User login
ERAS protocol for cesarean delivery reduces opioid usage
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – An enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathway for cesarean delivery decreased postoperative opioid usage by 62% in one health care organization, researchers reported at the Pregnancy Meeting. The protocol incorporates a stepwise approach to pain control with no scheduled postoperative opioids.
Abington Jefferson Health, which includes two hospitals in Pennsylvania, implemented an ERAS pathway for all cesarean deliveries in October 2018. Kathryn Ruymann, MD, said at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Dr. Ruymann is an obstetrics and gynecology resident at Abington Jefferson Health.
Prior to the ERAS protocol, 99%-100% of patients took an opioid during the postoperative period. “With ERAS, 26% of patients never took an opioid during the postop period,” Dr. Ruymann and her associates reported. “Pain scores decreased with ERAS for postoperative days 1-3 and remained unchanged on day 4.”
One in 300 opioid-naive patients who receives opioids after cesarean delivery becomes a persistent user, one study has shown (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep; 215(3):353.e1-18). “ERAS pathways integrate evidence-based interventions before, during, and after surgery to optimize outcomes, specifically to decrease postoperative opioid use,” the researchers said.
While other surgical fields have adopted ERAS pathways, more research is needed in obstetrics, said Dr. Ruymann. More than 4,500 women deliver at Abington Jefferson Health each year, and about a third undergo cesarean deliveries.
The organization’s ERAS pathway incorporates preoperative education, fasting guidelines, and intraoperative analgesia, nausea prophylaxis, and antimicrobial therapy. Under the new protocol, postoperative analgesia includes scheduled administration of nonopioid medications, including celecoxib and acetaminophen. In addition, patients may take 5-10 mg of oxycodone orally every 4 hours as needed, and hydromorphone 0.4 mg IV as needed may be used for refractory pain. In addition, patients should resume eating as soon as tolerated and be out of bed within 4 hours after surgery, according to the protocol. Postoperative management of pruritus and instructions on how to wean off opioids at home are among the other elements of the enhanced recovery plan.
To examine postoperative opioid usage before and after implementation of the ERAS pathway, the investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of 316 women who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months before the start of the ERAS pathway and 267 who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months after. The researchers used an application developed in Qlik Sense, a data analytics platform, to calculate opioid usage.
Mean postoperative opioid use decreased by 62%. The reduction in opioid use remained 8 months after starting the ERAS pathway.
“An ERAS pathway for [cesarean delivery] decreases postoperative opioid usage by integrating a multimodal stepwise approach to pain control and recovery,” the researchers said. “Standardized order sets and departmentwide education were crucial in the success of ERAS. Additional research is needed to evaluate the impact of unique components of ERAS in order to optimize this pathway.”
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Ruymann K et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S212, Abstract 315.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – An enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathway for cesarean delivery decreased postoperative opioid usage by 62% in one health care organization, researchers reported at the Pregnancy Meeting. The protocol incorporates a stepwise approach to pain control with no scheduled postoperative opioids.
Abington Jefferson Health, which includes two hospitals in Pennsylvania, implemented an ERAS pathway for all cesarean deliveries in October 2018. Kathryn Ruymann, MD, said at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Dr. Ruymann is an obstetrics and gynecology resident at Abington Jefferson Health.
Prior to the ERAS protocol, 99%-100% of patients took an opioid during the postoperative period. “With ERAS, 26% of patients never took an opioid during the postop period,” Dr. Ruymann and her associates reported. “Pain scores decreased with ERAS for postoperative days 1-3 and remained unchanged on day 4.”
One in 300 opioid-naive patients who receives opioids after cesarean delivery becomes a persistent user, one study has shown (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep; 215(3):353.e1-18). “ERAS pathways integrate evidence-based interventions before, during, and after surgery to optimize outcomes, specifically to decrease postoperative opioid use,” the researchers said.
While other surgical fields have adopted ERAS pathways, more research is needed in obstetrics, said Dr. Ruymann. More than 4,500 women deliver at Abington Jefferson Health each year, and about a third undergo cesarean deliveries.
The organization’s ERAS pathway incorporates preoperative education, fasting guidelines, and intraoperative analgesia, nausea prophylaxis, and antimicrobial therapy. Under the new protocol, postoperative analgesia includes scheduled administration of nonopioid medications, including celecoxib and acetaminophen. In addition, patients may take 5-10 mg of oxycodone orally every 4 hours as needed, and hydromorphone 0.4 mg IV as needed may be used for refractory pain. In addition, patients should resume eating as soon as tolerated and be out of bed within 4 hours after surgery, according to the protocol. Postoperative management of pruritus and instructions on how to wean off opioids at home are among the other elements of the enhanced recovery plan.
To examine postoperative opioid usage before and after implementation of the ERAS pathway, the investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of 316 women who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months before the start of the ERAS pathway and 267 who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months after. The researchers used an application developed in Qlik Sense, a data analytics platform, to calculate opioid usage.
Mean postoperative opioid use decreased by 62%. The reduction in opioid use remained 8 months after starting the ERAS pathway.
“An ERAS pathway for [cesarean delivery] decreases postoperative opioid usage by integrating a multimodal stepwise approach to pain control and recovery,” the researchers said. “Standardized order sets and departmentwide education were crucial in the success of ERAS. Additional research is needed to evaluate the impact of unique components of ERAS in order to optimize this pathway.”
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Ruymann K et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S212, Abstract 315.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – An enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathway for cesarean delivery decreased postoperative opioid usage by 62% in one health care organization, researchers reported at the Pregnancy Meeting. The protocol incorporates a stepwise approach to pain control with no scheduled postoperative opioids.
Abington Jefferson Health, which includes two hospitals in Pennsylvania, implemented an ERAS pathway for all cesarean deliveries in October 2018. Kathryn Ruymann, MD, said at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Dr. Ruymann is an obstetrics and gynecology resident at Abington Jefferson Health.
Prior to the ERAS protocol, 99%-100% of patients took an opioid during the postoperative period. “With ERAS, 26% of patients never took an opioid during the postop period,” Dr. Ruymann and her associates reported. “Pain scores decreased with ERAS for postoperative days 1-3 and remained unchanged on day 4.”
One in 300 opioid-naive patients who receives opioids after cesarean delivery becomes a persistent user, one study has shown (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep; 215(3):353.e1-18). “ERAS pathways integrate evidence-based interventions before, during, and after surgery to optimize outcomes, specifically to decrease postoperative opioid use,” the researchers said.
While other surgical fields have adopted ERAS pathways, more research is needed in obstetrics, said Dr. Ruymann. More than 4,500 women deliver at Abington Jefferson Health each year, and about a third undergo cesarean deliveries.
The organization’s ERAS pathway incorporates preoperative education, fasting guidelines, and intraoperative analgesia, nausea prophylaxis, and antimicrobial therapy. Under the new protocol, postoperative analgesia includes scheduled administration of nonopioid medications, including celecoxib and acetaminophen. In addition, patients may take 5-10 mg of oxycodone orally every 4 hours as needed, and hydromorphone 0.4 mg IV as needed may be used for refractory pain. In addition, patients should resume eating as soon as tolerated and be out of bed within 4 hours after surgery, according to the protocol. Postoperative management of pruritus and instructions on how to wean off opioids at home are among the other elements of the enhanced recovery plan.
To examine postoperative opioid usage before and after implementation of the ERAS pathway, the investigators conducted a retrospective cohort study of 316 women who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months before the start of the ERAS pathway and 267 who underwent cesarean delivery 3 months after. The researchers used an application developed in Qlik Sense, a data analytics platform, to calculate opioid usage.
Mean postoperative opioid use decreased by 62%. The reduction in opioid use remained 8 months after starting the ERAS pathway.
“An ERAS pathway for [cesarean delivery] decreases postoperative opioid usage by integrating a multimodal stepwise approach to pain control and recovery,” the researchers said. “Standardized order sets and departmentwide education were crucial in the success of ERAS. Additional research is needed to evaluate the impact of unique components of ERAS in order to optimize this pathway.”
The researchers had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Ruymann K et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jan;222(1):S212, Abstract 315.
REPORTING FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Refining your approach to hypothyroidism treatment
CASE
A 38-year-old woman presents for a routine physical. Other than urgent care visits for 1 episode of influenza and 2 upper respiratory illnesses, she has not seen a physician for a physical in 5 years. She denies any significant medical history. She takes naproxen occasionally for chronic right knee pain. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. Recently, she has started using a meal replacement shake at lunchtime for weight management. She performs aerobic exercise 30 to 40 minutes per day, 5 days per week. Her family history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, arthritis, heart disease, and hyperlipidemia on her mother’s side. She is single, is not currently sexually active, works as a pharmacy technician, and has no children. A high-risk human papillomavirus test was normal 4 years ago.
A review of systems is notable for a 20-pound weight gain over the past year, worsening heartburn over the past 2 weeks, and chronic knee pain, which is greater in the right knee than the left. She denies weakness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain. Vital signs reveal a blood pressure of 146/88 mm Hg, a heart rate of 63 bpm, a temperature of 98°F (36.7°C), a respiratory rate of 16, a height of 5’7’’ (1.7 m), a weight of 217 lbs (98.4 kg), and a peripheral capillary oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 99% on room air. The physical exam reveals a body mass index (BMI) of 34, warm dry skin, and coarse brittle hair.
Lab results reveal a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level of 11.17 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free thyroxine (T4) of 0.58 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). A basic metabolic panel and hemoglobin A1C level are normal.
What would you recommend?
In the United States, the prevalence of overt hypothyroidism (defined as a TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L and a low free T4) among people ≥ 12 years of age was estimated at 0.3% based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 1999-2002.1 Subclinical hypothyroidism (TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L but < 10 mIU/L and a normal T4 level) is even more common, with an estimated prevalence of 3.4%.1 Hypothyroidism is more common in females and occurs more frequently in Caucasian Americans and Mexican Americans than in African Americans.1
The most common etiologies of hypothyroidism include autoimmune thyroiditis (eg, Hashimoto thyroiditis, atrophic autoimmune thyroiditis) and iatrogenic causes (eg, after radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy) (TABLE 1).2-4
Initiating thyroid hormone replacement
Factors to consider when starting a patient on thyroid hormone replacement include age, weight, symptom severity, TSH level, goal TSH value, adverse effects from thyroid supplements, history of cardiac disease, and, for women of child-bearing age, the desire for pregnancy vs the use of contraceptives. Most adult patients < 50 years with overt hypothyroidism can begin a weight-based dose of levothyroxine: ~1.6 mcg/kg/d (based on ideal body weight).3
Continue to: For adults with cardiac disease...
For adults with cardiac disease, the risk of over-replacement limits initial dosing to 25 to 50 mcg/d for patients < 50 years (12.5-25 mcg/d; ≥ 50 years).3 For adults with subclinical hypothyroidism, it is reasonable to begin therapy at a lower daily dose (eg, 25-75 mcg/d) depending on baseline TSH level, symptoms (the patient may be asymptomatic), and the presence of cardiac disease (TABLE 23,4). Consider treatment in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism particularly when patients have a goiter or dyslipidemia and in women contemplating pregnancy in the near future. Elderly patients may require a dose 20% to 25% lower than younger adults because of decreased body mass.3
Levothyroxine is considered first-line therapy for hypothyroidism because of its low cost, dose consistency, low risk of allergic reactions, and potential to cause fewer cardiac adverse effects than triiodothyronine (T3) products such as desiccated thyroid extract.5 Although data have not shown an absolute increase in cardiovascular adverse effects, T3 products have a higher T3 vs T4 ratio, giving them a theoretically increased risk.5,6 Desiccated thyroid extract also has been associated with allergic reactions.5
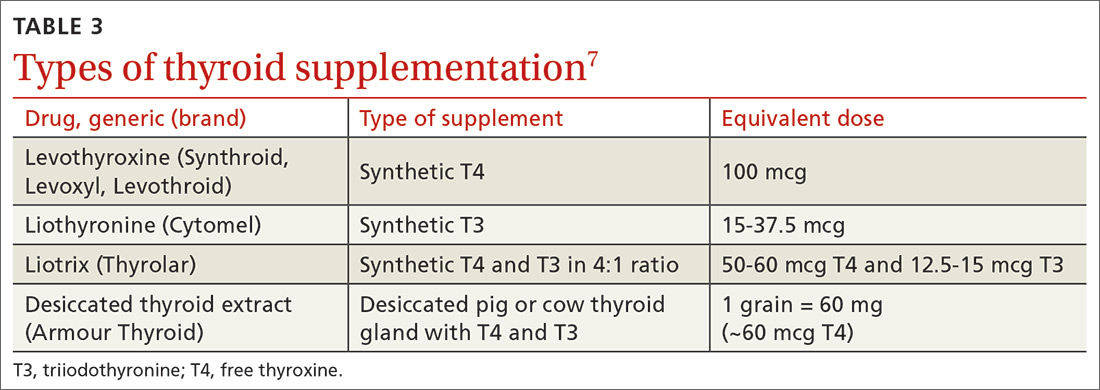
Use of liothyronine alone or in combination with levothyroxine lacks evidence and guideline support.4 Furthermore, it is dosed twice daily, which makes it less convenient, and concerns still exist that there may be an increase in cardiovascular adverse effects.4,6 See TABLE 37 for a summary of available products and their equivalent doses.
Maintaining patients on therapy
The maintenance phase begins once hypothyroidism is diagnosed and treatment is initiated. This phase includes regular monitoring with laboratory studies, office visits, and as-needed adjustments in hormone replacement dosing. The frequency at which all of these occur is variable and based on a number of factors including the patient’s other medical conditions, use of other medications including over-the-counter agents, the patient’s age, weight changes, and pregnancy status.3,4,8 In general, dosage adjustments of 12.5 to 25 mcg can be made at 6- to 8-week intervals based on repeat TSH measurements, patient symptoms, and comorbidities.3
Once a patient is symptomatically stable and laboratory values have normalized, the recommended frequency of laboratory evaluation and office visits is every 12 months, barring significant changes in any of the factors mentioned above. At each visit, physicians should perform medication (including supplements) reconciliation and discuss any health condition updates. Changes to the therapy plan, including frequency or timing of laboratory tests, may be necessary if patients begin taking medications that alter the absorption or function of levothyroxine (eg, steroids).
Continue to: To maximize absorption...
To maximize absorption, providers should review with patients the optimal way to take thyroid hormones. Levothyroxine is approximately 70% to 80% absorbed under ideal conditions, which means taking it in the morning at least 30 to 60 minutes before eating or 3 to 4 hours after the last meal of the day.3,9-13 Of note, TSH levels may increase slightly in patients taking proton pump inhibitors, but this does not usually require a dose increase of thyroid hormone.11 Given that some supplements, particularly iron and calcium, can interfere with absorption, it is recommended to maintain a 3- to 4-hour gap between taking those supplements and taking levothyroxine.12-14 For those patients unable or unwilling to adhere to these recommendations, an increase in levothyroxine dose may be required in order to compensate for the decreased absorption.
Don’t adjust hormone therapy based on clinical presentation alone. While clinical symptoms are important, it is not recommended to adjust hormone therapy based solely on clinical presentation. Common hypothyroid symptoms of dry skin, edema, weight gain, and fatigue may be caused by other medical conditions. While indices including Achilles reflex time and basal metabolic rate have shown some correlation to thyroid dysfunction, there has been limited evidence to show that longitudinal index changes reflect subtle changes in thyroid hormone levels.3
The most recent guidelines from the American Thyroid Association recommend that, “Symptoms should be followed, but considered in the context of serum thyrotropin values, relevant comorbidities, and other potential causes.”3
Special populations/circumstances to keep in mind
Malabsorption conditions. When a higher than expected weight-based dose of levothyroxine is required, physicians should review administration timing, adherence, and comorbid medical conditions that can affect absorption.
Several studies, for example, have demonstrated the impact of Helicobacter pylori gastritis on levothyroxine absorption and subsequent TSH levels.15-17 In one nonrandomized prospective study, patients with H pylori and hypothyroidism who were previously thought to be unresponsive to levothyroxine therapy had a decrease in average TSH level from 30.5 mIU/L to 4.2 mIU/L after H pylori was eradicated.15 Autoimmune atrophic gastritis and celiac disease, both of which are more common in those with other autoimmune diseases, are also associated with the need for higher than expected levothyroxine doses.17,18
Continue to: A history of gastric bypass surgery...
A history of gastric bypass surgery alone is not considered a risk factor for poor absorption of thyroid hormone, given that the majority of levothyroxine absorption occurs in the ileum.19,20 However, advancing age (> 70 years) and extreme obesity (BMI > 40) are independent risk factors for decreased levothyroxine absorption.20,21
Women of reproductive age and pregnant women. Overt untreated or undertreated hypothyroidism can be associated with increased risk of maternal and fetal complications including decreased fertility, miscarriage, preterm delivery, lower birth rates, and infant cognitive deficits.3,22 Therefore, the main focus should be optimization of thyroid hormone levels prior to and during pregnancy.3,4,8,22 Thyroid hormone replacement needs to be increased during pregnancy in approximately 50% to 85% of women using thyroid replacement prior to pregnancy, but the dose requirements vary based on the underlying etiology of thyroid dysfunction.
One initial option for patients on a stable dose before pregnancy is to increase their daily dose by a half tablet (1.5 × daily dose) immediately after home confirmation of pregnancy, until finer dose adjustments (usually increases of 25%-60% ) can be made by a physician. Experts recommend that a TSH level be obtained every 4 weeks until mid-gestation and then at least once around 30 weeks’ gestation to ensure specific targets are being met with dose adjustments.22 Optimal thyrotropin reference ranges during conception and pregnancy can be found in the literature.23
Patients who have positive antibodies and normal thyroid function tests. Patients who are screened for thyroid disorders may demonstrate normal thyroid function (ie, euthyroid) with TSH, free T4, and, if checked, free T3, all within normal ranges. Despite these normal lab results, patients may have additional test results that demonstrate positive thyroid autoantibodies including thyroglobulin antibodies and/or thyroid peroxidase antibodies. Thyroid autoimmunity itself has been associated with a range of other autoimmune conditions as well as an increased risk of thyroid cancer in those with Hashimoto thyroiditis.24 Two studies showed that prophylactic treatment of euthyroid patients with levothyroxine led to a reduction in antibody levels and a lower TSH level.25,26 However, no studies have focused on patient-oriented outcomes such as hospitalizations, quality of life, or symptoms. If the patient remains asymptomatic, we recommend no treatment, but that the patient’s TSH levels be monitored every 12 months.27
Elderly patients. Population data have shown that TSH increases normally with age, with a TSH level of 7.5 mIU/L being the upper limit of normal for a population of healthy adults > 80 years of age.28,29 Overall, studies have failed to show any benefit in treating elderly patients with subclinical hypothyroidism unless their TSH level exceeds 10 mIU/L.6,21 The one exception is elderly patients with heart failure in whom untreated subclinical hypothyroidism has been shown to be associated with higher mortality.30
Continue to: Elderly patients are at higher risk...
Elderly patients are at higher risk for adverse effects of thyroid over-replacement, including atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis. While there have been no randomized trials examining target TSH levels in this population, a reasonable recommendation is a goal TSH level of 4 to 6 mIU/L for elderly patients ≥ 70 years.4
CASE
As a result of the patient’s elevated TSH level and symptoms of hypothyroidism, you start levothyroxine 150 mcg/d by mouth, counsel her on potential adverse effects, and schedule a follow-up visit with another TSH check in 6 weeks.
Follow-up laboratory studies 6 weeks later reveal a TSH level of 5.86 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free T4 level of 0.74 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). Based on those results, you increase the dose of levothyroxine to 175 mcg/d.
At her follow-up visit 12 weeks after initial presentation, her TSH level is 3.85 mIU/L. She reports feeling better overall with less fatigue, and she has lost 5 pounds since her last visit. You recommend she continue levothyroxine 175 mcg/d after reviewing medication compliance with the patient and ensuring she is indeed taking it in the morning, at least 30 minutes prior to eating. With improved but not resolved symptoms, she agrees to follow-up with repeat TSH laboratory studies in 6 weeks to determine whether further dose adjustments are necessary. Given that she is of reproductive age and her TSH level is suboptimal for pregnancy, you caution her about heightened pregnancy/fetal risks with a suboptimal TSH and recommend that she use reliable contraception.
CORRESPONDENCE
Christopher Bunt, MD, FAAFP, 5 Charleston Center Drive, Suite 263, MSC 192,Charleston, SC 29425; [email protected]
1. Aoki Y, Belin RM, Clickner R, et al. Serum TSH and total T4 in the United States population and their association with participant characteristics: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 1999-2002). Thyroid. 2007;17:1211-1223.
2. Vaidya B, Pearce SH. Management of hypothyroidism in adults. BMJ. 2008;337:a801.
3. Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr Pract. 2012;18:988-1028.
4. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24:1670-1751.
5. Toft AD. Thyroxine therapy. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:174-180.
6. Floriani C, Gencer B, Collet TH, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases: 2016 update. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:503-507.
7. Lexi-Comp, Inc. (Lexi-Drugs®). https://online.lexi.com/lco/action/login. Accessed July 7, 2017.
8. Okosieme O, Gilbert J, Abraham P, et al. Management of primary hypothyroidism: statement by the British Thyroid Association Executive Committee. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016;84:799-808.
9. Fish LH, Schwartz HL, Cavanaugh J, et al. Replacement dose, metabolism, and bioavailability of levothyroxine in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Role of triiodothyronine in pituitary feedback in humans. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:764-770.
10. John-Kalarickal J, Pearlman G, Carlson HE. New medications which decrease levothyroxine absorption. Thyroid. 2007;17:763-765.
11. Sachmechi I, Reich DM, Aninyei M, et al. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level in euthyroid patients treated with levothyroxine for hypothyroidism. Endocr Pract. 2007;13:345-349.
12. Sperber AD, Liel Y. Evidence for interference with the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine sodium by aluminum hydroxide. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152:183-184.
13. Zamfirescu I, Carlson HE. Absorption of levothyroxine when coadministered with various calcium formulations. Thyroid. 2011;21:483-486.
14. Campbell NR, Hasinoff BB, Stalts H, et al. Ferrous sulfate reduces thyroxine efficacy in patients with hypothyroidism. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:1010-1013.
15. Bugdaci MS, Zuhur SS, Sokmen M, et al. The role of Helicobacter pylori in patients with hypothyroidism in whom could not be achieved normal thyrotropin levels despite treatment with high doses of thyroxine. Helicobacter. 2011;16:124-130.
16. Centanni M, Gargano L, Canettieri G, et al. Thyroxine in goiter, Helicobacter pylori infection, and chronic gastritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1787-1795.
17. Centanni M, Marignani M, Gargano L, et al. Atrophic body gastritis in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: an underdiagnosed association. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1726-1730.
18. Collins D, Wilcox R, Nathan M, et al. Celiac disease and hypothyroidism. Am J Med. 2012;125:278-282.
19. Azizi F, Belur R, Albano J. Malabsorption of thyroid hormones after jejunoileal bypass for obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:941-942.
20. Gkotsina M, Michalaki M, Mamali I, et al. Improved levothyroxine pharmacokinetics after bariatric surgery. Thyroid. 2013;23:414-419.
21. Hennessey JV, Espaillat R. Diagnosis and management of subclinical hypothyroidism in elderly adults: a review of the literature. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:1663-1673.
22. Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315-389.
23. Carney LA, Quinlan JD, West JM. Thyroid disease in pregnancy. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:273-278.
24. Fröhlich E, Wahl R. Thyroid autoimmunity: role of anti-thyroid antibodies in thyroid and extra-thyroidal diseases. Front Immunol. 2017;8:521.
25. Aksoy DY, Kerimoglu U, Okur H, et al. Effects of prophylactic thyroid hormone replacement in euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr J. 2005;52:337-343.
26. Padberg S, Heller K, Usadel KH, et al. One-year prophylactic treatment of euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients with levothyroxine: is there a benefit? Thyroid. 2001;11:249-255.
27. Rugge B, Balshem H, Sehgal R, et al. Screening and Treatment of Subclinical Hypothyroidism or Hyperthyroidism [Internet]. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 24. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; October 2011. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83492/. Accessed February 21, 2020.
28. Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:489-499.
29. Surks MI, Hollowell JG. Age-specific distribution of serum thyrotropin and antithyroid antibodies in the US population: implications for the prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4575-4582.
30. Pasqualetti G, Tognini S, Polini A, et al. Is subclinical hypothyroidism a cardiovascular risk factor in the elderly? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:2256-2266.
CASE
A 38-year-old woman presents for a routine physical. Other than urgent care visits for 1 episode of influenza and 2 upper respiratory illnesses, she has not seen a physician for a physical in 5 years. She denies any significant medical history. She takes naproxen occasionally for chronic right knee pain. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. Recently, she has started using a meal replacement shake at lunchtime for weight management. She performs aerobic exercise 30 to 40 minutes per day, 5 days per week. Her family history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, arthritis, heart disease, and hyperlipidemia on her mother’s side. She is single, is not currently sexually active, works as a pharmacy technician, and has no children. A high-risk human papillomavirus test was normal 4 years ago.
A review of systems is notable for a 20-pound weight gain over the past year, worsening heartburn over the past 2 weeks, and chronic knee pain, which is greater in the right knee than the left. She denies weakness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain. Vital signs reveal a blood pressure of 146/88 mm Hg, a heart rate of 63 bpm, a temperature of 98°F (36.7°C), a respiratory rate of 16, a height of 5’7’’ (1.7 m), a weight of 217 lbs (98.4 kg), and a peripheral capillary oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 99% on room air. The physical exam reveals a body mass index (BMI) of 34, warm dry skin, and coarse brittle hair.
Lab results reveal a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level of 11.17 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free thyroxine (T4) of 0.58 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). A basic metabolic panel and hemoglobin A1C level are normal.
What would you recommend?
In the United States, the prevalence of overt hypothyroidism (defined as a TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L and a low free T4) among people ≥ 12 years of age was estimated at 0.3% based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 1999-2002.1 Subclinical hypothyroidism (TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L but < 10 mIU/L and a normal T4 level) is even more common, with an estimated prevalence of 3.4%.1 Hypothyroidism is more common in females and occurs more frequently in Caucasian Americans and Mexican Americans than in African Americans.1
The most common etiologies of hypothyroidism include autoimmune thyroiditis (eg, Hashimoto thyroiditis, atrophic autoimmune thyroiditis) and iatrogenic causes (eg, after radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy) (TABLE 1).2-4

Initiating thyroid hormone replacement
Factors to consider when starting a patient on thyroid hormone replacement include age, weight, symptom severity, TSH level, goal TSH value, adverse effects from thyroid supplements, history of cardiac disease, and, for women of child-bearing age, the desire for pregnancy vs the use of contraceptives. Most adult patients < 50 years with overt hypothyroidism can begin a weight-based dose of levothyroxine: ~1.6 mcg/kg/d (based on ideal body weight).3
Continue to: For adults with cardiac disease...
For adults with cardiac disease, the risk of over-replacement limits initial dosing to 25 to 50 mcg/d for patients < 50 years (12.5-25 mcg/d; ≥ 50 years).3 For adults with subclinical hypothyroidism, it is reasonable to begin therapy at a lower daily dose (eg, 25-75 mcg/d) depending on baseline TSH level, symptoms (the patient may be asymptomatic), and the presence of cardiac disease (TABLE 23,4). Consider treatment in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism particularly when patients have a goiter or dyslipidemia and in women contemplating pregnancy in the near future. Elderly patients may require a dose 20% to 25% lower than younger adults because of decreased body mass.3

Levothyroxine is considered first-line therapy for hypothyroidism because of its low cost, dose consistency, low risk of allergic reactions, and potential to cause fewer cardiac adverse effects than triiodothyronine (T3) products such as desiccated thyroid extract.5 Although data have not shown an absolute increase in cardiovascular adverse effects, T3 products have a higher T3 vs T4 ratio, giving them a theoretically increased risk.5,6 Desiccated thyroid extract also has been associated with allergic reactions.5
Use of liothyronine alone or in combination with levothyroxine lacks evidence and guideline support.4 Furthermore, it is dosed twice daily, which makes it less convenient, and concerns still exist that there may be an increase in cardiovascular adverse effects.4,6 See TABLE 37 for a summary of available products and their equivalent doses.

Maintaining patients on therapy
The maintenance phase begins once hypothyroidism is diagnosed and treatment is initiated. This phase includes regular monitoring with laboratory studies, office visits, and as-needed adjustments in hormone replacement dosing. The frequency at which all of these occur is variable and based on a number of factors including the patient’s other medical conditions, use of other medications including over-the-counter agents, the patient’s age, weight changes, and pregnancy status.3,4,8 In general, dosage adjustments of 12.5 to 25 mcg can be made at 6- to 8-week intervals based on repeat TSH measurements, patient symptoms, and comorbidities.3
Once a patient is symptomatically stable and laboratory values have normalized, the recommended frequency of laboratory evaluation and office visits is every 12 months, barring significant changes in any of the factors mentioned above. At each visit, physicians should perform medication (including supplements) reconciliation and discuss any health condition updates. Changes to the therapy plan, including frequency or timing of laboratory tests, may be necessary if patients begin taking medications that alter the absorption or function of levothyroxine (eg, steroids).
Continue to: To maximize absorption...
To maximize absorption, providers should review with patients the optimal way to take thyroid hormones. Levothyroxine is approximately 70% to 80% absorbed under ideal conditions, which means taking it in the morning at least 30 to 60 minutes before eating or 3 to 4 hours after the last meal of the day.3,9-13 Of note, TSH levels may increase slightly in patients taking proton pump inhibitors, but this does not usually require a dose increase of thyroid hormone.11 Given that some supplements, particularly iron and calcium, can interfere with absorption, it is recommended to maintain a 3- to 4-hour gap between taking those supplements and taking levothyroxine.12-14 For those patients unable or unwilling to adhere to these recommendations, an increase in levothyroxine dose may be required in order to compensate for the decreased absorption.
Don’t adjust hormone therapy based on clinical presentation alone. While clinical symptoms are important, it is not recommended to adjust hormone therapy based solely on clinical presentation. Common hypothyroid symptoms of dry skin, edema, weight gain, and fatigue may be caused by other medical conditions. While indices including Achilles reflex time and basal metabolic rate have shown some correlation to thyroid dysfunction, there has been limited evidence to show that longitudinal index changes reflect subtle changes in thyroid hormone levels.3
The most recent guidelines from the American Thyroid Association recommend that, “Symptoms should be followed, but considered in the context of serum thyrotropin values, relevant comorbidities, and other potential causes.”3
Special populations/circumstances to keep in mind
Malabsorption conditions. When a higher than expected weight-based dose of levothyroxine is required, physicians should review administration timing, adherence, and comorbid medical conditions that can affect absorption.
Several studies, for example, have demonstrated the impact of Helicobacter pylori gastritis on levothyroxine absorption and subsequent TSH levels.15-17 In one nonrandomized prospective study, patients with H pylori and hypothyroidism who were previously thought to be unresponsive to levothyroxine therapy had a decrease in average TSH level from 30.5 mIU/L to 4.2 mIU/L after H pylori was eradicated.15 Autoimmune atrophic gastritis and celiac disease, both of which are more common in those with other autoimmune diseases, are also associated with the need for higher than expected levothyroxine doses.17,18
Continue to: A history of gastric bypass surgery...
A history of gastric bypass surgery alone is not considered a risk factor for poor absorption of thyroid hormone, given that the majority of levothyroxine absorption occurs in the ileum.19,20 However, advancing age (> 70 years) and extreme obesity (BMI > 40) are independent risk factors for decreased levothyroxine absorption.20,21
Women of reproductive age and pregnant women. Overt untreated or undertreated hypothyroidism can be associated with increased risk of maternal and fetal complications including decreased fertility, miscarriage, preterm delivery, lower birth rates, and infant cognitive deficits.3,22 Therefore, the main focus should be optimization of thyroid hormone levels prior to and during pregnancy.3,4,8,22 Thyroid hormone replacement needs to be increased during pregnancy in approximately 50% to 85% of women using thyroid replacement prior to pregnancy, but the dose requirements vary based on the underlying etiology of thyroid dysfunction.
One initial option for patients on a stable dose before pregnancy is to increase their daily dose by a half tablet (1.5 × daily dose) immediately after home confirmation of pregnancy, until finer dose adjustments (usually increases of 25%-60% ) can be made by a physician. Experts recommend that a TSH level be obtained every 4 weeks until mid-gestation and then at least once around 30 weeks’ gestation to ensure specific targets are being met with dose adjustments.22 Optimal thyrotropin reference ranges during conception and pregnancy can be found in the literature.23
Patients who have positive antibodies and normal thyroid function tests. Patients who are screened for thyroid disorders may demonstrate normal thyroid function (ie, euthyroid) with TSH, free T4, and, if checked, free T3, all within normal ranges. Despite these normal lab results, patients may have additional test results that demonstrate positive thyroid autoantibodies including thyroglobulin antibodies and/or thyroid peroxidase antibodies. Thyroid autoimmunity itself has been associated with a range of other autoimmune conditions as well as an increased risk of thyroid cancer in those with Hashimoto thyroiditis.24 Two studies showed that prophylactic treatment of euthyroid patients with levothyroxine led to a reduction in antibody levels and a lower TSH level.25,26 However, no studies have focused on patient-oriented outcomes such as hospitalizations, quality of life, or symptoms. If the patient remains asymptomatic, we recommend no treatment, but that the patient’s TSH levels be monitored every 12 months.27
Elderly patients. Population data have shown that TSH increases normally with age, with a TSH level of 7.5 mIU/L being the upper limit of normal for a population of healthy adults > 80 years of age.28,29 Overall, studies have failed to show any benefit in treating elderly patients with subclinical hypothyroidism unless their TSH level exceeds 10 mIU/L.6,21 The one exception is elderly patients with heart failure in whom untreated subclinical hypothyroidism has been shown to be associated with higher mortality.30
Continue to: Elderly patients are at higher risk...
Elderly patients are at higher risk for adverse effects of thyroid over-replacement, including atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis. While there have been no randomized trials examining target TSH levels in this population, a reasonable recommendation is a goal TSH level of 4 to 6 mIU/L for elderly patients ≥ 70 years.4
CASE
As a result of the patient’s elevated TSH level and symptoms of hypothyroidism, you start levothyroxine 150 mcg/d by mouth, counsel her on potential adverse effects, and schedule a follow-up visit with another TSH check in 6 weeks.
Follow-up laboratory studies 6 weeks later reveal a TSH level of 5.86 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free T4 level of 0.74 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). Based on those results, you increase the dose of levothyroxine to 175 mcg/d.
At her follow-up visit 12 weeks after initial presentation, her TSH level is 3.85 mIU/L. She reports feeling better overall with less fatigue, and she has lost 5 pounds since her last visit. You recommend she continue levothyroxine 175 mcg/d after reviewing medication compliance with the patient and ensuring she is indeed taking it in the morning, at least 30 minutes prior to eating. With improved but not resolved symptoms, she agrees to follow-up with repeat TSH laboratory studies in 6 weeks to determine whether further dose adjustments are necessary. Given that she is of reproductive age and her TSH level is suboptimal for pregnancy, you caution her about heightened pregnancy/fetal risks with a suboptimal TSH and recommend that she use reliable contraception.
CORRESPONDENCE
Christopher Bunt, MD, FAAFP, 5 Charleston Center Drive, Suite 263, MSC 192,Charleston, SC 29425; [email protected]
CASE
A 38-year-old woman presents for a routine physical. Other than urgent care visits for 1 episode of influenza and 2 upper respiratory illnesses, she has not seen a physician for a physical in 5 years. She denies any significant medical history. She takes naproxen occasionally for chronic right knee pain. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. Recently, she has started using a meal replacement shake at lunchtime for weight management. She performs aerobic exercise 30 to 40 minutes per day, 5 days per week. Her family history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, arthritis, heart disease, and hyperlipidemia on her mother’s side. She is single, is not currently sexually active, works as a pharmacy technician, and has no children. A high-risk human papillomavirus test was normal 4 years ago.
A review of systems is notable for a 20-pound weight gain over the past year, worsening heartburn over the past 2 weeks, and chronic knee pain, which is greater in the right knee than the left. She denies weakness, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain. Vital signs reveal a blood pressure of 146/88 mm Hg, a heart rate of 63 bpm, a temperature of 98°F (36.7°C), a respiratory rate of 16, a height of 5’7’’ (1.7 m), a weight of 217 lbs (98.4 kg), and a peripheral capillary oxygen saturation (SpO2) of 99% on room air. The physical exam reveals a body mass index (BMI) of 34, warm dry skin, and coarse brittle hair.
Lab results reveal a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level of 11.17 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free thyroxine (T4) of 0.58 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). A basic metabolic panel and hemoglobin A1C level are normal.
What would you recommend?
In the United States, the prevalence of overt hypothyroidism (defined as a TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L and a low free T4) among people ≥ 12 years of age was estimated at 0.3% based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 1999-2002.1 Subclinical hypothyroidism (TSH level > 4.5 mIU/L but < 10 mIU/L and a normal T4 level) is even more common, with an estimated prevalence of 3.4%.1 Hypothyroidism is more common in females and occurs more frequently in Caucasian Americans and Mexican Americans than in African Americans.1
The most common etiologies of hypothyroidism include autoimmune thyroiditis (eg, Hashimoto thyroiditis, atrophic autoimmune thyroiditis) and iatrogenic causes (eg, after radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy) (TABLE 1).2-4

Initiating thyroid hormone replacement
Factors to consider when starting a patient on thyroid hormone replacement include age, weight, symptom severity, TSH level, goal TSH value, adverse effects from thyroid supplements, history of cardiac disease, and, for women of child-bearing age, the desire for pregnancy vs the use of contraceptives. Most adult patients < 50 years with overt hypothyroidism can begin a weight-based dose of levothyroxine: ~1.6 mcg/kg/d (based on ideal body weight).3
Continue to: For adults with cardiac disease...
For adults with cardiac disease, the risk of over-replacement limits initial dosing to 25 to 50 mcg/d for patients < 50 years (12.5-25 mcg/d; ≥ 50 years).3 For adults with subclinical hypothyroidism, it is reasonable to begin therapy at a lower daily dose (eg, 25-75 mcg/d) depending on baseline TSH level, symptoms (the patient may be asymptomatic), and the presence of cardiac disease (TABLE 23,4). Consider treatment in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism particularly when patients have a goiter or dyslipidemia and in women contemplating pregnancy in the near future. Elderly patients may require a dose 20% to 25% lower than younger adults because of decreased body mass.3

Levothyroxine is considered first-line therapy for hypothyroidism because of its low cost, dose consistency, low risk of allergic reactions, and potential to cause fewer cardiac adverse effects than triiodothyronine (T3) products such as desiccated thyroid extract.5 Although data have not shown an absolute increase in cardiovascular adverse effects, T3 products have a higher T3 vs T4 ratio, giving them a theoretically increased risk.5,6 Desiccated thyroid extract also has been associated with allergic reactions.5
Use of liothyronine alone or in combination with levothyroxine lacks evidence and guideline support.4 Furthermore, it is dosed twice daily, which makes it less convenient, and concerns still exist that there may be an increase in cardiovascular adverse effects.4,6 See TABLE 37 for a summary of available products and their equivalent doses.

Maintaining patients on therapy
The maintenance phase begins once hypothyroidism is diagnosed and treatment is initiated. This phase includes regular monitoring with laboratory studies, office visits, and as-needed adjustments in hormone replacement dosing. The frequency at which all of these occur is variable and based on a number of factors including the patient’s other medical conditions, use of other medications including over-the-counter agents, the patient’s age, weight changes, and pregnancy status.3,4,8 In general, dosage adjustments of 12.5 to 25 mcg can be made at 6- to 8-week intervals based on repeat TSH measurements, patient symptoms, and comorbidities.3
Once a patient is symptomatically stable and laboratory values have normalized, the recommended frequency of laboratory evaluation and office visits is every 12 months, barring significant changes in any of the factors mentioned above. At each visit, physicians should perform medication (including supplements) reconciliation and discuss any health condition updates. Changes to the therapy plan, including frequency or timing of laboratory tests, may be necessary if patients begin taking medications that alter the absorption or function of levothyroxine (eg, steroids).
Continue to: To maximize absorption...
To maximize absorption, providers should review with patients the optimal way to take thyroid hormones. Levothyroxine is approximately 70% to 80% absorbed under ideal conditions, which means taking it in the morning at least 30 to 60 minutes before eating or 3 to 4 hours after the last meal of the day.3,9-13 Of note, TSH levels may increase slightly in patients taking proton pump inhibitors, but this does not usually require a dose increase of thyroid hormone.11 Given that some supplements, particularly iron and calcium, can interfere with absorption, it is recommended to maintain a 3- to 4-hour gap between taking those supplements and taking levothyroxine.12-14 For those patients unable or unwilling to adhere to these recommendations, an increase in levothyroxine dose may be required in order to compensate for the decreased absorption.
Don’t adjust hormone therapy based on clinical presentation alone. While clinical symptoms are important, it is not recommended to adjust hormone therapy based solely on clinical presentation. Common hypothyroid symptoms of dry skin, edema, weight gain, and fatigue may be caused by other medical conditions. While indices including Achilles reflex time and basal metabolic rate have shown some correlation to thyroid dysfunction, there has been limited evidence to show that longitudinal index changes reflect subtle changes in thyroid hormone levels.3
The most recent guidelines from the American Thyroid Association recommend that, “Symptoms should be followed, but considered in the context of serum thyrotropin values, relevant comorbidities, and other potential causes.”3
Special populations/circumstances to keep in mind
Malabsorption conditions. When a higher than expected weight-based dose of levothyroxine is required, physicians should review administration timing, adherence, and comorbid medical conditions that can affect absorption.
Several studies, for example, have demonstrated the impact of Helicobacter pylori gastritis on levothyroxine absorption and subsequent TSH levels.15-17 In one nonrandomized prospective study, patients with H pylori and hypothyroidism who were previously thought to be unresponsive to levothyroxine therapy had a decrease in average TSH level from 30.5 mIU/L to 4.2 mIU/L after H pylori was eradicated.15 Autoimmune atrophic gastritis and celiac disease, both of which are more common in those with other autoimmune diseases, are also associated with the need for higher than expected levothyroxine doses.17,18
Continue to: A history of gastric bypass surgery...
A history of gastric bypass surgery alone is not considered a risk factor for poor absorption of thyroid hormone, given that the majority of levothyroxine absorption occurs in the ileum.19,20 However, advancing age (> 70 years) and extreme obesity (BMI > 40) are independent risk factors for decreased levothyroxine absorption.20,21
Women of reproductive age and pregnant women. Overt untreated or undertreated hypothyroidism can be associated with increased risk of maternal and fetal complications including decreased fertility, miscarriage, preterm delivery, lower birth rates, and infant cognitive deficits.3,22 Therefore, the main focus should be optimization of thyroid hormone levels prior to and during pregnancy.3,4,8,22 Thyroid hormone replacement needs to be increased during pregnancy in approximately 50% to 85% of women using thyroid replacement prior to pregnancy, but the dose requirements vary based on the underlying etiology of thyroid dysfunction.
One initial option for patients on a stable dose before pregnancy is to increase their daily dose by a half tablet (1.5 × daily dose) immediately after home confirmation of pregnancy, until finer dose adjustments (usually increases of 25%-60% ) can be made by a physician. Experts recommend that a TSH level be obtained every 4 weeks until mid-gestation and then at least once around 30 weeks’ gestation to ensure specific targets are being met with dose adjustments.22 Optimal thyrotropin reference ranges during conception and pregnancy can be found in the literature.23
Patients who have positive antibodies and normal thyroid function tests. Patients who are screened for thyroid disorders may demonstrate normal thyroid function (ie, euthyroid) with TSH, free T4, and, if checked, free T3, all within normal ranges. Despite these normal lab results, patients may have additional test results that demonstrate positive thyroid autoantibodies including thyroglobulin antibodies and/or thyroid peroxidase antibodies. Thyroid autoimmunity itself has been associated with a range of other autoimmune conditions as well as an increased risk of thyroid cancer in those with Hashimoto thyroiditis.24 Two studies showed that prophylactic treatment of euthyroid patients with levothyroxine led to a reduction in antibody levels and a lower TSH level.25,26 However, no studies have focused on patient-oriented outcomes such as hospitalizations, quality of life, or symptoms. If the patient remains asymptomatic, we recommend no treatment, but that the patient’s TSH levels be monitored every 12 months.27
Elderly patients. Population data have shown that TSH increases normally with age, with a TSH level of 7.5 mIU/L being the upper limit of normal for a population of healthy adults > 80 years of age.28,29 Overall, studies have failed to show any benefit in treating elderly patients with subclinical hypothyroidism unless their TSH level exceeds 10 mIU/L.6,21 The one exception is elderly patients with heart failure in whom untreated subclinical hypothyroidism has been shown to be associated with higher mortality.30
Continue to: Elderly patients are at higher risk...
Elderly patients are at higher risk for adverse effects of thyroid over-replacement, including atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis. While there have been no randomized trials examining target TSH levels in this population, a reasonable recommendation is a goal TSH level of 4 to 6 mIU/L for elderly patients ≥ 70 years.4
CASE
As a result of the patient’s elevated TSH level and symptoms of hypothyroidism, you start levothyroxine 150 mcg/d by mouth, counsel her on potential adverse effects, and schedule a follow-up visit with another TSH check in 6 weeks.
Follow-up laboratory studies 6 weeks later reveal a TSH level of 5.86 mIU/L (reference range, 0.45-4.5 mIU/L) and a free T4 level of 0.74 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8-2.8 ng/dL). Based on those results, you increase the dose of levothyroxine to 175 mcg/d.
At her follow-up visit 12 weeks after initial presentation, her TSH level is 3.85 mIU/L. She reports feeling better overall with less fatigue, and she has lost 5 pounds since her last visit. You recommend she continue levothyroxine 175 mcg/d after reviewing medication compliance with the patient and ensuring she is indeed taking it in the morning, at least 30 minutes prior to eating. With improved but not resolved symptoms, she agrees to follow-up with repeat TSH laboratory studies in 6 weeks to determine whether further dose adjustments are necessary. Given that she is of reproductive age and her TSH level is suboptimal for pregnancy, you caution her about heightened pregnancy/fetal risks with a suboptimal TSH and recommend that she use reliable contraception.
CORRESPONDENCE
Christopher Bunt, MD, FAAFP, 5 Charleston Center Drive, Suite 263, MSC 192,Charleston, SC 29425; [email protected]
1. Aoki Y, Belin RM, Clickner R, et al. Serum TSH and total T4 in the United States population and their association with participant characteristics: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 1999-2002). Thyroid. 2007;17:1211-1223.
2. Vaidya B, Pearce SH. Management of hypothyroidism in adults. BMJ. 2008;337:a801.
3. Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr Pract. 2012;18:988-1028.
4. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24:1670-1751.
5. Toft AD. Thyroxine therapy. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:174-180.
6. Floriani C, Gencer B, Collet TH, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases: 2016 update. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:503-507.
7. Lexi-Comp, Inc. (Lexi-Drugs®). https://online.lexi.com/lco/action/login. Accessed July 7, 2017.
8. Okosieme O, Gilbert J, Abraham P, et al. Management of primary hypothyroidism: statement by the British Thyroid Association Executive Committee. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016;84:799-808.
9. Fish LH, Schwartz HL, Cavanaugh J, et al. Replacement dose, metabolism, and bioavailability of levothyroxine in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Role of triiodothyronine in pituitary feedback in humans. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:764-770.
10. John-Kalarickal J, Pearlman G, Carlson HE. New medications which decrease levothyroxine absorption. Thyroid. 2007;17:763-765.
11. Sachmechi I, Reich DM, Aninyei M, et al. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level in euthyroid patients treated with levothyroxine for hypothyroidism. Endocr Pract. 2007;13:345-349.
12. Sperber AD, Liel Y. Evidence for interference with the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine sodium by aluminum hydroxide. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152:183-184.
13. Zamfirescu I, Carlson HE. Absorption of levothyroxine when coadministered with various calcium formulations. Thyroid. 2011;21:483-486.
14. Campbell NR, Hasinoff BB, Stalts H, et al. Ferrous sulfate reduces thyroxine efficacy in patients with hypothyroidism. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:1010-1013.
15. Bugdaci MS, Zuhur SS, Sokmen M, et al. The role of Helicobacter pylori in patients with hypothyroidism in whom could not be achieved normal thyrotropin levels despite treatment with high doses of thyroxine. Helicobacter. 2011;16:124-130.
16. Centanni M, Gargano L, Canettieri G, et al. Thyroxine in goiter, Helicobacter pylori infection, and chronic gastritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1787-1795.
17. Centanni M, Marignani M, Gargano L, et al. Atrophic body gastritis in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: an underdiagnosed association. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1726-1730.
18. Collins D, Wilcox R, Nathan M, et al. Celiac disease and hypothyroidism. Am J Med. 2012;125:278-282.
19. Azizi F, Belur R, Albano J. Malabsorption of thyroid hormones after jejunoileal bypass for obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:941-942.
20. Gkotsina M, Michalaki M, Mamali I, et al. Improved levothyroxine pharmacokinetics after bariatric surgery. Thyroid. 2013;23:414-419.
21. Hennessey JV, Espaillat R. Diagnosis and management of subclinical hypothyroidism in elderly adults: a review of the literature. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:1663-1673.
22. Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315-389.
23. Carney LA, Quinlan JD, West JM. Thyroid disease in pregnancy. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:273-278.
24. Fröhlich E, Wahl R. Thyroid autoimmunity: role of anti-thyroid antibodies in thyroid and extra-thyroidal diseases. Front Immunol. 2017;8:521.
25. Aksoy DY, Kerimoglu U, Okur H, et al. Effects of prophylactic thyroid hormone replacement in euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr J. 2005;52:337-343.
26. Padberg S, Heller K, Usadel KH, et al. One-year prophylactic treatment of euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients with levothyroxine: is there a benefit? Thyroid. 2001;11:249-255.
27. Rugge B, Balshem H, Sehgal R, et al. Screening and Treatment of Subclinical Hypothyroidism or Hyperthyroidism [Internet]. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 24. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; October 2011. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83492/. Accessed February 21, 2020.
28. Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:489-499.
29. Surks MI, Hollowell JG. Age-specific distribution of serum thyrotropin and antithyroid antibodies in the US population: implications for the prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4575-4582.
30. Pasqualetti G, Tognini S, Polini A, et al. Is subclinical hypothyroidism a cardiovascular risk factor in the elderly? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:2256-2266.
1. Aoki Y, Belin RM, Clickner R, et al. Serum TSH and total T4 in the United States population and their association with participant characteristics: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 1999-2002). Thyroid. 2007;17:1211-1223.
2. Vaidya B, Pearce SH. Management of hypothyroidism in adults. BMJ. 2008;337:a801.
3. Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr Pract. 2012;18:988-1028.
4. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24:1670-1751.
5. Toft AD. Thyroxine therapy. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:174-180.
6. Floriani C, Gencer B, Collet TH, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases: 2016 update. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:503-507.
7. Lexi-Comp, Inc. (Lexi-Drugs®). https://online.lexi.com/lco/action/login. Accessed July 7, 2017.
8. Okosieme O, Gilbert J, Abraham P, et al. Management of primary hypothyroidism: statement by the British Thyroid Association Executive Committee. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016;84:799-808.
9. Fish LH, Schwartz HL, Cavanaugh J, et al. Replacement dose, metabolism, and bioavailability of levothyroxine in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Role of triiodothyronine in pituitary feedback in humans. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:764-770.
10. John-Kalarickal J, Pearlman G, Carlson HE. New medications which decrease levothyroxine absorption. Thyroid. 2007;17:763-765.
11. Sachmechi I, Reich DM, Aninyei M, et al. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level in euthyroid patients treated with levothyroxine for hypothyroidism. Endocr Pract. 2007;13:345-349.
12. Sperber AD, Liel Y. Evidence for interference with the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine sodium by aluminum hydroxide. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152:183-184.
13. Zamfirescu I, Carlson HE. Absorption of levothyroxine when coadministered with various calcium formulations. Thyroid. 2011;21:483-486.
14. Campbell NR, Hasinoff BB, Stalts H, et al. Ferrous sulfate reduces thyroxine efficacy in patients with hypothyroidism. Ann Intern Med. 1992;117:1010-1013.
15. Bugdaci MS, Zuhur SS, Sokmen M, et al. The role of Helicobacter pylori in patients with hypothyroidism in whom could not be achieved normal thyrotropin levels despite treatment with high doses of thyroxine. Helicobacter. 2011;16:124-130.
16. Centanni M, Gargano L, Canettieri G, et al. Thyroxine in goiter, Helicobacter pylori infection, and chronic gastritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1787-1795.
17. Centanni M, Marignani M, Gargano L, et al. Atrophic body gastritis in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease: an underdiagnosed association. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1726-1730.
18. Collins D, Wilcox R, Nathan M, et al. Celiac disease and hypothyroidism. Am J Med. 2012;125:278-282.
19. Azizi F, Belur R, Albano J. Malabsorption of thyroid hormones after jejunoileal bypass for obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90:941-942.
20. Gkotsina M, Michalaki M, Mamali I, et al. Improved levothyroxine pharmacokinetics after bariatric surgery. Thyroid. 2013;23:414-419.
21. Hennessey JV, Espaillat R. Diagnosis and management of subclinical hypothyroidism in elderly adults: a review of the literature. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:1663-1673.
22. Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315-389.
23. Carney LA, Quinlan JD, West JM. Thyroid disease in pregnancy. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:273-278.
24. Fröhlich E, Wahl R. Thyroid autoimmunity: role of anti-thyroid antibodies in thyroid and extra-thyroidal diseases. Front Immunol. 2017;8:521.
25. Aksoy DY, Kerimoglu U, Okur H, et al. Effects of prophylactic thyroid hormone replacement in euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr J. 2005;52:337-343.
26. Padberg S, Heller K, Usadel KH, et al. One-year prophylactic treatment of euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients with levothyroxine: is there a benefit? Thyroid. 2001;11:249-255.
27. Rugge B, Balshem H, Sehgal R, et al. Screening and Treatment of Subclinical Hypothyroidism or Hyperthyroidism [Internet]. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 24. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; October 2011. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83492/. Accessed February 21, 2020.
28. Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:489-499.
29. Surks MI, Hollowell JG. Age-specific distribution of serum thyrotropin and antithyroid antibodies in the US population: implications for the prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4575-4582.
30. Pasqualetti G, Tognini S, Polini A, et al. Is subclinical hypothyroidism a cardiovascular risk factor in the elderly? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:2256-2266.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Prescribe levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg/d for healthy adult patients < 50 years of age with overt hypothyroidism. B
› Consider lower initial doses of levothyroxine in patients with cardiac disease (12.5-50 mcg/d) or subclinical hypothyroidism (25-75 mcg/d). B
› Titrate levothyroxine by 12.5 to 25 mcg/d at 6- to 8-week intervals based on thyroid-stimulating hormone measurements, comorbidities, and symptoms. C
› Closely monitor and provide thyroid supplementation to female patients who are pregnant or of reproductive age with concomitant hypothyroidism. C
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Fever, abdominal pain, and adnexal mass
At the recommendation of her primary care physician, a 53-year-old perimenopausal woman sought care at the emergency department for the fever, abdominal pain, and pyuria that had persisted for 4 days despite outpatient treatment for pyelonephritis. On physical examination, she was febrile and tachycardic with abdominal tenderness of the left lower quadrant. Genitourinary examination revealed copious brown vaginal discharge, left adnexal tenderness, and no cervical motion tenderness.
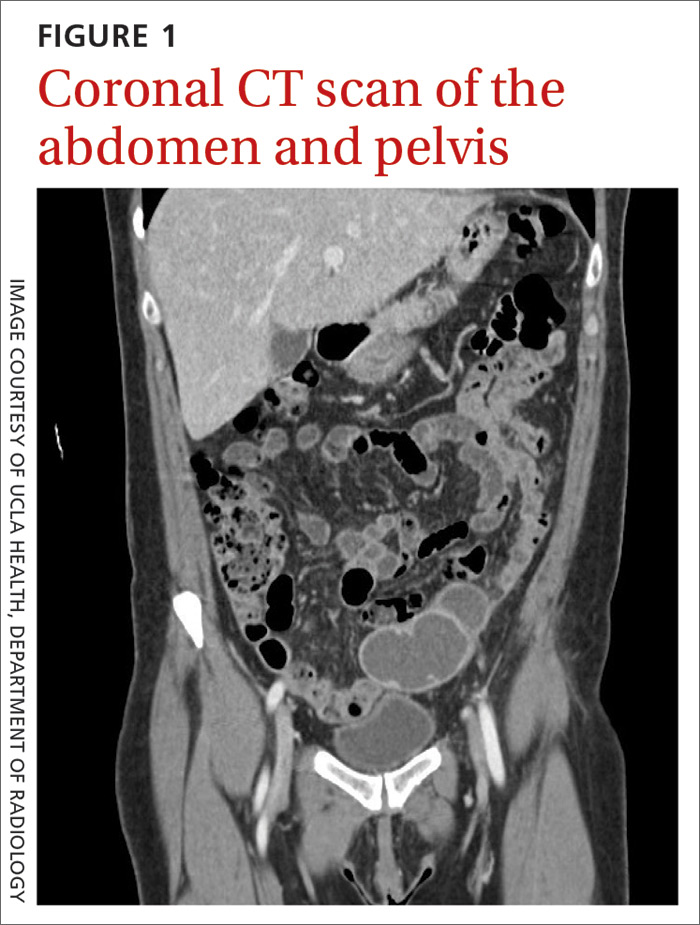
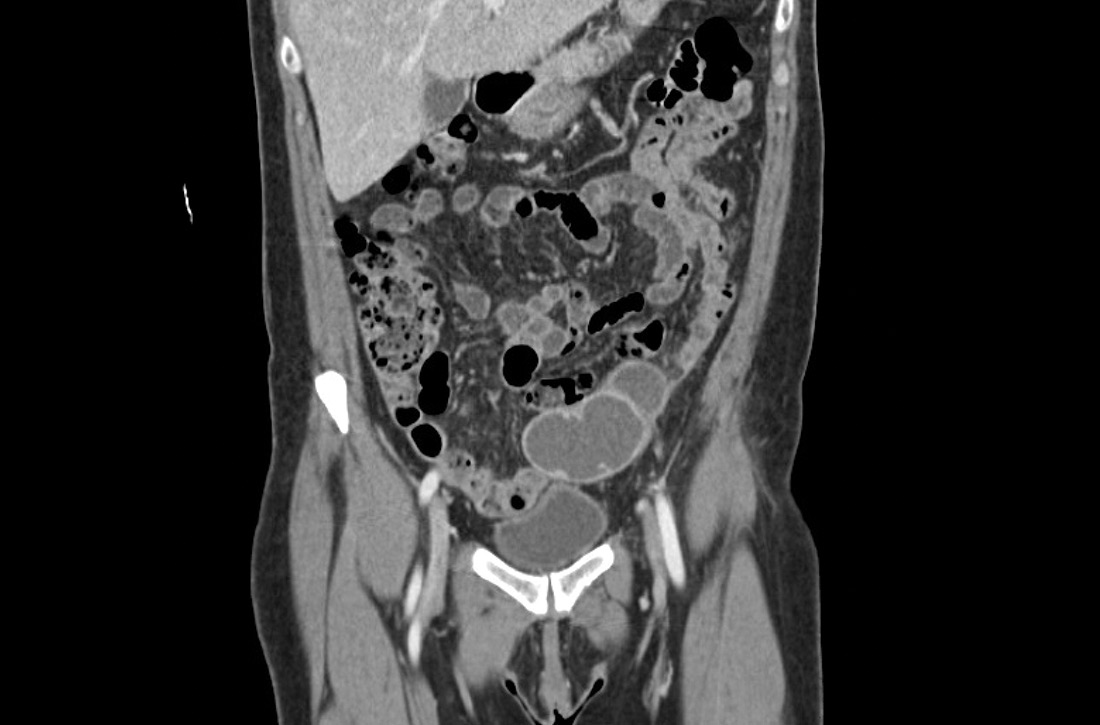
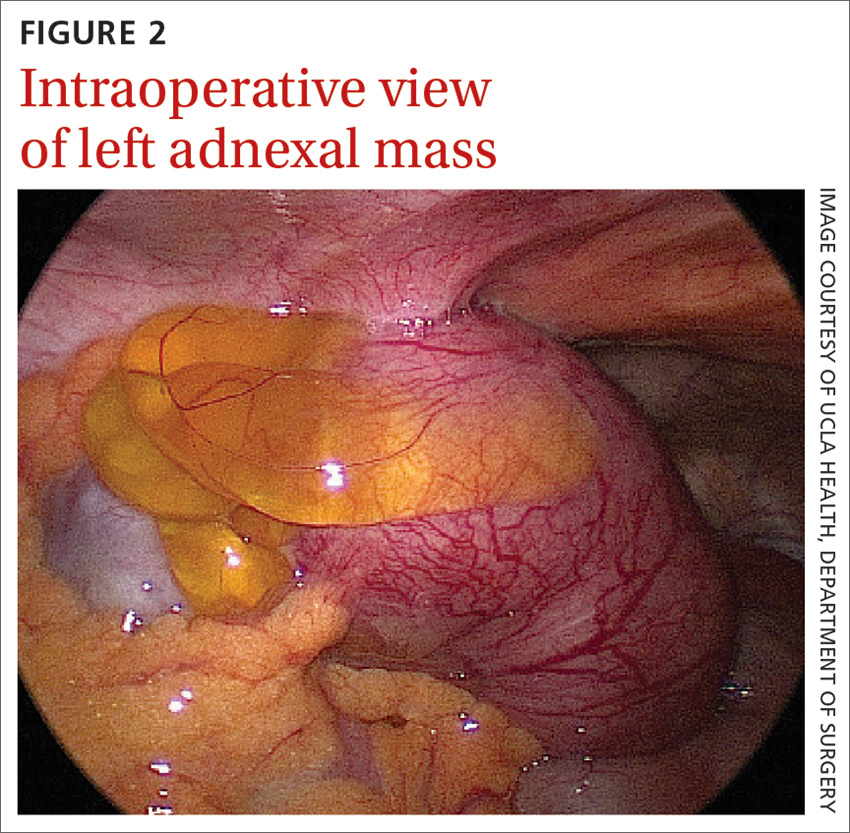
Laboratory testing revealed leukocytosis but otherwise normal electrolytes, liver function tests, and lactate levels. Urine culture obtained when she presented to an urgent care facility 3 days earlier had been negative. Computed tomography (CT) was performed and was read by Radiology as “closed loop small bowel obstruction in the left lower abdomen” (FIGURE 1). The patient was taken emergently to the operating room where her entire length of bowel was run without any obstruction found. Instead, the surgeons identified a mass in the left iliac fossa originating from the left ovary and fallopian tube (FIGURE 2).
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Pelvic inflammatory disease with tubo-ovarian abscess
The presence and location of this mass, paired with the patient’s symptoms, led to the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease. PID is an acute infection of the upper genital tract in women thought to be due to ascending infection from the lower genital tract. The prevalence of PID in reproductive-aged women in the United States is estimated to be 4.4%.1
Diagnosis of PID in middle-aged women is a challenge given the broad differential diagnosis of nonspecific presenting symptoms, lower index of suspicion in this age group, and unknown exact incidence of PID in postmenopausal women. While delay in diagnosis of PID in women of reproductive age is associated with increased infertility and ectopic pregnancy,2 delay in diagnosis in postmenopausal women also poses serious potential complications such as tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA)—as was seen with this patient—and concurrent gynecologic malignancy found on pathology of TOA specimens.3,4
Risk factors for PID in the postmenopausal population include recent uterine instrumentation, history of prior PID, and structural abnormalities such as cervical stenosis, uterine anatomic abnormalities, or tubal disease. The microbiology of PID in postmenopausal women differs from that of women of reproductive age. While sexually transmitted pathogens such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis most commonly are implicated in PID among premenopausal patients, aerobic gram-negative bacteria including Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae most frequently are associated in postmenopausal cases.
Differential diagnosis for abdominal pain is broad
The differential diagnosis for a patient with fever and abdominal pain includes PID, as well as the following:
Diverticulitis classically presents with left lower abdominal pain and a low-grade fever. Complications may include bowel obstruction, abscess, fistula, or perforation. Abdominal imaging such as a CT scan is required to establish the diagnosis.
Continue to: Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection should be suspected in a patient with dysuria, urinary frequency or urgency, and abdominal or flank pain. Urinalysis and culture should be performed and imaging may be considered for suspected obstruction, complication, or failure to improve on appropriate therapy.
Appendicitis may present as right lower quadrant pain with anorexia, fever, and nausea. Imaging studies such as CT or ultrasound can help support the diagnosis and rule out alternate etiologies of the presenting symptoms.
Ectopic pregnancy—while not considered in this case—should be suspected in a patient presenting with pelvic pain, missed menses or vaginal bleeding, and a positive pregnancy test. Further evaluation may be performed with a transvaginal ultrasound and serial measurement of serum quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin level.
Diagnosing PID is a clinical process
PID often is difficult to diagnose because of an absence of symptoms or the presence of symptoms that are subtle or nonspecific. Laparoscopy or endometrial biopsy can be useful but may not be justifiable due to their invasive nature when symptoms are mild or vague.5 Thus, a diagnosis of PID usually is based on clinical findings.
Clinical criteria to look for. Although PID commonly is attributed to N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis, fewer than 50% of those with a diagnosis of acute PID test positive for either of these organisms.5 As such, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines recommend presumptive treatment for PID in women with pelvic or lower abdominal pain with 1 or more of the following clinical criteria: cervical motion tenderness, uterine tenderness, or adnexal tenderness.
Continue to: The following criteria...
The following criteria enhance specificity and support the diagnosis5:
- oral temperature > 101°F (> 38.3°C),
- abnormal cervical mucopurulent discharge or cervical friability,
- presence of “abundant numbers of white blood cells on saline microscopy of vaginal fluid,”
- elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (reference range, 0–20 mm/hr),
- elevated C-reactive protein (reference range, 0.08-3.1 mg/L), and
- laboratory documentation of cervical infection with N gonorrhoeae or C trachomatis.
The CDC also suggests that the most specific criteria for PID include5
- endometrial biopsy consistent with endometritis,
- imaging (transvaginal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging) demonstrating fluid-filled tubes, or
- laparoscopic findings consistent with PID.
Treatment of PID includes IV antibiotics
Due to the polymicrobial nature of PID, antibiotics should cover not only gonorrhea and chlamydia but also anaerobic pathogens. CDC guidelines recommend the following treatment5,6:
- intravenous (IV) cefotetan (2 g bid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid),
- IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid), or
- IV clindamycin (900 mg tid) plus IV or intramuscular (IM) gentamicin loading dose (2 mg/kg) followed by a maintenance dose (1.5 mg/kg tid).
In mild-to-moderate PID cases deemed appropriate for outpatient therapy, the following regimens have been shown to have similar outcomes to IV therapy5,6:
- IM ceftriaxone (250 mg, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days,
- IM cefoxitin (2 g, single dose) and PO probenecid (1 g, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days, or
- other parenteral third-generation cephalosporin plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days.
Management in older women may be more intensive
Due to the increased risk of malignancy in postmenopausal women with TOA, surgical intervention may be needed.3,4
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent diagnostic laparoscopy, hysterectomy, left salpingo-oophorectomy, and right salpingectomy (with her right ovary left in place due to her perimenopausal status). Intraoperatively, she was found to have cervical stenosis. Postoperatively, she improved on IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) and IV doxycycline (100 mg bid), which was eventually transitioned to oral doxycycline (100 mg bid) and metronidazole (500 mg bid) on discharge.
Her final microbiology was negative for gonorrhea/chlamydia but the bacterial culture of peritoneal fluid grew E coli. Pathology was consistent with acute salpingitis, TOA, and acute cervicitis. She made a full recovery and is doing well.
CORRESPONDENCE
Catherine Peony Khoo, MD, 1920 Colorado Avenue, Santa Monica, CA 90404; [email protected]
1. Kreisel K, Torrone E, Bernstein K, et al. Prevalence of pelvic inflammatory disease in sexually experienced women of reproductive age—United States, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:80-83.
2. Weström L, Joesoef R, Reynolds G, et al. Pelvic inflammatory disease and fertility: a cohort study of 1,844 women with laparoscopically verified disease and 657 control women with normal laparoscopic results. Sex Transm Dis. 1992;19:185-192.
3. Jackson SL, Soper DE. Pelvic inflammatory disease in the postmenopausal woman. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7:248-252.
4. Protopas AG, Diakomanolis ES, Milingos SD, et al. Tubo-ovarian abscesses in postmenopausal women: gynecological malignancy until proven otherwise? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;114:203-209.
5. Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64:1-137.
6. Ness RB, Soper DE, Holley RL, et al. Effectiveness of inpatient and outpatient treatment strategies for women with pelvic inflammatory disease: results from the Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Evaluation and Clinical Health (PEACH) randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186:929-937 .
At the recommendation of her primary care physician, a 53-year-old perimenopausal woman sought care at the emergency department for the fever, abdominal pain, and pyuria that had persisted for 4 days despite outpatient treatment for pyelonephritis. On physical examination, she was febrile and tachycardic with abdominal tenderness of the left lower quadrant. Genitourinary examination revealed copious brown vaginal discharge, left adnexal tenderness, and no cervical motion tenderness.

Laboratory testing revealed leukocytosis but otherwise normal electrolytes, liver function tests, and lactate levels. Urine culture obtained when she presented to an urgent care facility 3 days earlier had been negative. Computed tomography (CT) was performed and was read by Radiology as “closed loop small bowel obstruction in the left lower abdomen” (FIGURE 1). The patient was taken emergently to the operating room where her entire length of bowel was run without any obstruction found. Instead, the surgeons identified a mass in the left iliac fossa originating from the left ovary and fallopian tube (FIGURE 2).

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Pelvic inflammatory disease with tubo-ovarian abscess
The presence and location of this mass, paired with the patient’s symptoms, led to the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease. PID is an acute infection of the upper genital tract in women thought to be due to ascending infection from the lower genital tract. The prevalence of PID in reproductive-aged women in the United States is estimated to be 4.4%.1
Diagnosis of PID in middle-aged women is a challenge given the broad differential diagnosis of nonspecific presenting symptoms, lower index of suspicion in this age group, and unknown exact incidence of PID in postmenopausal women. While delay in diagnosis of PID in women of reproductive age is associated with increased infertility and ectopic pregnancy,2 delay in diagnosis in postmenopausal women also poses serious potential complications such as tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA)—as was seen with this patient—and concurrent gynecologic malignancy found on pathology of TOA specimens.3,4
Risk factors for PID in the postmenopausal population include recent uterine instrumentation, history of prior PID, and structural abnormalities such as cervical stenosis, uterine anatomic abnormalities, or tubal disease. The microbiology of PID in postmenopausal women differs from that of women of reproductive age. While sexually transmitted pathogens such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis most commonly are implicated in PID among premenopausal patients, aerobic gram-negative bacteria including Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae most frequently are associated in postmenopausal cases.
Differential diagnosis for abdominal pain is broad
The differential diagnosis for a patient with fever and abdominal pain includes PID, as well as the following:
Diverticulitis classically presents with left lower abdominal pain and a low-grade fever. Complications may include bowel obstruction, abscess, fistula, or perforation. Abdominal imaging such as a CT scan is required to establish the diagnosis.
Continue to: Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection should be suspected in a patient with dysuria, urinary frequency or urgency, and abdominal or flank pain. Urinalysis and culture should be performed and imaging may be considered for suspected obstruction, complication, or failure to improve on appropriate therapy.
Appendicitis may present as right lower quadrant pain with anorexia, fever, and nausea. Imaging studies such as CT or ultrasound can help support the diagnosis and rule out alternate etiologies of the presenting symptoms.
Ectopic pregnancy—while not considered in this case—should be suspected in a patient presenting with pelvic pain, missed menses or vaginal bleeding, and a positive pregnancy test. Further evaluation may be performed with a transvaginal ultrasound and serial measurement of serum quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin level.
Diagnosing PID is a clinical process
PID often is difficult to diagnose because of an absence of symptoms or the presence of symptoms that are subtle or nonspecific. Laparoscopy or endometrial biopsy can be useful but may not be justifiable due to their invasive nature when symptoms are mild or vague.5 Thus, a diagnosis of PID usually is based on clinical findings.
Clinical criteria to look for. Although PID commonly is attributed to N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis, fewer than 50% of those with a diagnosis of acute PID test positive for either of these organisms.5 As such, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines recommend presumptive treatment for PID in women with pelvic or lower abdominal pain with 1 or more of the following clinical criteria: cervical motion tenderness, uterine tenderness, or adnexal tenderness.
Continue to: The following criteria...
The following criteria enhance specificity and support the diagnosis5:
- oral temperature > 101°F (> 38.3°C),
- abnormal cervical mucopurulent discharge or cervical friability,
- presence of “abundant numbers of white blood cells on saline microscopy of vaginal fluid,”
- elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (reference range, 0–20 mm/hr),
- elevated C-reactive protein (reference range, 0.08-3.1 mg/L), and
- laboratory documentation of cervical infection with N gonorrhoeae or C trachomatis.
The CDC also suggests that the most specific criteria for PID include5
- endometrial biopsy consistent with endometritis,
- imaging (transvaginal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging) demonstrating fluid-filled tubes, or
- laparoscopic findings consistent with PID.
Treatment of PID includes IV antibiotics
Due to the polymicrobial nature of PID, antibiotics should cover not only gonorrhea and chlamydia but also anaerobic pathogens. CDC guidelines recommend the following treatment5,6:
- intravenous (IV) cefotetan (2 g bid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid),
- IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid), or
- IV clindamycin (900 mg tid) plus IV or intramuscular (IM) gentamicin loading dose (2 mg/kg) followed by a maintenance dose (1.5 mg/kg tid).
In mild-to-moderate PID cases deemed appropriate for outpatient therapy, the following regimens have been shown to have similar outcomes to IV therapy5,6:
- IM ceftriaxone (250 mg, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days,
- IM cefoxitin (2 g, single dose) and PO probenecid (1 g, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days, or
- other parenteral third-generation cephalosporin plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days.
Management in older women may be more intensive
Due to the increased risk of malignancy in postmenopausal women with TOA, surgical intervention may be needed.3,4
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent diagnostic laparoscopy, hysterectomy, left salpingo-oophorectomy, and right salpingectomy (with her right ovary left in place due to her perimenopausal status). Intraoperatively, she was found to have cervical stenosis. Postoperatively, she improved on IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) and IV doxycycline (100 mg bid), which was eventually transitioned to oral doxycycline (100 mg bid) and metronidazole (500 mg bid) on discharge.
Her final microbiology was negative for gonorrhea/chlamydia but the bacterial culture of peritoneal fluid grew E coli. Pathology was consistent with acute salpingitis, TOA, and acute cervicitis. She made a full recovery and is doing well.
CORRESPONDENCE
Catherine Peony Khoo, MD, 1920 Colorado Avenue, Santa Monica, CA 90404; [email protected]
At the recommendation of her primary care physician, a 53-year-old perimenopausal woman sought care at the emergency department for the fever, abdominal pain, and pyuria that had persisted for 4 days despite outpatient treatment for pyelonephritis. On physical examination, she was febrile and tachycardic with abdominal tenderness of the left lower quadrant. Genitourinary examination revealed copious brown vaginal discharge, left adnexal tenderness, and no cervical motion tenderness.

Laboratory testing revealed leukocytosis but otherwise normal electrolytes, liver function tests, and lactate levels. Urine culture obtained when she presented to an urgent care facility 3 days earlier had been negative. Computed tomography (CT) was performed and was read by Radiology as “closed loop small bowel obstruction in the left lower abdomen” (FIGURE 1). The patient was taken emergently to the operating room where her entire length of bowel was run without any obstruction found. Instead, the surgeons identified a mass in the left iliac fossa originating from the left ovary and fallopian tube (FIGURE 2).

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Pelvic inflammatory disease with tubo-ovarian abscess
The presence and location of this mass, paired with the patient’s symptoms, led to the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease. PID is an acute infection of the upper genital tract in women thought to be due to ascending infection from the lower genital tract. The prevalence of PID in reproductive-aged women in the United States is estimated to be 4.4%.1
Diagnosis of PID in middle-aged women is a challenge given the broad differential diagnosis of nonspecific presenting symptoms, lower index of suspicion in this age group, and unknown exact incidence of PID in postmenopausal women. While delay in diagnosis of PID in women of reproductive age is associated with increased infertility and ectopic pregnancy,2 delay in diagnosis in postmenopausal women also poses serious potential complications such as tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA)—as was seen with this patient—and concurrent gynecologic malignancy found on pathology of TOA specimens.3,4
Risk factors for PID in the postmenopausal population include recent uterine instrumentation, history of prior PID, and structural abnormalities such as cervical stenosis, uterine anatomic abnormalities, or tubal disease. The microbiology of PID in postmenopausal women differs from that of women of reproductive age. While sexually transmitted pathogens such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis most commonly are implicated in PID among premenopausal patients, aerobic gram-negative bacteria including Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae most frequently are associated in postmenopausal cases.
Differential diagnosis for abdominal pain is broad
The differential diagnosis for a patient with fever and abdominal pain includes PID, as well as the following:
Diverticulitis classically presents with left lower abdominal pain and a low-grade fever. Complications may include bowel obstruction, abscess, fistula, or perforation. Abdominal imaging such as a CT scan is required to establish the diagnosis.
Continue to: Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection should be suspected in a patient with dysuria, urinary frequency or urgency, and abdominal or flank pain. Urinalysis and culture should be performed and imaging may be considered for suspected obstruction, complication, or failure to improve on appropriate therapy.
Appendicitis may present as right lower quadrant pain with anorexia, fever, and nausea. Imaging studies such as CT or ultrasound can help support the diagnosis and rule out alternate etiologies of the presenting symptoms.
Ectopic pregnancy—while not considered in this case—should be suspected in a patient presenting with pelvic pain, missed menses or vaginal bleeding, and a positive pregnancy test. Further evaluation may be performed with a transvaginal ultrasound and serial measurement of serum quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin level.
Diagnosing PID is a clinical process
PID often is difficult to diagnose because of an absence of symptoms or the presence of symptoms that are subtle or nonspecific. Laparoscopy or endometrial biopsy can be useful but may not be justifiable due to their invasive nature when symptoms are mild or vague.5 Thus, a diagnosis of PID usually is based on clinical findings.
Clinical criteria to look for. Although PID commonly is attributed to N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis, fewer than 50% of those with a diagnosis of acute PID test positive for either of these organisms.5 As such, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines recommend presumptive treatment for PID in women with pelvic or lower abdominal pain with 1 or more of the following clinical criteria: cervical motion tenderness, uterine tenderness, or adnexal tenderness.
Continue to: The following criteria...
The following criteria enhance specificity and support the diagnosis5:
- oral temperature > 101°F (> 38.3°C),
- abnormal cervical mucopurulent discharge or cervical friability,
- presence of “abundant numbers of white blood cells on saline microscopy of vaginal fluid,”
- elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (reference range, 0–20 mm/hr),
- elevated C-reactive protein (reference range, 0.08-3.1 mg/L), and
- laboratory documentation of cervical infection with N gonorrhoeae or C trachomatis.
The CDC also suggests that the most specific criteria for PID include5
- endometrial biopsy consistent with endometritis,
- imaging (transvaginal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging) demonstrating fluid-filled tubes, or
- laparoscopic findings consistent with PID.
Treatment of PID includes IV antibiotics
Due to the polymicrobial nature of PID, antibiotics should cover not only gonorrhea and chlamydia but also anaerobic pathogens. CDC guidelines recommend the following treatment5,6:
- intravenous (IV) cefotetan (2 g bid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid),
- IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO or IV bid), or
- IV clindamycin (900 mg tid) plus IV or intramuscular (IM) gentamicin loading dose (2 mg/kg) followed by a maintenance dose (1.5 mg/kg tid).
In mild-to-moderate PID cases deemed appropriate for outpatient therapy, the following regimens have been shown to have similar outcomes to IV therapy5,6:
- IM ceftriaxone (250 mg, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days,
- IM cefoxitin (2 g, single dose) and PO probenecid (1 g, single dose) plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days, or
- other parenteral third-generation cephalosporin plus PO doxycycline (100 mg bid) for 14 days with/without PO metronidazole (500 mg bid) for 14 days.
Management in older women may be more intensive
Due to the increased risk of malignancy in postmenopausal women with TOA, surgical intervention may be needed.3,4
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent diagnostic laparoscopy, hysterectomy, left salpingo-oophorectomy, and right salpingectomy (with her right ovary left in place due to her perimenopausal status). Intraoperatively, she was found to have cervical stenosis. Postoperatively, she improved on IV cefoxitin (2 g qid) and IV doxycycline (100 mg bid), which was eventually transitioned to oral doxycycline (100 mg bid) and metronidazole (500 mg bid) on discharge.
Her final microbiology was negative for gonorrhea/chlamydia but the bacterial culture of peritoneal fluid grew E coli. Pathology was consistent with acute salpingitis, TOA, and acute cervicitis. She made a full recovery and is doing well.
CORRESPONDENCE
Catherine Peony Khoo, MD, 1920 Colorado Avenue, Santa Monica, CA 90404; [email protected]
1. Kreisel K, Torrone E, Bernstein K, et al. Prevalence of pelvic inflammatory disease in sexually experienced women of reproductive age—United States, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:80-83.
2. Weström L, Joesoef R, Reynolds G, et al. Pelvic inflammatory disease and fertility: a cohort study of 1,844 women with laparoscopically verified disease and 657 control women with normal laparoscopic results. Sex Transm Dis. 1992;19:185-192.
3. Jackson SL, Soper DE. Pelvic inflammatory disease in the postmenopausal woman. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7:248-252.
4. Protopas AG, Diakomanolis ES, Milingos SD, et al. Tubo-ovarian abscesses in postmenopausal women: gynecological malignancy until proven otherwise? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;114:203-209.
5. Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64:1-137.
6. Ness RB, Soper DE, Holley RL, et al. Effectiveness of inpatient and outpatient treatment strategies for women with pelvic inflammatory disease: results from the Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Evaluation and Clinical Health (PEACH) randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186:929-937 .
1. Kreisel K, Torrone E, Bernstein K, et al. Prevalence of pelvic inflammatory disease in sexually experienced women of reproductive age—United States, 2013-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:80-83.
2. Weström L, Joesoef R, Reynolds G, et al. Pelvic inflammatory disease and fertility: a cohort study of 1,844 women with laparoscopically verified disease and 657 control women with normal laparoscopic results. Sex Transm Dis. 1992;19:185-192.
3. Jackson SL, Soper DE. Pelvic inflammatory disease in the postmenopausal woman. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1999;7:248-252.
4. Protopas AG, Diakomanolis ES, Milingos SD, et al. Tubo-ovarian abscesses in postmenopausal women: gynecological malignancy until proven otherwise? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2004;114:203-209.
5. Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64:1-137.
6. Ness RB, Soper DE, Holley RL, et al. Effectiveness of inpatient and outpatient treatment strategies for women with pelvic inflammatory disease: results from the Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Evaluation and Clinical Health (PEACH) randomized trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186:929-937 .
New guideline offers recommendations for reproductive health in patients with rheumatic diseases
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
A new guideline from the American College of Rheumatology offers the organization’s first clinical recommendations on how to manage reproductive health issues in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs).
“With the development of this guideline, the ACR recognizes the key role of clinical rheumatologists not only in managing disease activity but also in understanding the interactions of RMDs and their therapies in the context of reproductive health,” wrote Lisa R. Sammaritano, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine and the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and coauthors. The guideline was published in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
To develop an evidence-based guideline on reproductive health in RMD patients, the researchers embarked on a systematic review of studies in areas like contraception, pregnancy and lactation, assisted reproductive technology (ART), fertility preservation, and hormone therapy. The guideline contains 12 ungraded good practice statements and 131 graded recommendations, all developed through the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation methodology.
In counseling patients about these areas of care, the guideline says that rheumatologists and other clinicians “must collaborate with specialists in the fields of obstetrics-gynecology, maternal-fetal medicine, and reproductive endocrinology and infertility.”
“One thing this guideline does well is highlight the importance of involving maternal-fetal medicine colleagues,” Alison Cahill, MD, a professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist within UT Health Austin’s Women’s Health Institute, said when asked for comment on the guideline. “We’re always very happy to see patients ahead of time who are planning pregnancy to be able to discuss what the care plan would look like. And specifically, to address medications, if required, for their rheumatologic care.
“As we learn more and more,” she added, “we’ve come to understand that most treatments and medications are actually safe or relatively safe to take in pregnancy. Certainly, the benefit of taking them outweighs any small or theoretic risks. On the flip side, the guideline does a nice job of highlighting the importance of good disease control, both at the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
Contraception
In regard to contraception, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives – with a conditional recommendation of IUDs or a subdermal progestin implant – in fertile women with a RMD who have neither systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) nor positive antiphospholipid antibody (aPL). They also strongly recommend discussing the use of emergency contraception with all RMD patients.
For SLE patients, the guideline strongly recommends the use of effective contraceptives in those with stable or low disease activity who are not positive for aPL. They also strongly recommend progestin‐only or IUD contraceptives over combined estrogen‐progestin contraception. For aPL-positive patients, the guideline strongly recommends against combined estrogen‐progestin contraceptives and for levonorgestrel or copper IUDs or the progestin‐only pill.
Assisted reproductive technology
In regard to ART, the guideline strongly recommends proceeding as needed in aPL-negative women with uncomplicated, stable RMD who are on pregnancy‐compatible medications. They also strongly recommend deferring ART in any RMD patients with moderately or severely active disease.
For aPL-positive patients undergoing ART procedures, they strongly recommend prophylactic anticoagulation with heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in women with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and therapeutic anticoagulation in women with thrombotic APS. In patients undergoing embryo and oocyte cryopreservation, they strongly recommend continuing immunosuppressive and biologic therapies – the exception being cyclophosphamide (CYC) – for anyone in stable condition.
Fertility preservation
In regard to fertility preservation in patients taking CYC, the guideline strongly suggests sperm cryopreservation as good practice prior to treatment. They also conditionally recommend monthly gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist cotherapy in premenopausal women with RMD.
Hormone therapy
In regard to menopause and hormone therapy, the guideline strongly suggests hormone therapy as good practice in postmenopausal women with RMD, without SLE or positive aPL, and who have severe vasomotor symptoms. Hormone therapy is conditionally recommended in patients with SLE, without positive aPL, and with no contraindications. For aPL-positive patients, they strongly recommend against hormone therapy in women with obstetric and/or thrombotic APS.
Pregnancy assessment and management
Among the many recommendations regarding pregnancy assessment and management, the guideline strongly suggests counseling women with RMD who are considering pregnancy to take into account the improved outcomes for pregnant women with low disease activity. They strongly recommend that women considering pregnancy should switch to pregnancy‐compatible medication and pause to assess its efficacy and tolerability before moving forward, along with strongly recommending that pregnant women with active disease initiate or continue a pregnancy‐compatible steroid‐sparing medication. They also recommend testing for anti‐Ro/SS-A and anti‐La/SS-B in women with SLE, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or rheumatoid arthritis, but only once and only before or early in the pregnancy.
For women with systemic sclerosis who develop scleroderma renal crisis during pregnancy, the authors strongly advise using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers “because the risk of maternal or fetal death with untreated disease is higher than the risk associated with use of these medications during pregnancy.”
Among women with SLE, the recommendations strongly call for testing either before or early in pregnancy for anticardiolipin antibody, anti–beta2-glycoprotein I, or positive lupus anticoagulant, as well as initiating or continuing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) if possible. Starting in the first trimester, the authors also conditionally recommend that SLE patients take low-dose aspirin daily
For pregnant women who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the guideline conditionally recommends prophylactic treatment with low-dose aspirin daily to protect against preeclampsia. When obstetric APS criteria are met, the guideline strongly advises combined treatment with daily low-dose aspirin and prophylactic-dose heparin (or LMWH), as well as prophylactic-dose anticoagulation for 6-12 weeks post partum. When patients have thrombotic APS, this combination treatment should contain heparin dose at a therapeutic level throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, the authors conditionally recommend against giving low-dose aspirin plus prophylactic-dose heparin to women without obstetric APS. For refractory obstetric APS, the guideline also contains recommendations that are conditionally against treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin or an increased LMWH dose and strongly against adding prednisone to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin. In pregnant patients with primary APS, the authors conditionally advise adding HCQ to prophylactic-dose heparin or LMWH and low-dose aspirin therapy. However, women with aPL who do not meet APS criteria or have another indication for HCQ are conditionally advised against prophylactic treatment with the antimalarial.
For women with Anti-Ro/SS-A and/or anti-La/SS-B antibodies in pregnancy, there is conditional advice to use HCQ. When there is no history of an infant with complete heart block or neonatal lupus erythematosus among women with these antibodies, the guideline conditionally advises serial fetal echocardiography (less often than weekly) starting between 16 and 18 weeks and continuing through 26 weeks, but this should be weekly when there is a prior history. Treatment with oral dexamethasone 4 mg daily is conditionally advised when there is echocardiographic evidence of fetal first- or second-degree heart block, but dexamethasone is not recommended when complete heart block is present.
Finally, in regard to medication use, the authors strongly recommend that men who are planning to be fathers continue on HCQ, azathioprine, 6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Conditional treatment recommendations for men planning for pregnancy include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid (MMF), leflunomide, sulfasalazine, calcineurin inhibitors, and NSAIDs. They also strongly recommend that this group of men discontinue CYC and thalidomide.
Pregnant women are strongly recommended to discontinue methotrexate, leflunomide (with cholestyramine washout if there are detectable serum levels of its metabolite prior to pregnancy or as soon as it is confirmed), MMF, CYC, and thalidomide within 3 months prior to conception, and they strongly recommend HCQ (in women with SLE), azathioprine/6‐mercaptopurine, colchicine, or sulfasalazine for use throughout pregnancy. They strongly recommend a combination of low‐dose aspirin and prophylactic‐dose heparin for pregnant women with obstetric APS, along with low‐dose aspirin and therapeutic‐dose heparin for women with thrombotic APS throughout pregnancy and postpartum. However, for women with SLE and those who test positive for aPL but do not meet criteria for obstetric or thrombotic APS, the authors conditionally recommend low-dose aspirin starting in the first trimester.
The guideline suggests that women with RMD should be encouraged to breastfeed if they are willing and able; they also suggest that disease control be maintained through lactation‐compatible medications and that the risks and benefits be reviewed on a patient-by-patient basis. Treatment with HCQ, colchicine, sulfasalazine, rituximab, and all tumor necrosis factor inhibitors are strongly recommended as being compatible with breastfeeding, and they strongly recommend against using CYC, leflunomide, MMF, and thalidomide while breastfeeding.
The authors acknowledged the limitations of their guideline, including the literature review being conducted on studies involving adults and an “inability to include recommendations for uncommon but important clinical situations,” including those involving transgender patients and hormonal therapies.
The authors reported numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving research support, consulting fees, speaking fees, and honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Sammaritano LR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Feb 23. doi: 10.1002/art.41191.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
In gestational diabetes, early postpartum glucose testing is a winner
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – Early postpartum glucose tolerance testing for women with gestational diabetes resulted in a 99% adherence rate, with similar sensitivity and specificity as the currently recommended 4- to 12-week postpartum testing schedule.
“Two-day postpartum glucose tolerance testing has similar diagnostic utility as the 4- to 12-week postpartum glucose tolerance test to identify impaired glucose metabolism and diabetes at 1 year postpartum,” said Erika Werner, MD, speaking at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Overall, 29% of women studied had impaired glucose metabolism at 2 days postpartum, as did 25% in the 4- to 12-weeks postpartum window. At 1 year, that figure was 35%. The number of women meeting diagnostic criteria for diabetes held steady at 4% for all three time points.
The findings warrant “consideration for the 2-day postpartum glucose tolerance test (GTT) as the initial postpartum test for women who have gestational diabetes, with repeat testing at 1 year,” said Dr. Werner, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Glucose testing for women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is recommended at 4-12 weeks postpartum by both the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Testing can allow detection and treatment of impaired glucose metabolism, seen in 15%-40% of women with a history of GDM. Up to 1 in 20 women with GDM will receive a postpartum diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
However, fewer than one in five women will actually have postpartum glucose testing, representing a large missed opportunity, said Dr. Werner.
Several factors likely contribute to those screening failures, she added. In addition to the potential for public insurance to lapse at 6 weeks postpartum, the logistical realities and time demands of parenting a newborn are themselves a significant barrier.
“What if we changed the timing?” and shifted glucose testing to the early postpartum days, before hospital discharge, asked Dr. Werner. Several pilot studies had already compared glucose screening in the first few days postpartum with the routine schedule, finding good correlation between the early and routine GTT schedule.
Importantly, the earlier studies achieved an adherence rate of more than 90% for early GTT. By contrast, fewer than half of the participants in the usual-care arms actually returned for postpartum GTT in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, even under the optimized conditions associated with a medical study.
The single-center prospective cohort study conducted by Dr. Werner and collaborators enrolled 300 women with GDM. Women agreed to participate in glucose tolerance testing as inpatients, at 2 days postpartum, in addition to receiving a GTT between 4 and 12 weeks postpartum, and additional screening that included a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test at 1 year postpartum.
The investigators obtained postpartum day 2 GTTs for all but four of the patients. A total of 201 patients returned in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, and 168 of those participants returned for HbA1c testing at 1 year. Of the 95 patients who didn’t come back for the 4- to 12-week test, 33 did return at 1 year for HbA1c testing.
Dr. Werner and her coinvestigators included adult women who spoke either fluent Spanish or English and had GDM diagnosed by the Carpenter-Coustan criteria, or by having a blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or more in a 1-hour glucose challenge test.
The early GTT results weren’t shared with patients or their health care providers. For outpatient visits, participants were offered financial incentives and received multiple reminder phone calls and the offer of free transportation.
For the purposes of the study, impaired glucose metabolism was defined as fasting blood glucose of 100 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 140 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 5.7% or greater.
Participants were diagnosed with diabetes if they had a fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 6.5% or greater.
Dr. Werner and colleagues conducted two analyses of their results. In the first, they included only women in both arms who had complete data. In the second analysis, they looked at all women who had data for the 1-year postpartum mark, assuming that interval GTTs were negative for women who were missing these values.
The statistical analysis showed that, for women with complete data, both early and later postpartum GTTs were similar in predicting impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year postpartum (areas under the receiver operating curve [AUC], 0.63 and 0.60, respectively).
For identifying diabetes at 1 year, both early and late testing had high negative predictive value (98% and 99%, respectively), but the later testing strategy had higher sensitivity and specificity, yielding an AUC of 0.83, compared with 0.65 for early testing.
Turning to the second analysis that included all women who had 1-year postpartum HbA1c values, negative predictive values for diabetes were similarly high (98%) for both the early and late testing strategies. For identifying impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year in this group, both the positive and negative predictive value of the early and late strategies were similar.
Patients were about 32 years old at baseline, with a mean body mass index of 31.7 kg/m2. More than half of patients (52.3%) had private insurance, and 22% had GDM in a pregnancy prior to the index pregnancy. Black patients made up about 9% of the study population; 54% of participants were white, and 23% Hispanic. About one-third of patients were nulliparous, and two-thirds had education beyond high school.
During their pregnancies, about 44% of patients managed GDM by diet alone, 40% required insulin, with an additional 1% also requiring an oral agent. The remainder required oral agents alone. Patients delivered at a mean 38.3 weeks gestation, with about 40% receiving cesarean deliveries.
Some of the study’s strengths included its prospective nature, the diverse population recruited, and the fact that participants and providers were both blinded to the 2-day GTT results. Although more than half of participants completed the study – besting the previous pilots – 44% of patients still had incomplete data, noted Dr. Werner.
The American Diabetes Association sponsored the study. Dr. Werner reported no other conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Werner E et al. SMFM 2020. Abstract 72.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – Early postpartum glucose tolerance testing for women with gestational diabetes resulted in a 99% adherence rate, with similar sensitivity and specificity as the currently recommended 4- to 12-week postpartum testing schedule.
“Two-day postpartum glucose tolerance testing has similar diagnostic utility as the 4- to 12-week postpartum glucose tolerance test to identify impaired glucose metabolism and diabetes at 1 year postpartum,” said Erika Werner, MD, speaking at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Overall, 29% of women studied had impaired glucose metabolism at 2 days postpartum, as did 25% in the 4- to 12-weeks postpartum window. At 1 year, that figure was 35%. The number of women meeting diagnostic criteria for diabetes held steady at 4% for all three time points.
The findings warrant “consideration for the 2-day postpartum glucose tolerance test (GTT) as the initial postpartum test for women who have gestational diabetes, with repeat testing at 1 year,” said Dr. Werner, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Glucose testing for women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is recommended at 4-12 weeks postpartum by both the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Testing can allow detection and treatment of impaired glucose metabolism, seen in 15%-40% of women with a history of GDM. Up to 1 in 20 women with GDM will receive a postpartum diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
However, fewer than one in five women will actually have postpartum glucose testing, representing a large missed opportunity, said Dr. Werner.
Several factors likely contribute to those screening failures, she added. In addition to the potential for public insurance to lapse at 6 weeks postpartum, the logistical realities and time demands of parenting a newborn are themselves a significant barrier.
“What if we changed the timing?” and shifted glucose testing to the early postpartum days, before hospital discharge, asked Dr. Werner. Several pilot studies had already compared glucose screening in the first few days postpartum with the routine schedule, finding good correlation between the early and routine GTT schedule.
Importantly, the earlier studies achieved an adherence rate of more than 90% for early GTT. By contrast, fewer than half of the participants in the usual-care arms actually returned for postpartum GTT in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, even under the optimized conditions associated with a medical study.
The single-center prospective cohort study conducted by Dr. Werner and collaborators enrolled 300 women with GDM. Women agreed to participate in glucose tolerance testing as inpatients, at 2 days postpartum, in addition to receiving a GTT between 4 and 12 weeks postpartum, and additional screening that included a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test at 1 year postpartum.
The investigators obtained postpartum day 2 GTTs for all but four of the patients. A total of 201 patients returned in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, and 168 of those participants returned for HbA1c testing at 1 year. Of the 95 patients who didn’t come back for the 4- to 12-week test, 33 did return at 1 year for HbA1c testing.
Dr. Werner and her coinvestigators included adult women who spoke either fluent Spanish or English and had GDM diagnosed by the Carpenter-Coustan criteria, or by having a blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or more in a 1-hour glucose challenge test.
The early GTT results weren’t shared with patients or their health care providers. For outpatient visits, participants were offered financial incentives and received multiple reminder phone calls and the offer of free transportation.
For the purposes of the study, impaired glucose metabolism was defined as fasting blood glucose of 100 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 140 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 5.7% or greater.
Participants were diagnosed with diabetes if they had a fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 6.5% or greater.
Dr. Werner and colleagues conducted two analyses of their results. In the first, they included only women in both arms who had complete data. In the second analysis, they looked at all women who had data for the 1-year postpartum mark, assuming that interval GTTs were negative for women who were missing these values.
The statistical analysis showed that, for women with complete data, both early and later postpartum GTTs were similar in predicting impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year postpartum (areas under the receiver operating curve [AUC], 0.63 and 0.60, respectively).
For identifying diabetes at 1 year, both early and late testing had high negative predictive value (98% and 99%, respectively), but the later testing strategy had higher sensitivity and specificity, yielding an AUC of 0.83, compared with 0.65 for early testing.
Turning to the second analysis that included all women who had 1-year postpartum HbA1c values, negative predictive values for diabetes were similarly high (98%) for both the early and late testing strategies. For identifying impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year in this group, both the positive and negative predictive value of the early and late strategies were similar.
Patients were about 32 years old at baseline, with a mean body mass index of 31.7 kg/m2. More than half of patients (52.3%) had private insurance, and 22% had GDM in a pregnancy prior to the index pregnancy. Black patients made up about 9% of the study population; 54% of participants were white, and 23% Hispanic. About one-third of patients were nulliparous, and two-thirds had education beyond high school.
During their pregnancies, about 44% of patients managed GDM by diet alone, 40% required insulin, with an additional 1% also requiring an oral agent. The remainder required oral agents alone. Patients delivered at a mean 38.3 weeks gestation, with about 40% receiving cesarean deliveries.
Some of the study’s strengths included its prospective nature, the diverse population recruited, and the fact that participants and providers were both blinded to the 2-day GTT results. Although more than half of participants completed the study – besting the previous pilots – 44% of patients still had incomplete data, noted Dr. Werner.
The American Diabetes Association sponsored the study. Dr. Werner reported no other conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Werner E et al. SMFM 2020. Abstract 72.
GRAPEVINE, TEX. – Early postpartum glucose tolerance testing for women with gestational diabetes resulted in a 99% adherence rate, with similar sensitivity and specificity as the currently recommended 4- to 12-week postpartum testing schedule.
“Two-day postpartum glucose tolerance testing has similar diagnostic utility as the 4- to 12-week postpartum glucose tolerance test to identify impaired glucose metabolism and diabetes at 1 year postpartum,” said Erika Werner, MD, speaking at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Overall, 29% of women studied had impaired glucose metabolism at 2 days postpartum, as did 25% in the 4- to 12-weeks postpartum window. At 1 year, that figure was 35%. The number of women meeting diagnostic criteria for diabetes held steady at 4% for all three time points.
The findings warrant “consideration for the 2-day postpartum glucose tolerance test (GTT) as the initial postpartum test for women who have gestational diabetes, with repeat testing at 1 year,” said Dr. Werner, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Glucose testing for women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is recommended at 4-12 weeks postpartum by both the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Testing can allow detection and treatment of impaired glucose metabolism, seen in 15%-40% of women with a history of GDM. Up to 1 in 20 women with GDM will receive a postpartum diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
However, fewer than one in five women will actually have postpartum glucose testing, representing a large missed opportunity, said Dr. Werner.
Several factors likely contribute to those screening failures, she added. In addition to the potential for public insurance to lapse at 6 weeks postpartum, the logistical realities and time demands of parenting a newborn are themselves a significant barrier.
“What if we changed the timing?” and shifted glucose testing to the early postpartum days, before hospital discharge, asked Dr. Werner. Several pilot studies had already compared glucose screening in the first few days postpartum with the routine schedule, finding good correlation between the early and routine GTT schedule.
Importantly, the earlier studies achieved an adherence rate of more than 90% for early GTT. By contrast, fewer than half of the participants in the usual-care arms actually returned for postpartum GTT in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, even under the optimized conditions associated with a medical study.
The single-center prospective cohort study conducted by Dr. Werner and collaborators enrolled 300 women with GDM. Women agreed to participate in glucose tolerance testing as inpatients, at 2 days postpartum, in addition to receiving a GTT between 4 and 12 weeks postpartum, and additional screening that included a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test at 1 year postpartum.
The investigators obtained postpartum day 2 GTTs for all but four of the patients. A total of 201 patients returned in the 4- to 12-week postpartum window, and 168 of those participants returned for HbA1c testing at 1 year. Of the 95 patients who didn’t come back for the 4- to 12-week test, 33 did return at 1 year for HbA1c testing.
Dr. Werner and her coinvestigators included adult women who spoke either fluent Spanish or English and had GDM diagnosed by the Carpenter-Coustan criteria, or by having a blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or more in a 1-hour glucose challenge test.
The early GTT results weren’t shared with patients or their health care providers. For outpatient visits, participants were offered financial incentives and received multiple reminder phone calls and the offer of free transportation.
For the purposes of the study, impaired glucose metabolism was defined as fasting blood glucose of 100 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 140 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 5.7% or greater.
Participants were diagnosed with diabetes if they had a fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL or greater, a 2-hour GTT blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL or greater, or HbA1c of 6.5% or greater.
Dr. Werner and colleagues conducted two analyses of their results. In the first, they included only women in both arms who had complete data. In the second analysis, they looked at all women who had data for the 1-year postpartum mark, assuming that interval GTTs were negative for women who were missing these values.
The statistical analysis showed that, for women with complete data, both early and later postpartum GTTs were similar in predicting impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year postpartum (areas under the receiver operating curve [AUC], 0.63 and 0.60, respectively).
For identifying diabetes at 1 year, both early and late testing had high negative predictive value (98% and 99%, respectively), but the later testing strategy had higher sensitivity and specificity, yielding an AUC of 0.83, compared with 0.65 for early testing.
Turning to the second analysis that included all women who had 1-year postpartum HbA1c values, negative predictive values for diabetes were similarly high (98%) for both the early and late testing strategies. For identifying impaired glucose metabolism at 1 year in this group, both the positive and negative predictive value of the early and late strategies were similar.
Patients were about 32 years old at baseline, with a mean body mass index of 31.7 kg/m2. More than half of patients (52.3%) had private insurance, and 22% had GDM in a pregnancy prior to the index pregnancy. Black patients made up about 9% of the study population; 54% of participants were white, and 23% Hispanic. About one-third of patients were nulliparous, and two-thirds had education beyond high school.
During their pregnancies, about 44% of patients managed GDM by diet alone, 40% required insulin, with an additional 1% also requiring an oral agent. The remainder required oral agents alone. Patients delivered at a mean 38.3 weeks gestation, with about 40% receiving cesarean deliveries.
Some of the study’s strengths included its prospective nature, the diverse population recruited, and the fact that participants and providers were both blinded to the 2-day GTT results. Although more than half of participants completed the study – besting the previous pilots – 44% of patients still had incomplete data, noted Dr. Werner.
The American Diabetes Association sponsored the study. Dr. Werner reported no other conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Werner E et al. SMFM 2020. Abstract 72.
REPORTING FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
Increased risk of infection seen in patients with MS
womensWEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) are at increased risk for most types of infection, with the highest risk associated with renal tract infections, according to an analysis of Department of Defense data.
Susan Jick, DSc, director of the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program and professor of epidemiology and biostatistics at Boston University, and colleagues sought to understand the rates at which infections occur because they are known to be a common cause of comorbidity and death in patients with MS.
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Jick and associates presented rates of infection in patients with MS after MS diagnosis, compared with a matched population of patients without MS. The MS cohort included patients who had MS diagnosed and treated between January 2004 and August 2017. Patients had medical history available for at least 1 year before MS diagnosis and at least one prescription for an MS disease-modifying treatment.
Patients without MS were matched to patients with MS 10:1 based on age, sex, geographic region, and cohort entry date. For each patient, the researchers identified the first diagnosed infection of each type after cohort entry. They followed patients until loss of eligibility, death, or end of data collection.
In all, the study included 8,695 patients with MS and 86,934 matched patients without MS. The median age at cohort entry was 41 years, and 71% were female. Median duration of follow-up after study entry was about 6 years. Patients with MS were more likely to have an infection in the year before cohort entry, compared with non-MS patients (43.9% vs. 36.3%).
After cohort entry, the incidence rate of any infection was higher among patients with MS, compared with non-MS patients (4,805 vs. 2,731 per 10,000 person-years; IR ratio, 1.76). In addition, the IR of hospitalized infection was higher among MS patients (125 vs. 51.3 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 2.43). The IR also was increased for several other types of infections, including renal, skin, fungal, pneumonia or influenza, and other infections (such as rickettsial and spirochetal diseases, helminthiases, and nonsyphilitic and nongonococcal venereal diseases). Eye or ear, respiratory or throat, and viral IRRs “were marginally elevated,” the investigators wrote.
In both cohorts, females had a higher risk of infection than males did. The rate of renal tract infection was more than fourfold higher among females, compared with males, in both cohorts. Relative to non-MS patients, however, men with MS had a higher IRR for renal tract infection than women with MS did (2.47 vs. 1.90).
“The risk for any opportunistic infection was slightly increased among MS patients,” the researchers wrote (520 vs. 338 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.54). This was particularly true for candidiasis (252 vs. 166 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.52) and herpes virus infection (221 vs. 150 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.47). “There were few cases of tuberculosis, hepatitis B infection, or hepatitis C infection,” they noted.
The study was funded by a grant from Celgene, a subsidiary of Bristol-Myers Squibb. Four authors are employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb, and one author works for a company that does business with Celgene.
SOURCE: Jick S et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P086.
womensWEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) are at increased risk for most types of infection, with the highest risk associated with renal tract infections, according to an analysis of Department of Defense data.
Susan Jick, DSc, director of the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program and professor of epidemiology and biostatistics at Boston University, and colleagues sought to understand the rates at which infections occur because they are known to be a common cause of comorbidity and death in patients with MS.
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Jick and associates presented rates of infection in patients with MS after MS diagnosis, compared with a matched population of patients without MS. The MS cohort included patients who had MS diagnosed and treated between January 2004 and August 2017. Patients had medical history available for at least 1 year before MS diagnosis and at least one prescription for an MS disease-modifying treatment.
Patients without MS were matched to patients with MS 10:1 based on age, sex, geographic region, and cohort entry date. For each patient, the researchers identified the first diagnosed infection of each type after cohort entry. They followed patients until loss of eligibility, death, or end of data collection.
In all, the study included 8,695 patients with MS and 86,934 matched patients without MS. The median age at cohort entry was 41 years, and 71% were female. Median duration of follow-up after study entry was about 6 years. Patients with MS were more likely to have an infection in the year before cohort entry, compared with non-MS patients (43.9% vs. 36.3%).
After cohort entry, the incidence rate of any infection was higher among patients with MS, compared with non-MS patients (4,805 vs. 2,731 per 10,000 person-years; IR ratio, 1.76). In addition, the IR of hospitalized infection was higher among MS patients (125 vs. 51.3 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 2.43). The IR also was increased for several other types of infections, including renal, skin, fungal, pneumonia or influenza, and other infections (such as rickettsial and spirochetal diseases, helminthiases, and nonsyphilitic and nongonococcal venereal diseases). Eye or ear, respiratory or throat, and viral IRRs “were marginally elevated,” the investigators wrote.
In both cohorts, females had a higher risk of infection than males did. The rate of renal tract infection was more than fourfold higher among females, compared with males, in both cohorts. Relative to non-MS patients, however, men with MS had a higher IRR for renal tract infection than women with MS did (2.47 vs. 1.90).
“The risk for any opportunistic infection was slightly increased among MS patients,” the researchers wrote (520 vs. 338 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.54). This was particularly true for candidiasis (252 vs. 166 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.52) and herpes virus infection (221 vs. 150 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.47). “There were few cases of tuberculosis, hepatitis B infection, or hepatitis C infection,” they noted.
The study was funded by a grant from Celgene, a subsidiary of Bristol-Myers Squibb. Four authors are employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb, and one author works for a company that does business with Celgene.
SOURCE: Jick S et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P086.
womensWEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) are at increased risk for most types of infection, with the highest risk associated with renal tract infections, according to an analysis of Department of Defense data.
Susan Jick, DSc, director of the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program and professor of epidemiology and biostatistics at Boston University, and colleagues sought to understand the rates at which infections occur because they are known to be a common cause of comorbidity and death in patients with MS.
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Jick and associates presented rates of infection in patients with MS after MS diagnosis, compared with a matched population of patients without MS. The MS cohort included patients who had MS diagnosed and treated between January 2004 and August 2017. Patients had medical history available for at least 1 year before MS diagnosis and at least one prescription for an MS disease-modifying treatment.
Patients without MS were matched to patients with MS 10:1 based on age, sex, geographic region, and cohort entry date. For each patient, the researchers identified the first diagnosed infection of each type after cohort entry. They followed patients until loss of eligibility, death, or end of data collection.
In all, the study included 8,695 patients with MS and 86,934 matched patients without MS. The median age at cohort entry was 41 years, and 71% were female. Median duration of follow-up after study entry was about 6 years. Patients with MS were more likely to have an infection in the year before cohort entry, compared with non-MS patients (43.9% vs. 36.3%).
After cohort entry, the incidence rate of any infection was higher among patients with MS, compared with non-MS patients (4,805 vs. 2,731 per 10,000 person-years; IR ratio, 1.76). In addition, the IR of hospitalized infection was higher among MS patients (125 vs. 51.3 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 2.43). The IR also was increased for several other types of infections, including renal, skin, fungal, pneumonia or influenza, and other infections (such as rickettsial and spirochetal diseases, helminthiases, and nonsyphilitic and nongonococcal venereal diseases). Eye or ear, respiratory or throat, and viral IRRs “were marginally elevated,” the investigators wrote.
In both cohorts, females had a higher risk of infection than males did. The rate of renal tract infection was more than fourfold higher among females, compared with males, in both cohorts. Relative to non-MS patients, however, men with MS had a higher IRR for renal tract infection than women with MS did (2.47 vs. 1.90).
“The risk for any opportunistic infection was slightly increased among MS patients,” the researchers wrote (520 vs. 338 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.54). This was particularly true for candidiasis (252 vs. 166 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.52) and herpes virus infection (221 vs. 150 per 10,000 person-years; IRR, 1.47). “There were few cases of tuberculosis, hepatitis B infection, or hepatitis C infection,” they noted.
The study was funded by a grant from Celgene, a subsidiary of Bristol-Myers Squibb. Four authors are employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb, and one author works for a company that does business with Celgene.
SOURCE: Jick S et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P086.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2020
Endocrine Society advises on use of romosozumab for osteoporosis
Latest guidelines on the treatment of osteoporosis have been released that include new recommendations for the use of romosozumab (Evenity) in postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis, but they contain caveats as to which women should – and should not – receive the drug.
The updated clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society is in response to the approval of romosozumab by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2019, and more recently, by the European Medicines Agency.
It was published online February 18 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In the new guidelines, committee members recommend the use of romosozumab for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at very high risk of fracture. Candidates would include women with severe osteoporosis (T-score of less than –2.5 and a prior fracture) or women with a history of multiple vertebral fractures.
Women should be treated with romosozumab for up to 1 year, followed by an antiresorptive agent to maintain bone mineral density gains and further reduce fracture risk.
“The recommended dosage is 210 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection for 12 months,” the authors wrote.
However, and very importantly, romosozumab should not be considered for women at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cerebrovascular disease. A high risk of CVD includes women who have had a previous myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke.
Experts questioned by Medscape Medical News stressed that romosozumab should not be a first-line, or even generally a second-line, option for osteoporosis, but it can be a considered for select patients with severe osteoporosis, taking into account CV risk.
Boxed warning
In the Active-Controlled Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis at High Risk (ARCH), there were more major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in the first year of the trial with romosozumab, and patients had a 31% higher risk of MACE with romosozumab, compared with the bisphosphonate alendronate.
As a result, the drug was initially rejected by a number of regulatory agencies.
In the United States and Canada, it was eventually approved with a boxed warning, which cautions against the use of the drug in patients at risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD-related death.
“Romosozumab offers promising results for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis or who have a history of fractures,” Clifford Rosen, MD, Maine Medical Center Research Institute in Scarborough and chair of the writing committee, said in an Endocrine Society statement. “It does, however, come with a risk of heart disease, so clinicians need to be careful when selecting patients for this therapy.”
Exact risk unknown
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment, Kenneth Saag, MD, professor of medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham and principle investigator of the ARCH study, said that physicians needed more data from real-world studies to resolve the issue around whether romosozumab heightens the risk of CV events in women with osteoporosis or whether that particular finding from ARCH was an artifact.
“Women who have had a recent cardiovascular event should not receive the drug,” he said, agreeing with the new guidelines.
But it remains unclear, for example, whether women who are at slightly higher risk of having a CV event by virtue of their age alone, are also at risk, he noted.
In the meantime, results from the ARCH study clearly showed that not only was romosozumab more effective than alendronate, “but it is more effective than other bone-building drugs as well,” Dr. Saag observed, and it leads to a significantly greater reduction in vertebral, nonvertebral, and hip fractures, compared with the alendronate, the current standard of care in osteoporosis.
“In patients who have very severe osteoporosis and who have had a recent fracture or who are at risk for imminent future fracture, physicians need to balance the benefit versus the risk in favor of using romosozumab,” Dr. Saag suggested.
“And while I would say most women prefer not to inject themselves, the women I have put on this medicine have all had recent fractures and they are very aware of the pain and the disability of having a broken bone, so it is something they are willing to do,” he added.
Not for all women
Giving his opinion, Bart Clarke, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, underscored the fact that the Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis (FRAME), again conducted in postmenopausal women, showed no increase in CV events in patients treated with romosozumab compared with placebo.
“So there are questions about what this means, because if these events really were a drug effect, then that effect would be even more evident compared with placebo and they did not see any signal of CV events [in FRAME],” said Dr. Clarke, past president of the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research.
Like everything else in medicine, “there is always some risk,” Dr. Clarke observed.
However, what physicians should do is talk to women, ensure they have not had either an MI or stroke in the last year, and if patients have severe osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture, “then we can say, here’s another option,” he suggested.
“Then, if a woman develops chest pain or shortness of breath while on the drug, [she needs] to let us know ,and then we’ll stop the drug and reassess the situation,” he added.
Dr. Clarke also pointed out that if the FDA had received further reports of CV events linked to romosozumab, physicians would know about it by now, but to his knowledge, there has been no change to the drug’s current warning label.
Furthermore, neither he nor any of his colleagues who treat metabolic bone disease at the Mayo Clinic has seen a single CV event in patients prescribed the agent.
“This is not a drug we would use as first-line for most patients, and we don’t even use it as second-line for most patients, but in people who have not responded to other drugs or who have had terrible things happen to them already, hip fracture especially, then we are saying, you can consider this, he concluded.
The guidelines were supported by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Rosen and Dr. Clarke reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Saag reported receiving grants and personal fees from Amgen, personal fees from Radius, and is a consultant for Amgen, Radius, Roche, and Daiichi Sankyo.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Latest guidelines on the treatment of osteoporosis have been released that include new recommendations for the use of romosozumab (Evenity) in postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis, but they contain caveats as to which women should – and should not – receive the drug.
The updated clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society is in response to the approval of romosozumab by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2019, and more recently, by the European Medicines Agency.
It was published online February 18 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In the new guidelines, committee members recommend the use of romosozumab for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at very high risk of fracture. Candidates would include women with severe osteoporosis (T-score of less than –2.5 and a prior fracture) or women with a history of multiple vertebral fractures.
Women should be treated with romosozumab for up to 1 year, followed by an antiresorptive agent to maintain bone mineral density gains and further reduce fracture risk.
“The recommended dosage is 210 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection for 12 months,” the authors wrote.
However, and very importantly, romosozumab should not be considered for women at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cerebrovascular disease. A high risk of CVD includes women who have had a previous myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke.
Experts questioned by Medscape Medical News stressed that romosozumab should not be a first-line, or even generally a second-line, option for osteoporosis, but it can be a considered for select patients with severe osteoporosis, taking into account CV risk.
Boxed warning
In the Active-Controlled Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis at High Risk (ARCH), there were more major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in the first year of the trial with romosozumab, and patients had a 31% higher risk of MACE with romosozumab, compared with the bisphosphonate alendronate.
As a result, the drug was initially rejected by a number of regulatory agencies.
In the United States and Canada, it was eventually approved with a boxed warning, which cautions against the use of the drug in patients at risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD-related death.
“Romosozumab offers promising results for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis or who have a history of fractures,” Clifford Rosen, MD, Maine Medical Center Research Institute in Scarborough and chair of the writing committee, said in an Endocrine Society statement. “It does, however, come with a risk of heart disease, so clinicians need to be careful when selecting patients for this therapy.”
Exact risk unknown
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment, Kenneth Saag, MD, professor of medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham and principle investigator of the ARCH study, said that physicians needed more data from real-world studies to resolve the issue around whether romosozumab heightens the risk of CV events in women with osteoporosis or whether that particular finding from ARCH was an artifact.
“Women who have had a recent cardiovascular event should not receive the drug,” he said, agreeing with the new guidelines.
But it remains unclear, for example, whether women who are at slightly higher risk of having a CV event by virtue of their age alone, are also at risk, he noted.
In the meantime, results from the ARCH study clearly showed that not only was romosozumab more effective than alendronate, “but it is more effective than other bone-building drugs as well,” Dr. Saag observed, and it leads to a significantly greater reduction in vertebral, nonvertebral, and hip fractures, compared with the alendronate, the current standard of care in osteoporosis.
“In patients who have very severe osteoporosis and who have had a recent fracture or who are at risk for imminent future fracture, physicians need to balance the benefit versus the risk in favor of using romosozumab,” Dr. Saag suggested.
“And while I would say most women prefer not to inject themselves, the women I have put on this medicine have all had recent fractures and they are very aware of the pain and the disability of having a broken bone, so it is something they are willing to do,” he added.
Not for all women
Giving his opinion, Bart Clarke, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, underscored the fact that the Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis (FRAME), again conducted in postmenopausal women, showed no increase in CV events in patients treated with romosozumab compared with placebo.
“So there are questions about what this means, because if these events really were a drug effect, then that effect would be even more evident compared with placebo and they did not see any signal of CV events [in FRAME],” said Dr. Clarke, past president of the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research.
Like everything else in medicine, “there is always some risk,” Dr. Clarke observed.
However, what physicians should do is talk to women, ensure they have not had either an MI or stroke in the last year, and if patients have severe osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture, “then we can say, here’s another option,” he suggested.
“Then, if a woman develops chest pain or shortness of breath while on the drug, [she needs] to let us know ,and then we’ll stop the drug and reassess the situation,” he added.
Dr. Clarke also pointed out that if the FDA had received further reports of CV events linked to romosozumab, physicians would know about it by now, but to his knowledge, there has been no change to the drug’s current warning label.
Furthermore, neither he nor any of his colleagues who treat metabolic bone disease at the Mayo Clinic has seen a single CV event in patients prescribed the agent.
“This is not a drug we would use as first-line for most patients, and we don’t even use it as second-line for most patients, but in people who have not responded to other drugs or who have had terrible things happen to them already, hip fracture especially, then we are saying, you can consider this, he concluded.
The guidelines were supported by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Rosen and Dr. Clarke reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Saag reported receiving grants and personal fees from Amgen, personal fees from Radius, and is a consultant for Amgen, Radius, Roche, and Daiichi Sankyo.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Latest guidelines on the treatment of osteoporosis have been released that include new recommendations for the use of romosozumab (Evenity) in postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis, but they contain caveats as to which women should – and should not – receive the drug.
The updated clinical practice guideline from the Endocrine Society is in response to the approval of romosozumab by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2019, and more recently, by the European Medicines Agency.
It was published online February 18 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In the new guidelines, committee members recommend the use of romosozumab for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at very high risk of fracture. Candidates would include women with severe osteoporosis (T-score of less than –2.5 and a prior fracture) or women with a history of multiple vertebral fractures.
Women should be treated with romosozumab for up to 1 year, followed by an antiresorptive agent to maintain bone mineral density gains and further reduce fracture risk.
“The recommended dosage is 210 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection for 12 months,” the authors wrote.
However, and very importantly, romosozumab should not be considered for women at high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) or cerebrovascular disease. A high risk of CVD includes women who have had a previous myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke.
Experts questioned by Medscape Medical News stressed that romosozumab should not be a first-line, or even generally a second-line, option for osteoporosis, but it can be a considered for select patients with severe osteoporosis, taking into account CV risk.
Boxed warning
In the Active-Controlled Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis at High Risk (ARCH), there were more major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in the first year of the trial with romosozumab, and patients had a 31% higher risk of MACE with romosozumab, compared with the bisphosphonate alendronate.
As a result, the drug was initially rejected by a number of regulatory agencies.
In the United States and Canada, it was eventually approved with a boxed warning, which cautions against the use of the drug in patients at risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD-related death.
“Romosozumab offers promising results for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis or who have a history of fractures,” Clifford Rosen, MD, Maine Medical Center Research Institute in Scarborough and chair of the writing committee, said in an Endocrine Society statement. “It does, however, come with a risk of heart disease, so clinicians need to be careful when selecting patients for this therapy.”
Exact risk unknown
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment, Kenneth Saag, MD, professor of medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham and principle investigator of the ARCH study, said that physicians needed more data from real-world studies to resolve the issue around whether romosozumab heightens the risk of CV events in women with osteoporosis or whether that particular finding from ARCH was an artifact.
“Women who have had a recent cardiovascular event should not receive the drug,” he said, agreeing with the new guidelines.
But it remains unclear, for example, whether women who are at slightly higher risk of having a CV event by virtue of their age alone, are also at risk, he noted.
In the meantime, results from the ARCH study clearly showed that not only was romosozumab more effective than alendronate, “but it is more effective than other bone-building drugs as well,” Dr. Saag observed, and it leads to a significantly greater reduction in vertebral, nonvertebral, and hip fractures, compared with the alendronate, the current standard of care in osteoporosis.
“In patients who have very severe osteoporosis and who have had a recent fracture or who are at risk for imminent future fracture, physicians need to balance the benefit versus the risk in favor of using romosozumab,” Dr. Saag suggested.
“And while I would say most women prefer not to inject themselves, the women I have put on this medicine have all had recent fractures and they are very aware of the pain and the disability of having a broken bone, so it is something they are willing to do,” he added.
Not for all women
Giving his opinion, Bart Clarke, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, underscored the fact that the Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis (FRAME), again conducted in postmenopausal women, showed no increase in CV events in patients treated with romosozumab compared with placebo.
“So there are questions about what this means, because if these events really were a drug effect, then that effect would be even more evident compared with placebo and they did not see any signal of CV events [in FRAME],” said Dr. Clarke, past president of the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research.
Like everything else in medicine, “there is always some risk,” Dr. Clarke observed.
However, what physicians should do is talk to women, ensure they have not had either an MI or stroke in the last year, and if patients have severe osteoporosis and a high risk of fracture, “then we can say, here’s another option,” he suggested.
“Then, if a woman develops chest pain or shortness of breath while on the drug, [she needs] to let us know ,and then we’ll stop the drug and reassess the situation,” he added.
Dr. Clarke also pointed out that if the FDA had received further reports of CV events linked to romosozumab, physicians would know about it by now, but to his knowledge, there has been no change to the drug’s current warning label.
Furthermore, neither he nor any of his colleagues who treat metabolic bone disease at the Mayo Clinic has seen a single CV event in patients prescribed the agent.
“This is not a drug we would use as first-line for most patients, and we don’t even use it as second-line for most patients, but in people who have not responded to other drugs or who have had terrible things happen to them already, hip fracture especially, then we are saying, you can consider this, he concluded.
The guidelines were supported by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Rosen and Dr. Clarke reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Saag reported receiving grants and personal fees from Amgen, personal fees from Radius, and is a consultant for Amgen, Radius, Roche, and Daiichi Sankyo.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM
Abbreviated MRI bests digital breast tomosynthesis in finding cancer in dense breasts
For women with dense breasts, abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging was more effective than was digital breast tomosynthesis for detecting invasive breast cancer in a cross-sectional study of 1,444 women who underwent both procedures.
Dense breasts are a common reason for failed early diagnosis of breast cancer, wrote Christopher E. Comstock, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are becoming more popular as safe and cost-effective breast cancer screening options, but their effectiveness in women with dense breasts and average breast cancer risk has not been compared.
The researchers reviewed data from 1,444 women aged 40-75 years at 47 institutions in the United States and 1 in Germany. The women underwent both DBT and MRI. The primary endpoint was the detection of invasive cancers, of which 17 were identified at baseline screening. Abbreviated breast MRI detected all 17 cases of invasive cancer, compared with 7 detected by DBT. In addition, MRI detected six of seven women with ductal carcinoma in situ, while DBT identified two of the seven cases, according to the study, which was published in JAMA.
Overall, the invasive cancer detection rate was 11.8 per 1,000 women for MRI compared with 4.8 per 1,000 women for DBT. Sensitivity for MRI and DBT was 96% vs. 39%, and specificity was 87% vs. 97%.
The rate of recommendation for further screening was not significantly different between the procedures (8% for MRI and 10% for DBT). The most common adverse events were three cases of mild allergic reactions and two cases of anxiety.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show an association between abbreviated breast MRI and breast cancer mortality and the lack of cost-effectiveness comparisons for the two procedures. Because eligibility criteria required a prior breast mammogram to see if the breasts were dense, the study compared an incidence DBT screen to a prevalence abbreviated MRI screen, Dr. Comstock and associates noted.
However, the results show a significantly increased breast cancer detection rate with abbreviated MRI, which merits additional research to examine the relationship between screening strategies and clinical outcomes for women with dense breasts, they said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, and by Bracco Diagnostics through funding to the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group. Dr. Comstock disclosed financial relationships with Bracco Diagnostics and Bayer, and three coauthors disclosed financial relationships with other imaging companies. The remaining coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Comstock CK et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.0572.
For women with dense breasts, abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging was more effective than was digital breast tomosynthesis for detecting invasive breast cancer in a cross-sectional study of 1,444 women who underwent both procedures.
Dense breasts are a common reason for failed early diagnosis of breast cancer, wrote Christopher E. Comstock, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are becoming more popular as safe and cost-effective breast cancer screening options, but their effectiveness in women with dense breasts and average breast cancer risk has not been compared.
The researchers reviewed data from 1,444 women aged 40-75 years at 47 institutions in the United States and 1 in Germany. The women underwent both DBT and MRI. The primary endpoint was the detection of invasive cancers, of which 17 were identified at baseline screening. Abbreviated breast MRI detected all 17 cases of invasive cancer, compared with 7 detected by DBT. In addition, MRI detected six of seven women with ductal carcinoma in situ, while DBT identified two of the seven cases, according to the study, which was published in JAMA.
Overall, the invasive cancer detection rate was 11.8 per 1,000 women for MRI compared with 4.8 per 1,000 women for DBT. Sensitivity for MRI and DBT was 96% vs. 39%, and specificity was 87% vs. 97%.
The rate of recommendation for further screening was not significantly different between the procedures (8% for MRI and 10% for DBT). The most common adverse events were three cases of mild allergic reactions and two cases of anxiety.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show an association between abbreviated breast MRI and breast cancer mortality and the lack of cost-effectiveness comparisons for the two procedures. Because eligibility criteria required a prior breast mammogram to see if the breasts were dense, the study compared an incidence DBT screen to a prevalence abbreviated MRI screen, Dr. Comstock and associates noted.
However, the results show a significantly increased breast cancer detection rate with abbreviated MRI, which merits additional research to examine the relationship between screening strategies and clinical outcomes for women with dense breasts, they said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, and by Bracco Diagnostics through funding to the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group. Dr. Comstock disclosed financial relationships with Bracco Diagnostics and Bayer, and three coauthors disclosed financial relationships with other imaging companies. The remaining coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Comstock CK et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.0572.
For women with dense breasts, abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging was more effective than was digital breast tomosynthesis for detecting invasive breast cancer in a cross-sectional study of 1,444 women who underwent both procedures.
Dense breasts are a common reason for failed early diagnosis of breast cancer, wrote Christopher E. Comstock, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are becoming more popular as safe and cost-effective breast cancer screening options, but their effectiveness in women with dense breasts and average breast cancer risk has not been compared.
The researchers reviewed data from 1,444 women aged 40-75 years at 47 institutions in the United States and 1 in Germany. The women underwent both DBT and MRI. The primary endpoint was the detection of invasive cancers, of which 17 were identified at baseline screening. Abbreviated breast MRI detected all 17 cases of invasive cancer, compared with 7 detected by DBT. In addition, MRI detected six of seven women with ductal carcinoma in situ, while DBT identified two of the seven cases, according to the study, which was published in JAMA.
Overall, the invasive cancer detection rate was 11.8 per 1,000 women for MRI compared with 4.8 per 1,000 women for DBT. Sensitivity for MRI and DBT was 96% vs. 39%, and specificity was 87% vs. 97%.
The rate of recommendation for further screening was not significantly different between the procedures (8% for MRI and 10% for DBT). The most common adverse events were three cases of mild allergic reactions and two cases of anxiety.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to show an association between abbreviated breast MRI and breast cancer mortality and the lack of cost-effectiveness comparisons for the two procedures. Because eligibility criteria required a prior breast mammogram to see if the breasts were dense, the study compared an incidence DBT screen to a prevalence abbreviated MRI screen, Dr. Comstock and associates noted.
However, the results show a significantly increased breast cancer detection rate with abbreviated MRI, which merits additional research to examine the relationship between screening strategies and clinical outcomes for women with dense breasts, they said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, and by Bracco Diagnostics through funding to the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group. Dr. Comstock disclosed financial relationships with Bracco Diagnostics and Bayer, and three coauthors disclosed financial relationships with other imaging companies. The remaining coauthors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Comstock CK et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.0572.
FROM JAMA
Understanding the cervicovaginal microbiome and how it affects preterm birth
Prematurity remains the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality, accounting for $26 billion a year in immediate costs, despite the implementation in obstetrics of a host of risk stratification algorithms and strategies for risk reduction, including the use of some medications.
It now is questionable whether injectable 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate (Makena) truly is efficacious in women who’ve had a prior spontaneous preterm birth (sPTB) – a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee last year recommended withdrawing it from the market based on results of an FDA confirmatory study. Even if the drug were efficacious, only a small percentage of the women who have an sPTB have had a prior one. The majority of sPTB occurs among women without such a history.
Vaginal progesterone appears to confer some protection in women found to have a short cervix during the second trimester, but this approach also has limited reach: Only 9% of women with sPTB had an antecedent short cervix in a 2017 study.1 Like a history of sPTB, screening for short cervical length is a potentially helpful strategy for risk reduction, but it is not a strategy that will significantly impact the overall rate of prematurity.
We’ve fallen short in our goals to significantly reduce the public health impact of prematurity partly because we still do not understand the exact pathways and mechanisms by which sPTB occurs. The main working paradigm for myself and many other researchers over the past 2 decades has centered on infection in the uterus triggering inflammation, followed by cervical remodeling and ripening. Research in animal models, as well as human clinical trials targeting various infections and inflammation, have led to some insights and discoveries, but no successful interventions.
In the past decade, however, our research framework for understanding sPTB incorporates new questions about immunologic, microbiological, and molecular/cellular events that happen in the cervicovaginal space. We’ve learned more about the cervicovaginal microbiota, and most recently, our research at the University of Pennsylvania has elucidated the role that nonoptimal bacteria play in disrupting the cervical endothelial barrier and initiating the process of cervical remodeling that likely precedes sPTB.
We also know that this association is stronger in black women and may help explain some of the observed racial disparities in sPTB. Although more research is needed to determine specific therapeutic strategies, new doors are open.
Host immune-microbial interactions
This new research paradigm has involved stepping back and asking basic questions, such as, what do we really know about the cervicovaginal space? In actuality, we know very little. We know little about the immune function of the vaginal and cervical epithelial cells in pregnancy, for instance, and there is a large gap in knowledge regarding the biomechanics of the cervix – a remarkable organ that can change shape and function in a matter of minutes. Studies on the biomechanics of the cervix during pregnancy and in labor are still in their infancy.
However, lessons can be drawn from research on inflammatory bowel disease and other disorders involving the gut. In the gastrointestinal tract, epithelial cells have been found to act as sentinels, forming a mucosal barrier against bacterial pathogens and secreting various immune factors. Research in this field also has shown that microbes living in the gut produce metabolites; that these microbial metabolites may be the key messengers from the microbial communities to the epithelial barrier; and that the microbes, microbial metabolites, and immune responses are responsible for triggering inflammatory processes in the tissues underneath.
In 2011, Jacques Ravel, PhD, who was part of the National Institutes of Health’s Human Microbiome Project, characterized the vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women for the first time.2 His paper classified the vaginal microbial communities of approximately 400 asymptomatic women of various ethnicities into five “community state types” (CSTs) based on the predominant bacteria found in the cervicovaginal space.3
On the heels of his research, Dr. Ravel and I launched an NIH-funded study involving a prospective cohort of 2,000 women with singleton pregnancies – the Motherhood & Microbiome cohort – to look at the cervicovaginal microbiota, the local immune response, and the risk of sPTB.4 Cervicovaginal samples were collected at 16-20 weeks’ gestation and during two subsequent clinical visits. From this cohort, which was composed mostly of African American women (74.5%), we conducted a nested case-controlled study of 103 cases of sPTB and 432 women who delivered at term, matched for race.
We carefully adjudicated the deliveries in our 2,000-person cohort so that we homed in on sPTB as opposed to preterm births that are medically indicated for reasons such as fetal distress or preeclampsia. (Several prior studies looking at the associations between the cervicovaginal microbiome had a heterogeneous phenotyping of PTB that made it hard to draw definitive conclusions.)
Our focus in assessing the microbiome and immunologic profiles was on the samples collected at the earliest time points in pregnancy because we hoped to detect a “signature” that could predict an outcome months later. Indeed, we found that the nonoptimal microbiota, known in microbiological terms as CST IV, was associated with about a 150% increased risk of sPTB. This community comprises a dominant array of anaerobic bacteria and a paucity of Lactobacillus species.
We also found that a larger proportion of African American women, compared with non–African American women, had this nonoptimal microbiota early in pregnancy (40% vs. 15%), which is consistent with previous studies in pregnancy and nonpregnancy showing lower levels of Lactobacillus species in the cervicovaginal microbiome of African American women.
Even more interesting was the finding that, although the rate of sPTB was higher in African American women and the effect of CST IV on sPTB was stronger in these women, the risk of sPTB couldn’t be explained solely by the presence of CST IV. Some women with this nonoptimal microbiome delivered at term, whereas others with more optimal microbiome types had sPTBs. This suggests that other factors contribute to African American women having a nonoptimal microbiota and being especially predisposed to sPTB.
Through the study’s immunologic profiling, we found a significant difference in the cervicovaginal levels of an immune factor, beta-defensin 2, between African American women who delivered at term and those who had a sPTB. Women who had a sPTB, even those who had higher levels of Lactobacillus species, had lower levels of beta-defensin 2. This association was not found in non–African American women.
Beta-defensin 2 is a host-derived antimicrobial peptide that, like other antimicrobial peptides, works at epithelial-mucosal barriers to combat bacteria; we have knowledge of its action from research on the gut, as well as some studies of the vaginal space in nonpregnant women that have focused on sexually transmitted infections.
Most exciting for us was the finding that higher levels of beta-defensin 2 appeared to lower the risk of sPTB in women who had a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota. There’s an interplay between the host and the microbiota, in other words, and it’s one that could be essential to manipulate as we seek to reduce sPTB.
The cervical epithelial barrier
In the laboratory, meanwhile, we are learning how certain microbes are mechanistically involved in the pathogenesis of sPTB. Research over the last decade has suggested that disruption or breakdown of the cervical epithelial barrier drives cervical remodeling processes that precede sPTB. The question now is, do cervicovaginal bacteria associated with sPTB, or a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota, cause disruption of the vaginal and cervical epithelial barrier – and how?
Using an in vitro model system, we found that Mobiluncus curtisii/mulieris, the bacterial taxa with the strongest association with sPTB in our Motherhood & Microbiome cohort and one that has long been associated with bacterial vaginosis, had a plethora of effects. It increased cell permeability and the expression of inflammatory mediators associated with cervical epithelial breakdown, and it altered expression of microRNAs that have been associated with sPTB in human studies.
Our study on Mobiluncus has served as proof of concept to us that, not only is the bacteria associated with sPTB, but that there are multiple mechanisms by which it can disrupt the cervicovaginal barrier and lead to cervical remodeling.5
The findings echo previous in vitro research on Gardnerella vaginalis, another anaerobic bacterium that has been associated with bacterial vaginosis and adverse obstetric outcomes, including sPTB.6 Using similar models, we found that G. vaginalis disrupts the cervical epithelial barrier through diverse mechanisms including the cleavage of certain proteins, the up-regulation of proinflammatory immune mediators, and altered gene expression.
Lactobacillus crispatus, on the other hand, conferred protection to the cervical epithelial barrier in this study by mitigating various G. vaginalis–induced effects.
Learning more about host-microbe interactions and the role of microbial metabolites in these interactions, as well as the role of altered gene expression in cervical function, will help us to more fully understand the biological mechanisms regulating cervicovaginal epithelial cells. At this point, we know that, as in the gut, bacteria commonly found in the cervicovaginal space play a significant role in regulating the function of epithelial cells (in both optimal and nonoptimal microbiota), and that various bacteria associated with sPTB contribute to poor outcomes by breaking down the cervical epithelium.
Therapeutic implications
Our growing knowledge of the cervicovaginal microbiota does not yet support screening or any particular interventions. We don’t know, for instance, that administering probiotics or prebiotics orally or vaginally will have any effect on rates of sPTB.
Ongoing research at all levels holds promise, however, for the development of diagnostics to identify women at risk for sPTB, and for the development of therapeutic strategies that aim to modify the microbiome and/or modify the immune response. We know from other areas of medicine that there are realistic ways to modulate the immune response and/or microbiota in a system to alter risk.
We need to more thoroughly understand the risk of particular microbiota and immune response factors – and how they vary by race and ethnicity – and we need to study the cervicovaginal microbiota of women before and during pregnancy to learn whether there is something about pregnancy or even about intercourse that can change one’s microbiome to a less favorable state.
It may well be possible in the near future to identify high-risk states of nonoptimal microbiota before conception – microbiota that, in and of themselves, may not be pathogenic but that become detrimental during pregnancy – and it should be possible to screen women early in pregnancy for microbial or immune signatures or both.
The question often arises in medicine of the validity of screening without having achieved certainty about treatments. However, in obstetrics, where we have different levels of care and the ability to personalize monitoring and care, identifying those at greatest risk still has value. Ultimately, with enough investment in all levels of research (basic, translational, and clinical), we can develop interventions and therapeutics that address a biologically plausible mechanism of sPTB and, as a result, achieve significant reductions in the rate of prematurity.
Dr. Elovitz is the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She disclosed holding a patent on a method to determine risk of preterm birth that relates to the microbiome. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. JAMA. 2017 Mar 14;317(10):1047-56.
2. NIH Human Microbiome Project. https://hmpdacc.org/.
3. PNAS. 2011 Mar 15;108 (Supplement 1):4680-7.
4. Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 21. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09285-9.
5. Anaerobe. 2019 Nov 21. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102127.
6. Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02181.
Prematurity remains the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality, accounting for $26 billion a year in immediate costs, despite the implementation in obstetrics of a host of risk stratification algorithms and strategies for risk reduction, including the use of some medications.
It now is questionable whether injectable 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate (Makena) truly is efficacious in women who’ve had a prior spontaneous preterm birth (sPTB) – a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee last year recommended withdrawing it from the market based on results of an FDA confirmatory study. Even if the drug were efficacious, only a small percentage of the women who have an sPTB have had a prior one. The majority of sPTB occurs among women without such a history.
Vaginal progesterone appears to confer some protection in women found to have a short cervix during the second trimester, but this approach also has limited reach: Only 9% of women with sPTB had an antecedent short cervix in a 2017 study.1 Like a history of sPTB, screening for short cervical length is a potentially helpful strategy for risk reduction, but it is not a strategy that will significantly impact the overall rate of prematurity.
We’ve fallen short in our goals to significantly reduce the public health impact of prematurity partly because we still do not understand the exact pathways and mechanisms by which sPTB occurs. The main working paradigm for myself and many other researchers over the past 2 decades has centered on infection in the uterus triggering inflammation, followed by cervical remodeling and ripening. Research in animal models, as well as human clinical trials targeting various infections and inflammation, have led to some insights and discoveries, but no successful interventions.
In the past decade, however, our research framework for understanding sPTB incorporates new questions about immunologic, microbiological, and molecular/cellular events that happen in the cervicovaginal space. We’ve learned more about the cervicovaginal microbiota, and most recently, our research at the University of Pennsylvania has elucidated the role that nonoptimal bacteria play in disrupting the cervical endothelial barrier and initiating the process of cervical remodeling that likely precedes sPTB.
We also know that this association is stronger in black women and may help explain some of the observed racial disparities in sPTB. Although more research is needed to determine specific therapeutic strategies, new doors are open.
Host immune-microbial interactions
This new research paradigm has involved stepping back and asking basic questions, such as, what do we really know about the cervicovaginal space? In actuality, we know very little. We know little about the immune function of the vaginal and cervical epithelial cells in pregnancy, for instance, and there is a large gap in knowledge regarding the biomechanics of the cervix – a remarkable organ that can change shape and function in a matter of minutes. Studies on the biomechanics of the cervix during pregnancy and in labor are still in their infancy.
However, lessons can be drawn from research on inflammatory bowel disease and other disorders involving the gut. In the gastrointestinal tract, epithelial cells have been found to act as sentinels, forming a mucosal barrier against bacterial pathogens and secreting various immune factors. Research in this field also has shown that microbes living in the gut produce metabolites; that these microbial metabolites may be the key messengers from the microbial communities to the epithelial barrier; and that the microbes, microbial metabolites, and immune responses are responsible for triggering inflammatory processes in the tissues underneath.
In 2011, Jacques Ravel, PhD, who was part of the National Institutes of Health’s Human Microbiome Project, characterized the vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women for the first time.2 His paper classified the vaginal microbial communities of approximately 400 asymptomatic women of various ethnicities into five “community state types” (CSTs) based on the predominant bacteria found in the cervicovaginal space.3
On the heels of his research, Dr. Ravel and I launched an NIH-funded study involving a prospective cohort of 2,000 women with singleton pregnancies – the Motherhood & Microbiome cohort – to look at the cervicovaginal microbiota, the local immune response, and the risk of sPTB.4 Cervicovaginal samples were collected at 16-20 weeks’ gestation and during two subsequent clinical visits. From this cohort, which was composed mostly of African American women (74.5%), we conducted a nested case-controlled study of 103 cases of sPTB and 432 women who delivered at term, matched for race.
We carefully adjudicated the deliveries in our 2,000-person cohort so that we homed in on sPTB as opposed to preterm births that are medically indicated for reasons such as fetal distress or preeclampsia. (Several prior studies looking at the associations between the cervicovaginal microbiome had a heterogeneous phenotyping of PTB that made it hard to draw definitive conclusions.)
Our focus in assessing the microbiome and immunologic profiles was on the samples collected at the earliest time points in pregnancy because we hoped to detect a “signature” that could predict an outcome months later. Indeed, we found that the nonoptimal microbiota, known in microbiological terms as CST IV, was associated with about a 150% increased risk of sPTB. This community comprises a dominant array of anaerobic bacteria and a paucity of Lactobacillus species.
We also found that a larger proportion of African American women, compared with non–African American women, had this nonoptimal microbiota early in pregnancy (40% vs. 15%), which is consistent with previous studies in pregnancy and nonpregnancy showing lower levels of Lactobacillus species in the cervicovaginal microbiome of African American women.
Even more interesting was the finding that, although the rate of sPTB was higher in African American women and the effect of CST IV on sPTB was stronger in these women, the risk of sPTB couldn’t be explained solely by the presence of CST IV. Some women with this nonoptimal microbiome delivered at term, whereas others with more optimal microbiome types had sPTBs. This suggests that other factors contribute to African American women having a nonoptimal microbiota and being especially predisposed to sPTB.
Through the study’s immunologic profiling, we found a significant difference in the cervicovaginal levels of an immune factor, beta-defensin 2, between African American women who delivered at term and those who had a sPTB. Women who had a sPTB, even those who had higher levels of Lactobacillus species, had lower levels of beta-defensin 2. This association was not found in non–African American women.
Beta-defensin 2 is a host-derived antimicrobial peptide that, like other antimicrobial peptides, works at epithelial-mucosal barriers to combat bacteria; we have knowledge of its action from research on the gut, as well as some studies of the vaginal space in nonpregnant women that have focused on sexually transmitted infections.
Most exciting for us was the finding that higher levels of beta-defensin 2 appeared to lower the risk of sPTB in women who had a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota. There’s an interplay between the host and the microbiota, in other words, and it’s one that could be essential to manipulate as we seek to reduce sPTB.
The cervical epithelial barrier
In the laboratory, meanwhile, we are learning how certain microbes are mechanistically involved in the pathogenesis of sPTB. Research over the last decade has suggested that disruption or breakdown of the cervical epithelial barrier drives cervical remodeling processes that precede sPTB. The question now is, do cervicovaginal bacteria associated with sPTB, or a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota, cause disruption of the vaginal and cervical epithelial barrier – and how?
Using an in vitro model system, we found that Mobiluncus curtisii/mulieris, the bacterial taxa with the strongest association with sPTB in our Motherhood & Microbiome cohort and one that has long been associated with bacterial vaginosis, had a plethora of effects. It increased cell permeability and the expression of inflammatory mediators associated with cervical epithelial breakdown, and it altered expression of microRNAs that have been associated with sPTB in human studies.
Our study on Mobiluncus has served as proof of concept to us that, not only is the bacteria associated with sPTB, but that there are multiple mechanisms by which it can disrupt the cervicovaginal barrier and lead to cervical remodeling.5
The findings echo previous in vitro research on Gardnerella vaginalis, another anaerobic bacterium that has been associated with bacterial vaginosis and adverse obstetric outcomes, including sPTB.6 Using similar models, we found that G. vaginalis disrupts the cervical epithelial barrier through diverse mechanisms including the cleavage of certain proteins, the up-regulation of proinflammatory immune mediators, and altered gene expression.
Lactobacillus crispatus, on the other hand, conferred protection to the cervical epithelial barrier in this study by mitigating various G. vaginalis–induced effects.
Learning more about host-microbe interactions and the role of microbial metabolites in these interactions, as well as the role of altered gene expression in cervical function, will help us to more fully understand the biological mechanisms regulating cervicovaginal epithelial cells. At this point, we know that, as in the gut, bacteria commonly found in the cervicovaginal space play a significant role in regulating the function of epithelial cells (in both optimal and nonoptimal microbiota), and that various bacteria associated with sPTB contribute to poor outcomes by breaking down the cervical epithelium.
Therapeutic implications
Our growing knowledge of the cervicovaginal microbiota does not yet support screening or any particular interventions. We don’t know, for instance, that administering probiotics or prebiotics orally or vaginally will have any effect on rates of sPTB.
Ongoing research at all levels holds promise, however, for the development of diagnostics to identify women at risk for sPTB, and for the development of therapeutic strategies that aim to modify the microbiome and/or modify the immune response. We know from other areas of medicine that there are realistic ways to modulate the immune response and/or microbiota in a system to alter risk.
We need to more thoroughly understand the risk of particular microbiota and immune response factors – and how they vary by race and ethnicity – and we need to study the cervicovaginal microbiota of women before and during pregnancy to learn whether there is something about pregnancy or even about intercourse that can change one’s microbiome to a less favorable state.
It may well be possible in the near future to identify high-risk states of nonoptimal microbiota before conception – microbiota that, in and of themselves, may not be pathogenic but that become detrimental during pregnancy – and it should be possible to screen women early in pregnancy for microbial or immune signatures or both.
The question often arises in medicine of the validity of screening without having achieved certainty about treatments. However, in obstetrics, where we have different levels of care and the ability to personalize monitoring and care, identifying those at greatest risk still has value. Ultimately, with enough investment in all levels of research (basic, translational, and clinical), we can develop interventions and therapeutics that address a biologically plausible mechanism of sPTB and, as a result, achieve significant reductions in the rate of prematurity.
Dr. Elovitz is the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She disclosed holding a patent on a method to determine risk of preterm birth that relates to the microbiome. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. JAMA. 2017 Mar 14;317(10):1047-56.
2. NIH Human Microbiome Project. https://hmpdacc.org/.
3. PNAS. 2011 Mar 15;108 (Supplement 1):4680-7.
4. Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 21. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09285-9.
5. Anaerobe. 2019 Nov 21. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102127.
6. Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02181.
Prematurity remains the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality, accounting for $26 billion a year in immediate costs, despite the implementation in obstetrics of a host of risk stratification algorithms and strategies for risk reduction, including the use of some medications.
It now is questionable whether injectable 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate (Makena) truly is efficacious in women who’ve had a prior spontaneous preterm birth (sPTB) – a Food and Drug Administration advisory committee last year recommended withdrawing it from the market based on results of an FDA confirmatory study. Even if the drug were efficacious, only a small percentage of the women who have an sPTB have had a prior one. The majority of sPTB occurs among women without such a history.
Vaginal progesterone appears to confer some protection in women found to have a short cervix during the second trimester, but this approach also has limited reach: Only 9% of women with sPTB had an antecedent short cervix in a 2017 study.1 Like a history of sPTB, screening for short cervical length is a potentially helpful strategy for risk reduction, but it is not a strategy that will significantly impact the overall rate of prematurity.
We’ve fallen short in our goals to significantly reduce the public health impact of prematurity partly because we still do not understand the exact pathways and mechanisms by which sPTB occurs. The main working paradigm for myself and many other researchers over the past 2 decades has centered on infection in the uterus triggering inflammation, followed by cervical remodeling and ripening. Research in animal models, as well as human clinical trials targeting various infections and inflammation, have led to some insights and discoveries, but no successful interventions.
In the past decade, however, our research framework for understanding sPTB incorporates new questions about immunologic, microbiological, and molecular/cellular events that happen in the cervicovaginal space. We’ve learned more about the cervicovaginal microbiota, and most recently, our research at the University of Pennsylvania has elucidated the role that nonoptimal bacteria play in disrupting the cervical endothelial barrier and initiating the process of cervical remodeling that likely precedes sPTB.
We also know that this association is stronger in black women and may help explain some of the observed racial disparities in sPTB. Although more research is needed to determine specific therapeutic strategies, new doors are open.
Host immune-microbial interactions
This new research paradigm has involved stepping back and asking basic questions, such as, what do we really know about the cervicovaginal space? In actuality, we know very little. We know little about the immune function of the vaginal and cervical epithelial cells in pregnancy, for instance, and there is a large gap in knowledge regarding the biomechanics of the cervix – a remarkable organ that can change shape and function in a matter of minutes. Studies on the biomechanics of the cervix during pregnancy and in labor are still in their infancy.
However, lessons can be drawn from research on inflammatory bowel disease and other disorders involving the gut. In the gastrointestinal tract, epithelial cells have been found to act as sentinels, forming a mucosal barrier against bacterial pathogens and secreting various immune factors. Research in this field also has shown that microbes living in the gut produce metabolites; that these microbial metabolites may be the key messengers from the microbial communities to the epithelial barrier; and that the microbes, microbial metabolites, and immune responses are responsible for triggering inflammatory processes in the tissues underneath.
In 2011, Jacques Ravel, PhD, who was part of the National Institutes of Health’s Human Microbiome Project, characterized the vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women for the first time.2 His paper classified the vaginal microbial communities of approximately 400 asymptomatic women of various ethnicities into five “community state types” (CSTs) based on the predominant bacteria found in the cervicovaginal space.3
On the heels of his research, Dr. Ravel and I launched an NIH-funded study involving a prospective cohort of 2,000 women with singleton pregnancies – the Motherhood & Microbiome cohort – to look at the cervicovaginal microbiota, the local immune response, and the risk of sPTB.4 Cervicovaginal samples were collected at 16-20 weeks’ gestation and during two subsequent clinical visits. From this cohort, which was composed mostly of African American women (74.5%), we conducted a nested case-controlled study of 103 cases of sPTB and 432 women who delivered at term, matched for race.
We carefully adjudicated the deliveries in our 2,000-person cohort so that we homed in on sPTB as opposed to preterm births that are medically indicated for reasons such as fetal distress or preeclampsia. (Several prior studies looking at the associations between the cervicovaginal microbiome had a heterogeneous phenotyping of PTB that made it hard to draw definitive conclusions.)
Our focus in assessing the microbiome and immunologic profiles was on the samples collected at the earliest time points in pregnancy because we hoped to detect a “signature” that could predict an outcome months later. Indeed, we found that the nonoptimal microbiota, known in microbiological terms as CST IV, was associated with about a 150% increased risk of sPTB. This community comprises a dominant array of anaerobic bacteria and a paucity of Lactobacillus species.
We also found that a larger proportion of African American women, compared with non–African American women, had this nonoptimal microbiota early in pregnancy (40% vs. 15%), which is consistent with previous studies in pregnancy and nonpregnancy showing lower levels of Lactobacillus species in the cervicovaginal microbiome of African American women.
Even more interesting was the finding that, although the rate of sPTB was higher in African American women and the effect of CST IV on sPTB was stronger in these women, the risk of sPTB couldn’t be explained solely by the presence of CST IV. Some women with this nonoptimal microbiome delivered at term, whereas others with more optimal microbiome types had sPTBs. This suggests that other factors contribute to African American women having a nonoptimal microbiota and being especially predisposed to sPTB.
Through the study’s immunologic profiling, we found a significant difference in the cervicovaginal levels of an immune factor, beta-defensin 2, between African American women who delivered at term and those who had a sPTB. Women who had a sPTB, even those who had higher levels of Lactobacillus species, had lower levels of beta-defensin 2. This association was not found in non–African American women.
Beta-defensin 2 is a host-derived antimicrobial peptide that, like other antimicrobial peptides, works at epithelial-mucosal barriers to combat bacteria; we have knowledge of its action from research on the gut, as well as some studies of the vaginal space in nonpregnant women that have focused on sexually transmitted infections.
Most exciting for us was the finding that higher levels of beta-defensin 2 appeared to lower the risk of sPTB in women who had a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota. There’s an interplay between the host and the microbiota, in other words, and it’s one that could be essential to manipulate as we seek to reduce sPTB.
The cervical epithelial barrier
In the laboratory, meanwhile, we are learning how certain microbes are mechanistically involved in the pathogenesis of sPTB. Research over the last decade has suggested that disruption or breakdown of the cervical epithelial barrier drives cervical remodeling processes that precede sPTB. The question now is, do cervicovaginal bacteria associated with sPTB, or a nonoptimal cervicovaginal microbiota, cause disruption of the vaginal and cervical epithelial barrier – and how?
Using an in vitro model system, we found that Mobiluncus curtisii/mulieris, the bacterial taxa with the strongest association with sPTB in our Motherhood & Microbiome cohort and one that has long been associated with bacterial vaginosis, had a plethora of effects. It increased cell permeability and the expression of inflammatory mediators associated with cervical epithelial breakdown, and it altered expression of microRNAs that have been associated with sPTB in human studies.
Our study on Mobiluncus has served as proof of concept to us that, not only is the bacteria associated with sPTB, but that there are multiple mechanisms by which it can disrupt the cervicovaginal barrier and lead to cervical remodeling.5
The findings echo previous in vitro research on Gardnerella vaginalis, another anaerobic bacterium that has been associated with bacterial vaginosis and adverse obstetric outcomes, including sPTB.6 Using similar models, we found that G. vaginalis disrupts the cervical epithelial barrier through diverse mechanisms including the cleavage of certain proteins, the up-regulation of proinflammatory immune mediators, and altered gene expression.
Lactobacillus crispatus, on the other hand, conferred protection to the cervical epithelial barrier in this study by mitigating various G. vaginalis–induced effects.
Learning more about host-microbe interactions and the role of microbial metabolites in these interactions, as well as the role of altered gene expression in cervical function, will help us to more fully understand the biological mechanisms regulating cervicovaginal epithelial cells. At this point, we know that, as in the gut, bacteria commonly found in the cervicovaginal space play a significant role in regulating the function of epithelial cells (in both optimal and nonoptimal microbiota), and that various bacteria associated with sPTB contribute to poor outcomes by breaking down the cervical epithelium.
Therapeutic implications
Our growing knowledge of the cervicovaginal microbiota does not yet support screening or any particular interventions. We don’t know, for instance, that administering probiotics or prebiotics orally or vaginally will have any effect on rates of sPTB.
Ongoing research at all levels holds promise, however, for the development of diagnostics to identify women at risk for sPTB, and for the development of therapeutic strategies that aim to modify the microbiome and/or modify the immune response. We know from other areas of medicine that there are realistic ways to modulate the immune response and/or microbiota in a system to alter risk.
We need to more thoroughly understand the risk of particular microbiota and immune response factors – and how they vary by race and ethnicity – and we need to study the cervicovaginal microbiota of women before and during pregnancy to learn whether there is something about pregnancy or even about intercourse that can change one’s microbiome to a less favorable state.
It may well be possible in the near future to identify high-risk states of nonoptimal microbiota before conception – microbiota that, in and of themselves, may not be pathogenic but that become detrimental during pregnancy – and it should be possible to screen women early in pregnancy for microbial or immune signatures or both.
The question often arises in medicine of the validity of screening without having achieved certainty about treatments. However, in obstetrics, where we have different levels of care and the ability to personalize monitoring and care, identifying those at greatest risk still has value. Ultimately, with enough investment in all levels of research (basic, translational, and clinical), we can develop interventions and therapeutics that address a biologically plausible mechanism of sPTB and, as a result, achieve significant reductions in the rate of prematurity.
Dr. Elovitz is the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. She disclosed holding a patent on a method to determine risk of preterm birth that relates to the microbiome. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. JAMA. 2017 Mar 14;317(10):1047-56.
2. NIH Human Microbiome Project. https://hmpdacc.org/.
3. PNAS. 2011 Mar 15;108 (Supplement 1):4680-7.
4. Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 21. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09285-9.
5. Anaerobe. 2019 Nov 21. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102127.
6. Front Microbiol. 2018 Oct 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02181.
Preterm birth: Under the microscope
Preventing infant mortality remains a significant challenge for ob.gyns. Despite the availability of a multitude of preventive and treatment options and some of the best possible medical care offered in the world, the United States lags behind many other developed and developing countries in its rate of infant deaths, which was an estimated 5.8 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2017. We can, and must, do better.
One of the major contributing factors to infant mortality is preterm birth. Defined as birth occurring prior to 37 weeks’ gestation, preterm birth is associated with a myriad of severe neonatal sequelae: low birth weight, bacterial sepsis, neonatal hemorrhage, and respiratory distress syndrome, among others. Therefore, many within the clinical and biomedical research spheres recognize that preventing preterm birth means reducing infant deaths.
However, therein lies the conundrum. We know very little about what causes preterm birth, which renders the current therapeutic strategies – such as use of progesterone supplements or cerclage placement – good for some but not all patients. It is thus vital to continue research to unravel the underlying mechanisms of preterm birth.
A promising area of investigation is the field of microbiome research, which has made great strides in advancing our awareness of the critical role of the millions of organisms living on and within us in maintaining health and fighting disease. For example, we now realize that eradicating all the commensals in our gastrointestinal tract has unintended and very negative consequences and, for patients whose good bacteria have been eliminated, fecal transplant is a therapeutic option. Therefore, it stands to reason that the microbes found in the vagina contribute significantly to women’s overall reproductive health.
The publication of the groundbreaking study characterizing the vaginal microbiome species in reproductive-age women opened new avenues of research into how these organisms contribute to women’s health. Importantly, this work, led initially by Jacques Ravel, PhD, a professor in the department of microbiology & immunology and associate director of the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, has spawned additional investigations into the potential role of the vaginal microbiome in preterm birth.
To provide some insight into the research around how the microorganisms in the vagina may induce or prevent preterm birth is our guest author, Michal A. Elovitz, MD, the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].
Preventing infant mortality remains a significant challenge for ob.gyns. Despite the availability of a multitude of preventive and treatment options and some of the best possible medical care offered in the world, the United States lags behind many other developed and developing countries in its rate of infant deaths, which was an estimated 5.8 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2017. We can, and must, do better.
One of the major contributing factors to infant mortality is preterm birth. Defined as birth occurring prior to 37 weeks’ gestation, preterm birth is associated with a myriad of severe neonatal sequelae: low birth weight, bacterial sepsis, neonatal hemorrhage, and respiratory distress syndrome, among others. Therefore, many within the clinical and biomedical research spheres recognize that preventing preterm birth means reducing infant deaths.
However, therein lies the conundrum. We know very little about what causes preterm birth, which renders the current therapeutic strategies – such as use of progesterone supplements or cerclage placement – good for some but not all patients. It is thus vital to continue research to unravel the underlying mechanisms of preterm birth.
A promising area of investigation is the field of microbiome research, which has made great strides in advancing our awareness of the critical role of the millions of organisms living on and within us in maintaining health and fighting disease. For example, we now realize that eradicating all the commensals in our gastrointestinal tract has unintended and very negative consequences and, for patients whose good bacteria have been eliminated, fecal transplant is a therapeutic option. Therefore, it stands to reason that the microbes found in the vagina contribute significantly to women’s overall reproductive health.
The publication of the groundbreaking study characterizing the vaginal microbiome species in reproductive-age women opened new avenues of research into how these organisms contribute to women’s health. Importantly, this work, led initially by Jacques Ravel, PhD, a professor in the department of microbiology & immunology and associate director of the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, has spawned additional investigations into the potential role of the vaginal microbiome in preterm birth.
To provide some insight into the research around how the microorganisms in the vagina may induce or prevent preterm birth is our guest author, Michal A. Elovitz, MD, the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].
Preventing infant mortality remains a significant challenge for ob.gyns. Despite the availability of a multitude of preventive and treatment options and some of the best possible medical care offered in the world, the United States lags behind many other developed and developing countries in its rate of infant deaths, which was an estimated 5.8 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2017. We can, and must, do better.
One of the major contributing factors to infant mortality is preterm birth. Defined as birth occurring prior to 37 weeks’ gestation, preterm birth is associated with a myriad of severe neonatal sequelae: low birth weight, bacterial sepsis, neonatal hemorrhage, and respiratory distress syndrome, among others. Therefore, many within the clinical and biomedical research spheres recognize that preventing preterm birth means reducing infant deaths.
However, therein lies the conundrum. We know very little about what causes preterm birth, which renders the current therapeutic strategies – such as use of progesterone supplements or cerclage placement – good for some but not all patients. It is thus vital to continue research to unravel the underlying mechanisms of preterm birth.
A promising area of investigation is the field of microbiome research, which has made great strides in advancing our awareness of the critical role of the millions of organisms living on and within us in maintaining health and fighting disease. For example, we now realize that eradicating all the commensals in our gastrointestinal tract has unintended and very negative consequences and, for patients whose good bacteria have been eliminated, fecal transplant is a therapeutic option. Therefore, it stands to reason that the microbes found in the vagina contribute significantly to women’s overall reproductive health.
The publication of the groundbreaking study characterizing the vaginal microbiome species in reproductive-age women opened new avenues of research into how these organisms contribute to women’s health. Importantly, this work, led initially by Jacques Ravel, PhD, a professor in the department of microbiology & immunology and associate director of the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, has spawned additional investigations into the potential role of the vaginal microbiome in preterm birth.
To provide some insight into the research around how the microorganisms in the vagina may induce or prevent preterm birth is our guest author, Michal A. Elovitz, MD, the Hilarie L. Morgan and Mitchell L. Morgan President’s Distinguished Professor in Women’s Health, vice chair of translational research, and director of the Maternal and Child Health Research Center, department of obstetrics and gynecology, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].