User login
TIL for Melanoma: What Are the Costs and Other Challenges to Getting It to Patients?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.
Unleashing Our Immune Response to Quash Cancer
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
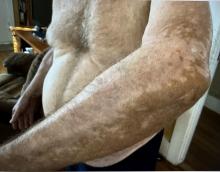
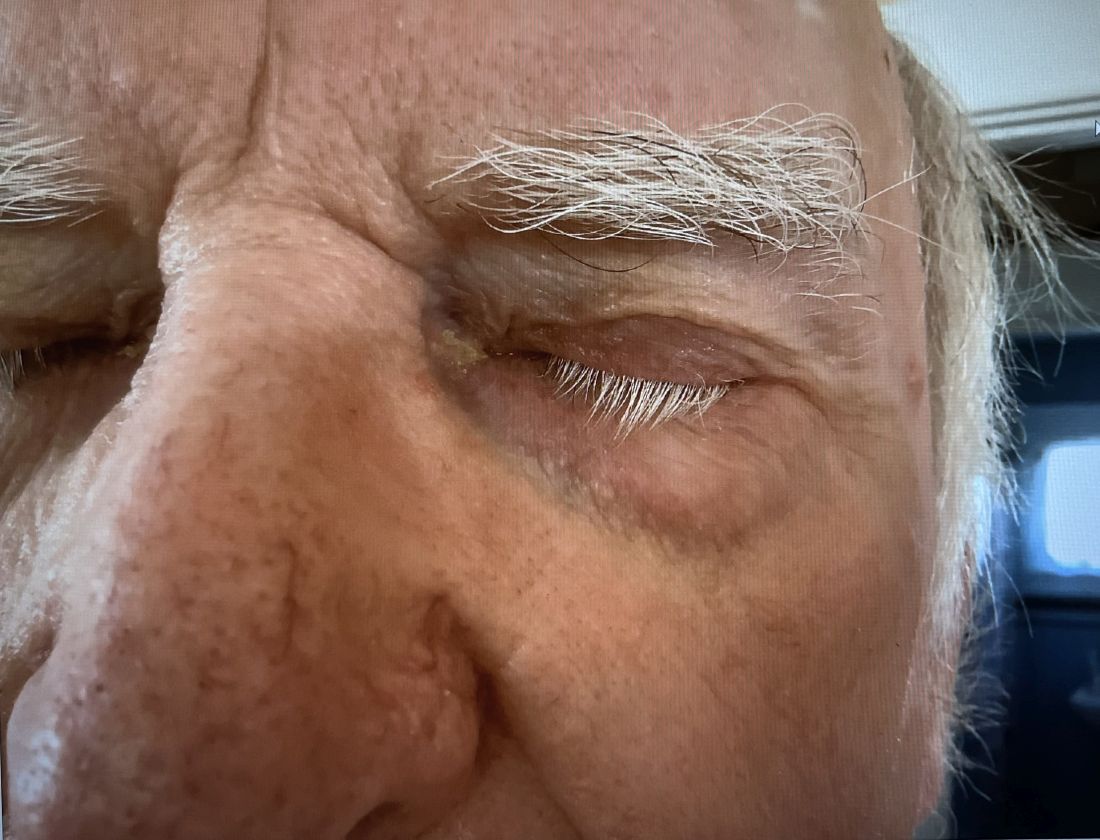
A 74-year-old White male presented with a 1-year history of depigmented patches on the hands, arms, and face, as well as white eyelashes and eyebrows
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
This patient showed no evidence of recurrence in the scar where the melanoma was excised, and had no enlarged lymph nodes on palpation. His complete blood count and liver function tests were normal. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan was ordered by Dr. Nasser that revealed hypermetabolic right paratracheal, right hilar, and subcarinal lymph nodes, highly suspicious for malignant lymph nodes. The patient was referred to oncology for metastatic melanoma treatment and has been doing well on ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition characterized by the progressive destruction of melanocytes resulting in hypopigmentation or depigmentation of the skin. Vitiligo has been associated with cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma-associated leukoderma occurs in a portion of patients with melanoma and is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, leukoderma has been described as a side effect of melanoma treatment itself. However, cases such as this one have also been reported of vitiligo-like depigmentation presenting prior to the diagnosis of metastatic melanoma.
Melanoma, like vitiligo, is considered highly immunogenic, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can recognize antigens in melanoma. Furthermore, studies have shown a vitiligo-like halo around melanoma tumors, likely caused by T-cell recruitment, and this may lead to tumor destruction, but rarely total clearance. It seems that the CTL infiltrate in both diseases is similar, but regulatory T cells are decreased in vitiligo, whereas they are present in melanomas and may contribute to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment found at the margin of these lesions.
Leukoderma is also associated with melanoma immunotherapy which may be described as drug-induced leukoderma. Additionally, the frequency of recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs leading to hypopigmentation appears to be higher in those with metastatic disease. High immune infiltrate with CTLs and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) expression by type 1 T helper cells is associated with favorable prognosis. Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in treatment augmentation for melanoma, but not all patients fully respond to therapy. Nonetheless, development of leukoderma with these treatments has been significantly associated with good therapeutic response. Depigmentation of hair and retinal epithelium has also been reported. However, drug-induced leukoderma and vitiligo seem to have clinical and biological differences, including family history of disease and serum chemokine levels. Vaccines are in production to aid in the treatment of melanoma, but researchers must first identify the appropriate antigen(s) to include.
Conversely, vitiligo-like depigmentation has been reported as a harbinger of metastatic melanoma. Patients with previous excision of primary melanoma have presented months or years later with depigmentation and, upon further evaluation, have been diagnosed with metastatic melanoma. The prevalence of depigmentation in melanoma patients is about 3%-6%, and is estimated to be 7-10 times more common in those with melanoma than in the general population. In most cases, hypopigmentation follows the diagnosis of melanoma, with an average of 4.8 years after the initial diagnosis and 1-2 years after lymph node or distant metastases. It is unclear whether hypopigmentation occurs before or after the growth of metastatic lesions, but this clinical finding in a patient with previous melanoma may serve as an important clue to conduct further investigation for metastasis.
This case and the photos were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Natalie Y. Nasser, MD, Kaiser Permanente Riverside Medical Center; Riverside, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cerci FB et al. Cutis. 2017 Jun;99(6):E1-E2. PMID: 28686764.
Cho EA et al. Ann Dermatol. 2009 May;21(2):178-181.
Failla CM et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 15;20(22):5731.
Small PFS gain in metastatic prostate cancer with TKI and ICI
The combination of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), cabozantinib (Cabometyx), and the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), atezolizumab (Tecentriq), was associated with a median PFS of 6.3 months vs 4.2 months for patients assigned to second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone (Zytiga) and prednisone, or enzalutamide (Xtandi) in the CONTACT-02 trial, Neeraj Agarwal, MD, reported at the ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.
“CONTACT 2 is the first phase 3 trial of the TKI/ICI combination to show statistically significant improvement in PFS in patients with mCRPC,” said Dr. Agarwal, of the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
The data support the combination of cabozantinib and atezolizumab as a potential new treatment option for patients with mCRPC that has progressed on novel hormonal therapy, he said.
Study Design Questioned
That opinion, however, was not shared by Kim N. Chi, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, BC, Canada, the invited discussant.
Dr. Chi acknowledged that the study results as presented were positive, but also pointed to several limitations, including the small difference between the treatment groups in radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS).
“I would say the rPFS benefit is modest, and in the absence of other improvements the difference in the median rPFS is equivalent from one scan to the next in the scanning cycle. I would argue about the clinical significance of that,” he said.
He also noted that there was no improvement in the investigational arm in patient-reported outcomes, and that pain progression and quality-of-life deterioration occurred within 2 to 4 months, which is “quite quick.”
Additionally, he questioned the choice of an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) switch as the control arm of the study.
“I’d also argue that ARPI switch is not the best standard of care for this patient population with measurable disease and 40% visceral metastases; there are better options,” he said.
For example, in phase 3 trials, docetaxel and cabazitaxel (Jevtana) have consistently demonstrated radiographic PFS of 8 to 9 months. In addition, lutetium-177–PSMA-617, a radioligand therapy that delivers beta-particle radiation to PSMA-expressing cells and the tumor microenvironment, has also been shown to have PFS and overall survival benefits, he said.
“Irrespective of regulatory decisions, I personally could not recommend this at this time, given the data that we’ve seen and the better options that are available for this patient population,” Dr. Chi said.
Real-World Practice
“Kim Chi offered a pretty fair critique and summary of the control arm, but in real world practice, ARPI switch, from abi [abiraterone] to enza [enzalutamide] or enza to abi continues to be used in routine clinical practice for various reasons,” Xin Gao, MD, a genitourinary oncologist at Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, said in an interview.
“There are patients who can’t tolerate chemotherapy or don’t want chemotherapy, and we do know also that there are patients who can benefit from an ARPI switch, especially some patients with more indolent disease,” said Dr. Gao, who attended the presentation but was not involved in the study.
He noted that some patients being switched from abiraterone to enzalutamide have clinical responses, and that the ARPIs are generally more tolerable than chemotherapy.
In addition, CONTACT-02 is one of a series of trials in which ARPI switch was used as the control arm, and many of these trials were initiated before there were data confirming the superior efficacy of some newer therapeutic options, Dr. Gao noted.
He agreed, however that there is growing evidence to show that ARPI switch may not be the optimal choice for patients with more measurable disease, especially visceral metastases, and other more aggressive forms of mCRPC.
CONTACT-02 Details
Investigators in the phase 3 study screened 866 men with mCRPC and after stratification by liver metastases, prior docetaxel use for castration-sensitive prostate cancer, and disease stage for which the first novel hormonal therapy was given. About 500 patients (507) were randomized to receive either oral cabozantinib 40 mg daily plus intravenous atezolizumab 1200 mg every 3 weeks or second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone 1000 mg with oral prednisone 5 mg twice daily, or oral enzalutamide 160 mg daily.
After a median follow-up of 14.3 months in the PFS intention-to-treat population, the median PFS by blinded central review was 6.3 months with cabozantinib/atezolizumab and 4.2 months with second hormonal therapy. This translated into a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .0002). The results were similar for a PFS analysis according to Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 criteria.
The combination was also associated with modest improvements in PFS in prespecified subgroups, including patients who had liver or bone metastases and those who had previously received docetaxel.
There were no significant differences in overall survival at the time of data cutoff. Overall survival data were not mature and will be reported at a later date.
Disease control rates, a composite of complete and partial responses and stable disease, were 73% with the combination and 55% with second hormonal therapy (P value not shown).
Safety Data
The safety analysis indicated that patients found the ARPI switch easier to tolerate than the combination.
Adverse events leading to dose reductions occurred in 40% of patients on the combination, vs 3% of patients on second hormonal therapy, and treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 13% and 2%, respectively.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 48% of patients assigned to the combination vs. 23% of patients assigned to the ARPI switch.
In all, 8% of patients on the combination and 12% on second hormonal therapy died on study, but none of the deaths were deemed to be treatment related.
CONTACT-02 was sponsored by Exelixis in partnerships with Ipsen and Takeda.
Dr. Agarwal disclosed institutional research funding from Exelixis, Roche, Takeda, and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer. Dr. Chi disclosed honoraria, a consulting/advisory role and institutional research funding with Roche and others. Dr. Gao has served as a consultant or advisor to several companies, not including the sponsors of the study, and has served as principal investigator at his institution, which has received research funding from Exelixis, Takeda, and others.
The combination of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), cabozantinib (Cabometyx), and the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), atezolizumab (Tecentriq), was associated with a median PFS of 6.3 months vs 4.2 months for patients assigned to second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone (Zytiga) and prednisone, or enzalutamide (Xtandi) in the CONTACT-02 trial, Neeraj Agarwal, MD, reported at the ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.
“CONTACT 2 is the first phase 3 trial of the TKI/ICI combination to show statistically significant improvement in PFS in patients with mCRPC,” said Dr. Agarwal, of the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
The data support the combination of cabozantinib and atezolizumab as a potential new treatment option for patients with mCRPC that has progressed on novel hormonal therapy, he said.
Study Design Questioned
That opinion, however, was not shared by Kim N. Chi, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, BC, Canada, the invited discussant.
Dr. Chi acknowledged that the study results as presented were positive, but also pointed to several limitations, including the small difference between the treatment groups in radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS).
“I would say the rPFS benefit is modest, and in the absence of other improvements the difference in the median rPFS is equivalent from one scan to the next in the scanning cycle. I would argue about the clinical significance of that,” he said.
He also noted that there was no improvement in the investigational arm in patient-reported outcomes, and that pain progression and quality-of-life deterioration occurred within 2 to 4 months, which is “quite quick.”
Additionally, he questioned the choice of an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) switch as the control arm of the study.
“I’d also argue that ARPI switch is not the best standard of care for this patient population with measurable disease and 40% visceral metastases; there are better options,” he said.
For example, in phase 3 trials, docetaxel and cabazitaxel (Jevtana) have consistently demonstrated radiographic PFS of 8 to 9 months. In addition, lutetium-177–PSMA-617, a radioligand therapy that delivers beta-particle radiation to PSMA-expressing cells and the tumor microenvironment, has also been shown to have PFS and overall survival benefits, he said.
“Irrespective of regulatory decisions, I personally could not recommend this at this time, given the data that we’ve seen and the better options that are available for this patient population,” Dr. Chi said.
Real-World Practice
“Kim Chi offered a pretty fair critique and summary of the control arm, but in real world practice, ARPI switch, from abi [abiraterone] to enza [enzalutamide] or enza to abi continues to be used in routine clinical practice for various reasons,” Xin Gao, MD, a genitourinary oncologist at Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, said in an interview.
“There are patients who can’t tolerate chemotherapy or don’t want chemotherapy, and we do know also that there are patients who can benefit from an ARPI switch, especially some patients with more indolent disease,” said Dr. Gao, who attended the presentation but was not involved in the study.
He noted that some patients being switched from abiraterone to enzalutamide have clinical responses, and that the ARPIs are generally more tolerable than chemotherapy.
In addition, CONTACT-02 is one of a series of trials in which ARPI switch was used as the control arm, and many of these trials were initiated before there were data confirming the superior efficacy of some newer therapeutic options, Dr. Gao noted.
He agreed, however that there is growing evidence to show that ARPI switch may not be the optimal choice for patients with more measurable disease, especially visceral metastases, and other more aggressive forms of mCRPC.
CONTACT-02 Details
Investigators in the phase 3 study screened 866 men with mCRPC and after stratification by liver metastases, prior docetaxel use for castration-sensitive prostate cancer, and disease stage for which the first novel hormonal therapy was given. About 500 patients (507) were randomized to receive either oral cabozantinib 40 mg daily plus intravenous atezolizumab 1200 mg every 3 weeks or second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone 1000 mg with oral prednisone 5 mg twice daily, or oral enzalutamide 160 mg daily.
After a median follow-up of 14.3 months in the PFS intention-to-treat population, the median PFS by blinded central review was 6.3 months with cabozantinib/atezolizumab and 4.2 months with second hormonal therapy. This translated into a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .0002). The results were similar for a PFS analysis according to Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 criteria.
The combination was also associated with modest improvements in PFS in prespecified subgroups, including patients who had liver or bone metastases and those who had previously received docetaxel.
There were no significant differences in overall survival at the time of data cutoff. Overall survival data were not mature and will be reported at a later date.
Disease control rates, a composite of complete and partial responses and stable disease, were 73% with the combination and 55% with second hormonal therapy (P value not shown).
Safety Data
The safety analysis indicated that patients found the ARPI switch easier to tolerate than the combination.
Adverse events leading to dose reductions occurred in 40% of patients on the combination, vs 3% of patients on second hormonal therapy, and treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 13% and 2%, respectively.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 48% of patients assigned to the combination vs. 23% of patients assigned to the ARPI switch.
In all, 8% of patients on the combination and 12% on second hormonal therapy died on study, but none of the deaths were deemed to be treatment related.
CONTACT-02 was sponsored by Exelixis in partnerships with Ipsen and Takeda.
Dr. Agarwal disclosed institutional research funding from Exelixis, Roche, Takeda, and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer. Dr. Chi disclosed honoraria, a consulting/advisory role and institutional research funding with Roche and others. Dr. Gao has served as a consultant or advisor to several companies, not including the sponsors of the study, and has served as principal investigator at his institution, which has received research funding from Exelixis, Takeda, and others.
The combination of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), cabozantinib (Cabometyx), and the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), atezolizumab (Tecentriq), was associated with a median PFS of 6.3 months vs 4.2 months for patients assigned to second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone (Zytiga) and prednisone, or enzalutamide (Xtandi) in the CONTACT-02 trial, Neeraj Agarwal, MD, reported at the ASCO Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.
“CONTACT 2 is the first phase 3 trial of the TKI/ICI combination to show statistically significant improvement in PFS in patients with mCRPC,” said Dr. Agarwal, of the Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City.
The data support the combination of cabozantinib and atezolizumab as a potential new treatment option for patients with mCRPC that has progressed on novel hormonal therapy, he said.
Study Design Questioned
That opinion, however, was not shared by Kim N. Chi, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, BC, Canada, the invited discussant.
Dr. Chi acknowledged that the study results as presented were positive, but also pointed to several limitations, including the small difference between the treatment groups in radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS).
“I would say the rPFS benefit is modest, and in the absence of other improvements the difference in the median rPFS is equivalent from one scan to the next in the scanning cycle. I would argue about the clinical significance of that,” he said.
He also noted that there was no improvement in the investigational arm in patient-reported outcomes, and that pain progression and quality-of-life deterioration occurred within 2 to 4 months, which is “quite quick.”
Additionally, he questioned the choice of an androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) switch as the control arm of the study.
“I’d also argue that ARPI switch is not the best standard of care for this patient population with measurable disease and 40% visceral metastases; there are better options,” he said.
For example, in phase 3 trials, docetaxel and cabazitaxel (Jevtana) have consistently demonstrated radiographic PFS of 8 to 9 months. In addition, lutetium-177–PSMA-617, a radioligand therapy that delivers beta-particle radiation to PSMA-expressing cells and the tumor microenvironment, has also been shown to have PFS and overall survival benefits, he said.
“Irrespective of regulatory decisions, I personally could not recommend this at this time, given the data that we’ve seen and the better options that are available for this patient population,” Dr. Chi said.
Real-World Practice
“Kim Chi offered a pretty fair critique and summary of the control arm, but in real world practice, ARPI switch, from abi [abiraterone] to enza [enzalutamide] or enza to abi continues to be used in routine clinical practice for various reasons,” Xin Gao, MD, a genitourinary oncologist at Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, said in an interview.
“There are patients who can’t tolerate chemotherapy or don’t want chemotherapy, and we do know also that there are patients who can benefit from an ARPI switch, especially some patients with more indolent disease,” said Dr. Gao, who attended the presentation but was not involved in the study.
He noted that some patients being switched from abiraterone to enzalutamide have clinical responses, and that the ARPIs are generally more tolerable than chemotherapy.
In addition, CONTACT-02 is one of a series of trials in which ARPI switch was used as the control arm, and many of these trials were initiated before there were data confirming the superior efficacy of some newer therapeutic options, Dr. Gao noted.
He agreed, however that there is growing evidence to show that ARPI switch may not be the optimal choice for patients with more measurable disease, especially visceral metastases, and other more aggressive forms of mCRPC.
CONTACT-02 Details
Investigators in the phase 3 study screened 866 men with mCRPC and after stratification by liver metastases, prior docetaxel use for castration-sensitive prostate cancer, and disease stage for which the first novel hormonal therapy was given. About 500 patients (507) were randomized to receive either oral cabozantinib 40 mg daily plus intravenous atezolizumab 1200 mg every 3 weeks or second hormonal therapy with either abiraterone 1000 mg with oral prednisone 5 mg twice daily, or oral enzalutamide 160 mg daily.
After a median follow-up of 14.3 months in the PFS intention-to-treat population, the median PFS by blinded central review was 6.3 months with cabozantinib/atezolizumab and 4.2 months with second hormonal therapy. This translated into a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .0002). The results were similar for a PFS analysis according to Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 criteria.
The combination was also associated with modest improvements in PFS in prespecified subgroups, including patients who had liver or bone metastases and those who had previously received docetaxel.
There were no significant differences in overall survival at the time of data cutoff. Overall survival data were not mature and will be reported at a later date.
Disease control rates, a composite of complete and partial responses and stable disease, were 73% with the combination and 55% with second hormonal therapy (P value not shown).
Safety Data
The safety analysis indicated that patients found the ARPI switch easier to tolerate than the combination.
Adverse events leading to dose reductions occurred in 40% of patients on the combination, vs 3% of patients on second hormonal therapy, and treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 13% and 2%, respectively.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 48% of patients assigned to the combination vs. 23% of patients assigned to the ARPI switch.
In all, 8% of patients on the combination and 12% on second hormonal therapy died on study, but none of the deaths were deemed to be treatment related.
CONTACT-02 was sponsored by Exelixis in partnerships with Ipsen and Takeda.
Dr. Agarwal disclosed institutional research funding from Exelixis, Roche, Takeda, and others, and travel expenses from Pfizer. Dr. Chi disclosed honoraria, a consulting/advisory role and institutional research funding with Roche and others. Dr. Gao has served as a consultant or advisor to several companies, not including the sponsors of the study, and has served as principal investigator at his institution, which has received research funding from Exelixis, Takeda, and others.
FROM ASCO GU 2024
How the microbiome influences the success of cancer therapy
HAMBURG, Germany — The human microbiome comprises 39 to 44 billion microbes. That is ten times more than the number of cells in our body. Hendrik Poeck, MD, managing senior physician of internal medicine at the University Hospital Regensburg, illustrated this point at the annual meeting of the German Society for Hematology and Medical Oncology. If the gut microbiome falls out of balance, then “intestinal dysbiosis potentially poses a risk for the pathogenesis of local and systemic diseases,” explained Dr. Poeck.
