User login
Progress in Management of Advanced Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Children
Incidence peaks in children aged 1-4 years, decreasing thereafter. Cases are highest among Native American/Alaskan Native and Hispanic children, and higher in White than Black children.4 ALL is seen more in patients with certain inherited conditions, including Down syndrome, ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, and Bloom syndrome.1
Treatment advances have improved remission rates and outcomes for patients. However, relapse is still a leading cause of death for patients of all ages.6 Prompt diagnosis and care are important to optimize outcomes, as treatment delay is associated with poorer survival.7
Pathophysiology
In ALL, abnormal, immature lymphocytes and progenitor B cells/T cells proliferate uncontrollably and eventually replace healthy cells in bone marrow and the lymphatic system. The loss of healthy cells leads to classic symptoms of cytopenia, splenomegaly, and hepatomegaly.1 B cells and T cells are descended from lymphoid stem cells (and are transformed by germline or somatic mutation into pathogenic cells, leading to symptom development and bone marrow dysfunction. Most pediatric patients have extensive bone marrow involvement at diagnosis, with > 25% blast cells in marrow (defined as M3 disease).4
Presentation
Patients usually present with signs and symptoms that are related to disease-associated anemia, thrombocytopenia, or neutropenia; these signs and symptoms may include fatigue or weakness, pale skin, bleeding or bruising easily, fever or infection, joint or extremity pain, B-cell symptoms such as night sweats or unintentional weight loss, and splenomegaly or hepatomegaly. Central nervous system (CNS) symptoms can include stroke-like symptoms due to leukemic cell invasion of CNS vasculature or neuropathies related to increased intracranial pressure. Sometimes, children may present with no symptoms other than joint or extremity pain.1,3,8
Classification
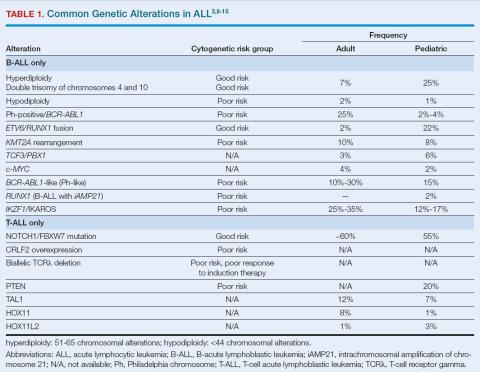
ALL is classified by whether it derives from B-cell or T-cell progenitor cells and, within these, by typical genetic alterations (Table 1).3,9-15 Some cytogenetics are associated with risk assessment as well. Well-identified B-ALL subtypes include Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome-positive, hyper- and hypodiploidy, and KMT2A rearranged, while newer classifications include Ph-like ALL and B-lymphoblastic leukemia with iAMP21. Provisional T-ALL subtypes include early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia and natural killer cell lymphoblastic leukemia.3
B-cell lineage is present in 88% of pediatric and 75%-80% of adult disease. T-ALL is found in about 12% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults.3,8 Familial syndromes associated with ALL are present in about 4% of pediatric patients, including autosomal dominant germline mutations in RUNX1 (T-cell ALL), ETV6 (B-ALL), PAX5 (B-ALL), IKZF1 (B-ALL and T-ALL), and TP53 (low-hypodiploid ALL).3 If a known-familial genotype is identified, families should be referred for genetic counseling and further testing if needed. If germline mutation is suspected, early identification is important; hereditary ALL can influence treatment choice and use of allogeneic transplantation or radiation.3
A third classification crucial to guiding treatment is Ph-positive vs Ph-negative or Ph-like, the latter strongly associated with abnormal B-cell development due to deletions in related genes.3,16 About 3% to 5% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults have Ph-positive ALL.17 The remission failure rate among pediatric patients treated with chemotherapy was 11% in one study, vs 2%-3% among patients with Ph-negative ALL.10
Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
Diagnosis is based on presentation and molecular features, requiring demonstration of ≥ 20% lymphoblasts in bone marrow biopsy or aspirate or ≥ 1,000 circulating lymphoblasts/mL in peripheral blood. Testing can include immunophenotyping using flow cytometry, molecular characterization of baseline leukemic clone, morphology using hematoxylin and eosin staining and Wright/Giemsa staining, and karyotyping.1,3 CNS involvement is assessed using a lumbar spinal tap.1
Risk stratification is based on molecular features (eg, high- and low-risk mutations, Table 1),3,9-15 which are assessed using fluorescence in-situ hybridization, broad-panel next-generation sequencing, and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of bone marrow or peripheral blood.3 Other risk factors include age, CNS involvement, white blood cell (WBC) count, and response to initial induction or consolidation therapy.3
Pediatric patients are assigned standard or high risk based on factors identified by the Children’s Oncology Group and National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Patients
aged 1 to < 10 years with WBC < 50 × 109/L are considered standard risk, and all others are considered high risk. Patients with ALL before age 1 have very high risk. All pediatric patients with T-ALL are considered high risk.3 Ph-positive, Ph-like, hypoploidy, failure to achieve remission with induction, and extramedullary disease are high-risk factors as well, whereas hyperploidy and certain mutations convey low risk.3
Newer treatment strategies for initial ALL diagnosis include targeted therapies. One goal of targeted therapy is avoidance of long-term toxicity, leading to improved survival outcomes. Well-studied targeted therapies include the tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in first-line and subsequent treatment of Ph-positive ALL.3
Treatment Options in Relapsed/Refractory ALL
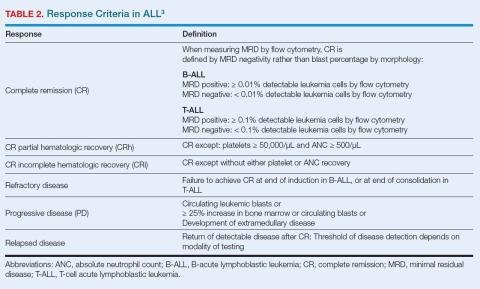
The initial treatment goal is complete remission (CR) defined as minimal residual disease (MRD) < 0.01% on flow cytometry (Table 2).3 Prognosis is dependent on time and location of relapse. Early relapse (< 18 months from diagnosis) predicts poor survival. Relapse in bone marrow is associated with poorer prognosis than relapse in CNS.11-18 Where possible, consolidation with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation improves survival for patients with early relapse.6 Three approaches have advanced treatment options for relapsed/refractory (R/R) B-ALL, all based around common cell markers seen in B-ALL.
The CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin is approved for adults with R/R B-ALL. In clinical trials, a higher percentage of patients had results below the MRD threshold, and longer progression-free survival and OS compared with standard care.19,20
Blinatumomab is a bispecific T-cell engager that binds to CD19 on the surface of B-ALL cells and to CD3 on T cells to trigger apoptosis.21 It was first approved for R/R ALL in adults or children, and is also now approved for treatment in remission with MRD ≥ 0.1%. Patients must demonstrate CD19-positive disease to qualify.15-22 For R/R ALL, blinatumomab improves OS and CR rates compared with standard chemotherapy.23
The use of CAR T-cell therapies has expanded greatly with increasing knowledge about their efficacy and safety. In R/R ALL, tisagenlecleucel (tisa-gen) is approved for treatment of patients aged ≤ 25 years, and brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexucel) is approved for treatment of adults.3,24,25 Patients undergoing the CAR T-cell process have apheresis to collect T cells, which are then manufactured before being reinfused into the patient. Depending on local capabilities, the time between T-cell harvest and reinfusion can extend to weeks.3,26,27 Cytoreduction with CAR T-cell therapy can allow previously ineligible patients (due to bulky disease) to undergo transplant. Patients treated in key clinical trials with tisa-gen or brexu-cel achieved high overall remission rates and improved event-free survival and OS rates compared with historical experience.25,28,29 Important toxicities with CAR T-cell therapy are cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity, which can develop rapidly. NCCN recommends hospitalizing patients at the first sign of either adverse event. Patients can be managed with tocilizumab or steroids for low-grade CRS or steroids for neurotoxicity. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and NCCN have guidelines on management of toxicities related to CAR T-cell therapy as well as management of symptoms and other adverse effects of CRS.5,23,24
Programs also incorporate telemedicine for symptom monitoring and follow-up.32-34 Centers providing CAR T-cell therapy must have a certified Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which ensures adherence to specific guidelines for administration, adverse event management, and patient education.35,36 Overcoming technical, social, and financial barriers to CAR T-cell therapy is an ongoing challenge of great interest.37
R/R T-Cell Precursor ALL
Patients with R/R T-ALL have poor prognosis, partly due to limited treatment options. Nelarabine, a nucleoside analog, is the only approved treatment for R/R T-ALL, but has increasingly been used in first-line therapy added to multiagent chemotherapy as a consolidation and maintenance approach to pediatric disease.3,38,39 Four-year DSF in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed T-ALL undergoing treatment incorporating nelarabine was 88.9%.39 Treatment is associated with grade ≥ 3 neurotoxicity in > 10% of patients, and can include CNS toxicity as well as neuropathy.3
In a recently completed phase 2 trial (NCT03384654), daratumumab was added to standard chemotherapy (vincristine, prednisone, PEG-asparaginase, doxorubicin) for R/R T-ALL in pediatric (ages 1-17 years) and young adult patients (age ≥ 18 years).40 Among 24 pediatric patients, CR was 41.7% and overall response rate (ORR; ORR = CR + CRi) was 83% after 1 cycle of treatment. Ten (41.7%) pediatric patients achieved MRD-negative status as well. ORR was 60% in the 5 older patients. All pediatric patients had at least 1 grade ≥ 3 toxicity, but none of the adverse events led to discontinuation.40
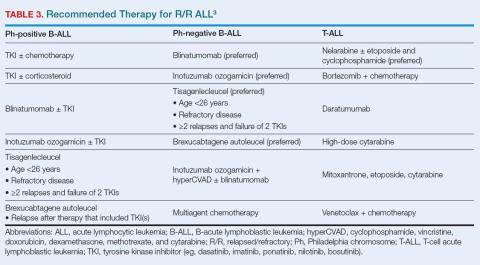
Success in achieving MRD-negative responses in patients treated for R/R ALL has increased interest in using targeted therapies for newly diagnosed patients. Recommended treatment approaches are summarized in Table 3.3
Long-Term Follow-Up and Survivorship
A study of > 500 pediatric patients followed for an average 23 years reassuringly found low prevalence of adverse outcomes related to disease or treatment. Major adverse outcomes such as death due to late relapse; secondary malignancy; or development of osteoporosis, cataracts, and diminished functional status were infrequent.41 Most prevalent were growth effects (short stature or growth hormone insufficiency), likely related to certain treatment approaches.41 Guidelines for long-term follow-up of pediatric patients are available from the Children’s Oncology Group.42
A 2017 systematic review concluded that the quality of life for survivors is diminished upon treatment, and persistently over time for some patients.43 In contrast, a 2022 comparison of long-term survivors (median 20.5 years since diagnosis) of pediatric ALL with healthy controls found that survivors had better quality of life in some domains, including general health, vitality, and mental health.44 Smaller percentages of survivors rated themselves happiest about sleep quality, absence of pain, and physical abilities.44
As therapy patterns and options evolve, continued follow-up is important to ensure patients derive optimal benefit from treatment and post-treatment life.
- Puckett Y, Chan O. Acute lymphocytic leukemia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated June 27, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459149/
- Cancer facts & figures 2023. American Cancer Society. 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2023/2023-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Version 1.2022. April 4, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/all.pdf
- Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 16, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: management of immunotherapy-related toxicities. Version 1.2023. March 10, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf
- DuVall AS, Sheade J, Anderson D, et al. Updates in the management of relapsed and refractory acute lymphoplastic leukemia: an urgent plea for new treatments is being answered! JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(7):479-487. doi:10.1200/OP.21.00843
- Baker JM, To T, Beyene J, Zagorski B, Greenberg ML, Sung L. Influence of length of time to diagnosis and treatment on the survival of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Leuk Res. 2014;38(2):204-209. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2013.11.014
- Acute adult lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 24, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/adult-all-treatment-pdq
- Trinquand A, Tanguy-Schmidt A, Ben Abdelali R, et al. Toward a NOTCH1/FBXW7/RAS/PTEN–based oncogenetic risk classification of adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Group for Research in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(34):4333-4342. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.48.5292
- Callens C, Baleydier F, Lengline E, et al. Clinical impact of NOTCH1 and/or FBXW7 mutations, FLASH deletion, and TCR status in pediatric T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(16):1966-1973. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.7661
- Gao C, Liu SG, Zhang RD, et al. NOTCH1 mutations are associated with favourable long-term prognosis in paediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a retrospective study of patients treated on BCH-2003 and CCLG-2008 protocol in China. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(2):221-228. doi:10.1111/bjh.12866
- Yang YL, Hsiao CC, Chen HY, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRγ deletion predicts induction failure and poorer outcomes in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;58(6):846-851. doi:10.1002/pbc.24021
- Gutierrez A, Dahlberg SE, Neuberg DS, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRgamma deletion predicts early treatment failure in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):3816-3823. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.3390
- Bandapalli OR, Zimmermann M, Kox C, et al. NOTCH1 activation clinically antagonizes the unfavorable effect of PTEN inactivation in BFM-treated children with precursor T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2013;98(6):928-936. doi:10.3324/haematol.2012.073585
- Palmi C, Savino AM, Silvestri D, et al. CRLF2 over-expression is a poor prognostic marker in children with high risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):59260-59272. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10610
- Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(2):125-134. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70339-5
- Aricò M, Schrappe M, Hunger SP, et al. Clinical outcome of children with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated between 1995 and 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(31):4755-4761. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1325
- Nguyen K, Devidas M, Cheng SC, et al.; Children’s Oncology Group. Factors influencing survival after relapse from acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children’s Oncology Group study. Leukemia. 2008;22(12):2142-2150. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.251
- Besponsa. Prescribing information. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2017. BESPONSA® (inotuzumab ozogamicin) Dosing & Administration |Safety Info (pfizerpro.com)
- Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(8):740-753. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1509277
- Lv M, Liu Y, Liu W, Xing Y, Zhang S. Immunotherapy for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: recent advances and future perspectives. Front Immunol. 2022;13:921894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.921894
- Blincyto. Prescribing information. Amgen; 2022. https://www.pi.amgen.com/-/media/Project/Amgen/Repository/pi-amgen-com/Blincyto/blincyto_pi_hcp_english.pdf
- Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(9):836-847. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1609783
- Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(5):439-448. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709866
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study. Lancet. 2021;398(10299):491-502. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01222-8
- Bhaskar ST, Dholaria BR, Singsayadeth S, Savani BN, Oluwole OO. Role of bridging therapy during chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. EJHaem. 2021;3(suppl 1):39-45. doi:10.1002/jha2.335
- Granroth G, Rosenthal A, McCallen M, et al. Supportive care for patients with lymphoma
undergoing CAR-T-cell therapy: the advanced practice provider’s perspective. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24(12):1863-1872. doi:10.1007/s11912-022-01330-z - Laetsch TW, Maude SL, Rives S, et al. Three-year update of tisagenlecleucel in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphocytic leukemia in the ELIANA trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(9):1664-1669. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.00642
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. Two-year follow-up of KTE-X19 in patients with relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in ZUMA-3 and its contextualization with SCHOLAR-3, an external historical control study. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):170. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01379-0
- Maus MV, Alexander S, Bishop MR, et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immune effector cell-related adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e001511. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-001511
- Santomasso BD, Nastoupil LJ, Adkins S, et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(35):3978-3992. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01992
- Borogovac A, Keruakous A, Bycko M, et al. Safety and feasibility of outpatient chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy: experience from a tertiary care center. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57(6):1025-1027. doi:10.1038/s41409-022-01664-z
- LeBar K, Murawski S, Umayam S, Quinn V. The role of advanced practice providers and telemedicine in reinventing care: the transition of a CAR T-cell transplantation program to the outpatient setting. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2020;11(7):757-763. doi:10.6004/jadpro.2020.11.7.8
- Myers GD, Verneris MR, Goy A, Maziarz RT. Perspectives on outpatient administration of CAR-T cell therapy for aggressive B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(4):e002056. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002056
- Kymriah. Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/107296/download
- Tecartus. Prescribing information. Kite Pharma, Inc; 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/140409/download
- Mikhael J, Fowler J, Shah N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies: barriers and solutions to access. JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(12):800-807. doi:10.1200/OP.22.00315
