User login
Has the VA Fulfilled its Commitment to Trust and Healing?
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
The Role of High Reliability Organization Foundational Practices in Building a Culture of Safety
Increasing complexities within health care systems are significant impediments to the consistent delivery of safe and effective patient care. These impediments include an increase in specialization of care, staff shortages, burnout, poor coordination of services and access to care, as well as rising costs.1 High reliability organizations (HROs) provide safe, high-quality, and effective care in highly complex and risk-prone environments without causing harm or experiencing catastrophic events.2
Within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) operates the nation’s largest integrated health care system, providing care to > 9 million veterans. The VHA formally launched plans for an enterprise-wide HRO in February 2019. During the first year, 18 medical facilities comprised cohort1 of the journey to high reliability. Cohort 2 began in October 2020 and consisted of 54 facilities. Cohort 3 started in October 2021 with 67 facilities.3
Health care organizations seeking high reliability exercise a philosophy aimed at learning from errors and addressing system failures. High reliability is accomplished by implementing 5 principles: (1) sensitivity to operations (a heightened understanding of the current state of systems); (2) preoccupation with failure (striving to anticipate risks that might suggest a much larger system problem); (3) reluctance to simplify (avoiding making any assumptions regarding the causes of failures); (4) commitment to resilience (preparing for potential failures and bouncing back when they occur); and (5) deference to expertise (deferring to individuals with the skills and proficiency to make the best decisions).2 The VHA also recognized that a successful journey to high reliability—in addition to achieving a culture of safety—relies on the implementation of foundational HRO practices: leader rounding, visual management systems, safety forums, and safety huddles. This article describes an initiative for how these foundational practices were implemented in a large integrated health care system.
BACKGROUND
The VHA has focused on 4 foundational components as part of its enterprise activities and support structure to implement HRO principles and practices. These components were selected based on pilot activities that preceded the enterprise-wide effort, reviews of the literature, and expert consultation with both government and private sector health systems. To support the implementation of these practices, the VHA provided training, toolkits, HRO executive leader coaching, and peer-to-peer mentoring. As the VHA enters its fifth year seeking high reliability, we undertook an initiative to reflect on our own experiences and refine our practices based on an updated literature review.
As part of this enterprise-wide initiative, we conducted a literature review from 2018 to March 2023 seeking recent evidence describing the value of implementing the 4 foundational HRO practices to advance high reliability and improve patient safety. A 5-year period was used to ensure recency and value of evidence.
Eligible literature was identified in PubMed, PsycINFO, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ScienceDirect, Scopus, the Cochrane Library, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were peer-reviewed interdisciplinary documents(eg, publications, dissertations, conference proceedings, and grey literature) written in English. Search terms included high reliability organizations, foundational practices, and patient safety. Boolean operators (AND, OR) were also used in the search. The search resulted in a dearth of evidence that addressed implementation of all 4 foundational practices across a health care system. Retrieved evidence focused on the implementation of only 1 particular foundational practice in a specific health care setting. In addition to describing the formal processes for the implementation of each foundational HRO practice, a brief description of representative examples of strong practices within the VHA is provided.
To support the implementation of HROs, the VHA paired HRO executive leader coaches with select medical center directors and their leadership teams. Executive leader coaches also support an organization’s HRO Lead and HRO Champion. The HRO Lead coordinates and facilitates the implementation of HRO principles and practices in pursuit of no harm across an organization. The HRO Champion supports the same as the HRO Lead, but typically has a different specialty background. For example, if the HRO Lead has an administrative background, the HRO Champion would have a clinical background.
Coaching focuses heavily on supporting site-specific implementation and sustainment of the 4 HRO foundational practices. The aim is to accelerate change, build enduring capacity, foster a safety culture, and accelerate HRO maturity. To measure change, HRO executive leader coaches track the progress of their aligned VA medical centers (VAMCs) using the Organizational Learning Tool (OLT). This tool was developed to provide information such as a facility summary and relationships between a medical center director, HRO Lead, HRO Champion, and the executive leader coach (Figure 1). The OLT also serves as a structured process to measure leader coaching performance against mutually agreed upon objectives that ultimately contribute to enterprise outcomes. It also collects data on the progress in implementing foundational practices, strong practices, needs and gaps, and more (Figure 2). Data collected from facilities supported by HRO executive leader coaches on whether foundational practices are in place are briefly described.
Leader Rounding
Leader rounding for high reliability ensures effective, bidirectional communication and collaboration among all disciplines to improve patient safety. It is an essential feature of a robust patient safety culture and an important method for demonstrating leadership engagement with high reliability.4,5 These rounds are conducted by organizational leadership (eg, executive teams, department/service chiefs, or unit managers) and frontline staff from different areas. They are specifically focused on high reliability, patient and staff safety, and improvement efforts. The aim is to learn about daily challenges that may contribute to patient harm.4
Leader rounding has been found to be highly effective at improving leadership visibility across the organization. It enhances interaction and open communication with frontline staff, fostering leader-staff collaboration and shared decision-making,as well as promoting leadership understanding of operational, clinical, nonclinical (eg, administrative, nutrition services, or facilities management), and patient/family experience issues.4 Collaboration among team members fosters the delivery of more effective and efficient care, increases staff satisfaction, and improves employee retention.6 Leader rounding for high reliability significantly contributes to the breakdown of power barriers by giving team members voice and agency, ultimately leading to deeper engagement.7
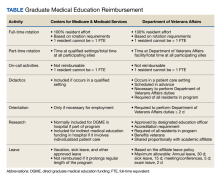
It is important that leader rounding for high reliability occurs as planned and when possible, scheduled in advance. This helps to avoid rounding at peak times when care activities are being performed.4,6 When scheduling conflicts arise, another leader should be sent to participate in rounds.4 Developing a list of questions in advance allows leadership to prepare messaging to share with staff as it relates to high reliability and patient safety (Table).4,6,8
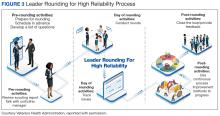
Closing the loop improves bidirectional communication and is critical to leader rounding for high reliability. Closed-loop communication and following up on and/or closing out issues raised during rounding empowers the sharing of information, which is critical for advancing a culture of safety.4,8 Enhanced feedback is also associated with greater workforce engagement, staff feeling more connected to quality improvement activities, and lower rates of employee burnout.7 It is important to recognize that senior leaders are not responsible for resolving all issues. If a team or manager can resolve concerns that are raised, this should be encouraged and supported. Maintaining accountability at the lowest level of the organization promotes principles and practices of high reliability (Figure 3).4,8
The VA Bedford Healthcare System created and implemented a strong practice for leader rounding for high reliability. This phased implementation involved creating an evidence-based process, deciding on an appropriate cadence, developing a tracking tool, and measuring impact to determine the overall effectiveness of leader rounding for high reliability.4
Visual Management Systems
A visual management system (VMS) displays clinical and operational performance aligned with HRO goals and practices. It is used to view and guide discussions between interdisciplinary teams during tiered safety huddles, leader rounds for high reliability, and frontline staff on the current status and safety trends in a particular area.8,9 A VMS is highly effective in creating an environment where all staff members, especially frontline workers, feel empowered to voice their concerns related to safety or to identify improvement opportunities.8,10 Increased leader engagement in patient safety and heightened transparency of information associated with the use of a VMS improves staff morale and professional satisfaction.10
A VMS may be a dry-erase or whiteboard display, paper-based display, or electronic status board.8 VMSs are usually located in or near work settings (eg, nurses’ station, staff break room, or conference room).8 Although they can take different forms and display several types of information, a VMS should be easy to update and meet the specific needs of a work area. In the VHA, a VMS displays: (1) essential information for staff members to effectively perform their work; (2) improvement project ideas; (3) current work in progress; (4) tracking of implemented improvement activities; (5) strong practices that have been effective; and (6) staff recognition for those who have enhanced patient safety, including the reporting of close calls and near misses.
The VHA uses the MESS (methods, equipment, staffing, and supplies) VMS format. This format empowers staff to identify whether proper procedures and practices are in place, essential equipment and supplies are readily available in the quantity needed, and appropriate staffing is on hand to provide safe, high-quality patient care.8 Colored magnets are used as visual cues in a stoplight classification system to identify low or no safety risks (green), at risk (yellow), or high risk (red). Green coded issues are addressed locally by a manager or supervisor. Yellow coded concerns require increased staff and leadership vigilance. Red coded issues indicate that patient care would be impacted that day and therefore need to be immediately escalated and addressed with senior leaders to mitigate the threat.4,11 Dayton VAMC successfully implemented a VMS, using both physical and electronic visual management boards. The Dayton VAMC VMS boards are closely tied to tiered safety huddles and leader rounding for high reliability.
Safety Forums
Safety forums are another foundational practice of VHA health care organizations seeking high reliability. Recurring monthly, safety forums focus on reinforcing HRO principles and practices, safety programs, the importance and appreciation of reporting, and just culture. The emphasis on just culture reminds staff that adverse events in the organization are viewed as valuable learning opportunities to understand the factors leading to the situation as opposed to immediately assigning blame.12
Psychological safety is another important focus. When individuals feel psychologically safe, they are more likely to voice concerns and act without fear of reprisal, which supports a culture of safety.13 Safety forums are open to all members of the health care organization, including both clinical and nonclinical staff. Forums can be conducted by an HRO Lead, HRO Champion, Patient Safety Manager, or even executive leadership. Rotating the responsibility of leading these forums demonstrates that high reliability and safety are everyone’s responsibility.
Safety forums publicly review and discuss errors, adverse events, close calls, and near misses. Time is also spent discussing root cause analysis trends and highlighting continuous process improvement principles and current projects. During safety forums, leaders should recognize individuals for safety behaviors and reward reporting through a safety awards program.14 All forums should conclude with a question-and-answer session. Forums typically occur in virtual 30-minute sessionsbut can last up to 60 minutes when guest speakers attend and continuing education credit is offered.
The Jesse Brown VAMC in Chicago developed an interactive monthly safety forum appealing to a broad audience. Each forum is attended by about 200 staff members and includes leader engagement and panel discussions led by the chief medical officer, with topics on both patient and team safety connecting with HRO principles. A planning committee prepares guest speakers and offers continuing education credits.
Tiered Safety Huddles
Based on the processes of high reliability industries like aviation and nuclear power, tiered safety huddles have been increasingly adopted in health care. Huddles (health care, utilizing, deliberate, discussion,linking, and events) are department-level interdisciplinary meetings that last no more than 15 minutes.15 Their purpose is to improve communication by sharing day-to-day information across multiple disciplines, identify issues that may impact the delivery of care (eg, patient and staff safety concerns, staffing issues, or inadequate supplies) and resolve problems.
Tiered safety huddles are gaining popularity, especially in organizations seeking high reliability. They are more complex than traditional huddles because of the mechanics of elevating safety issues (eg, bedside to executive leadership teams), feedback loops, and sequencing, among other factors.15,16
Tiered safety huddles are focused, transparent forums with multidisciplinary staff, including frontline workers, along with senior leadership.15,16 When initially implemented, tiered safety huddles may take longer than the suggested 15 minutes; however, as teams become more experienced, huddles become more efficient.15 The goal of tiered safety huddles is to proactively identify, share, address, and resolve problems that have the potential to impact the delivery of safe and quality patient care. This may include addressing staffing shortfalls, inadequate allocation of supplies and equipment, operational issues, etc.8,15 Critical to theeffective utilization of tiered safety huddles is the appropriate escalation of issues between tiers. The most critical issues are elevated to higher tiers so they are addressed by the most qualified person in the organization.
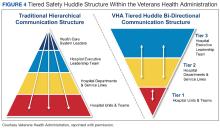
Deciding on the number of tiers typically depends on the size and scope of services provided by the health care organization or integrated system.For example, tiered huddles in the VHA originate at the point of service (eg, critical care unit). Tier 1 includes staff members at the unit/team level along with immediate supervisors/managers. Tier 2 involves departments and service lines (eg, pharmacy, podiatry, or internal medicine) including their respective leadership. Tier 3 is the executive leadership team. This process allows for bidirectional communication instead of the traditional hierarchical communication pathway (Figure 4). Issues identified that cannot be addressed at a particular tier are elevated to the next tier. Elevated issues typically involve systems or processes requiring attention and resolution by senior leadership.15 Tier 4 huddles at the Veterans Integrated Services Network level and Tier 5 huddles at the VHA Central Office level are being initiated. These additional levels will more effectively identify system-level risks and issues that may impact multiple VHA facilities and may be addressed through centralized functions and resources.
Tiered safety huddles have been found to be instrumental to ensuring the flow of information across organizations, improving multidisciplinary and leadership engagement and collaboration, as well as increasing accountability for safety.Tiered safety huddles increase situational awareness, which improves an organization’s ability to appropriately respond to safety concerns.Furthermore, tiered safety huddles enhance teamwork and interprofessional collaboration, and have been found to significantly increase the reporting of patient safety events.15-19
The VA Connecticut Healthcare System tiered huddles followed a pilot testing implementation process. After receiving executive-level commitment, an evidence-based process was enacted, including staff education, selecting a VMS, determining tier interaction, and deciding on metrics to track.15
Implementing Foundational Practices
To examine the progress of the implementation of the 4 foundational HRO practices, quarterly metrics derived from the OLT are reviewed to determine whether each is being implemented and sustained. The OLT also tracks progress over time. For example, at the 27 cohort 2 and lead sites that initiated leader coaching in 2021 and continued through 2022, coaches observed a 27% increase in leader rounding for high reliability and a 46% increase in the use of VMSs. For the 66 cohort 3 sites that began leader coaching in 2022, coaches documented similar changes, ranging from a 40% increase in leader rounding for high reliability to a 66% increase in the use of safety forums. Additional data continue to be collected and analyzed to publish more comprehensive findings.
DISCUSSION
Incorporating leader rounding for high reliability, VMSs, safety forums, and tiered safety huddles into daily operations is critical to building and sustaining a robust culture of safety.8 The 4 foundational HRO practices are instrumental in providing psychologically safe forums for staff to share concerns and actively participate. These practices also promote continual, efficient bidirectional communication throughout organizational lines and across services. The increased visibility and transparency of leaders demonstrate the importance of fostering trust, enhancing closed-loop communication with issues that arise, and building momentum to achieve high reliability. The interconnectedness of the foundational HRO practices identified and implemented by the VHA helps foster teamwork and collaboration built on trust, respect, enthusiasm for improvement, and the delivery of exceptional patient care.
CONCLUSIONS
Incorporating the 4 foundational practices into daily operations is beneficial to the delivery of safe, high-quality health care. This effective and sustained application can strengthen a health care organization on its journey to high reliability and establishing a culture of safety. To be effective, these foundational practices should be personalized to support the unique circumstances of every health care environment. While the exact methodology by which organizations implement these practices may differ, they will help organizations approach patient safety in a more transparent and thoughtful manner.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Aaron M. Sawyer, PhD, PMP, and Jessica Fankhauser, MA, for their unwavering administrative support, and Jeff Wright for exceptional graphic design support.
1. Figueroa CA, Harrison R, Chauhan A, Meyer L. Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: a rapid review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):239. Published 2019 Apr 24. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4080-7
2. What is a high reliability organization (HRO) in healthcare? Vizient. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.vizientinc.com/our-solutions/care-delivery-excellence/reliable-care-delivery
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VHA National Center for Patient Safety. VHA’s HRO journey officially begins. March 29, 2019. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.patientsafety.va.gov/features/VHA_s_HRO_journey_officially_begins.asp
4. Murray JS, Clifford J, Scott D, Kelly S, Hanover C. Leader rounding for high reliability and improved patient safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41(1):16-21. doi:10.12788/fp.0444
5. Ryan L, Jackson D, Woods C, Usher K. Intentional rounding – an integrative literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(6):1151-1161. doi:10.1111/jan.13897
6. Hedenstrom M, Harrilson A, Heath M, Dyess S. “What’s old is new again”: innovative health care leader rounding—a strategy to foster connection. Nurse
7. Blake PG, Bacon CT. Structured rounding to improve staff nurse satisfaction with leadership. Nurse Lead. 2020;18(5):461-466. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.04.009
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Leader’s guide to foundational high reliability organization (HRO) practices. https://dvagov.sharepoint.com/sites/OHT-PMO/high-reliability/Pages/default.aspx
9. Goyal A, Glanzman H, Quinn M, et al. Do bedside whiteboards enhance communication in hospitals? An exploratory multimethod study of patient and nurse perspectives. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-01020810. Williamsson A, Dellve L, Karltun A. Nurses’ use of visual management in hospitals-a longitudinal, quantitative study on its implications on systems performance and working conditions. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(4):760-771. doi:10.1111/jan.13855
11. Prineas S, Culwick M, Endlich Y. A proposed system for standardization of colour-coding stages of escalating criticality in clinical incidents. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(6):752-760. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000001071
12. Murray JS, Clifford J, Larson S, Lee JK, Sculli GL. Implementing just culture to improve patient safety. Mil Med. 2023;188(7-8):1596-1599. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac115
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Murray JS. Development of a safety awards program at a veterans affairs health care system: a quality improvement initiative. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2023;30(1):9-16. doi:10.12788/jcom.0120
15. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a veterans affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188(5-6):901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
16. Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(12):1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
17. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
18. Pimentel CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(9):2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
19. Adapa K, Ivester T, Shea C, et al. The effect of a system-level tiered huddle system on reporting patient safety events: an interrupted time series analysis. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2022;48(12):642-652. doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2022.08.005
Increasing complexities within health care systems are significant impediments to the consistent delivery of safe and effective patient care. These impediments include an increase in specialization of care, staff shortages, burnout, poor coordination of services and access to care, as well as rising costs.1 High reliability organizations (HROs) provide safe, high-quality, and effective care in highly complex and risk-prone environments without causing harm or experiencing catastrophic events.2
Within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) operates the nation’s largest integrated health care system, providing care to > 9 million veterans. The VHA formally launched plans for an enterprise-wide HRO in February 2019. During the first year, 18 medical facilities comprised cohort1 of the journey to high reliability. Cohort 2 began in October 2020 and consisted of 54 facilities. Cohort 3 started in October 2021 with 67 facilities.3
Health care organizations seeking high reliability exercise a philosophy aimed at learning from errors and addressing system failures. High reliability is accomplished by implementing 5 principles: (1) sensitivity to operations (a heightened understanding of the current state of systems); (2) preoccupation with failure (striving to anticipate risks that might suggest a much larger system problem); (3) reluctance to simplify (avoiding making any assumptions regarding the causes of failures); (4) commitment to resilience (preparing for potential failures and bouncing back when they occur); and (5) deference to expertise (deferring to individuals with the skills and proficiency to make the best decisions).2 The VHA also recognized that a successful journey to high reliability—in addition to achieving a culture of safety—relies on the implementation of foundational HRO practices: leader rounding, visual management systems, safety forums, and safety huddles. This article describes an initiative for how these foundational practices were implemented in a large integrated health care system.
BACKGROUND
The VHA has focused on 4 foundational components as part of its enterprise activities and support structure to implement HRO principles and practices. These components were selected based on pilot activities that preceded the enterprise-wide effort, reviews of the literature, and expert consultation with both government and private sector health systems. To support the implementation of these practices, the VHA provided training, toolkits, HRO executive leader coaching, and peer-to-peer mentoring. As the VHA enters its fifth year seeking high reliability, we undertook an initiative to reflect on our own experiences and refine our practices based on an updated literature review.
As part of this enterprise-wide initiative, we conducted a literature review from 2018 to March 2023 seeking recent evidence describing the value of implementing the 4 foundational HRO practices to advance high reliability and improve patient safety. A 5-year period was used to ensure recency and value of evidence.
Eligible literature was identified in PubMed, PsycINFO, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ScienceDirect, Scopus, the Cochrane Library, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were peer-reviewed interdisciplinary documents(eg, publications, dissertations, conference proceedings, and grey literature) written in English. Search terms included high reliability organizations, foundational practices, and patient safety. Boolean operators (AND, OR) were also used in the search. The search resulted in a dearth of evidence that addressed implementation of all 4 foundational practices across a health care system. Retrieved evidence focused on the implementation of only 1 particular foundational practice in a specific health care setting. In addition to describing the formal processes for the implementation of each foundational HRO practice, a brief description of representative examples of strong practices within the VHA is provided.
To support the implementation of HROs, the VHA paired HRO executive leader coaches with select medical center directors and their leadership teams. Executive leader coaches also support an organization’s HRO Lead and HRO Champion. The HRO Lead coordinates and facilitates the implementation of HRO principles and practices in pursuit of no harm across an organization. The HRO Champion supports the same as the HRO Lead, but typically has a different specialty background. For example, if the HRO Lead has an administrative background, the HRO Champion would have a clinical background.
Coaching focuses heavily on supporting site-specific implementation and sustainment of the 4 HRO foundational practices. The aim is to accelerate change, build enduring capacity, foster a safety culture, and accelerate HRO maturity. To measure change, HRO executive leader coaches track the progress of their aligned VA medical centers (VAMCs) using the Organizational Learning Tool (OLT). This tool was developed to provide information such as a facility summary and relationships between a medical center director, HRO Lead, HRO Champion, and the executive leader coach (Figure 1). The OLT also serves as a structured process to measure leader coaching performance against mutually agreed upon objectives that ultimately contribute to enterprise outcomes. It also collects data on the progress in implementing foundational practices, strong practices, needs and gaps, and more (Figure 2). Data collected from facilities supported by HRO executive leader coaches on whether foundational practices are in place are briefly described.
Leader Rounding
Leader rounding for high reliability ensures effective, bidirectional communication and collaboration among all disciplines to improve patient safety. It is an essential feature of a robust patient safety culture and an important method for demonstrating leadership engagement with high reliability.4,5 These rounds are conducted by organizational leadership (eg, executive teams, department/service chiefs, or unit managers) and frontline staff from different areas. They are specifically focused on high reliability, patient and staff safety, and improvement efforts. The aim is to learn about daily challenges that may contribute to patient harm.4
Leader rounding has been found to be highly effective at improving leadership visibility across the organization. It enhances interaction and open communication with frontline staff, fostering leader-staff collaboration and shared decision-making,as well as promoting leadership understanding of operational, clinical, nonclinical (eg, administrative, nutrition services, or facilities management), and patient/family experience issues.4 Collaboration among team members fosters the delivery of more effective and efficient care, increases staff satisfaction, and improves employee retention.6 Leader rounding for high reliability significantly contributes to the breakdown of power barriers by giving team members voice and agency, ultimately leading to deeper engagement.7
It is important that leader rounding for high reliability occurs as planned and when possible, scheduled in advance. This helps to avoid rounding at peak times when care activities are being performed.4,6 When scheduling conflicts arise, another leader should be sent to participate in rounds.4 Developing a list of questions in advance allows leadership to prepare messaging to share with staff as it relates to high reliability and patient safety (Table).4,6,8
Closing the loop improves bidirectional communication and is critical to leader rounding for high reliability. Closed-loop communication and following up on and/or closing out issues raised during rounding empowers the sharing of information, which is critical for advancing a culture of safety.4,8 Enhanced feedback is also associated with greater workforce engagement, staff feeling more connected to quality improvement activities, and lower rates of employee burnout.7 It is important to recognize that senior leaders are not responsible for resolving all issues. If a team or manager can resolve concerns that are raised, this should be encouraged and supported. Maintaining accountability at the lowest level of the organization promotes principles and practices of high reliability (Figure 3).4,8
The VA Bedford Healthcare System created and implemented a strong practice for leader rounding for high reliability. This phased implementation involved creating an evidence-based process, deciding on an appropriate cadence, developing a tracking tool, and measuring impact to determine the overall effectiveness of leader rounding for high reliability.4
Visual Management Systems
A visual management system (VMS) displays clinical and operational performance aligned with HRO goals and practices. It is used to view and guide discussions between interdisciplinary teams during tiered safety huddles, leader rounds for high reliability, and frontline staff on the current status and safety trends in a particular area.8,9 A VMS is highly effective in creating an environment where all staff members, especially frontline workers, feel empowered to voice their concerns related to safety or to identify improvement opportunities.8,10 Increased leader engagement in patient safety and heightened transparency of information associated with the use of a VMS improves staff morale and professional satisfaction.10
A VMS may be a dry-erase or whiteboard display, paper-based display, or electronic status board.8 VMSs are usually located in or near work settings (eg, nurses’ station, staff break room, or conference room).8 Although they can take different forms and display several types of information, a VMS should be easy to update and meet the specific needs of a work area. In the VHA, a VMS displays: (1) essential information for staff members to effectively perform their work; (2) improvement project ideas; (3) current work in progress; (4) tracking of implemented improvement activities; (5) strong practices that have been effective; and (6) staff recognition for those who have enhanced patient safety, including the reporting of close calls and near misses.
The VHA uses the MESS (methods, equipment, staffing, and supplies) VMS format. This format empowers staff to identify whether proper procedures and practices are in place, essential equipment and supplies are readily available in the quantity needed, and appropriate staffing is on hand to provide safe, high-quality patient care.8 Colored magnets are used as visual cues in a stoplight classification system to identify low or no safety risks (green), at risk (yellow), or high risk (red). Green coded issues are addressed locally by a manager or supervisor. Yellow coded concerns require increased staff and leadership vigilance. Red coded issues indicate that patient care would be impacted that day and therefore need to be immediately escalated and addressed with senior leaders to mitigate the threat.4,11 Dayton VAMC successfully implemented a VMS, using both physical and electronic visual management boards. The Dayton VAMC VMS boards are closely tied to tiered safety huddles and leader rounding for high reliability.
Safety Forums
Safety forums are another foundational practice of VHA health care organizations seeking high reliability. Recurring monthly, safety forums focus on reinforcing HRO principles and practices, safety programs, the importance and appreciation of reporting, and just culture. The emphasis on just culture reminds staff that adverse events in the organization are viewed as valuable learning opportunities to understand the factors leading to the situation as opposed to immediately assigning blame.12
Psychological safety is another important focus. When individuals feel psychologically safe, they are more likely to voice concerns and act without fear of reprisal, which supports a culture of safety.13 Safety forums are open to all members of the health care organization, including both clinical and nonclinical staff. Forums can be conducted by an HRO Lead, HRO Champion, Patient Safety Manager, or even executive leadership. Rotating the responsibility of leading these forums demonstrates that high reliability and safety are everyone’s responsibility.
Safety forums publicly review and discuss errors, adverse events, close calls, and near misses. Time is also spent discussing root cause analysis trends and highlighting continuous process improvement principles and current projects. During safety forums, leaders should recognize individuals for safety behaviors and reward reporting through a safety awards program.14 All forums should conclude with a question-and-answer session. Forums typically occur in virtual 30-minute sessionsbut can last up to 60 minutes when guest speakers attend and continuing education credit is offered.
The Jesse Brown VAMC in Chicago developed an interactive monthly safety forum appealing to a broad audience. Each forum is attended by about 200 staff members and includes leader engagement and panel discussions led by the chief medical officer, with topics on both patient and team safety connecting with HRO principles. A planning committee prepares guest speakers and offers continuing education credits.
Tiered Safety Huddles
Based on the processes of high reliability industries like aviation and nuclear power, tiered safety huddles have been increasingly adopted in health care. Huddles (health care, utilizing, deliberate, discussion,linking, and events) are department-level interdisciplinary meetings that last no more than 15 minutes.15 Their purpose is to improve communication by sharing day-to-day information across multiple disciplines, identify issues that may impact the delivery of care (eg, patient and staff safety concerns, staffing issues, or inadequate supplies) and resolve problems.
Tiered safety huddles are gaining popularity, especially in organizations seeking high reliability. They are more complex than traditional huddles because of the mechanics of elevating safety issues (eg, bedside to executive leadership teams), feedback loops, and sequencing, among other factors.15,16
Tiered safety huddles are focused, transparent forums with multidisciplinary staff, including frontline workers, along with senior leadership.15,16 When initially implemented, tiered safety huddles may take longer than the suggested 15 minutes; however, as teams become more experienced, huddles become more efficient.15 The goal of tiered safety huddles is to proactively identify, share, address, and resolve problems that have the potential to impact the delivery of safe and quality patient care. This may include addressing staffing shortfalls, inadequate allocation of supplies and equipment, operational issues, etc.8,15 Critical to theeffective utilization of tiered safety huddles is the appropriate escalation of issues between tiers. The most critical issues are elevated to higher tiers so they are addressed by the most qualified person in the organization.
Deciding on the number of tiers typically depends on the size and scope of services provided by the health care organization or integrated system.For example, tiered huddles in the VHA originate at the point of service (eg, critical care unit). Tier 1 includes staff members at the unit/team level along with immediate supervisors/managers. Tier 2 involves departments and service lines (eg, pharmacy, podiatry, or internal medicine) including their respective leadership. Tier 3 is the executive leadership team. This process allows for bidirectional communication instead of the traditional hierarchical communication pathway (Figure 4). Issues identified that cannot be addressed at a particular tier are elevated to the next tier. Elevated issues typically involve systems or processes requiring attention and resolution by senior leadership.15 Tier 4 huddles at the Veterans Integrated Services Network level and Tier 5 huddles at the VHA Central Office level are being initiated. These additional levels will more effectively identify system-level risks and issues that may impact multiple VHA facilities and may be addressed through centralized functions and resources.