Cancers and their therapies can also be influenced in this way. said Dr. Poeck.
Microbial diversity could be beneficial for cancer therapy, too. The composition of the microbiome varies significantly from host to host and can mutate. These properties make it a target for precision microbiotics, which involves using the gut microbiome as a biomarker to predict various physical reactions and to develop individualized diets.
Microbiome and Pathogenesis
The body’s microbiome fulfills a barrier function, especially where the body is exposed to an external environment: at the epidermis and the internal mucous membranes, in the gastrointestinal tract, and in the lungs, chest, and urogenital system.
Association studies on humans and experimental manipulations on mouse models of cancer showed that certain microorganisms can have either protective or harmful effects on cancer development, on the progression of a malignant disease, and on the response to therapy.
A Master Regulator?
Disruptions of the microbial system in the gut, as occur during antibiotic therapy, can have significant effects on a patient’s response to immunotherapy. Taking antibiotics shortly before or after starting therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly affected both overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), as reported in a recent review and meta-analysis, for example.
Proton pump inhibitors also affect the gut microbiome and reduce the response to immunotherapy; this effect was demonstrated by an analysis of data from more than 2700 cancer patients that was recently presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO).
The extent to which the gut microbiome influences the efficacy of an ICI or predicts said efficacy was examined in a retrospective analysis published in Science in 2018, which Dr. Poeck presented. Resistance to ICI correlated with the relative frequency of the bacteria Akkermansia muciniphila in the gut of patients with cancer. In mouse models, the researchers restored the efficacy of the PD-1 blockade through a stool transplant.
Predicting Immunotherapy Response
If A muciniphila is present, can the composition of the microbiome act as a predictor for an effective ICI therapy?
Laurence Zitvogel, MD, PhD, and her working group at the National Institute of Health and Medical Research in Villejuif, France, performed a prospective study in 338 patients with non–small cell lung cancer and examined the prognostic significance of the fecal bacteria A muciniphila (Akk). The “Akkerman status” (low Akk vs high Akk) in a patient’s stool correlated with an increased objective response rate and a longer OS, independently of PD-L1 expression, antibiotics, and performance status. The OS for low Akk was 13.4 months, vs 18.8 months for high Akk in first-line treatment.
These results are promising, said Dr. Poeck. But there is no one-size-fits-all solution. No conclusions can be drawn from one bacterium on the efficacy of therapies in humans, since “the entirety of the bacteria is decisive,” said Dr. Poeck. In addition to the gut microbiome, the composition of gut metabolites influences the response to immunotherapies, as shown in a study with ICI.
Therapeutic Interventions
One possible therapeutic intervention to restore the gut microbiome is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). In a phase 1 study presented by Dr. Poeck, FMT was effective in the treatment of 20 patients with melanoma with ICI in an advanced and treatment-naive stage. Seven days after the patients received FMT, the first cycle with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy was initiated, with a total administration of three to four cycles. After 12 weeks, most patients were in complete or partial remission, as evidenced on imaging.
However, FMT also carries some risks. Two cases of sepsis with multiresistant Escherichia coli occurred, as well as other serious infections. Since then, there has been an FDA condition for extended screening of the donor stool, said Dr. Poeck. Nevertheless, this intervention is promising. A search of the keywords “FMT in cancer/transplant setting” reveals 46 currently clinical studies on clinicaltrials.gov.
Nutritional Interventions
Dr. Poeck advises caution about over-the-counter products. These products usually contain only a few species, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “Over-the-counter probiotics can even delay the reconstitution of the microbiome after antibiotics,” said Dr. Poeck, according to a study. In some studies, the response rates were significantly lower after probiotic intake or led to controversial results, according to Dr. Poeck.
In contrast, Dr. Poeck said prebiotics (that is, a fiber-rich diet with indigestible carbohydrates) were promising. During digestion, prebiotics are split into short-chain fatty acids by bacterial enzymes and promote the growth of certain microbiota.
In this way, just 20 g of extremely fiber-rich food had a significant effect on PFS in 128 patients with melanoma undergoing anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. With 20 g of fiber-rich food per day, the PFS was stable over 60 months. The most significant benefit was observed in patients with a sufficient fiber intake who were not taking probiotics.
What to Recommend?
In summary, Dr. Poeck said that it is important to “budget” well, particularly with antibiotic administration, and to strive for calculated therapy with as narrow a spectrum as possible. For patients who experience complications such as cytokine release syndrome as a reaction to cell therapy, delaying the use of antibiotics is important. However, it is often difficult to differentiate this syndrome from neutropenic fever. The aim should be to avoid high-risk antibiotics, if clinically justifiable. Patients should avoid taking antibiotics for 30 days before starting immunotherapy.
Regarding nutritional interventions, Dr. Poeck referred to the recent Onkopedia recommendation for nutrition after cancer and the 10 nutritional rules of the German Nutrition Society. According to Dr. Poeck, the important aspects of these recommendations are a fiber-rich diet (> 20 g/d) from various plant products and avoiding artificial sweeteners and flavorings, as well as ultraprocessed (convenience) foods. In addition, meat should be consumed only in moderation, and as little processed meat as possible should be consumed. In addition, regular (aerobic and anaerobic) physical activity is important.
“Looking ahead into the future,” said Dr. Poeck, “we need a uniform and functional understanding and we need a randomized prediction for diagnosis.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany — The human microbiome comprises 39 to 44 billion microbes. That is ten times more than the number of cells in our body. Hendrik Poeck, MD, managing senior physician of internal medicine at the University Hospital Regensburg, illustrated this point at the annual meeting of the German Society for Hematology and Medical Oncology. If the gut microbiome falls out of balance, then “intestinal dysbiosis potentially poses a risk for the pathogenesis of local and systemic diseases,” explained Dr. Poeck.
Cancers and their therapies can also be influenced in this way. said Dr. Poeck.
Microbial diversity could be beneficial for cancer therapy, too. The composition of the microbiome varies significantly from host to host and can mutate. These properties make it a target for precision microbiotics, which involves using the gut microbiome as a biomarker to predict various physical reactions and to develop individualized diets.
Microbiome and Pathogenesis
The body’s microbiome fulfills a barrier function, especially where the body is exposed to an external environment: at the epidermis and the internal mucous membranes, in the gastrointestinal tract, and in the lungs, chest, and urogenital system.
Association studies on humans and experimental manipulations on mouse models of cancer showed that certain microorganisms can have either protective or harmful effects on cancer development, on the progression of a malignant disease, and on the response to therapy.
A Master Regulator?
Disruptions of the microbial system in the gut, as occur during antibiotic therapy, can have significant effects on a patient’s response to immunotherapy. Taking antibiotics shortly before or after starting therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly affected both overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), as reported in a recent review and meta-analysis, for example.
Proton pump inhibitors also affect the gut microbiome and reduce the response to immunotherapy; this effect was demonstrated by an analysis of data from more than 2700 cancer patients that was recently presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO).
The extent to which the gut microbiome influences the efficacy of an ICI or predicts said efficacy was examined in a retrospective analysis published in Science in 2018, which Dr. Poeck presented. Resistance to ICI correlated with the relative frequency of the bacteria Akkermansia muciniphila in the gut of patients with cancer. In mouse models, the researchers restored the efficacy of the PD-1 blockade through a stool transplant.
Predicting Immunotherapy Response
If A muciniphila is present, can the composition of the microbiome act as a predictor for an effective ICI therapy?
Laurence Zitvogel, MD, PhD, and her working group at the National Institute of Health and Medical Research in Villejuif, France, performed a prospective study in 338 patients with non–small cell lung cancer and examined the prognostic significance of the fecal bacteria A muciniphila (Akk). The “Akkerman status” (low Akk vs high Akk) in a patient’s stool correlated with an increased objective response rate and a longer OS, independently of PD-L1 expression, antibiotics, and performance status. The OS for low Akk was 13.4 months, vs 18.8 months for high Akk in first-line treatment.
These results are promising, said Dr. Poeck. But there is no one-size-fits-all solution. No conclusions can be drawn from one bacterium on the efficacy of therapies in humans, since “the entirety of the bacteria is decisive,” said Dr. Poeck. In addition to the gut microbiome, the composition of gut metabolites influences the response to immunotherapies, as shown in a study with ICI.
Therapeutic Interventions
One possible therapeutic intervention to restore the gut microbiome is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). In a phase 1 study presented by Dr. Poeck, FMT was effective in the treatment of 20 patients with melanoma with ICI in an advanced and treatment-naive stage. Seven days after the patients received FMT, the first cycle with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy was initiated, with a total administration of three to four cycles. After 12 weeks, most patients were in complete or partial remission, as evidenced on imaging.
However, FMT also carries some risks. Two cases of sepsis with multiresistant Escherichia coli occurred, as well as other serious infections. Since then, there has been an FDA condition for extended screening of the donor stool, said Dr. Poeck. Nevertheless, this intervention is promising. A search of the keywords “FMT in cancer/transplant setting” reveals 46 currently clinical studies on clinicaltrials.gov.
Nutritional Interventions
Dr. Poeck advises caution about over-the-counter products. These products usually contain only a few species, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “Over-the-counter probiotics can even delay the reconstitution of the microbiome after antibiotics,” said Dr. Poeck, according to a study. In some studies, the response rates were significantly lower after probiotic intake or led to controversial results, according to Dr. Poeck.
In contrast, Dr. Poeck said prebiotics (that is, a fiber-rich diet with indigestible carbohydrates) were promising. During digestion, prebiotics are split into short-chain fatty acids by bacterial enzymes and promote the growth of certain microbiota.
In this way, just 20 g of extremely fiber-rich food had a significant effect on PFS in 128 patients with melanoma undergoing anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. With 20 g of fiber-rich food per day, the PFS was stable over 60 months. The most significant benefit was observed in patients with a sufficient fiber intake who were not taking probiotics.
What to Recommend?
In summary, Dr. Poeck said that it is important to “budget” well, particularly with antibiotic administration, and to strive for calculated therapy with as narrow a spectrum as possible. For patients who experience complications such as cytokine release syndrome as a reaction to cell therapy, delaying the use of antibiotics is important. However, it is often difficult to differentiate this syndrome from neutropenic fever. The aim should be to avoid high-risk antibiotics, if clinically justifiable. Patients should avoid taking antibiotics for 30 days before starting immunotherapy.
Regarding nutritional interventions, Dr. Poeck referred to the recent Onkopedia recommendation for nutrition after cancer and the 10 nutritional rules of the German Nutrition Society. According to Dr. Poeck, the important aspects of these recommendations are a fiber-rich diet (> 20 g/d) from various plant products and avoiding artificial sweeteners and flavorings, as well as ultraprocessed (convenience) foods. In addition, meat should be consumed only in moderation, and as little processed meat as possible should be consumed. In addition, regular (aerobic and anaerobic) physical activity is important.
