User login
Cancer pain management inadequate in opioid-saturated areas
Patients with cancer who live in regions with high levels of opioid misuse may be undertreated for pain, according to investigators who studied opioid prescription patterns and cancer incidence in rural southwest Virginia.
Among 4,324 patients with cancer, only 22.16% were prescribed a Controlled Schedule II (C-II) prescription opioid medication at least 3 times in 1 year, from prescribers likely to be treating cancer pain. More than 60% of patients never received a C-II opioid prescription, reported Virginia T. LeBaron, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Nursing in Charlottesville, and colleagues.
“A clearer view of geographic patterns and predictors of both POM [prescription opioid medication] prescribing and potential harms can inform targeted interventions and policy initiatives that achieve a balanced approach to POMs – ensuring access for patients in need while reducing risk to both patients and communities. Our research makes an important contribution by exploring how the current ‘opioid epidemic’ relates to rural patients with cancer,” they wrote. Their report is in Journal of Oncology Practice.
The investigators studied the confluence of disproportionately high cancer mortality rates and opioid fatality rates in rural southwest Virginia, in the heart of Appalachia.
They conducted a longitudinal, exploratory secondary analysis of data from the Commonwealth of Virginia All Payer Claims database to look at opioid prescribing patterns and explore whether concerns about opioid misuse could result in undertreatment of pain in cancer patients.
They looked at prescribing patterns at the patient, provider, and insurance claim levels, predictors of opioid prescription frequency, opioid-related harms and patterns related to opioid prescribing, cancer incidence, and fatalities.
They identified 4,324 patients with cancer, 958 of whom (22.16%) received a C-II opioid at least three times in any study year. The majority of patients were in the 45-64 age range, and approximately 88% were diagnosed with solid malignancies, with breast cancer and lung cancer being the most frequent diagnoses.
As noted, more than 60% of patients never received a C-II prescription.
“The large percentages of cancer patients never prescribed a C-II are concerning for a number of reasons, especially when we consider the results per year,” the investigators wrote. “First, the ‘no C-II’ patients remain over 80% of the total sample, each year, even after accounting for the upscheduling (from C-III to C-II) of commonly-prescribed hydrocodone products in 2014. Second, anecdotal data and emerging empirical evidence demonstrate that patients with legitimate pain needs, including patients with cancer, experience significant difficulty accessing POMs.”
They noted that regulations regarding opioid prescriptions have become increasingly strict since the end date of their analysis in 2015, suggesting that the number of patients with cancer who are not receiving C-II opioids today may be even higher.
They also pointed to evidence of prescription practices suggesting suboptimal pain management or potential patient harm, such as frequent prescription of opioid-acetaminophen combinations that are dose-limited due to acetaminophen toxicity; coprescription of opioids and benzodiazepines, which is not recommended under current prescribing guidelines; and infrequent use of deterrent formulations of C-II opioids such as crush-resistant tablets.
The study was supported by the University of Virginia Cancer Center, Cancer Control & Population Health Division and the Virginia Tobacco Region Revitalization Commission. The authors reported having no disclaimers or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBaron VT et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Nov. 4. doi: 10.1200/JOP.19.00149.
Patients with cancer who live in regions with high levels of opioid misuse may be undertreated for pain, according to investigators who studied opioid prescription patterns and cancer incidence in rural southwest Virginia.
Among 4,324 patients with cancer, only 22.16% were prescribed a Controlled Schedule II (C-II) prescription opioid medication at least 3 times in 1 year, from prescribers likely to be treating cancer pain. More than 60% of patients never received a C-II opioid prescription, reported Virginia T. LeBaron, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Nursing in Charlottesville, and colleagues.
“A clearer view of geographic patterns and predictors of both POM [prescription opioid medication] prescribing and potential harms can inform targeted interventions and policy initiatives that achieve a balanced approach to POMs – ensuring access for patients in need while reducing risk to both patients and communities. Our research makes an important contribution by exploring how the current ‘opioid epidemic’ relates to rural patients with cancer,” they wrote. Their report is in Journal of Oncology Practice.
The investigators studied the confluence of disproportionately high cancer mortality rates and opioid fatality rates in rural southwest Virginia, in the heart of Appalachia.
They conducted a longitudinal, exploratory secondary analysis of data from the Commonwealth of Virginia All Payer Claims database to look at opioid prescribing patterns and explore whether concerns about opioid misuse could result in undertreatment of pain in cancer patients.
They looked at prescribing patterns at the patient, provider, and insurance claim levels, predictors of opioid prescription frequency, opioid-related harms and patterns related to opioid prescribing, cancer incidence, and fatalities.
They identified 4,324 patients with cancer, 958 of whom (22.16%) received a C-II opioid at least three times in any study year. The majority of patients were in the 45-64 age range, and approximately 88% were diagnosed with solid malignancies, with breast cancer and lung cancer being the most frequent diagnoses.
As noted, more than 60% of patients never received a C-II prescription.
“The large percentages of cancer patients never prescribed a C-II are concerning for a number of reasons, especially when we consider the results per year,” the investigators wrote. “First, the ‘no C-II’ patients remain over 80% of the total sample, each year, even after accounting for the upscheduling (from C-III to C-II) of commonly-prescribed hydrocodone products in 2014. Second, anecdotal data and emerging empirical evidence demonstrate that patients with legitimate pain needs, including patients with cancer, experience significant difficulty accessing POMs.”
They noted that regulations regarding opioid prescriptions have become increasingly strict since the end date of their analysis in 2015, suggesting that the number of patients with cancer who are not receiving C-II opioids today may be even higher.
They also pointed to evidence of prescription practices suggesting suboptimal pain management or potential patient harm, such as frequent prescription of opioid-acetaminophen combinations that are dose-limited due to acetaminophen toxicity; coprescription of opioids and benzodiazepines, which is not recommended under current prescribing guidelines; and infrequent use of deterrent formulations of C-II opioids such as crush-resistant tablets.
The study was supported by the University of Virginia Cancer Center, Cancer Control & Population Health Division and the Virginia Tobacco Region Revitalization Commission. The authors reported having no disclaimers or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBaron VT et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Nov. 4. doi: 10.1200/JOP.19.00149.
Patients with cancer who live in regions with high levels of opioid misuse may be undertreated for pain, according to investigators who studied opioid prescription patterns and cancer incidence in rural southwest Virginia.
Among 4,324 patients with cancer, only 22.16% were prescribed a Controlled Schedule II (C-II) prescription opioid medication at least 3 times in 1 year, from prescribers likely to be treating cancer pain. More than 60% of patients never received a C-II opioid prescription, reported Virginia T. LeBaron, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Nursing in Charlottesville, and colleagues.
“A clearer view of geographic patterns and predictors of both POM [prescription opioid medication] prescribing and potential harms can inform targeted interventions and policy initiatives that achieve a balanced approach to POMs – ensuring access for patients in need while reducing risk to both patients and communities. Our research makes an important contribution by exploring how the current ‘opioid epidemic’ relates to rural patients with cancer,” they wrote. Their report is in Journal of Oncology Practice.
The investigators studied the confluence of disproportionately high cancer mortality rates and opioid fatality rates in rural southwest Virginia, in the heart of Appalachia.
They conducted a longitudinal, exploratory secondary analysis of data from the Commonwealth of Virginia All Payer Claims database to look at opioid prescribing patterns and explore whether concerns about opioid misuse could result in undertreatment of pain in cancer patients.
They looked at prescribing patterns at the patient, provider, and insurance claim levels, predictors of opioid prescription frequency, opioid-related harms and patterns related to opioid prescribing, cancer incidence, and fatalities.
They identified 4,324 patients with cancer, 958 of whom (22.16%) received a C-II opioid at least three times in any study year. The majority of patients were in the 45-64 age range, and approximately 88% were diagnosed with solid malignancies, with breast cancer and lung cancer being the most frequent diagnoses.
As noted, more than 60% of patients never received a C-II prescription.
“The large percentages of cancer patients never prescribed a C-II are concerning for a number of reasons, especially when we consider the results per year,” the investigators wrote. “First, the ‘no C-II’ patients remain over 80% of the total sample, each year, even after accounting for the upscheduling (from C-III to C-II) of commonly-prescribed hydrocodone products in 2014. Second, anecdotal data and emerging empirical evidence demonstrate that patients with legitimate pain needs, including patients with cancer, experience significant difficulty accessing POMs.”
They noted that regulations regarding opioid prescriptions have become increasingly strict since the end date of their analysis in 2015, suggesting that the number of patients with cancer who are not receiving C-II opioids today may be even higher.
They also pointed to evidence of prescription practices suggesting suboptimal pain management or potential patient harm, such as frequent prescription of opioid-acetaminophen combinations that are dose-limited due to acetaminophen toxicity; coprescription of opioids and benzodiazepines, which is not recommended under current prescribing guidelines; and infrequent use of deterrent formulations of C-II opioids such as crush-resistant tablets.
The study was supported by the University of Virginia Cancer Center, Cancer Control & Population Health Division and the Virginia Tobacco Region Revitalization Commission. The authors reported having no disclaimers or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: LeBaron VT et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Nov. 4. doi: 10.1200/JOP.19.00149.
FROM JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Opioids, benzodiazepines carry greater risk of COPD-related hospitalization
according to recent research from Annals of the American Thoracic Society.
In addition, the risk of hospitalization because of respiratory events for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was greater when opioid and benzodiazepine medications were combined, compared with patients who did not take either medication, Jacques G. Baillargeon, PhD, of the department of preventive medicine and community health at the University of Texas, Galveston, and colleagues wrote.
“Patients with COPD and their physicians should judiciously assess the risks and benefits of opioids and benzodiazepines, alone and in combination, and preferentially recommend nonopioid and nonbenzodiazepine approaches for pain, sleep, and anxiety management in patients with COPD,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers performed a case-control study of 3,232 Medicare beneficiary cases of COPD patients who were aged at least 66 years. Patients were included if they experienced a hospitalization related to a COPD-related adverse event with a respiratory diagnosis in 2014 and then matched to one or two control patients (total, 6,247 patients) based on age at hospitalization, gender, COPD medication, COPD complexity, obstructive sleep apnea, and socioeconomic status. COPD complexity was assigned to three levels (low, moderate, high) and calculated using the patient’s comorbid respiratory conditions and associated medical procedures in the 12 months prior to their hospitalization.
They found that, in the 30 days before COPD-related hospitalization, use of opioids was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-1.97), as was use of benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.21-1.66). When patients used both opioids and benzodiazepines, they had a significantly higher risk of hospitalization, compared with patients who did not use opioids or benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.94-2.77).
In the 60 days prior to hospitalization, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization among COPD patients who used opioids (aOR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.47-1.88), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.24-1.67), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.93-2.67); at 90 days, this higher risk of hospitalization persisted among COPD patients taking opioids (aOR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.40-1.78), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.20-1.63), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.88-2.59).
The researchers acknowledged that one potential limitation in the study was how COPD diagnoses were obtained through coding performed by clinicians instead of from laboratory testing. Confounding by COPD indication and severity; use of over-the-counter medication or opioids and benzodiazepines received illegally; and lack of analyses of potential confounders such as diet, alcohol use, smoking status and herbal supplement use were other limitations.
This study was supported by an award from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Baillargeon had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baillargeon JG et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Oct 1. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-024OC.
according to recent research from Annals of the American Thoracic Society.
In addition, the risk of hospitalization because of respiratory events for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was greater when opioid and benzodiazepine medications were combined, compared with patients who did not take either medication, Jacques G. Baillargeon, PhD, of the department of preventive medicine and community health at the University of Texas, Galveston, and colleagues wrote.
“Patients with COPD and their physicians should judiciously assess the risks and benefits of opioids and benzodiazepines, alone and in combination, and preferentially recommend nonopioid and nonbenzodiazepine approaches for pain, sleep, and anxiety management in patients with COPD,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers performed a case-control study of 3,232 Medicare beneficiary cases of COPD patients who were aged at least 66 years. Patients were included if they experienced a hospitalization related to a COPD-related adverse event with a respiratory diagnosis in 2014 and then matched to one or two control patients (total, 6,247 patients) based on age at hospitalization, gender, COPD medication, COPD complexity, obstructive sleep apnea, and socioeconomic status. COPD complexity was assigned to three levels (low, moderate, high) and calculated using the patient’s comorbid respiratory conditions and associated medical procedures in the 12 months prior to their hospitalization.
They found that, in the 30 days before COPD-related hospitalization, use of opioids was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-1.97), as was use of benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.21-1.66). When patients used both opioids and benzodiazepines, they had a significantly higher risk of hospitalization, compared with patients who did not use opioids or benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.94-2.77).
In the 60 days prior to hospitalization, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization among COPD patients who used opioids (aOR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.47-1.88), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.24-1.67), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.93-2.67); at 90 days, this higher risk of hospitalization persisted among COPD patients taking opioids (aOR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.40-1.78), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.20-1.63), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.88-2.59).
The researchers acknowledged that one potential limitation in the study was how COPD diagnoses were obtained through coding performed by clinicians instead of from laboratory testing. Confounding by COPD indication and severity; use of over-the-counter medication or opioids and benzodiazepines received illegally; and lack of analyses of potential confounders such as diet, alcohol use, smoking status and herbal supplement use were other limitations.
This study was supported by an award from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Baillargeon had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baillargeon JG et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Oct 1. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-024OC.
according to recent research from Annals of the American Thoracic Society.
In addition, the risk of hospitalization because of respiratory events for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was greater when opioid and benzodiazepine medications were combined, compared with patients who did not take either medication, Jacques G. Baillargeon, PhD, of the department of preventive medicine and community health at the University of Texas, Galveston, and colleagues wrote.
