User login
Upcoming vaccine may offset surge in polio subtypes
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
Esophageal stricture signals urgent treatment in kids with butterfly skin
LONDON – A quarter of urgent contacts in 20 children with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (GS-RDEB) were tied to esophageal narrowing, according data from a 12-month review of electronic health records.
Urgent advice was sought 102 times outside of regular or scheduled appointments by the parents of 20 children with GS-RDEB, Christine Prodinger, MD, of the University Clinic of Dermatology at Paracelsus Medical University, Salzburg, Austria, and colleagues reported in a poster presentation at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). The researchers looked at the records from the EB clinic at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, London, during April 2018–April 2019.
The mean number of urgent contacts with the specialist unit was 5.1 per patient per year, the researchers reported, with 24 of the 102 contacts (23.5%) resulting in the child being admitted to a hospital. Most of the contacts were made via email or telephone to EB nurses (94%), by contacts during home visits (3%), or in an appointment with the palliative or symptom care team (3%).
“The most common reason [for the urgent contact] was acute dysphagia,” which was experienced as choking, throat pain, difficulty eating, reflux, and vomiting, the researchers observed. Dysphagia affected children in 27 of the contacts (26.5%), and resulted in esophageal dilatation in 90% of the cases. Other reasons for urgent contact were skin infection (15.7% of contacts), uncontrolled pain (15.7% of the contacts), and eye problems (11.8%).
Esophageal dilatation
Strictures are just one of the esophageal manifestations of the disease, noted Anna Bruckner, MD, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, during an oral presentation. Other possible manifestations include blisters and erosions, the formation of webs – a thin extension of esophageal tissue, perforations, and rupture. “These are primarily problems with dystrophic EB” but can occur with other EB subtypes, she noted.
“We don’t have great evidence” on whether the onset of esophageal strictures can be delayed or prevented, Dr. Bruckner observed. As for management, “fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation is probably best” for most patients, but the best procedural approach needs to be discussed on a patient-by-patient basis.
Citing a paper that documents her own experience on the use of esophageal dilatation in 24 children who underwent 231 fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation procedures, Dr. Bruckner noted that strictures were most commonly located in the proximal part of the esophagus, with a median distance of 13 cm down from the lips (J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67[6]:701-5).
The retrospective chart review reported by Dr. Bruckner showed that there were a median of seven dilatation procedures per patient, and 20 patients had repeated procedures at a median interval of 164 days. About 10% of procedures resulted in adverse events – mostly vomiting, pain, and fever – but there were no perforations or other serious effects, and the rate of subsequent hospitalization was 6.9%.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia was the predominant symptom caused by esophageal stricture in another dataset reported in a poster by Elena Pope, MD, MSc, of the Hospital for Sick Children at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
Of 125 EB patients who had experienced at least 1 esophageal stricture episode, 497 esophageal stricture events were reported, and 85.5% of patients had difficulty swallowing at presentation, with 29.8% unable to swallow solids and 7.2% unable to swallow liquids. Other symptoms at presentation were painful swallowing (11%), food being stuck in the esophagus (8%), regurgitation (5%), coughing (4.8%), and dyspepsia (2.8%).
The aim of the retrospective, multicenter cohort study was to determine the prevalence of, and predisposing factors for, restenosis of esophageal strictures and factors that may predispose to restenosis. The study population consisted of 66 men and 59 women who had experienced their esophageal stricture at around ages 12-13 years. The majority (98.4%) had dystrophic EB, of which almost half (46.5%) had GS-RDEB.
The researchers found that the location of the esophageal stricture was important for restenosis, and that strictures occurring in the lower esophagus were 67.5% less likely to result in restenosis than if they occurred in the upper esophagus (P = .057; hazard ratio, 0.675).
A higher number of strictures was associated with a higher rate of restenosis, they reported. Indeed, patients who had two esophageal strictures had a 29.4% increased risk of restenosis, compared with those who had just one stricture (P = .038; HR, 1.294), and those with three or more strictures had an increased risk of 78.5%, compared with those having one stricture (P = .005; HR, 1.785).
Strictures longer than 1 cm also were associated with a greater (34.7%) risk of restenosis, compared with shorter strictures (P = .032; HR, 1.347). Various methods of resolving the stricture were used, from fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation to retro- or antegrade endoscopy. “Irrespective of method, dilatations are successful,” Dr. Pope and colleagues reported. The overall success of dilatation was 99.3%, with full dilatation achieved in almost all of the patients (96%). Of note is that there was a low risk (2.6%) of complications, they observed.
Medications were used in 46.8% of the patients, with the most popular choice being corticosteroids (90.3%), but the researchers noted that the “potential benefit of periprocedural corticosteroids use in decreasing the risk of restenosis needs further exploration.”
Dr. Bruckner had noted in her presentation that her group did not favor the use of periprocedural corticosteroids, but that antifibrotic therapy “could be attractive” for preventing future strictures.
Dr. Prodinger, Dr. Pope, and their colleagues did not provide disclosure information. Dr. Bruckner is the principal investigator for the Epidermolysis Bullosa Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database. She disclosed the receipt of grants or research funding, honoraria, or consultation fees from a number of drug companies, as well as other support from the EB Research Partnership and the EB Medical Research Foundation.
SOURCES: Prodinger et al. EB 2020. Poster 3; Bruckner A et al. Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67(6):701-5; Pope et al. EB 2020. Poster 8.
LONDON – A quarter of urgent contacts in 20 children with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (GS-RDEB) were tied to esophageal narrowing, according data from a 12-month review of electronic health records.
Urgent advice was sought 102 times outside of regular or scheduled appointments by the parents of 20 children with GS-RDEB, Christine Prodinger, MD, of the University Clinic of Dermatology at Paracelsus Medical University, Salzburg, Austria, and colleagues reported in a poster presentation at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). The researchers looked at the records from the EB clinic at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, London, during April 2018–April 2019.
The mean number of urgent contacts with the specialist unit was 5.1 per patient per year, the researchers reported, with 24 of the 102 contacts (23.5%) resulting in the child being admitted to a hospital. Most of the contacts were made via email or telephone to EB nurses (94%), by contacts during home visits (3%), or in an appointment with the palliative or symptom care team (3%).
“The most common reason [for the urgent contact] was acute dysphagia,” which was experienced as choking, throat pain, difficulty eating, reflux, and vomiting, the researchers observed. Dysphagia affected children in 27 of the contacts (26.5%), and resulted in esophageal dilatation in 90% of the cases. Other reasons for urgent contact were skin infection (15.7% of contacts), uncontrolled pain (15.7% of the contacts), and eye problems (11.8%).
Esophageal dilatation
Strictures are just one of the esophageal manifestations of the disease, noted Anna Bruckner, MD, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, during an oral presentation. Other possible manifestations include blisters and erosions, the formation of webs – a thin extension of esophageal tissue, perforations, and rupture. “These are primarily problems with dystrophic EB” but can occur with other EB subtypes, she noted.
“We don’t have great evidence” on whether the onset of esophageal strictures can be delayed or prevented, Dr. Bruckner observed. As for management, “fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation is probably best” for most patients, but the best procedural approach needs to be discussed on a patient-by-patient basis.
Citing a paper that documents her own experience on the use of esophageal dilatation in 24 children who underwent 231 fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation procedures, Dr. Bruckner noted that strictures were most commonly located in the proximal part of the esophagus, with a median distance of 13 cm down from the lips (J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67[6]:701-5).
The retrospective chart review reported by Dr. Bruckner showed that there were a median of seven dilatation procedures per patient, and 20 patients had repeated procedures at a median interval of 164 days. About 10% of procedures resulted in adverse events – mostly vomiting, pain, and fever – but there were no perforations or other serious effects, and the rate of subsequent hospitalization was 6.9%.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia was the predominant symptom caused by esophageal stricture in another dataset reported in a poster by Elena Pope, MD, MSc, of the Hospital for Sick Children at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
Of 125 EB patients who had experienced at least 1 esophageal stricture episode, 497 esophageal stricture events were reported, and 85.5% of patients had difficulty swallowing at presentation, with 29.8% unable to swallow solids and 7.2% unable to swallow liquids. Other symptoms at presentation were painful swallowing (11%), food being stuck in the esophagus (8%), regurgitation (5%), coughing (4.8%), and dyspepsia (2.8%).
The aim of the retrospective, multicenter cohort study was to determine the prevalence of, and predisposing factors for, restenosis of esophageal strictures and factors that may predispose to restenosis. The study population consisted of 66 men and 59 women who had experienced their esophageal stricture at around ages 12-13 years. The majority (98.4%) had dystrophic EB, of which almost half (46.5%) had GS-RDEB.
The researchers found that the location of the esophageal stricture was important for restenosis, and that strictures occurring in the lower esophagus were 67.5% less likely to result in restenosis than if they occurred in the upper esophagus (P = .057; hazard ratio, 0.675).
A higher number of strictures was associated with a higher rate of restenosis, they reported. Indeed, patients who had two esophageal strictures had a 29.4% increased risk of restenosis, compared with those who had just one stricture (P = .038; HR, 1.294), and those with three or more strictures had an increased risk of 78.5%, compared with those having one stricture (P = .005; HR, 1.785).
Strictures longer than 1 cm also were associated with a greater (34.7%) risk of restenosis, compared with shorter strictures (P = .032; HR, 1.347). Various methods of resolving the stricture were used, from fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation to retro- or antegrade endoscopy. “Irrespective of method, dilatations are successful,” Dr. Pope and colleagues reported. The overall success of dilatation was 99.3%, with full dilatation achieved in almost all of the patients (96%). Of note is that there was a low risk (2.6%) of complications, they observed.
Medications were used in 46.8% of the patients, with the most popular choice being corticosteroids (90.3%), but the researchers noted that the “potential benefit of periprocedural corticosteroids use in decreasing the risk of restenosis needs further exploration.”
Dr. Bruckner had noted in her presentation that her group did not favor the use of periprocedural corticosteroids, but that antifibrotic therapy “could be attractive” for preventing future strictures.
Dr. Prodinger, Dr. Pope, and their colleagues did not provide disclosure information. Dr. Bruckner is the principal investigator for the Epidermolysis Bullosa Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database. She disclosed the receipt of grants or research funding, honoraria, or consultation fees from a number of drug companies, as well as other support from the EB Research Partnership and the EB Medical Research Foundation.
SOURCES: Prodinger et al. EB 2020. Poster 3; Bruckner A et al. Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67(6):701-5; Pope et al. EB 2020. Poster 8.
LONDON – A quarter of urgent contacts in 20 children with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (GS-RDEB) were tied to esophageal narrowing, according data from a 12-month review of electronic health records.
Urgent advice was sought 102 times outside of regular or scheduled appointments by the parents of 20 children with GS-RDEB, Christine Prodinger, MD, of the University Clinic of Dermatology at Paracelsus Medical University, Salzburg, Austria, and colleagues reported in a poster presentation at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). The researchers looked at the records from the EB clinic at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, London, during April 2018–April 2019.
The mean number of urgent contacts with the specialist unit was 5.1 per patient per year, the researchers reported, with 24 of the 102 contacts (23.5%) resulting in the child being admitted to a hospital. Most of the contacts were made via email or telephone to EB nurses (94%), by contacts during home visits (3%), or in an appointment with the palliative or symptom care team (3%).
“The most common reason [for the urgent contact] was acute dysphagia,” which was experienced as choking, throat pain, difficulty eating, reflux, and vomiting, the researchers observed. Dysphagia affected children in 27 of the contacts (26.5%), and resulted in esophageal dilatation in 90% of the cases. Other reasons for urgent contact were skin infection (15.7% of contacts), uncontrolled pain (15.7% of the contacts), and eye problems (11.8%).
Esophageal dilatation
Strictures are just one of the esophageal manifestations of the disease, noted Anna Bruckner, MD, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the department of dermatology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, during an oral presentation. Other possible manifestations include blisters and erosions, the formation of webs – a thin extension of esophageal tissue, perforations, and rupture. “These are primarily problems with dystrophic EB” but can occur with other EB subtypes, she noted.
“We don’t have great evidence” on whether the onset of esophageal strictures can be delayed or prevented, Dr. Bruckner observed. As for management, “fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation is probably best” for most patients, but the best procedural approach needs to be discussed on a patient-by-patient basis.
Citing a paper that documents her own experience on the use of esophageal dilatation in 24 children who underwent 231 fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation procedures, Dr. Bruckner noted that strictures were most commonly located in the proximal part of the esophagus, with a median distance of 13 cm down from the lips (J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67[6]:701-5).
The retrospective chart review reported by Dr. Bruckner showed that there were a median of seven dilatation procedures per patient, and 20 patients had repeated procedures at a median interval of 164 days. About 10% of procedures resulted in adverse events – mostly vomiting, pain, and fever – but there were no perforations or other serious effects, and the rate of subsequent hospitalization was 6.9%.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia was the predominant symptom caused by esophageal stricture in another dataset reported in a poster by Elena Pope, MD, MSc, of the Hospital for Sick Children at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
Of 125 EB patients who had experienced at least 1 esophageal stricture episode, 497 esophageal stricture events were reported, and 85.5% of patients had difficulty swallowing at presentation, with 29.8% unable to swallow solids and 7.2% unable to swallow liquids. Other symptoms at presentation were painful swallowing (11%), food being stuck in the esophagus (8%), regurgitation (5%), coughing (4.8%), and dyspepsia (2.8%).
The aim of the retrospective, multicenter cohort study was to determine the prevalence of, and predisposing factors for, restenosis of esophageal strictures and factors that may predispose to restenosis. The study population consisted of 66 men and 59 women who had experienced their esophageal stricture at around ages 12-13 years. The majority (98.4%) had dystrophic EB, of which almost half (46.5%) had GS-RDEB.
The researchers found that the location of the esophageal stricture was important for restenosis, and that strictures occurring in the lower esophagus were 67.5% less likely to result in restenosis than if they occurred in the upper esophagus (P = .057; hazard ratio, 0.675).
A higher number of strictures was associated with a higher rate of restenosis, they reported. Indeed, patients who had two esophageal strictures had a 29.4% increased risk of restenosis, compared with those who had just one stricture (P = .038; HR, 1.294), and those with three or more strictures had an increased risk of 78.5%, compared with those having one stricture (P = .005; HR, 1.785).
Strictures longer than 1 cm also were associated with a greater (34.7%) risk of restenosis, compared with shorter strictures (P = .032; HR, 1.347). Various methods of resolving the stricture were used, from fluoroscopy-guided balloon dilatation to retro- or antegrade endoscopy. “Irrespective of method, dilatations are successful,” Dr. Pope and colleagues reported. The overall success of dilatation was 99.3%, with full dilatation achieved in almost all of the patients (96%). Of note is that there was a low risk (2.6%) of complications, they observed.
Medications were used in 46.8% of the patients, with the most popular choice being corticosteroids (90.3%), but the researchers noted that the “potential benefit of periprocedural corticosteroids use in decreasing the risk of restenosis needs further exploration.”
