User login
Sex differences in pediatric B-ALL outcomes persist
Even in the age of intensive therapy and extensive risk stratification, there are small but significant differences in outcomes between boys and girls with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
This finding comes from a review of 10 years of clinical trials by the Children’s Oncology Group (COG), which showed that, among patients with B-ALL, 5-year event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were inferior with boys, compared with girls, even when adjusted for prognostic factors, reported Sumit Gupta, MD, PhD, FRCPC, from the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
“Inferior outcomes, although small in absolute terms, continue to exist among boys versus girls despite modern therapy and after adjusting for other risk factors. These persist also despite the longer duration of therapy among boys,” he said in an oral abstract presentation during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology. (Abstract 2025).
Among pediatric patients with T-cell lineage ALL (T-ALL), however, there were no significant sex-based differences in either EFS or OS, he said.
Although survival for children with ALL has continued to improve, previous studies found inferior survival outcomes in boys, and suggested that the difference might be explained by imbalances in risk factors.
To see whether sex-based disparities persist with modern intensive therapy protocols after adjustment for risk factors, and to determine whether there are sex-based differences in toxicities or patterns of treatment failure, Dr. Gupta and colleagues created a cohort of all patients age 1-30 years enrolled in frontline COG trial for B-ALL and T-ALL from 2004 to 2014.
During this period, boys received an extra year of maintenance. Cranial radiation was limited to B-ALL patients with slow treatment responses and central nervous system status 3, signifying definite CNS involvement. Among patients with T-ALL, cranial radiation was given to all intermediate- and high-risk patients.
Sex differences small, but significant
The investigators identified a total of 8,202 patients (4,463 males and 3,739 females) with B-ALL, and 1,562 (1,161 males and 401 females) with T-ALL. Boys were likely to be older (P < .0001), and to have a small but significantly greater likelihood of having unfavorable B-ALL cytogenetics, compared with girls (P = .05).
Boys with B-ALL were less likely to be negative for minimal residual disease (76.1% vs. 78.1%, P = .04), but the opposite was true for those with T-ALL (59% vs. 56.8%, P = .01).
As noted before, among pediatric patients with B-ALL, EFS and OS were both inferior for males, with a hazard ratio for higher EFS rates in girls of 1.19 (P = .001) and a HR for OS of 1.17 (P = .046).
Both EFS and OS were similar between the sexes among patients with T-ALL.
The differences in EFS in patients with B-ALL was attributable to higher CNS relapses among boys (4.2% vs. 2.5%, P < .0001). The CNS relapses occurred at a median of 2.5 years in boys versus 2.1 years in girls, although most relapses occurred during therapy.
There were no differences in cumulative isolated bone marrow relapses, however.
Treatment-related mortality rates were the same, but osteonecrosis rates were significantly lower for boys, with a 5-year cumulative incidence of 5.2% versus 6.7% for girls (P = .001).
Possible explanations
Dr. Gupta noted that the inferior outcomes among boys may be attributable to extramedullary relapses among patients with B-ALL.
In addition, the lack of sex-based differences in T-ALL may be caused in part by the increased use of CNS radiation in this population. Previous studies in which CNS radiation was omitted showed an increase in CNS relapsed rates among boys but not girls, he pointed out.
“This does imply that in the more recent generation of T-lineage ALL treatment trials that we’ll need to monitor sex-based differences in outcome, as fewer and fewer patients with T-ALL disease received cranial radiation in these more recent trials and in contemporary therapy,” he said.
One possible mechanism for sex-based outcome differences might be differences in steroid metabolism, as suggested by the higher osteonecrosis rate among girls, he added.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, William G. Woods, MD, from Emory University, Atlanta, asked what role testicular relapse played in outcomes.
Dr. Gupta replied that the investigators had considered that the excess risk for extramedullary relapse in boys might be accounted for by testicular relapse, but “when you take away testicular relapse from those numbers and really just concentrate on CNS, it’s still that substantial difference when you’re talking about B-lineage disease.”
In patients with T-ALL as well, CNS relapse was more common in boys after controlling for testicular relapse, he said.
Another audience member asked whether the data suggest a benefit to treating boys with CNS-penetrating drugs such as dexamethasone or high-dose methotrexate,
Dr. Gupta said that it’s still uncertain whether it is clinically sound to subject a boy with otherwise–standard-risk disease to more intensive high-risk therapy, given the relatively small absolute differences in outcomes between the sexes.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Gupta, Dr. Woods, and Dr. Meret had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
Even in the age of intensive therapy and extensive risk stratification, there are small but significant differences in outcomes between boys and girls with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
This finding comes from a review of 10 years of clinical trials by the Children’s Oncology Group (COG), which showed that, among patients with B-ALL, 5-year event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were inferior with boys, compared with girls, even when adjusted for prognostic factors, reported Sumit Gupta, MD, PhD, FRCPC, from the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
“Inferior outcomes, although small in absolute terms, continue to exist among boys versus girls despite modern therapy and after adjusting for other risk factors. These persist also despite the longer duration of therapy among boys,” he said in an oral abstract presentation during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology. (Abstract 2025).
Among pediatric patients with T-cell lineage ALL (T-ALL), however, there were no significant sex-based differences in either EFS or OS, he said.
Although survival for children with ALL has continued to improve, previous studies found inferior survival outcomes in boys, and suggested that the difference might be explained by imbalances in risk factors.
To see whether sex-based disparities persist with modern intensive therapy protocols after adjustment for risk factors, and to determine whether there are sex-based differences in toxicities or patterns of treatment failure, Dr. Gupta and colleagues created a cohort of all patients age 1-30 years enrolled in frontline COG trial for B-ALL and T-ALL from 2004 to 2014.
During this period, boys received an extra year of maintenance. Cranial radiation was limited to B-ALL patients with slow treatment responses and central nervous system status 3, signifying definite CNS involvement. Among patients with T-ALL, cranial radiation was given to all intermediate- and high-risk patients.
Sex differences small, but significant
The investigators identified a total of 8,202 patients (4,463 males and 3,739 females) with B-ALL, and 1,562 (1,161 males and 401 females) with T-ALL. Boys were likely to be older (P < .0001), and to have a small but significantly greater likelihood of having unfavorable B-ALL cytogenetics, compared with girls (P = .05).
Boys with B-ALL were less likely to be negative for minimal residual disease (76.1% vs. 78.1%, P = .04), but the opposite was true for those with T-ALL (59% vs. 56.8%, P = .01).
As noted before, among pediatric patients with B-ALL, EFS and OS were both inferior for males, with a hazard ratio for higher EFS rates in girls of 1.19 (P = .001) and a HR for OS of 1.17 (P = .046).
Both EFS and OS were similar between the sexes among patients with T-ALL.
The differences in EFS in patients with B-ALL was attributable to higher CNS relapses among boys (4.2% vs. 2.5%, P < .0001). The CNS relapses occurred at a median of 2.5 years in boys versus 2.1 years in girls, although most relapses occurred during therapy.
There were no differences in cumulative isolated bone marrow relapses, however.
Treatment-related mortality rates were the same, but osteonecrosis rates were significantly lower for boys, with a 5-year cumulative incidence of 5.2% versus 6.7% for girls (P = .001).
Possible explanations
Dr. Gupta noted that the inferior outcomes among boys may be attributable to extramedullary relapses among patients with B-ALL.
In addition, the lack of sex-based differences in T-ALL may be caused in part by the increased use of CNS radiation in this population. Previous studies in which CNS radiation was omitted showed an increase in CNS relapsed rates among boys but not girls, he pointed out.
“This does imply that in the more recent generation of T-lineage ALL treatment trials that we’ll need to monitor sex-based differences in outcome, as fewer and fewer patients with T-ALL disease received cranial radiation in these more recent trials and in contemporary therapy,” he said.
One possible mechanism for sex-based outcome differences might be differences in steroid metabolism, as suggested by the higher osteonecrosis rate among girls, he added.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, William G. Woods, MD, from Emory University, Atlanta, asked what role testicular relapse played in outcomes.
Dr. Gupta replied that the investigators had considered that the excess risk for extramedullary relapse in boys might be accounted for by testicular relapse, but “when you take away testicular relapse from those numbers and really just concentrate on CNS, it’s still that substantial difference when you’re talking about B-lineage disease.”
In patients with T-ALL as well, CNS relapse was more common in boys after controlling for testicular relapse, he said.
Another audience member asked whether the data suggest a benefit to treating boys with CNS-penetrating drugs such as dexamethasone or high-dose methotrexate,
Dr. Gupta said that it’s still uncertain whether it is clinically sound to subject a boy with otherwise–standard-risk disease to more intensive high-risk therapy, given the relatively small absolute differences in outcomes between the sexes.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Gupta, Dr. Woods, and Dr. Meret had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
Even in the age of intensive therapy and extensive risk stratification, there are small but significant differences in outcomes between boys and girls with B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
This finding comes from a review of 10 years of clinical trials by the Children’s Oncology Group (COG), which showed that, among patients with B-ALL, 5-year event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were inferior with boys, compared with girls, even when adjusted for prognostic factors, reported Sumit Gupta, MD, PhD, FRCPC, from the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
“Inferior outcomes, although small in absolute terms, continue to exist among boys versus girls despite modern therapy and after adjusting for other risk factors. These persist also despite the longer duration of therapy among boys,” he said in an oral abstract presentation during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology. (Abstract 2025).
Among pediatric patients with T-cell lineage ALL (T-ALL), however, there were no significant sex-based differences in either EFS or OS, he said.
Although survival for children with ALL has continued to improve, previous studies found inferior survival outcomes in boys, and suggested that the difference might be explained by imbalances in risk factors.
To see whether sex-based disparities persist with modern intensive therapy protocols after adjustment for risk factors, and to determine whether there are sex-based differences in toxicities or patterns of treatment failure, Dr. Gupta and colleagues created a cohort of all patients age 1-30 years enrolled in frontline COG trial for B-ALL and T-ALL from 2004 to 2014.
During this period, boys received an extra year of maintenance. Cranial radiation was limited to B-ALL patients with slow treatment responses and central nervous system status 3, signifying definite CNS involvement. Among patients with T-ALL, cranial radiation was given to all intermediate- and high-risk patients.
Sex differences small, but significant
The investigators identified a total of 8,202 patients (4,463 males and 3,739 females) with B-ALL, and 1,562 (1,161 males and 401 females) with T-ALL. Boys were likely to be older (P < .0001), and to have a small but significantly greater likelihood of having unfavorable B-ALL cytogenetics, compared with girls (P = .05).
Boys with B-ALL were less likely to be negative for minimal residual disease (76.1% vs. 78.1%, P = .04), but the opposite was true for those with T-ALL (59% vs. 56.8%, P = .01).
As noted before, among pediatric patients with B-ALL, EFS and OS were both inferior for males, with a hazard ratio for higher EFS rates in girls of 1.19 (P = .001) and a HR for OS of 1.17 (P = .046).
Both EFS and OS were similar between the sexes among patients with T-ALL.
The differences in EFS in patients with B-ALL was attributable to higher CNS relapses among boys (4.2% vs. 2.5%, P < .0001). The CNS relapses occurred at a median of 2.5 years in boys versus 2.1 years in girls, although most relapses occurred during therapy.
There were no differences in cumulative isolated bone marrow relapses, however.
Treatment-related mortality rates were the same, but osteonecrosis rates were significantly lower for boys, with a 5-year cumulative incidence of 5.2% versus 6.7% for girls (P = .001).
Possible explanations
Dr. Gupta noted that the inferior outcomes among boys may be attributable to extramedullary relapses among patients with B-ALL.
In addition, the lack of sex-based differences in T-ALL may be caused in part by the increased use of CNS radiation in this population. Previous studies in which CNS radiation was omitted showed an increase in CNS relapsed rates among boys but not girls, he pointed out.
“This does imply that in the more recent generation of T-lineage ALL treatment trials that we’ll need to monitor sex-based differences in outcome, as fewer and fewer patients with T-ALL disease received cranial radiation in these more recent trials and in contemporary therapy,” he said.
One possible mechanism for sex-based outcome differences might be differences in steroid metabolism, as suggested by the higher osteonecrosis rate among girls, he added.
In the question-and-answer following the presentation, William G. Woods, MD, from Emory University, Atlanta, asked what role testicular relapse played in outcomes.
Dr. Gupta replied that the investigators had considered that the excess risk for extramedullary relapse in boys might be accounted for by testicular relapse, but “when you take away testicular relapse from those numbers and really just concentrate on CNS, it’s still that substantial difference when you’re talking about B-lineage disease.”
In patients with T-ALL as well, CNS relapse was more common in boys after controlling for testicular relapse, he said.