Tiered safety huddles have been found to be instrumental to ensuring the flow of information across organizations, improving multidisciplinary and leadership engagement and collaboration, as well as increasing accountability for safety.Tiered safety huddles increase situational awareness, which improves an organization’s ability to appropriately respond to safety concerns.Furthermore, tiered safety huddles enhance teamwork and interprofessional collaboration, and have been found to significantly increase the reporting of patient safety events.15-19
The VA Connecticut Healthcare System tiered huddles followed a pilot testing implementation process. After receiving executive-level commitment, an evidence-based process was enacted, including staff education, selecting a VMS, determining tier interaction, and deciding on metrics to track.15
Implementing Foundational Practices
To examine the progress of the implementation of the 4 foundational HRO practices, quarterly metrics derived from the OLT are reviewed to determine whether each is being implemented and sustained. The OLT also tracks progress over time. For example, at the 27 cohort 2 and lead sites that initiated leader coaching in 2021 and continued through 2022, coaches observed a 27% increase in leader rounding for high reliability and a 46% increase in the use of VMSs. For the 66 cohort 3 sites that began leader coaching in 2022, coaches documented similar changes, ranging from a 40% increase in leader rounding for high reliability to a 66% increase in the use of safety forums. Additional data continue to be collected and analyzed to publish more comprehensive findings.
DISCUSSION
Incorporating leader rounding for high reliability, VMSs, safety forums, and tiered safety huddles into daily operations is critical to building and sustaining a robust culture of safety.8 The 4 foundational HRO practices are instrumental in providing psychologically safe forums for staff to share concerns and actively participate. These practices also promote continual, efficient bidirectional communication throughout organizational lines and across services. The increased visibility and transparency of leaders demonstrate the importance of fostering trust, enhancing closed-loop communication with issues that arise, and building momentum to achieve high reliability. The interconnectedness of the foundational HRO practices identified and implemented by the VHA helps foster teamwork and collaboration built on trust, respect, enthusiasm for improvement, and the delivery of exceptional patient care.
CONCLUSIONS
Incorporating the 4 foundational practices into daily operations is beneficial to the delivery of safe, high-quality health care. This effective and sustained application can strengthen a health care organization on its journey to high reliability and establishing a culture of safety. To be effective, these foundational practices should be personalized to support the unique circumstances of every health care environment. While the exact methodology by which organizations implement these practices may differ, they will help organizations approach patient safety in a more transparent and thoughtful manner.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Aaron M. Sawyer, PhD, PMP, and Jessica Fankhauser, MA, for their unwavering administrative support, and Jeff Wright for exceptional graphic design support.
Increasing complexities within health care systems are significant impediments to the consistent delivery of safe and effective patient care. These impediments include an increase in specialization of care, staff shortages, burnout, poor coordination of services and access to care, as well as rising costs.1 High reliability organizations (HROs) provide safe, high-quality, and effective care in highly complex and risk-prone environments without causing harm or experiencing catastrophic events.2
Within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) operates the nation’s largest integrated health care system, providing care to > 9 million veterans. The VHA formally launched plans for an enterprise-wide HRO in February 2019. During the first year, 18 medical facilities comprised cohort1 of the journey to high reliability. Cohort 2 began in October 2020 and consisted of 54 facilities. Cohort 3 started in October 2021 with 67 facilities.3
Health care organizations seeking high reliability exercise a philosophy aimed at learning from errors and addressing system failures. High reliability is accomplished by implementing 5 principles: (1) sensitivity to operations (a heightened understanding of the current state of systems); (2) preoccupation with failure (striving to anticipate risks that might suggest a much larger system problem); (3) reluctance to simplify (avoiding making any assumptions regarding the causes of failures); (4) commitment to resilience (preparing for potential failures and bouncing back when they occur); and (5) deference to expertise (deferring to individuals with the skills and proficiency to make the best decisions).2 The VHA also recognized that a successful journey to high reliability—in addition to achieving a culture of safety—relies on the implementation of foundational HRO practices: leader rounding, visual management systems, safety forums, and safety huddles. This article describes an initiative for how these foundational practices were implemented in a large integrated health care system.
BACKGROUND
The VHA has focused on 4 foundational components as part of its enterprise activities and support structure to implement HRO principles and practices. These components were selected based on pilot activities that preceded the enterprise-wide effort, reviews of the literature, and expert consultation with both government and private sector health systems. To support the implementation of these practices, the VHA provided training, toolkits, HRO executive leader coaching, and peer-to-peer mentoring. As the VHA enters its fifth year seeking high reliability, we undertook an initiative to reflect on our own experiences and refine our practices based on an updated literature review.
As part of this enterprise-wide initiative, we conducted a literature review from 2018 to March 2023 seeking recent evidence describing the value of implementing the 4 foundational HRO practices to advance high reliability and improve patient safety. A 5-year period was used to ensure recency and value of evidence.
Eligible literature was identified in PubMed, PsycINFO, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ScienceDirect, Scopus, the Cochrane Library, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were peer-reviewed interdisciplinary documents(eg, publications, dissertations, conference proceedings, and grey literature) written in English. Search terms included high reliability organizations, foundational practices, and patient safety. Boolean operators (AND, OR) were also used in the search. The search resulted in a dearth of evidence that addressed implementation of all 4 foundational practices across a health care system. Retrieved evidence focused on the implementation of only 1 particular foundational practice in a specific health care setting. In addition to describing the formal processes for the implementation of each foundational HRO practice, a brief description of representative examples of strong practices within the VHA is provided.
To support the implementation of HROs, the VHA paired HRO executive leader coaches with select medical center directors and their leadership teams. Executive leader coaches also support an organization’s HRO Lead and HRO Champion. The HRO Lead coordinates and facilitates the implementation of HRO principles and practices in pursuit of no harm across an organization. The HRO Champion supports the same as the HRO Lead, but typically has a different specialty background. For example, if the HRO Lead has an administrative background, the HRO Champion would have a clinical background.
Coaching focuses heavily on supporting site-specific implementation and sustainment of the 4 HRO foundational practices. The aim is to accelerate change, build enduring capacity, foster a safety culture, and accelerate HRO maturity. To measure change, HRO executive leader coaches track the progress of their aligned VA medical centers (VAMCs) using the Organizational Learning Tool (OLT). This tool was developed to provide information such as a facility summary and relationships between a medical center director, HRO Lead, HRO Champion, and the executive leader coach (Figure 1). The OLT also serves as a structured process to measure leader coaching performance against mutually agreed upon objectives that ultimately contribute to enterprise outcomes. It also collects data on the progress in implementing foundational practices, strong practices, needs and gaps, and more (Figure 2). Data collected from facilities supported by HRO executive leader coaches on whether foundational practices are in place are briefly described.
Leader Rounding
Leader rounding for high reliability ensures effective, bidirectional communication and collaboration among all disciplines to improve patient safety. It is an essential feature of a robust patient safety culture and an important method for demonstrating leadership engagement with high reliability.4,5 These rounds are conducted by organizational leadership (eg, executive teams, department/service chiefs, or unit managers) and frontline staff from different areas. They are specifically focused on high reliability, patient and staff safety, and improvement efforts. The aim is to learn about daily challenges that may contribute to patient harm.4
Leader rounding has been found to be highly effective at improving leadership visibility across the organization. It enhances interaction and open communication with frontline staff, fostering leader-staff collaboration and shared decision-making,as well as promoting leadership understanding of operational, clinical, nonclinical (eg, administrative, nutrition services, or facilities management), and patient/family experience issues.4 Collaboration among team members fosters the delivery of more effective and efficient care, increases staff satisfaction, and improves employee retention.6 Leader rounding for high reliability significantly contributes to the breakdown of power barriers by giving team members voice and agency, ultimately leading to deeper engagement.7
It is important that leader rounding for high reliability occurs as planned and when possible, scheduled in advance. This helps to avoid rounding at peak times when care activities are being performed.4,6 When scheduling conflicts arise, another leader should be sent to participate in rounds.4 Developing a list of questions in advance allows leadership to prepare messaging to share with staff as it relates to high reliability and patient safety (Table).4,6,8
Closing the loop improves bidirectional communication and is critical to leader rounding for high reliability. Closed-loop communication and following up on and/or closing out issues raised during rounding empowers the sharing of information, which is critical for advancing a culture of safety.4,8 Enhanced feedback is also associated with greater workforce engagement, staff feeling more connected to quality improvement activities, and lower rates of employee burnout.7 It is important to recognize that senior leaders are not responsible for resolving all issues. If a team or manager can resolve concerns that are raised, this should be encouraged and supported. Maintaining accountability at the lowest level of the organization promotes principles and practices of high reliability (Figure 3).4,8
The VA Bedford Healthcare System created and implemented a strong practice for leader rounding for high reliability. This phased implementation involved creating an evidence-based process, deciding on an appropriate cadence, developing a tracking tool, and measuring impact to determine the overall effectiveness of leader rounding for high reliability.4
Visual Management Systems
A visual management system (VMS) displays clinical and operational performance aligned with HRO goals and practices. It is used to view and guide discussions between interdisciplinary teams during tiered safety huddles, leader rounds for high reliability, and frontline staff on the current status and safety trends in a particular area.8,9 A VMS is highly effective in creating an environment where all staff members, especially frontline workers, feel empowered to voice their concerns related to safety or to identify improvement opportunities.8,10 Increased leader engagement in patient safety and heightened transparency of information associated with the use of a VMS improves staff morale and professional satisfaction.10
A VMS may be a dry-erase or whiteboard display, paper-based display, or electronic status board.8 VMSs are usually located in or near work settings (eg, nurses’ station, staff break room, or conference room).8 Although they can take different forms and display several types of information, a VMS should be easy to update and meet the specific needs of a work area. In the VHA, a VMS displays: (1) essential information for staff members to effectively perform their work; (2) improvement project ideas; (3) current work in progress; (4) tracking of implemented improvement activities; (5) strong practices that have been effective; and (6) staff recognition for those who have enhanced patient safety, including the reporting of close calls and near misses.
The VHA uses the MESS (methods, equipment, staffing, and supplies) VMS format. This format empowers staff to identify whether proper procedures and practices are in place, essential equipment and supplies are readily available in the quantity needed, and appropriate staffing is on hand to provide safe, high-quality patient care.8 Colored magnets are used as visual cues in a stoplight classification system to identify low or no safety risks (green), at risk (yellow), or high risk (red). Green coded issues are addressed locally by a manager or supervisor. Yellow coded concerns require increased staff and leadership vigilance. Red coded issues indicate that patient care would be impacted that day and therefore need to be immediately escalated and addressed with senior leaders to mitigate the threat.4,11 Dayton VAMC successfully implemented a VMS, using both physical and electronic visual management boards. The Dayton VAMC VMS boards are closely tied to tiered safety huddles and leader rounding for high reliability.
Safety Forums
Safety forums are another foundational practice of VHA health care organizations seeking high reliability. Recurring monthly, safety forums focus on reinforcing HRO principles and practices, safety programs, the importance and appreciation of reporting, and just culture. The emphasis on just culture reminds staff that adverse events in the organization are viewed as valuable learning opportunities to understand the factors leading to the situation as opposed to immediately assigning blame.12
Psychological safety is another important focus. When individuals feel psychologically safe, they are more likely to voice concerns and act without fear of reprisal, which supports a culture of safety.13 Safety forums are open to all members of the health care organization, including both clinical and nonclinical staff. Forums can be conducted by an HRO Lead, HRO Champion, Patient Safety Manager, or even executive leadership. Rotating the responsibility of leading these forums demonstrates that high reliability and safety are everyone’s responsibility.
Safety forums publicly review and discuss errors, adverse events, close calls, and near misses. Time is also spent discussing root cause analysis trends and highlighting continuous process improvement principles and current projects. During safety forums, leaders should recognize individuals for safety behaviors and reward reporting through a safety awards program.14 All forums should conclude with a question-and-answer session. Forums typically occur in virtual 30-minute sessionsbut can last up to 60 minutes when guest speakers attend and continuing education credit is offered.
The Jesse Brown VAMC in Chicago developed an interactive monthly safety forum appealing to a broad audience. Each forum is attended by about 200 staff members and includes leader engagement and panel discussions led by the chief medical officer, with topics on both patient and team safety connecting with HRO principles. A planning committee prepares guest speakers and offers continuing education credits.
Tiered Safety Huddles
Based on the processes of high reliability industries like aviation and nuclear power, tiered safety huddles have been increasingly adopted in health care. Huddles (health care, utilizing, deliberate, discussion,linking, and events) are department-level interdisciplinary meetings that last no more than 15 minutes.15 Their purpose is to improve communication by sharing day-to-day information across multiple disciplines, identify issues that may impact the delivery of care (eg, patient and staff safety concerns, staffing issues, or inadequate supplies) and resolve problems.
Tiered safety huddles are gaining popularity, especially in organizations seeking high reliability. They are more complex than traditional huddles because of the mechanics of elevating safety issues (eg, bedside to executive leadership teams), feedback loops, and sequencing, among other factors.15,16
Tiered safety huddles are focused, transparent forums with multidisciplinary staff, including frontline workers, along with senior leadership.15,16 When initially implemented, tiered safety huddles may take longer than the suggested 15 minutes; however, as teams become more experienced, huddles become more efficient.15 The goal of tiered safety huddles is to proactively identify, share, address, and resolve problems that have the potential to impact the delivery of safe and quality patient care. This may include addressing staffing shortfalls, inadequate allocation of supplies and equipment, operational issues, etc.8,15 Critical to theeffective utilization of tiered safety huddles is the appropriate escalation of issues between tiers. The most critical issues are elevated to higher tiers so they are addressed by the most qualified person in the organization.
Deciding on the number of tiers typically depends on the size and scope of services provided by the health care organization or integrated system.For example, tiered huddles in the VHA originate at the point of service (eg, critical care unit). Tier 1 includes staff members at the unit/team level along with immediate supervisors/managers. Tier 2 involves departments and service lines (eg, pharmacy, podiatry, or internal medicine) including their respective leadership. Tier 3 is the executive leadership team. This process allows for bidirectional communication instead of the traditional hierarchical communication pathway (Figure 4). Issues identified that cannot be addressed at a particular tier are elevated to the next tier. Elevated issues typically involve systems or processes requiring attention and resolution by senior leadership.15 Tier 4 huddles at the Veterans Integrated Services Network level and Tier 5 huddles at the VHA Central Office level are being initiated. These additional levels will more effectively identify system-level risks and issues that may impact multiple VHA facilities and may be addressed through centralized functions and resources.
Tiered safety huddles have been found to be instrumental to ensuring the flow of information across organizations, improving multidisciplinary and leadership engagement and collaboration, as well as increasing accountability for safety.Tiered safety huddles increase situational awareness, which improves an organization’s ability to appropriately respond to safety concerns.Furthermore, tiered safety huddles enhance teamwork and interprofessional collaboration, and have been found to significantly increase the reporting of patient safety events.15-19
The VA Connecticut Healthcare System tiered huddles followed a pilot testing implementation process. After receiving executive-level commitment, an evidence-based process was enacted, including staff education, selecting a VMS, determining tier interaction, and deciding on metrics to track.15
Implementing Foundational Practices
To examine the progress of the implementation of the 4 foundational HRO practices, quarterly metrics derived from the OLT are reviewed to determine whether each is being implemented and sustained. The OLT also tracks progress over time. For example, at the 27 cohort 2 and lead sites that initiated leader coaching in 2021 and continued through 2022, coaches observed a 27% increase in leader rounding for high reliability and a 46% increase in the use of VMSs. For the 66 cohort 3 sites that began leader coaching in 2022, coaches documented similar changes, ranging from a 40% increase in leader rounding for high reliability to a 66% increase in the use of safety forums. Additional data continue to be collected and analyzed to publish more comprehensive findings.
DISCUSSION
Incorporating leader rounding for high reliability, VMSs, safety forums, and tiered safety huddles into daily operations is critical to building and sustaining a robust culture of safety.8 The 4 foundational HRO practices are instrumental in providing psychologically safe forums for staff to share concerns and actively participate. These practices also promote continual, efficient bidirectional communication throughout organizational lines and across services. The increased visibility and transparency of leaders demonstrate the importance of fostering trust, enhancing closed-loop communication with issues that arise, and building momentum to achieve high reliability. The interconnectedness of the foundational HRO practices identified and implemented by the VHA helps foster teamwork and collaboration built on trust, respect, enthusiasm for improvement, and the delivery of exceptional patient care.
CONCLUSIONS
Incorporating the 4 foundational practices into daily operations is beneficial to the delivery of safe, high-quality health care. This effective and sustained application can strengthen a health care organization on its journey to high reliability and establishing a culture of safety. To be effective, these foundational practices should be personalized to support the unique circumstances of every health care environment. While the exact methodology by which organizations implement these practices may differ, they will help organizations approach patient safety in a more transparent and thoughtful manner.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Aaron M. Sawyer, PhD, PMP, and Jessica Fankhauser, MA, for their unwavering administrative support, and Jeff Wright for exceptional graphic design support.
1. Figueroa CA, Harrison R, Chauhan A, Meyer L. Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: a rapid review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):239. Published 2019 Apr 24. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4080-7
2. What is a high reliability organization (HRO) in healthcare? Vizient. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.vizientinc.com/our-solutions/care-delivery-excellence/reliable-care-delivery
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VHA National Center for Patient Safety. VHA’s HRO journey officially begins. March 29, 2019. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.patientsafety.va.gov/features/VHA_s_HRO_journey_officially_begins.asp
4. Murray JS, Clifford J, Scott D, Kelly S, Hanover C. Leader rounding for high reliability and improved patient safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41(1):16-21. doi:10.12788/fp.0444
5. Ryan L, Jackson D, Woods C, Usher K. Intentional rounding – an integrative literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(6):1151-1161. doi:10.1111/jan.13897
6. Hedenstrom M, Harrilson A, Heath M, Dyess S. “What’s old is new again”: innovative health care leader rounding—a strategy to foster connection. Nurse
7. Blake PG, Bacon CT. Structured rounding to improve staff nurse satisfaction with leadership. Nurse Lead. 2020;18(5):461-466. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.04.009
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Leader’s guide to foundational high reliability organization (HRO) practices. https://dvagov.sharepoint.com/sites/OHT-PMO/high-reliability/Pages/default.aspx
9. Goyal A, Glanzman H, Quinn M, et al. Do bedside whiteboards enhance communication in hospitals? An exploratory multimethod study of patient and nurse perspectives. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-01020810. Williamsson A, Dellve L, Karltun A. Nurses’ use of visual management in hospitals-a longitudinal, quantitative study on its implications on systems performance and working conditions. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(4):760-771. doi:10.1111/jan.13855
11. Prineas S, Culwick M, Endlich Y. A proposed system for standardization of colour-coding stages of escalating criticality in clinical incidents. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(6):752-760. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000001071
12. Murray JS, Clifford J, Larson S, Lee JK, Sculli GL. Implementing just culture to improve patient safety. Mil Med. 2023;188(7-8):1596-1599. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac115
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Murray JS. Development of a safety awards program at a veterans affairs health care system: a quality improvement initiative. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2023;30(1):9-16. doi:10.12788/jcom.0120
15. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a veterans affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188(5-6):901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
16. Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(12):1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
17. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
18. Pimentel CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(9):2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
19. Adapa K, Ivester T, Shea C, et al. The effect of a system-level tiered huddle system on reporting patient safety events: an interrupted time series analysis. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2022;48(12):642-652. doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2022.08.005
1. Figueroa CA, Harrison R, Chauhan A, Meyer L. Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: a rapid review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):239. Published 2019 Apr 24. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4080-7
2. What is a high reliability organization (HRO) in healthcare? Vizient. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.vizientinc.com/our-solutions/care-delivery-excellence/reliable-care-delivery
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VHA National Center for Patient Safety. VHA’s HRO journey officially begins. March 29, 2019. Accessed May 22, 2024. https://www.patientsafety.va.gov/features/VHA_s_HRO_journey_officially_begins.asp
4. Murray JS, Clifford J, Scott D, Kelly S, Hanover C. Leader rounding for high reliability and improved patient safety. Fed Pract. 2024;41(1):16-21. doi:10.12788/fp.0444
5. Ryan L, Jackson D, Woods C, Usher K. Intentional rounding – an integrative literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(6):1151-1161. doi:10.1111/jan.13897
6. Hedenstrom M, Harrilson A, Heath M, Dyess S. “What’s old is new again”: innovative health care leader rounding—a strategy to foster connection. Nurse
7. Blake PG, Bacon CT. Structured rounding to improve staff nurse satisfaction with leadership. Nurse Lead. 2020;18(5):461-466. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.04.009
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Leader’s guide to foundational high reliability organization (HRO) practices. https://dvagov.sharepoint.com/sites/OHT-PMO/high-reliability/Pages/default.aspx
9. Goyal A, Glanzman H, Quinn M, et al. Do bedside whiteboards enhance communication in hospitals? An exploratory multimethod study of patient and nurse perspectives. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-01020810. Williamsson A, Dellve L, Karltun A. Nurses’ use of visual management in hospitals-a longitudinal, quantitative study on its implications on systems performance and working conditions. J Adv Nurs. 2019;75(4):760-771. doi:10.1111/jan.13855
11. Prineas S, Culwick M, Endlich Y. A proposed system for standardization of colour-coding stages of escalating criticality in clinical incidents. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(6):752-760. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000001071
12. Murray JS, Clifford J, Larson S, Lee JK, Sculli GL. Implementing just culture to improve patient safety. Mil Med. 2023;188(7-8):1596-1599. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac115
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Murray JS. Development of a safety awards program at a veterans affairs health care system: a quality improvement initiative. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2023;30(1):9-16. doi:10.12788/jcom.0120
15. Merchant NB, O’Neal J, Montoya A, Cox GR, Murray JS. Creating a process for the implementation of tiered huddles in a veterans affairs medical center. Mil Med. 2023;188(5-6):901-906. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac073
16. Mihaljevic T. Tiered daily huddles: the power of teamwork in managing large healthcare organisations. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(12):1050-1052. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010575
17. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
18. Pimentel CB, Snow AL, Carnes SL, et al. Huddles and their effectiveness at the frontlines of clinical care: a scoping review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(9):2772-2783. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-06632-9
19. Adapa K, Ivester T, Shea C, et al. The effect of a system-level tiered huddle system on reporting patient safety events: an interrupted time series analysis. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2022;48(12):642-652. doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2022.08.005
Potential Impact of USPS Mail Delivery Delays on Colorectal Cancer Screening Programs
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States.1 In 2022, there were an estimated 151,030 new CRC cases and 52,580 deaths.1 Options for CRC screening of patients at average risk include stool tests (annual fecal immunochemical test [FIT], annual guaiac-based fecal occult blood test, or stool FIT-DNA test every 1 to 3 years), colonoscopies every 10 years, flexible sigmoidoscopies every 5 years (or every 10 years with annual FIT), and computed tomography (CT) colonography every 5 years.2 Many health care systems use annual FIT for patients at average risk. Compared with guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing, FIT does not require dietary or medication modifications and yields greater sensitivity and patient participation.3
The COVID-19 pandemic and staffing issues have caused a scheduling backlog for screening, diagnostic, and surveillance endoscopies at some medical centers. As a result, FIT has become the primary means of CRC screening at these institutions. FIT kits for home use are typically distributed to eligible patients at an office visit or by mail, and patients are then instructed to mail the kits back to the laboratory. For the test to be as sensitive as possible, FIT kit manufacturers advise laboratory analysis within 14 to 15 days of collection, if stored at ambient temperature, and to reject the sample if it does not meet testing criteria for stability. Delayed FIT sample analysis has been associated with higher false-negative rates because of hemoglobin degradation.4 FIT sample exposure to high ambient temperatures also has been linked to decreased sensitivity for detecting CRC.5
US Postal Service (USPS) mail delivery delays have plagued many areas of the country. A variety of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, understaffing, changes in USPS policies, closure of post offices, and changes in mail delivery standards, may also be contributory causes. According to the USPS website, delivery standard for first-class mail is 1 to 5 days, but this is not guaranteed.6
The Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JBVAMC) laboratory in Chicago has reported receiving FIT kit envelopes in batches by the USPS, with some prepaid first-class business reply envelopes delivered up to 60 days after the time of sample collection. Polymedco, a company that assists US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical centers with logistics of FIT programs for CRC screening, reports that USPS batching of FIT kits leading to delayed delivery has been a periodic problem for medical centers around the country. Polymedco staff remind USPS staff about 4 points when they encounter this issue: Mailers are first-class mail; mailers contain a human biologic specimen that has limited viability; the biological sample used for detecting cancer is time sensitive; and delays in delivery by holding/batching kits could impact morbidity and mortality. Reviewing these key points with local USPS staff usually helps, however, batching and delayed delivery of the FIT kits can sometimes recur with USPS staffing turnover.
Tracking and identifying when a patient receives the FIT kit is difficult. Patients are instructed to write the date of collection on the kit, so the receiving laboratory knows whether the sample can be reliably analyzed. When patients are notified about delayed delivery of their sample, a staff member asks if they postponed dropping the kit in the mail. Most patients report mailing the sample within 1 to 2 days of collection. Tracking and dating each step of FIT kit events is not feasible with a mass mailing campaign. In our experience, most patients write the date of collection on the kit. If a collection date is not provided, the laboratory will call the patient to confirm a date. Cheng and colleagues reviewed the causes for FIT specimen rejection in a laboratory analyzing specimens for VA patients and found that 14% of submitted samples were rejected because the specimen was received > 14 days after collection, and 6% because the patient did not record the collection date. With a series of interventions aimed at reminding patients and improving laboratory procedures, rates of rejection for these 2 causes were reduced to < 4%.7 USPS delays were not identified as a factor or tracked in this study.
It is unclear why the USPS sometimes holds FIT kits at their facilities and then delivers large bins of them at the same time. Because FIT kits should be analyzed within 14 to 15 days of sample collection to assure reliable results, mail delivery delays can result in increased sample rejection. Based on the JBVAMC experience, up to 30% of submitted samples might need to be discarded when batched delivery takes place. In these cases, patients need to be contacted, informed of the problem, and asked to submit new kits. Understandably, patients are reluctant to repeat this type of testing, and we are concerned this could lead to reduced rates of CRC screening in affected communities.
As an alternative to discarding delayed samples, laboratories could report the results of delayed FIT kits with an added comment that “negative test results may be less reliable due to delayed processing,” but this approach would raise quality and medicolegal concerns. Clinicians have reached out to local USPS supervisory personnel with mixed results. Sometimes batching and delayed deliveries stop for a few months, only to resume without warning. Dropping off the sample directly at the laboratory is not a realistic option for most patients. Some patients can be convinced to submit another sample, some elect to switch to other CRC screening strategies, while others, unfortunately, decline further screening efforts.
Laboratory staff can be overwhelmed with having to process hundreds of samples in a short time frame, especially because there is no way of knowing when USPS will make a batched delivery. Laboratory capacities can limit staff at some facilities to performing analysis of only 10 tests at a time. The FIT kits should be delivered on a rolling basis and without delay so that the samples can be reliably analyzed with a predictable workload for the laboratory personnel and without unexpected surges.
When health care facilities identify delayed mail delivery of FIT kits via USPS, laboratories should first ensure that the correct postage rates are used on the prepaid envelopes and that their USPS accounts are properly funded, so that insufficient funds are not contributing to delayed deliveries. Stakeholders should then reach out to local USPS supervisory staff and request that the practice of batching the delivery of FIT kits be stopped. Educating USPS supervisory staff about concerns related to decreased test reliability associated with delayed mail delivery can be a persuasive argument. Adding additional language to the preprinted envelopes, such as “time sensitive,” may also be helpful. Unfortunately, the JBVAMC experience has been that the problem initially gets better after contacting the USPS, only to unexpectedly resurface months later. This cycle has been repeated several times in the past 2 years at JBVAMC.
All clinicians involved in CRC screening and treatment at institutions that use FIT kits need to be aware of the impact that local USPS delays can have on the reliability of these results. Health care systems should be prepared to implement mitigation strategies if they encounter significant delays with mail delivery. If delays cannot be reliably resolved by working with the local USPS staff, consider involving national USPS oversight bodies. And if the problems persist despite an attempt to work with the USPS, some institutions might find it feasible to offer drop boxes at their clinics and instruct patients to drop off FIT kits immediately following collection, in lieu of mailing them. Switching to private carriers is not a cost-effective alternative for most health care systems, and some may exclude rural areas. Depending on the local availability and capacity of endoscopists, some clinicians might prioritize referring patients for screening colonoscopies or screening flexible sigmoidoscopies, and might deemphasize FIT kits as a preferred option for CRC screening. CT colonography is an alternative screening method that is not as widely offered, nor as widely accepted at this time.
