User login
Infective endocarditis with stroke after TAVR has ‘dismal’ prognosis
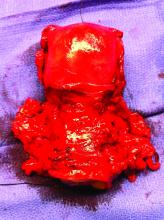
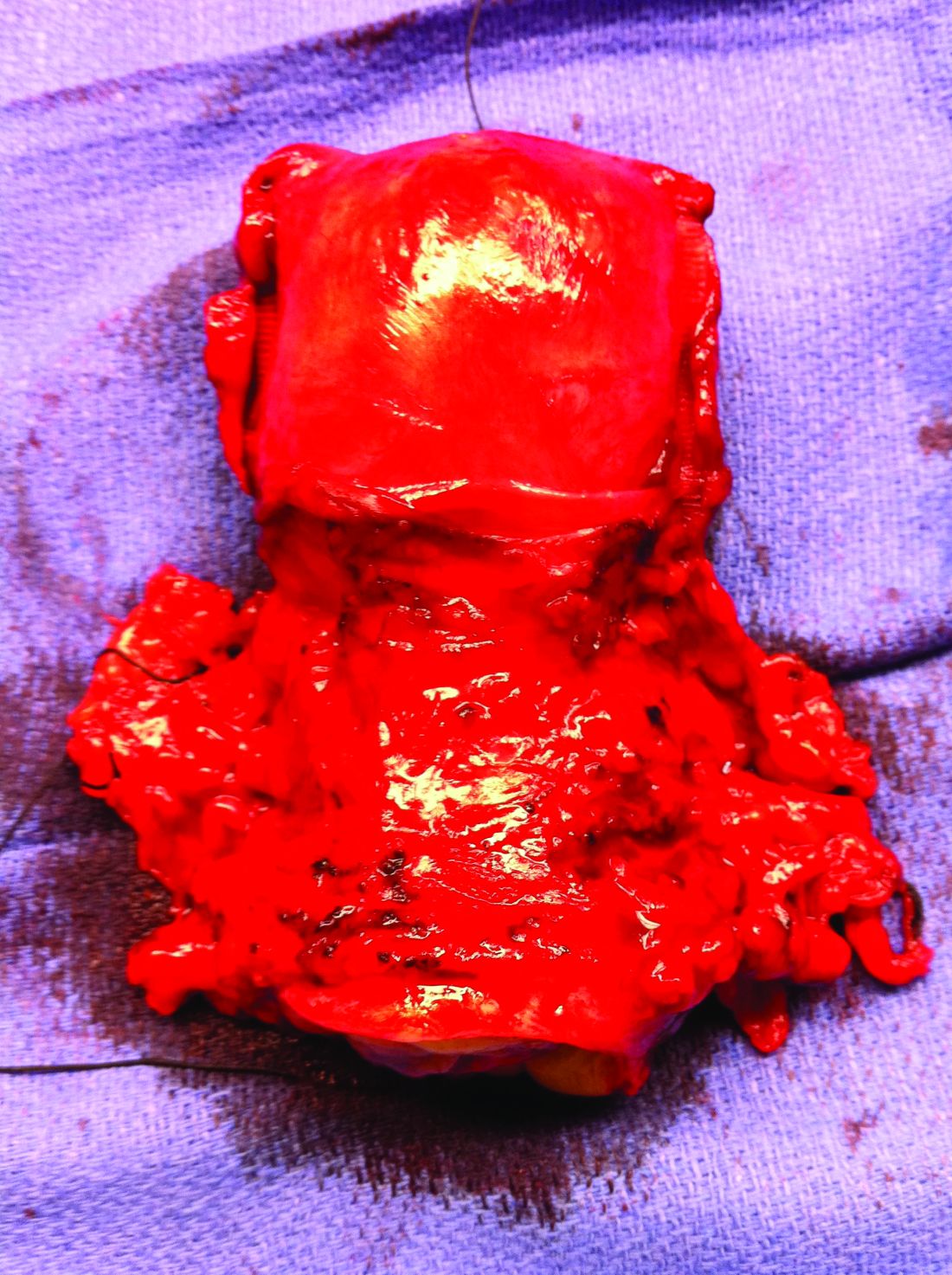
Patients who suffer a stroke during hospitalization for infective endocarditis (IE) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) have a dismal prognosis, with more than half dying during the index hospitalization and two-thirds within the first year, a new study shows.
The study – the first to evaluate stroke as an IE-related complication following TAVR in a large multicenter cohort – is published in the May 11 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, led by David del Val, MD, Quebec Heart & Lung Institute, Quebec City, explain that IE after TAVR is a rare but serious complication associated with a high mortality rate. Neurologic events, especially stroke, remain one of the most common and potentially disabling IE-related complications, but until now, no study has attempted to evaluate the predictors of stroke and outcomes in patients with IE following TAVR.
For the current study, the authors analyzed data from the Infectious Endocarditis after TAVR International Registry, including 569 patients who developed definite IE following TAVR from 59 centers in 11 countries.
Patients who experienced a stroke during IE admission were compared with patients who did not have a stroke.
Results showed that 57 patients (10%) had a stroke during IE hospitalization, with no differences in the causative microorganism between groups. Stroke patients had higher rates of acute renal failure, systemic embolization, and persistent bacteremia.
Factors associated with a higher risk for stroke during the index IE hospitalization included stroke before IE, moderate or higher residual aortic regurgitation after TAVR, balloon-expandable valves, IE within 30 days after TAVR, and vegetation size greater than 8 mm.
The stroke rate was 3.1% in patients with none of these risk factors; 6.1% with one risk factor; 13.1% with two risk factors; 28.9% with three risk factors, and 60% with four risk factors.
“The presence of such factors (particularly in combination) may be considered for determining an earlier and more aggressive (medical or surgical) treatment in these patients,” the researchers say.
IE patients with stroke had higher rates of in-hospital mortality (54.4% vs. 28.7%) and overall mortality at 1 year (66.3% vs. 45.6%).
Surgery rates were low (25%) even in the presence of stroke and failed to improve outcomes in this population.
Noting that consensus guidelines for managing patients with IE recommend surgery along with antibiotic treatment for patients developing systemic embolism, particularly stroke, the researchers say their findings suggest that such surgery recommendations may not be extrapolated to TAVR-IE patients, and specific guidelines are warranted for this particular population.
Furthermore, the possibility of early surgery in those patients with factors increasing the risk for stroke should be evaluated in future studies.
The authors note that TAVR has revolutionized the treatment of aortic stenosis and is currently moving toward less complex and younger patients with lower surgical risk. Despite the relatively low incidence of IE after TAVR, the number of procedures is expected to grow exponentially, increasing the number of patients at risk of developing this life-threatening complication. Therefore, detailed knowledge of this disease and its complications is essential to improve outcomes.
They point out that the 10% rate of stroke found in this study is substantially lower, compared with the largest surgical prosthetic-valve infective endocarditis registries, but they suggest that the unique clinical profile of TAVR patients may lead to an underdiagnosis of stroke, with a high proportion of elderly patients who more frequently present with nonspecific symptoms.
They conclude that “IE post-TAVR is associated with a poor prognosis with high in-hospital and late mortality rates. Our study reveals that patients with IE after TAVR complicated by stroke showed an even worse prognosis.”
“The progressive implementation of advanced imaging modalities for early IE diagnosis, especially nuclear imaging, may translate into a better prognosis in coming years. Close attention should be paid to early recognition of stroke-associated factors to improve clinical outcomes,” they add.
In an accompanying editorial, Vuyisile Nkomo, MD, Daniel DeSimone, MD, and William Miranda, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., say the current study “highlights the devastating consequences of IE after TAVR and the even worse consequences when IE was associated with stroke.”
This points to the critical importance of efforts to prevent IE with appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis and addressing potential sources of infection (for example, dental screening) before invasive cardiac procedures.
“Patient education is critical in regard to recognizing early signs and symptoms of IE. In particular, patients must be informed to obtain blood cultures with any episode of fever, as identification of bacteremia is critical in the diagnosis of IE,” the editorialists comment.
Endocarditis should also be suspected in afebrile patients with increasing transcatheter heart valve gradients or new or worsening regurgitation, they state.
Multimodality imaging is important for the early diagnosis of IE to facilitate prompt antibiotic treatment and potentially decrease the risk for IE complications, especially systemic embolization, they add.
“Despite the unequivocal advances in the safety and periprocedural complications of TAVR, IE with and without stroke in this TAVR population remains a dreadful complication,” they conclude.
Dr. Del Val was supported by a research grant from the Fundación Alfonso Martin Escudero. The editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who suffer a stroke during hospitalization for infective endocarditis (IE) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) have a dismal prognosis, with more than half dying during the index hospitalization and two-thirds within the first year, a new study shows.
The study – the first to evaluate stroke as an IE-related complication following TAVR in a large multicenter cohort – is published in the May 11 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, led by David del Val, MD, Quebec Heart & Lung Institute, Quebec City, explain that IE after TAVR is a rare but serious complication associated with a high mortality rate. Neurologic events, especially stroke, remain one of the most common and potentially disabling IE-related complications, but until now, no study has attempted to evaluate the predictors of stroke and outcomes in patients with IE following TAVR.
For the current study, the authors analyzed data from the Infectious Endocarditis after TAVR International Registry, including 569 patients who developed definite IE following TAVR from 59 centers in 11 countries.
Patients who experienced a stroke during IE admission were compared with patients who did not have a stroke.
Results showed that 57 patients (10%) had a stroke during IE hospitalization, with no differences in the causative microorganism between groups. Stroke patients had higher rates of acute renal failure, systemic embolization, and persistent bacteremia.
Factors associated with a higher risk for stroke during the index IE hospitalization included stroke before IE, moderate or higher residual aortic regurgitation after TAVR, balloon-expandable valves, IE within 30 days after TAVR, and vegetation size greater than 8 mm.
The stroke rate was 3.1% in patients with none of these risk factors; 6.1% with one risk factor; 13.1% with two risk factors; 28.9% with three risk factors, and 60% with four risk factors.
“The presence of such factors (particularly in combination) may be considered for determining an earlier and more aggressive (medical or surgical) treatment in these patients,” the researchers say.
IE patients with stroke had higher rates of in-hospital mortality (54.4% vs. 28.7%) and overall mortality at 1 year (66.3% vs. 45.6%).
Surgery rates were low (25%) even in the presence of stroke and failed to improve outcomes in this population.
Noting that consensus guidelines for managing patients with IE recommend surgery along with antibiotic treatment for patients developing systemic embolism, particularly stroke, the researchers say their findings suggest that such surgery recommendations may not be extrapolated to TAVR-IE patients, and specific guidelines are warranted for this particular population.
Furthermore, the possibility of early surgery in those patients with factors increasing the risk for stroke should be evaluated in future studies.
The authors note that TAVR has revolutionized the treatment of aortic stenosis and is currently moving toward less complex and younger patients with lower surgical risk. Despite the relatively low incidence of IE after TAVR, the number of procedures is expected to grow exponentially, increasing the number of patients at risk of developing this life-threatening complication. Therefore, detailed knowledge of this disease and its complications is essential to improve outcomes.
They point out that the 10% rate of stroke found in this study is substantially lower, compared with the largest surgical prosthetic-valve infective endocarditis registries, but they suggest that the unique clinical profile of TAVR patients may lead to an underdiagnosis of stroke, with a high proportion of elderly patients who more frequently present with nonspecific symptoms.
They conclude that “IE post-TAVR is associated with a poor prognosis with high in-hospital and late mortality rates. Our study reveals that patients with IE after TAVR complicated by stroke showed an even worse prognosis.”
“The progressive implementation of advanced imaging modalities for early IE diagnosis, especially nuclear imaging, may translate into a better prognosis in coming years. Close attention should be paid to early recognition of stroke-associated factors to improve clinical outcomes,” they add.
In an accompanying editorial, Vuyisile Nkomo, MD, Daniel DeSimone, MD, and William Miranda, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., say the current study “highlights the devastating consequences of IE after TAVR and the even worse consequences when IE was associated with stroke.”
This points to the critical importance of efforts to prevent IE with appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis and addressing potential sources of infection (for example, dental screening) before invasive cardiac procedures.
“Patient education is critical in regard to recognizing early signs and symptoms of IE. In particular, patients must be informed to obtain blood cultures with any episode of fever, as identification of bacteremia is critical in the diagnosis of IE,” the editorialists comment.
Endocarditis should also be suspected in afebrile patients with increasing transcatheter heart valve gradients or new or worsening regurgitation, they state.
Multimodality imaging is important for the early diagnosis of IE to facilitate prompt antibiotic treatment and potentially decrease the risk for IE complications, especially systemic embolization, they add.
“Despite the unequivocal advances in the safety and periprocedural complications of TAVR, IE with and without stroke in this TAVR population remains a dreadful complication,” they conclude.
Dr. Del Val was supported by a research grant from the Fundación Alfonso Martin Escudero. The editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who suffer a stroke during hospitalization for infective endocarditis (IE) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) have a dismal prognosis, with more than half dying during the index hospitalization and two-thirds within the first year, a new study shows.
The study – the first to evaluate stroke as an IE-related complication following TAVR in a large multicenter cohort – is published in the May 11 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors, led by David del Val, MD, Quebec Heart & Lung Institute, Quebec City, explain that IE after TAVR is a rare but serious complication associated with a high mortality rate. Neurologic events, especially stroke, remain one of the most common and potentially disabling IE-related complications, but until now, no study has attempted to evaluate the predictors of stroke and outcomes in patients with IE following TAVR.
For the current study, the authors analyzed data from the Infectious Endocarditis after TAVR International Registry, including 569 patients who developed definite IE following TAVR from 59 centers in 11 countries.
Patients who experienced a stroke during IE admission were compared with patients who did not have a stroke.
Results showed that 57 patients (10%) had a stroke during IE hospitalization, with no differences in the causative microorganism between groups. Stroke patients had higher rates of acute renal failure, systemic embolization, and persistent bacteremia.
Factors associated with a higher risk for stroke during the index IE hospitalization included stroke before IE, moderate or higher residual aortic regurgitation after TAVR, balloon-expandable valves, IE within 30 days after TAVR, and vegetation size greater than 8 mm.
The stroke rate was 3.1% in patients with none of these risk factors; 6.1% with one risk factor; 13.1% with two risk factors; 28.9% with three risk factors, and 60% with four risk factors.
“The presence of such factors (particularly in combination) may be considered for determining an earlier and more aggressive (medical or surgical) treatment in these patients,” the researchers say.
IE patients with stroke had higher rates of in-hospital mortality (54.4% vs. 28.7%) and overall mortality at 1 year (66.3% vs. 45.6%).
Surgery rates were low (25%) even in the presence of stroke and failed to improve outcomes in this population.
Noting that consensus guidelines for managing patients with IE recommend surgery along with antibiotic treatment for patients developing systemic embolism, particularly stroke, the researchers say their findings suggest that such surgery recommendations may not be extrapolated to TAVR-IE patients, and specific guidelines are warranted for this particular population.
Furthermore, the possibility of early surgery in those patients with factors increasing the risk for stroke should be evaluated in future studies.