Another audience member asked whether the data suggest a benefit to treating boys with CNS-penetrating drugs such as dexamethasone or high-dose methotrexate,
Dr. Gupta said that it’s still uncertain whether it is clinically sound to subject a boy with otherwise–standard-risk disease to more intensive high-risk therapy, given the relatively small absolute differences in outcomes between the sexes.
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation. Dr. Gupta, Dr. Woods, and Dr. Meret had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
FROM ASPHO 2021
Pediatric cancer survivors at risk for opioid misuse
Survivors of childhood cancers are at increased risk for prescription opioid misuse compared with their peers, a review of a claims database revealed.
Among more than 8,000 patients age 21 or younger who had completed treatment for hematologic, central nervous system, bone, or gonadal cancers, survivors were significantly more likely than were their peers to have an opioid prescription, longer duration of prescription, and higher daily doses of opioids, and to have opioid prescriptions overlapping for a week or more, reported Xu Ji, PhD, of Emory University in Atlanta.
Teenage and young adult patients were at higher risk than were patients younger than 12, and the risk was highest among patients who had been treated for bone malignancies, as well as those who had undergone any hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
“These findings suggest that health care providers who regularly see survivors should explore nonopioid options to help prevent opioid misuse, and screen for potential misuse in those who actually receive opioids,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
“This is a really important topic, and something that’s probably been underinvestigated and underexplored in our patient population,” said session comoderator Sheri Spunt, MD, Endowed Professor of Pediatric Cancer at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Database review
Dr. Ji and colleagues used the IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters database from 2009 to 2018 to examine prescription opioid use, potential misuse, and substance use disorders in pediatric cancer survivors in the first year after completion of therapy, and to identify factors associated with risk for misuse or substance use disorders. Specifically, the period of interest was the first year after completion of all treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and stem cell transplant (Abstract 2015).
They looked at deidentified records on any opioid prescription and for treatment of any opioid use or substance use disorder (alcohol, psychotherapeutic drugs, marijuana, or illicit drug use disorders).
They defined indicators of potential misuse as either prescriptions for long-acting or extended-release opioids for acute pain conditions; opioid and benzodiazepine prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; opioid prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; high daily opioid dosage (prescribed daily dose of 100 or greater morphine milligram equivalent [MME]; and/or opioid dose escalation (an increase of at least 50% in mean MMEs per month twice consecutively within 1 year).
They compared outcomes between a total of 8,635 survivors and 44,175 controls, matched on a 1:5 basis with survivors by age, sex, and region, and continuous enrollment during the 1-year posttherapy period.
In each of three age categories – 0 to 11 years, 12 to 17 years, and 18 years and older – survivors were significantly more likely to have received an opioid prescription, at 15% for the youngest survivors vs. 2% of controls, 25% vs. 8% for 12- to 17-year-olds, and 28% vs. 12% for those 18 and older (P < .01 for all three comparisons).
Survivors were also significantly more likely to have any indicator of potential misuse (1.6% vs. 0.1%, 4.6% vs. 0.5%, and 7.4% vs. 1.2%, respectively, P < .001 for all) and both the youngest and oldest groups (but not 12- to 17-year-olds) were significantly more like to have opioid or substance use disorder (0.4% vs. 0% for 0-11 years, 5.76% vs. 4.2% for 18 years and older, P < .001 for both).
Among patients with any opioid prescription, survivors were significantly more likely than were controls of any age to have indicators for potential misuse. For example, 13% of survivors aged 18 years and older had prescriptions for high opioid doses, compared with 5% of controls, and 12% had prescription overlap, vs. 2%.
Compared with patients with leukemia, patients treated for bone malignancies had a 6% greater risk for having any indicator of misuse, while patients with other malignancies were at slightly lower risk for misuse than those who completed leukemia therapy.
Patients who received any stem cell transplant had an 8.4% greater risk for misuse compared with patients who had surgery only.
Opioids pre- and posttreatment?
“Being someone who takes care of a lot of bone cancer patients, I do see patients with these issues,” Dr. Spunt said.
Audience member Jack H. Staddon, MD, PhD, of the Billings (Montana) Clinic, noted the possibility that opioid use during treatment may have been carried on into the posttreatment period, and asked whether use of narcotics during treatment was an independent risk factor for posttreatment narcotic use or misuse.
The researchers plan to investigate this question in future studies, Dr. Ji replied.
They did not report a study funding source. Dr. Ji and coauthors and Dr. Staddon reported no relevant disclosures.
Survivors of childhood cancers are at increased risk for prescription opioid misuse compared with their peers, a review of a claims database revealed.
Among more than 8,000 patients age 21 or younger who had completed treatment for hematologic, central nervous system, bone, or gonadal cancers, survivors were significantly more likely than were their peers to have an opioid prescription, longer duration of prescription, and higher daily doses of opioids, and to have opioid prescriptions overlapping for a week or more, reported Xu Ji, PhD, of Emory University in Atlanta.
Teenage and young adult patients were at higher risk than were patients younger than 12, and the risk was highest among patients who had been treated for bone malignancies, as well as those who had undergone any hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
“These findings suggest that health care providers who regularly see survivors should explore nonopioid options to help prevent opioid misuse, and screen for potential misuse in those who actually receive opioids,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
“This is a really important topic, and something that’s probably been underinvestigated and underexplored in our patient population,” said session comoderator Sheri Spunt, MD, Endowed Professor of Pediatric Cancer at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Database review
Dr. Ji and colleagues used the IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters database from 2009 to 2018 to examine prescription opioid use, potential misuse, and substance use disorders in pediatric cancer survivors in the first year after completion of therapy, and to identify factors associated with risk for misuse or substance use disorders. Specifically, the period of interest was the first year after completion of all treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and stem cell transplant (Abstract 2015).
They looked at deidentified records on any opioid prescription and for treatment of any opioid use or substance use disorder (alcohol, psychotherapeutic drugs, marijuana, or illicit drug use disorders).
They defined indicators of potential misuse as either prescriptions for long-acting or extended-release opioids for acute pain conditions; opioid and benzodiazepine prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; opioid prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; high daily opioid dosage (prescribed daily dose of 100 or greater morphine milligram equivalent [MME]; and/or opioid dose escalation (an increase of at least 50% in mean MMEs per month twice consecutively within 1 year).
They compared outcomes between a total of 8,635 survivors and 44,175 controls, matched on a 1:5 basis with survivors by age, sex, and region, and continuous enrollment during the 1-year posttherapy period.
In each of three age categories – 0 to 11 years, 12 to 17 years, and 18 years and older – survivors were significantly more likely to have received an opioid prescription, at 15% for the youngest survivors vs. 2% of controls, 25% vs. 8% for 12- to 17-year-olds, and 28% vs. 12% for those 18 and older (P < .01 for all three comparisons).
Survivors were also significantly more likely to have any indicator of potential misuse (1.6% vs. 0.1%, 4.6% vs. 0.5%, and 7.4% vs. 1.2%, respectively, P < .001 for all) and both the youngest and oldest groups (but not 12- to 17-year-olds) were significantly more like to have opioid or substance use disorder (0.4% vs. 0% for 0-11 years, 5.76% vs. 4.2% for 18 years and older, P < .001 for both).
Among patients with any opioid prescription, survivors were significantly more likely than were controls of any age to have indicators for potential misuse. For example, 13% of survivors aged 18 years and older had prescriptions for high opioid doses, compared with 5% of controls, and 12% had prescription overlap, vs. 2%.
Compared with patients with leukemia, patients treated for bone malignancies had a 6% greater risk for having any indicator of misuse, while patients with other malignancies were at slightly lower risk for misuse than those who completed leukemia therapy.
Patients who received any stem cell transplant had an 8.4% greater risk for misuse compared with patients who had surgery only.
Opioids pre- and posttreatment?
“Being someone who takes care of a lot of bone cancer patients, I do see patients with these issues,” Dr. Spunt said.
Audience member Jack H. Staddon, MD, PhD, of the Billings (Montana) Clinic, noted the possibility that opioid use during treatment may have been carried on into the posttreatment period, and asked whether use of narcotics during treatment was an independent risk factor for posttreatment narcotic use or misuse.
The researchers plan to investigate this question in future studies, Dr. Ji replied.
They did not report a study funding source. Dr. Ji and coauthors and Dr. Staddon reported no relevant disclosures.
Survivors of childhood cancers are at increased risk for prescription opioid misuse compared with their peers, a review of a claims database revealed.
Among more than 8,000 patients age 21 or younger who had completed treatment for hematologic, central nervous system, bone, or gonadal cancers, survivors were significantly more likely than were their peers to have an opioid prescription, longer duration of prescription, and higher daily doses of opioids, and to have opioid prescriptions overlapping for a week or more, reported Xu Ji, PhD, of Emory University in Atlanta.
Teenage and young adult patients were at higher risk than were patients younger than 12, and the risk was highest among patients who had been treated for bone malignancies, as well as those who had undergone any hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
“These findings suggest that health care providers who regularly see survivors should explore nonopioid options to help prevent opioid misuse, and screen for potential misuse in those who actually receive opioids,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
“This is a really important topic, and something that’s probably been underinvestigated and underexplored in our patient population,” said session comoderator Sheri Spunt, MD, Endowed Professor of Pediatric Cancer at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Database review
Dr. Ji and colleagues used the IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters database from 2009 to 2018 to examine prescription opioid use, potential misuse, and substance use disorders in pediatric cancer survivors in the first year after completion of therapy, and to identify factors associated with risk for misuse or substance use disorders. Specifically, the period of interest was the first year after completion of all treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and stem cell transplant (Abstract 2015).
They looked at deidentified records on any opioid prescription and for treatment of any opioid use or substance use disorder (alcohol, psychotherapeutic drugs, marijuana, or illicit drug use disorders).
They defined indicators of potential misuse as either prescriptions for long-acting or extended-release opioids for acute pain conditions; opioid and benzodiazepine prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; opioid prescriptions overlapping by a week or more; high daily opioid dosage (prescribed daily dose of 100 or greater morphine milligram equivalent [MME]; and/or opioid dose escalation (an increase of at least 50% in mean MMEs per month twice consecutively within 1 year).
They compared outcomes between a total of 8,635 survivors and 44,175 controls, matched on a 1:5 basis with survivors by age, sex, and region, and continuous enrollment during the 1-year posttherapy period.
In each of three age categories – 0 to 11 years, 12 to 17 years, and 18 years and older – survivors were significantly more likely to have received an opioid prescription, at 15% for the youngest survivors vs. 2% of controls, 25% vs. 8% for 12- to 17-year-olds, and 28% vs. 12% for those 18 and older (P < .01 for all three comparisons).
Survivors were also significantly more likely to have any indicator of potential misuse (1.6% vs. 0.1%, 4.6% vs. 0.5%, and 7.4% vs. 1.2%, respectively, P < .001 for all) and both the youngest and oldest groups (but not 12- to 17-year-olds) were significantly more like to have opioid or substance use disorder (0.4% vs. 0% for 0-11 years, 5.76% vs. 4.2% for 18 years and older, P < .001 for both).
Among patients with any opioid prescription, survivors were significantly more likely than were controls of any age to have indicators for potential misuse. For example, 13% of survivors aged 18 years and older had prescriptions for high opioid doses, compared with 5% of controls, and 12% had prescription overlap, vs. 2%.
Compared with patients with leukemia, patients treated for bone malignancies had a 6% greater risk for having any indicator of misuse, while patients with other malignancies were at slightly lower risk for misuse than those who completed leukemia therapy.
Patients who received any stem cell transplant had an 8.4% greater risk for misuse compared with patients who had surgery only.
Opioids pre- and posttreatment?
“Being someone who takes care of a lot of bone cancer patients, I do see patients with these issues,” Dr. Spunt said.
Audience member Jack H. Staddon, MD, PhD, of the Billings (Montana) Clinic, noted the possibility that opioid use during treatment may have been carried on into the posttreatment period, and asked whether use of narcotics during treatment was an independent risk factor for posttreatment narcotic use or misuse.
The researchers plan to investigate this question in future studies, Dr. Ji replied.