Conclusions
CRC screening is an essential part of preventive medicine, and the percentage of eligible patients screened is a well-established quality metric in primary care settings. Health care systems, clinicians, and laboratories must be vigilant to ensure that USPS delays in delivering FIT kits do not negatively impact their CRC screening programs. Facilities should actively monitor for delays in the return of FIT kits.
Despite the widespread use of mail-order pharmacies and the use of mail to communicate notifications about test results and follow-up appointments, unreliable or delayed mail delivery traditionally has not been considered a social determinant of health.8 This article highlights the impact delayed mail delivery can have on health outcomes. Disadvantaged communities in inner cities and rural areas have been disproportionately affected by the worsening performance of the USPS over the past few years.9 This represents an underappreciated public health concern in need of a sustainable solution.
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7-33. doi:10.3322/caac.21708
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer screening tests. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/basic_info/screening/tests.htm
3. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, Laheij RJ, et al. Random comparison of guaiac and immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for colorectal cancer in a screening population. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1):82-90. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.040
4. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, van Oijen MG, et al. False negative fecal occult blood tests due to delayed sample return in colorectal cancer screening. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(4):746-750. doi:10.1002/ijc.24458
5. Doubeni CA, Jensen CD, Fedewa SA, et al. Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) for colon cancer screening: variable performance with ambient temperature. J Am Board Fam Med. 2016;29(6):672-681. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2016.06.160060
6. United States Postal Service. Shipping and mailing with USPS. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.usps.com/ship
7. Cheng C, Ganz DA, Chang ET, Huynh A, De Peralta S. Reducing rejected fecal immunochemical tests received in the laboratory for colorectal cancer screening. J Healthc Qual. 2019;41(2):75-82.doi:10.1097/JHQ.0000000000000181
8. Hussaini SMQ, Alexander GC. The United States Postal Service: an essential public health agency? J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(12):3699-3701. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06275-2
9. Hampton DJ. Colorado mountain towns are plagued by post office delays as residents wait weeks for medication and retirement checks. NBC News. February 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/colo-mountain-towns-are-plagued-post-office-delays-residents-wait-week-rcna72085
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States.1 In 2022, there were an estimated 151,030 new CRC cases and 52,580 deaths.1 Options for CRC screening of patients at average risk include stool tests (annual fecal immunochemical test [FIT], annual guaiac-based fecal occult blood test, or stool FIT-DNA test every 1 to 3 years), colonoscopies every 10 years, flexible sigmoidoscopies every 5 years (or every 10 years with annual FIT), and computed tomography (CT) colonography every 5 years.2 Many health care systems use annual FIT for patients at average risk. Compared with guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing, FIT does not require dietary or medication modifications and yields greater sensitivity and patient participation.3
The COVID-19 pandemic and staffing issues have caused a scheduling backlog for screening, diagnostic, and surveillance endoscopies at some medical centers. As a result, FIT has become the primary means of CRC screening at these institutions. FIT kits for home use are typically distributed to eligible patients at an office visit or by mail, and patients are then instructed to mail the kits back to the laboratory. For the test to be as sensitive as possible, FIT kit manufacturers advise laboratory analysis within 14 to 15 days of collection, if stored at ambient temperature, and to reject the sample if it does not meet testing criteria for stability. Delayed FIT sample analysis has been associated with higher false-negative rates because of hemoglobin degradation.4 FIT sample exposure to high ambient temperatures also has been linked to decreased sensitivity for detecting CRC.5
US Postal Service (USPS) mail delivery delays have plagued many areas of the country. A variety of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, understaffing, changes in USPS policies, closure of post offices, and changes in mail delivery standards, may also be contributory causes. According to the USPS website, delivery standard for first-class mail is 1 to 5 days, but this is not guaranteed.6
The Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JBVAMC) laboratory in Chicago has reported receiving FIT kit envelopes in batches by the USPS, with some prepaid first-class business reply envelopes delivered up to 60 days after the time of sample collection. Polymedco, a company that assists US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical centers with logistics of FIT programs for CRC screening, reports that USPS batching of FIT kits leading to delayed delivery has been a periodic problem for medical centers around the country. Polymedco staff remind USPS staff about 4 points when they encounter this issue: Mailers are first-class mail; mailers contain a human biologic specimen that has limited viability; the biological sample used for detecting cancer is time sensitive; and delays in delivery by holding/batching kits could impact morbidity and mortality. Reviewing these key points with local USPS staff usually helps, however, batching and delayed delivery of the FIT kits can sometimes recur with USPS staffing turnover.
Tracking and identifying when a patient receives the FIT kit is difficult. Patients are instructed to write the date of collection on the kit, so the receiving laboratory knows whether the sample can be reliably analyzed. When patients are notified about delayed delivery of their sample, a staff member asks if they postponed dropping the kit in the mail. Most patients report mailing the sample within 1 to 2 days of collection. Tracking and dating each step of FIT kit events is not feasible with a mass mailing campaign. In our experience, most patients write the date of collection on the kit. If a collection date is not provided, the laboratory will call the patient to confirm a date. Cheng and colleagues reviewed the causes for FIT specimen rejection in a laboratory analyzing specimens for VA patients and found that 14% of submitted samples were rejected because the specimen was received > 14 days after collection, and 6% because the patient did not record the collection date. With a series of interventions aimed at reminding patients and improving laboratory procedures, rates of rejection for these 2 causes were reduced to < 4%.7 USPS delays were not identified as a factor or tracked in this study.
It is unclear why the USPS sometimes holds FIT kits at their facilities and then delivers large bins of them at the same time. Because FIT kits should be analyzed within 14 to 15 days of sample collection to assure reliable results, mail delivery delays can result in increased sample rejection. Based on the JBVAMC experience, up to 30% of submitted samples might need to be discarded when batched delivery takes place. In these cases, patients need to be contacted, informed of the problem, and asked to submit new kits. Understandably, patients are reluctant to repeat this type of testing, and we are concerned this could lead to reduced rates of CRC screening in affected communities.
As an alternative to discarding delayed samples, laboratories could report the results of delayed FIT kits with an added comment that “negative test results may be less reliable due to delayed processing,” but this approach would raise quality and medicolegal concerns. Clinicians have reached out to local USPS supervisory personnel with mixed results. Sometimes batching and delayed deliveries stop for a few months, only to resume without warning. Dropping off the sample directly at the laboratory is not a realistic option for most patients. Some patients can be convinced to submit another sample, some elect to switch to other CRC screening strategies, while others, unfortunately, decline further screening efforts.
Laboratory staff can be overwhelmed with having to process hundreds of samples in a short time frame, especially because there is no way of knowing when USPS will make a batched delivery. Laboratory capacities can limit staff at some facilities to performing analysis of only 10 tests at a time. The FIT kits should be delivered on a rolling basis and without delay so that the samples can be reliably analyzed with a predictable workload for the laboratory personnel and without unexpected surges.
When health care facilities identify delayed mail delivery of FIT kits via USPS, laboratories should first ensure that the correct postage rates are used on the prepaid envelopes and that their USPS accounts are properly funded, so that insufficient funds are not contributing to delayed deliveries. Stakeholders should then reach out to local USPS supervisory staff and request that the practice of batching the delivery of FIT kits be stopped. Educating USPS supervisory staff about concerns related to decreased test reliability associated with delayed mail delivery can be a persuasive argument. Adding additional language to the preprinted envelopes, such as “time sensitive,” may also be helpful. Unfortunately, the JBVAMC experience has been that the problem initially gets better after contacting the USPS, only to unexpectedly resurface months later. This cycle has been repeated several times in the past 2 years at JBVAMC.
All clinicians involved in CRC screening and treatment at institutions that use FIT kits need to be aware of the impact that local USPS delays can have on the reliability of these results. Health care systems should be prepared to implement mitigation strategies if they encounter significant delays with mail delivery. If delays cannot be reliably resolved by working with the local USPS staff, consider involving national USPS oversight bodies. And if the problems persist despite an attempt to work with the USPS, some institutions might find it feasible to offer drop boxes at their clinics and instruct patients to drop off FIT kits immediately following collection, in lieu of mailing them. Switching to private carriers is not a cost-effective alternative for most health care systems, and some may exclude rural areas. Depending on the local availability and capacity of endoscopists, some clinicians might prioritize referring patients for screening colonoscopies or screening flexible sigmoidoscopies, and might deemphasize FIT kits as a preferred option for CRC screening. CT colonography is an alternative screening method that is not as widely offered, nor as widely accepted at this time.
Conclusions
CRC screening is an essential part of preventive medicine, and the percentage of eligible patients screened is a well-established quality metric in primary care settings. Health care systems, clinicians, and laboratories must be vigilant to ensure that USPS delays in delivering FIT kits do not negatively impact their CRC screening programs. Facilities should actively monitor for delays in the return of FIT kits.
Despite the widespread use of mail-order pharmacies and the use of mail to communicate notifications about test results and follow-up appointments, unreliable or delayed mail delivery traditionally has not been considered a social determinant of health.8 This article highlights the impact delayed mail delivery can have on health outcomes. Disadvantaged communities in inner cities and rural areas have been disproportionately affected by the worsening performance of the USPS over the past few years.9 This represents an underappreciated public health concern in need of a sustainable solution.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States.1 In 2022, there were an estimated 151,030 new CRC cases and 52,580 deaths.1 Options for CRC screening of patients at average risk include stool tests (annual fecal immunochemical test [FIT], annual guaiac-based fecal occult blood test, or stool FIT-DNA test every 1 to 3 years), colonoscopies every 10 years, flexible sigmoidoscopies every 5 years (or every 10 years with annual FIT), and computed tomography (CT) colonography every 5 years.2 Many health care systems use annual FIT for patients at average risk. Compared with guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing, FIT does not require dietary or medication modifications and yields greater sensitivity and patient participation.3
The COVID-19 pandemic and staffing issues have caused a scheduling backlog for screening, diagnostic, and surveillance endoscopies at some medical centers. As a result, FIT has become the primary means of CRC screening at these institutions. FIT kits for home use are typically distributed to eligible patients at an office visit or by mail, and patients are then instructed to mail the kits back to the laboratory. For the test to be as sensitive as possible, FIT kit manufacturers advise laboratory analysis within 14 to 15 days of collection, if stored at ambient temperature, and to reject the sample if it does not meet testing criteria for stability. Delayed FIT sample analysis has been associated with higher false-negative rates because of hemoglobin degradation.4 FIT sample exposure to high ambient temperatures also has been linked to decreased sensitivity for detecting CRC.5
US Postal Service (USPS) mail delivery delays have plagued many areas of the country. A variety of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, understaffing, changes in USPS policies, closure of post offices, and changes in mail delivery standards, may also be contributory causes. According to the USPS website, delivery standard for first-class mail is 1 to 5 days, but this is not guaranteed.6
The Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center (JBVAMC) laboratory in Chicago has reported receiving FIT kit envelopes in batches by the USPS, with some prepaid first-class business reply envelopes delivered up to 60 days after the time of sample collection. Polymedco, a company that assists US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical centers with logistics of FIT programs for CRC screening, reports that USPS batching of FIT kits leading to delayed delivery has been a periodic problem for medical centers around the country. Polymedco staff remind USPS staff about 4 points when they encounter this issue: Mailers are first-class mail; mailers contain a human biologic specimen that has limited viability; the biological sample used for detecting cancer is time sensitive; and delays in delivery by holding/batching kits could impact morbidity and mortality. Reviewing these key points with local USPS staff usually helps, however, batching and delayed delivery of the FIT kits can sometimes recur with USPS staffing turnover.
Tracking and identifying when a patient receives the FIT kit is difficult. Patients are instructed to write the date of collection on the kit, so the receiving laboratory knows whether the sample can be reliably analyzed. When patients are notified about delayed delivery of their sample, a staff member asks if they postponed dropping the kit in the mail. Most patients report mailing the sample within 1 to 2 days of collection. Tracking and dating each step of FIT kit events is not feasible with a mass mailing campaign. In our experience, most patients write the date of collection on the kit. If a collection date is not provided, the laboratory will call the patient to confirm a date. Cheng and colleagues reviewed the causes for FIT specimen rejection in a laboratory analyzing specimens for VA patients and found that 14% of submitted samples were rejected because the specimen was received > 14 days after collection, and 6% because the patient did not record the collection date. With a series of interventions aimed at reminding patients and improving laboratory procedures, rates of rejection for these 2 causes were reduced to < 4%.7 USPS delays were not identified as a factor or tracked in this study.
It is unclear why the USPS sometimes holds FIT kits at their facilities and then delivers large bins of them at the same time. Because FIT kits should be analyzed within 14 to 15 days of sample collection to assure reliable results, mail delivery delays can result in increased sample rejection. Based on the JBVAMC experience, up to 30% of submitted samples might need to be discarded when batched delivery takes place. In these cases, patients need to be contacted, informed of the problem, and asked to submit new kits. Understandably, patients are reluctant to repeat this type of testing, and we are concerned this could lead to reduced rates of CRC screening in affected communities.
As an alternative to discarding delayed samples, laboratories could report the results of delayed FIT kits with an added comment that “negative test results may be less reliable due to delayed processing,” but this approach would raise quality and medicolegal concerns. Clinicians have reached out to local USPS supervisory personnel with mixed results. Sometimes batching and delayed deliveries stop for a few months, only to resume without warning. Dropping off the sample directly at the laboratory is not a realistic option for most patients. Some patients can be convinced to submit another sample, some elect to switch to other CRC screening strategies, while others, unfortunately, decline further screening efforts.
Laboratory staff can be overwhelmed with having to process hundreds of samples in a short time frame, especially because there is no way of knowing when USPS will make a batched delivery. Laboratory capacities can limit staff at some facilities to performing analysis of only 10 tests at a time. The FIT kits should be delivered on a rolling basis and without delay so that the samples can be reliably analyzed with a predictable workload for the laboratory personnel and without unexpected surges.
When health care facilities identify delayed mail delivery of FIT kits via USPS, laboratories should first ensure that the correct postage rates are used on the prepaid envelopes and that their USPS accounts are properly funded, so that insufficient funds are not contributing to delayed deliveries. Stakeholders should then reach out to local USPS supervisory staff and request that the practice of batching the delivery of FIT kits be stopped. Educating USPS supervisory staff about concerns related to decreased test reliability associated with delayed mail delivery can be a persuasive argument. Adding additional language to the preprinted envelopes, such as “time sensitive,” may also be helpful. Unfortunately, the JBVAMC experience has been that the problem initially gets better after contacting the USPS, only to unexpectedly resurface months later. This cycle has been repeated several times in the past 2 years at JBVAMC.
All clinicians involved in CRC screening and treatment at institutions that use FIT kits need to be aware of the impact that local USPS delays can have on the reliability of these results. Health care systems should be prepared to implement mitigation strategies if they encounter significant delays with mail delivery. If delays cannot be reliably resolved by working with the local USPS staff, consider involving national USPS oversight bodies. And if the problems persist despite an attempt to work with the USPS, some institutions might find it feasible to offer drop boxes at their clinics and instruct patients to drop off FIT kits immediately following collection, in lieu of mailing them. Switching to private carriers is not a cost-effective alternative for most health care systems, and some may exclude rural areas. Depending on the local availability and capacity of endoscopists, some clinicians might prioritize referring patients for screening colonoscopies or screening flexible sigmoidoscopies, and might deemphasize FIT kits as a preferred option for CRC screening. CT colonography is an alternative screening method that is not as widely offered, nor as widely accepted at this time.
Conclusions
CRC screening is an essential part of preventive medicine, and the percentage of eligible patients screened is a well-established quality metric in primary care settings. Health care systems, clinicians, and laboratories must be vigilant to ensure that USPS delays in delivering FIT kits do not negatively impact their CRC screening programs. Facilities should actively monitor for delays in the return of FIT kits.
Despite the widespread use of mail-order pharmacies and the use of mail to communicate notifications about test results and follow-up appointments, unreliable or delayed mail delivery traditionally has not been considered a social determinant of health.8 This article highlights the impact delayed mail delivery can have on health outcomes. Disadvantaged communities in inner cities and rural areas have been disproportionately affected by the worsening performance of the USPS over the past few years.9 This represents an underappreciated public health concern in need of a sustainable solution.
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7-33. doi:10.3322/caac.21708
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer screening tests. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/basic_info/screening/tests.htm
3. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, Laheij RJ, et al. Random comparison of guaiac and immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for colorectal cancer in a screening population. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1):82-90. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.040
4. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, van Oijen MG, et al. False negative fecal occult blood tests due to delayed sample return in colorectal cancer screening. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(4):746-750. doi:10.1002/ijc.24458
5. Doubeni CA, Jensen CD, Fedewa SA, et al. Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) for colon cancer screening: variable performance with ambient temperature. J Am Board Fam Med. 2016;29(6):672-681. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2016.06.160060
6. United States Postal Service. Shipping and mailing with USPS. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.usps.com/ship
7. Cheng C, Ganz DA, Chang ET, Huynh A, De Peralta S. Reducing rejected fecal immunochemical tests received in the laboratory for colorectal cancer screening. J Healthc Qual. 2019;41(2):75-82.doi:10.1097/JHQ.0000000000000181
8. Hussaini SMQ, Alexander GC. The United States Postal Service: an essential public health agency? J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(12):3699-3701. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06275-2
9. Hampton DJ. Colorado mountain towns are plagued by post office delays as residents wait weeks for medication and retirement checks. NBC News. February 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/colo-mountain-towns-are-plagued-post-office-delays-residents-wait-week-rcna72085
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7-33. doi:10.3322/caac.21708
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Colorectal cancer screening tests. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/colorectal/basic_info/screening/tests.htm
3. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, Laheij RJ, et al. Random comparison of guaiac and immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for colorectal cancer in a screening population. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1):82-90. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.040
4. van Rossum LG, van Rijn AF, van Oijen MG, et al. False negative fecal occult blood tests due to delayed sample return in colorectal cancer screening. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(4):746-750. doi:10.1002/ijc.24458
5. Doubeni CA, Jensen CD, Fedewa SA, et al. Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) for colon cancer screening: variable performance with ambient temperature. J Am Board Fam Med. 2016;29(6):672-681. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2016.06.160060
6. United States Postal Service. Shipping and mailing with USPS. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.usps.com/ship
7. Cheng C, Ganz DA, Chang ET, Huynh A, De Peralta S. Reducing rejected fecal immunochemical tests received in the laboratory for colorectal cancer screening. J Healthc Qual. 2019;41(2):75-82.doi:10.1097/JHQ.0000000000000181
8. Hussaini SMQ, Alexander GC. The United States Postal Service: an essential public health agency? J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(12):3699-3701. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06275-2
9. Hampton DJ. Colorado mountain towns are plagued by post office delays as residents wait weeks for medication and retirement checks. NBC News. February 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/colo-mountain-towns-are-plagued-post-office-delays-residents-wait-week-rcna72085
Moral Injury in Health Care: A Unified Definition and its Relationship to Burnout
Moral injury was identified by health care professionals (HCPs) as a driver of occupational distress prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, but the crisis expanded the appeal and investigation of the term.1 HCPs now consider moral injury an essential component of the framework to describe their distress, because using the term burnout alone fails to capture their full experience and has proven resistant to interventions.2 Moral injury goes beyond the transdiagnostic symptoms of exhaustion and cynicism and beyond operational, demand-resource mismatches that characterize burnout. It describes the frustration, anger, and helplessness associated with relational ruptures and the existential threats to a clinician’s professional identity as business interests erode their ability to put their patients’ needs ahead of corporate and health care system obligations.3
Proper characterization of moral injury in health care—separate from the military environments where it originated—is stymied by an ill-defined relationship between 2 definitions of the term and by an unclear relationship between moral injury and the long-standing body of scholarship in burnout. To clarify the concept, inform research agendas, and open avenues for more effective solutions to the crisis of HCP distress, we propose a unified conceptualization of moral injury and its association with burnout in health care.
CONTEXTUAL DISTINCTIONS
It is important to properly distinguish between the original use of moral injury in the military and its expanded use in civilian circumstances. Health care and the military are both professions whereupon donning the “uniform” of a physician—or soldier, sailor, airman, or marine—members must comport with strict expectations of behavior, including the refusal to engage in illegal actions or those contrary to professional ethics. Individuals in both professions acquire a highly specialized body of knowledge and enter an implied contract to provide critical services to society, specifically healing and protection, respectively. Members of both professions are trained to make complex judgments with integrity under conditions of technical and ethical uncertainty, upon which they take highly skilled action. Medical and military professionals must be free to act on their ethical principles, without confounding demands.4 However, the context of each profession’s commitment to society carries different moral implications.
The risk of moral injury is inherent in military service. The military promises protection with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. In contrast, HCPs promise healing and care. The military promises to protect our society, with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. Some military actions may inflict harm without the hope of benefitting an individual, and are therefore potentially morally injurious. The health care contract with society, promising healing and care, is devoid of inherent moral injury due to harm without potential individual benefit. Therefore, the presence of moral injury in health care settings are warning signs of a dysfunctional environment.
One complex example of the dysfunctional environments is illustrative. The military and health care are among the few industries where supply creates demand. For example, the more bad state actors there are, the more demand for the military. As we have seen since the 1950s, the more technology and therapeutics we create in health care, coupled with a larger share paid for by third parties, the greater the demand for and use of them.5 In a fee for service environment, corporate greed feeds on this reality. In most other environments, more technological and therapeutic options inevitably pit clinicians against multiple other factions: payers, who do not want to underwrite them; patients, who sometimes demand them without justification or later rail against spiraling health care costs; and administrators, especially in capitated systems, who watch their bottom lines erode. The moral injury risk in this instance demands a collective conversation among stakeholders regarding the structural determinants of health—how we choose to distribute limited resources. The intermediary of moral injury is a useful measure of the harm that results from ignoring or avoiding such challenges.
HARMONIZING DEFINITIONS
Moral injury is inherently nuanced. The 2 dominant definitions arise from work with combat veterans and create additional and perhaps unnecessary complexity. Unifying these 2 definitions eliminates inadvertent confusion, preventing the risk of unbridled interdisciplinary investigation which leads to a lack of precision in the meaning of moral injury and other related concepts, such as burnout.6
The first definition was developed by Jonathan Shay in 1994 and outlines 3 necessarycomponents, viewing the violator as a powerholder: (1) betrayal of what is right, (2) by someone who holds legitimate authority, (3) in a high stakes situation.7 Litz and colleagues describe moral injury another way: “Perpetrating, failing to prevent, bearing witness to, or learning about acts that transgress deeply held moral beliefs and expectations.”8 The violator is posited to be either the self or others.
Rather than representing “self” or “other” imposed moral injury, we propose the 2 definitions are related as exposure (ie, the perceived betrayal) and response (ie, the resulting transgression). An individual who experiences a betrayal by a legitimate authority has an opportunity to choose their response. They may acquiesce and transgress their moral beliefs (eg, their oath to provide ethical health care), or they could refuse, by speaking out, or in some way resisting the authority’s betrayal. The case of Ray Brovont is a useful illustration of reconciling the definitions (Box).9
Myriad factors—known as potentially morally injurious events—drive moral injury, such as resource-constrained decision making, witnessing the behaviors of colleagues that violate deeply held moral beliefs, questionable billing practices, and more. Each begins with a betrayal. Spotlighting the betrayal, refusing to perpetuate it, or taking actions toward change, may reduce the risk of experiencing moral injury.9 Conversely, acquiescing and transgressing one’s oath, the profession’s covenant with society, increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.8
Many HCPs believe they are not always free to resist betrayal, fearing retaliation, job loss, blacklisting, or worse. They feel constrained by debt accrued while receiving their education, being their household’s primary earner, community ties, practicing a niche specialty that requires working for a tertiary referral center, or perhaps believing the situation will be the same elsewhere. To not stand up or speak out is to choose complicity with corporate greed that uses HCPs to undermine their professional duties, which significantly increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.
MORAL INJURY AND BURNOUT
In addition to reconciling the definitions of moral injury, the relationship between moral injury and burnout are still being elucidated. We suggest that moral injury and burnout represent independent and potentially interrelated pathways to distress (Figure). Exposure to chronic, inconsonant, and transactional demands, which things like shorter work hours, better self-care, or improved health system operations might mitigate, manifests as burnout. In contrast, moral injury arises when a superior’s actions or a system’s policies and practices—such as justifiable but unnecessary testing, or referral restrictions to prevent revenue leakage—undermine one’s professional obligations to prioritize the patient’s best interest.
If concerns from HCPs about transactional demands are persistently dismissed, such inaction may be perceived as a betrayal, raising the risk of moral injury. Additionally, the resignation or helplessness of moral injury perceived as inescapable may present with emotional exhaustion, ineffectiveness, and depersonalization, all hallmarks of burnout. Both conditions can mediate and moderate the relationship between triggers for workplace distress and resulting psychological, physical, and existential harm.
CONCLUSIONS
Moral injury is increasingly recognized as a source of distress among HCPs, resulting from structural constraints on their ability to deliver optimal care and their own unwillingness to stand up for their patients, their oaths, and their professions.1 Unlike the military, where moral injury is inherent in the contract with society, moral injury in health care (and the relational rupture it connotes) is a signal of systemic dysfunction, fractured trust, and the need for relational repair.
Health care is at a crossroads, experiencing a workforce retention crisis while simultaneously predicting a significant increase in care needs by Baby Boomers over the next 3 decades.
Health care does not have the luxury of experimenting another 30 years with interventions that have limited impact. We must design a new generation of approaches, shaped by lessons learned from the pandemic while acknowledging that prepandemic standards were already failing the workforce. A unified definition of moral injury must be integrated to frame clinician distress alongside burnout, recentering ethical decision making, rather than profit, at the heart of health care. Harmonizing the definitions of moral injury and clarifying the relationship of moral injury with burnout reduces the need for further reinterpretations, allowing for more robust, easily comparable studies focused on identifying risk factors, as well as rapidly implementing effective mitigation strategies.
1. Griffin BJ, Weber MC, Hinkson KD, et al. Toward a dimensional contextual model of moral injury: a scoping review on healthcare workers. Curr Treat Options Psych. 2023;10:199-216. doi:10.1007/s40501-023-00296-4
2. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; National Academy of Medicine; Committee on Systems Approaches to Improve Patient Care by Supporting Clinician Well-Being. Taking Action Against Clinician Burnout: A Systems Approach to Professional Well-Being. The National Academies Press; 2019. doi:10.17226/25521
3. Dean W, Talbot S, Dean A. Reframing clinician distress: moral injury not burnout. Fed Pract. 2019;36(9):400-402.
4. Gardner HE, Schulman LS. The professions in America today: crucial but fragile. Daedalus. 2005;134(3):13-18. doi:10.1162/0011526054622132
5. Fuchs VR. Major trends in the U.S. health economy since 1950. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(11):973-977. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1200478
6. Molendijk T. Warnings against romanticising moral injury. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220(1):1-3. doi:10.1192/bjp.2021.114
7. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanalytic Psychol. 2014;31(2):182-191. doi:10.1037/a0036090
8. Litz BT, Stein N, Delaney E, et al. Moral injury and moral repair in war veterans: a preliminary model and intervention strategy. Clin Psychol Rev. 2009;29(8):695-706. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.07.003
9. Brovont v KS-I Med. Servs., P.A., 622 SW3d 671 (Mo Ct App 2020).
Moral injury was identified by health care professionals (HCPs) as a driver of occupational distress prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, but the crisis expanded the appeal and investigation of the term.1 HCPs now consider moral injury an essential component of the framework to describe their distress, because using the term burnout alone fails to capture their full experience and has proven resistant to interventions.2 Moral injury goes beyond the transdiagnostic symptoms of exhaustion and cynicism and beyond operational, demand-resource mismatches that characterize burnout. It describes the frustration, anger, and helplessness associated with relational ruptures and the existential threats to a clinician’s professional identity as business interests erode their ability to put their patients’ needs ahead of corporate and health care system obligations.3
Proper characterization of moral injury in health care—separate from the military environments where it originated—is stymied by an ill-defined relationship between 2 definitions of the term and by an unclear relationship between moral injury and the long-standing body of scholarship in burnout. To clarify the concept, inform research agendas, and open avenues for more effective solutions to the crisis of HCP distress, we propose a unified conceptualization of moral injury and its association with burnout in health care.
CONTEXTUAL DISTINCTIONS
It is important to properly distinguish between the original use of moral injury in the military and its expanded use in civilian circumstances. Health care and the military are both professions whereupon donning the “uniform” of a physician—or soldier, sailor, airman, or marine—members must comport with strict expectations of behavior, including the refusal to engage in illegal actions or those contrary to professional ethics. Individuals in both professions acquire a highly specialized body of knowledge and enter an implied contract to provide critical services to society, specifically healing and protection, respectively. Members of both professions are trained to make complex judgments with integrity under conditions of technical and ethical uncertainty, upon which they take highly skilled action. Medical and military professionals must be free to act on their ethical principles, without confounding demands.4 However, the context of each profession’s commitment to society carries different moral implications.
