User login
Restriction of Foley catheters in older trauma patients improved outcomes
and led to earlier discharge, findings from a study revealed. The results of the study were reported in an abstract scheduled for release at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The meeting was canceled because of COVID-19.
“We reduced the use of Foley catheters in our target population by more than 50%, which led to a decrease in the rate of hospital-acquired UTI and positively affected other perioperative outcomes,” reported Sanjit R. Konda, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with New York University Langone Health.
The quality initiative was introduced about 2 years ago specifically to reduce the risk of UTI in older patients admitted for femur or hip fractures. Previously at the level 1 trauma center where this quality initiative was introduced, placement of Foley catheters in these types of patients had been routine.
After the policy change, Foley catheters were only offered to these trauma patients 55 years of age or older when more than three episodes or urinary retention had been documented with a bladder scan. Urinary retention was defined as a volume of at least 600 mL.
When outcomes in 184 patients treated in the 15 months after the policy change were compared with 393 treated in the prior 38 months, Foley catheter use was substantially and significantly reduced (43.5% vs. 95.5%; P < .001), Dr. Konda said in an interview.
Although the lower rate of UTI following the policy change fell short of statistical significance (10.33% vs. 14.5%; P = .167), the policy change was associated with a decreased time to surgery (33.27 vs. 38.54 hours; P = .001), shorter length of stay (6.89 vs. 8.34 days; P < .001), and higher rate of home discharge (22.8% vs. 15.6%; P = .038).
When those who avoided a Foley catheter were compared with those who did not after the policy change, there was a significant reduction in UTI (4.81% vs. 17.4%; P = .014). In addition, patients who avoided a Foley catheter had a decreased time to surgery (P = .014), shorter length of stay (P < .001) and an almost 900% greater likelihood of home discharge (odds ratio, 9.9; P < .001).
“This quality initiative does increase the number of bladder scans required, meaning more work for nurses, but the program was developed in collaboration with our nursing staff, who were supportive of the goals,” Dr. Konda reported.
Reducing the incidence of UTI is an important initiative because the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other third-party payers employ this as a quality metric, according to Dr. Konda. This explains why hospital administrators generally embrace effective strategies to reduce UTI rates.
The improvement in outcomes, including the reduction in UTIs and length of stay, has cost implications, which will be evaluated in a future analysis, according to Dr. Konda.
Although this quality initiative was undertaken in a level 1 trauma center, Dr. Konda believes the same principles can be applied to other settings.
Jennifer A. Meddings, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, agreed. Active in the evaluation of strategies to reduce hospital-acquired complications, Dr. Meddings published a study of procedural appropriateness ratings to guide strategies for improving the likelihood that catheters are employed only when needed (BMJ Qual Saf. 2019;28:56-66).
“In addition to avoiding UTI, reducing unnecessary placement of Foley catheters also eliminates the risk of trauma to the urinary tract,” Dr. Meddings said. This is a complication that is not well appreciated because the trauma is not always documented, according to Dr. Meddings, who believes increased risk of both UTI and urinary tract trauma should discourage use of Foley catheters when there is not a specific indication.
Although there are criteria other than excess bladder volume to determine when to consider a Foley catheter, Dr. Meddings encourages any systematic approach that increases the likelihood that catheters are not placed unnecessarily. She emphasized that a hip fracture by itself “is not a criterion for catheterization.”
Dr. Konda reported a financial relationship with Stryker.
and led to earlier discharge, findings from a study revealed. The results of the study were reported in an abstract scheduled for release at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The meeting was canceled because of COVID-19.
“We reduced the use of Foley catheters in our target population by more than 50%, which led to a decrease in the rate of hospital-acquired UTI and positively affected other perioperative outcomes,” reported Sanjit R. Konda, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with New York University Langone Health.
The quality initiative was introduced about 2 years ago specifically to reduce the risk of UTI in older patients admitted for femur or hip fractures. Previously at the level 1 trauma center where this quality initiative was introduced, placement of Foley catheters in these types of patients had been routine.
After the policy change, Foley catheters were only offered to these trauma patients 55 years of age or older when more than three episodes or urinary retention had been documented with a bladder scan. Urinary retention was defined as a volume of at least 600 mL.
When outcomes in 184 patients treated in the 15 months after the policy change were compared with 393 treated in the prior 38 months, Foley catheter use was substantially and significantly reduced (43.5% vs. 95.5%; P < .001), Dr. Konda said in an interview.
Although the lower rate of UTI following the policy change fell short of statistical significance (10.33% vs. 14.5%; P = .167), the policy change was associated with a decreased time to surgery (33.27 vs. 38.54 hours; P = .001), shorter length of stay (6.89 vs. 8.34 days; P < .001), and higher rate of home discharge (22.8% vs. 15.6%; P = .038).
When those who avoided a Foley catheter were compared with those who did not after the policy change, there was a significant reduction in UTI (4.81% vs. 17.4%; P = .014). In addition, patients who avoided a Foley catheter had a decreased time to surgery (P = .014), shorter length of stay (P < .001) and an almost 900% greater likelihood of home discharge (odds ratio, 9.9; P < .001).
“This quality initiative does increase the number of bladder scans required, meaning more work for nurses, but the program was developed in collaboration with our nursing staff, who were supportive of the goals,” Dr. Konda reported.
Reducing the incidence of UTI is an important initiative because the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other third-party payers employ this as a quality metric, according to Dr. Konda. This explains why hospital administrators generally embrace effective strategies to reduce UTI rates.
The improvement in outcomes, including the reduction in UTIs and length of stay, has cost implications, which will be evaluated in a future analysis, according to Dr. Konda.
Although this quality initiative was undertaken in a level 1 trauma center, Dr. Konda believes the same principles can be applied to other settings.
Jennifer A. Meddings, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, agreed. Active in the evaluation of strategies to reduce hospital-acquired complications, Dr. Meddings published a study of procedural appropriateness ratings to guide strategies for improving the likelihood that catheters are employed only when needed (BMJ Qual Saf. 2019;28:56-66).
“In addition to avoiding UTI, reducing unnecessary placement of Foley catheters also eliminates the risk of trauma to the urinary tract,” Dr. Meddings said. This is a complication that is not well appreciated because the trauma is not always documented, according to Dr. Meddings, who believes increased risk of both UTI and urinary tract trauma should discourage use of Foley catheters when there is not a specific indication.
Although there are criteria other than excess bladder volume to determine when to consider a Foley catheter, Dr. Meddings encourages any systematic approach that increases the likelihood that catheters are not placed unnecessarily. She emphasized that a hip fracture by itself “is not a criterion for catheterization.”
Dr. Konda reported a financial relationship with Stryker.
and led to earlier discharge, findings from a study revealed. The results of the study were reported in an abstract scheduled for release at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The meeting was canceled because of COVID-19.
“We reduced the use of Foley catheters in our target population by more than 50%, which led to a decrease in the rate of hospital-acquired UTI and positively affected other perioperative outcomes,” reported Sanjit R. Konda, MD, an orthopedic surgeon with New York University Langone Health.
The quality initiative was introduced about 2 years ago specifically to reduce the risk of UTI in older patients admitted for femur or hip fractures. Previously at the level 1 trauma center where this quality initiative was introduced, placement of Foley catheters in these types of patients had been routine.
After the policy change, Foley catheters were only offered to these trauma patients 55 years of age or older when more than three episodes or urinary retention had been documented with a bladder scan. Urinary retention was defined as a volume of at least 600 mL.
When outcomes in 184 patients treated in the 15 months after the policy change were compared with 393 treated in the prior 38 months, Foley catheter use was substantially and significantly reduced (43.5% vs. 95.5%; P < .001), Dr. Konda said in an interview.
Although the lower rate of UTI following the policy change fell short of statistical significance (10.33% vs. 14.5%; P = .167), the policy change was associated with a decreased time to surgery (33.27 vs. 38.54 hours; P = .001), shorter length of stay (6.89 vs. 8.34 days; P < .001), and higher rate of home discharge (22.8% vs. 15.6%; P = .038).
When those who avoided a Foley catheter were compared with those who did not after the policy change, there was a significant reduction in UTI (4.81% vs. 17.4%; P = .014). In addition, patients who avoided a Foley catheter had a decreased time to surgery (P = .014), shorter length of stay (P < .001) and an almost 900% greater likelihood of home discharge (odds ratio, 9.9; P < .001).
“This quality initiative does increase the number of bladder scans required, meaning more work for nurses, but the program was developed in collaboration with our nursing staff, who were supportive of the goals,” Dr. Konda reported.
Reducing the incidence of UTI is an important initiative because the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other third-party payers employ this as a quality metric, according to Dr. Konda. This explains why hospital administrators generally embrace effective strategies to reduce UTI rates.
The improvement in outcomes, including the reduction in UTIs and length of stay, has cost implications, which will be evaluated in a future analysis, according to Dr. Konda.
Although this quality initiative was undertaken in a level 1 trauma center, Dr. Konda believes the same principles can be applied to other settings.
Jennifer A. Meddings, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, agreed. Active in the evaluation of strategies to reduce hospital-acquired complications, Dr. Meddings published a study of procedural appropriateness ratings to guide strategies for improving the likelihood that catheters are employed only when needed (BMJ Qual Saf. 2019;28:56-66).
“In addition to avoiding UTI, reducing unnecessary placement of Foley catheters also eliminates the risk of trauma to the urinary tract,” Dr. Meddings said. This is a complication that is not well appreciated because the trauma is not always documented, according to Dr. Meddings, who believes increased risk of both UTI and urinary tract trauma should discourage use of Foley catheters when there is not a specific indication.
Although there are criteria other than excess bladder volume to determine when to consider a Foley catheter, Dr. Meddings encourages any systematic approach that increases the likelihood that catheters are not placed unnecessarily. She emphasized that a hip fracture by itself “is not a criterion for catheterization.”
Dr. Konda reported a financial relationship with Stryker.
FROM AAOS 2020
COVID-19-related inflammatory condition more common in black children in small study
More evidence has linked the Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children to COVID-19 and suggests that black children have a greater risk of the condition, according to a study published in the BMJ.
A small observational study in Paris found more than half of the 21 children who were admitted for the condition at the city’s pediatric hospital for COVID-19 patients were of African ancestry.
“The observation of a higher proportion of patients of African ancestry is consistent with recent findings, suggesting an effect of either social and living conditions or genetic susceptibility,” wrote Julie Toubiana, MD, PhD, of the University of Paris and the Pasteur Institute, and colleagues.
The findings did not surprise Edward M. Behrens, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, whose institution has seen similar disparities that he attributes to social disadvantages.
“Infection rate will be higher in vulnerable populations that are less able to socially distance, have disproportionate numbers of essential workers, and have less access to health care and other resources,” Dr. Behrens said in an interview. “While there may be a role for genetics, environment – including social disparities – is almost certainly playing a role.”
Although the study’s small size is a limitation, he said, “the features described seem to mirror the experience of our center and what has been discussed more broadly amongst U.S. physicians.”
Byron Whyte, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in southeast Washington, found the differences in race interesting, but said the study was too small to draw any conclusions or generalize to the United States. But social disparities related to race are likely similar in France as they are in the United States, he said.
The prospective observational study assessed the clinical and demographic characteristics of all patients under age 18 who met the criteria for Kawasaki disease and were admitted between April 27 and May 20 to the Necker Hospital for Sick Children in Paris.
The 21 children had an average age of 8 years (ranging from 3 to 16), and 57% had at least one parent from sub-Saharan Africa or a Caribbean island; 14% had parents from Asia (two from China and one from Sri Lanka). The authors noted in their discussion that past U.S. and U.K. studies of Kawasaki disease have found a 2.5 times greater risk in Asian-American children and 1.5 times greater risk in African-American children compared with children with European ancestry.
Most of the patients (81%) needed intensive care, with 57% presenting with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome and 67% with myocarditis. Dr. Toubiana and associates also noted that “gastrointestinal symptoms were also unusually common, affecting all of our 21 patients.”
Only nine of the children reported having symptoms of a viral-like illness when they were admitted, primarily headache, cough, coryza, and fever, plus anosmia in one child. Among those children, the Kawasaki symptoms began a median 45 days after onset of the viral symptoms (range 18-79 days).
Only two children showed no positive test result for current COVID-19 infection or antibodies. Eight (38%) of the children had positive PCR tests for SARS-CoV2, and 19 (90%) had positive tests for IgG antibodies. The two patients with both negative tests did not require intensive care and did not have myocarditis.
About half the patients (52%) met all the criteria of Kawasaki disease, and the other 10 had “incomplete Kawasaki disease.” The most common Kawasaki symptoms were the polymorphous skin rash, occurring in 76% of the patients, changes to the lips and oral cavity (76%), and bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection (81%). Three patients (14%) had pleural effusion, and 10 of them (48%) had pericardial effusion, Dr. Toubiana and associates reported.
But Dr. Behrens said he disagrees with the assertion that the illness described in the paper and what he is seeing at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia is related to Kawasaki disease.
“Most experts here in the U.S. seem to agree this is not Kawasaki disease, but a distinct clinical syndrome called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, or MIS-C, that seems to have some overlap with the most nonspecific features of Kawasaki disease,” said Dr. Behrens, who is the Joseph Lee Hollander Chair in Pediatric Rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has coauthored a study currently under review and available as a preprint soon that examines the biologic mechanisms underlying MIS-C.
Neither Dr. Behrens nor Dr. Whyte believed the findings had clinical implications that might change practice, but Dr. Whyte said he will be paying closer attention to the black children he treats – 99% of his practice – who are recovering from COVID-19.
“And, because we know that the concerns of African Americans are often overlooked in health care,” Dr. Whyte said, physicians should “pay a little more attention to symptom reporting on those kids, since there is a possibility that those kids would need hospitalization.”