They did not report a study funding source. Dr. Ji and coauthors and Dr. Staddon reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM 2021 ASPHO CONFERENCE
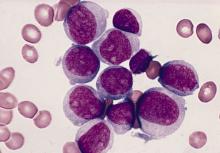
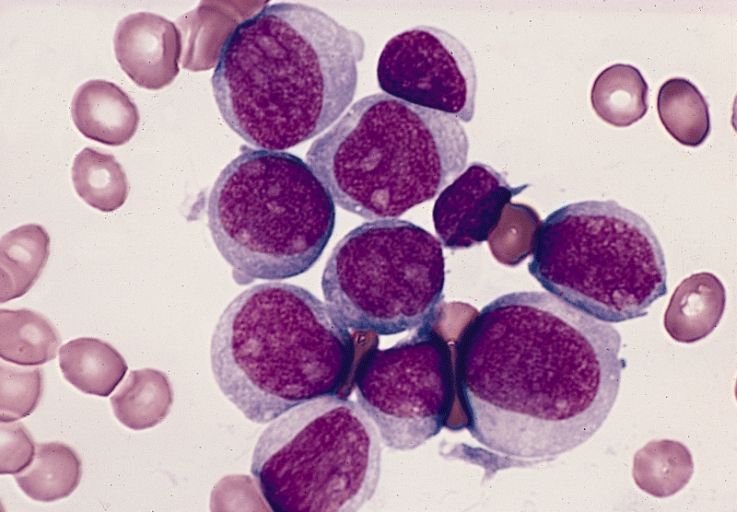
High MRD rates with CAR T in r/r B-ALL in kids
It’s early days, but preliminary data show that a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR T) product was associated with high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, and complete or near-complete responses in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Among 24 patients aged 3-20 years with relapsed or refractory B-ALL treated with the CAR T construct brexucabtagene autoleucel (KTE-X19; Tecartus), 16 had either a complete response or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), for a combined CR/CRi rate of 67%, reported Alan S. Wayne, MD, from Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, also in Los Angeles.
“Optimized KTE-X19 formulation of 40 mL and revised toxicity management were associated with an improved risk/benefit profile,” he said in audio narration accompanying a poster presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Although overall survival for children and adolescents receiving first-line therapy for B-ALL is associated with remission rates of 80% or more, the prognosis is poor following relapse, despite the availability of newer therapies such as blinatumomab (Blincyto) and inotuzumab (Besponsa), with a 1-year overall survival rate of approximately 36%, he said.
To see whether they could improve on these odds, Dr. Wayne and colleagues conducted the phase 1 Zuma-4 trial, a single-arm, open-label study in children and adolescents with relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
He reported long-term follow-up results from the study.
Zuma-4 details
A total of 24 patients, median age 14 (range 3 to 20) years, received the CAR T product. Four patients received the starting dose of 2 x 106 CAR T per kg (these patients were enrolled per protocol for evaluation of dose-limiting toxicities).
Following the initial dosing and evaluation of safety, 11 patients were treated with a dose of 1 x 106 cells per kg with a total volume of 68 mL, and 9 received 1 x 106 per kg at a volume of 40 mL (the dose being used in current phase 2 trials).
The median follow-up at the time of data cutoff in September 2020 was 36.1 months.
The combined CR/CRi rate was 75% for patients treated at the starting dose, 64% for patients treated at the 1 x 106 68-mL dose, and 67% for those who received the 48-mL dose.
The respective median durations of response were 4.14 months, 10.68 months, and not reached.
All patients who had an objective response had undetectable MRD assessed by flow cytometry with a sensitivity of .01%.
The therapy served as a bridge to allogeneic transplant in 16 patients, including 2 in the initial dose group, 8 in the 68-mL group, and 6 in the 40-mL group.
Median overall survival was not reached in either of the two 1 x 106–dose groups, but was 8 months in the 2 x 106 group.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities seen, and the adverse event profile was consistent with that seen with the use of CAR T therapy for other malignancies.
Patients treated at either the 68-mL or 40-mL 1 x 106–dose levels received tocilizumab only for neurologic events occurring in context with the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and were started on steroids for grade 2 or greater neurologic events.
Rates of grade 3 or greater neurologic events were 25% in the initial-dose group, 27% in the 68-mL group, and 11% in the 40-mL group. Respective rates of grade 3 or greater CRS were 75%, 27%, and 22%.
Four patients died on study, all from causes deemed unrelated to CAR T therapy: two from progressive disease, one from disseminated mucormycosis, and one from Escherichia sepsis.
Investigators are currently enrolling pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including patients with MRD-positive disease and early relapse after first-line therapy, in phase 2 of the Zuma-4 study.
How long will it last?
Howard Weinstein, MD, chief of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General for Children in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the response rate and comparatively low toxicity profile look good.
“One of the challenges, though, with CAR T-cell products has been relapse – almost half of the patients who go into remission relapse. Sometimes leukemic cells change their surface properties, resulting in antigen loss, there’s T-cell exhaustion, and other postulates for relapse,” he said.
He noted that due to the high number of patients who went on to transplant, the study lacks good data on the durability of remissions.
“One of the unknowns at the moment is whether CAR T cells are sufficient to cure a high percentage of children who have had a relapse, or do you need to follow it with a bone marrow transplant,” Dr. Weinstein said.
The ZUMA-4 trial is sponsored by Kite Pharma. Dr. Wayne disclosed research funding from Kite, Servier, and Institut de Recherches Internationales. Dr. Weinstein had no relevant disclosures.
It’s early days, but preliminary data show that a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR T) product was associated with high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, and complete or near-complete responses in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Among 24 patients aged 3-20 years with relapsed or refractory B-ALL treated with the CAR T construct brexucabtagene autoleucel (KTE-X19; Tecartus), 16 had either a complete response or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), for a combined CR/CRi rate of 67%, reported Alan S. Wayne, MD, from Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, also in Los Angeles.
“Optimized KTE-X19 formulation of 40 mL and revised toxicity management were associated with an improved risk/benefit profile,” he said in audio narration accompanying a poster presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Although overall survival for children and adolescents receiving first-line therapy for B-ALL is associated with remission rates of 80% or more, the prognosis is poor following relapse, despite the availability of newer therapies such as blinatumomab (Blincyto) and inotuzumab (Besponsa), with a 1-year overall survival rate of approximately 36%, he said.
To see whether they could improve on these odds, Dr. Wayne and colleagues conducted the phase 1 Zuma-4 trial, a single-arm, open-label study in children and adolescents with relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
He reported long-term follow-up results from the study.
Zuma-4 details
A total of 24 patients, median age 14 (range 3 to 20) years, received the CAR T product. Four patients received the starting dose of 2 x 106 CAR T per kg (these patients were enrolled per protocol for evaluation of dose-limiting toxicities).
Following the initial dosing and evaluation of safety, 11 patients were treated with a dose of 1 x 106 cells per kg with a total volume of 68 mL, and 9 received 1 x 106 per kg at a volume of 40 mL (the dose being used in current phase 2 trials).
The median follow-up at the time of data cutoff in September 2020 was 36.1 months.
The combined CR/CRi rate was 75% for patients treated at the starting dose, 64% for patients treated at the 1 x 106 68-mL dose, and 67% for those who received the 48-mL dose.
The respective median durations of response were 4.14 months, 10.68 months, and not reached.
All patients who had an objective response had undetectable MRD assessed by flow cytometry with a sensitivity of .01%.
The therapy served as a bridge to allogeneic transplant in 16 patients, including 2 in the initial dose group, 8 in the 68-mL group, and 6 in the 40-mL group.
Median overall survival was not reached in either of the two 1 x 106–dose groups, but was 8 months in the 2 x 106 group.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities seen, and the adverse event profile was consistent with that seen with the use of CAR T therapy for other malignancies.
Patients treated at either the 68-mL or 40-mL 1 x 106–dose levels received tocilizumab only for neurologic events occurring in context with the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and were started on steroids for grade 2 or greater neurologic events.
Rates of grade 3 or greater neurologic events were 25% in the initial-dose group, 27% in the 68-mL group, and 11% in the 40-mL group. Respective rates of grade 3 or greater CRS were 75%, 27%, and 22%.
Four patients died on study, all from causes deemed unrelated to CAR T therapy: two from progressive disease, one from disseminated mucormycosis, and one from Escherichia sepsis.
Investigators are currently enrolling pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including patients with MRD-positive disease and early relapse after first-line therapy, in phase 2 of the Zuma-4 study.
How long will it last?
Howard Weinstein, MD, chief of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General for Children in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the response rate and comparatively low toxicity profile look good.
“One of the challenges, though, with CAR T-cell products has been relapse – almost half of the patients who go into remission relapse. Sometimes leukemic cells change their surface properties, resulting in antigen loss, there’s T-cell exhaustion, and other postulates for relapse,” he said.
He noted that due to the high number of patients who went on to transplant, the study lacks good data on the durability of remissions.
“One of the unknowns at the moment is whether CAR T cells are sufficient to cure a high percentage of children who have had a relapse, or do you need to follow it with a bone marrow transplant,” Dr. Weinstein said.
The ZUMA-4 trial is sponsored by Kite Pharma. Dr. Wayne disclosed research funding from Kite, Servier, and Institut de Recherches Internationales. Dr. Weinstein had no relevant disclosures.
It’s early days, but preliminary data show that a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR T) product was associated with high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, and complete or near-complete responses in children and adolescents with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Among 24 patients aged 3-20 years with relapsed or refractory B-ALL treated with the CAR T construct brexucabtagene autoleucel (KTE-X19; Tecartus), 16 had either a complete response or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi), for a combined CR/CRi rate of 67%, reported Alan S. Wayne, MD, from Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, also in Los Angeles.
“Optimized KTE-X19 formulation of 40 mL and revised toxicity management were associated with an improved risk/benefit profile,” he said in audio narration accompanying a poster presented during the annual meeting of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Although overall survival for children and adolescents receiving first-line therapy for B-ALL is associated with remission rates of 80% or more, the prognosis is poor following relapse, despite the availability of newer therapies such as blinatumomab (Blincyto) and inotuzumab (Besponsa), with a 1-year overall survival rate of approximately 36%, he said.
To see whether they could improve on these odds, Dr. Wayne and colleagues conducted the phase 1 Zuma-4 trial, a single-arm, open-label study in children and adolescents with relapsed/refractory B-ALL.
He reported long-term follow-up results from the study.
Zuma-4 details
A total of 24 patients, median age 14 (range 3 to 20) years, received the CAR T product. Four patients received the starting dose of 2 x 106 CAR T per kg (these patients were enrolled per protocol for evaluation of dose-limiting toxicities).
Following the initial dosing and evaluation of safety, 11 patients were treated with a dose of 1 x 106 cells per kg with a total volume of 68 mL, and 9 received 1 x 106 per kg at a volume of 40 mL (the dose being used in current phase 2 trials).
The median follow-up at the time of data cutoff in September 2020 was 36.1 months.
The combined CR/CRi rate was 75% for patients treated at the starting dose, 64% for patients treated at the 1 x 106 68-mL dose, and 67% for those who received the 48-mL dose.
The respective median durations of response were 4.14 months, 10.68 months, and not reached.
All patients who had an objective response had undetectable MRD assessed by flow cytometry with a sensitivity of .01%.
The therapy served as a bridge to allogeneic transplant in 16 patients, including 2 in the initial dose group, 8 in the 68-mL group, and 6 in the 40-mL group.
Median overall survival was not reached in either of the two 1 x 106–dose groups, but was 8 months in the 2 x 106 group.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities seen, and the adverse event profile was consistent with that seen with the use of CAR T therapy for other malignancies.
Patients treated at either the 68-mL or 40-mL 1 x 106–dose levels received tocilizumab only for neurologic events occurring in context with the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and were started on steroids for grade 2 or greater neurologic events.
Rates of grade 3 or greater neurologic events were 25% in the initial-dose group, 27% in the 68-mL group, and 11% in the 40-mL group. Respective rates of grade 3 or greater CRS were 75%, 27%, and 22%.
Four patients died on study, all from causes deemed unrelated to CAR T therapy: two from progressive disease, one from disseminated mucormycosis, and one from Escherichia sepsis.
Investigators are currently enrolling pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including patients with MRD-positive disease and early relapse after first-line therapy, in phase 2 of the Zuma-4 study.
How long will it last?
Howard Weinstein, MD, chief of pediatric hematology/oncology at Mass General for Children in Boston, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that the response rate and comparatively low toxicity profile look good.
“One of the challenges, though, with CAR T-cell products has been relapse – almost half of the patients who go into remission relapse. Sometimes leukemic cells change their surface properties, resulting in antigen loss, there’s T-cell exhaustion, and other postulates for relapse,” he said.
He noted that due to the high number of patients who went on to transplant, the study lacks good data on the durability of remissions.
“One of the unknowns at the moment is whether CAR T cells are sufficient to cure a high percentage of children who have had a relapse, or do you need to follow it with a bone marrow transplant,” Dr. Weinstein said.
The ZUMA-4 trial is sponsored by Kite Pharma. Dr. Wayne disclosed research funding from Kite, Servier, and Institut de Recherches Internationales. Dr. Weinstein had no relevant disclosures.
FROM ASPHO 2021
The power and promise of social media in oncology
Mark A. Lewis, MD, explained to the COSMO meeting audience how storytelling on social media can educate and engage patients, advocates, and professional colleagues – advancing knowledge, dispelling misinformation, and promoting clinical research.