“Looking ahead into the future,” said Dr. Poeck, “we need a uniform and functional understanding and we need a randomized prediction for diagnosis.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany — The human microbiome comprises 39 to 44 billion microbes. That is ten times more than the number of cells in our body. Hendrik Poeck, MD, managing senior physician of internal medicine at the University Hospital Regensburg, illustrated this point at the annual meeting of the German Society for Hematology and Medical Oncology. If the gut microbiome falls out of balance, then “intestinal dysbiosis potentially poses a risk for the pathogenesis of local and systemic diseases,” explained Dr. Poeck.
Cancers and their therapies can also be influenced in this way. said Dr. Poeck.
Microbial diversity could be beneficial for cancer therapy, too. The composition of the microbiome varies significantly from host to host and can mutate. These properties make it a target for precision microbiotics, which involves using the gut microbiome as a biomarker to predict various physical reactions and to develop individualized diets.
Microbiome and Pathogenesis
The body’s microbiome fulfills a barrier function, especially where the body is exposed to an external environment: at the epidermis and the internal mucous membranes, in the gastrointestinal tract, and in the lungs, chest, and urogenital system.
Association studies on humans and experimental manipulations on mouse models of cancer showed that certain microorganisms can have either protective or harmful effects on cancer development, on the progression of a malignant disease, and on the response to therapy.
A Master Regulator?
Disruptions of the microbial system in the gut, as occur during antibiotic therapy, can have significant effects on a patient’s response to immunotherapy. Taking antibiotics shortly before or after starting therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly affected both overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), as reported in a recent review and meta-analysis, for example.
Proton pump inhibitors also affect the gut microbiome and reduce the response to immunotherapy; this effect was demonstrated by an analysis of data from more than 2700 cancer patients that was recently presented at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO).
The extent to which the gut microbiome influences the efficacy of an ICI or predicts said efficacy was examined in a retrospective analysis published in Science in 2018, which Dr. Poeck presented. Resistance to ICI correlated with the relative frequency of the bacteria Akkermansia muciniphila in the gut of patients with cancer. In mouse models, the researchers restored the efficacy of the PD-1 blockade through a stool transplant.
Predicting Immunotherapy Response
If A muciniphila is present, can the composition of the microbiome act as a predictor for an effective ICI therapy?
Laurence Zitvogel, MD, PhD, and her working group at the National Institute of Health and Medical Research in Villejuif, France, performed a prospective study in 338 patients with non–small cell lung cancer and examined the prognostic significance of the fecal bacteria A muciniphila (Akk). The “Akkerman status” (low Akk vs high Akk) in a patient’s stool correlated with an increased objective response rate and a longer OS, independently of PD-L1 expression, antibiotics, and performance status. The OS for low Akk was 13.4 months, vs 18.8 months for high Akk in first-line treatment.
These results are promising, said Dr. Poeck. But there is no one-size-fits-all solution. No conclusions can be drawn from one bacterium on the efficacy of therapies in humans, since “the entirety of the bacteria is decisive,” said Dr. Poeck. In addition to the gut microbiome, the composition of gut metabolites influences the response to immunotherapies, as shown in a study with ICI.
Therapeutic Interventions
One possible therapeutic intervention to restore the gut microbiome is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). In a phase 1 study presented by Dr. Poeck, FMT was effective in the treatment of 20 patients with melanoma with ICI in an advanced and treatment-naive stage. Seven days after the patients received FMT, the first cycle with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy was initiated, with a total administration of three to four cycles. After 12 weeks, most patients were in complete or partial remission, as evidenced on imaging.
However, FMT also carries some risks. Two cases of sepsis with multiresistant Escherichia coli occurred, as well as other serious infections. Since then, there has been an FDA condition for extended screening of the donor stool, said Dr. Poeck. Nevertheless, this intervention is promising. A search of the keywords “FMT in cancer/transplant setting” reveals 46 currently clinical studies on clinicaltrials.gov.
Nutritional Interventions
Dr. Poeck advises caution about over-the-counter products. These products usually contain only a few species, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. “Over-the-counter probiotics can even delay the reconstitution of the microbiome after antibiotics,” said Dr. Poeck, according to a study. In some studies, the response rates were significantly lower after probiotic intake or led to controversial results, according to Dr. Poeck.
In contrast, Dr. Poeck said prebiotics (that is, a fiber-rich diet with indigestible carbohydrates) were promising. During digestion, prebiotics are split into short-chain fatty acids by bacterial enzymes and promote the growth of certain microbiota.
In this way, just 20 g of extremely fiber-rich food had a significant effect on PFS in 128 patients with melanoma undergoing anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. With 20 g of fiber-rich food per day, the PFS was stable over 60 months. The most significant benefit was observed in patients with a sufficient fiber intake who were not taking probiotics.
What to Recommend?
In summary, Dr. Poeck said that it is important to “budget” well, particularly with antibiotic administration, and to strive for calculated therapy with as narrow a spectrum as possible. For patients who experience complications such as cytokine release syndrome as a reaction to cell therapy, delaying the use of antibiotics is important. However, it is often difficult to differentiate this syndrome from neutropenic fever. The aim should be to avoid high-risk antibiotics, if clinically justifiable. Patients should avoid taking antibiotics for 30 days before starting immunotherapy.
Regarding nutritional interventions, Dr. Poeck referred to the recent Onkopedia recommendation for nutrition after cancer and the 10 nutritional rules of the German Nutrition Society. According to Dr. Poeck, the important aspects of these recommendations are a fiber-rich diet (> 20 g/d) from various plant products and avoiding artificial sweeteners and flavorings, as well as ultraprocessed (convenience) foods. In addition, meat should be consumed only in moderation, and as little processed meat as possible should be consumed. In addition, regular (aerobic and anaerobic) physical activity is important.
“Looking ahead into the future,” said Dr. Poeck, “we need a uniform and functional understanding and we need a randomized prediction for diagnosis.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
These adverse events linked to improved cancer prognosis
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Emerging evidence suggests that the presence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events may be linked with favorable outcomes among patients with cancer who receive ICIs.
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that included 23 studies and a total of 22,749 patients with cancer who received ICI treatment; studies compared outcomes among patients with and those without cutaneous immune-related adverse events.
- The major outcomes evaluated in the analysis were overall survival and progression-free survival (PFS); subgroup analyses assessed cutaneous immune-related adverse event type, cancer type, and other factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The occurrence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events was associated with improved PFS (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.61; P < .001).
- In the subgroup analysis, patients with eczematous (HR, 0.69), lichenoid or lichen planus–like skin lesions (HR, 0.51), pruritus without rash (HR, 0.70), psoriasis (HR, 0.63), or vitiligo (HR, 0.30) demonstrated a significant overall survival advantage. Vitiligo was the only adverse event associated with a PFS advantage (HR, 0.28).
- Among patients with melanoma, analyses revealed a significant association between the incidence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events and improved overall survival (HR, 0.51) and PFS (HR, 0.45). The authors highlighted similar findings among patients with non–small cell lung cancer (HR, 0.50 for overall survival and 0.61 for PFS).
IN PRACTICE:
“These data suggest that [cutaneous immune-related adverse events] may have useful prognostic value in ICI treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Fei Wang, MD, Zhong Da Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most of the data came from retrospective studies, and there were limited data on specific patient subgroups. The Egger tests, used to assess potential publication bias in meta-analyses, revealed publication bias.
DISCLOSURES:
No disclosures were reported. The study was supported by a grant from the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Emerging evidence suggests that the presence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events may be linked with favorable outcomes among patients with cancer who receive ICIs.
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that included 23 studies and a total of 22,749 patients with cancer who received ICI treatment; studies compared outcomes among patients with and those without cutaneous immune-related adverse events.
- The major outcomes evaluated in the analysis were overall survival and progression-free survival (PFS); subgroup analyses assessed cutaneous immune-related adverse event type, cancer type, and other factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The occurrence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events was associated with improved PFS (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.61; P < .001).
- In the subgroup analysis, patients with eczematous (HR, 0.69), lichenoid or lichen planus–like skin lesions (HR, 0.51), pruritus without rash (HR, 0.70), psoriasis (HR, 0.63), or vitiligo (HR, 0.30) demonstrated a significant overall survival advantage. Vitiligo was the only adverse event associated with a PFS advantage (HR, 0.28).
- Among patients with melanoma, analyses revealed a significant association between the incidence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events and improved overall survival (HR, 0.51) and PFS (HR, 0.45). The authors highlighted similar findings among patients with non–small cell lung cancer (HR, 0.50 for overall survival and 0.61 for PFS).
IN PRACTICE:
“These data suggest that [cutaneous immune-related adverse events] may have useful prognostic value in ICI treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Fei Wang, MD, Zhong Da Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most of the data came from retrospective studies, and there were limited data on specific patient subgroups. The Egger tests, used to assess potential publication bias in meta-analyses, revealed publication bias.
DISCLOSURES:
No disclosures were reported. The study was supported by a grant from the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Emerging evidence suggests that the presence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events may be linked with favorable outcomes among patients with cancer who receive ICIs.
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that included 23 studies and a total of 22,749 patients with cancer who received ICI treatment; studies compared outcomes among patients with and those without cutaneous immune-related adverse events.
- The major outcomes evaluated in the analysis were overall survival and progression-free survival (PFS); subgroup analyses assessed cutaneous immune-related adverse event type, cancer type, and other factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- The occurrence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events was associated with improved PFS (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .001) and overall survival (HR, 0.61; P < .001).
- In the subgroup analysis, patients with eczematous (HR, 0.69), lichenoid or lichen planus–like skin lesions (HR, 0.51), pruritus without rash (HR, 0.70), psoriasis (HR, 0.63), or vitiligo (HR, 0.30) demonstrated a significant overall survival advantage. Vitiligo was the only adverse event associated with a PFS advantage (HR, 0.28).
- Among patients with melanoma, analyses revealed a significant association between the incidence of cutaneous immune-related adverse events and improved overall survival (HR, 0.51) and PFS (HR, 0.45). The authors highlighted similar findings among patients with non–small cell lung cancer (HR, 0.50 for overall survival and 0.61 for PFS).
IN PRACTICE:
“These data suggest that [cutaneous immune-related adverse events] may have useful prognostic value in ICI treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Fei Wang, MD, Zhong Da Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Most of the data came from retrospective studies, and there were limited data on specific patient subgroups. The Egger tests, used to assess potential publication bias in meta-analyses, revealed publication bias.
DISCLOSURES:
No disclosures were reported. The study was supported by a grant from the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy stewardship could save tens of millions a year
Implementing stewardship strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, including personalized weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and pharmacy-level vial sharing, could generate savings of as much as $74 million each year for the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), a new analysis suggests.
That $74 million in savings would translate to nearly 14% less spent on ICI therapy annually.
first author Alex Bryant, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published in Health Affairs.
ICI therapy is used in about 40 unique cancer indications and, in 2020, accounted for more than $6 billion in Medicare Part B spending.
Two of the most prescribed ICIs – pembrolizumab and nivolumab – initially received their U.S. approval at personalized weight-based doses. But at the request of the manufacturers, the Food and Drug Administration approved “one-size-fits-all” flat doses, despite a lack of data to support this strategy compared with weight-based dosing.