“Patients with COPD and their physicians should judiciously assess the risks and benefits of opioids and benzodiazepines, alone and in combination, and preferentially recommend nonopioid and nonbenzodiazepine approaches for pain, sleep, and anxiety management in patients with COPD,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers performed a case-control study of 3,232 Medicare beneficiary cases of COPD patients who were aged at least 66 years. Patients were included if they experienced a hospitalization related to a COPD-related adverse event with a respiratory diagnosis in 2014 and then matched to one or two control patients (total, 6,247 patients) based on age at hospitalization, gender, COPD medication, COPD complexity, obstructive sleep apnea, and socioeconomic status. COPD complexity was assigned to three levels (low, moderate, high) and calculated using the patient’s comorbid respiratory conditions and associated medical procedures in the 12 months prior to their hospitalization.
They found that, in the 30 days before COPD-related hospitalization, use of opioids was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (adjusted odds ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-1.97), as was use of benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.21-1.66). When patients used both opioids and benzodiazepines, they had a significantly higher risk of hospitalization, compared with patients who did not use opioids or benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.94-2.77).
In the 60 days prior to hospitalization, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization among COPD patients who used opioids (aOR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.47-1.88), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.24-1.67), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.27; 95% CI, 1.93-2.67); at 90 days, this higher risk of hospitalization persisted among COPD patients taking opioids (aOR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.40-1.78), benzodiazepines (aOR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.20-1.63), and both opioids and benzodiazepines (aOR, 2.21; 95% CI, 1.88-2.59).
The researchers acknowledged that one potential limitation in the study was how COPD diagnoses were obtained through coding performed by clinicians instead of from laboratory testing. Confounding by COPD indication and severity; use of over-the-counter medication or opioids and benzodiazepines received illegally; and lack of analyses of potential confounders such as diet, alcohol use, smoking status and herbal supplement use were other limitations.
This study was supported by an award from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and National Institutes of Health. Dr. Baillargeon had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Baillargeon JG et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Oct 1. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201901-024OC.
FROM ANNALS OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY
Clinical interventions for global drug use need updating
Public health approach requires greater emphasis on harms, benefits of substance use.
Strategies aimed at reducing drug-related harm should be informed by evidence, and recognize the contribution of social and economic factors to drug use, report the authors of a series of four papers published in The Lancet.
Louisa Degenhardt, PhD, and coauthors wrote in the first paper that, although the availability and use of drugs have been transformed over recent decades – including the emergence of hundreds of new psychoactive substances – professional and public policy has not yet adapted to those new realities (Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9).
, in a way that you don’t see in other areas of public health,” Dr. Degenhardt, of the National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, said in an interview. “There has been an increasing level of awareness of issues but also level of recognition that we need to have hard evidence to work out the best ways to respond.”
The paper by Dr. Degenhardt and coauthors addressed the issue of opioid use and dependence around the world, citing evidence that in 2017, 40.5 million people were dependent on opioids and 109,500 deaths were attributable to opioid overdose. An effective treatment exists in the form of opioid agonists methadone and buprenorphine, both of which are recognized as World Health Organization essential medicines.
While the best evidence for positive outcomes from opioid agonist treatment is in people using illicit opioids such as heroin, there is also evidence for their effectiveness in people with pharmaceutical opioid dependence. A study in Kentucky suggested that scaling up the use and retention of opioid agonist treatment, including in prison, could prevent 57% of overdose deaths among injecting drug users.
“Despite strong evidence for the effectiveness of a range of interventions to improve the health and well-being of people who are dependent on opioids, coverage is low, even in high-income countries,” the authors wrote. They also called for international efforts to eliminate marketing strategies that have contributed to the increase in opioid prescription and harms in North America.
The second paper examined the public health implications of legalizing cannabis for medicinal and recreational use (Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1). Cannabis has been considered an illicit drug for more than 50 years but recently has been decriminalized or legalized in many parts of the world in recognition of the lower levels of harm, compared with other illicit substances.
Cannabis is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis. It also is used to treat pain, nausea, and vomiting in palliative care, and to reduce seizures in epilepsy. However, the authors noted that the evidence for many medical applications was absent, and that weakly regulated medical cannabis programs in some U.S. states were blurring the boundaries between medicinal and nonmedicinal use.
They also wrote that the public health effects of legalization could not be assessed, because legalization had happened only in the last 5 years.
“A major determinant of the public health effect of cannabis legalization will be the effect that it has on alcohol use,” they wrote. “The substitution of cannabis for alcohol would produce substantial public health gains, but any increase in the combined use of alcohol and cannabis could increase harm.”
The authors also looked at the effect of use of stimulants such as cocaine and amphetamines. While their use is associated with higher mortality, increased incidence of HIV and hepatitis C infection, poor mental health, and increased risk of cardiovascular events, no effective pharmacotherapies are available, and psychosocial interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy have only a weak effect.
“Many governments rely on punitive responses, such as involuntary detention in drug centers, despite the absence of evidence for their effectiveness and their potential to increase harm,” the authors wrote. “Substantial research investment is needed to develop more effective, innovative, and impactful prevention and treatment” (Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5).
They focused on interventions to prevent the transmission of blood-borne and sexually transmitted infections – such as the provision of safe injecting equipment, condoms or pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV – and improve treatment of these, and interventions to prevent and treat overdose, injury, and other harms.
The final paper in the series explored new psychoactive substances, such as synthetic cannabinoids, stimulants, hallucinogens, and dissociative and depressant substances (Peacock A et al. Lancet 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7).
There really needs to be massive change in systems in terms of the way monitoring occurs and the speed with which new drugs are identified, Dr. Degenhardt said in the interview. She also said the risks that are identified need to be communicated more effectively.
“At the moment, the way that drug surveillance works in most countries, things come and then particular drugs may spread in use, cause massive harm, and all of our systems of detecting and responding are not fit to detect those things in a timely way and disseminate information to reduce those risks.”
The papers were supported by European Monitoring Centre on Drugs and Drug Addiction, and the Australian National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre. The authors declared support from a range of institutions and funding bodies, and several also declared unrelated grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector.
SOURCES: Degenhardt L et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9; Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1; Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5; and Peacock A et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7.
Public health approach requires greater emphasis on harms, benefits of substance use.
Public health approach requires greater emphasis on harms, benefits of substance use.
Strategies aimed at reducing drug-related harm should be informed by evidence, and recognize the contribution of social and economic factors to drug use, report the authors of a series of four papers published in The Lancet.
Louisa Degenhardt, PhD, and coauthors wrote in the first paper that, although the availability and use of drugs have been transformed over recent decades – including the emergence of hundreds of new psychoactive substances – professional and public policy has not yet adapted to those new realities (Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9).
, in a way that you don’t see in other areas of public health,” Dr. Degenhardt, of the National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, said in an interview. “There has been an increasing level of awareness of issues but also level of recognition that we need to have hard evidence to work out the best ways to respond.”
The paper by Dr. Degenhardt and coauthors addressed the issue of opioid use and dependence around the world, citing evidence that in 2017, 40.5 million people were dependent on opioids and 109,500 deaths were attributable to opioid overdose. An effective treatment exists in the form of opioid agonists methadone and buprenorphine, both of which are recognized as World Health Organization essential medicines.
While the best evidence for positive outcomes from opioid agonist treatment is in people using illicit opioids such as heroin, there is also evidence for their effectiveness in people with pharmaceutical opioid dependence. A study in Kentucky suggested that scaling up the use and retention of opioid agonist treatment, including in prison, could prevent 57% of overdose deaths among injecting drug users.
“Despite strong evidence for the effectiveness of a range of interventions to improve the health and well-being of people who are dependent on opioids, coverage is low, even in high-income countries,” the authors wrote. They also called for international efforts to eliminate marketing strategies that have contributed to the increase in opioid prescription and harms in North America.
The second paper examined the public health implications of legalizing cannabis for medicinal and recreational use (Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1). Cannabis has been considered an illicit drug for more than 50 years but recently has been decriminalized or legalized in many parts of the world in recognition of the lower levels of harm, compared with other illicit substances.
Cannabis is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis. It also is used to treat pain, nausea, and vomiting in palliative care, and to reduce seizures in epilepsy. However, the authors noted that the evidence for many medical applications was absent, and that weakly regulated medical cannabis programs in some U.S. states were blurring the boundaries between medicinal and nonmedicinal use.
They also wrote that the public health effects of legalization could not be assessed, because legalization had happened only in the last 5 years.
“A major determinant of the public health effect of cannabis legalization will be the effect that it has on alcohol use,” they wrote. “The substitution of cannabis for alcohol would produce substantial public health gains, but any increase in the combined use of alcohol and cannabis could increase harm.”
The authors also looked at the effect of use of stimulants such as cocaine and amphetamines. While their use is associated with higher mortality, increased incidence of HIV and hepatitis C infection, poor mental health, and increased risk of cardiovascular events, no effective pharmacotherapies are available, and psychosocial interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy have only a weak effect.
“Many governments rely on punitive responses, such as involuntary detention in drug centers, despite the absence of evidence for their effectiveness and their potential to increase harm,” the authors wrote. “Substantial research investment is needed to develop more effective, innovative, and impactful prevention and treatment” (Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5).
They focused on interventions to prevent the transmission of blood-borne and sexually transmitted infections – such as the provision of safe injecting equipment, condoms or pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV – and improve treatment of these, and interventions to prevent and treat overdose, injury, and other harms.
The final paper in the series explored new psychoactive substances, such as synthetic cannabinoids, stimulants, hallucinogens, and dissociative and depressant substances (Peacock A et al. Lancet 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7).
There really needs to be massive change in systems in terms of the way monitoring occurs and the speed with which new drugs are identified, Dr. Degenhardt said in the interview. She also said the risks that are identified need to be communicated more effectively.
“At the moment, the way that drug surveillance works in most countries, things come and then particular drugs may spread in use, cause massive harm, and all of our systems of detecting and responding are not fit to detect those things in a timely way and disseminate information to reduce those risks.”
The papers were supported by European Monitoring Centre on Drugs and Drug Addiction, and the Australian National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre. The authors declared support from a range of institutions and funding bodies, and several also declared unrelated grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector.
SOURCES: Degenhardt L et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9; Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1; Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5; and Peacock A et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7.
Strategies aimed at reducing drug-related harm should be informed by evidence, and recognize the contribution of social and economic factors to drug use, report the authors of a series of four papers published in The Lancet.
Louisa Degenhardt, PhD, and coauthors wrote in the first paper that, although the availability and use of drugs have been transformed over recent decades – including the emergence of hundreds of new psychoactive substances – professional and public policy has not yet adapted to those new realities (Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9).
, in a way that you don’t see in other areas of public health,” Dr. Degenhardt, of the National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre at the University of New South Wales in Sydney, said in an interview. “There has been an increasing level of awareness of issues but also level of recognition that we need to have hard evidence to work out the best ways to respond.”
The paper by Dr. Degenhardt and coauthors addressed the issue of opioid use and dependence around the world, citing evidence that in 2017, 40.5 million people were dependent on opioids and 109,500 deaths were attributable to opioid overdose. An effective treatment exists in the form of opioid agonists methadone and buprenorphine, both of which are recognized as World Health Organization essential medicines.
While the best evidence for positive outcomes from opioid agonist treatment is in people using illicit opioids such as heroin, there is also evidence for their effectiveness in people with pharmaceutical opioid dependence. A study in Kentucky suggested that scaling up the use and retention of opioid agonist treatment, including in prison, could prevent 57% of overdose deaths among injecting drug users.
“Despite strong evidence for the effectiveness of a range of interventions to improve the health and well-being of people who are dependent on opioids, coverage is low, even in high-income countries,” the authors wrote. They also called for international efforts to eliminate marketing strategies that have contributed to the increase in opioid prescription and harms in North America.
The second paper examined the public health implications of legalizing cannabis for medicinal and recreational use (Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1). Cannabis has been considered an illicit drug for more than 50 years but recently has been decriminalized or legalized in many parts of the world in recognition of the lower levels of harm, compared with other illicit substances.
Cannabis is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis. It also is used to treat pain, nausea, and vomiting in palliative care, and to reduce seizures in epilepsy. However, the authors noted that the evidence for many medical applications was absent, and that weakly regulated medical cannabis programs in some U.S. states were blurring the boundaries between medicinal and nonmedicinal use.
They also wrote that the public health effects of legalization could not be assessed, because legalization had happened only in the last 5 years.
“A major determinant of the public health effect of cannabis legalization will be the effect that it has on alcohol use,” they wrote. “The substitution of cannabis for alcohol would produce substantial public health gains, but any increase in the combined use of alcohol and cannabis could increase harm.”
The authors also looked at the effect of use of stimulants such as cocaine and amphetamines. While their use is associated with higher mortality, increased incidence of HIV and hepatitis C infection, poor mental health, and increased risk of cardiovascular events, no effective pharmacotherapies are available, and psychosocial interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy have only a weak effect.
“Many governments rely on punitive responses, such as involuntary detention in drug centers, despite the absence of evidence for their effectiveness and their potential to increase harm,” the authors wrote. “Substantial research investment is needed to develop more effective, innovative, and impactful prevention and treatment” (Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5).
They focused on interventions to prevent the transmission of blood-borne and sexually transmitted infections – such as the provision of safe injecting equipment, condoms or pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV – and improve treatment of these, and interventions to prevent and treat overdose, injury, and other harms.
The final paper in the series explored new psychoactive substances, such as synthetic cannabinoids, stimulants, hallucinogens, and dissociative and depressant substances (Peacock A et al. Lancet 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7).
There really needs to be massive change in systems in terms of the way monitoring occurs and the speed with which new drugs are identified, Dr. Degenhardt said in the interview. She also said the risks that are identified need to be communicated more effectively.
“At the moment, the way that drug surveillance works in most countries, things come and then particular drugs may spread in use, cause massive harm, and all of our systems of detecting and responding are not fit to detect those things in a timely way and disseminate information to reduce those risks.”
The papers were supported by European Monitoring Centre on Drugs and Drug Addiction, and the Australian National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre. The authors declared support from a range of institutions and funding bodies, and several also declared unrelated grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector.
SOURCES: Degenhardt L et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9; Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1; Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5; and Peacock A et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7.
FROM THE LANCET
Key clinical point: People with drug use disorders around the world need evidence-based and nonjudgmental clinical care.
