User login
Part 1: The ABCs of managing COPD exacerbations

Do you know the ABCs of medication management for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations?
Understanding how to effectively use the ABCs – antibiotics, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids – in COPD exacerbations can reduce morbidity and improve patient outcomes.
In the first episode of a two-part interview, Robert A. Wise, MD, outlines the evidence and best practices for treating patients with antibiotics and bronchodilators.
Dr. Wise is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is the coauthor of a review of medication regimens to manage COPD exacerbations (Respir Care. 2018 Jun;63[6]:773-82).

Do you know the ABCs of medication management for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations?
Understanding how to effectively use the ABCs – antibiotics, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids – in COPD exacerbations can reduce morbidity and improve patient outcomes.
In the first episode of a two-part interview, Robert A. Wise, MD, outlines the evidence and best practices for treating patients with antibiotics and bronchodilators.
Dr. Wise is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is the coauthor of a review of medication regimens to manage COPD exacerbations (Respir Care. 2018 Jun;63[6]:773-82).

Do you know the ABCs of medication management for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations?
Understanding how to effectively use the ABCs – antibiotics, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids – in COPD exacerbations can reduce morbidity and improve patient outcomes.
In the first episode of a two-part interview, Robert A. Wise, MD, outlines the evidence and best practices for treating patients with antibiotics and bronchodilators.
Dr. Wise is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is the coauthor of a review of medication regimens to manage COPD exacerbations (Respir Care. 2018 Jun;63[6]:773-82).
FDA noncommittal on e-cigarette action
on when the agency would act and what actions it was planning on taking.
“I was actually shocked that, in a hearing that is focused in part on the youth vaping epidemic [that] your testimony, both written and oral here, made no mention of the administration’s Sept. 11 announcement that it intended to clear the market of all unauthorized non–tobacco-flavored vaping products,” said Patty Murray (D-Wash.), ranking member of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, during a Nov. 13 hearing to Mitchell Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products. “Why is that not included in your testimony?”
Director Zeller would only offer a vague response, testifying that the agency is “committed to doing everything that we can to prevent kids from using any tobacco product, including e-cigarettes, and that we are continuing to develop a policy approach that aligns with that concern.”
When Sen. Murray pressed further, Director Zeller deflected: “I think that any questions that the committee has about the announcement that the White House and anything related to what remains a deliberative process on policy is best referred to the White House itself.”
He would not even offer any perspective on when the FDA might take actual regulatory action when asked about it by Sen. Murray.
“I can’t give you a specific timeline, Senator, other than to say that the deliberative process continues,” Director Zeller responded, telling her that “I really would refer you and the committee to the White House to ask specific questions about where we are.”
The hearing, called to examine the response to lung illnesses and rising youth e-cigarette usage, shed no new light on the issue. And while Director Zeller outlined the numerous educational campaigns being aimed at convincing youth to not use e-cigarettes, Committee Chairman Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.) questioned whether the FDA was doing an adequate job.
The FDA, from late 2017 to the end of 2020, “will wind up investing about $150 million in a massive, multimedia public education campaign to get the word out to kids” on the dangers of vaping, Director Zeller said, adding that the agency is “aggressively enforcing” youth access restrictions in targeting sellers of e-cigarette products to minors.
“Well, obviously we are not making much progress with youth use ... if one in four of American high schoolers, according to your statistics, are using e-cigarettes,” Sen. Alexander said.
While most on the committee were focused on the rising numbers of youth vaping and e-cigarette usage, Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) cautioned that any regulatory action, particularly a ban on all flavored e-cigarette products, would adversely affect adults, particularly those who are turning to e-cigarettes as a smoking cessation tool.
His solution, noting that it is already illegal for kids to be purchasing vaping and e-cigarette products, was to increase the penalties for those found selling to minors, adding that “most adults are using the flavors as well” and it could lead them back to combustible tobacco products if they are prevented from accessing flavored e-cigarettes.
on when the agency would act and what actions it was planning on taking.
“I was actually shocked that, in a hearing that is focused in part on the youth vaping epidemic [that] your testimony, both written and oral here, made no mention of the administration’s Sept. 11 announcement that it intended to clear the market of all unauthorized non–tobacco-flavored vaping products,” said Patty Murray (D-Wash.), ranking member of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, during a Nov. 13 hearing to Mitchell Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products. “Why is that not included in your testimony?”
Director Zeller would only offer a vague response, testifying that the agency is “committed to doing everything that we can to prevent kids from using any tobacco product, including e-cigarettes, and that we are continuing to develop a policy approach that aligns with that concern.”
When Sen. Murray pressed further, Director Zeller deflected: “I think that any questions that the committee has about the announcement that the White House and anything related to what remains a deliberative process on policy is best referred to the White House itself.”
He would not even offer any perspective on when the FDA might take actual regulatory action when asked about it by Sen. Murray.
“I can’t give you a specific timeline, Senator, other than to say that the deliberative process continues,” Director Zeller responded, telling her that “I really would refer you and the committee to the White House to ask specific questions about where we are.”
The hearing, called to examine the response to lung illnesses and rising youth e-cigarette usage, shed no new light on the issue. And while Director Zeller outlined the numerous educational campaigns being aimed at convincing youth to not use e-cigarettes, Committee Chairman Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.) questioned whether the FDA was doing an adequate job.
The FDA, from late 2017 to the end of 2020, “will wind up investing about $150 million in a massive, multimedia public education campaign to get the word out to kids” on the dangers of vaping, Director Zeller said, adding that the agency is “aggressively enforcing” youth access restrictions in targeting sellers of e-cigarette products to minors.
“Well, obviously we are not making much progress with youth use ... if one in four of American high schoolers, according to your statistics, are using e-cigarettes,” Sen. Alexander said.
While most on the committee were focused on the rising numbers of youth vaping and e-cigarette usage, Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) cautioned that any regulatory action, particularly a ban on all flavored e-cigarette products, would adversely affect adults, particularly those who are turning to e-cigarettes as a smoking cessation tool.
His solution, noting that it is already illegal for kids to be purchasing vaping and e-cigarette products, was to increase the penalties for those found selling to minors, adding that “most adults are using the flavors as well” and it could lead them back to combustible tobacco products if they are prevented from accessing flavored e-cigarettes.
on when the agency would act and what actions it was planning on taking.
“I was actually shocked that, in a hearing that is focused in part on the youth vaping epidemic [that] your testimony, both written and oral here, made no mention of the administration’s Sept. 11 announcement that it intended to clear the market of all unauthorized non–tobacco-flavored vaping products,” said Patty Murray (D-Wash.), ranking member of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, during a Nov. 13 hearing to Mitchell Zeller, director of the FDA’s Center for Tobacco Products. “Why is that not included in your testimony?”
Director Zeller would only offer a vague response, testifying that the agency is “committed to doing everything that we can to prevent kids from using any tobacco product, including e-cigarettes, and that we are continuing to develop a policy approach that aligns with that concern.”
When Sen. Murray pressed further, Director Zeller deflected: “I think that any questions that the committee has about the announcement that the White House and anything related to what remains a deliberative process on policy is best referred to the White House itself.”
He would not even offer any perspective on when the FDA might take actual regulatory action when asked about it by Sen. Murray.
“I can’t give you a specific timeline, Senator, other than to say that the deliberative process continues,” Director Zeller responded, telling her that “I really would refer you and the committee to the White House to ask specific questions about where we are.”
The hearing, called to examine the response to lung illnesses and rising youth e-cigarette usage, shed no new light on the issue. And while Director Zeller outlined the numerous educational campaigns being aimed at convincing youth to not use e-cigarettes, Committee Chairman Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.) questioned whether the FDA was doing an adequate job.
The FDA, from late 2017 to the end of 2020, “will wind up investing about $150 million in a massive, multimedia public education campaign to get the word out to kids” on the dangers of vaping, Director Zeller said, adding that the agency is “aggressively enforcing” youth access restrictions in targeting sellers of e-cigarette products to minors.
“Well, obviously we are not making much progress with youth use ... if one in four of American high schoolers, according to your statistics, are using e-cigarettes,” Sen. Alexander said.
While most on the committee were focused on the rising numbers of youth vaping and e-cigarette usage, Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) cautioned that any regulatory action, particularly a ban on all flavored e-cigarette products, would adversely affect adults, particularly those who are turning to e-cigarettes as a smoking cessation tool.
His solution, noting that it is already illegal for kids to be purchasing vaping and e-cigarette products, was to increase the penalties for those found selling to minors, adding that “most adults are using the flavors as well” and it could lead them back to combustible tobacco products if they are prevented from accessing flavored e-cigarettes.
REPORTING FROM A SENATE HELP COMMITTEE HEARING
Vaping-linked lung injury: 2,172 cases, 42 deaths
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
REPORTING FROM CDC
Transfusion-related lung injury is on the rise in elderly patients
SAN ANTONIO – Although there has been a general decline in transfusion-related anaphylaxis and acute infections over time among hospitalized older adults in the United States, incidence rates for both transfusion-related acute lung injury and transfusion-associated circulatory overload have risen over the last decade, according to researchers from the Food and Drug Administration.