The risk of moral injury is inherent in military service. The military promises protection with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. In contrast, HCPs promise healing and care. The military promises to protect our society, with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. Some military actions may inflict harm without the hope of benefitting an individual, and are therefore potentially morally injurious. The health care contract with society, promising healing and care, is devoid of inherent moral injury due to harm without potential individual benefit. Therefore, the presence of moral injury in health care settings are warning signs of a dysfunctional environment.
One complex example of the dysfunctional environments is illustrative. The military and health care are among the few industries where supply creates demand. For example, the more bad state actors there are, the more demand for the military. As we have seen since the 1950s, the more technology and therapeutics we create in health care, coupled with a larger share paid for by third parties, the greater the demand for and use of them.5 In a fee for service environment, corporate greed feeds on this reality. In most other environments, more technological and therapeutic options inevitably pit clinicians against multiple other factions: payers, who do not want to underwrite them; patients, who sometimes demand them without justification or later rail against spiraling health care costs; and administrators, especially in capitated systems, who watch their bottom lines erode. The moral injury risk in this instance demands a collective conversation among stakeholders regarding the structural determinants of health—how we choose to distribute limited resources. The intermediary of moral injury is a useful measure of the harm that results from ignoring or avoiding such challenges.
HARMONIZING DEFINITIONS
Moral injury is inherently nuanced. The 2 dominant definitions arise from work with combat veterans and create additional and perhaps unnecessary complexity. Unifying these 2 definitions eliminates inadvertent confusion, preventing the risk of unbridled interdisciplinary investigation which leads to a lack of precision in the meaning of moral injury and other related concepts, such as burnout.6
The first definition was developed by Jonathan Shay in 1994 and outlines 3 necessarycomponents, viewing the violator as a powerholder: (1) betrayal of what is right, (2) by someone who holds legitimate authority, (3) in a high stakes situation.7 Litz and colleagues describe moral injury another way: “Perpetrating, failing to prevent, bearing witness to, or learning about acts that transgress deeply held moral beliefs and expectations.”8 The violator is posited to be either the self or others.
Rather than representing “self” or “other” imposed moral injury, we propose the 2 definitions are related as exposure (ie, the perceived betrayal) and response (ie, the resulting transgression). An individual who experiences a betrayal by a legitimate authority has an opportunity to choose their response. They may acquiesce and transgress their moral beliefs (eg, their oath to provide ethical health care), or they could refuse, by speaking out, or in some way resisting the authority’s betrayal. The case of Ray Brovont is a useful illustration of reconciling the definitions (Box).9
Myriad factors—known as potentially morally injurious events—drive moral injury, such as resource-constrained decision making, witnessing the behaviors of colleagues that violate deeply held moral beliefs, questionable billing practices, and more. Each begins with a betrayal. Spotlighting the betrayal, refusing to perpetuate it, or taking actions toward change, may reduce the risk of experiencing moral injury.9 Conversely, acquiescing and transgressing one’s oath, the profession’s covenant with society, increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.8
Many HCPs believe they are not always free to resist betrayal, fearing retaliation, job loss, blacklisting, or worse. They feel constrained by debt accrued while receiving their education, being their household’s primary earner, community ties, practicing a niche specialty that requires working for a tertiary referral center, or perhaps believing the situation will be the same elsewhere. To not stand up or speak out is to choose complicity with corporate greed that uses HCPs to undermine their professional duties, which significantly increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.
MORAL INJURY AND BURNOUT
In addition to reconciling the definitions of moral injury, the relationship between moral injury and burnout are still being elucidated. We suggest that moral injury and burnout represent independent and potentially interrelated pathways to distress (Figure). Exposure to chronic, inconsonant, and transactional demands, which things like shorter work hours, better self-care, or improved health system operations might mitigate, manifests as burnout. In contrast, moral injury arises when a superior’s actions or a system’s policies and practices—such as justifiable but unnecessary testing, or referral restrictions to prevent revenue leakage—undermine one’s professional obligations to prioritize the patient’s best interest.
If concerns from HCPs about transactional demands are persistently dismissed, such inaction may be perceived as a betrayal, raising the risk of moral injury. Additionally, the resignation or helplessness of moral injury perceived as inescapable may present with emotional exhaustion, ineffectiveness, and depersonalization, all hallmarks of burnout. Both conditions can mediate and moderate the relationship between triggers for workplace distress and resulting psychological, physical, and existential harm.
CONCLUSIONS
Moral injury is increasingly recognized as a source of distress among HCPs, resulting from structural constraints on their ability to deliver optimal care and their own unwillingness to stand up for their patients, their oaths, and their professions.1 Unlike the military, where moral injury is inherent in the contract with society, moral injury in health care (and the relational rupture it connotes) is a signal of systemic dysfunction, fractured trust, and the need for relational repair.
Health care is at a crossroads, experiencing a workforce retention crisis while simultaneously predicting a significant increase in care needs by Baby Boomers over the next 3 decades.
Health care does not have the luxury of experimenting another 30 years with interventions that have limited impact. We must design a new generation of approaches, shaped by lessons learned from the pandemic while acknowledging that prepandemic standards were already failing the workforce. A unified definition of moral injury must be integrated to frame clinician distress alongside burnout, recentering ethical decision making, rather than profit, at the heart of health care. Harmonizing the definitions of moral injury and clarifying the relationship of moral injury with burnout reduces the need for further reinterpretations, allowing for more robust, easily comparable studies focused on identifying risk factors, as well as rapidly implementing effective mitigation strategies.
Moral injury was identified by health care professionals (HCPs) as a driver of occupational distress prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, but the crisis expanded the appeal and investigation of the term.1 HCPs now consider moral injury an essential component of the framework to describe their distress, because using the term burnout alone fails to capture their full experience and has proven resistant to interventions.2 Moral injury goes beyond the transdiagnostic symptoms of exhaustion and cynicism and beyond operational, demand-resource mismatches that characterize burnout. It describes the frustration, anger, and helplessness associated with relational ruptures and the existential threats to a clinician’s professional identity as business interests erode their ability to put their patients’ needs ahead of corporate and health care system obligations.3
Proper characterization of moral injury in health care—separate from the military environments where it originated—is stymied by an ill-defined relationship between 2 definitions of the term and by an unclear relationship between moral injury and the long-standing body of scholarship in burnout. To clarify the concept, inform research agendas, and open avenues for more effective solutions to the crisis of HCP distress, we propose a unified conceptualization of moral injury and its association with burnout in health care.
CONTEXTUAL DISTINCTIONS
It is important to properly distinguish between the original use of moral injury in the military and its expanded use in civilian circumstances. Health care and the military are both professions whereupon donning the “uniform” of a physician—or soldier, sailor, airman, or marine—members must comport with strict expectations of behavior, including the refusal to engage in illegal actions or those contrary to professional ethics. Individuals in both professions acquire a highly specialized body of knowledge and enter an implied contract to provide critical services to society, specifically healing and protection, respectively. Members of both professions are trained to make complex judgments with integrity under conditions of technical and ethical uncertainty, upon which they take highly skilled action. Medical and military professionals must be free to act on their ethical principles, without confounding demands.4 However, the context of each profession’s commitment to society carries different moral implications.
The risk of moral injury is inherent in military service. The military promises protection with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. In contrast, HCPs promise healing and care. The military promises to protect our society, with an implicit acknowledgment of the need to use lethal force to uphold the agreement. Some military actions may inflict harm without the hope of benefitting an individual, and are therefore potentially morally injurious. The health care contract with society, promising healing and care, is devoid of inherent moral injury due to harm without potential individual benefit. Therefore, the presence of moral injury in health care settings are warning signs of a dysfunctional environment.
One complex example of the dysfunctional environments is illustrative. The military and health care are among the few industries where supply creates demand. For example, the more bad state actors there are, the more demand for the military. As we have seen since the 1950s, the more technology and therapeutics we create in health care, coupled with a larger share paid for by third parties, the greater the demand for and use of them.5 In a fee for service environment, corporate greed feeds on this reality. In most other environments, more technological and therapeutic options inevitably pit clinicians against multiple other factions: payers, who do not want to underwrite them; patients, who sometimes demand them without justification or later rail against spiraling health care costs; and administrators, especially in capitated systems, who watch their bottom lines erode. The moral injury risk in this instance demands a collective conversation among stakeholders regarding the structural determinants of health—how we choose to distribute limited resources. The intermediary of moral injury is a useful measure of the harm that results from ignoring or avoiding such challenges.
HARMONIZING DEFINITIONS
Moral injury is inherently nuanced. The 2 dominant definitions arise from work with combat veterans and create additional and perhaps unnecessary complexity. Unifying these 2 definitions eliminates inadvertent confusion, preventing the risk of unbridled interdisciplinary investigation which leads to a lack of precision in the meaning of moral injury and other related concepts, such as burnout.6
The first definition was developed by Jonathan Shay in 1994 and outlines 3 necessarycomponents, viewing the violator as a powerholder: (1) betrayal of what is right, (2) by someone who holds legitimate authority, (3) in a high stakes situation.7 Litz and colleagues describe moral injury another way: “Perpetrating, failing to prevent, bearing witness to, or learning about acts that transgress deeply held moral beliefs and expectations.”8 The violator is posited to be either the self or others.
Rather than representing “self” or “other” imposed moral injury, we propose the 2 definitions are related as exposure (ie, the perceived betrayal) and response (ie, the resulting transgression). An individual who experiences a betrayal by a legitimate authority has an opportunity to choose their response. They may acquiesce and transgress their moral beliefs (eg, their oath to provide ethical health care), or they could refuse, by speaking out, or in some way resisting the authority’s betrayal. The case of Ray Brovont is a useful illustration of reconciling the definitions (Box).9
Myriad factors—known as potentially morally injurious events—drive moral injury, such as resource-constrained decision making, witnessing the behaviors of colleagues that violate deeply held moral beliefs, questionable billing practices, and more. Each begins with a betrayal. Spotlighting the betrayal, refusing to perpetuate it, or taking actions toward change, may reduce the risk of experiencing moral injury.9 Conversely, acquiescing and transgressing one’s oath, the profession’s covenant with society, increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.8
Many HCPs believe they are not always free to resist betrayal, fearing retaliation, job loss, blacklisting, or worse. They feel constrained by debt accrued while receiving their education, being their household’s primary earner, community ties, practicing a niche specialty that requires working for a tertiary referral center, or perhaps believing the situation will be the same elsewhere. To not stand up or speak out is to choose complicity with corporate greed that uses HCPs to undermine their professional duties, which significantly increases the risk of experiencing moral injury.
MORAL INJURY AND BURNOUT
In addition to reconciling the definitions of moral injury, the relationship between moral injury and burnout are still being elucidated. We suggest that moral injury and burnout represent independent and potentially interrelated pathways to distress (Figure). Exposure to chronic, inconsonant, and transactional demands, which things like shorter work hours, better self-care, or improved health system operations might mitigate, manifests as burnout. In contrast, moral injury arises when a superior’s actions or a system’s policies and practices—such as justifiable but unnecessary testing, or referral restrictions to prevent revenue leakage—undermine one’s professional obligations to prioritize the patient’s best interest.
If concerns from HCPs about transactional demands are persistently dismissed, such inaction may be perceived as a betrayal, raising the risk of moral injury. Additionally, the resignation or helplessness of moral injury perceived as inescapable may present with emotional exhaustion, ineffectiveness, and depersonalization, all hallmarks of burnout. Both conditions can mediate and moderate the relationship between triggers for workplace distress and resulting psychological, physical, and existential harm.
CONCLUSIONS
Moral injury is increasingly recognized as a source of distress among HCPs, resulting from structural constraints on their ability to deliver optimal care and their own unwillingness to stand up for their patients, their oaths, and their professions.1 Unlike the military, where moral injury is inherent in the contract with society, moral injury in health care (and the relational rupture it connotes) is a signal of systemic dysfunction, fractured trust, and the need for relational repair.
Health care is at a crossroads, experiencing a workforce retention crisis while simultaneously predicting a significant increase in care needs by Baby Boomers over the next 3 decades.
Health care does not have the luxury of experimenting another 30 years with interventions that have limited impact. We must design a new generation of approaches, shaped by lessons learned from the pandemic while acknowledging that prepandemic standards were already failing the workforce. A unified definition of moral injury must be integrated to frame clinician distress alongside burnout, recentering ethical decision making, rather than profit, at the heart of health care. Harmonizing the definitions of moral injury and clarifying the relationship of moral injury with burnout reduces the need for further reinterpretations, allowing for more robust, easily comparable studies focused on identifying risk factors, as well as rapidly implementing effective mitigation strategies.
1. Griffin BJ, Weber MC, Hinkson KD, et al. Toward a dimensional contextual model of moral injury: a scoping review on healthcare workers. Curr Treat Options Psych. 2023;10:199-216. doi:10.1007/s40501-023-00296-4
2. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; National Academy of Medicine; Committee on Systems Approaches to Improve Patient Care by Supporting Clinician Well-Being. Taking Action Against Clinician Burnout: A Systems Approach to Professional Well-Being. The National Academies Press; 2019. doi:10.17226/25521
3. Dean W, Talbot S, Dean A. Reframing clinician distress: moral injury not burnout. Fed Pract. 2019;36(9):400-402.
4. Gardner HE, Schulman LS. The professions in America today: crucial but fragile. Daedalus. 2005;134(3):13-18. doi:10.1162/0011526054622132
5. Fuchs VR. Major trends in the U.S. health economy since 1950. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(11):973-977. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1200478
6. Molendijk T. Warnings against romanticising moral injury. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220(1):1-3. doi:10.1192/bjp.2021.114
7. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanalytic Psychol. 2014;31(2):182-191. doi:10.1037/a0036090
8. Litz BT, Stein N, Delaney E, et al. Moral injury and moral repair in war veterans: a preliminary model and intervention strategy. Clin Psychol Rev. 2009;29(8):695-706. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.07.003
9. Brovont v KS-I Med. Servs., P.A., 622 SW3d 671 (Mo Ct App 2020).
1. Griffin BJ, Weber MC, Hinkson KD, et al. Toward a dimensional contextual model of moral injury: a scoping review on healthcare workers. Curr Treat Options Psych. 2023;10:199-216. doi:10.1007/s40501-023-00296-4
2. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; National Academy of Medicine; Committee on Systems Approaches to Improve Patient Care by Supporting Clinician Well-Being. Taking Action Against Clinician Burnout: A Systems Approach to Professional Well-Being. The National Academies Press; 2019. doi:10.17226/25521
3. Dean W, Talbot S, Dean A. Reframing clinician distress: moral injury not burnout. Fed Pract. 2019;36(9):400-402.
4. Gardner HE, Schulman LS. The professions in America today: crucial but fragile. Daedalus. 2005;134(3):13-18. doi:10.1162/0011526054622132
5. Fuchs VR. Major trends in the U.S. health economy since 1950. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(11):973-977. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1200478
6. Molendijk T. Warnings against romanticising moral injury. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220(1):1-3. doi:10.1192/bjp.2021.114
7. Shay J. Moral injury. Psychoanalytic Psychol. 2014;31(2):182-191. doi:10.1037/a0036090
8. Litz BT, Stein N, Delaney E, et al. Moral injury and moral repair in war veterans: a preliminary model and intervention strategy. Clin Psychol Rev. 2009;29(8):695-706. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.07.003
9. Brovont v KS-I Med. Servs., P.A., 622 SW3d 671 (Mo Ct App 2020).
Graduate Medical Education Financing in the US Department of Veterans Affairs
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has partnered with academic medical centers and programs since 1946 to provide clinical training for physician residents. Ranking second in federal graduate medical education (GME) funding to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the $850 million VA GME budget annually reimburses > 250 GME-sponsoring institutions (affiliates) of 8000 GME programs for the clinical training of 49,000 individual residents rotating through > 11,000 full-time equivalent (FTE) positions.1 The VA also distributes $1.6 billion to VA facilities to offset the costs of conducting health professions education (HPE) (eg, facility infrastructure, salary support for VA instructors and preceptors, education office administration, and instructional equipment).2 The VA financial and educational contributions account for payment of 11% of resident positions nationally and allow academic medical centers to be less reliant on CMS GME funding.3,4 The VA contributions also provide opportunities for GME expansion,1,5,6 educational innovations,5,7 interprofessional and team-based care,8,9 and quality and safety training.10,11 The Table provides a comparison of CMS and VA GME reimbursability based on activity.
GME financing is complex, particularly the formulaic approach used by CMS, the details of which are often obscured in federal regulations. Due to this complexity and the $16 billion CMS GME budget, academic publications have focused on CMS GME financing while not fully explaining the VA GME policies and processes.4,12-14 By comparison, the VA GME financing model is relatively straightforward and governed by different statues and VA regulations, yet sharing some of the same principles as CMS regulations. Given the challenges in CMS reimbursement to fully support the cost of resident education, as well as the educational opportunities at the VA, the VA designs its reimbursement model to assure that affiliates receive appropriate payments.4,12,15 To ensure the continued success of VA GME partnerships, knowledge of VA GME financing has become increasingly important for designated institutional officers (DIOs) and residency program directors, particularly in light of recent investigations into oversight of the VA’s reimbursement to academic affiliates.
VA AUTHORITY
While the VA’s primary mission is “to provide a complete hospital medical service for the medical care and treatment of veterans,”early VA leaders recognized the importance of affiliating with the nation’s academic institutions.19 In 1946, the VA Policy Memorandum Number 2 established a partnership between the VA and the academic medical community.20 Additional legislation authorized specific agreements with academic affiliates for the central administration of salary and benefits for residents rotating at VA facilities. This process, known as disbursement, is an alternative payroll mechanism whereby the VA reimburses the academic affiliate for resident salary and benefits and the affiliate acts as the disbursing agent, issuing paychecks to residents.21,22
Resident FUNDING
By policy, with rare exceptions, the VA does not sponsor residency programs due to the challenges of providing an appropriate patient mix of age, sex, and medical conditions to meet accreditation standards.4 Nearly all VA reimbursements are for residents in affiliate-sponsored programs, while just 1% pays for residents in legacy, VA-sponsored residency programs at 2 VA facilities. The VA budget for resident (including fellows) salary and benefits is managed by the VA Office of Academic Affiliations (OAA), the national VA office responsible for oversight, policy, and funding of VA HPE programs.
Resident Salaries and Benefits
VA funding of resident salary and benefits are analogous with CMS direct GME (DGME), which is designed to cover resident salary and benefits costs.4,14,23 CMS DGME payments depend on a hospital’s volume of CMS inpatients and are based on a statutory formula, which uses the hospital’s resident FTE positions, the per-resident amount, and Medicare’s share of inpatient beds (Medicare patient load) to determine payments.12 The per-resident amount is set by statute, varies geographically, and is calculated by dividing the hospital’s allowable costs of GME (percentage of CMS inpatient days) divided by the number of residents.12,24
By comparison, the VA GME payment reimburses for each FTE based on the salary and benefits rate set by the academic affiliate. Reimbursement is calculated based on resident time spent at the VA multiplied by a daily salary rate. The daily salary rate is determined by dividing the resident’s total compensation (salary and benefits) by the number of calendar days in an academic year. Resident time spent at the VA facility is determined by obtaining rotation schedules provided by the academic affiliate and verifying resident clinical and educational activity during scheduled rotations.
Indirect Medical Education Funding
In addition to resident salary and benefits, funds to offset the cost of conducting HPE are provided to VA facilities. These funds are intended to improve and maintain necessary infrastructure for all HPE programs not just GME, including education office administration needs, teaching costs (ie, a portion of VA preceptors salary), and instructional equipment.
The Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation (VERA) is a national budgeting process for VA medical facilities that funds facility operational needs such as staff salary and benefits, infrastructure, and equipment.2 The education portion of the VERA, the VERA Education Support Component (VESC), is not managed by the OAA, but rather is distributed through the VERA model to the general budget of VA facilities hosting HPE (Figure). VESC funding in the VA budget is based on labor mapping of physician time spent in education; other labor mapping categories include clinical care, research, and administration. VA facility VESC funding is calculated based on the number of paid health profession trainees (HPTs) from all professions, apportioned according to the number of FTEs for physician residents and VA-paid HPTs in other disciplines. In fiscal year 2024, VA facilities received $115,812 for each physician resident FTE position and $84,906 for each VA-paid, non-GME FTE position.
The VESC is like CMS's indirect GME funding, termed Indirect Medical Education (IME), an additional payment for each Medicare patient discharged reflecting teaching hospitals’ higher patient care costs relative to nonteaching hospitals. Described elsewhere, IME is calculated using a resident-to-bed ratio and a multiplier, which is set by statute.4,25 While IME can be used for reimbursement for some resident clinical and educational activities(eg, research), VA VESC funds cannot be used for such activities and are part of the general facility budget and appropriated per the discretion of the medical facility director.
ESTABLISHING GME PARTNERSHIPS
An affiliation agreement establishes the administrative and legal requirements for educational relationships with academic affiliates and includes standards for conducting HPE, responsibilities for accreditation standards, program leadership, faculty, resources, supervision, academic policies, and procedures. The VA uses standardized affiliation agreement templates that have been vetted with accrediting bodies and the VA Office of General Counsel.
A disbursement agreement authorizes the VA to reimburse affiliates for resident salary and benefits for VA clinical and educational activities. The disbursement agreement details the fiscal arrangements (eg, payment in advance vs arrears, salary, and benefit rates, leave) for the reimbursement payments. Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1400.05 provides the policy and procedures for calculating reimbursement for HPT educational activities.26
The VA facility designated education officer (DEO) oversees all HPE programs and coordinates the affiliation and disbursement agreement processes.27 The DEO, affiliate DIO, residency program director, and VA residency site director determine the physician resident FTE positions assigned to a VA facility based on educational objectives and availability of educational resources at the VA facility, such as patient care opportunities, faculty supervisors, space, and equipment. The VA facility requests for resident FTE positions are submitted to the OAA by the facility DEO.
Once GME FTE positions are approved by the OAA, VA facilities work with their academic affiliate to submit the physician resident salary and benefit rate. Affiliate DIOs attest to the accuracy of the salary rate schedule and the local DEO submits the budget request to the OAA. Upon approval, the funds are transferred to the VA facility each fiscal year, which begins October 1. DEOs report quarterly to the OAA both budget needs and excesses based on variations in the approved FTEs due to additional VA rotations, physician resident attrition, or reassignment.
Resident Position Allocation
VA GME financing provides flexibility through periodic needs assessments and expansion initiatives. In August and December, DEOs collaborate with an academic affiliate to submit reports to the OAA confirming their projected GME needs for the next academic year. Additional positions requests are reviewed by the OAA; funding depends on budget and the educational justification. The OAA periodically issues GME expansion requests for proposal, which typically arise from legislation to address specific VA workforce needs. The VA facility DEO and affiliate GME leaders collaborate to apply for additional positions. For example, a VA GME expansion under the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 added 1500 GME positions in 8 years for critically needed specialties and in rural and underserved areas.5 The Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018 authorized a pilot program for VA to fund residents at non-VA facilities with priority for Indian Health Services, Tribes and Tribal Organizations, Federally Qualified Health Centers, and US Department of Defense facilities to provide access to veterans in underserved areas.6
The VA GME financing system has flexibility to meet local needs for additional resident positions and to address broader VA workforce gaps through targeted expansion. Generally, CMS does not fund positions to address workforce needs, place residents in specific geographic areas, or require the training of certain types of residents.4 However, the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 has provided the opportunity to address rural workforce needs.28
Reimbursement
The VA provides reimbursement for clinical and educational activities performed in VA facilities for the benefit of veterans as well as research, didactics, meetings and conferences, annual and sick leave, and orientation. The VA also may provide reimbursement for educational activities that occur off VA grounds (eg, the VA proportional share of a residency program’s didactic sessions). The VA does not reimburse for affiliate clinical duties or administrative costs, although a national policy allows VA facilities to reimburse affiliates for some GME overhead costs.29
CMS similarly reimburses for residency training time spent in patient care activities as well as orientation activities, didactics, leave, and, in some cases, research.4,30,31 CMS makes payments to hospitals, which may include sponsoring institutions and Medicare-eligible participating training sites.4,30,31 For both the VA and CMS, residents may not be counted twice for reimbursement by 2 federal agencies; in other words, a resident may not count for > 1 FTE.4,30-32
GME Oversight
VA GME funding came under significant scrutiny. At a 2016 House Veterans Affairs Committee hearing, Representative Phil Roe, MD (R-Tennessee), noted that no process existed at many VA facilities for “determining trainee presence” and that many VA medical centers had “difficulty tracking resident rotations”16 A VA Office of the Inspector General investigation recommended that the VA implement policies and procedures to improve oversight to “ensure residents are fully participating in educational activities” and that the VA is “paying the correct amount” to the affiliate.17 A 2020 General Accountability Office report outlined unclear policy guidance, incomplete tracking of resident activities, and improper fiscal processes for reimbursement and reconciliation of affiliate invoices.18
In response, the OAA created an oversight and compliance unit, revised VHA Directive 1400.05 (the policy for disbursement), and improved resident tracking procedures.26 The standard operating procedure that accompanied VHA Directive 1400.05 provides detailed information for the DEO and VA facility staff for tracking resident clinical and educational activities. FTE counts are essential to both VA and CMS for accurate reimbursement. The eAppendix and the Table provide a guide to reimbursable activities in the VA for the calculation of reimbursement, with a comparison to CMS.33,34 The OAA in cooperation with other VA staff and officers periodically conducts audits to assess compliance with disbursement policy and affiliate reimbursement accuracy.
In the VA, resident activities are captured on the VA Educational Activity Record, a standardized spreadsheet to track activities and calculate reimbursement. Each VA facility hosting resident physicians manually records resident activity by the half-day. This process is labor intensive, involving both VA and affiliate staff to accurately reconcile payments. To address the workload demands, the OAA is developing an online tool that will automate aspects of the tracking process. Also, to ensure adequate staffing, the OAA is in the process of implementing an office optimization project, providing standardized position descriptions, an organizational chart, and staffing levels for DEO offices in VA facilities.
Conclusions
This report describes the key policies and principles of VA GME financing, highlighting the essential similarities and differences between VA and CMS. Neither the VA nor CMS regulations allow for reimbursement for > 1 FTE position per resident, a principle that underpins the assignment of resident rotations and federal funding for GME and are similar with respect to reimbursement for patient care activities, didactics, research, orientation, and scholarly activity. While reimbursable activities in the VA require physical presence and care of veteran patients, CMS also limits reimbursement to resident activities in the hospital and approved other settings if the hospital is paying for resident salary and benefits in these settings. The VA provides some flexibility for offsite activities including didactics and, in specific circumstances, remote care of veteran patients (eg, teleradiology).
The VA and CMS use different GME financing models. For example, the CMS calculations for resident FTEs are complex, whereas VA calculations reimburse the salary and benefits as set by the academic affiliate. The VA process accounts for local variation in salary rates, whereas the per-resident amount set by CMS varies regionally and does not fully account for differences in the cost of living.24 Because all patients in VA facilities are veterans, VA calculations for reimbursement do not involve ratios of beds like the CMS calculations to determine a proportional share of reimbursement. The VA GME expansion tends to be more directed to VA health workforce needs than CMS, specifying the types of programs and geographic locations to address these needs.
The VA regularly reevaluates how affiliates are reimbursed for VA resident activity, balancing compliance with VA policies and the workload for VA and its affiliates. The VA obtains input from key stakeholders including DEOs, DIOs, and professional organizations such as the Association of American Medical Colleges and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.35,36
Looking ahead, the VA is developing an online tool to improve the accuracy of affiliate reimbursement. The VA will also implement a standardized staffing model, organizational structure, and position descriptions for DEO offices. These initiatives will help reduce the burden of tracking and verifying resident activity and continue to support the 77-year partnership between VA and its affiliated institutions.
