User login
From Scrubs to Social Media: How Some Med Students Become Influencers
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No Surprises Act: Private Equity Scores Big in Arbitrations
Four organizations owned by private equity firms — including two provider groups — dominated the No Surprises Act’s disputed bill arbitration process in its first year, filing about 70% of 657,040 cases against insurers in 2023, a new report finds.
The findings, recently published in Health Affairs, suggest that private equity–owned organizations are forcefully challenging insurers about payments for certain kinds of out-of-network care.
Their fighting stance has paid off: The percentage of resolved arbitration cases won by providers jumped from 72% in the first quarter of 2023 to 85% in the last quarter, and they were awarded a median of more than 300% the contracted in-network rates for the services in question.
With many more out-of-network bills disputed by providers than expected, “the system is not working exactly the way it was anticipated when this law was written,” lead author Jack Hoadley, PhD, a research professor emeritus at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy, Washington, DC, told this news organization.
And, he said, the public and the federal government may end up paying a price.
Congress passed the No Surprises Act in 2020 and then-President Donald Trump signed it. The landmark bill, which went into effect in 2022, was designed to protect patients from unexpected and often exorbitant “surprise” bills after they received some kinds of out-of-network care.
Now, many types of providers are forbidden from billing patients beyond normal in-network costs. In these cases, health plans and out-of-network providers — who don’t have mutual agreements — must wrangle over payment amounts, which are intended to not exceed inflation-adjusted 2019 median levels.
A binding arbitration process kicks in when a provider and a health plan fail to agree about how much the plan will pay for a service. Then, a third-party arbitrator is called in to make a ruling that’s binding. The process is controversial, and a flurry of lawsuits from providers have challenged it.
The new report, which updates an earlier analysis, examines data about disputed cases from all of 2023.
Of the 657,040 new cases filed in 2023, about 70% came from four private equity-funded organizations: Team Health, SCP Health, Radiology Partners, and Envision, which each provide physician services.
About half of the 2023 cases were from just four states: Texas, Florida, Tennessee, and Georgia. The report says the four organizations are especially active in those states. In contrast, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Washington state each had just 1500 or fewer cases filed last year.
Health plans challenged a third of cases as ineligible, and 22% of all resolved cases were deemed ineligible.
Providers won 80% of resolved challenges in 2023, although it’s not clear how much money they reaped. Still, it’s clear that “in the vast majority of the cases, insurers have to pay larger amounts to the provider,” Dr. Hoadley said.
Radiologists made a median of at least 500% of the in-network rate in their cases. Surgeons and neurologists made even more money — a median of at least 800% of the in-network rate. Overall, providers made 322%-350% of in-network rates, depending on the quarter.
Dr. Hoadley cautioned that only a small percentage of medical payments are disputed. In those cases, “the amount that the insurer offers is accepted, and that’s the end of the story.”
Why are the providers often reaping much more than typical payments for in-network services? It’s “really hard to know,” Dr. Hoadley said. But one factor, he said, may be the fact that providers are able to offer evidence challenging that amounts that insurers say they paid previously: “Hey, when we were in network, we were paid this much.”
It’s not clear whether the dispute-and-arbitration system will cost insurers — and patients — more in the long run. The Congressional Budget Office actually thought the No Surprises Act might lower the growth of premiums slightly and save the federal government money, Dr. Hoadley said, but that could potentially not happen. The flood of litigation also contributes to uncertainty, he said.
Alan Sager, PhD, professor of Health Law, Policy, and Management at Boston University School of Public Health, told this news organization that premiums are bound to rise as insurers react to higher costs. He also expects that providers will question the value of being in-network. “If you’re out-of-network and can obtain much higher payments, why would any doctor or hospital remain in-network, especially since they don’t lose out on patient volume?”
Why are provider groups owned by private equity firms so aggressive at challenging health plans? Loren Adler, a fellow and associate director of the Brookings Institution’s Center on Health Policy, told this news organization that these companies play large roles in fields affected by the No Surprises Act. These include emergency medicine, radiology, and anesthesiology, said Mr. Adler, who’s also studied the No Surprises Act’s dispute/arbitration system.
Mr. Adler added that larger companies “are better suited to deal with technical complexities of this process and spend the sort of upfront money to go through it.”
In the big picture, Mr. Adler said, the new study “raises question of whether Congress at some point wants to try to basically bring prices from the arbitration process back in line with average in-network prices.”
The study was funded by the Commonwealth Fund and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Hoadley, Dr. Sager, and Mr. Adler had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four organizations owned by private equity firms — including two provider groups — dominated the No Surprises Act’s disputed bill arbitration process in its first year, filing about 70% of 657,040 cases against insurers in 2023, a new report finds.
The findings, recently published in Health Affairs, suggest that private equity–owned organizations are forcefully challenging insurers about payments for certain kinds of out-of-network care.
Their fighting stance has paid off: The percentage of resolved arbitration cases won by providers jumped from 72% in the first quarter of 2023 to 85% in the last quarter, and they were awarded a median of more than 300% the contracted in-network rates for the services in question.
With many more out-of-network bills disputed by providers than expected, “the system is not working exactly the way it was anticipated when this law was written,” lead author Jack Hoadley, PhD, a research professor emeritus at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy, Washington, DC, told this news organization.
And, he said, the public and the federal government may end up paying a price.
Congress passed the No Surprises Act in 2020 and then-President Donald Trump signed it. The landmark bill, which went into effect in 2022, was designed to protect patients from unexpected and often exorbitant “surprise” bills after they received some kinds of out-of-network care.
Now, many types of providers are forbidden from billing patients beyond normal in-network costs. In these cases, health plans and out-of-network providers — who don’t have mutual agreements — must wrangle over payment amounts, which are intended to not exceed inflation-adjusted 2019 median levels.
A binding arbitration process kicks in when a provider and a health plan fail to agree about how much the plan will pay for a service. Then, a third-party arbitrator is called in to make a ruling that’s binding. The process is controversial, and a flurry of lawsuits from providers have challenged it.
The new report, which updates an earlier analysis, examines data about disputed cases from all of 2023.
Of the 657,040 new cases filed in 2023, about 70% came from four private equity-funded organizations: Team Health, SCP Health, Radiology Partners, and Envision, which each provide physician services.
About half of the 2023 cases were from just four states: Texas, Florida, Tennessee, and Georgia. The report says the four organizations are especially active in those states. In contrast, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Washington state each had just 1500 or fewer cases filed last year.
Health plans challenged a third of cases as ineligible, and 22% of all resolved cases were deemed ineligible.
Providers won 80% of resolved challenges in 2023, although it’s not clear how much money they reaped. Still, it’s clear that “in the vast majority of the cases, insurers have to pay larger amounts to the provider,” Dr. Hoadley said.
Radiologists made a median of at least 500% of the in-network rate in their cases. Surgeons and neurologists made even more money — a median of at least 800% of the in-network rate. Overall, providers made 322%-350% of in-network rates, depending on the quarter.
Dr. Hoadley cautioned that only a small percentage of medical payments are disputed. In those cases, “the amount that the insurer offers is accepted, and that’s the end of the story.”
Why are the providers often reaping much more than typical payments for in-network services? It’s “really hard to know,” Dr. Hoadley said. But one factor, he said, may be the fact that providers are able to offer evidence challenging that amounts that insurers say they paid previously: “Hey, when we were in network, we were paid this much.”
It’s not clear whether the dispute-and-arbitration system will cost insurers — and patients — more in the long run. The Congressional Budget Office actually thought the No Surprises Act might lower the growth of premiums slightly and save the federal government money, Dr. Hoadley said, but that could potentially not happen. The flood of litigation also contributes to uncertainty, he said.
Alan Sager, PhD, professor of Health Law, Policy, and Management at Boston University School of Public Health, told this news organization that premiums are bound to rise as insurers react to higher costs. He also expects that providers will question the value of being in-network. “If you’re out-of-network and can obtain much higher payments, why would any doctor or hospital remain in-network, especially since they don’t lose out on patient volume?”
Why are provider groups owned by private equity firms so aggressive at challenging health plans? Loren Adler, a fellow and associate director of the Brookings Institution’s Center on Health Policy, told this news organization that these companies play large roles in fields affected by the No Surprises Act. These include emergency medicine, radiology, and anesthesiology, said Mr. Adler, who’s also studied the No Surprises Act’s dispute/arbitration system.
Mr. Adler added that larger companies “are better suited to deal with technical complexities of this process and spend the sort of upfront money to go through it.”
In the big picture, Mr. Adler said, the new study “raises question of whether Congress at some point wants to try to basically bring prices from the arbitration process back in line with average in-network prices.”
The study was funded by the Commonwealth Fund and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Hoadley, Dr. Sager, and Mr. Adler had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four organizations owned by private equity firms — including two provider groups — dominated the No Surprises Act’s disputed bill arbitration process in its first year, filing about 70% of 657,040 cases against insurers in 2023, a new report finds.
The findings, recently published in Health Affairs, suggest that private equity–owned organizations are forcefully challenging insurers about payments for certain kinds of out-of-network care.
Their fighting stance has paid off: The percentage of resolved arbitration cases won by providers jumped from 72% in the first quarter of 2023 to 85% in the last quarter, and they were awarded a median of more than 300% the contracted in-network rates for the services in question.
With many more out-of-network bills disputed by providers than expected, “the system is not working exactly the way it was anticipated when this law was written,” lead author Jack Hoadley, PhD, a research professor emeritus at Georgetown University’s McCourt School of Public Policy, Washington, DC, told this news organization.
And, he said, the public and the federal government may end up paying a price.
Congress passed the No Surprises Act in 2020 and then-President Donald Trump signed it. The landmark bill, which went into effect in 2022, was designed to protect patients from unexpected and often exorbitant “surprise” bills after they received some kinds of out-of-network care.
Now, many types of providers are forbidden from billing patients beyond normal in-network costs. In these cases, health plans and out-of-network providers — who don’t have mutual agreements — must wrangle over payment amounts, which are intended to not exceed inflation-adjusted 2019 median levels.
A binding arbitration process kicks in when a provider and a health plan fail to agree about how much the plan will pay for a service. Then, a third-party arbitrator is called in to make a ruling that’s binding. The process is controversial, and a flurry of lawsuits from providers have challenged it.
The new report, which updates an earlier analysis, examines data about disputed cases from all of 2023.
Of the 657,040 new cases filed in 2023, about 70% came from four private equity-funded organizations: Team Health, SCP Health, Radiology Partners, and Envision, which each provide physician services.
About half of the 2023 cases were from just four states: Texas, Florida, Tennessee, and Georgia. The report says the four organizations are especially active in those states. In contrast, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Washington state each had just 1500 or fewer cases filed last year.
Health plans challenged a third of cases as ineligible, and 22% of all resolved cases were deemed ineligible.
Providers won 80% of resolved challenges in 2023, although it’s not clear how much money they reaped. Still, it’s clear that “in the vast majority of the cases, insurers have to pay larger amounts to the provider,” Dr. Hoadley said.
Radiologists made a median of at least 500% of the in-network rate in their cases. Surgeons and neurologists made even more money — a median of at least 800% of the in-network rate. Overall, providers made 322%-350% of in-network rates, depending on the quarter.
Dr. Hoadley cautioned that only a small percentage of medical payments are disputed. In those cases, “the amount that the insurer offers is accepted, and that’s the end of the story.”
Why are the providers often reaping much more than typical payments for in-network services? It’s “really hard to know,” Dr. Hoadley said. But one factor, he said, may be the fact that providers are able to offer evidence challenging that amounts that insurers say they paid previously: “Hey, when we were in network, we were paid this much.”
It’s not clear whether the dispute-and-arbitration system will cost insurers — and patients — more in the long run. The Congressional Budget Office actually thought the No Surprises Act might lower the growth of premiums slightly and save the federal government money, Dr. Hoadley said, but that could potentially not happen. The flood of litigation also contributes to uncertainty, he said.
Alan Sager, PhD, professor of Health Law, Policy, and Management at Boston University School of Public Health, told this news organization that premiums are bound to rise as insurers react to higher costs. He also expects that providers will question the value of being in-network. “If you’re out-of-network and can obtain much higher payments, why would any doctor or hospital remain in-network, especially since they don’t lose out on patient volume?”
Why are provider groups owned by private equity firms so aggressive at challenging health plans? Loren Adler, a fellow and associate director of the Brookings Institution’s Center on Health Policy, told this news organization that these companies play large roles in fields affected by the No Surprises Act. These include emergency medicine, radiology, and anesthesiology, said Mr. Adler, who’s also studied the No Surprises Act’s dispute/arbitration system.
Mr. Adler added that larger companies “are better suited to deal with technical complexities of this process and spend the sort of upfront money to go through it.”
In the big picture, Mr. Adler said, the new study “raises question of whether Congress at some point wants to try to basically bring prices from the arbitration process back in line with average in-network prices.”
The study was funded by the Commonwealth Fund and Arnold Ventures. Dr. Hoadley, Dr. Sager, and Mr. Adler had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Baseline MRIs Reshape Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment?
The multicenter, real-world trial showed that men with low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease who had higher Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scores at baseline were more likely to be reclassified with more aggressive disease on a future biopsy, wrote lead author Kiran R. Nandalur, MD and colleagues. The study was published in The Journal of Urology.
This means that without MRI, some cases of prostate cancer are being labeled as lower-risk than they actually are.
The investigators noted that MRI is increasingly being used to choose patients who are appropriate for active surveillance instead of treatment, but related clinical data are scarce.
Although PI-RADS is the preferred metric for characterizing prostate tumors via MRI, “most previous studies on the prognostic implications of baseline PI-RADS score included smaller populations from academic centers, limited inclusion of clinical and pathologic data into models, and/or [are] ambiguous on the implications of PI-RADS score,” they wrote.
These knowledge gaps prompted the present study.
How Were Baseline MRI Findings Related to Prostate Cancer Disease Risk?
The dataset included 1491 men with prostate cancer that was diagnosed at 46 hospital-based, academic, or private practice urology groups. All had low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease and had undergone MRI within 6 months before or after initial biopsy, along with enrollment in active surveillance.
“A novel aspect of this study was that the MRIs were not read by dedicated prostate MRI experts at academic institutions, but rather a mix of community and academic radiologists,” Dr. Nandalur, medical director of Corewell Health East Radiology, Royal Oak, Michigan, said in an interview.
After traditional risk factors were accounted for, baseline PI-RADS (four or more lesions) was significantly associated with increased likelihood of biopsy reclassification to high-grade prostate cancer on surveillance biopsy (hazard ratio, 2.3; 95% CI 1.6-3.2; P < .001).
“These patients with suspicious lesions on their initial MRI were more than twice as likely to have higher-grade disease within 5 years,” Nandalur noted. “This result was not only seen in the low-risk group but also in the favorable intermediate-risk group, which hasn’t been shown before.”
Grade group 2 vs 1 and increasing age were also associated with significantly increased risk for reclassification to a more aggressive cancer type.
How Might These Findings Improve Outcomes in Patients With Prostate Cancer?
Currently, 60%-70% of patients with low-risk disease choose active surveillance over immediate treatment, whereas 20% with favorable intermediate-risk disease choose active surveillance, according to Dr. Nandalur.
For low-risk patients, PI-RADS score is unlikely to change this decision, although surveillance intervals could be adjusted in accordance with risk. More notably, those with favorable intermediate-risk disease may benefit from considering PI-RADS score when choosing between active surveillance and immediate treatment.
“Most of the management strategies for prostate cancer are based on just your lab values and your pathology,” Dr. Nandalur said, “but this study shows that maybe we should start taking MRI into account — into the general paradigm of management of prostate cancer.”
Ideally, he added, prospective studies will confirm these findings, although such studies can be challenging to perform and similar data have historically been sufficient to reshape clinical practice.
“We are hoping that [baseline PI-RADS score] will be adopted into the NCCN [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines,” Dr. Nandalur said.
How Likely Are These Findings to Reshape Clinical Practice?
“The study’s large, multicenter cohort and its focus on the prognostic value of baseline MRI in active surveillance make it a crucial contribution to the field, providing evidence that can potentially refine patient management strategies in clinical practice,” Ismail Baris Turkbey, MD, FSAR, head of MRI Section, Molecular Imaging Branch, National Cancer Institute, Rockville, Maryland, said in a written comment.
“The findings from this study are likely to have a significant impact on clinical practice and potentially influence future guidelines in the management of localized prostate cancer, particularly in the context of active surveillance,” Dr. Turkbey said. “MRI, already a commonly used imaging modality in prostate cancer management, may become an even more integral part of the initial assessment and ongoing monitoring of patients with low or favorable-intermediate risk prostate cancer.”
Dr. Turkbey noted several strengths of the study.
First, the size and the diversity of the cohort, along with the variety of treatment centers, support generalizability of findings. Second, the study pinpoints a “critical aspect” of active surveillance by uncovering the link between baseline MRI findings and later risk reclassification. Finally, the study also showed that increasing age was associated with higher likelihood of risk reclassification, “further emphasizing the need for personalized risk assessment” among these patients.
What Were Some Limitations of This Study?
“One important limitation is the lack of inter-reader agreement for PI-RADS evaluations for baseline MRIs,” Dr. Turkbey said. “Variation of PI-RADS is quite known, and centralized evaluations could have made this study stronger. Same applies for centralized quality evaluation of MRIs using The Prostate Imaging Quality (PI-QUAL) score. These items are difficult to do in a multicenter prospective data registry, and maybe authors will consider including these additional analyses in their future work.”
How Does This New Approach to Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment Compare With Recent Advances in AI-Based Risk Assessment?
Over the past few years, artificial intelligence (AI)–assisted risk assessment in prostate cancer has been gaining increasing attention. Recently, for example, Artera, a self-styled “precision medicine company,” released the first AI tool to help patients choose between active surveillance and active treatment on the basis of analysis of digital pathology images.
When asked to compare this approach with the methods used in the present study, Dr. Nandalur called the AI model “a step forward” but noted that it still relies on conventional risk criteria.
“Our data show imaging with MRI has independent prognostic information for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance, over and above these traditional factors,” he said. “Moreover, this predictive ability of MRI was seen in low and favorable intermediate risk groups, so the additive value is broad.”
Still, he predicted that the future will not involve a binary choice, but a combination approach.
“The exciting aspect is that MRI results can eventually be added to this novel AI model and further improve prediction models for patients,” Dr. Nandalur said. “The combination of recent AI models and MRI will likely represent the future paradigm for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance versus immediate treatment.”
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan. The investigators and Dr. Turkbey reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The multicenter, real-world trial showed that men with low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease who had higher Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scores at baseline were more likely to be reclassified with more aggressive disease on a future biopsy, wrote lead author Kiran R. Nandalur, MD and colleagues. The study was published in The Journal of Urology.
This means that without MRI, some cases of prostate cancer are being labeled as lower-risk than they actually are.
The investigators noted that MRI is increasingly being used to choose patients who are appropriate for active surveillance instead of treatment, but related clinical data are scarce.
Although PI-RADS is the preferred metric for characterizing prostate tumors via MRI, “most previous studies on the prognostic implications of baseline PI-RADS score included smaller populations from academic centers, limited inclusion of clinical and pathologic data into models, and/or [are] ambiguous on the implications of PI-RADS score,” they wrote.
These knowledge gaps prompted the present study.
How Were Baseline MRI Findings Related to Prostate Cancer Disease Risk?
The dataset included 1491 men with prostate cancer that was diagnosed at 46 hospital-based, academic, or private practice urology groups. All had low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease and had undergone MRI within 6 months before or after initial biopsy, along with enrollment in active surveillance.
“A novel aspect of this study was that the MRIs were not read by dedicated prostate MRI experts at academic institutions, but rather a mix of community and academic radiologists,” Dr. Nandalur, medical director of Corewell Health East Radiology, Royal Oak, Michigan, said in an interview.
After traditional risk factors were accounted for, baseline PI-RADS (four or more lesions) was significantly associated with increased likelihood of biopsy reclassification to high-grade prostate cancer on surveillance biopsy (hazard ratio, 2.3; 95% CI 1.6-3.2; P < .001).
“These patients with suspicious lesions on their initial MRI were more than twice as likely to have higher-grade disease within 5 years,” Nandalur noted. “This result was not only seen in the low-risk group but also in the favorable intermediate-risk group, which hasn’t been shown before.”
Grade group 2 vs 1 and increasing age were also associated with significantly increased risk for reclassification to a more aggressive cancer type.
How Might These Findings Improve Outcomes in Patients With Prostate Cancer?
Currently, 60%-70% of patients with low-risk disease choose active surveillance over immediate treatment, whereas 20% with favorable intermediate-risk disease choose active surveillance, according to Dr. Nandalur.
For low-risk patients, PI-RADS score is unlikely to change this decision, although surveillance intervals could be adjusted in accordance with risk. More notably, those with favorable intermediate-risk disease may benefit from considering PI-RADS score when choosing between active surveillance and immediate treatment.
“Most of the management strategies for prostate cancer are based on just your lab values and your pathology,” Dr. Nandalur said, “but this study shows that maybe we should start taking MRI into account — into the general paradigm of management of prostate cancer.”
Ideally, he added, prospective studies will confirm these findings, although such studies can be challenging to perform and similar data have historically been sufficient to reshape clinical practice.
“We are hoping that [baseline PI-RADS score] will be adopted into the NCCN [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines,” Dr. Nandalur said.
How Likely Are These Findings to Reshape Clinical Practice?
“The study’s large, multicenter cohort and its focus on the prognostic value of baseline MRI in active surveillance make it a crucial contribution to the field, providing evidence that can potentially refine patient management strategies in clinical practice,” Ismail Baris Turkbey, MD, FSAR, head of MRI Section, Molecular Imaging Branch, National Cancer Institute, Rockville, Maryland, said in a written comment.
“The findings from this study are likely to have a significant impact on clinical practice and potentially influence future guidelines in the management of localized prostate cancer, particularly in the context of active surveillance,” Dr. Turkbey said. “MRI, already a commonly used imaging modality in prostate cancer management, may become an even more integral part of the initial assessment and ongoing monitoring of patients with low or favorable-intermediate risk prostate cancer.”
Dr. Turkbey noted several strengths of the study.
First, the size and the diversity of the cohort, along with the variety of treatment centers, support generalizability of findings. Second, the study pinpoints a “critical aspect” of active surveillance by uncovering the link between baseline MRI findings and later risk reclassification. Finally, the study also showed that increasing age was associated with higher likelihood of risk reclassification, “further emphasizing the need for personalized risk assessment” among these patients.
What Were Some Limitations of This Study?
“One important limitation is the lack of inter-reader agreement for PI-RADS evaluations for baseline MRIs,” Dr. Turkbey said. “Variation of PI-RADS is quite known, and centralized evaluations could have made this study stronger. Same applies for centralized quality evaluation of MRIs using The Prostate Imaging Quality (PI-QUAL) score. These items are difficult to do in a multicenter prospective data registry, and maybe authors will consider including these additional analyses in their future work.”
How Does This New Approach to Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment Compare With Recent Advances in AI-Based Risk Assessment?
Over the past few years, artificial intelligence (AI)–assisted risk assessment in prostate cancer has been gaining increasing attention. Recently, for example, Artera, a self-styled “precision medicine company,” released the first AI tool to help patients choose between active surveillance and active treatment on the basis of analysis of digital pathology images.
When asked to compare this approach with the methods used in the present study, Dr. Nandalur called the AI model “a step forward” but noted that it still relies on conventional risk criteria.
“Our data show imaging with MRI has independent prognostic information for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance, over and above these traditional factors,” he said. “Moreover, this predictive ability of MRI was seen in low and favorable intermediate risk groups, so the additive value is broad.”
Still, he predicted that the future will not involve a binary choice, but a combination approach.
“The exciting aspect is that MRI results can eventually be added to this novel AI model and further improve prediction models for patients,” Dr. Nandalur said. “The combination of recent AI models and MRI will likely represent the future paradigm for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance versus immediate treatment.”
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan. The investigators and Dr. Turkbey reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The multicenter, real-world trial showed that men with low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease who had higher Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scores at baseline were more likely to be reclassified with more aggressive disease on a future biopsy, wrote lead author Kiran R. Nandalur, MD and colleagues. The study was published in The Journal of Urology.
This means that without MRI, some cases of prostate cancer are being labeled as lower-risk than they actually are.
The investigators noted that MRI is increasingly being used to choose patients who are appropriate for active surveillance instead of treatment, but related clinical data are scarce.
Although PI-RADS is the preferred metric for characterizing prostate tumors via MRI, “most previous studies on the prognostic implications of baseline PI-RADS score included smaller populations from academic centers, limited inclusion of clinical and pathologic data into models, and/or [are] ambiguous on the implications of PI-RADS score,” they wrote.
These knowledge gaps prompted the present study.
How Were Baseline MRI Findings Related to Prostate Cancer Disease Risk?
The dataset included 1491 men with prostate cancer that was diagnosed at 46 hospital-based, academic, or private practice urology groups. All had low-risk or favorable intermediate-risk disease and had undergone MRI within 6 months before or after initial biopsy, along with enrollment in active surveillance.
“A novel aspect of this study was that the MRIs were not read by dedicated prostate MRI experts at academic institutions, but rather a mix of community and academic radiologists,” Dr. Nandalur, medical director of Corewell Health East Radiology, Royal Oak, Michigan, said in an interview.
After traditional risk factors were accounted for, baseline PI-RADS (four or more lesions) was significantly associated with increased likelihood of biopsy reclassification to high-grade prostate cancer on surveillance biopsy (hazard ratio, 2.3; 95% CI 1.6-3.2; P < .001).
“These patients with suspicious lesions on their initial MRI were more than twice as likely to have higher-grade disease within 5 years,” Nandalur noted. “This result was not only seen in the low-risk group but also in the favorable intermediate-risk group, which hasn’t been shown before.”
Grade group 2 vs 1 and increasing age were also associated with significantly increased risk for reclassification to a more aggressive cancer type.
How Might These Findings Improve Outcomes in Patients With Prostate Cancer?
Currently, 60%-70% of patients with low-risk disease choose active surveillance over immediate treatment, whereas 20% with favorable intermediate-risk disease choose active surveillance, according to Dr. Nandalur.
For low-risk patients, PI-RADS score is unlikely to change this decision, although surveillance intervals could be adjusted in accordance with risk. More notably, those with favorable intermediate-risk disease may benefit from considering PI-RADS score when choosing between active surveillance and immediate treatment.
“Most of the management strategies for prostate cancer are based on just your lab values and your pathology,” Dr. Nandalur said, “but this study shows that maybe we should start taking MRI into account — into the general paradigm of management of prostate cancer.”
Ideally, he added, prospective studies will confirm these findings, although such studies can be challenging to perform and similar data have historically been sufficient to reshape clinical practice.
“We are hoping that [baseline PI-RADS score] will be adopted into the NCCN [National Comprehensive Cancer Network] guidelines,” Dr. Nandalur said.
How Likely Are These Findings to Reshape Clinical Practice?
“The study’s large, multicenter cohort and its focus on the prognostic value of baseline MRI in active surveillance make it a crucial contribution to the field, providing evidence that can potentially refine patient management strategies in clinical practice,” Ismail Baris Turkbey, MD, FSAR, head of MRI Section, Molecular Imaging Branch, National Cancer Institute, Rockville, Maryland, said in a written comment.
“The findings from this study are likely to have a significant impact on clinical practice and potentially influence future guidelines in the management of localized prostate cancer, particularly in the context of active surveillance,” Dr. Turkbey said. “MRI, already a commonly used imaging modality in prostate cancer management, may become an even more integral part of the initial assessment and ongoing monitoring of patients with low or favorable-intermediate risk prostate cancer.”
Dr. Turkbey noted several strengths of the study.
First, the size and the diversity of the cohort, along with the variety of treatment centers, support generalizability of findings. Second, the study pinpoints a “critical aspect” of active surveillance by uncovering the link between baseline MRI findings and later risk reclassification. Finally, the study also showed that increasing age was associated with higher likelihood of risk reclassification, “further emphasizing the need for personalized risk assessment” among these patients.
What Were Some Limitations of This Study?
“One important limitation is the lack of inter-reader agreement for PI-RADS evaluations for baseline MRIs,” Dr. Turkbey said. “Variation of PI-RADS is quite known, and centralized evaluations could have made this study stronger. Same applies for centralized quality evaluation of MRIs using The Prostate Imaging Quality (PI-QUAL) score. These items are difficult to do in a multicenter prospective data registry, and maybe authors will consider including these additional analyses in their future work.”
How Does This New Approach to Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment Compare With Recent Advances in AI-Based Risk Assessment?
Over the past few years, artificial intelligence (AI)–assisted risk assessment in prostate cancer has been gaining increasing attention. Recently, for example, Artera, a self-styled “precision medicine company,” released the first AI tool to help patients choose between active surveillance and active treatment on the basis of analysis of digital pathology images.
When asked to compare this approach with the methods used in the present study, Dr. Nandalur called the AI model “a step forward” but noted that it still relies on conventional risk criteria.
“Our data show imaging with MRI has independent prognostic information for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance, over and above these traditional factors,” he said. “Moreover, this predictive ability of MRI was seen in low and favorable intermediate risk groups, so the additive value is broad.”
Still, he predicted that the future will not involve a binary choice, but a combination approach.
“The exciting aspect is that MRI results can eventually be added to this novel AI model and further improve prediction models for patients,” Dr. Nandalur said. “The combination of recent AI models and MRI will likely represent the future paradigm for prostate cancer patients considering active surveillance versus immediate treatment.”
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan. The investigators and Dr. Turkbey reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY
Cancer Treatment 101: A Primer for Non-Oncologists
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
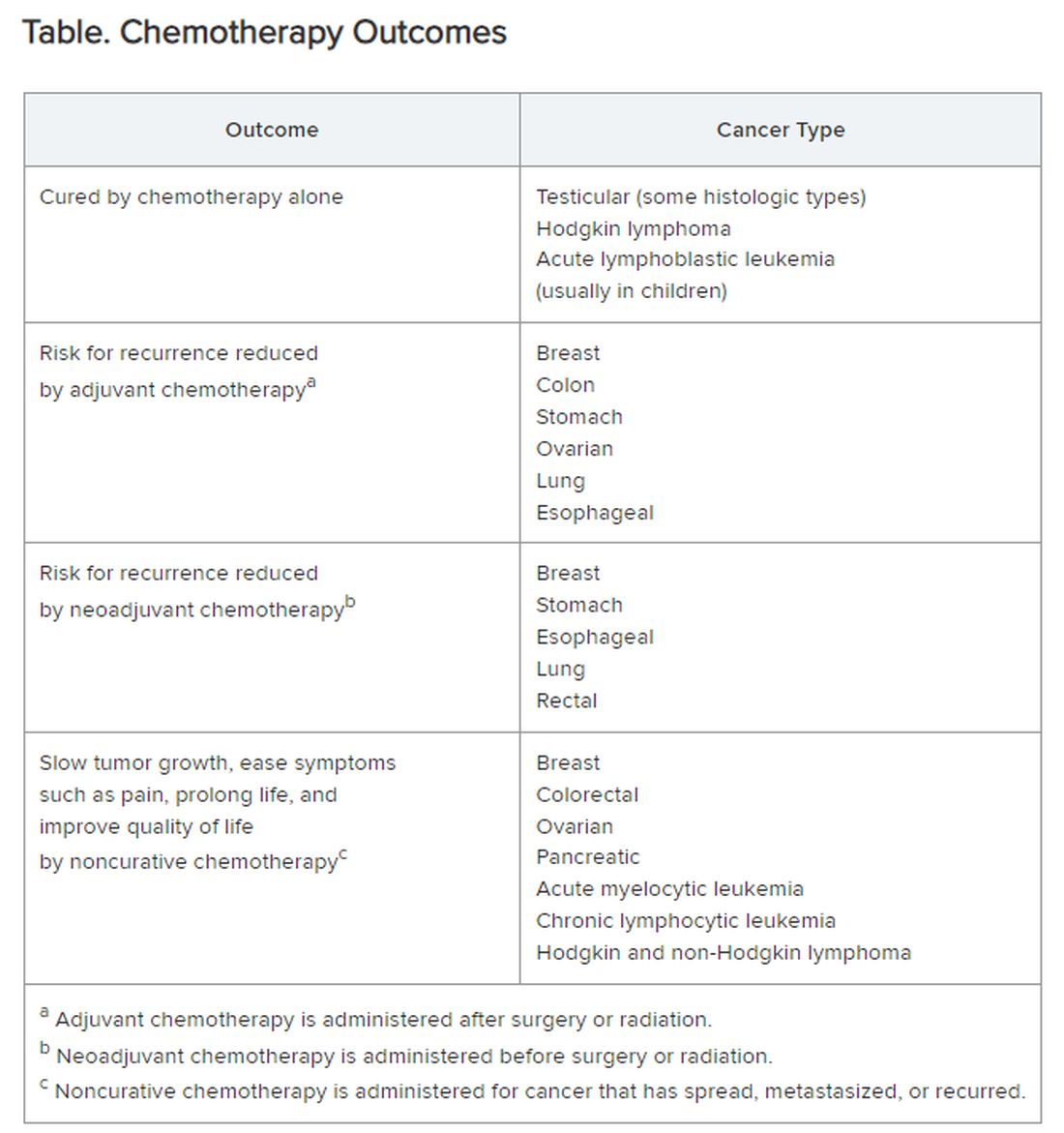
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians Lament Over Reliance on Relative Value Units: Survey
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs First-Line Lazertinib With Amivantamab for NSCLC
This marks the first approval for lazertinib. Amivantamab was initially approved by the FDA in 2021 and carries a few indications for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Both drugs are manufactured by Janssen Biotech Inc.
“Patients will now have the option of a potential new first-line standard of care with significant clinical benefits over osimertinib,” study investigator Alexander Spira, MD, PhD, director, Virginia Cancer Specialists Research Institute, said in a news release from Johnson & Johnson .
Lazertinib is an oral, highly selective, third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can penetrate the brain and amivantamab is a bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET.
The approval was based on results from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial, which showed that the combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 30% compared with osimertinib.
The MARIPOSA trial randomly allocated 1074 patients with exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC and no prior systemic therapy for advanced disease to amivantamab plus lazertinib, osimertinib alone, or lazertinib alone.
Lazertinib plus amivantamab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival compared with osimertinib (hazard ratio, 0.70; P < .001). Median progression-free survival was 23.7 months with the combination vs 16.6 months osimertinib alone and 18.5 months with lazertinib alone.
The median duration of response was 9 months longer with the combination compared with osimertinib (25.8 months vs 16.7 months).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were rash, nail toxicity, infusion-related reactions (amivantamab), musculoskeletal pain, edema, stomatitis, venous thromboembolism, paresthesia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, COVID-19, hemorrhage, dry skin, decreased appetite, pruritus, nausea, and ocular toxicity.
“A serious safety signal of venous thromboembolic events was observed with lazertinib in combination with amivantamab and prophylactic anticoagulation should be administered for the first four months of therapy,” the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
Results from MARIPOSA were first presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology 2023 Congress and published in The New England Journal of Medicine in June. Longer-term follow-up data from MARIPOSA will be presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2024 World Congress on Lung Cancer in September.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This marks the first approval for lazertinib. Amivantamab was initially approved by the FDA in 2021 and carries a few indications for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Both drugs are manufactured by Janssen Biotech Inc.
“Patients will now have the option of a potential new first-line standard of care with significant clinical benefits over osimertinib,” study investigator Alexander Spira, MD, PhD, director, Virginia Cancer Specialists Research Institute, said in a news release from Johnson & Johnson .
Lazertinib is an oral, highly selective, third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can penetrate the brain and amivantamab is a bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET.
The approval was based on results from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial, which showed that the combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 30% compared with osimertinib.
The MARIPOSA trial randomly allocated 1074 patients with exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC and no prior systemic therapy for advanced disease to amivantamab plus lazertinib, osimertinib alone, or lazertinib alone.
Lazertinib plus amivantamab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival compared with osimertinib (hazard ratio, 0.70; P < .001). Median progression-free survival was 23.7 months with the combination vs 16.6 months osimertinib alone and 18.5 months with lazertinib alone.
The median duration of response was 9 months longer with the combination compared with osimertinib (25.8 months vs 16.7 months).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were rash, nail toxicity, infusion-related reactions (amivantamab), musculoskeletal pain, edema, stomatitis, venous thromboembolism, paresthesia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, COVID-19, hemorrhage, dry skin, decreased appetite, pruritus, nausea, and ocular toxicity.
“A serious safety signal of venous thromboembolic events was observed with lazertinib in combination with amivantamab and prophylactic anticoagulation should be administered for the first four months of therapy,” the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
Results from MARIPOSA were first presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology 2023 Congress and published in The New England Journal of Medicine in June. Longer-term follow-up data from MARIPOSA will be presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2024 World Congress on Lung Cancer in September.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This marks the first approval for lazertinib. Amivantamab was initially approved by the FDA in 2021 and carries a few indications for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Both drugs are manufactured by Janssen Biotech Inc.
“Patients will now have the option of a potential new first-line standard of care with significant clinical benefits over osimertinib,” study investigator Alexander Spira, MD, PhD, director, Virginia Cancer Specialists Research Institute, said in a news release from Johnson & Johnson .
Lazertinib is an oral, highly selective, third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can penetrate the brain and amivantamab is a bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET.
The approval was based on results from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial, which showed that the combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 30% compared with osimertinib.
The MARIPOSA trial randomly allocated 1074 patients with exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R substitution mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC and no prior systemic therapy for advanced disease to amivantamab plus lazertinib, osimertinib alone, or lazertinib alone.
Lazertinib plus amivantamab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival compared with osimertinib (hazard ratio, 0.70; P < .001). Median progression-free survival was 23.7 months with the combination vs 16.6 months osimertinib alone and 18.5 months with lazertinib alone.
The median duration of response was 9 months longer with the combination compared with osimertinib (25.8 months vs 16.7 months).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) were rash, nail toxicity, infusion-related reactions (amivantamab), musculoskeletal pain, edema, stomatitis, venous thromboembolism, paresthesia, fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, COVID-19, hemorrhage, dry skin, decreased appetite, pruritus, nausea, and ocular toxicity.
“A serious safety signal of venous thromboembolic events was observed with lazertinib in combination with amivantamab and prophylactic anticoagulation should be administered for the first four months of therapy,” the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
Results from MARIPOSA were first presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology 2023 Congress and published in The New England Journal of Medicine in June. Longer-term follow-up data from MARIPOSA will be presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2024 World Congress on Lung Cancer in September.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do New Blood Tests for Cancer Meet the Right Standards?
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Biotech startups worldwide are rushing to market screening tests that they claim can detect various cancers in early stages with just a few drops of blood. The tests allegedly will simplify cancer care by eliminating tedious scans, scopes, and swabs at the doctor’s office.
The promise of these early detection tests is truly “enticing,” Hilary A. Robbins, PhD, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization in Lyon, France, said in an interview.
In an opinion article in The New England Journal of Medicine, she emphasized that the new cancer tests are much less cumbersome than traditional screening strategies for individual cancers. Moreover, they could enable the early detection of dozens of cancer types for which no screening has been available so far.
Meeting the Criteria
The problem is that these tests have not met the strict criteria typically required for traditional cancer screening tests. To be considered for introduction as a screening procedure, a test usually needs to meet the following four minimum requirements:
- The disease that the test screens for must have a presymptomatic form.
- The screening test must be able to identify this presymptomatic disease.
- Treating the disease in the presymptomatic phase improves prognosis (specifically, it affects cancer-specific mortality in a randomized controlled trial).
- The screening test is feasible, and the benefits outweigh potential risks.
“The new blood tests for multiple cancers have so far only met the second criteria, showing they can detect presymptomatic cancer,” Dr. Robbins wrote.
The next step would be to demonstrate that they affect cancer-specific mortality. “But currently, commercial interests seem to be influencing the evidence standards for these cancer tests,” said Dr. Robbins.
Inappropriate Endpoints?
Some proponents of such tests argue that, unlike for previous cancer screening procedures, initial approval should not depend on the endpoint of cancer-specific mortality. It would take too long to gather sufficient outcome data, and in the meantime, people would die, they argue.
Eric A. Klein, MD, from the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute in Cleveland, Ohio, and colleagues advocate for alternative endpoints such as the incidence of late-stage cancer in an article published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
“The concept would be,” they wrote, “that a negative signal would not indicate a mortality benefit, leading to the study being stopped. A positive signal, on the other hand, could result in provisional approval until mortality data and real-world evidence of effectiveness are available. This would resemble the accelerated approval of new cancer drugs, which often is based on progression-free survival until there postmarketing data on overall survival emerge.”
Dr. Klein is also employed at the US biotech start-up Grail, which developed the Galleri test, which is one of the best-known and most advanced cancer screening tests. The Galleri test uses cell-free DNA and machine learning to detect a common cancer signal in more than 50 cancer types and predict the origin of the cancer signal. Consumers in the United States can already order and perform the test.
An NHS Study
Arguments for different endpoints apparently resonated with the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS). Three years ago, they initiated the Galleri study, a large randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Grail’s cancer test. The primary endpoint was not cancer-specific mortality, but the incidence of stage III or IV cancer.
The results are expected in 2026. But recruitment was stopped after 140,000 participants were enrolled. The NHS reported that the initial results were not convincing enough to continue the trial. Exact numbers were not disclosed.
The Galleri study deviates from the standard randomized controlled trial design for cancer screening procedures not only in terms of the primary endpoint, but also in blinding. The only participants who were unblinded and informed of their test results are those in the intervention group with a positive cancer test.
False Security
This trial design encourages participants to undergo blood tests once per year. But according to Dr. Robbins, it prevents the exploration of the phenomenon of “false security,” which is a potential drawback of the new cancer tests.
“Women with a negative mammogram can reasonably assume that they probably do not have breast cancer. But individuals with a negative cancer blood test could mistakenly believe they cannot have any cancer at all. As a result, they may not undergo standard early detection screenings or seek medical help early enough for potential cancer symptoms,” said Dr. Robbins.
To assess the actual risk-benefit ratio of the Galleri test, participants must receive their test results, she said. “Under real-world conditions, benefits and risks can come from positive and negative results.”
Upcoming Trial
More illuminating results may come from a large trial planned by the National Cancer Institute in the United States. Several new cancer tests will be evaluated for their ability to reduce cancer-specific mortality. A pilot phase will start later in 2024. “This study may be the only one with sufficient statistical power to determine whether an approach based on these cancer tests can reduce cancer-specific mortality,” said Dr. Robbins.
For the new blood tests for multiple cancers, it is crucial that health authorities “set a high bar for a benefit,” she said. This, according to her, also means that they must show an effect on cancer-specific mortality before being introduced. “This evidence must come from studies in which commercial interests do not influence the design, execution, data management, or data analysis.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, Giant of Cancer Care, Dies
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dr. Weber, a melanoma and cancer immunotherapy specialist, served as deputy director of the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University (NYU) Langone Medical Center in New York City. He also held positions as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program, and co-leader of the Clinical Melanoma Program Board at NYU Langone Health.
Dr. Weber was a principal investigator on many studies, including pivotal clinical drug trials in melanoma and trials focused on managing autoimmune side effects from immunotherapy. He published more than 150 articles in top peer-reviewed journals.
For many years, Dr. Weber hosted the popular “Weber on Oncology” series of video contributions for Medscape Oncology, sharing updates and insights on noteworthy research and breakthroughs in melanoma.
“The Melanoma Research Alliance mourns the passing of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber, a true pioneer in the field of cancer immunotherapy and an extraordinary leader in melanoma research. His contributions have forever changed the landscape of melanoma treatment, bringing groundbreaking advances from the lab into clinical practice and offering hope to countless patients,” the Melanoma Research Alliance posted on LinkedIn.
Many X users also shared condolences and memories of Dr. Weber, praising his numerous contributions and accomplishments.
“[Cancer Research Institute] mourns the loss of Dr. Jeffrey S. Weber ... [a]s an accomplished physician scientist, Dr. Weber drove advances in melanoma research, and played an active role in educating patients about the lifesaving power of immunotherapy,” the Cancer Research Institute posted.
A colleague noted that “[h]e was involved in the early days of cytokine and cell therapy and most recently led studies of personalized vaccines for melanoma patients. ... He was a great friend and colleague to many of us in the melanoma and immunotherapy field and we will remember him as a pioneer, thought leader and compassionate physician.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low HPV Vaccination in the United States Is a Public Health ‘Failure’
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors Are Seeking Professional Coaches More Often. Here’s Why
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.