Dr. Lewis, an oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, reflected on the bifid roles of oncologists as scientists engaged in life-long learning and humanists who can internalize and appreciate the unique character and circumstances of their patients.
Patients who have serious illnesses are necessarily aggregated by statistics. However, in an essay published in 2011, Dr. Lewis noted that “each individual patient partakes in a unique, irreproducible experiment where n = 1” (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
Dr. Lewis highlighted the duality of individual data points on a survival curve as descriptors of common disease trajectories and treatment effects. However, those data points also conceal important narratives regarding the most highly valued aspects of the doctor-patient relationship and the impact of cancer treatment on patients’ lives.
In referring to the futuristic essay “Ars Brevis,” Dr. Lewis contrasted the humanism of oncology specialists in the present day with the fictional image of data-regurgitating robots programmed to maximize the efficiency of each patient encounter (J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 10;31[14]:1792-4).
Dr. Lewis reminded attendees that to practice medicine without using both “head and heart” undermines the inherent nature of medical care.
Unfortunately, that perspective may not match the public perception of oncologists. Dr. Lewis described his experience of typing “oncologists are” into an Internet search engine and seeing the auto-complete function prompt words such as “criminals,” “evil,” “murderers,” and “confused.”
Obviously, it is hard to establish a trusting patient-doctor relationship if that is the prima facie perception of the oncology specialty.
Dispelling myths and creating community via social media
A primary goal of consultation with a newly-diagnosed cancer patient is for the patient to feel that the oncologist will be there to take care of them, regardless of what the future holds.
Dr. Lewis has found that social media can potentially extend that feeling to a global community of patients, caregivers, and others seeking information relevant to a cancer diagnosis. He believes that oncologists have an opportunity to dispel myths and fears by being attentive to the real-life concerns of patients.
Dr. Lewis took advantage of this opportunity when he underwent a Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) for a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. He and the hospital’s media services staff “live-tweeted” his surgery and recovery.
With those tweets, Dr. Lewis demystified each step of a major surgical procedure. From messages he received on social media, Dr. Lewis knows he made the decision to have a Whipple procedure more acceptable to other patients.
His personal medical experience notwithstanding, Dr. Lewis acknowledged that every patient’s circumstances are unique.
Oncologists cannot possibly empathize with every circumstance. However, when they show sensitivity to personal elements of the cancer experience, they shed light on the complicated role they play in patient care and can facilitate good decision-making among patients across the globe.
Social media for professional development and patient care
The publication of his 2011 essay was gratifying for Dr. Lewis, but the finite number of comments he received thereafter illustrated the rather limited audience that traditional academic publications have and the laborious process for subsequent interaction (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
First as an observer and later as a participant on social media, Dr. Lewis appreciated that teaching points and publications can be amplified by global distribution and the potential for informal bidirectional communication.
Social media platforms enable physicians to connect with a larger audience through participative communication, in which users develop, share, and react to content (N Engl J Med. 2009 Aug 13;361[7]:649-51).
Dr. Lewis reflected on how oncologists are challenged to sort through the thousands of oncology-focused publications annually. Through social media, one can see the studies on which the experts are commenting and appreciate the nuances that contextualize the results. Focused interactions with renowned doctors, at regular intervals, require little formality.
Online journal clubs enable the sharing of ideas, opinions, multimedia resources, and references across institutional and international borders (J Gen Intern Med. 2014 Oct;29[10]:1317-8).
Social media in oncology: Accomplishments and promise
The development of broadband Internet, wireless connectivity, and social media for peer-to-peer and general communication are among the major technological advances that have transformed medical communication.
As an organization, COSMO aims to describe, understand, and improve the use of social media to increase the penetration of evidence-based guidelines and research insights into clinical practice (Future Oncol. 2017 Jun;13[15]:1281-5).
At the inaugural COSMO meeting, areas of progress since COSMO’s inception in 2015 were highlighted, including:
- The involvement of cancer professionals and advocates in multiple distinctive platforms.
- The development of hashtag libraries to aggregate interest groups and topics.
- The refinement of strategies for engaging advocates with attention to inclusiveness.
- A steady trajectory of growth in tweeting at scientific conferences.
An overarching theme of the COSMO meeting was “authenticity,” a virtue that is easy to admire but requires conscious, consistent effort to achieve.
Disclosure of conflicts of interest and avoiding using social media simply as a recruitment tool for clinical trials are basic components of accurate self-representation.
In addition, Dr. Lewis advocated for sharing personal experiences in a component of social media posts so oncologists can show humanity as a feature of their professional online identity and inherent nature.
Dr. Lewis disclosed consultancy with Medscape/WebMD, which are owned by the same parent company as MDedge. He also disclosed relationships with Foundation Medicine, Natera, Exelixis, QED, HalioDX, and Ipsen.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Mark A. Lewis, MD, explained to the COSMO meeting audience how storytelling on social media can educate and engage patients, advocates, and professional colleagues – advancing knowledge, dispelling misinformation, and promoting clinical research.
Dr. Lewis, an oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, reflected on the bifid roles of oncologists as scientists engaged in life-long learning and humanists who can internalize and appreciate the unique character and circumstances of their patients.
Patients who have serious illnesses are necessarily aggregated by statistics. However, in an essay published in 2011, Dr. Lewis noted that “each individual patient partakes in a unique, irreproducible experiment where n = 1” (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
Dr. Lewis highlighted the duality of individual data points on a survival curve as descriptors of common disease trajectories and treatment effects. However, those data points also conceal important narratives regarding the most highly valued aspects of the doctor-patient relationship and the impact of cancer treatment on patients’ lives.
In referring to the futuristic essay “Ars Brevis,” Dr. Lewis contrasted the humanism of oncology specialists in the present day with the fictional image of data-regurgitating robots programmed to maximize the efficiency of each patient encounter (J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 10;31[14]:1792-4).
Dr. Lewis reminded attendees that to practice medicine without using both “head and heart” undermines the inherent nature of medical care.
Unfortunately, that perspective may not match the public perception of oncologists. Dr. Lewis described his experience of typing “oncologists are” into an Internet search engine and seeing the auto-complete function prompt words such as “criminals,” “evil,” “murderers,” and “confused.”
Obviously, it is hard to establish a trusting patient-doctor relationship if that is the prima facie perception of the oncology specialty.
Dispelling myths and creating community via social media
A primary goal of consultation with a newly-diagnosed cancer patient is for the patient to feel that the oncologist will be there to take care of them, regardless of what the future holds.
Dr. Lewis has found that social media can potentially extend that feeling to a global community of patients, caregivers, and others seeking information relevant to a cancer diagnosis. He believes that oncologists have an opportunity to dispel myths and fears by being attentive to the real-life concerns of patients.
Dr. Lewis took advantage of this opportunity when he underwent a Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) for a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. He and the hospital’s media services staff “live-tweeted” his surgery and recovery.
With those tweets, Dr. Lewis demystified each step of a major surgical procedure. From messages he received on social media, Dr. Lewis knows he made the decision to have a Whipple procedure more acceptable to other patients.
His personal medical experience notwithstanding, Dr. Lewis acknowledged that every patient’s circumstances are unique.
Oncologists cannot possibly empathize with every circumstance. However, when they show sensitivity to personal elements of the cancer experience, they shed light on the complicated role they play in patient care and can facilitate good decision-making among patients across the globe.
Social media for professional development and patient care
The publication of his 2011 essay was gratifying for Dr. Lewis, but the finite number of comments he received thereafter illustrated the rather limited audience that traditional academic publications have and the laborious process for subsequent interaction (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
First as an observer and later as a participant on social media, Dr. Lewis appreciated that teaching points and publications can be amplified by global distribution and the potential for informal bidirectional communication.
Social media platforms enable physicians to connect with a larger audience through participative communication, in which users develop, share, and react to content (N Engl J Med. 2009 Aug 13;361[7]:649-51).
Dr. Lewis reflected on how oncologists are challenged to sort through the thousands of oncology-focused publications annually. Through social media, one can see the studies on which the experts are commenting and appreciate the nuances that contextualize the results. Focused interactions with renowned doctors, at regular intervals, require little formality.
Online journal clubs enable the sharing of ideas, opinions, multimedia resources, and references across institutional and international borders (J Gen Intern Med. 2014 Oct;29[10]:1317-8).
Social media in oncology: Accomplishments and promise
The development of broadband Internet, wireless connectivity, and social media for peer-to-peer and general communication are among the major technological advances that have transformed medical communication.
As an organization, COSMO aims to describe, understand, and improve the use of social media to increase the penetration of evidence-based guidelines and research insights into clinical practice (Future Oncol. 2017 Jun;13[15]:1281-5).
At the inaugural COSMO meeting, areas of progress since COSMO’s inception in 2015 were highlighted, including:
- The involvement of cancer professionals and advocates in multiple distinctive platforms.
- The development of hashtag libraries to aggregate interest groups and topics.
- The refinement of strategies for engaging advocates with attention to inclusiveness.
- A steady trajectory of growth in tweeting at scientific conferences.
An overarching theme of the COSMO meeting was “authenticity,” a virtue that is easy to admire but requires conscious, consistent effort to achieve.
Disclosure of conflicts of interest and avoiding using social media simply as a recruitment tool for clinical trials are basic components of accurate self-representation.
In addition, Dr. Lewis advocated for sharing personal experiences in a component of social media posts so oncologists can show humanity as a feature of their professional online identity and inherent nature.
Dr. Lewis disclosed consultancy with Medscape/WebMD, which are owned by the same parent company as MDedge. He also disclosed relationships with Foundation Medicine, Natera, Exelixis, QED, HalioDX, and Ipsen.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Mark A. Lewis, MD, explained to the COSMO meeting audience how storytelling on social media can educate and engage patients, advocates, and professional colleagues – advancing knowledge, dispelling misinformation, and promoting clinical research.
Dr. Lewis, an oncologist at Intermountain Healthcare in Salt Lake City, reflected on the bifid roles of oncologists as scientists engaged in life-long learning and humanists who can internalize and appreciate the unique character and circumstances of their patients.
Patients who have serious illnesses are necessarily aggregated by statistics. However, in an essay published in 2011, Dr. Lewis noted that “each individual patient partakes in a unique, irreproducible experiment where n = 1” (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
Dr. Lewis highlighted the duality of individual data points on a survival curve as descriptors of common disease trajectories and treatment effects. However, those data points also conceal important narratives regarding the most highly valued aspects of the doctor-patient relationship and the impact of cancer treatment on patients’ lives.
In referring to the futuristic essay “Ars Brevis,” Dr. Lewis contrasted the humanism of oncology specialists in the present day with the fictional image of data-regurgitating robots programmed to maximize the efficiency of each patient encounter (J Clin Oncol. 2013 May 10;31[14]:1792-4).
Dr. Lewis reminded attendees that to practice medicine without using both “head and heart” undermines the inherent nature of medical care.
Unfortunately, that perspective may not match the public perception of oncologists. Dr. Lewis described his experience of typing “oncologists are” into an Internet search engine and seeing the auto-complete function prompt words such as “criminals,” “evil,” “murderers,” and “confused.”
Obviously, it is hard to establish a trusting patient-doctor relationship if that is the prima facie perception of the oncology specialty.
Dispelling myths and creating community via social media
A primary goal of consultation with a newly-diagnosed cancer patient is for the patient to feel that the oncologist will be there to take care of them, regardless of what the future holds.
Dr. Lewis has found that social media can potentially extend that feeling to a global community of patients, caregivers, and others seeking information relevant to a cancer diagnosis. He believes that oncologists have an opportunity to dispel myths and fears by being attentive to the real-life concerns of patients.
Dr. Lewis took advantage of this opportunity when he underwent a Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) for a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. He and the hospital’s media services staff “live-tweeted” his surgery and recovery.
With those tweets, Dr. Lewis demystified each step of a major surgical procedure. From messages he received on social media, Dr. Lewis knows he made the decision to have a Whipple procedure more acceptable to other patients.
His personal medical experience notwithstanding, Dr. Lewis acknowledged that every patient’s circumstances are unique.
Oncologists cannot possibly empathize with every circumstance. However, when they show sensitivity to personal elements of the cancer experience, they shed light on the complicated role they play in patient care and can facilitate good decision-making among patients across the globe.
Social media for professional development and patient care
The publication of his 2011 essay was gratifying for Dr. Lewis, but the finite number of comments he received thereafter illustrated the rather limited audience that traditional academic publications have and the laborious process for subsequent interaction (J Clin Oncol. 2011 Aug 1;29[22]:3103-4).
First as an observer and later as a participant on social media, Dr. Lewis appreciated that teaching points and publications can be amplified by global distribution and the potential for informal bidirectional communication.
Social media platforms enable physicians to connect with a larger audience through participative communication, in which users develop, share, and react to content (N Engl J Med. 2009 Aug 13;361[7]:649-51).