All the patients in the study were treated with intravenous immunoglobulin, and corticosteroids were administered to 10 of them (48%). Their median hospital stay was 8 days (5 days in intensive care), and all were discharged without any deaths.
“Only one patient had symptoms suggestive of acute covid-19 and most had positive serum test results for IgG antibodies, suggesting that the development of Kawasaki disease in these patients is more likely to be the result of a postviral immunological reaction,” Dr. Toubiana and associates said.
The research received no external funding, and neither the authors nor other quoted physicians had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Toubiana J et al. BMJ. 2020 Jun 3, doi: 10.1136 bmj.m2094.
More evidence has linked the Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children to COVID-19 and suggests that black children have a greater risk of the condition, according to a study published in the BMJ.
A small observational study in Paris found more than half of the 21 children who were admitted for the condition at the city’s pediatric hospital for COVID-19 patients were of African ancestry.
“The observation of a higher proportion of patients of African ancestry is consistent with recent findings, suggesting an effect of either social and living conditions or genetic susceptibility,” wrote Julie Toubiana, MD, PhD, of the University of Paris and the Pasteur Institute, and colleagues.
The findings did not surprise Edward M. Behrens, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, whose institution has seen similar disparities that he attributes to social disadvantages.
“Infection rate will be higher in vulnerable populations that are less able to socially distance, have disproportionate numbers of essential workers, and have less access to health care and other resources,” Dr. Behrens said in an interview. “While there may be a role for genetics, environment – including social disparities – is almost certainly playing a role.”
Although the study’s small size is a limitation, he said, “the features described seem to mirror the experience of our center and what has been discussed more broadly amongst U.S. physicians.”
Byron Whyte, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in southeast Washington, found the differences in race interesting, but said the study was too small to draw any conclusions or generalize to the United States. But social disparities related to race are likely similar in France as they are in the United States, he said.
The prospective observational study assessed the clinical and demographic characteristics of all patients under age 18 who met the criteria for Kawasaki disease and were admitted between April 27 and May 20 to the Necker Hospital for Sick Children in Paris.
The 21 children had an average age of 8 years (ranging from 3 to 16), and 57% had at least one parent from sub-Saharan Africa or a Caribbean island; 14% had parents from Asia (two from China and one from Sri Lanka). The authors noted in their discussion that past U.S. and U.K. studies of Kawasaki disease have found a 2.5 times greater risk in Asian-American children and 1.5 times greater risk in African-American children compared with children with European ancestry.
Most of the patients (81%) needed intensive care, with 57% presenting with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome and 67% with myocarditis. Dr. Toubiana and associates also noted that “gastrointestinal symptoms were also unusually common, affecting all of our 21 patients.”
Only nine of the children reported having symptoms of a viral-like illness when they were admitted, primarily headache, cough, coryza, and fever, plus anosmia in one child. Among those children, the Kawasaki symptoms began a median 45 days after onset of the viral symptoms (range 18-79 days).
Only two children showed no positive test result for current COVID-19 infection or antibodies. Eight (38%) of the children had positive PCR tests for SARS-CoV2, and 19 (90%) had positive tests for IgG antibodies. The two patients with both negative tests did not require intensive care and did not have myocarditis.
About half the patients (52%) met all the criteria of Kawasaki disease, and the other 10 had “incomplete Kawasaki disease.” The most common Kawasaki symptoms were the polymorphous skin rash, occurring in 76% of the patients, changes to the lips and oral cavity (76%), and bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection (81%). Three patients (14%) had pleural effusion, and 10 of them (48%) had pericardial effusion, Dr. Toubiana and associates reported.
But Dr. Behrens said he disagrees with the assertion that the illness described in the paper and what he is seeing at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia is related to Kawasaki disease.
“Most experts here in the U.S. seem to agree this is not Kawasaki disease, but a distinct clinical syndrome called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, or MIS-C, that seems to have some overlap with the most nonspecific features of Kawasaki disease,” said Dr. Behrens, who is the Joseph Lee Hollander Chair in Pediatric Rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has coauthored a study currently under review and available as a preprint soon that examines the biologic mechanisms underlying MIS-C.
Neither Dr. Behrens nor Dr. Whyte believed the findings had clinical implications that might change practice, but Dr. Whyte said he will be paying closer attention to the black children he treats – 99% of his practice – who are recovering from COVID-19.
“And, because we know that the concerns of African Americans are often overlooked in health care,” Dr. Whyte said, physicians should “pay a little more attention to symptom reporting on those kids, since there is a possibility that those kids would need hospitalization.”
All the patients in the study were treated with intravenous immunoglobulin, and corticosteroids were administered to 10 of them (48%). Their median hospital stay was 8 days (5 days in intensive care), and all were discharged without any deaths.
“Only one patient had symptoms suggestive of acute covid-19 and most had positive serum test results for IgG antibodies, suggesting that the development of Kawasaki disease in these patients is more likely to be the result of a postviral immunological reaction,” Dr. Toubiana and associates said.
The research received no external funding, and neither the authors nor other quoted physicians had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Toubiana J et al. BMJ. 2020 Jun 3, doi: 10.1136 bmj.m2094.
More evidence has linked the Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children to COVID-19 and suggests that black children have a greater risk of the condition, according to a study published in the BMJ.
A small observational study in Paris found more than half of the 21 children who were admitted for the condition at the city’s pediatric hospital for COVID-19 patients were of African ancestry.
“The observation of a higher proportion of patients of African ancestry is consistent with recent findings, suggesting an effect of either social and living conditions or genetic susceptibility,” wrote Julie Toubiana, MD, PhD, of the University of Paris and the Pasteur Institute, and colleagues.
The findings did not surprise Edward M. Behrens, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, whose institution has seen similar disparities that he attributes to social disadvantages.
“Infection rate will be higher in vulnerable populations that are less able to socially distance, have disproportionate numbers of essential workers, and have less access to health care and other resources,” Dr. Behrens said in an interview. “While there may be a role for genetics, environment – including social disparities – is almost certainly playing a role.”
Although the study’s small size is a limitation, he said, “the features described seem to mirror the experience of our center and what has been discussed more broadly amongst U.S. physicians.”
Byron Whyte, MD, a pediatrician in private practice in southeast Washington, found the differences in race interesting, but said the study was too small to draw any conclusions or generalize to the United States. But social disparities related to race are likely similar in France as they are in the United States, he said.
The prospective observational study assessed the clinical and demographic characteristics of all patients under age 18 who met the criteria for Kawasaki disease and were admitted between April 27 and May 20 to the Necker Hospital for Sick Children in Paris.
The 21 children had an average age of 8 years (ranging from 3 to 16), and 57% had at least one parent from sub-Saharan Africa or a Caribbean island; 14% had parents from Asia (two from China and one from Sri Lanka). The authors noted in their discussion that past U.S. and U.K. studies of Kawasaki disease have found a 2.5 times greater risk in Asian-American children and 1.5 times greater risk in African-American children compared with children with European ancestry.
Most of the patients (81%) needed intensive care, with 57% presenting with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome and 67% with myocarditis. Dr. Toubiana and associates also noted that “gastrointestinal symptoms were also unusually common, affecting all of our 21 patients.”
Only nine of the children reported having symptoms of a viral-like illness when they were admitted, primarily headache, cough, coryza, and fever, plus anosmia in one child. Among those children, the Kawasaki symptoms began a median 45 days after onset of the viral symptoms (range 18-79 days).
Only two children showed no positive test result for current COVID-19 infection or antibodies. Eight (38%) of the children had positive PCR tests for SARS-CoV2, and 19 (90%) had positive tests for IgG antibodies. The two patients with both negative tests did not require intensive care and did not have myocarditis.
About half the patients (52%) met all the criteria of Kawasaki disease, and the other 10 had “incomplete Kawasaki disease.” The most common Kawasaki symptoms were the polymorphous skin rash, occurring in 76% of the patients, changes to the lips and oral cavity (76%), and bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection (81%). Three patients (14%) had pleural effusion, and 10 of them (48%) had pericardial effusion, Dr. Toubiana and associates reported.
But Dr. Behrens said he disagrees with the assertion that the illness described in the paper and what he is seeing at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia is related to Kawasaki disease.
“Most experts here in the U.S. seem to agree this is not Kawasaki disease, but a distinct clinical syndrome called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, or MIS-C, that seems to have some overlap with the most nonspecific features of Kawasaki disease,” said Dr. Behrens, who is the Joseph Lee Hollander Chair in Pediatric Rheumatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has coauthored a study currently under review and available as a preprint soon that examines the biologic mechanisms underlying MIS-C.
Neither Dr. Behrens nor Dr. Whyte believed the findings had clinical implications that might change practice, but Dr. Whyte said he will be paying closer attention to the black children he treats – 99% of his practice – who are recovering from COVID-19.
“And, because we know that the concerns of African Americans are often overlooked in health care,” Dr. Whyte said, physicians should “pay a little more attention to symptom reporting on those kids, since there is a possibility that those kids would need hospitalization.”
All the patients in the study were treated with intravenous immunoglobulin, and corticosteroids were administered to 10 of them (48%). Their median hospital stay was 8 days (5 days in intensive care), and all were discharged without any deaths.
“Only one patient had symptoms suggestive of acute covid-19 and most had positive serum test results for IgG antibodies, suggesting that the development of Kawasaki disease in these patients is more likely to be the result of a postviral immunological reaction,” Dr. Toubiana and associates said.
The research received no external funding, and neither the authors nor other quoted physicians had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Toubiana J et al. BMJ. 2020 Jun 3, doi: 10.1136 bmj.m2094.
FROM BMJ
COVID-19: Use these strategies to help parents with and without special needs children
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Most people can cope, to some degree, with the multiple weeks of social distancing and stressors related to the pandemic. But what if those stressors became a way of life for a year – or longer? What sorts of skills would be essential not only to survive but to have a renewed sense of resilience?
I know of one group that has had experiences that mirror the challenges faced by the parents of children: the parents of special needs children. As I argued previously, those parents have faced many of the challenges presented by COVID-19. Among those challenges are social distancing and difficulty accessing everyday common experiences. These parents know that they have to manage more areas of their children’s rearing than do their counterparts.
In addition to having to plan for how to deal with acute urgent or emergent medical situations involving their special needs children, these parents also must prepare for the long-term effects of managing children who require ongoing daily care, attention, and dedication.
These strategies can help the parents of special needs kids find a sense of mastery and comfort. The hope is that, after practicing them for long periods of time, the strategies become second nature.
Here are several strategies that might help patients with children during this pandemic:
- Take time to reset: Sometimes it is helpful for parents to take a minute away from a difficult impasse with their kids to reset and take their own “time out.” A few seconds of mental time away from the “scene” provides space and a mental reminder that the minute that just happened is finite, and that a whole new one is coming up next. The break provides a sense of hope. This cognitive reframing could be practiced often.
- Re-enter the challenging scene with a warm voice: Parents model for their children, but they also are telling their own brains that they, too, can calm down. This approach also de-escalates the situation and allows children to get used to hearing directions from someone who is in control – without hostility or irritability.
- Keep a sense of humor; it might come in handy: This is especially the case when tension is in the home, or when facing a set of challenging bad news. As an example, consider how some situations are so repetitive that they border on the ridiculous – such as a grown child having a tantrum at a store. Encourage the children to give themselves permission to cry first so they can laugh second, and then move on.
- Establish a routine for children that is self-reinforcing, and allows for together and separate times: They can, as an example: A) Get ready for the day all by themselves, or as much as they can do independently, before they come down and then B) have breakfast. Then, the child can C) do homework, and then D) go play outside. The routine would then continue on its own without outside reinforcers.
- Tell the children that they can get to the reinforcing activity only after completing the previous one. Over time, they learn to take pride in completing the first activity and doing so more independently. Not having to wait to be told what to do all the time fosters a sense of independence.
- Plan for meals and fun tasks together, and separate for individual work. This creates a sense of change and gives the day a certain flow. Establish routines that are predictable for the children that can be easily documented for the whole family on a calendar. Establish a beginning and an end time to the work day. Mark the end of the day with a chalk line establishing when the family can engage in a certain activity, for example, going for a family bike ride. Let the routine honor healthy circadian rhythms for sleep/wakeful times, and be consistent.
- Feed the brain and body the “good stuff”: Limit negative news, and surround the children with people who bring them joy or provide hope. Listen to inspirational messages and uplifting music. Give the children food that nourishes and energizes their bodies. Take in the view outside, the greenery, or the sky if there is no green around. Connect with family/friends who are far away.
- Make time to replenish with something that is meaningful/productive/helpful: Parents have very little time for themselves when they are “on,” so when they can actually take a little time to recharge, the activity should check many boxes. For example, encourage them to go for a walk (exercise) while listening to music (relax), make a phone call to someone who can relate to their situation (socialize), pray with someone (be spiritual), or sit in their rooms to get some alone quiet time (meditate). Reach out to those who are lonely. Network. Mentor. Volunteer.
- Develop an eye for noticing the positive: Instead of hoping for things to go back to the way they were, tell your patients to practice embracing without judgment the new norm. Get them to notice the time they spend with their families. Break all tasks into many smaller tasks, so there is more possibility of observing progress, and it is evident for everyone to see. Learn to notice the small changes that they want to see in their children. Celebrate all that can be celebrated by stating the obvious: “You wiped your face after eating. You are observant; you are noticing when you have something on your face.”
- State when a child is forgiving, helpful, or puts forward some effort. Label the growth witnessed. The child will learn that that is who they are over time (“observant”). Verbalizing these behaviors also will provide patients with a sense of mastery over parenting, because they are driving the emotional and behavioral development of their children in a way that also complements their family values.
- Make everyone in the family a contributor and foster a sense of gratitude: Give everyone a reason to claim that their collaboration and effort are a big part of the plan’s success. Take turns to lessen everyone’s burden and to thank them for their contributions. Older children can take on leadership roles, even in small ways. Younger children can practice being good listeners, following directions, and helping. Reverse the roles when possible.
Special needs families sometimes have to work harder than others to overcome obstacles, grow, and learn to support one another. Since the pandemic, many parents have been just as challenged. Mastering the above skills might provide a sense of fulfillment and agency, as well as an appreciation for the unexpected gifts that special children – and all children – have to offer.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist with a private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. She has no disclosures.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
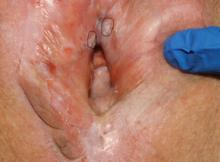
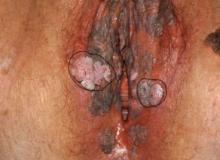
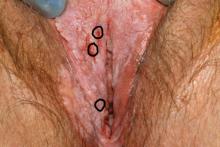
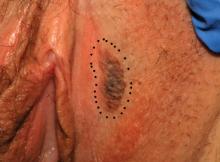
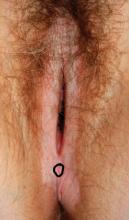
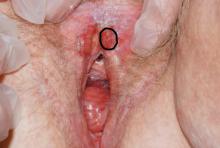
How to perform a vulvar biopsy
Many benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions can occur on the vulva. These can be challenging to differentiate by examination alone. A vulvar biopsy often is needed to appropriately diagnose—and ultimately treat—these various conditions.
In this article, we review vulvar biopsy procedures, describe how to prepare tissue specimens for the pathologist, and provide some brief case examples in which biopsy established the diagnosis.
Ask questions first
Prior to examining a patient with a vulvar lesion, obtain a detailed history. Asking specific questions may aid in making the correct diagnosis, such as:
- How long has the lesion been present? Has it changed? What color is it?
- Was any trigger, or trauma, associated with onset of the lesion?
- Does the lesion itch, burn, or cause pain? Is there any associated bleeding or discharge?
- Are other lesions present in the vagina, anus, or mouth, or are other skin lesions present?
- Are any systemic symptoms present, such as fever, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, or joint pain?
- What is the patient’s previous treatment history, including over-the-counter medications and prescribed medications?
- Has there been any incontinence of urine or stool? Does the patient use a pad?
- Is the patient scratching? Is there any nighttime scratching? It also can be useful to ask her partner, if she has one, about nighttime scratching.
- Is there a family history of vulvar conditions?
- Has there been any change in her use of products like soap, lotions, cleansing wipes, sprays, lubricants, or laundry detergent?
- Has the patient had any new partners or significant travel history?
Preprocedure counseling points
Prior to proceeding with a vulvar biopsy, review with the patient the risks, benefits, and alternatives and obtain patient consent for the procedure. Vulvar biopsy risks include pain, bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding tissue, and the need for further surgery. Make patients aware that some biopsies are nondiagnostic. We recommend that clinicians perform a time-out verification to ensure that the patient’s identity and planned procedure are correct.
Assess the biopsy site
A wide variety of lesions may require a biopsy for diagnosis. While it can be challenging to know where to biopsy, taking the time to determine the proper biopsy site may enhance pathology results.
When considering colored lesions, depth is the important factor, and a punch biopsy often is sufficient. A tumor should be biopsied in the thickest area. Lesions that are concerning for malignancy may require multiple biopsies. An erosion or ulcer is best biopsied on the edge, including a small amount of surrounding tissue. For most patients, biopsy of normal-appearing tissue is of low diagnostic yield. Lastly, we try to avoid biopsies directly on the midline to facilitate better healing.1
A photograph of the vulva prior to biopsy may be helpful for the pathologist to see the tissue. Some electronic medical records have the capability to include photographs. Due to the sensitive nature of these photographs, we prefer that a separate written patient consent be obtained prior to taking photographs. We find also that photos are a useful reference for progression of disease at follow-up in a shared care team.
Continue to: Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit...
Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit
Some patients may benefit from the application of topical lidocaine 4% cream (L.M.X.4) prior to the injection of a local anesthetic for tissue biopsy. Ideally, topical lidocaine should be placed on the vulva and covered with a dressing such as Tegaderm or cellophane up to 30 minutes before the anticipated biopsy procedure. The anesthetic effect generally lasts for about 60 minutes. Many patients report stinging for several seconds upon application. Due to clinic time restrictions, we tend to reserve this method for a limited subset of patients. If planning a return visit for a biopsy, the patient can place the topical anesthetic herself.
For the anesthetic injection, we recommend lidocaine 1% or 2% with epinephrine in all areas of the vulva except for the glans clitoris. For a punch biopsy, we draw up 1 to 3 mL in a 3-mL syringe and inject with a 21- to 30-gauge needle, using a lower gauge for thicker tissue. We have not found buffering the anesthetic with sodium bicarbonate to be of particular use. For the glans clitoris, lidocaine without epinephrine should be utilized.
Equipment. Depending on your office setting, having a premade instrument kit may be preferred to peel-pack equipment. We prefer a premade tray that contains sterile gauze, a hemostat, iris scissors, a needle driver, a scalpel handle, and Adson forceps (FIGURE 1).
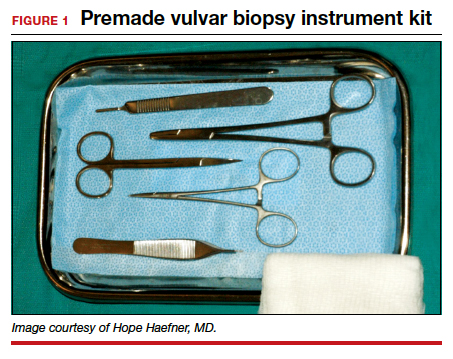
Types of biopsy procedures
Punch biopsy. We recommend a 4-mm Keyes biopsy punch. As mentioned, we use a biopsy kit to facilitate the procedure. After the tissue is properly anesthetized and prepped, we test the area via gentle touch to the skin with the hemostat or Adson forceps. To perform the punch biopsy, gentle, consistent pressure in a clockwise-counterclockwise fashion yields the best results. The goal is to obtain a 5-mm depth for hair-bearing skin and a 3-mm depth for all other tissue.2 The tissue should then be excised at the base with scissors, taking care not to crush the specimen with forceps.
Punch biopsy permits sampling of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Hemostasis is maintained with either silver nitrate, Monsel’s solution (ferric sulfate), or a dissolvable suture such as 4-0 Monocryl (poliglecaprone 25) or Vicryl Rapide (polyglactin 910).
Stitch biopsy. We find the stitch biopsy to be very useful given the architecture of the vulva. A modification of the shave biopsy, the stitch biopsy is depicted in FIGURE 2. A 3-0 or 4-0 dissolvable suture is placed through the intended area of biopsy. Iris scissors are used to undermine the tissue while the suture is held on tension. The goal is to remove the suture with the specimen. Separate sutures are used for hemostasis. The stitch does not cause the crushing artifacts on prepared specimens. Depending on the proceduralist’s comfort, a relatively large sample can be obtained in this fashion. If the suture held on tension is inadvertently cut, a second pass can be made with suture; alternatively, care can be used to remove remaining tissue with forceps and scissors, again avoiding crush injury to the tissue.

Excisional biopsy. Often, a larger area or margins are desired. We find that with adequate preparation, patients tolerate excisions in the office quite well. The planned area for excision can be marked with ink to ensure margins. Adequate anesthesia is instilled. A No. 15 blade scalpel is often the best size used to excise vulvar tissue in an elliptical fashion. Depending on depth of incision, the tissue may need to be approximated in layers for cosmesis and healing.
When planning an excisional biopsy, place a stitch on the excised tissue to mark orientation or pin out the entire specimen to a foam board to help your pathologist interpret tissue orientation.
The box "Vulvar biopsy established the diagnosis" at the end of this discussion provides 6 case examples of vulvar lesions and the respective diagnoses confirmed by biopsy.
Continue to: Preparing tissue for the pathologist...
Preparing tissue for the pathologist
Here are 5 tips for preparing the biopsied specimen for pathology:
- Include a question for the pathologist, such as “rule out lichen sclerosus or lichen simplex chronicus.” The majority of specimens should be sent in formalin. At times, frozen sections are done in the operating room.
- Double-check that the proper paperwork is included with every specimen and be very specific regarding the exact location of the lesion on the vulva. Include photographs whenever possible.
- Request that a dermatopathologist or a gynecologic pathologist with a special interest in vulvar dermatology, when feasible, review the tissue.
- Check your laboratory’s protocol for sending biopsies from areas around ulcerated tissue. Often, special medium is required for immunohistochemistry stains.
- Call your pathologist with questions about results; he or she often is happy to clarify, and together you may be able to arrive at a diagnosis to better serve your patient.3
Complications and how to avoid them
Bleeding. Any procedure has bleeding risks. To avoid bleeding, review the patient’s medication list and medical history prior to biopsy, as certain medications, such as blood thinners, increase risk for bleeding. Counseling a patient on applying direct pressure to the biopsy site for 2 minutes is generally sufficient for any bleeding that may occur once she is discharged from the clinic.
Infection. With aseptic technique, infection of a biopsy site is rare. We use nonsterile gloves for biopsy procedures. This does not increase the risk of infection.4 If a patient has iodine allergy, dilute chlorhexidine is a reasonable alternative for skin cleansing. Instruct the patient to keep the site clean and dry; if the biopsy proximity is close to the urethra or anus, use of a peri-bottle may be preferred after toileting. Instruct patients not to pull sutures. While instructions are specific for each patient, we generally advise that patients wait 4 to 7 days before resuming use of topical medications.
Scarring or tattooing. Avoid using dyed suture on skin surfaces and counsel the patient that silver nitrate can permanently stain tissue. Usually, small biopsies heal well but a small scar is possible.
Key points to keep in mind
- Counsel patients on biopsy risks, benefits, and alternatives. Counsel regarding possible inconclusive results.
- Take time in choosing the biopsy site and consider multiple biopsies.
- Have all anticipated equipment available; consider using premade biopsy kits.
- Consider performing a stitch biopsy to avoid crush injury.
- Take photographs of the area to be biopsied and communicate with your pathologist to facilitate diagnosis.
Case 1
Biopsies were obtained of the areas highlighted in the photo. Pathology shows dVIN.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 2
The examination is consistent with condylomata acuminata and biopsy is recommended with a 4-mm punch. Biopsy results are consistent with condylomata acuminata.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 3
The final pathology shows high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 4
This presentation is an excellent opportunity for an excisional biopsy of the vulva. A marking pen is used to draw margins. A No. 15 blade is used to outline and then undermine the lesion, removing it in its entirety.
Final pathology shows a compound nevus of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 5
A 4-mm punch biopsy result is consistent with a diagnosis of lichen sclerosus.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 6
A 4-mm punch biopsy result reveals that the pathology is significant for squamous cell carcinoma.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
- Edwards L, Lynch PJ. Genital Dermatology Atlas and Manual. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 93: Diagnosis and management of vulvar skin disorders. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1243-1253.
- Heller DS. Areas of confusion in pathologist-clinician communication as it relates to understanding the vulvar pathology report. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2017;21:327-328.
- Rietz A, Barzin A, Jones K, et al. Sterile or non-sterile gloves for minor skin excisions? J Fam Pract. 2015;64:723-727.
Many benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions can occur on the vulva. These can be challenging to differentiate by examination alone. A vulvar biopsy often is needed to appropriately diagnose—and ultimately treat—these various conditions.
In this article, we review vulvar biopsy procedures, describe how to prepare tissue specimens for the pathologist, and provide some brief case examples in which biopsy established the diagnosis.
Ask questions first
Prior to examining a patient with a vulvar lesion, obtain a detailed history. Asking specific questions may aid in making the correct diagnosis, such as:
- How long has the lesion been present? Has it changed? What color is it?
- Was any trigger, or trauma, associated with onset of the lesion?
- Does the lesion itch, burn, or cause pain? Is there any associated bleeding or discharge?
- Are other lesions present in the vagina, anus, or mouth, or are other skin lesions present?
- Are any systemic symptoms present, such as fever, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, or joint pain?
- What is the patient’s previous treatment history, including over-the-counter medications and prescribed medications?
- Has there been any incontinence of urine or stool? Does the patient use a pad?
- Is the patient scratching? Is there any nighttime scratching? It also can be useful to ask her partner, if she has one, about nighttime scratching.
- Is there a family history of vulvar conditions?
- Has there been any change in her use of products like soap, lotions, cleansing wipes, sprays, lubricants, or laundry detergent?
- Has the patient had any new partners or significant travel history?
Preprocedure counseling points
Prior to proceeding with a vulvar biopsy, review with the patient the risks, benefits, and alternatives and obtain patient consent for the procedure. Vulvar biopsy risks include pain, bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding tissue, and the need for further surgery. Make patients aware that some biopsies are nondiagnostic. We recommend that clinicians perform a time-out verification to ensure that the patient’s identity and planned procedure are correct.
Assess the biopsy site
A wide variety of lesions may require a biopsy for diagnosis. While it can be challenging to know where to biopsy, taking the time to determine the proper biopsy site may enhance pathology results.
When considering colored lesions, depth is the important factor, and a punch biopsy often is sufficient. A tumor should be biopsied in the thickest area. Lesions that are concerning for malignancy may require multiple biopsies. An erosion or ulcer is best biopsied on the edge, including a small amount of surrounding tissue. For most patients, biopsy of normal-appearing tissue is of low diagnostic yield. Lastly, we try to avoid biopsies directly on the midline to facilitate better healing.1
A photograph of the vulva prior to biopsy may be helpful for the pathologist to see the tissue. Some electronic medical records have the capability to include photographs. Due to the sensitive nature of these photographs, we prefer that a separate written patient consent be obtained prior to taking photographs. We find also that photos are a useful reference for progression of disease at follow-up in a shared care team.
Continue to: Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit...
Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit
Some patients may benefit from the application of topical lidocaine 4% cream (L.M.X.4) prior to the injection of a local anesthetic for tissue biopsy. Ideally, topical lidocaine should be placed on the vulva and covered with a dressing such as Tegaderm or cellophane up to 30 minutes before the anticipated biopsy procedure. The anesthetic effect generally lasts for about 60 minutes. Many patients report stinging for several seconds upon application. Due to clinic time restrictions, we tend to reserve this method for a limited subset of patients. If planning a return visit for a biopsy, the patient can place the topical anesthetic herself.
For the anesthetic injection, we recommend lidocaine 1% or 2% with epinephrine in all areas of the vulva except for the glans clitoris. For a punch biopsy, we draw up 1 to 3 mL in a 3-mL syringe and inject with a 21- to 30-gauge needle, using a lower gauge for thicker tissue. We have not found buffering the anesthetic with sodium bicarbonate to be of particular use. For the glans clitoris, lidocaine without epinephrine should be utilized.
Equipment. Depending on your office setting, having a premade instrument kit may be preferred to peel-pack equipment. We prefer a premade tray that contains sterile gauze, a hemostat, iris scissors, a needle driver, a scalpel handle, and Adson forceps (FIGURE 1).

Types of biopsy procedures
Punch biopsy. We recommend a 4-mm Keyes biopsy punch. As mentioned, we use a biopsy kit to facilitate the procedure. After the tissue is properly anesthetized and prepped, we test the area via gentle touch to the skin with the hemostat or Adson forceps. To perform the punch biopsy, gentle, consistent pressure in a clockwise-counterclockwise fashion yields the best results. The goal is to obtain a 5-mm depth for hair-bearing skin and a 3-mm depth for all other tissue.2 The tissue should then be excised at the base with scissors, taking care not to crush the specimen with forceps.
Punch biopsy permits sampling of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Hemostasis is maintained with either silver nitrate, Monsel’s solution (ferric sulfate), or a dissolvable suture such as 4-0 Monocryl (poliglecaprone 25) or Vicryl Rapide (polyglactin 910).
Stitch biopsy. We find the stitch biopsy to be very useful given the architecture of the vulva. A modification of the shave biopsy, the stitch biopsy is depicted in FIGURE 2. A 3-0 or 4-0 dissolvable suture is placed through the intended area of biopsy. Iris scissors are used to undermine the tissue while the suture is held on tension. The goal is to remove the suture with the specimen. Separate sutures are used for hemostasis. The stitch does not cause the crushing artifacts on prepared specimens. Depending on the proceduralist’s comfort, a relatively large sample can be obtained in this fashion. If the suture held on tension is inadvertently cut, a second pass can be made with suture; alternatively, care can be used to remove remaining tissue with forceps and scissors, again avoiding crush injury to the tissue.

Excisional biopsy. Often, a larger area or margins are desired. We find that with adequate preparation, patients tolerate excisions in the office quite well. The planned area for excision can be marked with ink to ensure margins. Adequate anesthesia is instilled. A No. 15 blade scalpel is often the best size used to excise vulvar tissue in an elliptical fashion. Depending on depth of incision, the tissue may need to be approximated in layers for cosmesis and healing.
When planning an excisional biopsy, place a stitch on the excised tissue to mark orientation or pin out the entire specimen to a foam board to help your pathologist interpret tissue orientation.
The box "Vulvar biopsy established the diagnosis" at the end of this discussion provides 6 case examples of vulvar lesions and the respective diagnoses confirmed by biopsy.
Continue to: Preparing tissue for the pathologist...
Preparing tissue for the pathologist
Here are 5 tips for preparing the biopsied specimen for pathology:
- Include a question for the pathologist, such as “rule out lichen sclerosus or lichen simplex chronicus.” The majority of specimens should be sent in formalin. At times, frozen sections are done in the operating room.
- Double-check that the proper paperwork is included with every specimen and be very specific regarding the exact location of the lesion on the vulva. Include photographs whenever possible.
- Request that a dermatopathologist or a gynecologic pathologist with a special interest in vulvar dermatology, when feasible, review the tissue.
- Check your laboratory’s protocol for sending biopsies from areas around ulcerated tissue. Often, special medium is required for immunohistochemistry stains.
- Call your pathologist with questions about results; he or she often is happy to clarify, and together you may be able to arrive at a diagnosis to better serve your patient.3
Complications and how to avoid them
Bleeding. Any procedure has bleeding risks. To avoid bleeding, review the patient’s medication list and medical history prior to biopsy, as certain medications, such as blood thinners, increase risk for bleeding. Counseling a patient on applying direct pressure to the biopsy site for 2 minutes is generally sufficient for any bleeding that may occur once she is discharged from the clinic.
Infection. With aseptic technique, infection of a biopsy site is rare. We use nonsterile gloves for biopsy procedures. This does not increase the risk of infection.4 If a patient has iodine allergy, dilute chlorhexidine is a reasonable alternative for skin cleansing. Instruct the patient to keep the site clean and dry; if the biopsy proximity is close to the urethra or anus, use of a peri-bottle may be preferred after toileting. Instruct patients not to pull sutures. While instructions are specific for each patient, we generally advise that patients wait 4 to 7 days before resuming use of topical medications.
Scarring or tattooing. Avoid using dyed suture on skin surfaces and counsel the patient that silver nitrate can permanently stain tissue. Usually, small biopsies heal well but a small scar is possible.
Key points to keep in mind
- Counsel patients on biopsy risks, benefits, and alternatives. Counsel regarding possible inconclusive results.
- Take time in choosing the biopsy site and consider multiple biopsies.
- Have all anticipated equipment available; consider using premade biopsy kits.
- Consider performing a stitch biopsy to avoid crush injury.
- Take photographs of the area to be biopsied and communicate with your pathologist to facilitate diagnosis.
Case 1
Biopsies were obtained of the areas highlighted in the photo. Pathology shows dVIN.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 2
The examination is consistent with condylomata acuminata and biopsy is recommended with a 4-mm punch. Biopsy results are consistent with condylomata acuminata.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 3
The final pathology shows high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 4
This presentation is an excellent opportunity for an excisional biopsy of the vulva. A marking pen is used to draw margins. A No. 15 blade is used to outline and then undermine the lesion, removing it in its entirety.
Final pathology shows a compound nevus of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 5
A 4-mm punch biopsy result is consistent with a diagnosis of lichen sclerosus.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 6
A 4-mm punch biopsy result reveals that the pathology is significant for squamous cell carcinoma.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Many benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions can occur on the vulva. These can be challenging to differentiate by examination alone. A vulvar biopsy often is needed to appropriately diagnose—and ultimately treat—these various conditions.
In this article, we review vulvar biopsy procedures, describe how to prepare tissue specimens for the pathologist, and provide some brief case examples in which biopsy established the diagnosis.
Ask questions first
Prior to examining a patient with a vulvar lesion, obtain a detailed history. Asking specific questions may aid in making the correct diagnosis, such as:
- How long has the lesion been present? Has it changed? What color is it?
- Was any trigger, or trauma, associated with onset of the lesion?
- Does the lesion itch, burn, or cause pain? Is there any associated bleeding or discharge?
- Are other lesions present in the vagina, anus, or mouth, or are other skin lesions present?
- Are any systemic symptoms present, such as fever, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, or joint pain?
- What is the patient’s previous treatment history, including over-the-counter medications and prescribed medications?
- Has there been any incontinence of urine or stool? Does the patient use a pad?
- Is the patient scratching? Is there any nighttime scratching? It also can be useful to ask her partner, if she has one, about nighttime scratching.
- Is there a family history of vulvar conditions?
- Has there been any change in her use of products like soap, lotions, cleansing wipes, sprays, lubricants, or laundry detergent?
- Has the patient had any new partners or significant travel history?
Preprocedure counseling points
Prior to proceeding with a vulvar biopsy, review with the patient the risks, benefits, and alternatives and obtain patient consent for the procedure. Vulvar biopsy risks include pain, bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding tissue, and the need for further surgery. Make patients aware that some biopsies are nondiagnostic. We recommend that clinicians perform a time-out verification to ensure that the patient’s identity and planned procedure are correct.
Assess the biopsy site
A wide variety of lesions may require a biopsy for diagnosis. While it can be challenging to know where to biopsy, taking the time to determine the proper biopsy site may enhance pathology results.
When considering colored lesions, depth is the important factor, and a punch biopsy often is sufficient. A tumor should be biopsied in the thickest area. Lesions that are concerning for malignancy may require multiple biopsies. An erosion or ulcer is best biopsied on the edge, including a small amount of surrounding tissue. For most patients, biopsy of normal-appearing tissue is of low diagnostic yield. Lastly, we try to avoid biopsies directly on the midline to facilitate better healing.1
A photograph of the vulva prior to biopsy may be helpful for the pathologist to see the tissue. Some electronic medical records have the capability to include photographs. Due to the sensitive nature of these photographs, we prefer that a separate written patient consent be obtained prior to taking photographs. We find also that photos are a useful reference for progression of disease at follow-up in a shared care team.
Continue to: Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit...
Anesthesia procedure and instrument kit
Some patients may benefit from the application of topical lidocaine 4% cream (L.M.X.4) prior to the injection of a local anesthetic for tissue biopsy. Ideally, topical lidocaine should be placed on the vulva and covered with a dressing such as Tegaderm or cellophane up to 30 minutes before the anticipated biopsy procedure. The anesthetic effect generally lasts for about 60 minutes. Many patients report stinging for several seconds upon application. Due to clinic time restrictions, we tend to reserve this method for a limited subset of patients. If planning a return visit for a biopsy, the patient can place the topical anesthetic herself.
For the anesthetic injection, we recommend lidocaine 1% or 2% with epinephrine in all areas of the vulva except for the glans clitoris. For a punch biopsy, we draw up 1 to 3 mL in a 3-mL syringe and inject with a 21- to 30-gauge needle, using a lower gauge for thicker tissue. We have not found buffering the anesthetic with sodium bicarbonate to be of particular use. For the glans clitoris, lidocaine without epinephrine should be utilized.
Equipment. Depending on your office setting, having a premade instrument kit may be preferred to peel-pack equipment. We prefer a premade tray that contains sterile gauze, a hemostat, iris scissors, a needle driver, a scalpel handle, and Adson forceps (FIGURE 1).

Types of biopsy procedures
Punch biopsy. We recommend a 4-mm Keyes biopsy punch. As mentioned, we use a biopsy kit to facilitate the procedure. After the tissue is properly anesthetized and prepped, we test the area via gentle touch to the skin with the hemostat or Adson forceps. To perform the punch biopsy, gentle, consistent pressure in a clockwise-counterclockwise fashion yields the best results. The goal is to obtain a 5-mm depth for hair-bearing skin and a 3-mm depth for all other tissue.2 The tissue should then be excised at the base with scissors, taking care not to crush the specimen with forceps.
Punch biopsy permits sampling of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Hemostasis is maintained with either silver nitrate, Monsel’s solution (ferric sulfate), or a dissolvable suture such as 4-0 Monocryl (poliglecaprone 25) or Vicryl Rapide (polyglactin 910).
Stitch biopsy. We find the stitch biopsy to be very useful given the architecture of the vulva. A modification of the shave biopsy, the stitch biopsy is depicted in FIGURE 2. A 3-0 or 4-0 dissolvable suture is placed through the intended area of biopsy. Iris scissors are used to undermine the tissue while the suture is held on tension. The goal is to remove the suture with the specimen. Separate sutures are used for hemostasis. The stitch does not cause the crushing artifacts on prepared specimens. Depending on the proceduralist’s comfort, a relatively large sample can be obtained in this fashion. If the suture held on tension is inadvertently cut, a second pass can be made with suture; alternatively, care can be used to remove remaining tissue with forceps and scissors, again avoiding crush injury to the tissue.

Excisional biopsy. Often, a larger area or margins are desired. We find that with adequate preparation, patients tolerate excisions in the office quite well. The planned area for excision can be marked with ink to ensure margins. Adequate anesthesia is instilled. A No. 15 blade scalpel is often the best size used to excise vulvar tissue in an elliptical fashion. Depending on depth of incision, the tissue may need to be approximated in layers for cosmesis and healing.
When planning an excisional biopsy, place a stitch on the excised tissue to mark orientation or pin out the entire specimen to a foam board to help your pathologist interpret tissue orientation.
The box "Vulvar biopsy established the diagnosis" at the end of this discussion provides 6 case examples of vulvar lesions and the respective diagnoses confirmed by biopsy.
Continue to: Preparing tissue for the pathologist...
Preparing tissue for the pathologist
Here are 5 tips for preparing the biopsied specimen for pathology:
- Include a question for the pathologist, such as “rule out lichen sclerosus or lichen simplex chronicus.” The majority of specimens should be sent in formalin. At times, frozen sections are done in the operating room.
- Double-check that the proper paperwork is included with every specimen and be very specific regarding the exact location of the lesion on the vulva. Include photographs whenever possible.
- Request that a dermatopathologist or a gynecologic pathologist with a special interest in vulvar dermatology, when feasible, review the tissue.
- Check your laboratory’s protocol for sending biopsies from areas around ulcerated tissue. Often, special medium is required for immunohistochemistry stains.
- Call your pathologist with questions about results; he or she often is happy to clarify, and together you may be able to arrive at a diagnosis to better serve your patient.3
Complications and how to avoid them
Bleeding. Any procedure has bleeding risks. To avoid bleeding, review the patient’s medication list and medical history prior to biopsy, as certain medications, such as blood thinners, increase risk for bleeding. Counseling a patient on applying direct pressure to the biopsy site for 2 minutes is generally sufficient for any bleeding that may occur once she is discharged from the clinic.
Infection. With aseptic technique, infection of a biopsy site is rare. We use nonsterile gloves for biopsy procedures. This does not increase the risk of infection.4 If a patient has iodine allergy, dilute chlorhexidine is a reasonable alternative for skin cleansing. Instruct the patient to keep the site clean and dry; if the biopsy proximity is close to the urethra or anus, use of a peri-bottle may be preferred after toileting. Instruct patients not to pull sutures. While instructions are specific for each patient, we generally advise that patients wait 4 to 7 days before resuming use of topical medications.
Scarring or tattooing. Avoid using dyed suture on skin surfaces and counsel the patient that silver nitrate can permanently stain tissue. Usually, small biopsies heal well but a small scar is possible.
Key points to keep in mind
- Counsel patients on biopsy risks, benefits, and alternatives. Counsel regarding possible inconclusive results.
- Take time in choosing the biopsy site and consider multiple biopsies.
- Have all anticipated equipment available; consider using premade biopsy kits.
- Consider performing a stitch biopsy to avoid crush injury.
- Take photographs of the area to be biopsied and communicate with your pathologist to facilitate diagnosis.
Case 1
Biopsies were obtained of the areas highlighted in the photo. Pathology shows dVIN.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 2
The examination is consistent with condylomata acuminata and biopsy is recommended with a 4-mm punch. Biopsy results are consistent with condylomata acuminata.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 3
The final pathology shows high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 4
This presentation is an excellent opportunity for an excisional biopsy of the vulva. A marking pen is used to draw margins. A No. 15 blade is used to outline and then undermine the lesion, removing it in its entirety.
Final pathology shows a compound nevus of the vulva.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 5
A 4-mm punch biopsy result is consistent with a diagnosis of lichen sclerosus.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
Case 6
A 4-mm punch biopsy result reveals that the pathology is significant for squamous cell carcinoma.
Image courtesy of Hope Haefner, MD.
- Edwards L, Lynch PJ. Genital Dermatology Atlas and Manual. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 93: Diagnosis and management of vulvar skin disorders. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1243-1253.
- Heller DS. Areas of confusion in pathologist-clinician communication as it relates to understanding the vulvar pathology report. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2017;21:327-328.
- Rietz A, Barzin A, Jones K, et al. Sterile or non-sterile gloves for minor skin excisions? J Fam Pract. 2015;64:723-727.
- Edwards L, Lynch PJ. Genital Dermatology Atlas and Manual. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; 2018.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 93: Diagnosis and management of vulvar skin disorders. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1243-1253.
- Heller DS. Areas of confusion in pathologist-clinician communication as it relates to understanding the vulvar pathology report. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2017;21:327-328.
- Rietz A, Barzin A, Jones K, et al. Sterile or non-sterile gloves for minor skin excisions? J Fam Pract. 2015;64:723-727.
Reducing low-value preop care for cataract surgery patients
Background: Although multiple randomized, controlled trials have shown that routine preoperative testing prior to cataract surgery has low yield, most Medicare beneficiaries continue to undergo this testing. The American Board of Internal Medicine started the Choosing Wisely campaign to help educate patients and providers about a crisis of unnecessary testing and procedures. This prompted multiple centers to create quality improvement (QI) projects to decrease low-value care.
_
Study design: Observational study of a health system quality improvement initiative.
Setting: Two academic, safety-net hospitals in Los Angeles.
Synopsis: The intervention hospital’s QI nurse underwent an extensive formal QI training program, followed by educating all health care team members involved in preoperative care for cataract patients. New guidelines were created and circulated, with a stated goal of eliminating routine preoperative visits and testing. The control hospital continued their usual preoperative care.
Preoperative visits decreased from 93% to 24% in the intervention group and increased from 89% to 91% in the control group (between-group difference, −71%; 95% confidence interval, –80% to –62%). Chest x-rays, laboratory tests, and electrocardiograms also had a similar decrease in the intervention group.
The intervention hospital lost $42,241 the first year because of training costs but 3-year projections estimated $67,241 in savings. The authors estimated $217,322 savings in 3 years from a societal perspective. Interestingly, the decrease in utilization would lead to financial loss in fee-for-service payment ($88,151 loss in 3 years).
No causal relationship can be established since this was an observational study. Several assumptions were made for the cost analysis. Results are less generalizable since the study was at hospitals in a single city and health system. It is unclear which component of the QI initiative was most effective.
Bottom line: A multidisciplinary, multicomponent initiative can be successful in decreasing low-value preoperative testing of patients undergoing cataract surgery. Although this results in cost savings overall and for capitated payment systems, it would actually cause revenue loss in fee-for-service systems. This emphasizes a potential barrier to eradicate low-value care.
Citation: Mafi JN et al. Evaluation of an intervention to reduce low-value preoperative care for patients undergoing cataract surgery at a safety-net health system. JAMA Intern Med. Published online 2019 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8358.
Dr. Menon is a hospitalist at Duke University Health System.
Background: Although multiple randomized, controlled trials have shown that routine preoperative testing prior to cataract surgery has low yield, most Medicare beneficiaries continue to undergo this testing. The American Board of Internal Medicine started the Choosing Wisely campaign to help educate patients and providers about a crisis of unnecessary testing and procedures. This prompted multiple centers to create quality improvement (QI) projects to decrease low-value care.
_
Study design: Observational study of a health system quality improvement initiative.
Setting: Two academic, safety-net hospitals in Los Angeles.
Synopsis: The intervention hospital’s QI nurse underwent an extensive formal QI training program, followed by educating all health care team members involved in preoperative care for cataract patients. New guidelines were created and circulated, with a stated goal of eliminating routine preoperative visits and testing. The control hospital continued their usual preoperative care.
Preoperative visits decreased from 93% to 24% in the intervention group and increased from 89% to 91% in the control group (between-group difference, −71%; 95% confidence interval, –80% to –62%). Chest x-rays, laboratory tests, and electrocardiograms also had a similar decrease in the intervention group.
The intervention hospital lost $42,241 the first year because of training costs but 3-year projections estimated $67,241 in savings. The authors estimated $217,322 savings in 3 years from a societal perspective. Interestingly, the decrease in utilization would lead to financial loss in fee-for-service payment ($88,151 loss in 3 years).
No causal relationship can be established since this was an observational study. Several assumptions were made for the cost analysis. Results are less generalizable since the study was at hospitals in a single city and health system. It is unclear which component of the QI initiative was most effective.
Bottom line: A multidisciplinary, multicomponent initiative can be successful in decreasing low-value preoperative testing of patients undergoing cataract surgery. Although this results in cost savings overall and for capitated payment systems, it would actually cause revenue loss in fee-for-service systems. This emphasizes a potential barrier to eradicate low-value care.
Citation: Mafi JN et al. Evaluation of an intervention to reduce low-value preoperative care for patients undergoing cataract surgery at a safety-net health system. JAMA Intern Med. Published online 2019 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8358.
Dr. Menon is a hospitalist at Duke University Health System.
Background: Although multiple randomized, controlled trials have shown that routine preoperative testing prior to cataract surgery has low yield, most Medicare beneficiaries continue to undergo this testing. The American Board of Internal Medicine started the Choosing Wisely campaign to help educate patients and providers about a crisis of unnecessary testing and procedures. This prompted multiple centers to create quality improvement (QI) projects to decrease low-value care.
_
Study design: Observational study of a health system quality improvement initiative.
Setting: Two academic, safety-net hospitals in Los Angeles.
Synopsis: The intervention hospital’s QI nurse underwent an extensive formal QI training program, followed by educating all health care team members involved in preoperative care for cataract patients. New guidelines were created and circulated, with a stated goal of eliminating routine preoperative visits and testing. The control hospital continued their usual preoperative care.
Preoperative visits decreased from 93% to 24% in the intervention group and increased from 89% to 91% in the control group (between-group difference, −71%; 95% confidence interval, –80% to –62%). Chest x-rays, laboratory tests, and electrocardiograms also had a similar decrease in the intervention group.
The intervention hospital lost $42,241 the first year because of training costs but 3-year projections estimated $67,241 in savings. The authors estimated $217,322 savings in 3 years from a societal perspective. Interestingly, the decrease in utilization would lead to financial loss in fee-for-service payment ($88,151 loss in 3 years).
No causal relationship can be established since this was an observational study. Several assumptions were made for the cost analysis. Results are less generalizable since the study was at hospitals in a single city and health system. It is unclear which component of the QI initiative was most effective.
Bottom line: A multidisciplinary, multicomponent initiative can be successful in decreasing low-value preoperative testing of patients undergoing cataract surgery. Although this results in cost savings overall and for capitated payment systems, it would actually cause revenue loss in fee-for-service systems. This emphasizes a potential barrier to eradicate low-value care.
Citation: Mafi JN et al. Evaluation of an intervention to reduce low-value preoperative care for patients undergoing cataract surgery at a safety-net health system. JAMA Intern Med. Published online 2019 Mar 25. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8358.
Dr. Menon is a hospitalist at Duke University Health System.
COVID-19 complicates prescribing for children with inflammatory skin disease
designed to offer guidance to specialists and nonspecialists faced with tough choices about risks.
Some 87% reported that they were reducing the frequency of lab monitoring for some medications, while more than half said they had reached out to patients and their families to discuss the implications of continuing or stopping a drug.
Virtually all – 97% – said that the COVID-19 crisis had affected their decision to initiate immunosuppressive medications, with 84% saying the decision depended on a patient’s risk factors for contracting COVID-19 infection, and also the potential consequences of infection while treated, compared with the risks of not optimally treating the skin condition.
To develop a consensus-based guidance for clinicians, published online April 22 in Pediatric Dermatology, Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, assembled a task force of pediatric dermatologists at academic institutions (the Pediatric Dermatology COVID-19 Response Task Force). Together with Sean Reynolds, MD, a pediatric dermatology fellow at UCSF and colleagues, they issued a survey to the 37 members of the task force with questions on how the pandemic has affected their prescribing decisions and certain therapies specifically. All the recipients responded.
The dermatologists were asked about conventional systemic and biologic medications. Most felt confident in continuing biologics, with 78% saying they would keep patients with no signs of COVID-19 exposure or infection on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. More than 90% of respondents said they would continue patients on dupilumab, as well as anti–interleukin (IL)–17, anti–IL-12/23, and anti–IL-23 therapies.
Responses varied more on approaches to the nonbiologic treatments. Fewer than half (46%) said they would continue patients without apparent COVID-19 exposure on systemic steroids, with another 46% saying it depended on the clinical context.
For other systemic therapies, respondents were more likely to want to continue their patients with no signs or symptoms of COVID-19 on methotrexate and apremilast (78% and 83%, respectively) than others (mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, cyclosporine, and JAK inhibitors), which saw between 50% and 60% support in the survey.
Patients on any immunosuppressive medications with likely exposure to COVID-19 or who test positive for the virus should be temporarily taken off their medications, the majority concurred. Exceptions were for systemic steroids, which must be tapered. And a significant minority of the dermatologists said that they would continue apremilast or dupilumab (24% and 16%, respectively) in the event of a confirmed COVID-19 infection.
In an interview, Dr. Cordoro commented that, even in normal times, most systemic or biological immunosuppressive treatments are used off-label by pediatric dermatologists. “There’s no way this could have been an evidence-based document, as we didn’t have the data to drive this. Many of the medications have been tested in children but not necessarily for dermatologic indications; some are chemotherapy agents or drugs used in rheumatologic diseases.”
The COVID-19 pandemic complicated an already difficult decision-making process, she said.
The researchers cautioned against attempting to make decisions about medications based on data on other infections from clinical trials. “Infection data from standard infections that were identified and watched for in clinical trials really still has no bearing on COVID-19 because it’s such a different virus,” Dr. Cordoro said.
And while some immunosuppressive medications could potentially attenuate a SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm, “we certainly don’t assume this is necessarily going to help.”
The authors advised that physicians anxious about initiating an immunosuppressive treatment should take into consideration whether early intervention could “prevent permanent physical impairment or disfigurement” in diseases such as erythrodermic pustular psoriasis or rapidly progressive linear morphea.
Other diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, “may be acceptably, though not optimally, managed with topical and other home-based therapeutic options” during the pandemic, they wrote.
Dr. Cordoro commented that, given how fast new findings are emerging from the pandemic, the guidance on medications could change. “We will know so much more 3 months from now,” she said. And while there are no formal plans to reissue the survey, “we’re maintaining communication and will have some kind of follow up” with the academic dermatologists.
“If we recognize any signals that are counter to what we say in this work we will immediately let people know,” she said.
The researchers received no outside funding for their study. Of the study’s 24 coauthors, nine disclosed financial relationships with industry.
SOURCE: Add the first auSOURCE: Reynolds et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020. doi: 10.1111/pde.14202.
designed to offer guidance to specialists and nonspecialists faced with tough choices about risks.
Some 87% reported that they were reducing the frequency of lab monitoring for some medications, while more than half said they had reached out to patients and their families to discuss the implications of continuing or stopping a drug.
Virtually all – 97% – said that the COVID-19 crisis had affected their decision to initiate immunosuppressive medications, with 84% saying the decision depended on a patient’s risk factors for contracting COVID-19 infection, and also the potential consequences of infection while treated, compared with the risks of not optimally treating the skin condition.
To develop a consensus-based guidance for clinicians, published online April 22 in Pediatric Dermatology, Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, assembled a task force of pediatric dermatologists at academic institutions (the Pediatric Dermatology COVID-19 Response Task Force). Together with Sean Reynolds, MD, a pediatric dermatology fellow at UCSF and colleagues, they issued a survey to the 37 members of the task force with questions on how the pandemic has affected their prescribing decisions and certain therapies specifically. All the recipients responded.
The dermatologists were asked about conventional systemic and biologic medications. Most felt confident in continuing biologics, with 78% saying they would keep patients with no signs of COVID-19 exposure or infection on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. More than 90% of respondents said they would continue patients on dupilumab, as well as anti–interleukin (IL)–17, anti–IL-12/23, and anti–IL-23 therapies.
Responses varied more on approaches to the nonbiologic treatments. Fewer than half (46%) said they would continue patients without apparent COVID-19 exposure on systemic steroids, with another 46% saying it depended on the clinical context.
For other systemic therapies, respondents were more likely to want to continue their patients with no signs or symptoms of COVID-19 on methotrexate and apremilast (78% and 83%, respectively) than others (mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, cyclosporine, and JAK inhibitors), which saw between 50% and 60% support in the survey.
Patients on any immunosuppressive medications with likely exposure to COVID-19 or who test positive for the virus should be temporarily taken off their medications, the majority concurred. Exceptions were for systemic steroids, which must be tapered. And a significant minority of the dermatologists said that they would continue apremilast or dupilumab (24% and 16%, respectively) in the event of a confirmed COVID-19 infection.
In an interview, Dr. Cordoro commented that, even in normal times, most systemic or biological immunosuppressive treatments are used off-label by pediatric dermatologists. “There’s no way this could have been an evidence-based document, as we didn’t have the data to drive this. Many of the medications have been tested in children but not necessarily for dermatologic indications; some are chemotherapy agents or drugs used in rheumatologic diseases.”
The COVID-19 pandemic complicated an already difficult decision-making process, she said.
The researchers cautioned against attempting to make decisions about medications based on data on other infections from clinical trials. “Infection data from standard infections that were identified and watched for in clinical trials really still has no bearing on COVID-19 because it’s such a different virus,” Dr. Cordoro said.
And while some immunosuppressive medications could potentially attenuate a SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm, “we certainly don’t assume this is necessarily going to help.”
The authors advised that physicians anxious about initiating an immunosuppressive treatment should take into consideration whether early intervention could “prevent permanent physical impairment or disfigurement” in diseases such as erythrodermic pustular psoriasis or rapidly progressive linear morphea.
Other diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, “may be acceptably, though not optimally, managed with topical and other home-based therapeutic options” during the pandemic, they wrote.
Dr. Cordoro commented that, given how fast new findings are emerging from the pandemic, the guidance on medications could change. “We will know so much more 3 months from now,” she said. And while there are no formal plans to reissue the survey, “we’re maintaining communication and will have some kind of follow up” with the academic dermatologists.
“If we recognize any signals that are counter to what we say in this work we will immediately let people know,” she said.
The researchers received no outside funding for their study. Of the study’s 24 coauthors, nine disclosed financial relationships with industry.
SOURCE: Add the first auSOURCE: Reynolds et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020. doi: 10.1111/pde.14202.
designed to offer guidance to specialists and nonspecialists faced with tough choices about risks.
Some 87% reported that they were reducing the frequency of lab monitoring for some medications, while more than half said they had reached out to patients and their families to discuss the implications of continuing or stopping a drug.
Virtually all – 97% – said that the COVID-19 crisis had affected their decision to initiate immunosuppressive medications, with 84% saying the decision depended on a patient’s risk factors for contracting COVID-19 infection, and also the potential consequences of infection while treated, compared with the risks of not optimally treating the skin condition.
To develop a consensus-based guidance for clinicians, published online April 22 in Pediatric Dermatology, Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, assembled a task force of pediatric dermatologists at academic institutions (the Pediatric Dermatology COVID-19 Response Task Force). Together with Sean Reynolds, MD, a pediatric dermatology fellow at UCSF and colleagues, they issued a survey to the 37 members of the task force with questions on how the pandemic has affected their prescribing decisions and certain therapies specifically. All the recipients responded.
The dermatologists were asked about conventional systemic and biologic medications. Most felt confident in continuing biologics, with 78% saying they would keep patients with no signs of COVID-19 exposure or infection on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. More than 90% of respondents said they would continue patients on dupilumab, as well as anti–interleukin (IL)–17, anti–IL-12/23, and anti–IL-23 therapies.
Responses varied more on approaches to the nonbiologic treatments. Fewer than half (46%) said they would continue patients without apparent COVID-19 exposure on systemic steroids, with another 46% saying it depended on the clinical context.
For other systemic therapies, respondents were more likely to want to continue their patients with no signs or symptoms of COVID-19 on methotrexate and apremilast (78% and 83%, respectively) than others (mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, cyclosporine, and JAK inhibitors), which saw between 50% and 60% support in the survey.
Patients on any immunosuppressive medications with likely exposure to COVID-19 or who test positive for the virus should be temporarily taken off their medications, the majority concurred. Exceptions were for systemic steroids, which must be tapered. And a significant minority of the dermatologists said that they would continue apremilast or dupilumab (24% and 16%, respectively) in the event of a confirmed COVID-19 infection.
In an interview, Dr. Cordoro commented that, even in normal times, most systemic or biological immunosuppressive treatments are used off-label by pediatric dermatologists. “There’s no way this could have been an evidence-based document, as we didn’t have the data to drive this. Many of the medications have been tested in children but not necessarily for dermatologic indications; some are chemotherapy agents or drugs used in rheumatologic diseases.”
The COVID-19 pandemic complicated an already difficult decision-making process, she said.
The researchers cautioned against attempting to make decisions about medications based on data on other infections from clinical trials. “Infection data from standard infections that were identified and watched for in clinical trials really still has no bearing on COVID-19 because it’s such a different virus,” Dr. Cordoro said.
And while some immunosuppressive medications could potentially attenuate a SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm, “we certainly don’t assume this is necessarily going to help.”
The authors advised that physicians anxious about initiating an immunosuppressive treatment should take into consideration whether early intervention could “prevent permanent physical impairment or disfigurement” in diseases such as erythrodermic pustular psoriasis or rapidly progressive linear morphea.
Other diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, “may be acceptably, though not optimally, managed with topical and other home-based therapeutic options” during the pandemic, they wrote.
Dr. Cordoro commented that, given how fast new findings are emerging from the pandemic, the guidance on medications could change. “We will know so much more 3 months from now,” she said. And while there are no formal plans to reissue the survey, “we’re maintaining communication and will have some kind of follow up” with the academic dermatologists.
“If we recognize any signals that are counter to what we say in this work we will immediately let people know,” she said.
The researchers received no outside funding for their study. Of the study’s 24 coauthors, nine disclosed financial relationships with industry.
SOURCE: Add the first auSOURCE: Reynolds et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020. doi: 10.1111/pde.14202.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Severe disease not uncommon in children hospitalized with COVID-19
Children with COVID-19 are more likely to develop severe illness and require intensive care than previously realized, data from a single-center study suggest.
Jerry Y. Chao, MD, of the department of anesthesiology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues reported their findings in an article published online May 11 in the Journal of Pediatrics.
“Thankfully most children with COVID-19 fare well, and some do not have any symptoms at all, but this research is a sobering reminder that children are not immune to this virus and some do require a higher level of care,” senior author Shivanand S. Medar, MD, FAAP, attending physician, Cardiac Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, and assistant professor of pediatrics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, said in a Montefiore Medical Center news release.
The study included 67 patients aged 1 month to 21 years (median, 13.1 years) who were treated for COVID-19 at a tertiary care children’s hospital between March 15 and April 13. Of those, 21 (31.3%) were treated as outpatients.
“As the number of patients screened for COVID-19 was restricted during the first weeks of the outbreak because of limited testing availability, the number of mildly symptomatic patients is not known, and therefore these 21 patients are not included in the analysis,” the authors wrote.
Of the 46 hospitalized patients, 33 (72%) were admitted to a general pediatric medical ward, and 13 (28%) were admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Almost one-third (14 children; 30.4%) of the admitted patients were obese, and almost one-quarter (11 children; 24.4%) had asthma, but neither factor was associated with an increased risk for PICU admission.
“We know that in adults, obesity is a risk factor for more severe disease, however, surprisingly, our study found that children admitted to the intensive care unit did not have a higher prevalence of obesity than those on the general unit,” Dr. Chao said in the news release.
Three of the PICU patients (25%) had preexisting seizure disorders, as did one (3%) patient on the general medical unit. “There was no significant difference in the usage of ibuprofen prior to hospitalization among patients admitted to medical unit compared with those admitted to the PICU,” the authors wrote.
Platelet counts were lower in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those on the general medical unit; however, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and pro–brain natriuretic peptide levels were all elevated in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those admitted to the general medical unit.
Patients admitted to the PICU were more likely to need high-flow nasal cannula. Ten (77%) patients in the PICU developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and six (46.2%) of them needed “invasive mechanical ventilation for a median of 9 days.”
The only clinical symptom significantly linked to PICU admission was shortness of breath (92.3% vs 30.3%; P < .001).
Eight (61.5%) of the 13 patients treated in the PICU were discharged to home; four (30.7%) were still hospitalized and receiving ventilatory support on day 14. One patient had metastatic cancer and died as a result of the cancer after life-sustaining therapy was withdrawn.
Those admitted to the PICU were more likely to receive treatment with remdesivir via compassionate use compared with those treated in the general medical unit. Seven (53.8%) patients in the PICU developed severe sepsis and septic shock syndromes.
The average hospital stay was 4 days longer for the children admitted to the PICU than for the children admitted to the general medical unit.
Cough (63%) and fever (60.9%) were the most frequently reported symptoms at admission. The median duration of symptoms before admission was 3 days. None of the children had traveled to an area affected by COVID-19 before becoming ill, and only 20 (43.5%) children were confirmed to have had contact with someone with COVID-19. “The lack of a known sick contact reported in our study may have implications for how healthcare providers identify and screen for potential cases,” the authors explained.
Although children are believed to experience milder SARS-CoV-2 illness, these results and those of an earlier study suggest that some pediatric patients develop illness severe enough to require PICU admission. “This subset had significantly higher markers of inflammation (CRP, pro-BNP, procalcitonin) compared with patients in the medical unit. Inflammation likely contributed to the high rate of ARDS we observed, although serum levels of IL-6 and other cytokines linked to ARDS were not determined,” the authors wrote.
A retrospective cohort study found that of 177 children and young adults treated in a single center, patients younger than 1 year and older than 15 years were more likely to become critically ill with COVID-19 (J Pediatr. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007).
Each of the two age groups accounted for 32% of the hospitalized patients.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with COVID-19 are more likely to develop severe illness and require intensive care than previously realized, data from a single-center study suggest.
Jerry Y. Chao, MD, of the department of anesthesiology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues reported their findings in an article published online May 11 in the Journal of Pediatrics.
“Thankfully most children with COVID-19 fare well, and some do not have any symptoms at all, but this research is a sobering reminder that children are not immune to this virus and some do require a higher level of care,” senior author Shivanand S. Medar, MD, FAAP, attending physician, Cardiac Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, and assistant professor of pediatrics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, said in a Montefiore Medical Center news release.
The study included 67 patients aged 1 month to 21 years (median, 13.1 years) who were treated for COVID-19 at a tertiary care children’s hospital between March 15 and April 13. Of those, 21 (31.3%) were treated as outpatients.
“As the number of patients screened for COVID-19 was restricted during the first weeks of the outbreak because of limited testing availability, the number of mildly symptomatic patients is not known, and therefore these 21 patients are not included in the analysis,” the authors wrote.
Of the 46 hospitalized patients, 33 (72%) were admitted to a general pediatric medical ward, and 13 (28%) were admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Almost one-third (14 children; 30.4%) of the admitted patients were obese, and almost one-quarter (11 children; 24.4%) had asthma, but neither factor was associated with an increased risk for PICU admission.
“We know that in adults, obesity is a risk factor for more severe disease, however, surprisingly, our study found that children admitted to the intensive care unit did not have a higher prevalence of obesity than those on the general unit,” Dr. Chao said in the news release.
Three of the PICU patients (25%) had preexisting seizure disorders, as did one (3%) patient on the general medical unit. “There was no significant difference in the usage of ibuprofen prior to hospitalization among patients admitted to medical unit compared with those admitted to the PICU,” the authors wrote.
Platelet counts were lower in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those on the general medical unit; however, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and pro–brain natriuretic peptide levels were all elevated in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those admitted to the general medical unit.
Patients admitted to the PICU were more likely to need high-flow nasal cannula. Ten (77%) patients in the PICU developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and six (46.2%) of them needed “invasive mechanical ventilation for a median of 9 days.”
The only clinical symptom significantly linked to PICU admission was shortness of breath (92.3% vs 30.3%; P < .001).
Eight (61.5%) of the 13 patients treated in the PICU were discharged to home; four (30.7%) were still hospitalized and receiving ventilatory support on day 14. One patient had metastatic cancer and died as a result of the cancer after life-sustaining therapy was withdrawn.
Those admitted to the PICU were more likely to receive treatment with remdesivir via compassionate use compared with those treated in the general medical unit. Seven (53.8%) patients in the PICU developed severe sepsis and septic shock syndromes.
The average hospital stay was 4 days longer for the children admitted to the PICU than for the children admitted to the general medical unit.
Cough (63%) and fever (60.9%) were the most frequently reported symptoms at admission. The median duration of symptoms before admission was 3 days. None of the children had traveled to an area affected by COVID-19 before becoming ill, and only 20 (43.5%) children were confirmed to have had contact with someone with COVID-19. “The lack of a known sick contact reported in our study may have implications for how healthcare providers identify and screen for potential cases,” the authors explained.
Although children are believed to experience milder SARS-CoV-2 illness, these results and those of an earlier study suggest that some pediatric patients develop illness severe enough to require PICU admission. “This subset had significantly higher markers of inflammation (CRP, pro-BNP, procalcitonin) compared with patients in the medical unit. Inflammation likely contributed to the high rate of ARDS we observed, although serum levels of IL-6 and other cytokines linked to ARDS were not determined,” the authors wrote.
A retrospective cohort study found that of 177 children and young adults treated in a single center, patients younger than 1 year and older than 15 years were more likely to become critically ill with COVID-19 (J Pediatr. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007).
Each of the two age groups accounted for 32% of the hospitalized patients.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with COVID-19 are more likely to develop severe illness and require intensive care than previously realized, data from a single-center study suggest.
Jerry Y. Chao, MD, of the department of anesthesiology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, and colleagues reported their findings in an article published online May 11 in the Journal of Pediatrics.
“Thankfully most children with COVID-19 fare well, and some do not have any symptoms at all, but this research is a sobering reminder that children are not immune to this virus and some do require a higher level of care,” senior author Shivanand S. Medar, MD, FAAP, attending physician, Cardiac Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, and assistant professor of pediatrics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, said in a Montefiore Medical Center news release.
The study included 67 patients aged 1 month to 21 years (median, 13.1 years) who were treated for COVID-19 at a tertiary care children’s hospital between March 15 and April 13. Of those, 21 (31.3%) were treated as outpatients.
“As the number of patients screened for COVID-19 was restricted during the first weeks of the outbreak because of limited testing availability, the number of mildly symptomatic patients is not known, and therefore these 21 patients are not included in the analysis,” the authors wrote.
Of the 46 hospitalized patients, 33 (72%) were admitted to a general pediatric medical ward, and 13 (28%) were admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Almost one-third (14 children; 30.4%) of the admitted patients were obese, and almost one-quarter (11 children; 24.4%) had asthma, but neither factor was associated with an increased risk for PICU admission.
“We know that in adults, obesity is a risk factor for more severe disease, however, surprisingly, our study found that children admitted to the intensive care unit did not have a higher prevalence of obesity than those on the general unit,” Dr. Chao said in the news release.
Three of the PICU patients (25%) had preexisting seizure disorders, as did one (3%) patient on the general medical unit. “There was no significant difference in the usage of ibuprofen prior to hospitalization among patients admitted to medical unit compared with those admitted to the PICU,” the authors wrote.
Platelet counts were lower in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those on the general medical unit; however, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and pro–brain natriuretic peptide levels were all elevated in patients admitted to the PICU compared with those admitted to the general medical unit.
Patients admitted to the PICU were more likely to need high-flow nasal cannula. Ten (77%) patients in the PICU developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and six (46.2%) of them needed “invasive mechanical ventilation for a median of 9 days.”
The only clinical symptom significantly linked to PICU admission was shortness of breath (92.3% vs 30.3%; P < .001).
Eight (61.5%) of the 13 patients treated in the PICU were discharged to home; four (30.7%) were still hospitalized and receiving ventilatory support on day 14. One patient had metastatic cancer and died as a result of the cancer after life-sustaining therapy was withdrawn.
Those admitted to the PICU were more likely to receive treatment with remdesivir via compassionate use compared with those treated in the general medical unit. Seven (53.8%) patients in the PICU developed severe sepsis and septic shock syndromes.
The average hospital stay was 4 days longer for the children admitted to the PICU than for the children admitted to the general medical unit.
Cough (63%) and fever (60.9%) were the most frequently reported symptoms at admission. The median duration of symptoms before admission was 3 days. None of the children had traveled to an area affected by COVID-19 before becoming ill, and only 20 (43.5%) children were confirmed to have had contact with someone with COVID-19. “The lack of a known sick contact reported in our study may have implications for how healthcare providers identify and screen for potential cases,” the authors explained.
Although children are believed to experience milder SARS-CoV-2 illness, these results and those of an earlier study suggest that some pediatric patients develop illness severe enough to require PICU admission. “This subset had significantly higher markers of inflammation (CRP, pro-BNP, procalcitonin) compared with patients in the medical unit. Inflammation likely contributed to the high rate of ARDS we observed, although serum levels of IL-6 and other cytokines linked to ARDS were not determined,” the authors wrote.
A retrospective cohort study found that of 177 children and young adults treated in a single center, patients younger than 1 year and older than 15 years were more likely to become critically ill with COVID-19 (J Pediatr. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007).
Each of the two age groups accounted for 32% of the hospitalized patients.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy, steroids had positive outcomes in COVID-19–associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome
According to study of a cluster of patients in France and Switzerland, children may experience an acute cardiac decompensation from the severe inflammatory state following SARS-CoV-2 infection, termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Treatment with immunoglobulin appears to be associated with recovery of left ventricular systolic function.
“The pediatric and cardiology communities should be acutely aware of this new disease probably related to SARS-CoV-2 infection (MIS-C), that shares similarities with Kawasaki disease but has specificities in its presentation,” researchers led by Zahra Belhadjer, MD, of Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital in Paris, wrote in a cases series report published online in Circulation “Early diagnosis and management appear to lead to favorable outcome using classical therapies. Elucidating the immune mechanisms of this disease will afford further insights for treatment and potential global prevention of severe forms.”
Over a 2-month period that coincided with the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in France and Switzerland, the researchers retrospectively collected clinical, biological, therapeutic, and early-outcomes data in 35 children who were admitted to pediatric ICUs in 14 centers for cardiogenic shock, left ventricular dysfunction, and severe inflammatory state. Their median age was 10 years, all presented with a fever, 80% had gastrointestinal symptoms of abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea, and 28% had comorbidities that included body mass index of greater than 25 kg/m2 (17%), asthma (9%), and lupus (3%), and overweight. Only 17% presented with chest pain. The researchers observed that left ventricular ejection fraction was less than 30% in 28% of patients, and 80% required inotropic support with 28% treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). All patients presented with a severe inflammatory state evidenced by elevated C-reactive protein and d-dimer. Interleukin 6 was elevated to a median of 135 pg/mL in 13 of the patients. Elevation of troponin I was constant but mild to moderate, and NT-proBNP or BNP elevation was present in all children.
Nearly all patients 35 (88%) patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction of nasopharyngeal swab or serology. Most patients (80%) received IV inotropic support, 71% received first-line IV immunoglobulin, 65% received anticoagulation with heparin, 34% received IV steroids having been considered high-risk patients with symptoms similar to an incomplete form of Kawasaki disease, and 8% received treatment with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist because of a persistent severe inflammatory state. Left ventricular function was restored in 71% of those discharged from the intensive care unit. No patient died, and all patients treated with ECMO were successfully weaned after a median of 4.5 days.
“Some aspects of this emerging pediatric disease (MIS-C) are similar to those of Kawasaki disease: prolonged fever, multisystem inflammation with skin rash, lymphadenopathy, diarrhea, meningism, and high levels of inflammatory biomarkers,” the researchers wrote. “But differences are important and raise the question as to whether this syndrome is Kawasaki disease with SARS-CoV-2 as the triggering agent, or represents a different syndrome (MIS-C). Kawasaki disease predominantly affects young children younger than 5 years, whereas the median age in our series is 10 years. Incomplete forms of Kawasaki disease occur in infants who may have fever as the sole clinical finding, whereas older patients are more prone to exhibit the complete form.”
They went on to note that the overlapping features between MIS-C and Kawasaki disease “may be due to similar pathophysiology. The etiologic agent of Kawasaki disease is unknown but likely to be ubiquitous, causing asymptomatic childhood infection but triggering the immunologic cascade of Kawasaki disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Please note that infection with a novel RNA virus that enters through the upper respiratory tract has been proposed to be the cause of the disease (see PLoS One. 2008 Feb 13;3:e1582 and J Infect Dis. 2011 Apr 1;203:1021-30).”
Based on the work of authors, it appears that a high index of suspicion for MIS-C is important for children who develop Kawasaki-like symptoms, David J. Goldberg, MD, said in an interview. “Although children have largely been spared from the acute respiratory presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the recognition and understanding of what appears to be a postviral inflammatory response is a critical first step in developing treatment algorithms for this disease process,” said Dr. Goldberg, a board-certified attending cardiologist in the cardiac center and fetal heart program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If inflammatory markers are elevated, particularly if there are accompanying gastrointestinal symptoms, the possibility of cardiac involvement suggests the utility of screening echocardiography. Given the potential need for inotropic or mechanical circulatory support, the presence of myocardial dysfunction dictates care in an intensive care unit capable of providing advanced therapies. While the evidence from Dr. Belhadjer’s cohort suggests that full recovery is probable, there is still much to be learned about this unique inflammatory syndrome and the alarm has rightly been sounded.”
The researchers and Dr. Goldberg reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Belhadjer Z et al. Circulation 2020 May 17; doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.048360.
According to study of a cluster of patients in France and Switzerland, children may experience an acute cardiac decompensation from the severe inflammatory state following SARS-CoV-2 infection, termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Treatment with immunoglobulin appears to be associated with recovery of left ventricular systolic function.
“The pediatric and cardiology communities should be acutely aware of this new disease probably related to SARS-CoV-2 infection (MIS-C), that shares similarities with Kawasaki disease but has specificities in its presentation,” researchers led by Zahra Belhadjer, MD, of Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital in Paris, wrote in a cases series report published online in Circulation “Early diagnosis and management appear to lead to favorable outcome using classical therapies. Elucidating the immune mechanisms of this disease will afford further insights for treatment and potential global prevention of severe forms.”
Over a 2-month period that coincided with the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in France and Switzerland, the researchers retrospectively collected clinical, biological, therapeutic, and early-outcomes data in 35 children who were admitted to pediatric ICUs in 14 centers for cardiogenic shock, left ventricular dysfunction, and severe inflammatory state. Their median age was 10 years, all presented with a fever, 80% had gastrointestinal symptoms of abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea, and 28% had comorbidities that included body mass index of greater than 25 kg/m2 (17%), asthma (9%), and lupus (3%), and overweight. Only 17% presented with chest pain. The researchers observed that left ventricular ejection fraction was less than 30% in 28% of patients, and 80% required inotropic support with 28% treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). All patients presented with a severe inflammatory state evidenced by elevated C-reactive protein and d-dimer. Interleukin 6 was elevated to a median of 135 pg/mL in 13 of the patients. Elevation of troponin I was constant but mild to moderate, and NT-proBNP or BNP elevation was present in all children.
Nearly all patients 35 (88%) patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction of nasopharyngeal swab or serology. Most patients (80%) received IV inotropic support, 71% received first-line IV immunoglobulin, 65% received anticoagulation with heparin, 34% received IV steroids having been considered high-risk patients with symptoms similar to an incomplete form of Kawasaki disease, and 8% received treatment with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist because of a persistent severe inflammatory state. Left ventricular function was restored in 71% of those discharged from the intensive care unit. No patient died, and all patients treated with ECMO were successfully weaned after a median of 4.5 days.
“Some aspects of this emerging pediatric disease (MIS-C) are similar to those of Kawasaki disease: prolonged fever, multisystem inflammation with skin rash, lymphadenopathy, diarrhea, meningism, and high levels of inflammatory biomarkers,” the researchers wrote. “But differences are important and raise the question as to whether this syndrome is Kawasaki disease with SARS-CoV-2 as the triggering agent, or represents a different syndrome (MIS-C). Kawasaki disease predominantly affects young children younger than 5 years, whereas the median age in our series is 10 years. Incomplete forms of Kawasaki disease occur in infants who may have fever as the sole clinical finding, whereas older patients are more prone to exhibit the complete form.”
They went on to note that the overlapping features between MIS-C and Kawasaki disease “may be due to similar pathophysiology. The etiologic agent of Kawasaki disease is unknown but likely to be ubiquitous, causing asymptomatic childhood infection but triggering the immunologic cascade of Kawasaki disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Please note that infection with a novel RNA virus that enters through the upper respiratory tract has been proposed to be the cause of the disease (see PLoS One. 2008 Feb 13;3:e1582 and J Infect Dis. 2011 Apr 1;203:1021-30).”
Based on the work of authors, it appears that a high index of suspicion for MIS-C is important for children who develop Kawasaki-like symptoms, David J. Goldberg, MD, said in an interview. “Although children have largely been spared from the acute respiratory presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the recognition and understanding of what appears to be a postviral inflammatory response is a critical first step in developing treatment algorithms for this disease process,” said Dr. Goldberg, a board-certified attending cardiologist in the cardiac center and fetal heart program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If inflammatory markers are elevated, particularly if there are accompanying gastrointestinal symptoms, the possibility of cardiac involvement suggests the utility of screening echocardiography. Given the potential need for inotropic or mechanical circulatory support, the presence of myocardial dysfunction dictates care in an intensive care unit capable of providing advanced therapies. While the evidence from Dr. Belhadjer’s cohort suggests that full recovery is probable, there is still much to be learned about this unique inflammatory syndrome and the alarm has rightly been sounded.”
The researchers and Dr. Goldberg reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Belhadjer Z et al. Circulation 2020 May 17; doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.048360.
According to study of a cluster of patients in France and Switzerland, children may experience an acute cardiac decompensation from the severe inflammatory state following SARS-CoV-2 infection, termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Treatment with immunoglobulin appears to be associated with recovery of left ventricular systolic function.
“The pediatric and cardiology communities should be acutely aware of this new disease probably related to SARS-CoV-2 infection (MIS-C), that shares similarities with Kawasaki disease but has specificities in its presentation,” researchers led by Zahra Belhadjer, MD, of Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital in Paris, wrote in a cases series report published online in Circulation “Early diagnosis and management appear to lead to favorable outcome using classical therapies. Elucidating the immune mechanisms of this disease will afford further insights for treatment and potential global prevention of severe forms.”
Over a 2-month period that coincided with the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in France and Switzerland, the researchers retrospectively collected clinical, biological, therapeutic, and early-outcomes data in 35 children who were admitted to pediatric ICUs in 14 centers for cardiogenic shock, left ventricular dysfunction, and severe inflammatory state. Their median age was 10 years, all presented with a fever, 80% had gastrointestinal symptoms of abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea, and 28% had comorbidities that included body mass index of greater than 25 kg/m2 (17%), asthma (9%), and lupus (3%), and overweight. Only 17% presented with chest pain. The researchers observed that left ventricular ejection fraction was less than 30% in 28% of patients, and 80% required inotropic support with 28% treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). All patients presented with a severe inflammatory state evidenced by elevated C-reactive protein and d-dimer. Interleukin 6 was elevated to a median of 135 pg/mL in 13 of the patients. Elevation of troponin I was constant but mild to moderate, and NT-proBNP or BNP elevation was present in all children.
Nearly all patients 35 (88%) patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction of nasopharyngeal swab or serology. Most patients (80%) received IV inotropic support, 71% received first-line IV immunoglobulin, 65% received anticoagulation with heparin, 34% received IV steroids having been considered high-risk patients with symptoms similar to an incomplete form of Kawasaki disease, and 8% received treatment with an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist because of a persistent severe inflammatory state. Left ventricular function was restored in 71% of those discharged from the intensive care unit. No patient died, and all patients treated with ECMO were successfully weaned after a median of 4.5 days.
“Some aspects of this emerging pediatric disease (MIS-C) are similar to those of Kawasaki disease: prolonged fever, multisystem inflammation with skin rash, lymphadenopathy, diarrhea, meningism, and high levels of inflammatory biomarkers,” the researchers wrote. “But differences are important and raise the question as to whether this syndrome is Kawasaki disease with SARS-CoV-2 as the triggering agent, or represents a different syndrome (MIS-C). Kawasaki disease predominantly affects young children younger than 5 years, whereas the median age in our series is 10 years. Incomplete forms of Kawasaki disease occur in infants who may have fever as the sole clinical finding, whereas older patients are more prone to exhibit the complete form.”
They went on to note that the overlapping features between MIS-C and Kawasaki disease “may be due to similar pathophysiology. The etiologic agent of Kawasaki disease is unknown but likely to be ubiquitous, causing asymptomatic childhood infection but triggering the immunologic cascade of Kawasaki disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Please note that infection with a novel RNA virus that enters through the upper respiratory tract has been proposed to be the cause of the disease (see PLoS One. 2008 Feb 13;3:e1582 and J Infect Dis. 2011 Apr 1;203:1021-30).”
Based on the work of authors, it appears that a high index of suspicion for MIS-C is important for children who develop Kawasaki-like symptoms, David J. Goldberg, MD, said in an interview. “Although children have largely been spared from the acute respiratory presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the recognition and understanding of what appears to be a postviral inflammatory response is a critical first step in developing treatment algorithms for this disease process,” said Dr. Goldberg, a board-certified attending cardiologist in the cardiac center and fetal heart program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “If inflammatory markers are elevated, particularly if there are accompanying gastrointestinal symptoms, the possibility of cardiac involvement suggests the utility of screening echocardiography. Given the potential need for inotropic or mechanical circulatory support, the presence of myocardial dysfunction dictates care in an intensive care unit capable of providing advanced therapies. While the evidence from Dr. Belhadjer’s cohort suggests that full recovery is probable, there is still much to be learned about this unique inflammatory syndrome and the alarm has rightly been sounded.”
The researchers and Dr. Goldberg reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Belhadjer Z et al. Circulation 2020 May 17; doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.048360.
FROM CIRCULATION
Timing of Surgery in Patients With Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
Study Overview
Objective. To determine the timing of surgical intervention in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Design. Open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled study.
Setting and participants. A total of 145 asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis were randomly assigned to early surgery or conservative care.
Main outcome measures. The primary endpoint was a composite of operative mortality or death from a cardiovascular cause during follow-up. The major secondary endpoint was death from any cause during follow-up.
Main results. The primary endpoint occurred in 1 of 73 patients (1%) in the early surgery group and 11 of 72 patients (15%) in the conservative care group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01-0.67, P = 0.003). The secondary endpoint occurred in 7% of patients in the early surgery group and 21% of patients in the conservative care group (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.12-0.90).
Conclusion. Among asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis, the incidence of the composite of operative mortality or death from cardiovascular causes during follow-up was significantly lower among those who underwent early valve replacement surgery compared to those who received conservative care.
Commentary
Aortic stenosis is a progressive disease that can lead to angina, heart failure, and death.1A higher mortality rate is reported in patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, as compared to patients with asymptomatic disease, and current guidelines require symptoms to be present in order to proceed with aortic valve replacement.2 Management of asymptomatic patients is often determined by the treating physician, with treatment decisions based on multiple factors, such as left ventricular function, stress test results, and the local level of expertise for surgery.2
In this context, the RECOVERY investigators report the findings of their well-designed randomized controlled study assessing patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis, which was defined as aortic valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 and either transvalvular velocity > 4.5 m/s or a mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg. Compared to patients who received conservative care, patients who underwent early valve surgery had a significantly lower rate of a composite of operative mortality or death from any cardiovascular causes during follow-up. Notably, the number needed to treat to prevent 1 death from cardiovascular causes within 4 years was 20.
The strengths of this trial include complete long-term follow-up (> 4 years) and low cross-over rates. Furthermore, as the study targeted a previously understudied population, there were a number of interesting observations, in addition to the primary endpoint. First, the risk of sudden death was high in patients who received conservative care, 4% at 4 years and 14% at 8 years, a finding contrary to the common belief that asymptomatic patients are at lower risk of sudden cardiac death. Second, 74% of patients assigned to initial conservative care required aortic valve replacement during the follow-up period. Furthermore, when the patients assigned to conservative care required surgery, it was often performed emergently (17%), which could have contributed to the higher mortality in this group of patients. Finally, hospitalization for heart failure was more common in patients randomized to conservative care compared to patients with early surgery. These findings will help physicians conduct detailed, informed discussions with their patients regarding the risks/benefits of early surgery versus conservative management.
There are a few limitations of the RECOVERY trial to consider. First, this study investigated the effect of surgical aortic valve replacement; whether its findings can be extended to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) requires further investigation. Patients who were enrolled in this study were younger and had fewer comorbidities than typical patients referred for TAVR. Second, all patients included in this study had the most severe form of aortic stenosis (valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 with either a peak velocity of ≥ 4.5 m/s or mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg). Finally, the study was performed in highly experienced centers, as evidenced by a very low (0%) mortality rate after aortic valve replacement. Therefore, the finding may not be applicable to centers that have less experience with aortic valve replacement surgery.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The findings of the RECOVERY trial strongly suggest a mortality benefit of early surgery compared to conservative management in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis.
–Taishi Hirai, MD
1. Otto CM, Prendergast B. Aortic-valve stenosis--from patients at risk to severe valve obstruction. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:744-756.
2. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e1159-e1195.
Study Overview
Objective. To determine the timing of surgical intervention in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Design. Open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled study.
Setting and participants. A total of 145 asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis were randomly assigned to early surgery or conservative care.
Main outcome measures. The primary endpoint was a composite of operative mortality or death from a cardiovascular cause during follow-up. The major secondary endpoint was death from any cause during follow-up.
Main results. The primary endpoint occurred in 1 of 73 patients (1%) in the early surgery group and 11 of 72 patients (15%) in the conservative care group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01-0.67, P = 0.003). The secondary endpoint occurred in 7% of patients in the early surgery group and 21% of patients in the conservative care group (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.12-0.90).
Conclusion. Among asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis, the incidence of the composite of operative mortality or death from cardiovascular causes during follow-up was significantly lower among those who underwent early valve replacement surgery compared to those who received conservative care.
Commentary
Aortic stenosis is a progressive disease that can lead to angina, heart failure, and death.1A higher mortality rate is reported in patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, as compared to patients with asymptomatic disease, and current guidelines require symptoms to be present in order to proceed with aortic valve replacement.2 Management of asymptomatic patients is often determined by the treating physician, with treatment decisions based on multiple factors, such as left ventricular function, stress test results, and the local level of expertise for surgery.2
In this context, the RECOVERY investigators report the findings of their well-designed randomized controlled study assessing patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis, which was defined as aortic valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 and either transvalvular velocity > 4.5 m/s or a mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg. Compared to patients who received conservative care, patients who underwent early valve surgery had a significantly lower rate of a composite of operative mortality or death from any cardiovascular causes during follow-up. Notably, the number needed to treat to prevent 1 death from cardiovascular causes within 4 years was 20.
The strengths of this trial include complete long-term follow-up (> 4 years) and low cross-over rates. Furthermore, as the study targeted a previously understudied population, there were a number of interesting observations, in addition to the primary endpoint. First, the risk of sudden death was high in patients who received conservative care, 4% at 4 years and 14% at 8 years, a finding contrary to the common belief that asymptomatic patients are at lower risk of sudden cardiac death. Second, 74% of patients assigned to initial conservative care required aortic valve replacement during the follow-up period. Furthermore, when the patients assigned to conservative care required surgery, it was often performed emergently (17%), which could have contributed to the higher mortality in this group of patients. Finally, hospitalization for heart failure was more common in patients randomized to conservative care compared to patients with early surgery. These findings will help physicians conduct detailed, informed discussions with their patients regarding the risks/benefits of early surgery versus conservative management.
There are a few limitations of the RECOVERY trial to consider. First, this study investigated the effect of surgical aortic valve replacement; whether its findings can be extended to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) requires further investigation. Patients who were enrolled in this study were younger and had fewer comorbidities than typical patients referred for TAVR. Second, all patients included in this study had the most severe form of aortic stenosis (valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 with either a peak velocity of ≥ 4.5 m/s or mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg). Finally, the study was performed in highly experienced centers, as evidenced by a very low (0%) mortality rate after aortic valve replacement. Therefore, the finding may not be applicable to centers that have less experience with aortic valve replacement surgery.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The findings of the RECOVERY trial strongly suggest a mortality benefit of early surgery compared to conservative management in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis.
–Taishi Hirai, MD
Study Overview
Objective. To determine the timing of surgical intervention in asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Design. Open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled study.
Setting and participants. A total of 145 asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis were randomly assigned to early surgery or conservative care.
Main outcome measures. The primary endpoint was a composite of operative mortality or death from a cardiovascular cause during follow-up. The major secondary endpoint was death from any cause during follow-up.
Main results. The primary endpoint occurred in 1 of 73 patients (1%) in the early surgery group and 11 of 72 patients (15%) in the conservative care group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01-0.67, P = 0.003). The secondary endpoint occurred in 7% of patients in the early surgery group and 21% of patients in the conservative care group (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.12-0.90).
Conclusion. Among asymptomatic patients with very severe aortic stenosis, the incidence of the composite of operative mortality or death from cardiovascular causes during follow-up was significantly lower among those who underwent early valve replacement surgery compared to those who received conservative care.
Commentary
Aortic stenosis is a progressive disease that can lead to angina, heart failure, and death.1A higher mortality rate is reported in patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, as compared to patients with asymptomatic disease, and current guidelines require symptoms to be present in order to proceed with aortic valve replacement.2 Management of asymptomatic patients is often determined by the treating physician, with treatment decisions based on multiple factors, such as left ventricular function, stress test results, and the local level of expertise for surgery.2
In this context, the RECOVERY investigators report the findings of their well-designed randomized controlled study assessing patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis, which was defined as aortic valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 and either transvalvular velocity > 4.5 m/s or a mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg. Compared to patients who received conservative care, patients who underwent early valve surgery had a significantly lower rate of a composite of operative mortality or death from any cardiovascular causes during follow-up. Notably, the number needed to treat to prevent 1 death from cardiovascular causes within 4 years was 20.
The strengths of this trial include complete long-term follow-up (> 4 years) and low cross-over rates. Furthermore, as the study targeted a previously understudied population, there were a number of interesting observations, in addition to the primary endpoint. First, the risk of sudden death was high in patients who received conservative care, 4% at 4 years and 14% at 8 years, a finding contrary to the common belief that asymptomatic patients are at lower risk of sudden cardiac death. Second, 74% of patients assigned to initial conservative care required aortic valve replacement during the follow-up period. Furthermore, when the patients assigned to conservative care required surgery, it was often performed emergently (17%), which could have contributed to the higher mortality in this group of patients. Finally, hospitalization for heart failure was more common in patients randomized to conservative care compared to patients with early surgery. These findings will help physicians conduct detailed, informed discussions with their patients regarding the risks/benefits of early surgery versus conservative management.
There are a few limitations of the RECOVERY trial to consider. First, this study investigated the effect of surgical aortic valve replacement; whether its findings can be extended to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) requires further investigation. Patients who were enrolled in this study were younger and had fewer comorbidities than typical patients referred for TAVR. Second, all patients included in this study had the most severe form of aortic stenosis (valve area ≤ 0.75 cm2 with either a peak velocity of ≥ 4.5 m/s or mean gradient ≥ 50 mm Hg). Finally, the study was performed in highly experienced centers, as evidenced by a very low (0%) mortality rate after aortic valve replacement. Therefore, the finding may not be applicable to centers that have less experience with aortic valve replacement surgery.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The findings of the RECOVERY trial strongly suggest a mortality benefit of early surgery compared to conservative management in patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis.
–Taishi Hirai, MD
1. Otto CM, Prendergast B. Aortic-valve stenosis--from patients at risk to severe valve obstruction. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:744-756.
2. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e1159-e1195.
1. Otto CM, Prendergast B. Aortic-valve stenosis--from patients at risk to severe valve obstruction. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:744-756.
2. Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e1159-e1195.