Dr. Bruckner had noted in her presentation that her group did not favor the use of periprocedural corticosteroids, but that antifibrotic therapy “could be attractive” for preventing future strictures.
Dr. Prodinger, Dr. Pope, and their colleagues did not provide disclosure information. Dr. Bruckner is the principal investigator for the Epidermolysis Bullosa Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database. She disclosed the receipt of grants or research funding, honoraria, or consultation fees from a number of drug companies, as well as other support from the EB Research Partnership and the EB Medical Research Foundation.
SOURCES: Prodinger et al. EB 2020. Poster 3; Bruckner A et al. Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67(6):701-5; Pope et al. EB 2020. Poster 8.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Inebilizumab benefits patients with NMOSD
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Compared with placebo, inebilizumab reduces the risk of attacks, the risk of disability worsening, the number of hospitalizations, and the number of new MRI lesions in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), according to a study presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The drug’s efficacy was sustained for one year in the study, and the treatment had an acceptable safety profile.
“Multiple lines of evidence suggest that NMO is predominantly a B-cell–mediated disorder,” said Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences. Inebilizumab depletes B cells and reduces inflammatory disease activity in NMO potentially by altering immune networks that are dependent on B cells for cytokine production or antigen presentation.” Inebilizumab is an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody.
Dr. Cree and colleagues conducted a randomized, controlled trial called N-MOmentum to characterize the long-term efficacy and safety of inebilizumab in patients with NMOSD. The investigators randomized patients with NMOSD to inebilizumab or placebo monotherapy in a 3:1 ratio for 6.5 months. The study’s primary outcome was the time to the first adjudicated attack. Patients who had an adjudicated attack or completed the trial could receive inebilizumab in an ongoing open-label extension.
The study was conducted at 99 sites in 25 countries. In all, 230 patients were randomized and dosed (174 received inebilizumab, and 56 received placebo). About 91% of the population was aquaporin-4-IgG–positive (AQP4-IgG+), and 91% was female. The population’s mean age at baseline was 43 years. The population’s median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale score was approximately 3.5, and the range was from 0 to 8.0. Approximately 50% of participants were white, 20% were Asian, and 9% were of African descent. “The demographic profile is similar to that of many published studies,” said Dr. Cree.
Because of clear evidence of efficacy, the independent data monitoring committee recommended that the study be stopped early. In the randomized, controlled trial, inebilizumab reduced the risk of attack by 77.3% among AQP4-IgG+ patients and by 72.8% in the total population. The number needed to treat for 6.5 months to prevent one attack was 3.2 for the AQP4-IgG+ group and 3.7 for the total population.
Furthermore, inebilizumab significantly reduced the risk of worsening disability, the number of new MRI lesions, and NMOSD-related hospitalizations. After 1 year on inebilizumab, 85% of patients were free of an NMOSD attack. In safety analyses that combined data from the randomized, controlled trial and interim data from the open-label extension, the mean duration of inebilizumab treatment was 1.5 years.
“The rapid effect of inebilizumab on attack prevention is not mediated by decreasing AQP4-IgG, although it is possible that long-term inebilizumab treatment might eventually reduce AQP4-IgG production,” said Dr. Cree.
The most common adverse events (AEs) were urinary tract infection (UTI, 19.6%), nasopharyngitis (12.9%), and infusion-related reactions (IRRs, 11.6%). IRRs were most common with the first infusion. The proportion of inebilizumab-treated patients with IgG levels below the lower limit of normal was 7.5% at 1 year and 13.4% at 2 years. Serious AEs occurred in 12% of patients, and UTI was the most common (2.2%). Two patients died in the open-label extension; one death resulted from NMOSD, and one from new presumed inflammatory brain lesions of undetermined etiology.
“The open-label results show a striking durability of treatment effect,” said Dr. Cree. “Most of the attacks that occurred during the open-label extension occurred early on, suggesting that the risk of attack decreases with duration of B-cell depletion. The open-label study also is important for assessing the longer-term AE profile of inebilizumab treatment. One potentially important observation from the open-label extension is that the extent of B-cell depletion correlates with reduced attack risk. Approximately 95% of participants with deep B-cell depletion were free of attacks. Participants who either incompletely depleted B cells or who began to reconstitute B cells more rapidly were at increased risk of attack. Therefore, by monitoring B-cell counts in inebilizumab-treated patients, it may be possible to further reduce the risk of attack in patients who partially deplete, or replete B cells early, with an extra inebilizumab treatment.”
Viela Bio, which is developing inebilizumab, and MedImmune sponsored the study. Dr. Cree has received compensation for consulting services that he provided to Alexion, Atara, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, and TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Cree BA et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P207.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Compared with placebo, inebilizumab reduces the risk of attacks, the risk of disability worsening, the number of hospitalizations, and the number of new MRI lesions in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), according to a study presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The drug’s efficacy was sustained for one year in the study, and the treatment had an acceptable safety profile.
“Multiple lines of evidence suggest that NMO is predominantly a B-cell–mediated disorder,” said Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences. Inebilizumab depletes B cells and reduces inflammatory disease activity in NMO potentially by altering immune networks that are dependent on B cells for cytokine production or antigen presentation.” Inebilizumab is an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody.
Dr. Cree and colleagues conducted a randomized, controlled trial called N-MOmentum to characterize the long-term efficacy and safety of inebilizumab in patients with NMOSD. The investigators randomized patients with NMOSD to inebilizumab or placebo monotherapy in a 3:1 ratio for 6.5 months. The study’s primary outcome was the time to the first adjudicated attack. Patients who had an adjudicated attack or completed the trial could receive inebilizumab in an ongoing open-label extension.
The study was conducted at 99 sites in 25 countries. In all, 230 patients were randomized and dosed (174 received inebilizumab, and 56 received placebo). About 91% of the population was aquaporin-4-IgG–positive (AQP4-IgG+), and 91% was female. The population’s mean age at baseline was 43 years. The population’s median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale score was approximately 3.5, and the range was from 0 to 8.0. Approximately 50% of participants were white, 20% were Asian, and 9% were of African descent. “The demographic profile is similar to that of many published studies,” said Dr. Cree.
Because of clear evidence of efficacy, the independent data monitoring committee recommended that the study be stopped early. In the randomized, controlled trial, inebilizumab reduced the risk of attack by 77.3% among AQP4-IgG+ patients and by 72.8% in the total population. The number needed to treat for 6.5 months to prevent one attack was 3.2 for the AQP4-IgG+ group and 3.7 for the total population.
Furthermore, inebilizumab significantly reduced the risk of worsening disability, the number of new MRI lesions, and NMOSD-related hospitalizations. After 1 year on inebilizumab, 85% of patients were free of an NMOSD attack. In safety analyses that combined data from the randomized, controlled trial and interim data from the open-label extension, the mean duration of inebilizumab treatment was 1.5 years.
“The rapid effect of inebilizumab on attack prevention is not mediated by decreasing AQP4-IgG, although it is possible that long-term inebilizumab treatment might eventually reduce AQP4-IgG production,” said Dr. Cree.
The most common adverse events (AEs) were urinary tract infection (UTI, 19.6%), nasopharyngitis (12.9%), and infusion-related reactions (IRRs, 11.6%). IRRs were most common with the first infusion. The proportion of inebilizumab-treated patients with IgG levels below the lower limit of normal was 7.5% at 1 year and 13.4% at 2 years. Serious AEs occurred in 12% of patients, and UTI was the most common (2.2%). Two patients died in the open-label extension; one death resulted from NMOSD, and one from new presumed inflammatory brain lesions of undetermined etiology.
“The open-label results show a striking durability of treatment effect,” said Dr. Cree. “Most of the attacks that occurred during the open-label extension occurred early on, suggesting that the risk of attack decreases with duration of B-cell depletion. The open-label study also is important for assessing the longer-term AE profile of inebilizumab treatment. One potentially important observation from the open-label extension is that the extent of B-cell depletion correlates with reduced attack risk. Approximately 95% of participants with deep B-cell depletion were free of attacks. Participants who either incompletely depleted B cells or who began to reconstitute B cells more rapidly were at increased risk of attack. Therefore, by monitoring B-cell counts in inebilizumab-treated patients, it may be possible to further reduce the risk of attack in patients who partially deplete, or replete B cells early, with an extra inebilizumab treatment.”
Viela Bio, which is developing inebilizumab, and MedImmune sponsored the study. Dr. Cree has received compensation for consulting services that he provided to Alexion, Atara, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, and TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Cree BA et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P207.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Compared with placebo, inebilizumab reduces the risk of attacks, the risk of disability worsening, the number of hospitalizations, and the number of new MRI lesions in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), according to a study presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The drug’s efficacy was sustained for one year in the study, and the treatment had an acceptable safety profile.
“Multiple lines of evidence suggest that NMO is predominantly a B-cell–mediated disorder,” said Bruce Cree, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neurosciences. Inebilizumab depletes B cells and reduces inflammatory disease activity in NMO potentially by altering immune networks that are dependent on B cells for cytokine production or antigen presentation.” Inebilizumab is an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody.
Dr. Cree and colleagues conducted a randomized, controlled trial called N-MOmentum to characterize the long-term efficacy and safety of inebilizumab in patients with NMOSD. The investigators randomized patients with NMOSD to inebilizumab or placebo monotherapy in a 3:1 ratio for 6.5 months. The study’s primary outcome was the time to the first adjudicated attack. Patients who had an adjudicated attack or completed the trial could receive inebilizumab in an ongoing open-label extension.
The study was conducted at 99 sites in 25 countries. In all, 230 patients were randomized and dosed (174 received inebilizumab, and 56 received placebo). About 91% of the population was aquaporin-4-IgG–positive (AQP4-IgG+), and 91% was female. The population’s mean age at baseline was 43 years. The population’s median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale score was approximately 3.5, and the range was from 0 to 8.0. Approximately 50% of participants were white, 20% were Asian, and 9% were of African descent. “The demographic profile is similar to that of many published studies,” said Dr. Cree.
Because of clear evidence of efficacy, the independent data monitoring committee recommended that the study be stopped early. In the randomized, controlled trial, inebilizumab reduced the risk of attack by 77.3% among AQP4-IgG+ patients and by 72.8% in the total population. The number needed to treat for 6.5 months to prevent one attack was 3.2 for the AQP4-IgG+ group and 3.7 for the total population.
Furthermore, inebilizumab significantly reduced the risk of worsening disability, the number of new MRI lesions, and NMOSD-related hospitalizations. After 1 year on inebilizumab, 85% of patients were free of an NMOSD attack. In safety analyses that combined data from the randomized, controlled trial and interim data from the open-label extension, the mean duration of inebilizumab treatment was 1.5 years.
“The rapid effect of inebilizumab on attack prevention is not mediated by decreasing AQP4-IgG, although it is possible that long-term inebilizumab treatment might eventually reduce AQP4-IgG production,” said Dr. Cree.
The most common adverse events (AEs) were urinary tract infection (UTI, 19.6%), nasopharyngitis (12.9%), and infusion-related reactions (IRRs, 11.6%). IRRs were most common with the first infusion. The proportion of inebilizumab-treated patients with IgG levels below the lower limit of normal was 7.5% at 1 year and 13.4% at 2 years. Serious AEs occurred in 12% of patients, and UTI was the most common (2.2%). Two patients died in the open-label extension; one death resulted from NMOSD, and one from new presumed inflammatory brain lesions of undetermined etiology.
“The open-label results show a striking durability of treatment effect,” said Dr. Cree. “Most of the attacks that occurred during the open-label extension occurred early on, suggesting that the risk of attack decreases with duration of B-cell depletion. The open-label study also is important for assessing the longer-term AE profile of inebilizumab treatment. One potentially important observation from the open-label extension is that the extent of B-cell depletion correlates with reduced attack risk. Approximately 95% of participants with deep B-cell depletion were free of attacks. Participants who either incompletely depleted B cells or who began to reconstitute B cells more rapidly were at increased risk of attack. Therefore, by monitoring B-cell counts in inebilizumab-treated patients, it may be possible to further reduce the risk of attack in patients who partially deplete, or replete B cells early, with an extra inebilizumab treatment.”
Viela Bio, which is developing inebilizumab, and MedImmune sponsored the study. Dr. Cree has received compensation for consulting services that he provided to Alexion, Atara, Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, and TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Cree BA et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P207.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2020
Eculizumab reduces relapse-related hospitalizations in patients with NMOSD
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – , according to research presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The results suggest that eculizumab may have a favorable effect on health-resource utilization.
Many patients with NMOSD, a rare autoimmune inflammatory disease, have relapses that result in hospitalization. Eculizumab (Soliris)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits the terminal complement protein C5. In the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PREVENT study, Dean M. Wingerchuk, MD, chair of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, , and colleagues found that eculizumab was associated with a 94% reduction in the risk of relapse, compared with placebo, in AQP4-IgG-positive patients with NMOSD.
In a new analysis of the PREVENT data, the investigators sought to evaluate rates of relapse-related hospitalization and associated treatment among study participants. The researchers chose time to first adjudicated relapse as their primary endpoint.
In the PREVENT study, Dr. Wingerchuk and colleagues randomized patients with AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD to eculizumab (1,200 mg/2 weeks) or placebo. The annualized relapse-related hospitalization and treatment rates were calculated as the number of relapses requiring hospitalization or treatment divided by the total number of patient-years during the study.
Approximately 91% of participants were female. Mean age at initial clinical presentation was about 37 years. Participants’ median Expanded Disability Status Scale score at baseline was 4, and their mean annualized relapse rate in the 24 months before screening was 2. In all, 96 patients received eculizumab, and 47 received placebo. The median length of exposure to treatment was 89.4 weeks in the eculizumab group and 41.3 weeks among controls.
The rate of adverse events requiring hospitalization was 29% in the eculizumab group and 53% in the placebo group. The most common events requiring hospitalization were physician-determined relapses. Infections were the next most common events requiring hospitalization.
The overall annualized hospitalization rate was 0.26 in the eculizumab group and 0.78 in the placebo group. The difference between groups was statistically significant. In addition, the annualized relapse-related hospitalization rate was lower in the eculizumab group than in the placebo group (0.04 vs. 0.31, respectively).
The annualized relapse-related use of intravenous methylprednisolone for the eculizumab and placebo groups were 0.07 and 0.42, respectively; for use of plasma exchange, 0.02 and 0.19; and for use of high-dose oral corticosteroids, 0.04 and 0.11. The differences between groups in use of intravenous methylprednisolone and plasma exchange were statistically significant.
Alexion Pharmaceuticals, which markets eculizumab, sponsored the study. Dr. Wingerchuk received grants from Alexion during the study. He also received personal fees from Biogen, BrainStorm Therapeutics, Celgene, MedImmune, Novartis, and ONO Pharmaceutical.
