User login
Severe Acute Systemic Reaction After the First Injections of Ixekizumab
Case Report
A 39-year-old woman who was otherwise healthy presented with fatigue, malaise, a resolving rash, focal lymphadenopathy, increasing distal arthritis, dactylitis, resolving ecchymoses, and acute onycholysis of 1 week’s duration that developed 13 days after initiating ixekizumab. The patient had a history of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis for more than 10 years. She had been successfully treated in the past for psoriasis with adalimumab for several years; however, adalimumab was discontinued after an episode of Clostridium difficile colitis. The patient had a negative purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test prior to starting biologics as she works in the health care field. Routine follow-up purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test was positive. She discontinued all therapy for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis prior to being appropriately treated for 6 months under the care of infectious disease physicians. She then had several pregnancies and chose to restart biologic treatment after weaning her third child from breastfeeding, as her skin and joint disease were notably flaring.
Ustekinumab was chosen to shift treatment away from tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors. The patient's condition was under relatively good control for 1 year; however, she experienced notable gastrointestinal tract upset (ie, intermittent diarrhea and constipation), despite multiple negative tests for C difficile. The patient was referred to see a gastroenterologist but never followed up. Due to long-term low-grade gastrointestinal problems, ustekinumab was discontinued, and the gastrointestinal symptoms resolved without treatment.
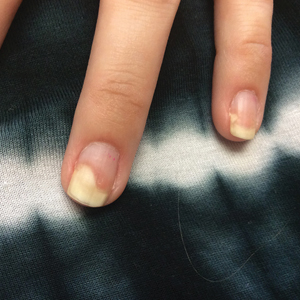
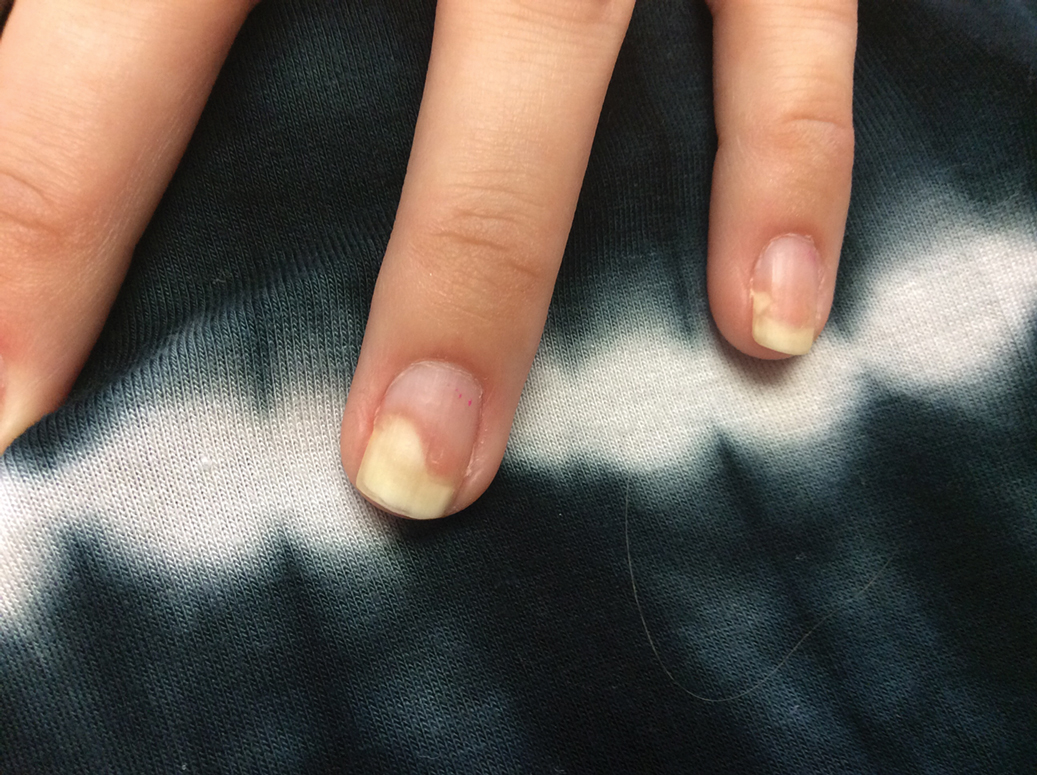
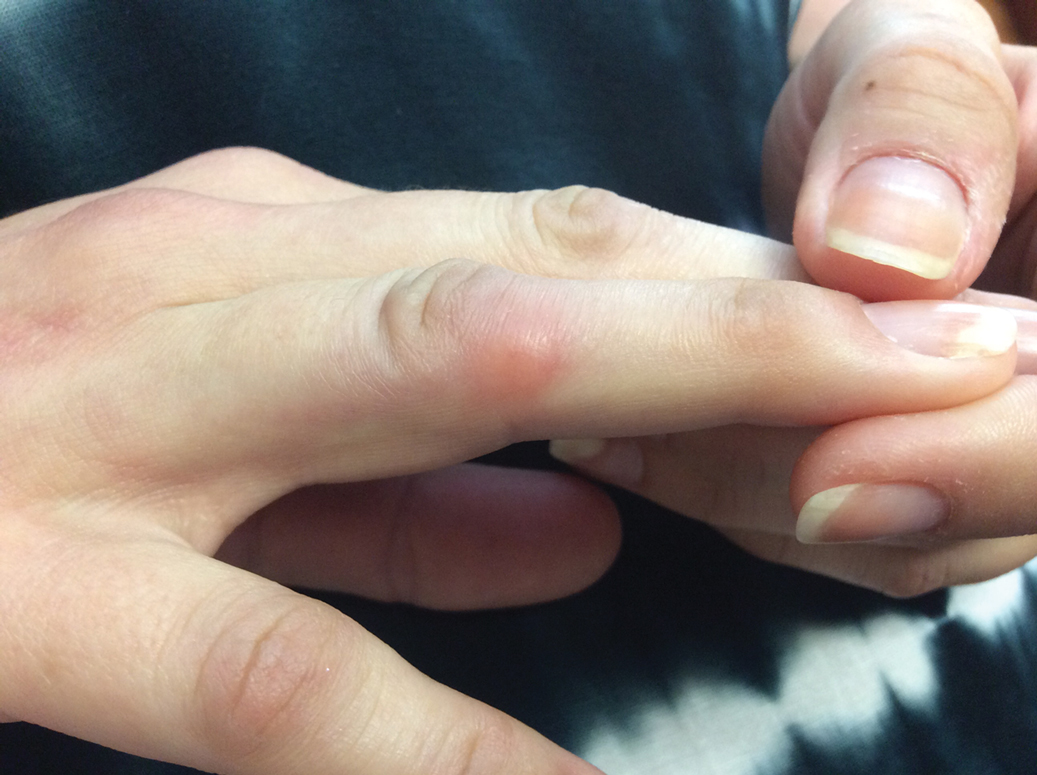
Given the side effects noted with TNF-α and IL-12/23 inhibitors and the fact that the patient’s cutaneous and joint disease were notable, the decision was made to start the IL-17A inhibitor ixekizumab. The patient administered 2 injections, one in each thigh. Within 12 hours, she experienced severe injection-site pain. The pain was so severe that it woke her from sleep the night of the first injections. She then developed severe pain in the right axilla that limited upper extremity mobility. Within 48 hours, she developed an erythematous, nonpruritic, nonscaly, mottled rash on the right breast that began to resolve within 24 hours without treatment. In addition, 3 days after the injections, she developed ecchymoses on the trunk and extremities without any identifiable trauma, severe acute onycholysis in several fingernails (Figure 1) and toenails, dactylitis such that she could not wear her wedding ring, and a flare of psoriatic arthritis in the fingers and ankles.
At the current presentation (2 weeks after the injections), the patient reported malaise, flulike symptoms, and low-grade intermittent fevers. Results from a hematology panel displayed leukopenia at 2.69×103/μL (reference range, 3.54–9.06×103/μL) and thrombocytopenia at 114×103/μL (reference range, 165–415×103/μL).1 Her most recent laboratory results before the ixekizumab injections displayed a white blood cell count level at 4.6×103/μL and platelet count at 159×103/μL. C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were within reference range. A shave biopsy of an erythematous nodule on the proximal interphalangeal joint of the fourth finger on the right hand displayed spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils (Figure 2).
Interestingly, the psoriatic plaques on the scalp, trunk, and extremities had nearly completely resolved after only the first 2 injections. However, given the side effects, the second dose of ixekizumab was held, repeat laboratory tests were ordered to ensure normalization of cytopenia, and the patient was transitioned to pulse-dose topical steroids to control the remaining psoriatic plaques.
One week after presentation (3 weeks after the initial injections), the patient’s systemic symptoms had almost completely resolved, and she denied any further concerns. Her fingernails and toenails, however, continued to show the changes of onycholysis noted at the visit.
Comment
Ixekizumab is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-17A, one of the cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. The monoclonal antibody prevents its attachment to the IL-17 receptor, which inhibits the release of further cytokines and chemokines, decreasing the inflammatory and immune response.2
Ixekizumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for plaque psoriasis after 3 clinical trials—UNCOVER-1, UNCOVER-2, and UNCOVER-3—were performed. In UNCOVER-3, the most common side effects that occurred—nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, injection-site reaction, arthralgia, headache, and infections (specifically candidiasis)—generally were well tolerated. More serious adverse events included cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, inflammatory bowel disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer.3
Notable laboratory abnormalities that have been documented from ixekizumab include elevated liver function tests (eg, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase), as well as leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.4 Although short-term thrombocytopenia, as described in our patient, provides an explanation for the bruising noted on observation, it is unusual to note such notable ecchymoses within days of the first injection.
Onycholysis has not been documented as a side effect of ixekizumab; however, it has been reported as an adverse event from other biologic medications. Sfikakis et al5 reported 5 patients who developed psoriatic skin lesions after treatment with 3 different anti-TNF biologics—infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—fo
The exact pathophysiology of these adverse events has not been clearly understood, but it has been proposed that anti-TNF biologics may initiate an autoimmune reaction in the skin and nails, leading to paradoxical psoriasis and nail changes such as onycholysis. Tumor necrosis factor may have a regulatory role in the skin that prevents autoreactive T cells, such as cutaneous lymphocyte antigen–expressing T cells that promote the formation of psoriasiform lesions. By inhibiting TNF, there can be an underlying activation of autoreactive T cells that leads to tissue destruction in the skin and nails.6 Anti-TNF biologics also could increase CXCR3, a chemokine receptor that allows autoreactive T cells to enter the skin and cause pathology.7
IL-17A and IL-17F also have been shown to upregulate the expression of TNF receptor II in synoviocytes,8 which demonstrates that IL-17 works in synergy with TNF-α to promote an inflammatory reaction.9 Due to the inhibitory effects of ixekizumab, psoriatic arthritis should theoretically improve. However, if there is an alteration in the inflammatory sequence, then the regulatory role of TNF could be suppressed and psoriatic arthritis could become exacerbated. Additionally, its associated symptoms, such as dactylitis, could develop, as seen in our patient.4 Because psoriatic arthritis is closely associated with nail changes of psoriasis, it is conceivable that acute arthritic flares and acute onycholysis are both induced by the same cytokine dysregulation. Further studies and a larger patient population need to be evaluated to determine the exact cause of the acute exacerbation of psoriatic arthritis with concomitant nail changes as noted in our patient.
Acute onycholysis (within 72 hours) is a rare side effect of ixekizumab. It can be postulated that our patient’s severe acute onycholysis associated with a flare of psoriatic arthritis could be due to idiosyncratic immune dysregulation, promoting the activity of autoreactive T cells. The pharmacologic effects of ixekizumab occur through the inhibition of IL-17. We propose that by inhibiting IL-17 with associated TNF alterations, an altered inflammatory cascade could promote an autoimmune reaction leading to the described pathology.
- Kratz A, Pesce MA, Basner RC, et al. Laboratory values of clinical importance. In: Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2014.
- Ixekizumab. Package insert. Eli Lilly & Co; 2017.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Papp KA, et al. Phase 3 trials of ixekizumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:345-356.
- Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190-1199.
- Sfikakis PP, Iliopoulos A, Elezoglou A, et al. Psoriasis induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: a paradoxical adverse reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2513-2518.
- Berg EL, Yoshino T, Rott LS, et al. The cutaneous lymphocyte antigen is a skin lymphocyte homing receptor for the vascular lectin endothelial cell-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Exp Med. 1991;174:1461-1466.
- Flier J, Boorsma DM, van Beek PJ, et al. Differential expression of CXCR3 targeting chemokines CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 in different types of skin inflammation. J Pathol. 2001;194:398-405.
- Zrioual S, Ecochard R, Tournadre A, et al. Genome-wide comparison between IL-17A- and IL-17F-induced effects in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol. 2009;182:3112-3120.
- Gaffen SL. The role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11:365-370.
Case Report
A 39-year-old woman who was otherwise healthy presented with fatigue, malaise, a resolving rash, focal lymphadenopathy, increasing distal arthritis, dactylitis, resolving ecchymoses, and acute onycholysis of 1 week’s duration that developed 13 days after initiating ixekizumab. The patient had a history of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis for more than 10 years. She had been successfully treated in the past for psoriasis with adalimumab for several years; however, adalimumab was discontinued after an episode of Clostridium difficile colitis. The patient had a negative purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test prior to starting biologics as she works in the health care field. Routine follow-up purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test was positive. She discontinued all therapy for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis prior to being appropriately treated for 6 months under the care of infectious disease physicians. She then had several pregnancies and chose to restart biologic treatment after weaning her third child from breastfeeding, as her skin and joint disease were notably flaring.
Ustekinumab was chosen to shift treatment away from tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors. The patient's condition was under relatively good control for 1 year; however, she experienced notable gastrointestinal tract upset (ie, intermittent diarrhea and constipation), despite multiple negative tests for C difficile. The patient was referred to see a gastroenterologist but never followed up. Due to long-term low-grade gastrointestinal problems, ustekinumab was discontinued, and the gastrointestinal symptoms resolved without treatment.
Given the side effects noted with TNF-α and IL-12/23 inhibitors and the fact that the patient’s cutaneous and joint disease were notable, the decision was made to start the IL-17A inhibitor ixekizumab. The patient administered 2 injections, one in each thigh. Within 12 hours, she experienced severe injection-site pain. The pain was so severe that it woke her from sleep the night of the first injections. She then developed severe pain in the right axilla that limited upper extremity mobility. Within 48 hours, she developed an erythematous, nonpruritic, nonscaly, mottled rash on the right breast that began to resolve within 24 hours without treatment. In addition, 3 days after the injections, she developed ecchymoses on the trunk and extremities without any identifiable trauma, severe acute onycholysis in several fingernails (Figure 1) and toenails, dactylitis such that she could not wear her wedding ring, and a flare of psoriatic arthritis in the fingers and ankles.

At the current presentation (2 weeks after the injections), the patient reported malaise, flulike symptoms, and low-grade intermittent fevers. Results from a hematology panel displayed leukopenia at 2.69×103/μL (reference range, 3.54–9.06×103/μL) and thrombocytopenia at 114×103/μL (reference range, 165–415×103/μL).1 Her most recent laboratory results before the ixekizumab injections displayed a white blood cell count level at 4.6×103/μL and platelet count at 159×103/μL. C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were within reference range. A shave biopsy of an erythematous nodule on the proximal interphalangeal joint of the fourth finger on the right hand displayed spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils (Figure 2).

Interestingly, the psoriatic plaques on the scalp, trunk, and extremities had nearly completely resolved after only the first 2 injections. However, given the side effects, the second dose of ixekizumab was held, repeat laboratory tests were ordered to ensure normalization of cytopenia, and the patient was transitioned to pulse-dose topical steroids to control the remaining psoriatic plaques.
One week after presentation (3 weeks after the initial injections), the patient’s systemic symptoms had almost completely resolved, and she denied any further concerns. Her fingernails and toenails, however, continued to show the changes of onycholysis noted at the visit.
Comment
Ixekizumab is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-17A, one of the cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. The monoclonal antibody prevents its attachment to the IL-17 receptor, which inhibits the release of further cytokines and chemokines, decreasing the inflammatory and immune response.2
Ixekizumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for plaque psoriasis after 3 clinical trials—UNCOVER-1, UNCOVER-2, and UNCOVER-3—were performed. In UNCOVER-3, the most common side effects that occurred—nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, injection-site reaction, arthralgia, headache, and infections (specifically candidiasis)—generally were well tolerated. More serious adverse events included cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, inflammatory bowel disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer.3
Notable laboratory abnormalities that have been documented from ixekizumab include elevated liver function tests (eg, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase), as well as leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.4 Although short-term thrombocytopenia, as described in our patient, provides an explanation for the bruising noted on observation, it is unusual to note such notable ecchymoses within days of the first injection.
Onycholysis has not been documented as a side effect of ixekizumab; however, it has been reported as an adverse event from other biologic medications. Sfikakis et al5 reported 5 patients who developed psoriatic skin lesions after treatment with 3 different anti-TNF biologics—infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—fo
The exact pathophysiology of these adverse events has not been clearly understood, but it has been proposed that anti-TNF biologics may initiate an autoimmune reaction in the skin and nails, leading to paradoxical psoriasis and nail changes such as onycholysis. Tumor necrosis factor may have a regulatory role in the skin that prevents autoreactive T cells, such as cutaneous lymphocyte antigen–expressing T cells that promote the formation of psoriasiform lesions. By inhibiting TNF, there can be an underlying activation of autoreactive T cells that leads to tissue destruction in the skin and nails.6 Anti-TNF biologics also could increase CXCR3, a chemokine receptor that allows autoreactive T cells to enter the skin and cause pathology.7
IL-17A and IL-17F also have been shown to upregulate the expression of TNF receptor II in synoviocytes,8 which demonstrates that IL-17 works in synergy with TNF-α to promote an inflammatory reaction.9 Due to the inhibitory effects of ixekizumab, psoriatic arthritis should theoretically improve. However, if there is an alteration in the inflammatory sequence, then the regulatory role of TNF could be suppressed and psoriatic arthritis could become exacerbated. Additionally, its associated symptoms, such as dactylitis, could develop, as seen in our patient.4 Because psoriatic arthritis is closely associated with nail changes of psoriasis, it is conceivable that acute arthritic flares and acute onycholysis are both induced by the same cytokine dysregulation. Further studies and a larger patient population need to be evaluated to determine the exact cause of the acute exacerbation of psoriatic arthritis with concomitant nail changes as noted in our patient.
Acute onycholysis (within 72 hours) is a rare side effect of ixekizumab. It can be postulated that our patient’s severe acute onycholysis associated with a flare of psoriatic arthritis could be due to idiosyncratic immune dysregulation, promoting the activity of autoreactive T cells. The pharmacologic effects of ixekizumab occur through the inhibition of IL-17. We propose that by inhibiting IL-17 with associated TNF alterations, an altered inflammatory cascade could promote an autoimmune reaction leading to the described pathology.
Case Report
A 39-year-old woman who was otherwise healthy presented with fatigue, malaise, a resolving rash, focal lymphadenopathy, increasing distal arthritis, dactylitis, resolving ecchymoses, and acute onycholysis of 1 week’s duration that developed 13 days after initiating ixekizumab. The patient had a history of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis for more than 10 years. She had been successfully treated in the past for psoriasis with adalimumab for several years; however, adalimumab was discontinued after an episode of Clostridium difficile colitis. The patient had a negative purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test prior to starting biologics as she works in the health care field. Routine follow-up purified protein derivative (tuberculin) test was positive. She discontinued all therapy for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis prior to being appropriately treated for 6 months under the care of infectious disease physicians. She then had several pregnancies and chose to restart biologic treatment after weaning her third child from breastfeeding, as her skin and joint disease were notably flaring.
Ustekinumab was chosen to shift treatment away from tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors. The patient's condition was under relatively good control for 1 year; however, she experienced notable gastrointestinal tract upset (ie, intermittent diarrhea and constipation), despite multiple negative tests for C difficile. The patient was referred to see a gastroenterologist but never followed up. Due to long-term low-grade gastrointestinal problems, ustekinumab was discontinued, and the gastrointestinal symptoms resolved without treatment.
Given the side effects noted with TNF-α and IL-12/23 inhibitors and the fact that the patient’s cutaneous and joint disease were notable, the decision was made to start the IL-17A inhibitor ixekizumab. The patient administered 2 injections, one in each thigh. Within 12 hours, she experienced severe injection-site pain. The pain was so severe that it woke her from sleep the night of the first injections. She then developed severe pain in the right axilla that limited upper extremity mobility. Within 48 hours, she developed an erythematous, nonpruritic, nonscaly, mottled rash on the right breast that began to resolve within 24 hours without treatment. In addition, 3 days after the injections, she developed ecchymoses on the trunk and extremities without any identifiable trauma, severe acute onycholysis in several fingernails (Figure 1) and toenails, dactylitis such that she could not wear her wedding ring, and a flare of psoriatic arthritis in the fingers and ankles.

At the current presentation (2 weeks after the injections), the patient reported malaise, flulike symptoms, and low-grade intermittent fevers. Results from a hematology panel displayed leukopenia at 2.69×103/μL (reference range, 3.54–9.06×103/μL) and thrombocytopenia at 114×103/μL (reference range, 165–415×103/μL).1 Her most recent laboratory results before the ixekizumab injections displayed a white blood cell count level at 4.6×103/μL and platelet count at 159×103/μL. C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were within reference range. A shave biopsy of an erythematous nodule on the proximal interphalangeal joint of the fourth finger on the right hand displayed spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils (Figure 2).

Interestingly, the psoriatic plaques on the scalp, trunk, and extremities had nearly completely resolved after only the first 2 injections. However, given the side effects, the second dose of ixekizumab was held, repeat laboratory tests were ordered to ensure normalization of cytopenia, and the patient was transitioned to pulse-dose topical steroids to control the remaining psoriatic plaques.
One week after presentation (3 weeks after the initial injections), the patient’s systemic symptoms had almost completely resolved, and she denied any further concerns. Her fingernails and toenails, however, continued to show the changes of onycholysis noted at the visit.
Comment
Ixekizumab is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to IL-17A, one of the cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. The monoclonal antibody prevents its attachment to the IL-17 receptor, which inhibits the release of further cytokines and chemokines, decreasing the inflammatory and immune response.2
Ixekizumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for plaque psoriasis after 3 clinical trials—UNCOVER-1, UNCOVER-2, and UNCOVER-3—were performed. In UNCOVER-3, the most common side effects that occurred—nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, injection-site reaction, arthralgia, headache, and infections (specifically candidiasis)—generally were well tolerated. More serious adverse events included cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, inflammatory bowel disease, and nonmelanoma skin cancer.3
Notable laboratory abnormalities that have been documented from ixekizumab include elevated liver function tests (eg, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase), as well as leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.4 Although short-term thrombocytopenia, as described in our patient, provides an explanation for the bruising noted on observation, it is unusual to note such notable ecchymoses within days of the first injection.
Onycholysis has not been documented as a side effect of ixekizumab; however, it has been reported as an adverse event from other biologic medications. Sfikakis et al5 reported 5 patients who developed psoriatic skin lesions after treatment with 3 different anti-TNF biologics—infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—fo
The exact pathophysiology of these adverse events has not been clearly understood, but it has been proposed that anti-TNF biologics may initiate an autoimmune reaction in the skin and nails, leading to paradoxical psoriasis and nail changes such as onycholysis. Tumor necrosis factor may have a regulatory role in the skin that prevents autoreactive T cells, such as cutaneous lymphocyte antigen–expressing T cells that promote the formation of psoriasiform lesions. By inhibiting TNF, there can be an underlying activation of autoreactive T cells that leads to tissue destruction in the skin and nails.6 Anti-TNF biologics also could increase CXCR3, a chemokine receptor that allows autoreactive T cells to enter the skin and cause pathology.7
IL-17A and IL-17F also have been shown to upregulate the expression of TNF receptor II in synoviocytes,8 which demonstrates that IL-17 works in synergy with TNF-α to promote an inflammatory reaction.9 Due to the inhibitory effects of ixekizumab, psoriatic arthritis should theoretically improve. However, if there is an alteration in the inflammatory sequence, then the regulatory role of TNF could be suppressed and psoriatic arthritis could become exacerbated. Additionally, its associated symptoms, such as dactylitis, could develop, as seen in our patient.4 Because psoriatic arthritis is closely associated with nail changes of psoriasis, it is conceivable that acute arthritic flares and acute onycholysis are both induced by the same cytokine dysregulation. Further studies and a larger patient population need to be evaluated to determine the exact cause of the acute exacerbation of psoriatic arthritis with concomitant nail changes as noted in our patient.
Acute onycholysis (within 72 hours) is a rare side effect of ixekizumab. It can be postulated that our patient’s severe acute onycholysis associated with a flare of psoriatic arthritis could be due to idiosyncratic immune dysregulation, promoting the activity of autoreactive T cells. The pharmacologic effects of ixekizumab occur through the inhibition of IL-17. We propose that by inhibiting IL-17 with associated TNF alterations, an altered inflammatory cascade could promote an autoimmune reaction leading to the described pathology.
- Kratz A, Pesce MA, Basner RC, et al. Laboratory values of clinical importance. In: Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2014.
- Ixekizumab. Package insert. Eli Lilly & Co; 2017.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Papp KA, et al. Phase 3 trials of ixekizumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:345-356.
- Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190-1199.
- Sfikakis PP, Iliopoulos A, Elezoglou A, et al. Psoriasis induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: a paradoxical adverse reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2513-2518.
- Berg EL, Yoshino T, Rott LS, et al. The cutaneous lymphocyte antigen is a skin lymphocyte homing receptor for the vascular lectin endothelial cell-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Exp Med. 1991;174:1461-1466.
- Flier J, Boorsma DM, van Beek PJ, et al. Differential expression of CXCR3 targeting chemokines CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 in different types of skin inflammation. J Pathol. 2001;194:398-405.
- Zrioual S, Ecochard R, Tournadre A, et al. Genome-wide comparison between IL-17A- and IL-17F-induced effects in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol. 2009;182:3112-3120.
- Gaffen SL. The role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11:365-370.
- Kratz A, Pesce MA, Basner RC, et al. Laboratory values of clinical importance. In: Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. McGraw-Hill; 2014.
- Ixekizumab. Package insert. Eli Lilly & Co; 2017.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Papp KA, et al. Phase 3 trials of ixekizumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:345-356.
- Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190-1199.
- Sfikakis PP, Iliopoulos A, Elezoglou A, et al. Psoriasis induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: a paradoxical adverse reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2513-2518.
- Berg EL, Yoshino T, Rott LS, et al. The cutaneous lymphocyte antigen is a skin lymphocyte homing receptor for the vascular lectin endothelial cell-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Exp Med. 1991;174:1461-1466.
- Flier J, Boorsma DM, van Beek PJ, et al. Differential expression of CXCR3 targeting chemokines CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 in different types of skin inflammation. J Pathol. 2001;194:398-405.
- Zrioual S, Ecochard R, Tournadre A, et al. Genome-wide comparison between IL-17A- and IL-17F-induced effects in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol. 2009;182:3112-3120.
- Gaffen SL. The role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11:365-370.
Practice Points
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder with a predominance of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that release cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor 11α and interleukins, which promote inflammation in the skin and joints and is associated with systemic inflammation predisposing patients to cardiovascular disease.
- Common adverse effects of most biologic medications for psoriasis include injection-site pain and rash, fever, malaise, back pain, urticaria and flushing, edema, dyspnea, and nausea.
- Ixekizumab is a humanized IL-17A antagonist intended for adults with moderate to severe psoriasis. Certain rare side effects specific to ixekizumab include inflammatory bowel disease, thrombocytopenia, severe injection-site reactions, and candidiasis.
- Acute onycholysis and acute exacerbation of arthritis/dactylitis are rare side effects of ixekizumab therapy.
A dermatologist-led model for CVD prevention in psoriasis may be feasible
A – may be feasible, given the positive perspectives expressed by both clinicians and patients in a set of electronic surveys, researchers say.
In an analysis of survey responses from 183 dermatologists and 322 patients, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, and coinvestigators found that more than two-thirds of dermatologists (69.3%) agreed it “seems doable” to check lipids and calculate a 10-year cardiovascular risk score, and over one-third (36.1%) agreed they could prescribe statins when indicated.
The patient survey was distributed through the National Psoriasis Foundation to individuals who were seeing a dermatologist or rheumatologist for psoriatic disease; the clinician survey was distributed through the American Academy of Dermatology to dermatologists who reported caring for patients with psoriasis. (A survey of rheumatologists was similarly conducted, but the number of participants fell short of the needed sample size.)
Most patients surveyed indicated they would be receptive to their dermatologist (or rheumatologist) playing a larger role in screening and managing CVD risk, and that they would be similarly likely to follow recommendations regarding risk screening and management whether the advice came their dermatologist/rheumatologist or from their PCP.
The clinician survey focused on lipids and statin use, and did not address other elements of risk management. Still, the researchers see their findings as an early but promising step in finding better models to improve cardiovascular outcomes for patients with psoriatic disease, who too often do not engage with their PCPs despite their increased risk of CVD and a higher risk of premature mortality from CVD.
Fewer than half of commercially insured adults aged under 65 years visit a PCP each year, the researchers noted. And among the patients in their survey, approximately 20% did not have a PCP or had not seen their PCP in the past year.
Other research has shown that only a small minority of patients with psoriasis have an encounter with their PCP within a year of establishing care with their dermatologist, and that “over half of patients with psoriasis have undetected risk factors like dyslipidemia or hypertension,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“There’s a gap here, a missing link in the chain of cardiovascular disease prevention,” he said. “What if the dermatologist or rheumatologist could be more engaged in [CV] risk protection? ... It’s the idea of meeting the patients where they are.”
The surveys
The clinician survey focused on statins because of their ease of use, efficacy and safety, and the need for minimal monitoring, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview. “On the spectrum of things you can do for cardiovascular disease prevention, it’s one of the easiest ones.”
In an accompanying editorial, cardiologists Michael S. Garshick, MD, MS, and Jeffrey S. Berger, MD, MS, both of the department of medicine, New York University, wrote that, “despite the well-described association between psoriasis and CVD, only 35% of patients with psoriasis diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.”
“For many of these patients, their dermatologist or rheumatologist may be their only source of contact with the health care system,” they added.
Most studies targeting CVD risk in psoriasis have focused on targeting psoriatic inflammation, and few studies have explored strategies to improve modifiable CVD risk factor control with pharmacological therapy, they said.
In addition to the questions about receptiveness to identifying and potentially treating CVD risk with statins, the dermatologist survey included a best-worst scaling choice experiment to assess preferences for implementation approaches. Dermatologists were asked to rank their preferences for eight implementation strategies that have been shown in published studies to help increase statin prescribing rates.
The three highest-ranked strategies among dermatologists were clinical decision support, physician educational outreach, and patient education materials. The lowest-ranked strategies were comparisons with peers, a pay-for-performance option, and a mobile app/texting service to remind patients to undergo CVD risk screening.
Of the 183 dermatologists in the survey, 28.4% were from academic settings, 11.5% were from multispecialty groups, and 45.4% were from dermatology groups. (A low response rate of 5.2% for dermatologists raises some questions about the generalizability of the findings, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger noted in their editorial.)
Where to go from here?
Asked to comment on the results, Jashin J. Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, Irvine, Calif., who was not involved with the study, said that a larger role in CVD risk management is “not likely to find traction with everyday dermatologists.”
“It’s already a big ask for community dermatologists to go through the approval process to get biologics for patients, so I don’t think many would be willing to add more to their plate by taking a bigger role in CVD management,” he said in an interview. He generally has not prescribed statins, “as I don’t feel that is in my scope of work.”
In the interview, Dr. Barbieri said that a parallel qualitative study, not yet published, has looked at the facilitators and barriers – including time constraints and concern about scope of practice – to statin prescribing and other elements of cardiovascular risk reduction.
All told, he said, a centralized care coordinator model may be the best approach to engage the dermatologist more in CVD prevention, including lipid management, but to also “offload some of the management responsibility.”
In this model, which is partially described by Dr. Barbieri and colleagues, the dermatologist (or rheumatologist) would educate the patient, measure blood pressure and check a lipid panel, and refer the patient to a coordinator who would, in turn, collect more information and calculate a 10-year CVD risk score.
Using a protocol-driven clinical decision support approach, the care coordinator would provide counseling about diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, and about whether statin therapy or blood pressure management is indicated.
“That coordinator would be in a good position to help the patient work with their PCP, if they have one, to find a PCP if they don’t, or to use telemedicine or work with their dermatologist or rheumatologist,” Dr. Barbieri said.
The centralized care coordinator service could be funded through grants, charitable funds, and patient assistance funds so that it is free to patients, he said, and could possibly be “housed in the National Psoriasis Foundation.”
Dr. Barbieri said he and his colleagues plan to design a clinical trial to test whether such a model can be adopted in practice and whether it can improve outcomes associated with CVD risk management.
In their editorial, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger, who is director of NYU Langone’s Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, wrote that many patients with psoriatic disease have or are at risk for cardiometabolic conditions, and that CVD risk reduction should extend beyond lipid management to include blood pressure, glucose lowering, obesity management, and antiplatelet therapy.
The joint AAD-NPF guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities, published in 2019, were among the first to formally recognize the enhanced CVD risk of patients with psoriasis, they noted.
The guidelines call upon dermatologists to inform patients of the psoriasis-CVD association and ensure their patients are engaged with their PCP or cardiologist for appropriate screening. Now, the editorialists say, “moving the needle forward includes refining and developing modifiable CVD risk reduction strategies for patients with psoriasis, and collaboration between the fields of dermatology, rheumatology, and cardiology is key.”
Incorporating a preventive cardiologist into combined dermatology-rheumatology clinics, or partnering as a freestanding cardioinflammatory clinic, also have potential to improve CVD risk, they wrote.
The survey study was supported by a grant from the NPF Psoriasis Prevention Initiative. Dr. Barbieri reported no conflicts of interest. Several authors disclosed consulting fees and grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Berger reported receiving personal fees from Janssen and grants from AstraZeneca outside of the submitted work. Dr. Garshick reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie outside of the submitted work.
A – may be feasible, given the positive perspectives expressed by both clinicians and patients in a set of electronic surveys, researchers say.
In an analysis of survey responses from 183 dermatologists and 322 patients, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, and coinvestigators found that more than two-thirds of dermatologists (69.3%) agreed it “seems doable” to check lipids and calculate a 10-year cardiovascular risk score, and over one-third (36.1%) agreed they could prescribe statins when indicated.
The patient survey was distributed through the National Psoriasis Foundation to individuals who were seeing a dermatologist or rheumatologist for psoriatic disease; the clinician survey was distributed through the American Academy of Dermatology to dermatologists who reported caring for patients with psoriasis. (A survey of rheumatologists was similarly conducted, but the number of participants fell short of the needed sample size.)
Most patients surveyed indicated they would be receptive to their dermatologist (or rheumatologist) playing a larger role in screening and managing CVD risk, and that they would be similarly likely to follow recommendations regarding risk screening and management whether the advice came their dermatologist/rheumatologist or from their PCP.
The clinician survey focused on lipids and statin use, and did not address other elements of risk management. Still, the researchers see their findings as an early but promising step in finding better models to improve cardiovascular outcomes for patients with psoriatic disease, who too often do not engage with their PCPs despite their increased risk of CVD and a higher risk of premature mortality from CVD.
Fewer than half of commercially insured adults aged under 65 years visit a PCP each year, the researchers noted. And among the patients in their survey, approximately 20% did not have a PCP or had not seen their PCP in the past year.
Other research has shown that only a small minority of patients with psoriasis have an encounter with their PCP within a year of establishing care with their dermatologist, and that “over half of patients with psoriasis have undetected risk factors like dyslipidemia or hypertension,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“There’s a gap here, a missing link in the chain of cardiovascular disease prevention,” he said. “What if the dermatologist or rheumatologist could be more engaged in [CV] risk protection? ... It’s the idea of meeting the patients where they are.”
The surveys
The clinician survey focused on statins because of their ease of use, efficacy and safety, and the need for minimal monitoring, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview. “On the spectrum of things you can do for cardiovascular disease prevention, it’s one of the easiest ones.”
In an accompanying editorial, cardiologists Michael S. Garshick, MD, MS, and Jeffrey S. Berger, MD, MS, both of the department of medicine, New York University, wrote that, “despite the well-described association between psoriasis and CVD, only 35% of patients with psoriasis diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.”
“For many of these patients, their dermatologist or rheumatologist may be their only source of contact with the health care system,” they added.
Most studies targeting CVD risk in psoriasis have focused on targeting psoriatic inflammation, and few studies have explored strategies to improve modifiable CVD risk factor control with pharmacological therapy, they said.
In addition to the questions about receptiveness to identifying and potentially treating CVD risk with statins, the dermatologist survey included a best-worst scaling choice experiment to assess preferences for implementation approaches. Dermatologists were asked to rank their preferences for eight implementation strategies that have been shown in published studies to help increase statin prescribing rates.
The three highest-ranked strategies among dermatologists were clinical decision support, physician educational outreach, and patient education materials. The lowest-ranked strategies were comparisons with peers, a pay-for-performance option, and a mobile app/texting service to remind patients to undergo CVD risk screening.
Of the 183 dermatologists in the survey, 28.4% were from academic settings, 11.5% were from multispecialty groups, and 45.4% were from dermatology groups. (A low response rate of 5.2% for dermatologists raises some questions about the generalizability of the findings, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger noted in their editorial.)
Where to go from here?
Asked to comment on the results, Jashin J. Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, Irvine, Calif., who was not involved with the study, said that a larger role in CVD risk management is “not likely to find traction with everyday dermatologists.”
“It’s already a big ask for community dermatologists to go through the approval process to get biologics for patients, so I don’t think many would be willing to add more to their plate by taking a bigger role in CVD management,” he said in an interview. He generally has not prescribed statins, “as I don’t feel that is in my scope of work.”
In the interview, Dr. Barbieri said that a parallel qualitative study, not yet published, has looked at the facilitators and barriers – including time constraints and concern about scope of practice – to statin prescribing and other elements of cardiovascular risk reduction.
All told, he said, a centralized care coordinator model may be the best approach to engage the dermatologist more in CVD prevention, including lipid management, but to also “offload some of the management responsibility.”
In this model, which is partially described by Dr. Barbieri and colleagues, the dermatologist (or rheumatologist) would educate the patient, measure blood pressure and check a lipid panel, and refer the patient to a coordinator who would, in turn, collect more information and calculate a 10-year CVD risk score.
Using a protocol-driven clinical decision support approach, the care coordinator would provide counseling about diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, and about whether statin therapy or blood pressure management is indicated.
“That coordinator would be in a good position to help the patient work with their PCP, if they have one, to find a PCP if they don’t, or to use telemedicine or work with their dermatologist or rheumatologist,” Dr. Barbieri said.
The centralized care coordinator service could be funded through grants, charitable funds, and patient assistance funds so that it is free to patients, he said, and could possibly be “housed in the National Psoriasis Foundation.”
Dr. Barbieri said he and his colleagues plan to design a clinical trial to test whether such a model can be adopted in practice and whether it can improve outcomes associated with CVD risk management.
In their editorial, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger, who is director of NYU Langone’s Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, wrote that many patients with psoriatic disease have or are at risk for cardiometabolic conditions, and that CVD risk reduction should extend beyond lipid management to include blood pressure, glucose lowering, obesity management, and antiplatelet therapy.
The joint AAD-NPF guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities, published in 2019, were among the first to formally recognize the enhanced CVD risk of patients with psoriasis, they noted.
The guidelines call upon dermatologists to inform patients of the psoriasis-CVD association and ensure their patients are engaged with their PCP or cardiologist for appropriate screening. Now, the editorialists say, “moving the needle forward includes refining and developing modifiable CVD risk reduction strategies for patients with psoriasis, and collaboration between the fields of dermatology, rheumatology, and cardiology is key.”
Incorporating a preventive cardiologist into combined dermatology-rheumatology clinics, or partnering as a freestanding cardioinflammatory clinic, also have potential to improve CVD risk, they wrote.
The survey study was supported by a grant from the NPF Psoriasis Prevention Initiative. Dr. Barbieri reported no conflicts of interest. Several authors disclosed consulting fees and grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Berger reported receiving personal fees from Janssen and grants from AstraZeneca outside of the submitted work. Dr. Garshick reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie outside of the submitted work.
A – may be feasible, given the positive perspectives expressed by both clinicians and patients in a set of electronic surveys, researchers say.
In an analysis of survey responses from 183 dermatologists and 322 patients, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, and coinvestigators found that more than two-thirds of dermatologists (69.3%) agreed it “seems doable” to check lipids and calculate a 10-year cardiovascular risk score, and over one-third (36.1%) agreed they could prescribe statins when indicated.
The patient survey was distributed through the National Psoriasis Foundation to individuals who were seeing a dermatologist or rheumatologist for psoriatic disease; the clinician survey was distributed through the American Academy of Dermatology to dermatologists who reported caring for patients with psoriasis. (A survey of rheumatologists was similarly conducted, but the number of participants fell short of the needed sample size.)
Most patients surveyed indicated they would be receptive to their dermatologist (or rheumatologist) playing a larger role in screening and managing CVD risk, and that they would be similarly likely to follow recommendations regarding risk screening and management whether the advice came their dermatologist/rheumatologist or from their PCP.
The clinician survey focused on lipids and statin use, and did not address other elements of risk management. Still, the researchers see their findings as an early but promising step in finding better models to improve cardiovascular outcomes for patients with psoriatic disease, who too often do not engage with their PCPs despite their increased risk of CVD and a higher risk of premature mortality from CVD.
Fewer than half of commercially insured adults aged under 65 years visit a PCP each year, the researchers noted. And among the patients in their survey, approximately 20% did not have a PCP or had not seen their PCP in the past year.
Other research has shown that only a small minority of patients with psoriasis have an encounter with their PCP within a year of establishing care with their dermatologist, and that “over half of patients with psoriasis have undetected risk factors like dyslipidemia or hypertension,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“There’s a gap here, a missing link in the chain of cardiovascular disease prevention,” he said. “What if the dermatologist or rheumatologist could be more engaged in [CV] risk protection? ... It’s the idea of meeting the patients where they are.”
The surveys
The clinician survey focused on statins because of their ease of use, efficacy and safety, and the need for minimal monitoring, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview. “On the spectrum of things you can do for cardiovascular disease prevention, it’s one of the easiest ones.”
In an accompanying editorial, cardiologists Michael S. Garshick, MD, MS, and Jeffrey S. Berger, MD, MS, both of the department of medicine, New York University, wrote that, “despite the well-described association between psoriasis and CVD, only 35% of patients with psoriasis diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.”
“For many of these patients, their dermatologist or rheumatologist may be their only source of contact with the health care system,” they added.
Most studies targeting CVD risk in psoriasis have focused on targeting psoriatic inflammation, and few studies have explored strategies to improve modifiable CVD risk factor control with pharmacological therapy, they said.
In addition to the questions about receptiveness to identifying and potentially treating CVD risk with statins, the dermatologist survey included a best-worst scaling choice experiment to assess preferences for implementation approaches. Dermatologists were asked to rank their preferences for eight implementation strategies that have been shown in published studies to help increase statin prescribing rates.
The three highest-ranked strategies among dermatologists were clinical decision support, physician educational outreach, and patient education materials. The lowest-ranked strategies were comparisons with peers, a pay-for-performance option, and a mobile app/texting service to remind patients to undergo CVD risk screening.
Of the 183 dermatologists in the survey, 28.4% were from academic settings, 11.5% were from multispecialty groups, and 45.4% were from dermatology groups. (A low response rate of 5.2% for dermatologists raises some questions about the generalizability of the findings, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger noted in their editorial.)
Where to go from here?
Asked to comment on the results, Jashin J. Wu, MD, founder and CEO of the Dermatology Research and Education Foundation, Irvine, Calif., who was not involved with the study, said that a larger role in CVD risk management is “not likely to find traction with everyday dermatologists.”
“It’s already a big ask for community dermatologists to go through the approval process to get biologics for patients, so I don’t think many would be willing to add more to their plate by taking a bigger role in CVD management,” he said in an interview. He generally has not prescribed statins, “as I don’t feel that is in my scope of work.”
In the interview, Dr. Barbieri said that a parallel qualitative study, not yet published, has looked at the facilitators and barriers – including time constraints and concern about scope of practice – to statin prescribing and other elements of cardiovascular risk reduction.
All told, he said, a centralized care coordinator model may be the best approach to engage the dermatologist more in CVD prevention, including lipid management, but to also “offload some of the management responsibility.”
In this model, which is partially described by Dr. Barbieri and colleagues, the dermatologist (or rheumatologist) would educate the patient, measure blood pressure and check a lipid panel, and refer the patient to a coordinator who would, in turn, collect more information and calculate a 10-year CVD risk score.
Using a protocol-driven clinical decision support approach, the care coordinator would provide counseling about diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, and about whether statin therapy or blood pressure management is indicated.
“That coordinator would be in a good position to help the patient work with their PCP, if they have one, to find a PCP if they don’t, or to use telemedicine or work with their dermatologist or rheumatologist,” Dr. Barbieri said.
The centralized care coordinator service could be funded through grants, charitable funds, and patient assistance funds so that it is free to patients, he said, and could possibly be “housed in the National Psoriasis Foundation.”
Dr. Barbieri said he and his colleagues plan to design a clinical trial to test whether such a model can be adopted in practice and whether it can improve outcomes associated with CVD risk management.
In their editorial, Dr. Garshick and Dr. Berger, who is director of NYU Langone’s Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, wrote that many patients with psoriatic disease have or are at risk for cardiometabolic conditions, and that CVD risk reduction should extend beyond lipid management to include blood pressure, glucose lowering, obesity management, and antiplatelet therapy.
The joint AAD-NPF guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities, published in 2019, were among the first to formally recognize the enhanced CVD risk of patients with psoriasis, they noted.
The guidelines call upon dermatologists to inform patients of the psoriasis-CVD association and ensure their patients are engaged with their PCP or cardiologist for appropriate screening. Now, the editorialists say, “moving the needle forward includes refining and developing modifiable CVD risk reduction strategies for patients with psoriasis, and collaboration between the fields of dermatology, rheumatology, and cardiology is key.”
Incorporating a preventive cardiologist into combined dermatology-rheumatology clinics, or partnering as a freestanding cardioinflammatory clinic, also have potential to improve CVD risk, they wrote.
The survey study was supported by a grant from the NPF Psoriasis Prevention Initiative. Dr. Barbieri reported no conflicts of interest. Several authors disclosed consulting fees and grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Berger reported receiving personal fees from Janssen and grants from AstraZeneca outside of the submitted work. Dr. Garshick reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie outside of the submitted work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
More frequent secukinumab dosing found to benefit overweight psoriasis patients
, results from a multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group trial showed.
The more frequent dosing was also associated with comparable safety, consistent with the established secukinumab safety profile.
“Weight may have an impact on pharmacokinetics and, therefore, on the clinical outcome of biologic treatment for psoriasis,” Matthias Augustin, MD, and colleagues wrote in the study, published recently in the British Journal of Dermatology. “Dose optimization may be highly beneficial for patients with higher body weight,” they noted, adding that their study supports previous study findings and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling data, showing that secukinumab dosed every 2 weeks “leads to a clinically and statistically significant advantage in PASI 90 response,” compared with standard dosing every 4 weeks in patients who weight 90 kg (about 198 pounds) or more, after 16 weeks of treatment, which was maintained until week 52.
For the study, Dr. Augustin, of the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing at University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), and colleagues randomized 331 patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who weighed 90 kg or more to receive secukinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks, or secukinumab 300 mg every 4 weeks. The mean age of the patients was 47 years, 75% were male, 92% were White, and their mean body weight was 111.1 kg, with a mean body mass index of 36.1 kg/m2.
Patients who did not achieve a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 at week 16 on the monthly regimen (Q4W) either remained on that regimen or were up-titrated to dosing every 2 weeks (Q2W). Of the 331 patients, 165 received Q2W dosing and 166 received Q4W dosing. The researchers found that, at 16 weeks, patients in the Q2W dosing group had significantly higher PASI 90 responses, compared with those in the Q4W group (73.2% vs. 55.5%, respectively; P = .0003; odds ratio estimate, 2.3).
At 52 weeks, a greater proportion of patients in the Q2W group maintained responses to several outcome measures, compared with those in the Q4W group, including PASI 75 (88.9% vs. 74.8%), PASI 90 (76.4% vs. 52.4%), and PASI 100 (46.7% vs. 27.3%) scores; Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1 (75.9% vs. 55.6%); and Dermatology Life Quality Index scores of 0 or 1 (66.1% vs. 48.8%).
In addition, those who had not had a PASI 90 response at week 16 who were up-titrated to Q2W dosing demonstrated higher efficacy responses at week 32, compared with those who remained on the Q4W regimen, with PASI 90 scores of 37.7% versus 16.5%, respectively.
Both regimens were well-tolerated, consistent with the known secukinumab safety profile; safety was comparable in the treatment arms, and there was “no clear dose-response relationship seen” for the incidence of overall adverse events, serious AEs, and AEs leading to discontinuation of the study treatment, “or AEs related to the identified risks” of infections, hypersensitivity, neutropenia and potential risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, the authors wrote.
“Despite more frequent dosing, the incidence of Candida infections was numerically lower in the Q2W group versus the Q4W group,” although there were not many cases, three patients versus six patients, respectively.
Need for individualized treatment
“Despite a decades-long revolution in development of highly efficacious biologic treatments for psoriasis, we are only in the early stages of developing personalized clinical approaches,” said Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. “The need for individualized treatment in psoriasis is very real; not every patient may respond to therapy in the same way. Obesity is one important comorbidity of psoriasis, and increased body mass index may be associated with variable treatment outcomes with systemic therapy.”
The data from this study, he added, “suggest that dose optimization may be an important strategy to enhance psoriasis clearance in patients with suboptimal treatment outcomes on standard dosing, including those with increased weight. Future studies should examine optimal regimen of biologic therapy across a variety of patient factors.”
The study was funded by Novartis, the manufacturer of secukinumab (Cosentyx); several authors were company employees. Dr. Augustin disclosed that he has served as a consultant for or has been a paid speaker for clinical trials sponsored by companies that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of psoriasis, including AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Centocor, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen-Cilag, LEO Pharma, Medac, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Xenoport. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
, results from a multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group trial showed.
The more frequent dosing was also associated with comparable safety, consistent with the established secukinumab safety profile.
“Weight may have an impact on pharmacokinetics and, therefore, on the clinical outcome of biologic treatment for psoriasis,” Matthias Augustin, MD, and colleagues wrote in the study, published recently in the British Journal of Dermatology. “Dose optimization may be highly beneficial for patients with higher body weight,” they noted, adding that their study supports previous study findings and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling data, showing that secukinumab dosed every 2 weeks “leads to a clinically and statistically significant advantage in PASI 90 response,” compared with standard dosing every 4 weeks in patients who weight 90 kg (about 198 pounds) or more, after 16 weeks of treatment, which was maintained until week 52.
For the study, Dr. Augustin, of the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing at University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), and colleagues randomized 331 patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who weighed 90 kg or more to receive secukinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks, or secukinumab 300 mg every 4 weeks. The mean age of the patients was 47 years, 75% were male, 92% were White, and their mean body weight was 111.1 kg, with a mean body mass index of 36.1 kg/m2.
Patients who did not achieve a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 at week 16 on the monthly regimen (Q4W) either remained on that regimen or were up-titrated to dosing every 2 weeks (Q2W). Of the 331 patients, 165 received Q2W dosing and 166 received Q4W dosing. The researchers found that, at 16 weeks, patients in the Q2W dosing group had significantly higher PASI 90 responses, compared with those in the Q4W group (73.2% vs. 55.5%, respectively; P = .0003; odds ratio estimate, 2.3).
At 52 weeks, a greater proportion of patients in the Q2W group maintained responses to several outcome measures, compared with those in the Q4W group, including PASI 75 (88.9% vs. 74.8%), PASI 90 (76.4% vs. 52.4%), and PASI 100 (46.7% vs. 27.3%) scores; Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1 (75.9% vs. 55.6%); and Dermatology Life Quality Index scores of 0 or 1 (66.1% vs. 48.8%).
In addition, those who had not had a PASI 90 response at week 16 who were up-titrated to Q2W dosing demonstrated higher efficacy responses at week 32, compared with those who remained on the Q4W regimen, with PASI 90 scores of 37.7% versus 16.5%, respectively.
Both regimens were well-tolerated, consistent with the known secukinumab safety profile; safety was comparable in the treatment arms, and there was “no clear dose-response relationship seen” for the incidence of overall adverse events, serious AEs, and AEs leading to discontinuation of the study treatment, “or AEs related to the identified risks” of infections, hypersensitivity, neutropenia and potential risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, the authors wrote.
“Despite more frequent dosing, the incidence of Candida infections was numerically lower in the Q2W group versus the Q4W group,” although there were not many cases, three patients versus six patients, respectively.
Need for individualized treatment
“Despite a decades-long revolution in development of highly efficacious biologic treatments for psoriasis, we are only in the early stages of developing personalized clinical approaches,” said Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. “The need for individualized treatment in psoriasis is very real; not every patient may respond to therapy in the same way. Obesity is one important comorbidity of psoriasis, and increased body mass index may be associated with variable treatment outcomes with systemic therapy.”
The data from this study, he added, “suggest that dose optimization may be an important strategy to enhance psoriasis clearance in patients with suboptimal treatment outcomes on standard dosing, including those with increased weight. Future studies should examine optimal regimen of biologic therapy across a variety of patient factors.”
The study was funded by Novartis, the manufacturer of secukinumab (Cosentyx); several authors were company employees. Dr. Augustin disclosed that he has served as a consultant for or has been a paid speaker for clinical trials sponsored by companies that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of psoriasis, including AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Centocor, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen-Cilag, LEO Pharma, Medac, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Xenoport. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
, results from a multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group trial showed.
The more frequent dosing was also associated with comparable safety, consistent with the established secukinumab safety profile.
“Weight may have an impact on pharmacokinetics and, therefore, on the clinical outcome of biologic treatment for psoriasis,” Matthias Augustin, MD, and colleagues wrote in the study, published recently in the British Journal of Dermatology. “Dose optimization may be highly beneficial for patients with higher body weight,” they noted, adding that their study supports previous study findings and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling data, showing that secukinumab dosed every 2 weeks “leads to a clinically and statistically significant advantage in PASI 90 response,” compared with standard dosing every 4 weeks in patients who weight 90 kg (about 198 pounds) or more, after 16 weeks of treatment, which was maintained until week 52.
For the study, Dr. Augustin, of the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing at University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), and colleagues randomized 331 patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who weighed 90 kg or more to receive secukinumab 300 mg every 2 weeks, or secukinumab 300 mg every 4 weeks. The mean age of the patients was 47 years, 75% were male, 92% were White, and their mean body weight was 111.1 kg, with a mean body mass index of 36.1 kg/m2.
Patients who did not achieve a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 at week 16 on the monthly regimen (Q4W) either remained on that regimen or were up-titrated to dosing every 2 weeks (Q2W). Of the 331 patients, 165 received Q2W dosing and 166 received Q4W dosing. The researchers found that, at 16 weeks, patients in the Q2W dosing group had significantly higher PASI 90 responses, compared with those in the Q4W group (73.2% vs. 55.5%, respectively; P = .0003; odds ratio estimate, 2.3).
At 52 weeks, a greater proportion of patients in the Q2W group maintained responses to several outcome measures, compared with those in the Q4W group, including PASI 75 (88.9% vs. 74.8%), PASI 90 (76.4% vs. 52.4%), and PASI 100 (46.7% vs. 27.3%) scores; Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1 (75.9% vs. 55.6%); and Dermatology Life Quality Index scores of 0 or 1 (66.1% vs. 48.8%).
In addition, those who had not had a PASI 90 response at week 16 who were up-titrated to Q2W dosing demonstrated higher efficacy responses at week 32, compared with those who remained on the Q4W regimen, with PASI 90 scores of 37.7% versus 16.5%, respectively.
Both regimens were well-tolerated, consistent with the known secukinumab safety profile; safety was comparable in the treatment arms, and there was “no clear dose-response relationship seen” for the incidence of overall adverse events, serious AEs, and AEs leading to discontinuation of the study treatment, “or AEs related to the identified risks” of infections, hypersensitivity, neutropenia and potential risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, the authors wrote.
“Despite more frequent dosing, the incidence of Candida infections was numerically lower in the Q2W group versus the Q4W group,” although there were not many cases, three patients versus six patients, respectively.
Need for individualized treatment
“Despite a decades-long revolution in development of highly efficacious biologic treatments for psoriasis, we are only in the early stages of developing personalized clinical approaches,” said Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study. “The need for individualized treatment in psoriasis is very real; not every patient may respond to therapy in the same way. Obesity is one important comorbidity of psoriasis, and increased body mass index may be associated with variable treatment outcomes with systemic therapy.”
The data from this study, he added, “suggest that dose optimization may be an important strategy to enhance psoriasis clearance in patients with suboptimal treatment outcomes on standard dosing, including those with increased weight. Future studies should examine optimal regimen of biologic therapy across a variety of patient factors.”
The study was funded by Novartis, the manufacturer of secukinumab (Cosentyx); several authors were company employees. Dr. Augustin disclosed that he has served as a consultant for or has been a paid speaker for clinical trials sponsored by companies that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of psoriasis, including AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Centocor, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen-Cilag, LEO Pharma, Medac, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Xenoport. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for AbbVie, Arcutis, Arena, Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi Genzyme.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Proactive infliximab monitoring found best for sustaining control of inflammatory diseases
A new study has found that proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) with maintenance infliximab is more effective than standard therapy in sustaining control of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
The findings from the Norwegian Drug Monitoring B (NOR-DRUM B) trial, published Dec. 21, 2021, in JAMA, provide greater support to the usefulness of TDM in proactively monitoring serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies to infliximab, which has been previously shown to have benefit in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, but leave the benefits of proactive versus reactive monitoring and the cost-effectiveness of the approach in individual immune-mediated inflammatory diseases still open to questioning.
TDM is ‘not the holy grail,’ and that’s OK
“This is an important milestone in the field of TDM with biologics for immunoinflammatory diseases,” Niels Vande Casteele, PharmD, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization. He was not involved in the study.
“When you read through the study, you can see the authors used the TAXIT trial results to inform their study design and the sample size,” he added, referencing his 2015 study on infliximab guide dosing for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, “the first-ever randomized, controlled trial of proactive TDM with any biologic.”
For the TAXIT study’s primary outcome of clinical and biochemical remission at 1 year, “continued concentration-based dosing was not superior to clinically based dosing for achieving remission.” But in regard to their secondary outcome of sustained remission, their results were quite similar to the results of NOR-DRUM B.
“If anything, we already showed a benefit of proactive TDM in 2015,” he said, “but I’m very glad that the authors looked at the trial design and teased out where TDM could be the most important and have the biggest impact, which is to maintain that sustained disease remission over a prolonged period.”
As for next steps, Dr. Vande Casteele noted that TDM isn’t a one-size-fits-all upgrade for drug treatments. But that doesn’t mean it won’t be very useful in many patients.
“What the paper is saying, and what we’ve been finding all along, is that TDM is not the holy grail,” he said. “But it is a tool in the physicians’ toolbox to optimize treatments and maximize efficacy, and there are some patients who truly benefit from it.”
Study details
To determine if proactive TDM with infliximab led to more sustained disease control than standard therapy, first author Silje Watterdal Syversen, MD, PhD, of Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, and coauthors conducted a 52-week, randomized, parallel-group, open-label trial. From 20 Norwegian hospitals, they recruited 458 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 80), spondyloarthritis (n = 138), psoriatic arthritis (n = 54), ulcerative colitis (n = 81), Crohn’s disease (n = 68), or psoriasis (n = 37) who were undergoing maintenance therapy with the biologic.
The 454 patients who received at least one randomly allocated dose of infliximab were treated with one of two strategies: TDM (n = 227) or standard therapy (n = 227). The TDM group received dose and interval adjustments based on an algorithm that factored in serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies. The standard therapy group was treated on the basis of clinical judgment and physician discretion. The average age across groups was roughly 45 years, and just under 50% were women.
Overall, sustained disease control without worsening was achieved in 167 patients (73.6%) in the TDM group and 127 patients (55.9%) in the standard therapy group, with an estimated adjusted difference of 17.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.0%-26.2%; P < .001). The estimated hazard ratio of disease worsening was 2.1 (95% CI, 1.5-2.9) for standard therapy, compared with TDM. A total of 27 patients (15%) in the standard therapy group and 21 patients (9.2%) in the TDM group developed significant levels of antidrug antibodies, defined here as 50 mcg/L or more.
A total of 34 patients discontinued infliximab in each group; in the TDM group, most discontinued because of antidrug antibody formation, while the main reason for discontinuing in the standard therapy group was disease worsening. Adverse events were reported in 137 patients (60%) in the TDM group and 142 patients (63%) in the standard therapy group.
Removing barriers to TDM
It’s not clear that proactive TDM will benefit treatment with all biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), but the findings from Dr. Syversen and colleagues state the clear value of using drug monitoring to guide maintenance therapy with infliximab, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The relatively large sample size and rigorous study design ... helped to overcome some limitations of previous observational studies and small clinical trials that yielded conflicting results regarding TDM,” they added, noting that these findings contrasted somewhat with the NOR-DRUM A trial in which TDM did not improve remission induction in patients initiating infliximab therapy.
Along those lines, they recognized that TDM appears to have a greater effect in patients on maintenance infliximab, compared with those just starting the drug, surmising – among several explanations – that achieving remission in someone beginning treatment is a more difficult outcome to achieve than controlling disease in a patient already in remission.
For now, more clinical trials assessing specific diseases and involving other bDMARDs are needed; Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks stated that it’s time to remove barriers to implementing TDM – including the need for medical insurance preauthorization before increasing drug doses – and potentially “introduce a new era in treatment approach to maintenance therapy for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including disease worsening being measured in part by patient-physician consensus and thus potentially subject to bias. In addition, they did not have the statistical ability to test TDM effectiveness in each of the six disease groups, noting that “these diseases have inherent differences, and findings may not be completely generalizable across groups.”
The study was funded by grants from the Norwegian Regional Health Authorities and the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authorities. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks also reported receiving research support and fees from pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Vande Casteele reported receiving research grants and personal fees from multiple pharmaceutical companies, all outside of the reviewed work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has found that proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) with maintenance infliximab is more effective than standard therapy in sustaining control of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
The findings from the Norwegian Drug Monitoring B (NOR-DRUM B) trial, published Dec. 21, 2021, in JAMA, provide greater support to the usefulness of TDM in proactively monitoring serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies to infliximab, which has been previously shown to have benefit in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, but leave the benefits of proactive versus reactive monitoring and the cost-effectiveness of the approach in individual immune-mediated inflammatory diseases still open to questioning.
TDM is ‘not the holy grail,’ and that’s OK
“This is an important milestone in the field of TDM with biologics for immunoinflammatory diseases,” Niels Vande Casteele, PharmD, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization. He was not involved in the study.
“When you read through the study, you can see the authors used the TAXIT trial results to inform their study design and the sample size,” he added, referencing his 2015 study on infliximab guide dosing for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, “the first-ever randomized, controlled trial of proactive TDM with any biologic.”
For the TAXIT study’s primary outcome of clinical and biochemical remission at 1 year, “continued concentration-based dosing was not superior to clinically based dosing for achieving remission.” But in regard to their secondary outcome of sustained remission, their results were quite similar to the results of NOR-DRUM B.
“If anything, we already showed a benefit of proactive TDM in 2015,” he said, “but I’m very glad that the authors looked at the trial design and teased out where TDM could be the most important and have the biggest impact, which is to maintain that sustained disease remission over a prolonged period.”
As for next steps, Dr. Vande Casteele noted that TDM isn’t a one-size-fits-all upgrade for drug treatments. But that doesn’t mean it won’t be very useful in many patients.
“What the paper is saying, and what we’ve been finding all along, is that TDM is not the holy grail,” he said. “But it is a tool in the physicians’ toolbox to optimize treatments and maximize efficacy, and there are some patients who truly benefit from it.”
Study details
To determine if proactive TDM with infliximab led to more sustained disease control than standard therapy, first author Silje Watterdal Syversen, MD, PhD, of Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, and coauthors conducted a 52-week, randomized, parallel-group, open-label trial. From 20 Norwegian hospitals, they recruited 458 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 80), spondyloarthritis (n = 138), psoriatic arthritis (n = 54), ulcerative colitis (n = 81), Crohn’s disease (n = 68), or psoriasis (n = 37) who were undergoing maintenance therapy with the biologic.
The 454 patients who received at least one randomly allocated dose of infliximab were treated with one of two strategies: TDM (n = 227) or standard therapy (n = 227). The TDM group received dose and interval adjustments based on an algorithm that factored in serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies. The standard therapy group was treated on the basis of clinical judgment and physician discretion. The average age across groups was roughly 45 years, and just under 50% were women.
Overall, sustained disease control without worsening was achieved in 167 patients (73.6%) in the TDM group and 127 patients (55.9%) in the standard therapy group, with an estimated adjusted difference of 17.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.0%-26.2%; P < .001). The estimated hazard ratio of disease worsening was 2.1 (95% CI, 1.5-2.9) for standard therapy, compared with TDM. A total of 27 patients (15%) in the standard therapy group and 21 patients (9.2%) in the TDM group developed significant levels of antidrug antibodies, defined here as 50 mcg/L or more.
A total of 34 patients discontinued infliximab in each group; in the TDM group, most discontinued because of antidrug antibody formation, while the main reason for discontinuing in the standard therapy group was disease worsening. Adverse events were reported in 137 patients (60%) in the TDM group and 142 patients (63%) in the standard therapy group.
Removing barriers to TDM
It’s not clear that proactive TDM will benefit treatment with all biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), but the findings from Dr. Syversen and colleagues state the clear value of using drug monitoring to guide maintenance therapy with infliximab, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The relatively large sample size and rigorous study design ... helped to overcome some limitations of previous observational studies and small clinical trials that yielded conflicting results regarding TDM,” they added, noting that these findings contrasted somewhat with the NOR-DRUM A trial in which TDM did not improve remission induction in patients initiating infliximab therapy.
Along those lines, they recognized that TDM appears to have a greater effect in patients on maintenance infliximab, compared with those just starting the drug, surmising – among several explanations – that achieving remission in someone beginning treatment is a more difficult outcome to achieve than controlling disease in a patient already in remission.
For now, more clinical trials assessing specific diseases and involving other bDMARDs are needed; Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks stated that it’s time to remove barriers to implementing TDM – including the need for medical insurance preauthorization before increasing drug doses – and potentially “introduce a new era in treatment approach to maintenance therapy for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including disease worsening being measured in part by patient-physician consensus and thus potentially subject to bias. In addition, they did not have the statistical ability to test TDM effectiveness in each of the six disease groups, noting that “these diseases have inherent differences, and findings may not be completely generalizable across groups.”
The study was funded by grants from the Norwegian Regional Health Authorities and the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authorities. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks also reported receiving research support and fees from pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Vande Casteele reported receiving research grants and personal fees from multiple pharmaceutical companies, all outside of the reviewed work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has found that proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) with maintenance infliximab is more effective than standard therapy in sustaining control of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
The findings from the Norwegian Drug Monitoring B (NOR-DRUM B) trial, published Dec. 21, 2021, in JAMA, provide greater support to the usefulness of TDM in proactively monitoring serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies to infliximab, which has been previously shown to have benefit in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, but leave the benefits of proactive versus reactive monitoring and the cost-effectiveness of the approach in individual immune-mediated inflammatory diseases still open to questioning.
TDM is ‘not the holy grail,’ and that’s OK
“This is an important milestone in the field of TDM with biologics for immunoinflammatory diseases,” Niels Vande Casteele, PharmD, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization. He was not involved in the study.
“When you read through the study, you can see the authors used the TAXIT trial results to inform their study design and the sample size,” he added, referencing his 2015 study on infliximab guide dosing for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, “the first-ever randomized, controlled trial of proactive TDM with any biologic.”
For the TAXIT study’s primary outcome of clinical and biochemical remission at 1 year, “continued concentration-based dosing was not superior to clinically based dosing for achieving remission.” But in regard to their secondary outcome of sustained remission, their results were quite similar to the results of NOR-DRUM B.
“If anything, we already showed a benefit of proactive TDM in 2015,” he said, “but I’m very glad that the authors looked at the trial design and teased out where TDM could be the most important and have the biggest impact, which is to maintain that sustained disease remission over a prolonged period.”
As for next steps, Dr. Vande Casteele noted that TDM isn’t a one-size-fits-all upgrade for drug treatments. But that doesn’t mean it won’t be very useful in many patients.
“What the paper is saying, and what we’ve been finding all along, is that TDM is not the holy grail,” he said. “But it is a tool in the physicians’ toolbox to optimize treatments and maximize efficacy, and there are some patients who truly benefit from it.”
Study details
To determine if proactive TDM with infliximab led to more sustained disease control than standard therapy, first author Silje Watterdal Syversen, MD, PhD, of Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, and coauthors conducted a 52-week, randomized, parallel-group, open-label trial. From 20 Norwegian hospitals, they recruited 458 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 80), spondyloarthritis (n = 138), psoriatic arthritis (n = 54), ulcerative colitis (n = 81), Crohn’s disease (n = 68), or psoriasis (n = 37) who were undergoing maintenance therapy with the biologic.
The 454 patients who received at least one randomly allocated dose of infliximab were treated with one of two strategies: TDM (n = 227) or standard therapy (n = 227). The TDM group received dose and interval adjustments based on an algorithm that factored in serum drug levels and antidrug antibodies. The standard therapy group was treated on the basis of clinical judgment and physician discretion. The average age across groups was roughly 45 years, and just under 50% were women.
Overall, sustained disease control without worsening was achieved in 167 patients (73.6%) in the TDM group and 127 patients (55.9%) in the standard therapy group, with an estimated adjusted difference of 17.6% (95% confidence interval, 9.0%-26.2%; P < .001). The estimated hazard ratio of disease worsening was 2.1 (95% CI, 1.5-2.9) for standard therapy, compared with TDM. A total of 27 patients (15%) in the standard therapy group and 21 patients (9.2%) in the TDM group developed significant levels of antidrug antibodies, defined here as 50 mcg/L or more.
A total of 34 patients discontinued infliximab in each group; in the TDM group, most discontinued because of antidrug antibody formation, while the main reason for discontinuing in the standard therapy group was disease worsening. Adverse events were reported in 137 patients (60%) in the TDM group and 142 patients (63%) in the standard therapy group.
Removing barriers to TDM
It’s not clear that proactive TDM will benefit treatment with all biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), but the findings from Dr. Syversen and colleagues state the clear value of using drug monitoring to guide maintenance therapy with infliximab, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
“The relatively large sample size and rigorous study design ... helped to overcome some limitations of previous observational studies and small clinical trials that yielded conflicting results regarding TDM,” they added, noting that these findings contrasted somewhat with the NOR-DRUM A trial in which TDM did not improve remission induction in patients initiating infliximab therapy.
Along those lines, they recognized that TDM appears to have a greater effect in patients on maintenance infliximab, compared with those just starting the drug, surmising – among several explanations – that achieving remission in someone beginning treatment is a more difficult outcome to achieve than controlling disease in a patient already in remission.
For now, more clinical trials assessing specific diseases and involving other bDMARDs are needed; Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks stated that it’s time to remove barriers to implementing TDM – including the need for medical insurance preauthorization before increasing drug doses – and potentially “introduce a new era in treatment approach to maintenance therapy for patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including disease worsening being measured in part by patient-physician consensus and thus potentially subject to bias. In addition, they did not have the statistical ability to test TDM effectiveness in each of the six disease groups, noting that “these diseases have inherent differences, and findings may not be completely generalizable across groups.”
The study was funded by grants from the Norwegian Regional Health Authorities and the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authorities. The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving personal fees and grants from various pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wallace and Dr. Sparks also reported receiving research support and fees from pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Vande Casteele reported receiving research grants and personal fees from multiple pharmaceutical companies, all outside of the reviewed work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Case series show no consensus on treatment for palmoplantar pustulosis, generalized pustular psoriasis
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
FDA to review PDE4-inhibitor roflumilast for psoriasis
The , according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Roflumilast cream (also known as ARQ-151) is a small molecule inhibitor of PDE4, an enzyme that increases proinflammatory mediators and decreases anti-inflammatory mediators. PDE4 is an established treatment target in dermatology: The FDA approved PDE-4 inhibitor crisaborole (Eucrisa) as a topical treatment for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in 2016, and an oral PDE-4 inhibitor, orismilast, is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Topical roflumilast, if approved, would be the first topical PDE4 inhibitor for psoriasis in particular, according to the Arcutis Biotherapeutics statement. The cream is designed for use on the entire body, including the face and sensitive intertriginous areas.
The NDA is based on data from a pair of phase 3 randomized, double-blind 8-week studies known as DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 (Trials of PDE4 Inhibition with Roflumilast for the Management of Plaque Psoriasis” One and Two) and a long-term phase 2b open-label study.
DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 were identical multinational, multicenter studies designed to assess the safety and efficacy of 0.3% roflumilast cream. In the studies, roflumilast met its primary endpoint and patients treated with it demonstrated an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) success rate of 42.4% compared with 6.1% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), and 37.5% compared with 6.9% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), in the DERMIS 1 and 2 trials, respectively, according to Arcutis.
In the phase 2b study, the treatment effect lasted for 52-64 weeks. Roflumilast was well tolerated across the three studies.
Overall, the most common adverse events reported in the studies were diarrhea (3%), headache (2%), insomnia (1%), nausea (1%), upper respiratory tract infections (1%), and urinary tract infections (1%).
Roflumilast also showed statistically significant improvement compared to a vehicle on secondary endpoints including Intertriginous IGA (I-IGA) Success, Psoriasis Area Severity Index-75 (PASI-75), reductions in itch as measured by the Worst Itch-Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS), and patient perceptions of symptoms based on the Psoriasis Symptoms Diary (PSD).
The FDA has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of July 29, 2022, according to the manufacturer’s statement. An oral formulation of roflumilast was approved by the FDA in 2011, for reducing the risk of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in patients with severe COPD.
The , according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Roflumilast cream (also known as ARQ-151) is a small molecule inhibitor of PDE4, an enzyme that increases proinflammatory mediators and decreases anti-inflammatory mediators. PDE4 is an established treatment target in dermatology: The FDA approved PDE-4 inhibitor crisaborole (Eucrisa) as a topical treatment for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in 2016, and an oral PDE-4 inhibitor, orismilast, is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Topical roflumilast, if approved, would be the first topical PDE4 inhibitor for psoriasis in particular, according to the Arcutis Biotherapeutics statement. The cream is designed for use on the entire body, including the face and sensitive intertriginous areas.
The NDA is based on data from a pair of phase 3 randomized, double-blind 8-week studies known as DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 (Trials of PDE4 Inhibition with Roflumilast for the Management of Plaque Psoriasis” One and Two) and a long-term phase 2b open-label study.
DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 were identical multinational, multicenter studies designed to assess the safety and efficacy of 0.3% roflumilast cream. In the studies, roflumilast met its primary endpoint and patients treated with it demonstrated an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) success rate of 42.4% compared with 6.1% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), and 37.5% compared with 6.9% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), in the DERMIS 1 and 2 trials, respectively, according to Arcutis.
In the phase 2b study, the treatment effect lasted for 52-64 weeks. Roflumilast was well tolerated across the three studies.
Overall, the most common adverse events reported in the studies were diarrhea (3%), headache (2%), insomnia (1%), nausea (1%), upper respiratory tract infections (1%), and urinary tract infections (1%).
Roflumilast also showed statistically significant improvement compared to a vehicle on secondary endpoints including Intertriginous IGA (I-IGA) Success, Psoriasis Area Severity Index-75 (PASI-75), reductions in itch as measured by the Worst Itch-Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS), and patient perceptions of symptoms based on the Psoriasis Symptoms Diary (PSD).
The FDA has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of July 29, 2022, according to the manufacturer’s statement. An oral formulation of roflumilast was approved by the FDA in 2011, for reducing the risk of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in patients with severe COPD.
The , according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Roflumilast cream (also known as ARQ-151) is a small molecule inhibitor of PDE4, an enzyme that increases proinflammatory mediators and decreases anti-inflammatory mediators. PDE4 is an established treatment target in dermatology: The FDA approved PDE-4 inhibitor crisaborole (Eucrisa) as a topical treatment for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in 2016, and an oral PDE-4 inhibitor, orismilast, is being studied for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Topical roflumilast, if approved, would be the first topical PDE4 inhibitor for psoriasis in particular, according to the Arcutis Biotherapeutics statement. The cream is designed for use on the entire body, including the face and sensitive intertriginous areas.
The NDA is based on data from a pair of phase 3 randomized, double-blind 8-week studies known as DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 (Trials of PDE4 Inhibition with Roflumilast for the Management of Plaque Psoriasis” One and Two) and a long-term phase 2b open-label study.
DERMIS 1 and DERMIS 2 were identical multinational, multicenter studies designed to assess the safety and efficacy of 0.3% roflumilast cream. In the studies, roflumilast met its primary endpoint and patients treated with it demonstrated an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) success rate of 42.4% compared with 6.1% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), and 37.5% compared with 6.9% for the vehicle control (P < .0001), in the DERMIS 1 and 2 trials, respectively, according to Arcutis.
In the phase 2b study, the treatment effect lasted for 52-64 weeks. Roflumilast was well tolerated across the three studies.
Overall, the most common adverse events reported in the studies were diarrhea (3%), headache (2%), insomnia (1%), nausea (1%), upper respiratory tract infections (1%), and urinary tract infections (1%).
Roflumilast also showed statistically significant improvement compared to a vehicle on secondary endpoints including Intertriginous IGA (I-IGA) Success, Psoriasis Area Severity Index-75 (PASI-75), reductions in itch as measured by the Worst Itch-Numerical Rating Scale (WI-NRS), and patient perceptions of symptoms based on the Psoriasis Symptoms Diary (PSD).
The FDA has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) target action date of July 29, 2022, according to the manufacturer’s statement. An oral formulation of roflumilast was approved by the FDA in 2011, for reducing the risk of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in patients with severe COPD.
Spesolimab speeds lesion clearance in generalized pustular psoriasis
GPP is a life-threatening skin condition involving the widespread eruption of sterile pustules, with a clinical course that “can be relapsing with recurrent flares or persistent with intermittent flares,” Hervé Bachelez, MD, of the Université de Paris and coauthors wrote. GPP patients are often hospitalized, and mortality ranges from 2% to 16% from causes that include sepsis and cardiorespiratory failure.
“The role of the interleukin-36 pathway in GPP is supported by the finding of loss-of-function mutations in the interleukin-36 receptor antagonist gene (IL36RN) and associated genes (CARD14, AP1S3, SERPINA3, and MPO) and by the overexpression of interleukin-36 cytokines in GPP skin lesions,” therefore, IL-36 is a potential treatment target to manage flares, they explained.
In the multicenter, double-blind trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 35 adults with GPP flares to a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab and 18 to placebo. Patients in both groups could receive an open-label dose of spesolimab after day 8; all patients were followed for 12 weeks.
The primary study endpoint was the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) pustulation subscore of 0 at 1 week after treatment. The GPPGA ranges from 0 (no visible pustules) to 4 (severe pustules). At baseline, 46% spesolimab patients and 39% placebo patients had a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 3, and 37% and 33%, respectively, had a pustulation subscore of 4.
After 1 week, 54% of the spesolimab patients had no visible pustules, compared with 6% of placebo patients; the difference was statistically significant (P < .001). The main secondary endpoint was a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the GPPGA total score after 1 week. Significantly more spesolimab patients had GPPGA total scores of 0 or 1, compared with placebo patients (43% vs. 11%, respectively; P = .02).
Overall, 6 of 35 spesolimab patients (17%) and 6% of those in the placebo groups developed infections during the first week, and 24 of 51 patients (47%) who had received spesolimab at any point during the study developed infections by week 12. Infections included urinary tract infections (three cases), influenza (three), otitis externa (two), folliculitis (two), upper respiratory tract infection (two), and pustule (two).
In the first week, 6% of spesolimab patients and none of the placebo patients reported serious adverse events; at week 12, 12% of patients who had received at least one spesolimab dose reported a serious adverse event. In addition, antidrug antibodies were identified in 23 (46%) of the 50 patients who received at least one dose of spesolimab.
“Symptoms that were observed in two patients who received spesolimab were reported as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS),” the authors noted. One patient had a RegiSCAR (European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions) score and the other had a score of 3; a score below 2 indicates no DRESS, and a score of 2 or 3 indicates “possible DRESS,” they added.
“Because 15 of the 18 patients who were assigned to the placebo group received open-label spesolimab, the effect of spesolimab as compared with that of placebo could not be determined after week 1,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short randomization period and small study population, the researchers noted. However, the effect sizes for both the primary and secondary endpoints were large, which strengthened the results.
The results support data from previous studies suggesting a role for IL-36 in the pathogenesis of GPP, and support the need for longer and larger studies of the safety and effectiveness of spesolimab for GPP patients, they concluded.
No FDA-approved therapy
“GPP is a very rare but devastating life-threatening disease that presents with the sudden onset of pustules throughout the skin,” Joel Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the psoriasis and phototherapy center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Without rapid treatment, GPP can result in death. Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved treatments for this orphan disease.”
Dr. Gelfand said he was surprised by the degree of efficacy and the speed of the patient response to spesolimab, compared with placebo, which he described as “truly remarkable.” Based on the current study results, “spesolimab offers a tremendous step forward for our patients,” he added.
Looking ahead, Dr. Gelfand noted that “longer-term studies with a comparator, such as a biologic that targets IL-17, would be helpful to more fully understand the safety, efficacy, and role that spesolimab will have in real-world patients.”
On Dec. 15, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that the FDA had granted priority review for spesolimab for treating GPP flares.
The study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim. Lead author Dr. Bachelez had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several authors are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gelfand is a consultant for the study sponsor Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim to his institution to support an investigator-initiated study. He also disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving research grants from other manufacturers of psoriasis products.
GPP is a life-threatening skin condition involving the widespread eruption of sterile pustules, with a clinical course that “can be relapsing with recurrent flares or persistent with intermittent flares,” Hervé Bachelez, MD, of the Université de Paris and coauthors wrote. GPP patients are often hospitalized, and mortality ranges from 2% to 16% from causes that include sepsis and cardiorespiratory failure.
“The role of the interleukin-36 pathway in GPP is supported by the finding of loss-of-function mutations in the interleukin-36 receptor antagonist gene (IL36RN) and associated genes (CARD14, AP1S3, SERPINA3, and MPO) and by the overexpression of interleukin-36 cytokines in GPP skin lesions,” therefore, IL-36 is a potential treatment target to manage flares, they explained.
In the multicenter, double-blind trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 35 adults with GPP flares to a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab and 18 to placebo. Patients in both groups could receive an open-label dose of spesolimab after day 8; all patients were followed for 12 weeks.
The primary study endpoint was the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) pustulation subscore of 0 at 1 week after treatment. The GPPGA ranges from 0 (no visible pustules) to 4 (severe pustules). At baseline, 46% spesolimab patients and 39% placebo patients had a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 3, and 37% and 33%, respectively, had a pustulation subscore of 4.
After 1 week, 54% of the spesolimab patients had no visible pustules, compared with 6% of placebo patients; the difference was statistically significant (P < .001). The main secondary endpoint was a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the GPPGA total score after 1 week. Significantly more spesolimab patients had GPPGA total scores of 0 or 1, compared with placebo patients (43% vs. 11%, respectively; P = .02).
Overall, 6 of 35 spesolimab patients (17%) and 6% of those in the placebo groups developed infections during the first week, and 24 of 51 patients (47%) who had received spesolimab at any point during the study developed infections by week 12. Infections included urinary tract infections (three cases), influenza (three), otitis externa (two), folliculitis (two), upper respiratory tract infection (two), and pustule (two).
In the first week, 6% of spesolimab patients and none of the placebo patients reported serious adverse events; at week 12, 12% of patients who had received at least one spesolimab dose reported a serious adverse event. In addition, antidrug antibodies were identified in 23 (46%) of the 50 patients who received at least one dose of spesolimab.
“Symptoms that were observed in two patients who received spesolimab were reported as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS),” the authors noted. One patient had a RegiSCAR (European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions) score and the other had a score of 3; a score below 2 indicates no DRESS, and a score of 2 or 3 indicates “possible DRESS,” they added.
“Because 15 of the 18 patients who were assigned to the placebo group received open-label spesolimab, the effect of spesolimab as compared with that of placebo could not be determined after week 1,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short randomization period and small study population, the researchers noted. However, the effect sizes for both the primary and secondary endpoints were large, which strengthened the results.
The results support data from previous studies suggesting a role for IL-36 in the pathogenesis of GPP, and support the need for longer and larger studies of the safety and effectiveness of spesolimab for GPP patients, they concluded.
No FDA-approved therapy
“GPP is a very rare but devastating life-threatening disease that presents with the sudden onset of pustules throughout the skin,” Joel Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the psoriasis and phototherapy center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Without rapid treatment, GPP can result in death. Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved treatments for this orphan disease.”
Dr. Gelfand said he was surprised by the degree of efficacy and the speed of the patient response to spesolimab, compared with placebo, which he described as “truly remarkable.” Based on the current study results, “spesolimab offers a tremendous step forward for our patients,” he added.
Looking ahead, Dr. Gelfand noted that “longer-term studies with a comparator, such as a biologic that targets IL-17, would be helpful to more fully understand the safety, efficacy, and role that spesolimab will have in real-world patients.”
On Dec. 15, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that the FDA had granted priority review for spesolimab for treating GPP flares.
The study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim. Lead author Dr. Bachelez had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several authors are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gelfand is a consultant for the study sponsor Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim to his institution to support an investigator-initiated study. He also disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving research grants from other manufacturers of psoriasis products.
GPP is a life-threatening skin condition involving the widespread eruption of sterile pustules, with a clinical course that “can be relapsing with recurrent flares or persistent with intermittent flares,” Hervé Bachelez, MD, of the Université de Paris and coauthors wrote. GPP patients are often hospitalized, and mortality ranges from 2% to 16% from causes that include sepsis and cardiorespiratory failure.
“The role of the interleukin-36 pathway in GPP is supported by the finding of loss-of-function mutations in the interleukin-36 receptor antagonist gene (IL36RN) and associated genes (CARD14, AP1S3, SERPINA3, and MPO) and by the overexpression of interleukin-36 cytokines in GPP skin lesions,” therefore, IL-36 is a potential treatment target to manage flares, they explained.
In the multicenter, double-blind trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers randomized 35 adults with GPP flares to a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab and 18 to placebo. Patients in both groups could receive an open-label dose of spesolimab after day 8; all patients were followed for 12 weeks.
The primary study endpoint was the Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) pustulation subscore of 0 at 1 week after treatment. The GPPGA ranges from 0 (no visible pustules) to 4 (severe pustules). At baseline, 46% spesolimab patients and 39% placebo patients had a GPPGA pustulation subscore of 3, and 37% and 33%, respectively, had a pustulation subscore of 4.
After 1 week, 54% of the spesolimab patients had no visible pustules, compared with 6% of placebo patients; the difference was statistically significant (P < .001). The main secondary endpoint was a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the GPPGA total score after 1 week. Significantly more spesolimab patients had GPPGA total scores of 0 or 1, compared with placebo patients (43% vs. 11%, respectively; P = .02).
Overall, 6 of 35 spesolimab patients (17%) and 6% of those in the placebo groups developed infections during the first week, and 24 of 51 patients (47%) who had received spesolimab at any point during the study developed infections by week 12. Infections included urinary tract infections (three cases), influenza (three), otitis externa (two), folliculitis (two), upper respiratory tract infection (two), and pustule (two).
In the first week, 6% of spesolimab patients and none of the placebo patients reported serious adverse events; at week 12, 12% of patients who had received at least one spesolimab dose reported a serious adverse event. In addition, antidrug antibodies were identified in 23 (46%) of the 50 patients who received at least one dose of spesolimab.
“Symptoms that were observed in two patients who received spesolimab were reported as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS),” the authors noted. One patient had a RegiSCAR (European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions) score and the other had a score of 3; a score below 2 indicates no DRESS, and a score of 2 or 3 indicates “possible DRESS,” they added.
“Because 15 of the 18 patients who were assigned to the placebo group received open-label spesolimab, the effect of spesolimab as compared with that of placebo could not be determined after week 1,” the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the short randomization period and small study population, the researchers noted. However, the effect sizes for both the primary and secondary endpoints were large, which strengthened the results.
The results support data from previous studies suggesting a role for IL-36 in the pathogenesis of GPP, and support the need for longer and larger studies of the safety and effectiveness of spesolimab for GPP patients, they concluded.
No FDA-approved therapy
“GPP is a very rare but devastating life-threatening disease that presents with the sudden onset of pustules throughout the skin,” Joel Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the psoriasis and phototherapy center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “Without rapid treatment, GPP can result in death. Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved treatments for this orphan disease.”
Dr. Gelfand said he was surprised by the degree of efficacy and the speed of the patient response to spesolimab, compared with placebo, which he described as “truly remarkable.” Based on the current study results, “spesolimab offers a tremendous step forward for our patients,” he added.
Looking ahead, Dr. Gelfand noted that “longer-term studies with a comparator, such as a biologic that targets IL-17, would be helpful to more fully understand the safety, efficacy, and role that spesolimab will have in real-world patients.”
On Dec. 15, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that the FDA had granted priority review for spesolimab for treating GPP flares.
The study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim. Lead author Dr. Bachelez had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several authors are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gelfand is a consultant for the study sponsor Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim to his institution to support an investigator-initiated study. He also disclosed serving as a consultant and receiving research grants from other manufacturers of psoriasis products.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
New option for flares in pustular psoriasis
according to a statement from manufacturer Boehringer Ingelheim. The FDA also granted Priority Review to spesolimab. Priority Review is a designation granted to medications that would offer significant improvement over the currently available treatments.
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), though rare, is a potentially life-threatening condition that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. Throughout the course of the disease, which is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin, patients may experience persistent disease with intermittent flares or relapsing disease with recurrent flares. The neutrophil accumulation results in the eruption of sterile, yet painful pustules across all parts of the body.
“While the severity of GPP flares can vary, if left untreated they can be life threatening due to complications such as sepsis and multisystem organ failure,” and have a significant impact on quality of life, according to the company statement.
The FDA also has granted spesolimab an Orphan Drug Designation for the treatment of GPP, and a Breakthrough Therapy Designation for the treatment of GPP flares in adults.
A marketing authorization application for spesolimab for the treatment of GPP was accepted for evaluation by the European Medicines Agency in October 2021, according to a company press release issued at that time.
A protocol for a phase 2 study of spesolimab versus placebo for treating acute flares in GPP patients was published in October in BMJ Open, after a phase 1 proof-of-concept study published in 2019 showed the potential of an IL-36 receptor antagonist to improve disease scores in adults with GPP.
More information is available on the Boehringer Ingelheim website.
according to a statement from manufacturer Boehringer Ingelheim. The FDA also granted Priority Review to spesolimab. Priority Review is a designation granted to medications that would offer significant improvement over the currently available treatments.
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), though rare, is a potentially life-threatening condition that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. Throughout the course of the disease, which is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin, patients may experience persistent disease with intermittent flares or relapsing disease with recurrent flares. The neutrophil accumulation results in the eruption of sterile, yet painful pustules across all parts of the body.
“While the severity of GPP flares can vary, if left untreated they can be life threatening due to complications such as sepsis and multisystem organ failure,” and have a significant impact on quality of life, according to the company statement.
The FDA also has granted spesolimab an Orphan Drug Designation for the treatment of GPP, and a Breakthrough Therapy Designation for the treatment of GPP flares in adults.
A marketing authorization application for spesolimab for the treatment of GPP was accepted for evaluation by the European Medicines Agency in October 2021, according to a company press release issued at that time.
A protocol for a phase 2 study of spesolimab versus placebo for treating acute flares in GPP patients was published in October in BMJ Open, after a phase 1 proof-of-concept study published in 2019 showed the potential of an IL-36 receptor antagonist to improve disease scores in adults with GPP.
More information is available on the Boehringer Ingelheim website.
according to a statement from manufacturer Boehringer Ingelheim. The FDA also granted Priority Review to spesolimab. Priority Review is a designation granted to medications that would offer significant improvement over the currently available treatments.
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), though rare, is a potentially life-threatening condition that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. Throughout the course of the disease, which is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin, patients may experience persistent disease with intermittent flares or relapsing disease with recurrent flares. The neutrophil accumulation results in the eruption of sterile, yet painful pustules across all parts of the body.
“While the severity of GPP flares can vary, if left untreated they can be life threatening due to complications such as sepsis and multisystem organ failure,” and have a significant impact on quality of life, according to the company statement.
The FDA also has granted spesolimab an Orphan Drug Designation for the treatment of GPP, and a Breakthrough Therapy Designation for the treatment of GPP flares in adults.
A marketing authorization application for spesolimab for the treatment of GPP was accepted for evaluation by the European Medicines Agency in October 2021, according to a company press release issued at that time.
A protocol for a phase 2 study of spesolimab versus placebo for treating acute flares in GPP patients was published in October in BMJ Open, after a phase 1 proof-of-concept study published in 2019 showed the potential of an IL-36 receptor antagonist to improve disease scores in adults with GPP.
More information is available on the Boehringer Ingelheim website.
Guselkumab’s efficacy, safety confirmed in patients with psoriatic arthritis and prior TNFi exposure
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Psoriasis December 2021
A retrospective observational study of nearly 1200 prior biologic-experienced adult patients with psoriasis now receiving either secukinumab (n=780) or ixekizumab (n=411), both of which inhibit IL-17A, examined drug persistence after 18 months. Ixekizumab was associated with significantly higher rates of high treatment adherence (42% vs 35%; P = .019) and persistence (44.9% vs 36.9%; P = .007) and lower discontinuation (48.4% vs 56.0%; P = .018) and switching (26.6% vs 34.0%; P = .009) rates than secukinumab. Both drugs are dosed monthly after an initial loading dose (Blauvelt A et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb).
With several biologic options available, patients may be switched from one biologic to another if they are not having an adequate response. Separate studies have shown that patients with an inadequate response to ustekinumab are likely to have a better response when switched to brodalumab or guselkumab, although this does not tell us if one is more likely to be effective than the other. In a recent matching-adjusted indirect comparison study using data for patients with psoriasis who responded inadequately to ustekinumab and switched to receive brodalumab (n=121) or guselkumab (n=135) the authors found that brodalumab was associated with greater improvements than guselkumab in inadequate responders to ustekinumab with a PASI 100 rate at week 36 of 40.3% for brodalumab vs 20.0% for guselkumab; P < 0.001. (Hampton P et al. Psoriasis (Auckl).
While biologics have revolutionized the treatment of psoriasis, not all patients with extensive disease desire or are appropriate for a systemic therapy. Topical steroids, the most commonly used topical psoriasis therapy, still carry some risk of systemic absorption and are associate with cutaneous side effects such as atrophy with prolonged use. Tarpinarof 1% cream is a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulating agent that has been shown in phase 3 studies to be an effective treatment for psoriasis when applied once a day. A recent open label study of 21 adult patients with extensive plaque psoriasis (20% or more body surface area (BSA) involvement, mean baseline BSA 27.2%) who applied tapinarof cream 1% QD daily showed that 94.7% of patients had a decrease in their PASI score (mean PASI decrease of 59.6%). Despite the large BSA being treated, tapinarof plasma concentration were low and remained below the quantification level in the majority (67.9%) of samples tested. There were also no concerning EKG changes such as QT prolongation. Folliculitis and headache were the most common adverse events (each reported by 4 patients) (Jett JE et al. Am J Clin Dermatol).
These studies all provide valuable data in helping us to make the best treatment decisions for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
A retrospective observational study of nearly 1200 prior biologic-experienced adult patients with psoriasis now receiving either secukinumab (n=780) or ixekizumab (n=411), both of which inhibit IL-17A, examined drug persistence after 18 months. Ixekizumab was associated with significantly higher rates of high treatment adherence (42% vs 35%; P = .019) and persistence (44.9% vs 36.9%; P = .007) and lower discontinuation (48.4% vs 56.0%; P = .018) and switching (26.6% vs 34.0%; P = .009) rates than secukinumab. Both drugs are dosed monthly after an initial loading dose (Blauvelt A et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb).
With several biologic options available, patients may be switched from one biologic to another if they are not having an adequate response. Separate studies have shown that patients with an inadequate response to ustekinumab are likely to have a better response when switched to brodalumab or guselkumab, although this does not tell us if one is more likely to be effective than the other. In a recent matching-adjusted indirect comparison study using data for patients with psoriasis who responded inadequately to ustekinumab and switched to receive brodalumab (n=121) or guselkumab (n=135) the authors found that brodalumab was associated with greater improvements than guselkumab in inadequate responders to ustekinumab with a PASI 100 rate at week 36 of 40.3% for brodalumab vs 20.0% for guselkumab; P < 0.001. (Hampton P et al. Psoriasis (Auckl).
While biologics have revolutionized the treatment of psoriasis, not all patients with extensive disease desire or are appropriate for a systemic therapy. Topical steroids, the most commonly used topical psoriasis therapy, still carry some risk of systemic absorption and are associate with cutaneous side effects such as atrophy with prolonged use. Tarpinarof 1% cream is a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulating agent that has been shown in phase 3 studies to be an effective treatment for psoriasis when applied once a day. A recent open label study of 21 adult patients with extensive plaque psoriasis (20% or more body surface area (BSA) involvement, mean baseline BSA 27.2%) who applied tapinarof cream 1% QD daily showed that 94.7% of patients had a decrease in their PASI score (mean PASI decrease of 59.6%). Despite the large BSA being treated, tapinarof plasma concentration were low and remained below the quantification level in the majority (67.9%) of samples tested. There were also no concerning EKG changes such as QT prolongation. Folliculitis and headache were the most common adverse events (each reported by 4 patients) (Jett JE et al. Am J Clin Dermatol).
These studies all provide valuable data in helping us to make the best treatment decisions for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
A retrospective observational study of nearly 1200 prior biologic-experienced adult patients with psoriasis now receiving either secukinumab (n=780) or ixekizumab (n=411), both of which inhibit IL-17A, examined drug persistence after 18 months. Ixekizumab was associated with significantly higher rates of high treatment adherence (42% vs 35%; P = .019) and persistence (44.9% vs 36.9%; P = .007) and lower discontinuation (48.4% vs 56.0%; P = .018) and switching (26.6% vs 34.0%; P = .009) rates than secukinumab. Both drugs are dosed monthly after an initial loading dose (Blauvelt A et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb).
With several biologic options available, patients may be switched from one biologic to another if they are not having an adequate response. Separate studies have shown that patients with an inadequate response to ustekinumab are likely to have a better response when switched to brodalumab or guselkumab, although this does not tell us if one is more likely to be effective than the other. In a recent matching-adjusted indirect comparison study using data for patients with psoriasis who responded inadequately to ustekinumab and switched to receive brodalumab (n=121) or guselkumab (n=135) the authors found that brodalumab was associated with greater improvements than guselkumab in inadequate responders to ustekinumab with a PASI 100 rate at week 36 of 40.3% for brodalumab vs 20.0% for guselkumab; P < 0.001. (Hampton P et al. Psoriasis (Auckl).
While biologics have revolutionized the treatment of psoriasis, not all patients with extensive disease desire or are appropriate for a systemic therapy. Topical steroids, the most commonly used topical psoriasis therapy, still carry some risk of systemic absorption and are associate with cutaneous side effects such as atrophy with prolonged use. Tarpinarof 1% cream is a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulating agent that has been shown in phase 3 studies to be an effective treatment for psoriasis when applied once a day. A recent open label study of 21 adult patients with extensive plaque psoriasis (20% or more body surface area (BSA) involvement, mean baseline BSA 27.2%) who applied tapinarof cream 1% QD daily showed that 94.7% of patients had a decrease in their PASI score (mean PASI decrease of 59.6%). Despite the large BSA being treated, tapinarof plasma concentration were low and remained below the quantification level in the majority (67.9%) of samples tested. There were also no concerning EKG changes such as QT prolongation. Folliculitis and headache were the most common adverse events (each reported by 4 patients) (Jett JE et al. Am J Clin Dermatol).
These studies all provide valuable data in helping us to make the best treatment decisions for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.