With a fixed dose strategy, “patients with cancer not only tend to get too high a dose of the drug, but costs go up significantly,” Daniel Goldstein, MD, a medical oncologist at the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, told this news organization last year. “Why should we give a higher dose with the same efficacy when that dose will cost significantly more and has the potential to increase adverse events?”
To compare the cost of a weight-based vs. fixed-dose strategy, Dr. Bryant and colleagues conducted a simulation analysis under four stewardship scenarios, using data from the VHA and Medicare drug prices. Strategy one looked at weight-based dosing; strategy two combined weight-based dosing and dose rounding but not single-use vial sharing; strategy three used weight-based dosing and single-use vial sharing but not dose rounding; and strategy four, the most aggressive, combined all three.
ICIs in the VHA national formulary included pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and cemiplimab-rwlc.
Using an algorithm to extract data, the team identified 49,851 administration events in 8,276 unique patients in 2021 – just over half were pembrolizumab, nearly 23% were nivolumab, and the remaining 26% largely included atezolizumab (12.1%) and durvalumab (11.9%).
The team found that the VHA spends roughly $537 million annually on ICIs. But implementing the stewardship measures that combined weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and vial sharing could save the VHA $74 million, or about 14%, annually on ICIs.
Most of the savings came from dosing changes to pembrolizumab and nivolumab, with greater savings achieved by combining more stewardship strategies. For instance, using strategy one (weight-based dosing alone) could lead to annual pembrolizumab savings of $14 million. Adding dose rounding (strategy two) could reduce pembrolizumab spending by $24 million. And using strategy four, with an unlimited window for vial sharing, could mean annual savings of nearly $60 million.
“Our results should prompt cost-conscious systems and payers to ask whether the amounts of drugs they’re providing to patients and how they go about making those doses are the most cost-effective approaches,” said corresponding author Garth W. Strohbehn, MD, of the University of Michigan and the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
Dr. Strohbehn said the prospect of adopting these strategies hinges on several factors, with financial incentives at the prescriber and medical center level likely being the most influential.
“In fee-for-service systems, reimbursement scales with the amount of drug administered, so there can be a financial disincentive to decreasing overall drug usage,” Dr. Strohbehn explained.
“Conversely, integrated systems such as Kaiser Permanente or the VHA and large self-insured employers are incentivized to contain costs and take great care of patients, so they may be more inclined to promote these strategies,” he added.
However, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president, Payer+Provider Syndicate, who wasn’t involved in the analysis, cautioned that such a shift may come with unintended consequences.
The Infrastructure, Investment, and Jobs Act of 2021 let the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services seek reimbursement for discarded drugs – in effect, changing the reimbursement model for medications. That led pharmaceutical manufacturers to respond in kind by changing the dosing model, Dr. Powell said.
“Drugs that previously had personalized weight-based dosing were moved to uniform flat dosing, eliminating the potential for the manufacturer to have to issue a reimbursement if the patient’s personalized dose fell short of the amount in the single-use vial,” Dr. Powell added.
If there is a substantial migration to weight-based dosing, “it is possible that pharmaceutical manufacturers will rethink their dosing and pricing models, just as happened previously,” he cautioned.
However, these strategies could also provide relief for another escalating issue: drug shortages. Especially in the current moment, having a stewardship mindset, “might be helpful in navigating drug shortages,” Dr. Strohbehn said.
This research had no commercial funding. Dr. Bryant, Dr. Strohbehn, and Dr. Powell report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Implementing stewardship strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, including personalized weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and pharmacy-level vial sharing, could generate savings of as much as $74 million each year for the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), a new analysis suggests.
That $74 million in savings would translate to nearly 14% less spent on ICI therapy annually.
first author Alex Bryant, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published in Health Affairs.
ICI therapy is used in about 40 unique cancer indications and, in 2020, accounted for more than $6 billion in Medicare Part B spending.
Two of the most prescribed ICIs – pembrolizumab and nivolumab – initially received their U.S. approval at personalized weight-based doses. But at the request of the manufacturers, the Food and Drug Administration approved “one-size-fits-all” flat doses, despite a lack of data to support this strategy compared with weight-based dosing.
With a fixed dose strategy, “patients with cancer not only tend to get too high a dose of the drug, but costs go up significantly,” Daniel Goldstein, MD, a medical oncologist at the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, told this news organization last year. “Why should we give a higher dose with the same efficacy when that dose will cost significantly more and has the potential to increase adverse events?”
To compare the cost of a weight-based vs. fixed-dose strategy, Dr. Bryant and colleagues conducted a simulation analysis under four stewardship scenarios, using data from the VHA and Medicare drug prices. Strategy one looked at weight-based dosing; strategy two combined weight-based dosing and dose rounding but not single-use vial sharing; strategy three used weight-based dosing and single-use vial sharing but not dose rounding; and strategy four, the most aggressive, combined all three.
ICIs in the VHA national formulary included pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and cemiplimab-rwlc.
Using an algorithm to extract data, the team identified 49,851 administration events in 8,276 unique patients in 2021 – just over half were pembrolizumab, nearly 23% were nivolumab, and the remaining 26% largely included atezolizumab (12.1%) and durvalumab (11.9%).
The team found that the VHA spends roughly $537 million annually on ICIs. But implementing the stewardship measures that combined weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and vial sharing could save the VHA $74 million, or about 14%, annually on ICIs.
Most of the savings came from dosing changes to pembrolizumab and nivolumab, with greater savings achieved by combining more stewardship strategies. For instance, using strategy one (weight-based dosing alone) could lead to annual pembrolizumab savings of $14 million. Adding dose rounding (strategy two) could reduce pembrolizumab spending by $24 million. And using strategy four, with an unlimited window for vial sharing, could mean annual savings of nearly $60 million.
“Our results should prompt cost-conscious systems and payers to ask whether the amounts of drugs they’re providing to patients and how they go about making those doses are the most cost-effective approaches,” said corresponding author Garth W. Strohbehn, MD, of the University of Michigan and the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
Dr. Strohbehn said the prospect of adopting these strategies hinges on several factors, with financial incentives at the prescriber and medical center level likely being the most influential.
“In fee-for-service systems, reimbursement scales with the amount of drug administered, so there can be a financial disincentive to decreasing overall drug usage,” Dr. Strohbehn explained.
“Conversely, integrated systems such as Kaiser Permanente or the VHA and large self-insured employers are incentivized to contain costs and take great care of patients, so they may be more inclined to promote these strategies,” he added.
However, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president, Payer+Provider Syndicate, who wasn’t involved in the analysis, cautioned that such a shift may come with unintended consequences.
The Infrastructure, Investment, and Jobs Act of 2021 let the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services seek reimbursement for discarded drugs – in effect, changing the reimbursement model for medications. That led pharmaceutical manufacturers to respond in kind by changing the dosing model, Dr. Powell said.
“Drugs that previously had personalized weight-based dosing were moved to uniform flat dosing, eliminating the potential for the manufacturer to have to issue a reimbursement if the patient’s personalized dose fell short of the amount in the single-use vial,” Dr. Powell added.
If there is a substantial migration to weight-based dosing, “it is possible that pharmaceutical manufacturers will rethink their dosing and pricing models, just as happened previously,” he cautioned.
However, these strategies could also provide relief for another escalating issue: drug shortages. Especially in the current moment, having a stewardship mindset, “might be helpful in navigating drug shortages,” Dr. Strohbehn said.
This research had no commercial funding. Dr. Bryant, Dr. Strohbehn, and Dr. Powell report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Implementing stewardship strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, including personalized weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and pharmacy-level vial sharing, could generate savings of as much as $74 million each year for the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), a new analysis suggests.
That $74 million in savings would translate to nearly 14% less spent on ICI therapy annually.
first author Alex Bryant, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
The study was published in Health Affairs.
ICI therapy is used in about 40 unique cancer indications and, in 2020, accounted for more than $6 billion in Medicare Part B spending.
Two of the most prescribed ICIs – pembrolizumab and nivolumab – initially received their U.S. approval at personalized weight-based doses. But at the request of the manufacturers, the Food and Drug Administration approved “one-size-fits-all” flat doses, despite a lack of data to support this strategy compared with weight-based dosing.
With a fixed dose strategy, “patients with cancer not only tend to get too high a dose of the drug, but costs go up significantly,” Daniel Goldstein, MD, a medical oncologist at the Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, told this news organization last year. “Why should we give a higher dose with the same efficacy when that dose will cost significantly more and has the potential to increase adverse events?”
To compare the cost of a weight-based vs. fixed-dose strategy, Dr. Bryant and colleagues conducted a simulation analysis under four stewardship scenarios, using data from the VHA and Medicare drug prices. Strategy one looked at weight-based dosing; strategy two combined weight-based dosing and dose rounding but not single-use vial sharing; strategy three used weight-based dosing and single-use vial sharing but not dose rounding; and strategy four, the most aggressive, combined all three.
ICIs in the VHA national formulary included pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and cemiplimab-rwlc.
Using an algorithm to extract data, the team identified 49,851 administration events in 8,276 unique patients in 2021 – just over half were pembrolizumab, nearly 23% were nivolumab, and the remaining 26% largely included atezolizumab (12.1%) and durvalumab (11.9%).
The team found that the VHA spends roughly $537 million annually on ICIs. But implementing the stewardship measures that combined weight-based dosing, dose rounding, and vial sharing could save the VHA $74 million, or about 14%, annually on ICIs.
Most of the savings came from dosing changes to pembrolizumab and nivolumab, with greater savings achieved by combining more stewardship strategies. For instance, using strategy one (weight-based dosing alone) could lead to annual pembrolizumab savings of $14 million. Adding dose rounding (strategy two) could reduce pembrolizumab spending by $24 million. And using strategy four, with an unlimited window for vial sharing, could mean annual savings of nearly $60 million.
“Our results should prompt cost-conscious systems and payers to ask whether the amounts of drugs they’re providing to patients and how they go about making those doses are the most cost-effective approaches,” said corresponding author Garth W. Strohbehn, MD, of the University of Michigan and the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System.
Dr. Strohbehn said the prospect of adopting these strategies hinges on several factors, with financial incentives at the prescriber and medical center level likely being the most influential.
“In fee-for-service systems, reimbursement scales with the amount of drug administered, so there can be a financial disincentive to decreasing overall drug usage,” Dr. Strohbehn explained.
“Conversely, integrated systems such as Kaiser Permanente or the VHA and large self-insured employers are incentivized to contain costs and take great care of patients, so they may be more inclined to promote these strategies,” he added.
However, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president, Payer+Provider Syndicate, who wasn’t involved in the analysis, cautioned that such a shift may come with unintended consequences.
The Infrastructure, Investment, and Jobs Act of 2021 let the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services seek reimbursement for discarded drugs – in effect, changing the reimbursement model for medications. That led pharmaceutical manufacturers to respond in kind by changing the dosing model, Dr. Powell said.
“Drugs that previously had personalized weight-based dosing were moved to uniform flat dosing, eliminating the potential for the manufacturer to have to issue a reimbursement if the patient’s personalized dose fell short of the amount in the single-use vial,” Dr. Powell added.
If there is a substantial migration to weight-based dosing, “it is possible that pharmaceutical manufacturers will rethink their dosing and pricing models, just as happened previously,” he cautioned.
However, these strategies could also provide relief for another escalating issue: drug shortages. Especially in the current moment, having a stewardship mindset, “might be helpful in navigating drug shortages,” Dr. Strohbehn said.
This research had no commercial funding. Dr. Bryant, Dr. Strohbehn, and Dr. Powell report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEALTH AFFAIRS
CAR T-cell benefit in lenalidomide-refractory myeloma
New results show that such patients benefit from treatment with the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) (Carvykti).
The finding comes from the phase 3 CARTITUDE-4 trial, which was reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who received a single infusion of ciltacabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a 74% reduction in the risk for disease progression or death, compared with patients who received the standard of care.
The hazard ratio for death or progression with cilta-cel was 0.26 (P < .001), which “is the best hazard ratio ever reported in this patient population in a randomized clinical setting,” said principal investigator Binod Dhakal, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
Dr. Dhakal reported data from the first analysis of the trial. At a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, had not been reached among 208 patients who received cilta-cel; PFS was 11.8 months for the 211 patients assigned to receive standard of care, which consisted of the physician’s choice of either pomalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (PVd), or daratumumab, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone (DPd).
Twelve-month PFS rates were 75.9% and 48.6%, respectively, and both the overall response rate (ORR) and the complete response (CR) rate were higher with the CAR T construct than with the standard of care (ORR, 84.6% vs. 67.3%; CR rates, 73.1% and 21.8%, respectively).
“My perspective on Dr. Dakhal and colleague’s data is that myeloma treatment should be revisited in the light of this,” commented invited discussant Asher Chanan-Khan, MD, from the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center in Jacksonville, Fla.
“Early CAR Ts demonstrating efficacy and safety and prior lines of treatment impact survival from CAR T in myeloma. In lymphoma, CAR T is almost replacing, if not already, autotransplant. Can this also be true for multiple myeloma?” he asked.
Dr. Chanan-Khan noted that there are at least four ongoing trials with CAR T targeting either the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) alone or in combination with an anti-CD19 CAR T, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or with bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone.
Also commenting on the new results, ASCO Expert Oreofe Odejide, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said in a statement: “Lenalidomide has become a foundation of care for people with myeloma, but as its use has expanded, so has the number of patients whose disease will no longer respond to the treatment. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel has not only shown that it delivers remarkably effective outcomes, compared with patients’ current options, but also that it can be used safely earlier in the treatment phase.”
Already approved for refractory myeloma
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T that contains two single-domain antibodies that target BCMA. This target was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
The product is already approved for use in myeloma; it was approved in March 2022 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with refractory/relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried four or more therapies. That approval was based on results from phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 trial, which, as previously reported by this news organization, showed that early and deep responses with cilta-cel proved to be durable.
Final results of CARTITUDE-1, reported in a scientific poster at ASCO 2023, showed that almost half of patients (47.5%) who were treated with cilta-cel were free of disease progression at 3 years, and 59.8% had sustained, complete responses. In addition, the median PFS was longer than for any previously reported therapy for heavily pretreated patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the authors said.
CARTITUDE-4 details
For the CARTITUDE-4 trial, the investigators enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who had experienced relapse after one to three prior lines of therapy that included a prosteasome inhibitor and immunomodulator. After stratification by the choice of PVd or DPd, Multiple Myeloma International Staging System, and number of prior lines of therapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive either cilta-cel or one of the two standard-of-care regimens previously described.
Patients assigned to cilta-cel received one or more cycles of either PVd or DPd as bridging therapy during the period from apheresis to infusion of the CAR T cells.
As already noted, cilta-cel showed superior PFS and response rates and was associated with a significantly higher rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, compared with standard of care, in the intention-to-treat population: 60.6% vs. 15.6%, which translates into an odds ratio for achieving MRD negativity with CAR T of 8.7 (P < .0001). Among the subset of patients evaluable for MRD, the respective rates were 87.5% and 32.7%.
Overall survival data were not mature at the time of presentation. In all, 39 patients in the cilta-cel arm and 47 in the standard-of-care arm died during the study.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 97% of patients who received cilta-cel and in 94% of those who received standard-of-care therapies. In the cilta-cel arm, 76.1% of patients had cytokine release syndrome (CRS), although only 1.1% of cases were of grade 3 or 4 in severity, and there were no CRS-associated deaths. Eight patients in this arm had immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome, all of grade 1 or 2. One patient had grade 1 movement and neurocognitive symptoms, 16 had grade 2 or 3 cranial nerve palsy, and 5 patients had CAR T–related peripheral neuropathy of grade 1, 2, or 3.
The investigators plan to follow patients to determine the long-term effects of ciltacabtagene autoleucel and are currently performing analyses of health-related quality of life, subgroups, and biomarkers.
The study was funded by Janssen and Legend Biotech, which market ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Dr. Dhakal disclosed consulting, speaker’s bureau participation, and institutional research funding from Janssen and others. Several coauthors are employees of the study funders. Dr. Chanan-Khan’s relevant financial information was not available. Dr. Odejide reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New results show that such patients benefit from treatment with the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) (Carvykti).
The finding comes from the phase 3 CARTITUDE-4 trial, which was reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who received a single infusion of ciltacabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a 74% reduction in the risk for disease progression or death, compared with patients who received the standard of care.
The hazard ratio for death or progression with cilta-cel was 0.26 (P < .001), which “is the best hazard ratio ever reported in this patient population in a randomized clinical setting,” said principal investigator Binod Dhakal, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
Dr. Dhakal reported data from the first analysis of the trial. At a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, had not been reached among 208 patients who received cilta-cel; PFS was 11.8 months for the 211 patients assigned to receive standard of care, which consisted of the physician’s choice of either pomalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (PVd), or daratumumab, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone (DPd).
Twelve-month PFS rates were 75.9% and 48.6%, respectively, and both the overall response rate (ORR) and the complete response (CR) rate were higher with the CAR T construct than with the standard of care (ORR, 84.6% vs. 67.3%; CR rates, 73.1% and 21.8%, respectively).
“My perspective on Dr. Dakhal and colleague’s data is that myeloma treatment should be revisited in the light of this,” commented invited discussant Asher Chanan-Khan, MD, from the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center in Jacksonville, Fla.
“Early CAR Ts demonstrating efficacy and safety and prior lines of treatment impact survival from CAR T in myeloma. In lymphoma, CAR T is almost replacing, if not already, autotransplant. Can this also be true for multiple myeloma?” he asked.
Dr. Chanan-Khan noted that there are at least four ongoing trials with CAR T targeting either the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) alone or in combination with an anti-CD19 CAR T, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or with bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone.
Also commenting on the new results, ASCO Expert Oreofe Odejide, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said in a statement: “Lenalidomide has become a foundation of care for people with myeloma, but as its use has expanded, so has the number of patients whose disease will no longer respond to the treatment. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel has not only shown that it delivers remarkably effective outcomes, compared with patients’ current options, but also that it can be used safely earlier in the treatment phase.”
Already approved for refractory myeloma
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T that contains two single-domain antibodies that target BCMA. This target was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
The product is already approved for use in myeloma; it was approved in March 2022 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with refractory/relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried four or more therapies. That approval was based on results from phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 trial, which, as previously reported by this news organization, showed that early and deep responses with cilta-cel proved to be durable.
Final results of CARTITUDE-1, reported in a scientific poster at ASCO 2023, showed that almost half of patients (47.5%) who were treated with cilta-cel were free of disease progression at 3 years, and 59.8% had sustained, complete responses. In addition, the median PFS was longer than for any previously reported therapy for heavily pretreated patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the authors said.
CARTITUDE-4 details
For the CARTITUDE-4 trial, the investigators enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who had experienced relapse after one to three prior lines of therapy that included a prosteasome inhibitor and immunomodulator. After stratification by the choice of PVd or DPd, Multiple Myeloma International Staging System, and number of prior lines of therapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive either cilta-cel or one of the two standard-of-care regimens previously described.
Patients assigned to cilta-cel received one or more cycles of either PVd or DPd as bridging therapy during the period from apheresis to infusion of the CAR T cells.
As already noted, cilta-cel showed superior PFS and response rates and was associated with a significantly higher rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, compared with standard of care, in the intention-to-treat population: 60.6% vs. 15.6%, which translates into an odds ratio for achieving MRD negativity with CAR T of 8.7 (P < .0001). Among the subset of patients evaluable for MRD, the respective rates were 87.5% and 32.7%.
Overall survival data were not mature at the time of presentation. In all, 39 patients in the cilta-cel arm and 47 in the standard-of-care arm died during the study.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 97% of patients who received cilta-cel and in 94% of those who received standard-of-care therapies. In the cilta-cel arm, 76.1% of patients had cytokine release syndrome (CRS), although only 1.1% of cases were of grade 3 or 4 in severity, and there were no CRS-associated deaths. Eight patients in this arm had immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome, all of grade 1 or 2. One patient had grade 1 movement and neurocognitive symptoms, 16 had grade 2 or 3 cranial nerve palsy, and 5 patients had CAR T–related peripheral neuropathy of grade 1, 2, or 3.
The investigators plan to follow patients to determine the long-term effects of ciltacabtagene autoleucel and are currently performing analyses of health-related quality of life, subgroups, and biomarkers.
The study was funded by Janssen and Legend Biotech, which market ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Dr. Dhakal disclosed consulting, speaker’s bureau participation, and institutional research funding from Janssen and others. Several coauthors are employees of the study funders. Dr. Chanan-Khan’s relevant financial information was not available. Dr. Odejide reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New results show that such patients benefit from treatment with the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) (Carvykti).
The finding comes from the phase 3 CARTITUDE-4 trial, which was reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Patients with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who received a single infusion of ciltacabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a 74% reduction in the risk for disease progression or death, compared with patients who received the standard of care.
The hazard ratio for death or progression with cilta-cel was 0.26 (P < .001), which “is the best hazard ratio ever reported in this patient population in a randomized clinical setting,” said principal investigator Binod Dhakal, MD, from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
Dr. Dhakal reported data from the first analysis of the trial. At a median follow-up of 15.9 months, median progression-free survival (PFS), the primary endpoint, had not been reached among 208 patients who received cilta-cel; PFS was 11.8 months for the 211 patients assigned to receive standard of care, which consisted of the physician’s choice of either pomalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (PVd), or daratumumab, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone (DPd).
Twelve-month PFS rates were 75.9% and 48.6%, respectively, and both the overall response rate (ORR) and the complete response (CR) rate were higher with the CAR T construct than with the standard of care (ORR, 84.6% vs. 67.3%; CR rates, 73.1% and 21.8%, respectively).
“My perspective on Dr. Dakhal and colleague’s data is that myeloma treatment should be revisited in the light of this,” commented invited discussant Asher Chanan-Khan, MD, from the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center in Jacksonville, Fla.