SOURCE: Kim H et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P197.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – , according to research presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The results suggest that eculizumab may have a favorable effect on health-resource utilization.
Many patients with NMOSD, a rare autoimmune inflammatory disease, have relapses that result in hospitalization. Eculizumab (Soliris)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits the terminal complement protein C5. In the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PREVENT study, Dean M. Wingerchuk, MD, chair of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, , and colleagues found that eculizumab was associated with a 94% reduction in the risk of relapse, compared with placebo, in AQP4-IgG-positive patients with NMOSD.
In a new analysis of the PREVENT data, the investigators sought to evaluate rates of relapse-related hospitalization and associated treatment among study participants. The researchers chose time to first adjudicated relapse as their primary endpoint.
In the PREVENT study, Dr. Wingerchuk and colleagues randomized patients with AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD to eculizumab (1,200 mg/2 weeks) or placebo. The annualized relapse-related hospitalization and treatment rates were calculated as the number of relapses requiring hospitalization or treatment divided by the total number of patient-years during the study.
Approximately 91% of participants were female. Mean age at initial clinical presentation was about 37 years. Participants’ median Expanded Disability Status Scale score at baseline was 4, and their mean annualized relapse rate in the 24 months before screening was 2. In all, 96 patients received eculizumab, and 47 received placebo. The median length of exposure to treatment was 89.4 weeks in the eculizumab group and 41.3 weeks among controls.
The rate of adverse events requiring hospitalization was 29% in the eculizumab group and 53% in the placebo group. The most common events requiring hospitalization were physician-determined relapses. Infections were the next most common events requiring hospitalization.
The overall annualized hospitalization rate was 0.26 in the eculizumab group and 0.78 in the placebo group. The difference between groups was statistically significant. In addition, the annualized relapse-related hospitalization rate was lower in the eculizumab group than in the placebo group (0.04 vs. 0.31, respectively).
The annualized relapse-related use of intravenous methylprednisolone for the eculizumab and placebo groups were 0.07 and 0.42, respectively; for use of plasma exchange, 0.02 and 0.19; and for use of high-dose oral corticosteroids, 0.04 and 0.11. The differences between groups in use of intravenous methylprednisolone and plasma exchange were statistically significant.
Alexion Pharmaceuticals, which markets eculizumab, sponsored the study. Dr. Wingerchuk received grants from Alexion during the study. He also received personal fees from Biogen, BrainStorm Therapeutics, Celgene, MedImmune, Novartis, and ONO Pharmaceutical.
SOURCE: Kim H et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P197.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – , according to research presented at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. The results suggest that eculizumab may have a favorable effect on health-resource utilization.
Many patients with NMOSD, a rare autoimmune inflammatory disease, have relapses that result in hospitalization. Eculizumab (Soliris)is a humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits the terminal complement protein C5. In the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PREVENT study, Dean M. Wingerchuk, MD, chair of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, , and colleagues found that eculizumab was associated with a 94% reduction in the risk of relapse, compared with placebo, in AQP4-IgG-positive patients with NMOSD.
In a new analysis of the PREVENT data, the investigators sought to evaluate rates of relapse-related hospitalization and associated treatment among study participants. The researchers chose time to first adjudicated relapse as their primary endpoint.
In the PREVENT study, Dr. Wingerchuk and colleagues randomized patients with AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD to eculizumab (1,200 mg/2 weeks) or placebo. The annualized relapse-related hospitalization and treatment rates were calculated as the number of relapses requiring hospitalization or treatment divided by the total number of patient-years during the study.
Approximately 91% of participants were female. Mean age at initial clinical presentation was about 37 years. Participants’ median Expanded Disability Status Scale score at baseline was 4, and their mean annualized relapse rate in the 24 months before screening was 2. In all, 96 patients received eculizumab, and 47 received placebo. The median length of exposure to treatment was 89.4 weeks in the eculizumab group and 41.3 weeks among controls.
The rate of adverse events requiring hospitalization was 29% in the eculizumab group and 53% in the placebo group. The most common events requiring hospitalization were physician-determined relapses. Infections were the next most common events requiring hospitalization.
The overall annualized hospitalization rate was 0.26 in the eculizumab group and 0.78 in the placebo group. The difference between groups was statistically significant. In addition, the annualized relapse-related hospitalization rate was lower in the eculizumab group than in the placebo group (0.04 vs. 0.31, respectively).
The annualized relapse-related use of intravenous methylprednisolone for the eculizumab and placebo groups were 0.07 and 0.42, respectively; for use of plasma exchange, 0.02 and 0.19; and for use of high-dose oral corticosteroids, 0.04 and 0.11. The differences between groups in use of intravenous methylprednisolone and plasma exchange were statistically significant.
Alexion Pharmaceuticals, which markets eculizumab, sponsored the study. Dr. Wingerchuk received grants from Alexion during the study. He also received personal fees from Biogen, BrainStorm Therapeutics, Celgene, MedImmune, Novartis, and ONO Pharmaceutical.
SOURCE: Kim H et al. ACTRIMS 2020. Abstract P197.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2020
SCC survival remains poor in epidermolysis bullosa
LONDON – Median survival among patients with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB-GS) after a first diagnosis of mucocutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) was 2.4 years in an observational, retrospective study.
The study, conducted at St. Thomas’ Hospital and Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, was a review of all individuals with EB who had developed the skin cancer over a 28-year period, from 1991 to 2019.
A total of 44 subjects were identified who together had 221 primary SCCs. Considering all study subjects, the median age at first diagnosis of SCC was 32.6 years, with a mean of five tumors present. Almost 40% had metastatic tumors, and of the 57% who died during the observation period, 88% of deaths were attributable to the SCC.
“EB-associated SCCs differ from those in the general population,” the study’s investigators wrote in a poster presented at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (debra). “They affect a younger age group, and there are often multiple primaries,” they added. Furthermore, “they behave aggressively and metastasize early despite being well differentiated.”
Most (31) of the study participants had RDEB-GS and tended to develop their first SCC at a younger age than the group overall, at a median of 29.5 years (compared with 32.6 years for the overall group). The mean number of tumors was 5.8 among those with RDEB-GS, with over half (53.4%) of the SCCs being well differentiated and located on the hands, upper arms, feet, and lower legs. Median survival after a first diagnosis in this group was 2.4 years. The short survival after a first diagnosis of SCC “underscores the poor prognosis in this group,” the researchers wrote.
“As the largest cohort of EB SCC patients with comprehensive data regarding clinical course and management to date, our data reinforce the need for regular clinical surveillance for SCCs in EB patients,” the team concluded. This surveillance should start in adolescence for those with the severe generalized RDEB subtype, they advise, and from the third or fourth decade for other at-risk groups.
These data also highlight “the pressing need for more effective treatments,” the investigators wrote. Most (86.4%) of the SCCs among the patients in the study had been surgically removed by wide local excision, with a few patients undergoing lymph node dissection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, electrochemotherapy, or receiving targeted cancer therapies such as erlotinib, cetuximab, or cemiplimab.
Surgery may not be an option for many patients, Jemima Mellerio, MD explained in an oral presentation at the meeting. Dr. Mellerio, a consultant dermatologist and chief of St John’s Institute of Dermatology at Guy’s & St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation, London, noted that the location of the tumor was important, as sometimes it was not physically possible to excise it completely.
Guidelines on how to manage SCCs in patients with EB were published a few years ago (Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:56-67) and noted that the clinical detection of SCCs could be difficult because of chronic wound ulceration in these patients. The “possibility of malignancy should be borne in mind, with suspicious lesions biopsied for histological evaluation,” the document states. Evidence for many of the nonsurgical options – radiotherapy, conventional chemotherapy, biologic therapies – was poor, according to the guidelines, and effective nonsurgical options are still desperately needed.
Several avenues of research are being investigated, Dr. Mellerio noted, such as targeting the fibrotic process and perhaps using a micro-RNA inhibitor to stop the upregulation of certain microRNAs in fibroblasts. Targeting inflammatory mechanisms such as thrombospondin 1, which can lead to elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor–beta and contribute to extracellular matrix stiffness, also is under investigation. Raised interleukin-6 may be another target to consider.
Research shows that similar genes are mutated in EB-related and ultraviolet-related SCCs, Dr. Mellerio said. Indeed, mutations in HRAS, NOTCH1, TP53, and CDKN2A have been reported, but mutations in these genes occur much earlier in life in patients with EB. “Something else is going on,” she added, commenting that researchers are looking at apolipoprotein B editing complex (APOBEC) enzymes, which modulate DNA and can cause “particular types of genetic changes in EB cancers.”
One investigator who is studying the genetics of EB SCCs and how APOBEC enzymes might be involved is Andrew South, PhD, an associate professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. APOBEC enzymes are a very prominent source of mutations in RDEB. These mutations are found in 10%-20% of squamous cell carcinomas not associated with RDEB, and 80%-90% of head and neck cancers, he said during a separate talk at the meeting.
Dr. South observed that “RDEB squamous cell carcinoma does not show any particular somatic mutation or upregulation or downregulation of genes that differentiates it from other squamous cell carcinomas, which might be disappointing on the front of it, but actually it does mean that precision therapies that have been developed for other squamous cell carcinomas have application in RDEB.”
RDEB SCC shows the greatest similarity with head and neck SCC, Dr. South said. He also stressed that fibrosis is a major driver of cancer development, SCC tumors in RDEB are homogenous, and that frontline therapy is still unclear.
What is clear, however, is that interdisciplinary management of patients is crucial, said Leena Bruckner-Tuderman, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University Medical Center, Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg, Germany.
“In severe RDEB, metastatic SCC is the leading cause of death at a young age. We need monitoring, careful diagnostics, and multidisciplinary treatment,” Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman said. The latter should be delivered by a coordinated team that consists of dermatologists, surgeons, radiologists, oncologists, pathologists, geneticists, and (molecular) tumor boards, she advised.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Mellerio disclosed financial relationships with Castle Creek Pharmaceuticals and ProQR Therapeutics, and acted as an unpaid advisor to Helpberby Therapeutics. Dr. South disclosed financial relationships with Krystal Biotech Inc. and Amryt Genetics and has been an advisory board member for Abeona Therapeutics and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman disclosed receiving grants or research support from Constant Pharmaceuticals/Tarix Orphan.
LONDON – Median survival among patients with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB-GS) after a first diagnosis of mucocutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) was 2.4 years in an observational, retrospective study.
The study, conducted at St. Thomas’ Hospital and Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, was a review of all individuals with EB who had developed the skin cancer over a 28-year period, from 1991 to 2019.
A total of 44 subjects were identified who together had 221 primary SCCs. Considering all study subjects, the median age at first diagnosis of SCC was 32.6 years, with a mean of five tumors present. Almost 40% had metastatic tumors, and of the 57% who died during the observation period, 88% of deaths were attributable to the SCC.
“EB-associated SCCs differ from those in the general population,” the study’s investigators wrote in a poster presented at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (debra). “They affect a younger age group, and there are often multiple primaries,” they added. Furthermore, “they behave aggressively and metastasize early despite being well differentiated.”
Most (31) of the study participants had RDEB-GS and tended to develop their first SCC at a younger age than the group overall, at a median of 29.5 years (compared with 32.6 years for the overall group). The mean number of tumors was 5.8 among those with RDEB-GS, with over half (53.4%) of the SCCs being well differentiated and located on the hands, upper arms, feet, and lower legs. Median survival after a first diagnosis in this group was 2.4 years. The short survival after a first diagnosis of SCC “underscores the poor prognosis in this group,” the researchers wrote.
“As the largest cohort of EB SCC patients with comprehensive data regarding clinical course and management to date, our data reinforce the need for regular clinical surveillance for SCCs in EB patients,” the team concluded. This surveillance should start in adolescence for those with the severe generalized RDEB subtype, they advise, and from the third or fourth decade for other at-risk groups.
These data also highlight “the pressing need for more effective treatments,” the investigators wrote. Most (86.4%) of the SCCs among the patients in the study had been surgically removed by wide local excision, with a few patients undergoing lymph node dissection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, electrochemotherapy, or receiving targeted cancer therapies such as erlotinib, cetuximab, or cemiplimab.
Surgery may not be an option for many patients, Jemima Mellerio, MD explained in an oral presentation at the meeting. Dr. Mellerio, a consultant dermatologist and chief of St John’s Institute of Dermatology at Guy’s & St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation, London, noted that the location of the tumor was important, as sometimes it was not physically possible to excise it completely.
Guidelines on how to manage SCCs in patients with EB were published a few years ago (Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:56-67) and noted that the clinical detection of SCCs could be difficult because of chronic wound ulceration in these patients. The “possibility of malignancy should be borne in mind, with suspicious lesions biopsied for histological evaluation,” the document states. Evidence for many of the nonsurgical options – radiotherapy, conventional chemotherapy, biologic therapies – was poor, according to the guidelines, and effective nonsurgical options are still desperately needed.
Several avenues of research are being investigated, Dr. Mellerio noted, such as targeting the fibrotic process and perhaps using a micro-RNA inhibitor to stop the upregulation of certain microRNAs in fibroblasts. Targeting inflammatory mechanisms such as thrombospondin 1, which can lead to elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor–beta and contribute to extracellular matrix stiffness, also is under investigation. Raised interleukin-6 may be another target to consider.
Research shows that similar genes are mutated in EB-related and ultraviolet-related SCCs, Dr. Mellerio said. Indeed, mutations in HRAS, NOTCH1, TP53, and CDKN2A have been reported, but mutations in these genes occur much earlier in life in patients with EB. “Something else is going on,” she added, commenting that researchers are looking at apolipoprotein B editing complex (APOBEC) enzymes, which modulate DNA and can cause “particular types of genetic changes in EB cancers.”
One investigator who is studying the genetics of EB SCCs and how APOBEC enzymes might be involved is Andrew South, PhD, an associate professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. APOBEC enzymes are a very prominent source of mutations in RDEB. These mutations are found in 10%-20% of squamous cell carcinomas not associated with RDEB, and 80%-90% of head and neck cancers, he said during a separate talk at the meeting.
Dr. South observed that “RDEB squamous cell carcinoma does not show any particular somatic mutation or upregulation or downregulation of genes that differentiates it from other squamous cell carcinomas, which might be disappointing on the front of it, but actually it does mean that precision therapies that have been developed for other squamous cell carcinomas have application in RDEB.”
RDEB SCC shows the greatest similarity with head and neck SCC, Dr. South said. He also stressed that fibrosis is a major driver of cancer development, SCC tumors in RDEB are homogenous, and that frontline therapy is still unclear.
What is clear, however, is that interdisciplinary management of patients is crucial, said Leena Bruckner-Tuderman, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University Medical Center, Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg, Germany.