1. Klink KA, Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM. Veterans Affairs graduate medical education expansion addresses US physician workforce needs. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1144-1150. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004545
2. Andrus CH, Johnson K, Pierce E, Romito PJ, Hartel P, Berrios‐Guccione S, Best W. Finance modeling in the delivery of medical care in tertiary‐care hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Surg Res. 2001;96(2):152-157. doi:10.1006/jsre.1999.5728
3. Petrakis IL, Kozal M. Academic medical centers and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a 75-year partnership influences medical education, scientific discovery, and clinical care. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1110-1113. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004734
4. Heisler EJ, Mendez BH, Mitchell A, Panangala SV, Villagrana MA. Federal support for graduate medical education: an overview (R44376). Congressional Research Service report R44376; version 11. Updated December 27, 2018. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R44376/11
5. Chang BK, Brannen JL. The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014: examining graduate medical education enhancement in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Acad Med. 2015;90(9):1196-1198. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000000795
6. Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
7. Lypson ML, Roberts LW. Valuing the partnership between the Veterans Health Administration and academic medicine. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1091-1093. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004748
8. Harada ND, Traylor L, Rugen KW, et al. Interprofessional transformation of clinical education: the first six years of the Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education. J Interprof Care. 2023;37(suppl 1):S86-S94. doi:10.1080/13561820.2018.1433642

9. Harada ND, Rajashekara S, Sansgiry S, et al. Developing interprofessional primary care teams: alumni evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education Program. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519875455. doi:10.1177/2382120519875455
10. Splaine ME, Ogrinc G, Gilman SC, et al. The Department of Veterans Affairs National Quality Scholars Fellowship Program: experience from 10 years of training quality scholars. Acad Med. 2009;84(12):1741-1748. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181bfdcef
11. Watts BV, Paull DE, Williams LC, Neily J, Hemphill RR, Brannen JL. Department of Veterans Affairs chief resident in quality and patient safety program: a model to spread change. Am J Med Qual. 2016;31(6):598-600. doi:10.1177/1062860616643403
12. He K, Whang E, Kristo G. Graduate medical education funding mechanisms, challenges, and solutions: a narrative review. Am J Surg. 2021;221(1):65-71. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.06.007
13. Villagrana M. Medicare graduate medical education payments: an overview. Congressional Research Service report IF10960. Updated September 29, 2022. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF10960
14. Committee on the Governance and Financing of Graduate Medical Education; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine. Graduate Medical Education That Meets the Nation’s Health Needs. Eden J, Berwick DM, Wilensky GR, eds. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2014. doi:10.17226/18754
15. Physician workforce: caps on Medicare-funded graduate medical education at teaching hospitals. Report to congressional requesters. GAO-21-391. May 21, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-21-391.pdf
16. VA and Academic Affiliates: Who Benefits? Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations of the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, 114th Cong, 2nd Sess (2016). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CHRG-115hhrg29685/html/CHRG-115hhrg29685.htm
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General (OIG). Veterans Health Administration. Review of resident and part-time physician time and attendance at the Oklahoma City VA Health Care System. OIG report 17-00253-93. March 28, 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.oversight.gov/sites/default/files/oig-reports/VAOIG-17-00253-93.pdf
18. VA health care: actions needed to improve oversight of graduate medical education reimbursement. Report to the ranking member, Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, House of Representatives. GAO-20-553. July 2020. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/710/708275.pdf
19. Functions of Veterans Health Administration: in general, 38 USC §7301 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap73-subchapI-sec7301.pdf
20. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Policy memorandum no. 2, policy in association of veterans’ hospitals with medical schools. January 30, 1946.
21. Veterans Health Care Expansion Act of 1973, Public Law 93-82. August 2, 1973. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-87/pdf/STATUTE-87-Pg179.pdf
22. Residencies and internships, 38 USC § 7406 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap74-subchapI-sec7406.pdf
23. Direct graduate medical education (DGME). Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services. Updated December 5, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/DGME
24. Drezdzon MK, Cowley NJ, Sweeney DP, et al. Going for broke: the impact of cost of living on surgery resident stipend value. Ann Surg. 2023;278(6):1053-1059. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000005923
25. Special treatment: hospitals that incur indirect costs for graduate medical education programs, 42 CFR § 412.105 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec412-105.pdf
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.05, Disbursement agreements for health professions trainees appointed under 38 U.S.C. § 7406. June 2, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9293
27. Harada ND, Sanders KM, Bowman MA. Health systems education leadership: learning from the VA designated education officer role. Fed Pract. 2022;39(6):266-273. doi:10.12788/fp.0278
28. Schleiter Hitchell K, Johnson L. CMS finalizes rules for distribution of 1000 new Medicare-funded residency positions and changes to rural training track programs. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14(2):245-249. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-22-00193.1

29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.10, Educational cost contracts for health professions education. September 25, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/VHAPUBLICATIONS/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11480
30. Direct GME payments: general requirements, 42 CFR § 413.75 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-75.pdf
31. Direct GME payments: determination of the total number of FTE residents, 42 CFR § 413.78 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-78.pdf
32. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare financial management manual, chapter 8. Contractor procedures for provider audits. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/regulations-and-guidance/guidance/manuals/downloads/fin106c08.pdf
33. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Inspector General. CMS did not always ensure hospitals complied with Medicare reimbursement requirements for graduate medical education. OIG report A-02-17-01017. November 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oas/reports/region2/21701017.pdf
34. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Interns and Residents Information System (IRIS) XML format. Publication 100-20. Transmittal 11418. Change request 12724. May 19, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/guidance/sites/default/files/hhs-guidance-documents/R11418OTN.pdf
35. Birnbaum AD, Byrne J, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. VHA Updates: Disbursement Policy and Education Cost Contracts. Presented at: American Association of Medical Colleges Webinar; June 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://vimeo.com/644415670
36. Byrne JM, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. Disbursement procedures update for AY 23-24. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/oaa/Videos/AffiliatePresentationDisbursementandEARsAY23-24.pptx
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has partnered with academic medical centers and programs since 1946 to provide clinical training for physician residents. Ranking second in federal graduate medical education (GME) funding to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the $850 million VA GME budget annually reimburses > 250 GME-sponsoring institutions (affiliates) of 8000 GME programs for the clinical training of 49,000 individual residents rotating through > 11,000 full-time equivalent (FTE) positions.1 The VA also distributes $1.6 billion to VA facilities to offset the costs of conducting health professions education (HPE) (eg, facility infrastructure, salary support for VA instructors and preceptors, education office administration, and instructional equipment).2 The VA financial and educational contributions account for payment of 11% of resident positions nationally and allow academic medical centers to be less reliant on CMS GME funding.3,4 The VA contributions also provide opportunities for GME expansion,1,5,6 educational innovations,5,7 interprofessional and team-based care,8,9 and quality and safety training.10,11 The Table provides a comparison of CMS and VA GME reimbursability based on activity.
GME financing is complex, particularly the formulaic approach used by CMS, the details of which are often obscured in federal regulations. Due to this complexity and the $16 billion CMS GME budget, academic publications have focused on CMS GME financing while not fully explaining the VA GME policies and processes.4,12-14 By comparison, the VA GME financing model is relatively straightforward and governed by different statues and VA regulations, yet sharing some of the same principles as CMS regulations. Given the challenges in CMS reimbursement to fully support the cost of resident education, as well as the educational opportunities at the VA, the VA designs its reimbursement model to assure that affiliates receive appropriate payments.4,12,15 To ensure the continued success of VA GME partnerships, knowledge of VA GME financing has become increasingly important for designated institutional officers (DIOs) and residency program directors, particularly in light of recent investigations into oversight of the VA’s reimbursement to academic affiliates.
VA AUTHORITY
While the VA’s primary mission is “to provide a complete hospital medical service for the medical care and treatment of veterans,”early VA leaders recognized the importance of affiliating with the nation’s academic institutions.19 In 1946, the VA Policy Memorandum Number 2 established a partnership between the VA and the academic medical community.20 Additional legislation authorized specific agreements with academic affiliates for the central administration of salary and benefits for residents rotating at VA facilities. This process, known as disbursement, is an alternative payroll mechanism whereby the VA reimburses the academic affiliate for resident salary and benefits and the affiliate acts as the disbursing agent, issuing paychecks to residents.21,22
Resident FUNDING
By policy, with rare exceptions, the VA does not sponsor residency programs due to the challenges of providing an appropriate patient mix of age, sex, and medical conditions to meet accreditation standards.4 Nearly all VA reimbursements are for residents in affiliate-sponsored programs, while just 1% pays for residents in legacy, VA-sponsored residency programs at 2 VA facilities. The VA budget for resident (including fellows) salary and benefits is managed by the VA Office of Academic Affiliations (OAA), the national VA office responsible for oversight, policy, and funding of VA HPE programs.
Resident Salaries and Benefits
VA funding of resident salary and benefits are analogous with CMS direct GME (DGME), which is designed to cover resident salary and benefits costs.4,14,23 CMS DGME payments depend on a hospital’s volume of CMS inpatients and are based on a statutory formula, which uses the hospital’s resident FTE positions, the per-resident amount, and Medicare’s share of inpatient beds (Medicare patient load) to determine payments.12 The per-resident amount is set by statute, varies geographically, and is calculated by dividing the hospital’s allowable costs of GME (percentage of CMS inpatient days) divided by the number of residents.12,24
By comparison, the VA GME payment reimburses for each FTE based on the salary and benefits rate set by the academic affiliate. Reimbursement is calculated based on resident time spent at the VA multiplied by a daily salary rate. The daily salary rate is determined by dividing the resident’s total compensation (salary and benefits) by the number of calendar days in an academic year. Resident time spent at the VA facility is determined by obtaining rotation schedules provided by the academic affiliate and verifying resident clinical and educational activity during scheduled rotations.
Indirect Medical Education Funding
In addition to resident salary and benefits, funds to offset the cost of conducting HPE are provided to VA facilities. These funds are intended to improve and maintain necessary infrastructure for all HPE programs not just GME, including education office administration needs, teaching costs (ie, a portion of VA preceptors salary), and instructional equipment.
The Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation (VERA) is a national budgeting process for VA medical facilities that funds facility operational needs such as staff salary and benefits, infrastructure, and equipment.2 The education portion of the VERA, the VERA Education Support Component (VESC), is not managed by the OAA, but rather is distributed through the VERA model to the general budget of VA facilities hosting HPE (Figure). VESC funding in the VA budget is based on labor mapping of physician time spent in education; other labor mapping categories include clinical care, research, and administration. VA facility VESC funding is calculated based on the number of paid health profession trainees (HPTs) from all professions, apportioned according to the number of FTEs for physician residents and VA-paid HPTs in other disciplines. In fiscal year 2024, VA facilities received $115,812 for each physician resident FTE position and $84,906 for each VA-paid, non-GME FTE position.
The VESC is like CMS's indirect GME funding, termed Indirect Medical Education (IME), an additional payment for each Medicare patient discharged reflecting teaching hospitals’ higher patient care costs relative to nonteaching hospitals. Described elsewhere, IME is calculated using a resident-to-bed ratio and a multiplier, which is set by statute.4,25 While IME can be used for reimbursement for some resident clinical and educational activities(eg, research), VA VESC funds cannot be used for such activities and are part of the general facility budget and appropriated per the discretion of the medical facility director.
ESTABLISHING GME PARTNERSHIPS
An affiliation agreement establishes the administrative and legal requirements for educational relationships with academic affiliates and includes standards for conducting HPE, responsibilities for accreditation standards, program leadership, faculty, resources, supervision, academic policies, and procedures. The VA uses standardized affiliation agreement templates that have been vetted with accrediting bodies and the VA Office of General Counsel.
A disbursement agreement authorizes the VA to reimburse affiliates for resident salary and benefits for VA clinical and educational activities. The disbursement agreement details the fiscal arrangements (eg, payment in advance vs arrears, salary, and benefit rates, leave) for the reimbursement payments. Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1400.05 provides the policy and procedures for calculating reimbursement for HPT educational activities.26
The VA facility designated education officer (DEO) oversees all HPE programs and coordinates the affiliation and disbursement agreement processes.27 The DEO, affiliate DIO, residency program director, and VA residency site director determine the physician resident FTE positions assigned to a VA facility based on educational objectives and availability of educational resources at the VA facility, such as patient care opportunities, faculty supervisors, space, and equipment. The VA facility requests for resident FTE positions are submitted to the OAA by the facility DEO.
Once GME FTE positions are approved by the OAA, VA facilities work with their academic affiliate to submit the physician resident salary and benefit rate. Affiliate DIOs attest to the accuracy of the salary rate schedule and the local DEO submits the budget request to the OAA. Upon approval, the funds are transferred to the VA facility each fiscal year, which begins October 1. DEOs report quarterly to the OAA both budget needs and excesses based on variations in the approved FTEs due to additional VA rotations, physician resident attrition, or reassignment.
Resident Position Allocation
VA GME financing provides flexibility through periodic needs assessments and expansion initiatives. In August and December, DEOs collaborate with an academic affiliate to submit reports to the OAA confirming their projected GME needs for the next academic year. Additional positions requests are reviewed by the OAA; funding depends on budget and the educational justification. The OAA periodically issues GME expansion requests for proposal, which typically arise from legislation to address specific VA workforce needs. The VA facility DEO and affiliate GME leaders collaborate to apply for additional positions. For example, a VA GME expansion under the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 added 1500 GME positions in 8 years for critically needed specialties and in rural and underserved areas.5 The Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018 authorized a pilot program for VA to fund residents at non-VA facilities with priority for Indian Health Services, Tribes and Tribal Organizations, Federally Qualified Health Centers, and US Department of Defense facilities to provide access to veterans in underserved areas.6
The VA GME financing system has flexibility to meet local needs for additional resident positions and to address broader VA workforce gaps through targeted expansion. Generally, CMS does not fund positions to address workforce needs, place residents in specific geographic areas, or require the training of certain types of residents.4 However, the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 has provided the opportunity to address rural workforce needs.28
Reimbursement
The VA provides reimbursement for clinical and educational activities performed in VA facilities for the benefit of veterans as well as research, didactics, meetings and conferences, annual and sick leave, and orientation. The VA also may provide reimbursement for educational activities that occur off VA grounds (eg, the VA proportional share of a residency program’s didactic sessions). The VA does not reimburse for affiliate clinical duties or administrative costs, although a national policy allows VA facilities to reimburse affiliates for some GME overhead costs.29
CMS similarly reimburses for residency training time spent in patient care activities as well as orientation activities, didactics, leave, and, in some cases, research.4,30,31 CMS makes payments to hospitals, which may include sponsoring institutions and Medicare-eligible participating training sites.4,30,31 For both the VA and CMS, residents may not be counted twice for reimbursement by 2 federal agencies; in other words, a resident may not count for > 1 FTE.4,30-32
GME Oversight
VA GME funding came under significant scrutiny. At a 2016 House Veterans Affairs Committee hearing, Representative Phil Roe, MD (R-Tennessee), noted that no process existed at many VA facilities for “determining trainee presence” and that many VA medical centers had “difficulty tracking resident rotations”16 A VA Office of the Inspector General investigation recommended that the VA implement policies and procedures to improve oversight to “ensure residents are fully participating in educational activities” and that the VA is “paying the correct amount” to the affiliate.17 A 2020 General Accountability Office report outlined unclear policy guidance, incomplete tracking of resident activities, and improper fiscal processes for reimbursement and reconciliation of affiliate invoices.18
In response, the OAA created an oversight and compliance unit, revised VHA Directive 1400.05 (the policy for disbursement), and improved resident tracking procedures.26 The standard operating procedure that accompanied VHA Directive 1400.05 provides detailed information for the DEO and VA facility staff for tracking resident clinical and educational activities. FTE counts are essential to both VA and CMS for accurate reimbursement. The eAppendix and the Table provide a guide to reimbursable activities in the VA for the calculation of reimbursement, with a comparison to CMS.33,34 The OAA in cooperation with other VA staff and officers periodically conducts audits to assess compliance with disbursement policy and affiliate reimbursement accuracy.
In the VA, resident activities are captured on the VA Educational Activity Record, a standardized spreadsheet to track activities and calculate reimbursement. Each VA facility hosting resident physicians manually records resident activity by the half-day. This process is labor intensive, involving both VA and affiliate staff to accurately reconcile payments. To address the workload demands, the OAA is developing an online tool that will automate aspects of the tracking process. Also, to ensure adequate staffing, the OAA is in the process of implementing an office optimization project, providing standardized position descriptions, an organizational chart, and staffing levels for DEO offices in VA facilities.
Conclusions
This report describes the key policies and principles of VA GME financing, highlighting the essential similarities and differences between VA and CMS. Neither the VA nor CMS regulations allow for reimbursement for > 1 FTE position per resident, a principle that underpins the assignment of resident rotations and federal funding for GME and are similar with respect to reimbursement for patient care activities, didactics, research, orientation, and scholarly activity. While reimbursable activities in the VA require physical presence and care of veteran patients, CMS also limits reimbursement to resident activities in the hospital and approved other settings if the hospital is paying for resident salary and benefits in these settings. The VA provides some flexibility for offsite activities including didactics and, in specific circumstances, remote care of veteran patients (eg, teleradiology).
The VA and CMS use different GME financing models. For example, the CMS calculations for resident FTEs are complex, whereas VA calculations reimburse the salary and benefits as set by the academic affiliate. The VA process accounts for local variation in salary rates, whereas the per-resident amount set by CMS varies regionally and does not fully account for differences in the cost of living.24 Because all patients in VA facilities are veterans, VA calculations for reimbursement do not involve ratios of beds like the CMS calculations to determine a proportional share of reimbursement. The VA GME expansion tends to be more directed to VA health workforce needs than CMS, specifying the types of programs and geographic locations to address these needs.
The VA regularly reevaluates how affiliates are reimbursed for VA resident activity, balancing compliance with VA policies and the workload for VA and its affiliates. The VA obtains input from key stakeholders including DEOs, DIOs, and professional organizations such as the Association of American Medical Colleges and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.35,36
Looking ahead, the VA is developing an online tool to improve the accuracy of affiliate reimbursement. The VA will also implement a standardized staffing model, organizational structure, and position descriptions for DEO offices. These initiatives will help reduce the burden of tracking and verifying resident activity and continue to support the 77-year partnership between VA and its affiliated institutions.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has partnered with academic medical centers and programs since 1946 to provide clinical training for physician residents. Ranking second in federal graduate medical education (GME) funding to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), the $850 million VA GME budget annually reimburses > 250 GME-sponsoring institutions (affiliates) of 8000 GME programs for the clinical training of 49,000 individual residents rotating through > 11,000 full-time equivalent (FTE) positions.1 The VA also distributes $1.6 billion to VA facilities to offset the costs of conducting health professions education (HPE) (eg, facility infrastructure, salary support for VA instructors and preceptors, education office administration, and instructional equipment).2 The VA financial and educational contributions account for payment of 11% of resident positions nationally and allow academic medical centers to be less reliant on CMS GME funding.3,4 The VA contributions also provide opportunities for GME expansion,1,5,6 educational innovations,5,7 interprofessional and team-based care,8,9 and quality and safety training.10,11 The Table provides a comparison of CMS and VA GME reimbursability based on activity.
GME financing is complex, particularly the formulaic approach used by CMS, the details of which are often obscured in federal regulations. Due to this complexity and the $16 billion CMS GME budget, academic publications have focused on CMS GME financing while not fully explaining the VA GME policies and processes.4,12-14 By comparison, the VA GME financing model is relatively straightforward and governed by different statues and VA regulations, yet sharing some of the same principles as CMS regulations. Given the challenges in CMS reimbursement to fully support the cost of resident education, as well as the educational opportunities at the VA, the VA designs its reimbursement model to assure that affiliates receive appropriate payments.4,12,15 To ensure the continued success of VA GME partnerships, knowledge of VA GME financing has become increasingly important for designated institutional officers (DIOs) and residency program directors, particularly in light of recent investigations into oversight of the VA’s reimbursement to academic affiliates.
VA AUTHORITY
While the VA’s primary mission is “to provide a complete hospital medical service for the medical care and treatment of veterans,”early VA leaders recognized the importance of affiliating with the nation’s academic institutions.19 In 1946, the VA Policy Memorandum Number 2 established a partnership between the VA and the academic medical community.20 Additional legislation authorized specific agreements with academic affiliates for the central administration of salary and benefits for residents rotating at VA facilities. This process, known as disbursement, is an alternative payroll mechanism whereby the VA reimburses the academic affiliate for resident salary and benefits and the affiliate acts as the disbursing agent, issuing paychecks to residents.21,22
Resident FUNDING
By policy, with rare exceptions, the VA does not sponsor residency programs due to the challenges of providing an appropriate patient mix of age, sex, and medical conditions to meet accreditation standards.4 Nearly all VA reimbursements are for residents in affiliate-sponsored programs, while just 1% pays for residents in legacy, VA-sponsored residency programs at 2 VA facilities. The VA budget for resident (including fellows) salary and benefits is managed by the VA Office of Academic Affiliations (OAA), the national VA office responsible for oversight, policy, and funding of VA HPE programs.
Resident Salaries and Benefits
VA funding of resident salary and benefits are analogous with CMS direct GME (DGME), which is designed to cover resident salary and benefits costs.4,14,23 CMS DGME payments depend on a hospital’s volume of CMS inpatients and are based on a statutory formula, which uses the hospital’s resident FTE positions, the per-resident amount, and Medicare’s share of inpatient beds (Medicare patient load) to determine payments.12 The per-resident amount is set by statute, varies geographically, and is calculated by dividing the hospital’s allowable costs of GME (percentage of CMS inpatient days) divided by the number of residents.12,24
By comparison, the VA GME payment reimburses for each FTE based on the salary and benefits rate set by the academic affiliate. Reimbursement is calculated based on resident time spent at the VA multiplied by a daily salary rate. The daily salary rate is determined by dividing the resident’s total compensation (salary and benefits) by the number of calendar days in an academic year. Resident time spent at the VA facility is determined by obtaining rotation schedules provided by the academic affiliate and verifying resident clinical and educational activity during scheduled rotations.
Indirect Medical Education Funding
In addition to resident salary and benefits, funds to offset the cost of conducting HPE are provided to VA facilities. These funds are intended to improve and maintain necessary infrastructure for all HPE programs not just GME, including education office administration needs, teaching costs (ie, a portion of VA preceptors salary), and instructional equipment.
The Veterans Equitable Resource Allocation (VERA) is a national budgeting process for VA medical facilities that funds facility operational needs such as staff salary and benefits, infrastructure, and equipment.2 The education portion of the VERA, the VERA Education Support Component (VESC), is not managed by the OAA, but rather is distributed through the VERA model to the general budget of VA facilities hosting HPE (Figure). VESC funding in the VA budget is based on labor mapping of physician time spent in education; other labor mapping categories include clinical care, research, and administration. VA facility VESC funding is calculated based on the number of paid health profession trainees (HPTs) from all professions, apportioned according to the number of FTEs for physician residents and VA-paid HPTs in other disciplines. In fiscal year 2024, VA facilities received $115,812 for each physician resident FTE position and $84,906 for each VA-paid, non-GME FTE position.
The VESC is like CMS's indirect GME funding, termed Indirect Medical Education (IME), an additional payment for each Medicare patient discharged reflecting teaching hospitals’ higher patient care costs relative to nonteaching hospitals. Described elsewhere, IME is calculated using a resident-to-bed ratio and a multiplier, which is set by statute.4,25 While IME can be used for reimbursement for some resident clinical and educational activities(eg, research), VA VESC funds cannot be used for such activities and are part of the general facility budget and appropriated per the discretion of the medical facility director.
ESTABLISHING GME PARTNERSHIPS
An affiliation agreement establishes the administrative and legal requirements for educational relationships with academic affiliates and includes standards for conducting HPE, responsibilities for accreditation standards, program leadership, faculty, resources, supervision, academic policies, and procedures. The VA uses standardized affiliation agreement templates that have been vetted with accrediting bodies and the VA Office of General Counsel.
A disbursement agreement authorizes the VA to reimburse affiliates for resident salary and benefits for VA clinical and educational activities. The disbursement agreement details the fiscal arrangements (eg, payment in advance vs arrears, salary, and benefit rates, leave) for the reimbursement payments. Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1400.05 provides the policy and procedures for calculating reimbursement for HPT educational activities.26
The VA facility designated education officer (DEO) oversees all HPE programs and coordinates the affiliation and disbursement agreement processes.27 The DEO, affiliate DIO, residency program director, and VA residency site director determine the physician resident FTE positions assigned to a VA facility based on educational objectives and availability of educational resources at the VA facility, such as patient care opportunities, faculty supervisors, space, and equipment. The VA facility requests for resident FTE positions are submitted to the OAA by the facility DEO.
Once GME FTE positions are approved by the OAA, VA facilities work with their academic affiliate to submit the physician resident salary and benefit rate. Affiliate DIOs attest to the accuracy of the salary rate schedule and the local DEO submits the budget request to the OAA. Upon approval, the funds are transferred to the VA facility each fiscal year, which begins October 1. DEOs report quarterly to the OAA both budget needs and excesses based on variations in the approved FTEs due to additional VA rotations, physician resident attrition, or reassignment.
Resident Position Allocation
VA GME financing provides flexibility through periodic needs assessments and expansion initiatives. In August and December, DEOs collaborate with an academic affiliate to submit reports to the OAA confirming their projected GME needs for the next academic year. Additional positions requests are reviewed by the OAA; funding depends on budget and the educational justification. The OAA periodically issues GME expansion requests for proposal, which typically arise from legislation to address specific VA workforce needs. The VA facility DEO and affiliate GME leaders collaborate to apply for additional positions. For example, a VA GME expansion under the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 added 1500 GME positions in 8 years for critically needed specialties and in rural and underserved areas.5 The Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Outside Networks (MISSION) Act of 2018 authorized a pilot program for VA to fund residents at non-VA facilities with priority for Indian Health Services, Tribes and Tribal Organizations, Federally Qualified Health Centers, and US Department of Defense facilities to provide access to veterans in underserved areas.6
The VA GME financing system has flexibility to meet local needs for additional resident positions and to address broader VA workforce gaps through targeted expansion. Generally, CMS does not fund positions to address workforce needs, place residents in specific geographic areas, or require the training of certain types of residents.4 However, the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 has provided the opportunity to address rural workforce needs.28
Reimbursement
The VA provides reimbursement for clinical and educational activities performed in VA facilities for the benefit of veterans as well as research, didactics, meetings and conferences, annual and sick leave, and orientation. The VA also may provide reimbursement for educational activities that occur off VA grounds (eg, the VA proportional share of a residency program’s didactic sessions). The VA does not reimburse for affiliate clinical duties or administrative costs, although a national policy allows VA facilities to reimburse affiliates for some GME overhead costs.29
CMS similarly reimburses for residency training time spent in patient care activities as well as orientation activities, didactics, leave, and, in some cases, research.4,30,31 CMS makes payments to hospitals, which may include sponsoring institutions and Medicare-eligible participating training sites.4,30,31 For both the VA and CMS, residents may not be counted twice for reimbursement by 2 federal agencies; in other words, a resident may not count for > 1 FTE.4,30-32
GME Oversight
VA GME funding came under significant scrutiny. At a 2016 House Veterans Affairs Committee hearing, Representative Phil Roe, MD (R-Tennessee), noted that no process existed at many VA facilities for “determining trainee presence” and that many VA medical centers had “difficulty tracking resident rotations”16 A VA Office of the Inspector General investigation recommended that the VA implement policies and procedures to improve oversight to “ensure residents are fully participating in educational activities” and that the VA is “paying the correct amount” to the affiliate.17 A 2020 General Accountability Office report outlined unclear policy guidance, incomplete tracking of resident activities, and improper fiscal processes for reimbursement and reconciliation of affiliate invoices.18
In response, the OAA created an oversight and compliance unit, revised VHA Directive 1400.05 (the policy for disbursement), and improved resident tracking procedures.26 The standard operating procedure that accompanied VHA Directive 1400.05 provides detailed information for the DEO and VA facility staff for tracking resident clinical and educational activities. FTE counts are essential to both VA and CMS for accurate reimbursement. The eAppendix and the Table provide a guide to reimbursable activities in the VA for the calculation of reimbursement, with a comparison to CMS.33,34 The OAA in cooperation with other VA staff and officers periodically conducts audits to assess compliance with disbursement policy and affiliate reimbursement accuracy.
In the VA, resident activities are captured on the VA Educational Activity Record, a standardized spreadsheet to track activities and calculate reimbursement. Each VA facility hosting resident physicians manually records resident activity by the half-day. This process is labor intensive, involving both VA and affiliate staff to accurately reconcile payments. To address the workload demands, the OAA is developing an online tool that will automate aspects of the tracking process. Also, to ensure adequate staffing, the OAA is in the process of implementing an office optimization project, providing standardized position descriptions, an organizational chart, and staffing levels for DEO offices in VA facilities.
Conclusions
This report describes the key policies and principles of VA GME financing, highlighting the essential similarities and differences between VA and CMS. Neither the VA nor CMS regulations allow for reimbursement for > 1 FTE position per resident, a principle that underpins the assignment of resident rotations and federal funding for GME and are similar with respect to reimbursement for patient care activities, didactics, research, orientation, and scholarly activity. While reimbursable activities in the VA require physical presence and care of veteran patients, CMS also limits reimbursement to resident activities in the hospital and approved other settings if the hospital is paying for resident salary and benefits in these settings. The VA provides some flexibility for offsite activities including didactics and, in specific circumstances, remote care of veteran patients (eg, teleradiology).
The VA and CMS use different GME financing models. For example, the CMS calculations for resident FTEs are complex, whereas VA calculations reimburse the salary and benefits as set by the academic affiliate. The VA process accounts for local variation in salary rates, whereas the per-resident amount set by CMS varies regionally and does not fully account for differences in the cost of living.24 Because all patients in VA facilities are veterans, VA calculations for reimbursement do not involve ratios of beds like the CMS calculations to determine a proportional share of reimbursement. The VA GME expansion tends to be more directed to VA health workforce needs than CMS, specifying the types of programs and geographic locations to address these needs.
The VA regularly reevaluates how affiliates are reimbursed for VA resident activity, balancing compliance with VA policies and the workload for VA and its affiliates. The VA obtains input from key stakeholders including DEOs, DIOs, and professional organizations such as the Association of American Medical Colleges and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.35,36
Looking ahead, the VA is developing an online tool to improve the accuracy of affiliate reimbursement. The VA will also implement a standardized staffing model, organizational structure, and position descriptions for DEO offices. These initiatives will help reduce the burden of tracking and verifying resident activity and continue to support the 77-year partnership between VA and its affiliated institutions.
1. Klink KA, Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM. Veterans Affairs graduate medical education expansion addresses US physician workforce needs. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1144-1150. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004545
2. Andrus CH, Johnson K, Pierce E, Romito PJ, Hartel P, Berrios‐Guccione S, Best W. Finance modeling in the delivery of medical care in tertiary‐care hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Surg Res. 2001;96(2):152-157. doi:10.1006/jsre.1999.5728
3. Petrakis IL, Kozal M. Academic medical centers and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a 75-year partnership influences medical education, scientific discovery, and clinical care. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1110-1113. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004734
4. Heisler EJ, Mendez BH, Mitchell A, Panangala SV, Villagrana MA. Federal support for graduate medical education: an overview (R44376). Congressional Research Service report R44376; version 11. Updated December 27, 2018. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R44376/11
5. Chang BK, Brannen JL. The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014: examining graduate medical education enhancement in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Acad Med. 2015;90(9):1196-1198. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000000795
6. Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
7. Lypson ML, Roberts LW. Valuing the partnership between the Veterans Health Administration and academic medicine. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1091-1093. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004748
8. Harada ND, Traylor L, Rugen KW, et al. Interprofessional transformation of clinical education: the first six years of the Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education. J Interprof Care. 2023;37(suppl 1):S86-S94. doi:10.1080/13561820.2018.1433642

9. Harada ND, Rajashekara S, Sansgiry S, et al. Developing interprofessional primary care teams: alumni evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education Program. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519875455. doi:10.1177/2382120519875455
10. Splaine ME, Ogrinc G, Gilman SC, et al. The Department of Veterans Affairs National Quality Scholars Fellowship Program: experience from 10 years of training quality scholars. Acad Med. 2009;84(12):1741-1748. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181bfdcef
11. Watts BV, Paull DE, Williams LC, Neily J, Hemphill RR, Brannen JL. Department of Veterans Affairs chief resident in quality and patient safety program: a model to spread change. Am J Med Qual. 2016;31(6):598-600. doi:10.1177/1062860616643403
12. He K, Whang E, Kristo G. Graduate medical education funding mechanisms, challenges, and solutions: a narrative review. Am J Surg. 2021;221(1):65-71. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.06.007
13. Villagrana M. Medicare graduate medical education payments: an overview. Congressional Research Service report IF10960. Updated September 29, 2022. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF10960
14. Committee on the Governance and Financing of Graduate Medical Education; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine. Graduate Medical Education That Meets the Nation’s Health Needs. Eden J, Berwick DM, Wilensky GR, eds. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2014. doi:10.17226/18754
15. Physician workforce: caps on Medicare-funded graduate medical education at teaching hospitals. Report to congressional requesters. GAO-21-391. May 21, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-21-391.pdf
16. VA and Academic Affiliates: Who Benefits? Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations of the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, 114th Cong, 2nd Sess (2016). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CHRG-115hhrg29685/html/CHRG-115hhrg29685.htm
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General (OIG). Veterans Health Administration. Review of resident and part-time physician time and attendance at the Oklahoma City VA Health Care System. OIG report 17-00253-93. March 28, 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.oversight.gov/sites/default/files/oig-reports/VAOIG-17-00253-93.pdf
18. VA health care: actions needed to improve oversight of graduate medical education reimbursement. Report to the ranking member, Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, House of Representatives. GAO-20-553. July 2020. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/710/708275.pdf
19. Functions of Veterans Health Administration: in general, 38 USC §7301 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap73-subchapI-sec7301.pdf
20. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Policy memorandum no. 2, policy in association of veterans’ hospitals with medical schools. January 30, 1946.
21. Veterans Health Care Expansion Act of 1973, Public Law 93-82. August 2, 1973. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-87/pdf/STATUTE-87-Pg179.pdf
22. Residencies and internships, 38 USC § 7406 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap74-subchapI-sec7406.pdf
23. Direct graduate medical education (DGME). Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services. Updated December 5, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/DGME
24. Drezdzon MK, Cowley NJ, Sweeney DP, et al. Going for broke: the impact of cost of living on surgery resident stipend value. Ann Surg. 2023;278(6):1053-1059. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000005923
25. Special treatment: hospitals that incur indirect costs for graduate medical education programs, 42 CFR § 412.105 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec412-105.pdf
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.05, Disbursement agreements for health professions trainees appointed under 38 U.S.C. § 7406. June 2, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9293
27. Harada ND, Sanders KM, Bowman MA. Health systems education leadership: learning from the VA designated education officer role. Fed Pract. 2022;39(6):266-273. doi:10.12788/fp.0278
28. Schleiter Hitchell K, Johnson L. CMS finalizes rules for distribution of 1000 new Medicare-funded residency positions and changes to rural training track programs. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14(2):245-249. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-22-00193.1

29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.10, Educational cost contracts for health professions education. September 25, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/VHAPUBLICATIONS/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11480
30. Direct GME payments: general requirements, 42 CFR § 413.75 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-75.pdf
31. Direct GME payments: determination of the total number of FTE residents, 42 CFR § 413.78 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-78.pdf
32. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare financial management manual, chapter 8. Contractor procedures for provider audits. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/regulations-and-guidance/guidance/manuals/downloads/fin106c08.pdf
33. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Inspector General. CMS did not always ensure hospitals complied with Medicare reimbursement requirements for graduate medical education. OIG report A-02-17-01017. November 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oas/reports/region2/21701017.pdf
34. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Interns and Residents Information System (IRIS) XML format. Publication 100-20. Transmittal 11418. Change request 12724. May 19, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/guidance/sites/default/files/hhs-guidance-documents/R11418OTN.pdf
35. Birnbaum AD, Byrne J, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. VHA Updates: Disbursement Policy and Education Cost Contracts. Presented at: American Association of Medical Colleges Webinar; June 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://vimeo.com/644415670
36. Byrne JM, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. Disbursement procedures update for AY 23-24. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/oaa/Videos/AffiliatePresentationDisbursementandEARsAY23-24.pptx
1. Klink KA, Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM. Veterans Affairs graduate medical education expansion addresses US physician workforce needs. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1144-1150. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004545
2. Andrus CH, Johnson K, Pierce E, Romito PJ, Hartel P, Berrios‐Guccione S, Best W. Finance modeling in the delivery of medical care in tertiary‐care hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Surg Res. 2001;96(2):152-157. doi:10.1006/jsre.1999.5728
3. Petrakis IL, Kozal M. Academic medical centers and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a 75-year partnership influences medical education, scientific discovery, and clinical care. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1110-1113. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004734
4. Heisler EJ, Mendez BH, Mitchell A, Panangala SV, Villagrana MA. Federal support for graduate medical education: an overview (R44376). Congressional Research Service report R44376; version 11. Updated December 27, 2018. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R44376/11
5. Chang BK, Brannen JL. The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014: examining graduate medical education enhancement in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Acad Med. 2015;90(9):1196-1198. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000000795
6. Albanese AP, Bope ET, Sanders KM, Bowman M. The VA MISSION Act of 2018: a potential game changer for rural GME expansion and veteran health care. J Rural Health. 2020;36(1):133-136. doi:10.1111/jrh.12360
7. Lypson ML, Roberts LW. Valuing the partnership between the Veterans Health Administration and academic medicine. Acad Med. 2022;97(8):1091-1093. doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000004748
8. Harada ND, Traylor L, Rugen KW, et al. Interprofessional transformation of clinical education: the first six years of the Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education. J Interprof Care. 2023;37(suppl 1):S86-S94. doi:10.1080/13561820.2018.1433642

9. Harada ND, Rajashekara S, Sansgiry S, et al. Developing interprofessional primary care teams: alumni evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Centers of Excellence in Primary Care Education Program. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2019;6:2382120519875455. doi:10.1177/2382120519875455
10. Splaine ME, Ogrinc G, Gilman SC, et al. The Department of Veterans Affairs National Quality Scholars Fellowship Program: experience from 10 years of training quality scholars. Acad Med. 2009;84(12):1741-1748. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181bfdcef
11. Watts BV, Paull DE, Williams LC, Neily J, Hemphill RR, Brannen JL. Department of Veterans Affairs chief resident in quality and patient safety program: a model to spread change. Am J Med Qual. 2016;31(6):598-600. doi:10.1177/1062860616643403
12. He K, Whang E, Kristo G. Graduate medical education funding mechanisms, challenges, and solutions: a narrative review. Am J Surg. 2021;221(1):65-71. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.06.007
13. Villagrana M. Medicare graduate medical education payments: an overview. Congressional Research Service report IF10960. Updated September 29, 2022. Accessed March 2, 2024. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF10960
14. Committee on the Governance and Financing of Graduate Medical Education; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine. Graduate Medical Education That Meets the Nation’s Health Needs. Eden J, Berwick DM, Wilensky GR, eds. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2014. doi:10.17226/18754
15. Physician workforce: caps on Medicare-funded graduate medical education at teaching hospitals. Report to congressional requesters. GAO-21-391. May 21, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-21-391.pdf
16. VA and Academic Affiliates: Who Benefits? Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations of the Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, 114th Cong, 2nd Sess (2016). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CHRG-115hhrg29685/html/CHRG-115hhrg29685.htm
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Inspector General (OIG). Veterans Health Administration. Review of resident and part-time physician time and attendance at the Oklahoma City VA Health Care System. OIG report 17-00253-93. March 28, 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.oversight.gov/sites/default/files/oig-reports/VAOIG-17-00253-93.pdf
18. VA health care: actions needed to improve oversight of graduate medical education reimbursement. Report to the ranking member, Committee on Veterans’ Affairs, House of Representatives. GAO-20-553. July 2020. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.gao.gov/assets/710/708275.pdf
19. Functions of Veterans Health Administration: in general, 38 USC §7301 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap73-subchapI-sec7301.pdf
20. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Policy memorandum no. 2, policy in association of veterans’ hospitals with medical schools. January 30, 1946.
21. Veterans Health Care Expansion Act of 1973, Public Law 93-82. August 2, 1973. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-87/pdf/STATUTE-87-Pg179.pdf
22. Residencies and internships, 38 USC § 7406 (2022). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/USCODE-2022-title38/pdf/USCODE-2022-title38-partV-chap74-subchapI-sec7406.pdf
23. Direct graduate medical education (DGME). Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services. Updated December 5, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/DGME
24. Drezdzon MK, Cowley NJ, Sweeney DP, et al. Going for broke: the impact of cost of living on surgery resident stipend value. Ann Surg. 2023;278(6):1053-1059. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000005923
25. Special treatment: hospitals that incur indirect costs for graduate medical education programs, 42 CFR § 412.105 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec412-105.pdf
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.05, Disbursement agreements for health professions trainees appointed under 38 U.S.C. § 7406. June 2, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9293
27. Harada ND, Sanders KM, Bowman MA. Health systems education leadership: learning from the VA designated education officer role. Fed Pract. 2022;39(6):266-273. doi:10.12788/fp.0278
28. Schleiter Hitchell K, Johnson L. CMS finalizes rules for distribution of 1000 new Medicare-funded residency positions and changes to rural training track programs. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14(2):245-249. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-22-00193.1

29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1400.10, Educational cost contracts for health professions education. September 25, 2023. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/VHAPUBLICATIONS/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11480
30. Direct GME payments: general requirements, 42 CFR § 413.75 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-75.pdf
31. Direct GME payments: determination of the total number of FTE residents, 42 CFR § 413.78 (2023). Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2023-title42-vol2/pdf/CFR-2023-title42-vol2-sec413-78.pdf
32. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare financial management manual, chapter 8. Contractor procedures for provider audits. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/regulations-and-guidance/guidance/manuals/downloads/fin106c08.pdf
33. US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Inspector General. CMS did not always ensure hospitals complied with Medicare reimbursement requirements for graduate medical education. OIG report A-02-17-01017. November 2018. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oas/reports/region2/21701017.pdf
34. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Interns and Residents Information System (IRIS) XML format. Publication 100-20. Transmittal 11418. Change request 12724. May 19, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/guidance/sites/default/files/hhs-guidance-documents/R11418OTN.pdf
35. Birnbaum AD, Byrne J, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. VHA Updates: Disbursement Policy and Education Cost Contracts. Presented at: American Association of Medical Colleges Webinar; June 2021. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://vimeo.com/644415670
36. Byrne JM, on behalf of the VA Office of Academic Affiliations. Disbursement procedures update for AY 23-24. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/oaa/Videos/AffiliatePresentationDisbursementandEARsAY23-24.pptx
Could EHR Pharmacy Errors Put Veterans at Risk?
Will the new US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacy software be safe and effective? That was the topic when David Case, the VA Deputy Inspector General, spoke in the US House of Representatives Veterans Affairs Committee technology modernization subcommittee hearing on February 15.
Questions like that have dogged the project since 2018, when the VA began rolling out the Oracle Cerner electronic health record (EHR) system as the successor to ViSTA.
The Oracle system has been beset by one glitch after another since its arrival. And in that time, Case said, the VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) has been engaging with VA employees at sites in Washington, Oregon, Ohio, Illinois, and other locations where the modernization program has been piloted.
The most recent OIG investigation of pharmacy-related patient safety issues began with a review of an allegation of a prescription backlog at Columbus, Ohio, where the system went live on April 30, 2022. The OIG found that facility leaders took “timely and sustainable steps” to manage that issue. However, other unresolved patient safety issues came to light, such as medication inaccuracies, inaccurate medication data, and insufficient staffing. The OIG also found staff were creating “numerous work arounds” to provide patient care, and that the volume of staff educational materials for pharmacy-related functions was “overwhelming.”
Those problems were just the latest in a long queue. In May 2021, after the first VA deployment of the new EHR at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, a pharmacy patient safety team under the VA National Center for Patient Safety (NCPS) also had identified patient safety issues and “multiple” concerns regarding the system’s usability. For example, updates to a patient’s active medication list were not routinely reflected at the patient’s next appointment. Despite knowing about such challenges, Case noted in his report, VA leaders deployed the new EHR at 4 more VA medical centers.
Cerner/ViSTA Communication
One major cause of the current problems is the way the systems “talk” to each other. EHR information is communicated between VHA facilities through channels that include the Joint Longitudinal Viewer (JLV) and the Health Data Repository, which stores patient-specific clinical information from both the legacy and the new EHR systems. The JLV application allows clinicians to access a read only version of a patient’s EHR from both systems.
Every medication used in VHA has a VA Unique Identifier (VUID). When a patient is prescribed a medication at a new EHR site, that medication’s VUID is sent to the Health Data Repository. If that patient seeks care from a legacy health care practitioner (HCP), and that HCP enters a medication order, a software interface accesses the VUID from the Health Data Repository to verify that the medication being prescribed is safe and compatible with the medications and allergies previously documented in the patient’s record.
However, on March 31, 2023, staff from a ViSTA site found an incorrect medication order when prescribing a new medication to a patient who had received care and medications at a new EHR site. This in turn led to the discovery that an error in Oracle software coding had resulted in the “widespread transmission” of incorrect VUIDs from new EHR sites to legacy EHR sites, the OIG found. VA leaders and HCPs were notified of the potential clinical impact and were given specific instructions on how to mitigate the issue. They were asked to “please share widely.”
On top of that, days later, patient safety managers across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) were told that drug-to-drug interactions, duplicate medication orders, and allergy checks were not functioning as expected, and they too were provided with remedial actions.
Oracle applied a successful software patch on in April 2023, to ensure accurate VUIDs were attached to all mail order pharmacy–processed prescriptions from that date forward. However, the OIG learned the incorrect VUIDs sent from new EHR sites and stored in the Health Data Repository from as far back as October 2020 had not been corrected. Case told the subcommittee that on November 29, 2023, the VHA Pharmacy Council reported withdrawing a request for Oracle to send corrected medication VUID data to the Health Data Repository, on the presumption that remaining inaccurate VUIDs would expire in early April 2024, and the data would be corrected at that time.
The OIG is concerned, Case said, that patient medication data remains inaccurate almost a year after VA learned of the issue. The mail order pharmacy-related data generated from approximately 120,000 patients served by new EHR sites are still incorrect. These patients face an ongoing risk of an adverse medication-related event if they receive care and medications from a VA medical center using the legacy EHR system.
The OIG also learned of other problems associated with transmission of medication and allergy information, which could have consequences such as:
- Patient medications being discontinued or stopped by new HCPs using Cerner that appear in ViSTA as active and current prescriptions;
- Allergy-warning messages not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong medication;
- Duplicate medication order checks not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong drug;
- Patient active medication lists having incomplete or inaccurate information, such as missing prescriptions, duplicate prescriptions, or incorrect medication order statuses.
The OIG warned VHA employees about the risks, although it wasn’t possible to determine who might actually be at risk. A VHA leader told the OIG that all patients who have been prescribed any medications or have medication allergies documented at a at a Cerner site are at risk. That could mean as many as 250,000 patients: As of September 2023, approximately 190,000 patients had a medication prescribed and 126,000 had an allergy documented at a new EHR site.
Case Example
Not surprisingly, “the OIG is not confident in [EHRM-Integration Office] leaders’ oversight and control of the new systems’ Health Data Repository interface programming,” Case said. He cited the case of a patient with posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury with adrenal insufficiency. Four days prior to admission, a ViSTA site pharmacist used the EHR to perform a medication reconciliation for the patient. The data available did not include the patient’s most recent prednisone prescription, which had been ordered by an HCP at a facility using Cerner.
A nurse practitioner performed another reconciliation when the patient was admitted to the residential program, but the patient was unsure of all their medications. Because the most recent prednisone prescription was not visible in ViSTA, the prednisone appeared to have been completed at least 3 months prior to admission and was therefore not prescribed in the admission medication orders.
Five days into the residential program, the patient began exhibiting unusual behaviors associated with the lack of prednisone. The patient realized they needed more prednisone, but the nurse explained there was no prednisone on the patient’s medication list. Eventually, the patient found the active prednisone order on their personal cell phone and was transferred to a local emergency department for care.
Work Arounds
The VHA’s efforts to forestall or mitigate system errors have in some cases had a cascade effect. For example, HCPs must essentially back up what the automated software is intended to do, with “complex, time-consuming” multistep manual safety checks when prescribing new medications for patients previously cared for at a Cerner site. The OIG is concerned that this increased vigilance is “unsustainable” by pharmacists and frontline staff and could lead to burnout and medication-related patient safety events. After the new EHR launched, the OIG found, burnout symptoms for pharmacy staff increased. Nonetheless, Case told the committee, OIG staff “have observed [employees’] unwavering commitment to prioritizing the care of patients while mitigating implementation challenges.”
EHR-related workload burdens have necessitated other adjustments. Columbus, for instance, hired 9 full-time clinical pharmacists—a 62% staffing increase—to help reduce the backlog. Pharmacy leaders created approximately 29 additional work-arounds to support pharmacy staff and prevent delays. Facility pharmacy leaders also developed approximately 25 educational materials, such as tip sheets, reference guides, and job aids. The OIG’s concern—apart from the overwhelming amount of information for staff to implement—is that such prophylactic measures may in fact give rise to inconsistent practices, which increase risks to patient safety.
Committed to Working With the VA
Mike Sicilia, executive vice president of Oracle Corporation, told lawmakers in the hearing, “After the initial deployments, it became clear that the pharmacy system needed to be enhanced to better meet VA’s needs. To that end, in August 2022, shortly after Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner, VA contracted with us for seven enhancements that overall would adapt the pharmacy system to a more bidirectional system between VA providers placing prescription orders and VA pharmacists fulfilling and dispensing them.” Those enhancements are all live for VA providers and pharmacists to use now, he said, except for one that is undergoing additional testing.
He added, “As with any healthcare technology system, there is a need for continuous improvements but that does not mean the system is not safe and effective in its current state. Oracle is committed to working with VA … throughout the reset period to identify workflows and other items that can be simplified or streamlined to improve the overall user and pharmacy experience.”
Standardizing workflows and ensuring training and communications to pharmacists about the latest updates will discourage use of work-arounds, Sicilia said, and “help with improving morale and satisfaction with the system.” During a visit in early February by VA and the Oracle team to the Lovell Federal Health Care Center in North Chicago, “feedback from pharmacists was positive about the training and readiness for using the new pharmacy system.”
The backlog, at least, may be resolved. Sicilia said on average more than 215,000 outpatient prescriptions are being filled each month. “The current live sites do not have a backlog in filling prescriptions. Recent data from this month show that three of the five live sites have zero prescriptions waiting to be processed that are older than seven days. The two other live sites have an average of two prescriptions older than seven days,” he said.
Although Oracle Health has since resolved some of the identified issues, the OIG is concerned that the new EHR will continue to be deployed at medical facilities despite “myriad” as-yet unresolved issues related to inaccurate medication ordering, reconciliation, and dispensing. The VHA has paused Cerner deployments multiple times.
“It is unclear whether identified problems are being adequately resolved before additional deployments,” Case said. “There is also the question of whether there is sufficient transparency and communication among EHRM-IO, VHA and facility leaders, VA leaders, and Oracle Health needed for quality control and critical coordination. Trust in VA is also dependent on patients being fully and quickly advised when issues affecting them are identified and addressed. As VA moves toward its deployment next month at a complex facility jointly operated with the Department of Defense, transparency, communication, and program management will be essential to getting it right. Failures in these areas risk cascading problems.”
Will the new US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacy software be safe and effective? That was the topic when David Case, the VA Deputy Inspector General, spoke in the US House of Representatives Veterans Affairs Committee technology modernization subcommittee hearing on February 15.
Questions like that have dogged the project since 2018, when the VA began rolling out the Oracle Cerner electronic health record (EHR) system as the successor to ViSTA.
The Oracle system has been beset by one glitch after another since its arrival. And in that time, Case said, the VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) has been engaging with VA employees at sites in Washington, Oregon, Ohio, Illinois, and other locations where the modernization program has been piloted.
The most recent OIG investigation of pharmacy-related patient safety issues began with a review of an allegation of a prescription backlog at Columbus, Ohio, where the system went live on April 30, 2022. The OIG found that facility leaders took “timely and sustainable steps” to manage that issue. However, other unresolved patient safety issues came to light, such as medication inaccuracies, inaccurate medication data, and insufficient staffing. The OIG also found staff were creating “numerous work arounds” to provide patient care, and that the volume of staff educational materials for pharmacy-related functions was “overwhelming.”
Those problems were just the latest in a long queue. In May 2021, after the first VA deployment of the new EHR at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, a pharmacy patient safety team under the VA National Center for Patient Safety (NCPS) also had identified patient safety issues and “multiple” concerns regarding the system’s usability. For example, updates to a patient’s active medication list were not routinely reflected at the patient’s next appointment. Despite knowing about such challenges, Case noted in his report, VA leaders deployed the new EHR at 4 more VA medical centers.
Cerner/ViSTA Communication
One major cause of the current problems is the way the systems “talk” to each other. EHR information is communicated between VHA facilities through channels that include the Joint Longitudinal Viewer (JLV) and the Health Data Repository, which stores patient-specific clinical information from both the legacy and the new EHR systems. The JLV application allows clinicians to access a read only version of a patient’s EHR from both systems.
Every medication used in VHA has a VA Unique Identifier (VUID). When a patient is prescribed a medication at a new EHR site, that medication’s VUID is sent to the Health Data Repository. If that patient seeks care from a legacy health care practitioner (HCP), and that HCP enters a medication order, a software interface accesses the VUID from the Health Data Repository to verify that the medication being prescribed is safe and compatible with the medications and allergies previously documented in the patient’s record.
However, on March 31, 2023, staff from a ViSTA site found an incorrect medication order when prescribing a new medication to a patient who had received care and medications at a new EHR site. This in turn led to the discovery that an error in Oracle software coding had resulted in the “widespread transmission” of incorrect VUIDs from new EHR sites to legacy EHR sites, the OIG found. VA leaders and HCPs were notified of the potential clinical impact and were given specific instructions on how to mitigate the issue. They were asked to “please share widely.”
On top of that, days later, patient safety managers across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) were told that drug-to-drug interactions, duplicate medication orders, and allergy checks were not functioning as expected, and they too were provided with remedial actions.
Oracle applied a successful software patch on in April 2023, to ensure accurate VUIDs were attached to all mail order pharmacy–processed prescriptions from that date forward. However, the OIG learned the incorrect VUIDs sent from new EHR sites and stored in the Health Data Repository from as far back as October 2020 had not been corrected. Case told the subcommittee that on November 29, 2023, the VHA Pharmacy Council reported withdrawing a request for Oracle to send corrected medication VUID data to the Health Data Repository, on the presumption that remaining inaccurate VUIDs would expire in early April 2024, and the data would be corrected at that time.
The OIG is concerned, Case said, that patient medication data remains inaccurate almost a year after VA learned of the issue. The mail order pharmacy-related data generated from approximately 120,000 patients served by new EHR sites are still incorrect. These patients face an ongoing risk of an adverse medication-related event if they receive care and medications from a VA medical center using the legacy EHR system.
The OIG also learned of other problems associated with transmission of medication and allergy information, which could have consequences such as:
- Patient medications being discontinued or stopped by new HCPs using Cerner that appear in ViSTA as active and current prescriptions;
- Allergy-warning messages not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong medication;
- Duplicate medication order checks not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong drug;
- Patient active medication lists having incomplete or inaccurate information, such as missing prescriptions, duplicate prescriptions, or incorrect medication order statuses.
The OIG warned VHA employees about the risks, although it wasn’t possible to determine who might actually be at risk. A VHA leader told the OIG that all patients who have been prescribed any medications or have medication allergies documented at a at a Cerner site are at risk. That could mean as many as 250,000 patients: As of September 2023, approximately 190,000 patients had a medication prescribed and 126,000 had an allergy documented at a new EHR site.
Case Example
Not surprisingly, “the OIG is not confident in [EHRM-Integration Office] leaders’ oversight and control of the new systems’ Health Data Repository interface programming,” Case said. He cited the case of a patient with posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury with adrenal insufficiency. Four days prior to admission, a ViSTA site pharmacist used the EHR to perform a medication reconciliation for the patient. The data available did not include the patient’s most recent prednisone prescription, which had been ordered by an HCP at a facility using Cerner.
A nurse practitioner performed another reconciliation when the patient was admitted to the residential program, but the patient was unsure of all their medications. Because the most recent prednisone prescription was not visible in ViSTA, the prednisone appeared to have been completed at least 3 months prior to admission and was therefore not prescribed in the admission medication orders.
Five days into the residential program, the patient began exhibiting unusual behaviors associated with the lack of prednisone. The patient realized they needed more prednisone, but the nurse explained there was no prednisone on the patient’s medication list. Eventually, the patient found the active prednisone order on their personal cell phone and was transferred to a local emergency department for care.
Work Arounds
The VHA’s efforts to forestall or mitigate system errors have in some cases had a cascade effect. For example, HCPs must essentially back up what the automated software is intended to do, with “complex, time-consuming” multistep manual safety checks when prescribing new medications for patients previously cared for at a Cerner site. The OIG is concerned that this increased vigilance is “unsustainable” by pharmacists and frontline staff and could lead to burnout and medication-related patient safety events. After the new EHR launched, the OIG found, burnout symptoms for pharmacy staff increased. Nonetheless, Case told the committee, OIG staff “have observed [employees’] unwavering commitment to prioritizing the care of patients while mitigating implementation challenges.”
EHR-related workload burdens have necessitated other adjustments. Columbus, for instance, hired 9 full-time clinical pharmacists—a 62% staffing increase—to help reduce the backlog. Pharmacy leaders created approximately 29 additional work-arounds to support pharmacy staff and prevent delays. Facility pharmacy leaders also developed approximately 25 educational materials, such as tip sheets, reference guides, and job aids. The OIG’s concern—apart from the overwhelming amount of information for staff to implement—is that such prophylactic measures may in fact give rise to inconsistent practices, which increase risks to patient safety.