The authors note that TAVR has revolutionized the treatment of aortic stenosis and is currently moving toward less complex and younger patients with lower surgical risk. Despite the relatively low incidence of IE after TAVR, the number of procedures is expected to grow exponentially, increasing the number of patients at risk of developing this life-threatening complication. Therefore, detailed knowledge of this disease and its complications is essential to improve outcomes.
They point out that the 10% rate of stroke found in this study is substantially lower, compared with the largest surgical prosthetic-valve infective endocarditis registries, but they suggest that the unique clinical profile of TAVR patients may lead to an underdiagnosis of stroke, with a high proportion of elderly patients who more frequently present with nonspecific symptoms.
They conclude that “IE post-TAVR is associated with a poor prognosis with high in-hospital and late mortality rates. Our study reveals that patients with IE after TAVR complicated by stroke showed an even worse prognosis.”
“The progressive implementation of advanced imaging modalities for early IE diagnosis, especially nuclear imaging, may translate into a better prognosis in coming years. Close attention should be paid to early recognition of stroke-associated factors to improve clinical outcomes,” they add.
In an accompanying editorial, Vuyisile Nkomo, MD, Daniel DeSimone, MD, and William Miranda, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., say the current study “highlights the devastating consequences of IE after TAVR and the even worse consequences when IE was associated with stroke.”
This points to the critical importance of efforts to prevent IE with appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis and addressing potential sources of infection (for example, dental screening) before invasive cardiac procedures.
“Patient education is critical in regard to recognizing early signs and symptoms of IE. In particular, patients must be informed to obtain blood cultures with any episode of fever, as identification of bacteremia is critical in the diagnosis of IE,” the editorialists comment.
Endocarditis should also be suspected in afebrile patients with increasing transcatheter heart valve gradients or new or worsening regurgitation, they state.
Multimodality imaging is important for the early diagnosis of IE to facilitate prompt antibiotic treatment and potentially decrease the risk for IE complications, especially systemic embolization, they add.
“Despite the unequivocal advances in the safety and periprocedural complications of TAVR, IE with and without stroke in this TAVR population remains a dreadful complication,” they conclude.
Dr. Del Val was supported by a research grant from the Fundación Alfonso Martin Escudero. The editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA and power morcellation, gel for vaginal odor, and an intrauterine electrosurgery system
FDA guidance for power morcellation
“The FDA has granted marketing authorization for one containment system and continues to encourage innovation in this area” said the report. Olympus’ Pneumoliner is the only FDA cleared containment device to provide a laparoscopic option for appropriately identified patients undergoing myomectomy and hysterectomy. The containment system is sold with Olympus’ PK Morcellator, but the company says that it has made the Pneumoliner available to physicians choosing an alternate to the PK Morcellator, provided that there is device compatibility. The Pneumoliner “reduces the spread of benign tissue into the abdominal cavity, in which pathologies, like fibroids, may regrow when tissue or cells are inadvertently left behind,” according to Olympus.
Vaginal odor elimination gel
The gel is sold in 7 single-day applications, with a single tube used per day at bedtime to eliminate unwanted odor. To maintain freshness and comfort, a single tube of Relactagel can be used for 2 to 3 days after a woman’s menstrual cycle, says Kora Healthcare. The company warns that mild irritation can occur with product use during fungal infections or when small tears are present in the vaginal tissue and that use should be discontinued if irritation occurs. In addition, if trying to become pregnant Relatagel should not be used, advises Kora Healthcare, although the gel is not a contraceptive.
Intrauterine electrosurgery system
FDA guidance for power morcellation
“The FDA has granted marketing authorization for one containment system and continues to encourage innovation in this area” said the report. Olympus’ Pneumoliner is the only FDA cleared containment device to provide a laparoscopic option for appropriately identified patients undergoing myomectomy and hysterectomy. The containment system is sold with Olympus’ PK Morcellator, but the company says that it has made the Pneumoliner available to physicians choosing an alternate to the PK Morcellator, provided that there is device compatibility. The Pneumoliner “reduces the spread of benign tissue into the abdominal cavity, in which pathologies, like fibroids, may regrow when tissue or cells are inadvertently left behind,” according to Olympus.
Vaginal odor elimination gel
The gel is sold in 7 single-day applications, with a single tube used per day at bedtime to eliminate unwanted odor. To maintain freshness and comfort, a single tube of Relactagel can be used for 2 to 3 days after a woman’s menstrual cycle, says Kora Healthcare. The company warns that mild irritation can occur with product use during fungal infections or when small tears are present in the vaginal tissue and that use should be discontinued if irritation occurs. In addition, if trying to become pregnant Relatagel should not be used, advises Kora Healthcare, although the gel is not a contraceptive.
Intrauterine electrosurgery system
FDA guidance for power morcellation
“The FDA has granted marketing authorization for one containment system and continues to encourage innovation in this area” said the report. Olympus’ Pneumoliner is the only FDA cleared containment device to provide a laparoscopic option for appropriately identified patients undergoing myomectomy and hysterectomy. The containment system is sold with Olympus’ PK Morcellator, but the company says that it has made the Pneumoliner available to physicians choosing an alternate to the PK Morcellator, provided that there is device compatibility. The Pneumoliner “reduces the spread of benign tissue into the abdominal cavity, in which pathologies, like fibroids, may regrow when tissue or cells are inadvertently left behind,” according to Olympus.
Vaginal odor elimination gel
The gel is sold in 7 single-day applications, with a single tube used per day at bedtime to eliminate unwanted odor. To maintain freshness and comfort, a single tube of Relactagel can be used for 2 to 3 days after a woman’s menstrual cycle, says Kora Healthcare. The company warns that mild irritation can occur with product use during fungal infections or when small tears are present in the vaginal tissue and that use should be discontinued if irritation occurs. In addition, if trying to become pregnant Relatagel should not be used, advises Kora Healthcare, although the gel is not a contraceptive.
Intrauterine electrosurgery system
Expert emphasizes importance of screening for OSA prior to surgery
If you don’t have a standardized process for obstructive sleep apnea screening of all patients heading into the operating room at your hospital you should, because perioperative pulmonary complications can occur, according to Efren C. Manjarrez MD, SFHM, FACP.
If OSA is not documented in the patient’s chart, you may find yourself making a bedside assessment. “I usually don’t ask the patients this because they can’t necessarily answer the questions,” Dr. Manjarrez, associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Miami, said at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. “So, I ask their partner: ‘Does your partner snore loudly? Are they sleepy during the daytime, or are they gasping or choking in the middle of the night?’”
The following factors have a relatively high specificity for OSA: a STOP-Bang score of 5 or greater, a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus male gender, and a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus a body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2. Clinicians can also check the Mallampati score on their patients by having them tilt their heads back and stick out their tongues.
“If the uvula is not touching the tongue, that’s a Mallampati score of 1; that’s a pretty wide-open airway,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “However, when you do not have any form of an airway and the palate is touching the tongue, that is a Mallampati score of 4, which indicates OSA.”
Other objective data suggestive of OSA include high blood pressure, a BMI over 35 kg/m2, a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, and male gender. In a study of patients who presented for surgery who did not have a diagnosis of sleep apnea, a high STOP-Bang score indicated a high probability of moderate to severe sleep apnea (Br J. Anaesth 2012;108[5]:768-75).
“If the STOP-Bang score is 0-2, your workup stops,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “If your STOP-Bang score is 5 or above, there’s a high likelihood they have moderate or severe sleep apnea. Patients who have a STOP-Bang of 3-4, calculate their STOP score. If the STOP score is 2 or more and they’re male, obese, and have a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, there’s a pretty good chance they’ve got OSA.”
Screening for OSA prior to surgery matters, because the potential pulmonary complications are fairly high, “anywhere from postoperative respiratory failure to COPD exacerbation and hypoxia to pneumonia,” he continued. “These patients very commonly desaturate and are difficult for the anesthesiologists to intubate. Fortunately, we have not found significant cardiac complications in the medical literature, but we do know that patients with OSA commonly get postoperative atrial fibrillation. There are also combined complications like desaturation and AFib and difficult intubations. Patients with sleep apnea do have a higher resource utilization perioperatively. Fortunately, at this point in time the data does not show that patients with OSA going in for surgery have an increased mortality.”
To optimize the care of these patients prior to surgery, Dr. Manjarrez recommends that hospitalists document that a patient either has known OSA or suspected OSA. “If possible, obtain their sleep study results and recommended PAP settings,” he said. “Ask patients to bring their PAP device to the hospital or to assure the hospital has appropriate surrogate devices available. You also want to advise the patient and the perioperative care team of the increased risk of complications in patients at high risk for OSA and optimize other conditions that may impair cardiorespiratory function.”
Perioperative risk reduction strategies include planning for difficult intubation and mask ventilation, using regional anesthesia and analgesia, using sedatives with caution, minimizing the use of opioids and anticipating variable opioid responses. “When I have a patient with suspected sleep apnea and no red flags I write down ‘OSA precautions,’ in the chart, which means elevate the head of the bed, perform continuous pulse oximetry, and cautiously supply supplemental oxygen as needed,” he said.
Postoperatively, he continued, minimize sedative agents and opioids, use regional and nonopioid analgesics when possible, provide supplemental oxygen until the patient is able to maintain baseline SaO2 on room air in a monitored setting, maintain the patient in nonsupine position when feasible, and continuously monitor pulse oximetry.
Consider delay of elective surgery and referral to a sleep medicine specialist in cases of uncontrolled systemic conditions or impaired gas exchange, including hypoventilation syndromes (a clue being a serum HC03 of 28 or higher), severe pulmonary hypertension (a clue being right ventricular systolic blood pressure or pulmonary systolic pressure of 70 mm Hg or above, or right ventricular dilatation/dysfunction), and hypoxemia not explained by cardiac disease.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of six studies that included 904 patients with sleep apnea found that there was no significant difference in the postoperative adverse events between CPAP and no-CPAP treatment (Anesth Analg 2015;120:1013-23). However, there was a significant reduction in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index postoperatively among those who used CPAP (37 vs. 12 events per hour; P less than .001), as well as a significant reduction in hospital length of stay 4 vs. 4.4 days; P = .05).
Dr. Manjarrez reported having no financial disclosures.
If you don’t have a standardized process for obstructive sleep apnea screening of all patients heading into the operating room at your hospital you should, because perioperative pulmonary complications can occur, according to Efren C. Manjarrez MD, SFHM, FACP.
If OSA is not documented in the patient’s chart, you may find yourself making a bedside assessment. “I usually don’t ask the patients this because they can’t necessarily answer the questions,” Dr. Manjarrez, associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Miami, said at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. “So, I ask their partner: ‘Does your partner snore loudly? Are they sleepy during the daytime, or are they gasping or choking in the middle of the night?’”
The following factors have a relatively high specificity for OSA: a STOP-Bang score of 5 or greater, a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus male gender, and a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus a body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2. Clinicians can also check the Mallampati score on their patients by having them tilt their heads back and stick out their tongues.
“If the uvula is not touching the tongue, that’s a Mallampati score of 1; that’s a pretty wide-open airway,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “However, when you do not have any form of an airway and the palate is touching the tongue, that is a Mallampati score of 4, which indicates OSA.”
Other objective data suggestive of OSA include high blood pressure, a BMI over 35 kg/m2, a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, and male gender. In a study of patients who presented for surgery who did not have a diagnosis of sleep apnea, a high STOP-Bang score indicated a high probability of moderate to severe sleep apnea (Br J. Anaesth 2012;108[5]:768-75).
“If the STOP-Bang score is 0-2, your workup stops,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “If your STOP-Bang score is 5 or above, there’s a high likelihood they have moderate or severe sleep apnea. Patients who have a STOP-Bang of 3-4, calculate their STOP score. If the STOP score is 2 or more and they’re male, obese, and have a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, there’s a pretty good chance they’ve got OSA.”
Screening for OSA prior to surgery matters, because the potential pulmonary complications are fairly high, “anywhere from postoperative respiratory failure to COPD exacerbation and hypoxia to pneumonia,” he continued. “These patients very commonly desaturate and are difficult for the anesthesiologists to intubate. Fortunately, we have not found significant cardiac complications in the medical literature, but we do know that patients with OSA commonly get postoperative atrial fibrillation. There are also combined complications like desaturation and AFib and difficult intubations. Patients with sleep apnea do have a higher resource utilization perioperatively. Fortunately, at this point in time the data does not show that patients with OSA going in for surgery have an increased mortality.”
To optimize the care of these patients prior to surgery, Dr. Manjarrez recommends that hospitalists document that a patient either has known OSA or suspected OSA. “If possible, obtain their sleep study results and recommended PAP settings,” he said. “Ask patients to bring their PAP device to the hospital or to assure the hospital has appropriate surrogate devices available. You also want to advise the patient and the perioperative care team of the increased risk of complications in patients at high risk for OSA and optimize other conditions that may impair cardiorespiratory function.”
Perioperative risk reduction strategies include planning for difficult intubation and mask ventilation, using regional anesthesia and analgesia, using sedatives with caution, minimizing the use of opioids and anticipating variable opioid responses. “When I have a patient with suspected sleep apnea and no red flags I write down ‘OSA precautions,’ in the chart, which means elevate the head of the bed, perform continuous pulse oximetry, and cautiously supply supplemental oxygen as needed,” he said.
Postoperatively, he continued, minimize sedative agents and opioids, use regional and nonopioid analgesics when possible, provide supplemental oxygen until the patient is able to maintain baseline SaO2 on room air in a monitored setting, maintain the patient in nonsupine position when feasible, and continuously monitor pulse oximetry.
Consider delay of elective surgery and referral to a sleep medicine specialist in cases of uncontrolled systemic conditions or impaired gas exchange, including hypoventilation syndromes (a clue being a serum HC03 of 28 or higher), severe pulmonary hypertension (a clue being right ventricular systolic blood pressure or pulmonary systolic pressure of 70 mm Hg or above, or right ventricular dilatation/dysfunction), and hypoxemia not explained by cardiac disease.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of six studies that included 904 patients with sleep apnea found that there was no significant difference in the postoperative adverse events between CPAP and no-CPAP treatment (Anesth Analg 2015;120:1013-23). However, there was a significant reduction in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index postoperatively among those who used CPAP (37 vs. 12 events per hour; P less than .001), as well as a significant reduction in hospital length of stay 4 vs. 4.4 days; P = .05).
Dr. Manjarrez reported having no financial disclosures.
If you don’t have a standardized process for obstructive sleep apnea screening of all patients heading into the operating room at your hospital you should, because perioperative pulmonary complications can occur, according to Efren C. Manjarrez MD, SFHM, FACP.
If OSA is not documented in the patient’s chart, you may find yourself making a bedside assessment. “I usually don’t ask the patients this because they can’t necessarily answer the questions,” Dr. Manjarrez, associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Miami, said at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. “So, I ask their partner: ‘Does your partner snore loudly? Are they sleepy during the daytime, or are they gasping or choking in the middle of the night?’”
The following factors have a relatively high specificity for OSA: a STOP-Bang score of 5 or greater, a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus male gender, and a STOP-Bang score of 2 or greater plus a body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2. Clinicians can also check the Mallampati score on their patients by having them tilt their heads back and stick out their tongues.
“If the uvula is not touching the tongue, that’s a Mallampati score of 1; that’s a pretty wide-open airway,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “However, when you do not have any form of an airway and the palate is touching the tongue, that is a Mallampati score of 4, which indicates OSA.”
Other objective data suggestive of OSA include high blood pressure, a BMI over 35 kg/m2, a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, and male gender. In a study of patients who presented for surgery who did not have a diagnosis of sleep apnea, a high STOP-Bang score indicated a high probability of moderate to severe sleep apnea (Br J. Anaesth 2012;108[5]:768-75).
“If the STOP-Bang score is 0-2, your workup stops,” Dr. Manjarrez said. “If your STOP-Bang score is 5 or above, there’s a high likelihood they have moderate or severe sleep apnea. Patients who have a STOP-Bang of 3-4, calculate their STOP score. If the STOP score is 2 or more and they’re male, obese, and have a neck circumference of greater than 40 cm, there’s a pretty good chance they’ve got OSA.”
Screening for OSA prior to surgery matters, because the potential pulmonary complications are fairly high, “anywhere from postoperative respiratory failure to COPD exacerbation and hypoxia to pneumonia,” he continued. “These patients very commonly desaturate and are difficult for the anesthesiologists to intubate. Fortunately, we have not found significant cardiac complications in the medical literature, but we do know that patients with OSA commonly get postoperative atrial fibrillation. There are also combined complications like desaturation and AFib and difficult intubations. Patients with sleep apnea do have a higher resource utilization perioperatively. Fortunately, at this point in time the data does not show that patients with OSA going in for surgery have an increased mortality.”
To optimize the care of these patients prior to surgery, Dr. Manjarrez recommends that hospitalists document that a patient either has known OSA or suspected OSA. “If possible, obtain their sleep study results and recommended PAP settings,” he said. “Ask patients to bring their PAP device to the hospital or to assure the hospital has appropriate surrogate devices available. You also want to advise the patient and the perioperative care team of the increased risk of complications in patients at high risk for OSA and optimize other conditions that may impair cardiorespiratory function.”
Perioperative risk reduction strategies include planning for difficult intubation and mask ventilation, using regional anesthesia and analgesia, using sedatives with caution, minimizing the use of opioids and anticipating variable opioid responses. “When I have a patient with suspected sleep apnea and no red flags I write down ‘OSA precautions,’ in the chart, which means elevate the head of the bed, perform continuous pulse oximetry, and cautiously supply supplemental oxygen as needed,” he said.
Postoperatively, he continued, minimize sedative agents and opioids, use regional and nonopioid analgesics when possible, provide supplemental oxygen until the patient is able to maintain baseline SaO2 on room air in a monitored setting, maintain the patient in nonsupine position when feasible, and continuously monitor pulse oximetry.
Consider delay of elective surgery and referral to a sleep medicine specialist in cases of uncontrolled systemic conditions or impaired gas exchange, including hypoventilation syndromes (a clue being a serum HC03 of 28 or higher), severe pulmonary hypertension (a clue being right ventricular systolic blood pressure or pulmonary systolic pressure of 70 mm Hg or above, or right ventricular dilatation/dysfunction), and hypoxemia not explained by cardiac disease.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of six studies that included 904 patients with sleep apnea found that there was no significant difference in the postoperative adverse events between CPAP and no-CPAP treatment (Anesth Analg 2015;120:1013-23). However, there was a significant reduction in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index postoperatively among those who used CPAP (37 vs. 12 events per hour; P less than .001), as well as a significant reduction in hospital length of stay 4 vs. 4.4 days; P = .05).
Dr. Manjarrez reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM SHM CONVERGE 2021
Surgery for early-stage cervical cancer: Are we still too radical?
It has been more than 120 years since Ernst Wertheim, a Viennese surgeon, performed and described what is considered to have been the first radical total hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy for early-stage cervical cancer, yet this morbid procedure remains the standard of care for most early-stage cervical cancers. The rationale for this procedure, which included removal of the parametrial tissue, uterosacral and cardinal ligaments, and upper vagina en bloc with the cervix and uterus, was to obtain margins around a cancer that has a dominant radial growth pattern. The morbidity associated with this procedure is substantial. The parametrium houses important vascular, neural, and urologic structures. Unlike extrafascial hysterectomy, often referred to as “simple” hysterectomy, in which surgeons follow a fascial plane, and therefore a relatively avascular dissection, surgeons performing radical hysterectomy must venture outside of these embryologic fusion planes into less well–defined anatomy. Therefore, surgical complications are relatively common including hemorrhage, ureteral and bladder injury, as well as late-onset devastating complications such as fistula, urinary retention, or incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.1 More recently, variations of the Wertheim-Meigs radical hysterectomy have been described, and objective classifications created, which include modified radical procedures (removing less parametria) and nerve-sparing procedures to facilitate standardized nomenclature for tailoring the most appropriate procedure for any given tumor.2
The trend, and a positive one at that, over the course of the past century, has been a move away from routine radical surgical procedures for most clinical stage 1 cancers. No better example exists than breast cancer, in which the Halsted radical mastectomy has been largely replaced by less morbid breast-conserving or nonradical procedures with adjunct medical and radiation therapies offered to achieve high rates of cure with far more acceptable patient-centered outcomes.3 And so why is it that radical hysterectomy is still considered the standard of care for all but the smallest of microscopic cervical cancers?
The risk of lymph node metastases or recurrence is exceptionally low for women with microscopic (stage IA1) cervical cancers that are less than 3 mm in depth. Therefore, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend nonradical surgical remedies (such as extrafascial hysterectomy, or cone biopsy or trachelectomy if fertility preservation is desired) for this earlier stage of disease.4 If there is lymphovascular space invasion (an indicator of poor prognosis and potential lymphatic involvement), a lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy is also recommended. For women with stage IA2 or IB lesions, radical excisions (either trachelectomy or hysterectomy) are considered the standard of care. However, this “gold standard” was achieved largely through legacy, and not a result of randomized trials comparing its outcomes with nonradical procedures.
Initial strides away from radical cervical cancer surgery focused on the goal of fertility preservation via radical trachelectomy which allowed women to preserve an intact uterine fundus. This was initially met with skepticism and concern that surgeons could be sacrificing oncologic outcomes in order to preserve a woman’s fertility. Thanks to pioneering work, including prospective research studies by surgeon innovators it has been shown that, in appropriately selected candidates with tumors less than 2 cm, it is an accepted standard of care.4 Radical vaginal or abdominal trachelectomy is associated with cancer recurrence rates of less than 5% and successful pregnancy in approximately three-quarters of patients in whom this is desired.5,6 However, full-term pregnancy is achieved in 50%-75% of cases, reflecting increased obstetric risk, and radical trachelectomy still subjects patients to the morbidity of a radical parametrial resection, despite the fact that many of them will have no residual carcinoma in their final pathological specimens.
Therefore, can we be even more conservative in our surgery for these patients? Are simple hysterectomy or conization potentially adequate treatments for small (<2 cm) stage IA2 and IB1 lesions that have favorable histology (<10 mm stromal invasion, low-risk histology, no lymphovascular space involvement, negative margins on conization and no lymph node metastases)? In patients whose tumor exhibits these histologic features, the likelihood of parametrial involvement is approximately 1%, calling into question the virtue of parametrial resection.7 Observational studies have identified mixed results on the safety of conservative surgical techniques in early-stage cervical cancer. In a study of the National Cancer Database, the outcomes of 2,543 radical hysterectomies and 1,388 extrafascial hysterectomies for women with stage IB1 disease were evaluated and observed a difference in 5-year survival (92.4% vs. 95.3%) favoring the radical procedure.8 Unfortunately, database analyses such as these are limited by potential confounders and discordance between the groups such as rates of lymphadenectomy, known involvement of oncologic surgeon specialists, and margin status. An alternative evaluation of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database including 2,571 patients with stage IB1 disease, all of whom had lymphadenectomy performed, showed no difference in 10-year disease-specific survival between the two surgical approaches.9
Ultimately, whether conservative procedures (such as conization or extrafascial hysterectomy) can be offered to women with small, low-risk IB1 or IA2 cervical cancers will be best determined by prospective single-arm or randomized trials. Fortunately, these are underway. Preliminary results from the ConCerv trial in which 100 women with early-stage, low-risk stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer were treated with either repeat conization or extrafascial hysterectomy with sentinel lymph node biopsy showed acceptably low rates of recurrence (3%) with this approach.10 If the mature data supports this finding, it seems that, for appropriately selected and well-counseled patients, conservative surgery may become more broadly accepted as a reasonable option for treatment that spares women not only loss of fertility, but also the early and late surgical morbidity from radical procedures.
In the meantime, until more is known about the oncologic safety of nonradical procedures for stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer, this option should not be considered standard of care, and only offered to patients with favorable tumor factors who are well counseled regarding the uncertainty of this approach. It is critical that patients with early-stage cervical cancer be evaluated by a gynecologic cancer specialist prior to definitive surgical treatment as they are best equipped to evaluate risk profiles and counsel about her options for surgery, its known and unknown consequences, and the appropriateness of fertility preservation or radicality of surgery. We eagerly await the results of trials evaluating the safety of conservative cervical cancer surgery, which promise to advance us from 19th-century practices, preserving not only fertility, but also quality of life.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She has no disclosures and can be contacted at [email protected].
References
1. Trimbos JB et al. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40(3):375-8.
2. Querleu D and Morrow CP. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:297-303.
3. Sakorafas GH and Safioleas M. Eur J Cancer Care. 2010 Mar;19(2):145-66.
4. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cervical Cancer (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cervical.pdf. Accessed 2021 Apr 21.
5. Plante M et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121:290-7.
6. Wethington SL et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22:1251-7.
7. Domgue J and Schmeler K. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019 Feb;55:79-92.
8. Sia TY et al. Obstet Gyenecol. 2019;134(6):1132.
9. Tseng J et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;150(1):44.
10. Schmeler K et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2019;29:A14-5.
It has been more than 120 years since Ernst Wertheim, a Viennese surgeon, performed and described what is considered to have been the first radical total hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy for early-stage cervical cancer, yet this morbid procedure remains the standard of care for most early-stage cervical cancers. The rationale for this procedure, which included removal of the parametrial tissue, uterosacral and cardinal ligaments, and upper vagina en bloc with the cervix and uterus, was to obtain margins around a cancer that has a dominant radial growth pattern. The morbidity associated with this procedure is substantial. The parametrium houses important vascular, neural, and urologic structures. Unlike extrafascial hysterectomy, often referred to as “simple” hysterectomy, in which surgeons follow a fascial plane, and therefore a relatively avascular dissection, surgeons performing radical hysterectomy must venture outside of these embryologic fusion planes into less well–defined anatomy. Therefore, surgical complications are relatively common including hemorrhage, ureteral and bladder injury, as well as late-onset devastating complications such as fistula, urinary retention, or incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.1 More recently, variations of the Wertheim-Meigs radical hysterectomy have been described, and objective classifications created, which include modified radical procedures (removing less parametria) and nerve-sparing procedures to facilitate standardized nomenclature for tailoring the most appropriate procedure for any given tumor.2
The trend, and a positive one at that, over the course of the past century, has been a move away from routine radical surgical procedures for most clinical stage 1 cancers. No better example exists than breast cancer, in which the Halsted radical mastectomy has been largely replaced by less morbid breast-conserving or nonradical procedures with adjunct medical and radiation therapies offered to achieve high rates of cure with far more acceptable patient-centered outcomes.3 And so why is it that radical hysterectomy is still considered the standard of care for all but the smallest of microscopic cervical cancers?
The risk of lymph node metastases or recurrence is exceptionally low for women with microscopic (stage IA1) cervical cancers that are less than 3 mm in depth. Therefore, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend nonradical surgical remedies (such as extrafascial hysterectomy, or cone biopsy or trachelectomy if fertility preservation is desired) for this earlier stage of disease.4 If there is lymphovascular space invasion (an indicator of poor prognosis and potential lymphatic involvement), a lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy is also recommended. For women with stage IA2 or IB lesions, radical excisions (either trachelectomy or hysterectomy) are considered the standard of care. However, this “gold standard” was achieved largely through legacy, and not a result of randomized trials comparing its outcomes with nonradical procedures.
Initial strides away from radical cervical cancer surgery focused on the goal of fertility preservation via radical trachelectomy which allowed women to preserve an intact uterine fundus. This was initially met with skepticism and concern that surgeons could be sacrificing oncologic outcomes in order to preserve a woman’s fertility. Thanks to pioneering work, including prospective research studies by surgeon innovators it has been shown that, in appropriately selected candidates with tumors less than 2 cm, it is an accepted standard of care.4 Radical vaginal or abdominal trachelectomy is associated with cancer recurrence rates of less than 5% and successful pregnancy in approximately three-quarters of patients in whom this is desired.5,6 However, full-term pregnancy is achieved in 50%-75% of cases, reflecting increased obstetric risk, and radical trachelectomy still subjects patients to the morbidity of a radical parametrial resection, despite the fact that many of them will have no residual carcinoma in their final pathological specimens.
Therefore, can we be even more conservative in our surgery for these patients? Are simple hysterectomy or conization potentially adequate treatments for small (<2 cm) stage IA2 and IB1 lesions that have favorable histology (<10 mm stromal invasion, low-risk histology, no lymphovascular space involvement, negative margins on conization and no lymph node metastases)? In patients whose tumor exhibits these histologic features, the likelihood of parametrial involvement is approximately 1%, calling into question the virtue of parametrial resection.7 Observational studies have identified mixed results on the safety of conservative surgical techniques in early-stage cervical cancer. In a study of the National Cancer Database, the outcomes of 2,543 radical hysterectomies and 1,388 extrafascial hysterectomies for women with stage IB1 disease were evaluated and observed a difference in 5-year survival (92.4% vs. 95.3%) favoring the radical procedure.8 Unfortunately, database analyses such as these are limited by potential confounders and discordance between the groups such as rates of lymphadenectomy, known involvement of oncologic surgeon specialists, and margin status. An alternative evaluation of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database including 2,571 patients with stage IB1 disease, all of whom had lymphadenectomy performed, showed no difference in 10-year disease-specific survival between the two surgical approaches.9
Ultimately, whether conservative procedures (such as conization or extrafascial hysterectomy) can be offered to women with small, low-risk IB1 or IA2 cervical cancers will be best determined by prospective single-arm or randomized trials. Fortunately, these are underway. Preliminary results from the ConCerv trial in which 100 women with early-stage, low-risk stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer were treated with either repeat conization or extrafascial hysterectomy with sentinel lymph node biopsy showed acceptably low rates of recurrence (3%) with this approach.10 If the mature data supports this finding, it seems that, for appropriately selected and well-counseled patients, conservative surgery may become more broadly accepted as a reasonable option for treatment that spares women not only loss of fertility, but also the early and late surgical morbidity from radical procedures.
In the meantime, until more is known about the oncologic safety of nonradical procedures for stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer, this option should not be considered standard of care, and only offered to patients with favorable tumor factors who are well counseled regarding the uncertainty of this approach. It is critical that patients with early-stage cervical cancer be evaluated by a gynecologic cancer specialist prior to definitive surgical treatment as they are best equipped to evaluate risk profiles and counsel about her options for surgery, its known and unknown consequences, and the appropriateness of fertility preservation or radicality of surgery. We eagerly await the results of trials evaluating the safety of conservative cervical cancer surgery, which promise to advance us from 19th-century practices, preserving not only fertility, but also quality of life.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She has no disclosures and can be contacted at [email protected].
References
1. Trimbos JB et al. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40(3):375-8.
2. Querleu D and Morrow CP. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:297-303.
3. Sakorafas GH and Safioleas M. Eur J Cancer Care. 2010 Mar;19(2):145-66.
4. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cervical Cancer (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cervical.pdf. Accessed 2021 Apr 21.
5. Plante M et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121:290-7.
6. Wethington SL et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22:1251-7.
7. Domgue J and Schmeler K. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019 Feb;55:79-92.
8. Sia TY et al. Obstet Gyenecol. 2019;134(6):1132.
9. Tseng J et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;150(1):44.
10. Schmeler K et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2019;29:A14-5.
It has been more than 120 years since Ernst Wertheim, a Viennese surgeon, performed and described what is considered to have been the first radical total hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy for early-stage cervical cancer, yet this morbid procedure remains the standard of care for most early-stage cervical cancers. The rationale for this procedure, which included removal of the parametrial tissue, uterosacral and cardinal ligaments, and upper vagina en bloc with the cervix and uterus, was to obtain margins around a cancer that has a dominant radial growth pattern. The morbidity associated with this procedure is substantial. The parametrium houses important vascular, neural, and urologic structures. Unlike extrafascial hysterectomy, often referred to as “simple” hysterectomy, in which surgeons follow a fascial plane, and therefore a relatively avascular dissection, surgeons performing radical hysterectomy must venture outside of these embryologic fusion planes into less well–defined anatomy. Therefore, surgical complications are relatively common including hemorrhage, ureteral and bladder injury, as well as late-onset devastating complications such as fistula, urinary retention, or incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.1 More recently, variations of the Wertheim-Meigs radical hysterectomy have been described, and objective classifications created, which include modified radical procedures (removing less parametria) and nerve-sparing procedures to facilitate standardized nomenclature for tailoring the most appropriate procedure for any given tumor.2
The trend, and a positive one at that, over the course of the past century, has been a move away from routine radical surgical procedures for most clinical stage 1 cancers. No better example exists than breast cancer, in which the Halsted radical mastectomy has been largely replaced by less morbid breast-conserving or nonradical procedures with adjunct medical and radiation therapies offered to achieve high rates of cure with far more acceptable patient-centered outcomes.3 And so why is it that radical hysterectomy is still considered the standard of care for all but the smallest of microscopic cervical cancers?
The risk of lymph node metastases or recurrence is exceptionally low for women with microscopic (stage IA1) cervical cancers that are less than 3 mm in depth. Therefore, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend nonradical surgical remedies (such as extrafascial hysterectomy, or cone biopsy or trachelectomy if fertility preservation is desired) for this earlier stage of disease.4 If there is lymphovascular space invasion (an indicator of poor prognosis and potential lymphatic involvement), a lymphadenectomy or sentinel lymph node biopsy is also recommended. For women with stage IA2 or IB lesions, radical excisions (either trachelectomy or hysterectomy) are considered the standard of care. However, this “gold standard” was achieved largely through legacy, and not a result of randomized trials comparing its outcomes with nonradical procedures.
Initial strides away from radical cervical cancer surgery focused on the goal of fertility preservation via radical trachelectomy which allowed women to preserve an intact uterine fundus. This was initially met with skepticism and concern that surgeons could be sacrificing oncologic outcomes in order to preserve a woman’s fertility. Thanks to pioneering work, including prospective research studies by surgeon innovators it has been shown that, in appropriately selected candidates with tumors less than 2 cm, it is an accepted standard of care.4 Radical vaginal or abdominal trachelectomy is associated with cancer recurrence rates of less than 5% and successful pregnancy in approximately three-quarters of patients in whom this is desired.5,6 However, full-term pregnancy is achieved in 50%-75% of cases, reflecting increased obstetric risk, and radical trachelectomy still subjects patients to the morbidity of a radical parametrial resection, despite the fact that many of them will have no residual carcinoma in their final pathological specimens.
Therefore, can we be even more conservative in our surgery for these patients? Are simple hysterectomy or conization potentially adequate treatments for small (<2 cm) stage IA2 and IB1 lesions that have favorable histology (<10 mm stromal invasion, low-risk histology, no lymphovascular space involvement, negative margins on conization and no lymph node metastases)? In patients whose tumor exhibits these histologic features, the likelihood of parametrial involvement is approximately 1%, calling into question the virtue of parametrial resection.7 Observational studies have identified mixed results on the safety of conservative surgical techniques in early-stage cervical cancer. In a study of the National Cancer Database, the outcomes of 2,543 radical hysterectomies and 1,388 extrafascial hysterectomies for women with stage IB1 disease were evaluated and observed a difference in 5-year survival (92.4% vs. 95.3%) favoring the radical procedure.8 Unfortunately, database analyses such as these are limited by potential confounders and discordance between the groups such as rates of lymphadenectomy, known involvement of oncologic surgeon specialists, and margin status. An alternative evaluation of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database including 2,571 patients with stage IB1 disease, all of whom had lymphadenectomy performed, showed no difference in 10-year disease-specific survival between the two surgical approaches.9
Ultimately, whether conservative procedures (such as conization or extrafascial hysterectomy) can be offered to women with small, low-risk IB1 or IA2 cervical cancers will be best determined by prospective single-arm or randomized trials. Fortunately, these are underway. Preliminary results from the ConCerv trial in which 100 women with early-stage, low-risk stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer were treated with either repeat conization or extrafascial hysterectomy with sentinel lymph node biopsy showed acceptably low rates of recurrence (3%) with this approach.10 If the mature data supports this finding, it seems that, for appropriately selected and well-counseled patients, conservative surgery may become more broadly accepted as a reasonable option for treatment that spares women not only loss of fertility, but also the early and late surgical morbidity from radical procedures.
In the meantime, until more is known about the oncologic safety of nonradical procedures for stage IA2 and IB1 cervical cancer, this option should not be considered standard of care, and only offered to patients with favorable tumor factors who are well counseled regarding the uncertainty of this approach. It is critical that patients with early-stage cervical cancer be evaluated by a gynecologic cancer specialist prior to definitive surgical treatment as they are best equipped to evaluate risk profiles and counsel about her options for surgery, its known and unknown consequences, and the appropriateness of fertility preservation or radicality of surgery. We eagerly await the results of trials evaluating the safety of conservative cervical cancer surgery, which promise to advance us from 19th-century practices, preserving not only fertility, but also quality of life.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She has no disclosures and can be contacted at [email protected].
References
1. Trimbos JB et al. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40(3):375-8.
2. Querleu D and Morrow CP. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:297-303.
3. Sakorafas GH and Safioleas M. Eur J Cancer Care. 2010 Mar;19(2):145-66.
4. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cervical Cancer (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cervical.pdf. Accessed 2021 Apr 21.
5. Plante M et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121:290-7.
6. Wethington SL et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22:1251-7.
7. Domgue J and Schmeler K. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019 Feb;55:79-92.
8. Sia TY et al. Obstet Gyenecol. 2019;134(6):1132.
9. Tseng J et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;150(1):44.
10. Schmeler K et al. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2019;29:A14-5.
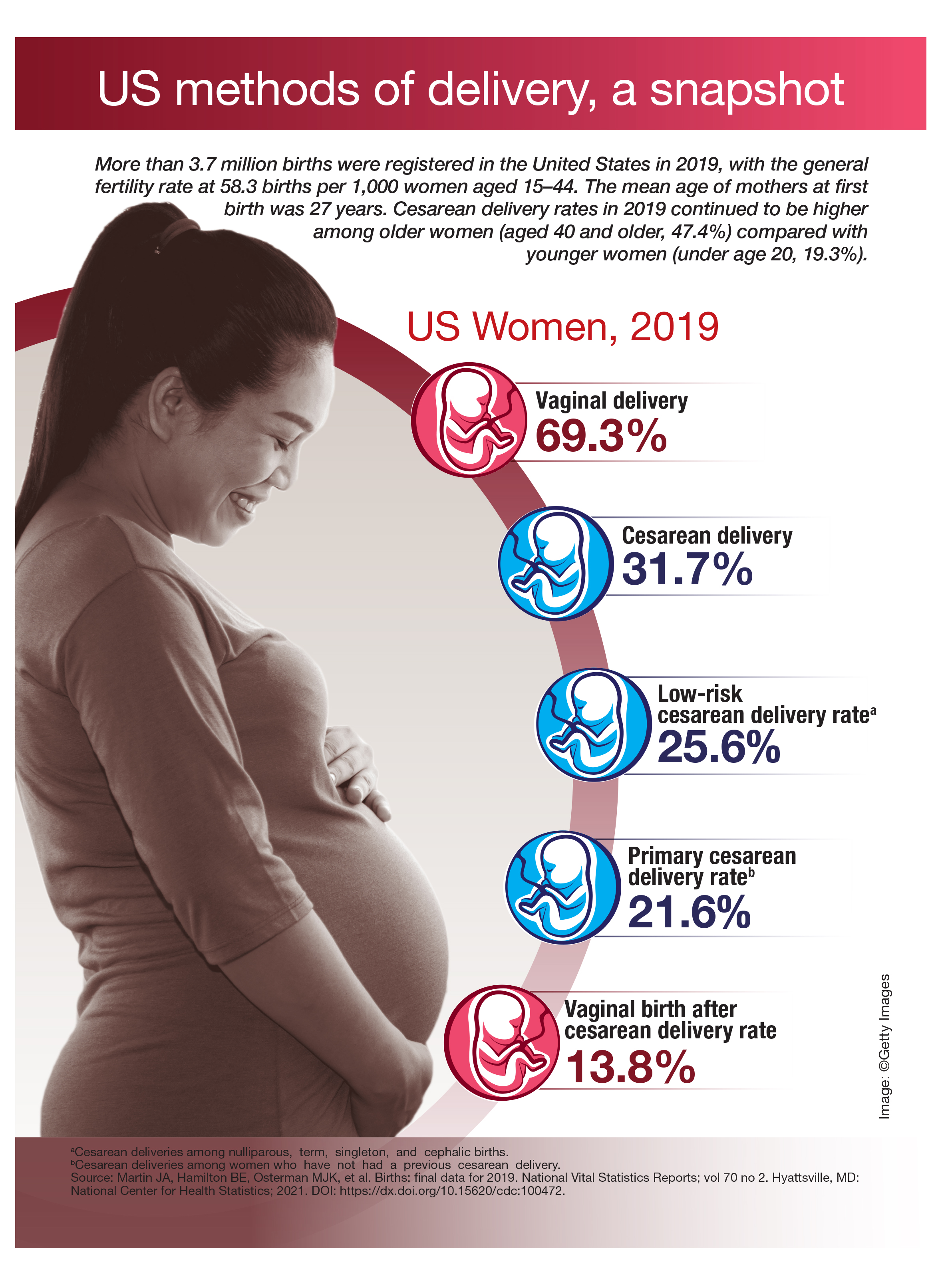
US methods of delivery, a snapshot


Data about COVID-19-related skin manifestations in children continue to emerge
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Two and stratifying children at risk for serious, systemic illness due to the virus.
In a single-center descriptive study carried out over a 9-month period, researchers in Madrid found that of 50 hospitalized children infected with COVID-19, 21 (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly exanthem, followed by conjunctival hyperemia without secretion and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue. In addition, 18 (36%) fulfilled criteria for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
“Based on findings in adult patients, the skin manifestations of COVID-19 have been classified under five categories: acral pseudo-chilblain, vesicular eruptions, urticarial lesions, maculopapular eruptions, and livedo or necrosis,” David Andina-Martinez, MD, of Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online on April 2 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Chilblain lesions in healthy children and adolescents have received much attention; these lesions resolve without complications after a few weeks,” they added. “Besides, other cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 in children have been the matter of case reports or small case series. Nevertheless, the mucocutaneous manifestations in hospitalized children infected with SARS-CoV-2 and their implications on the clinical course have not yet been extensively described.”
In an effort to describe the mucocutaneous manifestations in children hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers evaluated 50 children up to 18 years of age who were admitted between March 1 and Nov. 30, 2020, to Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, which was designated as a pediatric reference center during the peak of the pandemic. The main reasons for admission were respiratory illness (40%) and MIS-C (40%).
Of the 50 patients, 44 (88%) had a positive RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 and 6 (12%) met clinical suspicion criteria and had a negative RT-PCR with a positive IgG serology. In 34 patients (68%), a close contact with a suspected or confirmed case of COVID-19 was referred, while the source of the infection remained unknown in the remaining 16 patients (32%).
The researchers reported that 21 patients (42%) had mucocutaneous symptoms, most commonly maculopapular exanthem (86%), conjunctival hyperemia (81%), and red cracked lips or strawberry tongue (43%). In addition, 18 of the 21 patients (86%) fulfilled criteria for MIS-C.
“A tricky thing about MIS-C is that it often manifests 4-5 weeks after a child had COVID-19,” said Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study. “MIS-C is associated with characteristic bright red lips and a red tongue that might resemble a strawberry. Such oral findings should prompt rapid evaluation for other signs and symptoms. There can be redness of the eyes or other more nonspecific skin findings (large or small areas of redness on the trunk or limbs, sometimes with surface change), but more importantly, fever, a rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or breathing issues. The risk with MIS-C is a rapid decline in a child’s health, with admission to an intensive care unit.”
Dr. Andina-Martinez and his colleagues also contrast the skin findings of MIS-C, which are not generally on the hands or feet, with the so-called “COVID toe” or finger phenomenon, which has also been associated with SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. “Only one of the patients in this series had skin involvement of a finger, and it only appeared after recovery from MIS-C,” Dr. Ko noted. “Distinguishing COVID toes from MIS-C is important, as COVID toes has a very good outcome, while MIS-C can have severe consequences, including protracted heart disease.”
In other findings, patients who presented with mucocutaneous signs tended to be older than those without skin signs and they presented at the emergency department with poor general status and extreme tachycardia. They also had higher C-reactive protein and D-dimer levels and lower lymphocyte counts and faced a more than a 10-fold increased risk of being admitted to the PICU, compared with patients who did not have skin signs (OR, 10.24; P = .003).
In a separate study published online on April 7 in JAMA Dermatology, Zachary E. Holcomb, MD, of the combined dermatology residency program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues presented what is believed to be the first case report of reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. RIME is the preferred term for pediatric patients who present with mucositis and rash (often a scant or even absent skin eruption) triggered by various infectious agents.
The patient, a 17-year-old male, presented to the emergency department with 3 days of mouth pain and nonpainful penile erosions. “One week prior, he experienced transient anosmia and ageusia that had since spontaneously resolved,” the researchers wrote. “At that time, he was tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection via nasopharyngeal polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the results of which were positive.”
At presentation, the patient had no fever, his vital signs were normal, and the physical exam revealed shallow erosions of the vermilion lips and hard palate, circumferential erythematous erosions of the periurethral glans penis, and five small vesicles on the trunk and upper extremities. Serum analysis revealed a normal white blood cell count with mild absolute lymphopenia, slightly elevated creatinine level, normal liver function, slightly elevated C-reactive protein level, and normal ferritin level.
Dr. Holcomb and colleagues made a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2–associated RIME based on microbiological results, which revealed positive repeated SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal PCR and negative nasopharyngeal PCR testing for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, adenovirus, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, human metapneumovirus, influenza A/B, parainfluenza 1 to 4, rhinovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. In addition, titers of Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgM levels were negative, but Mycoplasma pneumoniae IgG levels were elevated.
The lesions resolved with 60 mg of oral prednisone taken daily for 4 days. A recurrence of oral mucositis 3 months later responded to 80 mg oral prednisone taken daily for 6 days.
“It’s not surprising that SARS-CoV-2 is yet another trigger for RIME,” said Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, chief of the division of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, who was asked to comment about the case report.
“The take-home message is for clinicians to be aware of this association and distinguish these patients from those with MIS-C, because patients with MIS-C require monitoring and urgent systemic treatment. RIME and MIS-C may potentially be distinguished clinically based on the nature of the mucositis (hemorrhagic and erosive in RIME, dry, cracked lips with ‘strawberry tongue’ in MIS-C) but more importantly patients with RIME lack laboratory evidence of severe systemic inflammation,” such as ESR, CRP, or ferritin, she said.
“A final interesting point in this article was the recurrence of mucositis in this patient, which could mean that recurrent mucositis/recurrent RIME might be yet another manifestation of ‘long-COVID’ (now called post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection) in some patients,” Dr. Kirkorian added. She noted that the American Academy of Dermatology–International League of Dermatologic Societies COVID-19 Dermatology Registry and articles like these “provide invaluable ‘hot off the presses’ information for clinicians who are facing the protean manifestations of a novel viral epidemic.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Can a once-daily oral formulation treat symptoms of uterine fibroids without causing hot flashes or bone loss?
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN 3rd, et al. Treatment of uterine fibroid symptoms with relugolix combination therapy. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:630-642. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2008283
Expert Commentary
By age 50, approximately 70% of White women and 80% of Black women will have uterine fibroids.1 Of these, about 25% will have symptoms—most often including heavy menstrual bleeding,2 and associated pain the second most common symptom.3 First-line treatment has traditionally been hormonal contraceptives. Injectable gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist like leuprolide acetate have been commonly employed, although their actual approved indication is “for concomitant use with iron therapy for preoperative hematologic improvement of patients with anemia caused by uterine leiomyomata (fibroids).”4 Recently, an oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, combined with estrogen and progestogen, was approved for treatment of uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. However, it is dosed twice per day because of its short half-life and results in a loss of bone mineral density at 1 year.5,6
Details of the studies
Al-Hendy and colleagues report on two double-blind 24-week phase 3 trials involving women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids. There were just under 400 women in each trial. There was a 1:1:1 randomization to: placebo, once-daily oral relugolix 40 mg with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate, or oral relugolix by itself for 12 weeks followed by the combination for 12 weeks (referred to as the “delayed relugolix combination therapy” arm).
Results. The primary end point was the percentage of patients who had a volume of menstrual blood loss less than 80 mL and a ≥50% reduction in blood loss volume as measured by the alkaline hematin method. The baseline blood loss in these studies ranged from approximately 210–250 mL. Secondary end points included amenorrhea, volume of menstrual blood loss, distress from bleeding and pelvic discomfort, anemia, pain, uterine volume, and the largest fibroid volume.
In trials one and two, 73% and 71% of patients in the relugolix combination groups, respectively, achieved the primary endpoint, compared with 19% and 15% in the placebo groups (P <.001). In addition, all secondary endpoints except largest fibroid volume were significantly improved versus placebo. Adverse events, including any change in bone mineral density, were no different between the combination and placebo groups. The delayed combination groups did have more hot flashes and diminished bone density compared with both the placebo and combination groups.
Strengths and weaknesses
The studies appropriately enrolled women with a mean age of 41–42 years and a mean BMI >30 kg/m2, and more than 50% were African American. Thus, the samples are adequately representative of the type of population most likely to have fibroids and associated symptoms. The results showed the advantages of built-in “add back therapy” with estrogen plus progestogen, as the vasomotor symptoms and bone loss that treatment with a GnRH antagonist alone produces were reduced.
Although the trials were only conducted for 24 weeks, efficacy was seen as early as 4 weeks, and was clearly maintained throughout the full trials—and there is no scientific reason to assume it would not be maintained indefinitely. However, one cannot make a similar assumption about long-term safety. As another GnRH antagonist, with a shorter half-life requiring twice-daily-dosing with add back therapy, has been approved for use for 2 years, it is likely that the once-daily formulation of combination relugolix will be approved for this timeframe as well. Still, with patients’ mean age of 41–42 years, what will clinicians do after 2-year treatment? Clearly, study of long-term safety would be valuable. ●
Fibroids are extremely common in clinical practice, with their associated symptoms depending greatly on size and location. In many patients, symptoms are serious enough to be the most common indication for hysterectomy. In the past, combination oral contraceptives, injectable leuprolide acetate, and more recently, a GnRH antagonist given twice daily with estrogen/progestogen add-back have been utilized. The formulation described in Al-Hendy and colleagues’ study, which is dosed once per day and appears to not increase vasomotor symptoms or diminish bone mass, may provide a very nice “tool” in the clinician’s toolbox to either avoid any surgery in some patients (likely those aged closer to menopause) or optimize other patients preoperatively in terms of reversing anemia and reducing uterine volume, thus making any planned surgical procedure safer.
STEVEN R. GOLDSTEIN, MD, NCMP, CCD
- Wise LA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK. Epidemiology of uterine fibroids: from menarche to menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2016;59:2-24.
- Borah BJ, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The impact of uterine leiomyomas: a national survey of affected women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:319.e1-319.e20.
- David M, Pitz CM, Mihaylova A, et al. Myoma-associated pain frequency and intensity: a retrospective evaluation of 1548 myoma patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:137-140.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2018.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2020.
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN 3rd, et al. Treatment of uterine fibroid symptoms with relugolix combination therapy. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:630-642. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2008283
Expert Commentary
By age 50, approximately 70% of White women and 80% of Black women will have uterine fibroids.1 Of these, about 25% will have symptoms—most often including heavy menstrual bleeding,2 and associated pain the second most common symptom.3 First-line treatment has traditionally been hormonal contraceptives. Injectable gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist like leuprolide acetate have been commonly employed, although their actual approved indication is “for concomitant use with iron therapy for preoperative hematologic improvement of patients with anemia caused by uterine leiomyomata (fibroids).”4 Recently, an oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, combined with estrogen and progestogen, was approved for treatment of uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. However, it is dosed twice per day because of its short half-life and results in a loss of bone mineral density at 1 year.5,6
Details of the studies
Al-Hendy and colleagues report on two double-blind 24-week phase 3 trials involving women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids. There were just under 400 women in each trial. There was a 1:1:1 randomization to: placebo, once-daily oral relugolix 40 mg with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate, or oral relugolix by itself for 12 weeks followed by the combination for 12 weeks (referred to as the “delayed relugolix combination therapy” arm).
Results. The primary end point was the percentage of patients who had a volume of menstrual blood loss less than 80 mL and a ≥50% reduction in blood loss volume as measured by the alkaline hematin method. The baseline blood loss in these studies ranged from approximately 210–250 mL. Secondary end points included amenorrhea, volume of menstrual blood loss, distress from bleeding and pelvic discomfort, anemia, pain, uterine volume, and the largest fibroid volume.
In trials one and two, 73% and 71% of patients in the relugolix combination groups, respectively, achieved the primary endpoint, compared with 19% and 15% in the placebo groups (P <.001). In addition, all secondary endpoints except largest fibroid volume were significantly improved versus placebo. Adverse events, including any change in bone mineral density, were no different between the combination and placebo groups. The delayed combination groups did have more hot flashes and diminished bone density compared with both the placebo and combination groups.
Strengths and weaknesses
The studies appropriately enrolled women with a mean age of 41–42 years and a mean BMI >30 kg/m2, and more than 50% were African American. Thus, the samples are adequately representative of the type of population most likely to have fibroids and associated symptoms. The results showed the advantages of built-in “add back therapy” with estrogen plus progestogen, as the vasomotor symptoms and bone loss that treatment with a GnRH antagonist alone produces were reduced.
Although the trials were only conducted for 24 weeks, efficacy was seen as early as 4 weeks, and was clearly maintained throughout the full trials—and there is no scientific reason to assume it would not be maintained indefinitely. However, one cannot make a similar assumption about long-term safety. As another GnRH antagonist, with a shorter half-life requiring twice-daily-dosing with add back therapy, has been approved for use for 2 years, it is likely that the once-daily formulation of combination relugolix will be approved for this timeframe as well. Still, with patients’ mean age of 41–42 years, what will clinicians do after 2-year treatment? Clearly, study of long-term safety would be valuable. ●
Fibroids are extremely common in clinical practice, with their associated symptoms depending greatly on size and location. In many patients, symptoms are serious enough to be the most common indication for hysterectomy. In the past, combination oral contraceptives, injectable leuprolide acetate, and more recently, a GnRH antagonist given twice daily with estrogen/progestogen add-back have been utilized. The formulation described in Al-Hendy and colleagues’ study, which is dosed once per day and appears to not increase vasomotor symptoms or diminish bone mass, may provide a very nice “tool” in the clinician’s toolbox to either avoid any surgery in some patients (likely those aged closer to menopause) or optimize other patients preoperatively in terms of reversing anemia and reducing uterine volume, thus making any planned surgical procedure safer.
STEVEN R. GOLDSTEIN, MD, NCMP, CCD
Al-Hendy A, Lukes AS, Poindexter AN 3rd, et al. Treatment of uterine fibroid symptoms with relugolix combination therapy. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:630-642. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2008283
Expert Commentary
By age 50, approximately 70% of White women and 80% of Black women will have uterine fibroids.1 Of these, about 25% will have symptoms—most often including heavy menstrual bleeding,2 and associated pain the second most common symptom.3 First-line treatment has traditionally been hormonal contraceptives. Injectable gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist like leuprolide acetate have been commonly employed, although their actual approved indication is “for concomitant use with iron therapy for preoperative hematologic improvement of patients with anemia caused by uterine leiomyomata (fibroids).”4 Recently, an oral GnRH antagonist, elagolix, combined with estrogen and progestogen, was approved for treatment of uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. However, it is dosed twice per day because of its short half-life and results in a loss of bone mineral density at 1 year.5,6
Details of the studies
Al-Hendy and colleagues report on two double-blind 24-week phase 3 trials involving women with heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids. There were just under 400 women in each trial. There was a 1:1:1 randomization to: placebo, once-daily oral relugolix 40 mg with 1 mg estradiol and 0.5 mg norethindrone acetate, or oral relugolix by itself for 12 weeks followed by the combination for 12 weeks (referred to as the “delayed relugolix combination therapy” arm).
Results. The primary end point was the percentage of patients who had a volume of menstrual blood loss less than 80 mL and a ≥50% reduction in blood loss volume as measured by the alkaline hematin method. The baseline blood loss in these studies ranged from approximately 210–250 mL. Secondary end points included amenorrhea, volume of menstrual blood loss, distress from bleeding and pelvic discomfort, anemia, pain, uterine volume, and the largest fibroid volume.
In trials one and two, 73% and 71% of patients in the relugolix combination groups, respectively, achieved the primary endpoint, compared with 19% and 15% in the placebo groups (P <.001). In addition, all secondary endpoints except largest fibroid volume were significantly improved versus placebo. Adverse events, including any change in bone mineral density, were no different between the combination and placebo groups. The delayed combination groups did have more hot flashes and diminished bone density compared with both the placebo and combination groups.
Strengths and weaknesses
The studies appropriately enrolled women with a mean age of 41–42 years and a mean BMI >30 kg/m2, and more than 50% were African American. Thus, the samples are adequately representative of the type of population most likely to have fibroids and associated symptoms. The results showed the advantages of built-in “add back therapy” with estrogen plus progestogen, as the vasomotor symptoms and bone loss that treatment with a GnRH antagonist alone produces were reduced.
Although the trials were only conducted for 24 weeks, efficacy was seen as early as 4 weeks, and was clearly maintained throughout the full trials—and there is no scientific reason to assume it would not be maintained indefinitely. However, one cannot make a similar assumption about long-term safety. As another GnRH antagonist, with a shorter half-life requiring twice-daily-dosing with add back therapy, has been approved for use for 2 years, it is likely that the once-daily formulation of combination relugolix will be approved for this timeframe as well. Still, with patients’ mean age of 41–42 years, what will clinicians do after 2-year treatment? Clearly, study of long-term safety would be valuable. ●
Fibroids are extremely common in clinical practice, with their associated symptoms depending greatly on size and location. In many patients, symptoms are serious enough to be the most common indication for hysterectomy. In the past, combination oral contraceptives, injectable leuprolide acetate, and more recently, a GnRH antagonist given twice daily with estrogen/progestogen add-back have been utilized. The formulation described in Al-Hendy and colleagues’ study, which is dosed once per day and appears to not increase vasomotor symptoms or diminish bone mass, may provide a very nice “tool” in the clinician’s toolbox to either avoid any surgery in some patients (likely those aged closer to menopause) or optimize other patients preoperatively in terms of reversing anemia and reducing uterine volume, thus making any planned surgical procedure safer.
STEVEN R. GOLDSTEIN, MD, NCMP, CCD
- Wise LA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK. Epidemiology of uterine fibroids: from menarche to menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2016;59:2-24.
- Borah BJ, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The impact of uterine leiomyomas: a national survey of affected women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:319.e1-319.e20.
- David M, Pitz CM, Mihaylova A, et al. Myoma-associated pain frequency and intensity: a retrospective evaluation of 1548 myoma patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:137-140.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2018.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2020.
- Wise LA, Laughlin-Tommaso SK. Epidemiology of uterine fibroids: from menarche to menopause. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2016;59:2-24.
- Borah BJ, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The impact of uterine leiomyomas: a national survey of affected women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;209:319.e1-319.e20.
- David M, Pitz CM, Mihaylova A, et al. Myoma-associated pain frequency and intensity: a retrospective evaluation of 1548 myoma patients. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:137-140.
- Lupron Depot [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2018.
- Schlaff WD, Ackerman RT, Al-Hendy A, et al. Elagolix for heavy menstrual bleeding in women with uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:328-340.
- Oriahnn [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2020.
Optimize your treatment of endometriosis by using an FDA-approved hormonal medication
Women with endometriosis often present for medical care for one or more of the following health issues: pelvic pain, infertility, and/or an adnexal cyst (endometrioma). For women with moderate or severe pelvic pain and laparoscopically diagnosed endometriosis, hormone therapy is often necessary to achieve maximal long-term reduction in pain and optimize health. I focus on opportunities to optimize hormonal treatment of endometriosis in this editorial.
When plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B
Cyclic or continuous combination estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Although endometriosis pain may initially improve with estrogen-progestin contraceptives, many women on this medication will eventually report that they have worsening pelvic pain that adversely impacts their daily activities. Surprisingly, clinicians often continue to prescribe estrogen-progestin contraceptives even after the patient reports that the treatment is not effective, and their pain continues to be bothersome.
Patients benefit when they have access to the full range of hormone treatments that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis (TABLE). In the situation where an estrogen-progestin contraceptive is no longer effective at reducing the pelvic pain, I will often offer the patient the option of norethindrone acetate (NEA) or elagolix treatment. My experience is that stopping the estrogen-progestin contraceptive and starting NEA or elagolix will result in a significant decrease in pain symptoms and improvement in the patient’s quality of life.

Other FDA-approved options to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis include depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension, depot leuprolide acetate, goserelin implant, and danazol. I do not routinely prescribe depot medroxyprogesterone acetate because some patients report new onset or worsening symptoms of depression on the medication. I prescribe depot-leuprolide acetate less often than in the past, because many patients report moderate to severe hypoestrogenic symptoms on this medication. In women taking depot-leuprolide acetate, moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms can be improved by prescribing NEA pills, but the alternative of norethindrone monotherapy is less expensive. I seldom use goserelin or danazol in my practice. The needle required to place the goserelin implant has a diameter of approximately 1.7 mm (16 gauge) or 2.1 mm (14 gauge), for the 3.6 mg and 10 mg doses, respectively. The large diameter of the needle can cause pain and bruising at the implant site. As a comparison, the progestin subdermal implant needle is approximately 2.1 mm in diameter. Danazol is associated with weight gain, and most women prefer to avoid this side effect.
Continue to: Norethindrone acetate...
Norethindrone acetate
NEA 5 mg daily is approved by the FDA to treat endometriosis.1 NEA was approved at a time when large controlled clinical trials were not routinely required for a medicine to be approved. The data to support NEA treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis is based on cohort studies. In a study of 194 women, median age 21 years with moderate to severe pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis, the effect of NEA on pelvic pain was explored.2 The initial dose of NEA was 5 mg daily. If the patient did not achieve a reduction in pelvic pain and amenorrhea on the NEA dose of 5 mg daily, the dose was increased by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks, up to a maximum of 15 mg, until amenorrhea and/or a decrease in pelvic pain was achieved. Ninety-five percent of the women in this cohort had previously been treated with an estrogen-progestin contraceptive or a GnRH antagonist and had discontinued those medications because of inadequate control of pelvic pain or because of side effects of the medication.
In this large cohort, 65% of women reported significant improvement in pelvic pain, with a median pain score of 5 before treatment and 0 following NEA treatment. About 55% of the women reported no side effects. The most commonly reported side effects were weight gain (16%; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%). (In this study women could report more than one side effect.)
In another cohort study of 52 women with pelvic pain and surgically confirmed endometriosis, NEA treatment resulted in pain relief in 94% of the women.3 Breakthrough bleeding was a common side effect, reported by 58% of participants. The investigators concluded that NEA treatment was a “cost-effective alternative with relatively mild side effects in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis.” A conclusion which I endorse.
NEA has been reported to effectively treat ovarian endometriomas and rectovaginal endometriosis.4,5 In a cohort of 18 women who had previously had the surgical resection of an ovarian endometriosis cyst and had postoperative recurrence of pelvic pain and ovarian endometriosis, treatment was initiated with an escalating NEA regimen.4 Treatment was initiated with NEA 5 mg daily, with the dosage increased every 2 weeks by 2.5 mg until amenorrhea was established. Most women achieved amenorrhea with NEA 5 mg daily, and 89% had reduced pelvic pain. The investigators reported complete regression of the endometriosis cyst(s) in 74% of the women. In my experience, NEA does not result in complete regression of endometriosis cysts, but it does cause a reduction in cyst diameter and total volume.
In a retrospective cohort study, 61 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis had 5 years of treatment with NEA 2.5 mg or 5.0 mg daily.5 NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, and dyschezia. The most common side effects attributed to NEA treatment were weight gain (30%), vaginal bleeding (23%), decreased libido (11%), headache (9%), bloating or swelling (8%), depression (7%), and acne (5%). In women who had sequential imaging studies, NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in rectovaginal lesion volume, stable disease volume, or an increase in lesion volume in 56%, 32%, and 12% of the women, respectively. The investigators concluded that for women with rectovaginal endometriosis, NEA treatment is a low-cost option for long-term treatment.
In my practice, I do not prescribe NEA at doses greater than 5 mg daily. There are case reports that NEA at a dose of ≥10 mg daily is associated with the development of a hepatic adenoma,6 elevated liver transaminase concentration,7 and jaundice.8 If NEA 5 mg daily is not effective in controlling pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, I stop the NEA and start a GnRH analogue, most often elagolix.
NEA 5 mg is not FDA approved as a contraceptive. However, norethindrone 0.35 mg daily, also known as the “mini-pill”, is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 NEA is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone, and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone.1 Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg has contraceptive properties if taken daily.
Continue to: Elagolix...
Elagolix
Elagolix is FDA approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. I reviewed the key studies resulting in FDA approval in the November 2018 issue of
In the Elaris Endometriosis-I study, 872 women with endometriosis and pelvic pain were randomly assigned to treatment with 1 of 2 doses of elagolix (high-dose [200 mg twice daily] and low-dose [150 mg once daily]) or placebo.11 After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in dysmenorrhea pain was reported by 76%, 46%, and 20% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.001 for comparisons of elagolix to placebo). After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in nonmenstrual pain or decreased or stable use of rescue analgesics was reported by 55%, 50%, and 37% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.01 low-dose elagolix vs placebo and P<.001 high-dose elagolix vs placebo).
Hot flashes that were severe enough to be reported as an adverse event by the study participants were reported by 42%, 24%, and 7% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups. Bone density was measured at baseline and after 6 months of treatment. Lumbar bone density changes were -2.61%, -0.32%, and +0.47% and hip femoral neck bone density changes were -1.89%, -0.39%, and +0.02% in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively.
Another large clinical trial of elagolix for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, Elaris EM-II, involving 817 women, produced results very similar to those reported in Elaris EM-I. The elagolix continuation studies, Elaris EM-III and -IV, demonstrated efficacy and safety of elagolix through 12 months of treatment.12
In my 2018 review,10 I noted that elagolix dose adjustment can be utilized to attempt to achieve maximal pain relief with minimal vasomotor symptoms. Elagolix at 200 mg twice daily produces a mean estradiol concentration of 12 pg/mL, whereas elagolix at 150 mg daily resulted in a mean estradiol concentration of 41 pg/mL.13 The estrogen threshold hypothesis posits that in women with endometriosis a stable estradiol concentration of 20 to 30 pg/mL is often associated with decreased pain and fewer vasomotor events.14 To achieve the target estradiol range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, I often initiate elagolix treatment with 200 mg twice daily. This enables a rapid onset of amenorrhea and a reduction in pelvic pain. Once amenorrhea has been achieved and a decrease in pelvic pain has occurred, I adjust the dose downward to 200 mg twice daily on even calendar days of each month and 200 mg once daily on odd calendar days each month. Some women will have continued pain relief and amenorrhea when the dose is further decreased to 200 mg once daily. If bothersome bleeding recurs and/or pain symptoms increase in severity, the dose can be increased to 200 mg twice daily or an alternating regimen of 200 mg twice daily and 200 mg once daily, every 2 days. An alternative to dose adjustment is to combine elagolix with NEA, which can reduce the severity of hot flashes and reduce bone loss caused by hypoestrogenism.15,16
Health insurers and pharmacy benefits managers may require a prior authorization before approving and dispensing elagolix. The prior authorization process can be burdensome for clinicians, consuming limited healthcare resources, contributing to burnout and frustrating patients.17 Elagolix is less expensive than depot-leuprolide acetate and nafarelin nasal spray and somewhat more expensive than a goserelin implant.18,19
Elagolix is not approved as a contraceptive. In the Elaris EM-I and -II trials women were advised to use 2 forms of contraception, although pregnancies did occur. There were 6 pregnancies among 475 women taking elagolix 150 mg daily and 2 pregnancies among 477 women taking elagolix 200 mg twice daily.20 Women taking elagolix should be advised to use a contraceptive, but not an estrogen-progestin contraceptive.
Continue to: Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis...
Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
One of the greatest public health tragedies of our era is the opioid misuse epidemic. Hundreds of thousands of deaths have been caused by opioid misuse. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that for the 12-month period ending in May 2020, there were 81,000 opioid-related deaths, the greatest number ever reported in a 12-month period.21 Many authorities believe that in the United States opioid medications have been over-prescribed, contributing to the opioid misuse epidemic. There is little evidence that chronic pelvic pain is optimally managed by chronic treatment with an opioid.22,23 Prescribing opioids to vulnerable individuals to treat chronic pelvic pain may result in opioid dependency and adversely affect the patient’s health. It is best to pledge not to prescribe an opioid medication for a woman with chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In situations when pelvic pain is difficult to control with hormonal therapy and nonopioid pain medications, referral to a specialty pain practice may be warranted.
Post–conservative surgery hormone treatment reduces pelvic pain recurrence
In a meta-analysis of 14 studies that reported on endometriosis recurrence rates following conservative surgery, recurrence (defined as recurrent pelvic pain or an imaging study showing recurrent endometriosis) was significantly reduced with the use of hormone treatment compared with expectant management or placebo treatment.24 The postoperative relative risk of endometriosis recurrence was reduced by 83% with progestin treatment, 64% with estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment, and 38% with GnRH analogue treatment. Overall, the number of patients that needed to be treated to prevent one endometriosis recurrence was 10, assuming a recurrence rate of 25% in the placebo treatment or expectant management groups.
For women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis who develop a recurrence of pelvic pain while on postoperative hormone treatment, it is important for the prescribing clinician to be flexible and consider changing the hormone regimen. For example, if a postoperative patient is treated with a continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive and develops recurrent pain, I will stop the contraceptive and initiate treatment with either NEA or elagolix.
Capitalize on opportunities to improve the medical care of women with endometriosis
Early diagnosis of endometriosis can be facilitated by recognizing that the condition is a common cause of moderate to severe dysmenorrhea. In 5 studies involving 1,187 women, the mean length of time from onset of pelvic pain symptoms to diagnosis of endometriosis was 8.6 years.25 If a woman with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis has not had sufficient pain relief with one brand of continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive, it is best not to prescribe an alternative brand but rather to switch to a progestin-only treatment or a GnRH antagonist. If plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B. ●
- Aygestin [package insert]. Barr Laboratories: Pomona, NY; 2007.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Karacan M. Effect of norethindrone acetate in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis. Int J Fertil Womens Med. 1998;43:24-27.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Anopa J, Charles C, et al. Medical management of recurrent endometrioma with long-term norethindrone acetate. Int J Women Health. 2012;4:149-154.
- Morotti M, Venturini PL, Biscaldi E, et al. Efficacy and acceptability of long-term norethindrone acetate for the treatment of rectovaginal endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Repro Biol. 2017;213:4-10.
- Brady PC, Missmer SA, Laufer MR. Hepatic adenomas in adolescents and young women with endometriosis treated with norethindrone acetate. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2017;30:422-424.
- Choudhary NS, Bodh V, Chaudhari S, et al. Norethisterone related drug induced liver injury: a series of 3 cases. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;7:266- 268.
- Perez-Mera RA, Shields CE. Jaundice associated with norethindrone acetate therapy. N Engl J Med. 1962;267:1137-1138.
- Camila [package insert]. Mayne Pharma Inc: Greenville, NC; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Elagolix: a new treatment for pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. OBG Manag. 2018;30:10,12-14, 20.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:147-160.
- Orilissa [package insert]. AbbVie Inc; North Chicago, IL; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Hormonal treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:740-745.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Gallagher JS, Missmer SA, Hornstein MD, et al. Long-term effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and add-back in adolescent endometriosis. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2018;31:376- 381.
- Miller A, Shor R, Waites T, et al. Prior authorization reform for better patient care. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:1937-1939.
- Depot-leuprolide acetate. Good Rx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
- Goserelin. Good Rx website. https://www .goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID19. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020 /p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html. Reviewed December 18, 2020. Accessed March 24, 2021.
- Till SR, As-Sanie S. 3 cases of chronic pelvic pain with nonsurgical, nonopioid therapies. OBG Manag. 2018;30:41-48.
- Steele A. Opioid use and depression in chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:491-501.
- Zakhari A, Delpero E, McKeown S, et al. Endometriosis recurrence following post-operative hormonal suppression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27:96- 107.
- Barbieri RL. Why are there delays in the diagnosis of endometriosis? OBG Manag. 2017;29:8, 10-11, 16.
Women with endometriosis often present for medical care for one or more of the following health issues: pelvic pain, infertility, and/or an adnexal cyst (endometrioma). For women with moderate or severe pelvic pain and laparoscopically diagnosed endometriosis, hormone therapy is often necessary to achieve maximal long-term reduction in pain and optimize health. I focus on opportunities to optimize hormonal treatment of endometriosis in this editorial.
When plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B
Cyclic or continuous combination estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Although endometriosis pain may initially improve with estrogen-progestin contraceptives, many women on this medication will eventually report that they have worsening pelvic pain that adversely impacts their daily activities. Surprisingly, clinicians often continue to prescribe estrogen-progestin contraceptives even after the patient reports that the treatment is not effective, and their pain continues to be bothersome.
Patients benefit when they have access to the full range of hormone treatments that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis (TABLE). In the situation where an estrogen-progestin contraceptive is no longer effective at reducing the pelvic pain, I will often offer the patient the option of norethindrone acetate (NEA) or elagolix treatment. My experience is that stopping the estrogen-progestin contraceptive and starting NEA or elagolix will result in a significant decrease in pain symptoms and improvement in the patient’s quality of life.

Other FDA-approved options to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis include depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension, depot leuprolide acetate, goserelin implant, and danazol. I do not routinely prescribe depot medroxyprogesterone acetate because some patients report new onset or worsening symptoms of depression on the medication. I prescribe depot-leuprolide acetate less often than in the past, because many patients report moderate to severe hypoestrogenic symptoms on this medication. In women taking depot-leuprolide acetate, moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms can be improved by prescribing NEA pills, but the alternative of norethindrone monotherapy is less expensive. I seldom use goserelin or danazol in my practice. The needle required to place the goserelin implant has a diameter of approximately 1.7 mm (16 gauge) or 2.1 mm (14 gauge), for the 3.6 mg and 10 mg doses, respectively. The large diameter of the needle can cause pain and bruising at the implant site. As a comparison, the progestin subdermal implant needle is approximately 2.1 mm in diameter. Danazol is associated with weight gain, and most women prefer to avoid this side effect.
Continue to: Norethindrone acetate...
Norethindrone acetate
NEA 5 mg daily is approved by the FDA to treat endometriosis.1 NEA was approved at a time when large controlled clinical trials were not routinely required for a medicine to be approved. The data to support NEA treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis is based on cohort studies. In a study of 194 women, median age 21 years with moderate to severe pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis, the effect of NEA on pelvic pain was explored.2 The initial dose of NEA was 5 mg daily. If the patient did not achieve a reduction in pelvic pain and amenorrhea on the NEA dose of 5 mg daily, the dose was increased by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks, up to a maximum of 15 mg, until amenorrhea and/or a decrease in pelvic pain was achieved. Ninety-five percent of the women in this cohort had previously been treated with an estrogen-progestin contraceptive or a GnRH antagonist and had discontinued those medications because of inadequate control of pelvic pain or because of side effects of the medication.
In this large cohort, 65% of women reported significant improvement in pelvic pain, with a median pain score of 5 before treatment and 0 following NEA treatment. About 55% of the women reported no side effects. The most commonly reported side effects were weight gain (16%; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%). (In this study women could report more than one side effect.)
In another cohort study of 52 women with pelvic pain and surgically confirmed endometriosis, NEA treatment resulted in pain relief in 94% of the women.3 Breakthrough bleeding was a common side effect, reported by 58% of participants. The investigators concluded that NEA treatment was a “cost-effective alternative with relatively mild side effects in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis.” A conclusion which I endorse.
NEA has been reported to effectively treat ovarian endometriomas and rectovaginal endometriosis.4,5 In a cohort of 18 women who had previously had the surgical resection of an ovarian endometriosis cyst and had postoperative recurrence of pelvic pain and ovarian endometriosis, treatment was initiated with an escalating NEA regimen.4 Treatment was initiated with NEA 5 mg daily, with the dosage increased every 2 weeks by 2.5 mg until amenorrhea was established. Most women achieved amenorrhea with NEA 5 mg daily, and 89% had reduced pelvic pain. The investigators reported complete regression of the endometriosis cyst(s) in 74% of the women. In my experience, NEA does not result in complete regression of endometriosis cysts, but it does cause a reduction in cyst diameter and total volume.
In a retrospective cohort study, 61 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis had 5 years of treatment with NEA 2.5 mg or 5.0 mg daily.5 NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, and dyschezia. The most common side effects attributed to NEA treatment were weight gain (30%), vaginal bleeding (23%), decreased libido (11%), headache (9%), bloating or swelling (8%), depression (7%), and acne (5%). In women who had sequential imaging studies, NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in rectovaginal lesion volume, stable disease volume, or an increase in lesion volume in 56%, 32%, and 12% of the women, respectively. The investigators concluded that for women with rectovaginal endometriosis, NEA treatment is a low-cost option for long-term treatment.
In my practice, I do not prescribe NEA at doses greater than 5 mg daily. There are case reports that NEA at a dose of ≥10 mg daily is associated with the development of a hepatic adenoma,6 elevated liver transaminase concentration,7 and jaundice.8 If NEA 5 mg daily is not effective in controlling pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, I stop the NEA and start a GnRH analogue, most often elagolix.
NEA 5 mg is not FDA approved as a contraceptive. However, norethindrone 0.35 mg daily, also known as the “mini-pill”, is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 NEA is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone, and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone.1 Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg has contraceptive properties if taken daily.
Continue to: Elagolix...
Elagolix
Elagolix is FDA approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. I reviewed the key studies resulting in FDA approval in the November 2018 issue of
In the Elaris Endometriosis-I study, 872 women with endometriosis and pelvic pain were randomly assigned to treatment with 1 of 2 doses of elagolix (high-dose [200 mg twice daily] and low-dose [150 mg once daily]) or placebo.11 After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in dysmenorrhea pain was reported by 76%, 46%, and 20% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.001 for comparisons of elagolix to placebo). After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in nonmenstrual pain or decreased or stable use of rescue analgesics was reported by 55%, 50%, and 37% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.01 low-dose elagolix vs placebo and P<.001 high-dose elagolix vs placebo).
Hot flashes that were severe enough to be reported as an adverse event by the study participants were reported by 42%, 24%, and 7% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups. Bone density was measured at baseline and after 6 months of treatment. Lumbar bone density changes were -2.61%, -0.32%, and +0.47% and hip femoral neck bone density changes were -1.89%, -0.39%, and +0.02% in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively.
Another large clinical trial of elagolix for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, Elaris EM-II, involving 817 women, produced results very similar to those reported in Elaris EM-I. The elagolix continuation studies, Elaris EM-III and -IV, demonstrated efficacy and safety of elagolix through 12 months of treatment.12
In my 2018 review,10 I noted that elagolix dose adjustment can be utilized to attempt to achieve maximal pain relief with minimal vasomotor symptoms. Elagolix at 200 mg twice daily produces a mean estradiol concentration of 12 pg/mL, whereas elagolix at 150 mg daily resulted in a mean estradiol concentration of 41 pg/mL.13 The estrogen threshold hypothesis posits that in women with endometriosis a stable estradiol concentration of 20 to 30 pg/mL is often associated with decreased pain and fewer vasomotor events.14 To achieve the target estradiol range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, I often initiate elagolix treatment with 200 mg twice daily. This enables a rapid onset of amenorrhea and a reduction in pelvic pain. Once amenorrhea has been achieved and a decrease in pelvic pain has occurred, I adjust the dose downward to 200 mg twice daily on even calendar days of each month and 200 mg once daily on odd calendar days each month. Some women will have continued pain relief and amenorrhea when the dose is further decreased to 200 mg once daily. If bothersome bleeding recurs and/or pain symptoms increase in severity, the dose can be increased to 200 mg twice daily or an alternating regimen of 200 mg twice daily and 200 mg once daily, every 2 days. An alternative to dose adjustment is to combine elagolix with NEA, which can reduce the severity of hot flashes and reduce bone loss caused by hypoestrogenism.15,16
Health insurers and pharmacy benefits managers may require a prior authorization before approving and dispensing elagolix. The prior authorization process can be burdensome for clinicians, consuming limited healthcare resources, contributing to burnout and frustrating patients.17 Elagolix is less expensive than depot-leuprolide acetate and nafarelin nasal spray and somewhat more expensive than a goserelin implant.18,19
Elagolix is not approved as a contraceptive. In the Elaris EM-I and -II trials women were advised to use 2 forms of contraception, although pregnancies did occur. There were 6 pregnancies among 475 women taking elagolix 150 mg daily and 2 pregnancies among 477 women taking elagolix 200 mg twice daily.20 Women taking elagolix should be advised to use a contraceptive, but not an estrogen-progestin contraceptive.
Continue to: Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis...
Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
One of the greatest public health tragedies of our era is the opioid misuse epidemic. Hundreds of thousands of deaths have been caused by opioid misuse. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that for the 12-month period ending in May 2020, there were 81,000 opioid-related deaths, the greatest number ever reported in a 12-month period.21 Many authorities believe that in the United States opioid medications have been over-prescribed, contributing to the opioid misuse epidemic. There is little evidence that chronic pelvic pain is optimally managed by chronic treatment with an opioid.22,23 Prescribing opioids to vulnerable individuals to treat chronic pelvic pain may result in opioid dependency and adversely affect the patient’s health. It is best to pledge not to prescribe an opioid medication for a woman with chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In situations when pelvic pain is difficult to control with hormonal therapy and nonopioid pain medications, referral to a specialty pain practice may be warranted.
Post–conservative surgery hormone treatment reduces pelvic pain recurrence
In a meta-analysis of 14 studies that reported on endometriosis recurrence rates following conservative surgery, recurrence (defined as recurrent pelvic pain or an imaging study showing recurrent endometriosis) was significantly reduced with the use of hormone treatment compared with expectant management or placebo treatment.24 The postoperative relative risk of endometriosis recurrence was reduced by 83% with progestin treatment, 64% with estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment, and 38% with GnRH analogue treatment. Overall, the number of patients that needed to be treated to prevent one endometriosis recurrence was 10, assuming a recurrence rate of 25% in the placebo treatment or expectant management groups.
For women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis who develop a recurrence of pelvic pain while on postoperative hormone treatment, it is important for the prescribing clinician to be flexible and consider changing the hormone regimen. For example, if a postoperative patient is treated with a continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive and develops recurrent pain, I will stop the contraceptive and initiate treatment with either NEA or elagolix.
Capitalize on opportunities to improve the medical care of women with endometriosis
Early diagnosis of endometriosis can be facilitated by recognizing that the condition is a common cause of moderate to severe dysmenorrhea. In 5 studies involving 1,187 women, the mean length of time from onset of pelvic pain symptoms to diagnosis of endometriosis was 8.6 years.25 If a woman with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis has not had sufficient pain relief with one brand of continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive, it is best not to prescribe an alternative brand but rather to switch to a progestin-only treatment or a GnRH antagonist. If plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B. ●
Women with endometriosis often present for medical care for one or more of the following health issues: pelvic pain, infertility, and/or an adnexal cyst (endometrioma). For women with moderate or severe pelvic pain and laparoscopically diagnosed endometriosis, hormone therapy is often necessary to achieve maximal long-term reduction in pain and optimize health. I focus on opportunities to optimize hormonal treatment of endometriosis in this editorial.
When plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B
Cyclic or continuous combination estrogen-progestin contraceptives are commonly prescribed to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. Although endometriosis pain may initially improve with estrogen-progestin contraceptives, many women on this medication will eventually report that they have worsening pelvic pain that adversely impacts their daily activities. Surprisingly, clinicians often continue to prescribe estrogen-progestin contraceptives even after the patient reports that the treatment is not effective, and their pain continues to be bothersome.
Patients benefit when they have access to the full range of hormone treatments that have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of moderate to severe pelvic pain caused by endometriosis (TABLE). In the situation where an estrogen-progestin contraceptive is no longer effective at reducing the pelvic pain, I will often offer the patient the option of norethindrone acetate (NEA) or elagolix treatment. My experience is that stopping the estrogen-progestin contraceptive and starting NEA or elagolix will result in a significant decrease in pain symptoms and improvement in the patient’s quality of life.

Other FDA-approved options to treat pelvic pain caused by endometriosis include depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension, depot leuprolide acetate, goserelin implant, and danazol. I do not routinely prescribe depot medroxyprogesterone acetate because some patients report new onset or worsening symptoms of depression on the medication. I prescribe depot-leuprolide acetate less often than in the past, because many patients report moderate to severe hypoestrogenic symptoms on this medication. In women taking depot-leuprolide acetate, moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms can be improved by prescribing NEA pills, but the alternative of norethindrone monotherapy is less expensive. I seldom use goserelin or danazol in my practice. The needle required to place the goserelin implant has a diameter of approximately 1.7 mm (16 gauge) or 2.1 mm (14 gauge), for the 3.6 mg and 10 mg doses, respectively. The large diameter of the needle can cause pain and bruising at the implant site. As a comparison, the progestin subdermal implant needle is approximately 2.1 mm in diameter. Danazol is associated with weight gain, and most women prefer to avoid this side effect.
Continue to: Norethindrone acetate...
Norethindrone acetate
NEA 5 mg daily is approved by the FDA to treat endometriosis.1 NEA was approved at a time when large controlled clinical trials were not routinely required for a medicine to be approved. The data to support NEA treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis is based on cohort studies. In a study of 194 women, median age 21 years with moderate to severe pelvic pain and surgically proven endometriosis, the effect of NEA on pelvic pain was explored.2 The initial dose of NEA was 5 mg daily. If the patient did not achieve a reduction in pelvic pain and amenorrhea on the NEA dose of 5 mg daily, the dose was increased by 2.5 mg every 2 weeks, up to a maximum of 15 mg, until amenorrhea and/or a decrease in pelvic pain was achieved. Ninety-five percent of the women in this cohort had previously been treated with an estrogen-progestin contraceptive or a GnRH antagonist and had discontinued those medications because of inadequate control of pelvic pain or because of side effects of the medication.
In this large cohort, 65% of women reported significant improvement in pelvic pain, with a median pain score of 5 before treatment and 0 following NEA treatment. About 55% of the women reported no side effects. The most commonly reported side effects were weight gain (16%; mean weight gain, 3.1 kg), acne (10%), mood lability (9%), hot flashes (8%), depression (6%), scalp hair loss (4%), headache (4%), nausea (3%), and deepening of the voice (1%). (In this study women could report more than one side effect.)
In another cohort study of 52 women with pelvic pain and surgically confirmed endometriosis, NEA treatment resulted in pain relief in 94% of the women.3 Breakthrough bleeding was a common side effect, reported by 58% of participants. The investigators concluded that NEA treatment was a “cost-effective alternative with relatively mild side effects in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis.” A conclusion which I endorse.
NEA has been reported to effectively treat ovarian endometriomas and rectovaginal endometriosis.4,5 In a cohort of 18 women who had previously had the surgical resection of an ovarian endometriosis cyst and had postoperative recurrence of pelvic pain and ovarian endometriosis, treatment was initiated with an escalating NEA regimen.4 Treatment was initiated with NEA 5 mg daily, with the dosage increased every 2 weeks by 2.5 mg until amenorrhea was established. Most women achieved amenorrhea with NEA 5 mg daily, and 89% had reduced pelvic pain. The investigators reported complete regression of the endometriosis cyst(s) in 74% of the women. In my experience, NEA does not result in complete regression of endometriosis cysts, but it does cause a reduction in cyst diameter and total volume.
In a retrospective cohort study, 61 women with pelvic pain and rectovaginal endometriosis had 5 years of treatment with NEA 2.5 mg or 5.0 mg daily.5 NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in dysmenorrhea, deep dyspareunia, and dyschezia. The most common side effects attributed to NEA treatment were weight gain (30%), vaginal bleeding (23%), decreased libido (11%), headache (9%), bloating or swelling (8%), depression (7%), and acne (5%). In women who had sequential imaging studies, NEA treatment resulted in a decrease in rectovaginal lesion volume, stable disease volume, or an increase in lesion volume in 56%, 32%, and 12% of the women, respectively. The investigators concluded that for women with rectovaginal endometriosis, NEA treatment is a low-cost option for long-term treatment.
In my practice, I do not prescribe NEA at doses greater than 5 mg daily. There are case reports that NEA at a dose of ≥10 mg daily is associated with the development of a hepatic adenoma,6 elevated liver transaminase concentration,7 and jaundice.8 If NEA 5 mg daily is not effective in controlling pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, I stop the NEA and start a GnRH analogue, most often elagolix.
NEA 5 mg is not FDA approved as a contraceptive. However, norethindrone 0.35 mg daily, also known as the “mini-pill”, is approved as a progestin-only contraceptive.9 NEA is rapidly and completely deacetylated to norethindrone, and the disposition of oral NEA is indistinguishable from that of norethindrone.1 Since norethindrone 0.35 mg daily is approved as a contraceptive, it is highly likely that NEA 5 mg has contraceptive properties if taken daily.
Continue to: Elagolix...
Elagolix
Elagolix is FDA approved for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. I reviewed the key studies resulting in FDA approval in the November 2018 issue of
In the Elaris Endometriosis-I study, 872 women with endometriosis and pelvic pain were randomly assigned to treatment with 1 of 2 doses of elagolix (high-dose [200 mg twice daily] and low-dose [150 mg once daily]) or placebo.11 After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in dysmenorrhea pain was reported by 76%, 46%, and 20% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.001 for comparisons of elagolix to placebo). After 3 months of therapy, a clinically meaningful reduction in nonmenstrual pain or decreased or stable use of rescue analgesics was reported by 55%, 50%, and 37% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively (P<.01 low-dose elagolix vs placebo and P<.001 high-dose elagolix vs placebo).
Hot flashes that were severe enough to be reported as an adverse event by the study participants were reported by 42%, 24%, and 7% of the women in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups. Bone density was measured at baseline and after 6 months of treatment. Lumbar bone density changes were -2.61%, -0.32%, and +0.47% and hip femoral neck bone density changes were -1.89%, -0.39%, and +0.02% in the high-dose elagolix, low-dose elagolix, and placebo groups, respectively.
Another large clinical trial of elagolix for the treatment of pelvic pain caused by endometriosis, Elaris EM-II, involving 817 women, produced results very similar to those reported in Elaris EM-I. The elagolix continuation studies, Elaris EM-III and -IV, demonstrated efficacy and safety of elagolix through 12 months of treatment.12
In my 2018 review,10 I noted that elagolix dose adjustment can be utilized to attempt to achieve maximal pain relief with minimal vasomotor symptoms. Elagolix at 200 mg twice daily produces a mean estradiol concentration of 12 pg/mL, whereas elagolix at 150 mg daily resulted in a mean estradiol concentration of 41 pg/mL.13 The estrogen threshold hypothesis posits that in women with endometriosis a stable estradiol concentration of 20 to 30 pg/mL is often associated with decreased pain and fewer vasomotor events.14 To achieve the target estradiol range of 20 to 30 pg/mL, I often initiate elagolix treatment with 200 mg twice daily. This enables a rapid onset of amenorrhea and a reduction in pelvic pain. Once amenorrhea has been achieved and a decrease in pelvic pain has occurred, I adjust the dose downward to 200 mg twice daily on even calendar days of each month and 200 mg once daily on odd calendar days each month. Some women will have continued pain relief and amenorrhea when the dose is further decreased to 200 mg once daily. If bothersome bleeding recurs and/or pain symptoms increase in severity, the dose can be increased to 200 mg twice daily or an alternating regimen of 200 mg twice daily and 200 mg once daily, every 2 days. An alternative to dose adjustment is to combine elagolix with NEA, which can reduce the severity of hot flashes and reduce bone loss caused by hypoestrogenism.15,16
Health insurers and pharmacy benefits managers may require a prior authorization before approving and dispensing elagolix. The prior authorization process can be burdensome for clinicians, consuming limited healthcare resources, contributing to burnout and frustrating patients.17 Elagolix is less expensive than depot-leuprolide acetate and nafarelin nasal spray and somewhat more expensive than a goserelin implant.18,19
Elagolix is not approved as a contraceptive. In the Elaris EM-I and -II trials women were advised to use 2 forms of contraception, although pregnancies did occur. There were 6 pregnancies among 475 women taking elagolix 150 mg daily and 2 pregnancies among 477 women taking elagolix 200 mg twice daily.20 Women taking elagolix should be advised to use a contraceptive, but not an estrogen-progestin contraceptive.
Continue to: Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis...
Do not use opioids to treat chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis
One of the greatest public health tragedies of our era is the opioid misuse epidemic. Hundreds of thousands of deaths have been caused by opioid misuse. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that for the 12-month period ending in May 2020, there were 81,000 opioid-related deaths, the greatest number ever reported in a 12-month period.21 Many authorities believe that in the United States opioid medications have been over-prescribed, contributing to the opioid misuse epidemic. There is little evidence that chronic pelvic pain is optimally managed by chronic treatment with an opioid.22,23 Prescribing opioids to vulnerable individuals to treat chronic pelvic pain may result in opioid dependency and adversely affect the patient’s health. It is best to pledge not to prescribe an opioid medication for a woman with chronic pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. In situations when pelvic pain is difficult to control with hormonal therapy and nonopioid pain medications, referral to a specialty pain practice may be warranted.
Post–conservative surgery hormone treatment reduces pelvic pain recurrence
In a meta-analysis of 14 studies that reported on endometriosis recurrence rates following conservative surgery, recurrence (defined as recurrent pelvic pain or an imaging study showing recurrent endometriosis) was significantly reduced with the use of hormone treatment compared with expectant management or placebo treatment.24 The postoperative relative risk of endometriosis recurrence was reduced by 83% with progestin treatment, 64% with estrogen-progestin contraceptive treatment, and 38% with GnRH analogue treatment. Overall, the number of patients that needed to be treated to prevent one endometriosis recurrence was 10, assuming a recurrence rate of 25% in the placebo treatment or expectant management groups.
For women with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis who develop a recurrence of pelvic pain while on postoperative hormone treatment, it is important for the prescribing clinician to be flexible and consider changing the hormone regimen. For example, if a postoperative patient is treated with a continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive and develops recurrent pain, I will stop the contraceptive and initiate treatment with either NEA or elagolix.
Capitalize on opportunities to improve the medical care of women with endometriosis
Early diagnosis of endometriosis can be facilitated by recognizing that the condition is a common cause of moderate to severe dysmenorrhea. In 5 studies involving 1,187 women, the mean length of time from onset of pelvic pain symptoms to diagnosis of endometriosis was 8.6 years.25 If a woman with pelvic pain caused by endometriosis has not had sufficient pain relief with one brand of continuous estrogen-progestin contraceptive, it is best not to prescribe an alternative brand but rather to switch to a progestin-only treatment or a GnRH antagonist. If plan A is not working, move expeditiously to plan B. ●
- Aygestin [package insert]. Barr Laboratories: Pomona, NY; 2007.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Karacan M. Effect of norethindrone acetate in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis. Int J Fertil Womens Med. 1998;43:24-27.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Anopa J, Charles C, et al. Medical management of recurrent endometrioma with long-term norethindrone acetate. Int J Women Health. 2012;4:149-154.
- Morotti M, Venturini PL, Biscaldi E, et al. Efficacy and acceptability of long-term norethindrone acetate for the treatment of rectovaginal endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Repro Biol. 2017;213:4-10.
- Brady PC, Missmer SA, Laufer MR. Hepatic adenomas in adolescents and young women with endometriosis treated with norethindrone acetate. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2017;30:422-424.
- Choudhary NS, Bodh V, Chaudhari S, et al. Norethisterone related drug induced liver injury: a series of 3 cases. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;7:266- 268.
- Perez-Mera RA, Shields CE. Jaundice associated with norethindrone acetate therapy. N Engl J Med. 1962;267:1137-1138.
- Camila [package insert]. Mayne Pharma Inc: Greenville, NC; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Elagolix: a new treatment for pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. OBG Manag. 2018;30:10,12-14, 20.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:147-160.
- Orilissa [package insert]. AbbVie Inc; North Chicago, IL; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Hormonal treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:740-745.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Gallagher JS, Missmer SA, Hornstein MD, et al. Long-term effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and add-back in adolescent endometriosis. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2018;31:376- 381.
- Miller A, Shor R, Waites T, et al. Prior authorization reform for better patient care. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:1937-1939.
- Depot-leuprolide acetate. Good Rx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
- Goserelin. Good Rx website. https://www .goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID19. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020 /p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html. Reviewed December 18, 2020. Accessed March 24, 2021.
- Till SR, As-Sanie S. 3 cases of chronic pelvic pain with nonsurgical, nonopioid therapies. OBG Manag. 2018;30:41-48.
- Steele A. Opioid use and depression in chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:491-501.
- Zakhari A, Delpero E, McKeown S, et al. Endometriosis recurrence following post-operative hormonal suppression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27:96- 107.
- Barbieri RL. Why are there delays in the diagnosis of endometriosis? OBG Manag. 2017;29:8, 10-11, 16.
- Aygestin [package insert]. Barr Laboratories: Pomona, NY; 2007.
- Kaser DJ, Missmer SA, Berry KF, et al. Use of norethindrone acetate alone for postoperative suppression of endometriosis symptoms. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2012;25:105-108.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Karacan M. Effect of norethindrone acetate in the treatment of symptomatic endometriosis. Int J Fertil Womens Med. 1998;43:24-27.
- Muneyyirci-Delale O, Anopa J, Charles C, et al. Medical management of recurrent endometrioma with long-term norethindrone acetate. Int J Women Health. 2012;4:149-154.
- Morotti M, Venturini PL, Biscaldi E, et al. Efficacy and acceptability of long-term norethindrone acetate for the treatment of rectovaginal endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Repro Biol. 2017;213:4-10.
- Brady PC, Missmer SA, Laufer MR. Hepatic adenomas in adolescents and young women with endometriosis treated with norethindrone acetate. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2017;30:422-424.
- Choudhary NS, Bodh V, Chaudhari S, et al. Norethisterone related drug induced liver injury: a series of 3 cases. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017;7:266- 268.
- Perez-Mera RA, Shields CE. Jaundice associated with norethindrone acetate therapy. N Engl J Med. 1962;267:1137-1138.
- Camila [package insert]. Mayne Pharma Inc: Greenville, NC; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Elagolix: a new treatment for pelvic pain caused by endometriosis. OBG Manag. 2018;30:10,12-14, 20.
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Surrey E, Taylor HS, Giudice L, et al. Long-term outcomes of elagolix in women with endometriosis: results from two extension studies. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:147-160.
- Orilissa [package insert]. AbbVie Inc; North Chicago, IL; 2018.
- Barbieri RL. Hormonal treatment of endometriosis: the estrogen threshold hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:740-745.
- Hornstein MD, Surrey ES, Weisberg GW, et al. Leuprolide acetate depot and hormonal add-back in endometriosis: a 12-month study. Lupron Add-Back Study Group. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;91:16-24.
- Gallagher JS, Missmer SA, Hornstein MD, et al. Long-term effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and add-back in adolescent endometriosis. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2018;31:376- 381.
- Miller A, Shor R, Waites T, et al. Prior authorization reform for better patient care. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:1937-1939.
- Depot-leuprolide acetate. Good Rx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
- Goserelin. Good Rx website. https://www .goodrx.com/. Accessed January 22, 2021
- Taylor HS, Giudice LC, Lessey BA, et al. Treatment of endometriosis-associated pain with elagolix, an oral GnRH antagonist. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:28-40.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overdose deaths accelerating during COVID19. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2020 /p1218-overdose-deaths-covid-19.html. Reviewed December 18, 2020. Accessed March 24, 2021.
- Till SR, As-Sanie S. 3 cases of chronic pelvic pain with nonsurgical, nonopioid therapies. OBG Manag. 2018;30:41-48.
- Steele A. Opioid use and depression in chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:491-501.
- Zakhari A, Delpero E, McKeown S, et al. Endometriosis recurrence following post-operative hormonal suppression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27:96- 107.
- Barbieri RL. Why are there delays in the diagnosis of endometriosis? OBG Manag. 2017;29:8, 10-11, 16.
Changes required for gynecologic surgeons to achieve greater pay equity
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Delay surgery by 7 weeks after COVID-19 diagnosis, study shows
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven weeks appears to be the ideal amount of time to delay surgery, when possible, after someone tests positive for COVID-19, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Risk for death was about 3.5 to 4 times higher in the first 6 weeks after surgery among more than 3,000 people with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis compared with patients without COVID-19. After 7 weeks, the 30-day mortality rate dropped to a baseline level.
The study was published online March 9 in Anaesthesia.
Surgery should be further delayed for people who remain symptomatic at 7 weeks post diagnosis, lead author Dmitri Nepogodiev, MBChB, said in an interview.
“In this group we recommend waiting until COVID-19 symptoms resolve, if possible. However, our study did not capture specific data on long COVID … so we are unable to make specific recommendations for this group,” said Dr. Nepogodiev, research fellow at the NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham (England).
“This should be an area for future research,” he added.
The international, multicenter, prospective cohort study is notable for its sheer size – more than 15,000 investigators reported outcomes for 140,231 surgical patients from 1,674 hospitals across 116 countries. In total, 2.2% of these patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 prior to surgery.
Surgery of any type performed in October 2020 was assessed. A greater proportion of patients with a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis had emergency surgery, 44%, compared with 30% of people who never had a COVID-19 diagnosis.
Most patients were asymptomatic at the time of surgery, either because they never experienced COVID-19 symptoms or their symptoms resolved. The 30-day mortality rate was the primary outcome.
Death rates among surgical patients with preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis
Comparing the timing of surgery after COVID-19 diagnosis vs. 30-day mortality yielded the following results:
- 0 to 2 weeks – 9.1% mortality.
- 3 to 4 weeks – 6.9%.
- 5 to 6 weeks – 5.5%.
- 7 weeks or longer – 2.0%..
For comparison, the 30-day mortality rate for surgical patients without a preoperative COVID-19 diagnosis was 1.4%. A COVID-19 diagnosis more than 7 weeks before surgery did not make a significant difference on outcomes.
The ‘why’ remains unknown
The reasons for the association between a COVID-19 diagnosis and higher postoperative death rates remain unknown. However, Dr. Nepogodiev speculated that it could be related to “some degree of lung injury, even if patients are initially asymptomatic.”
Intubation and mechanical ventilation during surgery could exacerbate the existing lung injury, he said, thereby leading to more severe COVID-19.
In fact, Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues found that postoperative pulmonary complications followed a pattern similar to the findings on death. They reported higher rates of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and unexpected reventilation in the first 6 weeks following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Again, at 7 weeks and beyond, the rates returned to be relatively the same as those for people who never had COVID-19.
“Waiting for 7 or more weeks may allow time for the initial COVID-19 injury to resolve,” Dr. Nepogodiev said.
‘An important study’
“This is an important study of postoperative mortality among patients recovered from COVID-19,” Adrian Diaz, MD, MPH, said in an interview when asked to comment.
The large cohort and numerous practice settings are among the strengths of the research, said Dr. Diaz, of the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor. He was lead author of a June 2020 review article on elective surgery in the time of COVID-19, published in The American Journal of Surgery.
“As with nearly all studies of this nature, results must be interpreted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients. However, this study does add important information for patients and providers in helping them have an informed discussion on the timing of surgery,” said Dr. Diaz, a fellow in the Center for Healthcare Outcomes and Policy and a resident in general surgery at the Ohio State University, Columbus.
Dr. Nepogodiev and colleagues included both urgent and elective surgeries in the study. Dr. Diaz said this was a potential limitation because emergency operations “should never be delayed, by definition.” Lack of indications for the surgeries and information on cause of death were additional limitations.
Future research should evaluate any benefit in delaying surgery longer than 7 or more weeks, Dr. Diaz added, perhaps looking specifically at 10, 12, or 14 weeks, or considering outcomes as a continuous variable. This would help health care providers “garner more insight into risk and benefits of delaying surgery beyond 7 weeks.”
Dr. Nepogodiev and Dr. Diaz disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The study had multiple funding sources, including the National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit, the Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons, the British Association of Surgical Oncology, and Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.