Major finding: Many interventions aimed at reducing the harm of illicit drug use are not informed by evidence.
Study details: Series of four papers reviewing the evidence on cannabinoids, opioids, new psychoactive substances, and stimulants.
Disclosures: The papers were supported by European Monitoring Centre on Drugs and Drug Addiction, and the Australian National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre. The authors declared support from a range of institutions and funding bodies, and several also declared unrelated grants, funding, and other support from the pharmaceutical sector.
Sources: Degenhardt L et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32229-9; Hall W et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31789-1; Farrell M et al. Lancet. 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32230-5; and Peacock A et al. Lancet 2019 Oct 23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32231-7.
Drug crisis continues to evolve beyond opioids
Almost three-quarters of primary care physicians believe that their patients will take their controlled medications as prescribed, but more than half of drug-monitoring lab tests show signs of misuse, according to a new report from Quest Diagnostics.
“ and may miss some of the drug misuse risks affecting their patients,” report coauthor Harvey W. Kaufman, MD, Quest’s senior medical director, said in a written statement.
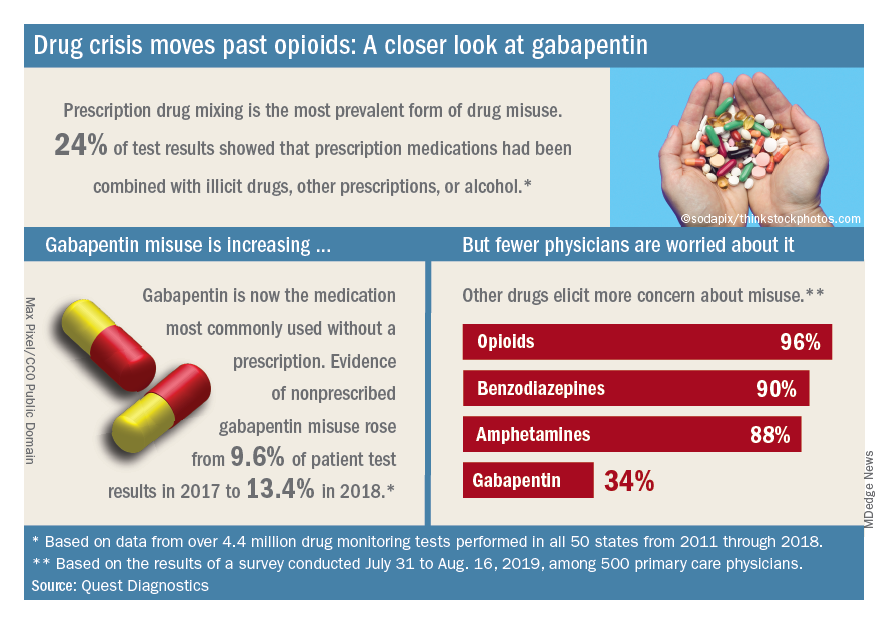
Analysis of more than 4.4 million drug-monitoring tests showed that 51% involved an inconsistent result, such as detection of a nonprescribed drug or nondetection of a drug that was prescribed. The report also included a survey of 500 primary care physicians, of whom 72% said they trusted their patents to properly use opioids and other controlled substances.
“The intersection of these two data sets reveals, for the first time, the contrast between physician expectations about patient drug use and the evolution of the drug epidemic and actual patient behavior, as revealed by objective lab data, amid a national drug crisis that claimed an estimated 68,500 lives last year,” the report said.
A majority (62%) of the physicians surveyed also said that the opioid crisis will evolve into a new prescription drug crisis, and even more (72%) think that patients with chronic pain will use illicit drugs if they cannot get prescription opioids. Evidence from the drug test dataset suggests that “misuse of nonprescribed fentanyl and nonprescribed gabapentin warrant[s] a closer look,” the report said. In the survey, 78% of respondents reported prescribing gabapentin as an alternative to opioids for patients with chronic pain.
Those two drugs, along with alcohol, are the only three drug groups for which misuse increased from 2017 to 2018, and both are frequently involved in drug mixing, which is the most common form of misuse. Gabapentin went from 9.6% of all nonprescribed misuse in 2017 to 13.4% in 2018, an increase of 40%. Nonprescribed fentanyl was found in 64% of test results that were positive for heroin and 24% that were positive for cocaine, the Quest data showed.
The survey results, however, suggest that gabapentin is not on physicians’ radar, as only 34% said that they were concerned about its misuse, compared with 96% for opioids and 90% for benzodiazepines, according to the report.
“While gabapentin may not have opioids’ addictive potential, it can exaggerate euphoric effects when combined with opioids or anxiety medications. This drug mixing is dangerous,” said report coauthor Jeffrey Gudin, MD, senior medical advisor, prescription drug monitoring, for Quest Diagnostics.
The survey was conducted online among family physicians, general practitioners, and internists from July 31 to Aug. 16, 2019, by the Harris Poll on behalf of Quest and Center for Addiction. The test result data were collected in all 50 states and Washington, D.C., from 2011 to 2018, and results from drug rehabilitation clinics and addiction specialists were excluded from the analysis, so actual misuse rates are probably higher than reported.
Almost three-quarters of primary care physicians believe that their patients will take their controlled medications as prescribed, but more than half of drug-monitoring lab tests show signs of misuse, according to a new report from Quest Diagnostics.

“ and may miss some of the drug misuse risks affecting their patients,” report coauthor Harvey W. Kaufman, MD, Quest’s senior medical director, said in a written statement.
Analysis of more than 4.4 million drug-monitoring tests showed that 51% involved an inconsistent result, such as detection of a nonprescribed drug or nondetection of a drug that was prescribed. The report also included a survey of 500 primary care physicians, of whom 72% said they trusted their patents to properly use opioids and other controlled substances.
“The intersection of these two data sets reveals, for the first time, the contrast between physician expectations about patient drug use and the evolution of the drug epidemic and actual patient behavior, as revealed by objective lab data, amid a national drug crisis that claimed an estimated 68,500 lives last year,” the report said.
A majority (62%) of the physicians surveyed also said that the opioid crisis will evolve into a new prescription drug crisis, and even more (72%) think that patients with chronic pain will use illicit drugs if they cannot get prescription opioids. Evidence from the drug test dataset suggests that “misuse of nonprescribed fentanyl and nonprescribed gabapentin warrant[s] a closer look,” the report said. In the survey, 78% of respondents reported prescribing gabapentin as an alternative to opioids for patients with chronic pain.
Those two drugs, along with alcohol, are the only three drug groups for which misuse increased from 2017 to 2018, and both are frequently involved in drug mixing, which is the most common form of misuse. Gabapentin went from 9.6% of all nonprescribed misuse in 2017 to 13.4% in 2018, an increase of 40%. Nonprescribed fentanyl was found in 64% of test results that were positive for heroin and 24% that were positive for cocaine, the Quest data showed.
The survey results, however, suggest that gabapentin is not on physicians’ radar, as only 34% said that they were concerned about its misuse, compared with 96% for opioids and 90% for benzodiazepines, according to the report.
“While gabapentin may not have opioids’ addictive potential, it can exaggerate euphoric effects when combined with opioids or anxiety medications. This drug mixing is dangerous,” said report coauthor Jeffrey Gudin, MD, senior medical advisor, prescription drug monitoring, for Quest Diagnostics.
The survey was conducted online among family physicians, general practitioners, and internists from July 31 to Aug. 16, 2019, by the Harris Poll on behalf of Quest and Center for Addiction. The test result data were collected in all 50 states and Washington, D.C., from 2011 to 2018, and results from drug rehabilitation clinics and addiction specialists were excluded from the analysis, so actual misuse rates are probably higher than reported.
Almost three-quarters of primary care physicians believe that their patients will take their controlled medications as prescribed, but more than half of drug-monitoring lab tests show signs of misuse, according to a new report from Quest Diagnostics.

“ and may miss some of the drug misuse risks affecting their patients,” report coauthor Harvey W. Kaufman, MD, Quest’s senior medical director, said in a written statement.
Analysis of more than 4.4 million drug-monitoring tests showed that 51% involved an inconsistent result, such as detection of a nonprescribed drug or nondetection of a drug that was prescribed. The report also included a survey of 500 primary care physicians, of whom 72% said they trusted their patents to properly use opioids and other controlled substances.
“The intersection of these two data sets reveals, for the first time, the contrast between physician expectations about patient drug use and the evolution of the drug epidemic and actual patient behavior, as revealed by objective lab data, amid a national drug crisis that claimed an estimated 68,500 lives last year,” the report said.
A majority (62%) of the physicians surveyed also said that the opioid crisis will evolve into a new prescription drug crisis, and even more (72%) think that patients with chronic pain will use illicit drugs if they cannot get prescription opioids. Evidence from the drug test dataset suggests that “misuse of nonprescribed fentanyl and nonprescribed gabapentin warrant[s] a closer look,” the report said. In the survey, 78% of respondents reported prescribing gabapentin as an alternative to opioids for patients with chronic pain.
Those two drugs, along with alcohol, are the only three drug groups for which misuse increased from 2017 to 2018, and both are frequently involved in drug mixing, which is the most common form of misuse. Gabapentin went from 9.6% of all nonprescribed misuse in 2017 to 13.4% in 2018, an increase of 40%. Nonprescribed fentanyl was found in 64% of test results that were positive for heroin and 24% that were positive for cocaine, the Quest data showed.
The survey results, however, suggest that gabapentin is not on physicians’ radar, as only 34% said that they were concerned about its misuse, compared with 96% for opioids and 90% for benzodiazepines, according to the report.
“While gabapentin may not have opioids’ addictive potential, it can exaggerate euphoric effects when combined with opioids or anxiety medications. This drug mixing is dangerous,” said report coauthor Jeffrey Gudin, MD, senior medical advisor, prescription drug monitoring, for Quest Diagnostics.
The survey was conducted online among family physicians, general practitioners, and internists from July 31 to Aug. 16, 2019, by the Harris Poll on behalf of Quest and Center for Addiction. The test result data were collected in all 50 states and Washington, D.C., from 2011 to 2018, and results from drug rehabilitation clinics and addiction specialists were excluded from the analysis, so actual misuse rates are probably higher than reported.
How to use lofexidine for quick opioid withdrawal
SAN DIEGO – Lofexidine (Lucemyra), the new kid on the block in the United States for opioid withdrawal, can help patients get through the process in a few days, instead of a week or more, according to Thomas Kosten, MD, a psychiatry professor and director of the division of addictions at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Lofexidine relieves symptom withdrawal and has significant advantages over clonidine, a similar drug, including easier dosing and no orthostatic hypertension.
In a video interview at the annual Psych Congress, Dr. Kosten went into the nuts and bolts of how to use lofexidine with buprenorphine and naltrexone – plus benzodiazepines when needed – to help people safely go through withdrawal and in just a few days.
Once chronic pain patients are off opioids, the next question is what to do for their pain. In a presentation before the interview, Dr. Kosten said he favors tricyclic antidepressants, especially desipramine because it has the fewest side effects. The effect size with tricyclic antidepressants is larger than with gabapentin and other options. They take a few weeks to kick in, however, so he’s thinking about a unique approach: using ketamine – either infusions or the new nasal spray esketamine (Spravato) – to tide people over in the meantime. It’s becoming well known that ketamine works amazingly fast for depression and suicidality, and there is emerging support that it might do the same for chronic pain. Dr. Kosten is a consultant for US Worldmeds, maker of lofexidine.
SAN DIEGO – Lofexidine (Lucemyra), the new kid on the block in the United States for opioid withdrawal, can help patients get through the process in a few days, instead of a week or more, according to Thomas Kosten, MD, a psychiatry professor and director of the division of addictions at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Lofexidine relieves symptom withdrawal and has significant advantages over clonidine, a similar drug, including easier dosing and no orthostatic hypertension.
In a video interview at the annual Psych Congress, Dr. Kosten went into the nuts and bolts of how to use lofexidine with buprenorphine and naltrexone – plus benzodiazepines when needed – to help people safely go through withdrawal and in just a few days.
Once chronic pain patients are off opioids, the next question is what to do for their pain. In a presentation before the interview, Dr. Kosten said he favors tricyclic antidepressants, especially desipramine because it has the fewest side effects. The effect size with tricyclic antidepressants is larger than with gabapentin and other options. They take a few weeks to kick in, however, so he’s thinking about a unique approach: using ketamine – either infusions or the new nasal spray esketamine (Spravato) – to tide people over in the meantime. It’s becoming well known that ketamine works amazingly fast for depression and suicidality, and there is emerging support that it might do the same for chronic pain. Dr. Kosten is a consultant for US Worldmeds, maker of lofexidine.
SAN DIEGO – Lofexidine (Lucemyra), the new kid on the block in the United States for opioid withdrawal, can help patients get through the process in a few days, instead of a week or more, according to Thomas Kosten, MD, a psychiatry professor and director of the division of addictions at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Lofexidine relieves symptom withdrawal and has significant advantages over clonidine, a similar drug, including easier dosing and no orthostatic hypertension.
In a video interview at the annual Psych Congress, Dr. Kosten went into the nuts and bolts of how to use lofexidine with buprenorphine and naltrexone – plus benzodiazepines when needed – to help people safely go through withdrawal and in just a few days.
Once chronic pain patients are off opioids, the next question is what to do for their pain. In a presentation before the interview, Dr. Kosten said he favors tricyclic antidepressants, especially desipramine because it has the fewest side effects. The effect size with tricyclic antidepressants is larger than with gabapentin and other options. They take a few weeks to kick in, however, so he’s thinking about a unique approach: using ketamine – either infusions or the new nasal spray esketamine (Spravato) – to tide people over in the meantime. It’s becoming well known that ketamine works amazingly fast for depression and suicidality, and there is emerging support that it might do the same for chronic pain. Dr. Kosten is a consultant for US Worldmeds, maker of lofexidine.
REPORTING FROM PSYCH CONGRESS 2019
Buprenorphine merits more attention for treatment of opioid use disorder
SAN DIEGO – Prescribing buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder requires strict discernment on the part of clinicians, Arwen Podesta, MD, said at the annual Psych Congress.
She encouraged clinicians to be prepared for a visit from the Drug Enforcement Administration, understand the unique properties of buprenorphine, and make sure that patients grasp the importance of sublingual administration.
Research shows that only 5% of physicians are allowed to prescribe buprenorphine – an opioid – by way of a DEA waiver, Dr. Podesta said. About half do not prescribe the drug. Barriers to prescribing buprenorphine include factors such as low reimbursement and untrained support staff, said Dr. Podesta, a board-certified psychiatrist who subspecializes in addiction medicine and practices in New Orleans.
But she noted that the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has recommended that medication-assisted therapy (MAT) – methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone – be considered in all patients with opioid use disorder. The drugs are safe and effective when used correctly, the federal agency has said.
Remember, Dr. Podesta said, that “patients taking MAT are considered to be in recovery.” In the big picture, she added, “we have to improve access to care because we have so many people who don’t have access to treatment.”
Getting permission from the DEA to prescribe buprenorphine – a schedule III controlled substance – comes with a price, Dr. Podesta said. “We have special scrutiny from the DEA,” she said. They come in and want to see your records. It sounds very punitive, although it’s their jobs.”
The best approach is to document that you know what you’re doing, she said. “It’s your job to educate them about why you’re using buprenorphine and produce the records to show that.”
Being aware of buprenorphine’s unique properties is important, she said. The drug is safer on the overdose front than are other opioids, Dr. Podesta said, but it can be very dangerous in patients without opioid tolerance. According to the DEA, as an analgesic, buprenorphine is 20-30 times more potent than morphine. Also, like morphine, patients who take buprenorphine are likely to experience euphoria, papillary restriction, and respiratory depression and sedation.
The buprenorphine/naloxone formulation is preferred to treat opioid use disorder, she noted.
The reason that naloxone, which treats opioid overdoses, is part of the drug combo is because as an add-on, it reduces the risk that buprenorphine will be crushed and snorted for an opioid high, she said. Those who take the combo drug via that method could end up with sudden and nasty withdrawal symptoms.
When the drug combo is administered sublingually, the idea is that the “good stuff” (buprenorphine) is absorbed in the mouth, while the “bad stuff” (naloxone) is harmlessly absorbed in the gut, Dr. Podesta said. This happens because the drugs are absorbed differently.
But patients can mistakenly trigger symptoms of withdrawal if, for example, they put the combo drug on their tongue and then go to sleep. “That’s a peril,” she said, and it’s important to make sure patients know what to do – and what not to do.
Dr. Podesta emphasized the importance of choosing language related to patients with addictions carefully and respectfully.
“We have stigma,” she said. “We have been saying that patients are ‘dirty’ or ‘clean,’ and if they’re ‘clean,’ they’re the opposite of ‘dirty.’
She also suggested that clinicians drop the use of the word “contract” to describe treatment agreements between patients and clinicians. “Call it an ‘agreement,’ ” she said. “It seems more mutual and less punitive or risky for the patient to sign, especially when they’re in a precarious comfort zone.”
And consider that even the words “substance abuse” can be misleading, she said. “Many [patients] are taking the medications that the doctor prescribed and following instructions to the letter.”
Dr. Podesta disclosed consulting with Kaleo, Pear Therapeutics, and JayMac, and serving on the speakers bureau of Alkermes, Orexo, and US WorldMeds. She is the author of “Hooked: A Concise Guide to the Underlying Mechanics of Addiction and Treatment for Patients, Families, and Providers” (Dog Ear Publishing, 2016).
SAN DIEGO – Prescribing buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder requires strict discernment on the part of clinicians, Arwen Podesta, MD, said at the annual Psych Congress.
She encouraged clinicians to be prepared for a visit from the Drug Enforcement Administration, understand the unique properties of buprenorphine, and make sure that patients grasp the importance of sublingual administration.
Research shows that only 5% of physicians are allowed to prescribe buprenorphine – an opioid – by way of a DEA waiver, Dr. Podesta said. About half do not prescribe the drug. Barriers to prescribing buprenorphine include factors such as low reimbursement and untrained support staff, said Dr. Podesta, a board-certified psychiatrist who subspecializes in addiction medicine and practices in New Orleans.
But she noted that the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has recommended that medication-assisted therapy (MAT) – methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone – be considered in all patients with opioid use disorder. The drugs are safe and effective when used correctly, the federal agency has said.
Remember, Dr. Podesta said, that “patients taking MAT are considered to be in recovery.” In the big picture, she added, “we have to improve access to care because we have so many people who don’t have access to treatment.”
Getting permission from the DEA to prescribe buprenorphine – a schedule III controlled substance – comes with a price, Dr. Podesta said. “We have special scrutiny from the DEA,” she said. They come in and want to see your records. It sounds very punitive, although it’s their jobs.”
The best approach is to document that you know what you’re doing, she said. “It’s your job to educate them about why you’re using buprenorphine and produce the records to show that.”
Being aware of buprenorphine’s unique properties is important, she said. The drug is safer on the overdose front than are other opioids, Dr. Podesta said, but it can be very dangerous in patients without opioid tolerance. According to the DEA, as an analgesic, buprenorphine is 20-30 times more potent than morphine. Also, like morphine, patients who take buprenorphine are likely to experience euphoria, papillary restriction, and respiratory depression and sedation.
The buprenorphine/naloxone formulation is preferred to treat opioid use disorder, she noted.
The reason that naloxone, which treats opioid overdoses, is part of the drug combo is because as an add-on, it reduces the risk that buprenorphine will be crushed and snorted for an opioid high, she said. Those who take the combo drug via that method could end up with sudden and nasty withdrawal symptoms.
When the drug combo is administered sublingually, the idea is that the “good stuff” (buprenorphine) is absorbed in the mouth, while the “bad stuff” (naloxone) is harmlessly absorbed in the gut, Dr. Podesta said. This happens because the drugs are absorbed differently.
But patients can mistakenly trigger symptoms of withdrawal if, for example, they put the combo drug on their tongue and then go to sleep. “That’s a peril,” she said, and it’s important to make sure patients know what to do – and what not to do.
Dr. Podesta emphasized the importance of choosing language related to patients with addictions carefully and respectfully.
“We have stigma,” she said. “We have been saying that patients are ‘dirty’ or ‘clean,’ and if they’re ‘clean,’ they’re the opposite of ‘dirty.’
She also suggested that clinicians drop the use of the word “contract” to describe treatment agreements between patients and clinicians. “Call it an ‘agreement,’ ” she said. “It seems more mutual and less punitive or risky for the patient to sign, especially when they’re in a precarious comfort zone.”
And consider that even the words “substance abuse” can be misleading, she said. “Many [patients] are taking the medications that the doctor prescribed and following instructions to the letter.”
Dr. Podesta disclosed consulting with Kaleo, Pear Therapeutics, and JayMac, and serving on the speakers bureau of Alkermes, Orexo, and US WorldMeds. She is the author of “Hooked: A Concise Guide to the Underlying Mechanics of Addiction and Treatment for Patients, Families, and Providers” (Dog Ear Publishing, 2016).
SAN DIEGO – Prescribing buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid use disorder requires strict discernment on the part of clinicians, Arwen Podesta, MD, said at the annual Psych Congress.
She encouraged clinicians to be prepared for a visit from the Drug Enforcement Administration, understand the unique properties of buprenorphine, and make sure that patients grasp the importance of sublingual administration.
Research shows that only 5% of physicians are allowed to prescribe buprenorphine – an opioid – by way of a DEA waiver, Dr. Podesta said. About half do not prescribe the drug. Barriers to prescribing buprenorphine include factors such as low reimbursement and untrained support staff, said Dr. Podesta, a board-certified psychiatrist who subspecializes in addiction medicine and practices in New Orleans.
But she noted that the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has recommended that medication-assisted therapy (MAT) – methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone – be considered in all patients with opioid use disorder. The drugs are safe and effective when used correctly, the federal agency has said.
Remember, Dr. Podesta said, that “patients taking MAT are considered to be in recovery.” In the big picture, she added, “we have to improve access to care because we have so many people who don’t have access to treatment.”
Getting permission from the DEA to prescribe buprenorphine – a schedule III controlled substance – comes with a price, Dr. Podesta said. “We have special scrutiny from the DEA,” she said. They come in and want to see your records. It sounds very punitive, although it’s their jobs.”
The best approach is to document that you know what you’re doing, she said. “It’s your job to educate them about why you’re using buprenorphine and produce the records to show that.”
Being aware of buprenorphine’s unique properties is important, she said. The drug is safer on the overdose front than are other opioids, Dr. Podesta said, but it can be very dangerous in patients without opioid tolerance. According to the DEA, as an analgesic, buprenorphine is 20-30 times more potent than morphine. Also, like morphine, patients who take buprenorphine are likely to experience euphoria, papillary restriction, and respiratory depression and sedation.
The buprenorphine/naloxone formulation is preferred to treat opioid use disorder, she noted.
The reason that naloxone, which treats opioid overdoses, is part of the drug combo is because as an add-on, it reduces the risk that buprenorphine will be crushed and snorted for an opioid high, she said. Those who take the combo drug via that method could end up with sudden and nasty withdrawal symptoms.
When the drug combo is administered sublingually, the idea is that the “good stuff” (buprenorphine) is absorbed in the mouth, while the “bad stuff” (naloxone) is harmlessly absorbed in the gut, Dr. Podesta said. This happens because the drugs are absorbed differently.
But patients can mistakenly trigger symptoms of withdrawal if, for example, they put the combo drug on their tongue and then go to sleep. “That’s a peril,” she said, and it’s important to make sure patients know what to do – and what not to do.
Dr. Podesta emphasized the importance of choosing language related to patients with addictions carefully and respectfully.
“We have stigma,” she said. “We have been saying that patients are ‘dirty’ or ‘clean,’ and if they’re ‘clean,’ they’re the opposite of ‘dirty.’
She also suggested that clinicians drop the use of the word “contract” to describe treatment agreements between patients and clinicians. “Call it an ‘agreement,’ ” she said. “It seems more mutual and less punitive or risky for the patient to sign, especially when they’re in a precarious comfort zone.”
And consider that even the words “substance abuse” can be misleading, she said. “Many [patients] are taking the medications that the doctor prescribed and following instructions to the letter.”
Dr. Podesta disclosed consulting with Kaleo, Pear Therapeutics, and JayMac, and serving on the speakers bureau of Alkermes, Orexo, and US WorldMeds. She is the author of “Hooked: A Concise Guide to the Underlying Mechanics of Addiction and Treatment for Patients, Families, and Providers” (Dog Ear Publishing, 2016).
REPORTING FROM PSYCH CONGRESS 2019
Long-term opioid use more common in hidradenitis suppurativa
, in a retrospective cohort study.
“These results suggest that periodic assessment of pain and screening for long-term opioid use may be warranted, particularly among patients who are older, who smoke tobacco, or who have depression and other medical comorbidities,” wrote the authors of the study (JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610).
Researchers led by Sarah Reddy, BA, of the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/ Northwell, New Hyde Park, N.Y., used data from a health-care database that represents an estimated 17% of the U.S. population. They focused on opioid-naive adults who were in the database for at least 3 years from 2008-2018 and monitored whether they began opioid use and then maintained use for at least 1 year.
Nearly 829,000 patients were in the control group, and 22,277 were in the HS group. The mean age of those with HS was 41 years, 76% were women, and 59% were white.
Over 1 year, the crude incidence of long-term opioid use among HS patients who were opioid naive was 0.33%, compared with 0.14% of controls (P less than .001).
An analysis, adjusted for potential confounding factors, found that compared with controls, those with HS were more likely to develop long-term opioid use (odds ratio [OR], 1.53, 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.95; P less than .001). In the adjusted analysis, long-term opioid use was increased among those in the HS group who had ever smoked tobacco (OR, 3.64, 95% CI, 2.06-6.41; P less than .001), compared with patients with HS who had never smoked; and those who had a history of depression (OR, 1.97, 95% CI, 1.21-3.19; P = .006), compared with HS patients who had not had depression.
The risk of long-term opioid use among those with HS increased by 2% with each additional year in age.
In addition, 5% of patients with HS and long-term opioid use were diagnosed with opioid use disorder over the study period. “Sex, race/ethnicity, disease duration, established dermatologic care, alcohol abuse, and nonopioid substance abuse were not associated with increased risk of long-term opioid use among patients with HS,” the authors wrote.
Emphasizing that these results “should not further stigmatize” people with HS, they said, “our hope is that the medical community, including dermatologists, will further embrace and engage in an integrated care plan that comprehensively supports the needs of patients with HS, including pain management.”
Future research, they added, “should include evaluating the association between disease severity and risk of opioid use, the role of disease-modifying therapies in reducing opioid use, and the development of effective and appropriate multimodal pain management strategies for HS.”
An educational grant to a study author from AbbVie partially funded the study. No other study funding was reported. Ms. Reddy had no disclosures; one author disclosed having received grants and personal fees from AbbVie and UCB during the study.
SOURCE: Reddy S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610.
, in a retrospective cohort study.
“These results suggest that periodic assessment of pain and screening for long-term opioid use may be warranted, particularly among patients who are older, who smoke tobacco, or who have depression and other medical comorbidities,” wrote the authors of the study (JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610).
Researchers led by Sarah Reddy, BA, of the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/ Northwell, New Hyde Park, N.Y., used data from a health-care database that represents an estimated 17% of the U.S. population. They focused on opioid-naive adults who were in the database for at least 3 years from 2008-2018 and monitored whether they began opioid use and then maintained use for at least 1 year.
Nearly 829,000 patients were in the control group, and 22,277 were in the HS group. The mean age of those with HS was 41 years, 76% were women, and 59% were white.
Over 1 year, the crude incidence of long-term opioid use among HS patients who were opioid naive was 0.33%, compared with 0.14% of controls (P less than .001).
An analysis, adjusted for potential confounding factors, found that compared with controls, those with HS were more likely to develop long-term opioid use (odds ratio [OR], 1.53, 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.95; P less than .001). In the adjusted analysis, long-term opioid use was increased among those in the HS group who had ever smoked tobacco (OR, 3.64, 95% CI, 2.06-6.41; P less than .001), compared with patients with HS who had never smoked; and those who had a history of depression (OR, 1.97, 95% CI, 1.21-3.19; P = .006), compared with HS patients who had not had depression.
The risk of long-term opioid use among those with HS increased by 2% with each additional year in age.
In addition, 5% of patients with HS and long-term opioid use were diagnosed with opioid use disorder over the study period. “Sex, race/ethnicity, disease duration, established dermatologic care, alcohol abuse, and nonopioid substance abuse were not associated with increased risk of long-term opioid use among patients with HS,” the authors wrote.
Emphasizing that these results “should not further stigmatize” people with HS, they said, “our hope is that the medical community, including dermatologists, will further embrace and engage in an integrated care plan that comprehensively supports the needs of patients with HS, including pain management.”
Future research, they added, “should include evaluating the association between disease severity and risk of opioid use, the role of disease-modifying therapies in reducing opioid use, and the development of effective and appropriate multimodal pain management strategies for HS.”
An educational grant to a study author from AbbVie partially funded the study. No other study funding was reported. Ms. Reddy had no disclosures; one author disclosed having received grants and personal fees from AbbVie and UCB during the study.
SOURCE: Reddy S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610.
, in a retrospective cohort study.
“These results suggest that periodic assessment of pain and screening for long-term opioid use may be warranted, particularly among patients who are older, who smoke tobacco, or who have depression and other medical comorbidities,” wrote the authors of the study (JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610).
Researchers led by Sarah Reddy, BA, of the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/ Northwell, New Hyde Park, N.Y., used data from a health-care database that represents an estimated 17% of the U.S. population. They focused on opioid-naive adults who were in the database for at least 3 years from 2008-2018 and monitored whether they began opioid use and then maintained use for at least 1 year.
Nearly 829,000 patients were in the control group, and 22,277 were in the HS group. The mean age of those with HS was 41 years, 76% were women, and 59% were white.
Over 1 year, the crude incidence of long-term opioid use among HS patients who were opioid naive was 0.33%, compared with 0.14% of controls (P less than .001).
An analysis, adjusted for potential confounding factors, found that compared with controls, those with HS were more likely to develop long-term opioid use (odds ratio [OR], 1.53, 95% confidence interval, 1.20-1.95; P less than .001). In the adjusted analysis, long-term opioid use was increased among those in the HS group who had ever smoked tobacco (OR, 3.64, 95% CI, 2.06-6.41; P less than .001), compared with patients with HS who had never smoked; and those who had a history of depression (OR, 1.97, 95% CI, 1.21-3.19; P = .006), compared with HS patients who had not had depression.
The risk of long-term opioid use among those with HS increased by 2% with each additional year in age.
In addition, 5% of patients with HS and long-term opioid use were diagnosed with opioid use disorder over the study period. “Sex, race/ethnicity, disease duration, established dermatologic care, alcohol abuse, and nonopioid substance abuse were not associated with increased risk of long-term opioid use among patients with HS,” the authors wrote.
Emphasizing that these results “should not further stigmatize” people with HS, they said, “our hope is that the medical community, including dermatologists, will further embrace and engage in an integrated care plan that comprehensively supports the needs of patients with HS, including pain management.”
Future research, they added, “should include evaluating the association between disease severity and risk of opioid use, the role of disease-modifying therapies in reducing opioid use, and the development of effective and appropriate multimodal pain management strategies for HS.”
An educational grant to a study author from AbbVie partially funded the study. No other study funding was reported. Ms. Reddy had no disclosures; one author disclosed having received grants and personal fees from AbbVie and UCB during the study.
SOURCE: Reddy S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Sep 11. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2610.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Assessing decisional capacity in patients with substance use disorders
Ms. B, age 31, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance after emergency medical technicians used naloxone nasal spray to revive her following an overdose on heroin. She reports daily IV heroin use for the last 4 years as well as frequent use of other illicit substances, including marijuana and alprazolam, for which she does not have
How can you determine if Ms. B has the capacity to make decisions regarding her care?
Decisional capacity is defined as a patient’s ability to use information about an illness and the proposed treatment options to make a choice that is congruent with one’s own values and preferences.1 Determining whether a patient has adequate capacity to make decisions regarding their care is an inherent aspect of all clinician-patient interactions.
Published reports have focused on the challenges clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with psychiatric and cognitive disorders. However, there is little evidence about assessing decisional capacity in patients with substance use disorders (SUDs), even though increasing numbers of patients with SUDs are presenting to EDs2 and being admitted as inpatients in general hospitals.3 In this article, I discuss:
- the biologic basis for impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs
- common substance use–related conditions that may impact a patient’s decisional capacity
- the clinical challenges and legal considerations clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with SUDs
- how to assess decisional capacity in such patients.
Decisional capacity vs competence
“Capacity” and “competence” are not the same. Decisional capacity, which refers to the ability to make decisions, is a clinical construct that is determined by clinicians and is generally used in the acute clinical setting. Because cognition is the main determinant of capacity, conditions or treatments that affect cognition can impair an individual’s decision-making capacity.1 Decisional capacity is not a global concept but a decision-specific one, subject to fluctuations depending on the time and the nature of the decision at hand. Therefore, requests for determination of decisional capacity in the clinical setting should be specific to an individual decision or set of decisions.
In contrast, competence is an enduring legal determination of incapacitation, typically made by a probate judge. It refers to the ability of an individual to perform actions needed to put decisions into effect. Decisional capacity as assessed by a clinician often serves as the basis for petitions submitted for the purpose of competency adjudication by the judicial system.
A biologic basis for impaired decision-making?
Jeste and Saks4 suggested that addiction itself is characterized by impaired decision-making because individuals keep using a substance despite experiencing recurrent physical, psychologic, or social problems caused or worsened by the substance. Several studies suggest there may be a biologic basis for impaired decision-making in these patients, even in the absence of severe psychiatric or cognitive disorders.
Continue to: Bechara and Damasio found...
Bechara and Damasio5 found that the decision-making impairment seen in some patients with SUDs was similar to that observed in patients who have lesions of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. In both groups of patients, the impaired decision-making was characterized by a preference to opt for high immediate reward despite even higher future losses.
These deficits were also observed by Grant et al.6 In this study, patients with SUDs displayed markedly impaired performance on the Gambling Task, which examines decisions that result in long-term losses that exceed short-term gains. However, patients with SUDs performed similarly to controls on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, which evaluates the ability to form abstract concepts and to shift from established response sets.
MacDonald et al7 used a laboratory experiment and 2 field studies to test the hypothesis that alcohol affects attitudes and intentions toward drinking and driving. Their findings support the concept that alcohol intoxication decreases cognitive capacity such that people are more likely to attend to only the most salient cues.7
Whether the impairment documented in such studies is a contributing factor in addiction or is a result of addiction remains uncertain. While individuals with SUDs may have some level of impairment in decision-making in general, particularly in regard to their substance use, their decisional capacity on specific clinical decisions should be assessed carefully. In a study of 300 consecutive psychiatric consultations for decisional capacity at an urban hospital, Boettger et al8 found that 41% were related to SUDs. Of these, 37% were found to have impaired decisional capacity.
Impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs may specifically pertain to choices related to their addiction, including9:
- consent for addiction treatment
- consistency in maintaining a choice of recovery
- changing values regarding treatment over time
- capacity to participate in addiction research involving the use of addictive substances.
Continue to: It is important to recognize...
It is important to recognize that this impairment may not necessarily translate into altered decisional capacity regarding other health care decisions, such as consenting to surgery or other necessary medical interventions.9
Substance-related disorders that affect decisional capacity
Substance-related syndromes can affect mood, reality testing, and/or cognitive function, thereby directly impacting a patient’s decisional capacity. Substance-related syndromes can be divided into 2 categories: 1) disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance, and 2) secondary disorders resulting from/or associated with substance use.
Disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance
Temporary/reversible incapacitation
- Acute intoxication or intoxication delirium may be the most frequent type of temporary incapacitation. It can result from toxic levels of licit or illicit substances; alcohol is likely the most frequent offending agent. Although some individuals who are intoxicated may appear to be alert, oriented, and able to engage in lengthy conversations, the majority do not possess adequate decisional capacity.10
- Withdrawal delirium, associated with longstanding alcohol, sedative-hypnotic, or barbiturate dependence, is typically prolonged, but usually resolves, either spontaneously or with treatment. Although most deliria resolve once the underlying etiology is corrected, vulnerable individuals may experience irreversible cognitive impairment and permanent decisional incapacitation.11,12
- Severe substance-induced depressive disorders, especially if accompanied by frank psychotic symptoms or severe depressive distortions of reality, may result in decisional incapacity. Substance abuse treatment that incorporates multiple strategies, sometimes in conjunction with pharmacotherapy to manage depression, should lead to sufficient recovery and restoration of decisional capacity.
- Transient psychotic disorders such as those associated with the use of stimulants are often treatable. Patients may recover decisional capacity spontaneously or with treatment.
Permanent incapacitation
- Dementia is associated with substance use, particularly alcohol use.13 For a patient who develops dementia, no appreciable recovery can be expected, even with prolonged abstinence.
- Persistent amnestic disorders (eg, Korsakoff syndrome) resulting from undiagnosed or untreated severe thiamine deficiency (Wernicke’s encephalopathy). Although an isolated Korsakoff syndrome consists primarily of anterograde amnesia, these patients may experience additional cognitive impairment resulting from years of alcohol consumption or associated with other neurodegenerative processes, and therefore are sufficiently impaired and lack decisional capacity. Even in the absence of such concomitant cognitive deficits, a very severe anterograde amnestic disorder directly impacts a patient’s capacity to perform the necessary tasks required to give informed consent. The inability to consolidate information about new medical developments, treatments, and procedures, even when they are thoroughly explained by the medical team, can pose serious challenges. For example, a patient may protest to being taken to surgery because he/she does not recall signing a consent form the previous day.
- Enduring severe and treatment-refractory psychotic disorders associated with drug use, specifically stimulants, can result in permanent incapacitation similar to that seen in severe primary psychotic disorders (such as treatment-resistant schizophrenia).
- Hepatic encephalopathy may be seen in patients with advanced cirrhosis of the liver (due to hepatitis C resulting from IV drug use, and/or alcohol use). In late stages of cirrhosis, the confusional state patients experience may become severe and may no longer be reversible unless liver transplantation is available and successful. This would therefore constitute a basis for permanent decisional incapacitation.
- Human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis or dementia can result from IV drug use.
Continue to: Clinical challenges
Clinical challenges
In intensive care settings, where a patient with a SUD may be treated for acute life-threatening intoxication or severe withdrawal delirium, an assumption of decisional incapacitation often exists as a result of medical acuity and impaired mentation. In these situations, treatment usually proceeds with consent obtained from next-of-kin, a guardian, or an administrative (hospital) authority when other substitute decision makers are unavailable or unwilling. In such cases, psychiatric consultation can play a dual role in documenting the patient’s decisional capacity and also in contributing to the care of patients with SUDs.
It is critical to perform a cognitive evaluation and mental status examination in a medically compromised patient with an SUD. Unfortunately, serious cognitive disorders can often be concealed by a superficially jovial or verbally skilled patient, or by an uncooperative individual who refuses to engage in a thorough conversation with his/her clinicians. These scenarios present significant challenges and may result in missed opportunities for care or premature discharges. Negative countertransference by clinicians toward patients with SUDs may also promote poor outcomes. For difficult cases, legal and ethical consultations may help mitigate risk and guide management approaches (Box14).
Box
The legal system rarely views patients with substance use disorders (SUDs) as lacking decisional capacity in the absence of overt psychiatric or cognitive deficits. The penal system offers little if any mitigation of liability on account of addiction in civil or criminal cases. On the contrary, intoxication is an aggravating factor in such settings. Despite extensive literature that questions the “free will,” accountability, and responsibility of patients with SUDs, the legal system takes an “all-or-none” approach to this issue. It assumes free choice and accountability for patients with SUDs, except when a clear superimposed psychiatric or cognitive disorder (such as psychosis or dementia) exists. Rarely, some jurisdictions may allow for mental health commitments on account of severe and persistent addictive behaviors that clearly pose a risk to the individual or to society, implicitly recognizing that incapacitation can result from severe addiction. Nevertheless, a finding of imminent or impending dangerousness is generally required for such commitments to be justified.
In other situations, individual health care settings may resort to local hospital policies that allow impaired patients with SUDs with a clearly altered mental status to be detained for the purpose of completing medical treatment. Presumably, discharge would occur when the medical and psychiatric acuity has resolved (often under the umbrella of a “Medical Hold” policy). Jain et al14 suggested that although such commitment laws for patients with SUDs may be appealing to some people, especially family members, specific statutes and their implementation are highly variable; the deprivation of liberty raises ethical concerns; and outcome data are limited. Conversely, most states either do not have such legislation, or rarely enforce it.
How to assess decisional capacity
A direct conclusion of incapacity in an individual cannot be determined solely on the knowledge of the patient having a SUD-related clinical condition. (The possible exception to this may be a patient with severe dementia.)
- understand the decision at hand
- discuss its benefits and risks
- describe alternatives
- demonstrate an appreciation of the implications of treatment or lack thereof
- communicate a clear and consistent choice.
Continue to: While most clinicians...
While most clinicians rely on a psychiatric interview (with or without a cognitive examination) to make these determinations, several instruments have been developed to aid these evaluations, such as the MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Treatment (Mac-CAT-T).15 In patients with potentially reversible incapacitating conditions, serial examinations over time, especially re-evaluation when a patient has achieved and maintained sobriety, may be necessary and helpful.
The Table offers a guide to assessing decisional capacity in a patient with an SUD.
Who should conduct the assessment?
Mental health professionals—usually psychiatrists or psychologists—are consulted when there is uncertainty about a patient’s decisional capacity, and when a more thorough mental status examination is warranted to formulate an informed opinion.16 Unfortunately, this typically occurs only if a patient refuses treatment or demands to be discharged before treatment has been completed, or there is a high level of risk to the patient or others after discharge.
In acute settings, when a patient consents to treatment, a psychiatric consultation regarding decisional capacity is rarely requested. While it is often tempting for medical or surgical teams to proceed with an intervention in a cooperative patient who willingly signs a consent form without a formal assessment of his/her decisional capacity, doing so raises challenging ethical and legal questions in the event of an adverse outcome. It is therefore prudent to strongly recommend that medical and surgical colleagues obtain a psychiatric consultation when an individual’s decisional capacity is uncertain, especially when a patient is known to have a psychiatric or neurocognitive disorder, or exhibits evidence of recent mental status changes. In cases of potentially reversible impairment (eg, delirium, psychosis, or acute anxiety), targeted interventions may help restore capacity and allow treatment to proceed.
No jurisdictions mandate that the determination of decisional capacity should be made exclusively by a mental health professional. Any treating health care professional (usually the attending physician) can make a determination of decisional capacity in scenarios where there is no overt evidence the patient has a mental or cognitive disorder and the patient is communicating clear and reasoned choices, or when a patient is profoundly impaired and no meaningful communication can take place.
Continue to: CASE CONTINUED
CASE CONTINUED
The emergency physician requests a psychiatric consultation. You assess Ms. B’s decisional capacity using the Mac-CAT-T along with a standard psychiatric evaluation. Her score of 14 reflects that she is able to understand the risks associated with her opioid use, and although irritated by engaging in such a discussion, is capable of reasoning through the various medical and psychosocial aspects of her addiction, and shows moderate appreciation of the impact of her choices on her future and that of significant others. The psychiatric evaluation fails to elicit any substantial mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders associated with/or resulting from her addiction, and her cognitive examination is within normal limits. She does not exhibit severe withdrawal and is not delirious on examination. Finally, she did not harbor thoughts of intentional harm to self or others and is not deemed imminently dangerous.
You document that in your opinion, despite Ms. B’s unfortunate choices and questionable judgment, she does have the capacity to make informed decisions regarding her care and could be released against medical advice if she so chooses, while providing her with information about available resources should she decide to seek rehabilitation in the future.
An increasingly common scenario
Decisional capacity assessment in patients with SUDs is an increasingly common reason for psychiatric consultations. Primary and secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. The same principles that guide the assessment of decisional capacity in patients with other psychiatric or cognitive disorders should be applied to compromised individuals with SUDs. In challenging cases, a skilled psychiatric evaluation that is supported by a thorough cognitive examination and, when required, complemented by a legal or ethical consultation, can help clinicians make safe and judicious decisions.
Bottom Line
Assessing the decisional capacity of a patient with a substance use disorder can be challenging. Primary or secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. A skilled psychiatric evaluation that includes a thorough cognitive examination and is complemented by legal or ethical consultation can help in making judicious decisions.
Related Resources
- Tan SY. Determining patients’ decisional capacity. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/137939/practice-management/determining-patients-decisional-capacity. Published May 10, 2017.
- Sorrentino R. Performing capacity evaluations: What’s expected from your consult. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(1):41-44.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Naloxone nasal spray • Narcan
1. Karlawish K. Assessment of decision-making capacity in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/assessment-of-decision-making-capacity-in-adults. Updated July 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
2. Owens PL, Mutter R, Stocks C. Mental health and substance abuse-related emergency department visits among adults, 2007. HCUP Statistical Brief #92. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK52659/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK52659.pdf. Published July 2010. Accessed August 19, 2019.
3. Smothers BA, Yahr HT. Alcohol use disorder and illicit drug use in admissions to general hospitals in the United States. Am J Addict. 2005;14(3):256-267.
4. Jeste DV, Saks E. Decisional capacity in mental illness and substance use disorders: empirical database and policy implications. Behav Sci Law. 2006;24(4):607-628.
5. Bechara A, Damasio H. Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia. 2002;40(10):1675-1689.
6. Grant S, Contoreggi C, London ED. Drug abusers show impaired performance in a laboratory test of decision making. Neuropsychologia. 2000;38(8):1180-1187.
7. MacDonald TK, Zanna MP, Fong GT. Decision making in altered states: effects of alcohol on attitudes toward drinking and driving. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1995;68(6):973-985.
8. Boettger S, Bergman M, Jenewein J, et al. Assessment of decisional capacity: prevalence of medical illness and psychiatric comorbidities. Palliat Support Care. 2015;13(5):1275-1281.
9. Charland LC. Chapter 6: Decision-making capacity and responsibility in addiction. In: Poland J, Graham G. Addiction and responsibility. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press Scholarship Online; 2011:139-158.
10. Martel ML, Klein LR, Miner JR, et al. A brief assessment of capacity to consent instrument in acutely intoxicated emergency department patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2018;36(1):18-23.
11. MacLullich AM, Beaglehole A, Hall RJ, et al. Delirium and long-term cognitive impairment. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21(1):30-42.
12. Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1306-1316.
13. Rehm J, Hasan OSM, Black SE, et al. Alcohol use and dementia: a systematic scoping review. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):1.
14. Jain A, Christopher P, Appelbaum PS. Civil commitment for opioid and other substance use disorders: does it work? Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(4):374-376.
15. Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Chapter 6: Using the MacArthur competence assessment tool – treatment. In: Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Assessing competence to consent to treatment: a guide for physicians and other health professionals. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1998:101-126.
16. Hazelton LD, Sterns GL, Chisholm T. Decision-making capacity and alcohol abuse: clinical and ethical considerations in personal care choices. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2003;25(2):130-135.
Ms. B, age 31, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance after emergency medical technicians used naloxone nasal spray to revive her following an overdose on heroin. She reports daily IV heroin use for the last 4 years as well as frequent use of other illicit substances, including marijuana and alprazolam, for which she does not have
How can you determine if Ms. B has the capacity to make decisions regarding her care?
Decisional capacity is defined as a patient’s ability to use information about an illness and the proposed treatment options to make a choice that is congruent with one’s own values and preferences.1 Determining whether a patient has adequate capacity to make decisions regarding their care is an inherent aspect of all clinician-patient interactions.
Published reports have focused on the challenges clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with psychiatric and cognitive disorders. However, there is little evidence about assessing decisional capacity in patients with substance use disorders (SUDs), even though increasing numbers of patients with SUDs are presenting to EDs2 and being admitted as inpatients in general hospitals.3 In this article, I discuss:
- the biologic basis for impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs
- common substance use–related conditions that may impact a patient’s decisional capacity
- the clinical challenges and legal considerations clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with SUDs
- how to assess decisional capacity in such patients.
Decisional capacity vs competence
“Capacity” and “competence” are not the same. Decisional capacity, which refers to the ability to make decisions, is a clinical construct that is determined by clinicians and is generally used in the acute clinical setting. Because cognition is the main determinant of capacity, conditions or treatments that affect cognition can impair an individual’s decision-making capacity.1 Decisional capacity is not a global concept but a decision-specific one, subject to fluctuations depending on the time and the nature of the decision at hand. Therefore, requests for determination of decisional capacity in the clinical setting should be specific to an individual decision or set of decisions.
In contrast, competence is an enduring legal determination of incapacitation, typically made by a probate judge. It refers to the ability of an individual to perform actions needed to put decisions into effect. Decisional capacity as assessed by a clinician often serves as the basis for petitions submitted for the purpose of competency adjudication by the judicial system.
A biologic basis for impaired decision-making?
Jeste and Saks4 suggested that addiction itself is characterized by impaired decision-making because individuals keep using a substance despite experiencing recurrent physical, psychologic, or social problems caused or worsened by the substance. Several studies suggest there may be a biologic basis for impaired decision-making in these patients, even in the absence of severe psychiatric or cognitive disorders.
Continue to: Bechara and Damasio found...
Bechara and Damasio5 found that the decision-making impairment seen in some patients with SUDs was similar to that observed in patients who have lesions of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. In both groups of patients, the impaired decision-making was characterized by a preference to opt for high immediate reward despite even higher future losses.
These deficits were also observed by Grant et al.6 In this study, patients with SUDs displayed markedly impaired performance on the Gambling Task, which examines decisions that result in long-term losses that exceed short-term gains. However, patients with SUDs performed similarly to controls on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, which evaluates the ability to form abstract concepts and to shift from established response sets.
MacDonald et al7 used a laboratory experiment and 2 field studies to test the hypothesis that alcohol affects attitudes and intentions toward drinking and driving. Their findings support the concept that alcohol intoxication decreases cognitive capacity such that people are more likely to attend to only the most salient cues.7
Whether the impairment documented in such studies is a contributing factor in addiction or is a result of addiction remains uncertain. While individuals with SUDs may have some level of impairment in decision-making in general, particularly in regard to their substance use, their decisional capacity on specific clinical decisions should be assessed carefully. In a study of 300 consecutive psychiatric consultations for decisional capacity at an urban hospital, Boettger et al8 found that 41% were related to SUDs. Of these, 37% were found to have impaired decisional capacity.
Impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs may specifically pertain to choices related to their addiction, including9:
- consent for addiction treatment
- consistency in maintaining a choice of recovery
- changing values regarding treatment over time
- capacity to participate in addiction research involving the use of addictive substances.
Continue to: It is important to recognize...
It is important to recognize that this impairment may not necessarily translate into altered decisional capacity regarding other health care decisions, such as consenting to surgery or other necessary medical interventions.9
Substance-related disorders that affect decisional capacity
Substance-related syndromes can affect mood, reality testing, and/or cognitive function, thereby directly impacting a patient’s decisional capacity. Substance-related syndromes can be divided into 2 categories: 1) disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance, and 2) secondary disorders resulting from/or associated with substance use.
Disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance
Temporary/reversible incapacitation
- Acute intoxication or intoxication delirium may be the most frequent type of temporary incapacitation. It can result from toxic levels of licit or illicit substances; alcohol is likely the most frequent offending agent. Although some individuals who are intoxicated may appear to be alert, oriented, and able to engage in lengthy conversations, the majority do not possess adequate decisional capacity.10
- Withdrawal delirium, associated with longstanding alcohol, sedative-hypnotic, or barbiturate dependence, is typically prolonged, but usually resolves, either spontaneously or with treatment. Although most deliria resolve once the underlying etiology is corrected, vulnerable individuals may experience irreversible cognitive impairment and permanent decisional incapacitation.11,12
- Severe substance-induced depressive disorders, especially if accompanied by frank psychotic symptoms or severe depressive distortions of reality, may result in decisional incapacity. Substance abuse treatment that incorporates multiple strategies, sometimes in conjunction with pharmacotherapy to manage depression, should lead to sufficient recovery and restoration of decisional capacity.
- Transient psychotic disorders such as those associated with the use of stimulants are often treatable. Patients may recover decisional capacity spontaneously or with treatment.
Permanent incapacitation
- Dementia is associated with substance use, particularly alcohol use.13 For a patient who develops dementia, no appreciable recovery can be expected, even with prolonged abstinence.
- Persistent amnestic disorders (eg, Korsakoff syndrome) resulting from undiagnosed or untreated severe thiamine deficiency (Wernicke’s encephalopathy). Although an isolated Korsakoff syndrome consists primarily of anterograde amnesia, these patients may experience additional cognitive impairment resulting from years of alcohol consumption or associated with other neurodegenerative processes, and therefore are sufficiently impaired and lack decisional capacity. Even in the absence of such concomitant cognitive deficits, a very severe anterograde amnestic disorder directly impacts a patient’s capacity to perform the necessary tasks required to give informed consent. The inability to consolidate information about new medical developments, treatments, and procedures, even when they are thoroughly explained by the medical team, can pose serious challenges. For example, a patient may protest to being taken to surgery because he/she does not recall signing a consent form the previous day.
- Enduring severe and treatment-refractory psychotic disorders associated with drug use, specifically stimulants, can result in permanent incapacitation similar to that seen in severe primary psychotic disorders (such as treatment-resistant schizophrenia).
- Hepatic encephalopathy may be seen in patients with advanced cirrhosis of the liver (due to hepatitis C resulting from IV drug use, and/or alcohol use). In late stages of cirrhosis, the confusional state patients experience may become severe and may no longer be reversible unless liver transplantation is available and successful. This would therefore constitute a basis for permanent decisional incapacitation.
- Human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis or dementia can result from IV drug use.
Continue to: Clinical challenges
Clinical challenges
In intensive care settings, where a patient with a SUD may be treated for acute life-threatening intoxication or severe withdrawal delirium, an assumption of decisional incapacitation often exists as a result of medical acuity and impaired mentation. In these situations, treatment usually proceeds with consent obtained from next-of-kin, a guardian, or an administrative (hospital) authority when other substitute decision makers are unavailable or unwilling. In such cases, psychiatric consultation can play a dual role in documenting the patient’s decisional capacity and also in contributing to the care of patients with SUDs.
It is critical to perform a cognitive evaluation and mental status examination in a medically compromised patient with an SUD. Unfortunately, serious cognitive disorders can often be concealed by a superficially jovial or verbally skilled patient, or by an uncooperative individual who refuses to engage in a thorough conversation with his/her clinicians. These scenarios present significant challenges and may result in missed opportunities for care or premature discharges. Negative countertransference by clinicians toward patients with SUDs may also promote poor outcomes. For difficult cases, legal and ethical consultations may help mitigate risk and guide management approaches (Box14).
Box
The legal system rarely views patients with substance use disorders (SUDs) as lacking decisional capacity in the absence of overt psychiatric or cognitive deficits. The penal system offers little if any mitigation of liability on account of addiction in civil or criminal cases. On the contrary, intoxication is an aggravating factor in such settings. Despite extensive literature that questions the “free will,” accountability, and responsibility of patients with SUDs, the legal system takes an “all-or-none” approach to this issue. It assumes free choice and accountability for patients with SUDs, except when a clear superimposed psychiatric or cognitive disorder (such as psychosis or dementia) exists. Rarely, some jurisdictions may allow for mental health commitments on account of severe and persistent addictive behaviors that clearly pose a risk to the individual or to society, implicitly recognizing that incapacitation can result from severe addiction. Nevertheless, a finding of imminent or impending dangerousness is generally required for such commitments to be justified.
In other situations, individual health care settings may resort to local hospital policies that allow impaired patients with SUDs with a clearly altered mental status to be detained for the purpose of completing medical treatment. Presumably, discharge would occur when the medical and psychiatric acuity has resolved (often under the umbrella of a “Medical Hold” policy). Jain et al14 suggested that although such commitment laws for patients with SUDs may be appealing to some people, especially family members, specific statutes and their implementation are highly variable; the deprivation of liberty raises ethical concerns; and outcome data are limited. Conversely, most states either do not have such legislation, or rarely enforce it.
How to assess decisional capacity
A direct conclusion of incapacity in an individual cannot be determined solely on the knowledge of the patient having a SUD-related clinical condition. (The possible exception to this may be a patient with severe dementia.)
- understand the decision at hand
- discuss its benefits and risks
- describe alternatives
- demonstrate an appreciation of the implications of treatment or lack thereof
- communicate a clear and consistent choice.
Continue to: While most clinicians...
While most clinicians rely on a psychiatric interview (with or without a cognitive examination) to make these determinations, several instruments have been developed to aid these evaluations, such as the MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Treatment (Mac-CAT-T).15 In patients with potentially reversible incapacitating conditions, serial examinations over time, especially re-evaluation when a patient has achieved and maintained sobriety, may be necessary and helpful.
The Table offers a guide to assessing decisional capacity in a patient with an SUD.
Who should conduct the assessment?
Mental health professionals—usually psychiatrists or psychologists—are consulted when there is uncertainty about a patient’s decisional capacity, and when a more thorough mental status examination is warranted to formulate an informed opinion.16 Unfortunately, this typically occurs only if a patient refuses treatment or demands to be discharged before treatment has been completed, or there is a high level of risk to the patient or others after discharge.
In acute settings, when a patient consents to treatment, a psychiatric consultation regarding decisional capacity is rarely requested. While it is often tempting for medical or surgical teams to proceed with an intervention in a cooperative patient who willingly signs a consent form without a formal assessment of his/her decisional capacity, doing so raises challenging ethical and legal questions in the event of an adverse outcome. It is therefore prudent to strongly recommend that medical and surgical colleagues obtain a psychiatric consultation when an individual’s decisional capacity is uncertain, especially when a patient is known to have a psychiatric or neurocognitive disorder, or exhibits evidence of recent mental status changes. In cases of potentially reversible impairment (eg, delirium, psychosis, or acute anxiety), targeted interventions may help restore capacity and allow treatment to proceed.
No jurisdictions mandate that the determination of decisional capacity should be made exclusively by a mental health professional. Any treating health care professional (usually the attending physician) can make a determination of decisional capacity in scenarios where there is no overt evidence the patient has a mental or cognitive disorder and the patient is communicating clear and reasoned choices, or when a patient is profoundly impaired and no meaningful communication can take place.
Continue to: CASE CONTINUED
CASE CONTINUED
The emergency physician requests a psychiatric consultation. You assess Ms. B’s decisional capacity using the Mac-CAT-T along with a standard psychiatric evaluation. Her score of 14 reflects that she is able to understand the risks associated with her opioid use, and although irritated by engaging in such a discussion, is capable of reasoning through the various medical and psychosocial aspects of her addiction, and shows moderate appreciation of the impact of her choices on her future and that of significant others. The psychiatric evaluation fails to elicit any substantial mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders associated with/or resulting from her addiction, and her cognitive examination is within normal limits. She does not exhibit severe withdrawal and is not delirious on examination. Finally, she did not harbor thoughts of intentional harm to self or others and is not deemed imminently dangerous.
You document that in your opinion, despite Ms. B’s unfortunate choices and questionable judgment, she does have the capacity to make informed decisions regarding her care and could be released against medical advice if she so chooses, while providing her with information about available resources should she decide to seek rehabilitation in the future.
An increasingly common scenario
Decisional capacity assessment in patients with SUDs is an increasingly common reason for psychiatric consultations. Primary and secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. The same principles that guide the assessment of decisional capacity in patients with other psychiatric or cognitive disorders should be applied to compromised individuals with SUDs. In challenging cases, a skilled psychiatric evaluation that is supported by a thorough cognitive examination and, when required, complemented by a legal or ethical consultation, can help clinicians make safe and judicious decisions.
Bottom Line
Assessing the decisional capacity of a patient with a substance use disorder can be challenging. Primary or secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. A skilled psychiatric evaluation that includes a thorough cognitive examination and is complemented by legal or ethical consultation can help in making judicious decisions.
Related Resources
- Tan SY. Determining patients’ decisional capacity. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/137939/practice-management/determining-patients-decisional-capacity. Published May 10, 2017.
- Sorrentino R. Performing capacity evaluations: What’s expected from your consult. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(1):41-44.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Naloxone nasal spray • Narcan
Ms. B, age 31, is brought to the emergency department (ED) via ambulance after emergency medical technicians used naloxone nasal spray to revive her following an overdose on heroin. She reports daily IV heroin use for the last 4 years as well as frequent use of other illicit substances, including marijuana and alprazolam, for which she does not have
How can you determine if Ms. B has the capacity to make decisions regarding her care?
Decisional capacity is defined as a patient’s ability to use information about an illness and the proposed treatment options to make a choice that is congruent with one’s own values and preferences.1 Determining whether a patient has adequate capacity to make decisions regarding their care is an inherent aspect of all clinician-patient interactions.
Published reports have focused on the challenges clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with psychiatric and cognitive disorders. However, there is little evidence about assessing decisional capacity in patients with substance use disorders (SUDs), even though increasing numbers of patients with SUDs are presenting to EDs2 and being admitted as inpatients in general hospitals.3 In this article, I discuss:
- the biologic basis for impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs
- common substance use–related conditions that may impact a patient’s decisional capacity
- the clinical challenges and legal considerations clinicians face when assessing decisional capacity in patients with SUDs
- how to assess decisional capacity in such patients.
Decisional capacity vs competence
“Capacity” and “competence” are not the same. Decisional capacity, which refers to the ability to make decisions, is a clinical construct that is determined by clinicians and is generally used in the acute clinical setting. Because cognition is the main determinant of capacity, conditions or treatments that affect cognition can impair an individual’s decision-making capacity.1 Decisional capacity is not a global concept but a decision-specific one, subject to fluctuations depending on the time and the nature of the decision at hand. Therefore, requests for determination of decisional capacity in the clinical setting should be specific to an individual decision or set of decisions.
In contrast, competence is an enduring legal determination of incapacitation, typically made by a probate judge. It refers to the ability of an individual to perform actions needed to put decisions into effect. Decisional capacity as assessed by a clinician often serves as the basis for petitions submitted for the purpose of competency adjudication by the judicial system.
A biologic basis for impaired decision-making?
Jeste and Saks4 suggested that addiction itself is characterized by impaired decision-making because individuals keep using a substance despite experiencing recurrent physical, psychologic, or social problems caused or worsened by the substance. Several studies suggest there may be a biologic basis for impaired decision-making in these patients, even in the absence of severe psychiatric or cognitive disorders.
Continue to: Bechara and Damasio found...
Bechara and Damasio5 found that the decision-making impairment seen in some patients with SUDs was similar to that observed in patients who have lesions of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. In both groups of patients, the impaired decision-making was characterized by a preference to opt for high immediate reward despite even higher future losses.
These deficits were also observed by Grant et al.6 In this study, patients with SUDs displayed markedly impaired performance on the Gambling Task, which examines decisions that result in long-term losses that exceed short-term gains. However, patients with SUDs performed similarly to controls on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, which evaluates the ability to form abstract concepts and to shift from established response sets.
MacDonald et al7 used a laboratory experiment and 2 field studies to test the hypothesis that alcohol affects attitudes and intentions toward drinking and driving. Their findings support the concept that alcohol intoxication decreases cognitive capacity such that people are more likely to attend to only the most salient cues.7
Whether the impairment documented in such studies is a contributing factor in addiction or is a result of addiction remains uncertain. While individuals with SUDs may have some level of impairment in decision-making in general, particularly in regard to their substance use, their decisional capacity on specific clinical decisions should be assessed carefully. In a study of 300 consecutive psychiatric consultations for decisional capacity at an urban hospital, Boettger et al8 found that 41% were related to SUDs. Of these, 37% were found to have impaired decisional capacity.
Impaired decision-making in patients with SUDs may specifically pertain to choices related to their addiction, including9:
- consent for addiction treatment
- consistency in maintaining a choice of recovery
- changing values regarding treatment over time
- capacity to participate in addiction research involving the use of addictive substances.
Continue to: It is important to recognize...
It is important to recognize that this impairment may not necessarily translate into altered decisional capacity regarding other health care decisions, such as consenting to surgery or other necessary medical interventions.9
Substance-related disorders that affect decisional capacity
Substance-related syndromes can affect mood, reality testing, and/or cognitive function, thereby directly impacting a patient’s decisional capacity. Substance-related syndromes can be divided into 2 categories: 1) disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance, and 2) secondary disorders resulting from/or associated with substance use.
Disorders resulting from the direct effects of the substance
Temporary/reversible incapacitation
- Acute intoxication or intoxication delirium may be the most frequent type of temporary incapacitation. It can result from toxic levels of licit or illicit substances; alcohol is likely the most frequent offending agent. Although some individuals who are intoxicated may appear to be alert, oriented, and able to engage in lengthy conversations, the majority do not possess adequate decisional capacity.10
- Withdrawal delirium, associated with longstanding alcohol, sedative-hypnotic, or barbiturate dependence, is typically prolonged, but usually resolves, either spontaneously or with treatment. Although most deliria resolve once the underlying etiology is corrected, vulnerable individuals may experience irreversible cognitive impairment and permanent decisional incapacitation.11,12
- Severe substance-induced depressive disorders, especially if accompanied by frank psychotic symptoms or severe depressive distortions of reality, may result in decisional incapacity. Substance abuse treatment that incorporates multiple strategies, sometimes in conjunction with pharmacotherapy to manage depression, should lead to sufficient recovery and restoration of decisional capacity.
- Transient psychotic disorders such as those associated with the use of stimulants are often treatable. Patients may recover decisional capacity spontaneously or with treatment.
Permanent incapacitation
- Dementia is associated with substance use, particularly alcohol use.13 For a patient who develops dementia, no appreciable recovery can be expected, even with prolonged abstinence.
- Persistent amnestic disorders (eg, Korsakoff syndrome) resulting from undiagnosed or untreated severe thiamine deficiency (Wernicke’s encephalopathy). Although an isolated Korsakoff syndrome consists primarily of anterograde amnesia, these patients may experience additional cognitive impairment resulting from years of alcohol consumption or associated with other neurodegenerative processes, and therefore are sufficiently impaired and lack decisional capacity. Even in the absence of such concomitant cognitive deficits, a very severe anterograde amnestic disorder directly impacts a patient’s capacity to perform the necessary tasks required to give informed consent. The inability to consolidate information about new medical developments, treatments, and procedures, even when they are thoroughly explained by the medical team, can pose serious challenges. For example, a patient may protest to being taken to surgery because he/she does not recall signing a consent form the previous day.
- Enduring severe and treatment-refractory psychotic disorders associated with drug use, specifically stimulants, can result in permanent incapacitation similar to that seen in severe primary psychotic disorders (such as treatment-resistant schizophrenia).
- Hepatic encephalopathy may be seen in patients with advanced cirrhosis of the liver (due to hepatitis C resulting from IV drug use, and/or alcohol use). In late stages of cirrhosis, the confusional state patients experience may become severe and may no longer be reversible unless liver transplantation is available and successful. This would therefore constitute a basis for permanent decisional incapacitation.
- Human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis or dementia can result from IV drug use.
Continue to: Clinical challenges
Clinical challenges
In intensive care settings, where a patient with a SUD may be treated for acute life-threatening intoxication or severe withdrawal delirium, an assumption of decisional incapacitation often exists as a result of medical acuity and impaired mentation. In these situations, treatment usually proceeds with consent obtained from next-of-kin, a guardian, or an administrative (hospital) authority when other substitute decision makers are unavailable or unwilling. In such cases, psychiatric consultation can play a dual role in documenting the patient’s decisional capacity and also in contributing to the care of patients with SUDs.
It is critical to perform a cognitive evaluation and mental status examination in a medically compromised patient with an SUD. Unfortunately, serious cognitive disorders can often be concealed by a superficially jovial or verbally skilled patient, or by an uncooperative individual who refuses to engage in a thorough conversation with his/her clinicians. These scenarios present significant challenges and may result in missed opportunities for care or premature discharges. Negative countertransference by clinicians toward patients with SUDs may also promote poor outcomes. For difficult cases, legal and ethical consultations may help mitigate risk and guide management approaches (Box14).
Box
The legal system rarely views patients with substance use disorders (SUDs) as lacking decisional capacity in the absence of overt psychiatric or cognitive deficits. The penal system offers little if any mitigation of liability on account of addiction in civil or criminal cases. On the contrary, intoxication is an aggravating factor in such settings. Despite extensive literature that questions the “free will,” accountability, and responsibility of patients with SUDs, the legal system takes an “all-or-none” approach to this issue. It assumes free choice and accountability for patients with SUDs, except when a clear superimposed psychiatric or cognitive disorder (such as psychosis or dementia) exists. Rarely, some jurisdictions may allow for mental health commitments on account of severe and persistent addictive behaviors that clearly pose a risk to the individual or to society, implicitly recognizing that incapacitation can result from severe addiction. Nevertheless, a finding of imminent or impending dangerousness is generally required for such commitments to be justified.