Committed to Working With the VA
Mike Sicilia, executive vice president of Oracle Corporation, told lawmakers in the hearing, “After the initial deployments, it became clear that the pharmacy system needed to be enhanced to better meet VA’s needs. To that end, in August 2022, shortly after Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner, VA contracted with us for seven enhancements that overall would adapt the pharmacy system to a more bidirectional system between VA providers placing prescription orders and VA pharmacists fulfilling and dispensing them.” Those enhancements are all live for VA providers and pharmacists to use now, he said, except for one that is undergoing additional testing.
He added, “As with any healthcare technology system, there is a need for continuous improvements but that does not mean the system is not safe and effective in its current state. Oracle is committed to working with VA … throughout the reset period to identify workflows and other items that can be simplified or streamlined to improve the overall user and pharmacy experience.”
Standardizing workflows and ensuring training and communications to pharmacists about the latest updates will discourage use of work-arounds, Sicilia said, and “help with improving morale and satisfaction with the system.” During a visit in early February by VA and the Oracle team to the Lovell Federal Health Care Center in North Chicago, “feedback from pharmacists was positive about the training and readiness for using the new pharmacy system.”
The backlog, at least, may be resolved. Sicilia said on average more than 215,000 outpatient prescriptions are being filled each month. “The current live sites do not have a backlog in filling prescriptions. Recent data from this month show that three of the five live sites have zero prescriptions waiting to be processed that are older than seven days. The two other live sites have an average of two prescriptions older than seven days,” he said.
Although Oracle Health has since resolved some of the identified issues, the OIG is concerned that the new EHR will continue to be deployed at medical facilities despite “myriad” as-yet unresolved issues related to inaccurate medication ordering, reconciliation, and dispensing. The VHA has paused Cerner deployments multiple times.
“It is unclear whether identified problems are being adequately resolved before additional deployments,” Case said. “There is also the question of whether there is sufficient transparency and communication among EHRM-IO, VHA and facility leaders, VA leaders, and Oracle Health needed for quality control and critical coordination. Trust in VA is also dependent on patients being fully and quickly advised when issues affecting them are identified and addressed. As VA moves toward its deployment next month at a complex facility jointly operated with the Department of Defense, transparency, communication, and program management will be essential to getting it right. Failures in these areas risk cascading problems.”
Will the new US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacy software be safe and effective? That was the topic when David Case, the VA Deputy Inspector General, spoke in the US House of Representatives Veterans Affairs Committee technology modernization subcommittee hearing on February 15.
Questions like that have dogged the project since 2018, when the VA began rolling out the Oracle Cerner electronic health record (EHR) system as the successor to ViSTA.
The Oracle system has been beset by one glitch after another since its arrival. And in that time, Case said, the VA Office of Inspector General (OIG) has been engaging with VA employees at sites in Washington, Oregon, Ohio, Illinois, and other locations where the modernization program has been piloted.
The most recent OIG investigation of pharmacy-related patient safety issues began with a review of an allegation of a prescription backlog at Columbus, Ohio, where the system went live on April 30, 2022. The OIG found that facility leaders took “timely and sustainable steps” to manage that issue. However, other unresolved patient safety issues came to light, such as medication inaccuracies, inaccurate medication data, and insufficient staffing. The OIG also found staff were creating “numerous work arounds” to provide patient care, and that the volume of staff educational materials for pharmacy-related functions was “overwhelming.”
Those problems were just the latest in a long queue. In May 2021, after the first VA deployment of the new EHR at the Mann-Grandstaff VA Medical Center in Spokane, Washington, a pharmacy patient safety team under the VA National Center for Patient Safety (NCPS) also had identified patient safety issues and “multiple” concerns regarding the system’s usability. For example, updates to a patient’s active medication list were not routinely reflected at the patient’s next appointment. Despite knowing about such challenges, Case noted in his report, VA leaders deployed the new EHR at 4 more VA medical centers.
Cerner/ViSTA Communication
One major cause of the current problems is the way the systems “talk” to each other. EHR information is communicated between VHA facilities through channels that include the Joint Longitudinal Viewer (JLV) and the Health Data Repository, which stores patient-specific clinical information from both the legacy and the new EHR systems. The JLV application allows clinicians to access a read only version of a patient’s EHR from both systems.
Every medication used in VHA has a VA Unique Identifier (VUID). When a patient is prescribed a medication at a new EHR site, that medication’s VUID is sent to the Health Data Repository. If that patient seeks care from a legacy health care practitioner (HCP), and that HCP enters a medication order, a software interface accesses the VUID from the Health Data Repository to verify that the medication being prescribed is safe and compatible with the medications and allergies previously documented in the patient’s record.
However, on March 31, 2023, staff from a ViSTA site found an incorrect medication order when prescribing a new medication to a patient who had received care and medications at a new EHR site. This in turn led to the discovery that an error in Oracle software coding had resulted in the “widespread transmission” of incorrect VUIDs from new EHR sites to legacy EHR sites, the OIG found. VA leaders and HCPs were notified of the potential clinical impact and were given specific instructions on how to mitigate the issue. They were asked to “please share widely.”
On top of that, days later, patient safety managers across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) were told that drug-to-drug interactions, duplicate medication orders, and allergy checks were not functioning as expected, and they too were provided with remedial actions.
Oracle applied a successful software patch on in April 2023, to ensure accurate VUIDs were attached to all mail order pharmacy–processed prescriptions from that date forward. However, the OIG learned the incorrect VUIDs sent from new EHR sites and stored in the Health Data Repository from as far back as October 2020 had not been corrected. Case told the subcommittee that on November 29, 2023, the VHA Pharmacy Council reported withdrawing a request for Oracle to send corrected medication VUID data to the Health Data Repository, on the presumption that remaining inaccurate VUIDs would expire in early April 2024, and the data would be corrected at that time.
The OIG is concerned, Case said, that patient medication data remains inaccurate almost a year after VA learned of the issue. The mail order pharmacy-related data generated from approximately 120,000 patients served by new EHR sites are still incorrect. These patients face an ongoing risk of an adverse medication-related event if they receive care and medications from a VA medical center using the legacy EHR system.
The OIG also learned of other problems associated with transmission of medication and allergy information, which could have consequences such as:
- Patient medications being discontinued or stopped by new HCPs using Cerner that appear in ViSTA as active and current prescriptions;
- Allergy-warning messages not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong medication;
- Duplicate medication order checks not appearing when intended or inappropriately appearing for the wrong drug;
- Patient active medication lists having incomplete or inaccurate information, such as missing prescriptions, duplicate prescriptions, or incorrect medication order statuses.
The OIG warned VHA employees about the risks, although it wasn’t possible to determine who might actually be at risk. A VHA leader told the OIG that all patients who have been prescribed any medications or have medication allergies documented at a at a Cerner site are at risk. That could mean as many as 250,000 patients: As of September 2023, approximately 190,000 patients had a medication prescribed and 126,000 had an allergy documented at a new EHR site.
Case Example
Not surprisingly, “the OIG is not confident in [EHRM-Integration Office] leaders’ oversight and control of the new systems’ Health Data Repository interface programming,” Case said. He cited the case of a patient with posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury with adrenal insufficiency. Four days prior to admission, a ViSTA site pharmacist used the EHR to perform a medication reconciliation for the patient. The data available did not include the patient’s most recent prednisone prescription, which had been ordered by an HCP at a facility using Cerner.
A nurse practitioner performed another reconciliation when the patient was admitted to the residential program, but the patient was unsure of all their medications. Because the most recent prednisone prescription was not visible in ViSTA, the prednisone appeared to have been completed at least 3 months prior to admission and was therefore not prescribed in the admission medication orders.
Five days into the residential program, the patient began exhibiting unusual behaviors associated with the lack of prednisone. The patient realized they needed more prednisone, but the nurse explained there was no prednisone on the patient’s medication list. Eventually, the patient found the active prednisone order on their personal cell phone and was transferred to a local emergency department for care.
Work Arounds
The VHA’s efforts to forestall or mitigate system errors have in some cases had a cascade effect. For example, HCPs must essentially back up what the automated software is intended to do, with “complex, time-consuming” multistep manual safety checks when prescribing new medications for patients previously cared for at a Cerner site. The OIG is concerned that this increased vigilance is “unsustainable” by pharmacists and frontline staff and could lead to burnout and medication-related patient safety events. After the new EHR launched, the OIG found, burnout symptoms for pharmacy staff increased. Nonetheless, Case told the committee, OIG staff “have observed [employees’] unwavering commitment to prioritizing the care of patients while mitigating implementation challenges.”
EHR-related workload burdens have necessitated other adjustments. Columbus, for instance, hired 9 full-time clinical pharmacists—a 62% staffing increase—to help reduce the backlog. Pharmacy leaders created approximately 29 additional work-arounds to support pharmacy staff and prevent delays. Facility pharmacy leaders also developed approximately 25 educational materials, such as tip sheets, reference guides, and job aids. The OIG’s concern—apart from the overwhelming amount of information for staff to implement—is that such prophylactic measures may in fact give rise to inconsistent practices, which increase risks to patient safety.
Committed to Working With the VA
Mike Sicilia, executive vice president of Oracle Corporation, told lawmakers in the hearing, “After the initial deployments, it became clear that the pharmacy system needed to be enhanced to better meet VA’s needs. To that end, in August 2022, shortly after Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner, VA contracted with us for seven enhancements that overall would adapt the pharmacy system to a more bidirectional system between VA providers placing prescription orders and VA pharmacists fulfilling and dispensing them.” Those enhancements are all live for VA providers and pharmacists to use now, he said, except for one that is undergoing additional testing.
He added, “As with any healthcare technology system, there is a need for continuous improvements but that does not mean the system is not safe and effective in its current state. Oracle is committed to working with VA … throughout the reset period to identify workflows and other items that can be simplified or streamlined to improve the overall user and pharmacy experience.”
Standardizing workflows and ensuring training and communications to pharmacists about the latest updates will discourage use of work-arounds, Sicilia said, and “help with improving morale and satisfaction with the system.” During a visit in early February by VA and the Oracle team to the Lovell Federal Health Care Center in North Chicago, “feedback from pharmacists was positive about the training and readiness for using the new pharmacy system.”
The backlog, at least, may be resolved. Sicilia said on average more than 215,000 outpatient prescriptions are being filled each month. “The current live sites do not have a backlog in filling prescriptions. Recent data from this month show that three of the five live sites have zero prescriptions waiting to be processed that are older than seven days. The two other live sites have an average of two prescriptions older than seven days,” he said.
Although Oracle Health has since resolved some of the identified issues, the OIG is concerned that the new EHR will continue to be deployed at medical facilities despite “myriad” as-yet unresolved issues related to inaccurate medication ordering, reconciliation, and dispensing. The VHA has paused Cerner deployments multiple times.
“It is unclear whether identified problems are being adequately resolved before additional deployments,” Case said. “There is also the question of whether there is sufficient transparency and communication among EHRM-IO, VHA and facility leaders, VA leaders, and Oracle Health needed for quality control and critical coordination. Trust in VA is also dependent on patients being fully and quickly advised when issues affecting them are identified and addressed. As VA moves toward its deployment next month at a complex facility jointly operated with the Department of Defense, transparency, communication, and program management will be essential to getting it right. Failures in these areas risk cascading problems.”
Implementing Trustworthy AI in VA High Reliability Health Care Organizations
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Age-Friendly Health Systems and Meeting the Principles of High Reliability Organizations in the VHA
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated health care system in the US, providing care to more than 9 million enrolled veterans at 1298 facilities.1 In February 2019, the VHA identified key action steps to become a high reliability organization (HRO), transforming how employees think about patient safety and care quality.2 The VHA is also working toward becoming the largest age-friendly health system in the US to be recognized by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) for its commitment to providing care guided by the 4Ms (what matters, medication, mentation, and mobility), causing no harm, and aligning care with what matters to older veterans.3 In this article, we describe how the Age-Friendly Health Systems (AFHS) movement supports the culture shift observed in HROs.
Age-Friendly Veteran Care
By 2060, the US population of adults aged ≥ 65 years is projected to increase to about 95 million.3 In the VHA, nearly half of veteran enrollees are aged ≥ 65 years, necessitating evidence-based models of care, such as the 4Ms, to meet their complex care needs.3 Historically, the VHA has been a leader in caring for older adults, recognizing the value of age-friendly care for veterans.4 In 1975, the VHA established the Geriatric Research, Education, and Clinical Centers (GRECCs) to serve as catalysts for developing, implementing, and refining enduring models of geriatric care.4 For 5 decades, GRECCs have driven innovations related to the 4Ms.
The VHA is well positioned to be a leader in the AFHS movement, building on decades of GRECC innovations and geriatric programs that align with the 4Ms and providing specialized geriatric training for health care professionals to expand age-friendly care to new settings and health systems.4 The AFHS movement organizes the 4Ms into a simple framework for frontline staff, and the VHA has recently begun tracking 4Ms care in the electronic health record (EHR) to facilitate evaluation and continuous improvement.
AFHS use the 4Ms as a framework to be implemented in every care setting, from the emergency department to inpatient units, outpatient settings, and postacute and long-term care. By assessing and acting on each M and practicing the 4Ms collectively, all members of the care team work to improve health outcomes and prevent avoidable harm.5
The 4Ms
What matters, is the driver of this person-centered approach. Any member of the care team may initiate a what matters conversation with the older adult to understand their personal values, health goals, and care preferences. When compared with usual care, care aligned with the older adult’s health priorities has been shown to decrease the use of high-risk medications and reduce treatment burden.6 The VHA has adopted Whole Health principles of care and the Patient Priorities Care approach to identify and support what matters to veterans.7,8
Addressing polypharmacy and identifying and deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications are essential in preventing adverse drug events, drug-drug interactions, and medication nonadherence.9 In the VHA, VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a rapidly expanding medication deprescribing program that exemplifies HRO principles.9 VIONE provides medication management that supports shared decision making, reducing risk and improving patient safety and quality of life.9 As of June 2023, > 600,000 unique veterans have benefited from VIONE, with an average of 2.2 medications deprescribed per patient with an annual cost avoidance of > $100 million.10
Assessing and acting on mentation includes preventing, identifying, and managing depression and dementia in outpatient settings and delirium in hospital and long-term care settings.5 There are many tools and clinical reminders available in the EHR so that interdisciplinary teams can document changes to mentation and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Closely aligned with mentation is mobility, with evidence suggesting that regular physical activity reduces the risk of falls (preventing associated complications), maintains physical functioning, and lowers the risk of cognitive impairment and depression.5 Ensuring early, frequent, and safe mobility helps patients achieve better health outcomes and prevent injury.5 Mobility programs within the VHA include the STRIDEprogram for the inpatient setting and Gerofit for outpatient settings.11,12
HRO Principles
An HRO is a complex environment of care that experiences fewer than anticipated accidents or adverse events by (1) establishing trust among leaders and staff by balancing individual accountability with systems thinking; (2) empowering staff to lead continuous process improvements; and (3) creating an environment where employees feel safe to report harm or near misses, focusing on the reasons errors occur.13 The work of AFHS incorporates HRO principles with an emphasis on 3 elements. First, it involves interactive systems and processes needed to support 4Ms care across care settings. Second, AFHS acknowledge the complexity of age-friendly work and deference to the expertise of interdisciplinary team members. Finally, AFHS are committed to resilience by overcoming failures and challenges to implementation and long-term sustainment as a standard of practice.
Case study
The names and details in this case have been modified to protect patient privacy. It is representative of many Community Living Centers (CLCs) involved in AFHS that work to create a safe, person-centered environment for veterans.
In a CLC team workroom, 2 nurses were discussing a long-term care resident. The nurses approached the attending physician and explained that they were worried about Sgt Johnson, who seemed depressed and sometimes combative. They had noticed a change in his behavior when they helped him clean up after an episode of incontinence and were concerned that he would try to get out of bed on his own and fall. The attending physician thanked them for sharing their concerns. Sgt Johnson was a retired Army veteran who had a long, decorated military career. His chronic health conditions had led to muscle weakness, and he fell and broke a hip before this admission. He had an uneventful hip replacement but was showing signs of depression due to his limited mobility, loss of independence, and inability to live at home without additional support.
The attending physician knocked on the door of his room, sat down next to the bed, and asked, “How are you feeling today?” Sgt Johnson tersely replied, “About the same.” The physician asked, “Sgt Johnson, what matters most to you related to your recovery? What is important to you?” Sgt Johnson responded, “Feeling like a man!” The doctor replied, “So what makes you feel ‘not like a man’?” The Sgt replied, “Having to be cleaned up by the nurses and not being able to use the toilet on my own.” The physician surmised that his decline in physical functioning had a connection to his worsening depression and combativeness and said to the Sgt, “Let’s get the team together and work out a plan to get you strong enough to use a bedside commode by yourself. Let’s make that the first goal in our plan to get you back to using the toilet independently. Can you work with us on that?” He smiled and said, “Sir, yes Sir!”
At the weekly interdisciplinary team meeting, the team discussed Sgt Johnson’s wishes and the nurses’ safety concerns. The physician reported to the team what mattered to the veteran. The nurses arranged for a bedside commode and supplies to be placed in his room, encouraged and assisted him, and provided a privacy screen. The physical therapist continued to support his mobility needs, concentrating on transfers, small steps like standing and turning with a walker to get in position to use the bedside commode, and later the bathroom toilet. The psychologist addressed what matters to Sgt Johnson and his mentation, health goals, and coping strategies. The social worker provided support and counseling for the veteran and his family. The pharmacist checked his medications to be sure that none were affecting his gastrointestinal tract and his ability to move safely and do what matters to him. Knowing what mattered to Sgt Johnson was the driver of the interdisciplinary care plan to provide 4Ms care.
The team worked collaboratively with the veteran to develop and set attainable goals around toileting and regaining his dignity. This improved his overall recovery. As Sgt Johnson became more independent, his mood gradually improved and he began to participate in other activities and interact with other residents on the unit, and he did not experience any falls. By addressing the 4Ms, the interdisciplinary team coordinated efforts to provide high-quality, person-centered care. They built trust with the veteran, shared accountability, and followed HRO principles to keep the veteran safe.
Becoming an Age-Friendly HRO
Becoming an HRO is a dynamic, ever-changing process to maintain high standards, improve care quality, and cause no harm. There are 3 pillars and 5 principles that guide an HRO. The pillars are critical areas of focus and include leadership commitment, culture of safety, and continuous process improvement.14 The first of 5 HRO principles is sensitivity to operations. This is defined as an awareness of how processes and systems impact the entire organization, the downstream impact.15 Focusing on the 4Ms helps develop the capability of frontline staff to provide high-quality care for older adults while ensuring that processes are in place to support the work. The 4Ms provide an efficient way to organize interdisciplinary team meetings, provide warm handoffs using Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation, and standardize documentation. Involvement in the AFHS movement improves communication, care quality, and patient and staff satisfaction to meet this HRO principle.15
The second HRO principle, reluctance to simplify, ensures that direct care staff and leaders delve further into issues to find solutions.15 AFHS use the Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle to put the 4Ms into practice; this cycle helps teams test small increments of change, study their performance, and act to ensure that all 4Ms are being practiced as a set. AFHS teams are encouraged to review at least 3 months of data after implementation of the 4Ms, working to find solutions if there are gaps or issues identified.
The third principle, preoccupation with failure, refers to shared attentiveness—being prepared for the unexpected and learning from mistakes.15 The entire AFHS team shares responsibility for providing 4Ms care, where staff are empowered to report any safety concerns or close calls. The fourth principle of deference to expertise includes listening to staff who have the most knowledge for the task at hand, which aligns with the collaborative interdisciplinary teamwork of age-friendly teams.15
The final HRO principle, commitment to resilience, includes continuous learning, interdisciplinary team training, and sharing of lessons learned.15 Although IHI offers 2 levels of AFHS recognition, teams are continuously learning to improve and sustain care beyond level 2, Committed to Care Excellence recognition.16
The Table shows the VHA’s AFHS implementation strategies and the HRO principles adapted from the Joint Commission’s High Reliability Health Care Maturity Model and the IHI’s Framework for Safe, Reliable, and Effective Care. The VHA is developing a national dashboard to capture age-friendly processes and health outcome measures that address patient safety and care quality.
Conclusions
AFHS empowers VHA teams to honor veterans’ care preferences and values, supporting their independence, dignity, and quality of life across care settings. The adoption of AFHS brings evidence-based practices to the point of care by addressing common pitfalls in the care of older adults, drawing attention to, and calling for action on inappropriate medication use, physical inactivity, and assessment of the vulnerable brain. The 4Ms also serve as a framework to continuously improve care and cause zero harm, reinforcing HRO pillars and principles across the VHA, and ensuring that older adults reliably receive the evidence-based, high-quality care they deserve.
1. Veterans Health Administration. Providing healthcare for veterans. Updated June 20, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.va.gov/health
2. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D. Evidence brief: implementation of high reliability organization principles. Washington, DC: Evidence Synthesis Program, Health Services Research and Development Service, Office of Research and Development, Department of Veterans Affairs. VA ESP Project #09-199; 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/high-reliability-org.cfm
3. Church K, Munro S, Shaughnessy M, Clancy C. Age-Friendly Health Systems: improving care for older adults in the Veterans Health Administration. Health Serv Res. 2023;58(suppl 1):5-8. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.14110
4. Farrell TW, Volden TA, Butler JM, et al. Age-friendly care in the Veterans Health Administration: past, present, and future. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(1):18-25. doi:10.1111/jgs.18070
5. Mate K, Fulmer T, Pelton L, et al. Evidence for the 4Ms: interactions and outcomes across the care continuum. J Aging Health. 2021;33(7-8):469-481. doi:10.1177/0898264321991658
6. Tinetti ME, Naik AD, Dindo L, et al. Association of patient priorities-aligned decision-making with patient outcomes and ambulatory health care burden among older adults with multiple chronic conditions: A nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12):1688-1697. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.4235
7. US Department of Veterans Affairs. What is whole health? Updated: October 31, 2023. November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth
8. Patient Priorities Care. Updated 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://patientprioritiescare.org
9. Battar S, Watson Dickerson KR, Sedgwick C, Cmelik T. Understanding principles of high reliability organizations through the eyes of VIONE: a clinical program to improve patient safety by deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications and reducing polypharmacy. Fed Pract. 2019;36(12):564-568.
10. VA Diffusion Marketplace. VIONE- medication optimization and polypharmacy reduction initiative. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://marketplace.va.gov/innovations/vione
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. STRIDE program to keep hospitalized veterans mobile. Updated November 6, 2018. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.research.va.gov/research_in_action/STRIDE-program-to-keep-hospitalized-Veterans-mobile.cfm
12. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Geriatrics and Extended Care. Gerofit: a program promoting exercise and health for older veterans. Updated August 2, 2023. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/GERIATRICS/pages/gerofit_Home.asp
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. VHA’s vision for a high reliability organization. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-1
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. Three HRO evaluation priorities. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-2
15. Oster CA, Deakins S. Practical application of high-reliability principles in healthcare to optimize quality and safety outcomes. J Nurs Adm. 2018;48(1):50-55. doi:10.1097/NNA.0000000000000570
16. Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Age-Friendly Health Systems recognitions. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.ihi.org/Engage/Initiatives/Age-Friendly-Health-Systems/Pages/Recognition.aspx
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated health care system in the US, providing care to more than 9 million enrolled veterans at 1298 facilities.1 In February 2019, the VHA identified key action steps to become a high reliability organization (HRO), transforming how employees think about patient safety and care quality.2 The VHA is also working toward becoming the largest age-friendly health system in the US to be recognized by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) for its commitment to providing care guided by the 4Ms (what matters, medication, mentation, and mobility), causing no harm, and aligning care with what matters to older veterans.3 In this article, we describe how the Age-Friendly Health Systems (AFHS) movement supports the culture shift observed in HROs.
Age-Friendly Veteran Care
By 2060, the US population of adults aged ≥ 65 years is projected to increase to about 95 million.3 In the VHA, nearly half of veteran enrollees are aged ≥ 65 years, necessitating evidence-based models of care, such as the 4Ms, to meet their complex care needs.3 Historically, the VHA has been a leader in caring for older adults, recognizing the value of age-friendly care for veterans.4 In 1975, the VHA established the Geriatric Research, Education, and Clinical Centers (GRECCs) to serve as catalysts for developing, implementing, and refining enduring models of geriatric care.4 For 5 decades, GRECCs have driven innovations related to the 4Ms.
The VHA is well positioned to be a leader in the AFHS movement, building on decades of GRECC innovations and geriatric programs that align with the 4Ms and providing specialized geriatric training for health care professionals to expand age-friendly care to new settings and health systems.4 The AFHS movement organizes the 4Ms into a simple framework for frontline staff, and the VHA has recently begun tracking 4Ms care in the electronic health record (EHR) to facilitate evaluation and continuous improvement.
AFHS use the 4Ms as a framework to be implemented in every care setting, from the emergency department to inpatient units, outpatient settings, and postacute and long-term care. By assessing and acting on each M and practicing the 4Ms collectively, all members of the care team work to improve health outcomes and prevent avoidable harm.5
The 4Ms
What matters, is the driver of this person-centered approach. Any member of the care team may initiate a what matters conversation with the older adult to understand their personal values, health goals, and care preferences. When compared with usual care, care aligned with the older adult’s health priorities has been shown to decrease the use of high-risk medications and reduce treatment burden.6 The VHA has adopted Whole Health principles of care and the Patient Priorities Care approach to identify and support what matters to veterans.7,8
Addressing polypharmacy and identifying and deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications are essential in preventing adverse drug events, drug-drug interactions, and medication nonadherence.9 In the VHA, VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a rapidly expanding medication deprescribing program that exemplifies HRO principles.9 VIONE provides medication management that supports shared decision making, reducing risk and improving patient safety and quality of life.9 As of June 2023, > 600,000 unique veterans have benefited from VIONE, with an average of 2.2 medications deprescribed per patient with an annual cost avoidance of > $100 million.10
Assessing and acting on mentation includes preventing, identifying, and managing depression and dementia in outpatient settings and delirium in hospital and long-term care settings.5 There are many tools and clinical reminders available in the EHR so that interdisciplinary teams can document changes to mentation and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Closely aligned with mentation is mobility, with evidence suggesting that regular physical activity reduces the risk of falls (preventing associated complications), maintains physical functioning, and lowers the risk of cognitive impairment and depression.5 Ensuring early, frequent, and safe mobility helps patients achieve better health outcomes and prevent injury.5 Mobility programs within the VHA include the STRIDEprogram for the inpatient setting and Gerofit for outpatient settings.11,12
HRO Principles
An HRO is a complex environment of care that experiences fewer than anticipated accidents or adverse events by (1) establishing trust among leaders and staff by balancing individual accountability with systems thinking; (2) empowering staff to lead continuous process improvements; and (3) creating an environment where employees feel safe to report harm or near misses, focusing on the reasons errors occur.13 The work of AFHS incorporates HRO principles with an emphasis on 3 elements. First, it involves interactive systems and processes needed to support 4Ms care across care settings. Second, AFHS acknowledge the complexity of age-friendly work and deference to the expertise of interdisciplinary team members. Finally, AFHS are committed to resilience by overcoming failures and challenges to implementation and long-term sustainment as a standard of practice.
Case study
The names and details in this case have been modified to protect patient privacy. It is representative of many Community Living Centers (CLCs) involved in AFHS that work to create a safe, person-centered environment for veterans.
In a CLC team workroom, 2 nurses were discussing a long-term care resident. The nurses approached the attending physician and explained that they were worried about Sgt Johnson, who seemed depressed and sometimes combative. They had noticed a change in his behavior when they helped him clean up after an episode of incontinence and were concerned that he would try to get out of bed on his own and fall. The attending physician thanked them for sharing their concerns. Sgt Johnson was a retired Army veteran who had a long, decorated military career. His chronic health conditions had led to muscle weakness, and he fell and broke a hip before this admission. He had an uneventful hip replacement but was showing signs of depression due to his limited mobility, loss of independence, and inability to live at home without additional support.
The attending physician knocked on the door of his room, sat down next to the bed, and asked, “How are you feeling today?” Sgt Johnson tersely replied, “About the same.” The physician asked, “Sgt Johnson, what matters most to you related to your recovery? What is important to you?” Sgt Johnson responded, “Feeling like a man!” The doctor replied, “So what makes you feel ‘not like a man’?” The Sgt replied, “Having to be cleaned up by the nurses and not being able to use the toilet on my own.” The physician surmised that his decline in physical functioning had a connection to his worsening depression and combativeness and said to the Sgt, “Let’s get the team together and work out a plan to get you strong enough to use a bedside commode by yourself. Let’s make that the first goal in our plan to get you back to using the toilet independently. Can you work with us on that?” He smiled and said, “Sir, yes Sir!”
At the weekly interdisciplinary team meeting, the team discussed Sgt Johnson’s wishes and the nurses’ safety concerns. The physician reported to the team what mattered to the veteran. The nurses arranged for a bedside commode and supplies to be placed in his room, encouraged and assisted him, and provided a privacy screen. The physical therapist continued to support his mobility needs, concentrating on transfers, small steps like standing and turning with a walker to get in position to use the bedside commode, and later the bathroom toilet. The psychologist addressed what matters to Sgt Johnson and his mentation, health goals, and coping strategies. The social worker provided support and counseling for the veteran and his family. The pharmacist checked his medications to be sure that none were affecting his gastrointestinal tract and his ability to move safely and do what matters to him. Knowing what mattered to Sgt Johnson was the driver of the interdisciplinary care plan to provide 4Ms care.
The team worked collaboratively with the veteran to develop and set attainable goals around toileting and regaining his dignity. This improved his overall recovery. As Sgt Johnson became more independent, his mood gradually improved and he began to participate in other activities and interact with other residents on the unit, and he did not experience any falls. By addressing the 4Ms, the interdisciplinary team coordinated efforts to provide high-quality, person-centered care. They built trust with the veteran, shared accountability, and followed HRO principles to keep the veteran safe.
Becoming an Age-Friendly HRO
Becoming an HRO is a dynamic, ever-changing process to maintain high standards, improve care quality, and cause no harm. There are 3 pillars and 5 principles that guide an HRO. The pillars are critical areas of focus and include leadership commitment, culture of safety, and continuous process improvement.14 The first of 5 HRO principles is sensitivity to operations. This is defined as an awareness of how processes and systems impact the entire organization, the downstream impact.15 Focusing on the 4Ms helps develop the capability of frontline staff to provide high-quality care for older adults while ensuring that processes are in place to support the work. The 4Ms provide an efficient way to organize interdisciplinary team meetings, provide warm handoffs using Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation, and standardize documentation. Involvement in the AFHS movement improves communication, care quality, and patient and staff satisfaction to meet this HRO principle.15
The second HRO principle, reluctance to simplify, ensures that direct care staff and leaders delve further into issues to find solutions.15 AFHS use the Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle to put the 4Ms into practice; this cycle helps teams test small increments of change, study their performance, and act to ensure that all 4Ms are being practiced as a set. AFHS teams are encouraged to review at least 3 months of data after implementation of the 4Ms, working to find solutions if there are gaps or issues identified.
The third principle, preoccupation with failure, refers to shared attentiveness—being prepared for the unexpected and learning from mistakes.15 The entire AFHS team shares responsibility for providing 4Ms care, where staff are empowered to report any safety concerns or close calls. The fourth principle of deference to expertise includes listening to staff who have the most knowledge for the task at hand, which aligns with the collaborative interdisciplinary teamwork of age-friendly teams.15
The final HRO principle, commitment to resilience, includes continuous learning, interdisciplinary team training, and sharing of lessons learned.15 Although IHI offers 2 levels of AFHS recognition, teams are continuously learning to improve and sustain care beyond level 2, Committed to Care Excellence recognition.16
The Table shows the VHA’s AFHS implementation strategies and the HRO principles adapted from the Joint Commission’s High Reliability Health Care Maturity Model and the IHI’s Framework for Safe, Reliable, and Effective Care. The VHA is developing a national dashboard to capture age-friendly processes and health outcome measures that address patient safety and care quality.
Conclusions
AFHS empowers VHA teams to honor veterans’ care preferences and values, supporting their independence, dignity, and quality of life across care settings. The adoption of AFHS brings evidence-based practices to the point of care by addressing common pitfalls in the care of older adults, drawing attention to, and calling for action on inappropriate medication use, physical inactivity, and assessment of the vulnerable brain. The 4Ms also serve as a framework to continuously improve care and cause zero harm, reinforcing HRO pillars and principles across the VHA, and ensuring that older adults reliably receive the evidence-based, high-quality care they deserve.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest integrated health care system in the US, providing care to more than 9 million enrolled veterans at 1298 facilities.1 In February 2019, the VHA identified key action steps to become a high reliability organization (HRO), transforming how employees think about patient safety and care quality.2 The VHA is also working toward becoming the largest age-friendly health system in the US to be recognized by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) for its commitment to providing care guided by the 4Ms (what matters, medication, mentation, and mobility), causing no harm, and aligning care with what matters to older veterans.3 In this article, we describe how the Age-Friendly Health Systems (AFHS) movement supports the culture shift observed in HROs.
Age-Friendly Veteran Care
By 2060, the US population of adults aged ≥ 65 years is projected to increase to about 95 million.3 In the VHA, nearly half of veteran enrollees are aged ≥ 65 years, necessitating evidence-based models of care, such as the 4Ms, to meet their complex care needs.3 Historically, the VHA has been a leader in caring for older adults, recognizing the value of age-friendly care for veterans.4 In 1975, the VHA established the Geriatric Research, Education, and Clinical Centers (GRECCs) to serve as catalysts for developing, implementing, and refining enduring models of geriatric care.4 For 5 decades, GRECCs have driven innovations related to the 4Ms.
The VHA is well positioned to be a leader in the AFHS movement, building on decades of GRECC innovations and geriatric programs that align with the 4Ms and providing specialized geriatric training for health care professionals to expand age-friendly care to new settings and health systems.4 The AFHS movement organizes the 4Ms into a simple framework for frontline staff, and the VHA has recently begun tracking 4Ms care in the electronic health record (EHR) to facilitate evaluation and continuous improvement.
AFHS use the 4Ms as a framework to be implemented in every care setting, from the emergency department to inpatient units, outpatient settings, and postacute and long-term care. By assessing and acting on each M and practicing the 4Ms collectively, all members of the care team work to improve health outcomes and prevent avoidable harm.5
The 4Ms
What matters, is the driver of this person-centered approach. Any member of the care team may initiate a what matters conversation with the older adult to understand their personal values, health goals, and care preferences. When compared with usual care, care aligned with the older adult’s health priorities has been shown to decrease the use of high-risk medications and reduce treatment burden.6 The VHA has adopted Whole Health principles of care and the Patient Priorities Care approach to identify and support what matters to veterans.7,8
Addressing polypharmacy and identifying and deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications are essential in preventing adverse drug events, drug-drug interactions, and medication nonadherence.9 In the VHA, VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a rapidly expanding medication deprescribing program that exemplifies HRO principles.9 VIONE provides medication management that supports shared decision making, reducing risk and improving patient safety and quality of life.9 As of June 2023, > 600,000 unique veterans have benefited from VIONE, with an average of 2.2 medications deprescribed per patient with an annual cost avoidance of > $100 million.10
Assessing and acting on mentation includes preventing, identifying, and managing depression and dementia in outpatient settings and delirium in hospital and long-term care settings.5 There are many tools and clinical reminders available in the EHR so that interdisciplinary teams can document changes to mentation and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Closely aligned with mentation is mobility, with evidence suggesting that regular physical activity reduces the risk of falls (preventing associated complications), maintains physical functioning, and lowers the risk of cognitive impairment and depression.5 Ensuring early, frequent, and safe mobility helps patients achieve better health outcomes and prevent injury.5 Mobility programs within the VHA include the STRIDEprogram for the inpatient setting and Gerofit for outpatient settings.11,12
HRO Principles
An HRO is a complex environment of care that experiences fewer than anticipated accidents or adverse events by (1) establishing trust among leaders and staff by balancing individual accountability with systems thinking; (2) empowering staff to lead continuous process improvements; and (3) creating an environment where employees feel safe to report harm or near misses, focusing on the reasons errors occur.13 The work of AFHS incorporates HRO principles with an emphasis on 3 elements. First, it involves interactive systems and processes needed to support 4Ms care across care settings. Second, AFHS acknowledge the complexity of age-friendly work and deference to the expertise of interdisciplinary team members. Finally, AFHS are committed to resilience by overcoming failures and challenges to implementation and long-term sustainment as a standard of practice.
Case study
The names and details in this case have been modified to protect patient privacy. It is representative of many Community Living Centers (CLCs) involved in AFHS that work to create a safe, person-centered environment for veterans.
In a CLC team workroom, 2 nurses were discussing a long-term care resident. The nurses approached the attending physician and explained that they were worried about Sgt Johnson, who seemed depressed and sometimes combative. They had noticed a change in his behavior when they helped him clean up after an episode of incontinence and were concerned that he would try to get out of bed on his own and fall. The attending physician thanked them for sharing their concerns. Sgt Johnson was a retired Army veteran who had a long, decorated military career. His chronic health conditions had led to muscle weakness, and he fell and broke a hip before this admission. He had an uneventful hip replacement but was showing signs of depression due to his limited mobility, loss of independence, and inability to live at home without additional support.
The attending physician knocked on the door of his room, sat down next to the bed, and asked, “How are you feeling today?” Sgt Johnson tersely replied, “About the same.” The physician asked, “Sgt Johnson, what matters most to you related to your recovery? What is important to you?” Sgt Johnson responded, “Feeling like a man!” The doctor replied, “So what makes you feel ‘not like a man’?” The Sgt replied, “Having to be cleaned up by the nurses and not being able to use the toilet on my own.” The physician surmised that his decline in physical functioning had a connection to his worsening depression and combativeness and said to the Sgt, “Let’s get the team together and work out a plan to get you strong enough to use a bedside commode by yourself. Let’s make that the first goal in our plan to get you back to using the toilet independently. Can you work with us on that?” He smiled and said, “Sir, yes Sir!”
At the weekly interdisciplinary team meeting, the team discussed Sgt Johnson’s wishes and the nurses’ safety concerns. The physician reported to the team what mattered to the veteran. The nurses arranged for a bedside commode and supplies to be placed in his room, encouraged and assisted him, and provided a privacy screen. The physical therapist continued to support his mobility needs, concentrating on transfers, small steps like standing and turning with a walker to get in position to use the bedside commode, and later the bathroom toilet. The psychologist addressed what matters to Sgt Johnson and his mentation, health goals, and coping strategies. The social worker provided support and counseling for the veteran and his family. The pharmacist checked his medications to be sure that none were affecting his gastrointestinal tract and his ability to move safely and do what matters to him. Knowing what mattered to Sgt Johnson was the driver of the interdisciplinary care plan to provide 4Ms care.
The team worked collaboratively with the veteran to develop and set attainable goals around toileting and regaining his dignity. This improved his overall recovery. As Sgt Johnson became more independent, his mood gradually improved and he began to participate in other activities and interact with other residents on the unit, and he did not experience any falls. By addressing the 4Ms, the interdisciplinary team coordinated efforts to provide high-quality, person-centered care. They built trust with the veteran, shared accountability, and followed HRO principles to keep the veteran safe.
Becoming an Age-Friendly HRO
Becoming an HRO is a dynamic, ever-changing process to maintain high standards, improve care quality, and cause no harm. There are 3 pillars and 5 principles that guide an HRO. The pillars are critical areas of focus and include leadership commitment, culture of safety, and continuous process improvement.14 The first of 5 HRO principles is sensitivity to operations. This is defined as an awareness of how processes and systems impact the entire organization, the downstream impact.15 Focusing on the 4Ms helps develop the capability of frontline staff to provide high-quality care for older adults while ensuring that processes are in place to support the work. The 4Ms provide an efficient way to organize interdisciplinary team meetings, provide warm handoffs using Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation, and standardize documentation. Involvement in the AFHS movement improves communication, care quality, and patient and staff satisfaction to meet this HRO principle.15
The second HRO principle, reluctance to simplify, ensures that direct care staff and leaders delve further into issues to find solutions.15 AFHS use the Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle to put the 4Ms into practice; this cycle helps teams test small increments of change, study their performance, and act to ensure that all 4Ms are being practiced as a set. AFHS teams are encouraged to review at least 3 months of data after implementation of the 4Ms, working to find solutions if there are gaps or issues identified.
The third principle, preoccupation with failure, refers to shared attentiveness—being prepared for the unexpected and learning from mistakes.15 The entire AFHS team shares responsibility for providing 4Ms care, where staff are empowered to report any safety concerns or close calls. The fourth principle of deference to expertise includes listening to staff who have the most knowledge for the task at hand, which aligns with the collaborative interdisciplinary teamwork of age-friendly teams.15
The final HRO principle, commitment to resilience, includes continuous learning, interdisciplinary team training, and sharing of lessons learned.15 Although IHI offers 2 levels of AFHS recognition, teams are continuously learning to improve and sustain care beyond level 2, Committed to Care Excellence recognition.16
The Table shows the VHA’s AFHS implementation strategies and the HRO principles adapted from the Joint Commission’s High Reliability Health Care Maturity Model and the IHI’s Framework for Safe, Reliable, and Effective Care. The VHA is developing a national dashboard to capture age-friendly processes and health outcome measures that address patient safety and care quality.
Conclusions
AFHS empowers VHA teams to honor veterans’ care preferences and values, supporting their independence, dignity, and quality of life across care settings. The adoption of AFHS brings evidence-based practices to the point of care by addressing common pitfalls in the care of older adults, drawing attention to, and calling for action on inappropriate medication use, physical inactivity, and assessment of the vulnerable brain. The 4Ms also serve as a framework to continuously improve care and cause zero harm, reinforcing HRO pillars and principles across the VHA, and ensuring that older adults reliably receive the evidence-based, high-quality care they deserve.
1. Veterans Health Administration. Providing healthcare for veterans. Updated June 20, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.va.gov/health
2. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D. Evidence brief: implementation of high reliability organization principles. Washington, DC: Evidence Synthesis Program, Health Services Research and Development Service, Office of Research and Development, Department of Veterans Affairs. VA ESP Project #09-199; 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/high-reliability-org.cfm
3. Church K, Munro S, Shaughnessy M, Clancy C. Age-Friendly Health Systems: improving care for older adults in the Veterans Health Administration. Health Serv Res. 2023;58(suppl 1):5-8. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.14110
4. Farrell TW, Volden TA, Butler JM, et al. Age-friendly care in the Veterans Health Administration: past, present, and future. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(1):18-25. doi:10.1111/jgs.18070
5. Mate K, Fulmer T, Pelton L, et al. Evidence for the 4Ms: interactions and outcomes across the care continuum. J Aging Health. 2021;33(7-8):469-481. doi:10.1177/0898264321991658
6. Tinetti ME, Naik AD, Dindo L, et al. Association of patient priorities-aligned decision-making with patient outcomes and ambulatory health care burden among older adults with multiple chronic conditions: A nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12):1688-1697. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.4235
7. US Department of Veterans Affairs. What is whole health? Updated: October 31, 2023. November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth
8. Patient Priorities Care. Updated 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://patientprioritiescare.org
9. Battar S, Watson Dickerson KR, Sedgwick C, Cmelik T. Understanding principles of high reliability organizations through the eyes of VIONE: a clinical program to improve patient safety by deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications and reducing polypharmacy. Fed Pract. 2019;36(12):564-568.
10. VA Diffusion Marketplace. VIONE- medication optimization and polypharmacy reduction initiative. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://marketplace.va.gov/innovations/vione
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. STRIDE program to keep hospitalized veterans mobile. Updated November 6, 2018. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.research.va.gov/research_in_action/STRIDE-program-to-keep-hospitalized-Veterans-mobile.cfm
12. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Geriatrics and Extended Care. Gerofit: a program promoting exercise and health for older veterans. Updated August 2, 2023. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/GERIATRICS/pages/gerofit_Home.asp
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. VHA’s vision for a high reliability organization. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-1
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. Three HRO evaluation priorities. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-2
15. Oster CA, Deakins S. Practical application of high-reliability principles in healthcare to optimize quality and safety outcomes. J Nurs Adm. 2018;48(1):50-55. doi:10.1097/NNA.0000000000000570
16. Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Age-Friendly Health Systems recognitions. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.ihi.org/Engage/Initiatives/Age-Friendly-Health-Systems/Pages/Recognition.aspx
1. Veterans Health Administration. Providing healthcare for veterans. Updated June 20, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2023. https://www.va.gov/health
2. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D. Evidence brief: implementation of high reliability organization principles. Washington, DC: Evidence Synthesis Program, Health Services Research and Development Service, Office of Research and Development, Department of Veterans Affairs. VA ESP Project #09-199; 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/high-reliability-org.cfm
3. Church K, Munro S, Shaughnessy M, Clancy C. Age-Friendly Health Systems: improving care for older adults in the Veterans Health Administration. Health Serv Res. 2023;58(suppl 1):5-8. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.14110
4. Farrell TW, Volden TA, Butler JM, et al. Age-friendly care in the Veterans Health Administration: past, present, and future. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(1):18-25. doi:10.1111/jgs.18070
5. Mate K, Fulmer T, Pelton L, et al. Evidence for the 4Ms: interactions and outcomes across the care continuum. J Aging Health. 2021;33(7-8):469-481. doi:10.1177/0898264321991658
6. Tinetti ME, Naik AD, Dindo L, et al. Association of patient priorities-aligned decision-making with patient outcomes and ambulatory health care burden among older adults with multiple chronic conditions: A nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12):1688-1697. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.4235
7. US Department of Veterans Affairs. What is whole health? Updated: October 31, 2023. November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/wholehealth
8. Patient Priorities Care. Updated 2019. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://patientprioritiescare.org
9. Battar S, Watson Dickerson KR, Sedgwick C, Cmelik T. Understanding principles of high reliability organizations through the eyes of VIONE: a clinical program to improve patient safety by deprescribing potentially inappropriate medications and reducing polypharmacy. Fed Pract. 2019;36(12):564-568.
10. VA Diffusion Marketplace. VIONE- medication optimization and polypharmacy reduction initiative. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://marketplace.va.gov/innovations/vione
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. STRIDE program to keep hospitalized veterans mobile. Updated November 6, 2018. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.research.va.gov/research_in_action/STRIDE-program-to-keep-hospitalized-Veterans-mobile.cfm
12. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Geriatrics and Extended Care. Gerofit: a program promoting exercise and health for older veterans. Updated August 2, 2023. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.va.gov/GERIATRICS/pages/gerofit_Home.asp
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. VHA’s vision for a high reliability organization. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-1
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development. Three HRO evaluation priorities. Updated August 14, 2020. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/forum/summer20/default.cfm?ForumMenu=summer20-2
15. Oster CA, Deakins S. Practical application of high-reliability principles in healthcare to optimize quality and safety outcomes. J Nurs Adm. 2018;48(1):50-55. doi:10.1097/NNA.0000000000000570
16. Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Age-Friendly Health Systems recognitions. Accessed November 30, 2023. https://www.ihi.org/Engage/Initiatives/Age-Friendly-Health-Systems/Pages/Recognition.aspx
Fellowships in Complex Medical Dermatology
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.
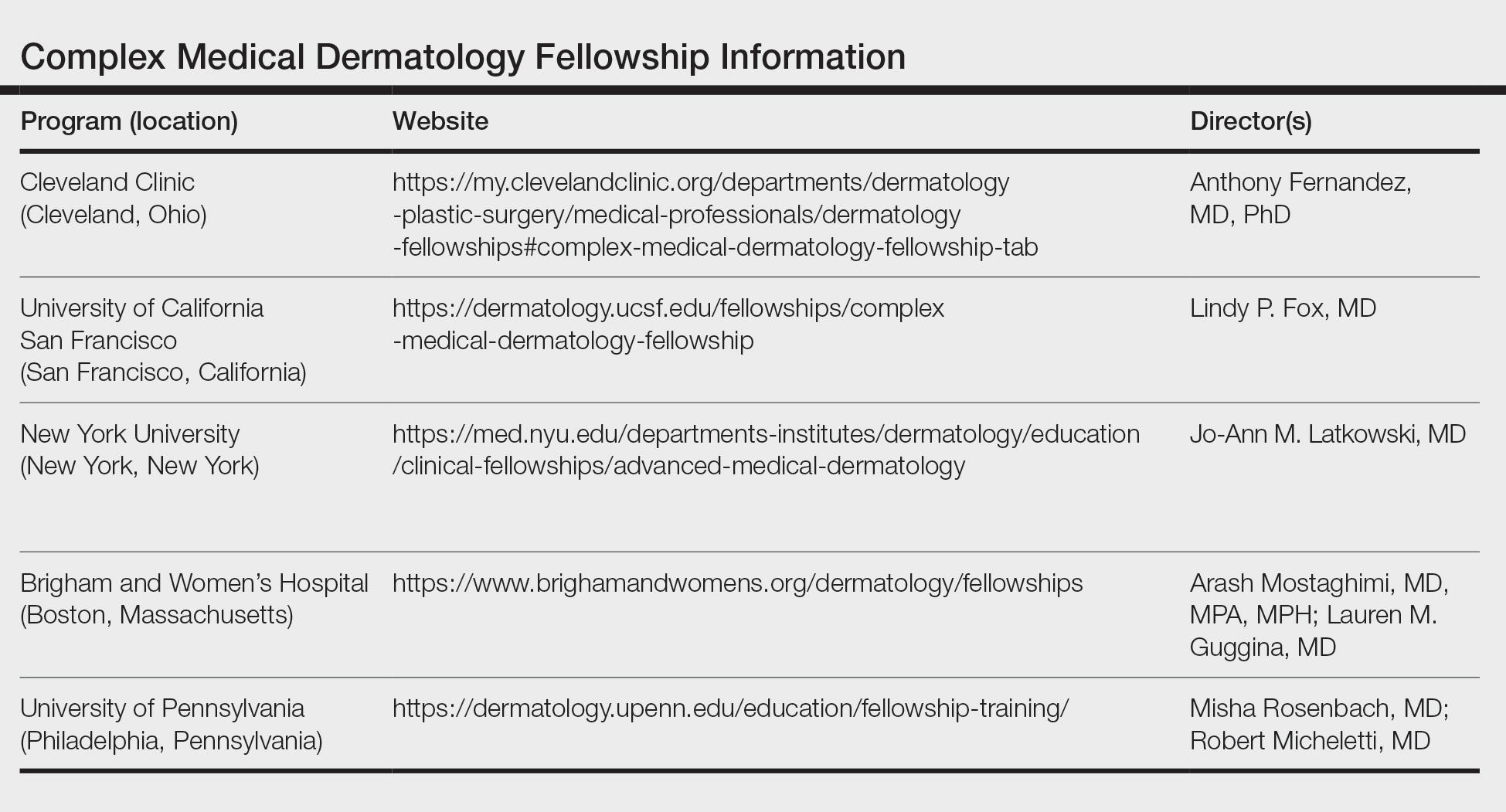
Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.

Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.

Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
RESIDENT PEARL
- Complex medical dermatology is a rewarding and fascinating subspecialty of dermatology, and additional training can be accomplished through a fellowship at a variety of prestigious institutions.
Camp Lejeune Family Members Now Eligible for Health Care Reimbursement Related to Parkinson Disease
Family members of veterans exposed to contaminated drinking water at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, Jacksonville, North Carolina, from August 1, 1953, to December 31, 1987, are now eligible for reimbursement of health care costs associated with Parkinson disease (PD) under the Camp Lejeune Family Member Program, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced.
That brings the number of illnesses or conditions those family members can be reimbursed for to 16: esophageal, lung, breast, bladder, and kidney cancer, leukemia, multiple myeloma, renal toxicity, miscarriage, hepatic steatosis, female infertility, myelodysplastic syndromes, scleroderma, neurobehavioral effects, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and Parkinson disease.
A recent JAMA study of 340,489 service members found that the risk of PD is 70% higher for veterans stationed at Camp Lejeune (n = 279) compared with veterans stationed at Camp Pendleton, California (n = 151).
The researchers say water supplies at Camp Lejeune were contaminated with several volatile organic compounds. They suggest that the risk of PD may be related to trichloroethylene exposure (TCE), a volatile organic compound widely used as a cleaning agent, in the manufacturing of some refrigerants, and found in paints and other products. In January, the US Environmental Protection Agency issued a revised risk determination saying that TCE presents an unreasonable risk to the health of workers, occupational nonusers (workers nearby but not in direct contact with this chemical), consumers, and bystanders.
Levels at Camp Lejeune were highest for TCE, with monthly median values greater than 70-fold the permissible amount.
Camp Lejeune veterans also had a significantly increased risk of prodromal PD diagnoses, including tremor, anxiety, and erectile dysfunction, and higher cumulative prodromal risk scores. No excess risk was found for other forms of neurodegenerative parkinsonism.
The PACT Act allows veterans and their families to file lawsuits for harm caused by exposure to contaminated water at Camp Lejeune. “Veterans and their families deserve no-cost health care for the conditions they developed due to the contaminated water at Camp Lejeune,” said VA’s Under Secretary for Health, Dr. Shereef Elnahal, MD. “We’re proud to add Parkinson disease to the list of conditions that are covered for veteran family members, and we implore anyone who may be living with this disease—or any of the other conditions covered by VA’s Camp Lejeune Family Member Program—to apply for assistance today.”
Family members of veterans exposed to contaminated drinking water at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, Jacksonville, North Carolina, from August 1, 1953, to December 31, 1987, are now eligible for reimbursement of health care costs associated with Parkinson disease (PD) under the Camp Lejeune Family Member Program, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced.
That brings the number of illnesses or conditions those family members can be reimbursed for to 16: esophageal, lung, breast, bladder, and kidney cancer, leukemia, multiple myeloma, renal toxicity, miscarriage, hepatic steatosis, female infertility, myelodysplastic syndromes, scleroderma, neurobehavioral effects, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and Parkinson disease.
A recent JAMA study of 340,489 service members found that the risk of PD is 70% higher for veterans stationed at Camp Lejeune (n = 279) compared with veterans stationed at Camp Pendleton, California (n = 151).
The researchers say water supplies at Camp Lejeune were contaminated with several volatile organic compounds. They suggest that the risk of PD may be related to trichloroethylene exposure (TCE), a volatile organic compound widely used as a cleaning agent, in the manufacturing of some refrigerants, and found in paints and other products. In January, the US Environmental Protection Agency issued a revised risk determination saying that TCE presents an unreasonable risk to the health of workers, occupational nonusers (workers nearby but not in direct contact with this chemical), consumers, and bystanders.
Levels at Camp Lejeune were highest for TCE, with monthly median values greater than 70-fold the permissible amount.
Camp Lejeune veterans also had a significantly increased risk of prodromal PD diagnoses, including tremor, anxiety, and erectile dysfunction, and higher cumulative prodromal risk scores. No excess risk was found for other forms of neurodegenerative parkinsonism.
The PACT Act allows veterans and their families to file lawsuits for harm caused by exposure to contaminated water at Camp Lejeune. “Veterans and their families deserve no-cost health care for the conditions they developed due to the contaminated water at Camp Lejeune,” said VA’s Under Secretary for Health, Dr. Shereef Elnahal, MD. “We’re proud to add Parkinson disease to the list of conditions that are covered for veteran family members, and we implore anyone who may be living with this disease—or any of the other conditions covered by VA’s Camp Lejeune Family Member Program—to apply for assistance today.”
Family members of veterans exposed to contaminated drinking water at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, Jacksonville, North Carolina, from August 1, 1953, to December 31, 1987, are now eligible for reimbursement of health care costs associated with Parkinson disease (PD) under the Camp Lejeune Family Member Program, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has announced.
That brings the number of illnesses or conditions those family members can be reimbursed for to 16: esophageal, lung, breast, bladder, and kidney cancer, leukemia, multiple myeloma, renal toxicity, miscarriage, hepatic steatosis, female infertility, myelodysplastic syndromes, scleroderma, neurobehavioral effects, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and Parkinson disease.
A recent JAMA study of 340,489 service members found that the risk of PD is 70% higher for veterans stationed at Camp Lejeune (n = 279) compared with veterans stationed at Camp Pendleton, California (n = 151).
The researchers say water supplies at Camp Lejeune were contaminated with several volatile organic compounds. They suggest that the risk of PD may be related to trichloroethylene exposure (TCE), a volatile organic compound widely used as a cleaning agent, in the manufacturing of some refrigerants, and found in paints and other products. In January, the US Environmental Protection Agency issued a revised risk determination saying that TCE presents an unreasonable risk to the health of workers, occupational nonusers (workers nearby but not in direct contact with this chemical), consumers, and bystanders.
Levels at Camp Lejeune were highest for TCE, with monthly median values greater than 70-fold the permissible amount.
Camp Lejeune veterans also had a significantly increased risk of prodromal PD diagnoses, including tremor, anxiety, and erectile dysfunction, and higher cumulative prodromal risk scores. No excess risk was found for other forms of neurodegenerative parkinsonism.
The PACT Act allows veterans and their families to file lawsuits for harm caused by exposure to contaminated water at Camp Lejeune. “Veterans and their families deserve no-cost health care for the conditions they developed due to the contaminated water at Camp Lejeune,” said VA’s Under Secretary for Health, Dr. Shereef Elnahal, MD. “We’re proud to add Parkinson disease to the list of conditions that are covered for veteran family members, and we implore anyone who may be living with this disease—or any of the other conditions covered by VA’s Camp Lejeune Family Member Program—to apply for assistance today.”