Dr. Lewis reflected on how oncologists are challenged to sort through the thousands of oncology-focused publications annually. Through social media, one can see the studies on which the experts are commenting and appreciate the nuances that contextualize the results. Focused interactions with renowned doctors, at regular intervals, require little formality.
Online journal clubs enable the sharing of ideas, opinions, multimedia resources, and references across institutional and international borders (J Gen Intern Med. 2014 Oct;29[10]:1317-8).
Social media in oncology: Accomplishments and promise
The development of broadband Internet, wireless connectivity, and social media for peer-to-peer and general communication are among the major technological advances that have transformed medical communication.
As an organization, COSMO aims to describe, understand, and improve the use of social media to increase the penetration of evidence-based guidelines and research insights into clinical practice (Future Oncol. 2017 Jun;13[15]:1281-5).
At the inaugural COSMO meeting, areas of progress since COSMO’s inception in 2015 were highlighted, including:
- The involvement of cancer professionals and advocates in multiple distinctive platforms.
- The development of hashtag libraries to aggregate interest groups and topics.
- The refinement of strategies for engaging advocates with attention to inclusiveness.
- A steady trajectory of growth in tweeting at scientific conferences.
An overarching theme of the COSMO meeting was “authenticity,” a virtue that is easy to admire but requires conscious, consistent effort to achieve.
Disclosure of conflicts of interest and avoiding using social media simply as a recruitment tool for clinical trials are basic components of accurate self-representation.
In addition, Dr. Lewis advocated for sharing personal experiences in a component of social media posts so oncologists can show humanity as a feature of their professional online identity and inherent nature.
Dr. Lewis disclosed consultancy with Medscape/WebMD, which are owned by the same parent company as MDedge. He also disclosed relationships with Foundation Medicine, Natera, Exelixis, QED, HalioDX, and Ipsen.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
FROM COSMO 2021
Atrial Fibrillation and Bleeding in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with Ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (FULL)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
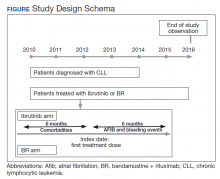
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
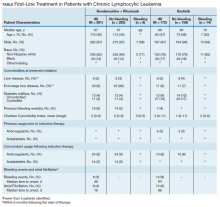
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
Mitochondrial DNA predicts survival in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number alterations are known to occur in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), however their biological significance has not been well studied. Pediatric AML has a distinct biology, different from adults, and with heterogeneous clinical outcomes, the biological basis of which are not well understood, according to researchers Shilpi Chaudhary, PhD, of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues.
Their analysis of 123 pediatric patients with AML found that mtDNA copy number was an independent predictor of aggressive disease, lower event-free survival, and overall survival, according to a report published in Mitochondrion.
In an attempt to find the biological factors involved in the increased mtDNA copy numbers and their effect on the development and aggressiveness of pediatric AML, the researchers studied the regulation and significance of mtDNA copy number in pediatric AML patients using quantitative real time–polymerase chain reaction, as well as in vitro studies. For patients, results were correlated with clinical outcomes.
Mitochondrial biogenesis genes (TFAM, POLG, POLRMT) and two regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, MYC and PGC1A, were also assessed, according to Dr. Chaudhary and colleagues.
Predictive results
MtDNA copy number was significantly higher in patients, compared with controls (P < .001) and was found to be an independent predictor of aggressive disease (P = .006), lower event-free survival (P = .033), and overall survival (P = .007).
TFAM, POLG & POLRMT and ND3 were also found to be significantly up-regulated in patients, compared with controls as was the expression of the mitochondrial biogenesis regulator MYC (P < .001). However, correlation analysis showed that mtDNA copy number was not associated with the expression of these genes.
In contrast, PGC1A expression was not significantly different in patients, compared with controls overall, although there was a subset of patients whose PGC1A expression was extremely high, according to the researchers.
Importantly, however, in the subset of patients with high PGC1A expression (n = 28), mtDNA copy number had a positive correlation with PGC1A expression (P = .013). On the other hand, among patients with low MYC expression (n = 27), there was no correlation of mtDNA copy number with either PGC1A or MYC expression.
These results were corroborated in in vitro studies, where treatment with the inhibitor tigecycline led to a significant decrease in expression of MYC (P < .001), TFAM (P = .037) and ND3 (P = .010) but resulted in no significant change in mtDNA copy number (P = .23) or expression of PGC1A (P = .10).
Therapeutic candidate?
In contrast to the case of MYC, in vitro PGC1A inhibition significantly reduced mtDNA copy number in along with expression of TFAM and even expression of POLG and POLRMT at higher concentration.
“This observation is in line with our finding in patient samples as well that PGC1A expression positively correlated with mtDNA copy number, more so in patients with higher PGC1A expression,” the researchers stated.
“This makes it plausible to infer that PGC1A may have a possible role in enhancing mtDNA copy number in AML patients, likely independent of MYC,” they added. “Therefore, a strategy of designing therapeutics using already approved inhibitors targeting PGC1A may be an exciting area of therapeutic intervention.”
The authors reported that they have no competing financial conflicts of interests.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number alterations are known to occur in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), however their biological significance has not been well studied. Pediatric AML has a distinct biology, different from adults, and with heterogeneous clinical outcomes, the biological basis of which are not well understood, according to researchers Shilpi Chaudhary, PhD, of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues.
Their analysis of 123 pediatric patients with AML found that mtDNA copy number was an independent predictor of aggressive disease, lower event-free survival, and overall survival, according to a report published in Mitochondrion.
In an attempt to find the biological factors involved in the increased mtDNA copy numbers and their effect on the development and aggressiveness of pediatric AML, the researchers studied the regulation and significance of mtDNA copy number in pediatric AML patients using quantitative real time–polymerase chain reaction, as well as in vitro studies. For patients, results were correlated with clinical outcomes.
Mitochondrial biogenesis genes (TFAM, POLG, POLRMT) and two regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, MYC and PGC1A, were also assessed, according to Dr. Chaudhary and colleagues.
Predictive results
MtDNA copy number was significantly higher in patients, compared with controls (P < .001) and was found to be an independent predictor of aggressive disease (P = .006), lower event-free survival (P = .033), and overall survival (P = .007).
TFAM, POLG & POLRMT and ND3 were also found to be significantly up-regulated in patients, compared with controls as was the expression of the mitochondrial biogenesis regulator MYC (P < .001). However, correlation analysis showed that mtDNA copy number was not associated with the expression of these genes.
In contrast, PGC1A expression was not significantly different in patients, compared with controls overall, although there was a subset of patients whose PGC1A expression was extremely high, according to the researchers.
Importantly, however, in the subset of patients with high PGC1A expression (n = 28), mtDNA copy number had a positive correlation with PGC1A expression (P = .013). On the other hand, among patients with low MYC expression (n = 27), there was no correlation of mtDNA copy number with either PGC1A or MYC expression.
These results were corroborated in in vitro studies, where treatment with the inhibitor tigecycline led to a significant decrease in expression of MYC (P < .001), TFAM (P = .037) and ND3 (P = .010) but resulted in no significant change in mtDNA copy number (P = .23) or expression of PGC1A (P = .10).
Therapeutic candidate?
In contrast to the case of MYC, in vitro PGC1A inhibition significantly reduced mtDNA copy number in along with expression of TFAM and even expression of POLG and POLRMT at higher concentration.
“This observation is in line with our finding in patient samples as well that PGC1A expression positively correlated with mtDNA copy number, more so in patients with higher PGC1A expression,” the researchers stated.
“This makes it plausible to infer that PGC1A may have a possible role in enhancing mtDNA copy number in AML patients, likely independent of MYC,” they added. “Therefore, a strategy of designing therapeutics using already approved inhibitors targeting PGC1A may be an exciting area of therapeutic intervention.”
The authors reported that they have no competing financial conflicts of interests.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number alterations are known to occur in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), however their biological significance has not been well studied. Pediatric AML has a distinct biology, different from adults, and with heterogeneous clinical outcomes, the biological basis of which are not well understood, according to researchers Shilpi Chaudhary, PhD, of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues.
Their analysis of 123 pediatric patients with AML found that mtDNA copy number was an independent predictor of aggressive disease, lower event-free survival, and overall survival, according to a report published in Mitochondrion.
In an attempt to find the biological factors involved in the increased mtDNA copy numbers and their effect on the development and aggressiveness of pediatric AML, the researchers studied the regulation and significance of mtDNA copy number in pediatric AML patients using quantitative real time–polymerase chain reaction, as well as in vitro studies. For patients, results were correlated with clinical outcomes.
Mitochondrial biogenesis genes (TFAM, POLG, POLRMT) and two regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, MYC and PGC1A, were also assessed, according to Dr. Chaudhary and colleagues.
Predictive results
MtDNA copy number was significantly higher in patients, compared with controls (P < .001) and was found to be an independent predictor of aggressive disease (P = .006), lower event-free survival (P = .033), and overall survival (P = .007).
TFAM, POLG & POLRMT and ND3 were also found to be significantly up-regulated in patients, compared with controls as was the expression of the mitochondrial biogenesis regulator MYC (P < .001). However, correlation analysis showed that mtDNA copy number was not associated with the expression of these genes.
In contrast, PGC1A expression was not significantly different in patients, compared with controls overall, although there was a subset of patients whose PGC1A expression was extremely high, according to the researchers.
Importantly, however, in the subset of patients with high PGC1A expression (n = 28), mtDNA copy number had a positive correlation with PGC1A expression (P = .013). On the other hand, among patients with low MYC expression (n = 27), there was no correlation of mtDNA copy number with either PGC1A or MYC expression.
These results were corroborated in in vitro studies, where treatment with the inhibitor tigecycline led to a significant decrease in expression of MYC (P < .001), TFAM (P = .037) and ND3 (P = .010) but resulted in no significant change in mtDNA copy number (P = .23) or expression of PGC1A (P = .10).
Therapeutic candidate?
In contrast to the case of MYC, in vitro PGC1A inhibition significantly reduced mtDNA copy number in along with expression of TFAM and even expression of POLG and POLRMT at higher concentration.
“This observation is in line with our finding in patient samples as well that PGC1A expression positively correlated with mtDNA copy number, more so in patients with higher PGC1A expression,” the researchers stated.
“This makes it plausible to infer that PGC1A may have a possible role in enhancing mtDNA copy number in AML patients, likely independent of MYC,” they added. “Therefore, a strategy of designing therapeutics using already approved inhibitors targeting PGC1A may be an exciting area of therapeutic intervention.”
The authors reported that they have no competing financial conflicts of interests.
FROM MITOCHONDRION
Predicting outcomes in therapy-related AML
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) occurs as a complication of chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy for previous cancer or for nonmalignant disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 10%-15% of all AML cases, according to Ram Vasudevan Nampoothiri, MD, and colleagues at the Princess Margaret Cancer Center, University of Toronto.
Dr. Nampoothiri and colleagues performed a retrospective study of 68 patients with t-AML who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at their institution. They found significant predictors of reduced overall survival, including chromosomal rearrangements, induction regimens, donor type, patient performance status, and the type of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis the patients received, as reported in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Some populations benefit
Among the 68 patients studied, a total of 59.9% were women; and the median age was 56.5 years. All patients were analyzed for prior malignancy, therapy, time to diagnosis of t-AML, transplant details, relapse-free survival, overall survival, and predictors of outcomes.
At 2 years, the cumulative incidence of relapse, nonrelapse mortality, relapse-free survival, and overall survival were 17.9%, 34.5%, 47.6%, and 49.3%, respectively. Overall, acute and chronic GVHD occurred in 39 (57.4%) and 23 (33.8%) patients, respectively, according to the researchers.
The significant predictors of reduced overall survival were the presence of the 11q23 chromosomal rearrangement (hazard ratio, 3.24), use of induction regimens other than fludarabine, cytarabine, idarubicin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or 7 + 3 (HR, 3.65), use of haploidentical donors (HR, 3.48), an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or higher (HR, 5.83), and use of cyclosporine A–methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis (HR, 2.41).
The researchers also found that a significant decrease in survival was seen with an increasing number of any of these prognostic factors.
A growing need
The incidence of t-AML is increasing because of longer life expectancy of the general population and also because of the improved survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation for prior malignancies, according to the researchers.
They concluded that, even with this increasing prevalence and normally poor prognosis, “patients of t-AML having good-risk karyotypes, good performance status, and having HLA-matched donors have favorable outcomes after allo-HSCT.”
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) occurs as a complication of chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy for previous cancer or for nonmalignant disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 10%-15% of all AML cases, according to Ram Vasudevan Nampoothiri, MD, and colleagues at the Princess Margaret Cancer Center, University of Toronto.