“Early CAR Ts demonstrating efficacy and safety and prior lines of treatment impact survival from CAR T in myeloma. In lymphoma, CAR T is almost replacing, if not already, autotransplant. Can this also be true for multiple myeloma?” he asked.
Dr. Chanan-Khan noted that there are at least four ongoing trials with CAR T targeting either the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) alone or in combination with an anti-CD19 CAR T, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or with bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone.
Also commenting on the new results, ASCO Expert Oreofe Odejide, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, said in a statement: “Lenalidomide has become a foundation of care for people with myeloma, but as its use has expanded, so has the number of patients whose disease will no longer respond to the treatment. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel has not only shown that it delivers remarkably effective outcomes, compared with patients’ current options, but also that it can be used safely earlier in the treatment phase.”
Already approved for refractory myeloma
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T that contains two single-domain antibodies that target BCMA. This target was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
The product is already approved for use in myeloma; it was approved in March 2022 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with refractory/relapsed multiple myeloma who have already tried four or more therapies. That approval was based on results from phase 1b/2 CARTITUDE-1 trial, which, as previously reported by this news organization, showed that early and deep responses with cilta-cel proved to be durable.
Final results of CARTITUDE-1, reported in a scientific poster at ASCO 2023, showed that almost half of patients (47.5%) who were treated with cilta-cel were free of disease progression at 3 years, and 59.8% had sustained, complete responses. In addition, the median PFS was longer than for any previously reported therapy for heavily pretreated patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the authors said.
CARTITUDE-4 details
For the CARTITUDE-4 trial, the investigators enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma who had experienced relapse after one to three prior lines of therapy that included a prosteasome inhibitor and immunomodulator. After stratification by the choice of PVd or DPd, Multiple Myeloma International Staging System, and number of prior lines of therapy, patients were randomly assigned to receive either cilta-cel or one of the two standard-of-care regimens previously described.
Patients assigned to cilta-cel received one or more cycles of either PVd or DPd as bridging therapy during the period from apheresis to infusion of the CAR T cells.
As already noted, cilta-cel showed superior PFS and response rates and was associated with a significantly higher rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, compared with standard of care, in the intention-to-treat population: 60.6% vs. 15.6%, which translates into an odds ratio for achieving MRD negativity with CAR T of 8.7 (P < .0001). Among the subset of patients evaluable for MRD, the respective rates were 87.5% and 32.7%.
Overall survival data were not mature at the time of presentation. In all, 39 patients in the cilta-cel arm and 47 in the standard-of-care arm died during the study.
Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 97% of patients who received cilta-cel and in 94% of those who received standard-of-care therapies. In the cilta-cel arm, 76.1% of patients had cytokine release syndrome (CRS), although only 1.1% of cases were of grade 3 or 4 in severity, and there were no CRS-associated deaths. Eight patients in this arm had immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome, all of grade 1 or 2. One patient had grade 1 movement and neurocognitive symptoms, 16 had grade 2 or 3 cranial nerve palsy, and 5 patients had CAR T–related peripheral neuropathy of grade 1, 2, or 3.
The investigators plan to follow patients to determine the long-term effects of ciltacabtagene autoleucel and are currently performing analyses of health-related quality of life, subgroups, and biomarkers.
The study was funded by Janssen and Legend Biotech, which market ciltacabtagene autoleucel. Dr. Dhakal disclosed consulting, speaker’s bureau participation, and institutional research funding from Janssen and others. Several coauthors are employees of the study funders. Dr. Chanan-Khan’s relevant financial information was not available. Dr. Odejide reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
Warts difficult to eradicate in immunocompromised children
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
.
Only a quarter of patients (24%) who were undergoing active cancer treatment experienced complete resolution of their warts, compared with 63.3% of patients who were not on active treatment.
In addition, warts persisted or worsened in 56.0% of patients receiving active treatment compared with 13.4% of those who were not receiving it.
“These data enable providers treating warts in children with cancer to have an educated discussion regarding the expected clinical progression of warts and the likelihood of response to wart therapy while on and off anti-cancer treatment,” the authors wrote in the study, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In immunocompromised children, warts are more common than in the general pediatric population, and more resistant to treatment. But as the authors noted, data on the course and prognosis of warts in pediatric patients who are actively receiving anti-cancer therapy compared with patients who have completed treatment are limited.
Tina Ho, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, and colleagues from Boston Children’s Hospital, sought to analyze the clinical course of warts treated in this patient population at their institution over a 10-year period. They conducted a retrospective study of 72 children who were treated for cancer between 2011 and 2021, and who had also been treated for warts.
The median age of the cohort was 12 years, and they were followed for a median of 2 years following their diagnosis of warts. Within this group, more than half (55%) had hematologic malignancies, while 27% had a history of bone marrow transplantation.
Of note, the authors pointed out, 54% of the patients had plantar warts, and 60% of patients (38 of 63) with a documented number of warts had more than five at the time of presentation.
The treatment regimens that the children had received varied, with 81% of patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy and 23% of patients on targeted therapies that included immunotherapy.
The warts were most commonly treated with cryotherapy and topical salicylic acid; this was the case for those actively receiving oncology treatment or those who had completed their treatment regimens.
Outcomes of wart treatments were available in 25 of the patients undergoing active cancer treatment and in 30 of those who had completed treatment. For children on active oncology treatment, 5 (20%) achieved partial resolution, 6 (24%) achieved complete resolution, and 14 (56%) experienced persistence or worsening of their warts following therapy. Those who had completed treatment had better outcomes: Seven (23.3%) had a partial response, 19 (63.3%) had complete resolution, and 4 (13.4%) had persistence or worsening of warts after treatment of warts.
The authors also pointed out the treatment of warts can be painful, expensive, and time-consuming. “It is thus imperative that the risks and benefits of these treatments are carefully considered before proceeding with treatment,” wrote Dr. Ho and colleagues. “This is especially true in medically complex children with cancer who may be fearful of procedures and spend significant portions of their young lives within the medical system.”
Limitations to the study include its retrospective design and small sample size. Clinical data were not uniformly complete, and follow-up intervals varied among the participants. Also, it was conducted at a single-institution and at a large tertiary center, so the results may not be fully generalizable.
The authors declared no conflict of interest. No outside funding source was listed.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Antibody-drug conjugate changes standard of care for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer
The conclusion of this study marks the first time that a novel therapy has demonstrated an overall survival (OS) improvement in any phase 3 trial in this population, according to lead investigator Kathleen Moore, MD.
“We believe these data are practice changing and position mirvetuximab [soravtansine] as the new standard of care for patients with folate receptor–alpha positive, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. Moore during a presentation of the study at a special session of the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology devoted solely to the MIRASOL study.
New standard of care
Following Dr. Moore’s presentation, Roisin Eilish O’Cearbhaill, MD, served as a discussant, and she confirmed the trial’s importance.
“It has firmly established the role of mirvetuximab [soravtansine] in folate receptor–alpha high-expression, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. O’Cearbhaill, who is Research director of the gynecologic medical oncology service and clinical director of the solid tumor, cellular therapy service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine received accelerated FDA approval in November based on the results of the single-arm SORAYA trial, which demonstrated a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit in platinum-resistant patients who had been previously treated with one to three treatment regimens, at least one of which having included bevacizumab.
The new study compared MIRV with physician choice chemotherapy and found both a PFS and OS benefit in the MIRV arm. The results garnered significant enthusiasm from the audience, and others reacted positively as well.
“The results that she presented are just astounding, with a significant improvement in both progression-free and overall survival. I think certainly the overall survival needs to be highlighted here, because this is a patient population that’s notoriously difficult to treat,” said Ana Valente, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. Dr. Valente, who did not attend the presentation but was asked to comment on the study, is also a member of the Society of Gynecological Oncologist communications committee.
Unlike SORAYA, MIRASOL was open to patients who had not received bevacizumab, and Dr. Moore and colleagues found similar survival benefits in patients who had not received bevacizumab as in those who had, said Dr. Moore, who is the associate director of clinical research at Stephenson Cancer Center and director of the Oklahoma TSET Phase 1 Program, both in Oklahoma City. This opens the possibility of using MIRV instead of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy in platinum-resistant patients.
“I think this data really shows you can move right to mirvetuximab [soravtansine] and feel pretty solid about the decision in a biomarker selected [population],” Dr. Moore said, during an interview.
Not just for high expression levels
MIRASOL was restricted to patients with high levels of expression of folate receptor–alpha, which is MIRV’s target on the surface of tumor cells. High expression is defined as at least 75% of viable tumor cells exhibiting a minimum of 2+ level membrane staining intensity by immunohistochemistry. That represents about 35% of patients, according to Dr. Moore, but she said that the drug also shows promise in patients with medium levels of folate receptor–alpha expression.
“I think it’s just going to be now starting to get those label extension studies launched to branch it out. Then you account for 60% of your population which [have] medium to high [expression levels], and that’s really where you see benefit,” said Dr. Moore. Medium expression levels of folate receptor–alpha are defined as 50% to greater than 75% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity.
She also noted that the FORWARD II trial combining mirvetuximab soravtansine with bevacizumab in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer is showing good results.
“We have really beautiful data [from FORWARD II]. If I have a medium expresser, I’m using the doublet [of MIRV and bevacizumab], and it works,” said Dr. Moore, while also pointing out that this remains an off-label use.
It’s possible that the drug could be extended even to low expression levels, defined as 25% to less than 50% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity. “[We are] currently working on that strategy with already available data,” said Dr. Moore.
She speculated that the improved OS may be attributed to the reduced toxicity of MIRV, compared with chemotherapy agents, which leaves patients feeling better and more able to pursue other treatments, which in turn may increase survival odds.
Dr. O’Cearbhaill touted the benefits of ADCs and their ability to target powerful cytotoxic agents while limiting side effects, and she is looking forward to more new therapies on the horizon.
“There are four [ADCs] in late stages of development [for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer], so hopefully there will be other ones coming online as well,” Dr. O’Cearbhaill said in an interview. “Then we’ll have to figure out how to sequence them, which drug will be best in class. Will we be just giving one or will be giving ADC followed by ADC?”
Study methods and results
The study enrolled 453 patients and randomized them to treatment with MIRV or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, which could be paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan. The MIRV dose was 6 mg/kg adjusted ideal body weight every 3 weeks. The median age was 62 in the chemotherapy arm and 63 years in the MIRV arm. About 63% of the chemotherapy arm had prior bevacizumab exposure, as did 61% of the MIRV arm.
Median PFS was 5.62 months in the MIRV arm and 3.98 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.65; P less than .0001). The overall response rate was 42% in the MIRV arm and 16% in the chemotherapy arm (P < .0001).
The safety outcomes also favored MIRV: 42% experienced grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) versus 54% in the chemotherapy group. Severe adverse events were also lower in MIRV, 24% versus 33%. Just 9% of patients in the MIRV discontinued because of TEAEs, compared with 16% in the chemotherapy arm.
