User login
Atrial Fibrillation and Bleeding in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with Ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (FULL)
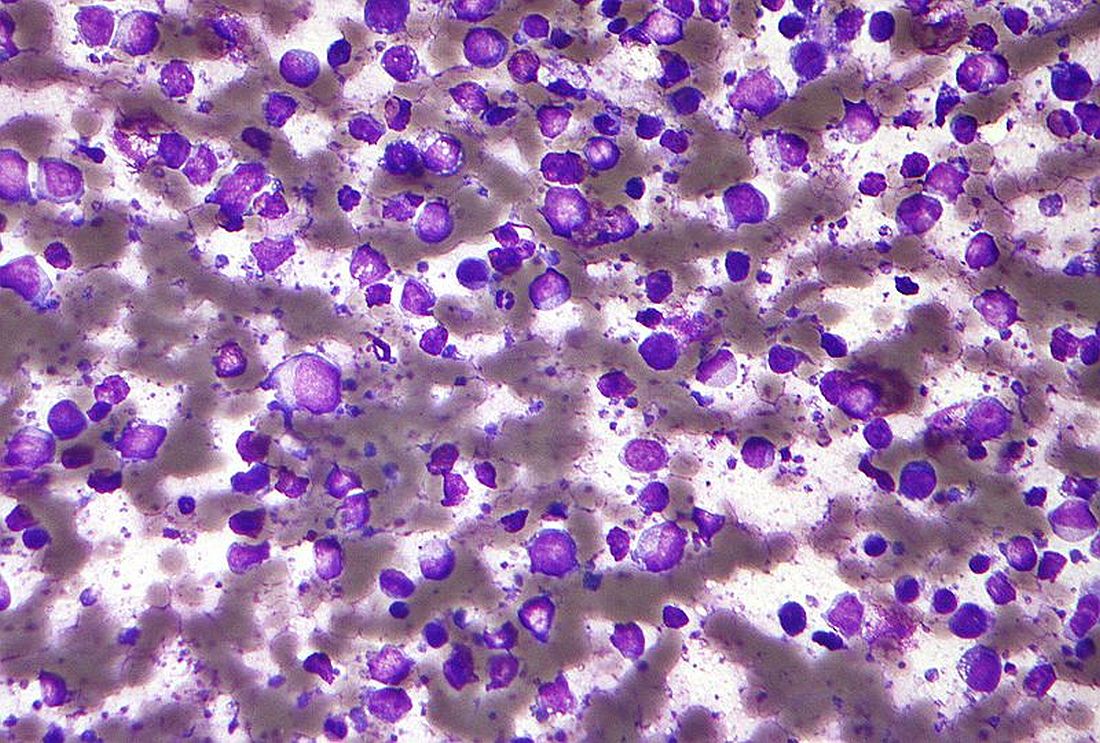
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
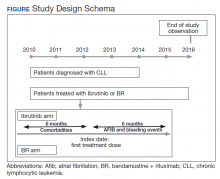
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
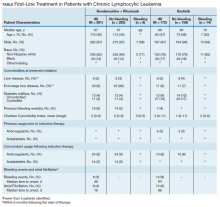
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia diagnosed in developed countries, with an estimated 21,040 new diagnoses of CLL expected in the US in 2020. 1-3 CLL is an indolent cancer characterized by the accumulation of B-lymphocytes in the blood, marrow, and lymphoid tissues. 4 It has a heterogeneous clinical course; the majority of patients are observed or receive delayed treatment following diagnosis, while a minority of patients require immediate treatment. After first-line treatment, some patients experience prolonged remissions while others require retreatment within 1 or 2 years. Fortunately, advances in cancer biology and therapeutics in the last decade have increased the number of treatment options available for patients with CLL.
Until recently, most CLL treatments relied on a chemotherapy or a chemoimmunotherapy backbone; however, the last few years have seen novel therapies introduced, such as small molecule inhibitors to target molecular pathways that promote the normal development, expansion, and survival of B-cells.5 One such therapy is ibrutinib, a targeted Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor that received accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2014 for patients with CLL who received at least 1 prior therapy. The FDA later expanded this approval to include use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL with relapsed or refractory disease, with or without chromosome 17p deletion. In 2016, based on data from the RESONATE-17 study, the FDA approved ibrutinib for first-line therapy in patients with CLL.6
Ibrutinib’s efficacy, ease of administration and dosing (all doses are oral and fixed, rather than based on weight or body surface area), and relatively favorable safety profile have resulted in a rapid growth in its adoption.7 Since its adverse event (AE) profile is generally more tolerable than that of a typical chemoimmunotherapy, its use in older patients with CLL and patients with significant comorbidities is particularly appealing.8
However, the results of some clinical trials suggest an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk of bleeding-related events of any grade (44%) and major bleeding events (4%).7,8 The incidence of major bleeding events was reported to be higher (9%) in one clinical trial and at 5-year follow-up, although this trial did not exclude patients receiving concomitant oral anticoagulation with warfarin.6,9
Heterogeneity in clinical trials’ definitions of major bleeding confounded the ability to calculate bleeding risk in patients treated with ibrutinib in a systematic review and meta-analysis that called for more data.10 Additionally, patients with factors that might increase the risk of major bleeding with ibrutinib treatment were likely underrepresented in clinical trials, given the carefully selected nature of clinical trial subjects. These factors include renal or hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disease, and use of a number of concomitant medications such as antiplatelets or anticoagulant medications. Accounting for use of the latter is particularly important because patients who develop atrial fibrillation (Afib), one of the recognized AEs of treatment with ibrutinib, often are treated with anticoagulant medications in order to decrease the risk of stroke or other thromboembolic complications.
A single-site observational study of patients treated with ibrutinib reported a high utilization rate of antiplatelet medications (70%), anticoagulant medications (17%), or both (13%) with a concomitant major bleeding rate of 18% of patients.11 Prevalence of bleeding events seemed to be highly affected by the presence of concomitant medications: 78% of patients treated with ibrutinib while concurrently receiving both antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications developed a major bleeding event, while none of the patients who were not receiving antiplatelets, anticoagulants, or medications that interact with cytochrome P450 (an enzyme that metabolized chemotherapeutic agents used to treat cancer) experienced a major bleeding event.11
The prevalence of major bleeding events, comorbidities, and utilization of medications that could increase the risk of major bleeding in patients with CLL on ibrutinib in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is not known. The VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the US. To address these knowledge gaps, a retrospective observational study was conducted using data on demographics, comorbidities that could affect bleeding, use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, and bleeding events in patients with CLL who were treated in the first year of ibrutinib availability from the VHA.
The first year of ibrutinib availability was chosen for this study since we anticipated that many health care providers would be unfamiliar with ibrutinib during that time given its novelty, and therefore more likely to codispense ibrutinib with medications that could increase the risk of a bleeding event. Since Afib is both an AE associated with ibrutinib treatment and a condition that often is treated with anticoagulants, the prevalence of Afib in this population was also included. For context, the incidence of bleeding and Afib and use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications during treatment in a cohort of patients with CLL treated with bendamustine + rituximab (BR) also was reported.
Methods
The VHA maintains the centralized US Department of Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry System (VACRS), with electronic medical record data and other sources captured in its Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). The VHA CDW is a national repository comprising data from several VHA clinical and administrative systems. The CDW includes patient identifiers; demographics; vital status; lab information; administrative information (such as diagnostic International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems [ICD-9] codes); medication dispensation tables (such as outpatient fill); IV package information; and notes from radiology, pathology, outpatient and inpatient admission, discharge, and daily progress.
Registrars abstract all cancer cases within the VHA system (or diagnosed outside the VHA, if patients subsequently receive treatment in the VHA). It is estimated that VACRS captures 3% of cancer cases in the US.12 Like most registries, VACRS captures data such as diagnosis, age, gender, race, and vital status.
The study received approval from the University of Utah Institutional Review Board and used individual patient-level historical administrative, cancer registry, and electronic health care record data. Patients diagnosed and treated for CLL at the VHA from 2010 to 2014 were identified through the VACRS and CDW; patients with a prior malignancy were excluded. Patients who received ibrutinib or BR based on pharmacy dispensation information were selected. Patients were followed until December 31, 2016 or death; patients with documentation of another cancer or lack of utilization of the VHA hematology or oncology services (defined as absence of any hematology and/or oncology clinic visits for ≥ 18 months) were omitted from the final analysis (Figure).
Previous and concomitant utilization of antiplatelet (aspirin, clopidogrel) or anticoagulant (dalteparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, heparin, rivaroxaban, and warfarin) medications was extracted 6 months before and after the first dispensation of ibrutinib or BR using pharmacy dispensation records.
Study Definitions
Prevalence of comorbidities that could increase bleeding risk was determined using administrative ICD-9-CM codes. Liver disease was identified by presence of cirrhosis, hepatitis C virus, or alcoholic liver disease using administrative codes validated by Kramer and colleagues, who reported positive and negative predictive values of 90% and 87% for cirrhosis, 93% and 92% for hepatitis C virus, and 71% and 98% for alcoholic liver disease.13 Similarly, end-stage liver disease was identified using a validated coding algorithm developed by Goldberg and colleagues, with a positive predictive value of 89.3%.14 The presence of controlled or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) was identified using the procedure described by Guzman and colleagues.15 Quan’s algorithm was used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) based on ICD-9-CM codes for inpatient and outpatient visits within a 6-month lookback period prior to treatment initiation.16
A major bleeding event was defined as a hospitalization with an ICD-9-CM code suggestive of major bleeding as the primary reason, as defined by Lane and colleagues in their study of major bleeding related to warfarin in a cohort of patients treated within the VHA.17 Incidence rates of major bleeding events were identified during the first 6 months of treatment. Incidence of Afib—defined as an inpatient or outpatient encounter with the 427.31 ICD-9-CM code—also was examined within the first 6 months after starting treatment. The period of 6 months was chosen because bendamustine must be discontinued after 6 months.
Study Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to examine patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment history from initial CLL diagnosis through end of study observation period. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and accompanying proportions, while a mean and standard deviation were used to summarize continuous variables. For the means of continuous variables and of categorical data, 95% CIs were used. Proportions and accompanying 95% CIs characterized treatment patterns, including line of therapy, comorbidities, and bleeding events. Treatment duration was described using mean and accompanying 95% CI. Statistical tests were not conducted for comparisons among treatment groups. Patients were censored at the end of follow-up, defined as the earliest of the following scenarios: (1) end of study observation period (December 31, 2016); (2) development of a secondary cancer; or (3) last day of contact given absence of care within the VHA for ≥ 18 months (with care defined as oncology and/or oncology/hematology visit with an associated note). Analysis was performed using R 3.4.0.
Results
Between 2010 and 2014, 2,796 patients were diagnosed and received care for CLL within the VHA. Overall, all 172 patients who were treated with ibrutinib during our inclusion period were selected. These patients were treated between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2016, following ibrutinib’s approval in early 2014. An additional 291 patients were selected who received BR (Table). Reflecting the predominantly male population of the VHA, 282 (97%) BR patients and 167 (97%) ibrutinib patients were male. The median age at diagnosis was 67 years for BR patients and 69 years for ibrutinib patients. About 76% of patients who received ibrutinib and 82% of patients who received BR were non-Hispanic white; 17% and 14% were African American, respectively.
Less than 10% of patients receiving either ibrutinib or BR had liver disease per criteria used by Kramer and colleagues, or end-stage liver disease using criteria developed by Goldberg and colleagues.12,13 About 5% of patients had a history of previous bleeding in the 6-month period prior to initiating either therapy. Mean CCI (excluding malignancy) score was 1.5 (range, 0-11) for the ibrutinib group, and 2.1 (range, 0-9) for the BR group. About 16% of the ibrutinib group had controlled DM and fewer than 10% had uncontrolled DM, while 4% of patients in the BR group met the criteria for controlled DM and another 4% met the criteria for uncontrolled DM.
There was very low utilization of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication prior to initiation of ibrutinib (2.9% and 2.3%, respectively) or BR (< 1% each). In the first 6 months after treatment initiation, about 8% of patients in both ibrutinib and BR cohorts received anticoagulant medication while antiplatelet utilization was < 5% in either group.