Dr. Nampoothiri and colleagues performed a retrospective study of 68 patients with t-AML who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at their institution. They found significant predictors of reduced overall survival, including chromosomal rearrangements, induction regimens, donor type, patient performance status, and the type of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis the patients received, as reported in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Some populations benefit
Among the 68 patients studied, a total of 59.9% were women; and the median age was 56.5 years. All patients were analyzed for prior malignancy, therapy, time to diagnosis of t-AML, transplant details, relapse-free survival, overall survival, and predictors of outcomes.
At 2 years, the cumulative incidence of relapse, nonrelapse mortality, relapse-free survival, and overall survival were 17.9%, 34.5%, 47.6%, and 49.3%, respectively. Overall, acute and chronic GVHD occurred in 39 (57.4%) and 23 (33.8%) patients, respectively, according to the researchers.
The significant predictors of reduced overall survival were the presence of the 11q23 chromosomal rearrangement (hazard ratio, 3.24), use of induction regimens other than fludarabine, cytarabine, idarubicin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or 7 + 3 (HR, 3.65), use of haploidentical donors (HR, 3.48), an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or higher (HR, 5.83), and use of cyclosporine A–methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis (HR, 2.41).
The researchers also found that a significant decrease in survival was seen with an increasing number of any of these prognostic factors.
A growing need
The incidence of t-AML is increasing because of longer life expectancy of the general population and also because of the improved survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation for prior malignancies, according to the researchers.
They concluded that, even with this increasing prevalence and normally poor prognosis, “patients of t-AML having good-risk karyotypes, good performance status, and having HLA-matched donors have favorable outcomes after allo-HSCT.”
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) occurs as a complication of chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy for previous cancer or for nonmalignant disorders, with an estimated prevalence of 10%-15% of all AML cases, according to Ram Vasudevan Nampoothiri, MD, and colleagues at the Princess Margaret Cancer Center, University of Toronto.
Dr. Nampoothiri and colleagues performed a retrospective study of 68 patients with t-AML who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) at their institution. They found significant predictors of reduced overall survival, including chromosomal rearrangements, induction regimens, donor type, patient performance status, and the type of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis the patients received, as reported in Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy.
Some populations benefit
Among the 68 patients studied, a total of 59.9% were women; and the median age was 56.5 years. All patients were analyzed for prior malignancy, therapy, time to diagnosis of t-AML, transplant details, relapse-free survival, overall survival, and predictors of outcomes.
At 2 years, the cumulative incidence of relapse, nonrelapse mortality, relapse-free survival, and overall survival were 17.9%, 34.5%, 47.6%, and 49.3%, respectively. Overall, acute and chronic GVHD occurred in 39 (57.4%) and 23 (33.8%) patients, respectively, according to the researchers.
The significant predictors of reduced overall survival were the presence of the 11q23 chromosomal rearrangement (hazard ratio, 3.24), use of induction regimens other than fludarabine, cytarabine, idarubicin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or 7 + 3 (HR, 3.65), use of haploidentical donors (HR, 3.48), an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or higher (HR, 5.83), and use of cyclosporine A–methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis (HR, 2.41).
The researchers also found that a significant decrease in survival was seen with an increasing number of any of these prognostic factors.
A growing need
The incidence of t-AML is increasing because of longer life expectancy of the general population and also because of the improved survival of patients treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation for prior malignancies, according to the researchers.
They concluded that, even with this increasing prevalence and normally poor prognosis, “patients of t-AML having good-risk karyotypes, good performance status, and having HLA-matched donors have favorable outcomes after allo-HSCT.”
The authors reported that they had no competing financial interests.
FROM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY AND STEM CELL THERAPY
GENUINE improvements: Ublituximab plus ibrutinib for CLL
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clinically heterogeneous disease associated with several known genetic abnormalities, including 17p deletion (del[17p]), 11q deletion (del[11q]), and TP53 gene mutations, which are adverse prognostic markers among patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib is approved for patients with untreated, relapsed, or refractory disease, including those with del(17p). Clinicians will soon have the chance to pair it with ublituximab, a next-generation, glycoengineered, type I, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that binds to a unique epitope on CD20, differentiating it from rituximab, ofatumumab, and obinutuzumab. Results from the phase 3 GENUINE trial, which were recently published in The Lancet Haematology, showed that ublituximab plus ibrutinib was superior to ibrutinib alone for patients with relapsed or refractory high-risk CLL.
This news organization spoke with Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, director of the CLL Center and institute physician at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, about the GENUINE trial and its potential impact on treatment choices going forward.
What type of patients were treated in the GENUINE trial?
Dr. Brown: This is a trial among relapsed/refractory CLL patients with 17p or 11q deletion or TP53 mutation. Patients aged 18 years or older with CLL who warranted treatment, as defined by International Workshop on CLL criteria, were eligible if they had previously received at least two cycles of at least one standard treatment regimen, had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or lower, and had high-risk cytogenetics, defined as the presence of at least one of del(17p), del(11q), or TP53 mutation confirmed by a central laboratory with fluorescence in situ hybridization and/or next-generation sequencing.
What were the main outcomes of the trial?
Originally, the GENUINE trial had coprimary endpoints of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall response rate. Because of slow accrual, it was amended to have one primary endpoint of independent review committee (IRC)–assessed ORR.
IRC-assessed ORR was improved from 65% to 83% with the addition of ublituximab. PFS also improved significantly in the ublituximab group, with an even greater improvement when the analysis was limited to those with del(17p) or TP53 aberrancy, but this outcome was limited by the reduced sample size of the study as well as the relatively short PFS of the ibrutinib arm.
After a median follow-up of 41.6 months, the median IRC-assessed PFS in all treated patients was not reached in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group after 15 PFS events but was 35.9 months in the ibrutinib group after 25 PFS events (hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.87; P = .016).
Undetectable minimal residual disease was also seen in 42% of the combination arm, compared with 6% of the ibrutinib arm.
What types of adverse events were found in the trial?
The researchers found mostly mild and known side effects of ibrutinib. More atrial fibrillation and neutropenia were seen in the antibody group, but this was not marked.
Most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2. The most common grade 3 and 4 adverse events were neutropenia (11 [19%] patients in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group and 7 [12%] in the ibrutinib group), anemia (5 [8%] and 5 [9%], respectively), and diarrhea (6 [10%] and 3 [5%], respectively).
What about serious adverse events?
Hospitalization from infection was seen, as expected. There were two cardiac arrests and an unexplained death, across both arms, which was concerning, given the known association of ibrutinib with ventricular arrhythmia and sudden death. There were also several hemorrhages, including one fatal one, which was again consistent with the known side effects of ibrutinib.
Are there treatments comparable with ublituximab plus ibrutinib that clinicians should perhaps first consider using?
In terms of other anti-CD20 antibodies, we have two randomized trials that have failed to show a benefit from adding rituximab to ibrutinib.
Obinutuzumab, like ublituximab, is also a next-generation glycoengineered antibody, and it is reasonably likely that it might lead to similar results. However, the only data we have on ibrutinib with obinutuzumab are from a single arm in a more heterogeneous, lower-risk patient population, and it is unlikely that a randomized comparison will ever be done.
On the basis of these trial results, how would you use the combination of ublituximab and ibrutinib for your patients?
I would consider the addition of ublituximab to a BTK inhibitor in high-risk patients (once ublituximab is approved). I already usually use a next-generation BTK inhibitor rather than ibrutinib.
Are there any other implications of the GENUINE trial?
I think this trial underscores the importance of studying genetic subgroups of patients separately. In this case, that was done in high-risk patients, but this observation likely also applies to low-risk patients.
Most trials to date have enrolled unselected patient populations, often without stratification, and their results therefore tend to obscure the outcomes in both the very high risk (as studied here) and in the low risk (patients with immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene mutations).
Dr. Brown has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Acerta/AstraZeneca, Beigene, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Juno/Celgene, Catapult, Genentech/Roche, Janssen, MEI Pharma, Morphosys, and Novartis, and has received research funding from Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, TG Therapeutics, Verastem/SecuraBio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clinically heterogeneous disease associated with several known genetic abnormalities, including 17p deletion (del[17p]), 11q deletion (del[11q]), and TP53 gene mutations, which are adverse prognostic markers among patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib is approved for patients with untreated, relapsed, or refractory disease, including those with del(17p). Clinicians will soon have the chance to pair it with ublituximab, a next-generation, glycoengineered, type I, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that binds to a unique epitope on CD20, differentiating it from rituximab, ofatumumab, and obinutuzumab. Results from the phase 3 GENUINE trial, which were recently published in The Lancet Haematology, showed that ublituximab plus ibrutinib was superior to ibrutinib alone for patients with relapsed or refractory high-risk CLL.
This news organization spoke with Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, director of the CLL Center and institute physician at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, about the GENUINE trial and its potential impact on treatment choices going forward.
What type of patients were treated in the GENUINE trial?
Dr. Brown: This is a trial among relapsed/refractory CLL patients with 17p or 11q deletion or TP53 mutation. Patients aged 18 years or older with CLL who warranted treatment, as defined by International Workshop on CLL criteria, were eligible if they had previously received at least two cycles of at least one standard treatment regimen, had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or lower, and had high-risk cytogenetics, defined as the presence of at least one of del(17p), del(11q), or TP53 mutation confirmed by a central laboratory with fluorescence in situ hybridization and/or next-generation sequencing.
What were the main outcomes of the trial?
Originally, the GENUINE trial had coprimary endpoints of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall response rate. Because of slow accrual, it was amended to have one primary endpoint of independent review committee (IRC)–assessed ORR.
IRC-assessed ORR was improved from 65% to 83% with the addition of ublituximab. PFS also improved significantly in the ublituximab group, with an even greater improvement when the analysis was limited to those with del(17p) or TP53 aberrancy, but this outcome was limited by the reduced sample size of the study as well as the relatively short PFS of the ibrutinib arm.
After a median follow-up of 41.6 months, the median IRC-assessed PFS in all treated patients was not reached in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group after 15 PFS events but was 35.9 months in the ibrutinib group after 25 PFS events (hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.87; P = .016).
Undetectable minimal residual disease was also seen in 42% of the combination arm, compared with 6% of the ibrutinib arm.
What types of adverse events were found in the trial?
The researchers found mostly mild and known side effects of ibrutinib. More atrial fibrillation and neutropenia were seen in the antibody group, but this was not marked.
Most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2. The most common grade 3 and 4 adverse events were neutropenia (11 [19%] patients in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group and 7 [12%] in the ibrutinib group), anemia (5 [8%] and 5 [9%], respectively), and diarrhea (6 [10%] and 3 [5%], respectively).
What about serious adverse events?
Hospitalization from infection was seen, as expected. There were two cardiac arrests and an unexplained death, across both arms, which was concerning, given the known association of ibrutinib with ventricular arrhythmia and sudden death. There were also several hemorrhages, including one fatal one, which was again consistent with the known side effects of ibrutinib.
Are there treatments comparable with ublituximab plus ibrutinib that clinicians should perhaps first consider using?
In terms of other anti-CD20 antibodies, we have two randomized trials that have failed to show a benefit from adding rituximab to ibrutinib.
Obinutuzumab, like ublituximab, is also a next-generation glycoengineered antibody, and it is reasonably likely that it might lead to similar results. However, the only data we have on ibrutinib with obinutuzumab are from a single arm in a more heterogeneous, lower-risk patient population, and it is unlikely that a randomized comparison will ever be done.
On the basis of these trial results, how would you use the combination of ublituximab and ibrutinib for your patients?
I would consider the addition of ublituximab to a BTK inhibitor in high-risk patients (once ublituximab is approved). I already usually use a next-generation BTK inhibitor rather than ibrutinib.
Are there any other implications of the GENUINE trial?
I think this trial underscores the importance of studying genetic subgroups of patients separately. In this case, that was done in high-risk patients, but this observation likely also applies to low-risk patients.
Most trials to date have enrolled unselected patient populations, often without stratification, and their results therefore tend to obscure the outcomes in both the very high risk (as studied here) and in the low risk (patients with immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene mutations).
Dr. Brown has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Acerta/AstraZeneca, Beigene, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Juno/Celgene, Catapult, Genentech/Roche, Janssen, MEI Pharma, Morphosys, and Novartis, and has received research funding from Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, TG Therapeutics, Verastem/SecuraBio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clinically heterogeneous disease associated with several known genetic abnormalities, including 17p deletion (del[17p]), 11q deletion (del[11q]), and TP53 gene mutations, which are adverse prognostic markers among patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib is approved for patients with untreated, relapsed, or refractory disease, including those with del(17p). Clinicians will soon have the chance to pair it with ublituximab, a next-generation, glycoengineered, type I, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that binds to a unique epitope on CD20, differentiating it from rituximab, ofatumumab, and obinutuzumab. Results from the phase 3 GENUINE trial, which were recently published in The Lancet Haematology, showed that ublituximab plus ibrutinib was superior to ibrutinib alone for patients with relapsed or refractory high-risk CLL.
This news organization spoke with Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, director of the CLL Center and institute physician at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, about the GENUINE trial and its potential impact on treatment choices going forward.
What type of patients were treated in the GENUINE trial?
Dr. Brown: This is a trial among relapsed/refractory CLL patients with 17p or 11q deletion or TP53 mutation. Patients aged 18 years or older with CLL who warranted treatment, as defined by International Workshop on CLL criteria, were eligible if they had previously received at least two cycles of at least one standard treatment regimen, had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2 or lower, and had high-risk cytogenetics, defined as the presence of at least one of del(17p), del(11q), or TP53 mutation confirmed by a central laboratory with fluorescence in situ hybridization and/or next-generation sequencing.
What were the main outcomes of the trial?
Originally, the GENUINE trial had coprimary endpoints of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall response rate. Because of slow accrual, it was amended to have one primary endpoint of independent review committee (IRC)–assessed ORR.
IRC-assessed ORR was improved from 65% to 83% with the addition of ublituximab. PFS also improved significantly in the ublituximab group, with an even greater improvement when the analysis was limited to those with del(17p) or TP53 aberrancy, but this outcome was limited by the reduced sample size of the study as well as the relatively short PFS of the ibrutinib arm.
After a median follow-up of 41.6 months, the median IRC-assessed PFS in all treated patients was not reached in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group after 15 PFS events but was 35.9 months in the ibrutinib group after 25 PFS events (hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.87; P = .016).
Undetectable minimal residual disease was also seen in 42% of the combination arm, compared with 6% of the ibrutinib arm.
What types of adverse events were found in the trial?
The researchers found mostly mild and known side effects of ibrutinib. More atrial fibrillation and neutropenia were seen in the antibody group, but this was not marked.
Most adverse events were of grade 1 or 2. The most common grade 3 and 4 adverse events were neutropenia (11 [19%] patients in the ublituximab plus ibrutinib group and 7 [12%] in the ibrutinib group), anemia (5 [8%] and 5 [9%], respectively), and diarrhea (6 [10%] and 3 [5%], respectively).
What about serious adverse events?
Hospitalization from infection was seen, as expected. There were two cardiac arrests and an unexplained death, across both arms, which was concerning, given the known association of ibrutinib with ventricular arrhythmia and sudden death. There were also several hemorrhages, including one fatal one, which was again consistent with the known side effects of ibrutinib.
Are there treatments comparable with ublituximab plus ibrutinib that clinicians should perhaps first consider using?
In terms of other anti-CD20 antibodies, we have two randomized trials that have failed to show a benefit from adding rituximab to ibrutinib.
Obinutuzumab, like ublituximab, is also a next-generation glycoengineered antibody, and it is reasonably likely that it might lead to similar results. However, the only data we have on ibrutinib with obinutuzumab are from a single arm in a more heterogeneous, lower-risk patient population, and it is unlikely that a randomized comparison will ever be done.
On the basis of these trial results, how would you use the combination of ublituximab and ibrutinib for your patients?
I would consider the addition of ublituximab to a BTK inhibitor in high-risk patients (once ublituximab is approved). I already usually use a next-generation BTK inhibitor rather than ibrutinib.
Are there any other implications of the GENUINE trial?
I think this trial underscores the importance of studying genetic subgroups of patients separately. In this case, that was done in high-risk patients, but this observation likely also applies to low-risk patients.
Most trials to date have enrolled unselected patient populations, often without stratification, and their results therefore tend to obscure the outcomes in both the very high risk (as studied here) and in the low risk (patients with immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene mutations).
Dr. Brown has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Acerta/AstraZeneca, Beigene, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Juno/Celgene, Catapult, Genentech/Roche, Janssen, MEI Pharma, Morphosys, and Novartis, and has received research funding from Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, TG Therapeutics, Verastem/SecuraBio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CLL patients: Diagnostic difficulties, treatment confusion with COVID-19
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients present significant problems with regard to COVID-19 disease, according to a literature review by Yousef Roosta, MD, of Urmia (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Diagnostic interaction between CLL and COVID-19 provides a major challenge. CLL patients have a lower rate of anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG development, and evidence shows worse therapeutic outcomes in these patients, according to study published in Leukemia Research Reports.
The researchers assessed 20 retrieved articles, 11 of which examined patients with CLL and with concomitant COVID-19; and 9 articles were designed as prospective or retrospective case series of such patients. The studies were assessed qualitatively by the QUADAS-2 tool.
Troubling results
Although the overall prevalence of CLL and COVID-19 concurrence was low, at 0.6% (95% confidence interval 0.5%-0.7%) according to the meta-analysis, the results showed some special challenges in the diagnosis and care of these patients.
Diagnostic difficulties are a unique problem. Lymphopenia is common in patients with COVID-19, while lymphocytosis may be considered a transient or even rare finding. The interplay between the two diseases is sometimes very misleading for specialists, and in patients with lymphocytosis, the diagnosis of CLL may be completely ignored, according to the researchers. They added that when performing a diagnostic approach for concurrent COVID-19 and CLL, due to differences in the amount and type of immune response, “relying on serological testing, and especially the evaluation of the anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels may not be beneficial,” they indicated.
In addition, studies showed unacceptable therapeutic outcome in patients with concurrent CLL and COVID-19, with mortality ranging from 33% to 41.7%, showing a need to revise current treatment protocols, according to the authors. In one study, 85.7% of surviving patients showed a considerable decrease in functional class and significant fatigue, with such a poor prognosis occurring more commonly in the elderly.
With regard to treatment, “it is quite obvious that despite the use of current standard protocols, the prognosis of these patients will be much worse than the prognosis of CLL patients with no evidence of COVID-19. Even in the first-line treatment protocol for these patients, there is no agreement in combination therapy with selected CLL drugs along with management protocols of COVID-19 patients,” the researchers stated.
“[The] different hematological behaviors of two diseases might mimic the detection of COVID-19 in the CLL state and vise versa. Also, due to the low level of immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in CLL patients, both scheduled immunological-based diagnosis and treatment may fail,” the researchers added.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients present significant problems with regard to COVID-19 disease, according to a literature review by Yousef Roosta, MD, of Urmia (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Diagnostic interaction between CLL and COVID-19 provides a major challenge. CLL patients have a lower rate of anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG development, and evidence shows worse therapeutic outcomes in these patients, according to study published in Leukemia Research Reports.
The researchers assessed 20 retrieved articles, 11 of which examined patients with CLL and with concomitant COVID-19; and 9 articles were designed as prospective or retrospective case series of such patients. The studies were assessed qualitatively by the QUADAS-2 tool.
Troubling results
Although the overall prevalence of CLL and COVID-19 concurrence was low, at 0.6% (95% confidence interval 0.5%-0.7%) according to the meta-analysis, the results showed some special challenges in the diagnosis and care of these patients.
Diagnostic difficulties are a unique problem. Lymphopenia is common in patients with COVID-19, while lymphocytosis may be considered a transient or even rare finding. The interplay between the two diseases is sometimes very misleading for specialists, and in patients with lymphocytosis, the diagnosis of CLL may be completely ignored, according to the researchers. They added that when performing a diagnostic approach for concurrent COVID-19 and CLL, due to differences in the amount and type of immune response, “relying on serological testing, and especially the evaluation of the anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels may not be beneficial,” they indicated.
In addition, studies showed unacceptable therapeutic outcome in patients with concurrent CLL and COVID-19, with mortality ranging from 33% to 41.7%, showing a need to revise current treatment protocols, according to the authors. In one study, 85.7% of surviving patients showed a considerable decrease in functional class and significant fatigue, with such a poor prognosis occurring more commonly in the elderly.
With regard to treatment, “it is quite obvious that despite the use of current standard protocols, the prognosis of these patients will be much worse than the prognosis of CLL patients with no evidence of COVID-19. Even in the first-line treatment protocol for these patients, there is no agreement in combination therapy with selected CLL drugs along with management protocols of COVID-19 patients,” the researchers stated.
“[The] different hematological behaviors of two diseases might mimic the detection of COVID-19 in the CLL state and vise versa. Also, due to the low level of immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in CLL patients, both scheduled immunological-based diagnosis and treatment may fail,” the researchers added.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients present significant problems with regard to COVID-19 disease, according to a literature review by Yousef Roosta, MD, of Urmia (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Diagnostic interaction between CLL and COVID-19 provides a major challenge. CLL patients have a lower rate of anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG development, and evidence shows worse therapeutic outcomes in these patients, according to study published in Leukemia Research Reports.
The researchers assessed 20 retrieved articles, 11 of which examined patients with CLL and with concomitant COVID-19; and 9 articles were designed as prospective or retrospective case series of such patients. The studies were assessed qualitatively by the QUADAS-2 tool.
Troubling results
Although the overall prevalence of CLL and COVID-19 concurrence was low, at 0.6% (95% confidence interval 0.5%-0.7%) according to the meta-analysis, the results showed some special challenges in the diagnosis and care of these patients.
Diagnostic difficulties are a unique problem. Lymphopenia is common in patients with COVID-19, while lymphocytosis may be considered a transient or even rare finding. The interplay between the two diseases is sometimes very misleading for specialists, and in patients with lymphocytosis, the diagnosis of CLL may be completely ignored, according to the researchers. They added that when performing a diagnostic approach for concurrent COVID-19 and CLL, due to differences in the amount and type of immune response, “relying on serological testing, and especially the evaluation of the anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels may not be beneficial,” they indicated.
In addition, studies showed unacceptable therapeutic outcome in patients with concurrent CLL and COVID-19, with mortality ranging from 33% to 41.7%, showing a need to revise current treatment protocols, according to the authors. In one study, 85.7% of surviving patients showed a considerable decrease in functional class and significant fatigue, with such a poor prognosis occurring more commonly in the elderly.
With regard to treatment, “it is quite obvious that despite the use of current standard protocols, the prognosis of these patients will be much worse than the prognosis of CLL patients with no evidence of COVID-19. Even in the first-line treatment protocol for these patients, there is no agreement in combination therapy with selected CLL drugs along with management protocols of COVID-19 patients,” the researchers stated.
“[The] different hematological behaviors of two diseases might mimic the detection of COVID-19 in the CLL state and vise versa. Also, due to the low level of immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in CLL patients, both scheduled immunological-based diagnosis and treatment may fail,” the researchers added.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH REPORTS
Low-calorie diet linked to improved chemo response in leukemia
Children and adolescents with leukemia who were placed on a restrictive diet and exercise regimen concurrent with starting chemotherapy showed responses to treatment that were better than those historically seen in such patients.
This apparently improved response suggests it is possible to boost treatment efficacy without raising the dose – or toxicity – of chemotherapy.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study in any hematologic malignancy to demonstrate potential benefit from caloric restriction via diet and exercise to augment chemotherapy efficacy and improve disease response, the authors reported.
The findings come from the IDEAL pilot trial, conducted in 40 young patients (mean age, 15 years; range, 10-21 years) diagnosed with high-risk B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The study was published online April 1 in Blood Advances.
The diet and exercise regimen is a departure from current recommendations for patients with leukemia.
“This was a major paradigm shift – until now, many oncologists encouraged ‘comfort foods’ and increased calories to get through the rigor of chemotherapy,” first author Etan Orgel, MD, of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California, also in Los Angeles.
The results from this pilot trial suggest that “the era of encouraging comfort food should be in the past; over-nutrition is likely harmful, and diet and exercise are important tools to harness during chemotherapy,” he said.
Dr. Orgel added that childhood ALL was selected because it is the most common cancer of childhood, but the findings could have potential relevance in other cancer types in children as well as adults.
Commenting on the study, Patrick Brown, MD, director of the pediatric leukemia program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said the findings are important, albeit preliminary.
“I think the most important contribution of this pilot study is to show that it is possible to change the nutrition and exercise habits of children and adolescents during the initial month of treatment for ALL,” he said in an interview.
“We have to be cautious about the preliminary finding that these changes resulted in deeper remissions – this will need to be confirmed in a larger study,” added Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research.
Dr. Orgel noted that a prospective, randomized trial, IDEAL-2, is launching later this year to further evaluate the intervention.
Obesity linked to poorer chemotherapy response
Among children and adolescents who start treatment for B-ALL, as many as 40% are overweight or obese, noted the study authors.
Those who are obese have more than a twofold greater risk of having persistent minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of chemotherapy, considered the strongest patient-level predictor of poor outcome and a common guide for therapy intensification.