- Teachey DT, O’Connor D. How I treat newly diagnosed T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in children. Blood. 2020;135(3):159-166. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001557
- Summers RJ, Teachey DT. SOHO state of the art updates and next questions: novel approaches to pediatric T-cell ALL and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022;22(10):718-725. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2022.07.010
- Hogan LE, Bhatla T, Teachey DT, et al. Efficacy and safety of daratumumab (DARA) in pediatric and young adult patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or lymphoblastic lymphoma (LL): results from the phase 2 DELPHINUS study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(16 suppl):Abstract 10001. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.10001
- Essig S, Li Q, Chen Y, et al. Risk of late effects of treatment in children newly diagnosed with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):841-851. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70265-7
- Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. Version 5.0. Children’s Oncology Group. October 2018. Accessed April 10, 2023. http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org
- Fardell JE, Vetsch J, Trahair T, et al. Health-related quality of life of children on treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a systematic review. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64(9). doi:10.1002/pbc.26489
- Chantziara S, Musoro J, Rowsell AC, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life (QLG) and Children’s Leukemia Group (CLG). Quality of life of long-term childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors: comparison with healthy controls. Psychooncology. 2022;31(12):2159-2168. doi:10.1002/pon.6060
Incidence peaks in children aged 1-4 years, decreasing thereafter. Cases are highest among Native American/Alaskan Native and Hispanic children, and higher in White than Black children.4 ALL is seen more in patients with certain inherited conditions, including Down syndrome, ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, and Bloom syndrome.1
Treatment advances have improved remission rates and outcomes for patients. However, relapse is still a leading cause of death for patients of all ages.6 Prompt diagnosis and care are important to optimize outcomes, as treatment delay is associated with poorer survival.7
Pathophysiology
In ALL, abnormal, immature lymphocytes and progenitor B cells/T cells proliferate uncontrollably and eventually replace healthy cells in bone marrow and the lymphatic system. The loss of healthy cells leads to classic symptoms of cytopenia, splenomegaly, and hepatomegaly.1 B cells and T cells are descended from lymphoid stem cells (and are transformed by germline or somatic mutation into pathogenic cells, leading to symptom development and bone marrow dysfunction. Most pediatric patients have extensive bone marrow involvement at diagnosis, with > 25% blast cells in marrow (defined as M3 disease).4
Presentation
Patients usually present with signs and symptoms that are related to disease-associated anemia, thrombocytopenia, or neutropenia; these signs and symptoms may include fatigue or weakness, pale skin, bleeding or bruising easily, fever or infection, joint or extremity pain, B-cell symptoms such as night sweats or unintentional weight loss, and splenomegaly or hepatomegaly. Central nervous system (CNS) symptoms can include stroke-like symptoms due to leukemic cell invasion of CNS vasculature or neuropathies related to increased intracranial pressure. Sometimes, children may present with no symptoms other than joint or extremity pain.1,3,8
Classification
ALL is classified by whether it derives from B-cell or T-cell progenitor cells and, within these, by typical genetic alterations (Table 1).3,9-15 Some cytogenetics are associated with risk assessment as well. Well-identified B-ALL subtypes include Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome-positive, hyper- and hypodiploidy, and KMT2A rearranged, while newer classifications include Ph-like ALL and B-lymphoblastic leukemia with iAMP21. Provisional T-ALL subtypes include early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia and natural killer cell lymphoblastic leukemia.3
B-cell lineage is present in 88% of pediatric and 75%-80% of adult disease. T-ALL is found in about 12% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults.3,8 Familial syndromes associated with ALL are present in about 4% of pediatric patients, including autosomal dominant germline mutations in RUNX1 (T-cell ALL), ETV6 (B-ALL), PAX5 (B-ALL), IKZF1 (B-ALL and T-ALL), and TP53 (low-hypodiploid ALL).3 If a known-familial genotype is identified, families should be referred for genetic counseling and further testing if needed. If germline mutation is suspected, early identification is important; hereditary ALL can influence treatment choice and use of allogeneic transplantation or radiation.3
A third classification crucial to guiding treatment is Ph-positive vs Ph-negative or Ph-like, the latter strongly associated with abnormal B-cell development due to deletions in related genes.3,16 About 3% to 5% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults have Ph-positive ALL.17 The remission failure rate among pediatric patients treated with chemotherapy was 11% in one study, vs 2%-3% among patients with Ph-negative ALL.10
Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
Diagnosis is based on presentation and molecular features, requiring demonstration of ≥ 20% lymphoblasts in bone marrow biopsy or aspirate or ≥ 1,000 circulating lymphoblasts/mL in peripheral blood. Testing can include immunophenotyping using flow cytometry, molecular characterization of baseline leukemic clone, morphology using hematoxylin and eosin staining and Wright/Giemsa staining, and karyotyping.1,3 CNS involvement is assessed using a lumbar spinal tap.1
Risk stratification is based on molecular features (eg, high- and low-risk mutations, Table 1),3,9-15 which are assessed using fluorescence in-situ hybridization, broad-panel next-generation sequencing, and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of bone marrow or peripheral blood.3 Other risk factors include age, CNS involvement, white blood cell (WBC) count, and response to initial induction or consolidation therapy.3
Pediatric patients are assigned standard or high risk based on factors identified by the Children’s Oncology Group and National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Patients
aged 1 to < 10 years with WBC < 50 × 109/L are considered standard risk, and all others are considered high risk. Patients with ALL before age 1 have very high risk. All pediatric patients with T-ALL are considered high risk.3 Ph-positive, Ph-like, hypoploidy, failure to achieve remission with induction, and extramedullary disease are high-risk factors as well, whereas hyperploidy and certain mutations convey low risk.3
Newer treatment strategies for initial ALL diagnosis include targeted therapies. One goal of targeted therapy is avoidance of long-term toxicity, leading to improved survival outcomes. Well-studied targeted therapies include the tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in first-line and subsequent treatment of Ph-positive ALL.3
Treatment Options in Relapsed/Refractory ALL
The initial treatment goal is complete remission (CR) defined as minimal residual disease (MRD) < 0.01% on flow cytometry (Table 2).3 Prognosis is dependent on time and location of relapse. Early relapse (< 18 months from diagnosis) predicts poor survival. Relapse in bone marrow is associated with poorer prognosis than relapse in CNS.11-18 Where possible, consolidation with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation improves survival for patients with early relapse.6 Three approaches have advanced treatment options for relapsed/refractory (R/R) B-ALL, all based around common cell markers seen in B-ALL.
The CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin is approved for adults with R/R B-ALL. In clinical trials, a higher percentage of patients had results below the MRD threshold, and longer progression-free survival and OS compared with standard care.19,20
Blinatumomab is a bispecific T-cell engager that binds to CD19 on the surface of B-ALL cells and to CD3 on T cells to trigger apoptosis.21 It was first approved for R/R ALL in adults or children, and is also now approved for treatment in remission with MRD ≥ 0.1%. Patients must demonstrate CD19-positive disease to qualify.15-22 For R/R ALL, blinatumomab improves OS and CR rates compared with standard chemotherapy.23
The use of CAR T-cell therapies has expanded greatly with increasing knowledge about their efficacy and safety. In R/R ALL, tisagenlecleucel (tisa-gen) is approved for treatment of patients aged ≤ 25 years, and brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexucel) is approved for treatment of adults.3,24,25 Patients undergoing the CAR T-cell process have apheresis to collect T cells, which are then manufactured before being reinfused into the patient. Depending on local capabilities, the time between T-cell harvest and reinfusion can extend to weeks.3,26,27 Cytoreduction with CAR T-cell therapy can allow previously ineligible patients (due to bulky disease) to undergo transplant. Patients treated in key clinical trials with tisa-gen or brexu-cel achieved high overall remission rates and improved event-free survival and OS rates compared with historical experience.25,28,29 Important toxicities with CAR T-cell therapy are cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity, which can develop rapidly. NCCN recommends hospitalizing patients at the first sign of either adverse event. Patients can be managed with tocilizumab or steroids for low-grade CRS or steroids for neurotoxicity. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and NCCN have guidelines on management of toxicities related to CAR T-cell therapy as well as management of symptoms and other adverse effects of CRS.5,23,24
Programs also incorporate telemedicine for symptom monitoring and follow-up.32-34 Centers providing CAR T-cell therapy must have a certified Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which ensures adherence to specific guidelines for administration, adverse event management, and patient education.35,36 Overcoming technical, social, and financial barriers to CAR T-cell therapy is an ongoing challenge of great interest.37
R/R T-Cell Precursor ALL
Patients with R/R T-ALL have poor prognosis, partly due to limited treatment options. Nelarabine, a nucleoside analog, is the only approved treatment for R/R T-ALL, but has increasingly been used in first-line therapy added to multiagent chemotherapy as a consolidation and maintenance approach to pediatric disease.3,38,39 Four-year DSF in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed T-ALL undergoing treatment incorporating nelarabine was 88.9%.39 Treatment is associated with grade ≥ 3 neurotoxicity in > 10% of patients, and can include CNS toxicity as well as neuropathy.3
In a recently completed phase 2 trial (NCT03384654), daratumumab was added to standard chemotherapy (vincristine, prednisone, PEG-asparaginase, doxorubicin) for R/R T-ALL in pediatric (ages 1-17 years) and young adult patients (age ≥ 18 years).40 Among 24 pediatric patients, CR was 41.7% and overall response rate (ORR; ORR = CR + CRi) was 83% after 1 cycle of treatment. Ten (41.7%) pediatric patients achieved MRD-negative status as well. ORR was 60% in the 5 older patients. All pediatric patients had at least 1 grade ≥ 3 toxicity, but none of the adverse events led to discontinuation.40
Success in achieving MRD-negative responses in patients treated for R/R ALL has increased interest in using targeted therapies for newly diagnosed patients. Recommended treatment approaches are summarized in Table 3.3
Long-Term Follow-Up and Survivorship
A study of > 500 pediatric patients followed for an average 23 years reassuringly found low prevalence of adverse outcomes related to disease or treatment. Major adverse outcomes such as death due to late relapse; secondary malignancy; or development of osteoporosis, cataracts, and diminished functional status were infrequent.41 Most prevalent were growth effects (short stature or growth hormone insufficiency), likely related to certain treatment approaches.41 Guidelines for long-term follow-up of pediatric patients are available from the Children’s Oncology Group.42
A 2017 systematic review concluded that the quality of life for survivors is diminished upon treatment, and persistently over time for some patients.43 In contrast, a 2022 comparison of long-term survivors (median 20.5 years since diagnosis) of pediatric ALL with healthy controls found that survivors had better quality of life in some domains, including general health, vitality, and mental health.44 Smaller percentages of survivors rated themselves happiest about sleep quality, absence of pain, and physical abilities.44
As therapy patterns and options evolve, continued follow-up is important to ensure patients derive optimal benefit from treatment and post-treatment life.
Incidence peaks in children aged 1-4 years, decreasing thereafter. Cases are highest among Native American/Alaskan Native and Hispanic children, and higher in White than Black children.4 ALL is seen more in patients with certain inherited conditions, including Down syndrome, ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, and Bloom syndrome.1
Treatment advances have improved remission rates and outcomes for patients. However, relapse is still a leading cause of death for patients of all ages.6 Prompt diagnosis and care are important to optimize outcomes, as treatment delay is associated with poorer survival.7
Pathophysiology
In ALL, abnormal, immature lymphocytes and progenitor B cells/T cells proliferate uncontrollably and eventually replace healthy cells in bone marrow and the lymphatic system. The loss of healthy cells leads to classic symptoms of cytopenia, splenomegaly, and hepatomegaly.1 B cells and T cells are descended from lymphoid stem cells (and are transformed by germline or somatic mutation into pathogenic cells, leading to symptom development and bone marrow dysfunction. Most pediatric patients have extensive bone marrow involvement at diagnosis, with > 25% blast cells in marrow (defined as M3 disease).4
Presentation
Patients usually present with signs and symptoms that are related to disease-associated anemia, thrombocytopenia, or neutropenia; these signs and symptoms may include fatigue or weakness, pale skin, bleeding or bruising easily, fever or infection, joint or extremity pain, B-cell symptoms such as night sweats or unintentional weight loss, and splenomegaly or hepatomegaly. Central nervous system (CNS) symptoms can include stroke-like symptoms due to leukemic cell invasion of CNS vasculature or neuropathies related to increased intracranial pressure. Sometimes, children may present with no symptoms other than joint or extremity pain.1,3,8
Classification
ALL is classified by whether it derives from B-cell or T-cell progenitor cells and, within these, by typical genetic alterations (Table 1).3,9-15 Some cytogenetics are associated with risk assessment as well. Well-identified B-ALL subtypes include Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome-positive, hyper- and hypodiploidy, and KMT2A rearranged, while newer classifications include Ph-like ALL and B-lymphoblastic leukemia with iAMP21. Provisional T-ALL subtypes include early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia and natural killer cell lymphoblastic leukemia.3
B-cell lineage is present in 88% of pediatric and 75%-80% of adult disease. T-ALL is found in about 12% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults.3,8 Familial syndromes associated with ALL are present in about 4% of pediatric patients, including autosomal dominant germline mutations in RUNX1 (T-cell ALL), ETV6 (B-ALL), PAX5 (B-ALL), IKZF1 (B-ALL and T-ALL), and TP53 (low-hypodiploid ALL).3 If a known-familial genotype is identified, families should be referred for genetic counseling and further testing if needed. If germline mutation is suspected, early identification is important; hereditary ALL can influence treatment choice and use of allogeneic transplantation or radiation.3
A third classification crucial to guiding treatment is Ph-positive vs Ph-negative or Ph-like, the latter strongly associated with abnormal B-cell development due to deletions in related genes.3,16 About 3% to 5% of pediatric patients and 25% of adults have Ph-positive ALL.17 The remission failure rate among pediatric patients treated with chemotherapy was 11% in one study, vs 2%-3% among patients with Ph-negative ALL.10
Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
Diagnosis is based on presentation and molecular features, requiring demonstration of ≥ 20% lymphoblasts in bone marrow biopsy or aspirate or ≥ 1,000 circulating lymphoblasts/mL in peripheral blood. Testing can include immunophenotyping using flow cytometry, molecular characterization of baseline leukemic clone, morphology using hematoxylin and eosin staining and Wright/Giemsa staining, and karyotyping.1,3 CNS involvement is assessed using a lumbar spinal tap.1
Risk stratification is based on molecular features (eg, high- and low-risk mutations, Table 1),3,9-15 which are assessed using fluorescence in-situ hybridization, broad-panel next-generation sequencing, and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of bone marrow or peripheral blood.3 Other risk factors include age, CNS involvement, white blood cell (WBC) count, and response to initial induction or consolidation therapy.3
Pediatric patients are assigned standard or high risk based on factors identified by the Children’s Oncology Group and National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Patients
aged 1 to < 10 years with WBC < 50 × 109/L are considered standard risk, and all others are considered high risk. Patients with ALL before age 1 have very high risk. All pediatric patients with T-ALL are considered high risk.3 Ph-positive, Ph-like, hypoploidy, failure to achieve remission with induction, and extramedullary disease are high-risk factors as well, whereas hyperploidy and certain mutations convey low risk.3
Newer treatment strategies for initial ALL diagnosis include targeted therapies. One goal of targeted therapy is avoidance of long-term toxicity, leading to improved survival outcomes. Well-studied targeted therapies include the tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in first-line and subsequent treatment of Ph-positive ALL.3
Treatment Options in Relapsed/Refractory ALL
The initial treatment goal is complete remission (CR) defined as minimal residual disease (MRD) < 0.01% on flow cytometry (Table 2).3 Prognosis is dependent on time and location of relapse. Early relapse (< 18 months from diagnosis) predicts poor survival. Relapse in bone marrow is associated with poorer prognosis than relapse in CNS.11-18 Where possible, consolidation with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation improves survival for patients with early relapse.6 Three approaches have advanced treatment options for relapsed/refractory (R/R) B-ALL, all based around common cell markers seen in B-ALL.
The CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin is approved for adults with R/R B-ALL. In clinical trials, a higher percentage of patients had results below the MRD threshold, and longer progression-free survival and OS compared with standard care.19,20
Blinatumomab is a bispecific T-cell engager that binds to CD19 on the surface of B-ALL cells and to CD3 on T cells to trigger apoptosis.21 It was first approved for R/R ALL in adults or children, and is also now approved for treatment in remission with MRD ≥ 0.1%. Patients must demonstrate CD19-positive disease to qualify.15-22 For R/R ALL, blinatumomab improves OS and CR rates compared with standard chemotherapy.23
The use of CAR T-cell therapies has expanded greatly with increasing knowledge about their efficacy and safety. In R/R ALL, tisagenlecleucel (tisa-gen) is approved for treatment of patients aged ≤ 25 years, and brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexucel) is approved for treatment of adults.3,24,25 Patients undergoing the CAR T-cell process have apheresis to collect T cells, which are then manufactured before being reinfused into the patient. Depending on local capabilities, the time between T-cell harvest and reinfusion can extend to weeks.3,26,27 Cytoreduction with CAR T-cell therapy can allow previously ineligible patients (due to bulky disease) to undergo transplant. Patients treated in key clinical trials with tisa-gen or brexu-cel achieved high overall remission rates and improved event-free survival and OS rates compared with historical experience.25,28,29 Important toxicities with CAR T-cell therapy are cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity, which can develop rapidly. NCCN recommends hospitalizing patients at the first sign of either adverse event. Patients can be managed with tocilizumab or steroids for low-grade CRS or steroids for neurotoxicity. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and NCCN have guidelines on management of toxicities related to CAR T-cell therapy as well as management of symptoms and other adverse effects of CRS.5,23,24
Programs also incorporate telemedicine for symptom monitoring and follow-up.32-34 Centers providing CAR T-cell therapy must have a certified Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which ensures adherence to specific guidelines for administration, adverse event management, and patient education.35,36 Overcoming technical, social, and financial barriers to CAR T-cell therapy is an ongoing challenge of great interest.37
R/R T-Cell Precursor ALL
Patients with R/R T-ALL have poor prognosis, partly due to limited treatment options. Nelarabine, a nucleoside analog, is the only approved treatment for R/R T-ALL, but has increasingly been used in first-line therapy added to multiagent chemotherapy as a consolidation and maintenance approach to pediatric disease.3,38,39 Four-year DSF in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed T-ALL undergoing treatment incorporating nelarabine was 88.9%.39 Treatment is associated with grade ≥ 3 neurotoxicity in > 10% of patients, and can include CNS toxicity as well as neuropathy.3
In a recently completed phase 2 trial (NCT03384654), daratumumab was added to standard chemotherapy (vincristine, prednisone, PEG-asparaginase, doxorubicin) for R/R T-ALL in pediatric (ages 1-17 years) and young adult patients (age ≥ 18 years).40 Among 24 pediatric patients, CR was 41.7% and overall response rate (ORR; ORR = CR + CRi) was 83% after 1 cycle of treatment. Ten (41.7%) pediatric patients achieved MRD-negative status as well. ORR was 60% in the 5 older patients. All pediatric patients had at least 1 grade ≥ 3 toxicity, but none of the adverse events led to discontinuation.40
Success in achieving MRD-negative responses in patients treated for R/R ALL has increased interest in using targeted therapies for newly diagnosed patients. Recommended treatment approaches are summarized in Table 3.3
Long-Term Follow-Up and Survivorship
A study of > 500 pediatric patients followed for an average 23 years reassuringly found low prevalence of adverse outcomes related to disease or treatment. Major adverse outcomes such as death due to late relapse; secondary malignancy; or development of osteoporosis, cataracts, and diminished functional status were infrequent.41 Most prevalent were growth effects (short stature or growth hormone insufficiency), likely related to certain treatment approaches.41 Guidelines for long-term follow-up of pediatric patients are available from the Children’s Oncology Group.42
A 2017 systematic review concluded that the quality of life for survivors is diminished upon treatment, and persistently over time for some patients.43 In contrast, a 2022 comparison of long-term survivors (median 20.5 years since diagnosis) of pediatric ALL with healthy controls found that survivors had better quality of life in some domains, including general health, vitality, and mental health.44 Smaller percentages of survivors rated themselves happiest about sleep quality, absence of pain, and physical abilities.44
As therapy patterns and options evolve, continued follow-up is important to ensure patients derive optimal benefit from treatment and post-treatment life.
- Puckett Y, Chan O. Acute lymphocytic leukemia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated June 27, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459149/
- Cancer facts & figures 2023. American Cancer Society. 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2023/2023-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Version 1.2022. April 4, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/all.pdf
- Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 16, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: management of immunotherapy-related toxicities. Version 1.2023. March 10, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf
- DuVall AS, Sheade J, Anderson D, et al. Updates in the management of relapsed and refractory acute lymphoplastic leukemia: an urgent plea for new treatments is being answered! JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(7):479-487. doi:10.1200/OP.21.00843
- Baker JM, To T, Beyene J, Zagorski B, Greenberg ML, Sung L. Influence of length of time to diagnosis and treatment on the survival of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Leuk Res. 2014;38(2):204-209. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2013.11.014
- Acute adult lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 24, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/adult-all-treatment-pdq
- Trinquand A, Tanguy-Schmidt A, Ben Abdelali R, et al. Toward a NOTCH1/FBXW7/RAS/PTEN–based oncogenetic risk classification of adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Group for Research in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(34):4333-4342. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.48.5292
- Callens C, Baleydier F, Lengline E, et al. Clinical impact of NOTCH1 and/or FBXW7 mutations, FLASH deletion, and TCR status in pediatric T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(16):1966-1973. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.7661
- Gao C, Liu SG, Zhang RD, et al. NOTCH1 mutations are associated with favourable long-term prognosis in paediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a retrospective study of patients treated on BCH-2003 and CCLG-2008 protocol in China. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(2):221-228. doi:10.1111/bjh.12866
- Yang YL, Hsiao CC, Chen HY, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRγ deletion predicts induction failure and poorer outcomes in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;58(6):846-851. doi:10.1002/pbc.24021
- Gutierrez A, Dahlberg SE, Neuberg DS, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRgamma deletion predicts early treatment failure in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):3816-3823. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.3390
- Bandapalli OR, Zimmermann M, Kox C, et al. NOTCH1 activation clinically antagonizes the unfavorable effect of PTEN inactivation in BFM-treated children with precursor T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2013;98(6):928-936. doi:10.3324/haematol.2012.073585
- Palmi C, Savino AM, Silvestri D, et al. CRLF2 over-expression is a poor prognostic marker in children with high risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):59260-59272. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10610
- Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(2):125-134. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70339-5
- Aricò M, Schrappe M, Hunger SP, et al. Clinical outcome of children with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated between 1995 and 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(31):4755-4761. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1325
- Nguyen K, Devidas M, Cheng SC, et al.; Children’s Oncology Group. Factors influencing survival after relapse from acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children’s Oncology Group study. Leukemia. 2008;22(12):2142-2150. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.251
- Besponsa. Prescribing information. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2017. BESPONSA® (inotuzumab ozogamicin) Dosing & Administration |Safety Info (pfizerpro.com)
- Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(8):740-753. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1509277
- Lv M, Liu Y, Liu W, Xing Y, Zhang S. Immunotherapy for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: recent advances and future perspectives. Front Immunol. 2022;13:921894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.921894
- Blincyto. Prescribing information. Amgen; 2022. https://www.pi.amgen.com/-/media/Project/Amgen/Repository/pi-amgen-com/Blincyto/blincyto_pi_hcp_english.pdf
- Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(9):836-847. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1609783
- Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(5):439-448. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709866
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study. Lancet. 2021;398(10299):491-502. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01222-8
- Bhaskar ST, Dholaria BR, Singsayadeth S, Savani BN, Oluwole OO. Role of bridging therapy during chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. EJHaem. 2021;3(suppl 1):39-45. doi:10.1002/jha2.335
- Granroth G, Rosenthal A, McCallen M, et al. Supportive care for patients with lymphoma
undergoing CAR-T-cell therapy: the advanced practice provider’s perspective. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24(12):1863-1872. doi:10.1007/s11912-022-01330-z - Laetsch TW, Maude SL, Rives S, et al. Three-year update of tisagenlecleucel in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphocytic leukemia in the ELIANA trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(9):1664-1669. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.00642
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. Two-year follow-up of KTE-X19 in patients with relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in ZUMA-3 and its contextualization with SCHOLAR-3, an external historical control study. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):170. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01379-0
- Maus MV, Alexander S, Bishop MR, et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immune effector cell-related adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e001511. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-001511
- Santomasso BD, Nastoupil LJ, Adkins S, et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(35):3978-3992. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01992
- Borogovac A, Keruakous A, Bycko M, et al. Safety and feasibility of outpatient chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy: experience from a tertiary care center. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57(6):1025-1027. doi:10.1038/s41409-022-01664-z
- LeBar K, Murawski S, Umayam S, Quinn V. The role of advanced practice providers and telemedicine in reinventing care: the transition of a CAR T-cell transplantation program to the outpatient setting. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2020;11(7):757-763. doi:10.6004/jadpro.2020.11.7.8
- Myers GD, Verneris MR, Goy A, Maziarz RT. Perspectives on outpatient administration of CAR-T cell therapy for aggressive B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(4):e002056. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002056
- Kymriah. Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/107296/download
- Tecartus. Prescribing information. Kite Pharma, Inc; 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/140409/download
- Mikhael J, Fowler J, Shah N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies: barriers and solutions to access. JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(12):800-807. doi:10.1200/OP.22.00315
- Teachey DT, O’Connor D. How I treat newly diagnosed T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in children. Blood. 2020;135(3):159-166. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001557
- Summers RJ, Teachey DT. SOHO state of the art updates and next questions: novel approaches to pediatric T-cell ALL and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022;22(10):718-725. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2022.07.010
- Hogan LE, Bhatla T, Teachey DT, et al. Efficacy and safety of daratumumab (DARA) in pediatric and young adult patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or lymphoblastic lymphoma (LL): results from the phase 2 DELPHINUS study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(16 suppl):Abstract 10001. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.10001
- Essig S, Li Q, Chen Y, et al. Risk of late effects of treatment in children newly diagnosed with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):841-851. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70265-7
- Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. Version 5.0. Children’s Oncology Group. October 2018. Accessed April 10, 2023. http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org
- Fardell JE, Vetsch J, Trahair T, et al. Health-related quality of life of children on treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a systematic review. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64(9). doi:10.1002/pbc.26489
- Chantziara S, Musoro J, Rowsell AC, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life (QLG) and Children’s Leukemia Group (CLG). Quality of life of long-term childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors: comparison with healthy controls. Psychooncology. 2022;31(12):2159-2168. doi:10.1002/pon.6060
- Puckett Y, Chan O. Acute lymphocytic leukemia. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Updated June 27, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459149/
- Cancer facts & figures 2023. American Cancer Society. 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2023/2023-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Version 1.2022. April 4, 2022. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/all.pdf
- Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 16, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: management of immunotherapy-related toxicities. Version 1.2023. March 10, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf
- DuVall AS, Sheade J, Anderson D, et al. Updates in the management of relapsed and refractory acute lymphoplastic leukemia: an urgent plea for new treatments is being answered! JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(7):479-487. doi:10.1200/OP.21.00843
- Baker JM, To T, Beyene J, Zagorski B, Greenberg ML, Sung L. Influence of length of time to diagnosis and treatment on the survival of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study. Leuk Res. 2014;38(2):204-209. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2013.11.014
- Acute adult lymphoblastic leukemia (PDQ)—Health Professional Version. National Cancer Institute. Updated February 24, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/adult-all-treatment-pdq
- Trinquand A, Tanguy-Schmidt A, Ben Abdelali R, et al. Toward a NOTCH1/FBXW7/RAS/PTEN–based oncogenetic risk classification of adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Group for Research in Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Study. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(34):4333-4342. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.48.5292
- Callens C, Baleydier F, Lengline E, et al. Clinical impact of NOTCH1 and/or FBXW7 mutations, FLASH deletion, and TCR status in pediatric T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(16):1966-1973. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.7661
- Gao C, Liu SG, Zhang RD, et al. NOTCH1 mutations are associated with favourable long-term prognosis in paediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a retrospective study of patients treated on BCH-2003 and CCLG-2008 protocol in China. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(2):221-228. doi:10.1111/bjh.12866
- Yang YL, Hsiao CC, Chen HY, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRγ deletion predicts induction failure and poorer outcomes in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;58(6):846-851. doi:10.1002/pbc.24021
- Gutierrez A, Dahlberg SE, Neuberg DS, et al. Absence of biallelic TCRgamma deletion predicts early treatment failure in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(24):3816-3823. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.3390
- Bandapalli OR, Zimmermann M, Kox C, et al. NOTCH1 activation clinically antagonizes the unfavorable effect of PTEN inactivation in BFM-treated children with precursor T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2013;98(6):928-936. doi:10.3324/haematol.2012.073585
- Palmi C, Savino AM, Silvestri D, et al. CRLF2 over-expression is a poor prognostic marker in children with high risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):59260-59272. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10610
- Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(2):125-134. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70339-5
- Aricò M, Schrappe M, Hunger SP, et al. Clinical outcome of children with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated between 1995 and 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(31):4755-4761. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1325
- Nguyen K, Devidas M, Cheng SC, et al.; Children’s Oncology Group. Factors influencing survival after relapse from acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children’s Oncology Group study. Leukemia. 2008;22(12):2142-2150. doi:10.1038/leu.2008.251
- Besponsa. Prescribing information. Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2017. BESPONSA® (inotuzumab ozogamicin) Dosing & Administration |Safety Info (pfizerpro.com)
- Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ, Stelljes M, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin versus standard therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(8):740-753. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1509277
- Lv M, Liu Y, Liu W, Xing Y, Zhang S. Immunotherapy for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: recent advances and future perspectives. Front Immunol. 2022;13:921894. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.921894
- Blincyto. Prescribing information. Amgen; 2022. https://www.pi.amgen.com/-/media/Project/Amgen/Repository/pi-amgen-com/Blincyto/blincyto_pi_hcp_english.pdf
- Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, et al. Blinatumomab versus chemotherapy for advanced acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(9):836-847. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1609783
- Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(5):439-448. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1709866
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study. Lancet. 2021;398(10299):491-502. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01222-8
- Bhaskar ST, Dholaria BR, Singsayadeth S, Savani BN, Oluwole OO. Role of bridging therapy during chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. EJHaem. 2021;3(suppl 1):39-45. doi:10.1002/jha2.335
- Granroth G, Rosenthal A, McCallen M, et al. Supportive care for patients with lymphoma
undergoing CAR-T-cell therapy: the advanced practice provider’s perspective. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24(12):1863-1872. doi:10.1007/s11912-022-01330-z - Laetsch TW, Maude SL, Rives S, et al. Three-year update of tisagenlecleucel in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphocytic leukemia in the ELIANA trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(9):1664-1669. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.00642
- Shah BD, Ghobadi A, Oluwole OO, et al. Two-year follow-up of KTE-X19 in patients with relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in ZUMA-3 and its contextualization with SCHOLAR-3, an external historical control study. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):170. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01379-0
- Maus MV, Alexander S, Bishop MR, et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immune effector cell-related adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e001511. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-001511
- Santomasso BD, Nastoupil LJ, Adkins S, et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(35):3978-3992. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01992
- Borogovac A, Keruakous A, Bycko M, et al. Safety and feasibility of outpatient chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy: experience from a tertiary care center. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57(6):1025-1027. doi:10.1038/s41409-022-01664-z
- LeBar K, Murawski S, Umayam S, Quinn V. The role of advanced practice providers and telemedicine in reinventing care: the transition of a CAR T-cell transplantation program to the outpatient setting. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2020;11(7):757-763. doi:10.6004/jadpro.2020.11.7.8
- Myers GD, Verneris MR, Goy A, Maziarz RT. Perspectives on outpatient administration of CAR-T cell therapy for aggressive B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(4):e002056. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002056
- Kymriah. Prescribing information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/107296/download
- Tecartus. Prescribing information. Kite Pharma, Inc; 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/140409/download
- Mikhael J, Fowler J, Shah N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies: barriers and solutions to access. JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(12):800-807. doi:10.1200/OP.22.00315
- Teachey DT, O’Connor D. How I treat newly diagnosed T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in children. Blood. 2020;135(3):159-166. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001557
- Summers RJ, Teachey DT. SOHO state of the art updates and next questions: novel approaches to pediatric T-cell ALL and T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022;22(10):718-725. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2022.07.010
- Hogan LE, Bhatla T, Teachey DT, et al. Efficacy and safety of daratumumab (DARA) in pediatric and young adult patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or lymphoblastic lymphoma (LL): results from the phase 2 DELPHINUS study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(16 suppl):Abstract 10001. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.10001
- Essig S, Li Q, Chen Y, et al. Risk of late effects of treatment in children newly diagnosed with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):841-851. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70265-7
- Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. Version 5.0. Children’s Oncology Group. October 2018. Accessed April 10, 2023. http://www.survivorshipguidelines.org
- Fardell JE, Vetsch J, Trahair T, et al. Health-related quality of life of children on treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a systematic review. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64(9). doi:10.1002/pbc.26489
- Chantziara S, Musoro J, Rowsell AC, et al; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life (QLG) and Children’s Leukemia Group (CLG). Quality of life of long-term childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors: comparison with healthy controls. Psychooncology. 2022;31(12):2159-2168. doi:10.1002/pon.6060
Treatment Needs of Older Adults With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Within the last 40 years, younger fit patients have benefited from intensive chemotherapy regimens for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with improved survival, and the possibility of long-term disease-free survival (DFS) (“cure”).1 Older patients are often considered too unfit for standard curative treatment with intensive induction chemotherapy followed by consolidation chemotherapy, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), or both.2-4 Higher induction mortality and poor overall survival (OS) are associated with worse performance status, organ impairment, significant comorbidities, and declining cognitive function, all of which are more common with advancing age. Although the suggested criteria for determining unfitness have not been validated (Table 1), they can provide guidance in clinical practice.2-5
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) panel recommends the consideration of a patient’s performance status and comorbid conditions in addition to their age to determine a patient’s fitness for intensive induction therapy.6 Adverse disease features should also be considered, because disease biology may make intensive chemotherapy futile or inappropriate. For example, the mutational driver tumor protein p53 (TP53) appears at a higher frequency in older adults than younger adults and is associated with dismal outcomes even with intensive chemotherapy. Likewise, the spliceosome and chromatin modifier gene mutations are more common in older patients with AML and confer a worse OS with intensive therapy.6,7 Older unfit patients faced a difficult decision: proceed with intensive therapy with some possibility of long-term survival but risk of early mortality and significant toxicity, or opt for supportive care and palliative chemotherapy, such as the hypomethylating agents (HMAs) or low-dose cytarabine, with much shorter survival.
Guidelines for Treating Older Unfit Patients
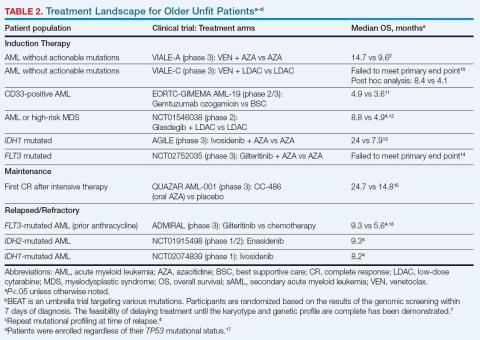
Evidence-based guidelines for managing older adults with newly diagnosed AML were developed by the American Society of Hematology in 2020; however, these guidelines were released prior to the results of several clinical trials involving older patients with AML (Table 2).8 In 2022, the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) recommendations were updated to include new therapeutic agents that target specific mutations in genes such as tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1), isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2). Given the important effects of genetic aberrations on disease phenotype, treatment options, and outcomes, screening for genetic aberrations at diagnosis is now essential.9
The potential for clonal evolution leading to new actionable targets that were not present at diagnosis highlights the importance of reevaluation of genetic aberrations throughout clinical progression. Actionable targets can include mutations in IDH1/IDH2, FLT3-internal tandem duplication or FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain.9
Treatment Landscape
Since 2018, several therapeutic agents have been added to the treatment armamentarium that can induce longer-term complete remission (CR) for older unfit patients with newly diagnosed AML (Table 2).4
Management of Primary AML With Less Intensive Induction Therapy
VIALE-A established a new standard of care for older unfit patients by demonstrating the benefit of adding the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax (VEN) to azacitidine (AZA).2 VIALE-A demonstrated that the rate of CR plus CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRi) was 65% for VEN plus AZA and 18% for AZA. Most remissions in the AZA/VEN arm occurred rapidly in the first 2 cycles. The median survival improved from 9.6 months with AZA to 14.7 months with AZA/VEN. An improvement in survival with VEN and low-dose cytarabine also emerged in a 6-month post hoc analysis of the VIALE-C trial.10 Various other trials examining targeted therapies on specific mutations have provided mixed results in the front-line setting.13,14,18 It is important to note that a recent systematic review found that 12% to 25% of patients who were unfit for intensive therapy were successfully bridged to HCT.19
Management of Postremission Response
Patients with a longer duration of first remission have demonstrated better survival outcomes.15 Two trials have examined postremission therapy in the setting of prior intensive therapy. HOVON97 enrolled older patients who achieved CR/CRi after 2 cycles of intensive therapy to receive either AZA postremission or no further treatment. The proportion of patients with DFS at 12 months was greater in the AZA maintenance group than in the observation group (64% vs 42%), but significant DFS improvement did not translate into improved OS.20 QUAZAR AML-001 demonstrated that OS was longer for older patients receiving maintenance therapy with CC-486 (a non-bioequivalent oral formulation of AZA) vs placebo (24.7 vs 14.8 months).15 CC-486 was FDA-approved for maintenance therapy after intensive induction with or without consolidation in patients who are not candidates for allo-HCT. However, limited evidence exists specifically for postremission therapy in unfit patients who have received less intensive therapy. Continuation of the lower intensive therapy is recommended until disease progression.6 No data are available to support the use of oral AZA therapy alone for maintenance of remission following HMA/VEN-induced remissions.
Management of Relapsed and Refractory AML
Nearly 50% of patients with AML experience relapse and up to 40% may be refractory.19 Importantly, patients who were considered fit for intensive therapy may not remain so with relapsed or refractory AML (r/rAML), so patients should be evaluated for fitness for an intensive salvage regimen. Similar to assessing fitness for induction therapy, no standard definition of fitness exists for r/rAML.19
Disease control is the goal for patients with r/rAML who are unfit for intensive salvage therapy; however, treatment options remain limited and prognosis is poor.19 Depending on the patient’s cytogenetic profile, management can include HMA with or without VEN, glasdegib with LDAC, gilteritinib, ivosidenib or enasidenib, or gemtuzumab ozogamicin.9 Only a few studies have been published involving the r/rAML population not eligible for intensive salvage regimen, and guidelines are needed for this population.19 Thus, the ELN recommends that clinical trial enrollment be considered for patients with r/rAML.9
Management of Secondary AML or High-risk AML
Compared with de novo AML, both secondary AML (sAML) and therapy-related AML (tAML) have been associated with inferior outcomes. Factors that influence poor outcomes can include older age, comorbidities, persistent malignant disease or relapse of primary malignancy, treatment-induced depletion of hematopoietic reserves and/or prolonged myelosuppression, and genetic abnormalities, such as TP53 mutations.21
CPX-351 is a dual drug that contains cytarabine and daunorubicin.9,22 An open-label study (NCT01696084) compared CPX-351 with conventional cytarabine and daunorubicin (induction and consolidation therapy) in older patients (aged 60-75 years) with newly diagnosed high-risk/sAML who were considered fit for intensive therapy. The OS for CPX-351 was longer (9.56 vs 5.95 months) and the safety profiles were similar between the treatment groups.23 Patients achieving CR/CRi received up to 2 cycles of consolidation with CPX-351. An exploratory analysis of this subgroup revealed median OS was longer with CPX-351 consolidation (25.43 vs 8.53 months).22 Patients with TP53 mutations had poor treatment outcomes regardless of treatment arm, whereas patients with sAML-type mutations including spliceosome and chromatin modifier genes had longer OS with CPX-351 therapy.24 The 5-year results of this trial indicate that the survival benefit of CPX-351 was maintained.25 However, data from a retrospective review involving 136 patients with either sAML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes revealed no difference in survival outcomes between patients treated with either HMA/VEN or CPX-351.26
Case Study: Elderly Woman With Newly Diagnosed AML
In 2018, Ms. W, age 69 years, was diagnosed with seropositive, non-erosive rheumatoid arthritis; she began methotrexate 17.5 mg per week split dosing in conjunction with oral folic acid 2 mg/d with varying doses based on symptoms. Her comorbidities included recurrent episodes of diverticulitis, hypertension, hypothyroidism, obstructive sleep apnea, and gastrointestinal reflux disease. On February 4, 2021, her methotrexate was increased to 20 mg and required intermittent prednisone tapers for flares. In November 2021, a blood test revealed she had a decreased white blood cell (WBC) count at 1.8 K/μL, and her methotrexate dose was decreased to 15 mg weekly. Despite the dose reduction, she had grade 3 neutropenia and anemia (WBC: 0.7 K/μL; HGB:10.5 g/dL) with a normal platelet count (PLT: 165,000/μL). Methotrexate was discontinued and leucovorin was initiated. She then had only modest improvement in her lab values and peripheral blood blasts.
On March 17, 2022, she underwent a bone marrow biopsy and aspirate, which resulted in a diagnosis of AML. She had 55% blasts in a 90% cellular bone marrow with mild reticulin fibrosis and numerous circulating blasts. She was classified as having AML without maturation (FAB AML-M1). Flow cytometry detected a phenotypically abnormal population with CD45 expression and side scatter/forward scatter features of small-to-medium sized blasts, accounting for 23% of total cells. The chromosome analysis demonstrated a normal female karyotype in all 19 available metaphases. Polymerase chain reaction analysis was negative for FLT3-ITD, FLT3-TKD, and NPM1 mutations and positive for an IDH1 R132C missense mutation. The myeloid gene panel identified only a single pathogenic variant, IDH1 R132C (variant allele frequency [VAF] 21.2%), and a variant of unknown significance DNMT3A A575P (VAF 25.7%).
Noting that she does not have favorable risk features, we discussed treatment options. Although she is a candidate for curative therapy, the patient was not interested in pursuing allo-HCT. Her history of diverticulitis is concerning for tolerating intensive chemotherapy. In addition, her immunosuppressive therapy increases her risk for opportunistic infections. Based on the available data from the AGILE and VIALE studies and associated potential adverse reactions, she opted for starting treatment with AZA and IVO.
On March 31, 2022, she began receiving AZA 75 mg/m2 intravenous (IV) once daily days 1-7 and oral IVO 500 mg once daily continuously. She has received 12 cycles and has not needed transfusion. She has not had febrile neutropenia or symptoms of differentiation syndrome. On March 24, 2023, she underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy, because an ultrasound revealed cholelithiasis, abnormal gallbladder wall thickening, and pericholecystic fluid. She was discharged home the following day and is continuing with AZA/ivosidenib.
- Schlenk RF. Acute myeloid leukemia: introduction to a series highlighting progress and ongoing challenges. Haematologica. 2023;108(2):306-307. doi:10.3324/haematol.2022.280803
- DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):617-629. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012971
- DiNardo CD, Wei AH. How I treat acute myeloid leukemia in the era of new drugs. Blood. 2020;135(2):85-96. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001239
- Huerga-Domínguez S, Villar S, Prósper F, Alfonso-Piérola A. Updates on the management of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4756. doi:10.3390/cancers14194756
- Ferrara F, Barosi G, Venditti A, et al. Consensus-based definition of unfitness to intensive and non-intensive chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: a project of SIE, SIES and GITMO group on a new tool for therapy decision making. Leukemia. 2013;27(5):997-999. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.303
- Tallman MS, Wang ES, Altman JK, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(6):721-749. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2019.0028
- Burd A, Levine RL, Ruppert AS, et al. Precision medicine treatment in acute myeloid leukemia using prospective genomic profiling: feasibility and preliminary efficacy of the Beat AML Master Trial. Nat Med. 2020;26(12):1852-1858. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1089-8
- Sekeres MA, Guyatt G, Abel G, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for treating newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in older adults. Blood Adv. 2020;4(15):3528-3549. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001920
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345-1377. doi:10.1182/blood.2022016867
- Wei AH, Montesinos P, Ivanov V, et al. Venetoclax plus LDAC for newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: a phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial. Blood. 2020;135(24):2137-2145. doi:10.1182/blood.2020004856
- Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0060
- Cortes JE, Heidel FH, Hellmann A, et al. Randomized comparison of low dose cytarabine with or without glasdegib in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2019;33(2):379-389. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0312-9
- Montesinos P, Recher C, Vives S, et al. Ivosidenib and azacitidine in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(16):1519-1531. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2117344
- Wang ES, Montesinos P, Minden MD, et al. Phase 3 trial of gilteritinib plus azacitidine vs azacitidine for newly diagnosed FLT3mut+ AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Blood. 2022;140(17):1845-1857. doi:10.1182/blood.2021014586
- Wei AH, Döhner H, Pocock C, et al; QUAZAR AML-001 Trial Investigators. Oral azacitidine maintenance therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(26):2526-2537. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004444
- Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, et al. Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1728-1740. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1902688
- Konopleva MY, Röllig C, Cavenagh J, et al. Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of the MIRROS trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6(14):4147-4156. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006303
- Pollyea DA, DiNardo CD, Arellano ML, et al. Impact of venetoclax and azacitidine in treatment-naïve patients with acute myeloid leukemia and IDH1/2 mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(13):2753-2761. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3467
- Russell-Smith TA, Gurskyte L, Muresan B, et al. Efficacy of non-intensive therapies approved for relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic literature review. Future Oncol. 2022;18(16):2029-2039. doi:10.2217/fon-2021-1355
- Huls G, Chitu DA, Havelange V, et al; Dutch-Belgian Hemato-Oncology Cooperative Group (HOVON). Azacitidine maintenance after intensive chemotherapy improves DFS in older AML patients. Blood. 2019;133(13):1457-1464. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-879866
- Granfeldt Østgård LS, Medeiros BC, Sengeløv H, et al. Epidemiology and clinical significance of secondary and therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia: a national population-based cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(31):3641-3649. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0890
- Kolitz JE, Strickland SA, Cortes JE, et al. Consolidation outcomes in CPX-351 versus cytarabine/daunorubicin-treated older patients with high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(3):631-640. doi:10.1080/1042819.2019.1688320
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Cortes JE, et al. CPX-351 (cytarabine and daunorubicin) liposome for injection versus conventional cytarabine plus daunorubicin in older patients with newly diagnosed secondary acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(26):2684-2692. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6112
- Lindsley RC, Gibson CJ, Murdock HM, et al. Genetic characteristics and outcomes by mutation status in a phase 3 study of CPX-351 versus 7+3 in older adults with newly diagnosed, high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):15. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-124500
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Newell LF, et al. CPX-351 versus 7+3 cytarabine and daunorubicin chemotherapy in older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia: 5-year results of a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(7):e481-e491. doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00134-4
- Alharthy H, Alkaabba F, Williams M, et al. Outcomes of newly diagnosed therapy-related AML and AML with myelodysplasia-related changes treated with 7+3, hypomethylating agents with or without venetoclax and CPX-351: a retrospective cohort study. Blood. 2022;140(suppl 1):9025-9026. doi:10.1182/blood-2022-170688
Within the last 40 years, younger fit patients have benefited from intensive chemotherapy regimens for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with improved survival, and the possibility of long-term disease-free survival (DFS) (“cure”).1 Older patients are often considered too unfit for standard curative treatment with intensive induction chemotherapy followed by consolidation chemotherapy, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), or both.2-4 Higher induction mortality and poor overall survival (OS) are associated with worse performance status, organ impairment, significant comorbidities, and declining cognitive function, all of which are more common with advancing age. Although the suggested criteria for determining unfitness have not been validated (Table 1), they can provide guidance in clinical practice.2-5
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) panel recommends the consideration of a patient’s performance status and comorbid conditions in addition to their age to determine a patient’s fitness for intensive induction therapy.6 Adverse disease features should also be considered, because disease biology may make intensive chemotherapy futile or inappropriate. For example, the mutational driver tumor protein p53 (TP53) appears at a higher frequency in older adults than younger adults and is associated with dismal outcomes even with intensive chemotherapy. Likewise, the spliceosome and chromatin modifier gene mutations are more common in older patients with AML and confer a worse OS with intensive therapy.6,7 Older unfit patients faced a difficult decision: proceed with intensive therapy with some possibility of long-term survival but risk of early mortality and significant toxicity, or opt for supportive care and palliative chemotherapy, such as the hypomethylating agents (HMAs) or low-dose cytarabine, with much shorter survival.
Guidelines for Treating Older Unfit Patients
Evidence-based guidelines for managing older adults with newly diagnosed AML were developed by the American Society of Hematology in 2020; however, these guidelines were released prior to the results of several clinical trials involving older patients with AML (Table 2).8 In 2022, the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) recommendations were updated to include new therapeutic agents that target specific mutations in genes such as tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1), isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2). Given the important effects of genetic aberrations on disease phenotype, treatment options, and outcomes, screening for genetic aberrations at diagnosis is now essential.9
The potential for clonal evolution leading to new actionable targets that were not present at diagnosis highlights the importance of reevaluation of genetic aberrations throughout clinical progression. Actionable targets can include mutations in IDH1/IDH2, FLT3-internal tandem duplication or FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain.9
Treatment Landscape
Since 2018, several therapeutic agents have been added to the treatment armamentarium that can induce longer-term complete remission (CR) for older unfit patients with newly diagnosed AML (Table 2).4
Management of Primary AML With Less Intensive Induction Therapy
VIALE-A established a new standard of care for older unfit patients by demonstrating the benefit of adding the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax (VEN) to azacitidine (AZA).2 VIALE-A demonstrated that the rate of CR plus CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRi) was 65% for VEN plus AZA and 18% for AZA. Most remissions in the AZA/VEN arm occurred rapidly in the first 2 cycles. The median survival improved from 9.6 months with AZA to 14.7 months with AZA/VEN. An improvement in survival with VEN and low-dose cytarabine also emerged in a 6-month post hoc analysis of the VIALE-C trial.10 Various other trials examining targeted therapies on specific mutations have provided mixed results in the front-line setting.13,14,18 It is important to note that a recent systematic review found that 12% to 25% of patients who were unfit for intensive therapy were successfully bridged to HCT.19
Management of Postremission Response
Patients with a longer duration of first remission have demonstrated better survival outcomes.15 Two trials have examined postremission therapy in the setting of prior intensive therapy. HOVON97 enrolled older patients who achieved CR/CRi after 2 cycles of intensive therapy to receive either AZA postremission or no further treatment. The proportion of patients with DFS at 12 months was greater in the AZA maintenance group than in the observation group (64% vs 42%), but significant DFS improvement did not translate into improved OS.20 QUAZAR AML-001 demonstrated that OS was longer for older patients receiving maintenance therapy with CC-486 (a non-bioequivalent oral formulation of AZA) vs placebo (24.7 vs 14.8 months).15 CC-486 was FDA-approved for maintenance therapy after intensive induction with or without consolidation in patients who are not candidates for allo-HCT. However, limited evidence exists specifically for postremission therapy in unfit patients who have received less intensive therapy. Continuation of the lower intensive therapy is recommended until disease progression.6 No data are available to support the use of oral AZA therapy alone for maintenance of remission following HMA/VEN-induced remissions.
Management of Relapsed and Refractory AML
Nearly 50% of patients with AML experience relapse and up to 40% may be refractory.19 Importantly, patients who were considered fit for intensive therapy may not remain so with relapsed or refractory AML (r/rAML), so patients should be evaluated for fitness for an intensive salvage regimen. Similar to assessing fitness for induction therapy, no standard definition of fitness exists for r/rAML.19
Disease control is the goal for patients with r/rAML who are unfit for intensive salvage therapy; however, treatment options remain limited and prognosis is poor.19 Depending on the patient’s cytogenetic profile, management can include HMA with or without VEN, glasdegib with LDAC, gilteritinib, ivosidenib or enasidenib, or gemtuzumab ozogamicin.9 Only a few studies have been published involving the r/rAML population not eligible for intensive salvage regimen, and guidelines are needed for this population.19 Thus, the ELN recommends that clinical trial enrollment be considered for patients with r/rAML.9
Management of Secondary AML or High-risk AML
Compared with de novo AML, both secondary AML (sAML) and therapy-related AML (tAML) have been associated with inferior outcomes. Factors that influence poor outcomes can include older age, comorbidities, persistent malignant disease or relapse of primary malignancy, treatment-induced depletion of hematopoietic reserves and/or prolonged myelosuppression, and genetic abnormalities, such as TP53 mutations.21
CPX-351 is a dual drug that contains cytarabine and daunorubicin.9,22 An open-label study (NCT01696084) compared CPX-351 with conventional cytarabine and daunorubicin (induction and consolidation therapy) in older patients (aged 60-75 years) with newly diagnosed high-risk/sAML who were considered fit for intensive therapy. The OS for CPX-351 was longer (9.56 vs 5.95 months) and the safety profiles were similar between the treatment groups.23 Patients achieving CR/CRi received up to 2 cycles of consolidation with CPX-351. An exploratory analysis of this subgroup revealed median OS was longer with CPX-351 consolidation (25.43 vs 8.53 months).22 Patients with TP53 mutations had poor treatment outcomes regardless of treatment arm, whereas patients with sAML-type mutations including spliceosome and chromatin modifier genes had longer OS with CPX-351 therapy.24 The 5-year results of this trial indicate that the survival benefit of CPX-351 was maintained.25 However, data from a retrospective review involving 136 patients with either sAML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes revealed no difference in survival outcomes between patients treated with either HMA/VEN or CPX-351.26
Case Study: Elderly Woman With Newly Diagnosed AML
In 2018, Ms. W, age 69 years, was diagnosed with seropositive, non-erosive rheumatoid arthritis; she began methotrexate 17.5 mg per week split dosing in conjunction with oral folic acid 2 mg/d with varying doses based on symptoms. Her comorbidities included recurrent episodes of diverticulitis, hypertension, hypothyroidism, obstructive sleep apnea, and gastrointestinal reflux disease. On February 4, 2021, her methotrexate was increased to 20 mg and required intermittent prednisone tapers for flares. In November 2021, a blood test revealed she had a decreased white blood cell (WBC) count at 1.8 K/μL, and her methotrexate dose was decreased to 15 mg weekly. Despite the dose reduction, she had grade 3 neutropenia and anemia (WBC: 0.7 K/μL; HGB:10.5 g/dL) with a normal platelet count (PLT: 165,000/μL). Methotrexate was discontinued and leucovorin was initiated. She then had only modest improvement in her lab values and peripheral blood blasts.
On March 17, 2022, she underwent a bone marrow biopsy and aspirate, which resulted in a diagnosis of AML. She had 55% blasts in a 90% cellular bone marrow with mild reticulin fibrosis and numerous circulating blasts. She was classified as having AML without maturation (FAB AML-M1). Flow cytometry detected a phenotypically abnormal population with CD45 expression and side scatter/forward scatter features of small-to-medium sized blasts, accounting for 23% of total cells. The chromosome analysis demonstrated a normal female karyotype in all 19 available metaphases. Polymerase chain reaction analysis was negative for FLT3-ITD, FLT3-TKD, and NPM1 mutations and positive for an IDH1 R132C missense mutation. The myeloid gene panel identified only a single pathogenic variant, IDH1 R132C (variant allele frequency [VAF] 21.2%), and a variant of unknown significance DNMT3A A575P (VAF 25.7%).
Noting that she does not have favorable risk features, we discussed treatment options. Although she is a candidate for curative therapy, the patient was not interested in pursuing allo-HCT. Her history of diverticulitis is concerning for tolerating intensive chemotherapy. In addition, her immunosuppressive therapy increases her risk for opportunistic infections. Based on the available data from the AGILE and VIALE studies and associated potential adverse reactions, she opted for starting treatment with AZA and IVO.
On March 31, 2022, she began receiving AZA 75 mg/m2 intravenous (IV) once daily days 1-7 and oral IVO 500 mg once daily continuously. She has received 12 cycles and has not needed transfusion. She has not had febrile neutropenia or symptoms of differentiation syndrome. On March 24, 2023, she underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy, because an ultrasound revealed cholelithiasis, abnormal gallbladder wall thickening, and pericholecystic fluid. She was discharged home the following day and is continuing with AZA/ivosidenib.
Within the last 40 years, younger fit patients have benefited from intensive chemotherapy regimens for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with improved survival, and the possibility of long-term disease-free survival (DFS) (“cure”).1 Older patients are often considered too unfit for standard curative treatment with intensive induction chemotherapy followed by consolidation chemotherapy, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT), or both.2-4 Higher induction mortality and poor overall survival (OS) are associated with worse performance status, organ impairment, significant comorbidities, and declining cognitive function, all of which are more common with advancing age. Although the suggested criteria for determining unfitness have not been validated (Table 1), they can provide guidance in clinical practice.2-5
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) panel recommends the consideration of a patient’s performance status and comorbid conditions in addition to their age to determine a patient’s fitness for intensive induction therapy.6 Adverse disease features should also be considered, because disease biology may make intensive chemotherapy futile or inappropriate. For example, the mutational driver tumor protein p53 (TP53) appears at a higher frequency in older adults than younger adults and is associated with dismal outcomes even with intensive chemotherapy. Likewise, the spliceosome and chromatin modifier gene mutations are more common in older patients with AML and confer a worse OS with intensive therapy.6,7 Older unfit patients faced a difficult decision: proceed with intensive therapy with some possibility of long-term survival but risk of early mortality and significant toxicity, or opt for supportive care and palliative chemotherapy, such as the hypomethylating agents (HMAs) or low-dose cytarabine, with much shorter survival.
Guidelines for Treating Older Unfit Patients
Evidence-based guidelines for managing older adults with newly diagnosed AML were developed by the American Society of Hematology in 2020; however, these guidelines were released prior to the results of several clinical trials involving older patients with AML (Table 2).8 In 2022, the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) recommendations were updated to include new therapeutic agents that target specific mutations in genes such as tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1), isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2), and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2). Given the important effects of genetic aberrations on disease phenotype, treatment options, and outcomes, screening for genetic aberrations at diagnosis is now essential.9
The potential for clonal evolution leading to new actionable targets that were not present at diagnosis highlights the importance of reevaluation of genetic aberrations throughout clinical progression. Actionable targets can include mutations in IDH1/IDH2, FLT3-internal tandem duplication or FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain.9
Treatment Landscape
Since 2018, several therapeutic agents have been added to the treatment armamentarium that can induce longer-term complete remission (CR) for older unfit patients with newly diagnosed AML (Table 2).4
Management of Primary AML With Less Intensive Induction Therapy
VIALE-A established a new standard of care for older unfit patients by demonstrating the benefit of adding the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax (VEN) to azacitidine (AZA).2 VIALE-A demonstrated that the rate of CR plus CR with partial hematologic recovery (CRi) was 65% for VEN plus AZA and 18% for AZA. Most remissions in the AZA/VEN arm occurred rapidly in the first 2 cycles. The median survival improved from 9.6 months with AZA to 14.7 months with AZA/VEN. An improvement in survival with VEN and low-dose cytarabine also emerged in a 6-month post hoc analysis of the VIALE-C trial.10 Various other trials examining targeted therapies on specific mutations have provided mixed results in the front-line setting.13,14,18 It is important to note that a recent systematic review found that 12% to 25% of patients who were unfit for intensive therapy were successfully bridged to HCT.19
Management of Postremission Response
Patients with a longer duration of first remission have demonstrated better survival outcomes.15 Two trials have examined postremission therapy in the setting of prior intensive therapy. HOVON97 enrolled older patients who achieved CR/CRi after 2 cycles of intensive therapy to receive either AZA postremission or no further treatment. The proportion of patients with DFS at 12 months was greater in the AZA maintenance group than in the observation group (64% vs 42%), but significant DFS improvement did not translate into improved OS.20 QUAZAR AML-001 demonstrated that OS was longer for older patients receiving maintenance therapy with CC-486 (a non-bioequivalent oral formulation of AZA) vs placebo (24.7 vs 14.8 months).15 CC-486 was FDA-approved for maintenance therapy after intensive induction with or without consolidation in patients who are not candidates for allo-HCT. However, limited evidence exists specifically for postremission therapy in unfit patients who have received less intensive therapy. Continuation of the lower intensive therapy is recommended until disease progression.6 No data are available to support the use of oral AZA therapy alone for maintenance of remission following HMA/VEN-induced remissions.
Management of Relapsed and Refractory AML
Nearly 50% of patients with AML experience relapse and up to 40% may be refractory.19 Importantly, patients who were considered fit for intensive therapy may not remain so with relapsed or refractory AML (r/rAML), so patients should be evaluated for fitness for an intensive salvage regimen. Similar to assessing fitness for induction therapy, no standard definition of fitness exists for r/rAML.19
Disease control is the goal for patients with r/rAML who are unfit for intensive salvage therapy; however, treatment options remain limited and prognosis is poor.19 Depending on the patient’s cytogenetic profile, management can include HMA with or without VEN, glasdegib with LDAC, gilteritinib, ivosidenib or enasidenib, or gemtuzumab ozogamicin.9 Only a few studies have been published involving the r/rAML population not eligible for intensive salvage regimen, and guidelines are needed for this population.19 Thus, the ELN recommends that clinical trial enrollment be considered for patients with r/rAML.9
Management of Secondary AML or High-risk AML
Compared with de novo AML, both secondary AML (sAML) and therapy-related AML (tAML) have been associated with inferior outcomes. Factors that influence poor outcomes can include older age, comorbidities, persistent malignant disease or relapse of primary malignancy, treatment-induced depletion of hematopoietic reserves and/or prolonged myelosuppression, and genetic abnormalities, such as TP53 mutations.21
CPX-351 is a dual drug that contains cytarabine and daunorubicin.9,22 An open-label study (NCT01696084) compared CPX-351 with conventional cytarabine and daunorubicin (induction and consolidation therapy) in older patients (aged 60-75 years) with newly diagnosed high-risk/sAML who were considered fit for intensive therapy. The OS for CPX-351 was longer (9.56 vs 5.95 months) and the safety profiles were similar between the treatment groups.23 Patients achieving CR/CRi received up to 2 cycles of consolidation with CPX-351. An exploratory analysis of this subgroup revealed median OS was longer with CPX-351 consolidation (25.43 vs 8.53 months).22 Patients with TP53 mutations had poor treatment outcomes regardless of treatment arm, whereas patients with sAML-type mutations including spliceosome and chromatin modifier genes had longer OS with CPX-351 therapy.24 The 5-year results of this trial indicate that the survival benefit of CPX-351 was maintained.25 However, data from a retrospective review involving 136 patients with either sAML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes revealed no difference in survival outcomes between patients treated with either HMA/VEN or CPX-351.26
Case Study: Elderly Woman With Newly Diagnosed AML
In 2018, Ms. W, age 69 years, was diagnosed with seropositive, non-erosive rheumatoid arthritis; she began methotrexate 17.5 mg per week split dosing in conjunction with oral folic acid 2 mg/d with varying doses based on symptoms. Her comorbidities included recurrent episodes of diverticulitis, hypertension, hypothyroidism, obstructive sleep apnea, and gastrointestinal reflux disease. On February 4, 2021, her methotrexate was increased to 20 mg and required intermittent prednisone tapers for flares. In November 2021, a blood test revealed she had a decreased white blood cell (WBC) count at 1.8 K/μL, and her methotrexate dose was decreased to 15 mg weekly. Despite the dose reduction, she had grade 3 neutropenia and anemia (WBC: 0.7 K/μL; HGB:10.5 g/dL) with a normal platelet count (PLT: 165,000/μL). Methotrexate was discontinued and leucovorin was initiated. She then had only modest improvement in her lab values and peripheral blood blasts.
On March 17, 2022, she underwent a bone marrow biopsy and aspirate, which resulted in a diagnosis of AML. She had 55% blasts in a 90% cellular bone marrow with mild reticulin fibrosis and numerous circulating blasts. She was classified as having AML without maturation (FAB AML-M1). Flow cytometry detected a phenotypically abnormal population with CD45 expression and side scatter/forward scatter features of small-to-medium sized blasts, accounting for 23% of total cells. The chromosome analysis demonstrated a normal female karyotype in all 19 available metaphases. Polymerase chain reaction analysis was negative for FLT3-ITD, FLT3-TKD, and NPM1 mutations and positive for an IDH1 R132C missense mutation. The myeloid gene panel identified only a single pathogenic variant, IDH1 R132C (variant allele frequency [VAF] 21.2%), and a variant of unknown significance DNMT3A A575P (VAF 25.7%).
Noting that she does not have favorable risk features, we discussed treatment options. Although she is a candidate for curative therapy, the patient was not interested in pursuing allo-HCT. Her history of diverticulitis is concerning for tolerating intensive chemotherapy. In addition, her immunosuppressive therapy increases her risk for opportunistic infections. Based on the available data from the AGILE and VIALE studies and associated potential adverse reactions, she opted for starting treatment with AZA and IVO.
On March 31, 2022, she began receiving AZA 75 mg/m2 intravenous (IV) once daily days 1-7 and oral IVO 500 mg once daily continuously. She has received 12 cycles and has not needed transfusion. She has not had febrile neutropenia or symptoms of differentiation syndrome. On March 24, 2023, she underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy, because an ultrasound revealed cholelithiasis, abnormal gallbladder wall thickening, and pericholecystic fluid. She was discharged home the following day and is continuing with AZA/ivosidenib.
- Schlenk RF. Acute myeloid leukemia: introduction to a series highlighting progress and ongoing challenges. Haematologica. 2023;108(2):306-307. doi:10.3324/haematol.2022.280803
- DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):617-629. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012971
- DiNardo CD, Wei AH. How I treat acute myeloid leukemia in the era of new drugs. Blood. 2020;135(2):85-96. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001239
- Huerga-Domínguez S, Villar S, Prósper F, Alfonso-Piérola A. Updates on the management of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4756. doi:10.3390/cancers14194756
- Ferrara F, Barosi G, Venditti A, et al. Consensus-based definition of unfitness to intensive and non-intensive chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: a project of SIE, SIES and GITMO group on a new tool for therapy decision making. Leukemia. 2013;27(5):997-999. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.303
- Tallman MS, Wang ES, Altman JK, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(6):721-749. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2019.0028
- Burd A, Levine RL, Ruppert AS, et al. Precision medicine treatment in acute myeloid leukemia using prospective genomic profiling: feasibility and preliminary efficacy of the Beat AML Master Trial. Nat Med. 2020;26(12):1852-1858. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1089-8
- Sekeres MA, Guyatt G, Abel G, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for treating newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in older adults. Blood Adv. 2020;4(15):3528-3549. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001920
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345-1377. doi:10.1182/blood.2022016867
- Wei AH, Montesinos P, Ivanov V, et al. Venetoclax plus LDAC for newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: a phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial. Blood. 2020;135(24):2137-2145. doi:10.1182/blood.2020004856
- Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0060
- Cortes JE, Heidel FH, Hellmann A, et al. Randomized comparison of low dose cytarabine with or without glasdegib in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2019;33(2):379-389. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0312-9
- Montesinos P, Recher C, Vives S, et al. Ivosidenib and azacitidine in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(16):1519-1531. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2117344
- Wang ES, Montesinos P, Minden MD, et al. Phase 3 trial of gilteritinib plus azacitidine vs azacitidine for newly diagnosed FLT3mut+ AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Blood. 2022;140(17):1845-1857. doi:10.1182/blood.2021014586
- Wei AH, Döhner H, Pocock C, et al; QUAZAR AML-001 Trial Investigators. Oral azacitidine maintenance therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(26):2526-2537. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004444
- Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, et al. Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1728-1740. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1902688
- Konopleva MY, Röllig C, Cavenagh J, et al. Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of the MIRROS trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6(14):4147-4156. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006303
- Pollyea DA, DiNardo CD, Arellano ML, et al. Impact of venetoclax and azacitidine in treatment-naïve patients with acute myeloid leukemia and IDH1/2 mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(13):2753-2761. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3467
- Russell-Smith TA, Gurskyte L, Muresan B, et al. Efficacy of non-intensive therapies approved for relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic literature review. Future Oncol. 2022;18(16):2029-2039. doi:10.2217/fon-2021-1355
- Huls G, Chitu DA, Havelange V, et al; Dutch-Belgian Hemato-Oncology Cooperative Group (HOVON). Azacitidine maintenance after intensive chemotherapy improves DFS in older AML patients. Blood. 2019;133(13):1457-1464. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-879866
- Granfeldt Østgård LS, Medeiros BC, Sengeløv H, et al. Epidemiology and clinical significance of secondary and therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia: a national population-based cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(31):3641-3649. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0890
- Kolitz JE, Strickland SA, Cortes JE, et al. Consolidation outcomes in CPX-351 versus cytarabine/daunorubicin-treated older patients with high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(3):631-640. doi:10.1080/1042819.2019.1688320
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Cortes JE, et al. CPX-351 (cytarabine and daunorubicin) liposome for injection versus conventional cytarabine plus daunorubicin in older patients with newly diagnosed secondary acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(26):2684-2692. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6112
- Lindsley RC, Gibson CJ, Murdock HM, et al. Genetic characteristics and outcomes by mutation status in a phase 3 study of CPX-351 versus 7+3 in older adults with newly diagnosed, high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):15. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-124500
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Newell LF, et al. CPX-351 versus 7+3 cytarabine and daunorubicin chemotherapy in older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia: 5-year results of a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(7):e481-e491. doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00134-4
- Alharthy H, Alkaabba F, Williams M, et al. Outcomes of newly diagnosed therapy-related AML and AML with myelodysplasia-related changes treated with 7+3, hypomethylating agents with or without venetoclax and CPX-351: a retrospective cohort study. Blood. 2022;140(suppl 1):9025-9026. doi:10.1182/blood-2022-170688
- Schlenk RF. Acute myeloid leukemia: introduction to a series highlighting progress and ongoing challenges. Haematologica. 2023;108(2):306-307. doi:10.3324/haematol.2022.280803
- DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):617-629. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012971
- DiNardo CD, Wei AH. How I treat acute myeloid leukemia in the era of new drugs. Blood. 2020;135(2):85-96. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001239
- Huerga-Domínguez S, Villar S, Prósper F, Alfonso-Piérola A. Updates on the management of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4756. doi:10.3390/cancers14194756
- Ferrara F, Barosi G, Venditti A, et al. Consensus-based definition of unfitness to intensive and non-intensive chemotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia: a project of SIE, SIES and GITMO group on a new tool for therapy decision making. Leukemia. 2013;27(5):997-999. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.303
- Tallman MS, Wang ES, Altman JK, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17(6):721-749. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2019.0028
- Burd A, Levine RL, Ruppert AS, et al. Precision medicine treatment in acute myeloid leukemia using prospective genomic profiling: feasibility and preliminary efficacy of the Beat AML Master Trial. Nat Med. 2020;26(12):1852-1858. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1089-8
- Sekeres MA, Guyatt G, Abel G, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for treating newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in older adults. Blood Adv. 2020;4(15):3528-3549. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001920
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345-1377. doi:10.1182/blood.2022016867
- Wei AH, Montesinos P, Ivanov V, et al. Venetoclax plus LDAC for newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: a phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial. Blood. 2020;135(24):2137-2145. doi:10.1182/blood.2020004856
- Amadori S, Suciu S, Selleslag D, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin versus best supportive care in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy: results of the randomized phase III EORTC-GIMEMA AML-19 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(9):972-979. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0060
- Cortes JE, Heidel FH, Hellmann A, et al. Randomized comparison of low dose cytarabine with or without glasdegib in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2019;33(2):379-389. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0312-9
- Montesinos P, Recher C, Vives S, et al. Ivosidenib and azacitidine in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(16):1519-1531. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2117344
- Wang ES, Montesinos P, Minden MD, et al. Phase 3 trial of gilteritinib plus azacitidine vs azacitidine for newly diagnosed FLT3mut+ AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Blood. 2022;140(17):1845-1857. doi:10.1182/blood.2021014586
- Wei AH, Döhner H, Pocock C, et al; QUAZAR AML-001 Trial Investigators. Oral azacitidine maintenance therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(26):2526-2537. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004444
- Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, et al. Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1728-1740. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1902688
- Konopleva MY, Röllig C, Cavenagh J, et al. Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: results of the MIRROS trial. Blood Adv. 2022;6(14):4147-4156. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006303
- Pollyea DA, DiNardo CD, Arellano ML, et al. Impact of venetoclax and azacitidine in treatment-naïve patients with acute myeloid leukemia and IDH1/2 mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(13):2753-2761. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3467
- Russell-Smith TA, Gurskyte L, Muresan B, et al. Efficacy of non-intensive therapies approved for relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic literature review. Future Oncol. 2022;18(16):2029-2039. doi:10.2217/fon-2021-1355
- Huls G, Chitu DA, Havelange V, et al; Dutch-Belgian Hemato-Oncology Cooperative Group (HOVON). Azacitidine maintenance after intensive chemotherapy improves DFS in older AML patients. Blood. 2019;133(13):1457-1464. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-10-879866
- Granfeldt Østgård LS, Medeiros BC, Sengeløv H, et al. Epidemiology and clinical significance of secondary and therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia: a national population-based cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(31):3641-3649. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0890
- Kolitz JE, Strickland SA, Cortes JE, et al. Consolidation outcomes in CPX-351 versus cytarabine/daunorubicin-treated older patients with high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(3):631-640. doi:10.1080/1042819.2019.1688320
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Cortes JE, et al. CPX-351 (cytarabine and daunorubicin) liposome for injection versus conventional cytarabine plus daunorubicin in older patients with newly diagnosed secondary acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(26):2684-2692. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6112
- Lindsley RC, Gibson CJ, Murdock HM, et al. Genetic characteristics and outcomes by mutation status in a phase 3 study of CPX-351 versus 7+3 in older adults with newly diagnosed, high-risk/secondary acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):15. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-124500
- Lancet JE, Uy GL, Newell LF, et al. CPX-351 versus 7+3 cytarabine and daunorubicin chemotherapy in older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia: 5-year results of a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(7):e481-e491. doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00134-4
- Alharthy H, Alkaabba F, Williams M, et al. Outcomes of newly diagnosed therapy-related AML and AML with myelodysplasia-related changes treated with 7+3, hypomethylating agents with or without venetoclax and CPX-351: a retrospective cohort study. Blood. 2022;140(suppl 1):9025-9026. doi:10.1182/blood-2022-170688
NORD: Making Progress Through Collaboration
While people living with rare cancers continue to face daunting obstacles, progress is being made, and there are reasons to hope for a better future. Advances in genomic testing and precision medicine provide increasing evidence that rare cancers can be more efficiently and effectively diagnosed and treated. Genomic tests examine tumor DNA to identify mutations that are unique to an individual’s cancer. This genetic information enables a more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment approach. Jim Palma, Co-Lead of the NORD Rare Cancer Coalition, said “There is promise for rare cancer patients due to increased legislative efforts to cover the costs of genomic testing coupled by an increase in FDA approvals for targeted and tissue agnostic therapies.”
In 2019, the National Cancer Institute established MyPART, a vast pediatric and adult rare tumor network that aims to bolster patient involvement in research and develop effective therapies through tumor sample collection, shared data, shared samples, new methods to test treatments, and new trial designs. In 2022, MyPART welcomed NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition as an advocacy partner.
Meanwhile, advocacy organizations are giving rare cancer a rising voice. NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition unites rare cancer patient advocacy organizations and helps them drive progress together. The coalition promotes research and awareness through its annual Rare Cancer Day (September 30) campaign. Additionally, NORD has produced over 22 continuing medical education modules on rare cancers in collaboration with PlatformQ Health, providing updates on new therapies and treatment approaches. NORD also offers rare disease reports and educational videos on rare cancers, sessions inclusive of rare cancer topics at the annual NORD Summit, and a quarterly e-newsletter, “Caring for Rare” for healthcare professionals. Please visit us at rarediseases.org to access these resources.
Much work on rare cancers remains to be done, but the progress over recent years points to better outcomes moving forward. We are grateful for the work you do and your dedication to your patients, including those with rare cancers and other rare conditions. We hope you will find the information in this special issue useful for your clinical practice.
– Katie Kowalski, MPH
Associate Director of Education
National Organization for Rare Disorders
- About Rare Cancers. National Cancer Institute. Posted February 27, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2023. http://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/about-rare-cancers
- Gatta G, Capocaccia R, Botta L, et al. Burden and centralized treatment in Europe of rare tumours: Results of RARECAREnet-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017,18(8):1022–1039. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30445-X
While people living with rare cancers continue to face daunting obstacles, progress is being made, and there are reasons to hope for a better future. Advances in genomic testing and precision medicine provide increasing evidence that rare cancers can be more efficiently and effectively diagnosed and treated. Genomic tests examine tumor DNA to identify mutations that are unique to an individual’s cancer. This genetic information enables a more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment approach. Jim Palma, Co-Lead of the NORD Rare Cancer Coalition, said “There is promise for rare cancer patients due to increased legislative efforts to cover the costs of genomic testing coupled by an increase in FDA approvals for targeted and tissue agnostic therapies.”
In 2019, the National Cancer Institute established MyPART, a vast pediatric and adult rare tumor network that aims to bolster patient involvement in research and develop effective therapies through tumor sample collection, shared data, shared samples, new methods to test treatments, and new trial designs. In 2022, MyPART welcomed NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition as an advocacy partner.
Meanwhile, advocacy organizations are giving rare cancer a rising voice. NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition unites rare cancer patient advocacy organizations and helps them drive progress together. The coalition promotes research and awareness through its annual Rare Cancer Day (September 30) campaign. Additionally, NORD has produced over 22 continuing medical education modules on rare cancers in collaboration with PlatformQ Health, providing updates on new therapies and treatment approaches. NORD also offers rare disease reports and educational videos on rare cancers, sessions inclusive of rare cancer topics at the annual NORD Summit, and a quarterly e-newsletter, “Caring for Rare” for healthcare professionals. Please visit us at rarediseases.org to access these resources.
Much work on rare cancers remains to be done, but the progress over recent years points to better outcomes moving forward. We are grateful for the work you do and your dedication to your patients, including those with rare cancers and other rare conditions. We hope you will find the information in this special issue useful for your clinical practice.
– Katie Kowalski, MPH
Associate Director of Education
National Organization for Rare Disorders
While people living with rare cancers continue to face daunting obstacles, progress is being made, and there are reasons to hope for a better future. Advances in genomic testing and precision medicine provide increasing evidence that rare cancers can be more efficiently and effectively diagnosed and treated. Genomic tests examine tumor DNA to identify mutations that are unique to an individual’s cancer. This genetic information enables a more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment approach. Jim Palma, Co-Lead of the NORD Rare Cancer Coalition, said “There is promise for rare cancer patients due to increased legislative efforts to cover the costs of genomic testing coupled by an increase in FDA approvals for targeted and tissue agnostic therapies.”
In 2019, the National Cancer Institute established MyPART, a vast pediatric and adult rare tumor network that aims to bolster patient involvement in research and develop effective therapies through tumor sample collection, shared data, shared samples, new methods to test treatments, and new trial designs. In 2022, MyPART welcomed NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition as an advocacy partner.
Meanwhile, advocacy organizations are giving rare cancer a rising voice. NORD’s Rare Cancer Coalition unites rare cancer patient advocacy organizations and helps them drive progress together. The coalition promotes research and awareness through its annual Rare Cancer Day (September 30) campaign. Additionally, NORD has produced over 22 continuing medical education modules on rare cancers in collaboration with PlatformQ Health, providing updates on new therapies and treatment approaches. NORD also offers rare disease reports and educational videos on rare cancers, sessions inclusive of rare cancer topics at the annual NORD Summit, and a quarterly e-newsletter, “Caring for Rare” for healthcare professionals. Please visit us at rarediseases.org to access these resources.
Much work on rare cancers remains to be done, but the progress over recent years points to better outcomes moving forward. We are grateful for the work you do and your dedication to your patients, including those with rare cancers and other rare conditions. We hope you will find the information in this special issue useful for your clinical practice.
– Katie Kowalski, MPH
Associate Director of Education
National Organization for Rare Disorders
- About Rare Cancers. National Cancer Institute. Posted February 27, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2023. http://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/about-rare-cancers
- Gatta G, Capocaccia R, Botta L, et al. Burden and centralized treatment in Europe of rare tumours: Results of RARECAREnet-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017,18(8):1022–1039. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30445-X
- About Rare Cancers. National Cancer Institute. Posted February 27, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2023. http://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/about-rare-cancers
- Gatta G, Capocaccia R, Botta L, et al. Burden and centralized treatment in Europe of rare tumours: Results of RARECAREnet-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017,18(8):1022–1039. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30445-X
2023 Rare Diseases Report: Cancers
This edition of Rare Diseases Report: Cancers highlights the latest breakthroughs and remaining unmet needs in the management of rare cancers. In addition to celebrating the great progress that has been made in recent years, we also discuss new challenges, such as how the healthcare system can prepare to manage the growing number of rare cancer survivors who are living longer due to improvements in disease management.
INTRODUCTION
NORD: Making Progress Through Collaboration
By Katie Kowalski, MPH
IN THIS ISSUE
The Complex Challenge of Survival After HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer
By Vlad C. Sandulache, MD, PhD
Progress in Ovarian Cancer: Discovery of Fallopian Tube Involvement
By Ronny Drapkin, MD, PhD
An Evolving Understanding of Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung
By Rajwanth Veluswamy, MD, MSCR
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Reflecting on 2 Decades of Clinical Advancements
By Jason K. Sicklick, MD, FACS
Progress in Treating Testicular Cancer
By Liang Cheng, MD
Strategies to Improve Long-Term Outcomes in Younger Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma
By Ann LaCasce, MD, MMSc
Targeted Therapies in Younger and Older Patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma
By Reem Karmali, MD, MS
Advances in Management of Relapsed/Refractory Hairy Cell Leukemia
By Robert J. Kreitman, MD
Treatment Needs of Older Adults With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
By Harry Erba, MD, PhD
Progress in Management of Advanced Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Children
By Susan Colace, MD, MSCI
This edition of Rare Diseases Report: Cancers highlights the latest breakthroughs and remaining unmet needs in the management of rare cancers. In addition to celebrating the great progress that has been made in recent years, we also discuss new challenges, such as how the healthcare system can prepare to manage the growing number of rare cancer survivors who are living longer due to improvements in disease management.
INTRODUCTION
NORD: Making Progress Through Collaboration
By Katie Kowalski, MPH
IN THIS ISSUE
The Complex Challenge of Survival After HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer
By Vlad C. Sandulache, MD, PhD
Progress in Ovarian Cancer: Discovery of Fallopian Tube Involvement
By Ronny Drapkin, MD, PhD
An Evolving Understanding of Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung
By Rajwanth Veluswamy, MD, MSCR
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Reflecting on 2 Decades of Clinical Advancements
By Jason K. Sicklick, MD, FACS
Progress in Treating Testicular Cancer
By Liang Cheng, MD
Strategies to Improve Long-Term Outcomes in Younger Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma
By Ann LaCasce, MD, MMSc
Targeted Therapies in Younger and Older Patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma
By Reem Karmali, MD, MS
Advances in Management of Relapsed/Refractory Hairy Cell Leukemia
By Robert J. Kreitman, MD
Treatment Needs of Older Adults With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
By Harry Erba, MD, PhD
Progress in Management of Advanced Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Children
By Susan Colace, MD, MSCI
This edition of Rare Diseases Report: Cancers highlights the latest breakthroughs and remaining unmet needs in the management of rare cancers. In addition to celebrating the great progress that has been made in recent years, we also discuss new challenges, such as how the healthcare system can prepare to manage the growing number of rare cancer survivors who are living longer due to improvements in disease management.
INTRODUCTION
NORD: Making Progress Through Collaboration
By Katie Kowalski, MPH
IN THIS ISSUE
The Complex Challenge of Survival After HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer
By Vlad C. Sandulache, MD, PhD
Progress in Ovarian Cancer: Discovery of Fallopian Tube Involvement
By Ronny Drapkin, MD, PhD
An Evolving Understanding of Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung
By Rajwanth Veluswamy, MD, MSCR
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Reflecting on 2 Decades of Clinical Advancements
By Jason K. Sicklick, MD, FACS
Progress in Treating Testicular Cancer
By Liang Cheng, MD
Strategies to Improve Long-Term Outcomes in Younger Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma
By Ann LaCasce, MD, MMSc
Targeted Therapies in Younger and Older Patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma
By Reem Karmali, MD, MS
Advances in Management of Relapsed/Refractory Hairy Cell Leukemia
By Robert J. Kreitman, MD
Treatment Needs of Older Adults With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
By Harry Erba, MD, PhD
Progress in Management of Advanced Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Children
By Susan Colace, MD, MSCI
Multiprong strategy makes clinical trials less White
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
CBSM phone app eases anxiety, depression in cancer patients
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
Huge underuse of germline testing for cancer patients
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
DEI training gives oncology fellows more confidence
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2023
Drugmakers are abandoning cheap generics, and now U.S. cancer patients can’t get meds
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Gilteritinib maintenance reduces relapse in MRD+ AML
The research was presented at the European Hematology Association Hybrid Congress 2023.
For the study, AML patients with the most common form of mutation in the proto-oncogene fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), known as the internal tandem duplication (ITD), were randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib or placebo.
The trial did not meet its primary endpoint, as there was no significant difference in relapse-free survival (RFS) between those assigned to the active drug and those given placebo, and there was no difference in overall survival rates.
However, subgroup analysis revealed that FLT3/ITD AML patients who were MRD+ after transplant, which represented approximately half of the participants, experienced a significant 48% improvement in RFS with gilteritinib versus placebo, while no benefit was seen in MRD– patients.
While acknowledging that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, presenter Mark J. Levis, MD, PhD, program leader, hematologic malignancies and bone marrow transplant program, Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, said it was nevertheless “a successful study.”
“We learned how to use these drugs and in whom,” he continued, adding: “No, not everybody needs and should get a FLT3 inhibitor post-transplant, but we can use this [MRD] assay to identify who.”
Consequently, Dr. Levis believes that gilteritinib “should be a standard of care for those who are MRD positive,” although the decision to use it “should be balanced against the potential for toxicity,” compared with not adding an additional treatment after HCT.
He told a press conference that “we’re going to certainly make sure that patients who are MRD positive get [gilteritinib],” although the MRD negative patients “are going to be more questionable,” especially because the assay that they used in the study is not “perfect.”
Dr. Levis also suggested that the trial did not meet its endpoint because of regional differences in the clinical practice, such as in the number of treatment cycles prior to HCT, the time to transplant, and the previous use of a FLT3 inhibitor, all of which may have skewed the findings.
“Everybody in the world is convinced that they’re the best transplanter,” he said, and yet “they all do it differently, and the heterogeneity is astounding.”
He added: “If we’d restricted everybody [to a] pretransplant regimen, I suspect we would have had a different result than what we’re getting here, but this is releasing the drug into the world and saying: ‘Here, transplant however you want, however it’s practiced in the real world. Tell us how this works.’ ”
Approached for comment, Claudio Brunstein, MD, PhD, vice-chair of the department of hematology and oncology in the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, said that while there was “some disappointment” with the results, he was “not surprised” that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint.
He said in an interview that the patient population was not of “high enough risk” to demonstrate an overall difference between gilteritinib and placebo, although he conceded that it is “hard to get to high-risk patients in a timely way” and so conduct a trial with them.
As to the notion that variations in clinical practice could have been responsible, Dr. Brunstein pointed out that it was a randomized trial, so the issue would have applied equally to both sides.
He nevertheless believes that it is “a very important study,” and “just the fact that it was done in the context of a number of drugs coming and being approved by the [U.S. Food and Drug Administration] in AML is quite remarkable.”
This is especially the case given that “many centers are already using [gilteritinib] as off-label maintenance therapy.”
Dr. Brunstein added that it is “good news” that the drug was effective in MRD+ patients, as it shows “you can overcome that with maintenance therapy rather than keeping giving more and more chemotherapy, especially as there are patients you’re worried about giving more intensive chemotherapy to make them MRD negative.”
He pointed out, however, that the assay used in the trial was “research grade” and very sensitive to MRD and “is not available everywhere, so there is an adjustment that the community will have to do to in order to apply this data.”
“But for those who are more obviously MRD positive with less sensitive assays, gilteritinib is already something that can be used,” Dr. Brunstein said.
Presenting the findings, Dr. Levis stated: “We all know that patients with FLT3/ITD AML have a high risk of relapse and are routinely referred for transplant. And we know that the detection of measurable residual disease pretransplant is highly predictive of outcome post-transplant.”
He continued that FLT3 inhibitors are “routinely given as post-transplant maintenance ... based on some prior trials, mostly with sorafenib.”
“But uncertainty exists as to the broad applicability of these trials,” Dr. Levis said. Moreover, the use of sorafenib in this context is “off label and can be difficult to tolerate,” and “we know that most patients are cured with allogeneic transplant alone.”
Gilteritinib is already known to be well tolerated as a monotherapy, and was approved by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with FLT3 mutation–positive relapsed or refractory AML in 2018.
The investigators therefore examined whether it would be beneficial as a post-HCT maintenance therapy in FLT3-ITD AML. Patients were required to be in morphologic remission after one or two courses of induction therapy, with Dr. Levis underlining: “We did not allow patients who had been salvaged onto the study.”
They subsequently had a marrow aspirate sample taken for MRD analysis before undergoing allogeneic transplant, with any conditioning regimen, donor, or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis allowed.
Between 30 and 90 days later, patients with successful engraftment who were able to take oral medication were then randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either gilteritinib or placebo.
Dr. Levis showed that, among 620 patients screened at 110 centers in 16 countries, 356 were randomized between Aug. 15, 2017, and July 8, 2020. The median age was 53 years, and 49% of gilteritinib patients and 48% of those given placebo were female.
He noted that there was a “fairly even global distribution” of patients from North America, Europe, and the Asia/Pacific region, and that 60% of patients underwent a myeloablative conditioning regimen. Approximately the same proportion had received an FLT3 inhibitor prior to HCT.
MRD positivity, assessed at a cell count of ≥ 10-6, was observed pre-HCT in 47% of patients in both treatment groups, and in 50% of gilteritinib patients and 51% of placebo patients at both pre- and post-transplant assessments.
The treatment regimen was completed by 52.8% of patients assigned to gilteritinib and 53.9% in the placebo arm. Dr. Levis said that 18.5% and 20.3% of patients, respectively, experienced a grade 3/4 treatment emergent acute GVHD event, while 32.6% and 21.5%, respectively, had a grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent infection.
He noted that “adverse events were clearly more common in the gilteritinib arm and often led to either dose reduction or interruption, or withdrawal of treatment.”
The most common grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent adverse event was a decrease in neutrophil count, seen in 24.7% of gilteritinib patients and 7.9% of those given placebo, followed by reduced platelet count, in 15.2% and 5.6%, respectively, and anemia, in 6.2% and 1.7%, respectively.
Turning to the efficacy outcomes, Dr. Levis reported that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, with no significant difference in RFS between the gilteritinib and placebo arms, at a hazard ratio of 0.679 (P = .0518). There was also no significant difference in the key secondary objective of overall survival, at a hazard ratio of 0.846 (P = .4394).
However, Dr. Levis noted that there was a “clear difference in the benefit of gilteritinib by region,” and, “at every level,” MRD predicted a benefit from gilteritinib, which he said was a “big surprise” and “really leapt out in the subgroup analysis.”
He explained that the researchers used a modified version of a two-step assay that has been used in previous studies, and was able to detect MRD at a sensitivity of approximately 1x10-6. “In our study, 98% of participants had samples pre- and post-[transplant].”
Regardless of treatment arm, MRD positivity measured at that sensitivity was associated with a significant reduction in overall survival, at a hazard ratio versus MRD– status of 0.514 (P = .0025).
When stratifying the patients by MRD status, the researchers found that, among MRD+ participants, gilteritinib was associated with a significant improvement in RFS, at a hazard ratio versus placebo of 0.515 (P = .0065), while there was no significant difference in MRD– patients.
Stratifying the patients by their conditioning regimen prior to HCT also revealed differences, with those undergoing myeloablative conditioning having significantly greater overall survival than those who underwent reduced-intensity conditioning, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.529 (P = .0027).
Dr. Levis said there is “no surprise there,” and the result could reflect the selection of fitter, younger patients to undergo the more intensive regimen.
He then showed that MRD+ patients who had undergone myeloablative conditioning had better overall survival with gilteritinib than placebo, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.418 (P = .0087). Again, the difference disappeared when looking at MRD– patients.
“So conditioning doesn’t help you in the setting of MRD,” Dr. Levis said.
Finally, he took a deeper dive into the regional differences in outcomes, noting that patients in the Asia/Pacific region, where gilteritinib showed no benefit over placebo, “were 10 years younger” than those in other regions, “tended to get myeloablative conditioning, and hardly ever used FLT3 inhibitors.”
In contrast, North American patients, who experienced a significant gilteritinib benefit in terms of RFS, underwent HCT an average of 26 days earlier than those elsewhere, and received fewer courses of chemotherapy pre-HCT. Moreover, 93.5% received an FLT3 inhibitor pretransplant.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma Global Development. Dr. Levis declares relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Jazz, Menarini, Pfizer, Sumitomo-Dainippon, Syndax, Takeda. Dr. Brunstein declares no relevant relationships.
The research was presented at the European Hematology Association Hybrid Congress 2023.
For the study, AML patients with the most common form of mutation in the proto-oncogene fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), known as the internal tandem duplication (ITD), were randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib or placebo.
The trial did not meet its primary endpoint, as there was no significant difference in relapse-free survival (RFS) between those assigned to the active drug and those given placebo, and there was no difference in overall survival rates.
However, subgroup analysis revealed that FLT3/ITD AML patients who were MRD+ after transplant, which represented approximately half of the participants, experienced a significant 48% improvement in RFS with gilteritinib versus placebo, while no benefit was seen in MRD– patients.
While acknowledging that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, presenter Mark J. Levis, MD, PhD, program leader, hematologic malignancies and bone marrow transplant program, Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, said it was nevertheless “a successful study.”
“We learned how to use these drugs and in whom,” he continued, adding: “No, not everybody needs and should get a FLT3 inhibitor post-transplant, but we can use this [MRD] assay to identify who.”
Consequently, Dr. Levis believes that gilteritinib “should be a standard of care for those who are MRD positive,” although the decision to use it “should be balanced against the potential for toxicity,” compared with not adding an additional treatment after HCT.
He told a press conference that “we’re going to certainly make sure that patients who are MRD positive get [gilteritinib],” although the MRD negative patients “are going to be more questionable,” especially because the assay that they used in the study is not “perfect.”
Dr. Levis also suggested that the trial did not meet its endpoint because of regional differences in the clinical practice, such as in the number of treatment cycles prior to HCT, the time to transplant, and the previous use of a FLT3 inhibitor, all of which may have skewed the findings.
“Everybody in the world is convinced that they’re the best transplanter,” he said, and yet “they all do it differently, and the heterogeneity is astounding.”
He added: “If we’d restricted everybody [to a] pretransplant regimen, I suspect we would have had a different result than what we’re getting here, but this is releasing the drug into the world and saying: ‘Here, transplant however you want, however it’s practiced in the real world. Tell us how this works.’ ”
Approached for comment, Claudio Brunstein, MD, PhD, vice-chair of the department of hematology and oncology in the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, said that while there was “some disappointment” with the results, he was “not surprised” that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint.
He said in an interview that the patient population was not of “high enough risk” to demonstrate an overall difference between gilteritinib and placebo, although he conceded that it is “hard to get to high-risk patients in a timely way” and so conduct a trial with them.
As to the notion that variations in clinical practice could have been responsible, Dr. Brunstein pointed out that it was a randomized trial, so the issue would have applied equally to both sides.
He nevertheless believes that it is “a very important study,” and “just the fact that it was done in the context of a number of drugs coming and being approved by the [U.S. Food and Drug Administration] in AML is quite remarkable.”
This is especially the case given that “many centers are already using [gilteritinib] as off-label maintenance therapy.”
Dr. Brunstein added that it is “good news” that the drug was effective in MRD+ patients, as it shows “you can overcome that with maintenance therapy rather than keeping giving more and more chemotherapy, especially as there are patients you’re worried about giving more intensive chemotherapy to make them MRD negative.”
He pointed out, however, that the assay used in the trial was “research grade” and very sensitive to MRD and “is not available everywhere, so there is an adjustment that the community will have to do to in order to apply this data.”
“But for those who are more obviously MRD positive with less sensitive assays, gilteritinib is already something that can be used,” Dr. Brunstein said.
Presenting the findings, Dr. Levis stated: “We all know that patients with FLT3/ITD AML have a high risk of relapse and are routinely referred for transplant. And we know that the detection of measurable residual disease pretransplant is highly predictive of outcome post-transplant.”
He continued that FLT3 inhibitors are “routinely given as post-transplant maintenance ... based on some prior trials, mostly with sorafenib.”
“But uncertainty exists as to the broad applicability of these trials,” Dr. Levis said. Moreover, the use of sorafenib in this context is “off label and can be difficult to tolerate,” and “we know that most patients are cured with allogeneic transplant alone.”
Gilteritinib is already known to be well tolerated as a monotherapy, and was approved by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with FLT3 mutation–positive relapsed or refractory AML in 2018.
The investigators therefore examined whether it would be beneficial as a post-HCT maintenance therapy in FLT3-ITD AML. Patients were required to be in morphologic remission after one or two courses of induction therapy, with Dr. Levis underlining: “We did not allow patients who had been salvaged onto the study.”
They subsequently had a marrow aspirate sample taken for MRD analysis before undergoing allogeneic transplant, with any conditioning regimen, donor, or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis allowed.
Between 30 and 90 days later, patients with successful engraftment who were able to take oral medication were then randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either gilteritinib or placebo.
Dr. Levis showed that, among 620 patients screened at 110 centers in 16 countries, 356 were randomized between Aug. 15, 2017, and July 8, 2020. The median age was 53 years, and 49% of gilteritinib patients and 48% of those given placebo were female.
He noted that there was a “fairly even global distribution” of patients from North America, Europe, and the Asia/Pacific region, and that 60% of patients underwent a myeloablative conditioning regimen. Approximately the same proportion had received an FLT3 inhibitor prior to HCT.
MRD positivity, assessed at a cell count of ≥ 10-6, was observed pre-HCT in 47% of patients in both treatment groups, and in 50% of gilteritinib patients and 51% of placebo patients at both pre- and post-transplant assessments.
The treatment regimen was completed by 52.8% of patients assigned to gilteritinib and 53.9% in the placebo arm. Dr. Levis said that 18.5% and 20.3% of patients, respectively, experienced a grade 3/4 treatment emergent acute GVHD event, while 32.6% and 21.5%, respectively, had a grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent infection.
He noted that “adverse events were clearly more common in the gilteritinib arm and often led to either dose reduction or interruption, or withdrawal of treatment.”
The most common grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent adverse event was a decrease in neutrophil count, seen in 24.7% of gilteritinib patients and 7.9% of those given placebo, followed by reduced platelet count, in 15.2% and 5.6%, respectively, and anemia, in 6.2% and 1.7%, respectively.
Turning to the efficacy outcomes, Dr. Levis reported that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, with no significant difference in RFS between the gilteritinib and placebo arms, at a hazard ratio of 0.679 (P = .0518). There was also no significant difference in the key secondary objective of overall survival, at a hazard ratio of 0.846 (P = .4394).
However, Dr. Levis noted that there was a “clear difference in the benefit of gilteritinib by region,” and, “at every level,” MRD predicted a benefit from gilteritinib, which he said was a “big surprise” and “really leapt out in the subgroup analysis.”
He explained that the researchers used a modified version of a two-step assay that has been used in previous studies, and was able to detect MRD at a sensitivity of approximately 1x10-6. “In our study, 98% of participants had samples pre- and post-[transplant].”
Regardless of treatment arm, MRD positivity measured at that sensitivity was associated with a significant reduction in overall survival, at a hazard ratio versus MRD– status of 0.514 (P = .0025).
When stratifying the patients by MRD status, the researchers found that, among MRD+ participants, gilteritinib was associated with a significant improvement in RFS, at a hazard ratio versus placebo of 0.515 (P = .0065), while there was no significant difference in MRD– patients.
Stratifying the patients by their conditioning regimen prior to HCT also revealed differences, with those undergoing myeloablative conditioning having significantly greater overall survival than those who underwent reduced-intensity conditioning, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.529 (P = .0027).
Dr. Levis said there is “no surprise there,” and the result could reflect the selection of fitter, younger patients to undergo the more intensive regimen.
He then showed that MRD+ patients who had undergone myeloablative conditioning had better overall survival with gilteritinib than placebo, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.418 (P = .0087). Again, the difference disappeared when looking at MRD– patients.
“So conditioning doesn’t help you in the setting of MRD,” Dr. Levis said.
Finally, he took a deeper dive into the regional differences in outcomes, noting that patients in the Asia/Pacific region, where gilteritinib showed no benefit over placebo, “were 10 years younger” than those in other regions, “tended to get myeloablative conditioning, and hardly ever used FLT3 inhibitors.”
In contrast, North American patients, who experienced a significant gilteritinib benefit in terms of RFS, underwent HCT an average of 26 days earlier than those elsewhere, and received fewer courses of chemotherapy pre-HCT. Moreover, 93.5% received an FLT3 inhibitor pretransplant.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma Global Development. Dr. Levis declares relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Jazz, Menarini, Pfizer, Sumitomo-Dainippon, Syndax, Takeda. Dr. Brunstein declares no relevant relationships.
The research was presented at the European Hematology Association Hybrid Congress 2023.
For the study, AML patients with the most common form of mutation in the proto-oncogene fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), known as the internal tandem duplication (ITD), were randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either the FLT3 inhibitor gilteritinib or placebo.
The trial did not meet its primary endpoint, as there was no significant difference in relapse-free survival (RFS) between those assigned to the active drug and those given placebo, and there was no difference in overall survival rates.
However, subgroup analysis revealed that FLT3/ITD AML patients who were MRD+ after transplant, which represented approximately half of the participants, experienced a significant 48% improvement in RFS with gilteritinib versus placebo, while no benefit was seen in MRD– patients.
While acknowledging that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, presenter Mark J. Levis, MD, PhD, program leader, hematologic malignancies and bone marrow transplant program, Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, said it was nevertheless “a successful study.”
“We learned how to use these drugs and in whom,” he continued, adding: “No, not everybody needs and should get a FLT3 inhibitor post-transplant, but we can use this [MRD] assay to identify who.”
Consequently, Dr. Levis believes that gilteritinib “should be a standard of care for those who are MRD positive,” although the decision to use it “should be balanced against the potential for toxicity,” compared with not adding an additional treatment after HCT.
He told a press conference that “we’re going to certainly make sure that patients who are MRD positive get [gilteritinib],” although the MRD negative patients “are going to be more questionable,” especially because the assay that they used in the study is not “perfect.”
Dr. Levis also suggested that the trial did not meet its endpoint because of regional differences in the clinical practice, such as in the number of treatment cycles prior to HCT, the time to transplant, and the previous use of a FLT3 inhibitor, all of which may have skewed the findings.
“Everybody in the world is convinced that they’re the best transplanter,” he said, and yet “they all do it differently, and the heterogeneity is astounding.”
He added: “If we’d restricted everybody [to a] pretransplant regimen, I suspect we would have had a different result than what we’re getting here, but this is releasing the drug into the world and saying: ‘Here, transplant however you want, however it’s practiced in the real world. Tell us how this works.’ ”
Approached for comment, Claudio Brunstein, MD, PhD, vice-chair of the department of hematology and oncology in the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, said that while there was “some disappointment” with the results, he was “not surprised” that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint.
He said in an interview that the patient population was not of “high enough risk” to demonstrate an overall difference between gilteritinib and placebo, although he conceded that it is “hard to get to high-risk patients in a timely way” and so conduct a trial with them.
As to the notion that variations in clinical practice could have been responsible, Dr. Brunstein pointed out that it was a randomized trial, so the issue would have applied equally to both sides.
He nevertheless believes that it is “a very important study,” and “just the fact that it was done in the context of a number of drugs coming and being approved by the [U.S. Food and Drug Administration] in AML is quite remarkable.”
This is especially the case given that “many centers are already using [gilteritinib] as off-label maintenance therapy.”
Dr. Brunstein added that it is “good news” that the drug was effective in MRD+ patients, as it shows “you can overcome that with maintenance therapy rather than keeping giving more and more chemotherapy, especially as there are patients you’re worried about giving more intensive chemotherapy to make them MRD negative.”
He pointed out, however, that the assay used in the trial was “research grade” and very sensitive to MRD and “is not available everywhere, so there is an adjustment that the community will have to do to in order to apply this data.”
“But for those who are more obviously MRD positive with less sensitive assays, gilteritinib is already something that can be used,” Dr. Brunstein said.
Presenting the findings, Dr. Levis stated: “We all know that patients with FLT3/ITD AML have a high risk of relapse and are routinely referred for transplant. And we know that the detection of measurable residual disease pretransplant is highly predictive of outcome post-transplant.”
He continued that FLT3 inhibitors are “routinely given as post-transplant maintenance ... based on some prior trials, mostly with sorafenib.”
“But uncertainty exists as to the broad applicability of these trials,” Dr. Levis said. Moreover, the use of sorafenib in this context is “off label and can be difficult to tolerate,” and “we know that most patients are cured with allogeneic transplant alone.”
Gilteritinib is already known to be well tolerated as a monotherapy, and was approved by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with FLT3 mutation–positive relapsed or refractory AML in 2018.
The investigators therefore examined whether it would be beneficial as a post-HCT maintenance therapy in FLT3-ITD AML. Patients were required to be in morphologic remission after one or two courses of induction therapy, with Dr. Levis underlining: “We did not allow patients who had been salvaged onto the study.”
They subsequently had a marrow aspirate sample taken for MRD analysis before undergoing allogeneic transplant, with any conditioning regimen, donor, or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis allowed.
Between 30 and 90 days later, patients with successful engraftment who were able to take oral medication were then randomized to 24 months of maintenance therapy with either gilteritinib or placebo.
Dr. Levis showed that, among 620 patients screened at 110 centers in 16 countries, 356 were randomized between Aug. 15, 2017, and July 8, 2020. The median age was 53 years, and 49% of gilteritinib patients and 48% of those given placebo were female.
He noted that there was a “fairly even global distribution” of patients from North America, Europe, and the Asia/Pacific region, and that 60% of patients underwent a myeloablative conditioning regimen. Approximately the same proportion had received an FLT3 inhibitor prior to HCT.
MRD positivity, assessed at a cell count of ≥ 10-6, was observed pre-HCT in 47% of patients in both treatment groups, and in 50% of gilteritinib patients and 51% of placebo patients at both pre- and post-transplant assessments.
The treatment regimen was completed by 52.8% of patients assigned to gilteritinib and 53.9% in the placebo arm. Dr. Levis said that 18.5% and 20.3% of patients, respectively, experienced a grade 3/4 treatment emergent acute GVHD event, while 32.6% and 21.5%, respectively, had a grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent infection.
He noted that “adverse events were clearly more common in the gilteritinib arm and often led to either dose reduction or interruption, or withdrawal of treatment.”
The most common grade ≥ 3 treatment emergent adverse event was a decrease in neutrophil count, seen in 24.7% of gilteritinib patients and 7.9% of those given placebo, followed by reduced platelet count, in 15.2% and 5.6%, respectively, and anemia, in 6.2% and 1.7%, respectively.
Turning to the efficacy outcomes, Dr. Levis reported that the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, with no significant difference in RFS between the gilteritinib and placebo arms, at a hazard ratio of 0.679 (P = .0518). There was also no significant difference in the key secondary objective of overall survival, at a hazard ratio of 0.846 (P = .4394).
However, Dr. Levis noted that there was a “clear difference in the benefit of gilteritinib by region,” and, “at every level,” MRD predicted a benefit from gilteritinib, which he said was a “big surprise” and “really leapt out in the subgroup analysis.”
He explained that the researchers used a modified version of a two-step assay that has been used in previous studies, and was able to detect MRD at a sensitivity of approximately 1x10-6. “In our study, 98% of participants had samples pre- and post-[transplant].”
Regardless of treatment arm, MRD positivity measured at that sensitivity was associated with a significant reduction in overall survival, at a hazard ratio versus MRD– status of 0.514 (P = .0025).
When stratifying the patients by MRD status, the researchers found that, among MRD+ participants, gilteritinib was associated with a significant improvement in RFS, at a hazard ratio versus placebo of 0.515 (P = .0065), while there was no significant difference in MRD– patients.
Stratifying the patients by their conditioning regimen prior to HCT also revealed differences, with those undergoing myeloablative conditioning having significantly greater overall survival than those who underwent reduced-intensity conditioning, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.529 (P = .0027).
Dr. Levis said there is “no surprise there,” and the result could reflect the selection of fitter, younger patients to undergo the more intensive regimen.
He then showed that MRD+ patients who had undergone myeloablative conditioning had better overall survival with gilteritinib than placebo, at a hazard ratio for death of 0.418 (P = .0087). Again, the difference disappeared when looking at MRD– patients.
“So conditioning doesn’t help you in the setting of MRD,” Dr. Levis said.
Finally, he took a deeper dive into the regional differences in outcomes, noting that patients in the Asia/Pacific region, where gilteritinib showed no benefit over placebo, “were 10 years younger” than those in other regions, “tended to get myeloablative conditioning, and hardly ever used FLT3 inhibitors.”
In contrast, North American patients, who experienced a significant gilteritinib benefit in terms of RFS, underwent HCT an average of 26 days earlier than those elsewhere, and received fewer courses of chemotherapy pre-HCT. Moreover, 93.5% received an FLT3 inhibitor pretransplant.
The study was funded by Astellas Pharma Global Development. Dr. Levis declares relationships with Abbvie, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Jazz, Menarini, Pfizer, Sumitomo-Dainippon, Syndax, Takeda. Dr. Brunstein declares no relevant relationships.
AT EHA 2023