“In severe RDEB, metastatic SCC is the leading cause of death at a young age. We need monitoring, careful diagnostics, and multidisciplinary treatment,” Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman said. The latter should be delivered by a coordinated team that consists of dermatologists, surgeons, radiologists, oncologists, pathologists, geneticists, and (molecular) tumor boards, she advised.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Mellerio disclosed financial relationships with Castle Creek Pharmaceuticals and ProQR Therapeutics, and acted as an unpaid advisor to Helpberby Therapeutics. Dr. South disclosed financial relationships with Krystal Biotech Inc. and Amryt Genetics and has been an advisory board member for Abeona Therapeutics and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman disclosed receiving grants or research support from Constant Pharmaceuticals/Tarix Orphan.
LONDON – Median survival among patients with generalized severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB-GS) after a first diagnosis of mucocutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) was 2.4 years in an observational, retrospective study.
The study, conducted at St. Thomas’ Hospital and Great Ormond Street Hospital in London, was a review of all individuals with EB who had developed the skin cancer over a 28-year period, from 1991 to 2019.
A total of 44 subjects were identified who together had 221 primary SCCs. Considering all study subjects, the median age at first diagnosis of SCC was 32.6 years, with a mean of five tumors present. Almost 40% had metastatic tumors, and of the 57% who died during the observation period, 88% of deaths were attributable to the SCC.
“EB-associated SCCs differ from those in the general population,” the study’s investigators wrote in a poster presented at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (debra). “They affect a younger age group, and there are often multiple primaries,” they added. Furthermore, “they behave aggressively and metastasize early despite being well differentiated.”
Most (31) of the study participants had RDEB-GS and tended to develop their first SCC at a younger age than the group overall, at a median of 29.5 years (compared with 32.6 years for the overall group). The mean number of tumors was 5.8 among those with RDEB-GS, with over half (53.4%) of the SCCs being well differentiated and located on the hands, upper arms, feet, and lower legs. Median survival after a first diagnosis in this group was 2.4 years. The short survival after a first diagnosis of SCC “underscores the poor prognosis in this group,” the researchers wrote.
“As the largest cohort of EB SCC patients with comprehensive data regarding clinical course and management to date, our data reinforce the need for regular clinical surveillance for SCCs in EB patients,” the team concluded. This surveillance should start in adolescence for those with the severe generalized RDEB subtype, they advise, and from the third or fourth decade for other at-risk groups.
These data also highlight “the pressing need for more effective treatments,” the investigators wrote. Most (86.4%) of the SCCs among the patients in the study had been surgically removed by wide local excision, with a few patients undergoing lymph node dissection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, electrochemotherapy, or receiving targeted cancer therapies such as erlotinib, cetuximab, or cemiplimab.
Surgery may not be an option for many patients, Jemima Mellerio, MD explained in an oral presentation at the meeting. Dr. Mellerio, a consultant dermatologist and chief of St John’s Institute of Dermatology at Guy’s & St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation, London, noted that the location of the tumor was important, as sometimes it was not physically possible to excise it completely.
Guidelines on how to manage SCCs in patients with EB were published a few years ago (Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:56-67) and noted that the clinical detection of SCCs could be difficult because of chronic wound ulceration in these patients. The “possibility of malignancy should be borne in mind, with suspicious lesions biopsied for histological evaluation,” the document states. Evidence for many of the nonsurgical options – radiotherapy, conventional chemotherapy, biologic therapies – was poor, according to the guidelines, and effective nonsurgical options are still desperately needed.
Several avenues of research are being investigated, Dr. Mellerio noted, such as targeting the fibrotic process and perhaps using a micro-RNA inhibitor to stop the upregulation of certain microRNAs in fibroblasts. Targeting inflammatory mechanisms such as thrombospondin 1, which can lead to elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor–beta and contribute to extracellular matrix stiffness, also is under investigation. Raised interleukin-6 may be another target to consider.
Research shows that similar genes are mutated in EB-related and ultraviolet-related SCCs, Dr. Mellerio said. Indeed, mutations in HRAS, NOTCH1, TP53, and CDKN2A have been reported, but mutations in these genes occur much earlier in life in patients with EB. “Something else is going on,” she added, commenting that researchers are looking at apolipoprotein B editing complex (APOBEC) enzymes, which modulate DNA and can cause “particular types of genetic changes in EB cancers.”
One investigator who is studying the genetics of EB SCCs and how APOBEC enzymes might be involved is Andrew South, PhD, an associate professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia. APOBEC enzymes are a very prominent source of mutations in RDEB. These mutations are found in 10%-20% of squamous cell carcinomas not associated with RDEB, and 80%-90% of head and neck cancers, he said during a separate talk at the meeting.
Dr. South observed that “RDEB squamous cell carcinoma does not show any particular somatic mutation or upregulation or downregulation of genes that differentiates it from other squamous cell carcinomas, which might be disappointing on the front of it, but actually it does mean that precision therapies that have been developed for other squamous cell carcinomas have application in RDEB.”
RDEB SCC shows the greatest similarity with head and neck SCC, Dr. South said. He also stressed that fibrosis is a major driver of cancer development, SCC tumors in RDEB are homogenous, and that frontline therapy is still unclear.
What is clear, however, is that interdisciplinary management of patients is crucial, said Leena Bruckner-Tuderman, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University Medical Center, Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg, Germany.
“In severe RDEB, metastatic SCC is the leading cause of death at a young age. We need monitoring, careful diagnostics, and multidisciplinary treatment,” Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman said. The latter should be delivered by a coordinated team that consists of dermatologists, surgeons, radiologists, oncologists, pathologists, geneticists, and (molecular) tumor boards, she advised.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Mellerio disclosed financial relationships with Castle Creek Pharmaceuticals and ProQR Therapeutics, and acted as an unpaid advisor to Helpberby Therapeutics. Dr. South disclosed financial relationships with Krystal Biotech Inc. and Amryt Genetics and has been an advisory board member for Abeona Therapeutics and Sanofi Genzyme. Dr. Bruckner-Tuderman disclosed receiving grants or research support from Constant Pharmaceuticals/Tarix Orphan.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Chronic Diarrhea in an Adolescent Girl With a Genetic Skin Condition
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder characterized by a clinical triad of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa; atopic diathesis; and hair shaft abnormalities, most classically trichorrhexis invaginata.1 Netherton syndrome is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal-type gene, SPINK5, which encodes LEKTI proteins and is found in all stratified epithelia as well as the thymus.2 A lack of functional LEKTI leads to the activation of a cascade of allergy and inflammation as well as uncontrolled proteolytic activity in the stratum corneum, which causes increased desquamation.1
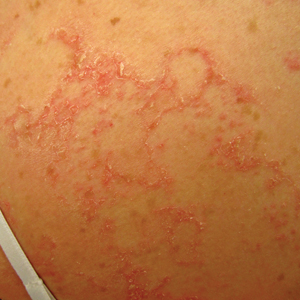
Netherton syndrome presents with serpiginous or circinate scaling plaques with double-edged scale referred to as ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (quiz image). Skin plaques are intensely pruritic and migratory with fluctuating severity. Alternately, patients may have a generalized scaling erythroderma. Infants are at an especially high risk for recurrent infections, sepsis, hypernatremic dehydration, and failure to thrive.2
Netherton syndrome often gradually improves over time, though adults with NS usually have intensely pruritic, localized patches of redness, scaling, or ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. Lichenification and eczematous plaques of the popliteal and antecubital fossae also are common.1 Therapeutic options for NS include emollients, topical steroids, phototherapy, and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe cases.3 Because there is skin barrier dysfunction in NS, supratherapeutic serum levels of tacrolimus following topical application have been reported.4 Topical pimecrolimus has been demonstrated as an effective and safer application.5 Trichorrhexis invaginata (also known as bamboo hair) of the hair and eyebrows is a pathognomonic finding in NS, involving invagination of the distal hair shaft into the proximal shaft on light microscopy examination.1
Histopathology is variable and nonspecific with psoriasiform hyperplasia as the most frequent finding. Other histologic findings include incomplete keratinization of the epidermis, incomplete cornification with a severely reduced granular layer, and mild to moderate inflammatory dermal infiltrate.6 LEKTI immunostaining is confirmatory and shows the reduction or complete absence of LEKTI in the granular layer and inner root sheath of follicles.1 Patchy LEKTI staining would be suggestive of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis instead of NS.2
Atopic manifestations include angioedema, urticaria, and anaphylaxis, as well as chronic diarrhea or vomiting due to food allergies.1 Elevated IgE levels for staple foods (eg, milk, wheat), elevated total serum IgE, and eosinophilia frequently are seen.7 Biopsy of the esophagus and colon likely would show mucosal eosinophilia.7,8 Elimination of major food triggers through specific serum IgE testing and oral allergen desensitization can lead to the reduction of digestive symptoms.9 Cisapride and omeprazole are effective treatments for gastroesophageal reflux and poor feeding.8 Biopsy of the intestines in this patient likely would not have shown total villous atrophy, which is rare and primarily reported in infants with NS who have failure to thrive.10 There is a limited association between NS and intestinal metaplasia, intraepithelial lymphocytes, and bacterial overgrowth.
The primary morphology of dyskeratosis follicularis includes keratotic papules developing in sebaceous areas of the skin rather than scaly serpiginous plaques as seen in NS. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is a perforating disorder seen in the context of several genetic conditions. It has a serpiginous appearance but, unlike NS, tends to be localized and features keratotic papules rather than patches with scale. Erythema marginatum is an uncommon feature of rheumatic fever and appears as pink annular macules and tends not to be pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus does feature scaly annular and serpiginous plaques but features trailing scale without the double-edge appearance of NS and is acquired rather than genetic.
- Hovnanian A. Netherton syndrome: skin inflammation and allergy by loss of protease inhibition. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351:289-300.
- Bitoun E, Micheloni A, Lamant L, et al. LEKTI proteolytic processing in human primary keratinocytes, tissue distribution and defective expression in Netherton syndrome. Human Mol Genet. 2003;12:2417-2430.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Shah KN, Yan AC. Low but detectable serum levels of tacrolimus seen with the use of very dilute, extemporaneously compounded formulations of tacrolimus ointment in the treatment of patients with Netherton syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1362-1363.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Leclerc-Mercier S, Bodemer C, Furio L, et al. Skin biopsy in Netherton syndrome: a histological review of a large series and new findings. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:83-91.
- Pauluel-Marmont C, Bellon N, Barbet P, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis and colonic mucosal eosinophilia in Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:2003-2005.e1.
- Hannula-Jouppi K, Laasanen SL, Heikkila H, et al. IgE allergen component-based profiling and atopic manifestations in patients with Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:985-988.
- Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1097-1102.
- Judge MR, Morgan G , Harper JI. A clinical and immunological study of Netherton's syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1994;131:615-21.
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder characterized by a clinical triad of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa; atopic diathesis; and hair shaft abnormalities, most classically trichorrhexis invaginata.1 Netherton syndrome is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal-type gene, SPINK5, which encodes LEKTI proteins and is found in all stratified epithelia as well as the thymus.2 A lack of functional LEKTI leads to the activation of a cascade of allergy and inflammation as well as uncontrolled proteolytic activity in the stratum corneum, which causes increased desquamation.1
Netherton syndrome presents with serpiginous or circinate scaling plaques with double-edged scale referred to as ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (quiz image). Skin plaques are intensely pruritic and migratory with fluctuating severity. Alternately, patients may have a generalized scaling erythroderma. Infants are at an especially high risk for recurrent infections, sepsis, hypernatremic dehydration, and failure to thrive.2
Netherton syndrome often gradually improves over time, though adults with NS usually have intensely pruritic, localized patches of redness, scaling, or ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. Lichenification and eczematous plaques of the popliteal and antecubital fossae also are common.1 Therapeutic options for NS include emollients, topical steroids, phototherapy, and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe cases.3 Because there is skin barrier dysfunction in NS, supratherapeutic serum levels of tacrolimus following topical application have been reported.4 Topical pimecrolimus has been demonstrated as an effective and safer application.5 Trichorrhexis invaginata (also known as bamboo hair) of the hair and eyebrows is a pathognomonic finding in NS, involving invagination of the distal hair shaft into the proximal shaft on light microscopy examination.1
Histopathology is variable and nonspecific with psoriasiform hyperplasia as the most frequent finding. Other histologic findings include incomplete keratinization of the epidermis, incomplete cornification with a severely reduced granular layer, and mild to moderate inflammatory dermal infiltrate.6 LEKTI immunostaining is confirmatory and shows the reduction or complete absence of LEKTI in the granular layer and inner root sheath of follicles.1 Patchy LEKTI staining would be suggestive of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis instead of NS.2
Atopic manifestations include angioedema, urticaria, and anaphylaxis, as well as chronic diarrhea or vomiting due to food allergies.1 Elevated IgE levels for staple foods (eg, milk, wheat), elevated total serum IgE, and eosinophilia frequently are seen.7 Biopsy of the esophagus and colon likely would show mucosal eosinophilia.7,8 Elimination of major food triggers through specific serum IgE testing and oral allergen desensitization can lead to the reduction of digestive symptoms.9 Cisapride and omeprazole are effective treatments for gastroesophageal reflux and poor feeding.8 Biopsy of the intestines in this patient likely would not have shown total villous atrophy, which is rare and primarily reported in infants with NS who have failure to thrive.10 There is a limited association between NS and intestinal metaplasia, intraepithelial lymphocytes, and bacterial overgrowth.
The primary morphology of dyskeratosis follicularis includes keratotic papules developing in sebaceous areas of the skin rather than scaly serpiginous plaques as seen in NS. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is a perforating disorder seen in the context of several genetic conditions. It has a serpiginous appearance but, unlike NS, tends to be localized and features keratotic papules rather than patches with scale. Erythema marginatum is an uncommon feature of rheumatic fever and appears as pink annular macules and tends not to be pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus does feature scaly annular and serpiginous plaques but features trailing scale without the double-edge appearance of NS and is acquired rather than genetic.
