User login
Sleep apnea and cognitive impairment are common bedfellows
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The study shows obstructive sleep apnea is common in patients with cognitive impairment. The results suggest that people with cognitive impairment should be assessed for sleep apnea if they have difficulty with sleep or if they demonstrate sleep-related symptoms,” said study investigator David Colelli, MSc, research coordinator at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto.
The findings were released ahead of the study’s scheduled presentation at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology..
Linked to cognitive impairment
OSA is a common sleep disorder and is associated with an increased risk of developing cognitive impairment. It is also prevalent in the general population, but even more common among patients with dementia.
However, the investigators noted, the frequency and predictors of OSA have not been well established in Alzheimer’s disease and other related conditions such as vascular dementia.
The investigators had conducted a previous feasibility study investigating a home sleep monitor as an OSA screening tool. The current research examined potential correlations between OSA detected by this monitor and cognitive impairment.
The study included 67 patients with cognitive impairment due to neurodegenerative or vascular disease. The range of disorders included Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment caused by Alzheimer’s disease, dementia caused by Parkinson’s or Lewy body disease, and vascular conditions.
Participants had a mean age of 72.8 years and 44.8% were male. The mean body mass index (BMI) was 25.6 kg/m2.
These participants completed a home sleep apnea test, which is an alternative to polysomnography for the detection of OSA.
Researchers identified OSA in 52.2% of the study population. This, Mr. Colelli said, “is in the range” of other research investigating sleep and cognitive impairment.
“In the general population, however, this number is a lot lower – in the 10%-20% range depending on the population or country you’re looking at,” Mr. Colelli said.
He emphasized that, without an objective sleep test, some patients may be unaware of their sleep issues. Those with cognitive impairment may “misjudge how they’re sleeping,” especially if they sleep without a partner, so it’s possible that sleep disorder symptoms often go undetected.
Bidirectional relationship?
Participants answered questionnaires on sleep, cognition, and mood. They also completed the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) to assess language, visuospatial abilities, memory and recall, and abstract thinking.
Scores on this test range from 0 to 30, with a score of 26 or higher signifying normal, 18-25 indicating mild cognitive impairment, and 17 or lower indicating moderate to severe cognitive impairment. The average score for study participants with OSA was 20.5, compared with 23.6 for those without the sleep disorder.
Results showed OSA was significantly associated with a lower score on the MoCA scale (odds ratio, 0.40; P = .048). “This demonstrated an association of OSA with lower cognitive scores,” Mr. Colelli said.
The analysis also showed that OSA severity was correlated with actigraphy-derived sleep variables, including lower total sleep time, greater sleep onset latency, lower sleep efficiency, and more awakenings.
The study was too small to determine whether a specific diagnosis of cognitive impairment affected the link to OSA, Mr. Colelli said. “But definitely future research should be directed towards looking at this.”
Obesity is a risk factor for OSA, but the mean BMI in the study was not in the obese range of 30 and over. This, Mr. Colelli said, suggests that sleep apnea may present differently in those with cognitive impairment.
“Sleep apnea in this population might not present with the typical risk factors of obesity or snoring or feeling tired.”
While the new study “adds to the understanding that there’s a link between sleep and cognitive impairment, the direction of that link isn’t entirely clear,” Mr. Colelli said.
“It’s slowly becoming appreciated that the relationship might be bidirectionality, where sleep apnea might be contributing to the cognitive impairment and cognitive impairment could be contributing to the sleep issues.”
The study highlights how essential sleep is to mental health, Mr. Colelli said. “I feel, and I’m sure you do too, that if you don’t get good sleep, you feel tired during the day and you may not have the best concentration or memory.”
Identifying sleep issues in patients with cognitive impairment is important, as treatment and management of these issues could affect outcomes including cognition and quality of life, he added.
“Future research should be directed to see if treatment of sleep disorders with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which is the gold standard, and various other treatments, can improve outcomes.” Future research should also examine OSA prevalence in larger cohorts.
Common, undertreated
Commenting on the resaerch, Lei Gao, MD, assistant professor of anesthesia at Harvard Medical School, Boston, whose areas of expertise include disorders of cognition, sleep, and circadian rhythm, believes the findings are important. “It highlights how common and potentially undertreated OSA is in this age group, and in particular, its link to cognitive impairment.”
OSA is often associated with significant comorbidities, as well as sleep disruption, Dr. Gao noted. One of the study’s strengths was including objective assessment of sleep using actigraphy. “It will be interesting to see to what extent the OSA link to cognitive impairment is via poor sleep or disrupted circadian rest/activity cycles.”
It would also be interesting “to tease out whether OSA is more linked to dementia of vascular etiologies due to common risk factors, or whether it is pervasive to all forms of dementia,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAN 2021
Severe atopic dermatitis often puts a dent in quality of life
In his role as head of the division of pediatric behavioral health at National Jewish Health, Denver, Bruce G. Bender, PhD, helps children and adults navigate the adverse effects of severe atopic dermatitis (AD) on their quality of life.
“There have been many surveys of adults with AD who report impairment of their sleep, reduced activity level, increased work absence, financial burden, emotional distress, and social avoidance,” he said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Similarly, children with AD or their parents report emotional distress, reduced activity, and increased school absence, social avoidance, and sleep disturbance. Families report financial burdens, conflict, particularly among the adults, social avoidance, sleep disturbance in the parents, and reduction of well-being in the siblings.”
In an effort to objectively measure sleep change in this population, Dr. Bender and colleagues recruited 14 adults with AD and 14 healthy controls who wore an ActiGraph for 1 week and completed questionnaires about sleep, itch, and quality of life. Patients with AD were awake almost twice as many minutes each night as the healthy controls (a mean of 57.3 vs. 32.3 minutes, respectively; P = .0480). Consequently, their sleep efficiency was significantly reduced based on the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (a mean of 90.6 vs. 95; P = .0305).
In another study, Dr. Bender and colleagues enrolled 20 adults with AD who underwent 2 nights of polysomnography and actigraphy. The lab was set up to measure a scratching event, which was recorded when a burst of electromyographic activity of at least 3 seconds was accompanied by a visible scratching motion. “We learned that sleep efficiency as measured by both PSG and actigraphy correlated with total body surface area and scratching index,” he said. “As we might assume, the more skin involved, the more patients scratch, the less well they sleep.”
Behavioral, neurocognitive effects
In a separate study of AD, sleep, and behavior, the researchers studied 1,041 children with asthma who were enrolled in the Childhood Asthma Management Program at eight North American sites. They used baseline parent ratings on standardized sleep and behavior rating scales and found that increased awakenings were associated with increased school absence and daytime behavior problems. “So, not only do children with AD sleep less well, but this shows up to impair their functioning during the day,” said Dr. Bender, professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado, Denver.
In a report from Australia, researchers set out to explore the association between sleep and neurocognitive function in 21 children with eczema and 20 healthy controls. Participants underwent cognitive testing and polysomnography. The authors found that the children with eczema demonstrated lower test scores. Reduced scores were correlated with parental reports of sleep problems but not polysomnography.
In a much larger study funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, investigators analyzed data on 354,416 children and 34,613 adults from 19 U.S. population surveys including the National Health Interview Survey 1997-2013 and the National Survey of Children’s Health 2003/4 and 2007/8. They found that AD was associated with ADHD in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.14) and adults (aOR, 1.61). Higher odds of ADHD were found in children who had significant sleep disturbance (aOR, 16.83) and other allergic disease and asthma (aOR, 1.61).
“All of these findings show that AD can impact quality of life, especially sleep, with the result of poorer daytime functioning,” Dr. Bender said. “But those studies don’t answer this question: Are patients with AD at increased risk for psychological disorders such as depression and anxiety?”
Impact on depression, anxiety
Two systematic reviews on the topic suggest that patients with AD are twice as likely to experience depression. One was published in 2018 and the other in 2019. The 2018 review reported a little more than a twofold increase (OR, 2.19), the 2019 review a little bit less (OR, 1.71).
“At the more severe end of the depression continuum, we sometimes see suicidal ideation and suicide attempts,” Dr. Bender said. “A number of studies have asked whether these are increased in patients with AD. Quite a few studies collectively show an increased incidence of suicidal ideation. The question of suicide attempts is reflected in fewer studies. And while the result is small, it is significant. There is a significant increase reported of suicide attempts in AD patients.”
The 2018 review also found an increased incidence of anxiety in AD patients: a little more than twofold in adults (OR, 2.19) and a little less than twofold in children (OR, 1.81).
“It’s a two-way relationship between AD and psychological factors,” Dr. Bender said. “We generally think about AD – the stress that it brings, the burden that it puts on children, adults, and families. But it can work the other way around,” he said, referring to patients who have psychological problems, experience a great deal of stress, have trouble being adherent to their treatment regimen, and find it difficult to resist scratching. “The behavioral/psychological characteristics of the patient also drive the AD. It is well established that acute and chronic stress can result in a worsening of skin conditions in AD patients.”
Behavioral health interventions that have been described in the literature include cognitive therapy, stress management, biofeedback, hypnotherapy, relaxation training, mindfulness, habit reversal, and patient education – some of which have been tested in randomized trials. “All of them report a decrease in scratching as a consequence of the behavioral intervention,” Dr. Bender said.
“Other studies have been reported that look at the impact of behavioral interventions on the severity of the skin condition. Most report an improvement in the skin condition from these behavioral interventions but it’s not a perfect literature.” Critiques of these studies include the fact that there is often not enough detail about the intervention or the framework for the intervention that would allow a clinician to test an intervention in another study or actually pull that intervention into clinical practice (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 7;2014[1]:CD004054), (Int Arch Allergy Immunol.2007;144[1]:1-9).
“Some of the studies lack rigorous designs, some have sampling bias, and some have inadequate outcome measurements,” he said. “We really need additional, high-quality studies to look at what is helpful for patients with AD.”
Dr. Bender reported having no financial disclosures.
In his role as head of the division of pediatric behavioral health at National Jewish Health, Denver, Bruce G. Bender, PhD, helps children and adults navigate the adverse effects of severe atopic dermatitis (AD) on their quality of life.
“There have been many surveys of adults with AD who report impairment of their sleep, reduced activity level, increased work absence, financial burden, emotional distress, and social avoidance,” he said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Similarly, children with AD or their parents report emotional distress, reduced activity, and increased school absence, social avoidance, and sleep disturbance. Families report financial burdens, conflict, particularly among the adults, social avoidance, sleep disturbance in the parents, and reduction of well-being in the siblings.”
In an effort to objectively measure sleep change in this population, Dr. Bender and colleagues recruited 14 adults with AD and 14 healthy controls who wore an ActiGraph for 1 week and completed questionnaires about sleep, itch, and quality of life. Patients with AD were awake almost twice as many minutes each night as the healthy controls (a mean of 57.3 vs. 32.3 minutes, respectively; P = .0480). Consequently, their sleep efficiency was significantly reduced based on the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (a mean of 90.6 vs. 95; P = .0305).
In another study, Dr. Bender and colleagues enrolled 20 adults with AD who underwent 2 nights of polysomnography and actigraphy. The lab was set up to measure a scratching event, which was recorded when a burst of electromyographic activity of at least 3 seconds was accompanied by a visible scratching motion. “We learned that sleep efficiency as measured by both PSG and actigraphy correlated with total body surface area and scratching index,” he said. “As we might assume, the more skin involved, the more patients scratch, the less well they sleep.”
Behavioral, neurocognitive effects
In a separate study of AD, sleep, and behavior, the researchers studied 1,041 children with asthma who were enrolled in the Childhood Asthma Management Program at eight North American sites. They used baseline parent ratings on standardized sleep and behavior rating scales and found that increased awakenings were associated with increased school absence and daytime behavior problems. “So, not only do children with AD sleep less well, but this shows up to impair their functioning during the day,” said Dr. Bender, professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado, Denver.
In a report from Australia, researchers set out to explore the association between sleep and neurocognitive function in 21 children with eczema and 20 healthy controls. Participants underwent cognitive testing and polysomnography. The authors found that the children with eczema demonstrated lower test scores. Reduced scores were correlated with parental reports of sleep problems but not polysomnography.
In a much larger study funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, investigators analyzed data on 354,416 children and 34,613 adults from 19 U.S. population surveys including the National Health Interview Survey 1997-2013 and the National Survey of Children’s Health 2003/4 and 2007/8. They found that AD was associated with ADHD in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.14) and adults (aOR, 1.61). Higher odds of ADHD were found in children who had significant sleep disturbance (aOR, 16.83) and other allergic disease and asthma (aOR, 1.61).
“All of these findings show that AD can impact quality of life, especially sleep, with the result of poorer daytime functioning,” Dr. Bender said. “But those studies don’t answer this question: Are patients with AD at increased risk for psychological disorders such as depression and anxiety?”
Impact on depression, anxiety
Two systematic reviews on the topic suggest that patients with AD are twice as likely to experience depression. One was published in 2018 and the other in 2019. The 2018 review reported a little more than a twofold increase (OR, 2.19), the 2019 review a little bit less (OR, 1.71).
“At the more severe end of the depression continuum, we sometimes see suicidal ideation and suicide attempts,” Dr. Bender said. “A number of studies have asked whether these are increased in patients with AD. Quite a few studies collectively show an increased incidence of suicidal ideation. The question of suicide attempts is reflected in fewer studies. And while the result is small, it is significant. There is a significant increase reported of suicide attempts in AD patients.”
The 2018 review also found an increased incidence of anxiety in AD patients: a little more than twofold in adults (OR, 2.19) and a little less than twofold in children (OR, 1.81).
“It’s a two-way relationship between AD and psychological factors,” Dr. Bender said. “We generally think about AD – the stress that it brings, the burden that it puts on children, adults, and families. But it can work the other way around,” he said, referring to patients who have psychological problems, experience a great deal of stress, have trouble being adherent to their treatment regimen, and find it difficult to resist scratching. “The behavioral/psychological characteristics of the patient also drive the AD. It is well established that acute and chronic stress can result in a worsening of skin conditions in AD patients.”
Behavioral health interventions that have been described in the literature include cognitive therapy, stress management, biofeedback, hypnotherapy, relaxation training, mindfulness, habit reversal, and patient education – some of which have been tested in randomized trials. “All of them report a decrease in scratching as a consequence of the behavioral intervention,” Dr. Bender said.
“Other studies have been reported that look at the impact of behavioral interventions on the severity of the skin condition. Most report an improvement in the skin condition from these behavioral interventions but it’s not a perfect literature.” Critiques of these studies include the fact that there is often not enough detail about the intervention or the framework for the intervention that would allow a clinician to test an intervention in another study or actually pull that intervention into clinical practice (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 7;2014[1]:CD004054), (Int Arch Allergy Immunol.2007;144[1]:1-9).
“Some of the studies lack rigorous designs, some have sampling bias, and some have inadequate outcome measurements,” he said. “We really need additional, high-quality studies to look at what is helpful for patients with AD.”
Dr. Bender reported having no financial disclosures.
In his role as head of the division of pediatric behavioral health at National Jewish Health, Denver, Bruce G. Bender, PhD, helps children and adults navigate the adverse effects of severe atopic dermatitis (AD) on their quality of life.
“There have been many surveys of adults with AD who report impairment of their sleep, reduced activity level, increased work absence, financial burden, emotional distress, and social avoidance,” he said at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “Similarly, children with AD or their parents report emotional distress, reduced activity, and increased school absence, social avoidance, and sleep disturbance. Families report financial burdens, conflict, particularly among the adults, social avoidance, sleep disturbance in the parents, and reduction of well-being in the siblings.”
In an effort to objectively measure sleep change in this population, Dr. Bender and colleagues recruited 14 adults with AD and 14 healthy controls who wore an ActiGraph for 1 week and completed questionnaires about sleep, itch, and quality of life. Patients with AD were awake almost twice as many minutes each night as the healthy controls (a mean of 57.3 vs. 32.3 minutes, respectively; P = .0480). Consequently, their sleep efficiency was significantly reduced based on the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (a mean of 90.6 vs. 95; P = .0305).
In another study, Dr. Bender and colleagues enrolled 20 adults with AD who underwent 2 nights of polysomnography and actigraphy. The lab was set up to measure a scratching event, which was recorded when a burst of electromyographic activity of at least 3 seconds was accompanied by a visible scratching motion. “We learned that sleep efficiency as measured by both PSG and actigraphy correlated with total body surface area and scratching index,” he said. “As we might assume, the more skin involved, the more patients scratch, the less well they sleep.”
Behavioral, neurocognitive effects
In a separate study of AD, sleep, and behavior, the researchers studied 1,041 children with asthma who were enrolled in the Childhood Asthma Management Program at eight North American sites. They used baseline parent ratings on standardized sleep and behavior rating scales and found that increased awakenings were associated with increased school absence and daytime behavior problems. “So, not only do children with AD sleep less well, but this shows up to impair their functioning during the day,” said Dr. Bender, professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado, Denver.
In a report from Australia, researchers set out to explore the association between sleep and neurocognitive function in 21 children with eczema and 20 healthy controls. Participants underwent cognitive testing and polysomnography. The authors found that the children with eczema demonstrated lower test scores. Reduced scores were correlated with parental reports of sleep problems but not polysomnography.
In a much larger study funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, investigators analyzed data on 354,416 children and 34,613 adults from 19 U.S. population surveys including the National Health Interview Survey 1997-2013 and the National Survey of Children’s Health 2003/4 and 2007/8. They found that AD was associated with ADHD in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.14) and adults (aOR, 1.61). Higher odds of ADHD were found in children who had significant sleep disturbance (aOR, 16.83) and other allergic disease and asthma (aOR, 1.61).
“All of these findings show that AD can impact quality of life, especially sleep, with the result of poorer daytime functioning,” Dr. Bender said. “But those studies don’t answer this question: Are patients with AD at increased risk for psychological disorders such as depression and anxiety?”
Impact on depression, anxiety
Two systematic reviews on the topic suggest that patients with AD are twice as likely to experience depression. One was published in 2018 and the other in 2019. The 2018 review reported a little more than a twofold increase (OR, 2.19), the 2019 review a little bit less (OR, 1.71).
“At the more severe end of the depression continuum, we sometimes see suicidal ideation and suicide attempts,” Dr. Bender said. “A number of studies have asked whether these are increased in patients with AD. Quite a few studies collectively show an increased incidence of suicidal ideation. The question of suicide attempts is reflected in fewer studies. And while the result is small, it is significant. There is a significant increase reported of suicide attempts in AD patients.”
The 2018 review also found an increased incidence of anxiety in AD patients: a little more than twofold in adults (OR, 2.19) and a little less than twofold in children (OR, 1.81).
“It’s a two-way relationship between AD and psychological factors,” Dr. Bender said. “We generally think about AD – the stress that it brings, the burden that it puts on children, adults, and families. But it can work the other way around,” he said, referring to patients who have psychological problems, experience a great deal of stress, have trouble being adherent to their treatment regimen, and find it difficult to resist scratching. “The behavioral/psychological characteristics of the patient also drive the AD. It is well established that acute and chronic stress can result in a worsening of skin conditions in AD patients.”
Behavioral health interventions that have been described in the literature include cognitive therapy, stress management, biofeedback, hypnotherapy, relaxation training, mindfulness, habit reversal, and patient education – some of which have been tested in randomized trials. “All of them report a decrease in scratching as a consequence of the behavioral intervention,” Dr. Bender said.
“Other studies have been reported that look at the impact of behavioral interventions on the severity of the skin condition. Most report an improvement in the skin condition from these behavioral interventions but it’s not a perfect literature.” Critiques of these studies include the fact that there is often not enough detail about the intervention or the framework for the intervention that would allow a clinician to test an intervention in another study or actually pull that intervention into clinical practice (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 7;2014[1]:CD004054), (Int Arch Allergy Immunol.2007;144[1]:1-9).
“Some of the studies lack rigorous designs, some have sampling bias, and some have inadequate outcome measurements,” he said. “We really need additional, high-quality studies to look at what is helpful for patients with AD.”
Dr. Bender reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2020
Telemedicine models show some benefit in OA
Remote interventions using an Internet-based app and telephone outreach to engage patients with osteoarthritis to self-manage their disease have demonstrated the potential to improve some symptoms, at least in the short term, showing the potential for tools to interact with OA patients without having them come into an office or clinic.
Remote interaction using these two forms of telemedicine – one a sophisticated digital platform, the other using a device that’s been around for almost 150 years – may have greater utility for keeping physicians connected with their OA patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, OA experts said in an interview.
“This is certainly relevant during the pandemic, but this has been of high interest for years as well, as researchers and clinicians have been seeking the best ways to reach patients with these types of programs,” said Kelli Allen, PhD, a research health scientist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Two separate studies evaluated the telemedicine platforms. In JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers reported that telephone-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for patients aged 60 and older with OA and insomnia led to improved sleep, fatigue and, to a lesser extent, pain, in a randomized, controlled trial with 327 patients.
A separate randomized, controlled trial of 105 OA patients at the University of Nottingham (England), published in JAMA Network Open, reported that users of a smartphone-based exercise intervention app had greater improvements in pain and function than did controls.
“I think these two studies represent a first step in terms of moving forward, and certainly the interventions could be refined and potentially combined together for patients in the future,” said C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center in Tucson.
Phone-based CBT study
The telephone-based CBT study consisted of two groups: the CBT group (n = 163) who completed six 20- to 30-minute telephone calls over 8 weeks, kept daily diaries, and received tailored educational materials and an education-only group (n = 164). At 2 months after treatment, Insomnia Severity Index scores decreased 8.1 points on average in the CBT group versus 4.8 points in the education-only patients (P < .001).
That variation between the intervention group and controls was sustained out to a year: 7.7 points lower than baseline versus 4.7 points lower. At the same time point, 56.3% of the CBT group remained in remission with Insomnia Severity Index scores less than 7 versus 25.8% of controls. Fatigue outcomes were similarly disparate between the groups.
Pain outcomes were a different story, however. “Post treatment, significant differences were observed for pain, but these differences were not sustained at 12-month follow-up,” first author Susan M. McCurry, PhD, a clinical psychologist and faculty member at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote.
“I think their positive findings illustrate that remotely delivered interventions can be ‘low tech’ and still effective,” Dr. Allen said of the CBT phone study. She noted that complete case data were available for 282 of 327 patients. “The high rate of session attendance suggests that they chose a delivery modality appropriate for their target patient group.”
The scalability of the telephone model is noteworthy, Dr. Kwoh said. “Having a telemedicine intervention that could be scaled a little more easily rather than an in-person intervention, and having individualized treatment, that’s beneficial, as is targeting two symptoms that are very bothersome and burdensome to patients with OA: insomnia and fatigue.” Following patients out to 12 months is a strength of the study, he added.
Smartphone app–based exercise study
The U.K. study evaluated 6-week outcomes of 48 patients with knee OA who used a proprietary app-based exercise program (Joint Academy) and 57 controls who used traditional self-management. The app provided daily exercises and texts, along with email and smartphone reminders. The app was derived from the Better Management of Patients with OA program initiated in Sweden in 2008 that used OA treatment guidelines for education and exercise in person in primary care clinics.
App users showed a 1.5-point reduction in numeric rating scale (NRS) pain score at 6 weeks versus virtually no change in controls (P < .001). In terms of secondary outcomes, pain scores improved 2.2 points on average for app users versus 1.2 for controls (P = .02), with similar improvements recorded in both stiffness and physical function.
Average change in the 30-second sit-to-stand test measured 4.5 for the app users and 1.2 for the usual-care group (P < .001). The study found no difference between the two groups in changes in temporal summation, conditional pain modulation, or Arthritis Research UK Musculoskeletal Health Questionnaire scores.
First author Sameer Akram Gohir, MSc, PhD, and colleagues wrote that the reasons for differences in outcomes between app users and controls aren’t clear. “The superior outcome in the intervention group may depend on the content and context in the app, including a combination of standardized exercises and information, as well as using a digital delivery system.”
Data gathering was cut short because of COVID-19 restrictions in the United Kingdom, as 27 patients missed their in-person follow-up visits. That was one shortcoming of the study, Dr. Kwoh noted.
“Given the caveats certainly they were able to show robust changes in terms of decreased pain, and also improvement in a variety of performance measures. Certainly this may be beneficial – we don’t know – in terms of cost-effectiveness, but it may be beneficial for insurance companies to adapt such a program,” he said, adding that future studies into the cost effectiveness of the digital platform would be in order.
“Certainly, if this program were to decrease physician visits or postpone the need for joint replacement for individuals, then it could be certainly very cost effective,” Dr. Kwoh said.
The completion rate among patients in the study – almost 90% – was “impressive,” Dr. Allen said. “However, this is a relatively short-term study, and I think an important question for future research is whether patients continue with this level of engagement for a longer period of time.”
Dr. McCurry had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. The CBT phone study received funding from the Public Health Service and the National Institute on Aging. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Campbell Alliance Group, Mapi Research Trust, and Pfizer. Dr. Gohir reported no relevant financial relationships. The study received funding from the Versus Arthritis UK Plan Center, the National Institute for Health Research Nottingham Biomedical Research Center, and Pfizer Global. The Joint Academy provided software for the study. A coauthor reported a financial relationships with Pfizer. Dr. Kwoh said that in the past year he has consulted for Express Scripts, Kolon Tissue Gene, LG Chem, and Regeneron. In the past year, he also received institutional grants for clinical trials from AbbVie, Cumberland, Eicos, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Mitsubishi, and Pfizer. Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Remote interventions using an Internet-based app and telephone outreach to engage patients with osteoarthritis to self-manage their disease have demonstrated the potential to improve some symptoms, at least in the short term, showing the potential for tools to interact with OA patients without having them come into an office or clinic.
Remote interaction using these two forms of telemedicine – one a sophisticated digital platform, the other using a device that’s been around for almost 150 years – may have greater utility for keeping physicians connected with their OA patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, OA experts said in an interview.
“This is certainly relevant during the pandemic, but this has been of high interest for years as well, as researchers and clinicians have been seeking the best ways to reach patients with these types of programs,” said Kelli Allen, PhD, a research health scientist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Two separate studies evaluated the telemedicine platforms. In JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers reported that telephone-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for patients aged 60 and older with OA and insomnia led to improved sleep, fatigue and, to a lesser extent, pain, in a randomized, controlled trial with 327 patients.
A separate randomized, controlled trial of 105 OA patients at the University of Nottingham (England), published in JAMA Network Open, reported that users of a smartphone-based exercise intervention app had greater improvements in pain and function than did controls.
“I think these two studies represent a first step in terms of moving forward, and certainly the interventions could be refined and potentially combined together for patients in the future,” said C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center in Tucson.
Phone-based CBT study
The telephone-based CBT study consisted of two groups: the CBT group (n = 163) who completed six 20- to 30-minute telephone calls over 8 weeks, kept daily diaries, and received tailored educational materials and an education-only group (n = 164). At 2 months after treatment, Insomnia Severity Index scores decreased 8.1 points on average in the CBT group versus 4.8 points in the education-only patients (P < .001).
That variation between the intervention group and controls was sustained out to a year: 7.7 points lower than baseline versus 4.7 points lower. At the same time point, 56.3% of the CBT group remained in remission with Insomnia Severity Index scores less than 7 versus 25.8% of controls. Fatigue outcomes were similarly disparate between the groups.
Pain outcomes were a different story, however. “Post treatment, significant differences were observed for pain, but these differences were not sustained at 12-month follow-up,” first author Susan M. McCurry, PhD, a clinical psychologist and faculty member at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote.
“I think their positive findings illustrate that remotely delivered interventions can be ‘low tech’ and still effective,” Dr. Allen said of the CBT phone study. She noted that complete case data were available for 282 of 327 patients. “The high rate of session attendance suggests that they chose a delivery modality appropriate for their target patient group.”
The scalability of the telephone model is noteworthy, Dr. Kwoh said. “Having a telemedicine intervention that could be scaled a little more easily rather than an in-person intervention, and having individualized treatment, that’s beneficial, as is targeting two symptoms that are very bothersome and burdensome to patients with OA: insomnia and fatigue.” Following patients out to 12 months is a strength of the study, he added.
Smartphone app–based exercise study
The U.K. study evaluated 6-week outcomes of 48 patients with knee OA who used a proprietary app-based exercise program (Joint Academy) and 57 controls who used traditional self-management. The app provided daily exercises and texts, along with email and smartphone reminders. The app was derived from the Better Management of Patients with OA program initiated in Sweden in 2008 that used OA treatment guidelines for education and exercise in person in primary care clinics.
App users showed a 1.5-point reduction in numeric rating scale (NRS) pain score at 6 weeks versus virtually no change in controls (P < .001). In terms of secondary outcomes, pain scores improved 2.2 points on average for app users versus 1.2 for controls (P = .02), with similar improvements recorded in both stiffness and physical function.
Average change in the 30-second sit-to-stand test measured 4.5 for the app users and 1.2 for the usual-care group (P < .001). The study found no difference between the two groups in changes in temporal summation, conditional pain modulation, or Arthritis Research UK Musculoskeletal Health Questionnaire scores.
First author Sameer Akram Gohir, MSc, PhD, and colleagues wrote that the reasons for differences in outcomes between app users and controls aren’t clear. “The superior outcome in the intervention group may depend on the content and context in the app, including a combination of standardized exercises and information, as well as using a digital delivery system.”
Data gathering was cut short because of COVID-19 restrictions in the United Kingdom, as 27 patients missed their in-person follow-up visits. That was one shortcoming of the study, Dr. Kwoh noted.
“Given the caveats certainly they were able to show robust changes in terms of decreased pain, and also improvement in a variety of performance measures. Certainly this may be beneficial – we don’t know – in terms of cost-effectiveness, but it may be beneficial for insurance companies to adapt such a program,” he said, adding that future studies into the cost effectiveness of the digital platform would be in order.
“Certainly, if this program were to decrease physician visits or postpone the need for joint replacement for individuals, then it could be certainly very cost effective,” Dr. Kwoh said.
The completion rate among patients in the study – almost 90% – was “impressive,” Dr. Allen said. “However, this is a relatively short-term study, and I think an important question for future research is whether patients continue with this level of engagement for a longer period of time.”
Dr. McCurry had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. The CBT phone study received funding from the Public Health Service and the National Institute on Aging. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Campbell Alliance Group, Mapi Research Trust, and Pfizer. Dr. Gohir reported no relevant financial relationships. The study received funding from the Versus Arthritis UK Plan Center, the National Institute for Health Research Nottingham Biomedical Research Center, and Pfizer Global. The Joint Academy provided software for the study. A coauthor reported a financial relationships with Pfizer. Dr. Kwoh said that in the past year he has consulted for Express Scripts, Kolon Tissue Gene, LG Chem, and Regeneron. In the past year, he also received institutional grants for clinical trials from AbbVie, Cumberland, Eicos, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Mitsubishi, and Pfizer. Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Remote interventions using an Internet-based app and telephone outreach to engage patients with osteoarthritis to self-manage their disease have demonstrated the potential to improve some symptoms, at least in the short term, showing the potential for tools to interact with OA patients without having them come into an office or clinic.
Remote interaction using these two forms of telemedicine – one a sophisticated digital platform, the other using a device that’s been around for almost 150 years – may have greater utility for keeping physicians connected with their OA patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, OA experts said in an interview.
“This is certainly relevant during the pandemic, but this has been of high interest for years as well, as researchers and clinicians have been seeking the best ways to reach patients with these types of programs,” said Kelli Allen, PhD, a research health scientist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Two separate studies evaluated the telemedicine platforms. In JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers reported that telephone-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for patients aged 60 and older with OA and insomnia led to improved sleep, fatigue and, to a lesser extent, pain, in a randomized, controlled trial with 327 patients.
A separate randomized, controlled trial of 105 OA patients at the University of Nottingham (England), published in JAMA Network Open, reported that users of a smartphone-based exercise intervention app had greater improvements in pain and function than did controls.
“I think these two studies represent a first step in terms of moving forward, and certainly the interventions could be refined and potentially combined together for patients in the future,” said C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center in Tucson.
Phone-based CBT study
The telephone-based CBT study consisted of two groups: the CBT group (n = 163) who completed six 20- to 30-minute telephone calls over 8 weeks, kept daily diaries, and received tailored educational materials and an education-only group (n = 164). At 2 months after treatment, Insomnia Severity Index scores decreased 8.1 points on average in the CBT group versus 4.8 points in the education-only patients (P < .001).
That variation between the intervention group and controls was sustained out to a year: 7.7 points lower than baseline versus 4.7 points lower. At the same time point, 56.3% of the CBT group remained in remission with Insomnia Severity Index scores less than 7 versus 25.8% of controls. Fatigue outcomes were similarly disparate between the groups.
Pain outcomes were a different story, however. “Post treatment, significant differences were observed for pain, but these differences were not sustained at 12-month follow-up,” first author Susan M. McCurry, PhD, a clinical psychologist and faculty member at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues wrote.
“I think their positive findings illustrate that remotely delivered interventions can be ‘low tech’ and still effective,” Dr. Allen said of the CBT phone study. She noted that complete case data were available for 282 of 327 patients. “The high rate of session attendance suggests that they chose a delivery modality appropriate for their target patient group.”
The scalability of the telephone model is noteworthy, Dr. Kwoh said. “Having a telemedicine intervention that could be scaled a little more easily rather than an in-person intervention, and having individualized treatment, that’s beneficial, as is targeting two symptoms that are very bothersome and burdensome to patients with OA: insomnia and fatigue.” Following patients out to 12 months is a strength of the study, he added.
Smartphone app–based exercise study
The U.K. study evaluated 6-week outcomes of 48 patients with knee OA who used a proprietary app-based exercise program (Joint Academy) and 57 controls who used traditional self-management. The app provided daily exercises and texts, along with email and smartphone reminders. The app was derived from the Better Management of Patients with OA program initiated in Sweden in 2008 that used OA treatment guidelines for education and exercise in person in primary care clinics.
App users showed a 1.5-point reduction in numeric rating scale (NRS) pain score at 6 weeks versus virtually no change in controls (P < .001). In terms of secondary outcomes, pain scores improved 2.2 points on average for app users versus 1.2 for controls (P = .02), with similar improvements recorded in both stiffness and physical function.
Average change in the 30-second sit-to-stand test measured 4.5 for the app users and 1.2 for the usual-care group (P < .001). The study found no difference between the two groups in changes in temporal summation, conditional pain modulation, or Arthritis Research UK Musculoskeletal Health Questionnaire scores.
First author Sameer Akram Gohir, MSc, PhD, and colleagues wrote that the reasons for differences in outcomes between app users and controls aren’t clear. “The superior outcome in the intervention group may depend on the content and context in the app, including a combination of standardized exercises and information, as well as using a digital delivery system.”
Data gathering was cut short because of COVID-19 restrictions in the United Kingdom, as 27 patients missed their in-person follow-up visits. That was one shortcoming of the study, Dr. Kwoh noted.
“Given the caveats certainly they were able to show robust changes in terms of decreased pain, and also improvement in a variety of performance measures. Certainly this may be beneficial – we don’t know – in terms of cost-effectiveness, but it may be beneficial for insurance companies to adapt such a program,” he said, adding that future studies into the cost effectiveness of the digital platform would be in order.
“Certainly, if this program were to decrease physician visits or postpone the need for joint replacement for individuals, then it could be certainly very cost effective,” Dr. Kwoh said.
The completion rate among patients in the study – almost 90% – was “impressive,” Dr. Allen said. “However, this is a relatively short-term study, and I think an important question for future research is whether patients continue with this level of engagement for a longer period of time.”
Dr. McCurry had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. The CBT phone study received funding from the Public Health Service and the National Institute on Aging. Coauthors disclosed relationships with Campbell Alliance Group, Mapi Research Trust, and Pfizer. Dr. Gohir reported no relevant financial relationships. The study received funding from the Versus Arthritis UK Plan Center, the National Institute for Health Research Nottingham Biomedical Research Center, and Pfizer Global. The Joint Academy provided software for the study. A coauthor reported a financial relationships with Pfizer. Dr. Kwoh said that in the past year he has consulted for Express Scripts, Kolon Tissue Gene, LG Chem, and Regeneron. In the past year, he also received institutional grants for clinical trials from AbbVie, Cumberland, Eicos, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Mitsubishi, and Pfizer. Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE AND JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Sleep disorders in older adults
As humans live longer, a renewed focus on quality of life has made the prompt diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related disorders in older adults increasingly necessary.1 Normative aging results in multiple changes in sleep architecture, including decreased total sleep time, decreased sleep efficiency, decreased slow-wave sleep (SWS), and increased awakenings after sleep onset.2 Sleep disturbances in older adults are increasingly recognized as multifactorial health conditions requiring comprehensive modification of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.3
In this article, we discuss the effects of aging on sleep architecture and provide an overview of primary sleep disorders in older adults. We also summarize strategies for diagnosing and treating sleep disorders in these patients.
Elements of the sleep cycle
The human sleep cycle begins with light sleep (sleep stages 1 and 2), progresses into SWS (sleep stage 3), and culminates in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The first 3 stages are referred to as non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM). Throughout the night, this coupling of NREM and REM cycles occurs 4 to 6 times, with each successive cycle decreasing in length until awakening.4
Two complex neurologic pathways intersect to regulate the timing of sleep and wakefulness on arousal. The first pathway, the circadian system, is located within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and is highly dependent on external stimuli (light, food, etc.) to synchronize sleep/wake cycles. The suprachiasmatic nucleus regulates melatonin secretion by the pineal gland, which signals day-night transitions. The other pathway, the homeostatic system, modifies the amount of sleep needed daily. When multiple days of poor sleep occur, homeostatic sleep pressure (colloquially described as sleep debt) compensates by increasing the amount of sleep required in the following days. Together, the circadian and homeostatic systems work in conjunction to regulate sleep quantity to approximately one-third of the total sleep-wake cycle.2,5
Age-related dysfunction of the regulatory sleep pathways leads to blunting of the ability to initiate and sustain high-quality sleep.6 Dysregulation of homeostatic sleep pressure decreases time spent in SWS, and failure of the circadian signaling apparatus results in delays in sleep/wake timing.2 While research into the underlying neurobiology of sleep reveals that some of these changes are inherent to aging (Box7-14), significant underdiagnosed pathologies may adversely affect sleep architecture, including polypharmacy, comorbid neuropathology (eg, synucleinopathies, tauopathies, etc.), and primary sleep disorders (insomnias, hypersomnias, and parasomnias).15
Box
It has long been known that sleep architecture changes significantly with age. One of the largest meta-analyses of sleep changes in healthy individuals throughout childhood into old age found that total sleep time, sleep efficiency, percentage of slow-wave sleep, percentage of rapid eye movement sleep (REM), and REM latency all decreased with normative aging.7 Other studies have also found a decreased ability to maintain sleep (increased frequency of awakenings and prolonged nocturnal awakenings).8
Based on several meta-analyses, the average total sleep time at night in the adult population decreases by approximately 10 minutes per decade in both men and women.7,9-11 However, this pattern is not observed after age 60, when the total sleep time plateaus.7 Similarly, the duration of wake after sleep onset increases by approximately 10 minutes every decade for adults age 30 to 60, and plateaus after that.7,8
Epidemiologic studies have suggested that the prevalence of daytime napping increases with age.8 This trend continues into older age without a noticeable plateau.
A study of a nationally representative sample of >7,000 Japanese participants found that a significantly higher proportion of older adults take daytime naps (27.4%) compared with middle-age adults (14.4%).12 Older adults nap more frequently because of both lifestyle and biologic changes that accompany normative aging. Polls in the United States have shown a correlation between frequent napping and an increase in excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia.13
While sleep latency steadily increases after age 50, recent studies have shown that in healthy individuals, these changes are modest at best,7,9,14 which suggests that other pathologic factors may be contributing to this problem. Although healthy older people were found to have more frequent arousals throughout the night, they retained the ability to reinitiate sleep as rapidly as younger adults.7,9
Primary sleep disorders
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is one of the most common, yet frequently underdiagnosed reversible causes of sleep disturbances. It is characterized by partial or complete airway obstruction culminating in periods of involuntary cessation of respirations during sleep. The resultant fragmentation in sleep leads to significant downstream effects over time, including excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, poor occupational and social performance, and substantial cognitive impairment.3 While it is well known that OSA increases in prevalence throughout middle age, this relationship plateaus after age 60.16 An estimated 40% to 60% of Americans age >60 are affected by OSA.17 The hypoxemia and fragmented sleep caused by unrecognized OSA are associated with a significant decline in activities of daily living (ADL).18 Untreated OSA is strongly linked to the development and progression of several major health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, stroke, and depression.19 In studies of long-term care facility residents—many of whom may have comorbid cognitive decline—researchers found that unrecognized OSA often mimics the progressive cognitive decline seen in major neurocognitive disorders.20 However, classic symptoms of OSA may not always be present in these patients, and their daytime sleepiness is often attributed to old age rather than to a pathological etiology.16 Screening for OSA and prompt initiation of the appropriate treatment may reverse OSA-induced cognitive changes in these patients.21
The primary presenting symptom of OSA is snoring, which is correlated with pauses in breathing. Risk factors include increased body mass index (BMI), thick neck circumference, male sex, and advanced age. In older adults, BMI has a lower impact on the Apnea-Hypopnea Index, an indicator of the number of pauses in breathing per hour, when compared with young and middle-age adults.16 Validated screening questionnaires for OSA include the STOP-Bang Questionnaire (Table 122), OSA50, Berlin Questionnaire, and Epworth Sleepiness Scale, each of which is used in different subpopulations. The current diagnostic standard for OSA is nocturnal polysomnography in a sleep laboratory, but recent advances in home sleep apnea testing have made it a viable, low-cost alternative for patients who do not have significant medical comorbidities.23 Standard utilized cutoffs for diagnosis are ≥5 events/hour (hypopneas associated with at least 4% oxygen desaturations) in conjunction with clinical symptoms of OSA.24

Continue to: Treatment
Treatment. First-line treatment for OSA is continuous positive airway pressure therapy, but adherence rates vary widely with patient education and regular follow-up.25 Adjunctive therapy includes weight loss, oral appliances, and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, a procedure in which tissue in the throat is remodeled or removed.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a pause in breathing without evidence of associated respiratory effort. In adults, the development of CSA is indicative of underlying lower brainstem dysfunction, due to intermittent failures in the pontomedullary centers responsible for regulation of rhythmic breathing.26 This can occur as a consequence of multiple diseases, including congestive heart failure, stroke, renal failure, chronic medication use (opioids), and brain tumors.
The Sleep Heart Health Study—the largest community-based cohort study to date examining CSA—estimated that the prevalence of CSA among adults age >65 was 1.1% (compared with 0.4% in those age <65).27 Subgroup analysis revealed that men had significantly higher rates of CSA compared with women (2.7% vs 0.2%, respectively).
CSA may present similarly to OSA (excessive daytime somnolence, insomnia, poor sleep quality, difficulties with attention and concentration). Symptoms may also mimic those of coexisting medical conditions in older adults, such as nocturnal angina or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.27 Any older patient with daytime sleepiness and risk factors for CSA should be referred for in-laboratory nocturnal polysomnography, the gold standard diagnostic test. Unlike in OSA, ambulatory diagnostic measures (home sleep apnea testing) have not been validated for this disorder.27
Treatment. The primary treatment for CSA is to address the underlying medical problem. Positive pressure ventilation has been attempted with mixed results. Supplemental oxygen and medical management (acetazolamide or theophylline) can help stimulate breathing. Newer studies have shown favorable outcomes with transvenous neurostimulation or adaptive servoventilation.28-30
Continue to: Insomnia
Insomnia. For a primary diagnosis of insomnia, DSM-5 requires at least 3 nights per week of sleep disturbances that induce distress or functional impairment for at least 3 months.31 The International Classification of Disease, 10th Edition requires at least 1 month of symptoms (lying awake for a long time before falling asleep, sleeping for short periods, being awake for most of the night, feeling lack of sleep, waking up early) after ruling out other sleep disorders, substance use, or other medical conditions.4 Clinically, insomnia tends to present in older adults as a subjective complaint of dissatisfaction with the quality and/or quantity of their sleep. Insomnia has been consistently shown to be a significant risk factor for both the development or exacerbation of depression in older adults.32-34
While the diagnosis of insomnia is mainly clinical via a thorough sleep and medication history, assistive ancillary testing can include wrist actigraphy and screening questionnaires (the Insomnia Severity Index and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index).4 Because population studies of older adults have found discrepancies between objective and subjective methods of assessing sleep quality, relying on the accuracy of self-reported symptoms alone is questionable.35
Treatment. Given that drug elimination half-life increases with age, and the risks of adverse effects are increased in older adults, the preferred treatment modalities for insomnia are nonpharmacologic.4 Sleep hygiene education (Table 2) and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia are often the first-line therapies.4,36,37 It is crucial to manage comorbidities such as heart disease and obesity, as well as sources of discomfort from conditions such as arthritic pain.38,39 If nonpharmacologic therapies are not effective, pharmacologic options can be considered.4 Before prescribing sleep medications, it may be more fruitful to treat underlying psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety with antidepressants.4 Although benzodiazepines are helpful for their sedative effects, they are not recommended for older adults because of an increased risk of falls, rebound insomnia, potential tolerance, and associated cognitive impairment.40 Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (eg, zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon) were initially developed as a first-line treatment for insomnia to replace the reliance on benzodiazepines, but these medications have a “black-box” warning of a serious risk of complex sleep behaviors, including life-threatening parasomnias.41 As a result, guidelines suggest a shorter duration of treatment with a benzodiazepine receptor agonist may still provide benefit while limiting the risk of adverse effects.42
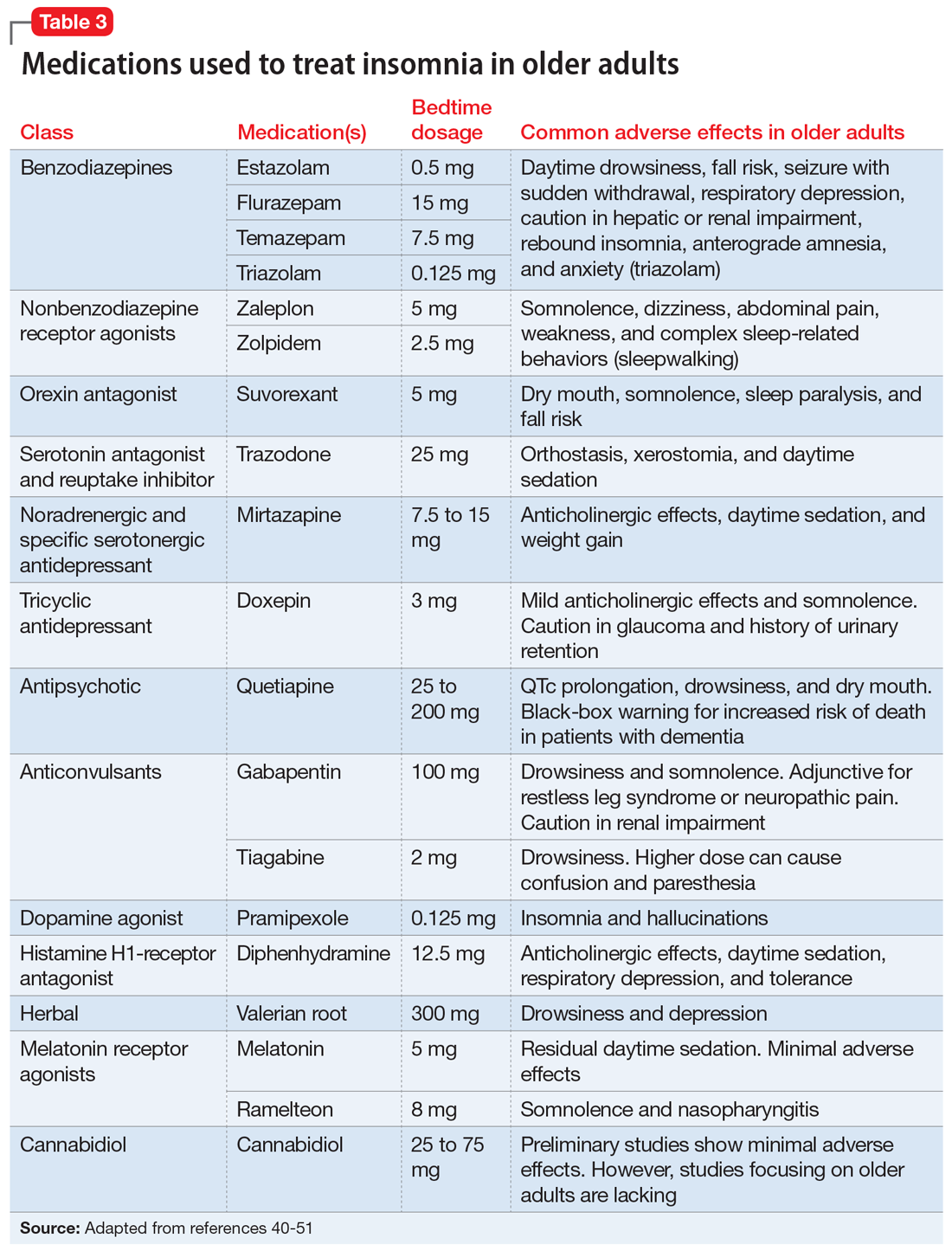
Doxepin is the only antidepressant FDA-approved for insomnia; it improves sleep latency (time taken to initiate sleep after lying down), duration, and quality in adults age >65.43 Melatonin receptor agonists such as ramelteon and melatonin have shown positive results in older patients with insomnia. In clinical trials of patients age ≥65, ramelteon, which is FDA-approved for insomnia, produced no rebound insomnia, withdrawal effects, memory impairment, or gait instability.44-46 Suvorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist, decreases sleep latency and increases total sleep time equally in both young and older adults.47-49Table 340-51 provides a list of medications used to treat insomnia (including off-label agents) and their common adverse effects in older adults.
Parasomnias are undesirable behaviors that occur during sleep, commonly associated with the sleep-wake transition period. These behaviors can occur during REM sleep (nightmare disorder, sleep paralysis, REM sleep behavior disorder) or NREM sleep (somnambulism [sleepwalking], confusional arousals, sleep terrors). According to a cross-sectional Norwegian study of parasomnias, the estimated lifetime prevalence of sleep walking is 22.4%; sleep talking, 66.8%; confusional arousal, 18.5%; and sleep terror, 10.4%.52
Continue to: When evaluating a patient...
When evaluating a patient with parasomnias, it is important to review their drug and substance use as well as coexisting medical conditions. Drugs and substances that can affect sleep include prescription medications (second-generation antidepressants, stimulants, dopamine agonists), excessive caffeine, alcohol, certain foods (coffee, chocolate milk, black tea, caffeinated soft drinks), environmental exposures (smoking, pesticides), and recreational drugs (amphetamines).53-56 Certain medical conditions are correlated with specific parasomnias (eg, sleep paralysis and narcolepsy, REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease [PD], etc.).54 Diagnosis of parasomnias is mainly clinical but supporting evidence can be obtained through in-lab polysomnography.
Treatment. For parasomnias, treatment is primarily supportive and includes creating a safe sleeping environment to reduce the risk of self-harm. Recommendations include sleeping in a room on the ground floor, minimizing furniture in the bedroom, padding any bedside furniture, child-proofing doorknobs, and locking up weapons and other dangerous household items.54
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). This disorder is characterized by a loss of the typical REM sleep-associated atonia and the presence of motor activity during dreaming (dream-enacted behaviors). While the estimated incidence of RBD in the general adult population is approximately 0.5%, it increases to 7.7% among those age >60.57 RBD occurs most commonly in the setting of the alpha-synucleinopathies (PD, Lewy body dementia, multisystem atrophy), but can also be found in patients with cerebral ischemia, demyelinating disorders, or alcohol misuse, or can be medication-induced (primarily antidepressants and antipsychotics).58 In patients with PD, the presence of RBD is associated with a more impaired cognitive profile, suggestive of widespread neurodegeneration.59 Recent studies revealed that RBD may also be a prodromal state of neurodegenerative diseases such as PD, which should prompt close monitoring and long-term follow up.60 Similar to other parasomnias, the diagnosis of RBD is primarily clinical, but polysomnography plays an important role in demonstrating loss of REM-related atonia.54
Treatment. Clonazepam and melatonin have been shown to be effective in treating the symptoms of RBD.54
Depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) affect sleep in patients of all ages, but are underreported in older adults. According to national epidemiologic surveys, the estimated prevalence of MDD and GAD among older adults is 13% and 11.4%, respectively.61,62 Rates as high as 42% and 39% have been reported in meta-regression analyses among patients with Alzheimer’s dementia.63
Continue to: Depression and anxiety
Depression and anxiety may have additive effects and manifest as poor sleep satisfaction, increased sleep latency, insomnia, and daytime sleepiness.64 However, they may also have independent effects. Studies showed that patients with depression alone reported overall poor sleep satisfaction, whereas patients with anxiety alone reported problems with sleep latency, daytime drowsiness, and waking up at night in addition to their overall poor sleep satisfaction.65-67 Both depression and anxiety are risk factors for developing cognitive decline, and may be an early sign/prodrome of neurodegenerative diseases (dementias).68 The bidirectional relationship between depression/anxiety and sleep is complex and needs further investigation.
Treatment. Pharmacologic treatments for patients with depression/anxiety and sleep disturbances include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and other serotonin receptor agonists.69-72 Nonpharmacologic treatments include CBT for both depression and anxiety, and problem-solving therapy for patients with mild cognitive impairment and depression.73,74 For severe depression and/or anxiety, electroconvulsive therapy is effective.75
Bottom Line
Sleep disorders in older adults are common but often underdiagnosed. Timely recognition of obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, insomnia, parasomnias, and other sleep disturbances can facilitate effective treatment and greatly improve older adults’ quality of life.
Related Resources
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition. https://aasm.org
- SleepFoundation.org. Sleep hygiene. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
Drug Brand Names
Acetazolamide • Diamox
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Doxepin • Silenor
Eszopiclone • Lunesta
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Pramipexole • Mirapex
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Ramelteon • Rozerem
Suvorexant • Belsomra
Temazepam • Restoril
Theophylline • Elixophyllin
Tiagabine • Gabitril
Trazadone • Desyrel
Triazolam • Halcion
Zaleplon • Sonata
Zolpidem • Ambien
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The state of aging and health in America. 2013. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/aging/pdf/state-aging-health-in-america-2013.pdf
2. Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Hirata K. Sleep disorders in the elderly: diagnosis and management. J Gen Fam Med. 2017;18(2):61-71.
3. Inouye SK, Studenski S, Tinetti ME, et al. Geriatric syndromes: clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55(5):780-791.
4. Patel D, Steinberg J, Patel P. Insomnia in the elderly: a review. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(6):1017-1024.
5. Neubauer DN. A review of ramelteon in the treatment of sleep disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008;4(1):69-79.
6. Mander BA, Winer JR, Walker MP. Sleep and human aging. Neuron. 2017;94(1):19-36.
7. Ohayon MM, Carskadon MA, Guilleminault C, et al. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep. 2004;27:1255-1273.
8. Li J, Vitiello MV, Gooneratne NS. Sleep in normal aging. Sleep Med Clin. 2018;13(1):1-11.
9. Floyd JA, Medler SM, Ager JW, et al. Age-related changes in initiation and maintenance of sleep: a meta-analysis. Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(2):106-117.
10. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Jenuwine ES, et al. Changes in REM-sleep percentage over the adult lifespan. Sleep. 2007;30(7):829-836.
11. Dorffner G, Vitr M, Anderer P. The effects of aging on sleep architecture in healthy subjects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;821:93-100.
12. Furihata R, Kaneita Y, Jike M, et al. Napping and associated factors: a Japanese nationwide general population survey. Sleep Med. 2016;20:72-79.
13. Foley DJ, Vitiello MV, Bliwise DL, et al. Frequent napping is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia in older adults: findings from the National Sleep Foundation ‘2003 Sleep in America’ Poll. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15(4):344-350.
14. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Marshall Medler S, et al. Nonlinear components of age-related change in sleep initiation. Nurs Res. 2000;49(5):290-294.
15. Miner B, Kryger MH. Sleep in the aging population. Sleep Med Clin. 2017;12(1):31-38.
16. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(9):1217-1239.
17. Ancoli-Israel S, Klauber MR, Butters N, et al. Dementia in institutionalized elderly: relation to sleep apnea. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(3):258-263.
18. Spira AP, Stone KL, Rebok GW, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing and functional decline in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(11):2040-2046.
19. Vijayan VK. Morbidities associated with obstructive sleep apnea. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2012;6(5):557-566.
20. Kerner NA, Roose SP. Obstructive sleep apnea is linked to depression and cognitive impairment: evidence and potential mechanisms. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;24(6):496-508.
21. Dalmases M, Solé-Padullés C, Torres M, et al. Effect of CPAP on cognition, brain function, and structure among elderly patients with OSA: a randomized pilot study. Chest. 2015;148(5):1214-1223.
22. Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network. University of Toronto. STOP-Bang Questionnaire. 2012. Accessed January 26, 2021. www.stopbang.ca
23. Freedman N. Doing it better for less: incorporating OSA management into alternative payment models. Chest. 2019;155(1):227-233.
24. Kapur VK, Auckley DH, Chowdhuri S, et al. Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017;13(3):479-504.
25. Semelka M, Wilson J, Floyd R. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94(5):355-360.
26. Javaheri S, Dempsey JA. Central sleep apnea. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):141-163.
27. Donovan LM, Kapur VK. Prevalence and characteristics of central compared to obstructive sleep apnea: analyses from the Sleep Heart Health Study cohort. Sleep. 2016;39(7):1353-1359.
28. Cao M, Cardell CY, Willes L, et al. A novel adaptive servoventilation (ASVAuto) for the treatment of central sleep apnea associated with chronic use of opioids. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(8):855-861.
29. Oldenburg O, Spießhöfer J, Fox H, et al. Performance of conventional and enhanced adaptive servoventilation (ASV) in heart failure patients with central sleep apnea who have adapted to conventional ASV. Sleep Breath. 2015;19(3):795-800.
30. Costanzo MR, Ponikowski P, Javaheri S, et al. Transvenous neurostimulation for central sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10048):974-982.
31. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:362.
32. Perlis ML, Smith LJ, Lyness JM, et al. Insomnia as a risk factor for onset of depression in the elderly. Behav Sleep Med. 2006;4(2):104-113.
33. Cole MG, Dendukuri N. Risk factors for depression among elderly community subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(6):1147-1156.
34. Pigeon WR, Hegel M, Unützer J, et al. Is insomnia a perpetuating factor for late-life depression in the IMPACT cohort? Sleep. 2008;31(4):481-488.
35. Hughes JM, Song Y, Fung CH, et al. Measuring sleep in vulnerable older adults: a comparison of subjective and objective sleep measures. Clin Gerontol. 2018;41(2):145-157.
36. Irish LA, Kline CE, Gunn HE, et al. The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: a review of empirical evidence. Sleep Med Rev. 2015;22:23-36.
37. Sleep Foundation. Sleep hygiene. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
38. Foley D, Ancoli-Israel S, Britz P, et al. Sleep disturbances and chronic disease in older adults: results of the 2003 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Survey. J Psychosom Res. 2004;56(5):497-502.
39. Eslami V, Zimmerman ME, Grewal T, et al. Pain grade and sleep disturbance in older adults: evaluation the role of pain, and stress for depressed and non-depressed individuals. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;31(5):450-457.
40. American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2015 updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(11):2227-2246.
41. United States Food & Drug Administration. FDA adds Boxed Warning for risk of serious injuries caused by sleepwalking with certain prescription insomnia medicines. 2019. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-adds-boxed-warning-risk-serious-injuries-caused-sleepwalking-certain-prescription-insomnia
42. Schroeck JL, Ford J, Conway EL, et al. Review of safety and efficacy of sleep medicines in older adults. Clin Ther. 2016;38(11):2340-2372.
43. Krystal AD, Lankford A, Durrence HH, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 3 and 6 mg in a 35-day sleep laboratory trial in adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1433-1442.
44. Roth T, Seiden D, Sainati S, et al. Effects of ramelteon on patient-reported sleep latency in older adults with chronic insomnia. Sleep Med. 2006;7(4):312-318.
45. Zammit G, Wang-Weigand S, Rosenthal M, et al. Effect of ramelteon on middle-of-the-night balance in older adults with chronic insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. 2009;5(1):34-40.
46. Mets MAJ, de Vries JM, de Senerpont Domis LM, et al. Next-day effects of ramelteon (8 mg), zopiclone (7.5 mg), and placebo on highway driving performance, memory functioning, psychomotor performance, and mood in healthy adult subjects. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1327-1334.
47. Rhyne DN, Anderson SL. Suvorexant in insomnia: efficacy, safety and place in therapy. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2015;6(5):189-195.
48. Norman JL, Anderson SL. Novel class of medications, orexin receptor antagonists, in the treatment of insomnia - critical appraisal of suvorexant. Nat Sci Sleep. 2016;8:239-247.
49. Owen RT. Suvorexant: efficacy and safety profile of a dual orexin receptor antagonist in treating insomnia. Drugs Today (Barc). 2016;52(1):29-40.
50. Shannon S, Lewis N, Lee H, et al. Cannabidiol in anxiety and sleep: a large case series. Perm J. 2019;23:18-041. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-041
51. Yunusa I, Alsumali A, Garba AE, et al. Assessment of reported comparative effectiveness and safety of atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a network meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190828.
52. Bjorvatn B, Gronli J, Pallesen S. Prevalence of different parasomnias in the general population. Sleep Med. 2010;11(10):1031-1034.
53. Postuma RB, Montplaisir JY, Pelletier A, et al. Environmental risk factors for REM sleep behavior disorder: a multicenter case-control study. Neurology. 2012;79(5):428-434.
54. Fleetham JA, Fleming JA. Parasomnias. CMAJ. 2014;186(8):E273-E280.
55. Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Caldas I, Carvalho F, et al. Bruxism after 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) abuse. Clin Toxicol (Phila.) 2010;48(8):863-864.
56. Irfan MH, Howell MJ. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: overview and current perspective. Curr Sleep Medicine Rep. 2016;2:64-73.
57. Mahlknecht P, Seppi K, Frauscher B, et al. Probable RBD and association with neurodegenerative disease markers: a population-based study. Mov Disord. 2015;30(10):1417-1421.
58. Oertel WH, Depboylu C, Krenzer M, et al. [REM sleep behavior disorder as a prodromal stage of α-synucleinopathies: symptoms, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and therapy]. Nervenarzt. 2014;85:19-25. German.
59. Jozwiak N, Postuma RB, Montplaisir J, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep. 2017;40(8):zsx101. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsx101
60. Claassen DO, Josephs KA, Ahlskog JE, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder preceding other aspects of synucleinopathies by up to half a century. Neurology 2010;75(6):494-499.
61. Reynolds K, Pietrzak RH, El-Gabalawy R, et al. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in U.S. older adults: findings from a nationally representative survey. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):74-81.
62. Lohman MC, Mezuk B, Dumenci L. Depression and frailty: concurrent risks for adverse health outcomes. Aging Ment Health. 2017;21(4):399-408.
63. Zhao QF, Tan L, Wang HF, et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;190:264-271.
64. Furihata R, Hall MH, Stone KL, et al. An aggregate measure of sleep health is associated with prevalent and incident clinically significant depression symptoms among community-dwelling older women. Sleep. 2017;40(3):zsw075. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw075
65. Spira AP, Stone K, Beaudreau SA, et al. Anxiety symptoms and objectively measured sleep quality in older women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17(2):136-143.
66. Press Y, Punchik B, Freud T. The association between subjectively impaired sleep and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a frail elderly population. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(7):755-765.
67. Gould CE, Spira AP, Liou-Johnson V, et al. Association of anxiety symptom clusters with sleep quality and daytime sleepiness. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2018;73(3):413-420.
68. Kassem AM, Ganguli M, Yaffe K, et al. Anxiety symptoms and risk of cognitive decline in older community-dwelling men. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(7):1137-1145.
69. Frank C. Pharmacologic treatment of depression in the elderly. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60(2):121-126.
70. Subramanyam AA, Kedare J, Singh OP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for geriatric anxiety disorders. Indian J Psychiatry. 2018;60(suppl 3):S371-S382.
71. Emsley R, Ahokas A, Suarez A, et al. Efficacy of tianeptine 25-50 mg in elderly patients with recurrent major depressive disorder: an 8-week placebo- and escitalopram-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(4):17m11741. doi: 10.4088/JCP.17m11741
72. Semel D, Murphy TK, Zlateva G, et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of pregabalin in older patients with neuropathic pain: results from a pooled analysis of 11 clinical studies. BMC Fam Pract. 2010;11:85.
73. Orgeta V, Qazi A, Spector A, et al. Psychological treatments for depression and anxiety in dementia and mild cognitive impairment: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(4):293-298.
74. Morimoto SS, Kanellopoulos D, Manning KJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of depression and cognitive impairment in late life. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1345(1):36-46.
75. Casey DA. Depression in older adults: a treatable medical condition. Prim Care. 2017;44(3):499-510.
As humans live longer, a renewed focus on quality of life has made the prompt diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related disorders in older adults increasingly necessary.1 Normative aging results in multiple changes in sleep architecture, including decreased total sleep time, decreased sleep efficiency, decreased slow-wave sleep (SWS), and increased awakenings after sleep onset.2 Sleep disturbances in older adults are increasingly recognized as multifactorial health conditions requiring comprehensive modification of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.3
In this article, we discuss the effects of aging on sleep architecture and provide an overview of primary sleep disorders in older adults. We also summarize strategies for diagnosing and treating sleep disorders in these patients.
Elements of the sleep cycle
The human sleep cycle begins with light sleep (sleep stages 1 and 2), progresses into SWS (sleep stage 3), and culminates in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The first 3 stages are referred to as non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM). Throughout the night, this coupling of NREM and REM cycles occurs 4 to 6 times, with each successive cycle decreasing in length until awakening.4
Two complex neurologic pathways intersect to regulate the timing of sleep and wakefulness on arousal. The first pathway, the circadian system, is located within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and is highly dependent on external stimuli (light, food, etc.) to synchronize sleep/wake cycles. The suprachiasmatic nucleus regulates melatonin secretion by the pineal gland, which signals day-night transitions. The other pathway, the homeostatic system, modifies the amount of sleep needed daily. When multiple days of poor sleep occur, homeostatic sleep pressure (colloquially described as sleep debt) compensates by increasing the amount of sleep required in the following days. Together, the circadian and homeostatic systems work in conjunction to regulate sleep quantity to approximately one-third of the total sleep-wake cycle.2,5
Age-related dysfunction of the regulatory sleep pathways leads to blunting of the ability to initiate and sustain high-quality sleep.6 Dysregulation of homeostatic sleep pressure decreases time spent in SWS, and failure of the circadian signaling apparatus results in delays in sleep/wake timing.2 While research into the underlying neurobiology of sleep reveals that some of these changes are inherent to aging (Box7-14), significant underdiagnosed pathologies may adversely affect sleep architecture, including polypharmacy, comorbid neuropathology (eg, synucleinopathies, tauopathies, etc.), and primary sleep disorders (insomnias, hypersomnias, and parasomnias).15
Box
It has long been known that sleep architecture changes significantly with age. One of the largest meta-analyses of sleep changes in healthy individuals throughout childhood into old age found that total sleep time, sleep efficiency, percentage of slow-wave sleep, percentage of rapid eye movement sleep (REM), and REM latency all decreased with normative aging.7 Other studies have also found a decreased ability to maintain sleep (increased frequency of awakenings and prolonged nocturnal awakenings).8
Based on several meta-analyses, the average total sleep time at night in the adult population decreases by approximately 10 minutes per decade in both men and women.7,9-11 However, this pattern is not observed after age 60, when the total sleep time plateaus.7 Similarly, the duration of wake after sleep onset increases by approximately 10 minutes every decade for adults age 30 to 60, and plateaus after that.7,8
Epidemiologic studies have suggested that the prevalence of daytime napping increases with age.8 This trend continues into older age without a noticeable plateau.
A study of a nationally representative sample of >7,000 Japanese participants found that a significantly higher proportion of older adults take daytime naps (27.4%) compared with middle-age adults (14.4%).12 Older adults nap more frequently because of both lifestyle and biologic changes that accompany normative aging. Polls in the United States have shown a correlation between frequent napping and an increase in excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia.13
While sleep latency steadily increases after age 50, recent studies have shown that in healthy individuals, these changes are modest at best,7,9,14 which suggests that other pathologic factors may be contributing to this problem. Although healthy older people were found to have more frequent arousals throughout the night, they retained the ability to reinitiate sleep as rapidly as younger adults.7,9
Primary sleep disorders
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is one of the most common, yet frequently underdiagnosed reversible causes of sleep disturbances. It is characterized by partial or complete airway obstruction culminating in periods of involuntary cessation of respirations during sleep. The resultant fragmentation in sleep leads to significant downstream effects over time, including excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, poor occupational and social performance, and substantial cognitive impairment.3 While it is well known that OSA increases in prevalence throughout middle age, this relationship plateaus after age 60.16 An estimated 40% to 60% of Americans age >60 are affected by OSA.17 The hypoxemia and fragmented sleep caused by unrecognized OSA are associated with a significant decline in activities of daily living (ADL).18 Untreated OSA is strongly linked to the development and progression of several major health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, stroke, and depression.19 In studies of long-term care facility residents—many of whom may have comorbid cognitive decline—researchers found that unrecognized OSA often mimics the progressive cognitive decline seen in major neurocognitive disorders.20 However, classic symptoms of OSA may not always be present in these patients, and their daytime sleepiness is often attributed to old age rather than to a pathological etiology.16 Screening for OSA and prompt initiation of the appropriate treatment may reverse OSA-induced cognitive changes in these patients.21
The primary presenting symptom of OSA is snoring, which is correlated with pauses in breathing. Risk factors include increased body mass index (BMI), thick neck circumference, male sex, and advanced age. In older adults, BMI has a lower impact on the Apnea-Hypopnea Index, an indicator of the number of pauses in breathing per hour, when compared with young and middle-age adults.16 Validated screening questionnaires for OSA include the STOP-Bang Questionnaire (Table 122), OSA50, Berlin Questionnaire, and Epworth Sleepiness Scale, each of which is used in different subpopulations. The current diagnostic standard for OSA is nocturnal polysomnography in a sleep laboratory, but recent advances in home sleep apnea testing have made it a viable, low-cost alternative for patients who do not have significant medical comorbidities.23 Standard utilized cutoffs for diagnosis are ≥5 events/hour (hypopneas associated with at least 4% oxygen desaturations) in conjunction with clinical symptoms of OSA.24

Continue to: Treatment
Treatment. First-line treatment for OSA is continuous positive airway pressure therapy, but adherence rates vary widely with patient education and regular follow-up.25 Adjunctive therapy includes weight loss, oral appliances, and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, a procedure in which tissue in the throat is remodeled or removed.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a pause in breathing without evidence of associated respiratory effort. In adults, the development of CSA is indicative of underlying lower brainstem dysfunction, due to intermittent failures in the pontomedullary centers responsible for regulation of rhythmic breathing.26 This can occur as a consequence of multiple diseases, including congestive heart failure, stroke, renal failure, chronic medication use (opioids), and brain tumors.
The Sleep Heart Health Study—the largest community-based cohort study to date examining CSA—estimated that the prevalence of CSA among adults age >65 was 1.1% (compared with 0.4% in those age <65).27 Subgroup analysis revealed that men had significantly higher rates of CSA compared with women (2.7% vs 0.2%, respectively).
CSA may present similarly to OSA (excessive daytime somnolence, insomnia, poor sleep quality, difficulties with attention and concentration). Symptoms may also mimic those of coexisting medical conditions in older adults, such as nocturnal angina or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.27 Any older patient with daytime sleepiness and risk factors for CSA should be referred for in-laboratory nocturnal polysomnography, the gold standard diagnostic test. Unlike in OSA, ambulatory diagnostic measures (home sleep apnea testing) have not been validated for this disorder.27
Treatment. The primary treatment for CSA is to address the underlying medical problem. Positive pressure ventilation has been attempted with mixed results. Supplemental oxygen and medical management (acetazolamide or theophylline) can help stimulate breathing. Newer studies have shown favorable outcomes with transvenous neurostimulation or adaptive servoventilation.28-30
Continue to: Insomnia
Insomnia. For a primary diagnosis of insomnia, DSM-5 requires at least 3 nights per week of sleep disturbances that induce distress or functional impairment for at least 3 months.31 The International Classification of Disease, 10th Edition requires at least 1 month of symptoms (lying awake for a long time before falling asleep, sleeping for short periods, being awake for most of the night, feeling lack of sleep, waking up early) after ruling out other sleep disorders, substance use, or other medical conditions.4 Clinically, insomnia tends to present in older adults as a subjective complaint of dissatisfaction with the quality and/or quantity of their sleep. Insomnia has been consistently shown to be a significant risk factor for both the development or exacerbation of depression in older adults.32-34
While the diagnosis of insomnia is mainly clinical via a thorough sleep and medication history, assistive ancillary testing can include wrist actigraphy and screening questionnaires (the Insomnia Severity Index and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index).4 Because population studies of older adults have found discrepancies between objective and subjective methods of assessing sleep quality, relying on the accuracy of self-reported symptoms alone is questionable.35
Treatment. Given that drug elimination half-life increases with age, and the risks of adverse effects are increased in older adults, the preferred treatment modalities for insomnia are nonpharmacologic.4 Sleep hygiene education (Table 2) and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia are often the first-line therapies.4,36,37 It is crucial to manage comorbidities such as heart disease and obesity, as well as sources of discomfort from conditions such as arthritic pain.38,39 If nonpharmacologic therapies are not effective, pharmacologic options can be considered.4 Before prescribing sleep medications, it may be more fruitful to treat underlying psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety with antidepressants.4 Although benzodiazepines are helpful for their sedative effects, they are not recommended for older adults because of an increased risk of falls, rebound insomnia, potential tolerance, and associated cognitive impairment.40 Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (eg, zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon) were initially developed as a first-line treatment for insomnia to replace the reliance on benzodiazepines, but these medications have a “black-box” warning of a serious risk of complex sleep behaviors, including life-threatening parasomnias.41 As a result, guidelines suggest a shorter duration of treatment with a benzodiazepine receptor agonist may still provide benefit while limiting the risk of adverse effects.42
Doxepin is the only antidepressant FDA-approved for insomnia; it improves sleep latency (time taken to initiate sleep after lying down), duration, and quality in adults age >65.43 Melatonin receptor agonists such as ramelteon and melatonin have shown positive results in older patients with insomnia. In clinical trials of patients age ≥65, ramelteon, which is FDA-approved for insomnia, produced no rebound insomnia, withdrawal effects, memory impairment, or gait instability.44-46 Suvorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist, decreases sleep latency and increases total sleep time equally in both young and older adults.47-49Table 340-51 provides a list of medications used to treat insomnia (including off-label agents) and their common adverse effects in older adults.

Parasomnias are undesirable behaviors that occur during sleep, commonly associated with the sleep-wake transition period. These behaviors can occur during REM sleep (nightmare disorder, sleep paralysis, REM sleep behavior disorder) or NREM sleep (somnambulism [sleepwalking], confusional arousals, sleep terrors). According to a cross-sectional Norwegian study of parasomnias, the estimated lifetime prevalence of sleep walking is 22.4%; sleep talking, 66.8%; confusional arousal, 18.5%; and sleep terror, 10.4%.52
Continue to: When evaluating a patient...
When evaluating a patient with parasomnias, it is important to review their drug and substance use as well as coexisting medical conditions. Drugs and substances that can affect sleep include prescription medications (second-generation antidepressants, stimulants, dopamine agonists), excessive caffeine, alcohol, certain foods (coffee, chocolate milk, black tea, caffeinated soft drinks), environmental exposures (smoking, pesticides), and recreational drugs (amphetamines).53-56 Certain medical conditions are correlated with specific parasomnias (eg, sleep paralysis and narcolepsy, REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease [PD], etc.).54 Diagnosis of parasomnias is mainly clinical but supporting evidence can be obtained through in-lab polysomnography.
Treatment. For parasomnias, treatment is primarily supportive and includes creating a safe sleeping environment to reduce the risk of self-harm. Recommendations include sleeping in a room on the ground floor, minimizing furniture in the bedroom, padding any bedside furniture, child-proofing doorknobs, and locking up weapons and other dangerous household items.54
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). This disorder is characterized by a loss of the typical REM sleep-associated atonia and the presence of motor activity during dreaming (dream-enacted behaviors). While the estimated incidence of RBD in the general adult population is approximately 0.5%, it increases to 7.7% among those age >60.57 RBD occurs most commonly in the setting of the alpha-synucleinopathies (PD, Lewy body dementia, multisystem atrophy), but can also be found in patients with cerebral ischemia, demyelinating disorders, or alcohol misuse, or can be medication-induced (primarily antidepressants and antipsychotics).58 In patients with PD, the presence of RBD is associated with a more impaired cognitive profile, suggestive of widespread neurodegeneration.59 Recent studies revealed that RBD may also be a prodromal state of neurodegenerative diseases such as PD, which should prompt close monitoring and long-term follow up.60 Similar to other parasomnias, the diagnosis of RBD is primarily clinical, but polysomnography plays an important role in demonstrating loss of REM-related atonia.54
Treatment. Clonazepam and melatonin have been shown to be effective in treating the symptoms of RBD.54
Depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) affect sleep in patients of all ages, but are underreported in older adults. According to national epidemiologic surveys, the estimated prevalence of MDD and GAD among older adults is 13% and 11.4%, respectively.61,62 Rates as high as 42% and 39% have been reported in meta-regression analyses among patients with Alzheimer’s dementia.63
Continue to: Depression and anxiety
Depression and anxiety may have additive effects and manifest as poor sleep satisfaction, increased sleep latency, insomnia, and daytime sleepiness.64 However, they may also have independent effects. Studies showed that patients with depression alone reported overall poor sleep satisfaction, whereas patients with anxiety alone reported problems with sleep latency, daytime drowsiness, and waking up at night in addition to their overall poor sleep satisfaction.65-67 Both depression and anxiety are risk factors for developing cognitive decline, and may be an early sign/prodrome of neurodegenerative diseases (dementias).68 The bidirectional relationship between depression/anxiety and sleep is complex and needs further investigation.
Treatment. Pharmacologic treatments for patients with depression/anxiety and sleep disturbances include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and other serotonin receptor agonists.69-72 Nonpharmacologic treatments include CBT for both depression and anxiety, and problem-solving therapy for patients with mild cognitive impairment and depression.73,74 For severe depression and/or anxiety, electroconvulsive therapy is effective.75
Bottom Line
Sleep disorders in older adults are common but often underdiagnosed. Timely recognition of obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, insomnia, parasomnias, and other sleep disturbances can facilitate effective treatment and greatly improve older adults’ quality of life.
Related Resources
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition. https://aasm.org
- SleepFoundation.org. Sleep hygiene. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
Drug Brand Names
Acetazolamide • Diamox
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Doxepin • Silenor
Eszopiclone • Lunesta
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Pramipexole • Mirapex
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Ramelteon • Rozerem
Suvorexant • Belsomra
Temazepam • Restoril
Theophylline • Elixophyllin
Tiagabine • Gabitril
Trazadone • Desyrel
Triazolam • Halcion
Zaleplon • Sonata
Zolpidem • Ambien
As humans live longer, a renewed focus on quality of life has made the prompt diagnosis and treatment of sleep-related disorders in older adults increasingly necessary.1 Normative aging results in multiple changes in sleep architecture, including decreased total sleep time, decreased sleep efficiency, decreased slow-wave sleep (SWS), and increased awakenings after sleep onset.2 Sleep disturbances in older adults are increasingly recognized as multifactorial health conditions requiring comprehensive modification of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.3
In this article, we discuss the effects of aging on sleep architecture and provide an overview of primary sleep disorders in older adults. We also summarize strategies for diagnosing and treating sleep disorders in these patients.
Elements of the sleep cycle
The human sleep cycle begins with light sleep (sleep stages 1 and 2), progresses into SWS (sleep stage 3), and culminates in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The first 3 stages are referred to as non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM). Throughout the night, this coupling of NREM and REM cycles occurs 4 to 6 times, with each successive cycle decreasing in length until awakening.4
Two complex neurologic pathways intersect to regulate the timing of sleep and wakefulness on arousal. The first pathway, the circadian system, is located within the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and is highly dependent on external stimuli (light, food, etc.) to synchronize sleep/wake cycles. The suprachiasmatic nucleus regulates melatonin secretion by the pineal gland, which signals day-night transitions. The other pathway, the homeostatic system, modifies the amount of sleep needed daily. When multiple days of poor sleep occur, homeostatic sleep pressure (colloquially described as sleep debt) compensates by increasing the amount of sleep required in the following days. Together, the circadian and homeostatic systems work in conjunction to regulate sleep quantity to approximately one-third of the total sleep-wake cycle.2,5
Age-related dysfunction of the regulatory sleep pathways leads to blunting of the ability to initiate and sustain high-quality sleep.6 Dysregulation of homeostatic sleep pressure decreases time spent in SWS, and failure of the circadian signaling apparatus results in delays in sleep/wake timing.2 While research into the underlying neurobiology of sleep reveals that some of these changes are inherent to aging (Box7-14), significant underdiagnosed pathologies may adversely affect sleep architecture, including polypharmacy, comorbid neuropathology (eg, synucleinopathies, tauopathies, etc.), and primary sleep disorders (insomnias, hypersomnias, and parasomnias).15
Box
It has long been known that sleep architecture changes significantly with age. One of the largest meta-analyses of sleep changes in healthy individuals throughout childhood into old age found that total sleep time, sleep efficiency, percentage of slow-wave sleep, percentage of rapid eye movement sleep (REM), and REM latency all decreased with normative aging.7 Other studies have also found a decreased ability to maintain sleep (increased frequency of awakenings and prolonged nocturnal awakenings).8
Based on several meta-analyses, the average total sleep time at night in the adult population decreases by approximately 10 minutes per decade in both men and women.7,9-11 However, this pattern is not observed after age 60, when the total sleep time plateaus.7 Similarly, the duration of wake after sleep onset increases by approximately 10 minutes every decade for adults age 30 to 60, and plateaus after that.7,8
Epidemiologic studies have suggested that the prevalence of daytime napping increases with age.8 This trend continues into older age without a noticeable plateau.
A study of a nationally representative sample of >7,000 Japanese participants found that a significantly higher proportion of older adults take daytime naps (27.4%) compared with middle-age adults (14.4%).12 Older adults nap more frequently because of both lifestyle and biologic changes that accompany normative aging. Polls in the United States have shown a correlation between frequent napping and an increase in excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia.13
While sleep latency steadily increases after age 50, recent studies have shown that in healthy individuals, these changes are modest at best,7,9,14 which suggests that other pathologic factors may be contributing to this problem. Although healthy older people were found to have more frequent arousals throughout the night, they retained the ability to reinitiate sleep as rapidly as younger adults.7,9
Primary sleep disorders
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is one of the most common, yet frequently underdiagnosed reversible causes of sleep disturbances. It is characterized by partial or complete airway obstruction culminating in periods of involuntary cessation of respirations during sleep. The resultant fragmentation in sleep leads to significant downstream effects over time, including excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, poor occupational and social performance, and substantial cognitive impairment.3 While it is well known that OSA increases in prevalence throughout middle age, this relationship plateaus after age 60.16 An estimated 40% to 60% of Americans age >60 are affected by OSA.17 The hypoxemia and fragmented sleep caused by unrecognized OSA are associated with a significant decline in activities of daily living (ADL).18 Untreated OSA is strongly linked to the development and progression of several major health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, stroke, and depression.19 In studies of long-term care facility residents—many of whom may have comorbid cognitive decline—researchers found that unrecognized OSA often mimics the progressive cognitive decline seen in major neurocognitive disorders.20 However, classic symptoms of OSA may not always be present in these patients, and their daytime sleepiness is often attributed to old age rather than to a pathological etiology.16 Screening for OSA and prompt initiation of the appropriate treatment may reverse OSA-induced cognitive changes in these patients.21
The primary presenting symptom of OSA is snoring, which is correlated with pauses in breathing. Risk factors include increased body mass index (BMI), thick neck circumference, male sex, and advanced age. In older adults, BMI has a lower impact on the Apnea-Hypopnea Index, an indicator of the number of pauses in breathing per hour, when compared with young and middle-age adults.16 Validated screening questionnaires for OSA include the STOP-Bang Questionnaire (Table 122), OSA50, Berlin Questionnaire, and Epworth Sleepiness Scale, each of which is used in different subpopulations. The current diagnostic standard for OSA is nocturnal polysomnography in a sleep laboratory, but recent advances in home sleep apnea testing have made it a viable, low-cost alternative for patients who do not have significant medical comorbidities.23 Standard utilized cutoffs for diagnosis are ≥5 events/hour (hypopneas associated with at least 4% oxygen desaturations) in conjunction with clinical symptoms of OSA.24

Continue to: Treatment
Treatment. First-line treatment for OSA is continuous positive airway pressure therapy, but adherence rates vary widely with patient education and regular follow-up.25 Adjunctive therapy includes weight loss, oral appliances, and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, a procedure in which tissue in the throat is remodeled or removed.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a pause in breathing without evidence of associated respiratory effort. In adults, the development of CSA is indicative of underlying lower brainstem dysfunction, due to intermittent failures in the pontomedullary centers responsible for regulation of rhythmic breathing.26 This can occur as a consequence of multiple diseases, including congestive heart failure, stroke, renal failure, chronic medication use (opioids), and brain tumors.
The Sleep Heart Health Study—the largest community-based cohort study to date examining CSA—estimated that the prevalence of CSA among adults age >65 was 1.1% (compared with 0.4% in those age <65).27 Subgroup analysis revealed that men had significantly higher rates of CSA compared with women (2.7% vs 0.2%, respectively).
CSA may present similarly to OSA (excessive daytime somnolence, insomnia, poor sleep quality, difficulties with attention and concentration). Symptoms may also mimic those of coexisting medical conditions in older adults, such as nocturnal angina or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.27 Any older patient with daytime sleepiness and risk factors for CSA should be referred for in-laboratory nocturnal polysomnography, the gold standard diagnostic test. Unlike in OSA, ambulatory diagnostic measures (home sleep apnea testing) have not been validated for this disorder.27
Treatment. The primary treatment for CSA is to address the underlying medical problem. Positive pressure ventilation has been attempted with mixed results. Supplemental oxygen and medical management (acetazolamide or theophylline) can help stimulate breathing. Newer studies have shown favorable outcomes with transvenous neurostimulation or adaptive servoventilation.28-30
Continue to: Insomnia
Insomnia. For a primary diagnosis of insomnia, DSM-5 requires at least 3 nights per week of sleep disturbances that induce distress or functional impairment for at least 3 months.31 The International Classification of Disease, 10th Edition requires at least 1 month of symptoms (lying awake for a long time before falling asleep, sleeping for short periods, being awake for most of the night, feeling lack of sleep, waking up early) after ruling out other sleep disorders, substance use, or other medical conditions.4 Clinically, insomnia tends to present in older adults as a subjective complaint of dissatisfaction with the quality and/or quantity of their sleep. Insomnia has been consistently shown to be a significant risk factor for both the development or exacerbation of depression in older adults.32-34
While the diagnosis of insomnia is mainly clinical via a thorough sleep and medication history, assistive ancillary testing can include wrist actigraphy and screening questionnaires (the Insomnia Severity Index and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index).4 Because population studies of older adults have found discrepancies between objective and subjective methods of assessing sleep quality, relying on the accuracy of self-reported symptoms alone is questionable.35
Treatment. Given that drug elimination half-life increases with age, and the risks of adverse effects are increased in older adults, the preferred treatment modalities for insomnia are nonpharmacologic.4 Sleep hygiene education (Table 2) and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia are often the first-line therapies.4,36,37 It is crucial to manage comorbidities such as heart disease and obesity, as well as sources of discomfort from conditions such as arthritic pain.38,39 If nonpharmacologic therapies are not effective, pharmacologic options can be considered.4 Before prescribing sleep medications, it may be more fruitful to treat underlying psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety with antidepressants.4 Although benzodiazepines are helpful for their sedative effects, they are not recommended for older adults because of an increased risk of falls, rebound insomnia, potential tolerance, and associated cognitive impairment.40 Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (eg, zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon) were initially developed as a first-line treatment for insomnia to replace the reliance on benzodiazepines, but these medications have a “black-box” warning of a serious risk of complex sleep behaviors, including life-threatening parasomnias.41 As a result, guidelines suggest a shorter duration of treatment with a benzodiazepine receptor agonist may still provide benefit while limiting the risk of adverse effects.42
Doxepin is the only antidepressant FDA-approved for insomnia; it improves sleep latency (time taken to initiate sleep after lying down), duration, and quality in adults age >65.43 Melatonin receptor agonists such as ramelteon and melatonin have shown positive results in older patients with insomnia. In clinical trials of patients age ≥65, ramelteon, which is FDA-approved for insomnia, produced no rebound insomnia, withdrawal effects, memory impairment, or gait instability.44-46 Suvorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist, decreases sleep latency and increases total sleep time equally in both young and older adults.47-49Table 340-51 provides a list of medications used to treat insomnia (including off-label agents) and their common adverse effects in older adults.

Parasomnias are undesirable behaviors that occur during sleep, commonly associated with the sleep-wake transition period. These behaviors can occur during REM sleep (nightmare disorder, sleep paralysis, REM sleep behavior disorder) or NREM sleep (somnambulism [sleepwalking], confusional arousals, sleep terrors). According to a cross-sectional Norwegian study of parasomnias, the estimated lifetime prevalence of sleep walking is 22.4%; sleep talking, 66.8%; confusional arousal, 18.5%; and sleep terror, 10.4%.52
Continue to: When evaluating a patient...
When evaluating a patient with parasomnias, it is important to review their drug and substance use as well as coexisting medical conditions. Drugs and substances that can affect sleep include prescription medications (second-generation antidepressants, stimulants, dopamine agonists), excessive caffeine, alcohol, certain foods (coffee, chocolate milk, black tea, caffeinated soft drinks), environmental exposures (smoking, pesticides), and recreational drugs (amphetamines).53-56 Certain medical conditions are correlated with specific parasomnias (eg, sleep paralysis and narcolepsy, REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease [PD], etc.).54 Diagnosis of parasomnias is mainly clinical but supporting evidence can be obtained through in-lab polysomnography.
Treatment. For parasomnias, treatment is primarily supportive and includes creating a safe sleeping environment to reduce the risk of self-harm. Recommendations include sleeping in a room on the ground floor, minimizing furniture in the bedroom, padding any bedside furniture, child-proofing doorknobs, and locking up weapons and other dangerous household items.54
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). This disorder is characterized by a loss of the typical REM sleep-associated atonia and the presence of motor activity during dreaming (dream-enacted behaviors). While the estimated incidence of RBD in the general adult population is approximately 0.5%, it increases to 7.7% among those age >60.57 RBD occurs most commonly in the setting of the alpha-synucleinopathies (PD, Lewy body dementia, multisystem atrophy), but can also be found in patients with cerebral ischemia, demyelinating disorders, or alcohol misuse, or can be medication-induced (primarily antidepressants and antipsychotics).58 In patients with PD, the presence of RBD is associated with a more impaired cognitive profile, suggestive of widespread neurodegeneration.59 Recent studies revealed that RBD may also be a prodromal state of neurodegenerative diseases such as PD, which should prompt close monitoring and long-term follow up.60 Similar to other parasomnias, the diagnosis of RBD is primarily clinical, but polysomnography plays an important role in demonstrating loss of REM-related atonia.54
Treatment. Clonazepam and melatonin have been shown to be effective in treating the symptoms of RBD.54
Depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances
Major depressive disorder (MDD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) affect sleep in patients of all ages, but are underreported in older adults. According to national epidemiologic surveys, the estimated prevalence of MDD and GAD among older adults is 13% and 11.4%, respectively.61,62 Rates as high as 42% and 39% have been reported in meta-regression analyses among patients with Alzheimer’s dementia.63
Continue to: Depression and anxiety
Depression and anxiety may have additive effects and manifest as poor sleep satisfaction, increased sleep latency, insomnia, and daytime sleepiness.64 However, they may also have independent effects. Studies showed that patients with depression alone reported overall poor sleep satisfaction, whereas patients with anxiety alone reported problems with sleep latency, daytime drowsiness, and waking up at night in addition to their overall poor sleep satisfaction.65-67 Both depression and anxiety are risk factors for developing cognitive decline, and may be an early sign/prodrome of neurodegenerative diseases (dementias).68 The bidirectional relationship between depression/anxiety and sleep is complex and needs further investigation.
Treatment. Pharmacologic treatments for patients with depression/anxiety and sleep disturbances include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and other serotonin receptor agonists.69-72 Nonpharmacologic treatments include CBT for both depression and anxiety, and problem-solving therapy for patients with mild cognitive impairment and depression.73,74 For severe depression and/or anxiety, electroconvulsive therapy is effective.75
Bottom Line
Sleep disorders in older adults are common but often underdiagnosed. Timely recognition of obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, insomnia, parasomnias, and other sleep disturbances can facilitate effective treatment and greatly improve older adults’ quality of life.
Related Resources
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition. https://aasm.org
- SleepFoundation.org. Sleep hygiene. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
Drug Brand Names
Acetazolamide • Diamox
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Doxepin • Silenor
Eszopiclone • Lunesta
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Pramipexole • Mirapex
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Ramelteon • Rozerem
Suvorexant • Belsomra
Temazepam • Restoril
Theophylline • Elixophyllin
Tiagabine • Gabitril
Trazadone • Desyrel
Triazolam • Halcion
Zaleplon • Sonata
Zolpidem • Ambien
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The state of aging and health in America. 2013. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/aging/pdf/state-aging-health-in-america-2013.pdf
2. Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Hirata K. Sleep disorders in the elderly: diagnosis and management. J Gen Fam Med. 2017;18(2):61-71.
3. Inouye SK, Studenski S, Tinetti ME, et al. Geriatric syndromes: clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55(5):780-791.
4. Patel D, Steinberg J, Patel P. Insomnia in the elderly: a review. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(6):1017-1024.
5. Neubauer DN. A review of ramelteon in the treatment of sleep disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008;4(1):69-79.
6. Mander BA, Winer JR, Walker MP. Sleep and human aging. Neuron. 2017;94(1):19-36.
7. Ohayon MM, Carskadon MA, Guilleminault C, et al. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep. 2004;27:1255-1273.
8. Li J, Vitiello MV, Gooneratne NS. Sleep in normal aging. Sleep Med Clin. 2018;13(1):1-11.
9. Floyd JA, Medler SM, Ager JW, et al. Age-related changes in initiation and maintenance of sleep: a meta-analysis. Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(2):106-117.
10. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Jenuwine ES, et al. Changes in REM-sleep percentage over the adult lifespan. Sleep. 2007;30(7):829-836.
11. Dorffner G, Vitr M, Anderer P. The effects of aging on sleep architecture in healthy subjects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;821:93-100.
12. Furihata R, Kaneita Y, Jike M, et al. Napping and associated factors: a Japanese nationwide general population survey. Sleep Med. 2016;20:72-79.
13. Foley DJ, Vitiello MV, Bliwise DL, et al. Frequent napping is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia in older adults: findings from the National Sleep Foundation ‘2003 Sleep in America’ Poll. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15(4):344-350.
14. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Marshall Medler S, et al. Nonlinear components of age-related change in sleep initiation. Nurs Res. 2000;49(5):290-294.
15. Miner B, Kryger MH. Sleep in the aging population. Sleep Med Clin. 2017;12(1):31-38.
16. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(9):1217-1239.
17. Ancoli-Israel S, Klauber MR, Butters N, et al. Dementia in institutionalized elderly: relation to sleep apnea. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(3):258-263.
18. Spira AP, Stone KL, Rebok GW, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing and functional decline in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(11):2040-2046.
19. Vijayan VK. Morbidities associated with obstructive sleep apnea. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2012;6(5):557-566.
20. Kerner NA, Roose SP. Obstructive sleep apnea is linked to depression and cognitive impairment: evidence and potential mechanisms. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;24(6):496-508.
21. Dalmases M, Solé-Padullés C, Torres M, et al. Effect of CPAP on cognition, brain function, and structure among elderly patients with OSA: a randomized pilot study. Chest. 2015;148(5):1214-1223.
22. Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network. University of Toronto. STOP-Bang Questionnaire. 2012. Accessed January 26, 2021. www.stopbang.ca
23. Freedman N. Doing it better for less: incorporating OSA management into alternative payment models. Chest. 2019;155(1):227-233.
24. Kapur VK, Auckley DH, Chowdhuri S, et al. Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017;13(3):479-504.
25. Semelka M, Wilson J, Floyd R. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94(5):355-360.
26. Javaheri S, Dempsey JA. Central sleep apnea. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):141-163.
27. Donovan LM, Kapur VK. Prevalence and characteristics of central compared to obstructive sleep apnea: analyses from the Sleep Heart Health Study cohort. Sleep. 2016;39(7):1353-1359.
28. Cao M, Cardell CY, Willes L, et al. A novel adaptive servoventilation (ASVAuto) for the treatment of central sleep apnea associated with chronic use of opioids. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(8):855-861.
29. Oldenburg O, Spießhöfer J, Fox H, et al. Performance of conventional and enhanced adaptive servoventilation (ASV) in heart failure patients with central sleep apnea who have adapted to conventional ASV. Sleep Breath. 2015;19(3):795-800.
30. Costanzo MR, Ponikowski P, Javaheri S, et al. Transvenous neurostimulation for central sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10048):974-982.
31. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:362.
32. Perlis ML, Smith LJ, Lyness JM, et al. Insomnia as a risk factor for onset of depression in the elderly. Behav Sleep Med. 2006;4(2):104-113.
33. Cole MG, Dendukuri N. Risk factors for depression among elderly community subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(6):1147-1156.
34. Pigeon WR, Hegel M, Unützer J, et al. Is insomnia a perpetuating factor for late-life depression in the IMPACT cohort? Sleep. 2008;31(4):481-488.
35. Hughes JM, Song Y, Fung CH, et al. Measuring sleep in vulnerable older adults: a comparison of subjective and objective sleep measures. Clin Gerontol. 2018;41(2):145-157.
36. Irish LA, Kline CE, Gunn HE, et al. The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: a review of empirical evidence. Sleep Med Rev. 2015;22:23-36.
37. Sleep Foundation. Sleep hygiene. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
38. Foley D, Ancoli-Israel S, Britz P, et al. Sleep disturbances and chronic disease in older adults: results of the 2003 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Survey. J Psychosom Res. 2004;56(5):497-502.
39. Eslami V, Zimmerman ME, Grewal T, et al. Pain grade and sleep disturbance in older adults: evaluation the role of pain, and stress for depressed and non-depressed individuals. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;31(5):450-457.
40. American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2015 updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(11):2227-2246.
41. United States Food & Drug Administration. FDA adds Boxed Warning for risk of serious injuries caused by sleepwalking with certain prescription insomnia medicines. 2019. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-adds-boxed-warning-risk-serious-injuries-caused-sleepwalking-certain-prescription-insomnia
42. Schroeck JL, Ford J, Conway EL, et al. Review of safety and efficacy of sleep medicines in older adults. Clin Ther. 2016;38(11):2340-2372.
43. Krystal AD, Lankford A, Durrence HH, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 3 and 6 mg in a 35-day sleep laboratory trial in adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1433-1442.
44. Roth T, Seiden D, Sainati S, et al. Effects of ramelteon on patient-reported sleep latency in older adults with chronic insomnia. Sleep Med. 2006;7(4):312-318.
45. Zammit G, Wang-Weigand S, Rosenthal M, et al. Effect of ramelteon on middle-of-the-night balance in older adults with chronic insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. 2009;5(1):34-40.
46. Mets MAJ, de Vries JM, de Senerpont Domis LM, et al. Next-day effects of ramelteon (8 mg), zopiclone (7.5 mg), and placebo on highway driving performance, memory functioning, psychomotor performance, and mood in healthy adult subjects. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1327-1334.
47. Rhyne DN, Anderson SL. Suvorexant in insomnia: efficacy, safety and place in therapy. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2015;6(5):189-195.
48. Norman JL, Anderson SL. Novel class of medications, orexin receptor antagonists, in the treatment of insomnia - critical appraisal of suvorexant. Nat Sci Sleep. 2016;8:239-247.
49. Owen RT. Suvorexant: efficacy and safety profile of a dual orexin receptor antagonist in treating insomnia. Drugs Today (Barc). 2016;52(1):29-40.
50. Shannon S, Lewis N, Lee H, et al. Cannabidiol in anxiety and sleep: a large case series. Perm J. 2019;23:18-041. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-041
51. Yunusa I, Alsumali A, Garba AE, et al. Assessment of reported comparative effectiveness and safety of atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a network meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190828.
52. Bjorvatn B, Gronli J, Pallesen S. Prevalence of different parasomnias in the general population. Sleep Med. 2010;11(10):1031-1034.
53. Postuma RB, Montplaisir JY, Pelletier A, et al. Environmental risk factors for REM sleep behavior disorder: a multicenter case-control study. Neurology. 2012;79(5):428-434.
54. Fleetham JA, Fleming JA. Parasomnias. CMAJ. 2014;186(8):E273-E280.
55. Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Caldas I, Carvalho F, et al. Bruxism after 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) abuse. Clin Toxicol (Phila.) 2010;48(8):863-864.
56. Irfan MH, Howell MJ. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: overview and current perspective. Curr Sleep Medicine Rep. 2016;2:64-73.
57. Mahlknecht P, Seppi K, Frauscher B, et al. Probable RBD and association with neurodegenerative disease markers: a population-based study. Mov Disord. 2015;30(10):1417-1421.
58. Oertel WH, Depboylu C, Krenzer M, et al. [REM sleep behavior disorder as a prodromal stage of α-synucleinopathies: symptoms, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and therapy]. Nervenarzt. 2014;85:19-25. German.
59. Jozwiak N, Postuma RB, Montplaisir J, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep. 2017;40(8):zsx101. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsx101
60. Claassen DO, Josephs KA, Ahlskog JE, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder preceding other aspects of synucleinopathies by up to half a century. Neurology 2010;75(6):494-499.
61. Reynolds K, Pietrzak RH, El-Gabalawy R, et al. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in U.S. older adults: findings from a nationally representative survey. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):74-81.
62. Lohman MC, Mezuk B, Dumenci L. Depression and frailty: concurrent risks for adverse health outcomes. Aging Ment Health. 2017;21(4):399-408.
63. Zhao QF, Tan L, Wang HF, et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;190:264-271.
64. Furihata R, Hall MH, Stone KL, et al. An aggregate measure of sleep health is associated with prevalent and incident clinically significant depression symptoms among community-dwelling older women. Sleep. 2017;40(3):zsw075. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw075
65. Spira AP, Stone K, Beaudreau SA, et al. Anxiety symptoms and objectively measured sleep quality in older women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17(2):136-143.
66. Press Y, Punchik B, Freud T. The association between subjectively impaired sleep and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a frail elderly population. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(7):755-765.
67. Gould CE, Spira AP, Liou-Johnson V, et al. Association of anxiety symptom clusters with sleep quality and daytime sleepiness. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2018;73(3):413-420.
68. Kassem AM, Ganguli M, Yaffe K, et al. Anxiety symptoms and risk of cognitive decline in older community-dwelling men. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(7):1137-1145.
69. Frank C. Pharmacologic treatment of depression in the elderly. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60(2):121-126.
70. Subramanyam AA, Kedare J, Singh OP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for geriatric anxiety disorders. Indian J Psychiatry. 2018;60(suppl 3):S371-S382.
71. Emsley R, Ahokas A, Suarez A, et al. Efficacy of tianeptine 25-50 mg in elderly patients with recurrent major depressive disorder: an 8-week placebo- and escitalopram-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(4):17m11741. doi: 10.4088/JCP.17m11741
72. Semel D, Murphy TK, Zlateva G, et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of pregabalin in older patients with neuropathic pain: results from a pooled analysis of 11 clinical studies. BMC Fam Pract. 2010;11:85.
73. Orgeta V, Qazi A, Spector A, et al. Psychological treatments for depression and anxiety in dementia and mild cognitive impairment: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(4):293-298.
74. Morimoto SS, Kanellopoulos D, Manning KJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of depression and cognitive impairment in late life. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1345(1):36-46.
75. Casey DA. Depression in older adults: a treatable medical condition. Prim Care. 2017;44(3):499-510.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The state of aging and health in America. 2013. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/aging/pdf/state-aging-health-in-america-2013.pdf
2. Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Hirata K. Sleep disorders in the elderly: diagnosis and management. J Gen Fam Med. 2017;18(2):61-71.
3. Inouye SK, Studenski S, Tinetti ME, et al. Geriatric syndromes: clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55(5):780-791.
4. Patel D, Steinberg J, Patel P. Insomnia in the elderly: a review. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018;14(6):1017-1024.
5. Neubauer DN. A review of ramelteon in the treatment of sleep disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008;4(1):69-79.
6. Mander BA, Winer JR, Walker MP. Sleep and human aging. Neuron. 2017;94(1):19-36.
7. Ohayon MM, Carskadon MA, Guilleminault C, et al. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep. 2004;27:1255-1273.
8. Li J, Vitiello MV, Gooneratne NS. Sleep in normal aging. Sleep Med Clin. 2018;13(1):1-11.
9. Floyd JA, Medler SM, Ager JW, et al. Age-related changes in initiation and maintenance of sleep: a meta-analysis. Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(2):106-117.
10. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Jenuwine ES, et al. Changes in REM-sleep percentage over the adult lifespan. Sleep. 2007;30(7):829-836.
11. Dorffner G, Vitr M, Anderer P. The effects of aging on sleep architecture in healthy subjects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;821:93-100.
12. Furihata R, Kaneita Y, Jike M, et al. Napping and associated factors: a Japanese nationwide general population survey. Sleep Med. 2016;20:72-79.
13. Foley DJ, Vitiello MV, Bliwise DL, et al. Frequent napping is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, pain, and nocturia in older adults: findings from the National Sleep Foundation ‘2003 Sleep in America’ Poll. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;15(4):344-350.
14. Floyd JA, Janisse JJ, Marshall Medler S, et al. Nonlinear components of age-related change in sleep initiation. Nurs Res. 2000;49(5):290-294.
15. Miner B, Kryger MH. Sleep in the aging population. Sleep Med Clin. 2017;12(1):31-38.
16. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(9):1217-1239.
17. Ancoli-Israel S, Klauber MR, Butters N, et al. Dementia in institutionalized elderly: relation to sleep apnea. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(3):258-263.
18. Spira AP, Stone KL, Rebok GW, et al. Sleep-disordered breathing and functional decline in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(11):2040-2046.
19. Vijayan VK. Morbidities associated with obstructive sleep apnea. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2012;6(5):557-566.
20. Kerner NA, Roose SP. Obstructive sleep apnea is linked to depression and cognitive impairment: evidence and potential mechanisms. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;24(6):496-508.
21. Dalmases M, Solé-Padullés C, Torres M, et al. Effect of CPAP on cognition, brain function, and structure among elderly patients with OSA: a randomized pilot study. Chest. 2015;148(5):1214-1223.
22. Toronto Western Hospital, University Health Network. University of Toronto. STOP-Bang Questionnaire. 2012. Accessed January 26, 2021. www.stopbang.ca
23. Freedman N. Doing it better for less: incorporating OSA management into alternative payment models. Chest. 2019;155(1):227-233.
24. Kapur VK, Auckley DH, Chowdhuri S, et al. Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017;13(3):479-504.
25. Semelka M, Wilson J, Floyd R. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94(5):355-360.
26. Javaheri S, Dempsey JA. Central sleep apnea. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):141-163.
27. Donovan LM, Kapur VK. Prevalence and characteristics of central compared to obstructive sleep apnea: analyses from the Sleep Heart Health Study cohort. Sleep. 2016;39(7):1353-1359.
28. Cao M, Cardell CY, Willes L, et al. A novel adaptive servoventilation (ASVAuto) for the treatment of central sleep apnea associated with chronic use of opioids. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(8):855-861.
29. Oldenburg O, Spießhöfer J, Fox H, et al. Performance of conventional and enhanced adaptive servoventilation (ASV) in heart failure patients with central sleep apnea who have adapted to conventional ASV. Sleep Breath. 2015;19(3):795-800.
30. Costanzo MR, Ponikowski P, Javaheri S, et al. Transvenous neurostimulation for central sleep apnoea: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10048):974-982.
31. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:362.
32. Perlis ML, Smith LJ, Lyness JM, et al. Insomnia as a risk factor for onset of depression in the elderly. Behav Sleep Med. 2006;4(2):104-113.
33. Cole MG, Dendukuri N. Risk factors for depression among elderly community subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(6):1147-1156.
34. Pigeon WR, Hegel M, Unützer J, et al. Is insomnia a perpetuating factor for late-life depression in the IMPACT cohort? Sleep. 2008;31(4):481-488.
35. Hughes JM, Song Y, Fung CH, et al. Measuring sleep in vulnerable older adults: a comparison of subjective and objective sleep measures. Clin Gerontol. 2018;41(2):145-157.
36. Irish LA, Kline CE, Gunn HE, et al. The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: a review of empirical evidence. Sleep Med Rev. 2015;22:23-36.
37. Sleep Foundation. Sleep hygiene. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/sleep-hygiene
38. Foley D, Ancoli-Israel S, Britz P, et al. Sleep disturbances and chronic disease in older adults: results of the 2003 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Survey. J Psychosom Res. 2004;56(5):497-502.
39. Eslami V, Zimmerman ME, Grewal T, et al. Pain grade and sleep disturbance in older adults: evaluation the role of pain, and stress for depressed and non-depressed individuals. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;31(5):450-457.
40. American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2015 updated Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63(11):2227-2246.
41. United States Food & Drug Administration. FDA adds Boxed Warning for risk of serious injuries caused by sleepwalking with certain prescription insomnia medicines. 2019. Accessed January 27, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-adds-boxed-warning-risk-serious-injuries-caused-sleepwalking-certain-prescription-insomnia
42. Schroeck JL, Ford J, Conway EL, et al. Review of safety and efficacy of sleep medicines in older adults. Clin Ther. 2016;38(11):2340-2372.
43. Krystal AD, Lankford A, Durrence HH, et al. Efficacy and safety of doxepin 3 and 6 mg in a 35-day sleep laboratory trial in adults with chronic primary insomnia. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1433-1442.
44. Roth T, Seiden D, Sainati S, et al. Effects of ramelteon on patient-reported sleep latency in older adults with chronic insomnia. Sleep Med. 2006;7(4):312-318.
45. Zammit G, Wang-Weigand S, Rosenthal M, et al. Effect of ramelteon on middle-of-the-night balance in older adults with chronic insomnia. J Clin Sleep Med. 2009;5(1):34-40.
46. Mets MAJ, de Vries JM, de Senerpont Domis LM, et al. Next-day effects of ramelteon (8 mg), zopiclone (7.5 mg), and placebo on highway driving performance, memory functioning, psychomotor performance, and mood in healthy adult subjects. Sleep. 2011;34(10):1327-1334.
47. Rhyne DN, Anderson SL. Suvorexant in insomnia: efficacy, safety and place in therapy. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2015;6(5):189-195.
48. Norman JL, Anderson SL. Novel class of medications, orexin receptor antagonists, in the treatment of insomnia - critical appraisal of suvorexant. Nat Sci Sleep. 2016;8:239-247.
49. Owen RT. Suvorexant: efficacy and safety profile of a dual orexin receptor antagonist in treating insomnia. Drugs Today (Barc). 2016;52(1):29-40.
50. Shannon S, Lewis N, Lee H, et al. Cannabidiol in anxiety and sleep: a large case series. Perm J. 2019;23:18-041. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-041
51. Yunusa I, Alsumali A, Garba AE, et al. Assessment of reported comparative effectiveness and safety of atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a network meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190828.
52. Bjorvatn B, Gronli J, Pallesen S. Prevalence of different parasomnias in the general population. Sleep Med. 2010;11(10):1031-1034.
53. Postuma RB, Montplaisir JY, Pelletier A, et al. Environmental risk factors for REM sleep behavior disorder: a multicenter case-control study. Neurology. 2012;79(5):428-434.
54. Fleetham JA, Fleming JA. Parasomnias. CMAJ. 2014;186(8):E273-E280.
55. Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Caldas I, Carvalho F, et al. Bruxism after 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) abuse. Clin Toxicol (Phila.) 2010;48(8):863-864.
56. Irfan MH, Howell MJ. Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: overview and current perspective. Curr Sleep Medicine Rep. 2016;2:64-73.
57. Mahlknecht P, Seppi K, Frauscher B, et al. Probable RBD and association with neurodegenerative disease markers: a population-based study. Mov Disord. 2015;30(10):1417-1421.
58. Oertel WH, Depboylu C, Krenzer M, et al. [REM sleep behavior disorder as a prodromal stage of α-synucleinopathies: symptoms, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and therapy]. Nervenarzt. 2014;85:19-25. German.
59. Jozwiak N, Postuma RB, Montplaisir J, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep. 2017;40(8):zsx101. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsx101
60. Claassen DO, Josephs KA, Ahlskog JE, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder preceding other aspects of synucleinopathies by up to half a century. Neurology 2010;75(6):494-499.
61. Reynolds K, Pietrzak RH, El-Gabalawy R, et al. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in U.S. older adults: findings from a nationally representative survey. World Psychiatry. 2015;14(1):74-81.
62. Lohman MC, Mezuk B, Dumenci L. Depression and frailty: concurrent risks for adverse health outcomes. Aging Ment Health. 2017;21(4):399-408.
63. Zhao QF, Tan L, Wang HF, et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;190:264-271.
64. Furihata R, Hall MH, Stone KL, et al. An aggregate measure of sleep health is associated with prevalent and incident clinically significant depression symptoms among community-dwelling older women. Sleep. 2017;40(3):zsw075. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw075
65. Spira AP, Stone K, Beaudreau SA, et al. Anxiety symptoms and objectively measured sleep quality in older women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17(2):136-143.
66. Press Y, Punchik B, Freud T. The association between subjectively impaired sleep and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a frail elderly population. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;30(7):755-765.
67. Gould CE, Spira AP, Liou-Johnson V, et al. Association of anxiety symptom clusters with sleep quality and daytime sleepiness. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2018;73(3):413-420.
68. Kassem AM, Ganguli M, Yaffe K, et al. Anxiety symptoms and risk of cognitive decline in older community-dwelling men. Int Psychogeriatr. 2017;29(7):1137-1145.
69. Frank C. Pharmacologic treatment of depression in the elderly. Can Fam Physician. 2014;60(2):121-126.
70. Subramanyam AA, Kedare J, Singh OP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for geriatric anxiety disorders. Indian J Psychiatry. 2018;60(suppl 3):S371-S382.
71. Emsley R, Ahokas A, Suarez A, et al. Efficacy of tianeptine 25-50 mg in elderly patients with recurrent major depressive disorder: an 8-week placebo- and escitalopram-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(4):17m11741. doi: 10.4088/JCP.17m11741
72. Semel D, Murphy TK, Zlateva G, et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of pregabalin in older patients with neuropathic pain: results from a pooled analysis of 11 clinical studies. BMC Fam Pract. 2010;11:85.
73. Orgeta V, Qazi A, Spector A, et al. Psychological treatments for depression and anxiety in dementia and mild cognitive impairment: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(4):293-298.
74. Morimoto SS, Kanellopoulos D, Manning KJ, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of depression and cognitive impairment in late life. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1345(1):36-46.
75. Casey DA. Depression in older adults: a treatable medical condition. Prim Care. 2017;44(3):499-510.
Study: Central sleep apnea is common in ticagrelor users post ACS
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
FROM SLEEP MEDICINE
Long-term CPAP use linked with more physical activity
in new research.
“The aim of this study was to determine whether long-term CPAP treatment affects self-reported physical activity among participants with moderate-severe OSA and comorbid CV disease,” wrote David Stevens, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and his colleagues. The findings were recently published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of the Sleep apnea cardiovascular endpoints (SAVE) trial that enrolled 2,687 adults aged 45-75 years old with OSA and confirmed CVD. In the study, participants were randomized to receive either CPAP plus usual care or usual care alone.
Physical activity levels were self-reported using the Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire (LTEQ) at baseline and at 6-, 24-, and 48-month follow-up intervals. The physical functioning subscale of the 36-item short form questionnaire (SF-36) was used to determine if activity levels were consistent with expert recommendations and to evaluate the effects on any self-perceived limitation of physical activity.
Moderate physical activity was higher among CPAP users
After a mean follow-up duration of 3.7 years, participants in the CPAP arm had approximately 20% higher levels of moderate physical activity, compared with the control arm (adjusted mean scores]: 8.7 points vs. 7.3 points; 95% confidence interval, 7.5-9.9 vs. 6.1-8.5; P = .003).
However, no significant difference was observed between treatment arms for mild physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 14.4 points vs. 14.2 points; 95% CI, 13.5-15.3 vs. 13.3-15.1; P = 0.599) or vigorous physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 3.4 points vs. 2.9 points; 95% CI 2.6-4.2 vs. 2.1-3.7; P = .125).
In addition, participants in the CPAP group reported less limitation in physical activity (adjusted between-group difference in SF-36 physical functioning subscale score = 1.66; 95% CI, 0.87-2.45; P < .001) and were more likely to report activity levels consistent with guideline recommendations.
“We were pleasantly surprised to find that people assigned to CPAP reported more physical activity than their counterparts who received usual care, despite being given no specific exercise instructions,” Kelly A. Loffler, PhD, a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
“While I don’t think this will result in any immediate changes to guidelines, it is a helpful reminder to clinicians who are treating such patients, that the symptomatic benefits people experience with CPAP present a window of opportunity to improve health more holistically,” Dr. Loffler explained.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the use of self-reported outcome measures. In future studies, they recommended that recent technological innovations, such as the availability of activity tracking devices, should be used to measure physical activity.
They also noted that patients with excessive sleepiness and severe hypoxemia were excluded from the SAVE trial; thus, the findings may not be generalizable to all patients.
Study reinforces CPAP’s health benefits
Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, explained that CPAP treatment is associated with well-documented health benefits among patients with CVD, as well as enhanced quality of life.
“These results provide further evidence that treating OSA can provide direct and indirect health benefits, suggesting that increased physical activity can be a vital pathway to improved cardiovascular health and enjoyment of life,” Dr. Wickwire, who is also director of the Insomnia Program at the University of Maryland Midtown Medical Center, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Steven M. Scharf, MD, a pulmonologist who is director of the Sleep Disorders Center (Adults) at the University of Maryland, also said the study findings were consistent with previous research involving patients treated for OSA.
“It is no surprise that treatment of OSA improves patient’s daily physical functioning,” explained Dr. Scharf, who is also a clinical professor, in an interview. “These results are expected, but very welcome, and I was glad to see them.”
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Respironics Sleep and Respiratory Research Foundation, and Philips Respironics. Some authors reported financial affiliations with medical device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Loffler, Dr. Wickwire, and Dr. Scharf reported no conflicts of interest related to this work.
in new research.
“The aim of this study was to determine whether long-term CPAP treatment affects self-reported physical activity among participants with moderate-severe OSA and comorbid CV disease,” wrote David Stevens, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and his colleagues. The findings were recently published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of the Sleep apnea cardiovascular endpoints (SAVE) trial that enrolled 2,687 adults aged 45-75 years old with OSA and confirmed CVD. In the study, participants were randomized to receive either CPAP plus usual care or usual care alone.
Physical activity levels were self-reported using the Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire (LTEQ) at baseline and at 6-, 24-, and 48-month follow-up intervals. The physical functioning subscale of the 36-item short form questionnaire (SF-36) was used to determine if activity levels were consistent with expert recommendations and to evaluate the effects on any self-perceived limitation of physical activity.
Moderate physical activity was higher among CPAP users
After a mean follow-up duration of 3.7 years, participants in the CPAP arm had approximately 20% higher levels of moderate physical activity, compared with the control arm (adjusted mean scores]: 8.7 points vs. 7.3 points; 95% confidence interval, 7.5-9.9 vs. 6.1-8.5; P = .003).
However, no significant difference was observed between treatment arms for mild physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 14.4 points vs. 14.2 points; 95% CI, 13.5-15.3 vs. 13.3-15.1; P = 0.599) or vigorous physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 3.4 points vs. 2.9 points; 95% CI 2.6-4.2 vs. 2.1-3.7; P = .125).
In addition, participants in the CPAP group reported less limitation in physical activity (adjusted between-group difference in SF-36 physical functioning subscale score = 1.66; 95% CI, 0.87-2.45; P < .001) and were more likely to report activity levels consistent with guideline recommendations.
“We were pleasantly surprised to find that people assigned to CPAP reported more physical activity than their counterparts who received usual care, despite being given no specific exercise instructions,” Kelly A. Loffler, PhD, a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
“While I don’t think this will result in any immediate changes to guidelines, it is a helpful reminder to clinicians who are treating such patients, that the symptomatic benefits people experience with CPAP present a window of opportunity to improve health more holistically,” Dr. Loffler explained.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the use of self-reported outcome measures. In future studies, they recommended that recent technological innovations, such as the availability of activity tracking devices, should be used to measure physical activity.
They also noted that patients with excessive sleepiness and severe hypoxemia were excluded from the SAVE trial; thus, the findings may not be generalizable to all patients.
Study reinforces CPAP’s health benefits
Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, explained that CPAP treatment is associated with well-documented health benefits among patients with CVD, as well as enhanced quality of life.
“These results provide further evidence that treating OSA can provide direct and indirect health benefits, suggesting that increased physical activity can be a vital pathway to improved cardiovascular health and enjoyment of life,” Dr. Wickwire, who is also director of the Insomnia Program at the University of Maryland Midtown Medical Center, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Steven M. Scharf, MD, a pulmonologist who is director of the Sleep Disorders Center (Adults) at the University of Maryland, also said the study findings were consistent with previous research involving patients treated for OSA.
“It is no surprise that treatment of OSA improves patient’s daily physical functioning,” explained Dr. Scharf, who is also a clinical professor, in an interview. “These results are expected, but very welcome, and I was glad to see them.”
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Respironics Sleep and Respiratory Research Foundation, and Philips Respironics. Some authors reported financial affiliations with medical device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Loffler, Dr. Wickwire, and Dr. Scharf reported no conflicts of interest related to this work.
in new research.
“The aim of this study was to determine whether long-term CPAP treatment affects self-reported physical activity among participants with moderate-severe OSA and comorbid CV disease,” wrote David Stevens, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and his colleagues. The findings were recently published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of the Sleep apnea cardiovascular endpoints (SAVE) trial that enrolled 2,687 adults aged 45-75 years old with OSA and confirmed CVD. In the study, participants were randomized to receive either CPAP plus usual care or usual care alone.
Physical activity levels were self-reported using the Leisure-Time Exercise Questionnaire (LTEQ) at baseline and at 6-, 24-, and 48-month follow-up intervals. The physical functioning subscale of the 36-item short form questionnaire (SF-36) was used to determine if activity levels were consistent with expert recommendations and to evaluate the effects on any self-perceived limitation of physical activity.
Moderate physical activity was higher among CPAP users
After a mean follow-up duration of 3.7 years, participants in the CPAP arm had approximately 20% higher levels of moderate physical activity, compared with the control arm (adjusted mean scores]: 8.7 points vs. 7.3 points; 95% confidence interval, 7.5-9.9 vs. 6.1-8.5; P = .003).
However, no significant difference was observed between treatment arms for mild physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 14.4 points vs. 14.2 points; 95% CI, 13.5-15.3 vs. 13.3-15.1; P = 0.599) or vigorous physical activity (adjusted mean scores, 3.4 points vs. 2.9 points; 95% CI 2.6-4.2 vs. 2.1-3.7; P = .125).
In addition, participants in the CPAP group reported less limitation in physical activity (adjusted between-group difference in SF-36 physical functioning subscale score = 1.66; 95% CI, 0.87-2.45; P < .001) and were more likely to report activity levels consistent with guideline recommendations.
“We were pleasantly surprised to find that people assigned to CPAP reported more physical activity than their counterparts who received usual care, despite being given no specific exercise instructions,” Kelly A. Loffler, PhD, a coauthor of the study, said in an interview.
“While I don’t think this will result in any immediate changes to guidelines, it is a helpful reminder to clinicians who are treating such patients, that the symptomatic benefits people experience with CPAP present a window of opportunity to improve health more holistically,” Dr. Loffler explained.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the use of self-reported outcome measures. In future studies, they recommended that recent technological innovations, such as the availability of activity tracking devices, should be used to measure physical activity.
They also noted that patients with excessive sleepiness and severe hypoxemia were excluded from the SAVE trial; thus, the findings may not be generalizable to all patients.
Study reinforces CPAP’s health benefits
Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, explained that CPAP treatment is associated with well-documented health benefits among patients with CVD, as well as enhanced quality of life.
“These results provide further evidence that treating OSA can provide direct and indirect health benefits, suggesting that increased physical activity can be a vital pathway to improved cardiovascular health and enjoyment of life,” Dr. Wickwire, who is also director of the Insomnia Program at the University of Maryland Midtown Medical Center, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Steven M. Scharf, MD, a pulmonologist who is director of the Sleep Disorders Center (Adults) at the University of Maryland, also said the study findings were consistent with previous research involving patients treated for OSA.
“It is no surprise that treatment of OSA improves patient’s daily physical functioning,” explained Dr. Scharf, who is also a clinical professor, in an interview. “These results are expected, but very welcome, and I was glad to see them.”
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Respironics Sleep and Respiratory Research Foundation, and Philips Respironics. Some authors reported financial affiliations with medical device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Loffler, Dr. Wickwire, and Dr. Scharf reported no conflicts of interest related to this work.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL SLEEP MEDICINE
Short sleep predicts incident dementia and all-cause mortality
More evidence has emerged linking sleep deficiency, dementia, and mortality.
“Sleep disturbance and insufficiency have been shown to be associated with both the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease and with all-cause mortality,” wrote Rebecca S. Robbins, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. However, research on this topic has yielded conflicting results, and “few studies have included a comprehensive set of sleep characteristics in a single examination of incident dementia and all-cause mortality.”
In a study published in Aging, the researchers identified 2,812 adults aged 65 years and older from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative longitudinal study of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older in the United States.
Participants completed surveys about sleep disturbance and duration in 2013 (1,575 individuals) and in 2014 (1,237 individuals), and the researchers examined the relationship between sleep disturbance and deficiency and incident dementia and all-cause mortality over the next 5 years. The average age of the study participants was 76.9 years, 60% were women, and 72% were White.
Overall, approximately 60% of the participants reported never or rarely having problems with alertness, approximately half said that they rarely or never napped, and more than half said they fell asleep in 15 minutes or less. Approximately 70% rated their sleep quality as good or very good, and more than 90% said they rarely or never snored.
The researchers examined the relationships between sleep characteristics and the development of incident dementia over 5 years. In a fully adjusted Cox multivariate analysis, individuals who slept 5 hours or less per night had approximately twice the risk for incident dementia as those who slept longer (hazard ratio, 2.04); risk of dementia also was higher among those who took 30 minutes or longer to fall asleep (HR, 1.45).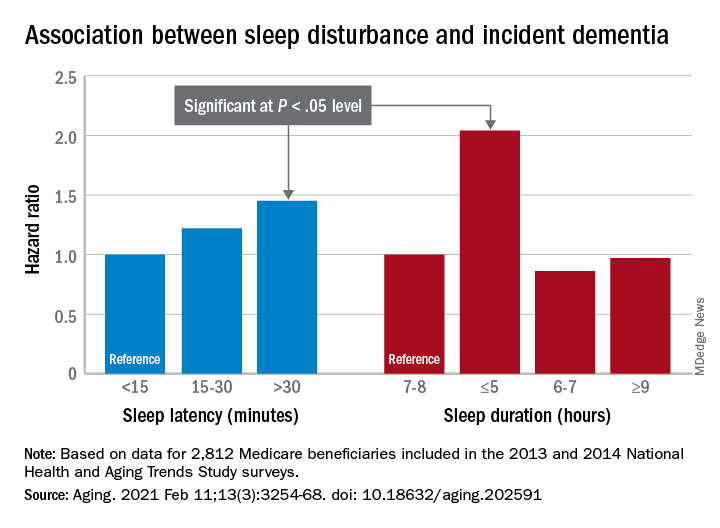
In addition, the risk of all-cause mortality was significantly higher among individuals who reported difficulty maintaining alertness some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.49 and HR, 1.65, respectively), routinely napping some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.38 and HR, 1.73, respectively), poor or very poor sleep quality (HR, 1.75), and sleeping 5 hours or less each night (HR, 2.38).
The study findings were limited by several factors including a population representing only one-quarter of the NHATS cohort, which prevented nationally representative estimates, the availability of only 2 years of sleep data, and small sample size for certain response categories, the researchers noted.
However, “our study offers a contribution to the literature on sleep among aging populations in its assessment of incident dementia and all-cause mortality and a range of sleep characteristics among older adults,” they said. In particular, “short sleep duration was a strong predictor of both incident dementia and all-cause mortality, suggesting this may be a sleep characteristic that is important – over and above the other predictors – of adverse outcomes among older adults,” and future areas for research include the development of novel behavioral interventions to improve sleep in this population.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute on Aging; and the Brigham Research Institute Fund to Sustain Research Excellence. Lead author Dr. Robbins disclosed fees from Denihan Hospitality, Rituals Cosmetics, Dagmejan, Asystem, and SleepCycle. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, and support from various philanthropic organizations.
More evidence has emerged linking sleep deficiency, dementia, and mortality.
“Sleep disturbance and insufficiency have been shown to be associated with both the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease and with all-cause mortality,” wrote Rebecca S. Robbins, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. However, research on this topic has yielded conflicting results, and “few studies have included a comprehensive set of sleep characteristics in a single examination of incident dementia and all-cause mortality.”
In a study published in Aging, the researchers identified 2,812 adults aged 65 years and older from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative longitudinal study of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older in the United States.
Participants completed surveys about sleep disturbance and duration in 2013 (1,575 individuals) and in 2014 (1,237 individuals), and the researchers examined the relationship between sleep disturbance and deficiency and incident dementia and all-cause mortality over the next 5 years. The average age of the study participants was 76.9 years, 60% were women, and 72% were White.
Overall, approximately 60% of the participants reported never or rarely having problems with alertness, approximately half said that they rarely or never napped, and more than half said they fell asleep in 15 minutes or less. Approximately 70% rated their sleep quality as good or very good, and more than 90% said they rarely or never snored.
The researchers examined the relationships between sleep characteristics and the development of incident dementia over 5 years. In a fully adjusted Cox multivariate analysis, individuals who slept 5 hours or less per night had approximately twice the risk for incident dementia as those who slept longer (hazard ratio, 2.04); risk of dementia also was higher among those who took 30 minutes or longer to fall asleep (HR, 1.45).
In addition, the risk of all-cause mortality was significantly higher among individuals who reported difficulty maintaining alertness some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.49 and HR, 1.65, respectively), routinely napping some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.38 and HR, 1.73, respectively), poor or very poor sleep quality (HR, 1.75), and sleeping 5 hours or less each night (HR, 2.38).
The study findings were limited by several factors including a population representing only one-quarter of the NHATS cohort, which prevented nationally representative estimates, the availability of only 2 years of sleep data, and small sample size for certain response categories, the researchers noted.
However, “our study offers a contribution to the literature on sleep among aging populations in its assessment of incident dementia and all-cause mortality and a range of sleep characteristics among older adults,” they said. In particular, “short sleep duration was a strong predictor of both incident dementia and all-cause mortality, suggesting this may be a sleep characteristic that is important – over and above the other predictors – of adverse outcomes among older adults,” and future areas for research include the development of novel behavioral interventions to improve sleep in this population.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute on Aging; and the Brigham Research Institute Fund to Sustain Research Excellence. Lead author Dr. Robbins disclosed fees from Denihan Hospitality, Rituals Cosmetics, Dagmejan, Asystem, and SleepCycle. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, and support from various philanthropic organizations.
More evidence has emerged linking sleep deficiency, dementia, and mortality.
“Sleep disturbance and insufficiency have been shown to be associated with both the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease and with all-cause mortality,” wrote Rebecca S. Robbins, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues. However, research on this topic has yielded conflicting results, and “few studies have included a comprehensive set of sleep characteristics in a single examination of incident dementia and all-cause mortality.”
In a study published in Aging, the researchers identified 2,812 adults aged 65 years and older from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative longitudinal study of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older in the United States.
Participants completed surveys about sleep disturbance and duration in 2013 (1,575 individuals) and in 2014 (1,237 individuals), and the researchers examined the relationship between sleep disturbance and deficiency and incident dementia and all-cause mortality over the next 5 years. The average age of the study participants was 76.9 years, 60% were women, and 72% were White.
Overall, approximately 60% of the participants reported never or rarely having problems with alertness, approximately half said that they rarely or never napped, and more than half said they fell asleep in 15 minutes or less. Approximately 70% rated their sleep quality as good or very good, and more than 90% said they rarely or never snored.
The researchers examined the relationships between sleep characteristics and the development of incident dementia over 5 years. In a fully adjusted Cox multivariate analysis, individuals who slept 5 hours or less per night had approximately twice the risk for incident dementia as those who slept longer (hazard ratio, 2.04); risk of dementia also was higher among those who took 30 minutes or longer to fall asleep (HR, 1.45).
In addition, the risk of all-cause mortality was significantly higher among individuals who reported difficulty maintaining alertness some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.49 and HR, 1.65, respectively), routinely napping some days or most days/every day (HR, 1.38 and HR, 1.73, respectively), poor or very poor sleep quality (HR, 1.75), and sleeping 5 hours or less each night (HR, 2.38).
The study findings were limited by several factors including a population representing only one-quarter of the NHATS cohort, which prevented nationally representative estimates, the availability of only 2 years of sleep data, and small sample size for certain response categories, the researchers noted.
However, “our study offers a contribution to the literature on sleep among aging populations in its assessment of incident dementia and all-cause mortality and a range of sleep characteristics among older adults,” they said. In particular, “short sleep duration was a strong predictor of both incident dementia and all-cause mortality, suggesting this may be a sleep characteristic that is important – over and above the other predictors – of adverse outcomes among older adults,” and future areas for research include the development of novel behavioral interventions to improve sleep in this population.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute on Aging; and the Brigham Research Institute Fund to Sustain Research Excellence. Lead author Dr. Robbins disclosed fees from Denihan Hospitality, Rituals Cosmetics, Dagmejan, Asystem, and SleepCycle. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, and support from various philanthropic organizations.
FROM AGING
FDA clears novel daytime device for obstructive sleep apnea
eXciteOSA (Signifier Medical Technologies) is a prescription-only, neuromuscular stimulation device designed to improve tongue muscle function, which, over time, can help prevent the tongue from collapsing backwards and obstructing the airway during sleep, the FDA said.
The eXciteOSA mouthpiece has four electrodes that deliver a series of electrical pulses with rest periods in between. Two electrodes are located above the tongue and two are located below the tongue.
The patient uses the device for 20 minutes once a day while awake for 6 weeks, and once a week thereafter. It is indicated for adults aged 18 and older with snoring and mild OSA.
OSA is marked by the recurring collapse of the upper airways during sleep, intermittently reducing or completely blocking airflow. Common symptoms include snoring, restless sleep and daytime sleepiness. Untreated OSA can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease and cognitive and behavioral disorders.
Continuous positive airway pressure therapy, administered through a face mask that is worn while asleep, is a first-line treatment for OSA.
The eXciteOSA device “offers a new option for the thousands of individuals who experience snoring or mild sleep apnea,” Malvina Eydelman, MD, director, FDA Office of Ophthalmic, Anesthesia, Respiratory, ENT, and Dental Devices, said in a news release.
The FDA reviewed data on the safety and effectiveness of the eXciteOSA device in 115 patients with snoring, including 48 patients with snoring and mild OSA. All patients used the device for 20 minutes once a day for 6 weeks, then stopped using it for 2 weeks before they were reassessed.
Overall, the percentage of time spent snoring at levels louder than 40 decibels was reduced by more than 20% in 87 out of the 115 patients.
In the subset of patients with snoring and mild OSA, the average apnea-hypopnea index score was reduced by 48%, from 10.21 to 5.27, in 41 of 48 patients. Mild OSA is defined as an AHI score greater than 5 but less than 15.
The most common adverse events were excessive salivation, tongue or tooth discomfort, tongue tingling, dental filling sensitivity, metallic taste, gagging, and tight jaw.
Before using the eXciteOSA device, patients should receive a comprehensive dental examination, the FDA said.
The device should not be used in patients with pacemakers or implanted pacing leads, or women who are pregnant. The device is also contraindicated in patients with temporary or permanent implants, dental braces, intraoral metal prosthesis/restorations, or ulcerations in or around the mouth.
The eXciteOSA device was approved under the de novo premarket review pathway for new low- to moderate-risk devices. More information on the device is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
eXciteOSA (Signifier Medical Technologies) is a prescription-only, neuromuscular stimulation device designed to improve tongue muscle function, which, over time, can help prevent the tongue from collapsing backwards and obstructing the airway during sleep, the FDA said.
The eXciteOSA mouthpiece has four electrodes that deliver a series of electrical pulses with rest periods in between. Two electrodes are located above the tongue and two are located below the tongue.
The patient uses the device for 20 minutes once a day while awake for 6 weeks, and once a week thereafter. It is indicated for adults aged 18 and older with snoring and mild OSA.
OSA is marked by the recurring collapse of the upper airways during sleep, intermittently reducing or completely blocking airflow. Common symptoms include snoring, restless sleep and daytime sleepiness. Untreated OSA can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease and cognitive and behavioral disorders.
Continuous positive airway pressure therapy, administered through a face mask that is worn while asleep, is a first-line treatment for OSA.
The eXciteOSA device “offers a new option for the thousands of individuals who experience snoring or mild sleep apnea,” Malvina Eydelman, MD, director, FDA Office of Ophthalmic, Anesthesia, Respiratory, ENT, and Dental Devices, said in a news release.
The FDA reviewed data on the safety and effectiveness of the eXciteOSA device in 115 patients with snoring, including 48 patients with snoring and mild OSA. All patients used the device for 20 minutes once a day for 6 weeks, then stopped using it for 2 weeks before they were reassessed.
Overall, the percentage of time spent snoring at levels louder than 40 decibels was reduced by more than 20% in 87 out of the 115 patients.
In the subset of patients with snoring and mild OSA, the average apnea-hypopnea index score was reduced by 48%, from 10.21 to 5.27, in 41 of 48 patients. Mild OSA is defined as an AHI score greater than 5 but less than 15.
The most common adverse events were excessive salivation, tongue or tooth discomfort, tongue tingling, dental filling sensitivity, metallic taste, gagging, and tight jaw.
Before using the eXciteOSA device, patients should receive a comprehensive dental examination, the FDA said.
The device should not be used in patients with pacemakers or implanted pacing leads, or women who are pregnant. The device is also contraindicated in patients with temporary or permanent implants, dental braces, intraoral metal prosthesis/restorations, or ulcerations in or around the mouth.
The eXciteOSA device was approved under the de novo premarket review pathway for new low- to moderate-risk devices. More information on the device is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
eXciteOSA (Signifier Medical Technologies) is a prescription-only, neuromuscular stimulation device designed to improve tongue muscle function, which, over time, can help prevent the tongue from collapsing backwards and obstructing the airway during sleep, the FDA said.
The eXciteOSA mouthpiece has four electrodes that deliver a series of electrical pulses with rest periods in between. Two electrodes are located above the tongue and two are located below the tongue.
The patient uses the device for 20 minutes once a day while awake for 6 weeks, and once a week thereafter. It is indicated for adults aged 18 and older with snoring and mild OSA.
OSA is marked by the recurring collapse of the upper airways during sleep, intermittently reducing or completely blocking airflow. Common symptoms include snoring, restless sleep and daytime sleepiness. Untreated OSA can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease and cognitive and behavioral disorders.
Continuous positive airway pressure therapy, administered through a face mask that is worn while asleep, is a first-line treatment for OSA.
The eXciteOSA device “offers a new option for the thousands of individuals who experience snoring or mild sleep apnea,” Malvina Eydelman, MD, director, FDA Office of Ophthalmic, Anesthesia, Respiratory, ENT, and Dental Devices, said in a news release.
The FDA reviewed data on the safety and effectiveness of the eXciteOSA device in 115 patients with snoring, including 48 patients with snoring and mild OSA. All patients used the device for 20 minutes once a day for 6 weeks, then stopped using it for 2 weeks before they were reassessed.
Overall, the percentage of time spent snoring at levels louder than 40 decibels was reduced by more than 20% in 87 out of the 115 patients.
In the subset of patients with snoring and mild OSA, the average apnea-hypopnea index score was reduced by 48%, from 10.21 to 5.27, in 41 of 48 patients. Mild OSA is defined as an AHI score greater than 5 but less than 15.
The most common adverse events were excessive salivation, tongue or tooth discomfort, tongue tingling, dental filling sensitivity, metallic taste, gagging, and tight jaw.
Before using the eXciteOSA device, patients should receive a comprehensive dental examination, the FDA said.
The device should not be used in patients with pacemakers or implanted pacing leads, or women who are pregnant. The device is also contraindicated in patients with temporary or permanent implants, dental braces, intraoral metal prosthesis/restorations, or ulcerations in or around the mouth.
The eXciteOSA device was approved under the de novo premarket review pathway for new low- to moderate-risk devices. More information on the device is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women increasingly turn to CBD, with or without doc’s blessing
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 42-year-old Danielle Simone Brand started having hormonal migraines, she first turned to cannabidiol (CBD) oil, eventually adding an occasional pull on a prefilled tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) vape for nighttime use. She was careful to avoid THC during work hours. A parenting and cannabis writer, Ms. Brand had more than a cursory background in cannabinoid medicine and had spent time at her local California dispensary discussing various cannabinoid components that might help alleviate her pain.
A self-professed “do-it-yourselfer,” Ms. Brand continues to use cannabinoids for her monthly headaches, forgoing any other pain medication. “There are times for conventional medicine in partnership with your doctor, but when it comes to health and wellness, women should be empowered to make decisions and self-experiment,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Brand is not alone. Significant numbers of women are replacing or supplementing prescription medications with cannabinoids, often without consulting their primary care physician, ob.gyn., or other specialist. At times, women have tried to have these conversations, only to be met with silence or worse.
Take Linda Fuller, a 58-year-old yoga instructor from Long Island who says that she uses CBD and THC for chronic sacroiliac pain after a car accident and to alleviate stress-triggered eczema flares. “I’ve had doctors turn their backs on me; I’ve had nurse practitioners walk out on me in the middle of a sentence,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Fuller said her conversion to cannabinoid medicine is relatively new; she never used cannabis recreationally before her accident but now considers it a gift. She doesn’t keep aspirin in the house and refused pain medication immediately after she injured her back.
Diana Krach, a 34-year-old writer from Maryland, says she’s encountered roadblocks about her decision to use cannabinoids for endometriosis and for pain from Crohn’s disease. When she tried to discuss her CBD use with a gastroenterologist, he interrupted her: “Whatever pot you’re smoking isn’t going to work, you’re going on biologics.”
Ms. Krach had not been smoking anything but had turned to a CBD tincture for symptom relief after prescription pain medications failed to help.
Ms. Brand, Ms. Fuller, and Ms. Krach are the tip of the iceberg when it comes to women seeking symptom relief outside the medicine cabinet. A recent survey in the Journal of Women’s Health of almost 1,000 women show that 90% (most between the ages of 35 and 44) had used cannabis and would consider using it to treat gynecologic pain. Roughly 80% said they would consider using it for procedure-related pain or other conditions. Additionally, women have reported using cannabinoids for PTSD, sleep disturbances or insomnia, anxiety, and migraine headaches.
Observational survey data have likewise shown that 80% of women with advanced or recurrent gynecologic malignancies who were prescribed cannabis reported that it was equivalent or superior to other medications for relieving pain, neuropathy, nausea, insomnia, decreased appetite, and anxiety.
In another survey, almost half (45%) of women with gynecologic malignancies who used nonprescribed cannabis for the same symptoms reported that they had reduced their use of prescription narcotics after initiating use of cannabis.
The gray zone
There has been a surge in self-reported cannabis use among pregnant women in particular. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health findings for the periods 2002-2003 and 2016-2017 highlight increases in adjusted prevalence rates from 3.4% to 7% in past-month use among pregnant women overall and from 5.7% to 12.1% during the first trimester alone.
“The more that you talk to pregnant women, the more that you realize that a lot are using cannabinoids for something that is basically medicinal, for sleep, for anxiety, or for nausea,” Katrina Mark, MD, an ob.gyn. and associate professor of medicine at the University of Maryland, College Park, said in an interview. “I’m not saying it’s fine to use drugs in pregnancy, but it is a grayer conversation than a lot of colleagues want to believe. Telling women to quit seems foolish since the alternative is to be anxious, don’t sleep, don’t eat, or use a medication that also has risks to it.”
One observational study shows that pregnant women themselves are conflicted. Although the majority believe that cannabis is “natural” and “safe,” compared with prescription drugs, they aren’t entirely in the dark about potential risks. They often express frustration with practitioners’ responses when these topics are broached during office visits. An observational survey among women and practitioners published in 2020 highlights that only half of doctors openly discouraged perinatal cannabis use and that others opted out of the discussion entirely.
This is the experience of many of the women that this news organization spoke with. Ms. Krach pointed out that “there’s a big deficit in listening; the doctor is supposed to be working for our behalf, especially when it comes to reproductive health.”
Dr. Mark believed that a lot of the conversation has been clouded by the illegality of the substance but that cannabinoids deserve as much of a fair chance for discussion and consideration as other medicines, which also carry risks in pregnancy. “There’s literally no evidence that it will work in pregnancy [for these symptoms], but there’s no evidence that it doesn’t, either,” she said in an interview. “When I have this conversation with colleagues who do not share my views, I try to encourage them to look at the actual risks versus the benefits versus the alternatives.”
The ‘entourage effect’
Data supporting cannabinoids have been mostly laboratory based, case based, or observational. However, several well-designed (albeit small) trials have demonstrated efficacy for chronic pain conditions, including neuropathic and headache pain, as well as in Crohn’s disease. Most investigators have concluded that dosage is important and that there is a synergistic interaction between compounds (known as the “entourage effect”) that relates to cannabinoid efficacy or lack thereof, as well as possible adverse effects.
In addition to legality issues, the entourage effect is one of the most important factors related to the medical use of cannabinoids. “There are literally thousands of cultivars of cannabis, each with their own phytocannabinoid and terpenic profiles that may produce distinct therapeutic effects, [so] it is misguided to speak of cannabis in monolithic terms. It is like making broad claims about soup,” wrote coauthor Samoon Ahmad, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook.
Additionally, the role that reproductive hormones play is not entirely understood. Reproductive-aged women appear to be more susceptible to a “telescoping” (gender-related progression to dependence) effect in comparison with men. Ziva Cooper, PhD, director of the Cannabis Research Initiative at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. She explained that research has shown that factors such as the degree of exposure, frequency of use, and menses confound this susceptibility.
It’s the data
Frustration over cannabinoid therapeutics abound, especially when it comes to data, legal issues, and lack of training. “The feedback that I hear from providers is that there isn’t enough information; we just don’t know enough about it,” Dr. Mark said, “but there is information that we do have, and ignoring it is not beneficial.”
Dr. Cooper concurred. Although she readily acknowledges that data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials are mostly lacking, she says, “There are signals in the literature providing evidence for the utility of cannabis and cannabinoids for pain and some other effects.”
Other practitioners said in an interview that some patients admit to using cannabinoids but that they lack the ample information to guide these patients. By and large, many women equate “natural” with “safe,” and some will experiment on their own to see what works.
Those experiments are not without risk, which is why “it’s just as important for physicians to talk to their patients about cannabis use as it is for patients to be forthcoming about that use,” said Dr. Cooper. “It could have implications on their overall health as well as interactions with other drugs that they’re using.”
That balance from a clinical perspective on cannabis is crucial, wrote coauthor Kenneth Hill, MD, in Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook. “Without it,” he wrote, “the window of opportunity for a patient to accept treatment that she needs may not be open very long.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Afternoon napping associated with better cognition in elderly, study shows
according to a new study in General Psychiatry.
The findings add to those seen in other observational studies showing afternoon napping promotes cognitive function, said the authors of the paper, published in General Psychiatry.
“The prevalence of afternoon napping has been increasing in older adults much more than in younger individuals,” wrote Han Cai, MS, of the department of geriatrics at The Fourth People’s Hospital of Wuhu, Anhui, China, and coauthors. “The elderly individuals who took afternoon naps showed significantly higher cognitive performance compared with those who did not nap.”
The researchers enrolled 2,214 people in the study – all Han Chinese and aged 60 or older. Afternoon napping was considered any period of inactivity of at least 5 minutes but less than 2 hours after lunch and outside of the person’s main sleep schedule. Those who reported ever napping – 1,534 subjects – were included in the napping group, and the others – 680 – in the nonnapping group. Patients with major physical conditions were excluded.
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and the Neuropsychological Test Battery (NTB) were used to measure cognitive function, and 739 patients agreed to blood tests for lipid values.
The average total MMSE score was higher for the napping group at 25.3 points out of 30, than for the nonnapping group, at 24.56 (P = .003). Those in the napping group also had significantly higher scores in the orientation portion of the MoCA test, at 5.55 out of 6 points, compared with 5.41 for the nonnapping group (P = .006).
Those in the napping group scored significantly higher on the digit span and language fluency parts of the Neuropsychological Test Battery (P = .009 and .020, respectively).
Dementia was assessed with face-to-face visits with clinicians, but diagnoses of dementia were not different between the groups.
Triglycerides were found to be higher – though still in the normal range – in the napping group compared with the nonnapping group, 1.80 mmol/L to 1.75 mmol/L, the researchers found (P = .001). No differences were seen for HDL or LDL cholesterol levels, or in hypertension or diabetes, the researchers reported.
The authors noted that inflammation is likely an important feature in the relationship between napping and cognitive function. Inflammatory cytokines have been found to play a role in sleep disorders, and strong inflammatory responses can lead to adverse events, including cognitive impairment.
“Sleep is known to be a regulator of the immune response that counters these inflammatory mediators, whereas napping, in particular, is thought to be an evolved response to inflammation,” they said.
The average age of patients in the napping group was 72.8 years, slightly older than those in the nonnapping group at 71.3 years, and this was a significant difference (P = .016).
The researchers acknowledged that the study “could not show direct causality of napping, whether beneficial or harmful,” and that “a lack of detailed information regarding napping duration ... also limited the description of napping status.”
Junxin Li, PhD, RN, assistant professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing, Baltimore, who has studied napping and cognition, said that previous research generally supports a U-shaped relationship between napping and mental acuity, with shorter or medium-length naps benefiting cognition and no naps or naps that are too long being detrimental.
“This study looked at no nap versus naps of less than 2 hours and may not be able to capture this potential U-shaped association,” she said.
For clinicians, the duration, timing, frequency, and purpose of naps are important factors in making recommendations to patients, she said.
“For example, timing – napping in the early evening close to older adult’s bedtime may delay their bedtime and interfere with their nighttime sleep quality. Taking naps after lunchtime is hypothesized to provide the most therapeutic values to the health and usually recommended,” she said. Regular napping is better than “randomly dozing off,” Dr. Li added.
There are also cultural considerations – in east Asia, napping tends to be considered part of a healthy lifestyle, while in western countries it is not – and this could impact napping behaviors and how these behaviors affect cognition, she said.
Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at the Northwestern University, Chicago, said the results are consistent with early cross-sectional studies that showed that regular, scheduled naps in the afternoon were associated with positive cognitive performance and lower cardiometabolic disease risk.
Dr. Zee noted that it’s important to recognize that the positive data are associated with naps that are planned, while older adults napping because of excess sleepiness are at a higher risk for cognitive impairment and other health issues.
The study authors, Dr. Li, and Dr. Zee reported no relevant financial disclosures.
according to a new study in General Psychiatry.
The findings add to those seen in other observational studies showing afternoon napping promotes cognitive function, said the authors of the paper, published in General Psychiatry.
“The prevalence of afternoon napping has been increasing in older adults much more than in younger individuals,” wrote Han Cai, MS, of the department of geriatrics at The Fourth People’s Hospital of Wuhu, Anhui, China, and coauthors. “The elderly individuals who took afternoon naps showed significantly higher cognitive performance compared with those who did not nap.”
The researchers enrolled 2,214 people in the study – all Han Chinese and aged 60 or older. Afternoon napping was considered any period of inactivity of at least 5 minutes but less than 2 hours after lunch and outside of the person’s main sleep schedule. Those who reported ever napping – 1,534 subjects – were included in the napping group, and the others – 680 – in the nonnapping group. Patients with major physical conditions were excluded.
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and the Neuropsychological Test Battery (NTB) were used to measure cognitive function, and 739 patients agreed to blood tests for lipid values.
The average total MMSE score was higher for the napping group at 25.3 points out of 30, than for the nonnapping group, at 24.56 (P = .003). Those in the napping group also had significantly higher scores in the orientation portion of the MoCA test, at 5.55 out of 6 points, compared with 5.41 for the nonnapping group (P = .006).
Those in the napping group scored significantly higher on the digit span and language fluency parts of the Neuropsychological Test Battery (P = .009 and .020, respectively).
Dementia was assessed with face-to-face visits with clinicians, but diagnoses of dementia were not different between the groups.
Triglycerides were found to be higher – though still in the normal range – in the napping group compared with the nonnapping group, 1.80 mmol/L to 1.75 mmol/L, the researchers found (P = .001). No differences were seen for HDL or LDL cholesterol levels, or in hypertension or diabetes, the researchers reported.
The authors noted that inflammation is likely an important feature in the relationship between napping and cognitive function. Inflammatory cytokines have been found to play a role in sleep disorders, and strong inflammatory responses can lead to adverse events, including cognitive impairment.
“Sleep is known to be a regulator of the immune response that counters these inflammatory mediators, whereas napping, in particular, is thought to be an evolved response to inflammation,” they said.
The average age of patients in the napping group was 72.8 years, slightly older than those in the nonnapping group at 71.3 years, and this was a significant difference (P = .016).
The researchers acknowledged that the study “could not show direct causality of napping, whether beneficial or harmful,” and that “a lack of detailed information regarding napping duration ... also limited the description of napping status.”
Junxin Li, PhD, RN, assistant professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing, Baltimore, who has studied napping and cognition, said that previous research generally supports a U-shaped relationship between napping and mental acuity, with shorter or medium-length naps benefiting cognition and no naps or naps that are too long being detrimental.
“This study looked at no nap versus naps of less than 2 hours and may not be able to capture this potential U-shaped association,” she said.
For clinicians, the duration, timing, frequency, and purpose of naps are important factors in making recommendations to patients, she said.
“For example, timing – napping in the early evening close to older adult’s bedtime may delay their bedtime and interfere with their nighttime sleep quality. Taking naps after lunchtime is hypothesized to provide the most therapeutic values to the health and usually recommended,” she said. Regular napping is better than “randomly dozing off,” Dr. Li added.
There are also cultural considerations – in east Asia, napping tends to be considered part of a healthy lifestyle, while in western countries it is not – and this could impact napping behaviors and how these behaviors affect cognition, she said.
Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at the Northwestern University, Chicago, said the results are consistent with early cross-sectional studies that showed that regular, scheduled naps in the afternoon were associated with positive cognitive performance and lower cardiometabolic disease risk.
Dr. Zee noted that it’s important to recognize that the positive data are associated with naps that are planned, while older adults napping because of excess sleepiness are at a higher risk for cognitive impairment and other health issues.
The study authors, Dr. Li, and Dr. Zee reported no relevant financial disclosures.
according to a new study in General Psychiatry.
The findings add to those seen in other observational studies showing afternoon napping promotes cognitive function, said the authors of the paper, published in General Psychiatry.
“The prevalence of afternoon napping has been increasing in older adults much more than in younger individuals,” wrote Han Cai, MS, of the department of geriatrics at The Fourth People’s Hospital of Wuhu, Anhui, China, and coauthors. “The elderly individuals who took afternoon naps showed significantly higher cognitive performance compared with those who did not nap.”
The researchers enrolled 2,214 people in the study – all Han Chinese and aged 60 or older. Afternoon napping was considered any period of inactivity of at least 5 minutes but less than 2 hours after lunch and outside of the person’s main sleep schedule. Those who reported ever napping – 1,534 subjects – were included in the napping group, and the others – 680 – in the nonnapping group. Patients with major physical conditions were excluded.
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and the Neuropsychological Test Battery (NTB) were used to measure cognitive function, and 739 patients agreed to blood tests for lipid values.
The average total MMSE score was higher for the napping group at 25.3 points out of 30, than for the nonnapping group, at 24.56 (P = .003). Those in the napping group also had significantly higher scores in the orientation portion of the MoCA test, at 5.55 out of 6 points, compared with 5.41 for the nonnapping group (P = .006).
Those in the napping group scored significantly higher on the digit span and language fluency parts of the Neuropsychological Test Battery (P = .009 and .020, respectively).
Dementia was assessed with face-to-face visits with clinicians, but diagnoses of dementia were not different between the groups.
Triglycerides were found to be higher – though still in the normal range – in the napping group compared with the nonnapping group, 1.80 mmol/L to 1.75 mmol/L, the researchers found (P = .001). No differences were seen for HDL or LDL cholesterol levels, or in hypertension or diabetes, the researchers reported.
The authors noted that inflammation is likely an important feature in the relationship between napping and cognitive function. Inflammatory cytokines have been found to play a role in sleep disorders, and strong inflammatory responses can lead to adverse events, including cognitive impairment.
“Sleep is known to be a regulator of the immune response that counters these inflammatory mediators, whereas napping, in particular, is thought to be an evolved response to inflammation,” they said.
The average age of patients in the napping group was 72.8 years, slightly older than those in the nonnapping group at 71.3 years, and this was a significant difference (P = .016).
The researchers acknowledged that the study “could not show direct causality of napping, whether beneficial or harmful,” and that “a lack of detailed information regarding napping duration ... also limited the description of napping status.”
Junxin Li, PhD, RN, assistant professor at Johns Hopkins School of Nursing, Baltimore, who has studied napping and cognition, said that previous research generally supports a U-shaped relationship between napping and mental acuity, with shorter or medium-length naps benefiting cognition and no naps or naps that are too long being detrimental.
“This study looked at no nap versus naps of less than 2 hours and may not be able to capture this potential U-shaped association,” she said.
For clinicians, the duration, timing, frequency, and purpose of naps are important factors in making recommendations to patients, she said.
“For example, timing – napping in the early evening close to older adult’s bedtime may delay their bedtime and interfere with their nighttime sleep quality. Taking naps after lunchtime is hypothesized to provide the most therapeutic values to the health and usually recommended,” she said. Regular napping is better than “randomly dozing off,” Dr. Li added.
There are also cultural considerations – in east Asia, napping tends to be considered part of a healthy lifestyle, while in western countries it is not – and this could impact napping behaviors and how these behaviors affect cognition, she said.
Phyllis C. Zee, MD, PhD, director of the Center for Circadian and Sleep Medicine at the Northwestern University, Chicago, said the results are consistent with early cross-sectional studies that showed that regular, scheduled naps in the afternoon were associated with positive cognitive performance and lower cardiometabolic disease risk.
Dr. Zee noted that it’s important to recognize that the positive data are associated with naps that are planned, while older adults napping because of excess sleepiness are at a higher risk for cognitive impairment and other health issues.
The study authors, Dr. Li, and Dr. Zee reported no relevant financial disclosures.




