The problem is compounded by weight gain that is common during treatment as a result of prolonged chemotherapy and sedentary behavior, they commented.
With studies of obese mice linking calorie and fat restriction to improved survival after chemotherapy, the authors theorized that a calorie- and fat-restrictive diet and exercise could help improve outcomes after chemotherapy in humans.
Participants were enrolled at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and City of Hope National Medical Center in nearby Duarte. After they were started on chemotherapy, they were placed on a low-carb, low-fat, and low-sugar diet tailored to patient needs and preferences, as well as a moderate daily exercise regimen, and continued on this regimen throughout the 4-week induction phase.
Following the intervention, there were no significant reductions observed in median gain of fat mass at the end of the intervention, compared with baseline (P = .13). However, in the subgroup of patients who were overweight or obese at baseline, the reduction in fat mass was indeed significant versus baseline (+1.5% vs. +9.7% at baseline; P = .02).
Importantly, after adjustment for prognostic factors, adherence to the intervention was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of MRD, compared with recent historical controls who received the same induction therapy at the same institution, but no intervention (odds ratio, 0.30; P = .02).
The intervention was also associated with a lower detectable MRD, compared with the historical controls (OR, 0.16; one-sided P = .002).
“Most importantly, the IDEAL intervention reduced risk of MRD at the end of induction in all patients, irrespective of starting [body mass index] and after accounting for prognostic features,” the authors noted.
Adherence to diet high, exercise low
As many as 82% of study participants achieved the goal of 20% or more caloric deficit throughout the chemotherapy.
“Adherence to the diet was excellent, with caloric deficits and macronutrient goals achieved in nearly all patients, including in the lean group,” the authors reported.
Dr. Orgel added that families embraced the chance to play an active role in the cancer therapy. “In our view, they couldn’t control their disease or their chemotherapy, but this, they could,” he said.
Conversely, adherence to the prescribed exercise was low – just 31.2%, with the inactivity during the first month likely contributed to the similar loss of muscle mass that occurred in both cohorts, Dr. Orgel noted.
“The [low exercise adherence] unfortunately was not a surprise, as it is often difficult to exercise and be active during chemotherapy,” he said.
Key aspects of physical activity will be refined in further studies, Dr. Orgel added.
Insulin sensitivity, adiponectin key factors?
Patients receiving the intervention showed improved insulin sensitivity and reductions in circulating insulin, which are notable in that insulin has been linked to mechanisms that counter chemoresistance, the authors noted.
Furthermore, the decreases in insulin were accompanied by notable elevations in circulating adiponectin, a protein hormone produced and secreted by fat cells.
“Adiponectin was certainly a surprise, as until now it did not appear to play a major role in cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy,” Dr. Orgel said.
“It is too soon to say they are central to the mechanism of the intervention, but the large differences in adiponectin and insulin sensitivity found in children in the trial have definitely highlighted these as important for future study,” he added.
Dr. Orgel, the study coauthors, and Dr. Brown disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and adolescents with leukemia who were placed on a restrictive diet and exercise regimen concurrent with starting chemotherapy showed responses to treatment that were better than those historically seen in such patients.
This apparently improved response suggests it is possible to boost treatment efficacy without raising the dose – or toxicity – of chemotherapy.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study in any hematologic malignancy to demonstrate potential benefit from caloric restriction via diet and exercise to augment chemotherapy efficacy and improve disease response, the authors reported.
The findings come from the IDEAL pilot trial, conducted in 40 young patients (mean age, 15 years; range, 10-21 years) diagnosed with high-risk B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The study was published online April 1 in Blood Advances.
The diet and exercise regimen is a departure from current recommendations for patients with leukemia.
“This was a major paradigm shift – until now, many oncologists encouraged ‘comfort foods’ and increased calories to get through the rigor of chemotherapy,” first author Etan Orgel, MD, of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California, also in Los Angeles.
The results from this pilot trial suggest that “the era of encouraging comfort food should be in the past; over-nutrition is likely harmful, and diet and exercise are important tools to harness during chemotherapy,” he said.
Dr. Orgel added that childhood ALL was selected because it is the most common cancer of childhood, but the findings could have potential relevance in other cancer types in children as well as adults.
Commenting on the study, Patrick Brown, MD, director of the pediatric leukemia program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said the findings are important, albeit preliminary.
“I think the most important contribution of this pilot study is to show that it is possible to change the nutrition and exercise habits of children and adolescents during the initial month of treatment for ALL,” he said in an interview.
“We have to be cautious about the preliminary finding that these changes resulted in deeper remissions – this will need to be confirmed in a larger study,” added Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research.
Dr. Orgel noted that a prospective, randomized trial, IDEAL-2, is launching later this year to further evaluate the intervention.
Obesity linked to poorer chemotherapy response
Among children and adolescents who start treatment for B-ALL, as many as 40% are overweight or obese, noted the study authors.
Those who are obese have more than a twofold greater risk of having persistent minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of chemotherapy, considered the strongest patient-level predictor of poor outcome and a common guide for therapy intensification.
The problem is compounded by weight gain that is common during treatment as a result of prolonged chemotherapy and sedentary behavior, they commented.
With studies of obese mice linking calorie and fat restriction to improved survival after chemotherapy, the authors theorized that a calorie- and fat-restrictive diet and exercise could help improve outcomes after chemotherapy in humans.
Participants were enrolled at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and City of Hope National Medical Center in nearby Duarte. After they were started on chemotherapy, they were placed on a low-carb, low-fat, and low-sugar diet tailored to patient needs and preferences, as well as a moderate daily exercise regimen, and continued on this regimen throughout the 4-week induction phase.
Following the intervention, there were no significant reductions observed in median gain of fat mass at the end of the intervention, compared with baseline (P = .13). However, in the subgroup of patients who were overweight or obese at baseline, the reduction in fat mass was indeed significant versus baseline (+1.5% vs. +9.7% at baseline; P = .02).
Importantly, after adjustment for prognostic factors, adherence to the intervention was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of MRD, compared with recent historical controls who received the same induction therapy at the same institution, but no intervention (odds ratio, 0.30; P = .02).
The intervention was also associated with a lower detectable MRD, compared with the historical controls (OR, 0.16; one-sided P = .002).
“Most importantly, the IDEAL intervention reduced risk of MRD at the end of induction in all patients, irrespective of starting [body mass index] and after accounting for prognostic features,” the authors noted.
Adherence to diet high, exercise low
As many as 82% of study participants achieved the goal of 20% or more caloric deficit throughout the chemotherapy.
“Adherence to the diet was excellent, with caloric deficits and macronutrient goals achieved in nearly all patients, including in the lean group,” the authors reported.
Dr. Orgel added that families embraced the chance to play an active role in the cancer therapy. “In our view, they couldn’t control their disease or their chemotherapy, but this, they could,” he said.
Conversely, adherence to the prescribed exercise was low – just 31.2%, with the inactivity during the first month likely contributed to the similar loss of muscle mass that occurred in both cohorts, Dr. Orgel noted.
“The [low exercise adherence] unfortunately was not a surprise, as it is often difficult to exercise and be active during chemotherapy,” he said.
Key aspects of physical activity will be refined in further studies, Dr. Orgel added.
Insulin sensitivity, adiponectin key factors?
Patients receiving the intervention showed improved insulin sensitivity and reductions in circulating insulin, which are notable in that insulin has been linked to mechanisms that counter chemoresistance, the authors noted.
Furthermore, the decreases in insulin were accompanied by notable elevations in circulating adiponectin, a protein hormone produced and secreted by fat cells.
“Adiponectin was certainly a surprise, as until now it did not appear to play a major role in cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy,” Dr. Orgel said.
“It is too soon to say they are central to the mechanism of the intervention, but the large differences in adiponectin and insulin sensitivity found in children in the trial have definitely highlighted these as important for future study,” he added.
Dr. Orgel, the study coauthors, and Dr. Brown disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and adolescents with leukemia who were placed on a restrictive diet and exercise regimen concurrent with starting chemotherapy showed responses to treatment that were better than those historically seen in such patients.
This apparently improved response suggests it is possible to boost treatment efficacy without raising the dose – or toxicity – of chemotherapy.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study in any hematologic malignancy to demonstrate potential benefit from caloric restriction via diet and exercise to augment chemotherapy efficacy and improve disease response, the authors reported.
The findings come from the IDEAL pilot trial, conducted in 40 young patients (mean age, 15 years; range, 10-21 years) diagnosed with high-risk B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
The study was published online April 1 in Blood Advances.
The diet and exercise regimen is a departure from current recommendations for patients with leukemia.
“This was a major paradigm shift – until now, many oncologists encouraged ‘comfort foods’ and increased calories to get through the rigor of chemotherapy,” first author Etan Orgel, MD, of Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California, also in Los Angeles.
The results from this pilot trial suggest that “the era of encouraging comfort food should be in the past; over-nutrition is likely harmful, and diet and exercise are important tools to harness during chemotherapy,” he said.
Dr. Orgel added that childhood ALL was selected because it is the most common cancer of childhood, but the findings could have potential relevance in other cancer types in children as well as adults.
Commenting on the study, Patrick Brown, MD, director of the pediatric leukemia program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said the findings are important, albeit preliminary.
“I think the most important contribution of this pilot study is to show that it is possible to change the nutrition and exercise habits of children and adolescents during the initial month of treatment for ALL,” he said in an interview.
“We have to be cautious about the preliminary finding that these changes resulted in deeper remissions – this will need to be confirmed in a larger study,” added Dr. Brown, who was not involved with the research.
Dr. Orgel noted that a prospective, randomized trial, IDEAL-2, is launching later this year to further evaluate the intervention.
Obesity linked to poorer chemotherapy response
Among children and adolescents who start treatment for B-ALL, as many as 40% are overweight or obese, noted the study authors.
Those who are obese have more than a twofold greater risk of having persistent minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of chemotherapy, considered the strongest patient-level predictor of poor outcome and a common guide for therapy intensification.
The problem is compounded by weight gain that is common during treatment as a result of prolonged chemotherapy and sedentary behavior, they commented.
With studies of obese mice linking calorie and fat restriction to improved survival after chemotherapy, the authors theorized that a calorie- and fat-restrictive diet and exercise could help improve outcomes after chemotherapy in humans.
Participants were enrolled at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and City of Hope National Medical Center in nearby Duarte. After they were started on chemotherapy, they were placed on a low-carb, low-fat, and low-sugar diet tailored to patient needs and preferences, as well as a moderate daily exercise regimen, and continued on this regimen throughout the 4-week induction phase.
Following the intervention, there were no significant reductions observed in median gain of fat mass at the end of the intervention, compared with baseline (P = .13). However, in the subgroup of patients who were overweight or obese at baseline, the reduction in fat mass was indeed significant versus baseline (+1.5% vs. +9.7% at baseline; P = .02).
Importantly, after adjustment for prognostic factors, adherence to the intervention was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of MRD, compared with recent historical controls who received the same induction therapy at the same institution, but no intervention (odds ratio, 0.30; P = .02).
The intervention was also associated with a lower detectable MRD, compared with the historical controls (OR, 0.16; one-sided P = .002).
“Most importantly, the IDEAL intervention reduced risk of MRD at the end of induction in all patients, irrespective of starting [body mass index] and after accounting for prognostic features,” the authors noted.
Adherence to diet high, exercise low
As many as 82% of study participants achieved the goal of 20% or more caloric deficit throughout the chemotherapy.
“Adherence to the diet was excellent, with caloric deficits and macronutrient goals achieved in nearly all patients, including in the lean group,” the authors reported.
Dr. Orgel added that families embraced the chance to play an active role in the cancer therapy. “In our view, they couldn’t control their disease or their chemotherapy, but this, they could,” he said.
Conversely, adherence to the prescribed exercise was low – just 31.2%, with the inactivity during the first month likely contributed to the similar loss of muscle mass that occurred in both cohorts, Dr. Orgel noted.
“The [low exercise adherence] unfortunately was not a surprise, as it is often difficult to exercise and be active during chemotherapy,” he said.
Key aspects of physical activity will be refined in further studies, Dr. Orgel added.
Insulin sensitivity, adiponectin key factors?
Patients receiving the intervention showed improved insulin sensitivity and reductions in circulating insulin, which are notable in that insulin has been linked to mechanisms that counter chemoresistance, the authors noted.
Furthermore, the decreases in insulin were accompanied by notable elevations in circulating adiponectin, a protein hormone produced and secreted by fat cells.
“Adiponectin was certainly a surprise, as until now it did not appear to play a major role in cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy,” Dr. Orgel said.
“It is too soon to say they are central to the mechanism of the intervention, but the large differences in adiponectin and insulin sensitivity found in children in the trial have definitely highlighted these as important for future study,” he added.
Dr. Orgel, the study coauthors, and Dr. Brown disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.