In the BR group, 8 patients (2.7%) experienced a major bleeding event, while 14 patients (8.1%) in the ibrutinib group experienced a bleeding event (P = .008). While these numbers were too low to perform a formal statistical analysis of the association between clinical covariates and bleeding in either group, there did not seem to be an association between bleeding and liver disease or DM. Of patients who experienced a bleeding event, about 1 in 4 patients had had a prior bleeding event in both the ibrutinib and the BR groups. Interestingly, while none of the patients who experienced a bleeding event while receiving BR were taking concomitant anticoagulant medication, 3 of the 14 patients who experienced a bleeding event in the ibrutinib group showed evidence of anticoagulant utilization. Finally, the incidence of Afib (defined as patients with no evidence of Afib in the 6 months prior to treatment but with evidence of Afib in the 6 months following treatment initiation) was 4% in the BR group, and about 8% in the ibrutinib group (P = .003).
Discussion
To the authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to examine the real-world incidence of bleeding and Afib in veterans who received ibrutinib for CLL in the first year of its availability. The study found minimal use of anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents prior to receiving first-line ibrutinib or BR, and very low use of these agents in the first 6 months following the initiation of first-line treatment. This finding suggests a high awareness among VA providers of potential adverse effects (AEs) of ibrutinib and chemotherapy, and a careful selection of patients that lack risk factors for AEs.
In patients treated with first-line ibrutinib when compared with patients treated with first-line BR, moderate increases in bleeding (2.7% vs 8.1%, P = .008) and Afib (10.5% vs 3%, P = .003) also were observed. These results are concordant with previous findings examining the use of ibrutinib in patients with CLL.18-20
Limitations
The results of this study should be interpreted with caution, as some limitations must be considered. The study was conducted in the early days of ibrutinib adoption. Since then, more patients have been treated with ibrutinib and for longer durations. As clinicians gain more familiarity and with ibrutinib, and as additional novel therapeutics emerge, it is possible that the initial awareness about risks for possible AEs may diminish; patients with high comorbidity burdens and concomitant medications would be especially vulnerable in cases of reduced physician vigilance.
Another limitation of this study stems from the potential for dual system use among patients treated in the VHA. Concurrent or alternating use of multiple health care systems (use of VHA and private-sector facilities) may present gaps in the reconstruction of patient histories, resulting in missing data as patients transition between commercial, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and VHA care. As a result, the results presented here do not reflect instances where a patient experienced a bleeding event treated outside the VA.
Problems with missing data also may occur due to incomplete extraction from the electronic health record; these issues were addressed by leveraging an understanding of the multiple data marts within the CDW environment to harmonize missing and/or erroneous information through use of other data marts when possible. Lastly, this research represents a population-level study of the VHA, thus all findings are directly relevant to the VHA. The generalizability of the findings outside the VHA would depend on the characteristics of the external population.
Conclusion
Real-world evidence from a nationwide cohort of veteran patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib suggest that, while there is an association of increased bleeding-related events and Afib, the risk is comparable to those reported in previous studies.18-20 These findings suggest that patients in real-world clinical care settings with higher levels of comorbidities may be at a slight increased risk for bleeding events and Afib.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
1. Scarfò L, Ferreri AJ, Ghia P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;104:169-182.
2. Devereux S, Cuthill K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;45(5):292-296.
3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2020. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2020/cancer-facts-and-figures-2020.pdf. Accessed April 24, 2020.
4. Kipps TJ, Stevenson FK, Wu CJ, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:16096.
5. Owen C, Assouline S, Kuruvilla J, Uchida C, Bellingham C, Sehn L. Novel therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a Canadian perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015;15(11):627-634.e5.
6. O’Brien S, Jones JA, Coutre SE, et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): a phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(10):1409–1418.
7. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al; RESONATE-2 Investigators. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425-2437.
8. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(1):32-42.
9. O’Brien S, Furman R, Coutre S, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib in treatment-naive and relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a 5-year experience. Blood. 2018;131(17):1910-1919.
10. Caron F, Leong DP, Hillis C, Fraser G, Siegal D. Current understanding of bleeding with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(12):772-778.
11. Kunk PR, Mock J, Devitt ME, Palkimas S, et al. Major bleeding with ibrutinib: more than expected. Blood. 2016;128(22):3229.
12. Zullig LL, Jackson GL, Dorn RA, et al. Cancer incidence among patients of the U.S. Veterans Affairs Health Care System. Mil Med. 2012;177(6):693-701.
13. Kramer JR, Davila JA, Miller ED, Richardson P, Giordano TP, El-Serag HB. The validity of viral hepatitis and chronic liver disease diagnoses in Veterans Affairs administrative databases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(3):274-282.
14. Goldberg D, Lewis JD, Halpern SD, Weiner M, Lo Re V 3rd. Validation of three coding algorithms to identify patients with end-stage liver disease in an administrative database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21(7):765-769.
15. Guzman JZ, Iatridis JC, Skovrlj B, et al. Outcomes and complications of diabetes mellitus on patients undergoing degenerative lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(19):1596-1604.
16. Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43(11):1130-1139.
17. Lane MA, Zeringue A, McDonald JR. Serious bleeding events due to warfarin and antibiotic co-prescription in a cohort of veterans. Am J Med. 2014;127(7):657–663.e2.
18. Leong DP, Caron F, Hillis C, et al. The risk of atrial fibrillation with ibrutinib use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2016;128(1):138-140.
19. Lipsky AH, Farooqui MZ, Tian X, et al. Incidence and risk factors of bleeding-related adverse events in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with ibrutinib. Haematologica. 2015;100(12):1571-1578.
20. Brown JR, Moslehi J, O’Brien S, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation adverse events reported in ibrutinib randomized controlled registration trials. Haematologica. 2017;102(10):1796-1805.
Hyperprogression on immunotherapy: When outcomes are much worse
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has ushered in a new era of cancer therapy, with some patients showing dramatic responses and significantly better outcomes than with other therapies across many cancer types. But some patients do worse, sometimes much worse.
A subset of patients who undergo immunotherapy experience unexpected, rapid disease progression, with a dramatic acceleration of disease trajectory. They also have a shorter progression-free survival and overall survival than would have been expected.
This has been described as hyperprogression and has been termed “hyperprogressive disease” (HPD). It has been seen in a variety of cancers; the incidence ranges from 4% to 29% in the studies reported to date.
There has been some debate over whether this is a real phenomenon or whether it is part of the natural course of disease.
HPD is a “provocative phenomenon,” wrote the authors of a recent commentary entitled “Hyperprogression and Immunotherapy: Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?”
“This phenomenon has polarized oncologists who debate that this could still reflect the natural history of the disease,” said the author of another commentary.
But the tide is now turning toward acceptance of HPD, said Kartik Sehgal, MD, an oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard University, both in Boston.
“With publication of multiple clinical reports of different cancer types worldwide, hyperprogression is now accepted by most oncologists to be a true phenomenon rather than natural progression of disease,” Dr. Sehgal said.
He authored an invited commentary in JAMA Network Openabout one of the latest meta-analyses (JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4[3]:e211136) to investigate HPD during immunotherapy. One of the biggest issues is that the studies that have reported on HPD have been retrospective, with a lack of comparator groups and a lack of a standardized definition of hyperprogression. Dr. Sehgal emphasized the need to study hyperprogression in well-designed prospective studies.
Existing data on HPD
HPD was described as “a new pattern of progression” seen in patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in a 2017 article published in Clinical Cancer Research. Authors Stephane Champiat, MD, PhD, of Institut Gustave Roussy, Universite Paris Saclay, Villejuif, France, and colleagues cited “anecdotal occurrences” of HPD among patients in phase 1 trials of anti–PD-1/PD-L1 agents.
In that study, HPD was defined by tumor growth rate ratio. The incidence was 9% among 213 patients.
The findings raised concerns about treating elderly patients with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy, according to the authors, who called for further study.
That same year, Roberto Ferrara, MD, and colleagues from the Insitut Gustave Roussy reported additional data indicating an incidence of HPD of 16% among 333 patients with non–small cell lung cancer who underwent immunotherapy at eight centers from 2012 to 2017. The findings, which were presented at the 2017 World Conference on Lung Cancer and reported at the time by this news organization, also showed that the incidence of HPD was higher with immunotherapy than with single-agent chemotherapy (5%).
Median overall survival (OS) was just 3.4 months among those with HPD, compared with 13 months in the overall study population – worse, even, than the median 5.4-month OS observed among patients with progressive disease who received immunotherapy.
In the wake of these findings, numerous researchers have attempted to better define HPD, its incidence, and patient factors associated with developing HPD while undergoing immunotherapy.
However, there is little so far to show for those efforts, Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in an interview.
“Many questions remain to be answered,” said Dr. Subbiah, clinical medical director of the Clinical Center for Targeted Therapy in the division of cancer medicine at MD Anderson. He was the senior author of the “Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?” commentary.
Work is underway to elucidate biological mechanisms. Some groups have implicated the Fc region of antibodies. Another group has reported EGFR and MDM2/MDM4 amplifications in patients with HPD, Dr. Subbiah and colleagues noted.
Other “proposed contributing pathological mechanisms include modulation of tumor immune microenvironment through macrophages and regulatory T cells as well as activation of oncogenic signaling pathways,” noted Dr. Sehgal.
Both groups of authors emphasize the urgent need for prospective studies.
It is imperative to confirm underlying biology, predict which patients are at risk, and identify therapeutic directions for patients who experience HPD, Dr. Subbiah said.
The main challenge is defining HPD, he added. Definitions that have been proposed include tumor growth at least two times greater than in control persons, a 15% increase in tumor burden in a set period, and disease progression of 50% from the first evaluation before treatment, he said.
The recent meta-analysis by Hyo Jung Park, MD, PhD, and colleagues, which Dr. Sehgal addressed in his invited commentary, highlights the many approaches used for defining HPD.
Depending on the definition used, the incidence of HPD across 24 studies involving more than 3,100 patients ranged from 5.9% to 43.1%.
“Hyperprogressive disease could be overestimated or underestimated based on current assessment,” Dr. Park and colleagues concluded. They highlighted the importance of “establishing uniform and clinically relevant criteria based on currently available evidence.”
Steps for solving the HPD mystery
“I think we need to come up with consensus criteria for an HPD definition. We need a unified definition,” Dr. Subbiah said. “We also need to design prospective studies to prove or disprove the immunotherapy-HPD association.”
Prospective registries with independent review of patients with suspected immunotherapy-related HPD would be useful for assessing the true incidence and the biology of HPD among patients undergoing immunotherapy, he suggested.
“We need to know the immunologic signals of HPD. This can give us an idea if patients can be prospectively identified for being at risk,” he said. “We also need to know what to do if they are at risk.”
Dr. Sehgal also called for consensus on an HPD definition, with input from a multidisciplinary group that includes “colleagues from radiology, medical oncology, radiation oncology. Getting expertise from different disciplines would be helpful,” he said.
Dr. Park and colleagues suggested several key requirements for an optimal HP definition, such as the inclusion of multiple variables for measuring tumor growth acceleration, “sufficiently quantitative” criteria for determining time to failure, and establishment of a standardized measure of tumor growth acceleration.
The agreed-upon definition of HPD could be applied to patients in a prospective registry and to existing trial data, Dr. Sehgal said.
“Eventually, the goal of this exercise is to [determine] how we can help our patients the best, having a biomarker that can at least inform us in terms of being aware and being proactive in terms of looking for this ... so that interventions can be brought on earlier,” he said.
“If we know what may be a biological mechanism, we can design trials that are designed to look at how to overcome that HPD,” he said.
Dr. Sehgal said he believes HPD is triggered in some way by treatment, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, but perhaps in different ways for each.
He estimated the true incidence of immunotherapy-related HPD will be in the 9%-10% range.
“This is a substantial number of patients, so it’s important that we try to understand this phenomenon, using, again, uniform criteria,” he said.
Current treatment decision-making
Until more is known, Dr. Sehgal said he considers the potential risk factors when treating patients with immunotherapy.
For example, the presence of MDM2 or MDM4 amplification on a genomic profile may factor into his treatment decision-making when it comes to using immunotherapy or immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy, he said.
“Is that the only factor that is going to make me choose one thing or another? No,” Dr. Sehgal said. However, he said it would make him more “proactive in making sure the patient is doing clinically okay” and in determining when to obtain on-treatment imaging studies.
Dr. Subbiah emphasized the relative benefit of immunotherapy, noting that survival with chemotherapy for many difficult-to-treat cancers in the relapsed/refractory metastatic setting is less than 2 years.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has allowed some of these patients to live longer (with survival reported to be more than 10 years for patients with metastatic melanoma).
“Immunotherapy has been a game changer; it has been transformative in the lives of these patients,” Dr. Subbiah said. “So unless there is any other contraindication, the benefit of receiving immunotherapy for an approved indication far outweighs the risk of HPD.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has ushered in a new era of cancer therapy, with some patients showing dramatic responses and significantly better outcomes than with other therapies across many cancer types. But some patients do worse, sometimes much worse.
A subset of patients who undergo immunotherapy experience unexpected, rapid disease progression, with a dramatic acceleration of disease trajectory. They also have a shorter progression-free survival and overall survival than would have been expected.
This has been described as hyperprogression and has been termed “hyperprogressive disease” (HPD). It has been seen in a variety of cancers; the incidence ranges from 4% to 29% in the studies reported to date.
There has been some debate over whether this is a real phenomenon or whether it is part of the natural course of disease.
HPD is a “provocative phenomenon,” wrote the authors of a recent commentary entitled “Hyperprogression and Immunotherapy: Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?”
“This phenomenon has polarized oncologists who debate that this could still reflect the natural history of the disease,” said the author of another commentary.
But the tide is now turning toward acceptance of HPD, said Kartik Sehgal, MD, an oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard University, both in Boston.
“With publication of multiple clinical reports of different cancer types worldwide, hyperprogression is now accepted by most oncologists to be a true phenomenon rather than natural progression of disease,” Dr. Sehgal said.
He authored an invited commentary in JAMA Network Openabout one of the latest meta-analyses (JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4[3]:e211136) to investigate HPD during immunotherapy. One of the biggest issues is that the studies that have reported on HPD have been retrospective, with a lack of comparator groups and a lack of a standardized definition of hyperprogression. Dr. Sehgal emphasized the need to study hyperprogression in well-designed prospective studies.
Existing data on HPD
HPD was described as “a new pattern of progression” seen in patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in a 2017 article published in Clinical Cancer Research. Authors Stephane Champiat, MD, PhD, of Institut Gustave Roussy, Universite Paris Saclay, Villejuif, France, and colleagues cited “anecdotal occurrences” of HPD among patients in phase 1 trials of anti–PD-1/PD-L1 agents.
In that study, HPD was defined by tumor growth rate ratio. The incidence was 9% among 213 patients.
The findings raised concerns about treating elderly patients with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy, according to the authors, who called for further study.
That same year, Roberto Ferrara, MD, and colleagues from the Insitut Gustave Roussy reported additional data indicating an incidence of HPD of 16% among 333 patients with non–small cell lung cancer who underwent immunotherapy at eight centers from 2012 to 2017. The findings, which were presented at the 2017 World Conference on Lung Cancer and reported at the time by this news organization, also showed that the incidence of HPD was higher with immunotherapy than with single-agent chemotherapy (5%).
Median overall survival (OS) was just 3.4 months among those with HPD, compared with 13 months in the overall study population – worse, even, than the median 5.4-month OS observed among patients with progressive disease who received immunotherapy.
In the wake of these findings, numerous researchers have attempted to better define HPD, its incidence, and patient factors associated with developing HPD while undergoing immunotherapy.
However, there is little so far to show for those efforts, Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in an interview.
“Many questions remain to be answered,” said Dr. Subbiah, clinical medical director of the Clinical Center for Targeted Therapy in the division of cancer medicine at MD Anderson. He was the senior author of the “Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?” commentary.
Work is underway to elucidate biological mechanisms. Some groups have implicated the Fc region of antibodies. Another group has reported EGFR and MDM2/MDM4 amplifications in patients with HPD, Dr. Subbiah and colleagues noted.
Other “proposed contributing pathological mechanisms include modulation of tumor immune microenvironment through macrophages and regulatory T cells as well as activation of oncogenic signaling pathways,” noted Dr. Sehgal.
Both groups of authors emphasize the urgent need for prospective studies.
It is imperative to confirm underlying biology, predict which patients are at risk, and identify therapeutic directions for patients who experience HPD, Dr. Subbiah said.
The main challenge is defining HPD, he added. Definitions that have been proposed include tumor growth at least two times greater than in control persons, a 15% increase in tumor burden in a set period, and disease progression of 50% from the first evaluation before treatment, he said.
The recent meta-analysis by Hyo Jung Park, MD, PhD, and colleagues, which Dr. Sehgal addressed in his invited commentary, highlights the many approaches used for defining HPD.
Depending on the definition used, the incidence of HPD across 24 studies involving more than 3,100 patients ranged from 5.9% to 43.1%.
“Hyperprogressive disease could be overestimated or underestimated based on current assessment,” Dr. Park and colleagues concluded. They highlighted the importance of “establishing uniform and clinically relevant criteria based on currently available evidence.”
Steps for solving the HPD mystery
“I think we need to come up with consensus criteria for an HPD definition. We need a unified definition,” Dr. Subbiah said. “We also need to design prospective studies to prove or disprove the immunotherapy-HPD association.”
Prospective registries with independent review of patients with suspected immunotherapy-related HPD would be useful for assessing the true incidence and the biology of HPD among patients undergoing immunotherapy, he suggested.
“We need to know the immunologic signals of HPD. This can give us an idea if patients can be prospectively identified for being at risk,” he said. “We also need to know what to do if they are at risk.”
Dr. Sehgal also called for consensus on an HPD definition, with input from a multidisciplinary group that includes “colleagues from radiology, medical oncology, radiation oncology. Getting expertise from different disciplines would be helpful,” he said.
Dr. Park and colleagues suggested several key requirements for an optimal HP definition, such as the inclusion of multiple variables for measuring tumor growth acceleration, “sufficiently quantitative” criteria for determining time to failure, and establishment of a standardized measure of tumor growth acceleration.
The agreed-upon definition of HPD could be applied to patients in a prospective registry and to existing trial data, Dr. Sehgal said.
“Eventually, the goal of this exercise is to [determine] how we can help our patients the best, having a biomarker that can at least inform us in terms of being aware and being proactive in terms of looking for this ... so that interventions can be brought on earlier,” he said.
“If we know what may be a biological mechanism, we can design trials that are designed to look at how to overcome that HPD,” he said.
Dr. Sehgal said he believes HPD is triggered in some way by treatment, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, but perhaps in different ways for each.
He estimated the true incidence of immunotherapy-related HPD will be in the 9%-10% range.
“This is a substantial number of patients, so it’s important that we try to understand this phenomenon, using, again, uniform criteria,” he said.
Current treatment decision-making
Until more is known, Dr. Sehgal said he considers the potential risk factors when treating patients with immunotherapy.
For example, the presence of MDM2 or MDM4 amplification on a genomic profile may factor into his treatment decision-making when it comes to using immunotherapy or immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy, he said.
“Is that the only factor that is going to make me choose one thing or another? No,” Dr. Sehgal said. However, he said it would make him more “proactive in making sure the patient is doing clinically okay” and in determining when to obtain on-treatment imaging studies.
Dr. Subbiah emphasized the relative benefit of immunotherapy, noting that survival with chemotherapy for many difficult-to-treat cancers in the relapsed/refractory metastatic setting is less than 2 years.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has allowed some of these patients to live longer (with survival reported to be more than 10 years for patients with metastatic melanoma).
“Immunotherapy has been a game changer; it has been transformative in the lives of these patients,” Dr. Subbiah said. “So unless there is any other contraindication, the benefit of receiving immunotherapy for an approved indication far outweighs the risk of HPD.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has ushered in a new era of cancer therapy, with some patients showing dramatic responses and significantly better outcomes than with other therapies across many cancer types. But some patients do worse, sometimes much worse.
A subset of patients who undergo immunotherapy experience unexpected, rapid disease progression, with a dramatic acceleration of disease trajectory. They also have a shorter progression-free survival and overall survival than would have been expected.
This has been described as hyperprogression and has been termed “hyperprogressive disease” (HPD). It has been seen in a variety of cancers; the incidence ranges from 4% to 29% in the studies reported to date.
There has been some debate over whether this is a real phenomenon or whether it is part of the natural course of disease.
HPD is a “provocative phenomenon,” wrote the authors of a recent commentary entitled “Hyperprogression and Immunotherapy: Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?”
“This phenomenon has polarized oncologists who debate that this could still reflect the natural history of the disease,” said the author of another commentary.
But the tide is now turning toward acceptance of HPD, said Kartik Sehgal, MD, an oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard University, both in Boston.
“With publication of multiple clinical reports of different cancer types worldwide, hyperprogression is now accepted by most oncologists to be a true phenomenon rather than natural progression of disease,” Dr. Sehgal said.
He authored an invited commentary in JAMA Network Openabout one of the latest meta-analyses (JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4[3]:e211136) to investigate HPD during immunotherapy. One of the biggest issues is that the studies that have reported on HPD have been retrospective, with a lack of comparator groups and a lack of a standardized definition of hyperprogression. Dr. Sehgal emphasized the need to study hyperprogression in well-designed prospective studies.
Existing data on HPD
HPD was described as “a new pattern of progression” seen in patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in a 2017 article published in Clinical Cancer Research. Authors Stephane Champiat, MD, PhD, of Institut Gustave Roussy, Universite Paris Saclay, Villejuif, France, and colleagues cited “anecdotal occurrences” of HPD among patients in phase 1 trials of anti–PD-1/PD-L1 agents.
In that study, HPD was defined by tumor growth rate ratio. The incidence was 9% among 213 patients.
The findings raised concerns about treating elderly patients with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy, according to the authors, who called for further study.
That same year, Roberto Ferrara, MD, and colleagues from the Insitut Gustave Roussy reported additional data indicating an incidence of HPD of 16% among 333 patients with non–small cell lung cancer who underwent immunotherapy at eight centers from 2012 to 2017. The findings, which were presented at the 2017 World Conference on Lung Cancer and reported at the time by this news organization, also showed that the incidence of HPD was higher with immunotherapy than with single-agent chemotherapy (5%).
Median overall survival (OS) was just 3.4 months among those with HPD, compared with 13 months in the overall study population – worse, even, than the median 5.4-month OS observed among patients with progressive disease who received immunotherapy.
In the wake of these findings, numerous researchers have attempted to better define HPD, its incidence, and patient factors associated with developing HPD while undergoing immunotherapy.
However, there is little so far to show for those efforts, Vivek Subbiah, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in an interview.
“Many questions remain to be answered,” said Dr. Subbiah, clinical medical director of the Clinical Center for Targeted Therapy in the division of cancer medicine at MD Anderson. He was the senior author of the “Fact, Fiction, or Alternative Fact?” commentary.
Work is underway to elucidate biological mechanisms. Some groups have implicated the Fc region of antibodies. Another group has reported EGFR and MDM2/MDM4 amplifications in patients with HPD, Dr. Subbiah and colleagues noted.
Other “proposed contributing pathological mechanisms include modulation of tumor immune microenvironment through macrophages and regulatory T cells as well as activation of oncogenic signaling pathways,” noted Dr. Sehgal.
Both groups of authors emphasize the urgent need for prospective studies.
It is imperative to confirm underlying biology, predict which patients are at risk, and identify therapeutic directions for patients who experience HPD, Dr. Subbiah said.
The main challenge is defining HPD, he added. Definitions that have been proposed include tumor growth at least two times greater than in control persons, a 15% increase in tumor burden in a set period, and disease progression of 50% from the first evaluation before treatment, he said.
The recent meta-analysis by Hyo Jung Park, MD, PhD, and colleagues, which Dr. Sehgal addressed in his invited commentary, highlights the many approaches used for defining HPD.
Depending on the definition used, the incidence of HPD across 24 studies involving more than 3,100 patients ranged from 5.9% to 43.1%.
“Hyperprogressive disease could be overestimated or underestimated based on current assessment,” Dr. Park and colleagues concluded. They highlighted the importance of “establishing uniform and clinically relevant criteria based on currently available evidence.”
Steps for solving the HPD mystery
“I think we need to come up with consensus criteria for an HPD definition. We need a unified definition,” Dr. Subbiah said. “We also need to design prospective studies to prove or disprove the immunotherapy-HPD association.”
Prospective registries with independent review of patients with suspected immunotherapy-related HPD would be useful for assessing the true incidence and the biology of HPD among patients undergoing immunotherapy, he suggested.
“We need to know the immunologic signals of HPD. This can give us an idea if patients can be prospectively identified for being at risk,” he said. “We also need to know what to do if they are at risk.”
Dr. Sehgal also called for consensus on an HPD definition, with input from a multidisciplinary group that includes “colleagues from radiology, medical oncology, radiation oncology. Getting expertise from different disciplines would be helpful,” he said.
Dr. Park and colleagues suggested several key requirements for an optimal HP definition, such as the inclusion of multiple variables for measuring tumor growth acceleration, “sufficiently quantitative” criteria for determining time to failure, and establishment of a standardized measure of tumor growth acceleration.
The agreed-upon definition of HPD could be applied to patients in a prospective registry and to existing trial data, Dr. Sehgal said.
“Eventually, the goal of this exercise is to [determine] how we can help our patients the best, having a biomarker that can at least inform us in terms of being aware and being proactive in terms of looking for this ... so that interventions can be brought on earlier,” he said.
“If we know what may be a biological mechanism, we can design trials that are designed to look at how to overcome that HPD,” he said.
Dr. Sehgal said he believes HPD is triggered in some way by treatment, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, but perhaps in different ways for each.
He estimated the true incidence of immunotherapy-related HPD will be in the 9%-10% range.
“This is a substantial number of patients, so it’s important that we try to understand this phenomenon, using, again, uniform criteria,” he said.
Current treatment decision-making
Until more is known, Dr. Sehgal said he considers the potential risk factors when treating patients with immunotherapy.
For example, the presence of MDM2 or MDM4 amplification on a genomic profile may factor into his treatment decision-making when it comes to using immunotherapy or immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy, he said.
“Is that the only factor that is going to make me choose one thing or another? No,” Dr. Sehgal said. However, he said it would make him more “proactive in making sure the patient is doing clinically okay” and in determining when to obtain on-treatment imaging studies.
Dr. Subbiah emphasized the relative benefit of immunotherapy, noting that survival with chemotherapy for many difficult-to-treat cancers in the relapsed/refractory metastatic setting is less than 2 years.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has allowed some of these patients to live longer (with survival reported to be more than 10 years for patients with metastatic melanoma).
“Immunotherapy has been a game changer; it has been transformative in the lives of these patients,” Dr. Subbiah said. “So unless there is any other contraindication, the benefit of receiving immunotherapy for an approved indication far outweighs the risk of HPD.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves loncastuximab for diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
The Food and Drug Administration granted an accelerated approval April 24, 2021, for a new drug for use in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) who have tried at least two prior systemic therapies.
The new product, loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl (Zynlonta, ADC Therapeutics), is the first and only CD19-targeted antibody-drug conjugate approved for this disease.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States, but the indication also includes DLBCL not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
“There is a significant unmet need for treatment options for patients with [relapsed or refractory] DLBCL, including those who have been heavily pretreated and have difficult-to-treat disease,” Paolo F. Caimi, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in a company press release.
The company also cited data from previous clinical trials showing that more than 40% of first-line DLBCL treatments fail, and that these patients have a poor prognosis, worsening with each line of therapy that is tried.
Accelerated approval based on ORR
The accelerated approval was based on overall response rate data from the single-arm LOTIS-2 trial. All patients received the new drug, administered as a 30-minute infusion once every 3 weeks for 1 year.
The trial was conducted in 145 patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had already tried at least two lines of systemic therapy. Dr. Caimi noted that this included patients who had been heavily pretreated, as the population included patients who previously received stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
The ORR was 48.3% (70/145 patients), which included a complete response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients) and a partial response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients).
Patients had a median time to response of 1.3 months and the median duration of response for the 70 responders was 10.3 months.
“Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial,” the company noted.
A phase 3 confirmatory is underway: the LOTIS 5 trial (NCT04384484) compares the combination of loncastuximab tesirine and rituximab versus chemoimmunotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
The company also noted that in a pooled safety population the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were thrombocytopenia, an increase in levels of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase, neutropenia, anemia, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevation, fatigue, hypoalbuminemia, rash, edema, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain.
In the LOTIS-2 trial, the most common (≥10%) grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (26.2%), thrombocytopenia (17.9%), GGT increase (17.2%) and anemia (10.3%).
Permanent treatment discontinuation as the result of an adverse reaction occurred in 19% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, edema, and effusion.
Dose reductions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients, and most were the result of a GGT increase. Dosage interruptions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 49% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and edema.
Warnings on effusions, infections, and skin reactions
The product carries a warning that serious effusion and edema has been reported. Grade 3 edema occurred in 3% (primarily peripheral edema or ascites), grade 3 pleural effusion occurred in 3%, and grade 3 or 4 pericardial effusion occurred in 1%.
Prescribers are recommended to monitor patients for new or worsening edema or effusions, and to consider diagnostic imaging in patients who develop symptoms of pleural effusion or pericardial effusion, such as new or worsened dyspnea, chest pain, and/or ascites such as swelling in the abdomen and bloating.
The product also carries a warning about fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, and serious cutaneous reactions, including photosensitivity reaction, rash (including exfoliative and maculopapular), and erythema.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration granted an accelerated approval April 24, 2021, for a new drug for use in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) who have tried at least two prior systemic therapies.
The new product, loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl (Zynlonta, ADC Therapeutics), is the first and only CD19-targeted antibody-drug conjugate approved for this disease.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States, but the indication also includes DLBCL not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
“There is a significant unmet need for treatment options for patients with [relapsed or refractory] DLBCL, including those who have been heavily pretreated and have difficult-to-treat disease,” Paolo F. Caimi, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in a company press release.
The company also cited data from previous clinical trials showing that more than 40% of first-line DLBCL treatments fail, and that these patients have a poor prognosis, worsening with each line of therapy that is tried.
Accelerated approval based on ORR
The accelerated approval was based on overall response rate data from the single-arm LOTIS-2 trial. All patients received the new drug, administered as a 30-minute infusion once every 3 weeks for 1 year.
The trial was conducted in 145 patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had already tried at least two lines of systemic therapy. Dr. Caimi noted that this included patients who had been heavily pretreated, as the population included patients who previously received stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
The ORR was 48.3% (70/145 patients), which included a complete response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients) and a partial response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients).
Patients had a median time to response of 1.3 months and the median duration of response for the 70 responders was 10.3 months.
“Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial,” the company noted.
A phase 3 confirmatory is underway: the LOTIS 5 trial (NCT04384484) compares the combination of loncastuximab tesirine and rituximab versus chemoimmunotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
The company also noted that in a pooled safety population the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were thrombocytopenia, an increase in levels of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase, neutropenia, anemia, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevation, fatigue, hypoalbuminemia, rash, edema, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain.
In the LOTIS-2 trial, the most common (≥10%) grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (26.2%), thrombocytopenia (17.9%), GGT increase (17.2%) and anemia (10.3%).
Permanent treatment discontinuation as the result of an adverse reaction occurred in 19% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, edema, and effusion.
Dose reductions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients, and most were the result of a GGT increase. Dosage interruptions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 49% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and edema.
Warnings on effusions, infections, and skin reactions
The product carries a warning that serious effusion and edema has been reported. Grade 3 edema occurred in 3% (primarily peripheral edema or ascites), grade 3 pleural effusion occurred in 3%, and grade 3 or 4 pericardial effusion occurred in 1%.
Prescribers are recommended to monitor patients for new or worsening edema or effusions, and to consider diagnostic imaging in patients who develop symptoms of pleural effusion or pericardial effusion, such as new or worsened dyspnea, chest pain, and/or ascites such as swelling in the abdomen and bloating.
The product also carries a warning about fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, and serious cutaneous reactions, including photosensitivity reaction, rash (including exfoliative and maculopapular), and erythema.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration granted an accelerated approval April 24, 2021, for a new drug for use in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) who have tried at least two prior systemic therapies.
The new product, loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl (Zynlonta, ADC Therapeutics), is the first and only CD19-targeted antibody-drug conjugate approved for this disease.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States, but the indication also includes DLBCL not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
“There is a significant unmet need for treatment options for patients with [relapsed or refractory] DLBCL, including those who have been heavily pretreated and have difficult-to-treat disease,” Paolo F. Caimi, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in a company press release.
The company also cited data from previous clinical trials showing that more than 40% of first-line DLBCL treatments fail, and that these patients have a poor prognosis, worsening with each line of therapy that is tried.
Accelerated approval based on ORR
The accelerated approval was based on overall response rate data from the single-arm LOTIS-2 trial. All patients received the new drug, administered as a 30-minute infusion once every 3 weeks for 1 year.
The trial was conducted in 145 patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who had already tried at least two lines of systemic therapy. Dr. Caimi noted that this included patients who had been heavily pretreated, as the population included patients who previously received stem cell transplant or chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
The ORR was 48.3% (70/145 patients), which included a complete response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients) and a partial response rate of 24.1% (35/145 patients).
Patients had a median time to response of 1.3 months and the median duration of response for the 70 responders was 10.3 months.
“Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial,” the company noted.
A phase 3 confirmatory is underway: the LOTIS 5 trial (NCT04384484) compares the combination of loncastuximab tesirine and rituximab versus chemoimmunotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL.
The company also noted that in a pooled safety population the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were thrombocytopenia, an increase in levels of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase, neutropenia, anemia, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevation, fatigue, hypoalbuminemia, rash, edema, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain.
In the LOTIS-2 trial, the most common (≥10%) grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (26.2%), thrombocytopenia (17.9%), GGT increase (17.2%) and anemia (10.3%).
Permanent treatment discontinuation as the result of an adverse reaction occurred in 19% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, edema, and effusion.
Dose reductions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients, and most were the result of a GGT increase. Dosage interruptions because of an adverse reaction occurred in 49% of patients, and these included a GGT increase, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and edema.
Warnings on effusions, infections, and skin reactions
The product carries a warning that serious effusion and edema has been reported. Grade 3 edema occurred in 3% (primarily peripheral edema or ascites), grade 3 pleural effusion occurred in 3%, and grade 3 or 4 pericardial effusion occurred in 1%.
Prescribers are recommended to monitor patients for new or worsening edema or effusions, and to consider diagnostic imaging in patients who develop symptoms of pleural effusion or pericardial effusion, such as new or worsened dyspnea, chest pain, and/or ascites such as swelling in the abdomen and bloating.
The product also carries a warning about fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, and serious cutaneous reactions, including photosensitivity reaction, rash (including exfoliative and maculopapular), and erythema.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Frontline brentuximab vedotin shows promise in high-risk pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma
A frontline treatment regimen including brentuximab vedotin (Bv) was well tolerated, was highly effective, and significantly reduced radiation exposure in pediatric patients with high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the results of an open-label, phase 2 trial.
Of 77 patients enrolled in the investigator-initiated, single-arm, multicenter trial, 27 (35%) achieved complete remission (CR) without radiation at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy, reported Monika L. Metzger, MD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn. and colleagues. The report was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The addition of Bv also resulted in superior event-free survival (97.4%) and overall survival (98.7%) at median follow-up of 3.4 years, compared with previously published pediatric trials, such as the HOD99 trial (EFS and OS of 80.8% and 96.5%, respectively), the authors noted.
Bv chemotherapy
Bv, a targeted anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate, received expanded Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2018 for frontline use in combination with chemotherapy in adults with stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). The current study is the first to include Bv as part of a chemotherapy regimen in the frontline setting for pediatric classical HL, the authors noted, adding that their primary aim was to reduce prescribed radiation thereby limiting late toxicities associated with radiation in this population.
Patients enrolled were children and adolescents aged 18 years and under with stage IIB, IIIB, or IV classical HL. Bv was used in place of vincristine in the standard OEPA/COPDac (vincristine, etoposide, prednisone, and doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone, and dacarbazine) frontline regimen for pediatric HL.
The Bv-based chemotherapy regimen was well tolerated and mostly limited to low-grade nausea, vomiting, and constipation, and the most common adverse events were hematologic events occurring mainly during the first two cycles of chemotherapy.
“Notably, we observed a very low incidence of neuropathy (4%) by both clinician and patient report, and no participants required Bv dose reduction or discontinuation,” they wrote, explaining that neuropathy is more common with vincristine.
Radiation exposure
Residual node radiotherapy (RNRT) was delivered at a prescribed dose of 25.5 Gy in 17 fractions of 1.5 Gy, 2-4 weeks after completion of chemotherapy only to nodal sites that did not achieve a CR at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy.
“Patients treated with RNRT had significantly lower integral radiation dose compared with patients treated on HOD99 with [involved-field radiation therapy] (78.1 J vs. 249.6 J),” the authors wrote. “Doses to specific organs were also compared ... [t]he mean heart dose was reduced to 5.29 Gy from 16.9 Gy, and the mean thyroid dose was reduced to 4.46 Gy from 25.9 Gy.”
Women also had significantly less breast radiation exposure (mean of 3.21 Gy vs. 6.85 Gy in HOD99).
One irradiated patient experienced disease progression at the end of therapy, but remained disease free more than 6 years following salvage therapy, and one unexpected death occurred, the authors said.
“We have already reduced the use of radiation for low-risk Hodgkin lymphoma patients. In this study we’ve shown that it is also possible to either omit or reduce the extent of radiation for high-risk patients, using highly focal methods such as proton beam radiation or intensity modulated radiation,” co–senior author Matthew Krasin, MD, of St. Jude’s department of radiation oncology, stated in a press release.
Next steps
Co–senior author Melissa Hudson, MD, the St. Jude cancer survivorship division director, added that “[b]eing able to offer Hodgkin lymphoma patients a targeted therapy in the frontline setting is an exciting development.
“The favorable safety and toxicity profile of Bv in combination with chemotherapy for high-risk pediatric patients supports its prospective evaluation in a randomized trial,” the authors concluded, noting that “[l]onger follow-up is required to establish if this approach reduces risk of late-occurring toxicities such as second malignant neoplasms in this cohort of minimally irradiated patients.”
The study was sponsored by Seattle Genetics. The research at St. Jude was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute and ALSAC (American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities), St. Jude’s fundraising and awareness organization. Dr. Metzger reported research funding from Seattle Genetics. Dr. Krasin reported a consulting or advisory role for Debiopharm Group. Dr. Hudson reported a consulting or advisory role for Oncology Research Information Exchange Network, Princess Máxima Center.
A frontline treatment regimen including brentuximab vedotin (Bv) was well tolerated, was highly effective, and significantly reduced radiation exposure in pediatric patients with high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the results of an open-label, phase 2 trial.
Of 77 patients enrolled in the investigator-initiated, single-arm, multicenter trial, 27 (35%) achieved complete remission (CR) without radiation at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy, reported Monika L. Metzger, MD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn. and colleagues. The report was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The addition of Bv also resulted in superior event-free survival (97.4%) and overall survival (98.7%) at median follow-up of 3.4 years, compared with previously published pediatric trials, such as the HOD99 trial (EFS and OS of 80.8% and 96.5%, respectively), the authors noted.
Bv chemotherapy
Bv, a targeted anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate, received expanded Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2018 for frontline use in combination with chemotherapy in adults with stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). The current study is the first to include Bv as part of a chemotherapy regimen in the frontline setting for pediatric classical HL, the authors noted, adding that their primary aim was to reduce prescribed radiation thereby limiting late toxicities associated with radiation in this population.
Patients enrolled were children and adolescents aged 18 years and under with stage IIB, IIIB, or IV classical HL. Bv was used in place of vincristine in the standard OEPA/COPDac (vincristine, etoposide, prednisone, and doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone, and dacarbazine) frontline regimen for pediatric HL.
The Bv-based chemotherapy regimen was well tolerated and mostly limited to low-grade nausea, vomiting, and constipation, and the most common adverse events were hematologic events occurring mainly during the first two cycles of chemotherapy.
“Notably, we observed a very low incidence of neuropathy (4%) by both clinician and patient report, and no participants required Bv dose reduction or discontinuation,” they wrote, explaining that neuropathy is more common with vincristine.
Radiation exposure
Residual node radiotherapy (RNRT) was delivered at a prescribed dose of 25.5 Gy in 17 fractions of 1.5 Gy, 2-4 weeks after completion of chemotherapy only to nodal sites that did not achieve a CR at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy.
“Patients treated with RNRT had significantly lower integral radiation dose compared with patients treated on HOD99 with [involved-field radiation therapy] (78.1 J vs. 249.6 J),” the authors wrote. “Doses to specific organs were also compared ... [t]he mean heart dose was reduced to 5.29 Gy from 16.9 Gy, and the mean thyroid dose was reduced to 4.46 Gy from 25.9 Gy.”
Women also had significantly less breast radiation exposure (mean of 3.21 Gy vs. 6.85 Gy in HOD99).
One irradiated patient experienced disease progression at the end of therapy, but remained disease free more than 6 years following salvage therapy, and one unexpected death occurred, the authors said.
“We have already reduced the use of radiation for low-risk Hodgkin lymphoma patients. In this study we’ve shown that it is also possible to either omit or reduce the extent of radiation for high-risk patients, using highly focal methods such as proton beam radiation or intensity modulated radiation,” co–senior author Matthew Krasin, MD, of St. Jude’s department of radiation oncology, stated in a press release.
Next steps
Co–senior author Melissa Hudson, MD, the St. Jude cancer survivorship division director, added that “[b]eing able to offer Hodgkin lymphoma patients a targeted therapy in the frontline setting is an exciting development.
“The favorable safety and toxicity profile of Bv in combination with chemotherapy for high-risk pediatric patients supports its prospective evaluation in a randomized trial,” the authors concluded, noting that “[l]onger follow-up is required to establish if this approach reduces risk of late-occurring toxicities such as second malignant neoplasms in this cohort of minimally irradiated patients.”
The study was sponsored by Seattle Genetics. The research at St. Jude was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute and ALSAC (American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities), St. Jude’s fundraising and awareness organization. Dr. Metzger reported research funding from Seattle Genetics. Dr. Krasin reported a consulting or advisory role for Debiopharm Group. Dr. Hudson reported a consulting or advisory role for Oncology Research Information Exchange Network, Princess Máxima Center.
A frontline treatment regimen including brentuximab vedotin (Bv) was well tolerated, was highly effective, and significantly reduced radiation exposure in pediatric patients with high-risk Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the results of an open-label, phase 2 trial.
Of 77 patients enrolled in the investigator-initiated, single-arm, multicenter trial, 27 (35%) achieved complete remission (CR) without radiation at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy, reported Monika L. Metzger, MD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn. and colleagues. The report was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The addition of Bv also resulted in superior event-free survival (97.4%) and overall survival (98.7%) at median follow-up of 3.4 years, compared with previously published pediatric trials, such as the HOD99 trial (EFS and OS of 80.8% and 96.5%, respectively), the authors noted.
Bv chemotherapy
Bv, a targeted anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate, received expanded Food and Drug Administration approval in March 2018 for frontline use in combination with chemotherapy in adults with stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). The current study is the first to include Bv as part of a chemotherapy regimen in the frontline setting for pediatric classical HL, the authors noted, adding that their primary aim was to reduce prescribed radiation thereby limiting late toxicities associated with radiation in this population.
Patients enrolled were children and adolescents aged 18 years and under with stage IIB, IIIB, or IV classical HL. Bv was used in place of vincristine in the standard OEPA/COPDac (vincristine, etoposide, prednisone, and doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone, and dacarbazine) frontline regimen for pediatric HL.
The Bv-based chemotherapy regimen was well tolerated and mostly limited to low-grade nausea, vomiting, and constipation, and the most common adverse events were hematologic events occurring mainly during the first two cycles of chemotherapy.
“Notably, we observed a very low incidence of neuropathy (4%) by both clinician and patient report, and no participants required Bv dose reduction or discontinuation,” they wrote, explaining that neuropathy is more common with vincristine.
Radiation exposure
Residual node radiotherapy (RNRT) was delivered at a prescribed dose of 25.5 Gy in 17 fractions of 1.5 Gy, 2-4 weeks after completion of chemotherapy only to nodal sites that did not achieve a CR at the early response assessment (ERA) after two cycles of therapy.
“Patients treated with RNRT had significantly lower integral radiation dose compared with patients treated on HOD99 with [involved-field radiation therapy] (78.1 J vs. 249.6 J),” the authors wrote. “Doses to specific organs were also compared ... [t]he mean heart dose was reduced to 5.29 Gy from 16.9 Gy, and the mean thyroid dose was reduced to 4.46 Gy from 25.9 Gy.”
Women also had significantly less breast radiation exposure (mean of 3.21 Gy vs. 6.85 Gy in HOD99).
One irradiated patient experienced disease progression at the end of therapy, but remained disease free more than 6 years following salvage therapy, and one unexpected death occurred, the authors said.
“We have already reduced the use of radiation for low-risk Hodgkin lymphoma patients. In this study we’ve shown that it is also possible to either omit or reduce the extent of radiation for high-risk patients, using highly focal methods such as proton beam radiation or intensity modulated radiation,” co–senior author Matthew Krasin, MD, of St. Jude’s department of radiation oncology, stated in a press release.
Next steps
Co–senior author Melissa Hudson, MD, the St. Jude cancer survivorship division director, added that “[b]eing able to offer Hodgkin lymphoma patients a targeted therapy in the frontline setting is an exciting development.
“The favorable safety and toxicity profile of Bv in combination with chemotherapy for high-risk pediatric patients supports its prospective evaluation in a randomized trial,” the authors concluded, noting that “[l]onger follow-up is required to establish if this approach reduces risk of late-occurring toxicities such as second malignant neoplasms in this cohort of minimally irradiated patients.”
The study was sponsored by Seattle Genetics. The research at St. Jude was funded in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute and ALSAC (American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities), St. Jude’s fundraising and awareness organization. Dr. Metzger reported research funding from Seattle Genetics. Dr. Krasin reported a consulting or advisory role for Debiopharm Group. Dr. Hudson reported a consulting or advisory role for Oncology Research Information Exchange Network, Princess Máxima Center.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Personalized cancer vaccine shows early promise across tumor types
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
FROM AACR 2021
Evidence favors lower-dose R-CHOP for fit, very elderly DLBCL patients
A dose-adjusted R-CHOP may be the best treatment for elderly patients with diffuse large beta-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a review of 38 studies that examined this aged population.
In addition, treatment choices based on new tools such as the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment appeared to provide useful guidance based on the comorbidities and frailty index of this group of patients, according to Alda Tavares, MD, of Hospital Pedro Hispano, Matosinhos (Portugal) Local Health Unit, and Ilídia Moreira, MD, of the Portuguese Institute of Oncology of Porto.
Study characteristics
Of the 38 studies assessed, 13 were retrospective and 25 were phase II/III clinical trials. Most of these studies investigated the efficacy of dose-adjusted R-CHOP regimen, according to the review published online in Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.
Alternative therapeutic drugs as well as the use of geriatric assessment were also investigated.
In terms of the elderly populations assessed, 11 out of 38 studies included at least 30 patients over age 80 years, although 11 other studies did not specify the number of patients older than 80 years. Eight of the studies included exclusively patients aged 80 years and over. Three of these studies were phase II trials.
Only six of the clinical trials required a geriatric assessment tool for inclusion criteria or therapeutic regime choice, using the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale–Geriatric (CIRS-G), the performance in activities of daily living (ADL) and/or instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) tools.
Most of the studies investigated the efficacy of R-CHOP regimen at different doses and variations, with 11 studies using alternative anthracycline in place of doxorubicin.
MiniCHOP mattered
Elderly patients over 80 years achieved complete response (CR) rates from 37.2% to 66.7% and 2-year overall survival (OS) from 31.9% to 64.7% across the studies reviewed. Overall, for fit patients aged 80 and over, the strongest evidence favored the use of an R-miniCHOP regimen, according to the authors.
In the 25 studies with treatment based on R-CHOP/modified R-CHOP or immunochemotherapy with an alternative anthracycline, the CR rate was below 50% in three studies and over 60% in the majority. Higher CR rates of 71%-88.9% were achieved in eight studies.
For patients over 80 years, the strongest evidence favored rituximab/ofatumumab-miniCHOP, based on two studies. In both studies, patients over 80 years old, without significant comorbidities, received CHOP regime with a dose reduction of about 50% (miniCHOP: cyclophosphamide 400 mg/m2, doxorubicin 25 mg/m2, and 1 mg vincristine on day 1 of each cycle, and prednisone 40 mg/m2 on days 1-5) plus an anti–CD-20 antibody (rituximab 375 mg/m2 or ofatumumab 1,000 mg). The first of these studies obtained CR rate of 62% and 2-year OS of 59% with low toxicities. The second study achieved slightly better results, according to the reviewers, who suggested the difference was possibly because of a prephase treatment and/or the use of ofatumumab.
One study group developed a simple prognostic model based on multivariate analysis of 108 patients aged 80 years and older treated in their study with R-CHOP at full (48%) or reduced dose (51%). Patients with at least two out of three risk factors (age > 85 years, revised International Prognostic Index score 3-5 and CIRS > 5) had worse survival than did those with 0-1 risk factors, with a median OS of 12 months vs. 45 months, P = .001, respectively).
“All these studies results favor the tailored treatment approach,” the reviewers stated. “More prospective studies are still needed to demonstrate and validate the adequate tools for the selection of patients and their optimal treatment. They would provide the grounds for clinical therapeutic decision, aiming for tailored treatment and fulfilling best individual expectations and outcome,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no research funds for the study and that they had no disclosures.
A dose-adjusted R-CHOP may be the best treatment for elderly patients with diffuse large beta-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a review of 38 studies that examined this aged population.
In addition, treatment choices based on new tools such as the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment appeared to provide useful guidance based on the comorbidities and frailty index of this group of patients, according to Alda Tavares, MD, of Hospital Pedro Hispano, Matosinhos (Portugal) Local Health Unit, and Ilídia Moreira, MD, of the Portuguese Institute of Oncology of Porto.
Study characteristics
Of the 38 studies assessed, 13 were retrospective and 25 were phase II/III clinical trials. Most of these studies investigated the efficacy of dose-adjusted R-CHOP regimen, according to the review published online in Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.
Alternative therapeutic drugs as well as the use of geriatric assessment were also investigated.
In terms of the elderly populations assessed, 11 out of 38 studies included at least 30 patients over age 80 years, although 11 other studies did not specify the number of patients older than 80 years. Eight of the studies included exclusively patients aged 80 years and over. Three of these studies were phase II trials.
Only six of the clinical trials required a geriatric assessment tool for inclusion criteria or therapeutic regime choice, using the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale–Geriatric (CIRS-G), the performance in activities of daily living (ADL) and/or instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) tools.
Most of the studies investigated the efficacy of R-CHOP regimen at different doses and variations, with 11 studies using alternative anthracycline in place of doxorubicin.
MiniCHOP mattered
Elderly patients over 80 years achieved complete response (CR) rates from 37.2% to 66.7% and 2-year overall survival (OS) from 31.9% to 64.7% across the studies reviewed. Overall, for fit patients aged 80 and over, the strongest evidence favored the use of an R-miniCHOP regimen, according to the authors.
In the 25 studies with treatment based on R-CHOP/modified R-CHOP or immunochemotherapy with an alternative anthracycline, the CR rate was below 50% in three studies and over 60% in the majority. Higher CR rates of 71%-88.9% were achieved in eight studies.
For patients over 80 years, the strongest evidence favored rituximab/ofatumumab-miniCHOP, based on two studies. In both studies, patients over 80 years old, without significant comorbidities, received CHOP regime with a dose reduction of about 50% (miniCHOP: cyclophosphamide 400 mg/m2, doxorubicin 25 mg/m2, and 1 mg vincristine on day 1 of each cycle, and prednisone 40 mg/m2 on days 1-5) plus an anti–CD-20 antibody (rituximab 375 mg/m2 or ofatumumab 1,000 mg). The first of these studies obtained CR rate of 62% and 2-year OS of 59% with low toxicities. The second study achieved slightly better results, according to the reviewers, who suggested the difference was possibly because of a prephase treatment and/or the use of ofatumumab.
One study group developed a simple prognostic model based on multivariate analysis of 108 patients aged 80 years and older treated in their study with R-CHOP at full (48%) or reduced dose (51%). Patients with at least two out of three risk factors (age > 85 years, revised International Prognostic Index score 3-5 and CIRS > 5) had worse survival than did those with 0-1 risk factors, with a median OS of 12 months vs. 45 months, P = .001, respectively).
“All these studies results favor the tailored treatment approach,” the reviewers stated. “More prospective studies are still needed to demonstrate and validate the adequate tools for the selection of patients and their optimal treatment. They would provide the grounds for clinical therapeutic decision, aiming for tailored treatment and fulfilling best individual expectations and outcome,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no research funds for the study and that they had no disclosures.
A dose-adjusted R-CHOP may be the best treatment for elderly patients with diffuse large beta-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to a review of 38 studies that examined this aged population.
In addition, treatment choices based on new tools such as the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment appeared to provide useful guidance based on the comorbidities and frailty index of this group of patients, according to Alda Tavares, MD, of Hospital Pedro Hispano, Matosinhos (Portugal) Local Health Unit, and Ilídia Moreira, MD, of the Portuguese Institute of Oncology of Porto.
Study characteristics
Of the 38 studies assessed, 13 were retrospective and 25 were phase II/III clinical trials. Most of these studies investigated the efficacy of dose-adjusted R-CHOP regimen, according to the review published online in Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.
Alternative therapeutic drugs as well as the use of geriatric assessment were also investigated.
In terms of the elderly populations assessed, 11 out of 38 studies included at least 30 patients over age 80 years, although 11 other studies did not specify the number of patients older than 80 years. Eight of the studies included exclusively patients aged 80 years and over. Three of these studies were phase II trials.
Only six of the clinical trials required a geriatric assessment tool for inclusion criteria or therapeutic regime choice, using the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale–Geriatric (CIRS-G), the performance in activities of daily living (ADL) and/or instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) tools.
Most of the studies investigated the efficacy of R-CHOP regimen at different doses and variations, with 11 studies using alternative anthracycline in place of doxorubicin.
MiniCHOP mattered
Elderly patients over 80 years achieved complete response (CR) rates from 37.2% to 66.7% and 2-year overall survival (OS) from 31.9% to 64.7% across the studies reviewed. Overall, for fit patients aged 80 and over, the strongest evidence favored the use of an R-miniCHOP regimen, according to the authors.
In the 25 studies with treatment based on R-CHOP/modified R-CHOP or immunochemotherapy with an alternative anthracycline, the CR rate was below 50% in three studies and over 60% in the majority. Higher CR rates of 71%-88.9% were achieved in eight studies.
For patients over 80 years, the strongest evidence favored rituximab/ofatumumab-miniCHOP, based on two studies. In both studies, patients over 80 years old, without significant comorbidities, received CHOP regime with a dose reduction of about 50% (miniCHOP: cyclophosphamide 400 mg/m2, doxorubicin 25 mg/m2, and 1 mg vincristine on day 1 of each cycle, and prednisone 40 mg/m2 on days 1-5) plus an anti–CD-20 antibody (rituximab 375 mg/m2 or ofatumumab 1,000 mg). The first of these studies obtained CR rate of 62% and 2-year OS of 59% with low toxicities. The second study achieved slightly better results, according to the reviewers, who suggested the difference was possibly because of a prephase treatment and/or the use of ofatumumab.
One study group developed a simple prognostic model based on multivariate analysis of 108 patients aged 80 years and older treated in their study with R-CHOP at full (48%) or reduced dose (51%). Patients with at least two out of three risk factors (age > 85 years, revised International Prognostic Index score 3-5 and CIRS > 5) had worse survival than did those with 0-1 risk factors, with a median OS of 12 months vs. 45 months, P = .001, respectively).
“All these studies results favor the tailored treatment approach,” the reviewers stated. “More prospective studies are still needed to demonstrate and validate the adequate tools for the selection of patients and their optimal treatment. They would provide the grounds for clinical therapeutic decision, aiming for tailored treatment and fulfilling best individual expectations and outcome,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no research funds for the study and that they had no disclosures.
FROM CRITICAL REVIEWS IN ONCOLOGY/HEMATOLOGY
Combo provides ‘broad benefit’ across NHL subtypes
The trial, dubbed CHRONOS-3, is the first to report “a broad benefit” across histologic subtypes of relapsed, indolent NHL, and the results are “essentially a long-awaited proof of concept” for combining a PI3K inhibitor with rituximab, according to investigator Matthew Matasar, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Matasar presented results from CHRONOS-3 at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT001). The findings were simultaneously published in The Lancet Oncology.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, called the results “strongly positive” and said the copanlisib-rituximab combination is “a potential new treatment option” for indolent NHL in patients with a long remission after first-line therapy or those who are unfit for chemotherapy.
Dr. Swanton noted, however, that “one should also bear in mind” the serious adverse events (AEs) seen with copanlisib, particularly hypertension and hyperglycemia. When asked about these AEs, Dr. Matasar said he thinks the combination would be appropriate for patients who meet the study criteria as long as they don’t have severe baseline diabetes or uncontrolled hypertension.
Patient and treatment details
The study included 458 patients with CD20-positive, relapsed, indolent, B-cell NHL. Subtypes included follicular lymphoma (n = 275), marginal zone lymphoma (n = 95), small lymphocytic lymphoma (n = 50), and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (n = 38).
All patients were progression free and treatment free before their relapse for at least 12 months after their last rituximab-containing regimen, or at least 6 months before relapse if they were unwilling or unable to undergo chemotherapy.
The patients’ median age was 63 years, and just over half of them were men (52%). About 37% of patients had a history of hypertension at baseline, and about 15% had a history of diabetes.
Patients were randomized to receive copanlisib plus rituximab (n = 307) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 151). Copanlisib was given at 60 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle. In both arms, rituximab was given at 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, and 9.
Progression-free survival benefit
At a median follow-up of 19.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 21.5 months in the copanlisib-rituximab arm and 13.8 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .0001).
The PFS advantage with copanlisib was seen across subtypes:
- Follicular lymphoma – 22.2 months vs. 18.7 months (P = .001)
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma – 14.2 months vs. 5.7 months (P < .0001)
- Marginal zone lymphoma – 22.1 months vs. 11.5 months (P = .012)
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia – 33.4 months vs. 16.6 months (P = .054)
The PFS difference among patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia was likely not statistically significant because of the small sample size, Dr. Matasar said.
He reported that the overall response rate was 81% with copanlisib-rituximab, including a 34% complete response rate. In the placebo arm, the overall response rate was 48%, and 15% of patients had a complete response.
The median overall survival was not estimable in either treatment arm. At a median follow-up of 30.1 months, 14% of patients in the copanlisib arm and 13.2% of patients in the placebo arm had died.
More than double the rate of serious AEs
The rate of serious treatment-emergent AEs was 47.2% in the combination arm and 18.5% in the placebo arm.
There were six grade 5 treatment-emergent AEs in the combination arm. One of these – pneumonitis – was deemed treatment related. There was one treatment-emergent death in the placebo arm.
Hyperglycemia and hypertension were the most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent AEs with the combination. Diarrhea, nausea, neutropenia, and pyrexia were also more frequent with the combination than with rituximab-placebo.
More than half of patients in the combination arm (56.3%) developed grade 3/4 hyperglycemia. In the placebo arm, the incidence of grade 3 hyperglycemia was 8.2%, and there was no grade 4 hyperglycemia.
Rates of grade 3 hypertension were 39.7% in the combination arm and 8.9% in the placebo arm. There was no grade 4 hypertension.
In the combination arm, 2.6% of patients stopped treatment because of hyperglycemia and 0.7% stopped because of hypertension.
Any-grade pneumonitis occurred in 6.8% of patients in the combination arm and 1.4% of those in the placebo arm. The rate of grade 3/4 pneumonitis was 2.7% in the copanlisib arm, and the rate of grade 3 pneumonitis was 0.7% in the placebo arm.
The study was funded by Bayer, the company developing copanlisib. Dr. Matasar disclosed relationships with Bayer, its subsidiaries, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
The trial, dubbed CHRONOS-3, is the first to report “a broad benefit” across histologic subtypes of relapsed, indolent NHL, and the results are “essentially a long-awaited proof of concept” for combining a PI3K inhibitor with rituximab, according to investigator Matthew Matasar, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Matasar presented results from CHRONOS-3 at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT001). The findings were simultaneously published in The Lancet Oncology.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, called the results “strongly positive” and said the copanlisib-rituximab combination is “a potential new treatment option” for indolent NHL in patients with a long remission after first-line therapy or those who are unfit for chemotherapy.
Dr. Swanton noted, however, that “one should also bear in mind” the serious adverse events (AEs) seen with copanlisib, particularly hypertension and hyperglycemia. When asked about these AEs, Dr. Matasar said he thinks the combination would be appropriate for patients who meet the study criteria as long as they don’t have severe baseline diabetes or uncontrolled hypertension.
Patient and treatment details
The study included 458 patients with CD20-positive, relapsed, indolent, B-cell NHL. Subtypes included follicular lymphoma (n = 275), marginal zone lymphoma (n = 95), small lymphocytic lymphoma (n = 50), and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (n = 38).
All patients were progression free and treatment free before their relapse for at least 12 months after their last rituximab-containing regimen, or at least 6 months before relapse if they were unwilling or unable to undergo chemotherapy.
The patients’ median age was 63 years, and just over half of them were men (52%). About 37% of patients had a history of hypertension at baseline, and about 15% had a history of diabetes.
Patients were randomized to receive copanlisib plus rituximab (n = 307) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 151). Copanlisib was given at 60 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle. In both arms, rituximab was given at 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, and 9.
Progression-free survival benefit
At a median follow-up of 19.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 21.5 months in the copanlisib-rituximab arm and 13.8 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .0001).
The PFS advantage with copanlisib was seen across subtypes:
- Follicular lymphoma – 22.2 months vs. 18.7 months (P = .001)
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma – 14.2 months vs. 5.7 months (P < .0001)
- Marginal zone lymphoma – 22.1 months vs. 11.5 months (P = .012)
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia – 33.4 months vs. 16.6 months (P = .054)
The PFS difference among patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia was likely not statistically significant because of the small sample size, Dr. Matasar said.
He reported that the overall response rate was 81% with copanlisib-rituximab, including a 34% complete response rate. In the placebo arm, the overall response rate was 48%, and 15% of patients had a complete response.
The median overall survival was not estimable in either treatment arm. At a median follow-up of 30.1 months, 14% of patients in the copanlisib arm and 13.2% of patients in the placebo arm had died.
More than double the rate of serious AEs
The rate of serious treatment-emergent AEs was 47.2% in the combination arm and 18.5% in the placebo arm.
There were six grade 5 treatment-emergent AEs in the combination arm. One of these – pneumonitis – was deemed treatment related. There was one treatment-emergent death in the placebo arm.
Hyperglycemia and hypertension were the most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent AEs with the combination. Diarrhea, nausea, neutropenia, and pyrexia were also more frequent with the combination than with rituximab-placebo.
More than half of patients in the combination arm (56.3%) developed grade 3/4 hyperglycemia. In the placebo arm, the incidence of grade 3 hyperglycemia was 8.2%, and there was no grade 4 hyperglycemia.
Rates of grade 3 hypertension were 39.7% in the combination arm and 8.9% in the placebo arm. There was no grade 4 hypertension.
In the combination arm, 2.6% of patients stopped treatment because of hyperglycemia and 0.7% stopped because of hypertension.
Any-grade pneumonitis occurred in 6.8% of patients in the combination arm and 1.4% of those in the placebo arm. The rate of grade 3/4 pneumonitis was 2.7% in the copanlisib arm, and the rate of grade 3 pneumonitis was 0.7% in the placebo arm.
The study was funded by Bayer, the company developing copanlisib. Dr. Matasar disclosed relationships with Bayer, its subsidiaries, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
The trial, dubbed CHRONOS-3, is the first to report “a broad benefit” across histologic subtypes of relapsed, indolent NHL, and the results are “essentially a long-awaited proof of concept” for combining a PI3K inhibitor with rituximab, according to investigator Matthew Matasar, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Matasar presented results from CHRONOS-3 at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT001). The findings were simultaneously published in The Lancet Oncology.
Charles Swanton, MBPhD, of the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Cancer Institute in London, called the results “strongly positive” and said the copanlisib-rituximab combination is “a potential new treatment option” for indolent NHL in patients with a long remission after first-line therapy or those who are unfit for chemotherapy.
Dr. Swanton noted, however, that “one should also bear in mind” the serious adverse events (AEs) seen with copanlisib, particularly hypertension and hyperglycemia. When asked about these AEs, Dr. Matasar said he thinks the combination would be appropriate for patients who meet the study criteria as long as they don’t have severe baseline diabetes or uncontrolled hypertension.
Patient and treatment details
The study included 458 patients with CD20-positive, relapsed, indolent, B-cell NHL. Subtypes included follicular lymphoma (n = 275), marginal zone lymphoma (n = 95), small lymphocytic lymphoma (n = 50), and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (n = 38).
All patients were progression free and treatment free before their relapse for at least 12 months after their last rituximab-containing regimen, or at least 6 months before relapse if they were unwilling or unable to undergo chemotherapy.
The patients’ median age was 63 years, and just over half of them were men (52%). About 37% of patients had a history of hypertension at baseline, and about 15% had a history of diabetes.
Patients were randomized to receive copanlisib plus rituximab (n = 307) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 151). Copanlisib was given at 60 mg IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle. In both arms, rituximab was given at 375 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 during cycle 1 and on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, and 9.
Progression-free survival benefit
At a median follow-up of 19.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 21.5 months in the copanlisib-rituximab arm and 13.8 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (hazard ratio, 0.52; P < .0001).
The PFS advantage with copanlisib was seen across subtypes:
- Follicular lymphoma – 22.2 months vs. 18.7 months (P = .001)
- Small lymphocytic lymphoma – 14.2 months vs. 5.7 months (P < .0001)
- Marginal zone lymphoma – 22.1 months vs. 11.5 months (P = .012)
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia – 33.4 months vs. 16.6 months (P = .054)
The PFS difference among patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia was likely not statistically significant because of the small sample size, Dr. Matasar said.
He reported that the overall response rate was 81% with copanlisib-rituximab, including a 34% complete response rate. In the placebo arm, the overall response rate was 48%, and 15% of patients had a complete response.
The median overall survival was not estimable in either treatment arm. At a median follow-up of 30.1 months, 14% of patients in the copanlisib arm and 13.2% of patients in the placebo arm had died.
More than double the rate of serious AEs
The rate of serious treatment-emergent AEs was 47.2% in the combination arm and 18.5% in the placebo arm.
There were six grade 5 treatment-emergent AEs in the combination arm. One of these – pneumonitis – was deemed treatment related. There was one treatment-emergent death in the placebo arm.
Hyperglycemia and hypertension were the most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent AEs with the combination. Diarrhea, nausea, neutropenia, and pyrexia were also more frequent with the combination than with rituximab-placebo.
More than half of patients in the combination arm (56.3%) developed grade 3/4 hyperglycemia. In the placebo arm, the incidence of grade 3 hyperglycemia was 8.2%, and there was no grade 4 hyperglycemia.
Rates of grade 3 hypertension were 39.7% in the combination arm and 8.9% in the placebo arm. There was no grade 4 hypertension.
In the combination arm, 2.6% of patients stopped treatment because of hyperglycemia and 0.7% stopped because of hypertension.
Any-grade pneumonitis occurred in 6.8% of patients in the combination arm and 1.4% of those in the placebo arm. The rate of grade 3/4 pneumonitis was 2.7% in the copanlisib arm, and the rate of grade 3 pneumonitis was 0.7% in the placebo arm.
The study was funded by Bayer, the company developing copanlisib. Dr. Matasar disclosed relationships with Bayer, its subsidiaries, and Roche/Genentech. Dr. Swanton disclosed relationships with numerous companies, including Pfizer, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline.
FROM AACR 2021
Steroid-refractory pneumonitis from ICIs: Experience at major centers
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Cancer screening stopped by pandemic: Repercussions to come?
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Steroids can be stopped in some older multiple myeloma patients
For select older patients, it is safe to switch to a lower dose of lenalidomide maintenance therapy and discontinue dexamethasone after 9 months. The regimen is safe and yields outcomes similar to those of standard, continuous lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd), according to new findings.
At a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the experimental arm in which dexamethasone therapy was stopped (Rd-R) versus 6.9 months for standard therapy. The tailored approach also resulted in fewer adverse effects.
The authors noted that there was no difference in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival between the two groups.
“These results may be useful for the treatment of myeloma patients, since approximately one-third of patients not eligible for stem cell transplantation are intermediate fit, the population in our study,” said lead author Alessandra Larocca, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology-oncology of the University Hospital Città della Salute e della Scienza, Torino, Italy.
She said in an interview that they expect that these findings “may help to optimize the treatment of less-fit elderly patients by reducing the occurrence of adverse events and thus improving outcomes and preserving quality of life of these patients.”
This approach is a viable option for clinicians to consider for some patient subgroups. “This steroid-sparing approach can also be used in other combinations,” she said. “Ongoing trials are now evaluating steroid sparing in combination with monoclonal antibodies or the role of frailty-guided treatment.”
The study was published March 19, 2021, in Blood.
Curtailing steroids
Myeloma patients aged 75 years or older or who have comorbidities and functional impairments are an understudied population. They are more susceptible to adverse events that may negatively affect the duration of treatment and outcomes. Steroids are “scarcely tolerated” in the long term, even among younger patients, and “whether sparing dexamethasone is as effective as prolonged steroid exposure remains an open issue,” the authors wrote. There are still no clear data on the advantage of continuous steroid treatment as opposed to fixed-duration treatment for newly diagnosed patients.
In 2010, a study compared high-dose with low-dose dexamethasone. As expected, the rate of adverse events was lower among patients who received the low-dose steroid, but quite unexpectedly, deaths with high-dose dexamethasone were significantly higher than with low-dose dexamethasone.
The 1-year overall survival was 96% among patients who received the low dose of dexamethasone versus 87% with the standard high dose.
S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who was the lead author of the 2010 study, spoke with this new organization about the current study. “This is an important and practice-changing study,” he said. “We have already changed our practice and recommendations based on this study.”
He explained that, for transplant-ineligible patients, instead of initial therapy with bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone followed by Rd, they use lenalidomide alone without steroids.
“After 9 months of initial therapy, I now recommend we stop dexamethasone unless we are having problems controlling the myeloma, such as progressive disease,” Dr. Rajkumar said. “I congratulate the authors on a study that will improve the quality of life for our patients.”
Improved event-free survival
In this study, Dr. Larocca and colleagues investigated the efficacy and feasibility of a dose- and schedule-adjusted Rd regimen that was followed by maintenance Rd-R 10 mg/d and compared the regimen with continuous Rd in elderly, intermediate-fit patients who were newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma.
The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as progression/death from any cause, lenalidomide discontinuation, and any hematologic grade 4 or nonhematologic grade 3-4 adverse events.
The cohort consisted of 199 patients who were randomly assigned to receive either Rd-R (n = 101) or continuous Rd (n = 98). The median age was 75 years in the Rd-R arm and 76 years in the Rd arm; 52% of patients in the Rd-R group and 43% in the Rd group were classified as being intermediate fit not for age but for geriatric impairments.
With a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the Rd-R arm versus 6.9 months in the Rd arm (hazard ratio, 0.70; P = .02). This benefit was maintained beyond nine cycles (median: 19.8 vs. 10.6 months for Rd-R vs. Rd; HR, 0.55; P = .03)
The median PFS was 20.2 months with Rd-R and 18.3 months with Rd (HR, 0.78; P = .16). The median overall survival was not reached. The 3-year overall survival was 74% with Rd-R and 63% with continuous Rd (HR, 0.62; P = .06). Among patients remaining on therapy after nine cycles, no difference in median PFS was observed between the two groups (24.3 vs. 18.7 months; HR, 0.73; P = .19).
Best response was similar for both groups, with an overall response rate of 78% versus 68% (P = .15). The very good partial response rate was 51% in the Rd-R arm versus 39% in the continuous Rd arm (P = .09).
Toxicities were similar between the two groups. Hematologic adverse events of at least grade 3 were reported in 26% of Rd-R patients versus 20% of Rd patients (P = .40). In both groups, the most frequent grade ≥3 hematologic toxicity was neutropenia (21% vs 18%). The most frequent grade ≥3 toxicities were nonhematologic. They occurred in 33% of Rd-R patients and 43% of Rd patients (P = .15). The most frequent nonhematologic toxicities were infections (10% vs. 12%), constitutional (3% vs. 12%), dermatologic (7% vs. 3%), and central nervous toxicities (2% vs. 6%).
The study was sponsored by Fondazione EMN Italy Onlus. Dr. Larocca has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and GlaxoSmithKline, and has served on the advisory boards for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. Several coauthors also have disclosed relationships with industry. Dr. Rajkumar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For select older patients, it is safe to switch to a lower dose of lenalidomide maintenance therapy and discontinue dexamethasone after 9 months. The regimen is safe and yields outcomes similar to those of standard, continuous lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd), according to new findings.
At a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the experimental arm in which dexamethasone therapy was stopped (Rd-R) versus 6.9 months for standard therapy. The tailored approach also resulted in fewer adverse effects.
The authors noted that there was no difference in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival between the two groups.
“These results may be useful for the treatment of myeloma patients, since approximately one-third of patients not eligible for stem cell transplantation are intermediate fit, the population in our study,” said lead author Alessandra Larocca, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology-oncology of the University Hospital Città della Salute e della Scienza, Torino, Italy.
She said in an interview that they expect that these findings “may help to optimize the treatment of less-fit elderly patients by reducing the occurrence of adverse events and thus improving outcomes and preserving quality of life of these patients.”
This approach is a viable option for clinicians to consider for some patient subgroups. “This steroid-sparing approach can also be used in other combinations,” she said. “Ongoing trials are now evaluating steroid sparing in combination with monoclonal antibodies or the role of frailty-guided treatment.”
The study was published March 19, 2021, in Blood.
Curtailing steroids
Myeloma patients aged 75 years or older or who have comorbidities and functional impairments are an understudied population. They are more susceptible to adverse events that may negatively affect the duration of treatment and outcomes. Steroids are “scarcely tolerated” in the long term, even among younger patients, and “whether sparing dexamethasone is as effective as prolonged steroid exposure remains an open issue,” the authors wrote. There are still no clear data on the advantage of continuous steroid treatment as opposed to fixed-duration treatment for newly diagnosed patients.
In 2010, a study compared high-dose with low-dose dexamethasone. As expected, the rate of adverse events was lower among patients who received the low-dose steroid, but quite unexpectedly, deaths with high-dose dexamethasone were significantly higher than with low-dose dexamethasone.
The 1-year overall survival was 96% among patients who received the low dose of dexamethasone versus 87% with the standard high dose.
S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who was the lead author of the 2010 study, spoke with this new organization about the current study. “This is an important and practice-changing study,” he said. “We have already changed our practice and recommendations based on this study.”
He explained that, for transplant-ineligible patients, instead of initial therapy with bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone followed by Rd, they use lenalidomide alone without steroids.
“After 9 months of initial therapy, I now recommend we stop dexamethasone unless we are having problems controlling the myeloma, such as progressive disease,” Dr. Rajkumar said. “I congratulate the authors on a study that will improve the quality of life for our patients.”
Improved event-free survival
In this study, Dr. Larocca and colleagues investigated the efficacy and feasibility of a dose- and schedule-adjusted Rd regimen that was followed by maintenance Rd-R 10 mg/d and compared the regimen with continuous Rd in elderly, intermediate-fit patients who were newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma.
The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as progression/death from any cause, lenalidomide discontinuation, and any hematologic grade 4 or nonhematologic grade 3-4 adverse events.
The cohort consisted of 199 patients who were randomly assigned to receive either Rd-R (n = 101) or continuous Rd (n = 98). The median age was 75 years in the Rd-R arm and 76 years in the Rd arm; 52% of patients in the Rd-R group and 43% in the Rd group were classified as being intermediate fit not for age but for geriatric impairments.
With a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the Rd-R arm versus 6.9 months in the Rd arm (hazard ratio, 0.70; P = .02). This benefit was maintained beyond nine cycles (median: 19.8 vs. 10.6 months for Rd-R vs. Rd; HR, 0.55; P = .03)
The median PFS was 20.2 months with Rd-R and 18.3 months with Rd (HR, 0.78; P = .16). The median overall survival was not reached. The 3-year overall survival was 74% with Rd-R and 63% with continuous Rd (HR, 0.62; P = .06). Among patients remaining on therapy after nine cycles, no difference in median PFS was observed between the two groups (24.3 vs. 18.7 months; HR, 0.73; P = .19).
Best response was similar for both groups, with an overall response rate of 78% versus 68% (P = .15). The very good partial response rate was 51% in the Rd-R arm versus 39% in the continuous Rd arm (P = .09).
Toxicities were similar between the two groups. Hematologic adverse events of at least grade 3 were reported in 26% of Rd-R patients versus 20% of Rd patients (P = .40). In both groups, the most frequent grade ≥3 hematologic toxicity was neutropenia (21% vs 18%). The most frequent grade ≥3 toxicities were nonhematologic. They occurred in 33% of Rd-R patients and 43% of Rd patients (P = .15). The most frequent nonhematologic toxicities were infections (10% vs. 12%), constitutional (3% vs. 12%), dermatologic (7% vs. 3%), and central nervous toxicities (2% vs. 6%).
The study was sponsored by Fondazione EMN Italy Onlus. Dr. Larocca has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and GlaxoSmithKline, and has served on the advisory boards for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. Several coauthors also have disclosed relationships with industry. Dr. Rajkumar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For select older patients, it is safe to switch to a lower dose of lenalidomide maintenance therapy and discontinue dexamethasone after 9 months. The regimen is safe and yields outcomes similar to those of standard, continuous lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd), according to new findings.
At a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the experimental arm in which dexamethasone therapy was stopped (Rd-R) versus 6.9 months for standard therapy. The tailored approach also resulted in fewer adverse effects.
The authors noted that there was no difference in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival between the two groups.
“These results may be useful for the treatment of myeloma patients, since approximately one-third of patients not eligible for stem cell transplantation are intermediate fit, the population in our study,” said lead author Alessandra Larocca, MD, PhD, from the department of hematology-oncology of the University Hospital Città della Salute e della Scienza, Torino, Italy.
She said in an interview that they expect that these findings “may help to optimize the treatment of less-fit elderly patients by reducing the occurrence of adverse events and thus improving outcomes and preserving quality of life of these patients.”
This approach is a viable option for clinicians to consider for some patient subgroups. “This steroid-sparing approach can also be used in other combinations,” she said. “Ongoing trials are now evaluating steroid sparing in combination with monoclonal antibodies or the role of frailty-guided treatment.”
The study was published March 19, 2021, in Blood.
Curtailing steroids
Myeloma patients aged 75 years or older or who have comorbidities and functional impairments are an understudied population. They are more susceptible to adverse events that may negatively affect the duration of treatment and outcomes. Steroids are “scarcely tolerated” in the long term, even among younger patients, and “whether sparing dexamethasone is as effective as prolonged steroid exposure remains an open issue,” the authors wrote. There are still no clear data on the advantage of continuous steroid treatment as opposed to fixed-duration treatment for newly diagnosed patients.
In 2010, a study compared high-dose with low-dose dexamethasone. As expected, the rate of adverse events was lower among patients who received the low-dose steroid, but quite unexpectedly, deaths with high-dose dexamethasone were significantly higher than with low-dose dexamethasone.
The 1-year overall survival was 96% among patients who received the low dose of dexamethasone versus 87% with the standard high dose.
S. Vincent Rajkumar, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who was the lead author of the 2010 study, spoke with this new organization about the current study. “This is an important and practice-changing study,” he said. “We have already changed our practice and recommendations based on this study.”
He explained that, for transplant-ineligible patients, instead of initial therapy with bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone followed by Rd, they use lenalidomide alone without steroids.
“After 9 months of initial therapy, I now recommend we stop dexamethasone unless we are having problems controlling the myeloma, such as progressive disease,” Dr. Rajkumar said. “I congratulate the authors on a study that will improve the quality of life for our patients.”
Improved event-free survival
In this study, Dr. Larocca and colleagues investigated the efficacy and feasibility of a dose- and schedule-adjusted Rd regimen that was followed by maintenance Rd-R 10 mg/d and compared the regimen with continuous Rd in elderly, intermediate-fit patients who were newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma.
The primary endpoint was event-free survival, defined as progression/death from any cause, lenalidomide discontinuation, and any hematologic grade 4 or nonhematologic grade 3-4 adverse events.
The cohort consisted of 199 patients who were randomly assigned to receive either Rd-R (n = 101) or continuous Rd (n = 98). The median age was 75 years in the Rd-R arm and 76 years in the Rd arm; 52% of patients in the Rd-R group and 43% in the Rd group were classified as being intermediate fit not for age but for geriatric impairments.
With a median follow-up of 37 months, event-free survival was 10.4 months in the Rd-R arm versus 6.9 months in the Rd arm (hazard ratio, 0.70; P = .02). This benefit was maintained beyond nine cycles (median: 19.8 vs. 10.6 months for Rd-R vs. Rd; HR, 0.55; P = .03)
The median PFS was 20.2 months with Rd-R and 18.3 months with Rd (HR, 0.78; P = .16). The median overall survival was not reached. The 3-year overall survival was 74% with Rd-R and 63% with continuous Rd (HR, 0.62; P = .06). Among patients remaining on therapy after nine cycles, no difference in median PFS was observed between the two groups (24.3 vs. 18.7 months; HR, 0.73; P = .19).
Best response was similar for both groups, with an overall response rate of 78% versus 68% (P = .15). The very good partial response rate was 51% in the Rd-R arm versus 39% in the continuous Rd arm (P = .09).
Toxicities were similar between the two groups. Hematologic adverse events of at least grade 3 were reported in 26% of Rd-R patients versus 20% of Rd patients (P = .40). In both groups, the most frequent grade ≥3 hematologic toxicity was neutropenia (21% vs 18%). The most frequent grade ≥3 toxicities were nonhematologic. They occurred in 33% of Rd-R patients and 43% of Rd patients (P = .15). The most frequent nonhematologic toxicities were infections (10% vs. 12%), constitutional (3% vs. 12%), dermatologic (7% vs. 3%), and central nervous toxicities (2% vs. 6%).
The study was sponsored by Fondazione EMN Italy Onlus. Dr. Larocca has received honoraria from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and GlaxoSmithKline, and has served on the advisory boards for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. Several coauthors also have disclosed relationships with industry. Dr. Rajkumar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.