MIRV was associated with blurred vision (41%), keratopathy (32%), and dry eye (28%), but these issues were generally manageable through collaboration with optometrists or ophthalmologists.
Dr. Moore and Dr. O’Cearbhaill reported receiving honoraria, research funding, and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. O’Cearbhaill has consulted for or advised Aptitude Health, Bayer, Carina Biotech, Fresenius Kabi, GlaxoSmithKline, GOG Foundation, Immunogen, R-Pharm, Regeneron, and Seagen.
The conclusion of this study marks the first time that a novel therapy has demonstrated an overall survival (OS) improvement in any phase 3 trial in this population, according to lead investigator Kathleen Moore, MD.
“We believe these data are practice changing and position mirvetuximab [soravtansine] as the new standard of care for patients with folate receptor–alpha positive, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. Moore during a presentation of the study at a special session of the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology devoted solely to the MIRASOL study.
New standard of care
Following Dr. Moore’s presentation, Roisin Eilish O’Cearbhaill, MD, served as a discussant, and she confirmed the trial’s importance.
“It has firmly established the role of mirvetuximab [soravtansine] in folate receptor–alpha high-expression, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. O’Cearbhaill, who is Research director of the gynecologic medical oncology service and clinical director of the solid tumor, cellular therapy service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine received accelerated FDA approval in November based on the results of the single-arm SORAYA trial, which demonstrated a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit in platinum-resistant patients who had been previously treated with one to three treatment regimens, at least one of which having included bevacizumab.
The new study compared MIRV with physician choice chemotherapy and found both a PFS and OS benefit in the MIRV arm. The results garnered significant enthusiasm from the audience, and others reacted positively as well.
“The results that she presented are just astounding, with a significant improvement in both progression-free and overall survival. I think certainly the overall survival needs to be highlighted here, because this is a patient population that’s notoriously difficult to treat,” said Ana Valente, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. Dr. Valente, who did not attend the presentation but was asked to comment on the study, is also a member of the Society of Gynecological Oncologist communications committee.
Unlike SORAYA, MIRASOL was open to patients who had not received bevacizumab, and Dr. Moore and colleagues found similar survival benefits in patients who had not received bevacizumab as in those who had, said Dr. Moore, who is the associate director of clinical research at Stephenson Cancer Center and director of the Oklahoma TSET Phase 1 Program, both in Oklahoma City. This opens the possibility of using MIRV instead of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy in platinum-resistant patients.
“I think this data really shows you can move right to mirvetuximab [soravtansine] and feel pretty solid about the decision in a biomarker selected [population],” Dr. Moore said, during an interview.
Not just for high expression levels
MIRASOL was restricted to patients with high levels of expression of folate receptor–alpha, which is MIRV’s target on the surface of tumor cells. High expression is defined as at least 75% of viable tumor cells exhibiting a minimum of 2+ level membrane staining intensity by immunohistochemistry. That represents about 35% of patients, according to Dr. Moore, but she said that the drug also shows promise in patients with medium levels of folate receptor–alpha expression.
“I think it’s just going to be now starting to get those label extension studies launched to branch it out. Then you account for 60% of your population which [have] medium to high [expression levels], and that’s really where you see benefit,” said Dr. Moore. Medium expression levels of folate receptor–alpha are defined as 50% to greater than 75% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity.
She also noted that the FORWARD II trial combining mirvetuximab soravtansine with bevacizumab in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer is showing good results.
“We have really beautiful data [from FORWARD II]. If I have a medium expresser, I’m using the doublet [of MIRV and bevacizumab], and it works,” said Dr. Moore, while also pointing out that this remains an off-label use.
It’s possible that the drug could be extended even to low expression levels, defined as 25% to less than 50% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity. “[We are] currently working on that strategy with already available data,” said Dr. Moore.
She speculated that the improved OS may be attributed to the reduced toxicity of MIRV, compared with chemotherapy agents, which leaves patients feeling better and more able to pursue other treatments, which in turn may increase survival odds.
Dr. O’Cearbhaill touted the benefits of ADCs and their ability to target powerful cytotoxic agents while limiting side effects, and she is looking forward to more new therapies on the horizon.
“There are four [ADCs] in late stages of development [for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer], so hopefully there will be other ones coming online as well,” Dr. O’Cearbhaill said in an interview. “Then we’ll have to figure out how to sequence them, which drug will be best in class. Will we be just giving one or will be giving ADC followed by ADC?”
Study methods and results
The study enrolled 453 patients and randomized them to treatment with MIRV or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, which could be paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan. The MIRV dose was 6 mg/kg adjusted ideal body weight every 3 weeks. The median age was 62 in the chemotherapy arm and 63 years in the MIRV arm. About 63% of the chemotherapy arm had prior bevacizumab exposure, as did 61% of the MIRV arm.
Median PFS was 5.62 months in the MIRV arm and 3.98 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.65; P less than .0001). The overall response rate was 42% in the MIRV arm and 16% in the chemotherapy arm (P < .0001).
The safety outcomes also favored MIRV: 42% experienced grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) versus 54% in the chemotherapy group. Severe adverse events were also lower in MIRV, 24% versus 33%. Just 9% of patients in the MIRV discontinued because of TEAEs, compared with 16% in the chemotherapy arm.
MIRV was associated with blurred vision (41%), keratopathy (32%), and dry eye (28%), but these issues were generally manageable through collaboration with optometrists or ophthalmologists.
Dr. Moore and Dr. O’Cearbhaill reported receiving honoraria, research funding, and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. O’Cearbhaill has consulted for or advised Aptitude Health, Bayer, Carina Biotech, Fresenius Kabi, GlaxoSmithKline, GOG Foundation, Immunogen, R-Pharm, Regeneron, and Seagen.
The conclusion of this study marks the first time that a novel therapy has demonstrated an overall survival (OS) improvement in any phase 3 trial in this population, according to lead investigator Kathleen Moore, MD.
“We believe these data are practice changing and position mirvetuximab [soravtansine] as the new standard of care for patients with folate receptor–alpha positive, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. Moore during a presentation of the study at a special session of the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology devoted solely to the MIRASOL study.
New standard of care
Following Dr. Moore’s presentation, Roisin Eilish O’Cearbhaill, MD, served as a discussant, and she confirmed the trial’s importance.
“It has firmly established the role of mirvetuximab [soravtansine] in folate receptor–alpha high-expression, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer,” said Dr. O’Cearbhaill, who is Research director of the gynecologic medical oncology service and clinical director of the solid tumor, cellular therapy service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
Mirvetuximab soravtansine received accelerated FDA approval in November based on the results of the single-arm SORAYA trial, which demonstrated a progression-free survival (PFS) benefit in platinum-resistant patients who had been previously treated with one to three treatment regimens, at least one of which having included bevacizumab.
The new study compared MIRV with physician choice chemotherapy and found both a PFS and OS benefit in the MIRV arm. The results garnered significant enthusiasm from the audience, and others reacted positively as well.
“The results that she presented are just astounding, with a significant improvement in both progression-free and overall survival. I think certainly the overall survival needs to be highlighted here, because this is a patient population that’s notoriously difficult to treat,” said Ana Valente, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at the Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. Dr. Valente, who did not attend the presentation but was asked to comment on the study, is also a member of the Society of Gynecological Oncologist communications committee.
Unlike SORAYA, MIRASOL was open to patients who had not received bevacizumab, and Dr. Moore and colleagues found similar survival benefits in patients who had not received bevacizumab as in those who had, said Dr. Moore, who is the associate director of clinical research at Stephenson Cancer Center and director of the Oklahoma TSET Phase 1 Program, both in Oklahoma City. This opens the possibility of using MIRV instead of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy in platinum-resistant patients.
“I think this data really shows you can move right to mirvetuximab [soravtansine] and feel pretty solid about the decision in a biomarker selected [population],” Dr. Moore said, during an interview.
Not just for high expression levels
MIRASOL was restricted to patients with high levels of expression of folate receptor–alpha, which is MIRV’s target on the surface of tumor cells. High expression is defined as at least 75% of viable tumor cells exhibiting a minimum of 2+ level membrane staining intensity by immunohistochemistry. That represents about 35% of patients, according to Dr. Moore, but she said that the drug also shows promise in patients with medium levels of folate receptor–alpha expression.
“I think it’s just going to be now starting to get those label extension studies launched to branch it out. Then you account for 60% of your population which [have] medium to high [expression levels], and that’s really where you see benefit,” said Dr. Moore. Medium expression levels of folate receptor–alpha are defined as 50% to greater than 75% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity.
She also noted that the FORWARD II trial combining mirvetuximab soravtansine with bevacizumab in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer is showing good results.
“We have really beautiful data [from FORWARD II]. If I have a medium expresser, I’m using the doublet [of MIRV and bevacizumab], and it works,” said Dr. Moore, while also pointing out that this remains an off-label use.
It’s possible that the drug could be extended even to low expression levels, defined as 25% to less than 50% of tumor cells with 2+ level membrane staining intensity. “[We are] currently working on that strategy with already available data,” said Dr. Moore.
She speculated that the improved OS may be attributed to the reduced toxicity of MIRV, compared with chemotherapy agents, which leaves patients feeling better and more able to pursue other treatments, which in turn may increase survival odds.
Dr. O’Cearbhaill touted the benefits of ADCs and their ability to target powerful cytotoxic agents while limiting side effects, and she is looking forward to more new therapies on the horizon.
“There are four [ADCs] in late stages of development [for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer], so hopefully there will be other ones coming online as well,” Dr. O’Cearbhaill said in an interview. “Then we’ll have to figure out how to sequence them, which drug will be best in class. Will we be just giving one or will be giving ADC followed by ADC?”
Study methods and results
The study enrolled 453 patients and randomized them to treatment with MIRV or investigator’s choice of chemotherapy, which could be paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan. The MIRV dose was 6 mg/kg adjusted ideal body weight every 3 weeks. The median age was 62 in the chemotherapy arm and 63 years in the MIRV arm. About 63% of the chemotherapy arm had prior bevacizumab exposure, as did 61% of the MIRV arm.
Median PFS was 5.62 months in the MIRV arm and 3.98 months in the chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.65; P less than .0001). The overall response rate was 42% in the MIRV arm and 16% in the chemotherapy arm (P < .0001).
The safety outcomes also favored MIRV: 42% experienced grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) versus 54% in the chemotherapy group. Severe adverse events were also lower in MIRV, 24% versus 33%. Just 9% of patients in the MIRV discontinued because of TEAEs, compared with 16% in the chemotherapy arm.
MIRV was associated with blurred vision (41%), keratopathy (32%), and dry eye (28%), but these issues were generally manageable through collaboration with optometrists or ophthalmologists.
Dr. Moore and Dr. O’Cearbhaill reported receiving honoraria, research funding, and travel expenses from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. O’Cearbhaill has consulted for or advised Aptitude Health, Bayer, Carina Biotech, Fresenius Kabi, GlaxoSmithKline, GOG Foundation, Immunogen, R-Pharm, Regeneron, and Seagen.
AT ASCO 2023