User login
Giving flu and COVID-19 shots at same time appears safe, effective: Study
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Extensive limb swelling after vaccines – including SARS-CoV-2 vaccine
A 19-month-old boy comes to the office with a large firm erythematous swelling of his anterior left thigh that reaches from just below the inguinal crease to the patella. He got his routine immunizations 2 days prior to this visit including the fourth DTaP dose in his left thigh. Clinicians who care for children and who give routine immunizations occasionally see such an adverse effect following immunization (AEFI). These large local reactions have been described for many decades and occur after many vaccines.
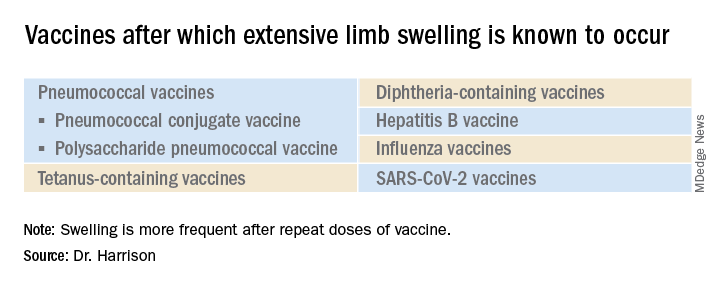
What is extensive limb swelling (ELS)? ELS is defined as erythema/swelling crossing a joint or extending mostly joint to joint. It is a subset of large local AEFIs. ELS is generally firm and often erythematous with varying degrees of pain. ELS is now most frequent after pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) and DTaP, with a 1%-4% rate after DTaP boosters.1-3 ELS and other large local swelling reactions occur at nearly any age.1 And yet there is still much that is not known about their true pathogenesis. Likewise, there are no accurate predictors of which vaccinees will develop large inflammatory processes at or near the site of immunization.
ELS after standard vaccines
The largest report to date on AEFI of all ages, including ELS, covered 1990-2003.1 Two upfront caveats are: This study evaluated ELS before PCVs were available, and in adults, repeat 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine was the most common cause of ELS in this study, comprising 45% of all adult ELS.
Considering all ages, ELS onset was nearly always greater than 1 hour and was less than 24 hours post vaccine in almost 75% of patients. However, for those aged under 2 years, onset in less than 24 hours was even more frequent (84%). Interestingly, concomitant fever occurred in less than 25% regardless of age. In adults, ELS after tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines occurred mostly in women (75%); whereas for ELS under 8 years of age, males predominated (about 60%). Of note, tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines were the most frequent ELS-inducing vaccines in children, that is, 75% aged under 8 years and 55% for those aged 8-17 years. Focusing on pediatric ELS after DTaP by dose, 33% were after the fourth, 31% after the fifth, 12% after the second, 10% after the first, and 3% after the third dose. In the case above, ELS was after the fourth dose.
Clinicians caring for children know how to manage ELS after DTaP or PCVs. They understand that ELS looks scary and is uncomfortable but is not dangerous and requires no specific treatment. Supportive management, that is, pain reliever, cool compresses, and TLC, are warranted. ELS is not a contraindication to subsequent immunization with the same vaccine. That said, large local reactions or ELS do occur with subsequent doses of that same vaccine at varying rates up to 66% of the time. Management is the same with repeat episodes, and no sequelae are expected. Supportive management only is standard unless one suspects a very rare Arthus reaction. If central necrosis occurs or swelling evolution/resolution is not per expectations, referral to a vaccine expert can sort out if it is an Arthus reaction, in which case, subsequent use of the same vaccine in not recommended.
ELS and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
With SARS-CoV-2 vaccines now authorized for adolescents and expected in a few months for younger children, large local AEFI reactions related to pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are expected, given that “COVID arm” is now well described in adults.4 Overall, ELS/large local reactions have been reported more frequently with the Moderna than Pfizer mRNA vaccine.4 In the almost 42% of adults having ELS post first dose, repeat ELS post second dose often appears sooner but also resolves more quickly, with no known sequelae.5
Some biopsies have shown delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (DTH) (superficial perivascular and perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrates with rare eosinophils and scattered mast cells),6,7 while others show no DTH but these patients have findings of immediate hypersensitivity findings and negative skin testing to the vaccine.8 With regard to sex, Dutch ELS data in White adults reveal 90% occur in females – higher than the 75% female rate after standard vaccines.7 Onset of ELS data show that Pfizer mRNA vaccinees had onset on average at 38 hours (range, <1 hr to 12 days). Boston data mostly in White adults reveal later onset (median, 6 days; range, 2-12 days).4 In contrast, adults of color appear to have later onset (mean, 8 days; range, 4-14 days).9
In addition to the local swelling, patients had concurrent injection-site AEFIs of pain (65%), warmth (63%), and pruritus (26%), plus myalgia (51%), headache (48%), malaise (45%), fatigue (43%), chills (33%), arthralgia (30%), and fever (28%).7
What should we tell families about pediatric ELS before we give SARS-CoV-2 vaccines to children? Clinical pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccine trials are smaller “immunologic bridging” studies, not requiring proof of efficacy. So, the precise incidence of pediatric ELS (adult rate is estimated under 1/100,000) may not be known until months after general use. Nevertheless, part of our counseling of families will need to include ELS/large local reactions. Unless new data show otherwise, the spiel that clinicians have developed to counsel about the rare chance of ELS after routine vaccines should also be useful to inform families of the rare chance of ELS post SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
The bottom line is that the management of pediatric ELS after SARS-CoV-2 vaccines should be the same as after standard vaccines. And remember, whether the reactions are DTH or not, neither immediate local injection-site reactions nor DTH reactions are contraindications to subsequent vaccination unless anaphylaxis or Arthus reaction is suspected.10,11
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Woo EJ and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System Working Group. Clin Infect Dis 2003;37:351-8.
2. Rennels MB et al. Pediatrics 2000;105:e12.
3. Huber BM, Goetschel P. J Pediatr. 2011;158:1033.
4. Blumenthal KG et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1273-7.
5. McMahon DE et al. J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2021;85(1):46-55. 6. Johnston MS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(6):716-20 .
7. ELS associated with the administration of Comirnaty®. WHO database Vigilyze (cited 2021 Feb 22). Available from https://vigilyze.who-umc.org/.
8. Baeck M et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2104751.
9. Samarakoon U et al. N Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108620.
10. Kelso JM et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:25-43.
11. Zafack JG et al. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20163707.
A 19-month-old boy comes to the office with a large firm erythematous swelling of his anterior left thigh that reaches from just below the inguinal crease to the patella. He got his routine immunizations 2 days prior to this visit including the fourth DTaP dose in his left thigh. Clinicians who care for children and who give routine immunizations occasionally see such an adverse effect following immunization (AEFI). These large local reactions have been described for many decades and occur after many vaccines.

What is extensive limb swelling (ELS)? ELS is defined as erythema/swelling crossing a joint or extending mostly joint to joint. It is a subset of large local AEFIs. ELS is generally firm and often erythematous with varying degrees of pain. ELS is now most frequent after pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) and DTaP, with a 1%-4% rate after DTaP boosters.1-3 ELS and other large local swelling reactions occur at nearly any age.1 And yet there is still much that is not known about their true pathogenesis. Likewise, there are no accurate predictors of which vaccinees will develop large inflammatory processes at or near the site of immunization.
ELS after standard vaccines
The largest report to date on AEFI of all ages, including ELS, covered 1990-2003.1 Two upfront caveats are: This study evaluated ELS before PCVs were available, and in adults, repeat 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine was the most common cause of ELS in this study, comprising 45% of all adult ELS.
Considering all ages, ELS onset was nearly always greater than 1 hour and was less than 24 hours post vaccine in almost 75% of patients. However, for those aged under 2 years, onset in less than 24 hours was even more frequent (84%). Interestingly, concomitant fever occurred in less than 25% regardless of age. In adults, ELS after tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines occurred mostly in women (75%); whereas for ELS under 8 years of age, males predominated (about 60%). Of note, tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines were the most frequent ELS-inducing vaccines in children, that is, 75% aged under 8 years and 55% for those aged 8-17 years. Focusing on pediatric ELS after DTaP by dose, 33% were after the fourth, 31% after the fifth, 12% after the second, 10% after the first, and 3% after the third dose. In the case above, ELS was after the fourth dose.
Clinicians caring for children know how to manage ELS after DTaP or PCVs. They understand that ELS looks scary and is uncomfortable but is not dangerous and requires no specific treatment. Supportive management, that is, pain reliever, cool compresses, and TLC, are warranted. ELS is not a contraindication to subsequent immunization with the same vaccine. That said, large local reactions or ELS do occur with subsequent doses of that same vaccine at varying rates up to 66% of the time. Management is the same with repeat episodes, and no sequelae are expected. Supportive management only is standard unless one suspects a very rare Arthus reaction. If central necrosis occurs or swelling evolution/resolution is not per expectations, referral to a vaccine expert can sort out if it is an Arthus reaction, in which case, subsequent use of the same vaccine in not recommended.
ELS and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
With SARS-CoV-2 vaccines now authorized for adolescents and expected in a few months for younger children, large local AEFI reactions related to pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are expected, given that “COVID arm” is now well described in adults.4 Overall, ELS/large local reactions have been reported more frequently with the Moderna than Pfizer mRNA vaccine.4 In the almost 42% of adults having ELS post first dose, repeat ELS post second dose often appears sooner but also resolves more quickly, with no known sequelae.5
Some biopsies have shown delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (DTH) (superficial perivascular and perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrates with rare eosinophils and scattered mast cells),6,7 while others show no DTH but these patients have findings of immediate hypersensitivity findings and negative skin testing to the vaccine.8 With regard to sex, Dutch ELS data in White adults reveal 90% occur in females – higher than the 75% female rate after standard vaccines.7 Onset of ELS data show that Pfizer mRNA vaccinees had onset on average at 38 hours (range, <1 hr to 12 days). Boston data mostly in White adults reveal later onset (median, 6 days; range, 2-12 days).4 In contrast, adults of color appear to have later onset (mean, 8 days; range, 4-14 days).9
In addition to the local swelling, patients had concurrent injection-site AEFIs of pain (65%), warmth (63%), and pruritus (26%), plus myalgia (51%), headache (48%), malaise (45%), fatigue (43%), chills (33%), arthralgia (30%), and fever (28%).7
What should we tell families about pediatric ELS before we give SARS-CoV-2 vaccines to children? Clinical pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccine trials are smaller “immunologic bridging” studies, not requiring proof of efficacy. So, the precise incidence of pediatric ELS (adult rate is estimated under 1/100,000) may not be known until months after general use. Nevertheless, part of our counseling of families will need to include ELS/large local reactions. Unless new data show otherwise, the spiel that clinicians have developed to counsel about the rare chance of ELS after routine vaccines should also be useful to inform families of the rare chance of ELS post SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
The bottom line is that the management of pediatric ELS after SARS-CoV-2 vaccines should be the same as after standard vaccines. And remember, whether the reactions are DTH or not, neither immediate local injection-site reactions nor DTH reactions are contraindications to subsequent vaccination unless anaphylaxis or Arthus reaction is suspected.10,11
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Woo EJ and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System Working Group. Clin Infect Dis 2003;37:351-8.
2. Rennels MB et al. Pediatrics 2000;105:e12.
3. Huber BM, Goetschel P. J Pediatr. 2011;158:1033.
4. Blumenthal KG et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1273-7.
5. McMahon DE et al. J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2021;85(1):46-55. 6. Johnston MS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(6):716-20 .
7. ELS associated with the administration of Comirnaty®. WHO database Vigilyze (cited 2021 Feb 22). Available from https://vigilyze.who-umc.org/.
8. Baeck M et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2104751.
9. Samarakoon U et al. N Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108620.
10. Kelso JM et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:25-43.
11. Zafack JG et al. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20163707.
A 19-month-old boy comes to the office with a large firm erythematous swelling of his anterior left thigh that reaches from just below the inguinal crease to the patella. He got his routine immunizations 2 days prior to this visit including the fourth DTaP dose in his left thigh. Clinicians who care for children and who give routine immunizations occasionally see such an adverse effect following immunization (AEFI). These large local reactions have been described for many decades and occur after many vaccines.

What is extensive limb swelling (ELS)? ELS is defined as erythema/swelling crossing a joint or extending mostly joint to joint. It is a subset of large local AEFIs. ELS is generally firm and often erythematous with varying degrees of pain. ELS is now most frequent after pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) and DTaP, with a 1%-4% rate after DTaP boosters.1-3 ELS and other large local swelling reactions occur at nearly any age.1 And yet there is still much that is not known about their true pathogenesis. Likewise, there are no accurate predictors of which vaccinees will develop large inflammatory processes at or near the site of immunization.
ELS after standard vaccines
The largest report to date on AEFI of all ages, including ELS, covered 1990-2003.1 Two upfront caveats are: This study evaluated ELS before PCVs were available, and in adults, repeat 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine was the most common cause of ELS in this study, comprising 45% of all adult ELS.
Considering all ages, ELS onset was nearly always greater than 1 hour and was less than 24 hours post vaccine in almost 75% of patients. However, for those aged under 2 years, onset in less than 24 hours was even more frequent (84%). Interestingly, concomitant fever occurred in less than 25% regardless of age. In adults, ELS after tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines occurred mostly in women (75%); whereas for ELS under 8 years of age, males predominated (about 60%). Of note, tetanus- and diphtheria-containing vaccines were the most frequent ELS-inducing vaccines in children, that is, 75% aged under 8 years and 55% for those aged 8-17 years. Focusing on pediatric ELS after DTaP by dose, 33% were after the fourth, 31% after the fifth, 12% after the second, 10% after the first, and 3% after the third dose. In the case above, ELS was after the fourth dose.
Clinicians caring for children know how to manage ELS after DTaP or PCVs. They understand that ELS looks scary and is uncomfortable but is not dangerous and requires no specific treatment. Supportive management, that is, pain reliever, cool compresses, and TLC, are warranted. ELS is not a contraindication to subsequent immunization with the same vaccine. That said, large local reactions or ELS do occur with subsequent doses of that same vaccine at varying rates up to 66% of the time. Management is the same with repeat episodes, and no sequelae are expected. Supportive management only is standard unless one suspects a very rare Arthus reaction. If central necrosis occurs or swelling evolution/resolution is not per expectations, referral to a vaccine expert can sort out if it is an Arthus reaction, in which case, subsequent use of the same vaccine in not recommended.
ELS and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
With SARS-CoV-2 vaccines now authorized for adolescents and expected in a few months for younger children, large local AEFI reactions related to pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are expected, given that “COVID arm” is now well described in adults.4 Overall, ELS/large local reactions have been reported more frequently with the Moderna than Pfizer mRNA vaccine.4 In the almost 42% of adults having ELS post first dose, repeat ELS post second dose often appears sooner but also resolves more quickly, with no known sequelae.5
Some biopsies have shown delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (DTH) (superficial perivascular and perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrates with rare eosinophils and scattered mast cells),6,7 while others show no DTH but these patients have findings of immediate hypersensitivity findings and negative skin testing to the vaccine.8 With regard to sex, Dutch ELS data in White adults reveal 90% occur in females – higher than the 75% female rate after standard vaccines.7 Onset of ELS data show that Pfizer mRNA vaccinees had onset on average at 38 hours (range, <1 hr to 12 days). Boston data mostly in White adults reveal later onset (median, 6 days; range, 2-12 days).4 In contrast, adults of color appear to have later onset (mean, 8 days; range, 4-14 days).9
In addition to the local swelling, patients had concurrent injection-site AEFIs of pain (65%), warmth (63%), and pruritus (26%), plus myalgia (51%), headache (48%), malaise (45%), fatigue (43%), chills (33%), arthralgia (30%), and fever (28%).7
What should we tell families about pediatric ELS before we give SARS-CoV-2 vaccines to children? Clinical pediatric SARS-CoV-2 vaccine trials are smaller “immunologic bridging” studies, not requiring proof of efficacy. So, the precise incidence of pediatric ELS (adult rate is estimated under 1/100,000) may not be known until months after general use. Nevertheless, part of our counseling of families will need to include ELS/large local reactions. Unless new data show otherwise, the spiel that clinicians have developed to counsel about the rare chance of ELS after routine vaccines should also be useful to inform families of the rare chance of ELS post SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
The bottom line is that the management of pediatric ELS after SARS-CoV-2 vaccines should be the same as after standard vaccines. And remember, whether the reactions are DTH or not, neither immediate local injection-site reactions nor DTH reactions are contraindications to subsequent vaccination unless anaphylaxis or Arthus reaction is suspected.10,11
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Woo EJ and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System Working Group. Clin Infect Dis 2003;37:351-8.
2. Rennels MB et al. Pediatrics 2000;105:e12.
3. Huber BM, Goetschel P. J Pediatr. 2011;158:1033.
4. Blumenthal KG et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1273-7.
5. McMahon DE et al. J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2021;85(1):46-55. 6. Johnston MS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(6):716-20 .
7. ELS associated with the administration of Comirnaty®. WHO database Vigilyze (cited 2021 Feb 22). Available from https://vigilyze.who-umc.org/.
8. Baeck M et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2104751.
9. Samarakoon U et al. N Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108620.
10. Kelso JM et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:25-43.
11. Zafack JG et al. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20163707.
Back-to-school threat: Missed vaccinations in children, teens
U.S. children and adolescents may be at higher risk for vaccine-preventable diseases this fall as vaccination levels have not caught up with prepandemic coverage, according to a study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Pediatric outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases have the potential to derail efforts to reopen schools for the 2021-22 academic year and further delay nationwide efforts to return students to the classroom,” wrote Bhavini Patel Murthy, MD, with the immunization services division, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, and colleagues.
The number of children getting routine vaccinations plummeted between March and May 2020, compared with the same months in 2019. Although vaccination rates increased again from June 2020 to September 2020, the rebound was not enough to reach prepandemic levels, according to the study.
At the beginning of the June–September 2020 period, the news was good, the authors wrote. After most stay-at-home orders were lifted, the number of weekly routine pediatric vaccinations started to approach, and even surpass, baseline prepandemic levels in most of the 10 jurisdictions studied.
“However,” the authors wrote, “across all age groups and across all vaccine types, none of the jurisdictions demonstrated a sustained or prolonged increase in the number of weekly doses administered above prepandemic administration levels, which would have been necessary to catch up children and adolescents who missed routine vaccinations.”
To overcome the gap, the authors said that clinicians should take the initiative. “Health care providers should assess the vaccination status of all pediatric patients, including adolescents, and contact those who are behind schedule to ensure that all children are fully vaccinated.”
As COVID-19 vaccinations become more readily available to children, the CDC recommends that providers consider giving COVID-19 shots along with other routinely recommended vaccines.
Martha Perry, MD, associate professor and medical director at the University of North Carolina Children’s Primary Care Clinic, Chapel Hill, said in an interview that getting the message out about the need to get children and adolescents caught up may require a national messaging campaign similar to that for COVID-19 vaccinations, as well as opening mass vaccination sites rather than families seeking vaccinations from individual providers.
She noted that, although schools may offer a checks and balances system for required vaccinations, children who are not yet school age depend on families getting individual appointments.
Size of the gaps
The MMWR article shows that the shortfall in vaccinations in June–September 2020, compared with those months the year before are striking.
For children younger than 2 years old and aged 2-6 years, diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DtaP) vaccinations declined an average of 9.1% and 6.7%, respectively.
Among children aged 12-23 months and 2-8 years, MMR vaccinations decreased 8.8% and 11.3%, respectively.
Among children aged 9-12 years and adolescents 13-17 years, human papillomavirus vaccinations decreased an average 12.2% and 28.1%, respectively. Among the same age groups, Tdap vaccinations dropped 21.3% and 30.0%, respectively.
Dr. Perry said that, although all the shortfalls are important, lags in vaccinations for measles and pertussis are particularly alarming in light of outbreaks in recent years.
Additionally, she said, as COVID-19 restrictions are lifting, some of the mitigation strategies, such as mask wearing, that kept other diseases at bay will not be in place, heightening the risk for infection.
The authors chose to measure weekly doses in March–May 2020, and June–September 2020 because many jurisdictions imposed and then lifted stay-at-home orders during these times. They analyzed data from 10 jurisdictions with high-performing information systems (Idaho, Iowa, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York City, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin).
Adults missing vaccinations as well
Another analysis, commissioned by GlaxoSmithKline and conducted by Avalere Health, calculated 8.8 million missed adolescent vaccine doses and 17.2 million missed adult vaccine doses as a result of the pandemic and ongoing government restrictions and public health measures.
That study examined claims for CDC-recommended vaccines across commercial, managed Medicaid, Medicare Advantage, and Medicare fee-for-service Part B for January–November 2020, compared with the same period in 2019.
It also found that vaccine claims remain well below 2019 levels. Total noninfluenza vaccine claims submissions were down by between 13% and 35% among adolescents and 17% and 40% among adults, compared with the same period in 2019.
Dr. Perry said it will be critical for schools across the nation to enforce their policies on requiring up-to-date vaccinations even if online attendance is offered.
The workforce needed for this will be challenging, she noted.
“We’ve lost a lot of workforce in the health care field in the pandemic for a variety of reasons and it may be challenging to fill those positions,” she said.
She also said the study underlines the importance of each state having a vaccine registry so each provider can determine what vaccinations a child needs.
The study authors and Dr. Perry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. children and adolescents may be at higher risk for vaccine-preventable diseases this fall as vaccination levels have not caught up with prepandemic coverage, according to a study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Pediatric outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases have the potential to derail efforts to reopen schools for the 2021-22 academic year and further delay nationwide efforts to return students to the classroom,” wrote Bhavini Patel Murthy, MD, with the immunization services division, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, and colleagues.
The number of children getting routine vaccinations plummeted between March and May 2020, compared with the same months in 2019. Although vaccination rates increased again from June 2020 to September 2020, the rebound was not enough to reach prepandemic levels, according to the study.
At the beginning of the June–September 2020 period, the news was good, the authors wrote. After most stay-at-home orders were lifted, the number of weekly routine pediatric vaccinations started to approach, and even surpass, baseline prepandemic levels in most of the 10 jurisdictions studied.
“However,” the authors wrote, “across all age groups and across all vaccine types, none of the jurisdictions demonstrated a sustained or prolonged increase in the number of weekly doses administered above prepandemic administration levels, which would have been necessary to catch up children and adolescents who missed routine vaccinations.”
To overcome the gap, the authors said that clinicians should take the initiative. “Health care providers should assess the vaccination status of all pediatric patients, including adolescents, and contact those who are behind schedule to ensure that all children are fully vaccinated.”
As COVID-19 vaccinations become more readily available to children, the CDC recommends that providers consider giving COVID-19 shots along with other routinely recommended vaccines.
Martha Perry, MD, associate professor and medical director at the University of North Carolina Children’s Primary Care Clinic, Chapel Hill, said in an interview that getting the message out about the need to get children and adolescents caught up may require a national messaging campaign similar to that for COVID-19 vaccinations, as well as opening mass vaccination sites rather than families seeking vaccinations from individual providers.
She noted that, although schools may offer a checks and balances system for required vaccinations, children who are not yet school age depend on families getting individual appointments.
Size of the gaps
The MMWR article shows that the shortfall in vaccinations in June–September 2020, compared with those months the year before are striking.
For children younger than 2 years old and aged 2-6 years, diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DtaP) vaccinations declined an average of 9.1% and 6.7%, respectively.
Among children aged 12-23 months and 2-8 years, MMR vaccinations decreased 8.8% and 11.3%, respectively.
Among children aged 9-12 years and adolescents 13-17 years, human papillomavirus vaccinations decreased an average 12.2% and 28.1%, respectively. Among the same age groups, Tdap vaccinations dropped 21.3% and 30.0%, respectively.
Dr. Perry said that, although all the shortfalls are important, lags in vaccinations for measles and pertussis are particularly alarming in light of outbreaks in recent years.
Additionally, she said, as COVID-19 restrictions are lifting, some of the mitigation strategies, such as mask wearing, that kept other diseases at bay will not be in place, heightening the risk for infection.
The authors chose to measure weekly doses in March–May 2020, and June–September 2020 because many jurisdictions imposed and then lifted stay-at-home orders during these times. They analyzed data from 10 jurisdictions with high-performing information systems (Idaho, Iowa, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York City, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin).
Adults missing vaccinations as well
Another analysis, commissioned by GlaxoSmithKline and conducted by Avalere Health, calculated 8.8 million missed adolescent vaccine doses and 17.2 million missed adult vaccine doses as a result of the pandemic and ongoing government restrictions and public health measures.
That study examined claims for CDC-recommended vaccines across commercial, managed Medicaid, Medicare Advantage, and Medicare fee-for-service Part B for January–November 2020, compared with the same period in 2019.
It also found that vaccine claims remain well below 2019 levels. Total noninfluenza vaccine claims submissions were down by between 13% and 35% among adolescents and 17% and 40% among adults, compared with the same period in 2019.
Dr. Perry said it will be critical for schools across the nation to enforce their policies on requiring up-to-date vaccinations even if online attendance is offered.
The workforce needed for this will be challenging, she noted.
“We’ve lost a lot of workforce in the health care field in the pandemic for a variety of reasons and it may be challenging to fill those positions,” she said.
She also said the study underlines the importance of each state having a vaccine registry so each provider can determine what vaccinations a child needs.
The study authors and Dr. Perry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. children and adolescents may be at higher risk for vaccine-preventable diseases this fall as vaccination levels have not caught up with prepandemic coverage, according to a study published in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Pediatric outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases have the potential to derail efforts to reopen schools for the 2021-22 academic year and further delay nationwide efforts to return students to the classroom,” wrote Bhavini Patel Murthy, MD, with the immunization services division, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, and colleagues.
The number of children getting routine vaccinations plummeted between March and May 2020, compared with the same months in 2019. Although vaccination rates increased again from June 2020 to September 2020, the rebound was not enough to reach prepandemic levels, according to the study.
At the beginning of the June–September 2020 period, the news was good, the authors wrote. After most stay-at-home orders were lifted, the number of weekly routine pediatric vaccinations started to approach, and even surpass, baseline prepandemic levels in most of the 10 jurisdictions studied.
“However,” the authors wrote, “across all age groups and across all vaccine types, none of the jurisdictions demonstrated a sustained or prolonged increase in the number of weekly doses administered above prepandemic administration levels, which would have been necessary to catch up children and adolescents who missed routine vaccinations.”
To overcome the gap, the authors said that clinicians should take the initiative. “Health care providers should assess the vaccination status of all pediatric patients, including adolescents, and contact those who are behind schedule to ensure that all children are fully vaccinated.”
As COVID-19 vaccinations become more readily available to children, the CDC recommends that providers consider giving COVID-19 shots along with other routinely recommended vaccines.
Martha Perry, MD, associate professor and medical director at the University of North Carolina Children’s Primary Care Clinic, Chapel Hill, said in an interview that getting the message out about the need to get children and adolescents caught up may require a national messaging campaign similar to that for COVID-19 vaccinations, as well as opening mass vaccination sites rather than families seeking vaccinations from individual providers.
She noted that, although schools may offer a checks and balances system for required vaccinations, children who are not yet school age depend on families getting individual appointments.
Size of the gaps
The MMWR article shows that the shortfall in vaccinations in June–September 2020, compared with those months the year before are striking.
For children younger than 2 years old and aged 2-6 years, diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DtaP) vaccinations declined an average of 9.1% and 6.7%, respectively.
Among children aged 12-23 months and 2-8 years, MMR vaccinations decreased 8.8% and 11.3%, respectively.
Among children aged 9-12 years and adolescents 13-17 years, human papillomavirus vaccinations decreased an average 12.2% and 28.1%, respectively. Among the same age groups, Tdap vaccinations dropped 21.3% and 30.0%, respectively.
Dr. Perry said that, although all the shortfalls are important, lags in vaccinations for measles and pertussis are particularly alarming in light of outbreaks in recent years.
Additionally, she said, as COVID-19 restrictions are lifting, some of the mitigation strategies, such as mask wearing, that kept other diseases at bay will not be in place, heightening the risk for infection.
The authors chose to measure weekly doses in March–May 2020, and June–September 2020 because many jurisdictions imposed and then lifted stay-at-home orders during these times. They analyzed data from 10 jurisdictions with high-performing information systems (Idaho, Iowa, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York City, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin).
Adults missing vaccinations as well
Another analysis, commissioned by GlaxoSmithKline and conducted by Avalere Health, calculated 8.8 million missed adolescent vaccine doses and 17.2 million missed adult vaccine doses as a result of the pandemic and ongoing government restrictions and public health measures.
That study examined claims for CDC-recommended vaccines across commercial, managed Medicaid, Medicare Advantage, and Medicare fee-for-service Part B for January–November 2020, compared with the same period in 2019.
It also found that vaccine claims remain well below 2019 levels. Total noninfluenza vaccine claims submissions were down by between 13% and 35% among adolescents and 17% and 40% among adults, compared with the same period in 2019.
Dr. Perry said it will be critical for schools across the nation to enforce their policies on requiring up-to-date vaccinations even if online attendance is offered.
The workforce needed for this will be challenging, she noted.
“We’ve lost a lot of workforce in the health care field in the pandemic for a variety of reasons and it may be challenging to fill those positions,” she said.
She also said the study underlines the importance of each state having a vaccine registry so each provider can determine what vaccinations a child needs.
The study authors and Dr. Perry reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Third COVID-19 vaccine dose helped some transplant recipients
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
More evidence links COVID vaccines to rare cases of myocarditis in youth
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NIAID advances universal flu vaccine candidate into phase 1 trial
Last month, U.S. government researchers began a test of an experimental influenza vaccine that they hope will provide long-lasting immunity against multiple strains of the virus. Their project adds to the many approaches that have been tried in the decades-long quest for a universal flu shot.
For the first time, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is testing an investigational flu vaccine, known as FluMos-v1, on people. Researchers in recent years have targeted the stalk or stem of an influenza surface protein called hemagglutinin (HA) in trying to develop better flu vaccines. NIAID said FluMos-v1 is designed to spark production of antibodies against the HA protein from different virus strains, which could make it superior to vaccines now available, NIAID said.
“It could be longer lasting than the traditional flu vaccine and give us what we call super seasonal protection that might go beyond just one flu season to next year’s or the year after, or offer additional protection in a pandemic setting,” Alicia T. Widge, MD, of NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center, who is the principal investigator of the trial, said in an interview.
The phase 1 study (NCT04896086) aims to enroll 35 participants, 15 of whom will receive a single intramuscular injection of a comparator treatment, Flucelvax, which has already been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The FluMos-v1 group will start with five participants who will receive one 20-μg dose. If no safety problems emerge at that dosage, another 15 volunteers will receive one 60-μg dose of the investigational vaccine.
The incorporation of a comparator group in the phase 1 study may help investigators get an early idea of how well FluMos-v1 compares to a marketed product, Dr. Widge said. The test will be carried out through the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center.
‘Renaissance’ of flu-vaccine research?
Currently, flu vaccines are reformulated each year in an attempt to match the dominant strain for the upcoming season, an effort that often falls notably short. The estimated vaccine effectiveness rate in the United States has ranged from a low of 19% to a high of 60% in recent years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Scientists have been working for decades on a universal flu vaccine that would offer better results but haven’t yet identified the right strategy to outwit mutations in the virus. Recent setbacks include BiondVax Pharmaceuticals’ October 2020 announcement of a failed phase 3 trial of its experimental M-001 universal flu vaccine candidate.
But advances in understanding the immune system may set the stage for a “renaissance” in efforts to develop a universal flu vaccine, Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, said in an interview.
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred greater interest in the need to develop a universal flu vaccine, he said. Dr. Osterholm said he is “more optimistic now than ever” about the chances for developing vaccines that can fend off multiple strains over longer periods, although the goal of a shot that can ward off influenza in all cases may remain elusive.
“How good can we make them? Will they ever be really universal? Will they have long periods of protection? I don’t think any of us know that yet,” Dr. Osterholm said. “But this is not the influenza vaccine world of 5 or 7 years ago.”
The mRNA technology used to develop the world’s first approved COVID-19 vaccines, for example, may be applied against influenza, Dr. Osterholm said.
In January 2021, Moderna announced plans to test three development candidates for a seasonal influenza vaccine and aims to start a phase 1 study this year. In an April interview on CNBC’s Squawk Box program, Moderna’s chief executive, Stephané Bancel, spoke about the company’s plans to eventually create a combination vaccine for SARS-Cov-2 and flu viruses.
SARS-CoV-2 “is not going away.” Like flu, this virus will persist and change forms, Ms. Bancel said. Creating a flu shot that outperforms the existing ones would boost confidence in influenza vaccines, which many people now skip, Ms. Bancel said. People might someday be able to get a combination of this more effective flu shot with a COVID-19 vaccine booster in their local pharmacies.
“You can take one dose and then have a nice winter,” Ms. Bancel said of Moderna’s goal for a combination vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, U.S. government researchers began a test of an experimental influenza vaccine that they hope will provide long-lasting immunity against multiple strains of the virus. Their project adds to the many approaches that have been tried in the decades-long quest for a universal flu shot.
For the first time, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is testing an investigational flu vaccine, known as FluMos-v1, on people. Researchers in recent years have targeted the stalk or stem of an influenza surface protein called hemagglutinin (HA) in trying to develop better flu vaccines. NIAID said FluMos-v1 is designed to spark production of antibodies against the HA protein from different virus strains, which could make it superior to vaccines now available, NIAID said.
“It could be longer lasting than the traditional flu vaccine and give us what we call super seasonal protection that might go beyond just one flu season to next year’s or the year after, or offer additional protection in a pandemic setting,” Alicia T. Widge, MD, of NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center, who is the principal investigator of the trial, said in an interview.
The phase 1 study (NCT04896086) aims to enroll 35 participants, 15 of whom will receive a single intramuscular injection of a comparator treatment, Flucelvax, which has already been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The FluMos-v1 group will start with five participants who will receive one 20-μg dose. If no safety problems emerge at that dosage, another 15 volunteers will receive one 60-μg dose of the investigational vaccine.
The incorporation of a comparator group in the phase 1 study may help investigators get an early idea of how well FluMos-v1 compares to a marketed product, Dr. Widge said. The test will be carried out through the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center.
‘Renaissance’ of flu-vaccine research?
Currently, flu vaccines are reformulated each year in an attempt to match the dominant strain for the upcoming season, an effort that often falls notably short. The estimated vaccine effectiveness rate in the United States has ranged from a low of 19% to a high of 60% in recent years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Scientists have been working for decades on a universal flu vaccine that would offer better results but haven’t yet identified the right strategy to outwit mutations in the virus. Recent setbacks include BiondVax Pharmaceuticals’ October 2020 announcement of a failed phase 3 trial of its experimental M-001 universal flu vaccine candidate.
But advances in understanding the immune system may set the stage for a “renaissance” in efforts to develop a universal flu vaccine, Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, said in an interview.
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred greater interest in the need to develop a universal flu vaccine, he said. Dr. Osterholm said he is “more optimistic now than ever” about the chances for developing vaccines that can fend off multiple strains over longer periods, although the goal of a shot that can ward off influenza in all cases may remain elusive.
“How good can we make them? Will they ever be really universal? Will they have long periods of protection? I don’t think any of us know that yet,” Dr. Osterholm said. “But this is not the influenza vaccine world of 5 or 7 years ago.”
The mRNA technology used to develop the world’s first approved COVID-19 vaccines, for example, may be applied against influenza, Dr. Osterholm said.
In January 2021, Moderna announced plans to test three development candidates for a seasonal influenza vaccine and aims to start a phase 1 study this year. In an April interview on CNBC’s Squawk Box program, Moderna’s chief executive, Stephané Bancel, spoke about the company’s plans to eventually create a combination vaccine for SARS-Cov-2 and flu viruses.
SARS-CoV-2 “is not going away.” Like flu, this virus will persist and change forms, Ms. Bancel said. Creating a flu shot that outperforms the existing ones would boost confidence in influenza vaccines, which many people now skip, Ms. Bancel said. People might someday be able to get a combination of this more effective flu shot with a COVID-19 vaccine booster in their local pharmacies.
“You can take one dose and then have a nice winter,” Ms. Bancel said of Moderna’s goal for a combination vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, U.S. government researchers began a test of an experimental influenza vaccine that they hope will provide long-lasting immunity against multiple strains of the virus. Their project adds to the many approaches that have been tried in the decades-long quest for a universal flu shot.
For the first time, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is testing an investigational flu vaccine, known as FluMos-v1, on people. Researchers in recent years have targeted the stalk or stem of an influenza surface protein called hemagglutinin (HA) in trying to develop better flu vaccines. NIAID said FluMos-v1 is designed to spark production of antibodies against the HA protein from different virus strains, which could make it superior to vaccines now available, NIAID said.
“It could be longer lasting than the traditional flu vaccine and give us what we call super seasonal protection that might go beyond just one flu season to next year’s or the year after, or offer additional protection in a pandemic setting,” Alicia T. Widge, MD, of NIAID’s Vaccine Research Center, who is the principal investigator of the trial, said in an interview.
The phase 1 study (NCT04896086) aims to enroll 35 participants, 15 of whom will receive a single intramuscular injection of a comparator treatment, Flucelvax, which has already been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The FluMos-v1 group will start with five participants who will receive one 20-μg dose. If no safety problems emerge at that dosage, another 15 volunteers will receive one 60-μg dose of the investigational vaccine.
The incorporation of a comparator group in the phase 1 study may help investigators get an early idea of how well FluMos-v1 compares to a marketed product, Dr. Widge said. The test will be carried out through the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center.
‘Renaissance’ of flu-vaccine research?
Currently, flu vaccines are reformulated each year in an attempt to match the dominant strain for the upcoming season, an effort that often falls notably short. The estimated vaccine effectiveness rate in the United States has ranged from a low of 19% to a high of 60% in recent years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Scientists have been working for decades on a universal flu vaccine that would offer better results but haven’t yet identified the right strategy to outwit mutations in the virus. Recent setbacks include BiondVax Pharmaceuticals’ October 2020 announcement of a failed phase 3 trial of its experimental M-001 universal flu vaccine candidate.
But advances in understanding the immune system may set the stage for a “renaissance” in efforts to develop a universal flu vaccine, Michael Osterholm, PhD, MPH, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota, said in an interview.
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred greater interest in the need to develop a universal flu vaccine, he said. Dr. Osterholm said he is “more optimistic now than ever” about the chances for developing vaccines that can fend off multiple strains over longer periods, although the goal of a shot that can ward off influenza in all cases may remain elusive.
“How good can we make them? Will they ever be really universal? Will they have long periods of protection? I don’t think any of us know that yet,” Dr. Osterholm said. “But this is not the influenza vaccine world of 5 or 7 years ago.”
The mRNA technology used to develop the world’s first approved COVID-19 vaccines, for example, may be applied against influenza, Dr. Osterholm said.
In January 2021, Moderna announced plans to test three development candidates for a seasonal influenza vaccine and aims to start a phase 1 study this year. In an April interview on CNBC’s Squawk Box program, Moderna’s chief executive, Stephané Bancel, spoke about the company’s plans to eventually create a combination vaccine for SARS-Cov-2 and flu viruses.
SARS-CoV-2 “is not going away.” Like flu, this virus will persist and change forms, Ms. Bancel said. Creating a flu shot that outperforms the existing ones would boost confidence in influenza vaccines, which many people now skip, Ms. Bancel said. People might someday be able to get a combination of this more effective flu shot with a COVID-19 vaccine booster in their local pharmacies.
“You can take one dose and then have a nice winter,” Ms. Bancel said of Moderna’s goal for a combination vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC director cites rise in hospitalizations in urging teen vaccinations
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
“I am deeply concerned by the numbers of hospitalized adolescents and saddened to see the number of adolescents who required treatment in intensive care units or mechanical ventilation,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said in a statement.
While urging teenagers to wear masks and take precautions around others, she asked “parents, relatives, and close friends to join me and talk with teens about the importance of these prevention strategies and to encourage them to get vaccinated.”
Dr. Walensky referred to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that showed adolescent hospitalizations peaked at 2.1 per 100,000 in early January 2021, then dropped to 0.6 per 100,000 in mid-March.
Alarmingly, hospitalizations rose to 1.3 per 100,000 in April, and a number of teens required serious interventions.
“Among hospitalized adolescents, nearly one-third required intensive care unit admission, and 5% required invasive mechanical ventilation,” the report said. No deaths occurred.
The study looked at 376 adolescents aged 12-17 who were hospitalized and tested positive for coronavirus. Of that group, 204 were hospitalized for COVID-19 and the other 172 were hospitalized for reasons not directly related to COVID-19.
Of the 204 hospitalized for COVID-19, 70.6% had an underlying medical condition such as obesity or chronic lung disease.
The study noted that children and teenagers have lower hospitalization rates and generally show less severe symptoms than do older people.
Possible causes for the rise in adolescent COVID-19 hospitalizations include the arrival of variants, the growing number of children returning to in-person education, and the changes in mask-wearing and other safety precautions, the study said.
The American Academy of Pediatrics said that as of May 27, 4 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the pandemic began, with about 34,500 new child cases reported for the week ending May 27.
The AAP said children have represented 14.1% of total cases since the pandemic began, but for the week ending May 27, children represented 24.3% of new reported weekly COVID-19 cases.
On May 10, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children aged 12-15 years. Previously, the FDA had authorized the Pfizer vaccine for people aged 16 years and up, whereas the Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people aged 18 years and up.
“Vaccination is our way out of this pandemic,” Dr. Walensky said in her statement. “I continue to see promising signs in CDC data that we are nearing the end of this pandemic in this country; however, we all have to do our part and get vaccinated to cross the finish line.”
A version of this article was first published on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 vaccine update: Uptake, effectiveness, and safety concerns
REFERENCES
- CDC. COVID Data Tracker. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid19.who.int/
- CDC. Demographic trends of people receiving COVID-19 vaccinations in the United States. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-demographics-trends
- Shimabukuro T. Update: thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) following COVID-19 vaccination. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/07-COVID-Shimabukuro-508.pdf
- Fleming-Dutra K. CDC COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness studies. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/09-COVID-Fleming-Dutra-508.pdf
- Scobie H. Update on emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and vaccine considerations. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/10-COVID-Scobie-508.pdf
REFERENCES
- CDC. COVID Data Tracker. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid19.who.int/
- CDC. Demographic trends of people receiving COVID-19 vaccinations in the United States. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-demographics-trends
- Shimabukuro T. Update: thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) following COVID-19 vaccination. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/07-COVID-Shimabukuro-508.pdf
- Fleming-Dutra K. CDC COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness studies. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/09-COVID-Fleming-Dutra-508.pdf
- Scobie H. Update on emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and vaccine considerations. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/10-COVID-Scobie-508.pdf
REFERENCES
- CDC. COVID Data Tracker. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid19.who.int/
- CDC. Demographic trends of people receiving COVID-19 vaccinations in the United States. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccination-demographics-trends
- Shimabukuro T. Update: thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) following COVID-19 vaccination. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/07-COVID-Shimabukuro-508.pdf
- Fleming-Dutra K. CDC COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness studies. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/09-COVID-Fleming-Dutra-508.pdf
- Scobie H. Update on emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and vaccine considerations. Presentation to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, May 12, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-05-12/10-COVID-Scobie-508.pdf
In Zambia, PCR tracks pertussis
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ESPID 2021
Children aged 12-15 years continue to close COVID-19 vaccination gap
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.