Mikhail Menis, PharmD, an epidemiologist at the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) and colleagues queried large Medicare databases to assess trends in transfusion-related adverse events among adults aged 65 years and older.
The investigators saw “substantially higher risk of all outcomes among immunocompromised beneficiaries, which could be related to higher blood use of all blood components, especially platelets, underlying conditions such as malignancies, and treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, which need further investigation,” Dr. Menis said at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
He reported data from a series of studies on four categories of transfusion-related events that may be life-threatening or fatal: transfusion-related anaphylaxis (TRA), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), and acute infection following transfusion (AIFT).
For each type of event, the researchers looked at overall incidence and the incidence by immune status, calendar year, blood components transfused, number of units transfused, age, sex, and race.
Anaphylaxis (TRA)
TRA may be caused by preformed immunoglobin E (IgE) antibodies to proteins in the plasma in transfused blood products or by preformed IgA antibodies in patients who are likely IgA deficient, Dr. Menis said.
The overall incidence of TRA among 8,833,817 inpatient transfusions stays for elderly beneficiaries from 2012 through 2018 was 7.1 per 100,000 stays. The rate was higher for immunocompromised patients, at 9.6, than it was among nonimmunocompromised patients, at 6.5.
The rates varied by every subgroup measured except immune status. Annual rates showed a downward trend, from 8.7 per 100,000 in 2012, to 5.1 in 2017 and 6.4 in 2018. The decline in occurrence may be caused by a decline in inpatient blood utilization during the study period, particularly among immunocompromised patients.
TRA rates increased with five or more units transfused. The risk was significantly reduced in the oldest group of patients versus the youngest (P less than .001), which supports the immune-based mechanism of action of anaphylaxis, Dr. Menis said.
They also found that TRA rates were substantially higher among patients who had received platelet and/or plasma transfusions, compared with patients who received only red blood cells (RBCs).
Additionally, risk for TRA was significantly higher among men than it was among women (9.3 vs. 5.4) and among white versus nonwhite patients (7.8 vs. 3.8).
The evidence suggested TRA cases are likely to be severe in this population, with inpatient mortality of 7.1%, and hospital stays of 7 days or longer in about 58% of cases, indicating the importance of TRA prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The investigators plan to perform multivariate regression analyses to assess potential risk factors, including underlying comorbidities and health histories for TRA occurrence for both the overall population and by immune status.
Acute lung injury (TRALI)
TRALI is a rare but serious adverse event, a clinical syndrome with onset within 6 hours of transfusion that presents as acute hypoxemia, respiratory distress, and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Among 17,771,193 total inpatient transfusion stays, the overall incidence of TRALI was 33.2 per 100,000. The rate was 55.9 for immunocompromised patients versus 28.4 for nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio was 2.0 (P less than .001).
The difference by immune status may be caused by higher blood utilizations with more units transfused per stay among immunocompromised patients, a higher incidence of prior transfusions among these patients, higher use of irradiated blood components that may lead to accumulation of proinflammatory mediators in blood products during storage, or underlying comorbidities.
The overall rate increased from 14.3 in 2007 to 56.4 in 2018. The rates increased proportionally among both immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients.
As with TRA, the incidence of TRALI was higher in patients with five or more units transfused, while the incidence declined with age, likely caused by declining blood use and age-related changes in neutrophil function, Dr. Menis said.
TRALI rates were slightly higher among men than among women, as well as higher among white patients than among nonwhite patients.
Overall, TRALI rates were higher for patients who received platelets either alone or in combination with RBCs and/or plasma. The highest rates were among patients who received RBCs, plasma and platelets.
Dr. Menis called for studies to determine what effects the processing and storage of blood components may have on TRALI occurrence; he and his colleagues also are planning regression analyses to assess potential risk factors for this complication.
Circulatory overload (TACO)
TACO is one of the leading reported causes of transfusion-related fatalities in the U.S., with onset usually occurring within 6 hours of transfusion, presenting as acute respiratory distress with dyspnea, orthopnea, increased blood pressure, and cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
The overall incidence of TACO among hospitalized patients aged 65 years and older from 2011 through 2018 was 86.3 per 100,000 stays. The incidences were 128.3 in immunocompromised and 76.0 in nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio for TACO in immunocompromised versus nonimmunocompromised patients was 1.70 (P less than .001).
Overall incidence rates of TACO rose from 62 per 100,000 stays in 2011 to 119.8 in 2018. As with other adverse events, incident rates rose with the number of units transfused.
Rates of TACO were significantly higher among women than they were among men (94.6 vs. 75.9 per 100,000; P less than .001), which could be caused by the higher mean age of women and/or a lower tolerance for increased blood volume from transfusion.
The study results also suggested that TACO and TRALI may coexist, based on evidence that 3.5% of all TACO stays also had diagnostic codes for TRALI. The frequency of co-occurrence of these two adverse events also increased over time, which may be caused by improved awareness, Dr. Menis said.
Infections (AIFT)
Acute infections following transfusion can lead to prolonged hospitalizations, sepsis, septic shock, and death. Those most at risk include elderly and immunocompromised patients because of high utilization of blood products, comorbidities, and decreased immune function.
Among 8,833,817 stays, the overall rate per 100,000 stays was 2.1. The rate for immunocompromised patients was 5.4, compared with 1.2 for nonimmunocompromised patients, for a rate ratio of 4.4 (P less than .001).
The incidence rate declined significantly (P = .03) over the study period, with the 3 latest years having the lowest rates.
Rates increased substantially among immunocompromised patients by the number of units transfused, but remained relatively stable among nonimmunocompromised patients.
Infection rates declined with age, from 2.7 per 100,000 stays for patients aged 65-68 years to 1.2 per 100,000 for those aged 85 years and older.
As with other adverse events, AIFT rates were likely related to the blood components transfused, with substantially higher rates for stays during which platelets were transfused either alone or with RBCs, compared with RBCs alone. This could be caused by the room-temperature storage of platelets and higher number of platelets units transfused, compared with RBCs alone, especially among immunocompromised patients.
In all, 51.9% of AIFT cases also had sepsis noted in the medical record, indicating high severity and emphasizing the importance of AIFT prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The studies were funded by the FDA, and Dr. Menis is an FDA employee. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
SAN ANTONIO – Although there has been a general decline in transfusion-related anaphylaxis and acute infections over time among hospitalized older adults in the United States, incidence rates for both transfusion-related acute lung injury and transfusion-associated circulatory overload have risen over the last decade, according to researchers from the Food and Drug Administration.
Mikhail Menis, PharmD, an epidemiologist at the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) and colleagues queried large Medicare databases to assess trends in transfusion-related adverse events among adults aged 65 years and older.
The investigators saw “substantially higher risk of all outcomes among immunocompromised beneficiaries, which could be related to higher blood use of all blood components, especially platelets, underlying conditions such as malignancies, and treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, which need further investigation,” Dr. Menis said at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
He reported data from a series of studies on four categories of transfusion-related events that may be life-threatening or fatal: transfusion-related anaphylaxis (TRA), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), and acute infection following transfusion (AIFT).
For each type of event, the researchers looked at overall incidence and the incidence by immune status, calendar year, blood components transfused, number of units transfused, age, sex, and race.
Anaphylaxis (TRA)
TRA may be caused by preformed immunoglobin E (IgE) antibodies to proteins in the plasma in transfused blood products or by preformed IgA antibodies in patients who are likely IgA deficient, Dr. Menis said.
The overall incidence of TRA among 8,833,817 inpatient transfusions stays for elderly beneficiaries from 2012 through 2018 was 7.1 per 100,000 stays. The rate was higher for immunocompromised patients, at 9.6, than it was among nonimmunocompromised patients, at 6.5.
The rates varied by every subgroup measured except immune status. Annual rates showed a downward trend, from 8.7 per 100,000 in 2012, to 5.1 in 2017 and 6.4 in 2018. The decline in occurrence may be caused by a decline in inpatient blood utilization during the study period, particularly among immunocompromised patients.
TRA rates increased with five or more units transfused. The risk was significantly reduced in the oldest group of patients versus the youngest (P less than .001), which supports the immune-based mechanism of action of anaphylaxis, Dr. Menis said.
They also found that TRA rates were substantially higher among patients who had received platelet and/or plasma transfusions, compared with patients who received only red blood cells (RBCs).
Additionally, risk for TRA was significantly higher among men than it was among women (9.3 vs. 5.4) and among white versus nonwhite patients (7.8 vs. 3.8).
The evidence suggested TRA cases are likely to be severe in this population, with inpatient mortality of 7.1%, and hospital stays of 7 days or longer in about 58% of cases, indicating the importance of TRA prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The investigators plan to perform multivariate regression analyses to assess potential risk factors, including underlying comorbidities and health histories for TRA occurrence for both the overall population and by immune status.
Acute lung injury (TRALI)
TRALI is a rare but serious adverse event, a clinical syndrome with onset within 6 hours of transfusion that presents as acute hypoxemia, respiratory distress, and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Among 17,771,193 total inpatient transfusion stays, the overall incidence of TRALI was 33.2 per 100,000. The rate was 55.9 for immunocompromised patients versus 28.4 for nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio was 2.0 (P less than .001).
The difference by immune status may be caused by higher blood utilizations with more units transfused per stay among immunocompromised patients, a higher incidence of prior transfusions among these patients, higher use of irradiated blood components that may lead to accumulation of proinflammatory mediators in blood products during storage, or underlying comorbidities.
The overall rate increased from 14.3 in 2007 to 56.4 in 2018. The rates increased proportionally among both immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients.
As with TRA, the incidence of TRALI was higher in patients with five or more units transfused, while the incidence declined with age, likely caused by declining blood use and age-related changes in neutrophil function, Dr. Menis said.
TRALI rates were slightly higher among men than among women, as well as higher among white patients than among nonwhite patients.
Overall, TRALI rates were higher for patients who received platelets either alone or in combination with RBCs and/or plasma. The highest rates were among patients who received RBCs, plasma and platelets.
Dr. Menis called for studies to determine what effects the processing and storage of blood components may have on TRALI occurrence; he and his colleagues also are planning regression analyses to assess potential risk factors for this complication.
Circulatory overload (TACO)
TACO is one of the leading reported causes of transfusion-related fatalities in the U.S., with onset usually occurring within 6 hours of transfusion, presenting as acute respiratory distress with dyspnea, orthopnea, increased blood pressure, and cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
The overall incidence of TACO among hospitalized patients aged 65 years and older from 2011 through 2018 was 86.3 per 100,000 stays. The incidences were 128.3 in immunocompromised and 76.0 in nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio for TACO in immunocompromised versus nonimmunocompromised patients was 1.70 (P less than .001).
Overall incidence rates of TACO rose from 62 per 100,000 stays in 2011 to 119.8 in 2018. As with other adverse events, incident rates rose with the number of units transfused.
Rates of TACO were significantly higher among women than they were among men (94.6 vs. 75.9 per 100,000; P less than .001), which could be caused by the higher mean age of women and/or a lower tolerance for increased blood volume from transfusion.
The study results also suggested that TACO and TRALI may coexist, based on evidence that 3.5% of all TACO stays also had diagnostic codes for TRALI. The frequency of co-occurrence of these two adverse events also increased over time, which may be caused by improved awareness, Dr. Menis said.
Infections (AIFT)
Acute infections following transfusion can lead to prolonged hospitalizations, sepsis, septic shock, and death. Those most at risk include elderly and immunocompromised patients because of high utilization of blood products, comorbidities, and decreased immune function.
Among 8,833,817 stays, the overall rate per 100,000 stays was 2.1. The rate for immunocompromised patients was 5.4, compared with 1.2 for nonimmunocompromised patients, for a rate ratio of 4.4 (P less than .001).
The incidence rate declined significantly (P = .03) over the study period, with the 3 latest years having the lowest rates.
Rates increased substantially among immunocompromised patients by the number of units transfused, but remained relatively stable among nonimmunocompromised patients.
Infection rates declined with age, from 2.7 per 100,000 stays for patients aged 65-68 years to 1.2 per 100,000 for those aged 85 years and older.
As with other adverse events, AIFT rates were likely related to the blood components transfused, with substantially higher rates for stays during which platelets were transfused either alone or with RBCs, compared with RBCs alone. This could be caused by the room-temperature storage of platelets and higher number of platelets units transfused, compared with RBCs alone, especially among immunocompromised patients.
In all, 51.9% of AIFT cases also had sepsis noted in the medical record, indicating high severity and emphasizing the importance of AIFT prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The studies were funded by the FDA, and Dr. Menis is an FDA employee. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
SAN ANTONIO – Although there has been a general decline in transfusion-related anaphylaxis and acute infections over time among hospitalized older adults in the United States, incidence rates for both transfusion-related acute lung injury and transfusion-associated circulatory overload have risen over the last decade, according to researchers from the Food and Drug Administration.
Mikhail Menis, PharmD, an epidemiologist at the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) and colleagues queried large Medicare databases to assess trends in transfusion-related adverse events among adults aged 65 years and older.
The investigators saw “substantially higher risk of all outcomes among immunocompromised beneficiaries, which could be related to higher blood use of all blood components, especially platelets, underlying conditions such as malignancies, and treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, which need further investigation,” Dr. Menis said at the annual meeting of AABB, the group formerly known as the American Association of Blood Banks.
He reported data from a series of studies on four categories of transfusion-related events that may be life-threatening or fatal: transfusion-related anaphylaxis (TRA), transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), and acute infection following transfusion (AIFT).
For each type of event, the researchers looked at overall incidence and the incidence by immune status, calendar year, blood components transfused, number of units transfused, age, sex, and race.
Anaphylaxis (TRA)
TRA may be caused by preformed immunoglobin E (IgE) antibodies to proteins in the plasma in transfused blood products or by preformed IgA antibodies in patients who are likely IgA deficient, Dr. Menis said.
The overall incidence of TRA among 8,833,817 inpatient transfusions stays for elderly beneficiaries from 2012 through 2018 was 7.1 per 100,000 stays. The rate was higher for immunocompromised patients, at 9.6, than it was among nonimmunocompromised patients, at 6.5.
The rates varied by every subgroup measured except immune status. Annual rates showed a downward trend, from 8.7 per 100,000 in 2012, to 5.1 in 2017 and 6.4 in 2018. The decline in occurrence may be caused by a decline in inpatient blood utilization during the study period, particularly among immunocompromised patients.
TRA rates increased with five or more units transfused. The risk was significantly reduced in the oldest group of patients versus the youngest (P less than .001), which supports the immune-based mechanism of action of anaphylaxis, Dr. Menis said.
They also found that TRA rates were substantially higher among patients who had received platelet and/or plasma transfusions, compared with patients who received only red blood cells (RBCs).
Additionally, risk for TRA was significantly higher among men than it was among women (9.3 vs. 5.4) and among white versus nonwhite patients (7.8 vs. 3.8).
The evidence suggested TRA cases are likely to be severe in this population, with inpatient mortality of 7.1%, and hospital stays of 7 days or longer in about 58% of cases, indicating the importance of TRA prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The investigators plan to perform multivariate regression analyses to assess potential risk factors, including underlying comorbidities and health histories for TRA occurrence for both the overall population and by immune status.
Acute lung injury (TRALI)
TRALI is a rare but serious adverse event, a clinical syndrome with onset within 6 hours of transfusion that presents as acute hypoxemia, respiratory distress, and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Among 17,771,193 total inpatient transfusion stays, the overall incidence of TRALI was 33.2 per 100,000. The rate was 55.9 for immunocompromised patients versus 28.4 for nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio was 2.0 (P less than .001).
The difference by immune status may be caused by higher blood utilizations with more units transfused per stay among immunocompromised patients, a higher incidence of prior transfusions among these patients, higher use of irradiated blood components that may lead to accumulation of proinflammatory mediators in blood products during storage, or underlying comorbidities.
The overall rate increased from 14.3 in 2007 to 56.4 in 2018. The rates increased proportionally among both immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients.
As with TRA, the incidence of TRALI was higher in patients with five or more units transfused, while the incidence declined with age, likely caused by declining blood use and age-related changes in neutrophil function, Dr. Menis said.
TRALI rates were slightly higher among men than among women, as well as higher among white patients than among nonwhite patients.
Overall, TRALI rates were higher for patients who received platelets either alone or in combination with RBCs and/or plasma. The highest rates were among patients who received RBCs, plasma and platelets.
Dr. Menis called for studies to determine what effects the processing and storage of blood components may have on TRALI occurrence; he and his colleagues also are planning regression analyses to assess potential risk factors for this complication.
Circulatory overload (TACO)
TACO is one of the leading reported causes of transfusion-related fatalities in the U.S., with onset usually occurring within 6 hours of transfusion, presenting as acute respiratory distress with dyspnea, orthopnea, increased blood pressure, and cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
The overall incidence of TACO among hospitalized patients aged 65 years and older from 2011 through 2018 was 86.3 per 100,000 stays. The incidences were 128.3 in immunocompromised and 76.0 in nonimmunocompromised patients. The rate ratio for TACO in immunocompromised versus nonimmunocompromised patients was 1.70 (P less than .001).
Overall incidence rates of TACO rose from 62 per 100,000 stays in 2011 to 119.8 in 2018. As with other adverse events, incident rates rose with the number of units transfused.
Rates of TACO were significantly higher among women than they were among men (94.6 vs. 75.9 per 100,000; P less than .001), which could be caused by the higher mean age of women and/or a lower tolerance for increased blood volume from transfusion.
The study results also suggested that TACO and TRALI may coexist, based on evidence that 3.5% of all TACO stays also had diagnostic codes for TRALI. The frequency of co-occurrence of these two adverse events also increased over time, which may be caused by improved awareness, Dr. Menis said.
Infections (AIFT)
Acute infections following transfusion can lead to prolonged hospitalizations, sepsis, septic shock, and death. Those most at risk include elderly and immunocompromised patients because of high utilization of blood products, comorbidities, and decreased immune function.
Among 8,833,817 stays, the overall rate per 100,000 stays was 2.1. The rate for immunocompromised patients was 5.4, compared with 1.2 for nonimmunocompromised patients, for a rate ratio of 4.4 (P less than .001).
The incidence rate declined significantly (P = .03) over the study period, with the 3 latest years having the lowest rates.
Rates increased substantially among immunocompromised patients by the number of units transfused, but remained relatively stable among nonimmunocompromised patients.
Infection rates declined with age, from 2.7 per 100,000 stays for patients aged 65-68 years to 1.2 per 100,000 for those aged 85 years and older.
As with other adverse events, AIFT rates were likely related to the blood components transfused, with substantially higher rates for stays during which platelets were transfused either alone or with RBCs, compared with RBCs alone. This could be caused by the room-temperature storage of platelets and higher number of platelets units transfused, compared with RBCs alone, especially among immunocompromised patients.
In all, 51.9% of AIFT cases also had sepsis noted in the medical record, indicating high severity and emphasizing the importance of AIFT prevention, Dr. Menis said.
The studies were funded by the FDA, and Dr. Menis is an FDA employee. He reported having no conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM AABB 2019
Monoclonal Antibodies in MS
A 19-year-old man was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 7 and is currently being treated with an infusible monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy. Early in the day, he receives an infusion at an outpatient clinic. That night, he begins to experience numbness and tingling in his right upper extremity, which prompts a visit to an urgent care clinic. There, the clinician administers IV fluids to the patient. After his symptoms improve, the patient is discharged home.
The next morning, he has a new onset of left-side shoulder and neck pain with a pulsating headache. The patient reports his symptoms to his primary care provider (PCP), who instructs him to visit the emergency department (ED) for evaluation and treatment of a possible infection.
EXAMINATION
The patient arrives at the ED with a 102.4°F fever, vomiting, cough, mild congestion, diaphoresis, generalized myalgias, and chills. He also reports depression and anxiety, saying that for the past 7 days, “I haven’t felt like my normal self.”
Medical history includes moderate persistent asthma that is not well controlled, status asthmaticus, and use of an electronic vaporizing device for inhaling nicotine and marijuana/tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Besides mAb infusions, his medications include hydrocodone/acetaminophen, prochlorperazine, gabapentin, hydroxyzine, trazodone, albuterol, and montelukast.
Examination reveals vital signs within normal limits. Lab work confirms elevated white blood cell count and absolute neutrophil count. Chest x-ray shows diffuse bilateral interstitial and patchy airspace opacities. He is diagnosed with bilateral pneumonia and is admitted and started on an IV antibiotic.
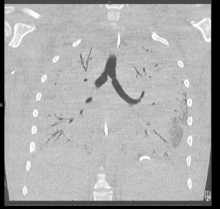
Within 24 hours, a new chest x-ray shows worsening symptoms. CT of the chest with contrast reveals diffuse bilateral ground-glass and airspace opacities suggestive of acute respiratory distress syndrome; bilateral thickening of the pulmonary interstitium; trace bilateral pleural effusions; increased caliber of the main pulmonary artery; and mediastinal and right hilar lymphadenopathy.
Subsequently, the patient developed sepsis and went into acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. He is transferred to the ICU, and pulmonology is consulted. A bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) reveals neutrophil predominance; fungal, bacterial, and viral cultures are negative. The patient is started on broad-spectrum IV antibiotics and high-dose IV steroids. After 4 days, he begins to improve and is transferred out of the ICU. He is discharged with oral steroids and antibiotics.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Fortunately, the PCP and the ED provider identified risk factors that contributed to the patient’s pneumonia and its subsequent worsening to sepsis and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. The immunosuppressive/immunomodulatory effect of mAb therapy increased the patient’s risk for infection and the severity of infection, which is why vigilant safety monitoring and surveillance is essential with mAb treatment.1 Bloodwork should be performed at least every 6 months and include a complete blood count, complete metabolic panel with differential, and JC virus antibody test. Additionally, urinalysis should be performed prior to every mAb infusion. All testing recommended in the package insert for the patient’s prescribed therapy should be performed.
The patient’s history of asthma and his chronic vaping predisposed him to respiratory infections. In mice studies, exposure to e-cigarette vapor has been shown to be cytotoxic to airway cells and to decrease macrophage and neutrophil antimicrobial function.2 Exposure also alters immunomodulating cytokines in the airway, increases inflammatory markers seen in BAL and serum samples, and increases the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus
TREATMENT AND PATIENT EDUCATION
The PCP’s treatment plan included patient education about the importance of infection control measures when receiving a mAb; this includes practicing good hand and environmental hygiene, maintaining vaccinations, avoiding or reducing exposure to individuals who have infections or colds, avoiding large crowds (especially during flu season), and following recommendations for nutrition and hydration. The PCP also discussed how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an infection—and the need for vigilant safety monitoring. The PCP described available options for smoking cessation, including nicotine replacement products, prescription non-nicotine medications, behavioral therapy, and/or counseling (individual, group or telephone) and discussed the risks associated with consuming nicotine and/or marijuana/THC and using electronic vaporizing devices.
The PCP emphasized the importance of completing the entire course of the oral antibiotics prescribed at discharge. The patient and the PCP agreed to the following plan of care: appointments with a pulmonologist and a neurologist within the next 2 weeks, and follow-up visits with the
1. Celius EG. Infections in patients with multiple sclerosis: implications for disease-modifying therapy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;136(suppl 201):34-36.
2. Hwang JH, Lyes M, Sladewski K, et al. Electronic cigarette inhalation alters innate immunity and airway cytokines while increasing the virulence of colonizing bacteria. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94(6):667-679.
A 19-year-old man was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 7 and is currently being treated with an infusible monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy. Early in the day, he receives an infusion at an outpatient clinic. That night, he begins to experience numbness and tingling in his right upper extremity, which prompts a visit to an urgent care clinic. There, the clinician administers IV fluids to the patient. After his symptoms improve, the patient is discharged home.
The next morning, he has a new onset of left-side shoulder and neck pain with a pulsating headache. The patient reports his symptoms to his primary care provider (PCP), who instructs him to visit the emergency department (ED) for evaluation and treatment of a possible infection.
EXAMINATION
The patient arrives at the ED with a 102.4°F fever, vomiting, cough, mild congestion, diaphoresis, generalized myalgias, and chills. He also reports depression and anxiety, saying that for the past 7 days, “I haven’t felt like my normal self.”
Medical history includes moderate persistent asthma that is not well controlled, status asthmaticus, and use of an electronic vaporizing device for inhaling nicotine and marijuana/tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Besides mAb infusions, his medications include hydrocodone/acetaminophen, prochlorperazine, gabapentin, hydroxyzine, trazodone, albuterol, and montelukast.
Examination reveals vital signs within normal limits. Lab work confirms elevated white blood cell count and absolute neutrophil count. Chest x-ray shows diffuse bilateral interstitial and patchy airspace opacities. He is diagnosed with bilateral pneumonia and is admitted and started on an IV antibiotic.
Within 24 hours, a new chest x-ray shows worsening symptoms. CT of the chest with contrast reveals diffuse bilateral ground-glass and airspace opacities suggestive of acute respiratory distress syndrome; bilateral thickening of the pulmonary interstitium; trace bilateral pleural effusions; increased caliber of the main pulmonary artery; and mediastinal and right hilar lymphadenopathy.
Subsequently, the patient developed sepsis and went into acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. He is transferred to the ICU, and pulmonology is consulted. A bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) reveals neutrophil predominance; fungal, bacterial, and viral cultures are negative. The patient is started on broad-spectrum IV antibiotics and high-dose IV steroids. After 4 days, he begins to improve and is transferred out of the ICU. He is discharged with oral steroids and antibiotics.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Fortunately, the PCP and the ED provider identified risk factors that contributed to the patient’s pneumonia and its subsequent worsening to sepsis and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. The immunosuppressive/immunomodulatory effect of mAb therapy increased the patient’s risk for infection and the severity of infection, which is why vigilant safety monitoring and surveillance is essential with mAb treatment.1 Bloodwork should be performed at least every 6 months and include a complete blood count, complete metabolic panel with differential, and JC virus antibody test. Additionally, urinalysis should be performed prior to every mAb infusion. All testing recommended in the package insert for the patient’s prescribed therapy should be performed.
The patient’s history of asthma and his chronic vaping predisposed him to respiratory infections. In mice studies, exposure to e-cigarette vapor has been shown to be cytotoxic to airway cells and to decrease macrophage and neutrophil antimicrobial function.2 Exposure also alters immunomodulating cytokines in the airway, increases inflammatory markers seen in BAL and serum samples, and increases the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus
TREATMENT AND PATIENT EDUCATION
The PCP’s treatment plan included patient education about the importance of infection control measures when receiving a mAb; this includes practicing good hand and environmental hygiene, maintaining vaccinations, avoiding or reducing exposure to individuals who have infections or colds, avoiding large crowds (especially during flu season), and following recommendations for nutrition and hydration. The PCP also discussed how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an infection—and the need for vigilant safety monitoring. The PCP described available options for smoking cessation, including nicotine replacement products, prescription non-nicotine medications, behavioral therapy, and/or counseling (individual, group or telephone) and discussed the risks associated with consuming nicotine and/or marijuana/THC and using electronic vaporizing devices.
The PCP emphasized the importance of completing the entire course of the oral antibiotics prescribed at discharge. The patient and the PCP agreed to the following plan of care: appointments with a pulmonologist and a neurologist within the next 2 weeks, and follow-up visits with the
A 19-year-old man was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 7 and is currently being treated with an infusible monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy. Early in the day, he receives an infusion at an outpatient clinic. That night, he begins to experience numbness and tingling in his right upper extremity, which prompts a visit to an urgent care clinic. There, the clinician administers IV fluids to the patient. After his symptoms improve, the patient is discharged home.
The next morning, he has a new onset of left-side shoulder and neck pain with a pulsating headache. The patient reports his symptoms to his primary care provider (PCP), who instructs him to visit the emergency department (ED) for evaluation and treatment of a possible infection.
EXAMINATION
The patient arrives at the ED with a 102.4°F fever, vomiting, cough, mild congestion, diaphoresis, generalized myalgias, and chills. He also reports depression and anxiety, saying that for the past 7 days, “I haven’t felt like my normal self.”
Medical history includes moderate persistent asthma that is not well controlled, status asthmaticus, and use of an electronic vaporizing device for inhaling nicotine and marijuana/tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Besides mAb infusions, his medications include hydrocodone/acetaminophen, prochlorperazine, gabapentin, hydroxyzine, trazodone, albuterol, and montelukast.
Examination reveals vital signs within normal limits. Lab work confirms elevated white blood cell count and absolute neutrophil count. Chest x-ray shows diffuse bilateral interstitial and patchy airspace opacities. He is diagnosed with bilateral pneumonia and is admitted and started on an IV antibiotic.
Within 24 hours, a new chest x-ray shows worsening symptoms. CT of the chest with contrast reveals diffuse bilateral ground-glass and airspace opacities suggestive of acute respiratory distress syndrome; bilateral thickening of the pulmonary interstitium; trace bilateral pleural effusions; increased caliber of the main pulmonary artery; and mediastinal and right hilar lymphadenopathy.
Subsequently, the patient developed sepsis and went into acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. He is transferred to the ICU, and pulmonology is consulted. A bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) reveals neutrophil predominance; fungal, bacterial, and viral cultures are negative. The patient is started on broad-spectrum IV antibiotics and high-dose IV steroids. After 4 days, he begins to improve and is transferred out of the ICU. He is discharged with oral steroids and antibiotics.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Fortunately, the PCP and the ED provider identified risk factors that contributed to the patient’s pneumonia and its subsequent worsening to sepsis and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. The immunosuppressive/immunomodulatory effect of mAb therapy increased the patient’s risk for infection and the severity of infection, which is why vigilant safety monitoring and surveillance is essential with mAb treatment.1 Bloodwork should be performed at least every 6 months and include a complete blood count, complete metabolic panel with differential, and JC virus antibody test. Additionally, urinalysis should be performed prior to every mAb infusion. All testing recommended in the package insert for the patient’s prescribed therapy should be performed.
The patient’s history of asthma and his chronic vaping predisposed him to respiratory infections. In mice studies, exposure to e-cigarette vapor has been shown to be cytotoxic to airway cells and to decrease macrophage and neutrophil antimicrobial function.2 Exposure also alters immunomodulating cytokines in the airway, increases inflammatory markers seen in BAL and serum samples, and increases the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus
TREATMENT AND PATIENT EDUCATION
The PCP’s treatment plan included patient education about the importance of infection control measures when receiving a mAb; this includes practicing good hand and environmental hygiene, maintaining vaccinations, avoiding or reducing exposure to individuals who have infections or colds, avoiding large crowds (especially during flu season), and following recommendations for nutrition and hydration. The PCP also discussed how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an infection—and the need for vigilant safety monitoring. The PCP described available options for smoking cessation, including nicotine replacement products, prescription non-nicotine medications, behavioral therapy, and/or counseling (individual, group or telephone) and discussed the risks associated with consuming nicotine and/or marijuana/THC and using electronic vaporizing devices.
The PCP emphasized the importance of completing the entire course of the oral antibiotics prescribed at discharge. The patient and the PCP agreed to the following plan of care: appointments with a pulmonologist and a neurologist within the next 2 weeks, and follow-up visits with the
1. Celius EG. Infections in patients with multiple sclerosis: implications for disease-modifying therapy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;136(suppl 201):34-36.
2. Hwang JH, Lyes M, Sladewski K, et al. Electronic cigarette inhalation alters innate immunity and airway cytokines while increasing the virulence of colonizing bacteria. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94(6):667-679.
1. Celius EG. Infections in patients with multiple sclerosis: implications for disease-modifying therapy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;136(suppl 201):34-36.
2. Hwang JH, Lyes M, Sladewski K, et al. Electronic cigarette inhalation alters innate immunity and airway cytokines while increasing the virulence of colonizing bacteria. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94(6):667-679.
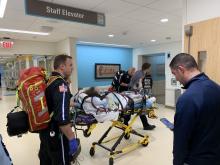
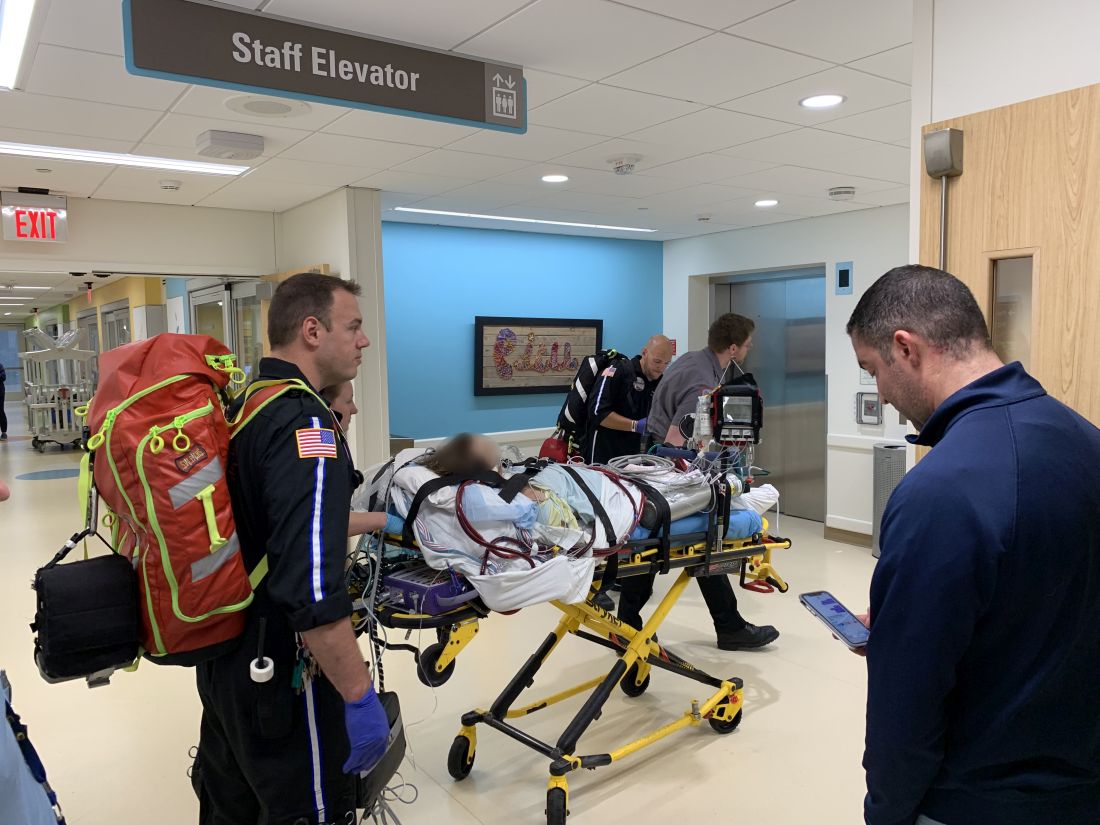
Teen survives double lung transplant after vaping injury
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
Worse air quality linked to premature deaths
, according to a working paper issued by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
The increase in air pollution, defined as the amount of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the air, was associated with an additional 9,700 premature deaths from 2016 to 2018, representing damages totaling $89 billion, wrote Karen Clay and Nicholas C. Miller of Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh. The increase may reflect in part the impact of the a major wildfire that occurred in the fall of 2018.
“These increases are worrisome, because previous studies have shown that PM2.5 increases premature mortality risk,” the researchers wrote. To assess the changes in air quality, they reviewed data from the Air Quality System (AQS) database including total PM2.5 and three PM2.5 species: ammonium nitrate, sulfate, and elemental carbon.
To examine the impact of pollution on public health, the researchers used data from the damage function approach used in the Environmental Protection Agency’s Benefit-Cost Analysis of the Clean Air Act, the Regulatory Impact Analysis for PM2.5, and multiple academic studies.
The number of premature deaths linked to PM2.5 increased by approximately 4,900 between 2016 and 2017 and by 9,700 from 2016 to 2018 in U.S. counties with monitors.
Elderly individuals are especially vulnerable to particulate matter exposure and experience approximately 80% of the burden of disease related to pollution, the researchers said.
“While some deaths among the elderly are shifted by days or weeks, recent research suggests that the burden is ‘concentrated among the elderly with 5-10 years of remaining life expectancy, followed by those with 2-5 years remaining, because these groups represent a large fraction of the Medicare population and are also vulnerable to acute particulate matter exposure,’” they said.
Overall, pollution levels across the United States stopped declining in 2016. When broken down by four Census regions, no change in PM2.5 levels occurred in the Northeast and South between 2016 and 2018; the Midwest and West showed increases in PM2.5 of 9.3% and 11.5%, respectively.
The researchers suggested three possible factors affecting the increase in pollution: economic activity, wildfires, and air quality enforcement. They noted that increases in PM2.5 were especially high in California, and that California accounted for 43% of the increase in pollution-related premature deaths nationwide between 2016 and 2018. When the researchers examined PM2.5 month by month, “November 2018 had an outsized effect on our mortality calculations,” largely because the devastating Camp Fire occurred in California at that time, they said.
With regard to the impact of economic activity on pollution, the researchers reviewed data from the National Highway Administration and Energy Information Administration that showed increased use of natural gas and increased vehicle travel as contributing to higher levels of nitrate and elemental carbon in the air.
Finally, the researchers reported that enforcement of the Clean Air Act appeared to have declined since 2013, and this decline, although it might reflect increased compliance in some areas “is concerning in light of the increases in air pollution in both attainment and nonattainment counties after 2016,” they said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Clay K, Miller NZ. NBER 2019. Working Paper 26381. doi: 10.3386/w26381.
, according to a working paper issued by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
The increase in air pollution, defined as the amount of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the air, was associated with an additional 9,700 premature deaths from 2016 to 2018, representing damages totaling $89 billion, wrote Karen Clay and Nicholas C. Miller of Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh. The increase may reflect in part the impact of the a major wildfire that occurred in the fall of 2018.
“These increases are worrisome, because previous studies have shown that PM2.5 increases premature mortality risk,” the researchers wrote. To assess the changes in air quality, they reviewed data from the Air Quality System (AQS) database including total PM2.5 and three PM2.5 species: ammonium nitrate, sulfate, and elemental carbon.
To examine the impact of pollution on public health, the researchers used data from the damage function approach used in the Environmental Protection Agency’s Benefit-Cost Analysis of the Clean Air Act, the Regulatory Impact Analysis for PM2.5, and multiple academic studies.
The number of premature deaths linked to PM2.5 increased by approximately 4,900 between 2016 and 2017 and by 9,700 from 2016 to 2018 in U.S. counties with monitors.
Elderly individuals are especially vulnerable to particulate matter exposure and experience approximately 80% of the burden of disease related to pollution, the researchers said.
“While some deaths among the elderly are shifted by days or weeks, recent research suggests that the burden is ‘concentrated among the elderly with 5-10 years of remaining life expectancy, followed by those with 2-5 years remaining, because these groups represent a large fraction of the Medicare population and are also vulnerable to acute particulate matter exposure,’” they said.
Overall, pollution levels across the United States stopped declining in 2016. When broken down by four Census regions, no change in PM2.5 levels occurred in the Northeast and South between 2016 and 2018; the Midwest and West showed increases in PM2.5 of 9.3% and 11.5%, respectively.
The researchers suggested three possible factors affecting the increase in pollution: economic activity, wildfires, and air quality enforcement. They noted that increases in PM2.5 were especially high in California, and that California accounted for 43% of the increase in pollution-related premature deaths nationwide between 2016 and 2018. When the researchers examined PM2.5 month by month, “November 2018 had an outsized effect on our mortality calculations,” largely because the devastating Camp Fire occurred in California at that time, they said.
With regard to the impact of economic activity on pollution, the researchers reviewed data from the National Highway Administration and Energy Information Administration that showed increased use of natural gas and increased vehicle travel as contributing to higher levels of nitrate and elemental carbon in the air.
Finally, the researchers reported that enforcement of the Clean Air Act appeared to have declined since 2013, and this decline, although it might reflect increased compliance in some areas “is concerning in light of the increases in air pollution in both attainment and nonattainment counties after 2016,” they said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Clay K, Miller NZ. NBER 2019. Working Paper 26381. doi: 10.3386/w26381.
, according to a working paper issued by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
The increase in air pollution, defined as the amount of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the air, was associated with an additional 9,700 premature deaths from 2016 to 2018, representing damages totaling $89 billion, wrote Karen Clay and Nicholas C. Miller of Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh. The increase may reflect in part the impact of the a major wildfire that occurred in the fall of 2018.
“These increases are worrisome, because previous studies have shown that PM2.5 increases premature mortality risk,” the researchers wrote. To assess the changes in air quality, they reviewed data from the Air Quality System (AQS) database including total PM2.5 and three PM2.5 species: ammonium nitrate, sulfate, and elemental carbon.
To examine the impact of pollution on public health, the researchers used data from the damage function approach used in the Environmental Protection Agency’s Benefit-Cost Analysis of the Clean Air Act, the Regulatory Impact Analysis for PM2.5, and multiple academic studies.
The number of premature deaths linked to PM2.5 increased by approximately 4,900 between 2016 and 2017 and by 9,700 from 2016 to 2018 in U.S. counties with monitors.
Elderly individuals are especially vulnerable to particulate matter exposure and experience approximately 80% of the burden of disease related to pollution, the researchers said.
“While some deaths among the elderly are shifted by days or weeks, recent research suggests that the burden is ‘concentrated among the elderly with 5-10 years of remaining life expectancy, followed by those with 2-5 years remaining, because these groups represent a large fraction of the Medicare population and are also vulnerable to acute particulate matter exposure,’” they said.
Overall, pollution levels across the United States stopped declining in 2016. When broken down by four Census regions, no change in PM2.5 levels occurred in the Northeast and South between 2016 and 2018; the Midwest and West showed increases in PM2.5 of 9.3% and 11.5%, respectively.
The researchers suggested three possible factors affecting the increase in pollution: economic activity, wildfires, and air quality enforcement. They noted that increases in PM2.5 were especially high in California, and that California accounted for 43% of the increase in pollution-related premature deaths nationwide between 2016 and 2018. When the researchers examined PM2.5 month by month, “November 2018 had an outsized effect on our mortality calculations,” largely because the devastating Camp Fire occurred in California at that time, they said.
With regard to the impact of economic activity on pollution, the researchers reviewed data from the National Highway Administration and Energy Information Administration that showed increased use of natural gas and increased vehicle travel as contributing to higher levels of nitrate and elemental carbon in the air.
Finally, the researchers reported that enforcement of the Clean Air Act appeared to have declined since 2013, and this decline, although it might reflect increased compliance in some areas “is concerning in light of the increases in air pollution in both attainment and nonattainment counties after 2016,” they said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Clay K, Miller NZ. NBER 2019. Working Paper 26381. doi: 10.3386/w26381.
FROM AN NBER AIR QUALITY STUDY
Benefits of BGF triple fixed-dose therapy consistent in COPD patients without exacerbation history
NEW ORLEANS – When looking specifically at the subgroup patients with no recent exacerbations, in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), an analysis of the phase 3 KRONOS study shows.
For that subgroup of patients with no moderate to severe exacerbations in the past year, BGF MDI was associated with a nominally significant reduction in the rate of subsequent COPD exacerbations, compared with glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (GFF) MDI, according to investigator Fernando J. Martinez MD, of Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
Results for the COPD patients with no recent history of exacerbation were consistent with the overall results of KRONOS, suggesting that the benefits of BGF MDI shown in that study were not driven by patients with a recent exacerbation history, Dr. Martinez said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It was clear that the effect of this particular triple did not really appear to be dramatically different by the prior history or not in the comparison of the triple versus dual bronchodilator,” he said in a late-breaking clinical trial session.
About three-quarters of the patients in KRONOS (1,411 out of 1,896) lacked a recent exacerbation history. These patients had a mean age of 65.5 years, 72.8% were male, and 69.9% used inhaled corticosteroids at screening, which are demographics were similar to the overall KRONOS patient population, Dr. Martinez said.
In this subset of patients with no recent exacerbation history, treatment with BGF MDI significantly reduced the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with GFF MDI, with a treatment incidence rate ratio of 0.52 (95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.72; P = .0001).
“The results were remarkably similar,” Dr. Martinez said. “I was surprised, to be honest with you, when I saw these results. I did not anticipate that would be the case.”
By contrast, BGF MDI did not significantly reduce the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with budesonide/formoterol fumarate (BFF) MDI or open-label budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate dry-powder inhaler (BUD/FORM DPI) as studied in KRONOS, Dr. Martinez said.
The change from baseline in morning predose trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) at week 24 was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI, according to the investigator. Similarly, the FEV1 area under the curve from 0 to 4 hours was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI.
Dr. Martinez reported disclosures related to AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Sunovion, and Teva.
SOURCE: Martinez FJ et al. CHEST 2019, Abstract.
NEW ORLEANS – When looking specifically at the subgroup patients with no recent exacerbations, in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), an analysis of the phase 3 KRONOS study shows.
For that subgroup of patients with no moderate to severe exacerbations in the past year, BGF MDI was associated with a nominally significant reduction in the rate of subsequent COPD exacerbations, compared with glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (GFF) MDI, according to investigator Fernando J. Martinez MD, of Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
Results for the COPD patients with no recent history of exacerbation were consistent with the overall results of KRONOS, suggesting that the benefits of BGF MDI shown in that study were not driven by patients with a recent exacerbation history, Dr. Martinez said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It was clear that the effect of this particular triple did not really appear to be dramatically different by the prior history or not in the comparison of the triple versus dual bronchodilator,” he said in a late-breaking clinical trial session.
About three-quarters of the patients in KRONOS (1,411 out of 1,896) lacked a recent exacerbation history. These patients had a mean age of 65.5 years, 72.8% were male, and 69.9% used inhaled corticosteroids at screening, which are demographics were similar to the overall KRONOS patient population, Dr. Martinez said.
In this subset of patients with no recent exacerbation history, treatment with BGF MDI significantly reduced the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with GFF MDI, with a treatment incidence rate ratio of 0.52 (95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.72; P = .0001).
“The results were remarkably similar,” Dr. Martinez said. “I was surprised, to be honest with you, when I saw these results. I did not anticipate that would be the case.”
By contrast, BGF MDI did not significantly reduce the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with budesonide/formoterol fumarate (BFF) MDI or open-label budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate dry-powder inhaler (BUD/FORM DPI) as studied in KRONOS, Dr. Martinez said.
The change from baseline in morning predose trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) at week 24 was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI, according to the investigator. Similarly, the FEV1 area under the curve from 0 to 4 hours was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI.
Dr. Martinez reported disclosures related to AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Sunovion, and Teva.
SOURCE: Martinez FJ et al. CHEST 2019, Abstract.
NEW ORLEANS – When looking specifically at the subgroup patients with no recent exacerbations, in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), an analysis of the phase 3 KRONOS study shows.
For that subgroup of patients with no moderate to severe exacerbations in the past year, BGF MDI was associated with a nominally significant reduction in the rate of subsequent COPD exacerbations, compared with glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate (GFF) MDI, according to investigator Fernando J. Martinez MD, of Weill Cornell Medical College, New York.
Results for the COPD patients with no recent history of exacerbation were consistent with the overall results of KRONOS, suggesting that the benefits of BGF MDI shown in that study were not driven by patients with a recent exacerbation history, Dr. Martinez said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It was clear that the effect of this particular triple did not really appear to be dramatically different by the prior history or not in the comparison of the triple versus dual bronchodilator,” he said in a late-breaking clinical trial session.
About three-quarters of the patients in KRONOS (1,411 out of 1,896) lacked a recent exacerbation history. These patients had a mean age of 65.5 years, 72.8% were male, and 69.9% used inhaled corticosteroids at screening, which are demographics were similar to the overall KRONOS patient population, Dr. Martinez said.
In this subset of patients with no recent exacerbation history, treatment with BGF MDI significantly reduced the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with GFF MDI, with a treatment incidence rate ratio of 0.52 (95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.72; P = .0001).
“The results were remarkably similar,” Dr. Martinez said. “I was surprised, to be honest with you, when I saw these results. I did not anticipate that would be the case.”
By contrast, BGF MDI did not significantly reduce the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, compared with budesonide/formoterol fumarate (BFF) MDI or open-label budesonide/formoterol fumarate dihydrate dry-powder inhaler (BUD/FORM DPI) as studied in KRONOS, Dr. Martinez said.
The change from baseline in morning predose trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) at week 24 was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI, according to the investigator. Similarly, the FEV1 area under the curve from 0 to 4 hours was significantly improved for BGF MDI, compared with BFF MDI and BUD/FORM DPI, but not compared with GFF MDI.
Dr. Martinez reported disclosures related to AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Sunovion, and Teva.
SOURCE: Martinez FJ et al. CHEST 2019, Abstract.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2019
Smokers with PE have higher rate of hospital readmission
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a retrospective study.
The rate of readmission was significantly higher among patients with tobacco dependence, and tobacco dependence was independently associated with an increased risk of readmission.
“This is the first study to quantify the increased rate of hospital readmission due to smoking,” said study investigator Kam Sing Ho, MD, of Mount Sinai St. Luke’s and Mount Sinai West, New York.
Dr. Ho and colleagues described this study and its results in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The researchers analyzed data on 168,891 hospital admissions of adults with PE, 34.2% of whom had tobacco dependence. Patients with and without tobacco dependence were propensity matched for baseline characteristics (n = 24,262 in each group).
The 30-day readmission rate was significantly higher in patients with tobacco dependence than in those without it – 11.0% and 8.9%, respectively (P less than .001). The most common reason for readmission in both groups was PE.
Dr. Ho said the higher readmission rate among patients with tobacco dependence might be explained by the fact that smokers have a higher level of fibrinogen, which may affect blood viscosity and contribute to thrombus formation (Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2[1]:71-7).
The investigators also found that tobacco dependence was an independent predictor of readmission (hazard ratio, 1.43; P less than .001). And the mortality rate was significantly higher after readmission than after index admission – 6.27% and 3.15%, respectively (P less than .001).
The increased risk of readmission and death among smokers highlights the importance of smoking cessation services. Dr. Ho cited previous research suggesting these services are underused in the hospital setting (BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2014;3[1]:u204964.w2110).
“Given that smoking is a common phenomenon among patients admitted with pulmonary embolism, we suggest that more rigorous smoking cessation services are implemented prior to discharge for all active smokers,” Dr. Ho said. “[P]atients have the right to be informed on the benefits of smoking cessation and the autonomy to choose. Future research will focus on implementing inpatient smoking cessation at our hospital and its effect on local readmission rate, health resources utilization, and mortality.”
Dr. Ho has no relevant relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ho KS et al. CHEST 2019 October. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.1551.
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a retrospective study.
The rate of readmission was significantly higher among patients with tobacco dependence, and tobacco dependence was independently associated with an increased risk of readmission.
“This is the first study to quantify the increased rate of hospital readmission due to smoking,” said study investigator Kam Sing Ho, MD, of Mount Sinai St. Luke’s and Mount Sinai West, New York.
Dr. Ho and colleagues described this study and its results in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The researchers analyzed data on 168,891 hospital admissions of adults with PE, 34.2% of whom had tobacco dependence. Patients with and without tobacco dependence were propensity matched for baseline characteristics (n = 24,262 in each group).
The 30-day readmission rate was significantly higher in patients with tobacco dependence than in those without it – 11.0% and 8.9%, respectively (P less than .001). The most common reason for readmission in both groups was PE.
Dr. Ho said the higher readmission rate among patients with tobacco dependence might be explained by the fact that smokers have a higher level of fibrinogen, which may affect blood viscosity and contribute to thrombus formation (Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2[1]:71-7).
The investigators also found that tobacco dependence was an independent predictor of readmission (hazard ratio, 1.43; P less than .001). And the mortality rate was significantly higher after readmission than after index admission – 6.27% and 3.15%, respectively (P less than .001).
The increased risk of readmission and death among smokers highlights the importance of smoking cessation services. Dr. Ho cited previous research suggesting these services are underused in the hospital setting (BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2014;3[1]:u204964.w2110).
“Given that smoking is a common phenomenon among patients admitted with pulmonary embolism, we suggest that more rigorous smoking cessation services are implemented prior to discharge for all active smokers,” Dr. Ho said. “[P]atients have the right to be informed on the benefits of smoking cessation and the autonomy to choose. Future research will focus on implementing inpatient smoking cessation at our hospital and its effect on local readmission rate, health resources utilization, and mortality.”
Dr. Ho has no relevant relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ho KS et al. CHEST 2019 October. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.1551.
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a retrospective study.
The rate of readmission was significantly higher among patients with tobacco dependence, and tobacco dependence was independently associated with an increased risk of readmission.
“This is the first study to quantify the increased rate of hospital readmission due to smoking,” said study investigator Kam Sing Ho, MD, of Mount Sinai St. Luke’s and Mount Sinai West, New York.
Dr. Ho and colleagues described this study and its results in a poster presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The researchers analyzed data on 168,891 hospital admissions of adults with PE, 34.2% of whom had tobacco dependence. Patients with and without tobacco dependence were propensity matched for baseline characteristics (n = 24,262 in each group).
The 30-day readmission rate was significantly higher in patients with tobacco dependence than in those without it – 11.0% and 8.9%, respectively (P less than .001). The most common reason for readmission in both groups was PE.
Dr. Ho said the higher readmission rate among patients with tobacco dependence might be explained by the fact that smokers have a higher level of fibrinogen, which may affect blood viscosity and contribute to thrombus formation (Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2[1]:71-7).
The investigators also found that tobacco dependence was an independent predictor of readmission (hazard ratio, 1.43; P less than .001). And the mortality rate was significantly higher after readmission than after index admission – 6.27% and 3.15%, respectively (P less than .001).
The increased risk of readmission and death among smokers highlights the importance of smoking cessation services. Dr. Ho cited previous research suggesting these services are underused in the hospital setting (BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2014;3[1]:u204964.w2110).
“Given that smoking is a common phenomenon among patients admitted with pulmonary embolism, we suggest that more rigorous smoking cessation services are implemented prior to discharge for all active smokers,” Dr. Ho said. “[P]atients have the right to be informed on the benefits of smoking cessation and the autonomy to choose. Future research will focus on implementing inpatient smoking cessation at our hospital and its effect on local readmission rate, health resources utilization, and mortality.”
Dr. Ho has no relevant relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Ho KS et al. CHEST 2019 October. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.1551.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2019
One in five chest tube placements/removals goes awry
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to a prospective observational study conducted at 14 adult trauma centers.
“The sad part is, I don’t know if it was surprisingly high, but I’m glad somebody has taken the time to document it,” said Robert Sawyer, MD, professor of surgery at Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, Mich., who comoderated the session at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons, where the study was presented.
The researchers examined error rates in both insertions and removals, and compared some of the practices and characteristics of trauma centers with unusually good or poor records. The work could begin to inform quality improvement initiatives. “That’s very parallel to where we were 20 or 25 years ago with central venous catheters. We used to put them in and thought it was never a problem, and then we started taking a close look at it and found out, yeah, there was a problem. We systematically made our procedures more consistent and had better outcomes. I think chest tubes is going to be ripe for that,” Dr. Sawyer said in an interview.
“In some ways we have been lying to ourselves. We acknowledge that trainees have a high rate of complications in chest tube insertion and removal, but we haven’t fixed it as a systematic problem. We’re behind in our work to reduce complications for this bedside procedure,” echoed the session’s other comoderator, Tam Pham, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview.
The researchers defined chest tube errors as anything that resulted in a need to manipulate, replace, or revise an existing tube; a worsening of the condition that the tube was intended to address; or complications that resulted in additional length of stay or interventions. A total of 381 chest tubes were placed in 273 patients over a 3-month period, about 55% by residents and about 28% by trauma attending physicians. Around 80% were traditional chest tubes, and most of the rest were Pigtail, with a very small fraction of Trocar chest tubes, according to a pie chart displayed by Michaela West, MD, a trauma surgeon at North Memorial Health, Robbinsdale, Minn., who presented the research.
Dr. West reported a wide range of complication rates among the 14 institutions, ranging from under 10% to nearly 60%, and some centers reported far more complications with removal or insertion, while some had closer to an even split. The overall average rate of insertion complications was 18.7%, and the average for removal was 17.7%.
When the researchers looked at some of the best and worst performing centers, they identified some trends. A total of 98.6% of chest tubes were tunneled in the best-performing centers, while 14.3% were tunneled in the worst. An initial air leak was more common in the best performing centers (52.5% versus 21.7%). Higher performing centers had a greater percentage of patients with gunshot wounds (24.3% versus 13%), and had a longer duration of stay (5.3 days versus 3.4 days; P less than .05 for all).
In the single highest performing center, all chest tubes were removed by midlevel individuals, and the other two best performing centers relied on an attending physician or resident. The worst performing centers often had postgraduate year 1 and 2 residents removing the chest tubes.
Dr. West, Dr. Pham, and Dr. Sawyer have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: West M et al. Clinical Congress 2019 Abstract.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to a prospective observational study conducted at 14 adult trauma centers.
“The sad part is, I don’t know if it was surprisingly high, but I’m glad somebody has taken the time to document it,” said Robert Sawyer, MD, professor of surgery at Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, Mich., who comoderated the session at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons, where the study was presented.
The researchers examined error rates in both insertions and removals, and compared some of the practices and characteristics of trauma centers with unusually good or poor records. The work could begin to inform quality improvement initiatives. “That’s very parallel to where we were 20 or 25 years ago with central venous catheters. We used to put them in and thought it was never a problem, and then we started taking a close look at it and found out, yeah, there was a problem. We systematically made our procedures more consistent and had better outcomes. I think chest tubes is going to be ripe for that,” Dr. Sawyer said in an interview.
“In some ways we have been lying to ourselves. We acknowledge that trainees have a high rate of complications in chest tube insertion and removal, but we haven’t fixed it as a systematic problem. We’re behind in our work to reduce complications for this bedside procedure,” echoed the session’s other comoderator, Tam Pham, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview.
The researchers defined chest tube errors as anything that resulted in a need to manipulate, replace, or revise an existing tube; a worsening of the condition that the tube was intended to address; or complications that resulted in additional length of stay or interventions. A total of 381 chest tubes were placed in 273 patients over a 3-month period, about 55% by residents and about 28% by trauma attending physicians. Around 80% were traditional chest tubes, and most of the rest were Pigtail, with a very small fraction of Trocar chest tubes, according to a pie chart displayed by Michaela West, MD, a trauma surgeon at North Memorial Health, Robbinsdale, Minn., who presented the research.
Dr. West reported a wide range of complication rates among the 14 institutions, ranging from under 10% to nearly 60%, and some centers reported far more complications with removal or insertion, while some had closer to an even split. The overall average rate of insertion complications was 18.7%, and the average for removal was 17.7%.
When the researchers looked at some of the best and worst performing centers, they identified some trends. A total of 98.6% of chest tubes were tunneled in the best-performing centers, while 14.3% were tunneled in the worst. An initial air leak was more common in the best performing centers (52.5% versus 21.7%). Higher performing centers had a greater percentage of patients with gunshot wounds (24.3% versus 13%), and had a longer duration of stay (5.3 days versus 3.4 days; P less than .05 for all).
In the single highest performing center, all chest tubes were removed by midlevel individuals, and the other two best performing centers relied on an attending physician or resident. The worst performing centers often had postgraduate year 1 and 2 residents removing the chest tubes.
Dr. West, Dr. Pham, and Dr. Sawyer have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: West M et al. Clinical Congress 2019 Abstract.
SAN FRANCISCO – , according to a prospective observational study conducted at 14 adult trauma centers.
“The sad part is, I don’t know if it was surprisingly high, but I’m glad somebody has taken the time to document it,” said Robert Sawyer, MD, professor of surgery at Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, Mich., who comoderated the session at the annual clinical congress of the American College of Surgeons, where the study was presented.
The researchers examined error rates in both insertions and removals, and compared some of the practices and characteristics of trauma centers with unusually good or poor records. The work could begin to inform quality improvement initiatives. “That’s very parallel to where we were 20 or 25 years ago with central venous catheters. We used to put them in and thought it was never a problem, and then we started taking a close look at it and found out, yeah, there was a problem. We systematically made our procedures more consistent and had better outcomes. I think chest tubes is going to be ripe for that,” Dr. Sawyer said in an interview.
“In some ways we have been lying to ourselves. We acknowledge that trainees have a high rate of complications in chest tube insertion and removal, but we haven’t fixed it as a systematic problem. We’re behind in our work to reduce complications for this bedside procedure,” echoed the session’s other comoderator, Tam Pham, MD, professor of surgery at the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview.
The researchers defined chest tube errors as anything that resulted in a need to manipulate, replace, or revise an existing tube; a worsening of the condition that the tube was intended to address; or complications that resulted in additional length of stay or interventions. A total of 381 chest tubes were placed in 273 patients over a 3-month period, about 55% by residents and about 28% by trauma attending physicians. Around 80% were traditional chest tubes, and most of the rest were Pigtail, with a very small fraction of Trocar chest tubes, according to a pie chart displayed by Michaela West, MD, a trauma surgeon at North Memorial Health, Robbinsdale, Minn., who presented the research.
Dr. West reported a wide range of complication rates among the 14 institutions, ranging from under 10% to nearly 60%, and some centers reported far more complications with removal or insertion, while some had closer to an even split. The overall average rate of insertion complications was 18.7%, and the average for removal was 17.7%.
When the researchers looked at some of the best and worst performing centers, they identified some trends. A total of 98.6% of chest tubes were tunneled in the best-performing centers, while 14.3% were tunneled in the worst. An initial air leak was more common in the best performing centers (52.5% versus 21.7%). Higher performing centers had a greater percentage of patients with gunshot wounds (24.3% versus 13%), and had a longer duration of stay (5.3 days versus 3.4 days; P less than .05 for all).
In the single highest performing center, all chest tubes were removed by midlevel individuals, and the other two best performing centers relied on an attending physician or resident. The worst performing centers often had postgraduate year 1 and 2 residents removing the chest tubes.
Dr. West, Dr. Pham, and Dr. Sawyer have no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: West M et al. Clinical Congress 2019 Abstract.
REPORTING FROM CLINICAL CONGRESS 2019