User login
Use hospital MRSA rates to guide pediatric osteomyelitis treatment
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PHM 2019
Mysterious vaping lung injuries may have flown under regulatory radar
It was the arrival of the second man in his early 20s gasping for air that alarmed Dixie Harris, MD. Young patients rarely get so sick, so fast, with a severe lung illness, and this was her second case in a matter of days.
Then she saw three more patients at her Utah telehealth clinic with similar symptoms. They did not have infections, but all had been vaping. When Dr. Harris heard several teenagers in Wisconsin had been hospitalized in similar cases, she quickly alerted her state health department.
As patients in hospitals across the country combat a mysterious illness linked to e-cigarettes, federal and state investigators are frantically trying to trace the outbreaks to specific vaping products that, until recently, were virtually unregulated.
As of Aug. 22, 2019, 193 potential vaping-related illnesses in 22 states had been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Wisconsin, which first put out an alert in July, has at least 16 confirmed and 15 suspected cases. Illinois has reported 34 patients, 1 of whom has died. Indiana is investigating 24 cases.
Lung doctors said they had seen warning signs for years that vaping could be hazardous as they treated patients. Medically it seemed problematic since it often involved inhaling chemicals not normally inhaled into the lungs. Despite that, assessing the safety of a new product storming the market fell between regulatory cracks, leaving doctors unsure where to register concerns before the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration took years to regulate e-cigarettes once a court determined it had the authority to do so.
“You don’t know what you’re putting into your lungs when you vape,” said Dr. Harris, a critical care pulmonologist. “It’s purported to be safe, but how do you know if it’s safe? To me, it’s a very dangerous thing.”
Off the radar
When e-cigarettes came to market about a decade ago, they fell into a regulatory no man’s land. They are not a food, not a drug, and not a medical device, any of which would have put them immediately in the FDA’s purview. And, until a few years ago, they weren’t even lumped in with tobacco products.
As a result, billions of dollars of vaping products have been sold online, at big-box retailers, and in corner stores without going through the FDA’s rigorous review process to assess their safety. Companies like Juul, Blu, and NJoy quickly established their brands of devices and cartridges, or pods. And thousands of related products are sold, sometimes on the black market, over the Internet, or beyond.
“It makes it really tough because we don’t know what we’re looking for,” said Ruth Lynfield, MD, the state epidemiologist for Minnesota, where several patients were admitted to the ICU as a result of the illness. She added that, if it turns out that the products in question were sold by unregistered retailers and manufacturers “on the street,” outbreak sleuths will have a harder time figuring out exactly what is in them.
With e-cigarettes, people can vape – or smoke – nicotine products, selecting flavorings like mint, mango, blueberry crème brûlée, or cookies and milk. They can also inhale cannabis products. Many are hopeful that e-cigarettes might be useful smoking cessation tools, but some research has called that into question.
The mysterious pulmonary disease cases have been linked to vaping, but it’s unclear whether there is a common device or chemical. In some states, including California and Utah, all of the patients had vaped cannabis products. One or more substances could be involved, health officials have said. The products used by several victims are being tested to see what they contained.
And this has apparently been the case for years.
Multiple doctors described seeing earlier cases of severe lung problems linked to vaping that were not officially reported or included in the current CDC count.
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a pulmonologist and researcher with the University of California, San Diego, said she saw her first case about 2 years ago. A young man had been vaping for months with the same device but developed acute lung injury when he switched flavors. She strongly suspected a link, but did not report the illness anywhere.
“It wasn’t that I didn’t want to report it, it’s that there’s no pathway” to do so, Dr. Alexander said.
She said she’s concerned that many physicians haven’t been asking patients about e-cigarette use and that there’s no way to document a case like this in the medical coding system.
John E. Parker, MD, of West Virginia University, Morgantown, said he saw his first patient with pneumonia tied to vaping in 2015. Doctors there were intrigued enough to report on the case at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. Dr. Parker and his team didn’t contact a federal agency, and Dr. Parker said it was unclear whom to call.
Numerous other cases have been reported in medical journals and at professional conferences in the years since. The FDA’s voluntary system for reporting tobacco-related health problems included 96 seizures and only 1 lung ailment tied to e-cigarettes between April and June 2019. The system appears to be utilized most by concerned citizens, rather than manufacturers or health care professionals.
But several lung specialists said that due to the patchwork nature of regulatory oversight over the years, the true scope of the problem is yet to be identified.
“We do know that e-cigarettes do not emit a harmless aerosol,” said Brian King, PhD, MPH, a deputy director in the Office on Smoking and Health at the CDC in a call with media on Aug. 23 about the outbreak. “It is possible that some of these cases were already occurring but we were not picking them up.”
Regulatory limits
The FDA has had limited authority to regulate e-cigarettes over the years.
In 2009, Congress passed the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, empowering the FDA to oversee the safety and sale of tobacco products. But e-cigarettes, still new, were not top of mind.
Later that year, the FDA tried to block imports of e-cigarettes, saying the combination drug-device products were unapproved and therefore illegal for sale in the United States. Two vaping companies, Smoking Everywhere and NJoy, sued, and a federal judge ruled in 2010 that the FDA should regulate e-cigarettes as tobacco products.
It took the agency 6 years to finalize what’s become known as the “deeming rule,” in which it formally began regulating e-cigarettes and e-liquids.
By then, it was May 2016, and the e-cigarette market had swelled to an estimated $4.1 billion, Wells Fargo Securities analyst Bonnie Herzog said at the time. Market researchers now project that the global industry could reach $48 billion by 2023.
Critics say the FDA took too long to act.
“I think the fact that FDA has been dillydallying [has made] figuring out what’s going on [with this outbreak] much harder,” said Stanton Glantz, PhD, a University of California, San Francisco, professor in its Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. “No question.”
The agency began by banning e-cigarette sales to minors and requiring all new vaping products to submit applications for authorization before they could come to market. Companies and retailers with thousands of products already on the market were granted 2 years to submit applications, and the FDA would get an additional year to evaluate the applications. Meanwhile, existing products could still be sold.
But when Scott Gottlieb, MD, arrived as the new FDA commissioner in 2017, the rule hadn’t been implemented and there was no formal guidance for companies to file applications, he said. As a result, he pushed the deadline back to 2022, drawing ire from public health advocates, who called foul over his previous ties to an e-cigarette retailer called Kure.
“I thought e-cigarettes at the time – and I still believe – that they represent an opportunity for currently addicted adult smokers to transition off of combustible tobacco,” he said in an interview, adding that other parts of the deeming rule went into effect as planned. “All I did was delay the application deadline.”
Dr. Gottlieb’s thinking changed the following year, when a national survey showed a sharp rise in teen vaping, which he called an “epidemic.” He announced that the agency would rethink the extended deadline and weigh whether to take flavors that appeal to kids off the market.
A judge ruled last month that e-cigarette makers would have only 10 more months to submit applications to the FDA. They’re now due in May 2020.
Asked about the lung injuries appearing now, Dr. Gottlieb, who left the FDA in April 2019, said he suspected counterfeit pods are to blame, given the geographic clustering of cases and the fact that, overall, the FDA is inspecting registered e-cigarette makers and retailers to make sure they’re complying with existing regulations.
“I think the manufacturers are culpable if their products are being used, whether the liquids are counterfeit or real,” he said. “Ultimately, they’re responsible for keeping their products out of the hands of kids.”
Juul, the leading e-cigarette maker, agreed that children shouldn’t be able to vape its products, and said curtailing access should be done “through significant regulation” and “enforcement.”
“When people say ‘Why aren’t these being regulated?’ They actually are all being regulated,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
For example, companies are required to label their products as potentially addictive, sell only to adults and comply with manufacturing standards. The agency has conducted thousands of inspections of e-cigarette manufacturers and retailers and taken enforcement actions against companies selling e-cigarettes that look like juice boxes, and against a company that was putting the ingredients found in erectile dysfunction drugs into its vape liquid.
Health departments investigating the outbreak told Kaiser Health News that e-cigarettes’ niche as a tobacco product instead of a drug has presented challenges. Most weren’t aware that adverse events could be reported to a database that tracks problems with tobacco products. And, because e-cigarettes never went through the FDA’s “gold-standard” approval process for drugs, doctors can’t readily look up a detailed list of known side effects.
But like other arms of the FDA, the tobacco office has tools and a team to investigate a public health threat just as the teams for drugs and devices do, Dr. Gottlieb said. It may even be better equipped because of its funding.
“I don’t think FDA is operating in any way with hands tied behind its back because of the way that the statute is set up,” he said.
Teen vaping has exploded during this regulatory tussle. In 2011, 1.5% of high school students reported vaping. By 2018, it was 20.8%, according to a CDC report.
Unknown components
Still, doctors and researchers are concerned about the ingredients in e-cigarettes and how little the public knows about the risks of vaping.
In Juul’s terms and conditions, posted on its website, it says, “We encourage consumers to do their own research regarding vapor products and what is right for them.” Many ingredients in e-cigarette products, however, are protected as trade secrets.
Since at least 2013, the flavor industry has expressed concern about the use of flavoring chemicals in vaping products.
The vast majority of the chemicals have been tested only by ingesting them in small quantities because they’re encountered in foods. For most of these chemicals, there have been no tests to determine whether it is safe to inhale them, as happens daily by millions when they use e-cigarettes.
“Many of the ingredients of vaping products, including flavoring substances, have not been tested for … the exposure one would get from using a vaping device,” said John Hallagan, a senior adviser to the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. The group has sent cease-and-desist letters to e-cigarette companies in previous years for using the food safety certification of the flavor industry to imply that the chemicals are also safe in e-cigarettes.
Some flavor chemicals are thought to be harmful when inhaled in high doses. Research suggests that cinnamaldehyde, the main component of many cinnamon flavors, may impair lung function when inhaled. Sven-Eric Jordt, PhD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., says he presented evidence of its dangers at an FDA meeting in 2015 — and its relative abundance in many e-cigarette vaping liquids. In response, one major e-cigarette liquid seller, Tasty Vapor, voluntarily took its cinnamon-flavored liquid off the shelves.
In 2017, when Dr. Gottlieb delayed the FDA application deadline, the product was back. A company email to its customers put it this way: “Two years ago, Tasty Vapor allowed itself to be intimidated by scaremongering tactics. … We lost a lot of sales as well as a good number of long-time customers. We no long see reason to disappoint our customers hostage for these shady tactics.”
At the time of publication, Tasty Vapor’s owner did not reply to a request for comment.
Dr. Jordt said he is frustrated by the delays in the regulatory approval process.
“As a parent, I would say that the government has not acted on this,” he said. “You’re basically left to act alone with your addicted kid. It’s kind of terrifying that this was allowed to happen. The industry needs to be held to account.”
Kaiser Health News correspondents Cara Anthony, Markian Hawryluk, and Lauren Weber, as well as reporter Victoria Knight contributed to this report. This story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Kaiser Health News is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
It was the arrival of the second man in his early 20s gasping for air that alarmed Dixie Harris, MD. Young patients rarely get so sick, so fast, with a severe lung illness, and this was her second case in a matter of days.
Then she saw three more patients at her Utah telehealth clinic with similar symptoms. They did not have infections, but all had been vaping. When Dr. Harris heard several teenagers in Wisconsin had been hospitalized in similar cases, she quickly alerted her state health department.
As patients in hospitals across the country combat a mysterious illness linked to e-cigarettes, federal and state investigators are frantically trying to trace the outbreaks to specific vaping products that, until recently, were virtually unregulated.
As of Aug. 22, 2019, 193 potential vaping-related illnesses in 22 states had been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Wisconsin, which first put out an alert in July, has at least 16 confirmed and 15 suspected cases. Illinois has reported 34 patients, 1 of whom has died. Indiana is investigating 24 cases.
Lung doctors said they had seen warning signs for years that vaping could be hazardous as they treated patients. Medically it seemed problematic since it often involved inhaling chemicals not normally inhaled into the lungs. Despite that, assessing the safety of a new product storming the market fell between regulatory cracks, leaving doctors unsure where to register concerns before the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration took years to regulate e-cigarettes once a court determined it had the authority to do so.
“You don’t know what you’re putting into your lungs when you vape,” said Dr. Harris, a critical care pulmonologist. “It’s purported to be safe, but how do you know if it’s safe? To me, it’s a very dangerous thing.”
Off the radar
When e-cigarettes came to market about a decade ago, they fell into a regulatory no man’s land. They are not a food, not a drug, and not a medical device, any of which would have put them immediately in the FDA’s purview. And, until a few years ago, they weren’t even lumped in with tobacco products.
As a result, billions of dollars of vaping products have been sold online, at big-box retailers, and in corner stores without going through the FDA’s rigorous review process to assess their safety. Companies like Juul, Blu, and NJoy quickly established their brands of devices and cartridges, or pods. And thousands of related products are sold, sometimes on the black market, over the Internet, or beyond.
“It makes it really tough because we don’t know what we’re looking for,” said Ruth Lynfield, MD, the state epidemiologist for Minnesota, where several patients were admitted to the ICU as a result of the illness. She added that, if it turns out that the products in question were sold by unregistered retailers and manufacturers “on the street,” outbreak sleuths will have a harder time figuring out exactly what is in them.
With e-cigarettes, people can vape – or smoke – nicotine products, selecting flavorings like mint, mango, blueberry crème brûlée, or cookies and milk. They can also inhale cannabis products. Many are hopeful that e-cigarettes might be useful smoking cessation tools, but some research has called that into question.
The mysterious pulmonary disease cases have been linked to vaping, but it’s unclear whether there is a common device or chemical. In some states, including California and Utah, all of the patients had vaped cannabis products. One or more substances could be involved, health officials have said. The products used by several victims are being tested to see what they contained.
And this has apparently been the case for years.
Multiple doctors described seeing earlier cases of severe lung problems linked to vaping that were not officially reported or included in the current CDC count.
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a pulmonologist and researcher with the University of California, San Diego, said she saw her first case about 2 years ago. A young man had been vaping for months with the same device but developed acute lung injury when he switched flavors. She strongly suspected a link, but did not report the illness anywhere.
“It wasn’t that I didn’t want to report it, it’s that there’s no pathway” to do so, Dr. Alexander said.
She said she’s concerned that many physicians haven’t been asking patients about e-cigarette use and that there’s no way to document a case like this in the medical coding system.
John E. Parker, MD, of West Virginia University, Morgantown, said he saw his first patient with pneumonia tied to vaping in 2015. Doctors there were intrigued enough to report on the case at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. Dr. Parker and his team didn’t contact a federal agency, and Dr. Parker said it was unclear whom to call.
Numerous other cases have been reported in medical journals and at professional conferences in the years since. The FDA’s voluntary system for reporting tobacco-related health problems included 96 seizures and only 1 lung ailment tied to e-cigarettes between April and June 2019. The system appears to be utilized most by concerned citizens, rather than manufacturers or health care professionals.
But several lung specialists said that due to the patchwork nature of regulatory oversight over the years, the true scope of the problem is yet to be identified.
“We do know that e-cigarettes do not emit a harmless aerosol,” said Brian King, PhD, MPH, a deputy director in the Office on Smoking and Health at the CDC in a call with media on Aug. 23 about the outbreak. “It is possible that some of these cases were already occurring but we were not picking them up.”
Regulatory limits
The FDA has had limited authority to regulate e-cigarettes over the years.
In 2009, Congress passed the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, empowering the FDA to oversee the safety and sale of tobacco products. But e-cigarettes, still new, were not top of mind.
Later that year, the FDA tried to block imports of e-cigarettes, saying the combination drug-device products were unapproved and therefore illegal for sale in the United States. Two vaping companies, Smoking Everywhere and NJoy, sued, and a federal judge ruled in 2010 that the FDA should regulate e-cigarettes as tobacco products.
It took the agency 6 years to finalize what’s become known as the “deeming rule,” in which it formally began regulating e-cigarettes and e-liquids.
By then, it was May 2016, and the e-cigarette market had swelled to an estimated $4.1 billion, Wells Fargo Securities analyst Bonnie Herzog said at the time. Market researchers now project that the global industry could reach $48 billion by 2023.
Critics say the FDA took too long to act.
“I think the fact that FDA has been dillydallying [has made] figuring out what’s going on [with this outbreak] much harder,” said Stanton Glantz, PhD, a University of California, San Francisco, professor in its Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. “No question.”
The agency began by banning e-cigarette sales to minors and requiring all new vaping products to submit applications for authorization before they could come to market. Companies and retailers with thousands of products already on the market were granted 2 years to submit applications, and the FDA would get an additional year to evaluate the applications. Meanwhile, existing products could still be sold.
But when Scott Gottlieb, MD, arrived as the new FDA commissioner in 2017, the rule hadn’t been implemented and there was no formal guidance for companies to file applications, he said. As a result, he pushed the deadline back to 2022, drawing ire from public health advocates, who called foul over his previous ties to an e-cigarette retailer called Kure.
“I thought e-cigarettes at the time – and I still believe – that they represent an opportunity for currently addicted adult smokers to transition off of combustible tobacco,” he said in an interview, adding that other parts of the deeming rule went into effect as planned. “All I did was delay the application deadline.”
Dr. Gottlieb’s thinking changed the following year, when a national survey showed a sharp rise in teen vaping, which he called an “epidemic.” He announced that the agency would rethink the extended deadline and weigh whether to take flavors that appeal to kids off the market.
A judge ruled last month that e-cigarette makers would have only 10 more months to submit applications to the FDA. They’re now due in May 2020.
Asked about the lung injuries appearing now, Dr. Gottlieb, who left the FDA in April 2019, said he suspected counterfeit pods are to blame, given the geographic clustering of cases and the fact that, overall, the FDA is inspecting registered e-cigarette makers and retailers to make sure they’re complying with existing regulations.
“I think the manufacturers are culpable if their products are being used, whether the liquids are counterfeit or real,” he said. “Ultimately, they’re responsible for keeping their products out of the hands of kids.”
Juul, the leading e-cigarette maker, agreed that children shouldn’t be able to vape its products, and said curtailing access should be done “through significant regulation” and “enforcement.”
“When people say ‘Why aren’t these being regulated?’ They actually are all being regulated,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
For example, companies are required to label their products as potentially addictive, sell only to adults and comply with manufacturing standards. The agency has conducted thousands of inspections of e-cigarette manufacturers and retailers and taken enforcement actions against companies selling e-cigarettes that look like juice boxes, and against a company that was putting the ingredients found in erectile dysfunction drugs into its vape liquid.
Health departments investigating the outbreak told Kaiser Health News that e-cigarettes’ niche as a tobacco product instead of a drug has presented challenges. Most weren’t aware that adverse events could be reported to a database that tracks problems with tobacco products. And, because e-cigarettes never went through the FDA’s “gold-standard” approval process for drugs, doctors can’t readily look up a detailed list of known side effects.
But like other arms of the FDA, the tobacco office has tools and a team to investigate a public health threat just as the teams for drugs and devices do, Dr. Gottlieb said. It may even be better equipped because of its funding.
“I don’t think FDA is operating in any way with hands tied behind its back because of the way that the statute is set up,” he said.
Teen vaping has exploded during this regulatory tussle. In 2011, 1.5% of high school students reported vaping. By 2018, it was 20.8%, according to a CDC report.
Unknown components
Still, doctors and researchers are concerned about the ingredients in e-cigarettes and how little the public knows about the risks of vaping.
In Juul’s terms and conditions, posted on its website, it says, “We encourage consumers to do their own research regarding vapor products and what is right for them.” Many ingredients in e-cigarette products, however, are protected as trade secrets.
Since at least 2013, the flavor industry has expressed concern about the use of flavoring chemicals in vaping products.
The vast majority of the chemicals have been tested only by ingesting them in small quantities because they’re encountered in foods. For most of these chemicals, there have been no tests to determine whether it is safe to inhale them, as happens daily by millions when they use e-cigarettes.
“Many of the ingredients of vaping products, including flavoring substances, have not been tested for … the exposure one would get from using a vaping device,” said John Hallagan, a senior adviser to the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. The group has sent cease-and-desist letters to e-cigarette companies in previous years for using the food safety certification of the flavor industry to imply that the chemicals are also safe in e-cigarettes.
Some flavor chemicals are thought to be harmful when inhaled in high doses. Research suggests that cinnamaldehyde, the main component of many cinnamon flavors, may impair lung function when inhaled. Sven-Eric Jordt, PhD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., says he presented evidence of its dangers at an FDA meeting in 2015 — and its relative abundance in many e-cigarette vaping liquids. In response, one major e-cigarette liquid seller, Tasty Vapor, voluntarily took its cinnamon-flavored liquid off the shelves.
In 2017, when Dr. Gottlieb delayed the FDA application deadline, the product was back. A company email to its customers put it this way: “Two years ago, Tasty Vapor allowed itself to be intimidated by scaremongering tactics. … We lost a lot of sales as well as a good number of long-time customers. We no long see reason to disappoint our customers hostage for these shady tactics.”
At the time of publication, Tasty Vapor’s owner did not reply to a request for comment.
Dr. Jordt said he is frustrated by the delays in the regulatory approval process.
“As a parent, I would say that the government has not acted on this,” he said. “You’re basically left to act alone with your addicted kid. It’s kind of terrifying that this was allowed to happen. The industry needs to be held to account.”
Kaiser Health News correspondents Cara Anthony, Markian Hawryluk, and Lauren Weber, as well as reporter Victoria Knight contributed to this report. This story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Kaiser Health News is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
It was the arrival of the second man in his early 20s gasping for air that alarmed Dixie Harris, MD. Young patients rarely get so sick, so fast, with a severe lung illness, and this was her second case in a matter of days.
Then she saw three more patients at her Utah telehealth clinic with similar symptoms. They did not have infections, but all had been vaping. When Dr. Harris heard several teenagers in Wisconsin had been hospitalized in similar cases, she quickly alerted her state health department.
As patients in hospitals across the country combat a mysterious illness linked to e-cigarettes, federal and state investigators are frantically trying to trace the outbreaks to specific vaping products that, until recently, were virtually unregulated.
As of Aug. 22, 2019, 193 potential vaping-related illnesses in 22 states had been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Wisconsin, which first put out an alert in July, has at least 16 confirmed and 15 suspected cases. Illinois has reported 34 patients, 1 of whom has died. Indiana is investigating 24 cases.
Lung doctors said they had seen warning signs for years that vaping could be hazardous as they treated patients. Medically it seemed problematic since it often involved inhaling chemicals not normally inhaled into the lungs. Despite that, assessing the safety of a new product storming the market fell between regulatory cracks, leaving doctors unsure where to register concerns before the outbreak. The Food and Drug Administration took years to regulate e-cigarettes once a court determined it had the authority to do so.
“You don’t know what you’re putting into your lungs when you vape,” said Dr. Harris, a critical care pulmonologist. “It’s purported to be safe, but how do you know if it’s safe? To me, it’s a very dangerous thing.”
Off the radar
When e-cigarettes came to market about a decade ago, they fell into a regulatory no man’s land. They are not a food, not a drug, and not a medical device, any of which would have put them immediately in the FDA’s purview. And, until a few years ago, they weren’t even lumped in with tobacco products.
As a result, billions of dollars of vaping products have been sold online, at big-box retailers, and in corner stores without going through the FDA’s rigorous review process to assess their safety. Companies like Juul, Blu, and NJoy quickly established their brands of devices and cartridges, or pods. And thousands of related products are sold, sometimes on the black market, over the Internet, or beyond.
“It makes it really tough because we don’t know what we’re looking for,” said Ruth Lynfield, MD, the state epidemiologist for Minnesota, where several patients were admitted to the ICU as a result of the illness. She added that, if it turns out that the products in question were sold by unregistered retailers and manufacturers “on the street,” outbreak sleuths will have a harder time figuring out exactly what is in them.
With e-cigarettes, people can vape – or smoke – nicotine products, selecting flavorings like mint, mango, blueberry crème brûlée, or cookies and milk. They can also inhale cannabis products. Many are hopeful that e-cigarettes might be useful smoking cessation tools, but some research has called that into question.
The mysterious pulmonary disease cases have been linked to vaping, but it’s unclear whether there is a common device or chemical. In some states, including California and Utah, all of the patients had vaped cannabis products. One or more substances could be involved, health officials have said. The products used by several victims are being tested to see what they contained.
And this has apparently been the case for years.
Multiple doctors described seeing earlier cases of severe lung problems linked to vaping that were not officially reported or included in the current CDC count.
Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, a pulmonologist and researcher with the University of California, San Diego, said she saw her first case about 2 years ago. A young man had been vaping for months with the same device but developed acute lung injury when he switched flavors. She strongly suspected a link, but did not report the illness anywhere.
“It wasn’t that I didn’t want to report it, it’s that there’s no pathway” to do so, Dr. Alexander said.
She said she’s concerned that many physicians haven’t been asking patients about e-cigarette use and that there’s no way to document a case like this in the medical coding system.
John E. Parker, MD, of West Virginia University, Morgantown, said he saw his first patient with pneumonia tied to vaping in 2015. Doctors there were intrigued enough to report on the case at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. Dr. Parker and his team didn’t contact a federal agency, and Dr. Parker said it was unclear whom to call.
Numerous other cases have been reported in medical journals and at professional conferences in the years since. The FDA’s voluntary system for reporting tobacco-related health problems included 96 seizures and only 1 lung ailment tied to e-cigarettes between April and June 2019. The system appears to be utilized most by concerned citizens, rather than manufacturers or health care professionals.
But several lung specialists said that due to the patchwork nature of regulatory oversight over the years, the true scope of the problem is yet to be identified.
“We do know that e-cigarettes do not emit a harmless aerosol,” said Brian King, PhD, MPH, a deputy director in the Office on Smoking and Health at the CDC in a call with media on Aug. 23 about the outbreak. “It is possible that some of these cases were already occurring but we were not picking them up.”
Regulatory limits
The FDA has had limited authority to regulate e-cigarettes over the years.
In 2009, Congress passed the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, empowering the FDA to oversee the safety and sale of tobacco products. But e-cigarettes, still new, were not top of mind.
Later that year, the FDA tried to block imports of e-cigarettes, saying the combination drug-device products were unapproved and therefore illegal for sale in the United States. Two vaping companies, Smoking Everywhere and NJoy, sued, and a federal judge ruled in 2010 that the FDA should regulate e-cigarettes as tobacco products.
It took the agency 6 years to finalize what’s become known as the “deeming rule,” in which it formally began regulating e-cigarettes and e-liquids.
By then, it was May 2016, and the e-cigarette market had swelled to an estimated $4.1 billion, Wells Fargo Securities analyst Bonnie Herzog said at the time. Market researchers now project that the global industry could reach $48 billion by 2023.
Critics say the FDA took too long to act.
“I think the fact that FDA has been dillydallying [has made] figuring out what’s going on [with this outbreak] much harder,” said Stanton Glantz, PhD, a University of California, San Francisco, professor in its Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education. “No question.”
The agency began by banning e-cigarette sales to minors and requiring all new vaping products to submit applications for authorization before they could come to market. Companies and retailers with thousands of products already on the market were granted 2 years to submit applications, and the FDA would get an additional year to evaluate the applications. Meanwhile, existing products could still be sold.
But when Scott Gottlieb, MD, arrived as the new FDA commissioner in 2017, the rule hadn’t been implemented and there was no formal guidance for companies to file applications, he said. As a result, he pushed the deadline back to 2022, drawing ire from public health advocates, who called foul over his previous ties to an e-cigarette retailer called Kure.
“I thought e-cigarettes at the time – and I still believe – that they represent an opportunity for currently addicted adult smokers to transition off of combustible tobacco,” he said in an interview, adding that other parts of the deeming rule went into effect as planned. “All I did was delay the application deadline.”
Dr. Gottlieb’s thinking changed the following year, when a national survey showed a sharp rise in teen vaping, which he called an “epidemic.” He announced that the agency would rethink the extended deadline and weigh whether to take flavors that appeal to kids off the market.
A judge ruled last month that e-cigarette makers would have only 10 more months to submit applications to the FDA. They’re now due in May 2020.
Asked about the lung injuries appearing now, Dr. Gottlieb, who left the FDA in April 2019, said he suspected counterfeit pods are to blame, given the geographic clustering of cases and the fact that, overall, the FDA is inspecting registered e-cigarette makers and retailers to make sure they’re complying with existing regulations.
“I think the manufacturers are culpable if their products are being used, whether the liquids are counterfeit or real,” he said. “Ultimately, they’re responsible for keeping their products out of the hands of kids.”
Juul, the leading e-cigarette maker, agreed that children shouldn’t be able to vape its products, and said curtailing access should be done “through significant regulation” and “enforcement.”
“When people say ‘Why aren’t these being regulated?’ They actually are all being regulated,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
For example, companies are required to label their products as potentially addictive, sell only to adults and comply with manufacturing standards. The agency has conducted thousands of inspections of e-cigarette manufacturers and retailers and taken enforcement actions against companies selling e-cigarettes that look like juice boxes, and against a company that was putting the ingredients found in erectile dysfunction drugs into its vape liquid.
Health departments investigating the outbreak told Kaiser Health News that e-cigarettes’ niche as a tobacco product instead of a drug has presented challenges. Most weren’t aware that adverse events could be reported to a database that tracks problems with tobacco products. And, because e-cigarettes never went through the FDA’s “gold-standard” approval process for drugs, doctors can’t readily look up a detailed list of known side effects.
But like other arms of the FDA, the tobacco office has tools and a team to investigate a public health threat just as the teams for drugs and devices do, Dr. Gottlieb said. It may even be better equipped because of its funding.
“I don’t think FDA is operating in any way with hands tied behind its back because of the way that the statute is set up,” he said.
Teen vaping has exploded during this regulatory tussle. In 2011, 1.5% of high school students reported vaping. By 2018, it was 20.8%, according to a CDC report.
Unknown components
Still, doctors and researchers are concerned about the ingredients in e-cigarettes and how little the public knows about the risks of vaping.
In Juul’s terms and conditions, posted on its website, it says, “We encourage consumers to do their own research regarding vapor products and what is right for them.” Many ingredients in e-cigarette products, however, are protected as trade secrets.
Since at least 2013, the flavor industry has expressed concern about the use of flavoring chemicals in vaping products.
The vast majority of the chemicals have been tested only by ingesting them in small quantities because they’re encountered in foods. For most of these chemicals, there have been no tests to determine whether it is safe to inhale them, as happens daily by millions when they use e-cigarettes.
“Many of the ingredients of vaping products, including flavoring substances, have not been tested for … the exposure one would get from using a vaping device,” said John Hallagan, a senior adviser to the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. The group has sent cease-and-desist letters to e-cigarette companies in previous years for using the food safety certification of the flavor industry to imply that the chemicals are also safe in e-cigarettes.
Some flavor chemicals are thought to be harmful when inhaled in high doses. Research suggests that cinnamaldehyde, the main component of many cinnamon flavors, may impair lung function when inhaled. Sven-Eric Jordt, PhD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., says he presented evidence of its dangers at an FDA meeting in 2015 — and its relative abundance in many e-cigarette vaping liquids. In response, one major e-cigarette liquid seller, Tasty Vapor, voluntarily took its cinnamon-flavored liquid off the shelves.
In 2017, when Dr. Gottlieb delayed the FDA application deadline, the product was back. A company email to its customers put it this way: “Two years ago, Tasty Vapor allowed itself to be intimidated by scaremongering tactics. … We lost a lot of sales as well as a good number of long-time customers. We no long see reason to disappoint our customers hostage for these shady tactics.”
At the time of publication, Tasty Vapor’s owner did not reply to a request for comment.
Dr. Jordt said he is frustrated by the delays in the regulatory approval process.
“As a parent, I would say that the government has not acted on this,” he said. “You’re basically left to act alone with your addicted kid. It’s kind of terrifying that this was allowed to happen. The industry needs to be held to account.”
Kaiser Health News correspondents Cara Anthony, Markian Hawryluk, and Lauren Weber, as well as reporter Victoria Knight contributed to this report. This story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Kaiser Health News is a national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
ACOG advises bleeding disorder screening for teens with heavy menstruation
Adolescent girls with heavy menstrual bleeding should be assessed for bleeding disorders, according to a Committee Opinion issued by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A bleeding disorder is secondary only to anovulation as a cause of heavy menstrual bleeding in adolescents.
Bleeding disorders affect 1%-2% of the general population, but are “found in approximately 20% of adolescent girls who present for evaluation of heavy menstrual bleeding and in 33% of adolescent girls hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding,” wrote Oluyemisi Adeyemi-Fowode, MD, and Judith Simms-Cendan, MD, and members of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care in the opinion, published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
The committee advised that physical examination of teens with acute heavy menstrual bleeding should include assessment of hemodynamic stability with orthostatic blood pressure and pulse measurements. A speculum exam is not usually needed in teen girls with heavy menstrual bleeding. Evaluation should include screening for anemia attributable to blood loss with serum ferritin, endocrine disorders, and bleeding disorders. In suspected cases of bleeding disorders, laboratory evaluation and medical management should be done in consultation with a hematologist.
Those who are actively bleeding or hemodynamically unstable should be hospitalized for medical management, they said.
Ultrasonography is not necessary for an initial work-up of teens with heavy menstrual bleeding, but could be useful in patients who fail to respond to medical management.
Adolescent girls without contraindications to estrogen can be treated with hormone therapy in various forms including intravenous conjugated estrogen every 4-6 hours or oral 30-50 mg ethinyl estradiol every 6-8 hours until cessation of bleeding. Antifibrinolytics also can be used to stop bleeding.
Maintenance therapy after correction of acute heavy bleeding can include a combination of treatments such as hormonal contraceptives, oral and injectable progestins, and levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices, the committee wrote. They also recommended oral iron replacement therapy for all women of reproductive age with anemia caused by menstrual bleeding.
If a patient fails to respond to medical therapy, nonmedical options or surgery may be considered, according to the committee. In addition, all teen girls with bleeding disorders should be advised about safe medication use, including the use of aspirin or NSAIDs only on the recommendation of a hematologist.
Patients and their families need education on menstrual issues including possible options for surgery in the future if heavy menstruation does not resolve. If a patient has a known bleeding disorder and is considering surgery, preoperative evaluation should include a consultation with a hematologist and an anesthesiologist, the committee noted.
Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, said in an interview, “Every ob.gyn. will see a young patient with ‘heavy menstrual bleeding.’ And it becomes part of the art and challenge to work with the patient and family to collectively explore if this is, indeed, ‘heavy’ and of concern … or is it is a ‘normal’ menstrual period and simply reflects a newer life experience that would benefit from some education? And the stakes are high. Young people who have heavy menstrual cycles are much more likely to have an underlying bleeding disorder than the general population (20% vs. 1%-2%), and 75%-80% of adolescents with bleeding disorders report heavy menses as the most common clinical manifestation of their disorder.
“Fortunately, Committee Opinion 785, ‘Screening and Management of Bleeding Disorders in Adolescents with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding’ from the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care is detailed and pragmatic. It outlines how to translate everyday conversations with young people about their menses into a quantifiable estimate of bleeding, including a very teen-friendly Pictorial Blood Loss Assessment Chart. It also gives ob.gyns. ever-important guidance about what to do next for evaluation and diagnosis. This committee opinion nicely outlines how to help manage heavy bleeding in an adolescent with a detailed algorithm. And very importantly, it gives clear management guidance and encourages ob.gyns. to avoid frequently unnecessary (speculum exams and ultrasounds) and excessive (early transfusion or surgical interventions) approaches to management for the young patient. I think it will be a great resource for any provider who is taking care of heavy menstrual bleeding for a young person,” said Dr. Kottke, who is director of the Jane Fonda Center for Adolescent Reproductive Health and associate professor of gynecology and obstetrics, both at Emory University, Atlanta. Dr. Kottke is not a member of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health and was asked to comment on the opinion.*
The complete opinion, ACOG Committee Opinion number 785, includes recommended laboratory tests, an eight-question screening tool, and a management algorithm.
The committee members had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kottke said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adeyemi-Fowode O and Simms-Cendan J. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Sep. 134:e71-83.
*This article was updated on 9/9/2019.
Adolescent girls with heavy menstrual bleeding should be assessed for bleeding disorders, according to a Committee Opinion issued by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A bleeding disorder is secondary only to anovulation as a cause of heavy menstrual bleeding in adolescents.
Bleeding disorders affect 1%-2% of the general population, but are “found in approximately 20% of adolescent girls who present for evaluation of heavy menstrual bleeding and in 33% of adolescent girls hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding,” wrote Oluyemisi Adeyemi-Fowode, MD, and Judith Simms-Cendan, MD, and members of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care in the opinion, published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
The committee advised that physical examination of teens with acute heavy menstrual bleeding should include assessment of hemodynamic stability with orthostatic blood pressure and pulse measurements. A speculum exam is not usually needed in teen girls with heavy menstrual bleeding. Evaluation should include screening for anemia attributable to blood loss with serum ferritin, endocrine disorders, and bleeding disorders. In suspected cases of bleeding disorders, laboratory evaluation and medical management should be done in consultation with a hematologist.
Those who are actively bleeding or hemodynamically unstable should be hospitalized for medical management, they said.
Ultrasonography is not necessary for an initial work-up of teens with heavy menstrual bleeding, but could be useful in patients who fail to respond to medical management.
Adolescent girls without contraindications to estrogen can be treated with hormone therapy in various forms including intravenous conjugated estrogen every 4-6 hours or oral 30-50 mg ethinyl estradiol every 6-8 hours until cessation of bleeding. Antifibrinolytics also can be used to stop bleeding.
Maintenance therapy after correction of acute heavy bleeding can include a combination of treatments such as hormonal contraceptives, oral and injectable progestins, and levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices, the committee wrote. They also recommended oral iron replacement therapy for all women of reproductive age with anemia caused by menstrual bleeding.
If a patient fails to respond to medical therapy, nonmedical options or surgery may be considered, according to the committee. In addition, all teen girls with bleeding disorders should be advised about safe medication use, including the use of aspirin or NSAIDs only on the recommendation of a hematologist.
Patients and their families need education on menstrual issues including possible options for surgery in the future if heavy menstruation does not resolve. If a patient has a known bleeding disorder and is considering surgery, preoperative evaluation should include a consultation with a hematologist and an anesthesiologist, the committee noted.
Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, said in an interview, “Every ob.gyn. will see a young patient with ‘heavy menstrual bleeding.’ And it becomes part of the art and challenge to work with the patient and family to collectively explore if this is, indeed, ‘heavy’ and of concern … or is it is a ‘normal’ menstrual period and simply reflects a newer life experience that would benefit from some education? And the stakes are high. Young people who have heavy menstrual cycles are much more likely to have an underlying bleeding disorder than the general population (20% vs. 1%-2%), and 75%-80% of adolescents with bleeding disorders report heavy menses as the most common clinical manifestation of their disorder.
“Fortunately, Committee Opinion 785, ‘Screening and Management of Bleeding Disorders in Adolescents with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding’ from the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care is detailed and pragmatic. It outlines how to translate everyday conversations with young people about their menses into a quantifiable estimate of bleeding, including a very teen-friendly Pictorial Blood Loss Assessment Chart. It also gives ob.gyns. ever-important guidance about what to do next for evaluation and diagnosis. This committee opinion nicely outlines how to help manage heavy bleeding in an adolescent with a detailed algorithm. And very importantly, it gives clear management guidance and encourages ob.gyns. to avoid frequently unnecessary (speculum exams and ultrasounds) and excessive (early transfusion or surgical interventions) approaches to management for the young patient. I think it will be a great resource for any provider who is taking care of heavy menstrual bleeding for a young person,” said Dr. Kottke, who is director of the Jane Fonda Center for Adolescent Reproductive Health and associate professor of gynecology and obstetrics, both at Emory University, Atlanta. Dr. Kottke is not a member of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health and was asked to comment on the opinion.*
The complete opinion, ACOG Committee Opinion number 785, includes recommended laboratory tests, an eight-question screening tool, and a management algorithm.
The committee members had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kottke said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adeyemi-Fowode O and Simms-Cendan J. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Sep. 134:e71-83.
*This article was updated on 9/9/2019.
Adolescent girls with heavy menstrual bleeding should be assessed for bleeding disorders, according to a Committee Opinion issued by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A bleeding disorder is secondary only to anovulation as a cause of heavy menstrual bleeding in adolescents.
Bleeding disorders affect 1%-2% of the general population, but are “found in approximately 20% of adolescent girls who present for evaluation of heavy menstrual bleeding and in 33% of adolescent girls hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding,” wrote Oluyemisi Adeyemi-Fowode, MD, and Judith Simms-Cendan, MD, and members of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care in the opinion, published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
The committee advised that physical examination of teens with acute heavy menstrual bleeding should include assessment of hemodynamic stability with orthostatic blood pressure and pulse measurements. A speculum exam is not usually needed in teen girls with heavy menstrual bleeding. Evaluation should include screening for anemia attributable to blood loss with serum ferritin, endocrine disorders, and bleeding disorders. In suspected cases of bleeding disorders, laboratory evaluation and medical management should be done in consultation with a hematologist.
Those who are actively bleeding or hemodynamically unstable should be hospitalized for medical management, they said.
Ultrasonography is not necessary for an initial work-up of teens with heavy menstrual bleeding, but could be useful in patients who fail to respond to medical management.
Adolescent girls without contraindications to estrogen can be treated with hormone therapy in various forms including intravenous conjugated estrogen every 4-6 hours or oral 30-50 mg ethinyl estradiol every 6-8 hours until cessation of bleeding. Antifibrinolytics also can be used to stop bleeding.
Maintenance therapy after correction of acute heavy bleeding can include a combination of treatments such as hormonal contraceptives, oral and injectable progestins, and levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices, the committee wrote. They also recommended oral iron replacement therapy for all women of reproductive age with anemia caused by menstrual bleeding.
If a patient fails to respond to medical therapy, nonmedical options or surgery may be considered, according to the committee. In addition, all teen girls with bleeding disorders should be advised about safe medication use, including the use of aspirin or NSAIDs only on the recommendation of a hematologist.
Patients and their families need education on menstrual issues including possible options for surgery in the future if heavy menstruation does not resolve. If a patient has a known bleeding disorder and is considering surgery, preoperative evaluation should include a consultation with a hematologist and an anesthesiologist, the committee noted.
Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, said in an interview, “Every ob.gyn. will see a young patient with ‘heavy menstrual bleeding.’ And it becomes part of the art and challenge to work with the patient and family to collectively explore if this is, indeed, ‘heavy’ and of concern … or is it is a ‘normal’ menstrual period and simply reflects a newer life experience that would benefit from some education? And the stakes are high. Young people who have heavy menstrual cycles are much more likely to have an underlying bleeding disorder than the general population (20% vs. 1%-2%), and 75%-80% of adolescents with bleeding disorders report heavy menses as the most common clinical manifestation of their disorder.
“Fortunately, Committee Opinion 785, ‘Screening and Management of Bleeding Disorders in Adolescents with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding’ from the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health Care is detailed and pragmatic. It outlines how to translate everyday conversations with young people about their menses into a quantifiable estimate of bleeding, including a very teen-friendly Pictorial Blood Loss Assessment Chart. It also gives ob.gyns. ever-important guidance about what to do next for evaluation and diagnosis. This committee opinion nicely outlines how to help manage heavy bleeding in an adolescent with a detailed algorithm. And very importantly, it gives clear management guidance and encourages ob.gyns. to avoid frequently unnecessary (speculum exams and ultrasounds) and excessive (early transfusion or surgical interventions) approaches to management for the young patient. I think it will be a great resource for any provider who is taking care of heavy menstrual bleeding for a young person,” said Dr. Kottke, who is director of the Jane Fonda Center for Adolescent Reproductive Health and associate professor of gynecology and obstetrics, both at Emory University, Atlanta. Dr. Kottke is not a member of the ACOG Committee on Adolescent Health and was asked to comment on the opinion.*
The complete opinion, ACOG Committee Opinion number 785, includes recommended laboratory tests, an eight-question screening tool, and a management algorithm.
The committee members had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kottke said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Adeyemi-Fowode O and Simms-Cendan J. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Sep. 134:e71-83.
*This article was updated on 9/9/2019.
FROM OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Blood test may reveal brain injury
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
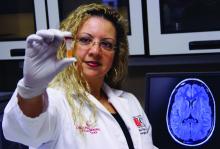
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
FROM BMJ PAEDIATRICS OPEN
Key clinical point: Levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) are lowest in patients with nonconcussive body trauma, higher in patients with nonconcussive head trauma, and highest in patients with concussion.
Major finding: GFAP was fair to excellent at distinguishing concussion from body trauma, with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves of 0.75-0.89.
Study details: A prospective cohort study of 712 trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. The study included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and presented within 4 hours of injury.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers. Coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
Source: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
CPAP safety for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floor
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PHM 2019
Granuloma Annulare Presenting as Firm Nodules on the Forehead and Scalp in a Child
To the Editor:
A 3.5-year-old boy presented with asymptomatic subcutaneous nodules on the left side of the forehead and frontal scalp of approximately 6 months’ duration. There was no history of trauma or preceding rash. His medical history was remarkable only for allergic rhinitis. A review of systems was otherwise negative. Computed tomography ordered by the patient’s pediatrician prior to referral to dermatology showed soft tissue masses on the forehead and frontal scalp with no associated bone or brain parenchymal signal abnormalities.
At presentation to dermatology, physical examination revealed a 6×7-cm, flesh-colored cluster of firm, nontender, fixed, subcutaneous nodules on the left superior forehead and anterior part of the left frontal scalp (Figure 1A), as well as 2×1.5-cm, firm, fixed, flesh-colored nodule inferior to the larger cluster of lesions (Figure 1B). The remainder of the skin examination was unremarkable.
The patient was referred to plastic surgery for an incisional biopsy. The histopathologic findings demonstrated a marked mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and histiocytes with rare eosinophils and neutrophils in the subcutaneous tissue. The histiocytes were arranged in a palisading pattern surrounding central areas of necrosis (Figure 2). These features were consistent with a diagnosis of subcutaneous granuloma annulare (GA).
After the histologic diagnosis was elucidated, the patient’s family was provided reassurance regarding the benign nature and self-resolving course of GA in most children. No treatment was initiated, and no further laboratory studies or imaging were performed. At 9-month follow-up, the nodules were considerably smaller, and the patient remained asymptomatic.
Granuloma annulare is a benign dermatosis that presents in various forms, including localized, generalized, perforating, and subcutaneous subtypes. Subcutaneous GA (SGA) occurs most commonly in young children. The typical presentation of SGA is single or multiple flesh-colored to pink subcutaneous nodules on the arms, legs, or scalp.1 On the scalp, SGA has a predilection for the parietal and occipital regions. In some cases, there may be a history of preceding trauma to the area. Typically, lesions on the arms and legs are mobile whereas lesions on the scalp may be fixed due to their close proximity to the periosteum. Patients often are asymptomatic, and in the majority of cases, lesions resolve spontaneously over several months to years. Approximately 50% of cases resolve within 2 years of onset.2
Histologically, SGA appears as a nodule of fibrinoid or necrotic degeneration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes in the deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare is an accurate term for our case due to the subcutaneous location of the granulomatous change; however, some practitioners may prefer to use the term deep GA when the histologic findings are in the deep dermis vs the subcutis. Often, prominent deposition of mucin may be found. Histologically, SGA can closely resemble a rheumatoid nodule or necrobiosis lipoidica.1
Subcutaneous GA presenting on the scalp and forehead, such as in our case, can present a diagnostic challenge due to the extensive differential diagnoses that must be considered, including trauma, infection, bone or skin disease, and inflammatory or autoimmune disease.2,3 Additionally, the firm fixed characteristics of some lesions may raise additional concerns for possible malignant diagnoses such as epithelial sarcoma, peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, or Langerhans cell histiocytosis, as highlighted by Agrawal et al.4 For these reasons, imaging and biopsy often are necessary for histologic diagnosis.
There is no consensus on the etiology of SGA, and no specific disease associations have been proven. Some case reports and case series have proposed a link between SGA and type 1 diabetes mellitus.1,4 In one retrospective case series, Grogg and Nascimento1 found that 2 of 34 (5.9%) pediatric patients with SGA had known or subsequently diagnosed diabetes mellitus; however, a definitive association between the 2 entities has not been elucidated. Underlying type 1 diabetes mellitus should be considered in patients with isolated SGA, but laboratory screening for diabetes is not necessary in patients with a negative review of systems.
Treatment of SGA typically is not required, as it is a self-limited condition. Often, once a histologic diagnosis is established, no further evaluation or treatment is warranted. Multiple treatment modalities have been reported, including intralesional and topical corticosteroids, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and systemic agents such as isotretinoin or corticosteroids; however, no treatment has been shown to be consistently efficacious.5 Excision of the lesions may be performed, but the risk for recurrence often precludes it as a viable option. In some case series, there have been recurrence rates as high as 40% to 75% in the months to years following surgical excision/biopsy.1,6
Patients presenting with presumed SGA should undergo a thorough history, review of systems, and full-body skin examination. In some cases, imaging and biopsy may be necessary to make a definitive diagnosis and exclude a more serious condition.
- Grogg KL, Nascimento AG. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare in childhood: clinicopathologic features in 34 cases. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E42.
- Sabuncuoglu H, Oge K, Soylemezoglu F, et al. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare of the scalp in childhood: a case report and review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2007;17:19-22.
- Whelan JP, Zembowicz A. A 22-month-old boy with the rapid growth of subcutaneous nodules. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2697-2704.
- Agrawal AK, Kammen BF, Guo H, et al. An unusual presentation of subcutaneous granuloma annulare in association with juvenile-onset diabetes: case report and literature review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:202-205.
- Cronquist SD, Stashower ME, Benson PM. Deep dermal granuloma annulare presenting as an eyelid tumor in a child, with review of pediatric eyelid lesions. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:377-380.
- Jankowski PP, Krishna PH, Rutledge JC, et al. Surgical management and outcome of scalp subcutaneous granuloma annulare in children: case report. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:E1002, discussion E1002.
To the Editor:
A 3.5-year-old boy presented with asymptomatic subcutaneous nodules on the left side of the forehead and frontal scalp of approximately 6 months’ duration. There was no history of trauma or preceding rash. His medical history was remarkable only for allergic rhinitis. A review of systems was otherwise negative. Computed tomography ordered by the patient’s pediatrician prior to referral to dermatology showed soft tissue masses on the forehead and frontal scalp with no associated bone or brain parenchymal signal abnormalities.
At presentation to dermatology, physical examination revealed a 6×7-cm, flesh-colored cluster of firm, nontender, fixed, subcutaneous nodules on the left superior forehead and anterior part of the left frontal scalp (Figure 1A), as well as 2×1.5-cm, firm, fixed, flesh-colored nodule inferior to the larger cluster of lesions (Figure 1B). The remainder of the skin examination was unremarkable.

The patient was referred to plastic surgery for an incisional biopsy. The histopathologic findings demonstrated a marked mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and histiocytes with rare eosinophils and neutrophils in the subcutaneous tissue. The histiocytes were arranged in a palisading pattern surrounding central areas of necrosis (Figure 2). These features were consistent with a diagnosis of subcutaneous granuloma annulare (GA).

After the histologic diagnosis was elucidated, the patient’s family was provided reassurance regarding the benign nature and self-resolving course of GA in most children. No treatment was initiated, and no further laboratory studies or imaging were performed. At 9-month follow-up, the nodules were considerably smaller, and the patient remained asymptomatic.
Granuloma annulare is a benign dermatosis that presents in various forms, including localized, generalized, perforating, and subcutaneous subtypes. Subcutaneous GA (SGA) occurs most commonly in young children. The typical presentation of SGA is single or multiple flesh-colored to pink subcutaneous nodules on the arms, legs, or scalp.1 On the scalp, SGA has a predilection for the parietal and occipital regions. In some cases, there may be a history of preceding trauma to the area. Typically, lesions on the arms and legs are mobile whereas lesions on the scalp may be fixed due to their close proximity to the periosteum. Patients often are asymptomatic, and in the majority of cases, lesions resolve spontaneously over several months to years. Approximately 50% of cases resolve within 2 years of onset.2
Histologically, SGA appears as a nodule of fibrinoid or necrotic degeneration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes in the deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare is an accurate term for our case due to the subcutaneous location of the granulomatous change; however, some practitioners may prefer to use the term deep GA when the histologic findings are in the deep dermis vs the subcutis. Often, prominent deposition of mucin may be found. Histologically, SGA can closely resemble a rheumatoid nodule or necrobiosis lipoidica.1
Subcutaneous GA presenting on the scalp and forehead, such as in our case, can present a diagnostic challenge due to the extensive differential diagnoses that must be considered, including trauma, infection, bone or skin disease, and inflammatory or autoimmune disease.2,3 Additionally, the firm fixed characteristics of some lesions may raise additional concerns for possible malignant diagnoses such as epithelial sarcoma, peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, or Langerhans cell histiocytosis, as highlighted by Agrawal et al.4 For these reasons, imaging and biopsy often are necessary for histologic diagnosis.
There is no consensus on the etiology of SGA, and no specific disease associations have been proven. Some case reports and case series have proposed a link between SGA and type 1 diabetes mellitus.1,4 In one retrospective case series, Grogg and Nascimento1 found that 2 of 34 (5.9%) pediatric patients with SGA had known or subsequently diagnosed diabetes mellitus; however, a definitive association between the 2 entities has not been elucidated. Underlying type 1 diabetes mellitus should be considered in patients with isolated SGA, but laboratory screening for diabetes is not necessary in patients with a negative review of systems.
Treatment of SGA typically is not required, as it is a self-limited condition. Often, once a histologic diagnosis is established, no further evaluation or treatment is warranted. Multiple treatment modalities have been reported, including intralesional and topical corticosteroids, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and systemic agents such as isotretinoin or corticosteroids; however, no treatment has been shown to be consistently efficacious.5 Excision of the lesions may be performed, but the risk for recurrence often precludes it as a viable option. In some case series, there have been recurrence rates as high as 40% to 75% in the months to years following surgical excision/biopsy.1,6
Patients presenting with presumed SGA should undergo a thorough history, review of systems, and full-body skin examination. In some cases, imaging and biopsy may be necessary to make a definitive diagnosis and exclude a more serious condition.
To the Editor:
A 3.5-year-old boy presented with asymptomatic subcutaneous nodules on the left side of the forehead and frontal scalp of approximately 6 months’ duration. There was no history of trauma or preceding rash. His medical history was remarkable only for allergic rhinitis. A review of systems was otherwise negative. Computed tomography ordered by the patient’s pediatrician prior to referral to dermatology showed soft tissue masses on the forehead and frontal scalp with no associated bone or brain parenchymal signal abnormalities.
At presentation to dermatology, physical examination revealed a 6×7-cm, flesh-colored cluster of firm, nontender, fixed, subcutaneous nodules on the left superior forehead and anterior part of the left frontal scalp (Figure 1A), as well as 2×1.5-cm, firm, fixed, flesh-colored nodule inferior to the larger cluster of lesions (Figure 1B). The remainder of the skin examination was unremarkable.

The patient was referred to plastic surgery for an incisional biopsy. The histopathologic findings demonstrated a marked mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and histiocytes with rare eosinophils and neutrophils in the subcutaneous tissue. The histiocytes were arranged in a palisading pattern surrounding central areas of necrosis (Figure 2). These features were consistent with a diagnosis of subcutaneous granuloma annulare (GA).

After the histologic diagnosis was elucidated, the patient’s family was provided reassurance regarding the benign nature and self-resolving course of GA in most children. No treatment was initiated, and no further laboratory studies or imaging were performed. At 9-month follow-up, the nodules were considerably smaller, and the patient remained asymptomatic.
Granuloma annulare is a benign dermatosis that presents in various forms, including localized, generalized, perforating, and subcutaneous subtypes. Subcutaneous GA (SGA) occurs most commonly in young children. The typical presentation of SGA is single or multiple flesh-colored to pink subcutaneous nodules on the arms, legs, or scalp.1 On the scalp, SGA has a predilection for the parietal and occipital regions. In some cases, there may be a history of preceding trauma to the area. Typically, lesions on the arms and legs are mobile whereas lesions on the scalp may be fixed due to their close proximity to the periosteum. Patients often are asymptomatic, and in the majority of cases, lesions resolve spontaneously over several months to years. Approximately 50% of cases resolve within 2 years of onset.2
Histologically, SGA appears as a nodule of fibrinoid or necrotic degeneration surrounded by palisaded histiocytes and lymphocytes in the deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare is an accurate term for our case due to the subcutaneous location of the granulomatous change; however, some practitioners may prefer to use the term deep GA when the histologic findings are in the deep dermis vs the subcutis. Often, prominent deposition of mucin may be found. Histologically, SGA can closely resemble a rheumatoid nodule or necrobiosis lipoidica.1
Subcutaneous GA presenting on the scalp and forehead, such as in our case, can present a diagnostic challenge due to the extensive differential diagnoses that must be considered, including trauma, infection, bone or skin disease, and inflammatory or autoimmune disease.2,3 Additionally, the firm fixed characteristics of some lesions may raise additional concerns for possible malignant diagnoses such as epithelial sarcoma, peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, or Langerhans cell histiocytosis, as highlighted by Agrawal et al.4 For these reasons, imaging and biopsy often are necessary for histologic diagnosis.
There is no consensus on the etiology of SGA, and no specific disease associations have been proven. Some case reports and case series have proposed a link between SGA and type 1 diabetes mellitus.1,4 In one retrospective case series, Grogg and Nascimento1 found that 2 of 34 (5.9%) pediatric patients with SGA had known or subsequently diagnosed diabetes mellitus; however, a definitive association between the 2 entities has not been elucidated. Underlying type 1 diabetes mellitus should be considered in patients with isolated SGA, but laboratory screening for diabetes is not necessary in patients with a negative review of systems.
Treatment of SGA typically is not required, as it is a self-limited condition. Often, once a histologic diagnosis is established, no further evaluation or treatment is warranted. Multiple treatment modalities have been reported, including intralesional and topical corticosteroids, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and systemic agents such as isotretinoin or corticosteroids; however, no treatment has been shown to be consistently efficacious.5 Excision of the lesions may be performed, but the risk for recurrence often precludes it as a viable option. In some case series, there have been recurrence rates as high as 40% to 75% in the months to years following surgical excision/biopsy.1,6
Patients presenting with presumed SGA should undergo a thorough history, review of systems, and full-body skin examination. In some cases, imaging and biopsy may be necessary to make a definitive diagnosis and exclude a more serious condition.
- Grogg KL, Nascimento AG. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare in childhood: clinicopathologic features in 34 cases. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E42.
- Sabuncuoglu H, Oge K, Soylemezoglu F, et al. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare of the scalp in childhood: a case report and review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2007;17:19-22.
- Whelan JP, Zembowicz A. A 22-month-old boy with the rapid growth of subcutaneous nodules. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2697-2704.
- Agrawal AK, Kammen BF, Guo H, et al. An unusual presentation of subcutaneous granuloma annulare in association with juvenile-onset diabetes: case report and literature review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:202-205.
- Cronquist SD, Stashower ME, Benson PM. Deep dermal granuloma annulare presenting as an eyelid tumor in a child, with review of pediatric eyelid lesions. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:377-380.
- Jankowski PP, Krishna PH, Rutledge JC, et al. Surgical management and outcome of scalp subcutaneous granuloma annulare in children: case report. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:E1002, discussion E1002.
- Grogg KL, Nascimento AG. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare in childhood: clinicopathologic features in 34 cases. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E42.
- Sabuncuoglu H, Oge K, Soylemezoglu F, et al. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare of the scalp in childhood: a case report and review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2007;17:19-22.
- Whelan JP, Zembowicz A. A 22-month-old boy with the rapid growth of subcutaneous nodules. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2697-2704.
- Agrawal AK, Kammen BF, Guo H, et al. An unusual presentation of subcutaneous granuloma annulare in association with juvenile-onset diabetes: case report and literature review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:202-205.
- Cronquist SD, Stashower ME, Benson PM. Deep dermal granuloma annulare presenting as an eyelid tumor in a child, with review of pediatric eyelid lesions. Pediatr Dermatol. 1999;16:377-380.
- Jankowski PP, Krishna PH, Rutledge JC, et al. Surgical management and outcome of scalp subcutaneous granuloma annulare in children: case report. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:E1002, discussion E1002.
Practice Points
- Subcutaneous granuloma annulare (GA) is an important diagnosis to consider in the differential of subcutaneous nodules in children.
- The subcutaneous variant of GA can present without any typical GA lesions.
- Subcutaneous GA typically has a self-resolving course in most children.
Pediatric hospitalist certification beset by gender bias concerns
Are women unfairly penalized?
More than 1,625 pediatricians have applied to take the first pediatric hospitalist certification exam in November 2019, and approximately 93% of them have been accepted, according to a statement from the American Board of Pediatrics.
It was the rejection of the 7%, however, that set off a firestorm on the electronic discussion board for American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) hospital medicine this summer, and led to a petition to the board to revise its eligibility requirements, ensure that the requirements are fair to women, and bring transparency to its decision process. The petition has more than 1,400 signatures.
Seattle Children’s Hospital and Yale New Haven (Conn.) Children’s Hospital have both said they will not consider board certification in hiring decisions until the situation is resolved.
The American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) declined an interview request pending its formal response to the Aug. 6 petition, but in a statement to this news organization, executive vice president Suzanne Woods, MD, said, “The percentage of women and men meeting the eligibility requirements for the exam did not differ. We stress this point because a concern about possible gender bias appears to have been the principal reason for this ... petition, and we wanted to offer immediate reassurance that no unintended bias has occurred.”
“We are carefully considering the requests and will release detailed data to hospitalists on the AAP’s [pediatric hospital medicine (PHM) electronic discussion board] ... and on the ABP’s website. We are conferring with ABP PHM subboard members as well as leaders from our volunteer community. We expect to provide a thoughtful response within the next 3 weeks,” Dr. Woods said in the Aug. 15 statement.
“Case-by-case” exceptions
The backstory is that, for better or worse depending on who you talk to, pediatric hospital medicine is becoming a board certified subspecialty. A fellowship will be required to sit for the exam after a few years, which is standard for subspecialties.
What’s generated concern is how the board is grandfathering current pediatric hospitalists into certification via a “practice pathway” until the fellowship requirement takes hold after 2023.
To qualify for the November test, hospitalists had to complete 4 years of full-time practice by June 30, 2019, which has been understood to mean 48 months of continual employment. At least 50% of that time had to be devoted to “professional activities ... related to the care of hospitalized children,” and at least 25% of that “devoted to direct patient care.” Assuming about 2,000 work hours per year, it translated to “450-500 hours” of direct patient care “per year over the most recent four years” to sit for the test, the board said.
“For individuals who have interrupted practice during the most recent four years for family leave or other such circumstances, an exception may be considered if there is substantial prior experience in pediatric hospital medicine. ... Such exceptions are made at the discretion of the ABP and will be considered on a case-by-case basis.” Specific criteria for exceptions were not spelled out.
In the end, there were more than a few surprises when denial letters went out in recent months, and scores of appeals have been filed. There’s “a lot of tension and a lot of confusion” about why some people with practice gaps during the 4 years were approved, but others were denied. There’s been “a lack of transparency on the ABP’s part,” said H. Barrett Fromme, MD, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Chicago.
“The standard has to be reasonable”
There are concerns about the availability of fellowship slots and other issues, but the 4-year rule – instead of averaging clinical hours over 4 or 5 years, for instance – is the main sticking point. It’s a gender issue because “women take maternity; women move with their spouse; women take care of elders; women tend to be in these roles that require time off” more than men do, Dr. Fromme said.
Until the board releases its data, the gender breakdown of the denials and the degree to which practice gaps due to such issues led to them is unknown. There’s concern that women have been unfairly penalized.
The storm was set off on the discussion board this summer by stories from physicians such as Chandani DeZure, MD, a pediatric hospitalist currently working in the neonatal ICU at Stanford (Calif.) University. She was denied a seat at the table in November, appealed, and was denied again.
She was a full-time pediatric hospitalist at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, from 2014, when she graduated residency, until Oct. 2018, when her husband, also a doctor, was offered a promising research position in California, and “we decided to take it,” Dr. DeZure said.
They moved to California with their young son in November. Dr. DeZure got her California medical license in 6 weeks, was hired by Stanford in January, and started her new postion in mid-April.
Because of the move, she worked only 3.5 years in the board’s 4 year practice window, but, as is common with young physicians, that time was spent in direct patient care, for a total of over 6,000 hours.
“How is that not good enough? How is a person that worked 500 hours with patients for 4 years” – for a total of 2,000 hours – “better qualified than someone who worked 100% for 3 and a half years? Nobody is saying there shouldn’t be a standard, but the standard has to be reasonable,” Dr. DeZure said.
“Illegal regardless of intent”
It’s situations like Dr. DeZure’s that led to the petition. One of demands is that ABP “revise the practice pathway criteria to be more inclusive of applicants with interrupted practice and varied clinical experience, to include clear-cut parameters rather than considering these applications on a closed-door ‘case-by-case basis...at the discretion of the ABP.’ ” Also, the petition asks the board to “clarify the appeals process and improve responsiveness to appeals and inquiries regarding denials.”
As ABP noted in its statement, however, the major demand is that the board “facilitate a timely analysis to determine if gender bias is present.” The petition noted that signers “do not suspect intentional bias on the part of the ABP; however, if gender bias is present it is unethical and potentially illegal regardless of intent.”
For now, the perception is that the board has “a hard 48-month rule” with not many exceptions; there are people who are “very concerned that, ‘Oh my gosh, I can’t have children for 4 years because I won’t be able to sit for the boards.’ No one should ever have to have that in their head,” Dr. Fromme said. At this point, it seems that 3 months off for maternity is being grandfathered in, but perhaps not 6 months for a second child; no one knows for sure.
Dr. DeZure, meanwhile, continues to study for the board exam, just in case.
Looking back over the past year, she said “I could have somehow picked up one shift a week moonlighting that would have kept me eligible, but the [board] didn’t respond to me” when contacted about her situation during the California move.
“The other option was for me was to live cross country from my husband with a small child,” she said.
Are women unfairly penalized?
Are women unfairly penalized?
More than 1,625 pediatricians have applied to take the first pediatric hospitalist certification exam in November 2019, and approximately 93% of them have been accepted, according to a statement from the American Board of Pediatrics.
It was the rejection of the 7%, however, that set off a firestorm on the electronic discussion board for American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) hospital medicine this summer, and led to a petition to the board to revise its eligibility requirements, ensure that the requirements are fair to women, and bring transparency to its decision process. The petition has more than 1,400 signatures.
Seattle Children’s Hospital and Yale New Haven (Conn.) Children’s Hospital have both said they will not consider board certification in hiring decisions until the situation is resolved.
The American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) declined an interview request pending its formal response to the Aug. 6 petition, but in a statement to this news organization, executive vice president Suzanne Woods, MD, said, “The percentage of women and men meeting the eligibility requirements for the exam did not differ. We stress this point because a concern about possible gender bias appears to have been the principal reason for this ... petition, and we wanted to offer immediate reassurance that no unintended bias has occurred.”
“We are carefully considering the requests and will release detailed data to hospitalists on the AAP’s [pediatric hospital medicine (PHM) electronic discussion board] ... and on the ABP’s website. We are conferring with ABP PHM subboard members as well as leaders from our volunteer community. We expect to provide a thoughtful response within the next 3 weeks,” Dr. Woods said in the Aug. 15 statement.
“Case-by-case” exceptions
The backstory is that, for better or worse depending on who you talk to, pediatric hospital medicine is becoming a board certified subspecialty. A fellowship will be required to sit for the exam after a few years, which is standard for subspecialties.
What’s generated concern is how the board is grandfathering current pediatric hospitalists into certification via a “practice pathway” until the fellowship requirement takes hold after 2023.
To qualify for the November test, hospitalists had to complete 4 years of full-time practice by June 30, 2019, which has been understood to mean 48 months of continual employment. At least 50% of that time had to be devoted to “professional activities ... related to the care of hospitalized children,” and at least 25% of that “devoted to direct patient care.” Assuming about 2,000 work hours per year, it translated to “450-500 hours” of direct patient care “per year over the most recent four years” to sit for the test, the board said.
“For individuals who have interrupted practice during the most recent four years for family leave or other such circumstances, an exception may be considered if there is substantial prior experience in pediatric hospital medicine. ... Such exceptions are made at the discretion of the ABP and will be considered on a case-by-case basis.” Specific criteria for exceptions were not spelled out.
In the end, there were more than a few surprises when denial letters went out in recent months, and scores of appeals have been filed. There’s “a lot of tension and a lot of confusion” about why some people with practice gaps during the 4 years were approved, but others were denied. There’s been “a lack of transparency on the ABP’s part,” said H. Barrett Fromme, MD, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Chicago.
“The standard has to be reasonable”
There are concerns about the availability of fellowship slots and other issues, but the 4-year rule – instead of averaging clinical hours over 4 or 5 years, for instance – is the main sticking point. It’s a gender issue because “women take maternity; women move with their spouse; women take care of elders; women tend to be in these roles that require time off” more than men do, Dr. Fromme said.
Until the board releases its data, the gender breakdown of the denials and the degree to which practice gaps due to such issues led to them is unknown. There’s concern that women have been unfairly penalized.
The storm was set off on the discussion board this summer by stories from physicians such as Chandani DeZure, MD, a pediatric hospitalist currently working in the neonatal ICU at Stanford (Calif.) University. She was denied a seat at the table in November, appealed, and was denied again.
She was a full-time pediatric hospitalist at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, from 2014, when she graduated residency, until Oct. 2018, when her husband, also a doctor, was offered a promising research position in California, and “we decided to take it,” Dr. DeZure said.
They moved to California with their young son in November. Dr. DeZure got her California medical license in 6 weeks, was hired by Stanford in January, and started her new postion in mid-April.
Because of the move, she worked only 3.5 years in the board’s 4 year practice window, but, as is common with young physicians, that time was spent in direct patient care, for a total of over 6,000 hours.
“How is that not good enough? How is a person that worked 500 hours with patients for 4 years” – for a total of 2,000 hours – “better qualified than someone who worked 100% for 3 and a half years? Nobody is saying there shouldn’t be a standard, but the standard has to be reasonable,” Dr. DeZure said.
“Illegal regardless of intent”
It’s situations like Dr. DeZure’s that led to the petition. One of demands is that ABP “revise the practice pathway criteria to be more inclusive of applicants with interrupted practice and varied clinical experience, to include clear-cut parameters rather than considering these applications on a closed-door ‘case-by-case basis...at the discretion of the ABP.’ ” Also, the petition asks the board to “clarify the appeals process and improve responsiveness to appeals and inquiries regarding denials.”
As ABP noted in its statement, however, the major demand is that the board “facilitate a timely analysis to determine if gender bias is present.” The petition noted that signers “do not suspect intentional bias on the part of the ABP; however, if gender bias is present it is unethical and potentially illegal regardless of intent.”
For now, the perception is that the board has “a hard 48-month rule” with not many exceptions; there are people who are “very concerned that, ‘Oh my gosh, I can’t have children for 4 years because I won’t be able to sit for the boards.’ No one should ever have to have that in their head,” Dr. Fromme said. At this point, it seems that 3 months off for maternity is being grandfathered in, but perhaps not 6 months for a second child; no one knows for sure.
Dr. DeZure, meanwhile, continues to study for the board exam, just in case.
Looking back over the past year, she said “I could have somehow picked up one shift a week moonlighting that would have kept me eligible, but the [board] didn’t respond to me” when contacted about her situation during the California move.
“The other option was for me was to live cross country from my husband with a small child,” she said.
More than 1,625 pediatricians have applied to take the first pediatric hospitalist certification exam in November 2019, and approximately 93% of them have been accepted, according to a statement from the American Board of Pediatrics.
It was the rejection of the 7%, however, that set off a firestorm on the electronic discussion board for American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) hospital medicine this summer, and led to a petition to the board to revise its eligibility requirements, ensure that the requirements are fair to women, and bring transparency to its decision process. The petition has more than 1,400 signatures.
Seattle Children’s Hospital and Yale New Haven (Conn.) Children’s Hospital have both said they will not consider board certification in hiring decisions until the situation is resolved.
The American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) declined an interview request pending its formal response to the Aug. 6 petition, but in a statement to this news organization, executive vice president Suzanne Woods, MD, said, “The percentage of women and men meeting the eligibility requirements for the exam did not differ. We stress this point because a concern about possible gender bias appears to have been the principal reason for this ... petition, and we wanted to offer immediate reassurance that no unintended bias has occurred.”
“We are carefully considering the requests and will release detailed data to hospitalists on the AAP’s [pediatric hospital medicine (PHM) electronic discussion board] ... and on the ABP’s website. We are conferring with ABP PHM subboard members as well as leaders from our volunteer community. We expect to provide a thoughtful response within the next 3 weeks,” Dr. Woods said in the Aug. 15 statement.
“Case-by-case” exceptions
The backstory is that, for better or worse depending on who you talk to, pediatric hospital medicine is becoming a board certified subspecialty. A fellowship will be required to sit for the exam after a few years, which is standard for subspecialties.
What’s generated concern is how the board is grandfathering current pediatric hospitalists into certification via a “practice pathway” until the fellowship requirement takes hold after 2023.
To qualify for the November test, hospitalists had to complete 4 years of full-time practice by June 30, 2019, which has been understood to mean 48 months of continual employment. At least 50% of that time had to be devoted to “professional activities ... related to the care of hospitalized children,” and at least 25% of that “devoted to direct patient care.” Assuming about 2,000 work hours per year, it translated to “450-500 hours” of direct patient care “per year over the most recent four years” to sit for the test, the board said.
“For individuals who have interrupted practice during the most recent four years for family leave or other such circumstances, an exception may be considered if there is substantial prior experience in pediatric hospital medicine. ... Such exceptions are made at the discretion of the ABP and will be considered on a case-by-case basis.” Specific criteria for exceptions were not spelled out.
In the end, there were more than a few surprises when denial letters went out in recent months, and scores of appeals have been filed. There’s “a lot of tension and a lot of confusion” about why some people with practice gaps during the 4 years were approved, but others were denied. There’s been “a lack of transparency on the ABP’s part,” said H. Barrett Fromme, MD, section chief of pediatric hospital medicine and a professor of pediatrics at the University of Chicago.
“The standard has to be reasonable”
There are concerns about the availability of fellowship slots and other issues, but the 4-year rule – instead of averaging clinical hours over 4 or 5 years, for instance – is the main sticking point. It’s a gender issue because “women take maternity; women move with their spouse; women take care of elders; women tend to be in these roles that require time off” more than men do, Dr. Fromme said.
Until the board releases its data, the gender breakdown of the denials and the degree to which practice gaps due to such issues led to them is unknown. There’s concern that women have been unfairly penalized.
The storm was set off on the discussion board this summer by stories from physicians such as Chandani DeZure, MD, a pediatric hospitalist currently working in the neonatal ICU at Stanford (Calif.) University. She was denied a seat at the table in November, appealed, and was denied again.
She was a full-time pediatric hospitalist at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, from 2014, when she graduated residency, until Oct. 2018, when her husband, also a doctor, was offered a promising research position in California, and “we decided to take it,” Dr. DeZure said.
They moved to California with their young son in November. Dr. DeZure got her California medical license in 6 weeks, was hired by Stanford in January, and started her new postion in mid-April.
Because of the move, she worked only 3.5 years in the board’s 4 year practice window, but, as is common with young physicians, that time was spent in direct patient care, for a total of over 6,000 hours.
“How is that not good enough? How is a person that worked 500 hours with patients for 4 years” – for a total of 2,000 hours – “better qualified than someone who worked 100% for 3 and a half years? Nobody is saying there shouldn’t be a standard, but the standard has to be reasonable,” Dr. DeZure said.
“Illegal regardless of intent”
It’s situations like Dr. DeZure’s that led to the petition. One of demands is that ABP “revise the practice pathway criteria to be more inclusive of applicants with interrupted practice and varied clinical experience, to include clear-cut parameters rather than considering these applications on a closed-door ‘case-by-case basis...at the discretion of the ABP.’ ” Also, the petition asks the board to “clarify the appeals process and improve responsiveness to appeals and inquiries regarding denials.”
As ABP noted in its statement, however, the major demand is that the board “facilitate a timely analysis to determine if gender bias is present.” The petition noted that signers “do not suspect intentional bias on the part of the ABP; however, if gender bias is present it is unethical and potentially illegal regardless of intent.”
For now, the perception is that the board has “a hard 48-month rule” with not many exceptions; there are people who are “very concerned that, ‘Oh my gosh, I can’t have children for 4 years because I won’t be able to sit for the boards.’ No one should ever have to have that in their head,” Dr. Fromme said. At this point, it seems that 3 months off for maternity is being grandfathered in, but perhaps not 6 months for a second child; no one knows for sure.
Dr. DeZure, meanwhile, continues to study for the board exam, just in case.
Looking back over the past year, she said “I could have somehow picked up one shift a week moonlighting that would have kept me eligible, but the [board] didn’t respond to me” when contacted about her situation during the California move.
“The other option was for me was to live cross country from my husband with a small child,” she said.
A practical tool predicts childhood epilepsy diagnosis
BANGKOK – A prediction tool that determines the risk of a pediatric epilepsy diagnosis eventually being made in a child who has had one or more paroxysmal events of possible epileptic origin is now available, and the clarity it provides makes life considerably easier for physicians and worried parents, Kees P. Braun, MD, PhD, said at the International Epilepsy Congress.
This prediction tool is highly practical. It relies upon certain clinical characteristics and a first interictal EEG, all information readily available at the time of the family’s first consultation with a neurologist or pediatrician with access to EEG, noted Dr. Braun, professor of neurology at Utrecht (the Netherlands) University.
The tool is freely available online (http://epilepsypredictiontools.info/first-consultation). The details of how Dr. Braun and coinvestigators developed the prediction tool have been published (Pediatrics. 2018 Dec;142[6]:e20180931. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-0931), he said at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
Early and accurate diagnosis or exclusion of epilepsy following a suspicious paroxysmal event deserves to be a high priority. Diagnostic delay is common, with resultant unrecognized recurrent epileptic seizures that can cause cognitive and behavioral impairments. And overdiagnosis of pediatric epilepsy unnecessarily exposes a child to the risks of antiepileptic drug therapy, not to mention the potential social stigma.
The predictive tool was developed through retrospective, multidimensional analysis of detailed data on 451 children who visited the outpatient pediatric neurology clinic at University Medical Center Utrecht for a diagnostic work-up after one or more paroxysmal events that might have been seizures, all of whom were subsequently followed for a year or longer. The resultant predictive model was then independently validated in a separate cohort of 187 children seen for the same reason at another Dutch university.
The model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.86, which statisticians consider to be excellent discriminatory power. The tool’s sensitivity and specificity varied according to the diagnostic probability threshold selected by the parents and physicians. For example, the predictive tool had a sensitivity of 18%, specificity of 99%, positive predictive value of 94%, and negative predictive value of 80% for identification of individuals with a greater than 80% probability of being diagnosed with epilepsy. For identification of all patients with a greater than 20% likelihood of receiving the diagnosis, the sensitivity was 73%, specificity 82%, positive predictive value 76%, and negative predictive value 79%.
The clinical characteristics incorporated in the predictive model include age at first seizure, gender, details of the paroxysmal event, and specifics of the child’s medical history. The relevant features of the standard interictal EEG recorded at the time of consultation include the presence or absence of focal epileptiform abnormalities if focal spikes or spike-wave complexes were detected, generalized epileptiform abnormalities in the presence of generalized spikes or spike-wave complexes, and nonspecific nonepileptiform abnormalities.
Future predictive refinements are under study
Dr. Braun and coworkers have reported that examining EEG functional network characteristics – that is, the functional networks of correlated brain activity in an individual patient’s brain – improves the EEG’s predictive value for epilepsy (PLoS One. 2013;8[4]:e59764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059764), a conclusion further reinforced in their systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating 11 additional studies (PLoS One. 2014 Dec 10;9[12]:e114606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114606).
In addition, the Dutch investigators have shown that ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes seen in scalp EEG recordings have prognostic significance. An absence of ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes identified children without epilepsy. In contrast, more than five ripples predicted atypical and symptomatic rolandic epilepsy with a substantial seizure risk warranting consideration of antiepileptic drug therapy (Epilepsia. 2016 Jul;57[7]:1179-89).
A Boston group using a fully automated spike ripple detector subsequently confirmed that ripples occurring in conjunction with epileptiform discharges on scalp EEG constitute a noninvasive biomarker for seizure risk that outperforms analysis of spikes alone and could potentially be useful in guiding medication tapering decisions in children (Brain. 2019 May 1;142[5]:1296-1309).
Dr. Braun reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
BANGKOK – A prediction tool that determines the risk of a pediatric epilepsy diagnosis eventually being made in a child who has had one or more paroxysmal events of possible epileptic origin is now available, and the clarity it provides makes life considerably easier for physicians and worried parents, Kees P. Braun, MD, PhD, said at the International Epilepsy Congress.
This prediction tool is highly practical. It relies upon certain clinical characteristics and a first interictal EEG, all information readily available at the time of the family’s first consultation with a neurologist or pediatrician with access to EEG, noted Dr. Braun, professor of neurology at Utrecht (the Netherlands) University.
The tool is freely available online (http://epilepsypredictiontools.info/first-consultation). The details of how Dr. Braun and coinvestigators developed the prediction tool have been published (Pediatrics. 2018 Dec;142[6]:e20180931. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-0931), he said at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
Early and accurate diagnosis or exclusion of epilepsy following a suspicious paroxysmal event deserves to be a high priority. Diagnostic delay is common, with resultant unrecognized recurrent epileptic seizures that can cause cognitive and behavioral impairments. And overdiagnosis of pediatric epilepsy unnecessarily exposes a child to the risks of antiepileptic drug therapy, not to mention the potential social stigma.
The predictive tool was developed through retrospective, multidimensional analysis of detailed data on 451 children who visited the outpatient pediatric neurology clinic at University Medical Center Utrecht for a diagnostic work-up after one or more paroxysmal events that might have been seizures, all of whom were subsequently followed for a year or longer. The resultant predictive model was then independently validated in a separate cohort of 187 children seen for the same reason at another Dutch university.
The model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.86, which statisticians consider to be excellent discriminatory power. The tool’s sensitivity and specificity varied according to the diagnostic probability threshold selected by the parents and physicians. For example, the predictive tool had a sensitivity of 18%, specificity of 99%, positive predictive value of 94%, and negative predictive value of 80% for identification of individuals with a greater than 80% probability of being diagnosed with epilepsy. For identification of all patients with a greater than 20% likelihood of receiving the diagnosis, the sensitivity was 73%, specificity 82%, positive predictive value 76%, and negative predictive value 79%.
The clinical characteristics incorporated in the predictive model include age at first seizure, gender, details of the paroxysmal event, and specifics of the child’s medical history. The relevant features of the standard interictal EEG recorded at the time of consultation include the presence or absence of focal epileptiform abnormalities if focal spikes or spike-wave complexes were detected, generalized epileptiform abnormalities in the presence of generalized spikes or spike-wave complexes, and nonspecific nonepileptiform abnormalities.
Future predictive refinements are under study
Dr. Braun and coworkers have reported that examining EEG functional network characteristics – that is, the functional networks of correlated brain activity in an individual patient’s brain – improves the EEG’s predictive value for epilepsy (PLoS One. 2013;8[4]:e59764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059764), a conclusion further reinforced in their systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating 11 additional studies (PLoS One. 2014 Dec 10;9[12]:e114606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114606).
In addition, the Dutch investigators have shown that ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes seen in scalp EEG recordings have prognostic significance. An absence of ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes identified children without epilepsy. In contrast, more than five ripples predicted atypical and symptomatic rolandic epilepsy with a substantial seizure risk warranting consideration of antiepileptic drug therapy (Epilepsia. 2016 Jul;57[7]:1179-89).
A Boston group using a fully automated spike ripple detector subsequently confirmed that ripples occurring in conjunction with epileptiform discharges on scalp EEG constitute a noninvasive biomarker for seizure risk that outperforms analysis of spikes alone and could potentially be useful in guiding medication tapering decisions in children (Brain. 2019 May 1;142[5]:1296-1309).
Dr. Braun reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
BANGKOK – A prediction tool that determines the risk of a pediatric epilepsy diagnosis eventually being made in a child who has had one or more paroxysmal events of possible epileptic origin is now available, and the clarity it provides makes life considerably easier for physicians and worried parents, Kees P. Braun, MD, PhD, said at the International Epilepsy Congress.
This prediction tool is highly practical. It relies upon certain clinical characteristics and a first interictal EEG, all information readily available at the time of the family’s first consultation with a neurologist or pediatrician with access to EEG, noted Dr. Braun, professor of neurology at Utrecht (the Netherlands) University.
The tool is freely available online (http://epilepsypredictiontools.info/first-consultation). The details of how Dr. Braun and coinvestigators developed the prediction tool have been published (Pediatrics. 2018 Dec;142[6]:e20180931. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-0931), he said at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
Early and accurate diagnosis or exclusion of epilepsy following a suspicious paroxysmal event deserves to be a high priority. Diagnostic delay is common, with resultant unrecognized recurrent epileptic seizures that can cause cognitive and behavioral impairments. And overdiagnosis of pediatric epilepsy unnecessarily exposes a child to the risks of antiepileptic drug therapy, not to mention the potential social stigma.
The predictive tool was developed through retrospective, multidimensional analysis of detailed data on 451 children who visited the outpatient pediatric neurology clinic at University Medical Center Utrecht for a diagnostic work-up after one or more paroxysmal events that might have been seizures, all of whom were subsequently followed for a year or longer. The resultant predictive model was then independently validated in a separate cohort of 187 children seen for the same reason at another Dutch university.
The model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.86, which statisticians consider to be excellent discriminatory power. The tool’s sensitivity and specificity varied according to the diagnostic probability threshold selected by the parents and physicians. For example, the predictive tool had a sensitivity of 18%, specificity of 99%, positive predictive value of 94%, and negative predictive value of 80% for identification of individuals with a greater than 80% probability of being diagnosed with epilepsy. For identification of all patients with a greater than 20% likelihood of receiving the diagnosis, the sensitivity was 73%, specificity 82%, positive predictive value 76%, and negative predictive value 79%.
The clinical characteristics incorporated in the predictive model include age at first seizure, gender, details of the paroxysmal event, and specifics of the child’s medical history. The relevant features of the standard interictal EEG recorded at the time of consultation include the presence or absence of focal epileptiform abnormalities if focal spikes or spike-wave complexes were detected, generalized epileptiform abnormalities in the presence of generalized spikes or spike-wave complexes, and nonspecific nonepileptiform abnormalities.
Future predictive refinements are under study
Dr. Braun and coworkers have reported that examining EEG functional network characteristics – that is, the functional networks of correlated brain activity in an individual patient’s brain – improves the EEG’s predictive value for epilepsy (PLoS One. 2013;8[4]:e59764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059764), a conclusion further reinforced in their systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating 11 additional studies (PLoS One. 2014 Dec 10;9[12]:e114606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114606).
In addition, the Dutch investigators have shown that ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes seen in scalp EEG recordings have prognostic significance. An absence of ripples superimposed on rolandic spikes identified children without epilepsy. In contrast, more than five ripples predicted atypical and symptomatic rolandic epilepsy with a substantial seizure risk warranting consideration of antiepileptic drug therapy (Epilepsia. 2016 Jul;57[7]:1179-89).
A Boston group using a fully automated spike ripple detector subsequently confirmed that ripples occurring in conjunction with epileptiform discharges on scalp EEG constitute a noninvasive biomarker for seizure risk that outperforms analysis of spikes alone and could potentially be useful in guiding medication tapering decisions in children (Brain. 2019 May 1;142[5]:1296-1309).
Dr. Braun reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
REPORTING FROM IEC 2019
‘Pot’ is still hot for Dravet, Lennox-Gastaut
BANGKOK – Interim results of long-term, open-label extension trials of add-on prescription cannabidiol in patients with Dravet syndrome or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome show sustained, clinically meaningful seizure reductions with no new safety concerns, Anup D. Patel, MD, reported at the International Epilepsy Congress.
“Overall, this is a very promising and sustainable result that we were happy to see,” said Dr. Patel, chief of child neurology at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
Epidiolex is the brand name for the plant-derived, highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) in an oil-based oral solution at 100 mg/mL. Dr. Patel has been involved in the medication’s development program since the earliest open-label compassionate use study, which was followed by rigorous phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trials, eventually leading to Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the treatment of Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients 2 years of age or older.
“On June 25th, 2018, history was made: for the first time in United States history, a plant-based derivative of marijuana was approved for use as a medication, and it was also the first FDA-approved treatment for Dravet syndrome,” Dr. Patel noted at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
A total of 96% of the 289 children with Dravet syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, controlled randomized trials enrolled in the open-label, long-term extension study, during which they were on a median of three concurrent antiepileptic drugs along with a mean modal dose of CBD at 22 mg/kg/day. Although the target maintenance dose of CBD was 20 mg/kg/day, as advised in the product labeling, physicians could reduce or increase the dose up to 30 mg/kg/day.
“In the initial compassionate-use study, our site could go up to 50 mg/kg/day,” according to Dr. Patel. “We have plenty of data showing efficacy and continued safety beyond the FDA-recommended dose.”
In the open-label extension study, the median reduction from baseline in monthly seizure frequency assessed in 12-week intervals up to a maximum of week 72 was 44%-57% for convulsive seizures and 49%-67% for total seizures. More than 80% of patients and/or caregivers reported improvement in the patient’s overall condition as assessed on the Subject/Caregiver Global Impression of Change scale.
The pattern of adverse events associated with CBD has been consistent across all of the studies. The most common side effects are diarrhea in about one-third of patients, sleepiness in one-quarter, and decreased appetite in about one-quarter. Seven percent of patients discontinued the long-term extension trial because of adverse events.
Seventy percent of patients remained in the long-term extension study at 1 year.
Twenty-six patients developed liver transaminase levels greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and of note, 23 of the 26 were on concomitant valproic acid. None met criteria for severe drug-induced liver injury, and all recovered either spontaneously or after a reduction in the dose of CBD or valproic acid. But this association between CBD, valproic acid, and increased risk of mild liver injury has been a consistent finding across the clinical trials program.
“This is a very important clinical pearl to take away,” commented Dr. Patel, who is also a pediatric neurologist at Ohio State University.
The interim results of the long-term, open-label extension study of add-on CBD in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are similar to the Dravet syndrome study. Overall, 99% of the 368 patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, randomized trials signed up for the open-label extension. During a median follow-up of 61 weeks, the median percent reduction in seizure frequency as assessed in serial 12-week windows was 48%-70% for drop seizures and 48%-63% for total seizures. Twenty-four percent of patients withdrew from the study. Eighty-eight percent of patients or caregivers reported an improvement in overall condition when assessed at weeks 24 and 48. Forty-seven patients developed elevated transaminase levels – typically within the first 2 months on CBD – and 35 of them were on concomitant valproic acid.
More on drug-drug interactions
Elsewhere at IEC 2019, Gilmour Morrison of GW Pharmaceuticals, the Cambridge, England, company that markets Epidiolex, presented the findings of a series of drug-drug interaction studies involving coadministration of their CBD with clobazam (Sympazan and Onfi), valproate, stiripentol (Diacomit), or midazolam (Versed) in adult epilepsy patients and healthy volunteers. The researchers reported a bidirectional drug-drug interaction between Epidiolex and clobazam resulting in increased levels of the active metabolites of both drugs. The mechanism is believed to involve inhibition of cytochrome P450 2C19. However, there were no interactions with midazolam or valproate, and the slight bump in stiripentol levels when given with CBD didn’t reach the level of a clinically meaningful drug-drug interaction, according to the investigators.
On the horizon, Canadian researchers are investigating the possibility that since both the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD components of marijuana have been shown to have anticonvulsant effects, adding a bit of THC to CBD will result in even better seizure control than with pure CBD in patients with Dravet syndrome. Investigators at Toronto’s Hospital for Sick Children have conducted a prospective, open-label study of a product containing CBD and THC in a 50:1 ratio as add-on therapy in 20 children with Dravet syndrome. The dose was 2-16 mg/kg/day of CBD and 0.04-0.32 mg/kg/day of THC. The cannabis plant extract used in the study was produced by Tilray, a Canadian pharmaceutical company.
Nineteen of the 20 patients completed the 20-week study. The sole noncompleter died of SUDEP (sudden unexpected death in epilepsy) deemed treatment unrelated. Patients experienced a median 71% reduction in motor seizures, compared with baseline. Sixty-three percent of patients had at least a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. Elevated liver transaminases occurred in patients on concomitant valproic acid, as did platelet abnormalities, which have not been seen in the Epidiolex studies, noted Dr. Patel, who was not involved in the Canadian study (Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Aug 1;5[9]:1077-88).
Dr. Patel reported serving as a consultant to Greenwich Biosciences, a U.S. offshoot of GW Pharmaceuticals. He receives research grants from that company as well as from the National Institutes of Health and the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation.
BANGKOK – Interim results of long-term, open-label extension trials of add-on prescription cannabidiol in patients with Dravet syndrome or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome show sustained, clinically meaningful seizure reductions with no new safety concerns, Anup D. Patel, MD, reported at the International Epilepsy Congress.
“Overall, this is a very promising and sustainable result that we were happy to see,” said Dr. Patel, chief of child neurology at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
Epidiolex is the brand name for the plant-derived, highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) in an oil-based oral solution at 100 mg/mL. Dr. Patel has been involved in the medication’s development program since the earliest open-label compassionate use study, which was followed by rigorous phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trials, eventually leading to Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the treatment of Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients 2 years of age or older.
“On June 25th, 2018, history was made: for the first time in United States history, a plant-based derivative of marijuana was approved for use as a medication, and it was also the first FDA-approved treatment for Dravet syndrome,” Dr. Patel noted at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
A total of 96% of the 289 children with Dravet syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, controlled randomized trials enrolled in the open-label, long-term extension study, during which they were on a median of three concurrent antiepileptic drugs along with a mean modal dose of CBD at 22 mg/kg/day. Although the target maintenance dose of CBD was 20 mg/kg/day, as advised in the product labeling, physicians could reduce or increase the dose up to 30 mg/kg/day.
“In the initial compassionate-use study, our site could go up to 50 mg/kg/day,” according to Dr. Patel. “We have plenty of data showing efficacy and continued safety beyond the FDA-recommended dose.”
In the open-label extension study, the median reduction from baseline in monthly seizure frequency assessed in 12-week intervals up to a maximum of week 72 was 44%-57% for convulsive seizures and 49%-67% for total seizures. More than 80% of patients and/or caregivers reported improvement in the patient’s overall condition as assessed on the Subject/Caregiver Global Impression of Change scale.
The pattern of adverse events associated with CBD has been consistent across all of the studies. The most common side effects are diarrhea in about one-third of patients, sleepiness in one-quarter, and decreased appetite in about one-quarter. Seven percent of patients discontinued the long-term extension trial because of adverse events.
Seventy percent of patients remained in the long-term extension study at 1 year.
Twenty-six patients developed liver transaminase levels greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and of note, 23 of the 26 were on concomitant valproic acid. None met criteria for severe drug-induced liver injury, and all recovered either spontaneously or after a reduction in the dose of CBD or valproic acid. But this association between CBD, valproic acid, and increased risk of mild liver injury has been a consistent finding across the clinical trials program.
“This is a very important clinical pearl to take away,” commented Dr. Patel, who is also a pediatric neurologist at Ohio State University.
The interim results of the long-term, open-label extension study of add-on CBD in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are similar to the Dravet syndrome study. Overall, 99% of the 368 patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, randomized trials signed up for the open-label extension. During a median follow-up of 61 weeks, the median percent reduction in seizure frequency as assessed in serial 12-week windows was 48%-70% for drop seizures and 48%-63% for total seizures. Twenty-four percent of patients withdrew from the study. Eighty-eight percent of patients or caregivers reported an improvement in overall condition when assessed at weeks 24 and 48. Forty-seven patients developed elevated transaminase levels – typically within the first 2 months on CBD – and 35 of them were on concomitant valproic acid.
More on drug-drug interactions
Elsewhere at IEC 2019, Gilmour Morrison of GW Pharmaceuticals, the Cambridge, England, company that markets Epidiolex, presented the findings of a series of drug-drug interaction studies involving coadministration of their CBD with clobazam (Sympazan and Onfi), valproate, stiripentol (Diacomit), or midazolam (Versed) in adult epilepsy patients and healthy volunteers. The researchers reported a bidirectional drug-drug interaction between Epidiolex and clobazam resulting in increased levels of the active metabolites of both drugs. The mechanism is believed to involve inhibition of cytochrome P450 2C19. However, there were no interactions with midazolam or valproate, and the slight bump in stiripentol levels when given with CBD didn’t reach the level of a clinically meaningful drug-drug interaction, according to the investigators.
On the horizon, Canadian researchers are investigating the possibility that since both the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD components of marijuana have been shown to have anticonvulsant effects, adding a bit of THC to CBD will result in even better seizure control than with pure CBD in patients with Dravet syndrome. Investigators at Toronto’s Hospital for Sick Children have conducted a prospective, open-label study of a product containing CBD and THC in a 50:1 ratio as add-on therapy in 20 children with Dravet syndrome. The dose was 2-16 mg/kg/day of CBD and 0.04-0.32 mg/kg/day of THC. The cannabis plant extract used in the study was produced by Tilray, a Canadian pharmaceutical company.
Nineteen of the 20 patients completed the 20-week study. The sole noncompleter died of SUDEP (sudden unexpected death in epilepsy) deemed treatment unrelated. Patients experienced a median 71% reduction in motor seizures, compared with baseline. Sixty-three percent of patients had at least a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. Elevated liver transaminases occurred in patients on concomitant valproic acid, as did platelet abnormalities, which have not been seen in the Epidiolex studies, noted Dr. Patel, who was not involved in the Canadian study (Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Aug 1;5[9]:1077-88).
Dr. Patel reported serving as a consultant to Greenwich Biosciences, a U.S. offshoot of GW Pharmaceuticals. He receives research grants from that company as well as from the National Institutes of Health and the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation.
BANGKOK – Interim results of long-term, open-label extension trials of add-on prescription cannabidiol in patients with Dravet syndrome or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome show sustained, clinically meaningful seizure reductions with no new safety concerns, Anup D. Patel, MD, reported at the International Epilepsy Congress.
“Overall, this is a very promising and sustainable result that we were happy to see,” said Dr. Patel, chief of child neurology at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio.
Epidiolex is the brand name for the plant-derived, highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) in an oil-based oral solution at 100 mg/mL. Dr. Patel has been involved in the medication’s development program since the earliest open-label compassionate use study, which was followed by rigorous phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trials, eventually leading to Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the treatment of Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in patients 2 years of age or older.
“On June 25th, 2018, history was made: for the first time in United States history, a plant-based derivative of marijuana was approved for use as a medication, and it was also the first FDA-approved treatment for Dravet syndrome,” Dr. Patel noted at the congress sponsored by the International League Against Epilepsy.
A total of 96% of the 289 children with Dravet syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, controlled randomized trials enrolled in the open-label, long-term extension study, during which they were on a median of three concurrent antiepileptic drugs along with a mean modal dose of CBD at 22 mg/kg/day. Although the target maintenance dose of CBD was 20 mg/kg/day, as advised in the product labeling, physicians could reduce or increase the dose up to 30 mg/kg/day.
“In the initial compassionate-use study, our site could go up to 50 mg/kg/day,” according to Dr. Patel. “We have plenty of data showing efficacy and continued safety beyond the FDA-recommended dose.”
In the open-label extension study, the median reduction from baseline in monthly seizure frequency assessed in 12-week intervals up to a maximum of week 72 was 44%-57% for convulsive seizures and 49%-67% for total seizures. More than 80% of patients and/or caregivers reported improvement in the patient’s overall condition as assessed on the Subject/Caregiver Global Impression of Change scale.
The pattern of adverse events associated with CBD has been consistent across all of the studies. The most common side effects are diarrhea in about one-third of patients, sleepiness in one-quarter, and decreased appetite in about one-quarter. Seven percent of patients discontinued the long-term extension trial because of adverse events.
Seventy percent of patients remained in the long-term extension study at 1 year.
Twenty-six patients developed liver transaminase levels greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and of note, 23 of the 26 were on concomitant valproic acid. None met criteria for severe drug-induced liver injury, and all recovered either spontaneously or after a reduction in the dose of CBD or valproic acid. But this association between CBD, valproic acid, and increased risk of mild liver injury has been a consistent finding across the clinical trials program.
“This is a very important clinical pearl to take away,” commented Dr. Patel, who is also a pediatric neurologist at Ohio State University.
The interim results of the long-term, open-label extension study of add-on CBD in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome are similar to the Dravet syndrome study. Overall, 99% of the 368 patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome who completed the 14-week, double-blind, randomized trials signed up for the open-label extension. During a median follow-up of 61 weeks, the median percent reduction in seizure frequency as assessed in serial 12-week windows was 48%-70% for drop seizures and 48%-63% for total seizures. Twenty-four percent of patients withdrew from the study. Eighty-eight percent of patients or caregivers reported an improvement in overall condition when assessed at weeks 24 and 48. Forty-seven patients developed elevated transaminase levels – typically within the first 2 months on CBD – and 35 of them were on concomitant valproic acid.
More on drug-drug interactions
Elsewhere at IEC 2019, Gilmour Morrison of GW Pharmaceuticals, the Cambridge, England, company that markets Epidiolex, presented the findings of a series of drug-drug interaction studies involving coadministration of their CBD with clobazam (Sympazan and Onfi), valproate, stiripentol (Diacomit), or midazolam (Versed) in adult epilepsy patients and healthy volunteers. The researchers reported a bidirectional drug-drug interaction between Epidiolex and clobazam resulting in increased levels of the active metabolites of both drugs. The mechanism is believed to involve inhibition of cytochrome P450 2C19. However, there were no interactions with midazolam or valproate, and the slight bump in stiripentol levels when given with CBD didn’t reach the level of a clinically meaningful drug-drug interaction, according to the investigators.
On the horizon, Canadian researchers are investigating the possibility that since both the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD components of marijuana have been shown to have anticonvulsant effects, adding a bit of THC to CBD will result in even better seizure control than with pure CBD in patients with Dravet syndrome. Investigators at Toronto’s Hospital for Sick Children have conducted a prospective, open-label study of a product containing CBD and THC in a 50:1 ratio as add-on therapy in 20 children with Dravet syndrome. The dose was 2-16 mg/kg/day of CBD and 0.04-0.32 mg/kg/day of THC. The cannabis plant extract used in the study was produced by Tilray, a Canadian pharmaceutical company.
Nineteen of the 20 patients completed the 20-week study. The sole noncompleter died of SUDEP (sudden unexpected death in epilepsy) deemed treatment unrelated. Patients experienced a median 71% reduction in motor seizures, compared with baseline. Sixty-three percent of patients had at least a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. Elevated liver transaminases occurred in patients on concomitant valproic acid, as did platelet abnormalities, which have not been seen in the Epidiolex studies, noted Dr. Patel, who was not involved in the Canadian study (Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018 Aug 1;5[9]:1077-88).
Dr. Patel reported serving as a consultant to Greenwich Biosciences, a U.S. offshoot of GW Pharmaceuticals. He receives research grants from that company as well as from the National Institutes of Health and the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation.
REPORTING FROM IEC 2019
Fifty-one percent of U.S. adolescents fully vaccinated against HPV
according to a report published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Researchers analyzed data from 18,700 adolescents aged 13-17 years – 48% of whom were female – in the 2018 National Immunization Survey–Teen to discover that 51% of adolescents were up to date with the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, and 68% had received at least one dose of the vaccine.
There was an increase in HPV vaccination coverage from 2017 to 2018, but this was attributable to a 4.4 percentage point increase in males who were up to date, compared with a 0.6 percentage point increase in females.
“Although HPV vaccination coverage improved, increases among all adolescents were modest compared with increases in previous years and were observed only among males,” wrote Tanja Y. Walker of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors.
The number of adolescents who had at least one dose of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate (4MenB) vaccine increased by 1.5 percentage points to 86.6%, while among individuals aged 17 years, coverage with two or more doses of 4MenB vaccine increased by 6.5 percentage points to 50.8%. Tdap coverage remained the same at 89% (MMWR 2019;68(33):718-23).
However, the study saw no significant increases in coverage with three or more hepatitis B vaccine doses, two or more MMR vaccine doses, or with one or more varicella vaccine doses in adolescents without a history of varicella disease.
Adolescents with Medicaid had higher HPV vaccination coverage than did adolescents with private health insurance. Uninsured adolescents had lower coverage overall, ranging from 4 percentage points lower for one or more varicella vaccine doses to 19 percentage points lower for two or more 4MenB vaccines, compared with adolescents with private health insurance.
Vaccination rates were lower among adolescents outside metropolitan areas, particularly when it came to being up to date with HPV vaccination, where there was a 15 percentage point difference, and with two or more doses of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine, where there was a 20 percentage point difference.
Provider recommendations to parents were associated with a higher rate of coverage with one or more doses of the HPV vaccine, but the prevalence of provider recommendations varied significantly from state to state. Overall, 78% of parents said they received a provider recommendation for the adolescent HPV vaccine, but that figure was as low as 60% in Mississippi and as high as 91% in Massachusetts.
Parents living in nonmetropolitan areas were less likely to report receiving a provider recommendation than were those in metropolitan principal cities.
“Equipping providers with the tools they need to give strong recommendations that emphasize the importance of HPV vaccination in preventing cancer and effectively address parental concerns is a priority, especially in states where provider recommendations were less commonly reported,” Ms. Walker and associates said.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
according to a report published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Researchers analyzed data from 18,700 adolescents aged 13-17 years – 48% of whom were female – in the 2018 National Immunization Survey–Teen to discover that 51% of adolescents were up to date with the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, and 68% had received at least one dose of the vaccine.
There was an increase in HPV vaccination coverage from 2017 to 2018, but this was attributable to a 4.4 percentage point increase in males who were up to date, compared with a 0.6 percentage point increase in females.
“Although HPV vaccination coverage improved, increases among all adolescents were modest compared with increases in previous years and were observed only among males,” wrote Tanja Y. Walker of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors.
The number of adolescents who had at least one dose of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate (4MenB) vaccine increased by 1.5 percentage points to 86.6%, while among individuals aged 17 years, coverage with two or more doses of 4MenB vaccine increased by 6.5 percentage points to 50.8%. Tdap coverage remained the same at 89% (MMWR 2019;68(33):718-23).
However, the study saw no significant increases in coverage with three or more hepatitis B vaccine doses, two or more MMR vaccine doses, or with one or more varicella vaccine doses in adolescents without a history of varicella disease.
Adolescents with Medicaid had higher HPV vaccination coverage than did adolescents with private health insurance. Uninsured adolescents had lower coverage overall, ranging from 4 percentage points lower for one or more varicella vaccine doses to 19 percentage points lower for two or more 4MenB vaccines, compared with adolescents with private health insurance.
Vaccination rates were lower among adolescents outside metropolitan areas, particularly when it came to being up to date with HPV vaccination, where there was a 15 percentage point difference, and with two or more doses of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine, where there was a 20 percentage point difference.
Provider recommendations to parents were associated with a higher rate of coverage with one or more doses of the HPV vaccine, but the prevalence of provider recommendations varied significantly from state to state. Overall, 78% of parents said they received a provider recommendation for the adolescent HPV vaccine, but that figure was as low as 60% in Mississippi and as high as 91% in Massachusetts.
Parents living in nonmetropolitan areas were less likely to report receiving a provider recommendation than were those in metropolitan principal cities.
“Equipping providers with the tools they need to give strong recommendations that emphasize the importance of HPV vaccination in preventing cancer and effectively address parental concerns is a priority, especially in states where provider recommendations were less commonly reported,” Ms. Walker and associates said.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
according to a report published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Researchers analyzed data from 18,700 adolescents aged 13-17 years – 48% of whom were female – in the 2018 National Immunization Survey–Teen to discover that 51% of adolescents were up to date with the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, and 68% had received at least one dose of the vaccine.
There was an increase in HPV vaccination coverage from 2017 to 2018, but this was attributable to a 4.4 percentage point increase in males who were up to date, compared with a 0.6 percentage point increase in females.
“Although HPV vaccination coverage improved, increases among all adolescents were modest compared with increases in previous years and were observed only among males,” wrote Tanja Y. Walker of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors.
The number of adolescents who had at least one dose of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate (4MenB) vaccine increased by 1.5 percentage points to 86.6%, while among individuals aged 17 years, coverage with two or more doses of 4MenB vaccine increased by 6.5 percentage points to 50.8%. Tdap coverage remained the same at 89% (MMWR 2019;68(33):718-23).
However, the study saw no significant increases in coverage with three or more hepatitis B vaccine doses, two or more MMR vaccine doses, or with one or more varicella vaccine doses in adolescents without a history of varicella disease.
Adolescents with Medicaid had higher HPV vaccination coverage than did adolescents with private health insurance. Uninsured adolescents had lower coverage overall, ranging from 4 percentage points lower for one or more varicella vaccine doses to 19 percentage points lower for two or more 4MenB vaccines, compared with adolescents with private health insurance.
Vaccination rates were lower among adolescents outside metropolitan areas, particularly when it came to being up to date with HPV vaccination, where there was a 15 percentage point difference, and with two or more doses of the quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine, where there was a 20 percentage point difference.
Provider recommendations to parents were associated with a higher rate of coverage with one or more doses of the HPV vaccine, but the prevalence of provider recommendations varied significantly from state to state. Overall, 78% of parents said they received a provider recommendation for the adolescent HPV vaccine, but that figure was as low as 60% in Mississippi and as high as 91% in Massachusetts.
Parents living in nonmetropolitan areas were less likely to report receiving a provider recommendation than were those in metropolitan principal cities.
“Equipping providers with the tools they need to give strong recommendations that emphasize the importance of HPV vaccination in preventing cancer and effectively address parental concerns is a priority, especially in states where provider recommendations were less commonly reported,” Ms. Walker and associates said.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM MMWR
Key clinical point: Slightly more than half of adolescents in the United States are fully vaccinated with the HPV vaccine.
Major finding: Rates of full HPV vaccination are 51% among adolescents aged 13-17 years.
Study details: Analysis of data from 18,700 adolescents aged 13-17 years in the 2018 National Immunization Survey–Teen.
Disclosures: No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Walker T et al. MMWR 2019 Aug 23;68(33):718-23.