User login
Gene Tests Could Predict if a Drug Will Work for a Patient
What if there were tests that could tell you whether the following drugs were a good match for your patients: Antidepressants, statins, painkillers, anticlotting medicines, chemotherapy agents, HIV treatments, organ transplant antirejection drugs, proton pump inhibitors for heartburn, and more?
That’s quite a list. And that’s pharmacogenetics, testing patients for genetic differences that affect how well a given drug will work for them and what kind of side effects to expect.
“About 9 out of 10 people will have a genetic difference in their DNA that can impact how they respond to common medications,” said Emily J. Cicali, PharmD, a clinical associate at the University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
Dr. Cicali is the clinical director of UF Health’s MyRx, a virtual program that gives Florida and New Jersey residents access to pharmacogenetic (PGx) tests plus expert interpretation by the health system’s pharmacists. Genetic factors are thought to contribute to about 25% or more of inappropriate drug responses or adverse events, said Kristin Wiisanen, PharmD, dean of the College of Pharmacy at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science in North Chicago.
Dr. Cicali said.
Through a cheek swab or blood sample, the MyRx program — and a growing number of health system programs, doctors’ offices, and home tests available across the United States — gives consumers a window on inherited gene variants that can affect how their body activates, metabolizes, and clears away medications from a long list of widely used drugs.
Why PGx Tests Can Have a Big Impact
These tests work by looking for genes that control drug metabolism.
“You have several different drug-metabolizing enzymes in your liver,” Dr. Cicali explained. “Pharmacogenetic tests look for gene variants that encode for these enzymes. If you’re an ultrarapid metabolizer, you have more of the enzymes that metabolize certain drugs, and there could be a risk the drug won’t work well because it doesn’t stay in the body long enough. On the other end of the spectrum, poor metabolizers have low levels of enzymes that affect certain drugs, so the drugs hang around longer and cause side effects.”
While pharmacogenetics is still considered an emerging science, it’s becoming more mainstream as test prices drop, insurance coverage expands, and an explosion of new research boosts understanding of gene-drug interactions, Dr. Wiisanen said.
Politicians are trying to extend its reach, too. The Right Drug Dose Now Act of 2024, introduced in Congress in late March, aims to accelerate the use of PGx by boosting public awareness and by inserting PGx test results into consumers’ electronic health records. (Though a similar bill died in a US House subcommittee in 2023.)
“The use of pharmacogenetic data to guide prescribing is growing rapidly,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “It’s becoming a routine part of drug therapy for many medications.”
What the Research Shows
When researchers sequenced the DNA of more than 10,000 Mayo Clinic patients, they made a discovery that might surprise many Americans: Gene variants that affect the effectiveness and safety of widely used drugs are not rare glitches. More than 99% of study participants had at least one. And 79% had three or more.
The Mayo-Baylor RIGHT 10K Study — one of the largest PGx studies ever conducted in the United States — looked at 77 gene variants, most involved with drug metabolism in the liver. Researchers focused closely on 13 with extensively studied, gene-based prescribing recommendations for 21 drugs including antidepressants, statins, pain killers, anticlotting medications for heart conditions, HIV treatments, chemotherapy agents, and antirejection drugs for organ transplants.
When researchers added participants’ genetic data to their electronic health records, they also sent semi-urgent alerts, which are alerts with the potential for severe harm, to the clinicians of 61 study volunteers. Over half changed patients’ drugs or doses.
The changes made a difference. One participant taking the pain drug tramadol turned out to be a poor metabolizer and was having dizzy spells because blood levels of the drug stayed high for long periods. Stopping tramadol stopped the dizziness. A participant taking escitalopram plus bupropion for major depression found out that the combo was likely ineffective because they metabolized escitalopram rapidly. A switch to a higher dose of bupropion alone put their depression into full remission.
“So many factors play into how you respond to medications,” said Mayo Clinic pharmacogenomics pharmacist Jessica Wright, PharmD, BCACP, one of the study authors. “Genetics is one of those pieces. Pharmacogenetic testing can reveal things that clinicians may not have been aware of or could help explain a patient’s exaggerated side effect.”
Pharmacogenetics is also called pharmacogenomics. The terms are often used interchangeably, even among PGx pharmacists, though the first refers to how individual genes influence drug response and the second to the effects of multiple genes, said Kelly E. Caudle, PharmD, PhD, an associate member of the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee. Dr. Caudle is also co-principal investigator and director of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). The group creates, publishes, and posts evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for drugs with well-researched PGx influences.
By any name, PGx may help explain, predict, and sidestep unpredictable responses to a variety of drugs:
- In a 2023 multicenter study of 6944 people from seven European countries in The Lancet, those given customized drug treatments based on a 12-gene PGx panel had 30% fewer side effects than those who didn’t get this personalized prescribing. People in the study were being treated for cancer, heart disease, and mental health issues, among other conditions.
- In a 2023 from China’s Tongji University, Shanghai, of 650 survivors of strokes and transient ischemic attacks, those whose antiplatelet drugs (such as clopidogrel) were customized based on PGx testing had a lower risk for stroke and other vascular events in the next 90 days. The study was published in Frontiers in Pharmacology.
- In a University of Pennsylvania of 1944 adults with major depression, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, those whose antidepressants were guided by PGx test results were 28% more likely to go into remission during the first 24 weeks of treatment than those in a control group. But by 24 weeks, equal numbers were in remission. A 2023 Chinese of 11 depression studies, published in BMC Psychiatry, came to a similar conclusion: PGx-guided antidepressant prescriptions may help people feel better quicker, perhaps by avoiding some of the usual trial-and-error of different depression drugs.
PGx checks are already strongly recommended or considered routine before some medications are prescribed. These include abacavir (Ziagen), an antiviral treatment for HIV that can have severe side effects in people with one gene variant.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends genetic testing for people with colon cancer before starting the drug irinotecan (Camptosar), which can cause severe diarrhea and raise infection risk in people with a gene variant that slows the drug’s elimination from the body.
Genetic testing is also recommended by the FDA for people with acute lymphoblastic leukemia before receiving the chemotherapy drug mercaptopurine (Purinethol) because a gene variant that affects drug processing can trigger serious side effects and raise the risk for infection at standard dosages.
“One of the key benefits of pharmacogenomic testing is in preventing adverse drug reactions,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “Testing of the thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme to guide dosing with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine can help prevent myelosuppression, a serious adverse drug reaction caused by lower production of blood cells in bone marrow.”
When, Why, and How to Test
“A family doctor should consider a PGx test if a patient is planning on taking a medication for which there is a CPIC guideline with a dosing recommendation,” said Teri Klein, PhD, professor of biomedical data science at Stanford University in California, and principal investigator at PharmGKB, an online resource funded by the NIH that provides information for healthcare practitioners, researchers, and consumers about PGx. Affiliated with CPIC, it’s based at Stanford University.
You might also consider it for patients already on a drug who are “not responding or experiencing side effects,” Dr. Caudle said.
Here’s how four PGx experts suggest consumers and physicians approach this option.
Find a Test
More than a dozen PGx tests are on the market — some only a provider can order, others a consumer can order after a review by their provider or by a provider from the testing company. Some of the tests (using saliva) may be administered at home, while blood tests are done in a doctor’s office or laboratory. Companies that offer the tests include ARUP Laboratories, Genomind, Labcorp, Mayo Clinic Laboratories, Myriad Neuroscience, Precision Sciences Inc., Tempus, and OneOme, but there are many others online. (Keep in mind that many laboratories offer “lab-developed tests” — created for use in a single laboratory — but these can be harder to verify. “The FDA regulates pharmacogenomic testing in laboratories,” Dr. Wiisanen said, “but many of the regulatory parameters are still being defined.”)
Because PGx is so new, there is no official list of recommended tests. So you’ll have to do a little homework. You can check that the laboratory is accredited by searching for it in the NIH Genetic Testing Laboratory Registry database. Beyond that, you’ll have to consult other evidence-based resources to confirm that the drug you’re interested in has research-backed data about specific gene variants (alleles) that affect metabolism as well as research-based clinical guidelines for using PGx results to make prescribing decisions.
The CPIC’s guidelines include dosing and alternate drug recommendations for more than 100 antidepressants, chemotherapy drugs, the antiplatelet and anticlotting drugs clopidogrel and warfarin, local anesthetics, antivirals and antibacterials, pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and some cholesterol-lowering statins such as lovastatin and fluvastatin.
For help figuring out if a test looks for the right gene variants, Dr. Caudle and Dr. Wright recommended checking with the Association for Molecular Pathology’s website. The group published a brief list of best practices for pharmacogenomic testing in 2019. And it keeps a list of gene variants (alleles) that should be included in tests. Clinical guidelines from the CPIC and other groups, available on PharmGKB’s website, also list gene variants that affect the metabolism of the drug.
Consider Cost
The price tag for a test is typically several hundred dollars — but it can run as high as $1000-$2500. And health insurance doesn’t always pick up the tab.
In a 2023 University of Florida study of more than 1000 insurance claims for PGx testing, the number reimbursed varied from 72% for a pain diagnosis to 52% for cardiology to 46% for psychiatry.
Medicare covers some PGx testing when a consumer and their providers meet certain criteria, including whether a drug being considered has a significant gene-drug interaction. California’s Medi-Cal health insurance program covers PGx as do Medicaid programs in some states, including Arkansas and Rhode Island. You can find state-by-state coverage information on the Genetics Policy Hub’s website.
Understand the Results
As more insurers cover PGx, Dr. Klein and Dr. Wiisanen say the field will grow and more providers will use it to inform prescribing. But some health systems aren’t waiting.
In addition to UF Health’s MyRx, PGx is part of personalized medicine programs at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, Endeavor Health in Chicago, the Mayo Clinic, the University of California, San Francisco, Sanford Health in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Beyond testing, they offer a very useful service: A consult with a pharmacogenetics pharmacist to review the results and explain what they mean for a consumer’s current and future medications.
Physicians and curious consumers can also consult CPIC’s guidelines, which give recommendations about how to interpret the results of a PGx test, said Dr. Klein, a co-principal investigator at CPIC. CPIC has a grading system for both the evidence that supports the recommendation (high, moderate, or weak) and the recommendation itself (strong, moderate, or optional).
Currently, labeling for 456 prescription drugs sold in the United States includes some type of PGx information, according to the FDA’s Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Drug Labeling and an annotated guide from PharmGKB.
Just 108 drug labels currently tell doctors and patients what to do with the information — such as requiring or suggesting testing or offering prescribing recommendations, according to PharmGKB. In contrast, PharmGKB’s online resources include evidence-based clinical guidelines for 201 drugs from CPIC and from professional PGx societies in the Netherlands, Canada, France, and elsewhere.
Consumers and physicians can also look for a pharmacist with pharmacogenetics training in their area or through a nearby medical center to learn more, Dr. Wright suggested. And while consumers can test without working with their own physician, the experts advise against it. Don’t stop or change the dose of medications you already take on your own, they say . And do work with your primary care practitioner or specialist to get tested and understand how the results fit into the bigger picture of how your body responds to your medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What if there were tests that could tell you whether the following drugs were a good match for your patients: Antidepressants, statins, painkillers, anticlotting medicines, chemotherapy agents, HIV treatments, organ transplant antirejection drugs, proton pump inhibitors for heartburn, and more?
That’s quite a list. And that’s pharmacogenetics, testing patients for genetic differences that affect how well a given drug will work for them and what kind of side effects to expect.
“About 9 out of 10 people will have a genetic difference in their DNA that can impact how they respond to common medications,” said Emily J. Cicali, PharmD, a clinical associate at the University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
Dr. Cicali is the clinical director of UF Health’s MyRx, a virtual program that gives Florida and New Jersey residents access to pharmacogenetic (PGx) tests plus expert interpretation by the health system’s pharmacists. Genetic factors are thought to contribute to about 25% or more of inappropriate drug responses or adverse events, said Kristin Wiisanen, PharmD, dean of the College of Pharmacy at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science in North Chicago.
Dr. Cicali said.
Through a cheek swab or blood sample, the MyRx program — and a growing number of health system programs, doctors’ offices, and home tests available across the United States — gives consumers a window on inherited gene variants that can affect how their body activates, metabolizes, and clears away medications from a long list of widely used drugs.
Why PGx Tests Can Have a Big Impact
These tests work by looking for genes that control drug metabolism.
“You have several different drug-metabolizing enzymes in your liver,” Dr. Cicali explained. “Pharmacogenetic tests look for gene variants that encode for these enzymes. If you’re an ultrarapid metabolizer, you have more of the enzymes that metabolize certain drugs, and there could be a risk the drug won’t work well because it doesn’t stay in the body long enough. On the other end of the spectrum, poor metabolizers have low levels of enzymes that affect certain drugs, so the drugs hang around longer and cause side effects.”
While pharmacogenetics is still considered an emerging science, it’s becoming more mainstream as test prices drop, insurance coverage expands, and an explosion of new research boosts understanding of gene-drug interactions, Dr. Wiisanen said.
Politicians are trying to extend its reach, too. The Right Drug Dose Now Act of 2024, introduced in Congress in late March, aims to accelerate the use of PGx by boosting public awareness and by inserting PGx test results into consumers’ electronic health records. (Though a similar bill died in a US House subcommittee in 2023.)
“The use of pharmacogenetic data to guide prescribing is growing rapidly,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “It’s becoming a routine part of drug therapy for many medications.”
What the Research Shows
When researchers sequenced the DNA of more than 10,000 Mayo Clinic patients, they made a discovery that might surprise many Americans: Gene variants that affect the effectiveness and safety of widely used drugs are not rare glitches. More than 99% of study participants had at least one. And 79% had three or more.
The Mayo-Baylor RIGHT 10K Study — one of the largest PGx studies ever conducted in the United States — looked at 77 gene variants, most involved with drug metabolism in the liver. Researchers focused closely on 13 with extensively studied, gene-based prescribing recommendations for 21 drugs including antidepressants, statins, pain killers, anticlotting medications for heart conditions, HIV treatments, chemotherapy agents, and antirejection drugs for organ transplants.
When researchers added participants’ genetic data to their electronic health records, they also sent semi-urgent alerts, which are alerts with the potential for severe harm, to the clinicians of 61 study volunteers. Over half changed patients’ drugs or doses.
The changes made a difference. One participant taking the pain drug tramadol turned out to be a poor metabolizer and was having dizzy spells because blood levels of the drug stayed high for long periods. Stopping tramadol stopped the dizziness. A participant taking escitalopram plus bupropion for major depression found out that the combo was likely ineffective because they metabolized escitalopram rapidly. A switch to a higher dose of bupropion alone put their depression into full remission.
“So many factors play into how you respond to medications,” said Mayo Clinic pharmacogenomics pharmacist Jessica Wright, PharmD, BCACP, one of the study authors. “Genetics is one of those pieces. Pharmacogenetic testing can reveal things that clinicians may not have been aware of or could help explain a patient’s exaggerated side effect.”
Pharmacogenetics is also called pharmacogenomics. The terms are often used interchangeably, even among PGx pharmacists, though the first refers to how individual genes influence drug response and the second to the effects of multiple genes, said Kelly E. Caudle, PharmD, PhD, an associate member of the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee. Dr. Caudle is also co-principal investigator and director of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). The group creates, publishes, and posts evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for drugs with well-researched PGx influences.
By any name, PGx may help explain, predict, and sidestep unpredictable responses to a variety of drugs:
- In a 2023 multicenter study of 6944 people from seven European countries in The Lancet, those given customized drug treatments based on a 12-gene PGx panel had 30% fewer side effects than those who didn’t get this personalized prescribing. People in the study were being treated for cancer, heart disease, and mental health issues, among other conditions.
- In a 2023 from China’s Tongji University, Shanghai, of 650 survivors of strokes and transient ischemic attacks, those whose antiplatelet drugs (such as clopidogrel) were customized based on PGx testing had a lower risk for stroke and other vascular events in the next 90 days. The study was published in Frontiers in Pharmacology.
- In a University of Pennsylvania of 1944 adults with major depression, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, those whose antidepressants were guided by PGx test results were 28% more likely to go into remission during the first 24 weeks of treatment than those in a control group. But by 24 weeks, equal numbers were in remission. A 2023 Chinese of 11 depression studies, published in BMC Psychiatry, came to a similar conclusion: PGx-guided antidepressant prescriptions may help people feel better quicker, perhaps by avoiding some of the usual trial-and-error of different depression drugs.
PGx checks are already strongly recommended or considered routine before some medications are prescribed. These include abacavir (Ziagen), an antiviral treatment for HIV that can have severe side effects in people with one gene variant.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends genetic testing for people with colon cancer before starting the drug irinotecan (Camptosar), which can cause severe diarrhea and raise infection risk in people with a gene variant that slows the drug’s elimination from the body.
Genetic testing is also recommended by the FDA for people with acute lymphoblastic leukemia before receiving the chemotherapy drug mercaptopurine (Purinethol) because a gene variant that affects drug processing can trigger serious side effects and raise the risk for infection at standard dosages.
“One of the key benefits of pharmacogenomic testing is in preventing adverse drug reactions,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “Testing of the thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme to guide dosing with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine can help prevent myelosuppression, a serious adverse drug reaction caused by lower production of blood cells in bone marrow.”
When, Why, and How to Test
“A family doctor should consider a PGx test if a patient is planning on taking a medication for which there is a CPIC guideline with a dosing recommendation,” said Teri Klein, PhD, professor of biomedical data science at Stanford University in California, and principal investigator at PharmGKB, an online resource funded by the NIH that provides information for healthcare practitioners, researchers, and consumers about PGx. Affiliated with CPIC, it’s based at Stanford University.
You might also consider it for patients already on a drug who are “not responding or experiencing side effects,” Dr. Caudle said.
Here’s how four PGx experts suggest consumers and physicians approach this option.
Find a Test
More than a dozen PGx tests are on the market — some only a provider can order, others a consumer can order after a review by their provider or by a provider from the testing company. Some of the tests (using saliva) may be administered at home, while blood tests are done in a doctor’s office or laboratory. Companies that offer the tests include ARUP Laboratories, Genomind, Labcorp, Mayo Clinic Laboratories, Myriad Neuroscience, Precision Sciences Inc., Tempus, and OneOme, but there are many others online. (Keep in mind that many laboratories offer “lab-developed tests” — created for use in a single laboratory — but these can be harder to verify. “The FDA regulates pharmacogenomic testing in laboratories,” Dr. Wiisanen said, “but many of the regulatory parameters are still being defined.”)
Because PGx is so new, there is no official list of recommended tests. So you’ll have to do a little homework. You can check that the laboratory is accredited by searching for it in the NIH Genetic Testing Laboratory Registry database. Beyond that, you’ll have to consult other evidence-based resources to confirm that the drug you’re interested in has research-backed data about specific gene variants (alleles) that affect metabolism as well as research-based clinical guidelines for using PGx results to make prescribing decisions.
The CPIC’s guidelines include dosing and alternate drug recommendations for more than 100 antidepressants, chemotherapy drugs, the antiplatelet and anticlotting drugs clopidogrel and warfarin, local anesthetics, antivirals and antibacterials, pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and some cholesterol-lowering statins such as lovastatin and fluvastatin.
For help figuring out if a test looks for the right gene variants, Dr. Caudle and Dr. Wright recommended checking with the Association for Molecular Pathology’s website. The group published a brief list of best practices for pharmacogenomic testing in 2019. And it keeps a list of gene variants (alleles) that should be included in tests. Clinical guidelines from the CPIC and other groups, available on PharmGKB’s website, also list gene variants that affect the metabolism of the drug.
Consider Cost
The price tag for a test is typically several hundred dollars — but it can run as high as $1000-$2500. And health insurance doesn’t always pick up the tab.
In a 2023 University of Florida study of more than 1000 insurance claims for PGx testing, the number reimbursed varied from 72% for a pain diagnosis to 52% for cardiology to 46% for psychiatry.
Medicare covers some PGx testing when a consumer and their providers meet certain criteria, including whether a drug being considered has a significant gene-drug interaction. California’s Medi-Cal health insurance program covers PGx as do Medicaid programs in some states, including Arkansas and Rhode Island. You can find state-by-state coverage information on the Genetics Policy Hub’s website.
Understand the Results
As more insurers cover PGx, Dr. Klein and Dr. Wiisanen say the field will grow and more providers will use it to inform prescribing. But some health systems aren’t waiting.
In addition to UF Health’s MyRx, PGx is part of personalized medicine programs at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, Endeavor Health in Chicago, the Mayo Clinic, the University of California, San Francisco, Sanford Health in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Beyond testing, they offer a very useful service: A consult with a pharmacogenetics pharmacist to review the results and explain what they mean for a consumer’s current and future medications.
Physicians and curious consumers can also consult CPIC’s guidelines, which give recommendations about how to interpret the results of a PGx test, said Dr. Klein, a co-principal investigator at CPIC. CPIC has a grading system for both the evidence that supports the recommendation (high, moderate, or weak) and the recommendation itself (strong, moderate, or optional).
Currently, labeling for 456 prescription drugs sold in the United States includes some type of PGx information, according to the FDA’s Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Drug Labeling and an annotated guide from PharmGKB.
Just 108 drug labels currently tell doctors and patients what to do with the information — such as requiring or suggesting testing or offering prescribing recommendations, according to PharmGKB. In contrast, PharmGKB’s online resources include evidence-based clinical guidelines for 201 drugs from CPIC and from professional PGx societies in the Netherlands, Canada, France, and elsewhere.
Consumers and physicians can also look for a pharmacist with pharmacogenetics training in their area or through a nearby medical center to learn more, Dr. Wright suggested. And while consumers can test without working with their own physician, the experts advise against it. Don’t stop or change the dose of medications you already take on your own, they say . And do work with your primary care practitioner or specialist to get tested and understand how the results fit into the bigger picture of how your body responds to your medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What if there were tests that could tell you whether the following drugs were a good match for your patients: Antidepressants, statins, painkillers, anticlotting medicines, chemotherapy agents, HIV treatments, organ transplant antirejection drugs, proton pump inhibitors for heartburn, and more?
That’s quite a list. And that’s pharmacogenetics, testing patients for genetic differences that affect how well a given drug will work for them and what kind of side effects to expect.
“About 9 out of 10 people will have a genetic difference in their DNA that can impact how they respond to common medications,” said Emily J. Cicali, PharmD, a clinical associate at the University of Florida College of Pharmacy, Gainesville.
Dr. Cicali is the clinical director of UF Health’s MyRx, a virtual program that gives Florida and New Jersey residents access to pharmacogenetic (PGx) tests plus expert interpretation by the health system’s pharmacists. Genetic factors are thought to contribute to about 25% or more of inappropriate drug responses or adverse events, said Kristin Wiisanen, PharmD, dean of the College of Pharmacy at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science in North Chicago.
Dr. Cicali said.
Through a cheek swab or blood sample, the MyRx program — and a growing number of health system programs, doctors’ offices, and home tests available across the United States — gives consumers a window on inherited gene variants that can affect how their body activates, metabolizes, and clears away medications from a long list of widely used drugs.
Why PGx Tests Can Have a Big Impact
These tests work by looking for genes that control drug metabolism.
“You have several different drug-metabolizing enzymes in your liver,” Dr. Cicali explained. “Pharmacogenetic tests look for gene variants that encode for these enzymes. If you’re an ultrarapid metabolizer, you have more of the enzymes that metabolize certain drugs, and there could be a risk the drug won’t work well because it doesn’t stay in the body long enough. On the other end of the spectrum, poor metabolizers have low levels of enzymes that affect certain drugs, so the drugs hang around longer and cause side effects.”
While pharmacogenetics is still considered an emerging science, it’s becoming more mainstream as test prices drop, insurance coverage expands, and an explosion of new research boosts understanding of gene-drug interactions, Dr. Wiisanen said.
Politicians are trying to extend its reach, too. The Right Drug Dose Now Act of 2024, introduced in Congress in late March, aims to accelerate the use of PGx by boosting public awareness and by inserting PGx test results into consumers’ electronic health records. (Though a similar bill died in a US House subcommittee in 2023.)
“The use of pharmacogenetic data to guide prescribing is growing rapidly,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “It’s becoming a routine part of drug therapy for many medications.”
What the Research Shows
When researchers sequenced the DNA of more than 10,000 Mayo Clinic patients, they made a discovery that might surprise many Americans: Gene variants that affect the effectiveness and safety of widely used drugs are not rare glitches. More than 99% of study participants had at least one. And 79% had three or more.
The Mayo-Baylor RIGHT 10K Study — one of the largest PGx studies ever conducted in the United States — looked at 77 gene variants, most involved with drug metabolism in the liver. Researchers focused closely on 13 with extensively studied, gene-based prescribing recommendations for 21 drugs including antidepressants, statins, pain killers, anticlotting medications for heart conditions, HIV treatments, chemotherapy agents, and antirejection drugs for organ transplants.
When researchers added participants’ genetic data to their electronic health records, they also sent semi-urgent alerts, which are alerts with the potential for severe harm, to the clinicians of 61 study volunteers. Over half changed patients’ drugs or doses.
The changes made a difference. One participant taking the pain drug tramadol turned out to be a poor metabolizer and was having dizzy spells because blood levels of the drug stayed high for long periods. Stopping tramadol stopped the dizziness. A participant taking escitalopram plus bupropion for major depression found out that the combo was likely ineffective because they metabolized escitalopram rapidly. A switch to a higher dose of bupropion alone put their depression into full remission.
“So many factors play into how you respond to medications,” said Mayo Clinic pharmacogenomics pharmacist Jessica Wright, PharmD, BCACP, one of the study authors. “Genetics is one of those pieces. Pharmacogenetic testing can reveal things that clinicians may not have been aware of or could help explain a patient’s exaggerated side effect.”
Pharmacogenetics is also called pharmacogenomics. The terms are often used interchangeably, even among PGx pharmacists, though the first refers to how individual genes influence drug response and the second to the effects of multiple genes, said Kelly E. Caudle, PharmD, PhD, an associate member of the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee. Dr. Caudle is also co-principal investigator and director of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). The group creates, publishes, and posts evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for drugs with well-researched PGx influences.
By any name, PGx may help explain, predict, and sidestep unpredictable responses to a variety of drugs:
- In a 2023 multicenter study of 6944 people from seven European countries in The Lancet, those given customized drug treatments based on a 12-gene PGx panel had 30% fewer side effects than those who didn’t get this personalized prescribing. People in the study were being treated for cancer, heart disease, and mental health issues, among other conditions.
- In a 2023 from China’s Tongji University, Shanghai, of 650 survivors of strokes and transient ischemic attacks, those whose antiplatelet drugs (such as clopidogrel) were customized based on PGx testing had a lower risk for stroke and other vascular events in the next 90 days. The study was published in Frontiers in Pharmacology.
- In a University of Pennsylvania of 1944 adults with major depression, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, those whose antidepressants were guided by PGx test results were 28% more likely to go into remission during the first 24 weeks of treatment than those in a control group. But by 24 weeks, equal numbers were in remission. A 2023 Chinese of 11 depression studies, published in BMC Psychiatry, came to a similar conclusion: PGx-guided antidepressant prescriptions may help people feel better quicker, perhaps by avoiding some of the usual trial-and-error of different depression drugs.
PGx checks are already strongly recommended or considered routine before some medications are prescribed. These include abacavir (Ziagen), an antiviral treatment for HIV that can have severe side effects in people with one gene variant.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends genetic testing for people with colon cancer before starting the drug irinotecan (Camptosar), which can cause severe diarrhea and raise infection risk in people with a gene variant that slows the drug’s elimination from the body.
Genetic testing is also recommended by the FDA for people with acute lymphoblastic leukemia before receiving the chemotherapy drug mercaptopurine (Purinethol) because a gene variant that affects drug processing can trigger serious side effects and raise the risk for infection at standard dosages.
“One of the key benefits of pharmacogenomic testing is in preventing adverse drug reactions,” Dr. Wiisanen said. “Testing of the thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme to guide dosing with 6-mercaptopurine or azathioprine can help prevent myelosuppression, a serious adverse drug reaction caused by lower production of blood cells in bone marrow.”
When, Why, and How to Test
“A family doctor should consider a PGx test if a patient is planning on taking a medication for which there is a CPIC guideline with a dosing recommendation,” said Teri Klein, PhD, professor of biomedical data science at Stanford University in California, and principal investigator at PharmGKB, an online resource funded by the NIH that provides information for healthcare practitioners, researchers, and consumers about PGx. Affiliated with CPIC, it’s based at Stanford University.
You might also consider it for patients already on a drug who are “not responding or experiencing side effects,” Dr. Caudle said.
Here’s how four PGx experts suggest consumers and physicians approach this option.
Find a Test
More than a dozen PGx tests are on the market — some only a provider can order, others a consumer can order after a review by their provider or by a provider from the testing company. Some of the tests (using saliva) may be administered at home, while blood tests are done in a doctor’s office or laboratory. Companies that offer the tests include ARUP Laboratories, Genomind, Labcorp, Mayo Clinic Laboratories, Myriad Neuroscience, Precision Sciences Inc., Tempus, and OneOme, but there are many others online. (Keep in mind that many laboratories offer “lab-developed tests” — created for use in a single laboratory — but these can be harder to verify. “The FDA regulates pharmacogenomic testing in laboratories,” Dr. Wiisanen said, “but many of the regulatory parameters are still being defined.”)
Because PGx is so new, there is no official list of recommended tests. So you’ll have to do a little homework. You can check that the laboratory is accredited by searching for it in the NIH Genetic Testing Laboratory Registry database. Beyond that, you’ll have to consult other evidence-based resources to confirm that the drug you’re interested in has research-backed data about specific gene variants (alleles) that affect metabolism as well as research-based clinical guidelines for using PGx results to make prescribing decisions.
The CPIC’s guidelines include dosing and alternate drug recommendations for more than 100 antidepressants, chemotherapy drugs, the antiplatelet and anticlotting drugs clopidogrel and warfarin, local anesthetics, antivirals and antibacterials, pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and some cholesterol-lowering statins such as lovastatin and fluvastatin.
For help figuring out if a test looks for the right gene variants, Dr. Caudle and Dr. Wright recommended checking with the Association for Molecular Pathology’s website. The group published a brief list of best practices for pharmacogenomic testing in 2019. And it keeps a list of gene variants (alleles) that should be included in tests. Clinical guidelines from the CPIC and other groups, available on PharmGKB’s website, also list gene variants that affect the metabolism of the drug.
Consider Cost
The price tag for a test is typically several hundred dollars — but it can run as high as $1000-$2500. And health insurance doesn’t always pick up the tab.
In a 2023 University of Florida study of more than 1000 insurance claims for PGx testing, the number reimbursed varied from 72% for a pain diagnosis to 52% for cardiology to 46% for psychiatry.
Medicare covers some PGx testing when a consumer and their providers meet certain criteria, including whether a drug being considered has a significant gene-drug interaction. California’s Medi-Cal health insurance program covers PGx as do Medicaid programs in some states, including Arkansas and Rhode Island. You can find state-by-state coverage information on the Genetics Policy Hub’s website.
Understand the Results
As more insurers cover PGx, Dr. Klein and Dr. Wiisanen say the field will grow and more providers will use it to inform prescribing. But some health systems aren’t waiting.
In addition to UF Health’s MyRx, PGx is part of personalized medicine programs at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, Endeavor Health in Chicago, the Mayo Clinic, the University of California, San Francisco, Sanford Health in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee.
Beyond testing, they offer a very useful service: A consult with a pharmacogenetics pharmacist to review the results and explain what they mean for a consumer’s current and future medications.
Physicians and curious consumers can also consult CPIC’s guidelines, which give recommendations about how to interpret the results of a PGx test, said Dr. Klein, a co-principal investigator at CPIC. CPIC has a grading system for both the evidence that supports the recommendation (high, moderate, or weak) and the recommendation itself (strong, moderate, or optional).
Currently, labeling for 456 prescription drugs sold in the United States includes some type of PGx information, according to the FDA’s Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Drug Labeling and an annotated guide from PharmGKB.
Just 108 drug labels currently tell doctors and patients what to do with the information — such as requiring or suggesting testing or offering prescribing recommendations, according to PharmGKB. In contrast, PharmGKB’s online resources include evidence-based clinical guidelines for 201 drugs from CPIC and from professional PGx societies in the Netherlands, Canada, France, and elsewhere.
Consumers and physicians can also look for a pharmacist with pharmacogenetics training in their area or through a nearby medical center to learn more, Dr. Wright suggested. And while consumers can test without working with their own physician, the experts advise against it. Don’t stop or change the dose of medications you already take on your own, they say . And do work with your primary care practitioner or specialist to get tested and understand how the results fit into the bigger picture of how your body responds to your medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Roche Blood Test for Lp(a) Designated Breakthrough Device
The Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay, developed by Roche in partnership with Amgen, is designed to identify adults with elevated Lp(a) levels who may benefit from lipid-lowering therapies currently in development.
Lp(a) is a type of lipoprotein that is genetically inherited. Elevated levels have been associated with an increased risk for heart disease, stroke, and other blood vessel diseases.
Worldwide, about 1 in 5 people have high Lp(a) levels that are not significantly affected by lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. Elevated Lp(a) is particularly prevalent among women and people of African descent.
Lp(a) testing is “an important tool for clinicians, enabling them to make a more accurate assessment of [cardiovascular] risk, and it is expected to become a part of regular diagnostic testing in the coming years,” Roche said in a news release announcing the breakthrough designation for the Lp(a) blood test.
If approved, the Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay will be available on select Roche cobas platforms, the company reported.
Although low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol particles are much more abundant than Lp(a) particles and carry the greatest overall risk for heart disease, on a per-particle basis, atherogenic risk associated with Lp(a) is about six times higher than that associated with LDL cholesterol, a recent study showed.
There currently are no approved pharmacologic therapies to lower Lp(a) levels in the United States, but several hopefuls are in development.
One is zerlasiran (Silence Therapeutics), a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “gene silencing” therapy, which binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene, which encodes for apolipoprotein A, a dominant and rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
Treatment with zerlasiran produced significant and sustained reductions in Lp(a) concentrations in adults with elevated Lp(a) in the phase 1 APOLLO trial and the phase 2 ALPACAR-360 trial.
Other siRNA agents in development to lower Lp(a) levels include pelacarsen, lepodisiran, olpasiran, and muvalaplin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay, developed by Roche in partnership with Amgen, is designed to identify adults with elevated Lp(a) levels who may benefit from lipid-lowering therapies currently in development.
Lp(a) is a type of lipoprotein that is genetically inherited. Elevated levels have been associated with an increased risk for heart disease, stroke, and other blood vessel diseases.
Worldwide, about 1 in 5 people have high Lp(a) levels that are not significantly affected by lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. Elevated Lp(a) is particularly prevalent among women and people of African descent.
Lp(a) testing is “an important tool for clinicians, enabling them to make a more accurate assessment of [cardiovascular] risk, and it is expected to become a part of regular diagnostic testing in the coming years,” Roche said in a news release announcing the breakthrough designation for the Lp(a) blood test.
If approved, the Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay will be available on select Roche cobas platforms, the company reported.
Although low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol particles are much more abundant than Lp(a) particles and carry the greatest overall risk for heart disease, on a per-particle basis, atherogenic risk associated with Lp(a) is about six times higher than that associated with LDL cholesterol, a recent study showed.
There currently are no approved pharmacologic therapies to lower Lp(a) levels in the United States, but several hopefuls are in development.
One is zerlasiran (Silence Therapeutics), a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “gene silencing” therapy, which binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene, which encodes for apolipoprotein A, a dominant and rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
Treatment with zerlasiran produced significant and sustained reductions in Lp(a) concentrations in adults with elevated Lp(a) in the phase 1 APOLLO trial and the phase 2 ALPACAR-360 trial.
Other siRNA agents in development to lower Lp(a) levels include pelacarsen, lepodisiran, olpasiran, and muvalaplin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay, developed by Roche in partnership with Amgen, is designed to identify adults with elevated Lp(a) levels who may benefit from lipid-lowering therapies currently in development.
Lp(a) is a type of lipoprotein that is genetically inherited. Elevated levels have been associated with an increased risk for heart disease, stroke, and other blood vessel diseases.
Worldwide, about 1 in 5 people have high Lp(a) levels that are not significantly affected by lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. Elevated Lp(a) is particularly prevalent among women and people of African descent.
Lp(a) testing is “an important tool for clinicians, enabling them to make a more accurate assessment of [cardiovascular] risk, and it is expected to become a part of regular diagnostic testing in the coming years,” Roche said in a news release announcing the breakthrough designation for the Lp(a) blood test.
If approved, the Tina-quant Lp(a) RxDx assay will be available on select Roche cobas platforms, the company reported.
Although low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol particles are much more abundant than Lp(a) particles and carry the greatest overall risk for heart disease, on a per-particle basis, atherogenic risk associated with Lp(a) is about six times higher than that associated with LDL cholesterol, a recent study showed.
There currently are no approved pharmacologic therapies to lower Lp(a) levels in the United States, but several hopefuls are in development.
One is zerlasiran (Silence Therapeutics), a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “gene silencing” therapy, which binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene, which encodes for apolipoprotein A, a dominant and rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
Treatment with zerlasiran produced significant and sustained reductions in Lp(a) concentrations in adults with elevated Lp(a) in the phase 1 APOLLO trial and the phase 2 ALPACAR-360 trial.
Other siRNA agents in development to lower Lp(a) levels include pelacarsen, lepodisiran, olpasiran, and muvalaplin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
No Routine Cancer Screening Option? New MCED Tests May Help
Analyses presented during a session at the American Association for Cancer Research annual meeting, revealed that three new MCED tests — CanScan, MERCURY, and OncoSeek — could detect a range of cancers and recognize the tissue of origin with high accuracy. One — OncoSeek — could also provide an affordable cancer screening option for individuals living in lower-income countries.
The need for these noninvasive liquid biopsy tests that can accurately identify multiple cancer types with a single blood draw, especially cancers without routine screening strategies, is pressing. “We know that the current cancer standard of care screening will identify less than 50% of all cancers, while more than 50% of all cancer deaths occur in types of cancer with no recommended screening,” said co-moderator Marie E. Wood, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, in Aurora, Colorado.
That being said, “the clinical utility of multicancer detection tests has not been established and we’re concerned about issues of overdiagnosis and overtreatment,” she noted.
The Early Data
One new MCED test called CanScan, developed by Geneseeq Technology, uses plasma cell-free DNA fragment patterns to detect cancer signals as well as identify the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
Overall, the CanScan test covers cancer types that contribute to two thirds of new cancer cases and 74% of morality globally, said presenter Shanshan Yang, of Geneseeq Research Institute, in Nanjing, China.
However, only five of these cancer types have screening recommendations issued by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), Dr. Yang added.
The interim data comes from an ongoing large-scale prospective study evaluating the MCED test in a cohort of asymptomatic individuals between ages 45 and 75 years with an average risk for cancer and no cancer-related symptoms on enrollment.
Patients at baseline had their blood collected for the CanScan test and subsequently received annual routine physical exams once a year for 3 consecutive years, with an additional 2 years of follow-up.
The analysis included 3724 participants with analyzable samples at the data cutoff in September 2023. Among the 3724 participants, 29 had confirmed cancer diagnoses. Among these cases, 14 patients had their cancer confirmed through USPSTF recommended screening and 15 were detected through outside of standard USPSTF screening, such as a thyroid ultrasound, Dr. Yang explained.
Almost 90% of the cancers (26 of 29) were detected in the stage I or II, and eight (27.5%) were not one of the test’s 13 targeted cancer types.
The CanScan test had a sensitivity of 55.2%, identifying 16 of 29 of the patients with cancer, including 10 of 21 individuals with stage I (47.6%), and two of three with stage II (66.7%).
The test had a high specificity of 97.9%, meaning out of 100 people screened, only two had false negative findings.
Among the 15 patients who had their cancer detected outside of USPSTF screening recommendations, eight (53.3%) were found using a CanScan test, including patients with liver and endometrial cancers.
Compared with a positive predictive value of (PPV) of 1.6% with screening or physical exam methods alone, the CanScan test had a PPV of 17.4%, Dr. Yang reported.
“The MCED test holds significant potential for early cancer screening in asymptomatic populations,” Dr. Yang and colleagues concluded.
Another new MCED test called MERCURY, also developed by Geneseeq Technology and presented during the session, used a similar method to detect cancer signals and predict the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
The researchers initially validated the test using 3076 patients with cancer and 3477 healthy controls with a target specificity of 99%. In this group, researchers reported a sensitivity of 0.865 and a specificity of 0.989.
The team then performed an independent validation analysis with 1465 participants, 732 with cancer and 733 with no cancer, and confirmed a high sensitivity and specificity of 0.874 and 0.978, respectively. The sensitivity increased incrementally by cancer stage — 0.768 for stage I, 0.840 for stage II, 0.923 for stage III, and 0.971 for stage IV.
The test identified the tissue of origin with high accuracy, the researchers noted, but cautioned that the test needs “to be further validated in a prospective cohort study.”
MCED in Low-Income Settings
The session also featured findings on a new affordable MCED test called OncoSeek, which could provide greater access to cancer testing in low- and middle-income countries.
The OncoSeek algorithm identifies the presence of cancer using seven protein tumor markers alongside clinical information, such as gender and age. Like other tests, the test also predicts the possible tissue of origin.
The test can be run on clinical protein assay instruments that are already widely available, such as Roche cobas analyzer, Mao Mao, MD, PhD, the founder and CEO of SeekIn, of Shenzhen, China, told this news organization.
This “feature makes the test accessible worldwide, even in low- and middle-income countries,” he said. “These instruments are fully-automated and part of today’s clinical practice. Therefore, the test does not require additional infrastructure building and lab personal training.”
Another notable advantage: the OncoSeek test only costs about $20, compared with other MCED tests, which can cost anywhere from $200 to $1000.
To validate the technology in a large, diverse cohort, Dr. Mao and colleagues enrolled approximately 10,000 participants, including 2003 cancer cases and 7888 non-cancer cases.
Peripheral blood was collected from each participant and analyzed using a panel of the seven protein tumor markers — AFP, CA125, CA15-3, CA19-9, CA72-4, CEA, and CYFRA 21-1.
To reduce the risk for false positive findings, the team designed the OncoSeek algorithm to achieve a specificity of 93%. Dr. Mao and colleagues found a sensitivity of 51.7%, resulting in an overall accuracy of 84.6%.
The performance was consistent in additional validation cohorts in Brazil, China, and the United States, with sensitivities ranging from 39.0% to 77.6% for detecting nine common cancer types, including breast, colorectal, liver, lung, lymphoma, esophagus, ovary, pancreas, and stomach. The sensitivity for pancreatic cancer was at the high end of 77.6%.
The test could predict the tissue of origin in about two thirds of cases.
Given its low cost, OncoSeek represents an affordable and accessible option for cancer screening, the authors concluded.
Overall, “I think MCEDs have the potential to enhance cancer screening,” Dr. Wood told this news organization.
Still, questions remain about the optimal use of these tests, such as whether they are best for average-risk or higher risk populations, and how to integrate them into standard screening, she said.
Dr. Wood also cautioned that the studies presented in the session represent early data, and it is likely that the numbers, such as sensitivity and specificity, will change with further prospective analyses.
And ultimately, these tests should complement, not replace, standard screening. “A negative testing should not be taken as a sign to avoid standard screening,” Dr. Wood said.
Dr. Yang is an employee of Geneseeq Technology, Inc., and Dr. Mao is an employee of SeekIn. Dr. Wood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analyses presented during a session at the American Association for Cancer Research annual meeting, revealed that three new MCED tests — CanScan, MERCURY, and OncoSeek — could detect a range of cancers and recognize the tissue of origin with high accuracy. One — OncoSeek — could also provide an affordable cancer screening option for individuals living in lower-income countries.
The need for these noninvasive liquid biopsy tests that can accurately identify multiple cancer types with a single blood draw, especially cancers without routine screening strategies, is pressing. “We know that the current cancer standard of care screening will identify less than 50% of all cancers, while more than 50% of all cancer deaths occur in types of cancer with no recommended screening,” said co-moderator Marie E. Wood, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, in Aurora, Colorado.
That being said, “the clinical utility of multicancer detection tests has not been established and we’re concerned about issues of overdiagnosis and overtreatment,” she noted.
The Early Data
One new MCED test called CanScan, developed by Geneseeq Technology, uses plasma cell-free DNA fragment patterns to detect cancer signals as well as identify the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
Overall, the CanScan test covers cancer types that contribute to two thirds of new cancer cases and 74% of morality globally, said presenter Shanshan Yang, of Geneseeq Research Institute, in Nanjing, China.
However, only five of these cancer types have screening recommendations issued by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), Dr. Yang added.
The interim data comes from an ongoing large-scale prospective study evaluating the MCED test in a cohort of asymptomatic individuals between ages 45 and 75 years with an average risk for cancer and no cancer-related symptoms on enrollment.
Patients at baseline had their blood collected for the CanScan test and subsequently received annual routine physical exams once a year for 3 consecutive years, with an additional 2 years of follow-up.
The analysis included 3724 participants with analyzable samples at the data cutoff in September 2023. Among the 3724 participants, 29 had confirmed cancer diagnoses. Among these cases, 14 patients had their cancer confirmed through USPSTF recommended screening and 15 were detected through outside of standard USPSTF screening, such as a thyroid ultrasound, Dr. Yang explained.
Almost 90% of the cancers (26 of 29) were detected in the stage I or II, and eight (27.5%) were not one of the test’s 13 targeted cancer types.
The CanScan test had a sensitivity of 55.2%, identifying 16 of 29 of the patients with cancer, including 10 of 21 individuals with stage I (47.6%), and two of three with stage II (66.7%).
The test had a high specificity of 97.9%, meaning out of 100 people screened, only two had false negative findings.
Among the 15 patients who had their cancer detected outside of USPSTF screening recommendations, eight (53.3%) were found using a CanScan test, including patients with liver and endometrial cancers.
Compared with a positive predictive value of (PPV) of 1.6% with screening or physical exam methods alone, the CanScan test had a PPV of 17.4%, Dr. Yang reported.
“The MCED test holds significant potential for early cancer screening in asymptomatic populations,” Dr. Yang and colleagues concluded.
Another new MCED test called MERCURY, also developed by Geneseeq Technology and presented during the session, used a similar method to detect cancer signals and predict the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
The researchers initially validated the test using 3076 patients with cancer and 3477 healthy controls with a target specificity of 99%. In this group, researchers reported a sensitivity of 0.865 and a specificity of 0.989.
The team then performed an independent validation analysis with 1465 participants, 732 with cancer and 733 with no cancer, and confirmed a high sensitivity and specificity of 0.874 and 0.978, respectively. The sensitivity increased incrementally by cancer stage — 0.768 for stage I, 0.840 for stage II, 0.923 for stage III, and 0.971 for stage IV.
The test identified the tissue of origin with high accuracy, the researchers noted, but cautioned that the test needs “to be further validated in a prospective cohort study.”
MCED in Low-Income Settings
The session also featured findings on a new affordable MCED test called OncoSeek, which could provide greater access to cancer testing in low- and middle-income countries.
The OncoSeek algorithm identifies the presence of cancer using seven protein tumor markers alongside clinical information, such as gender and age. Like other tests, the test also predicts the possible tissue of origin.
The test can be run on clinical protein assay instruments that are already widely available, such as Roche cobas analyzer, Mao Mao, MD, PhD, the founder and CEO of SeekIn, of Shenzhen, China, told this news organization.
This “feature makes the test accessible worldwide, even in low- and middle-income countries,” he said. “These instruments are fully-automated and part of today’s clinical practice. Therefore, the test does not require additional infrastructure building and lab personal training.”
Another notable advantage: the OncoSeek test only costs about $20, compared with other MCED tests, which can cost anywhere from $200 to $1000.
To validate the technology in a large, diverse cohort, Dr. Mao and colleagues enrolled approximately 10,000 participants, including 2003 cancer cases and 7888 non-cancer cases.
Peripheral blood was collected from each participant and analyzed using a panel of the seven protein tumor markers — AFP, CA125, CA15-3, CA19-9, CA72-4, CEA, and CYFRA 21-1.
To reduce the risk for false positive findings, the team designed the OncoSeek algorithm to achieve a specificity of 93%. Dr. Mao and colleagues found a sensitivity of 51.7%, resulting in an overall accuracy of 84.6%.
The performance was consistent in additional validation cohorts in Brazil, China, and the United States, with sensitivities ranging from 39.0% to 77.6% for detecting nine common cancer types, including breast, colorectal, liver, lung, lymphoma, esophagus, ovary, pancreas, and stomach. The sensitivity for pancreatic cancer was at the high end of 77.6%.
The test could predict the tissue of origin in about two thirds of cases.
Given its low cost, OncoSeek represents an affordable and accessible option for cancer screening, the authors concluded.
Overall, “I think MCEDs have the potential to enhance cancer screening,” Dr. Wood told this news organization.
Still, questions remain about the optimal use of these tests, such as whether they are best for average-risk or higher risk populations, and how to integrate them into standard screening, she said.
Dr. Wood also cautioned that the studies presented in the session represent early data, and it is likely that the numbers, such as sensitivity and specificity, will change with further prospective analyses.
And ultimately, these tests should complement, not replace, standard screening. “A negative testing should not be taken as a sign to avoid standard screening,” Dr. Wood said.
Dr. Yang is an employee of Geneseeq Technology, Inc., and Dr. Mao is an employee of SeekIn. Dr. Wood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Analyses presented during a session at the American Association for Cancer Research annual meeting, revealed that three new MCED tests — CanScan, MERCURY, and OncoSeek — could detect a range of cancers and recognize the tissue of origin with high accuracy. One — OncoSeek — could also provide an affordable cancer screening option for individuals living in lower-income countries.
The need for these noninvasive liquid biopsy tests that can accurately identify multiple cancer types with a single blood draw, especially cancers without routine screening strategies, is pressing. “We know that the current cancer standard of care screening will identify less than 50% of all cancers, while more than 50% of all cancer deaths occur in types of cancer with no recommended screening,” said co-moderator Marie E. Wood, MD, of the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, in Aurora, Colorado.
That being said, “the clinical utility of multicancer detection tests has not been established and we’re concerned about issues of overdiagnosis and overtreatment,” she noted.
The Early Data
One new MCED test called CanScan, developed by Geneseeq Technology, uses plasma cell-free DNA fragment patterns to detect cancer signals as well as identify the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
Overall, the CanScan test covers cancer types that contribute to two thirds of new cancer cases and 74% of morality globally, said presenter Shanshan Yang, of Geneseeq Research Institute, in Nanjing, China.
However, only five of these cancer types have screening recommendations issued by the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), Dr. Yang added.
The interim data comes from an ongoing large-scale prospective study evaluating the MCED test in a cohort of asymptomatic individuals between ages 45 and 75 years with an average risk for cancer and no cancer-related symptoms on enrollment.
Patients at baseline had their blood collected for the CanScan test and subsequently received annual routine physical exams once a year for 3 consecutive years, with an additional 2 years of follow-up.
The analysis included 3724 participants with analyzable samples at the data cutoff in September 2023. Among the 3724 participants, 29 had confirmed cancer diagnoses. Among these cases, 14 patients had their cancer confirmed through USPSTF recommended screening and 15 were detected through outside of standard USPSTF screening, such as a thyroid ultrasound, Dr. Yang explained.
Almost 90% of the cancers (26 of 29) were detected in the stage I or II, and eight (27.5%) were not one of the test’s 13 targeted cancer types.
The CanScan test had a sensitivity of 55.2%, identifying 16 of 29 of the patients with cancer, including 10 of 21 individuals with stage I (47.6%), and two of three with stage II (66.7%).
The test had a high specificity of 97.9%, meaning out of 100 people screened, only two had false negative findings.
Among the 15 patients who had their cancer detected outside of USPSTF screening recommendations, eight (53.3%) were found using a CanScan test, including patients with liver and endometrial cancers.
Compared with a positive predictive value of (PPV) of 1.6% with screening or physical exam methods alone, the CanScan test had a PPV of 17.4%, Dr. Yang reported.
“The MCED test holds significant potential for early cancer screening in asymptomatic populations,” Dr. Yang and colleagues concluded.
Another new MCED test called MERCURY, also developed by Geneseeq Technology and presented during the session, used a similar method to detect cancer signals and predict the tissue of origin across 13 cancer types.
The researchers initially validated the test using 3076 patients with cancer and 3477 healthy controls with a target specificity of 99%. In this group, researchers reported a sensitivity of 0.865 and a specificity of 0.989.
The team then performed an independent validation analysis with 1465 participants, 732 with cancer and 733 with no cancer, and confirmed a high sensitivity and specificity of 0.874 and 0.978, respectively. The sensitivity increased incrementally by cancer stage — 0.768 for stage I, 0.840 for stage II, 0.923 for stage III, and 0.971 for stage IV.
The test identified the tissue of origin with high accuracy, the researchers noted, but cautioned that the test needs “to be further validated in a prospective cohort study.”
MCED in Low-Income Settings
The session also featured findings on a new affordable MCED test called OncoSeek, which could provide greater access to cancer testing in low- and middle-income countries.
The OncoSeek algorithm identifies the presence of cancer using seven protein tumor markers alongside clinical information, such as gender and age. Like other tests, the test also predicts the possible tissue of origin.
The test can be run on clinical protein assay instruments that are already widely available, such as Roche cobas analyzer, Mao Mao, MD, PhD, the founder and CEO of SeekIn, of Shenzhen, China, told this news organization.
This “feature makes the test accessible worldwide, even in low- and middle-income countries,” he said. “These instruments are fully-automated and part of today’s clinical practice. Therefore, the test does not require additional infrastructure building and lab personal training.”
Another notable advantage: the OncoSeek test only costs about $20, compared with other MCED tests, which can cost anywhere from $200 to $1000.
To validate the technology in a large, diverse cohort, Dr. Mao and colleagues enrolled approximately 10,000 participants, including 2003 cancer cases and 7888 non-cancer cases.
Peripheral blood was collected from each participant and analyzed using a panel of the seven protein tumor markers — AFP, CA125, CA15-3, CA19-9, CA72-4, CEA, and CYFRA 21-1.
To reduce the risk for false positive findings, the team designed the OncoSeek algorithm to achieve a specificity of 93%. Dr. Mao and colleagues found a sensitivity of 51.7%, resulting in an overall accuracy of 84.6%.
The performance was consistent in additional validation cohorts in Brazil, China, and the United States, with sensitivities ranging from 39.0% to 77.6% for detecting nine common cancer types, including breast, colorectal, liver, lung, lymphoma, esophagus, ovary, pancreas, and stomach. The sensitivity for pancreatic cancer was at the high end of 77.6%.
The test could predict the tissue of origin in about two thirds of cases.
Given its low cost, OncoSeek represents an affordable and accessible option for cancer screening, the authors concluded.
Overall, “I think MCEDs have the potential to enhance cancer screening,” Dr. Wood told this news organization.
Still, questions remain about the optimal use of these tests, such as whether they are best for average-risk or higher risk populations, and how to integrate them into standard screening, she said.
Dr. Wood also cautioned that the studies presented in the session represent early data, and it is likely that the numbers, such as sensitivity and specificity, will change with further prospective analyses.
And ultimately, these tests should complement, not replace, standard screening. “A negative testing should not be taken as a sign to avoid standard screening,” Dr. Wood said.
Dr. Yang is an employee of Geneseeq Technology, Inc., and Dr. Mao is an employee of SeekIn. Dr. Wood had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs Danicopan Add-On for Extravascular Hemolysis in Adults With PNH
PNH is a rare blood disorder affecting 1-10 individuals per million. The condition, which eliminates red blood cells and leads to blood clots and impaired bone marrow function, can cause life-threatening anemia, thrombosis, and bone marrow dysfunction. About half of people with the condition die from thrombotic complications.
Ravulizumab and eculizumab, also both made by AstraZeneca, inhibit the destruction of red blood cells. However, 10%-20% of patients treated with the antibody infusions experience significant extravascular hemolysis, in which these surviving red blood cells are eliminated by the spleen and liver. Extravascular hemolysis can lead to ongoing anemia, which can lead patients to require blood transfusions.
Danicopan, an investigational, first-in-class, oral complement factor D inhibitor, is designed to control intravascular hemolysis and prevent extravascular hemolysis.
Approval of the oral medication was based on the phase 3 ALPHA trial in 63 patients with PNH who received ravulizumab or eculizumab and experienced significant extravascular hemolysis. These patients were randomized 2:1 to either danicopan or placebo.
Danicopan add-on significantly improved hemoglobin concentrations at 12 weeks (least squares mean improvement from baseline: 2.94 g/dL with danicopan vs 0.50 g/dL with placebo) and made transfusions less likely.
Headache, nausea, arthralgia, and diarrhea were the most common treatment-emergent side effects. Serious adverse events in the danicopan group included cholecystitis and COVID-19 in one patient each.
Danicopan carries a boxed warning of serious infections and is available only through a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PNH is a rare blood disorder affecting 1-10 individuals per million. The condition, which eliminates red blood cells and leads to blood clots and impaired bone marrow function, can cause life-threatening anemia, thrombosis, and bone marrow dysfunction. About half of people with the condition die from thrombotic complications.
Ravulizumab and eculizumab, also both made by AstraZeneca, inhibit the destruction of red blood cells. However, 10%-20% of patients treated with the antibody infusions experience significant extravascular hemolysis, in which these surviving red blood cells are eliminated by the spleen and liver. Extravascular hemolysis can lead to ongoing anemia, which can lead patients to require blood transfusions.
Danicopan, an investigational, first-in-class, oral complement factor D inhibitor, is designed to control intravascular hemolysis and prevent extravascular hemolysis.
Approval of the oral medication was based on the phase 3 ALPHA trial in 63 patients with PNH who received ravulizumab or eculizumab and experienced significant extravascular hemolysis. These patients were randomized 2:1 to either danicopan or placebo.
Danicopan add-on significantly improved hemoglobin concentrations at 12 weeks (least squares mean improvement from baseline: 2.94 g/dL with danicopan vs 0.50 g/dL with placebo) and made transfusions less likely.
Headache, nausea, arthralgia, and diarrhea were the most common treatment-emergent side effects. Serious adverse events in the danicopan group included cholecystitis and COVID-19 in one patient each.
Danicopan carries a boxed warning of serious infections and is available only through a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PNH is a rare blood disorder affecting 1-10 individuals per million. The condition, which eliminates red blood cells and leads to blood clots and impaired bone marrow function, can cause life-threatening anemia, thrombosis, and bone marrow dysfunction. About half of people with the condition die from thrombotic complications.
Ravulizumab and eculizumab, also both made by AstraZeneca, inhibit the destruction of red blood cells. However, 10%-20% of patients treated with the antibody infusions experience significant extravascular hemolysis, in which these surviving red blood cells are eliminated by the spleen and liver. Extravascular hemolysis can lead to ongoing anemia, which can lead patients to require blood transfusions.
Danicopan, an investigational, first-in-class, oral complement factor D inhibitor, is designed to control intravascular hemolysis and prevent extravascular hemolysis.
Approval of the oral medication was based on the phase 3 ALPHA trial in 63 patients with PNH who received ravulizumab or eculizumab and experienced significant extravascular hemolysis. These patients were randomized 2:1 to either danicopan or placebo.
Danicopan add-on significantly improved hemoglobin concentrations at 12 weeks (least squares mean improvement from baseline: 2.94 g/dL with danicopan vs 0.50 g/dL with placebo) and made transfusions less likely.
Headache, nausea, arthralgia, and diarrhea were the most common treatment-emergent side effects. Serious adverse events in the danicopan group included cholecystitis and COVID-19 in one patient each.
Danicopan carries a boxed warning of serious infections and is available only through a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Anticoagulants Safe With Enzyme-Inducing Meds for Epilepsy
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AES 2023
Hematology is in the Brodsky family’s blood
In interviews, Robert and Max Brodsky spoke about the appeal of hematology and the threads that unite them with family members who came before. The elder Brodsky also talked about the work that’s made him the proudest during his year-long presidency at ASH.
Robert A. Brodsky is professor of medicine and director of hematology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is stepping down as ASH president at its annual meeting in San Diego, December 9-12. Here are excerpts from our conversation:
Q: What drew your dad into medicine?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: He was going through his medical training at the University of Pennsylvania, then the Vietnam War came, and he served at the National Institutes of Health in what they referred to as the Yellow Berets. He got very interested in retroviruses and viruses that lead to cancer, which was a foreign idea at the time. This led him into hematology, stem cells, and myeloproliferative disorders.
He had a very successful career in hematology and just loved it. He performed the first bone marrow transplant in the tristate area of Pennsylvania, Delaware, and New Jersey.
Q: What did he like about hematology specifically?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: It’s a fascinating field, probably the most scientific area of medicine. It’s so easy to access blood and bone marrow. You can grow it, you can look at it, you can see it. It’s hard to do that with a lung, heart, kidney, or brain. Even back then, they could translate some of the science. What really drew him to hematology — and me, for that matter — was looking at a blood smear or bone marrow and being able to make a diagnosis. The other thing is the personal aspect. Hematologists tend to like the long-term relationships that they develop with their patients over the years.
Q: What were the biggest transformations in hematology during his career?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: Bone marrow transplant had the biggest impact, and it’s an area he really pioneered. He was very much involved in some of the early bone marrow transplants and was very close with Dr. George W. Santos, who was at Johns Hopkins and one of the big pioneers in that area as well. To be able to take marrow from related donors, get it to grow without the patient rejecting it, and cure a disease, was really huge. When he started doing this, patients had no other option. To see patients be cured was incredibly satisfying to him.
Q: How did you end up following your father into hematology?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: My brother Jeff, who’s a surgeon and older than me, knew he was going into medicine — probably about 3 hours after he was born. I came to it late. I was a political science major as an undergrad and really trying to figure out what I wanted to do. In my sophomore year, I decided I wanted to give this a shot. My dad worked very hard, long hours, but you could tell he loved what he did. And he was never absent, always involved in our lives and still made time for everyone. At some level, that must have had an influence on me.
Q: What has changed in hematology over your 30-plus years in medicine?
A: When I look back at when I was a fellow, it’s just mind-boggling how many lethal or life-threatening diseases are now pretty easy to treat. I studied disorders like aplastic anemia, which was very fatal. Without treatment, patients would die within a year. Now, over 95% are cured. Another classic examples is chronic myeloid leukemia disorder. Back when I was a fellow, the median survival for CML was maybe 4 to 6 years. Now, Kareem Abdul Jabbar has had this[for about 15 years]. Also a lot of hematologic malignancies are being cured with immunotherapy approaches. We’ve figured out the pathophysiology of a lot of diseases, and there are incredible genetic diagnostic assays.
Q: What was your father’s relationship with ASH?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: The first ASH meeting was 1958 in Atlantic City, New Jersey. There were 300 hematologists there, and my dad was one of them. We’re going to have over 30,000 people in San Diego, which is a record, and another 5,000 or 6,000 virtually.
Q: As ASH president, what are your biggest accomplishments when it comes to addressing the shortage of hematologists and other issues?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH is investing $19 million to develop fellowships with a focus on hematology.* This is going to put lots of new hematologists into the workforce over the next 5 to 10 years. We’ve also been working on the Maintenance of Certification [MOC] process to make it less onerous on physicians. It’s really a bad process, and it’s not just ASH [that’s complaining], it’s all of medicine. We’re hearing this from GI, endocrine, renal and the general internists.
[In a September 2023 letter to the American Board of Internal Medicine’s president and chief officer, Dr. Brodsky wrote that “ASH continues to support the importance of lifelong learning for hematologists via a program that is evidence-based, relevant to one’s practice, and transparent; however, these three basic requirements are not met by the current ABIM MOC program.” ASH is calling for a new and reformed MOC program.]
Q: What convinced ASH to expand its journals by adding Blood Neoplasia and Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH has two flagship journals right now, Blood and Blood Advances, and they’re both very competitive, high-impact journals. It turns out there’s not enough room to publish all the new science, and they end up rejecting the majority of the submissions that come to them. We decided to keep these journals in the ASH family because there’s some fantastic clinical trials and science that would be going elsewhere.
Dr. Brodsky’s sons both have medical degrees: Brett Brodsky, DO, is a resident at Virginia Commonwealth University who plans to become a sports medicine specialist, and Max Brodsky, MD, is a second-year fellow in hematology at Johns Hopkins University.
In an interview, Max Brodsky, MD, talked about the roots of his family’s dedication to caring for others.
Q: What drew you to hematology?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’ve watched both my dad and my grandfather be leaders in the field as both physicians and scientists, and that was very inspirational for me to see. And I went to a medical school [Drexel University College of Medicine] that my dad went to and where my grandfather was on faculty. That was like walking in their footsteps in a major way.
Q: What do you hope to focus on as a hematologist?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’m still working through that, but I am really interested in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Patients used to not be able to survive their initial episodes, but now we have good treatments and are able to follow them as outpatients. With this whole cohort of patients that are surviving, we’re seeing that they have more health problems — more heart disease, more strokes and kidney disease. There’s a whole growing field exploring how to treat these patients for their lifespan.
Q: How do you deal with the reality that more of your patients will die than in some other medical fields?
Dr. Max Brodsky: It is challenging, but I also see those moments as opportunities to support patients and families. I’m good at connecting to patients and families who are in scary situations. I’ve always had that skill of putting people at ease, making people feel calm, knowing that they can trust me, and I have their best interests in mind.
Q: Why do you think your family is so committed to medicine?
Dr. Max Brodsky: We’re Jewish, and looking to help the world is one of the main core values of Judaism. The Torah expects us to make this world better. Actually, my great-grandfather Max, whom I’m named after, used to dig tunnels to help people escape Ukraine and get to freedom. He was always looking to help others as well. My great-grandmother was shot crossing the border escaping from Ukraine, and he carried her the whole way to the boat. They lived in very poor West Philadelphia and poured everything into my grandfather. He became a great doctor, and his sons and his grandchildren are in medicine today.
*Correction, 12/11: A previous version of this story misstated the amount of ASH’s $19 million investment in developing fellowships with a focus on hematology.
In interviews, Robert and Max Brodsky spoke about the appeal of hematology and the threads that unite them with family members who came before. The elder Brodsky also talked about the work that’s made him the proudest during his year-long presidency at ASH.
Robert A. Brodsky is professor of medicine and director of hematology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is stepping down as ASH president at its annual meeting in San Diego, December 9-12. Here are excerpts from our conversation:
Q: What drew your dad into medicine?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: He was going through his medical training at the University of Pennsylvania, then the Vietnam War came, and he served at the National Institutes of Health in what they referred to as the Yellow Berets. He got very interested in retroviruses and viruses that lead to cancer, which was a foreign idea at the time. This led him into hematology, stem cells, and myeloproliferative disorders.
He had a very successful career in hematology and just loved it. He performed the first bone marrow transplant in the tristate area of Pennsylvania, Delaware, and New Jersey.
Q: What did he like about hematology specifically?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: It’s a fascinating field, probably the most scientific area of medicine. It’s so easy to access blood and bone marrow. You can grow it, you can look at it, you can see it. It’s hard to do that with a lung, heart, kidney, or brain. Even back then, they could translate some of the science. What really drew him to hematology — and me, for that matter — was looking at a blood smear or bone marrow and being able to make a diagnosis. The other thing is the personal aspect. Hematologists tend to like the long-term relationships that they develop with their patients over the years.
Q: What were the biggest transformations in hematology during his career?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: Bone marrow transplant had the biggest impact, and it’s an area he really pioneered. He was very much involved in some of the early bone marrow transplants and was very close with Dr. George W. Santos, who was at Johns Hopkins and one of the big pioneers in that area as well. To be able to take marrow from related donors, get it to grow without the patient rejecting it, and cure a disease, was really huge. When he started doing this, patients had no other option. To see patients be cured was incredibly satisfying to him.
Q: How did you end up following your father into hematology?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: My brother Jeff, who’s a surgeon and older than me, knew he was going into medicine — probably about 3 hours after he was born. I came to it late. I was a political science major as an undergrad and really trying to figure out what I wanted to do. In my sophomore year, I decided I wanted to give this a shot. My dad worked very hard, long hours, but you could tell he loved what he did. And he was never absent, always involved in our lives and still made time for everyone. At some level, that must have had an influence on me.
Q: What has changed in hematology over your 30-plus years in medicine?
A: When I look back at when I was a fellow, it’s just mind-boggling how many lethal or life-threatening diseases are now pretty easy to treat. I studied disorders like aplastic anemia, which was very fatal. Without treatment, patients would die within a year. Now, over 95% are cured. Another classic examples is chronic myeloid leukemia disorder. Back when I was a fellow, the median survival for CML was maybe 4 to 6 years. Now, Kareem Abdul Jabbar has had this[for about 15 years]. Also a lot of hematologic malignancies are being cured with immunotherapy approaches. We’ve figured out the pathophysiology of a lot of diseases, and there are incredible genetic diagnostic assays.
Q: What was your father’s relationship with ASH?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: The first ASH meeting was 1958 in Atlantic City, New Jersey. There were 300 hematologists there, and my dad was one of them. We’re going to have over 30,000 people in San Diego, which is a record, and another 5,000 or 6,000 virtually.
Q: As ASH president, what are your biggest accomplishments when it comes to addressing the shortage of hematologists and other issues?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH is investing $19 million to develop fellowships with a focus on hematology.* This is going to put lots of new hematologists into the workforce over the next 5 to 10 years. We’ve also been working on the Maintenance of Certification [MOC] process to make it less onerous on physicians. It’s really a bad process, and it’s not just ASH [that’s complaining], it’s all of medicine. We’re hearing this from GI, endocrine, renal and the general internists.
[In a September 2023 letter to the American Board of Internal Medicine’s president and chief officer, Dr. Brodsky wrote that “ASH continues to support the importance of lifelong learning for hematologists via a program that is evidence-based, relevant to one’s practice, and transparent; however, these three basic requirements are not met by the current ABIM MOC program.” ASH is calling for a new and reformed MOC program.]
Q: What convinced ASH to expand its journals by adding Blood Neoplasia and Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH has two flagship journals right now, Blood and Blood Advances, and they’re both very competitive, high-impact journals. It turns out there’s not enough room to publish all the new science, and they end up rejecting the majority of the submissions that come to them. We decided to keep these journals in the ASH family because there’s some fantastic clinical trials and science that would be going elsewhere.
Dr. Brodsky’s sons both have medical degrees: Brett Brodsky, DO, is a resident at Virginia Commonwealth University who plans to become a sports medicine specialist, and Max Brodsky, MD, is a second-year fellow in hematology at Johns Hopkins University.
In an interview, Max Brodsky, MD, talked about the roots of his family’s dedication to caring for others.
Q: What drew you to hematology?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’ve watched both my dad and my grandfather be leaders in the field as both physicians and scientists, and that was very inspirational for me to see. And I went to a medical school [Drexel University College of Medicine] that my dad went to and where my grandfather was on faculty. That was like walking in their footsteps in a major way.
Q: What do you hope to focus on as a hematologist?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’m still working through that, but I am really interested in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Patients used to not be able to survive their initial episodes, but now we have good treatments and are able to follow them as outpatients. With this whole cohort of patients that are surviving, we’re seeing that they have more health problems — more heart disease, more strokes and kidney disease. There’s a whole growing field exploring how to treat these patients for their lifespan.
Q: How do you deal with the reality that more of your patients will die than in some other medical fields?
Dr. Max Brodsky: It is challenging, but I also see those moments as opportunities to support patients and families. I’m good at connecting to patients and families who are in scary situations. I’ve always had that skill of putting people at ease, making people feel calm, knowing that they can trust me, and I have their best interests in mind.
Q: Why do you think your family is so committed to medicine?
Dr. Max Brodsky: We’re Jewish, and looking to help the world is one of the main core values of Judaism. The Torah expects us to make this world better. Actually, my great-grandfather Max, whom I’m named after, used to dig tunnels to help people escape Ukraine and get to freedom. He was always looking to help others as well. My great-grandmother was shot crossing the border escaping from Ukraine, and he carried her the whole way to the boat. They lived in very poor West Philadelphia and poured everything into my grandfather. He became a great doctor, and his sons and his grandchildren are in medicine today.
*Correction, 12/11: A previous version of this story misstated the amount of ASH’s $19 million investment in developing fellowships with a focus on hematology.
In interviews, Robert and Max Brodsky spoke about the appeal of hematology and the threads that unite them with family members who came before. The elder Brodsky also talked about the work that’s made him the proudest during his year-long presidency at ASH.
Robert A. Brodsky is professor of medicine and director of hematology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He is stepping down as ASH president at its annual meeting in San Diego, December 9-12. Here are excerpts from our conversation:
Q: What drew your dad into medicine?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: He was going through his medical training at the University of Pennsylvania, then the Vietnam War came, and he served at the National Institutes of Health in what they referred to as the Yellow Berets. He got very interested in retroviruses and viruses that lead to cancer, which was a foreign idea at the time. This led him into hematology, stem cells, and myeloproliferative disorders.
He had a very successful career in hematology and just loved it. He performed the first bone marrow transplant in the tristate area of Pennsylvania, Delaware, and New Jersey.
Q: What did he like about hematology specifically?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: It’s a fascinating field, probably the most scientific area of medicine. It’s so easy to access blood and bone marrow. You can grow it, you can look at it, you can see it. It’s hard to do that with a lung, heart, kidney, or brain. Even back then, they could translate some of the science. What really drew him to hematology — and me, for that matter — was looking at a blood smear or bone marrow and being able to make a diagnosis. The other thing is the personal aspect. Hematologists tend to like the long-term relationships that they develop with their patients over the years.
Q: What were the biggest transformations in hematology during his career?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: Bone marrow transplant had the biggest impact, and it’s an area he really pioneered. He was very much involved in some of the early bone marrow transplants and was very close with Dr. George W. Santos, who was at Johns Hopkins and one of the big pioneers in that area as well. To be able to take marrow from related donors, get it to grow without the patient rejecting it, and cure a disease, was really huge. When he started doing this, patients had no other option. To see patients be cured was incredibly satisfying to him.
Q: How did you end up following your father into hematology?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: My brother Jeff, who’s a surgeon and older than me, knew he was going into medicine — probably about 3 hours after he was born. I came to it late. I was a political science major as an undergrad and really trying to figure out what I wanted to do. In my sophomore year, I decided I wanted to give this a shot. My dad worked very hard, long hours, but you could tell he loved what he did. And he was never absent, always involved in our lives and still made time for everyone. At some level, that must have had an influence on me.
Q: What has changed in hematology over your 30-plus years in medicine?
A: When I look back at when I was a fellow, it’s just mind-boggling how many lethal or life-threatening diseases are now pretty easy to treat. I studied disorders like aplastic anemia, which was very fatal. Without treatment, patients would die within a year. Now, over 95% are cured. Another classic examples is chronic myeloid leukemia disorder. Back when I was a fellow, the median survival for CML was maybe 4 to 6 years. Now, Kareem Abdul Jabbar has had this[for about 15 years]. Also a lot of hematologic malignancies are being cured with immunotherapy approaches. We’ve figured out the pathophysiology of a lot of diseases, and there are incredible genetic diagnostic assays.
Q: What was your father’s relationship with ASH?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: The first ASH meeting was 1958 in Atlantic City, New Jersey. There were 300 hematologists there, and my dad was one of them. We’re going to have over 30,000 people in San Diego, which is a record, and another 5,000 or 6,000 virtually.
Q: As ASH president, what are your biggest accomplishments when it comes to addressing the shortage of hematologists and other issues?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH is investing $19 million to develop fellowships with a focus on hematology.* This is going to put lots of new hematologists into the workforce over the next 5 to 10 years. We’ve also been working on the Maintenance of Certification [MOC] process to make it less onerous on physicians. It’s really a bad process, and it’s not just ASH [that’s complaining], it’s all of medicine. We’re hearing this from GI, endocrine, renal and the general internists.
[In a September 2023 letter to the American Board of Internal Medicine’s president and chief officer, Dr. Brodsky wrote that “ASH continues to support the importance of lifelong learning for hematologists via a program that is evidence-based, relevant to one’s practice, and transparent; however, these three basic requirements are not met by the current ABIM MOC program.” ASH is calling for a new and reformed MOC program.]
Q: What convinced ASH to expand its journals by adding Blood Neoplasia and Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis?
Dr. Robert A. Brodsky: ASH has two flagship journals right now, Blood and Blood Advances, and they’re both very competitive, high-impact journals. It turns out there’s not enough room to publish all the new science, and they end up rejecting the majority of the submissions that come to them. We decided to keep these journals in the ASH family because there’s some fantastic clinical trials and science that would be going elsewhere.
Dr. Brodsky’s sons both have medical degrees: Brett Brodsky, DO, is a resident at Virginia Commonwealth University who plans to become a sports medicine specialist, and Max Brodsky, MD, is a second-year fellow in hematology at Johns Hopkins University.
In an interview, Max Brodsky, MD, talked about the roots of his family’s dedication to caring for others.
Q: What drew you to hematology?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’ve watched both my dad and my grandfather be leaders in the field as both physicians and scientists, and that was very inspirational for me to see. And I went to a medical school [Drexel University College of Medicine] that my dad went to and where my grandfather was on faculty. That was like walking in their footsteps in a major way.
Q: What do you hope to focus on as a hematologist?
Dr. Max Brodsky: I’m still working through that, but I am really interested in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Patients used to not be able to survive their initial episodes, but now we have good treatments and are able to follow them as outpatients. With this whole cohort of patients that are surviving, we’re seeing that they have more health problems — more heart disease, more strokes and kidney disease. There’s a whole growing field exploring how to treat these patients for their lifespan.
Q: How do you deal with the reality that more of your patients will die than in some other medical fields?
Dr. Max Brodsky: It is challenging, but I also see those moments as opportunities to support patients and families. I’m good at connecting to patients and families who are in scary situations. I’ve always had that skill of putting people at ease, making people feel calm, knowing that they can trust me, and I have their best interests in mind.
Q: Why do you think your family is so committed to medicine?
Dr. Max Brodsky: We’re Jewish, and looking to help the world is one of the main core values of Judaism. The Torah expects us to make this world better. Actually, my great-grandfather Max, whom I’m named after, used to dig tunnels to help people escape Ukraine and get to freedom. He was always looking to help others as well. My great-grandmother was shot crossing the border escaping from Ukraine, and he carried her the whole way to the boat. They lived in very poor West Philadelphia and poured everything into my grandfather. He became a great doctor, and his sons and his grandchildren are in medicine today.
*Correction, 12/11: A previous version of this story misstated the amount of ASH’s $19 million investment in developing fellowships with a focus on hematology.
FROM ASH 2023
ASH 2023: Equity, Sickle Cell, and Real-Life Outcomes
Cynthia E. Dunbar, MD, chief of the Translational Stem Cell Biology Branch at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and secretary of ASH, added that insight into actual patient experiences also will be a major theme at ASH 2023.
“There is a huge growth in research on outcomes and focusing on using real-world data and how important that is,” Dr. Dunbar said. “Academic research and hematology is really focusing on patient-reported outcomes and how care is delivered in a real-world setting – actually looking at what matters to patients. Are they alive in a certain number of years? And how are they feeling?”
As an example, Dr. Dunbar pointed to an abstract that examined clinical databases in Canada and found that real-world outcomes in multiple myeloma treatments were much worse than those in the original clinical trials for the therapies. Patients reached relapse 44% faster and their overall survival was 75% worse.
In the media briefing, ASH chair of communications Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, of the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami, noted that patients in these types of clinical trials “are just these pristine specimens of human beings except for the cancer that’s being treated.”
Dr. Dunbar agreed, noting that “patients who are able to enroll in clinical trials are more likely to be able to show up at the treatment center at the right time and for every dose, have transportation, and afford drugs to prevent side effects. They might stay on the drug for longer, or they have nurses who are always encouraging them of how to make it through a toxicity.”
Hematologists and patients should consider randomized controlled trials to be “the best possible outcome, and perhaps adjust their thinking if an individual patient is older, sicker, or less able to follow a regimen exactly,” she said.
Another highlighted study linked worse outcomes in African-Americans with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia to genetic traits that are more common in that population. The traits “likely explain at least in part the worst outcomes in Black patients in prior studies and on some regimens,” Dr. Dunbar said.
She added that the findings emphasize how testing for genetic variants and biomarkers that impact outcomes should be performed “instead of assuming that a certain dose should be given simply based on perceived or reported race or ethnicity.”
ASH President Robert A. Brodsky, MD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, highlighted an abstract that reported on the use of AI as a clinical decision support tool to differentiate two easily confused conditions — prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia.
AI “is a tool that’s going to help pathologists make more accurate and faster diagnoses,” he said. He also spotlighted an abstract about the use of “social media listening” to understand the experiences of patients with SCD and their caregivers. “There can be a lot of misuse and waste of time with social media, but they used this in a way to try and gain insight as to what’s really important to the patients and the caregiver.”
Also, in regard to SCD, Dr. Dunbar pointed to a study that reports on outcomes in patients who received lovotibeglogene autotemcel (lovo-cel) gene therapy for up to 60 months. Both this treatment and a CRISPR-based therapy called exa-cel “appear to result in comparable very impressive efficacy in terms of pain crises and organ dysfunction,” she said. “The hurdle is going to be figuring out how to deliver what will be very expensive and complicated therapies — but likely curative — therapies to patients.”
Another study to be presented at ASH — coauthored by Dr. Brodsky — shows promising results from reduced-intensity haploidentical bone marrow transplantation in adults with severe SCD. Results were similar to those seen with bone marrow from matched siblings, Dr. Sekeres said.
He added that more clarity is needed about new treatment options for SCD, perhaps through a “randomized trial where patients upfront get a haploidentical bone marrow transplant or fully matched bone marrow transplant. Then other patients are randomized to some of these other, newer technology therapies, and we follow them over time. We’re looking not only for overall survival but complications of the therapy itself and how many patients relapse from the treatment.”
Cynthia E. Dunbar, MD, chief of the Translational Stem Cell Biology Branch at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and secretary of ASH, added that insight into actual patient experiences also will be a major theme at ASH 2023.
“There is a huge growth in research on outcomes and focusing on using real-world data and how important that is,” Dr. Dunbar said. “Academic research and hematology is really focusing on patient-reported outcomes and how care is delivered in a real-world setting – actually looking at what matters to patients. Are they alive in a certain number of years? And how are they feeling?”
As an example, Dr. Dunbar pointed to an abstract that examined clinical databases in Canada and found that real-world outcomes in multiple myeloma treatments were much worse than those in the original clinical trials for the therapies. Patients reached relapse 44% faster and their overall survival was 75% worse.
In the media briefing, ASH chair of communications Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, of the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami, noted that patients in these types of clinical trials “are just these pristine specimens of human beings except for the cancer that’s being treated.”
Dr. Dunbar agreed, noting that “patients who are able to enroll in clinical trials are more likely to be able to show up at the treatment center at the right time and for every dose, have transportation, and afford drugs to prevent side effects. They might stay on the drug for longer, or they have nurses who are always encouraging them of how to make it through a toxicity.”
Hematologists and patients should consider randomized controlled trials to be “the best possible outcome, and perhaps adjust their thinking if an individual patient is older, sicker, or less able to follow a regimen exactly,” she said.
Another highlighted study linked worse outcomes in African-Americans with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia to genetic traits that are more common in that population. The traits “likely explain at least in part the worst outcomes in Black patients in prior studies and on some regimens,” Dr. Dunbar said.
She added that the findings emphasize how testing for genetic variants and biomarkers that impact outcomes should be performed “instead of assuming that a certain dose should be given simply based on perceived or reported race or ethnicity.”
ASH President Robert A. Brodsky, MD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, highlighted an abstract that reported on the use of AI as a clinical decision support tool to differentiate two easily confused conditions — prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia.
AI “is a tool that’s going to help pathologists make more accurate and faster diagnoses,” he said. He also spotlighted an abstract about the use of “social media listening” to understand the experiences of patients with SCD and their caregivers. “There can be a lot of misuse and waste of time with social media, but they used this in a way to try and gain insight as to what’s really important to the patients and the caregiver.”
Also, in regard to SCD, Dr. Dunbar pointed to a study that reports on outcomes in patients who received lovotibeglogene autotemcel (lovo-cel) gene therapy for up to 60 months. Both this treatment and a CRISPR-based therapy called exa-cel “appear to result in comparable very impressive efficacy in terms of pain crises and organ dysfunction,” she said. “The hurdle is going to be figuring out how to deliver what will be very expensive and complicated therapies — but likely curative — therapies to patients.”
Another study to be presented at ASH — coauthored by Dr. Brodsky — shows promising results from reduced-intensity haploidentical bone marrow transplantation in adults with severe SCD. Results were similar to those seen with bone marrow from matched siblings, Dr. Sekeres said.
He added that more clarity is needed about new treatment options for SCD, perhaps through a “randomized trial where patients upfront get a haploidentical bone marrow transplant or fully matched bone marrow transplant. Then other patients are randomized to some of these other, newer technology therapies, and we follow them over time. We’re looking not only for overall survival but complications of the therapy itself and how many patients relapse from the treatment.”
Cynthia E. Dunbar, MD, chief of the Translational Stem Cell Biology Branch at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and secretary of ASH, added that insight into actual patient experiences also will be a major theme at ASH 2023.
“There is a huge growth in research on outcomes and focusing on using real-world data and how important that is,” Dr. Dunbar said. “Academic research and hematology is really focusing on patient-reported outcomes and how care is delivered in a real-world setting – actually looking at what matters to patients. Are they alive in a certain number of years? And how are they feeling?”
As an example, Dr. Dunbar pointed to an abstract that examined clinical databases in Canada and found that real-world outcomes in multiple myeloma treatments were much worse than those in the original clinical trials for the therapies. Patients reached relapse 44% faster and their overall survival was 75% worse.
In the media briefing, ASH chair of communications Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, MS, of the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami, noted that patients in these types of clinical trials “are just these pristine specimens of human beings except for the cancer that’s being treated.”
Dr. Dunbar agreed, noting that “patients who are able to enroll in clinical trials are more likely to be able to show up at the treatment center at the right time and for every dose, have transportation, and afford drugs to prevent side effects. They might stay on the drug for longer, or they have nurses who are always encouraging them of how to make it through a toxicity.”
Hematologists and patients should consider randomized controlled trials to be “the best possible outcome, and perhaps adjust their thinking if an individual patient is older, sicker, or less able to follow a regimen exactly,” she said.
Another highlighted study linked worse outcomes in African-Americans with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia to genetic traits that are more common in that population. The traits “likely explain at least in part the worst outcomes in Black patients in prior studies and on some regimens,” Dr. Dunbar said.
She added that the findings emphasize how testing for genetic variants and biomarkers that impact outcomes should be performed “instead of assuming that a certain dose should be given simply based on perceived or reported race or ethnicity.”
ASH President Robert A. Brodsky, MD, of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, highlighted an abstract that reported on the use of AI as a clinical decision support tool to differentiate two easily confused conditions — prefibrotic primary myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia.
AI “is a tool that’s going to help pathologists make more accurate and faster diagnoses,” he said. He also spotlighted an abstract about the use of “social media listening” to understand the experiences of patients with SCD and their caregivers. “There can be a lot of misuse and waste of time with social media, but they used this in a way to try and gain insight as to what’s really important to the patients and the caregiver.”
Also, in regard to SCD, Dr. Dunbar pointed to a study that reports on outcomes in patients who received lovotibeglogene autotemcel (lovo-cel) gene therapy for up to 60 months. Both this treatment and a CRISPR-based therapy called exa-cel “appear to result in comparable very impressive efficacy in terms of pain crises and organ dysfunction,” she said. “The hurdle is going to be figuring out how to deliver what will be very expensive and complicated therapies — but likely curative — therapies to patients.”
Another study to be presented at ASH — coauthored by Dr. Brodsky — shows promising results from reduced-intensity haploidentical bone marrow transplantation in adults with severe SCD. Results were similar to those seen with bone marrow from matched siblings, Dr. Sekeres said.
He added that more clarity is needed about new treatment options for SCD, perhaps through a “randomized trial where patients upfront get a haploidentical bone marrow transplant or fully matched bone marrow transplant. Then other patients are randomized to some of these other, newer technology therapies, and we follow them over time. We’re looking not only for overall survival but complications of the therapy itself and how many patients relapse from the treatment.”
AT ASH 2023
FDA approves first tx for rare, deadly clotting disorder
Congenital TTP affects fewer than 1,000 people in the United States and is caused by a mutation in the ADAMTS13 gene, which makes an enzyme that regulates blood clotting. Patients with the congenital TTP typically receive prophylactic plasma-based therapy to replenish the ADAMTS13 enzyme and reduce the risk for clotting and bleeding. The condition, however, can be fatal if left untreated.
The new agent is a purified recombinant form of the ADAMTS13 enzyme that works by replacing low levels of the deficient enzyme in patients with congenital TTP. Adzynma is given prophylactically to reduce the risk for disease symptoms and on demand when a patient is experiencing an acute event, according to the FDA approval announcement.
The approval was based on a global randomized phase 3 study comparing the product with plasma-based therapies in 46 patients with congenital TTP. Patients in the trial were randomized to receive 6 months of treatment with either intravenous Adzynma — given once every other week as prophylactic enzyme replacement therapy or once daily as on-demand enzyme replacement therapy — or plasma-based therapies. The patients then crossed over to the other treatment for 6 months.
Interim findings from the study showed that Adzynma reduced the incidence of thrombocytopenia — the most common symptom of congenital TTP — by 60% compared with plasma-based therapy (rate ratio, 0.40). No patients experienced an acute TTP event during Adzynma prophylaxis, Takeda said.
Significantly more patients receiving plasma-based therapies experienced treatment-emergent adverse events compared with those receiving the biologic.
The most common side effects associated with the biologic were headache (31.3%), diarrhea (16.7%), migraine (14.6%), abdominal pain (12.5%), nausea (12.5%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.5%), dizziness (10.4%), and vomiting (10.4%). No treatment-related adverse events, including allergic reactions, were observed during administration.
“The FDA remains deeply committed in our efforts to help facilitate the development and approval of safe and effective therapies for patients with rare diseases,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, stated. The “approval reflects important progress in the development of much-needed treatment options for patients affected by this life-threatening disorder.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Congenital TTP affects fewer than 1,000 people in the United States and is caused by a mutation in the ADAMTS13 gene, which makes an enzyme that regulates blood clotting. Patients with the congenital TTP typically receive prophylactic plasma-based therapy to replenish the ADAMTS13 enzyme and reduce the risk for clotting and bleeding. The condition, however, can be fatal if left untreated.
The new agent is a purified recombinant form of the ADAMTS13 enzyme that works by replacing low levels of the deficient enzyme in patients with congenital TTP. Adzynma is given prophylactically to reduce the risk for disease symptoms and on demand when a patient is experiencing an acute event, according to the FDA approval announcement.
The approval was based on a global randomized phase 3 study comparing the product with plasma-based therapies in 46 patients with congenital TTP. Patients in the trial were randomized to receive 6 months of treatment with either intravenous Adzynma — given once every other week as prophylactic enzyme replacement therapy or once daily as on-demand enzyme replacement therapy — or plasma-based therapies. The patients then crossed over to the other treatment for 6 months.
Interim findings from the study showed that Adzynma reduced the incidence of thrombocytopenia — the most common symptom of congenital TTP — by 60% compared with plasma-based therapy (rate ratio, 0.40). No patients experienced an acute TTP event during Adzynma prophylaxis, Takeda said.
Significantly more patients receiving plasma-based therapies experienced treatment-emergent adverse events compared with those receiving the biologic.
The most common side effects associated with the biologic were headache (31.3%), diarrhea (16.7%), migraine (14.6%), abdominal pain (12.5%), nausea (12.5%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.5%), dizziness (10.4%), and vomiting (10.4%). No treatment-related adverse events, including allergic reactions, were observed during administration.
“The FDA remains deeply committed in our efforts to help facilitate the development and approval of safe and effective therapies for patients with rare diseases,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, stated. The “approval reflects important progress in the development of much-needed treatment options for patients affected by this life-threatening disorder.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Congenital TTP affects fewer than 1,000 people in the United States and is caused by a mutation in the ADAMTS13 gene, which makes an enzyme that regulates blood clotting. Patients with the congenital TTP typically receive prophylactic plasma-based therapy to replenish the ADAMTS13 enzyme and reduce the risk for clotting and bleeding. The condition, however, can be fatal if left untreated.
The new agent is a purified recombinant form of the ADAMTS13 enzyme that works by replacing low levels of the deficient enzyme in patients with congenital TTP. Adzynma is given prophylactically to reduce the risk for disease symptoms and on demand when a patient is experiencing an acute event, according to the FDA approval announcement.
The approval was based on a global randomized phase 3 study comparing the product with plasma-based therapies in 46 patients with congenital TTP. Patients in the trial were randomized to receive 6 months of treatment with either intravenous Adzynma — given once every other week as prophylactic enzyme replacement therapy or once daily as on-demand enzyme replacement therapy — or plasma-based therapies. The patients then crossed over to the other treatment for 6 months.
Interim findings from the study showed that Adzynma reduced the incidence of thrombocytopenia — the most common symptom of congenital TTP — by 60% compared with plasma-based therapy (rate ratio, 0.40). No patients experienced an acute TTP event during Adzynma prophylaxis, Takeda said.
Significantly more patients receiving plasma-based therapies experienced treatment-emergent adverse events compared with those receiving the biologic.
The most common side effects associated with the biologic were headache (31.3%), diarrhea (16.7%), migraine (14.6%), abdominal pain (12.5%), nausea (12.5%), upper respiratory tract infection (12.5%), dizziness (10.4%), and vomiting (10.4%). No treatment-related adverse events, including allergic reactions, were observed during administration.
“The FDA remains deeply committed in our efforts to help facilitate the development and approval of safe and effective therapies for patients with rare diseases,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, stated. The “approval reflects important progress in the development of much-needed treatment options for patients affected by this life-threatening disorder.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnancy in rheumatic disease quadruples risk of cardiovascular events
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
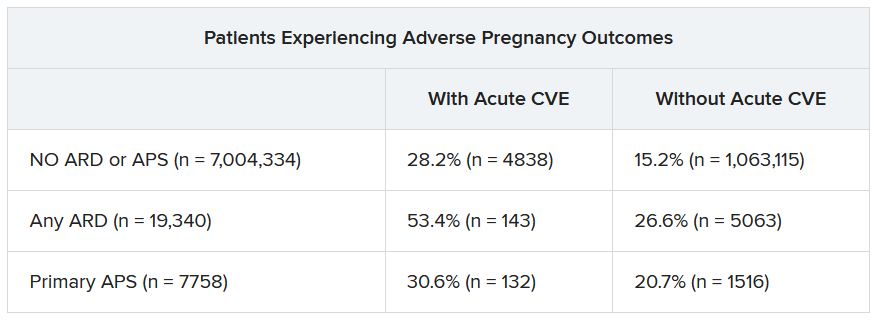
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.

Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.

Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2023
Review finds no CV or VTE risk signal with use of JAK inhibitors for skin indications
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
, results from a systematic literature review, and meta-analysis showed.
“There remains a knowledge gap regarding the risk of JAK inhibitor use and VTE and/or MACE in the dermatologic population,” researchers led by Michael S. Garshick, MD, a cardiologist at New York University Langone Health, wrote in their study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology . “Pooled safety studies suggest that the risk of MACE and VTE may be lower in patients treated with JAK inhibitors for a dermatologic indication than the risk observed in the ORAL Surveillance study, which may be related to the younger age and better health status of those enrolled in trials for dermatologic indications.” The results of that study, which included patients with rheumatoid arthritis only, resulted in the addition of a boxed warning in the labels for topical and oral JAK inhibitors regarding the increased risk of MACE, VTE, serious infections, malignancies, and death .
For the review – thought to be the first to specifically evaluate these risks for dermatologic indications – the researchers searched PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception through April 1, 2023, for phase 3 dermatology randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the risk of MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality with JAK inhibitors, compared with placebo or an active comparator in the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases. They followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and used a random-effects model and the DerSimonian-Laird method to calculate adverse events with odds ratios.
The database search yielded 35 RCTs with a total of 20,651 patients. Their mean age was 38.5 years, 54% were male, and the mean follow-up time was 4.9 months. Of the 35 trials, most (21) involved patients with atopic dermatitis, followed by psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (9 trials), alopecia areata (3 trials) and vitiligo (2 trials).
The researchers found no significant difference between JAK inhibitors and placebo/active comparator in composite MACE and all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.57) or in VTE (OR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.26-1.04).
In a secondary analysis, which included additional psoriatic arthritis RCTs, no significant differences between the treatment and placebo/active comparator groups were observed. Similarly, subgroup analyses of oral versus topical JAK inhibitors and a sensitivity analysis that excluded pediatric trials showed no significant differences between patients exposed to JAK inhibitors and those not exposed.
The researchers acknowledged certain limitations of the review, including the lack of access to patient-level data, the fact that most trials only included short-term follow-up, and that the findings have limited generalizability to an older patient population. “It remains unclear if the cardiovascular risks of JAK inhibitors are primarily due to patient level cardiovascular risk factors or are drug mediated,” they concluded. “Dermatologists should carefully select patients and assess baseline cardiovascular risk factors when considering JAK therapy. Cardiovascular risk assessment should continue for the duration of treatment.”
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology and director of the center for eczema and itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study results, characterized the findings as reassuring to dermatologists who may be reluctant to initiate therapy with JAK inhibitors based on concerns about safety signals for MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality.
“These data systematically show that across medications and across conditions, there doesn’t appear to be an increased signal for these events during the short-term, placebo-controlled period which generally spans a few months in most studies,” he told this news organization. The findings, he added, “align well with our clinical experience to date for JAK inhibitor use in inflammatory skin disease. Short-term safety, particularly in relation to boxed warning events such MACE, VTE, and all-cause mortality, have generally been favorable with real-world use. It’s good to have a rigorous statistical analysis to refer to when setting patient expectations.”
However, he noted that these data only examined short-term safety during the placebo or active comparator-controlled periods. “Considering that events like MACE or VTE may take many months or years to manifest, continued long-term data generation is needed to fully answer the question of risk,” he said.
Dr. Garshick disclosed that he received grants from Pfizer and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Several other coauthors reported having advisory board roles and/or having received funding or support from several pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, investigator, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including those that develop JAK inhibitors.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY