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder characterized by a clinical triad of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa; atopic diathesis; and hair shaft abnormalities, most classically trichorrhexis invaginata.1 Netherton syndrome is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal-type gene, SPINK5, which encodes LEKTI proteins and is found in all stratified epithelia as well as the thymus.2 A lack of functional LEKTI leads to the activation of a cascade of allergy and inflammation as well as uncontrolled proteolytic activity in the stratum corneum, which causes increased desquamation.1
Netherton syndrome presents with serpiginous or circinate scaling plaques with double-edged scale referred to as ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (quiz image). Skin plaques are intensely pruritic and migratory with fluctuating severity. Alternately, patients may have a generalized scaling erythroderma. Infants are at an especially high risk for recurrent infections, sepsis, hypernatremic dehydration, and failure to thrive.2
Netherton syndrome often gradually improves over time, though adults with NS usually have intensely pruritic, localized patches of redness, scaling, or ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. Lichenification and eczematous plaques of the popliteal and antecubital fossae also are common.1 Therapeutic options for NS include emollients, topical steroids, phototherapy, and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe cases.3 Because there is skin barrier dysfunction in NS, supratherapeutic serum levels of tacrolimus following topical application have been reported.4 Topical pimecrolimus has been demonstrated as an effective and safer application.5 Trichorrhexis invaginata (also known as bamboo hair) of the hair and eyebrows is a pathognomonic finding in NS, involving invagination of the distal hair shaft into the proximal shaft on light microscopy examination.1
Histopathology is variable and nonspecific with psoriasiform hyperplasia as the most frequent finding. Other histologic findings include incomplete keratinization of the epidermis, incomplete cornification with a severely reduced granular layer, and mild to moderate inflammatory dermal infiltrate.6 LEKTI immunostaining is confirmatory and shows the reduction or complete absence of LEKTI in the granular layer and inner root sheath of follicles.1 Patchy LEKTI staining would be suggestive of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis instead of NS.2
Atopic manifestations include angioedema, urticaria, and anaphylaxis, as well as chronic diarrhea or vomiting due to food allergies.1 Elevated IgE levels for staple foods (eg, milk, wheat), elevated total serum IgE, and eosinophilia frequently are seen.7 Biopsy of the esophagus and colon likely would show mucosal eosinophilia.7,8 Elimination of major food triggers through specific serum IgE testing and oral allergen desensitization can lead to the reduction of digestive symptoms.9 Cisapride and omeprazole are effective treatments for gastroesophageal reflux and poor feeding.8 Biopsy of the intestines in this patient likely would not have shown total villous atrophy, which is rare and primarily reported in infants with NS who have failure to thrive.10 There is a limited association between NS and intestinal metaplasia, intraepithelial lymphocytes, and bacterial overgrowth.
The primary morphology of dyskeratosis follicularis includes keratotic papules developing in sebaceous areas of the skin rather than scaly serpiginous plaques as seen in NS. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is a perforating disorder seen in the context of several genetic conditions. It has a serpiginous appearance but, unlike NS, tends to be localized and features keratotic papules rather than patches with scale. Erythema marginatum is an uncommon feature of rheumatic fever and appears as pink annular macules and tends not to be pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus does feature scaly annular and serpiginous plaques but features trailing scale without the double-edge appearance of NS and is acquired rather than genetic.
- Hovnanian A. Netherton syndrome: skin inflammation and allergy by loss of protease inhibition. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351:289-300.
- Bitoun E, Micheloni A, Lamant L, et al. LEKTI proteolytic processing in human primary keratinocytes, tissue distribution and defective expression in Netherton syndrome. Human Mol Genet. 2003;12:2417-2430.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Shah KN, Yan AC. Low but detectable serum levels of tacrolimus seen with the use of very dilute, extemporaneously compounded formulations of tacrolimus ointment in the treatment of patients with Netherton syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1362-1363.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Leclerc-Mercier S, Bodemer C, Furio L, et al. Skin biopsy in Netherton syndrome: a histological review of a large series and new findings. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:83-91.
- Pauluel-Marmont C, Bellon N, Barbet P, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis and colonic mucosal eosinophilia in Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:2003-2005.e1.
- Hannula-Jouppi K, Laasanen SL, Heikkila H, et al. IgE allergen component-based profiling and atopic manifestations in patients with Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:985-988.
- Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1097-1102.
- Judge MR, Morgan G , Harper JI. A clinical and immunological study of Netherton's syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1994;131:615-21.
- Hovnanian A. Netherton syndrome: skin inflammation and allergy by loss of protease inhibition. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351:289-300.
- Bitoun E, Micheloni A, Lamant L, et al. LEKTI proteolytic processing in human primary keratinocytes, tissue distribution and defective expression in Netherton syndrome. Human Mol Genet. 2003;12:2417-2430.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Shah KN, Yan AC. Low but detectable serum levels of tacrolimus seen with the use of very dilute, extemporaneously compounded formulations of tacrolimus ointment in the treatment of patients with Netherton syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1362-1363.
- Yan AC, Honig PJ, Ming ME, et al. The safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus, 1%, cream for the treatment of Netherton syndrome: results from an exploratory study. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:57-62.
- Leclerc-Mercier S, Bodemer C, Furio L, et al. Skin biopsy in Netherton syndrome: a histological review of a large series and new findings. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:83-91.
- Pauluel-Marmont C, Bellon N, Barbet P, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis and colonic mucosal eosinophilia in Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:2003-2005.e1.
- Hannula-Jouppi K, Laasanen SL, Heikkila H, et al. IgE allergen component-based profiling and atopic manifestations in patients with Netherton syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:985-988.
- Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1097-1102.
- Judge MR, Morgan G , Harper JI. A clinical and immunological study of Netherton's syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1994;131:615-21.
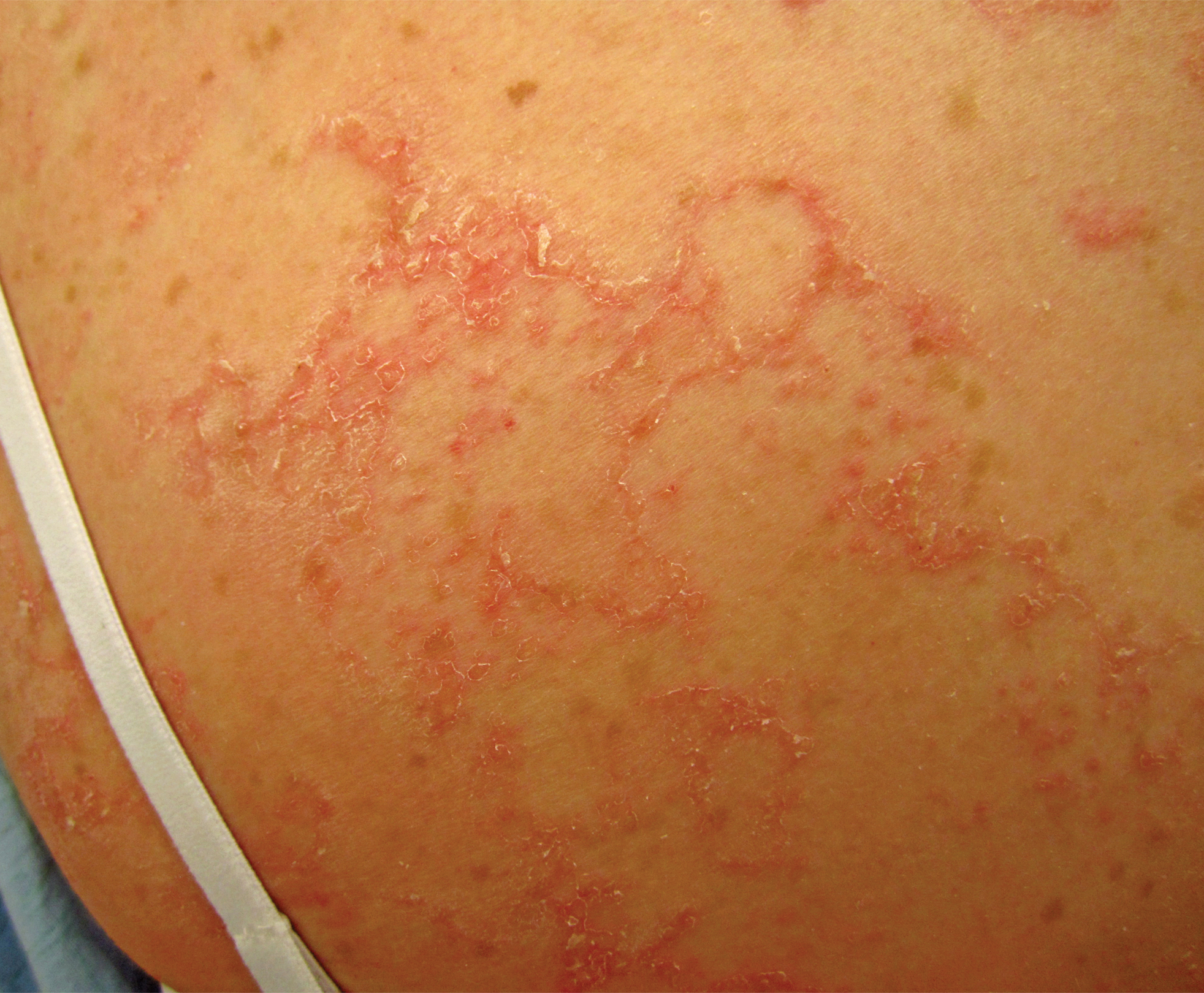
A 17-year-old adolescent girl visited our clinic to establish care for her genetic skin condition. She exhibited red scaly plaques and patches over much of the body surface area consistent with atopic dermatitis but also had areas on the trunk with serpiginous red plaques with scale on the leading and trailing edges. She also noted fragile hair with sparse eyebrows. The patient reported that she had experienced chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain since childhood. She asked if it could be related to her genetic condition.
Prioritize oral health in children with DEB
LONDON – , pediatric dentist Susanne Krämer told attendees at the first EB World Congress.
While it may not be the first thing on the minds of families coming to terms with their children having a chronic and potentially debilitating skin disease, it is important to consider oral health early to ensure healthy dentition and mouth function, both of which will affect the ability to eat and thus nutrition.
When there are a lot of other health issues, “dentistry is not a priority,” Dr. Krämer acknowledged in an interview at the meeting, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
Something as simple as brushing teeth can be very distressing for parents of a child with EB, she observed, especially if there is dysphagia and toothpaste may be getting into the airways accidentally.
Oral health was one of the topics that patients with EB and their families said would be good to have some guidance on when they were surveyed by DEBRA International. This led the charity to develop its first clinical practice guideline in 2012. Dr. Krämer was the lead author of the guidelines, which are about to be updated and republished.
The “Oral Health for Patients with Epidermolysis Bullosa – Best Clinical Practice Guidelines” (Int J Paediatr Dent. 2012;22 Suppl 1:1-35) are in the final stages of being revised, said Dr. Krämer, who is head of the department of pediatric dentistry at the University of Chile in Santiago. Although there is not much new evidence since the guidelines were first published, “we do have a lot of new technologies within dentistry that can aid the care of EB,” she said.
An important addition to the upcoming 2020 guidelines is a chapter on the patient-clinician partnership. This was added because “you can have fantastic technologies, but if you don’t have a confident relationship with the family and the patient, you won’t be able to proceed.” Dr. Krämer explained: “Patients with EB are so fragile and so afraid of being hurt that they won’t open their mouth unless there is a confidence with the clinician and they trust [him or her]; once they trust, they [will] open the mouth and you can work.”
Dr. Krämer noted that timing of the first dental appointment will depend on the referral pathway for every country and then every service. In her specialist practice the aim is to see newly diagnosed babies before the age of 3 months. “Lots of people would argue they don’t have teeth, but I need to educate the families on several aspects of oral health from early on.”
Older patients with EB may be more aware of the importance of a healthy mouth from a functional point of view and the need to eat and swallow normally, Dr. Krämer said, adding that the “social aspects of having a healthy smile are very important as well.”
Oral care in EB has come a long way since the 1970s when teeth extraction was recommended as the primary dental treatment option. “If you refer to literature in the 90s, that said we can actually restore the teeth in the patients with EB, and what we are now saying is that we have to prevent oral disease,” Dr. Krämer said.
Can oral disease be prevented completely? Yes, she said, but only in a few patients. “We still have decay in a lot of our patients, but far less than what we have had before. It will depend on the compliance of the family and the patient,” Dr. Krämer noted.
Compliance also is a factor in improving mouth function after surgery, which may be done to prevent the tongue from fusing to the bottom of the mouth and to relieve or prevent microstomia, which limits mouth opening.
“We are doing a lot of surgeries to release the fibrotic scars ... we have done it in both children and adults, but there have been better results in adults, because they are able to comply with the course of exercises” after surgery, Dr. Krämer said.
Results of an as-yet unpublished randomized controlled trial of postoperative mouth exercises demonstrate that patients who did the exercises, which involved using a device to stretch the mouth three times a day for 3 months, saw improvements in mouth opening. Once they stopped doing the exercises, however, these improvements faded. Considering the time spent on dressing changes and other exercises, this is perhaps understandable, she acknowledged.
Prevention, education, continual follow-up, and early referral are key to good oral health, Dr. Krämer emphasized. “If there is patient-clinician partnership confidence, they can have regular checkups with dental cleaning, with a fluoride varnish, different preventive strategies so they do not need to get to the point where they need general anesthesia or extractions.” Extractions still will be done, she added, but more for orthodontic reasons, because the teeth do not fit in the mouth. “That is our ideal world, that is where we want to go.”
LONDON – , pediatric dentist Susanne Krämer told attendees at the first EB World Congress.
While it may not be the first thing on the minds of families coming to terms with their children having a chronic and potentially debilitating skin disease, it is important to consider oral health early to ensure healthy dentition and mouth function, both of which will affect the ability to eat and thus nutrition.
When there are a lot of other health issues, “dentistry is not a priority,” Dr. Krämer acknowledged in an interview at the meeting, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
Something as simple as brushing teeth can be very distressing for parents of a child with EB, she observed, especially if there is dysphagia and toothpaste may be getting into the airways accidentally.
Oral health was one of the topics that patients with EB and their families said would be good to have some guidance on when they were surveyed by DEBRA International. This led the charity to develop its first clinical practice guideline in 2012. Dr. Krämer was the lead author of the guidelines, which are about to be updated and republished.
The “Oral Health for Patients with Epidermolysis Bullosa – Best Clinical Practice Guidelines” (Int J Paediatr Dent. 2012;22 Suppl 1:1-35) are in the final stages of being revised, said Dr. Krämer, who is head of the department of pediatric dentistry at the University of Chile in Santiago. Although there is not much new evidence since the guidelines were first published, “we do have a lot of new technologies within dentistry that can aid the care of EB,” she said.
An important addition to the upcoming 2020 guidelines is a chapter on the patient-clinician partnership. This was added because “you can have fantastic technologies, but if you don’t have a confident relationship with the family and the patient, you won’t be able to proceed.” Dr. Krämer explained: “Patients with EB are so fragile and so afraid of being hurt that they won’t open their mouth unless there is a confidence with the clinician and they trust [him or her]; once they trust, they [will] open the mouth and you can work.”
Dr. Krämer noted that timing of the first dental appointment will depend on the referral pathway for every country and then every service. In her specialist practice the aim is to see newly diagnosed babies before the age of 3 months. “Lots of people would argue they don’t have teeth, but I need to educate the families on several aspects of oral health from early on.”
Older patients with EB may be more aware of the importance of a healthy mouth from a functional point of view and the need to eat and swallow normally, Dr. Krämer said, adding that the “social aspects of having a healthy smile are very important as well.”
Oral care in EB has come a long way since the 1970s when teeth extraction was recommended as the primary dental treatment option. “If you refer to literature in the 90s, that said we can actually restore the teeth in the patients with EB, and what we are now saying is that we have to prevent oral disease,” Dr. Krämer said.