In other situations, individual health care settings may resort to local hospital policies that allow impaired patients with SUDs with a clearly altered mental status to be detained for the purpose of completing medical treatment. Presumably, discharge would occur when the medical and psychiatric acuity has resolved (often under the umbrella of a “Medical Hold” policy). Jain et al14 suggested that although such commitment laws for patients with SUDs may be appealing to some people, especially family members, specific statutes and their implementation are highly variable; the deprivation of liberty raises ethical concerns; and outcome data are limited. Conversely, most states either do not have such legislation, or rarely enforce it.
How to assess decisional capacity
A direct conclusion of incapacity in an individual cannot be determined solely on the knowledge of the patient having a SUD-related clinical condition. (The possible exception to this may be a patient with severe dementia.)
- understand the decision at hand
- discuss its benefits and risks
- describe alternatives
- demonstrate an appreciation of the implications of treatment or lack thereof
- communicate a clear and consistent choice.
Continue to: While most clinicians...
While most clinicians rely on a psychiatric interview (with or without a cognitive examination) to make these determinations, several instruments have been developed to aid these evaluations, such as the MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool for Treatment (Mac-CAT-T).15 In patients with potentially reversible incapacitating conditions, serial examinations over time, especially re-evaluation when a patient has achieved and maintained sobriety, may be necessary and helpful.
The Table offers a guide to assessing decisional capacity in a patient with an SUD.
Who should conduct the assessment?
Mental health professionals—usually psychiatrists or psychologists—are consulted when there is uncertainty about a patient’s decisional capacity, and when a more thorough mental status examination is warranted to formulate an informed opinion.16 Unfortunately, this typically occurs only if a patient refuses treatment or demands to be discharged before treatment has been completed, or there is a high level of risk to the patient or others after discharge.
In acute settings, when a patient consents to treatment, a psychiatric consultation regarding decisional capacity is rarely requested. While it is often tempting for medical or surgical teams to proceed with an intervention in a cooperative patient who willingly signs a consent form without a formal assessment of his/her decisional capacity, doing so raises challenging ethical and legal questions in the event of an adverse outcome. It is therefore prudent to strongly recommend that medical and surgical colleagues obtain a psychiatric consultation when an individual’s decisional capacity is uncertain, especially when a patient is known to have a psychiatric or neurocognitive disorder, or exhibits evidence of recent mental status changes. In cases of potentially reversible impairment (eg, delirium, psychosis, or acute anxiety), targeted interventions may help restore capacity and allow treatment to proceed.
No jurisdictions mandate that the determination of decisional capacity should be made exclusively by a mental health professional. Any treating health care professional (usually the attending physician) can make a determination of decisional capacity in scenarios where there is no overt evidence the patient has a mental or cognitive disorder and the patient is communicating clear and reasoned choices, or when a patient is profoundly impaired and no meaningful communication can take place.
Continue to: CASE CONTINUED
CASE CONTINUED
The emergency physician requests a psychiatric consultation. You assess Ms. B’s decisional capacity using the Mac-CAT-T along with a standard psychiatric evaluation. Her score of 14 reflects that she is able to understand the risks associated with her opioid use, and although irritated by engaging in such a discussion, is capable of reasoning through the various medical and psychosocial aspects of her addiction, and shows moderate appreciation of the impact of her choices on her future and that of significant others. The psychiatric evaluation fails to elicit any substantial mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorders associated with/or resulting from her addiction, and her cognitive examination is within normal limits. She does not exhibit severe withdrawal and is not delirious on examination. Finally, she did not harbor thoughts of intentional harm to self or others and is not deemed imminently dangerous.
You document that in your opinion, despite Ms. B’s unfortunate choices and questionable judgment, she does have the capacity to make informed decisions regarding her care and could be released against medical advice if she so chooses, while providing her with information about available resources should she decide to seek rehabilitation in the future.
An increasingly common scenario
Decisional capacity assessment in patients with SUDs is an increasingly common reason for psychiatric consultations. Primary and secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. The same principles that guide the assessment of decisional capacity in patients with other psychiatric or cognitive disorders should be applied to compromised individuals with SUDs. In challenging cases, a skilled psychiatric evaluation that is supported by a thorough cognitive examination and, when required, complemented by a legal or ethical consultation, can help clinicians make safe and judicious decisions.
Bottom Line
Assessing the decisional capacity of a patient with a substance use disorder can be challenging. Primary or secondary conditions related to substance use can affect a patient’s decisional capacity on a temporary or permanent basis. A skilled psychiatric evaluation that includes a thorough cognitive examination and is complemented by legal or ethical consultation can help in making judicious decisions.
Related Resources
- Tan SY. Determining patients’ decisional capacity. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/137939/practice-management/determining-patients-decisional-capacity. Published May 10, 2017.
- Sorrentino R. Performing capacity evaluations: What’s expected from your consult. Current Psychiatry. 2014;13(1):41-44.
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Naloxone nasal spray • Narcan
1. Karlawish K. Assessment of decision-making capacity in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/assessment-of-decision-making-capacity-in-adults. Updated July 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
2. Owens PL, Mutter R, Stocks C. Mental health and substance abuse-related emergency department visits among adults, 2007. HCUP Statistical Brief #92. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK52659/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK52659.pdf. Published July 2010. Accessed August 19, 2019.
3. Smothers BA, Yahr HT. Alcohol use disorder and illicit drug use in admissions to general hospitals in the United States. Am J Addict. 2005;14(3):256-267.
4. Jeste DV, Saks E. Decisional capacity in mental illness and substance use disorders: empirical database and policy implications. Behav Sci Law. 2006;24(4):607-628.
5. Bechara A, Damasio H. Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia. 2002;40(10):1675-1689.
6. Grant S, Contoreggi C, London ED. Drug abusers show impaired performance in a laboratory test of decision making. Neuropsychologia. 2000;38(8):1180-1187.
7. MacDonald TK, Zanna MP, Fong GT. Decision making in altered states: effects of alcohol on attitudes toward drinking and driving. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1995;68(6):973-985.
8. Boettger S, Bergman M, Jenewein J, et al. Assessment of decisional capacity: prevalence of medical illness and psychiatric comorbidities. Palliat Support Care. 2015;13(5):1275-1281.
9. Charland LC. Chapter 6: Decision-making capacity and responsibility in addiction. In: Poland J, Graham G. Addiction and responsibility. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press Scholarship Online; 2011:139-158.
10. Martel ML, Klein LR, Miner JR, et al. A brief assessment of capacity to consent instrument in acutely intoxicated emergency department patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2018;36(1):18-23.
11. MacLullich AM, Beaglehole A, Hall RJ, et al. Delirium and long-term cognitive impairment. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21(1):30-42.
12. Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1306-1316.
13. Rehm J, Hasan OSM, Black SE, et al. Alcohol use and dementia: a systematic scoping review. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):1.
14. Jain A, Christopher P, Appelbaum PS. Civil commitment for opioid and other substance use disorders: does it work? Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(4):374-376.
15. Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Chapter 6: Using the MacArthur competence assessment tool – treatment. In: Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Assessing competence to consent to treatment: a guide for physicians and other health professionals. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1998:101-126.
16. Hazelton LD, Sterns GL, Chisholm T. Decision-making capacity and alcohol abuse: clinical and ethical considerations in personal care choices. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2003;25(2):130-135.
1. Karlawish K. Assessment of decision-making capacity in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/assessment-of-decision-making-capacity-in-adults. Updated July 2019. Accessed August 19, 2019.
2. Owens PL, Mutter R, Stocks C. Mental health and substance abuse-related emergency department visits among adults, 2007. HCUP Statistical Brief #92. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK52659/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK52659.pdf. Published July 2010. Accessed August 19, 2019.
3. Smothers BA, Yahr HT. Alcohol use disorder and illicit drug use in admissions to general hospitals in the United States. Am J Addict. 2005;14(3):256-267.
4. Jeste DV, Saks E. Decisional capacity in mental illness and substance use disorders: empirical database and policy implications. Behav Sci Law. 2006;24(4):607-628.
5. Bechara A, Damasio H. Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia. 2002;40(10):1675-1689.
6. Grant S, Contoreggi C, London ED. Drug abusers show impaired performance in a laboratory test of decision making. Neuropsychologia. 2000;38(8):1180-1187.
7. MacDonald TK, Zanna MP, Fong GT. Decision making in altered states: effects of alcohol on attitudes toward drinking and driving. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1995;68(6):973-985.
8. Boettger S, Bergman M, Jenewein J, et al. Assessment of decisional capacity: prevalence of medical illness and psychiatric comorbidities. Palliat Support Care. 2015;13(5):1275-1281.
9. Charland LC. Chapter 6: Decision-making capacity and responsibility in addiction. In: Poland J, Graham G. Addiction and responsibility. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press Scholarship Online; 2011:139-158.
10. Martel ML, Klein LR, Miner JR, et al. A brief assessment of capacity to consent instrument in acutely intoxicated emergency department patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2018;36(1):18-23.
11. MacLullich AM, Beaglehole A, Hall RJ, et al. Delirium and long-term cognitive impairment. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21(1):30-42.
12. Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1306-1316.
13. Rehm J, Hasan OSM, Black SE, et al. Alcohol use and dementia: a systematic scoping review. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):1.
14. Jain A, Christopher P, Appelbaum PS. Civil commitment for opioid and other substance use disorders: does it work? Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69(4):374-376.
15. Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Chapter 6: Using the MacArthur competence assessment tool – treatment. In: Grisso T, Appelbaum PS. Assessing competence to consent to treatment: a guide for physicians and other health professionals. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1998:101-126.
16. Hazelton LD, Sterns GL, Chisholm T. Decision-making capacity and alcohol abuse: clinical and ethical considerations in personal care choices. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2003;25(2):130-135.
Drug abuse–linked infective endocarditis spiking in U.S.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC increased from 48 cases/100,000 in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study identifying about a more than 950,000 cases of IC from the National Inpatient Sample registry.
Disclosures: None.
Source: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
CDC, SAMHSA commit $1.8 billion to combat opioid crisis
More financial reinforcements are arriving in the battle against the opioid crisis, with the Trump administration promising more than $1.8 billion in new funds to help states address the crisis.
Speaking at a Sept. 4 press conference announcing the funding, President Donald Trump said the money will be used “to increase access to medication and medication-assisted treatment and mental health resources, which are critical for ending homelessness and getting people the help they deserve.” The president added that the grants also will help state and local governments obtain high-quality, comprehensive data.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will provide more than $900 million in new funding over the next 3 years to “advance the understanding of the opioid overdose epidemic and to scale-up prevention and response activities,” the Department of Health & Human Services said in a statement announcing the funding.
“This money will help states and local communities track overdose data and develop strategies that save lives,” HHS Secretary Alex Azar said during the press conference.
He noted that, when the Trump administration began, overdose data were published with a 12-month lag. That lag has since shortened to 6 months. One of the goals with the new funding is to bring data publishing as close to real time as possible.
Separately, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration awarded $932 million to all 50 states as part of its State Opioid Response grants, which “provide flexible funding to state governments to support prevention, treatment, and recovery services in the ways that meet the needs of their state,” according to the HHS statement.
That flexibility “can mean everything from expanding the use of medication-assisted treatment in criminal justice settings or in rural areas via telemedicine, to youth-focused community-based prevention efforts,” Secretary Azar explained. The funds can also support employment coaching and naloxone distribution, he added.
More financial reinforcements are arriving in the battle against the opioid crisis, with the Trump administration promising more than $1.8 billion in new funds to help states address the crisis.
Speaking at a Sept. 4 press conference announcing the funding, President Donald Trump said the money will be used “to increase access to medication and medication-assisted treatment and mental health resources, which are critical for ending homelessness and getting people the help they deserve.” The president added that the grants also will help state and local governments obtain high-quality, comprehensive data.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will provide more than $900 million in new funding over the next 3 years to “advance the understanding of the opioid overdose epidemic and to scale-up prevention and response activities,” the Department of Health & Human Services said in a statement announcing the funding.
“This money will help states and local communities track overdose data and develop strategies that save lives,” HHS Secretary Alex Azar said during the press conference.
He noted that, when the Trump administration began, overdose data were published with a 12-month lag. That lag has since shortened to 6 months. One of the goals with the new funding is to bring data publishing as close to real time as possible.
Separately, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration awarded $932 million to all 50 states as part of its State Opioid Response grants, which “provide flexible funding to state governments to support prevention, treatment, and recovery services in the ways that meet the needs of their state,” according to the HHS statement.
That flexibility “can mean everything from expanding the use of medication-assisted treatment in criminal justice settings or in rural areas via telemedicine, to youth-focused community-based prevention efforts,” Secretary Azar explained. The funds can also support employment coaching and naloxone distribution, he added.
More financial reinforcements are arriving in the battle against the opioid crisis, with the Trump administration promising more than $1.8 billion in new funds to help states address the crisis.
Speaking at a Sept. 4 press conference announcing the funding, President Donald Trump said the money will be used “to increase access to medication and medication-assisted treatment and mental health resources, which are critical for ending homelessness and getting people the help they deserve.” The president added that the grants also will help state and local governments obtain high-quality, comprehensive data.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will provide more than $900 million in new funding over the next 3 years to “advance the understanding of the opioid overdose epidemic and to scale-up prevention and response activities,” the Department of Health & Human Services said in a statement announcing the funding.
“This money will help states and local communities track overdose data and develop strategies that save lives,” HHS Secretary Alex Azar said during the press conference.
He noted that, when the Trump administration began, overdose data were published with a 12-month lag. That lag has since shortened to 6 months. One of the goals with the new funding is to bring data publishing as close to real time as possible.
Separately, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration awarded $932 million to all 50 states as part of its State Opioid Response grants, which “provide flexible funding to state governments to support prevention, treatment, and recovery services in the ways that meet the needs of their state,” according to the HHS statement.
That flexibility “can mean everything from expanding the use of medication-assisted treatment in criminal justice settings or in rural areas via telemedicine, to youth-focused community-based prevention efforts,” Secretary Azar explained. The funds can also support employment coaching and naloxone distribution, he added.