Can oral disease be prevented completely? Yes, she said, but only in a few patients. “We still have decay in a lot of our patients, but far less than what we have had before. It will depend on the compliance of the family and the patient,” Dr. Krämer noted.
Compliance also is a factor in improving mouth function after surgery, which may be done to prevent the tongue from fusing to the bottom of the mouth and to relieve or prevent microstomia, which limits mouth opening.
“We are doing a lot of surgeries to release the fibrotic scars ... we have done it in both children and adults, but there have been better results in adults, because they are able to comply with the course of exercises” after surgery, Dr. Krämer said.
Results of an as-yet unpublished randomized controlled trial of postoperative mouth exercises demonstrate that patients who did the exercises, which involved using a device to stretch the mouth three times a day for 3 months, saw improvements in mouth opening. Once they stopped doing the exercises, however, these improvements faded. Considering the time spent on dressing changes and other exercises, this is perhaps understandable, she acknowledged.
Prevention, education, continual follow-up, and early referral are key to good oral health, Dr. Krämer emphasized. “If there is patient-clinician partnership confidence, they can have regular checkups with dental cleaning, with a fluoride varnish, different preventive strategies so they do not need to get to the point where they need general anesthesia or extractions.” Extractions still will be done, she added, but more for orthodontic reasons, because the teeth do not fit in the mouth. “That is our ideal world, that is where we want to go.”
LONDON – , pediatric dentist Susanne Krämer told attendees at the first EB World Congress.
While it may not be the first thing on the minds of families coming to terms with their children having a chronic and potentially debilitating skin disease, it is important to consider oral health early to ensure healthy dentition and mouth function, both of which will affect the ability to eat and thus nutrition.
When there are a lot of other health issues, “dentistry is not a priority,” Dr. Krämer acknowledged in an interview at the meeting, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
Something as simple as brushing teeth can be very distressing for parents of a child with EB, she observed, especially if there is dysphagia and toothpaste may be getting into the airways accidentally.
Oral health was one of the topics that patients with EB and their families said would be good to have some guidance on when they were surveyed by DEBRA International. This led the charity to develop its first clinical practice guideline in 2012. Dr. Krämer was the lead author of the guidelines, which are about to be updated and republished.
The “Oral Health for Patients with Epidermolysis Bullosa – Best Clinical Practice Guidelines” (Int J Paediatr Dent. 2012;22 Suppl 1:1-35) are in the final stages of being revised, said Dr. Krämer, who is head of the department of pediatric dentistry at the University of Chile in Santiago. Although there is not much new evidence since the guidelines were first published, “we do have a lot of new technologies within dentistry that can aid the care of EB,” she said.
An important addition to the upcoming 2020 guidelines is a chapter on the patient-clinician partnership. This was added because “you can have fantastic technologies, but if you don’t have a confident relationship with the family and the patient, you won’t be able to proceed.” Dr. Krämer explained: “Patients with EB are so fragile and so afraid of being hurt that they won’t open their mouth unless there is a confidence with the clinician and they trust [him or her]; once they trust, they [will] open the mouth and you can work.”
Dr. Krämer noted that timing of the first dental appointment will depend on the referral pathway for every country and then every service. In her specialist practice the aim is to see newly diagnosed babies before the age of 3 months. “Lots of people would argue they don’t have teeth, but I need to educate the families on several aspects of oral health from early on.”
Older patients with EB may be more aware of the importance of a healthy mouth from a functional point of view and the need to eat and swallow normally, Dr. Krämer said, adding that the “social aspects of having a healthy smile are very important as well.”
Oral care in EB has come a long way since the 1970s when teeth extraction was recommended as the primary dental treatment option. “If you refer to literature in the 90s, that said we can actually restore the teeth in the patients with EB, and what we are now saying is that we have to prevent oral disease,” Dr. Krämer said.
Can oral disease be prevented completely? Yes, she said, but only in a few patients. “We still have decay in a lot of our patients, but far less than what we have had before. It will depend on the compliance of the family and the patient,” Dr. Krämer noted.
Compliance also is a factor in improving mouth function after surgery, which may be done to prevent the tongue from fusing to the bottom of the mouth and to relieve or prevent microstomia, which limits mouth opening.
“We are doing a lot of surgeries to release the fibrotic scars ... we have done it in both children and adults, but there have been better results in adults, because they are able to comply with the course of exercises” after surgery, Dr. Krämer said.
Results of an as-yet unpublished randomized controlled trial of postoperative mouth exercises demonstrate that patients who did the exercises, which involved using a device to stretch the mouth three times a day for 3 months, saw improvements in mouth opening. Once they stopped doing the exercises, however, these improvements faded. Considering the time spent on dressing changes and other exercises, this is perhaps understandable, she acknowledged.
Prevention, education, continual follow-up, and early referral are key to good oral health, Dr. Krämer emphasized. “If there is patient-clinician partnership confidence, they can have regular checkups with dental cleaning, with a fluoride varnish, different preventive strategies so they do not need to get to the point where they need general anesthesia or extractions.” Extractions still will be done, she added, but more for orthodontic reasons, because the teeth do not fit in the mouth. “That is our ideal world, that is where we want to go.”
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Target plantar keratoderma when managing ‘mild’ EBS
LONDON – Hardened feet are a major determinant of the clinical course of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), according to research presented by a German team of investigators at the EB World Congress.
In a study of 157 individuals with EBS, 75.8% had plantar keratoderma, a condition associated with a vicious circle of pain, reduced mobility, subsequent weight gain, and further foot problems.
“EBS has severe impacts on various aspects of everyday life,” Antonia Reimer, MD, and associates at the University of Freiburg, Germany, reported in a poster presentation. “Plantar involvement and [plantar keratoderma] are serious complications of all EBS subtypes, correlating with excessive weight gain, pain, local infections, and limited mobility.”
The researchers suggested that “targeting [plantar keratoderma] should be a priority in EBS therapy and research.”
In their retrospective cohort study, clinical and molecular data were retrieved from patient records, and major determinants of the clinical course of EBS investigated. As such, the researchers looked at how weight changes affected EBS, the effect of hardening skin on the feet, pain, mobility, and working life.
“EB simplex is generally regarded as the ‘mildest’ EB type,” Dr. Reimer and colleagues wrote, “however, individuals with EBS report a high disease burden and frequent pain.” The team found that just under 30% of patients (n = 46) experienced frequent pain, particularly those with localized and severe EBS. Of the patients experiencing pain, the majority (75.2%) had plantar keratoderma. Furthermore, those with blisters underneath the hardened skin reported having the most painful lesions.
Palmoplantar hyperhidrosis was present in slightly more than 40% of cases, and was especially common in individuals with localized EBS, Dr. Reimer and colleagues found. They also found that bacterial and fungal infections occurred in 14% and 7% of patients, respectively, and this correlated significantly with diffuse plantar keratoderma.
A third of patients experience mobility problems, and 8.2% required a wheelchair; 16.4% “were in occupational disability,” the team reported.
“Hyperkeratosis is important because it isn’t just about treating the hyperkeratosis, it’s also looking at the mechanical balance of the foot,” Tariq Khan, PhD, said during an unrelated oral presentation. Dr. Khan, a consultant podiatrist specializing in EB at Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, discussed how to best manage the feet of people with EB.
“Podiatry technology and how we treat can often be detrimental to an EB patient,” Dr. Khan cautioned at the meeting, which was organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
For example, “certain devices, certain types of material, will add more friction and pressure and cause more blistering,” he added, making treatment challenging.
Having worked with the EB community for the past 22 years, he noted that he had seen how podiatry practices had been refined to deal with this patient population. Dr. Khan is one of several experts behind EB podiatry guidelines issued by DEBRA International last year (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Aug 9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18381) and has run the charity’s first practical EB podiatry skills course to educate more podiatrists on the intricacies of managing EB feet.
During his talk, Dr. Kahn mentioned several innovations that came about by working with external companies, such as the production of special cotton socks containing silver fibers to help reduce the symptom of hot feet, and development of a cooling insole that helped draw moisture and odor away from the foot while providing comfort to the wearer.
One of the main problems for those with EB is finding comfortable footwear that doesn’t aggravate their symptoms, Dr. Khan emphasized.
According to the EB podiatry guidelines, footwear needs to be supportive, and “its primary focus should be aimed at minimizing blistering by reducing friction.” If blisters are already present, the guidelines note that dressings and topical antiseptics or antibiotics might be used until the blisters heal. “Therefore, suitable shoes or footwear are essential to accommodate dressings and not lead to further trauma to the damaged area. Footwear that is adjustable may be beneficial in these circumstances.”
What constitutes appropriate footwear is open to debate and was the topic of a separate poster presentation at meeting. Mark O’Sullivan, EB team podiatrist at Solihull and Birmingham Women’s and Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, and associates looked at whether wearing rocker bottom footwear could ease the formation of blisters in patients with EBS.
The team studied nine patients who reported regular plantar blistering. An in-shoe measurement system was devised to measure patients’ plantar pressure while they were wearing their existing footwear and then again when they were wearing new footwear with a rocker bottom. Participants completed questionnaires about the development of blisters on their feet, their activity levels, and pain.
The rocker bottom footwear reduced the peak plantar pressure by 30.5% and the total plantar pressure by 31.8%, compared with regular footwear. A shift in the average pressure under the foot was seen, moving from the heels of the feet to the midfoot area, while remaining similar in the front foot area.
“Patient feedback has been mixed,” Mr. O’Sullivan said when presenting the poster. “Patients state that blisters have often reduced in the heels and forefoot, but new blisters have developed in the midfoot.” As a result, some study participants chose to alternate wearing the rocker bottom footwear with their normal shoes, to even out the places where blisters might form.
Although the jury is still out on the benefit of rocker bottom footwear, one thing that might help those with EBS who develop regular foot blisters may be to keep their weight in check. In a separate poster presentation given by Lynn Hubbard, a specialist EB dietitian in the department of nutrition and dietetics at St. Thomas’ Hospital in London, it was shown that almost a third of patients with EB simplex were obese, compared with 26% of adults in the general U.K. population.
“People with EBS are known to have hyperkeratosis and foot-blistering,” Ms. Hubbard observed in the poster. This can lead to reduce mobility and pain, which “may in turn have an impact on body weight, and an increased BMI [body mass index] may further affect mobility.”
Data were collected on 90 patients who attended a U.K. EBS clinic over an 11-month period. While 45.5% of patients had a normal weight, the majority was overweight (21.1%), obese (21.1%), or morbidly obese (10%).
Fifteen patients completed questionnaires about their mobility, and almost all felt that their weight had an adverse effect on their feet, as did EBS. Several also noted problems with their EBS, in the skin folds around the bra, waist, and sock lines.
“We now plan to begin a pilot study to establish a supportive weight management program for people with EBS and evaluate both weight loss and impact on mobility,” Ms. Hubbard reported.
No conflicts of interest were declared by any of the speakers.
SOURCES: EB 2020. Reimer A et al. Poster 26; Khan T. oral presentation; O’Sullivan M et al. Poster 93; Hubbard L. Poster 19.
LONDON – Hardened feet are a major determinant of the clinical course of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), according to research presented by a German team of investigators at the EB World Congress.
In a study of 157 individuals with EBS, 75.8% had plantar keratoderma, a condition associated with a vicious circle of pain, reduced mobility, subsequent weight gain, and further foot problems.
“EBS has severe impacts on various aspects of everyday life,” Antonia Reimer, MD, and associates at the University of Freiburg, Germany, reported in a poster presentation. “Plantar involvement and [plantar keratoderma] are serious complications of all EBS subtypes, correlating with excessive weight gain, pain, local infections, and limited mobility.”
The researchers suggested that “targeting [plantar keratoderma] should be a priority in EBS therapy and research.”
In their retrospective cohort study, clinical and molecular data were retrieved from patient records, and major determinants of the clinical course of EBS investigated. As such, the researchers looked at how weight changes affected EBS, the effect of hardening skin on the feet, pain, mobility, and working life.
“EB simplex is generally regarded as the ‘mildest’ EB type,” Dr. Reimer and colleagues wrote, “however, individuals with EBS report a high disease burden and frequent pain.” The team found that just under 30% of patients (n = 46) experienced frequent pain, particularly those with localized and severe EBS. Of the patients experiencing pain, the majority (75.2%) had plantar keratoderma. Furthermore, those with blisters underneath the hardened skin reported having the most painful lesions.
Palmoplantar hyperhidrosis was present in slightly more than 40% of cases, and was especially common in individuals with localized EBS, Dr. Reimer and colleagues found. They also found that bacterial and fungal infections occurred in 14% and 7% of patients, respectively, and this correlated significantly with diffuse plantar keratoderma.
A third of patients experience mobility problems, and 8.2% required a wheelchair; 16.4% “were in occupational disability,” the team reported.
“Hyperkeratosis is important because it isn’t just about treating the hyperkeratosis, it’s also looking at the mechanical balance of the foot,” Tariq Khan, PhD, said during an unrelated oral presentation. Dr. Khan, a consultant podiatrist specializing in EB at Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, discussed how to best manage the feet of people with EB.
“Podiatry technology and how we treat can often be detrimental to an EB patient,” Dr. Khan cautioned at the meeting, which was organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
For example, “certain devices, certain types of material, will add more friction and pressure and cause more blistering,” he added, making treatment challenging.
Having worked with the EB community for the past 22 years, he noted that he had seen how podiatry practices had been refined to deal with this patient population. Dr. Khan is one of several experts behind EB podiatry guidelines issued by DEBRA International last year (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Aug 9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18381) and has run the charity’s first practical EB podiatry skills course to educate more podiatrists on the intricacies of managing EB feet.
During his talk, Dr. Kahn mentioned several innovations that came about by working with external companies, such as the production of special cotton socks containing silver fibers to help reduce the symptom of hot feet, and development of a cooling insole that helped draw moisture and odor away from the foot while providing comfort to the wearer.
One of the main problems for those with EB is finding comfortable footwear that doesn’t aggravate their symptoms, Dr. Khan emphasized.
According to the EB podiatry guidelines, footwear needs to be supportive, and “its primary focus should be aimed at minimizing blistering by reducing friction.” If blisters are already present, the guidelines note that dressings and topical antiseptics or antibiotics might be used until the blisters heal. “Therefore, suitable shoes or footwear are essential to accommodate dressings and not lead to further trauma to the damaged area. Footwear that is adjustable may be beneficial in these circumstances.”
What constitutes appropriate footwear is open to debate and was the topic of a separate poster presentation at meeting. Mark O’Sullivan, EB team podiatrist at Solihull and Birmingham Women’s and Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, and associates looked at whether wearing rocker bottom footwear could ease the formation of blisters in patients with EBS.
The team studied nine patients who reported regular plantar blistering. An in-shoe measurement system was devised to measure patients’ plantar pressure while they were wearing their existing footwear and then again when they were wearing new footwear with a rocker bottom. Participants completed questionnaires about the development of blisters on their feet, their activity levels, and pain.
The rocker bottom footwear reduced the peak plantar pressure by 30.5% and the total plantar pressure by 31.8%, compared with regular footwear. A shift in the average pressure under the foot was seen, moving from the heels of the feet to the midfoot area, while remaining similar in the front foot area.
“Patient feedback has been mixed,” Mr. O’Sullivan said when presenting the poster. “Patients state that blisters have often reduced in the heels and forefoot, but new blisters have developed in the midfoot.” As a result, some study participants chose to alternate wearing the rocker bottom footwear with their normal shoes, to even out the places where blisters might form.
Although the jury is still out on the benefit of rocker bottom footwear, one thing that might help those with EBS who develop regular foot blisters may be to keep their weight in check. In a separate poster presentation given by Lynn Hubbard, a specialist EB dietitian in the department of nutrition and dietetics at St. Thomas’ Hospital in London, it was shown that almost a third of patients with EB simplex were obese, compared with 26% of adults in the general U.K. population.
“People with EBS are known to have hyperkeratosis and foot-blistering,” Ms. Hubbard observed in the poster. This can lead to reduce mobility and pain, which “may in turn have an impact on body weight, and an increased BMI [body mass index] may further affect mobility.”
Data were collected on 90 patients who attended a U.K. EBS clinic over an 11-month period. While 45.5% of patients had a normal weight, the majority was overweight (21.1%), obese (21.1%), or morbidly obese (10%).
Fifteen patients completed questionnaires about their mobility, and almost all felt that their weight had an adverse effect on their feet, as did EBS. Several also noted problems with their EBS, in the skin folds around the bra, waist, and sock lines.
“We now plan to begin a pilot study to establish a supportive weight management program for people with EBS and evaluate both weight loss and impact on mobility,” Ms. Hubbard reported.
No conflicts of interest were declared by any of the speakers.
SOURCES: EB 2020. Reimer A et al. Poster 26; Khan T. oral presentation; O’Sullivan M et al. Poster 93; Hubbard L. Poster 19.
LONDON – Hardened feet are a major determinant of the clinical course of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), according to research presented by a German team of investigators at the EB World Congress.
In a study of 157 individuals with EBS, 75.8% had plantar keratoderma, a condition associated with a vicious circle of pain, reduced mobility, subsequent weight gain, and further foot problems.
“EBS has severe impacts on various aspects of everyday life,” Antonia Reimer, MD, and associates at the University of Freiburg, Germany, reported in a poster presentation. “Plantar involvement and [plantar keratoderma] are serious complications of all EBS subtypes, correlating with excessive weight gain, pain, local infections, and limited mobility.”
The researchers suggested that “targeting [plantar keratoderma] should be a priority in EBS therapy and research.”
In their retrospective cohort study, clinical and molecular data were retrieved from patient records, and major determinants of the clinical course of EBS investigated. As such, the researchers looked at how weight changes affected EBS, the effect of hardening skin on the feet, pain, mobility, and working life.
“EB simplex is generally regarded as the ‘mildest’ EB type,” Dr. Reimer and colleagues wrote, “however, individuals with EBS report a high disease burden and frequent pain.” The team found that just under 30% of patients (n = 46) experienced frequent pain, particularly those with localized and severe EBS. Of the patients experiencing pain, the majority (75.2%) had plantar keratoderma. Furthermore, those with blisters underneath the hardened skin reported having the most painful lesions.
Palmoplantar hyperhidrosis was present in slightly more than 40% of cases, and was especially common in individuals with localized EBS, Dr. Reimer and colleagues found. They also found that bacterial and fungal infections occurred in 14% and 7% of patients, respectively, and this correlated significantly with diffuse plantar keratoderma.
A third of patients experience mobility problems, and 8.2% required a wheelchair; 16.4% “were in occupational disability,” the team reported.
“Hyperkeratosis is important because it isn’t just about treating the hyperkeratosis, it’s also looking at the mechanical balance of the foot,” Tariq Khan, PhD, said during an unrelated oral presentation. Dr. Khan, a consultant podiatrist specializing in EB at Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, discussed how to best manage the feet of people with EB.
“Podiatry technology and how we treat can often be detrimental to an EB patient,” Dr. Khan cautioned at the meeting, which was organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA).
For example, “certain devices, certain types of material, will add more friction and pressure and cause more blistering,” he added, making treatment challenging.
Having worked with the EB community for the past 22 years, he noted that he had seen how podiatry practices had been refined to deal with this patient population. Dr. Khan is one of several experts behind EB podiatry guidelines issued by DEBRA International last year (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Aug 9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18381) and has run the charity’s first practical EB podiatry skills course to educate more podiatrists on the intricacies of managing EB feet.
During his talk, Dr. Kahn mentioned several innovations that came about by working with external companies, such as the production of special cotton socks containing silver fibers to help reduce the symptom of hot feet, and development of a cooling insole that helped draw moisture and odor away from the foot while providing comfort to the wearer.
One of the main problems for those with EB is finding comfortable footwear that doesn’t aggravate their symptoms, Dr. Khan emphasized.
According to the EB podiatry guidelines, footwear needs to be supportive, and “its primary focus should be aimed at minimizing blistering by reducing friction.” If blisters are already present, the guidelines note that dressings and topical antiseptics or antibiotics might be used until the blisters heal. “Therefore, suitable shoes or footwear are essential to accommodate dressings and not lead to further trauma to the damaged area. Footwear that is adjustable may be beneficial in these circumstances.”
What constitutes appropriate footwear is open to debate and was the topic of a separate poster presentation at meeting. Mark O’Sullivan, EB team podiatrist at Solihull and Birmingham Women’s and Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, and associates looked at whether wearing rocker bottom footwear could ease the formation of blisters in patients with EBS.
The team studied nine patients who reported regular plantar blistering. An in-shoe measurement system was devised to measure patients’ plantar pressure while they were wearing their existing footwear and then again when they were wearing new footwear with a rocker bottom. Participants completed questionnaires about the development of blisters on their feet, their activity levels, and pain.
The rocker bottom footwear reduced the peak plantar pressure by 30.5% and the total plantar pressure by 31.8%, compared with regular footwear. A shift in the average pressure under the foot was seen, moving from the heels of the feet to the midfoot area, while remaining similar in the front foot area.
“Patient feedback has been mixed,” Mr. O’Sullivan said when presenting the poster. “Patients state that blisters have often reduced in the heels and forefoot, but new blisters have developed in the midfoot.” As a result, some study participants chose to alternate wearing the rocker bottom footwear with their normal shoes, to even out the places where blisters might form.
Although the jury is still out on the benefit of rocker bottom footwear, one thing that might help those with EBS who develop regular foot blisters may be to keep their weight in check. In a separate poster presentation given by Lynn Hubbard, a specialist EB dietitian in the department of nutrition and dietetics at St. Thomas’ Hospital in London, it was shown that almost a third of patients with EB simplex were obese, compared with 26% of adults in the general U.K. population.
“People with EBS are known to have hyperkeratosis and foot-blistering,” Ms. Hubbard observed in the poster. This can lead to reduce mobility and pain, which “may in turn have an impact on body weight, and an increased BMI [body mass index] may further affect mobility.”
Data were collected on 90 patients who attended a U.K. EBS clinic over an 11-month period. While 45.5% of patients had a normal weight, the majority was overweight (21.1%), obese (21.1%), or morbidly obese (10%).
Fifteen patients completed questionnaires about their mobility, and almost all felt that their weight had an adverse effect on their feet, as did EBS. Several also noted problems with their EBS, in the skin folds around the bra, waist, and sock lines.
“We now plan to begin a pilot study to establish a supportive weight management program for people with EBS and evaluate both weight loss and impact on mobility,” Ms. Hubbard reported.
No conflicts of interest were declared by any of the speakers.
SOURCES: EB 2020. Reimer A et al. Poster 26; Khan T. oral presentation; O’Sullivan M et al. Poster 93; Hubbard L. Poster 19.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Hand deformity happens early in children with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
London – A predictable course of hand contracture was seen in a U.K. study of children with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), with all children experiencing moderate or severe hand deformity by the age of 12 years.
This stark finding, reported at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), highlighted the importance of intervening early with surgical methods that aim to prevent the pseudosyndactyly, or “mitten” hand deformity, which is an unfortunate characteristic of the genetic skin condition.
The investigative team, from the plastic and reconstructive surgery department at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, London, presented data from a retrospective case review of 24 children who attended their specialist pediatric EB center between 2010 and 2019. Of these, seven children had surgery to release hand contractures.
A total of 250 hand assessments were made via the novel Assessment of the Component Hand Contractures in Epidermolysis Bullosa (ACE). The assessment provides a hand deformity grade (HDG) – none, mild, moderate, and severe –based on the typical contractures that are seen in RDEB, such as between the fingers (web space contractures), finger flexion contractures, and thumb adduction contractures.
Using the ACE tool, “we found four significant time points regarding hand contracture development,” Catherine Miller, one of the team’s occupational therapists, said during a poster presentation. At birth, none of the children had any signs of hand deformity, but by 2 years of age half had mild hand contracture. By age 6, all children had some form of hand deformity, Ms. Miller said, and by age 12 all had moderate to severe hand deformity, “so adding to the data that hand deformities really are inevitable.”
Other findings were that the thumb and finger web spaces were the first to contract, Ms. Miller said. “So they tend to develop earlier and progress relatively slowly.” By contrast the finger flexion contractures occurred later on, “but progress more relatively rapidly,” she observed.
“Our data are limited as not every child is included at every age, and out tool has not yet been validated,” Ms. Miller and team acknowledged in the poster. “We assume that hand contractures do not improve, and therefore have included operated hands (mean age 6 years) at their last preoperative HDG in order to represent older children and more advanced hand deformities.”
In an interview, Ms. Miller noted that families have a lot going on when their newborn is diagnosed with RDEB, so introducing the idea that there will be substantial hand deformities in the future “is a difficult conversation. We have to take that gently.”
There are nonsurgical approaches to keeping the hands open, such as “encouraging them to open their hands in play, daily stretches; we can make splints with a silicon substance and other thermoplastic materials,” Ms. Miller said.
Hand surgery is a ‘blunt tool’
“The primary problem, of course, is the dermal fibrosis that we see that creates scarring and secondary problems,” said Gill Smith, a plastic surgery consultant who works with Ms. Miller at the hospital.
“In an ideal world, you would bandage up [the children] so that they could never injure their hands, but then they couldn’t use them, they couldn’t grow properly, and they could not develop,” Ms. Smith said in an oral presentation about hand surgery in children with RDEB. “You do not want them to get to the secondary stage, because the secondary stage is a real problem – you get all these impairments of hand function – pseudosyndactyly, finger contraction, and first web contracture, and ending up in a ‘mitten’ hand.”
Surgery is a very “crude” and “blunt tool,” Ms. Smith emphasized. Prevention is key, and perhaps in the future gene therapy, mesenchymal stem cells, and the like will mean that there is less need for hand surgery, she intimated. Until then, there are some things that can be done surgically – such as wrapping the hands, using gloves to protect the skin, stretching out the web spaces of the palm, and using splints. “All of these things we are trying to improve all the time, and come up with new ideas.”
The question is when to intervene? Ms. Smith said that in any other type of hand surgery, particularly in children where growth and function might be affected, the aim would be to “go in early.” In children with RDEB, however, the timing is not so clear: “Should we be going in early, before secondary joint changes, before we get secondary tendon shortening?” Perhaps this would result in less complex surgery, she suggested, but “it is a really huge deal for families and for children. For the moment we are still only really doing it when there [are] quite significant functional difficulties.”
When it comes to the type of surgery done to release the hands, “everyone has variants on the release technique,” but none are known to be better than any other, Ms. Smith said. Surgical release deals with consequences of dermal fibrosis but also creates more fibrosis, she cautioned.
Effects of hand surgery do not last long
How long the surgery’s effect will last is “what everyone wants to know, and I don’t think anyone has found a really good answer. It is variable, but unfortunately it’s a lot shorter than we’d like,” said Ms. Smith.
Indeed, data in another poster presentation by Ms. Smith and colleagues showed that the situation can be ‘back to square one’ within just a couple of years. Of the seven patients who had surgery at a mean 7 years of age (range 6-10 years), “most had returned to their original total score by 2 years post surgery,” the team wrote. All children “were initially happy with both appearance and function after surgery” they added; however, “happiness gradually decreased with time as they lost function and their scores increased with recurrence of contracture.”
The team noted that “sometimes after surgery a different component of the hand contracture worsened but function was preserved.”
While the ACE tool used by the team has not yet been validated, they believe it to be “a systematic tool with a structured method of administration.” As such it can help with informed decision making, they believe, and it could be used with functional measures to see how hand contractures might be impacting hand function and quality of life.
The ACE tool can be downloaded for free from the GOSH website.
SOURCE: Jessop N et al. EB 2020. Posters 42 and 43; Smith G et al. Poster 63.
London – A predictable course of hand contracture was seen in a U.K. study of children with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), with all children experiencing moderate or severe hand deformity by the age of 12 years.
This stark finding, reported at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), highlighted the importance of intervening early with surgical methods that aim to prevent the pseudosyndactyly, or “mitten” hand deformity, which is an unfortunate characteristic of the genetic skin condition.
The investigative team, from the plastic and reconstructive surgery department at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, London, presented data from a retrospective case review of 24 children who attended their specialist pediatric EB center between 2010 and 2019. Of these, seven children had surgery to release hand contractures.
A total of 250 hand assessments were made via the novel Assessment of the Component Hand Contractures in Epidermolysis Bullosa (ACE). The assessment provides a hand deformity grade (HDG) – none, mild, moderate, and severe –based on the typical contractures that are seen in RDEB, such as between the fingers (web space contractures), finger flexion contractures, and thumb adduction contractures.
Using the ACE tool, “we found four significant time points regarding hand contracture development,” Catherine Miller, one of the team’s occupational therapists, said during a poster presentation. At birth, none of the children had any signs of hand deformity, but by 2 years of age half had mild hand contracture. By age 6, all children had some form of hand deformity, Ms. Miller said, and by age 12 all had moderate to severe hand deformity, “so adding to the data that hand deformities really are inevitable.”
Other findings were that the thumb and finger web spaces were the first to contract, Ms. Miller said. “So they tend to develop earlier and progress relatively slowly.” By contrast the finger flexion contractures occurred later on, “but progress more relatively rapidly,” she observed.
“Our data are limited as not every child is included at every age, and out tool has not yet been validated,” Ms. Miller and team acknowledged in the poster. “We assume that hand contractures do not improve, and therefore have included operated hands (mean age 6 years) at their last preoperative HDG in order to represent older children and more advanced hand deformities.”
In an interview, Ms. Miller noted that families have a lot going on when their newborn is diagnosed with RDEB, so introducing the idea that there will be substantial hand deformities in the future “is a difficult conversation. We have to take that gently.”
There are nonsurgical approaches to keeping the hands open, such as “encouraging them to open their hands in play, daily stretches; we can make splints with a silicon substance and other thermoplastic materials,” Ms. Miller said.
Hand surgery is a ‘blunt tool’
“The primary problem, of course, is the dermal fibrosis that we see that creates scarring and secondary problems,” said Gill Smith, a plastic surgery consultant who works with Ms. Miller at the hospital.
“In an ideal world, you would bandage up [the children] so that they could never injure their hands, but then they couldn’t use them, they couldn’t grow properly, and they could not develop,” Ms. Smith said in an oral presentation about hand surgery in children with RDEB. “You do not want them to get to the secondary stage, because the secondary stage is a real problem – you get all these impairments of hand function – pseudosyndactyly, finger contraction, and first web contracture, and ending up in a ‘mitten’ hand.”
Surgery is a very “crude” and “blunt tool,” Ms. Smith emphasized. Prevention is key, and perhaps in the future gene therapy, mesenchymal stem cells, and the like will mean that there is less need for hand surgery, she intimated. Until then, there are some things that can be done surgically – such as wrapping the hands, using gloves to protect the skin, stretching out the web spaces of the palm, and using splints. “All of these things we are trying to improve all the time, and come up with new ideas.”
The question is when to intervene? Ms. Smith said that in any other type of hand surgery, particularly in children where growth and function might be affected, the aim would be to “go in early.” In children with RDEB, however, the timing is not so clear: “Should we be going in early, before secondary joint changes, before we get secondary tendon shortening?” Perhaps this would result in less complex surgery, she suggested, but “it is a really huge deal for families and for children. For the moment we are still only really doing it when there [are] quite significant functional difficulties.”
When it comes to the type of surgery done to release the hands, “everyone has variants on the release technique,” but none are known to be better than any other, Ms. Smith said. Surgical release deals with consequences of dermal fibrosis but also creates more fibrosis, she cautioned.
Effects of hand surgery do not last long
How long the surgery’s effect will last is “what everyone wants to know, and I don’t think anyone has found a really good answer. It is variable, but unfortunately it’s a lot shorter than we’d like,” said Ms. Smith.
Indeed, data in another poster presentation by Ms. Smith and colleagues showed that the situation can be ‘back to square one’ within just a couple of years. Of the seven patients who had surgery at a mean 7 years of age (range 6-10 years), “most had returned to their original total score by 2 years post surgery,” the team wrote. All children “were initially happy with both appearance and function after surgery” they added; however, “happiness gradually decreased with time as they lost function and their scores increased with recurrence of contracture.”
The team noted that “sometimes after surgery a different component of the hand contracture worsened but function was preserved.”
While the ACE tool used by the team has not yet been validated, they believe it to be “a systematic tool with a structured method of administration.” As such it can help with informed decision making, they believe, and it could be used with functional measures to see how hand contractures might be impacting hand function and quality of life.
The ACE tool can be downloaded for free from the GOSH website.
SOURCE: Jessop N et al. EB 2020. Posters 42 and 43; Smith G et al. Poster 63.
London – A predictable course of hand contracture was seen in a U.K. study of children with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), with all children experiencing moderate or severe hand deformity by the age of 12 years.
This stark finding, reported at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), highlighted the importance of intervening early with surgical methods that aim to prevent the pseudosyndactyly, or “mitten” hand deformity, which is an unfortunate characteristic of the genetic skin condition.
The investigative team, from the plastic and reconstructive surgery department at Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, London, presented data from a retrospective case review of 24 children who attended their specialist pediatric EB center between 2010 and 2019. Of these, seven children had surgery to release hand contractures.
A total of 250 hand assessments were made via the novel Assessment of the Component Hand Contractures in Epidermolysis Bullosa (ACE). The assessment provides a hand deformity grade (HDG) – none, mild, moderate, and severe –based on the typical contractures that are seen in RDEB, such as between the fingers (web space contractures), finger flexion contractures, and thumb adduction contractures.
Using the ACE tool, “we found four significant time points regarding hand contracture development,” Catherine Miller, one of the team’s occupational therapists, said during a poster presentation. At birth, none of the children had any signs of hand deformity, but by 2 years of age half had mild hand contracture. By age 6, all children had some form of hand deformity, Ms. Miller said, and by age 12 all had moderate to severe hand deformity, “so adding to the data that hand deformities really are inevitable.”
Other findings were that the thumb and finger web spaces were the first to contract, Ms. Miller said. “So they tend to develop earlier and progress relatively slowly.” By contrast the finger flexion contractures occurred later on, “but progress more relatively rapidly,” she observed.
“Our data are limited as not every child is included at every age, and out tool has not yet been validated,” Ms. Miller and team acknowledged in the poster. “We assume that hand contractures do not improve, and therefore have included operated hands (mean age 6 years) at their last preoperative HDG in order to represent older children and more advanced hand deformities.”
In an interview, Ms. Miller noted that families have a lot going on when their newborn is diagnosed with RDEB, so introducing the idea that there will be substantial hand deformities in the future “is a difficult conversation. We have to take that gently.”
There are nonsurgical approaches to keeping the hands open, such as “encouraging them to open their hands in play, daily stretches; we can make splints with a silicon substance and other thermoplastic materials,” Ms. Miller said.
Hand surgery is a ‘blunt tool’
“The primary problem, of course, is the dermal fibrosis that we see that creates scarring and secondary problems,” said Gill Smith, a plastic surgery consultant who works with Ms. Miller at the hospital.
“In an ideal world, you would bandage up [the children] so that they could never injure their hands, but then they couldn’t use them, they couldn’t grow properly, and they could not develop,” Ms. Smith said in an oral presentation about hand surgery in children with RDEB. “You do not want them to get to the secondary stage, because the secondary stage is a real problem – you get all these impairments of hand function – pseudosyndactyly, finger contraction, and first web contracture, and ending up in a ‘mitten’ hand.”
Surgery is a very “crude” and “blunt tool,” Ms. Smith emphasized. Prevention is key, and perhaps in the future gene therapy, mesenchymal stem cells, and the like will mean that there is less need for hand surgery, she intimated. Until then, there are some things that can be done surgically – such as wrapping the hands, using gloves to protect the skin, stretching out the web spaces of the palm, and using splints. “All of these things we are trying to improve all the time, and come up with new ideas.”
The question is when to intervene? Ms. Smith said that in any other type of hand surgery, particularly in children where growth and function might be affected, the aim would be to “go in early.” In children with RDEB, however, the timing is not so clear: “Should we be going in early, before secondary joint changes, before we get secondary tendon shortening?” Perhaps this would result in less complex surgery, she suggested, but “it is a really huge deal for families and for children. For the moment we are still only really doing it when there [are] quite significant functional difficulties.”
When it comes to the type of surgery done to release the hands, “everyone has variants on the release technique,” but none are known to be better than any other, Ms. Smith said. Surgical release deals with consequences of dermal fibrosis but also creates more fibrosis, she cautioned.
Effects of hand surgery do not last long
How long the surgery’s effect will last is “what everyone wants to know, and I don’t think anyone has found a really good answer. It is variable, but unfortunately it’s a lot shorter than we’d like,” said Ms. Smith.
Indeed, data in another poster presentation by Ms. Smith and colleagues showed that the situation can be ‘back to square one’ within just a couple of years. Of the seven patients who had surgery at a mean 7 years of age (range 6-10 years), “most had returned to their original total score by 2 years post surgery,” the team wrote. All children “were initially happy with both appearance and function after surgery” they added; however, “happiness gradually decreased with time as they lost function and their scores increased with recurrence of contracture.”
The team noted that “sometimes after surgery a different component of the hand contracture worsened but function was preserved.”
While the ACE tool used by the team has not yet been validated, they believe it to be “a systematic tool with a structured method of administration.” As such it can help with informed decision making, they believe, and it could be used with functional measures to see how hand contractures might be impacting hand function and quality of life.
The ACE tool can be downloaded for free from the GOSH website.
SOURCE: Jessop N et al. EB 2020. Posters 42 and 43; Smith G et al. Poster 63.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Zilucoplan improved efficacy outcomes in myasthenia gravis
The clinical effect of the self-administered macrocyclic peptide inhibitor was “similar,” the investigators wrote, to what was seen in studies of the intravenously administered complement inhibitor eculizumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of gMG.
While eculizumab studies were restricted to patients with refractory gMG, the investigators wrote that their study of zilucoplan included a broader population, including patients who had not failed prior therapies, who were earlier in their disease course, and who had a history of thymoma.
“This observation is important because in gMG, disease severity frequently peaks within the first few years after diagnosis, before all treatment options have been exhausted, and before patients may be formally declared treatment refractory,” wrote James F. Howard Jr, MD, of the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, and coauthors.
Complement inhibition is a “targeted approach” that addresses the primary mechanism of tissue damage in gMG, the investigators wrote.
That stands in contrast to conventional gMG treatments including pyridostigmine, corticosteroids, and other immunosuppressants. “These treatments lack strong evidence from clinical trials to support their efficacy, are often poorly tolerated, and can be associated with considerable long-term toxicities,” Dr. Howard and colleagues wrote in their report, which was published in JAMA Neurology.
A total of 44 adult patients with gMG were randomized to receive daily zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, or placebo for 12 weeks in this 25-center North American study. All patients had acetylcholine receptor autoantibody–positive disease and a Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) score of 12 or higher. The QMG score ranges from 0, indicating no muscle weakness, to 39, or severe weakness.
Per the study protocol, patients had to keep taking their current gMG medication without changing the dose.
Change in QMG score from baseline to 12 weeks, the primary efficacy endpoint of the study, showed a significant and clinically meaningful difference favoring zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg over placebo, according to the investigators.
The mean change was –6.0 points for zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg and –3.2 for placebo (P = .05), according to their report, which indicated a rapid onset of action apparent 1 week after starting treatment.
Zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg also yielded a significant and clinically meaningful improvement versus placebo, but its magnitude was smaller and took 4 weeks to become apparent.
Treatment with zilucoplan also significantly improved MG Activities of Daily Living scores versus placebo, a key secondary endpoint of the trial, according to the researchers.
Treatment-emergent adverse events, which included local injection-site reactions, were mild and judged to be unrelated to the study treatment, according to the report.
Ra Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Howard reported disclosures related to Ra Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, argenx, Viela Bio, and others.
SOURCE: Howard Jr JF et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.5125.
The clinical effect of the self-administered macrocyclic peptide inhibitor was “similar,” the investigators wrote, to what was seen in studies of the intravenously administered complement inhibitor eculizumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of gMG.
While eculizumab studies were restricted to patients with refractory gMG, the investigators wrote that their study of zilucoplan included a broader population, including patients who had not failed prior therapies, who were earlier in their disease course, and who had a history of thymoma.
“This observation is important because in gMG, disease severity frequently peaks within the first few years after diagnosis, before all treatment options have been exhausted, and before patients may be formally declared treatment refractory,” wrote James F. Howard Jr, MD, of the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, and coauthors.
Complement inhibition is a “targeted approach” that addresses the primary mechanism of tissue damage in gMG, the investigators wrote.
That stands in contrast to conventional gMG treatments including pyridostigmine, corticosteroids, and other immunosuppressants. “These treatments lack strong evidence from clinical trials to support their efficacy, are often poorly tolerated, and can be associated with considerable long-term toxicities,” Dr. Howard and colleagues wrote in their report, which was published in JAMA Neurology.
A total of 44 adult patients with gMG were randomized to receive daily zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, or placebo for 12 weeks in this 25-center North American study. All patients had acetylcholine receptor autoantibody–positive disease and a Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) score of 12 or higher. The QMG score ranges from 0, indicating no muscle weakness, to 39, or severe weakness.
Per the study protocol, patients had to keep taking their current gMG medication without changing the dose.
Change in QMG score from baseline to 12 weeks, the primary efficacy endpoint of the study, showed a significant and clinically meaningful difference favoring zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg over placebo, according to the investigators.
The mean change was –6.0 points for zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg and –3.2 for placebo (P = .05), according to their report, which indicated a rapid onset of action apparent 1 week after starting treatment.
Zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg also yielded a significant and clinically meaningful improvement versus placebo, but its magnitude was smaller and took 4 weeks to become apparent.
Treatment with zilucoplan also significantly improved MG Activities of Daily Living scores versus placebo, a key secondary endpoint of the trial, according to the researchers.
Treatment-emergent adverse events, which included local injection-site reactions, were mild and judged to be unrelated to the study treatment, according to the report.
Ra Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Howard reported disclosures related to Ra Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, argenx, Viela Bio, and others.
SOURCE: Howard Jr JF et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.5125.
The clinical effect of the self-administered macrocyclic peptide inhibitor was “similar,” the investigators wrote, to what was seen in studies of the intravenously administered complement inhibitor eculizumab, which is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of gMG.
While eculizumab studies were restricted to patients with refractory gMG, the investigators wrote that their study of zilucoplan included a broader population, including patients who had not failed prior therapies, who were earlier in their disease course, and who had a history of thymoma.
“This observation is important because in gMG, disease severity frequently peaks within the first few years after diagnosis, before all treatment options have been exhausted, and before patients may be formally declared treatment refractory,” wrote James F. Howard Jr, MD, of the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, and coauthors.
Complement inhibition is a “targeted approach” that addresses the primary mechanism of tissue damage in gMG, the investigators wrote.
That stands in contrast to conventional gMG treatments including pyridostigmine, corticosteroids, and other immunosuppressants. “These treatments lack strong evidence from clinical trials to support their efficacy, are often poorly tolerated, and can be associated with considerable long-term toxicities,” Dr. Howard and colleagues wrote in their report, which was published in JAMA Neurology.
A total of 44 adult patients with gMG were randomized to receive daily zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, or placebo for 12 weeks in this 25-center North American study. All patients had acetylcholine receptor autoantibody–positive disease and a Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) score of 12 or higher. The QMG score ranges from 0, indicating no muscle weakness, to 39, or severe weakness.
Per the study protocol, patients had to keep taking their current gMG medication without changing the dose.
Change in QMG score from baseline to 12 weeks, the primary efficacy endpoint of the study, showed a significant and clinically meaningful difference favoring zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg over placebo, according to the investigators.
The mean change was –6.0 points for zilucoplan 0.3 mg/kg and –3.2 for placebo (P = .05), according to their report, which indicated a rapid onset of action apparent 1 week after starting treatment.
Zilucoplan 0.1 mg/kg also yielded a significant and clinically meaningful improvement versus placebo, but its magnitude was smaller and took 4 weeks to become apparent.
Treatment with zilucoplan also significantly improved MG Activities of Daily Living scores versus placebo, a key secondary endpoint of the trial, according to the researchers.
Treatment-emergent adverse events, which included local injection-site reactions, were mild and judged to be unrelated to the study treatment, according to the report.
Ra Pharmaceuticals funded the study. Dr. Howard reported disclosures related to Ra Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, argenx, Viela Bio, and others.
SOURCE: Howard Jr JF et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.5125.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY