User login
Omit radiation in older women with low-risk, ER+ breast cancer
say researchers reporting 10-year outcomes from the large phase 3 trial known as PRIME II.
“Our trial provides robust evidence indicating that irradiation can be safely omitted in women 65 years of age or older who have grade 1 or 2 ER-high cancers treated by breast-conserving therapy, provided that they receive 5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy,” concluded investigators led by Ian Kunkler, MB, a clinical oncology professor at the University of Edinburgh.
The trial randomly assigned 1,326 women who had undergone a lumpectomy to either whole-breast irradiation or no radiation on a background of tamoxifen.
The incidence of local recurrence was lower with radiation (0.9% vs. 9.5%), but there was no significant difference in distant metastases or breast cancer–specific or overall survival.
The findings will “help clinicians guide older patients on whether this particular aspect of early breast cancer treatment can be omitted,” Dr. Kunkler said in a press release. Radiation carries risks of heart and lung damage, and these results show that skipping it does not increase the odds of dying from breast cancer.
The new study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any doubt that radiotherapy cannot be omitted in women” who meet the criteria “can be put to rest,” commented breast radiation oncologists Alice Ho, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., and Jennifer Bellon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Clinical guidelines already support omitting radiation therapy in older women with low-risk tumors treated with lumpectomy and endocrine therapy, but the move has been controversial owing to a lack of long-term data, and use of radiation for such women remains common in the United States, the investigators explain.
The “highly anticipated” results for 10-year outcomes from this trial should help address that issue, as well as “the long-standing problem of overtreatment in older women with low-risk breast cancer,” the editorialists comment.
Study details
PRIME II was conducted from 2003 to 2009 mainly in the United Kingdom. Participants were aged 65 years or older and had T1 or T2 ER-positive tumors no larger than 3 cm and were without nodal involvement.
Following lumpectomies with clear margins, the women underwent endocrine therapy; the investigators recommended tamoxifen at 20 mg/day for 5 years.
Women who were randomly assigned to radiation also received 40-50 Gy of whole-breast irradiation in 20-25 fractions over 3-5 weeks.
At 10 years, 1.6% of women in the no-radiation arm had distant metastases as their first recurrence vs. 3% of women who underwent radiation.
Ten-year breast cancer–specific survival was 97.9% with radiation and 97.4% with no radiation. Ten-year overall survival was 80.7% in the radiotherapy arm vs. 80.8% in the no-radiotherapy group.
In addition, the recurrence rate was lower after radiation. The investigators suggest that lower adherence to endocrine therapy and lower levels of ER positivity increased the risk of local recurrence among women who didn’t receive radiation.
Almost 10% of the women who did not receive radiation had local recurrences by 10 years, but the investigators note that if tumors do recur locally, women still have the option of a second lumpectomy, and if they so choose, they can then receive radiation, so local recurrence “does not necessarily mean loss of the breast.”
PRIME II was funded by the Scottish Government’s chief scientist office and the Breast Cancer Institute at Western General Hospital, Edinburgh. Dr. Kunkler reported no conflicts of interest. A coauthor has acted as a speaker, adviser, and/or researcher for many companies, including Hoffmann-La Roche, Exact Sciences, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Ho reported grants from and/or being a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Merck, and others. Dr. Bellon reported ties to Varian Medical Systems and Veracyte.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers reporting 10-year outcomes from the large phase 3 trial known as PRIME II.
“Our trial provides robust evidence indicating that irradiation can be safely omitted in women 65 years of age or older who have grade 1 or 2 ER-high cancers treated by breast-conserving therapy, provided that they receive 5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy,” concluded investigators led by Ian Kunkler, MB, a clinical oncology professor at the University of Edinburgh.
The trial randomly assigned 1,326 women who had undergone a lumpectomy to either whole-breast irradiation or no radiation on a background of tamoxifen.
The incidence of local recurrence was lower with radiation (0.9% vs. 9.5%), but there was no significant difference in distant metastases or breast cancer–specific or overall survival.
The findings will “help clinicians guide older patients on whether this particular aspect of early breast cancer treatment can be omitted,” Dr. Kunkler said in a press release. Radiation carries risks of heart and lung damage, and these results show that skipping it does not increase the odds of dying from breast cancer.
The new study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any doubt that radiotherapy cannot be omitted in women” who meet the criteria “can be put to rest,” commented breast radiation oncologists Alice Ho, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., and Jennifer Bellon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Clinical guidelines already support omitting radiation therapy in older women with low-risk tumors treated with lumpectomy and endocrine therapy, but the move has been controversial owing to a lack of long-term data, and use of radiation for such women remains common in the United States, the investigators explain.
The “highly anticipated” results for 10-year outcomes from this trial should help address that issue, as well as “the long-standing problem of overtreatment in older women with low-risk breast cancer,” the editorialists comment.
Study details
PRIME II was conducted from 2003 to 2009 mainly in the United Kingdom. Participants were aged 65 years or older and had T1 or T2 ER-positive tumors no larger than 3 cm and were without nodal involvement.
Following lumpectomies with clear margins, the women underwent endocrine therapy; the investigators recommended tamoxifen at 20 mg/day for 5 years.
Women who were randomly assigned to radiation also received 40-50 Gy of whole-breast irradiation in 20-25 fractions over 3-5 weeks.
At 10 years, 1.6% of women in the no-radiation arm had distant metastases as their first recurrence vs. 3% of women who underwent radiation.
Ten-year breast cancer–specific survival was 97.9% with radiation and 97.4% with no radiation. Ten-year overall survival was 80.7% in the radiotherapy arm vs. 80.8% in the no-radiotherapy group.
In addition, the recurrence rate was lower after radiation. The investigators suggest that lower adherence to endocrine therapy and lower levels of ER positivity increased the risk of local recurrence among women who didn’t receive radiation.
Almost 10% of the women who did not receive radiation had local recurrences by 10 years, but the investigators note that if tumors do recur locally, women still have the option of a second lumpectomy, and if they so choose, they can then receive radiation, so local recurrence “does not necessarily mean loss of the breast.”
PRIME II was funded by the Scottish Government’s chief scientist office and the Breast Cancer Institute at Western General Hospital, Edinburgh. Dr. Kunkler reported no conflicts of interest. A coauthor has acted as a speaker, adviser, and/or researcher for many companies, including Hoffmann-La Roche, Exact Sciences, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Ho reported grants from and/or being a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Merck, and others. Dr. Bellon reported ties to Varian Medical Systems and Veracyte.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
say researchers reporting 10-year outcomes from the large phase 3 trial known as PRIME II.
“Our trial provides robust evidence indicating that irradiation can be safely omitted in women 65 years of age or older who have grade 1 or 2 ER-high cancers treated by breast-conserving therapy, provided that they receive 5 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy,” concluded investigators led by Ian Kunkler, MB, a clinical oncology professor at the University of Edinburgh.
The trial randomly assigned 1,326 women who had undergone a lumpectomy to either whole-breast irradiation or no radiation on a background of tamoxifen.
The incidence of local recurrence was lower with radiation (0.9% vs. 9.5%), but there was no significant difference in distant metastases or breast cancer–specific or overall survival.
The findings will “help clinicians guide older patients on whether this particular aspect of early breast cancer treatment can be omitted,” Dr. Kunkler said in a press release. Radiation carries risks of heart and lung damage, and these results show that skipping it does not increase the odds of dying from breast cancer.
The new study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Any doubt that radiotherapy cannot be omitted in women” who meet the criteria “can be put to rest,” commented breast radiation oncologists Alice Ho, MD, of Duke University in Durham, N.C., and Jennifer Bellon, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Clinical guidelines already support omitting radiation therapy in older women with low-risk tumors treated with lumpectomy and endocrine therapy, but the move has been controversial owing to a lack of long-term data, and use of radiation for such women remains common in the United States, the investigators explain.
The “highly anticipated” results for 10-year outcomes from this trial should help address that issue, as well as “the long-standing problem of overtreatment in older women with low-risk breast cancer,” the editorialists comment.
Study details
PRIME II was conducted from 2003 to 2009 mainly in the United Kingdom. Participants were aged 65 years or older and had T1 or T2 ER-positive tumors no larger than 3 cm and were without nodal involvement.
Following lumpectomies with clear margins, the women underwent endocrine therapy; the investigators recommended tamoxifen at 20 mg/day for 5 years.
Women who were randomly assigned to radiation also received 40-50 Gy of whole-breast irradiation in 20-25 fractions over 3-5 weeks.
At 10 years, 1.6% of women in the no-radiation arm had distant metastases as their first recurrence vs. 3% of women who underwent radiation.
Ten-year breast cancer–specific survival was 97.9% with radiation and 97.4% with no radiation. Ten-year overall survival was 80.7% in the radiotherapy arm vs. 80.8% in the no-radiotherapy group.
In addition, the recurrence rate was lower after radiation. The investigators suggest that lower adherence to endocrine therapy and lower levels of ER positivity increased the risk of local recurrence among women who didn’t receive radiation.
Almost 10% of the women who did not receive radiation had local recurrences by 10 years, but the investigators note that if tumors do recur locally, women still have the option of a second lumpectomy, and if they so choose, they can then receive radiation, so local recurrence “does not necessarily mean loss of the breast.”
PRIME II was funded by the Scottish Government’s chief scientist office and the Breast Cancer Institute at Western General Hospital, Edinburgh. Dr. Kunkler reported no conflicts of interest. A coauthor has acted as a speaker, adviser, and/or researcher for many companies, including Hoffmann-La Roche, Exact Sciences, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Ho reported grants from and/or being a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Merck, and others. Dr. Bellon reported ties to Varian Medical Systems and Veracyte.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Immunodeficiencies tied to psychiatric disorders in offspring
new research suggests.
Results from a cohort study of more than 4.2 million individuals showed that offspring of mothers with PIDs had a 17% increased risk for a psychiatric disorder and a 20% increased risk for suicidal behavior, compared with their peers with mothers who did not have PIDs.
The risk was more pronounced in offspring of mothers with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases. These risks remained after strictly controlling for different covariates, such as the parents’ psychiatric history, offspring PIDs, and offspring autoimmune diseases.
The investigators, led by Josef Isung, MD, PhD, Centre for Psychiatry Research, department of clinical neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, noted that they could not “pinpoint a precise causal mechanism” underlying these findings.
Still, “the results add to the existing literature suggesting that the intrauterine immune environment may have implications for fetal neurodevelopment and that a compromised maternal immune system during pregnancy may be a risk factor for psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior in their offspring in the long term,” they wrote.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Natural experiment’
Maternal immune activation (MIA) is “an overarching term for aberrant and disrupted immune activity in the mother during gestation [and] has long been of interest in relation to adverse health outcomes in the offspring,” Dr. Isung noted.
“In relation to negative psychiatric outcomes, there is an abundance of preclinical evidence that has shown a negative impact on offspring secondary to MIA. And in humans, there are several observational studies supporting this link,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Isung added that PIDs are “rare conditions” known to be associated with repeated infections and high rates of autoimmune diseases, causing substantial disability.
“PIDs represent an interesting ‘natural experiment’ for researchers to understand more about the association between immune system dysfunctions and mental health,” he said.
Dr. Isung’s group previously showed that individuals with PIDs have increased odds of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior. The link was more pronounced in women with PIDs – and was even more pronounced in those with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases.
In the current study, “we wanted to see whether offspring of individuals were differentially at risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior, depending on being offspring of mothers or fathers with PIDs,” Dr. Isung said.
“Our hypothesis was that mothers with PIDs would have an increased risk of having offspring with neuropsychiatric outcomes, and that this risk could be due to MIA,” he added.
The researchers turned to Swedish nationwide health and administrative registers. They analyzed data on all individuals with diagnoses of PIDs identified between 1973 and 2013. Offspring born prior to 2003 were included, and parent-offspring pairs in which both parents had a history of PIDs were excluded.
The final study sample consisted of 4,294,169 offspring (51.4% boys). Of these participants, 7,270 (0.17%) had a parent with PIDs.
The researchers identified lifetime records of 10 psychiatric disorders: obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, major depressive disorder and other mood disorders, anxiety and stress-related disorders, eating disorders, substance use disorders, and Tourette syndrome and chronic tic disorders.
The investigators included parental birth year, psychopathology, suicide attempts, suicide deaths, and autoimmune diseases as covariates, as well as offsprings’ birth year and gender.
Elucidation needed
Results showed that, of the 4,676 offspring of mothers with PID, 17.1% had a psychiatric disorder versus 12.7% of offspring of mothers without PIDs. This translated “into a 17% increased risk for offspring of mothers with PIDs in the fully adjusted model,” the investigators reported.
The risk was even higher for offspring of mothers who had not only PIDs but also one of six of the individual psychiatric disorders, with incident rate ratios ranging from 1.15 to 1.71.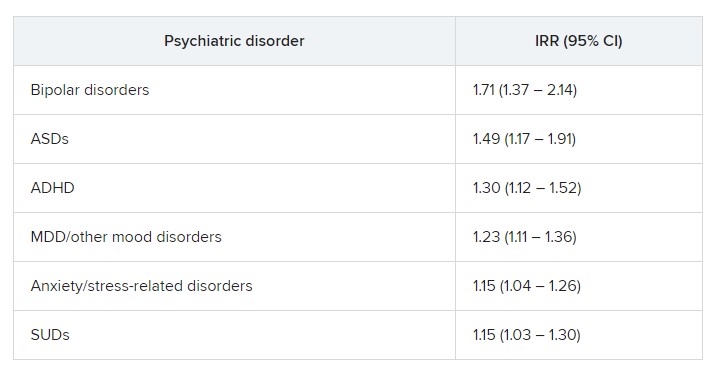
“In fully adjusted models, offspring of mothers with PIDs had an increased risk of any psychiatric disorder, while no such risks were observed in offspring of fathers with PIDs” (IRR, 1.17 vs. 1.03; P < .001), the researchers reported.
A higher risk for suicidal behavior was also observed among offspring of mothers with PIDS, in contrast to those of fathers with PIDs (IRR, 1.2 vs. 1.1; P = .01).
The greatest risk for any psychiatric disorder, as well as suicidal behavior, was found in offspring of mothers who had both PIDs and autoimmune diseases (IRRs, 1.24 and 1.44, respectively).
“The results could be seen as substantiating the hypothesis that immune disruption may be important in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior,” Dr. Isung said.
“Furthermore, the fact that only offspring of mothers and not offspring of fathers with PIDs had this association would align with our hypothesis that MIA is of importance,” he added.
However, he noted that “the specific mechanisms are most likely multifactorial and remain to be elucidated.”
Important piece of the puzzle?
In a comment, Michael Eriksen Benros, MD, PhD, professor of immunopsychiatry, department of immunology and microbiology, health, and medical sciences, University of Copenhagen, said this was a “high-quality study” that used a “rich data source.”
Dr. Benros, who is also head of research (biological and precision psychiatry) at the Copenhagen Research Centre for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, was not involved with the current study.
He noted that prior studies, including some conducted by his own group, have shown that maternal infections overall did not seem to be “specifically linked to mental disorders in the offspring.”
However, “specific maternal infections or specific brain-reactive antibodies during the pregnancy period have been shown to be associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes among the children,” such as intellectual disability, he said.
Regarding direct clinical implications of the study, “it is important to note that the increased risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidality in the offspring of mothers with PID were small,” Dr. Benros said.
“However, it adds an important part to the scientific puzzle regarding the role of maternal immune activation during pregnancy and the risk of mental disorders,” he added.
The study was funded by the Söderström König Foundation and the Fredrik and Ingrid Thuring Foundation. Neither Dr. Isung nor Dr. Benros reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a cohort study of more than 4.2 million individuals showed that offspring of mothers with PIDs had a 17% increased risk for a psychiatric disorder and a 20% increased risk for suicidal behavior, compared with their peers with mothers who did not have PIDs.
The risk was more pronounced in offspring of mothers with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases. These risks remained after strictly controlling for different covariates, such as the parents’ psychiatric history, offspring PIDs, and offspring autoimmune diseases.
The investigators, led by Josef Isung, MD, PhD, Centre for Psychiatry Research, department of clinical neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, noted that they could not “pinpoint a precise causal mechanism” underlying these findings.
Still, “the results add to the existing literature suggesting that the intrauterine immune environment may have implications for fetal neurodevelopment and that a compromised maternal immune system during pregnancy may be a risk factor for psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior in their offspring in the long term,” they wrote.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Natural experiment’
Maternal immune activation (MIA) is “an overarching term for aberrant and disrupted immune activity in the mother during gestation [and] has long been of interest in relation to adverse health outcomes in the offspring,” Dr. Isung noted.
“In relation to negative psychiatric outcomes, there is an abundance of preclinical evidence that has shown a negative impact on offspring secondary to MIA. And in humans, there are several observational studies supporting this link,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Isung added that PIDs are “rare conditions” known to be associated with repeated infections and high rates of autoimmune diseases, causing substantial disability.
“PIDs represent an interesting ‘natural experiment’ for researchers to understand more about the association between immune system dysfunctions and mental health,” he said.
Dr. Isung’s group previously showed that individuals with PIDs have increased odds of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior. The link was more pronounced in women with PIDs – and was even more pronounced in those with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases.
In the current study, “we wanted to see whether offspring of individuals were differentially at risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior, depending on being offspring of mothers or fathers with PIDs,” Dr. Isung said.
“Our hypothesis was that mothers with PIDs would have an increased risk of having offspring with neuropsychiatric outcomes, and that this risk could be due to MIA,” he added.
The researchers turned to Swedish nationwide health and administrative registers. They analyzed data on all individuals with diagnoses of PIDs identified between 1973 and 2013. Offspring born prior to 2003 were included, and parent-offspring pairs in which both parents had a history of PIDs were excluded.
The final study sample consisted of 4,294,169 offspring (51.4% boys). Of these participants, 7,270 (0.17%) had a parent with PIDs.
The researchers identified lifetime records of 10 psychiatric disorders: obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, major depressive disorder and other mood disorders, anxiety and stress-related disorders, eating disorders, substance use disorders, and Tourette syndrome and chronic tic disorders.
The investigators included parental birth year, psychopathology, suicide attempts, suicide deaths, and autoimmune diseases as covariates, as well as offsprings’ birth year and gender.
Elucidation needed
Results showed that, of the 4,676 offspring of mothers with PID, 17.1% had a psychiatric disorder versus 12.7% of offspring of mothers without PIDs. This translated “into a 17% increased risk for offspring of mothers with PIDs in the fully adjusted model,” the investigators reported.
The risk was even higher for offspring of mothers who had not only PIDs but also one of six of the individual psychiatric disorders, with incident rate ratios ranging from 1.15 to 1.71.
“In fully adjusted models, offspring of mothers with PIDs had an increased risk of any psychiatric disorder, while no such risks were observed in offspring of fathers with PIDs” (IRR, 1.17 vs. 1.03; P < .001), the researchers reported.
A higher risk for suicidal behavior was also observed among offspring of mothers with PIDS, in contrast to those of fathers with PIDs (IRR, 1.2 vs. 1.1; P = .01).
The greatest risk for any psychiatric disorder, as well as suicidal behavior, was found in offspring of mothers who had both PIDs and autoimmune diseases (IRRs, 1.24 and 1.44, respectively).
“The results could be seen as substantiating the hypothesis that immune disruption may be important in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior,” Dr. Isung said.
“Furthermore, the fact that only offspring of mothers and not offspring of fathers with PIDs had this association would align with our hypothesis that MIA is of importance,” he added.
However, he noted that “the specific mechanisms are most likely multifactorial and remain to be elucidated.”
Important piece of the puzzle?
In a comment, Michael Eriksen Benros, MD, PhD, professor of immunopsychiatry, department of immunology and microbiology, health, and medical sciences, University of Copenhagen, said this was a “high-quality study” that used a “rich data source.”
Dr. Benros, who is also head of research (biological and precision psychiatry) at the Copenhagen Research Centre for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, was not involved with the current study.
He noted that prior studies, including some conducted by his own group, have shown that maternal infections overall did not seem to be “specifically linked to mental disorders in the offspring.”
However, “specific maternal infections or specific brain-reactive antibodies during the pregnancy period have been shown to be associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes among the children,” such as intellectual disability, he said.
Regarding direct clinical implications of the study, “it is important to note that the increased risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidality in the offspring of mothers with PID were small,” Dr. Benros said.
“However, it adds an important part to the scientific puzzle regarding the role of maternal immune activation during pregnancy and the risk of mental disorders,” he added.
The study was funded by the Söderström König Foundation and the Fredrik and Ingrid Thuring Foundation. Neither Dr. Isung nor Dr. Benros reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a cohort study of more than 4.2 million individuals showed that offspring of mothers with PIDs had a 17% increased risk for a psychiatric disorder and a 20% increased risk for suicidal behavior, compared with their peers with mothers who did not have PIDs.
The risk was more pronounced in offspring of mothers with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases. These risks remained after strictly controlling for different covariates, such as the parents’ psychiatric history, offspring PIDs, and offspring autoimmune diseases.
The investigators, led by Josef Isung, MD, PhD, Centre for Psychiatry Research, department of clinical neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, noted that they could not “pinpoint a precise causal mechanism” underlying these findings.
Still, “the results add to the existing literature suggesting that the intrauterine immune environment may have implications for fetal neurodevelopment and that a compromised maternal immune system during pregnancy may be a risk factor for psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior in their offspring in the long term,” they wrote.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Natural experiment’
Maternal immune activation (MIA) is “an overarching term for aberrant and disrupted immune activity in the mother during gestation [and] has long been of interest in relation to adverse health outcomes in the offspring,” Dr. Isung noted.
“In relation to negative psychiatric outcomes, there is an abundance of preclinical evidence that has shown a negative impact on offspring secondary to MIA. And in humans, there are several observational studies supporting this link,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Isung added that PIDs are “rare conditions” known to be associated with repeated infections and high rates of autoimmune diseases, causing substantial disability.
“PIDs represent an interesting ‘natural experiment’ for researchers to understand more about the association between immune system dysfunctions and mental health,” he said.
Dr. Isung’s group previously showed that individuals with PIDs have increased odds of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior. The link was more pronounced in women with PIDs – and was even more pronounced in those with both PIDs and autoimmune diseases.
In the current study, “we wanted to see whether offspring of individuals were differentially at risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior, depending on being offspring of mothers or fathers with PIDs,” Dr. Isung said.
“Our hypothesis was that mothers with PIDs would have an increased risk of having offspring with neuropsychiatric outcomes, and that this risk could be due to MIA,” he added.
The researchers turned to Swedish nationwide health and administrative registers. They analyzed data on all individuals with diagnoses of PIDs identified between 1973 and 2013. Offspring born prior to 2003 were included, and parent-offspring pairs in which both parents had a history of PIDs were excluded.
The final study sample consisted of 4,294,169 offspring (51.4% boys). Of these participants, 7,270 (0.17%) had a parent with PIDs.
The researchers identified lifetime records of 10 psychiatric disorders: obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, bipolar disorders, major depressive disorder and other mood disorders, anxiety and stress-related disorders, eating disorders, substance use disorders, and Tourette syndrome and chronic tic disorders.
The investigators included parental birth year, psychopathology, suicide attempts, suicide deaths, and autoimmune diseases as covariates, as well as offsprings’ birth year and gender.
Elucidation needed
Results showed that, of the 4,676 offspring of mothers with PID, 17.1% had a psychiatric disorder versus 12.7% of offspring of mothers without PIDs. This translated “into a 17% increased risk for offspring of mothers with PIDs in the fully adjusted model,” the investigators reported.
The risk was even higher for offspring of mothers who had not only PIDs but also one of six of the individual psychiatric disorders, with incident rate ratios ranging from 1.15 to 1.71.
“In fully adjusted models, offspring of mothers with PIDs had an increased risk of any psychiatric disorder, while no such risks were observed in offspring of fathers with PIDs” (IRR, 1.17 vs. 1.03; P < .001), the researchers reported.
A higher risk for suicidal behavior was also observed among offspring of mothers with PIDS, in contrast to those of fathers with PIDs (IRR, 1.2 vs. 1.1; P = .01).
The greatest risk for any psychiatric disorder, as well as suicidal behavior, was found in offspring of mothers who had both PIDs and autoimmune diseases (IRRs, 1.24 and 1.44, respectively).
“The results could be seen as substantiating the hypothesis that immune disruption may be important in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders and suicidal behavior,” Dr. Isung said.
“Furthermore, the fact that only offspring of mothers and not offspring of fathers with PIDs had this association would align with our hypothesis that MIA is of importance,” he added.
However, he noted that “the specific mechanisms are most likely multifactorial and remain to be elucidated.”
Important piece of the puzzle?
In a comment, Michael Eriksen Benros, MD, PhD, professor of immunopsychiatry, department of immunology and microbiology, health, and medical sciences, University of Copenhagen, said this was a “high-quality study” that used a “rich data source.”
Dr. Benros, who is also head of research (biological and precision psychiatry) at the Copenhagen Research Centre for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, was not involved with the current study.
He noted that prior studies, including some conducted by his own group, have shown that maternal infections overall did not seem to be “specifically linked to mental disorders in the offspring.”
However, “specific maternal infections or specific brain-reactive antibodies during the pregnancy period have been shown to be associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes among the children,” such as intellectual disability, he said.
Regarding direct clinical implications of the study, “it is important to note that the increased risk of psychiatric disorders and suicidality in the offspring of mothers with PID were small,” Dr. Benros said.
“However, it adds an important part to the scientific puzzle regarding the role of maternal immune activation during pregnancy and the risk of mental disorders,” he added.
The study was funded by the Söderström König Foundation and the Fredrik and Ingrid Thuring Foundation. Neither Dr. Isung nor Dr. Benros reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Obstetric violence: How it’s defined and how we face it
In a recent, tragic case, a newborn died from being crushed by its mother, who fell asleep from the fatigue of numerous hours of labor. The case has brought the issue of obstetric violence (OV) to the attention of the Italian media. OV is defined as neglect, physical abuse, or disrespect during childbirth, according to the World Health Organization. The WHO outlined fundamental actions to be taken at various levels for its prevention, especially by health care systems, in a 2014 position paper.
Gender-based abuse
Considered a form of gender-based abuse, OV was first described in Latin America in the early 2000s. It is widespread and is increasing in European countries.
From the scientific literature on the subject, OV seems to be strongly associated with a lack of communication between health care personnel and pregnant women. It appears to have more to do with authoritarian and paternalistic behavior than actual real-life medical issues. Actively involving women in decision-making regarding childbirth and postpartum care seems to reduce the incidence of OV. Pregnant women who are more involved appear to trust health care professionals more and are therefore less likely to report disrespectful and abusive behavior.
Estimates of the prevalence of OV vary, depending on the country, the childbirth facility, and its definition. In Italy, inspired by the web campaign “#Bastatacere: le madri hanno voce [#EnoughSilence: mothers have a voice],” in 2017, the Obstetric Violence Database (OVO) investigated perceptions of having been a victim of OV in a representative sample of Italian women aged 18-54 years who had at least one child.
In 2017, just over 20% of the women interviewed considered themselves victims of OV; 33% felt they had not received adequate care; and around 35% reported serious problems concerning privacy or trust. Following the treatment received, approximately 15% of the women decided not to return to the same health care facility, and 6% did not want to proceed with further pregnancies.
At the time of publication, the results sparked a debate among relevant medical associations (the Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Italian Hospitals, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and the Association of Italian University Gynecologists), which immediately recognized the importance of the topic and accepted an invitation for further discussion on physician-patient relationships. They expressed reservations concerning the methodologies used by the OVO for data collection, especially regarding the representativeness of the sample.
Lack of communication
“In general, women who claim to have suffered from obstetric violence do not do so because they have been denied an aspect of care but because they have had an overall experience that, for whatever reason, did not conform with their expectations,” said Irene Cetin, MD, PhD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Milan and director of the obstetrics and gynecology unit of the Buzzi Hospital in Milan. “Following the OVO’s exposé, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics also conducted a large-scale study throughout Italy on all women who had given birth within a 3-month period. That investigation painted a very different picture. It wasn’t the case that no instances of obstetric violence were found, but the results were more contained. This is a very delicate subject, given that every report that we receive in hospital is always valued and looked into in detail, and women come to speak to us about errors and things that were missed.”
She added, “Experience leads me to say that complaints about what happens in the delivery room are extremely rare. What we hear more of, but still not often, are problems experienced during days spent in hospital immediately after childbirth.” There are never enough resources, which is the reason behind most problems. “The real hardships are found in the wards,” continued Dr. Cetin, “where the midwife-to-bed ratio is one or two to 30, and therefore this is where it is more difficult to feel like you’re being listened to. With COVID-19, the situation has gotten even worse, even though in my hospital we have always guaranteed, not without struggle, the presence of the partner in the delivery room.”
Only relatively recently have women’s partners been allowed into the hospital. In addition, a number of services, such as having the right beds and giving the correct explanations and information on how to establish a relationship with the child, are now being offered. These steps are necessary to guarantee what is referred to as a “humanizing birth,” a process in which the woman is at the center of the experience and is the main protagonist of the birth.
Lack of resources
This trend also is observed at the systemic level, where there is a lack of organization and resources. Few staff members are in the ward, even fewer specialists are in the psychological field, and contact is almost nonexistent after discharge from many hospitals and in many regions across Italy. There are, however, some positive aspects and hope for the future. “Just think,” said Dr. Cetin, “of how degree courses in obstetrics have changed over time, with a large part of teaching and training now being centered around the emotional aspects of birth.” From the gynecologist’s side, “most of the problems have been inherited from the past,” said Dr. Cetin. “Let’s not forget that we have only recently been giving birth in hospital. The so-called medicalization of childbirth has been responsible for a decline in the death rate and morbidity rate of pregnant women, but initially, there was little interest or care in how women felt in this situation, including with regard to physical pain. Since the 1970s, with Leboyer from France and Miraglia from Italy [promoters of so-called sweet birth], a path was cleared for a different line of thought. For this reason, I believe that the situation will improve over time.
“To continuously improve physician-patient communication,” concluded Dr. Cetin, “it would perhaps be appropriate to make sure that, even in the preparatory phase, women are well aware of possible complications and of the necessary and rapid emergency procedures that must be implemented by health care personnel. This way, a trusting relationship could be maintained, and the perception of having suffered abuse due to not being involved in strictly medical decisions could be stemmed.”
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recent, tragic case, a newborn died from being crushed by its mother, who fell asleep from the fatigue of numerous hours of labor. The case has brought the issue of obstetric violence (OV) to the attention of the Italian media. OV is defined as neglect, physical abuse, or disrespect during childbirth, according to the World Health Organization. The WHO outlined fundamental actions to be taken at various levels for its prevention, especially by health care systems, in a 2014 position paper.
Gender-based abuse
Considered a form of gender-based abuse, OV was first described in Latin America in the early 2000s. It is widespread and is increasing in European countries.
From the scientific literature on the subject, OV seems to be strongly associated with a lack of communication between health care personnel and pregnant women. It appears to have more to do with authoritarian and paternalistic behavior than actual real-life medical issues. Actively involving women in decision-making regarding childbirth and postpartum care seems to reduce the incidence of OV. Pregnant women who are more involved appear to trust health care professionals more and are therefore less likely to report disrespectful and abusive behavior.
Estimates of the prevalence of OV vary, depending on the country, the childbirth facility, and its definition. In Italy, inspired by the web campaign “#Bastatacere: le madri hanno voce [#EnoughSilence: mothers have a voice],” in 2017, the Obstetric Violence Database (OVO) investigated perceptions of having been a victim of OV in a representative sample of Italian women aged 18-54 years who had at least one child.
In 2017, just over 20% of the women interviewed considered themselves victims of OV; 33% felt they had not received adequate care; and around 35% reported serious problems concerning privacy or trust. Following the treatment received, approximately 15% of the women decided not to return to the same health care facility, and 6% did not want to proceed with further pregnancies.
At the time of publication, the results sparked a debate among relevant medical associations (the Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Italian Hospitals, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and the Association of Italian University Gynecologists), which immediately recognized the importance of the topic and accepted an invitation for further discussion on physician-patient relationships. They expressed reservations concerning the methodologies used by the OVO for data collection, especially regarding the representativeness of the sample.
Lack of communication
“In general, women who claim to have suffered from obstetric violence do not do so because they have been denied an aspect of care but because they have had an overall experience that, for whatever reason, did not conform with their expectations,” said Irene Cetin, MD, PhD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Milan and director of the obstetrics and gynecology unit of the Buzzi Hospital in Milan. “Following the OVO’s exposé, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics also conducted a large-scale study throughout Italy on all women who had given birth within a 3-month period. That investigation painted a very different picture. It wasn’t the case that no instances of obstetric violence were found, but the results were more contained. This is a very delicate subject, given that every report that we receive in hospital is always valued and looked into in detail, and women come to speak to us about errors and things that were missed.”
She added, “Experience leads me to say that complaints about what happens in the delivery room are extremely rare. What we hear more of, but still not often, are problems experienced during days spent in hospital immediately after childbirth.” There are never enough resources, which is the reason behind most problems. “The real hardships are found in the wards,” continued Dr. Cetin, “where the midwife-to-bed ratio is one or two to 30, and therefore this is where it is more difficult to feel like you’re being listened to. With COVID-19, the situation has gotten even worse, even though in my hospital we have always guaranteed, not without struggle, the presence of the partner in the delivery room.”
Only relatively recently have women’s partners been allowed into the hospital. In addition, a number of services, such as having the right beds and giving the correct explanations and information on how to establish a relationship with the child, are now being offered. These steps are necessary to guarantee what is referred to as a “humanizing birth,” a process in which the woman is at the center of the experience and is the main protagonist of the birth.
Lack of resources
This trend also is observed at the systemic level, where there is a lack of organization and resources. Few staff members are in the ward, even fewer specialists are in the psychological field, and contact is almost nonexistent after discharge from many hospitals and in many regions across Italy. There are, however, some positive aspects and hope for the future. “Just think,” said Dr. Cetin, “of how degree courses in obstetrics have changed over time, with a large part of teaching and training now being centered around the emotional aspects of birth.” From the gynecologist’s side, “most of the problems have been inherited from the past,” said Dr. Cetin. “Let’s not forget that we have only recently been giving birth in hospital. The so-called medicalization of childbirth has been responsible for a decline in the death rate and morbidity rate of pregnant women, but initially, there was little interest or care in how women felt in this situation, including with regard to physical pain. Since the 1970s, with Leboyer from France and Miraglia from Italy [promoters of so-called sweet birth], a path was cleared for a different line of thought. For this reason, I believe that the situation will improve over time.
“To continuously improve physician-patient communication,” concluded Dr. Cetin, “it would perhaps be appropriate to make sure that, even in the preparatory phase, women are well aware of possible complications and of the necessary and rapid emergency procedures that must be implemented by health care personnel. This way, a trusting relationship could be maintained, and the perception of having suffered abuse due to not being involved in strictly medical decisions could be stemmed.”
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recent, tragic case, a newborn died from being crushed by its mother, who fell asleep from the fatigue of numerous hours of labor. The case has brought the issue of obstetric violence (OV) to the attention of the Italian media. OV is defined as neglect, physical abuse, or disrespect during childbirth, according to the World Health Organization. The WHO outlined fundamental actions to be taken at various levels for its prevention, especially by health care systems, in a 2014 position paper.
Gender-based abuse
Considered a form of gender-based abuse, OV was first described in Latin America in the early 2000s. It is widespread and is increasing in European countries.
From the scientific literature on the subject, OV seems to be strongly associated with a lack of communication between health care personnel and pregnant women. It appears to have more to do with authoritarian and paternalistic behavior than actual real-life medical issues. Actively involving women in decision-making regarding childbirth and postpartum care seems to reduce the incidence of OV. Pregnant women who are more involved appear to trust health care professionals more and are therefore less likely to report disrespectful and abusive behavior.
Estimates of the prevalence of OV vary, depending on the country, the childbirth facility, and its definition. In Italy, inspired by the web campaign “#Bastatacere: le madri hanno voce [#EnoughSilence: mothers have a voice],” in 2017, the Obstetric Violence Database (OVO) investigated perceptions of having been a victim of OV in a representative sample of Italian women aged 18-54 years who had at least one child.
In 2017, just over 20% of the women interviewed considered themselves victims of OV; 33% felt they had not received adequate care; and around 35% reported serious problems concerning privacy or trust. Following the treatment received, approximately 15% of the women decided not to return to the same health care facility, and 6% did not want to proceed with further pregnancies.
At the time of publication, the results sparked a debate among relevant medical associations (the Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Italian Hospitals, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and the Association of Italian University Gynecologists), which immediately recognized the importance of the topic and accepted an invitation for further discussion on physician-patient relationships. They expressed reservations concerning the methodologies used by the OVO for data collection, especially regarding the representativeness of the sample.
Lack of communication
“In general, women who claim to have suffered from obstetric violence do not do so because they have been denied an aspect of care but because they have had an overall experience that, for whatever reason, did not conform with their expectations,” said Irene Cetin, MD, PhD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Milan and director of the obstetrics and gynecology unit of the Buzzi Hospital in Milan. “Following the OVO’s exposé, the Italian Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics also conducted a large-scale study throughout Italy on all women who had given birth within a 3-month period. That investigation painted a very different picture. It wasn’t the case that no instances of obstetric violence were found, but the results were more contained. This is a very delicate subject, given that every report that we receive in hospital is always valued and looked into in detail, and women come to speak to us about errors and things that were missed.”
She added, “Experience leads me to say that complaints about what happens in the delivery room are extremely rare. What we hear more of, but still not often, are problems experienced during days spent in hospital immediately after childbirth.” There are never enough resources, which is the reason behind most problems. “The real hardships are found in the wards,” continued Dr. Cetin, “where the midwife-to-bed ratio is one or two to 30, and therefore this is where it is more difficult to feel like you’re being listened to. With COVID-19, the situation has gotten even worse, even though in my hospital we have always guaranteed, not without struggle, the presence of the partner in the delivery room.”
Only relatively recently have women’s partners been allowed into the hospital. In addition, a number of services, such as having the right beds and giving the correct explanations and information on how to establish a relationship with the child, are now being offered. These steps are necessary to guarantee what is referred to as a “humanizing birth,” a process in which the woman is at the center of the experience and is the main protagonist of the birth.
Lack of resources
This trend also is observed at the systemic level, where there is a lack of organization and resources. Few staff members are in the ward, even fewer specialists are in the psychological field, and contact is almost nonexistent after discharge from many hospitals and in many regions across Italy. There are, however, some positive aspects and hope for the future. “Just think,” said Dr. Cetin, “of how degree courses in obstetrics have changed over time, with a large part of teaching and training now being centered around the emotional aspects of birth.” From the gynecologist’s side, “most of the problems have been inherited from the past,” said Dr. Cetin. “Let’s not forget that we have only recently been giving birth in hospital. The so-called medicalization of childbirth has been responsible for a decline in the death rate and morbidity rate of pregnant women, but initially, there was little interest or care in how women felt in this situation, including with regard to physical pain. Since the 1970s, with Leboyer from France and Miraglia from Italy [promoters of so-called sweet birth], a path was cleared for a different line of thought. For this reason, I believe that the situation will improve over time.
“To continuously improve physician-patient communication,” concluded Dr. Cetin, “it would perhaps be appropriate to make sure that, even in the preparatory phase, women are well aware of possible complications and of the necessary and rapid emergency procedures that must be implemented by health care personnel. This way, a trusting relationship could be maintained, and the perception of having suffered abuse due to not being involved in strictly medical decisions could be stemmed.”
This article was translated from Univadis Italy. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Genomic clues to poor outcomes in young breast cancer patients
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
and offer clues about molecular targets for future trials.
Compared with older women with early stage HR-positive breast cancer, women under 40 years of age had significantly higher frequencies of certain mutations, such as GATA3, as well as genomic features associated with a poor prognosis. Notably, the researchers found that women with such poor prognostic features vs. those with none had a significantly worse 8-year distant recurrence-free interval and overall survival.
“We have demonstrated age-related differences in genomic profiles with enrichment of genomic features associated with poor prognosis in these younger premenopausal women compared with older premenopausal and postmenopausal women,” the authors wrote in the study, published in the Annals of Oncology. Importantly, the genomic features highlight “the potential for age-focused treatment strategies.”
Charis Eng, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, Ohio, noted that the findings are promising but need further validation.
“With time and the appropriate clinical trials in place, I envision that these findings will enable the personalized genomics-driven management of these cancers – not only treatment, but also toward prevention,” said Dr. Eng, who was not involved in the study.
Young premenopausal women, particularly those with HR-positive, luminal breast cancer, are known to have significantly higher recurrence rates and worse survival, compared with older women, but the reasons have remained unclear.
Although previous studies have identified key gene expression signatures linked to worse outcomes in younger patients with breast cancer, there are limited data on this younger patient population, especially by breast cancer subtype. Given that breast cancer treatment strategies are often similar across age groups, such evidence gaps could represent missed opportunities for developing more targeted treatment strategies for this high-risk population of young women.
To further investigate the cancer-specific genetic profiles in younger women, Sherene Loi, MD, PhD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, University of Melbourne, and colleagues turned to data from the pivotal, multicenter Suppression of Ovarian Function Trial (SOFT).
Using next-generation sequencing, Dr. Loi and colleagues evaluated HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors among a subset of 1,276 premenopausal women who were diagnosed with early stage breast cancer. The study employed deep-targeted sequencing for most patients (n = 1,258) as well as whole-exome sequencing in a matched case-control subsample of young women with a median age of 38 years (n = 82).
Compared with women aged 40 and older, those under 40 years of age (n = 359) had significantly higher frequencies of mutations in GATA3 (19% vs. 16%) and copy number-amplifications (47% vs. 26%).
Younger women also had significantly higher features suggestive of homologous recombination deficiency (27% vs. 21% in older women), and a higher proportion of PIK3CA mutations with concurrent copy number-amplifications (23% vs. 11%, respectively), all considered to be poor prognostic features.
In addition, younger women had significantly lower frequencies of certain mutations, including PIK3CA (32% vs. 47%), CDH1 (3% vs. 9%), and MAP3K1 (7% vs. 12%), compared with older women.
Overall, 46% of women had poor prognostic features. These poor prognostic features were observed in 72% of patients under age 35, compared with 54% aged 35-39, and 40% of those 40 and over.
Compared with women without those features, women with poor prognostic features had a lower 8-year distant recurrence-free interval of 84% vs. 94% (hazard ratio, 1.85), and worse 8-year overall survival of 88% vs. 96%, respectively (HR, 2.20). Notably, younger women under age 40 had the poorest outcomes, with an 8-year distant recurrence-free interval rate of 74% vs. 85% in older women, and an 8-year overall survival of 80% vs. 93%, respectively.
How might these results inform potential therapeutics?
Drugs targeting the homologous recombination deficiency pathway are well established, and up to 36% of very young patients in the study showed genomic features of homologous recombination deficiency, the authors noted.
In addition, Dr. Eng explained, there are other Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments that can target the copy number amplified, PIK3CA-mutated tumors, including therapies that target PIK3CA itself, or proteins downstream of it. However, use of such therapies would need “to be tested experimentally, especially since pathway inhibition sometimes may result in rebound signaling to promote tumor growth,” Dr. Eng said.
An important caveat is that patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations may be underrepresented in the SOFT clinical trial, as the trial excluded patients who already had bilateral oophorectomy or planned to within 5 years, the authors noted.
Nevertheless, Dr. Loi said that the study is important because “there are no other datasets as large or with this long follow-up for very young women with breast cancer.”
Furthermore, “the SOFT clinical trial was practice-changing, so using the tumor samples associated with this study is more impactful than smaller cohorts with no outcome data or institutional retrospective cohorts,” she said.
Dr. Eng agreed that the study’s size is an important attribute, allowing the authors to “identify differences that would have been missed in a smaller and more heterogeneous series.”
She added that future research should also include ancestry and racial diversity.
“While young women have higher occurrences of aggressive breast cancers, mortality is twice as likely in young Black women, compared to young White women,” Dr. Eng said.
The study received funding from a Susan G. Komen for the Cure Promise Grant, the National Health and Research Council of Australia, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the National Breast Cancer Foundation of Australia, and support from the family of Judy Eisman in Australia. Dr. Loi and Dr. Eng report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF ONCOLOGY
Doctors are disappearing from emergency departments as hospitals look to cut costs
She didn’t know much about miscarriage, but this seemed like one.
In the emergency department, she was examined then sent home, she said. She went back when her cramping became excruciating. Then home again. It ultimately took three trips to the ED on 3 consecutive days, generating three separate bills, before she saw a doctor who looked at her blood work and confirmed her fears.
“At the time I wasn’t thinking, ‘Oh, I need to see a doctor,’ ” Ms. Valle recalled. “But when you think about it, it’s like, ‘Well, dang – why didn’t I see a doctor?’ ” It’s unclear whether the repeat visits were due to delays in seeing a physician, but the experience worried her. And she’s still paying the bills.
The hospital declined to discuss Ms. Valle’s care, citing patient privacy. But 17 months before her 3-day ordeal, Tennova had outsourced its emergency departments to American Physician Partners, a medical staffing company owned by private equity investors. APP employs fewer doctors in its EDs as one of its cost-saving initiatives to increase earnings, according to a confidential company document obtained by KHN and NPR.
This staffing strategy has permeated hospitals, and particularly emergency departments, that seek to reduce their top expense: physician labor. While diagnosing and treating patients was once their domain, doctors are increasingly being replaced by nurse practitioners and physician assistants, collectively known as “midlevel practitioners,” who can perform many of the same duties and generate much of the same revenue for less than half of the pay.
“APP has numerous cost saving initiatives underway as part of the Company’s continual focus on cost optimization,” the document says, including a “shift of staffing” between doctors and midlevel practitioners.
In a statement to KHN, American Physician Partners said this strategy is a way to ensure all EDs remain fully staffed, calling it a “blended model” that allows doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants “to provide care to their fullest potential.”
Critics of this strategy say the quest to save money results in treatment meted out by someone with far less training than a physician, leaving patients vulnerable to misdiagnoses, higher medical bills, and inadequate care. And these fears are bolstered by evidence that suggests dropping doctors from EDs may not be good for patients.
A working paper, published in October by the National Bureau of Economic Research, analyzed roughly 1.1 million visits to 44 EDs throughout the Veterans Health Administration, where nurse practitioners can treat patients without oversight from doctors.
Researchers found that treatment by a nurse practitioner resulted on average in a 7% increase in cost of care and an 11% increase in length of stay, extending patients’ time in the ED by minutes for minor visits and hours for longer ones. These gaps widened among patients with more severe diagnoses, the study said, but could be somewhat mitigated by nurse practitioners with more experience.
The study also found that ED patients treated by a nurse practitioner were 20% more likely to be readmitted to the hospital for a preventable reason within 30 days, although the overall risk of readmission remained very small.
Yiqun Chen, PhD, who is an assistant professor of economics at the University of Illinois at Chicago and coauthored the study, said these findings are not an indictment of nurse practitioners in the ED. Instead, she said, she hopes the study will guide how to best deploy nurse practitioners: in treatment of simpler patients or circumstances when no doctor is available.
“It’s not just a simple question of if we can substitute physicians with nurse practitioners or not,” Dr. Chen said. “It depends on how we use them. If we just use them as independent providers, especially ... for relatively complicated patients, it doesn’t seem to be a very good use.”
Dr. Chen’s research echoes smaller studies, like one from The Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute that found nonphysician practitioners in EDs were associated with a 5.3% increase in imaging, which could unnecessarily increase bills for patients. Separately, a study at the Hattiesburg Clinic in Mississippi found that midlevel practitioners in primary care – not in the emergency department – increased the out-of-pocket costs to patients while also leading to worse performance on 9 of 10 quality-of-care metrics, including cancer screenings and vaccination rates.
But definitive evidence remains elusive that replacing ER doctors with nonphysicians has a negative impact on patients, said Cameron Gettel, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. Private equity investment and the use of midlevel practitioners rose in lockstep in the ED, Dr. Gettel said, and in the absence of game-changing research, the pattern will likely continue.
“Worse patient outcomes haven’t really been shown across the board,” he said. “And I think until that is shown, then they will continue to play an increasing role.”
For private equity, dropping ED docs is a “simple equation”
Private equity companies pool money from wealthy investors to buy their way into various industries, often slashing spending and seeking to flip businesses in 3 to 7 years. While this business model is a proven moneymaker on Wall Street, it raises concerns in health care, where critics worry the pressure to turn big profits will influence life-or-death decisions that were once left solely to medical professionals.
Nearly $1 trillion in private equity funds have gone into almost 8,000 health care transactions over the past decade, according to industry tracker PitchBook, including buying into medical staffing companies that many hospitals hire to manage their emergency departments.
Two firms dominate the ED staffing industry: TeamHealth, bought by private equity firm Blackstone in 2016, and Envision Healthcare, bought by KKR in 2018. Trying to undercut these staffing giants is American Physician Partners, a rapidly expanding company that runs EDs in at least 17 states and is 50% owned by private equity firm BBH Capital Partners.
These staffing companies have been among the most aggressive in replacing doctors to cut costs, said Robert McNamara, MD, a founder of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia.
“It’s a relatively simple equation,” Dr. McNamara said. “Their No. 1 expense is the board-certified emergency physician. So they are going to want to keep that expense as low as possible.”
Not everyone sees the trend of private equity in ED staffing in a negative light. Jennifer Orozco, president of the American Academy of Physician Associates, which represents physician assistants, said even if the change – to use more nonphysician providers – is driven by the staffing firms’ desire to make more money, patients are still well served by a team approach that includes nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
“Though I see that shift, it’s not about profits at the end of the day,” Ms. Orozco said. “It’s about the patient.”
The “shift” is nearly invisible to patients because hospitals rarely promote branding from their ED staffing firms and there is little public documentation of private equity investments.
Arthur Smolensky, MD, a Tennessee emergency medicine specialist attempting to measure private equity’s intrusion into EDs, said his review of hospital job postings and employment contracts in 14 major metropolitan areas found that 43% of ED patients were seen in EDs staffed by companies with nonphysician owners, nearly all of whom are private equity investors.
Dr. Smolensky hopes to publish his full study, expanding to 55 metro areas, later this year. But this research will merely quantify what many doctors already know: The ED has changed. Demoralized by an increased focus on profit, and wary of a looming surplus of emergency medicine residents because there are fewer jobs to fill, many experienced doctors are leaving the ED on their own, he said.
“Most of us didn’t go into medicine to supervise an army of people that are not as well trained as we are,” Dr. Smolensky said. “We want to take care of patients.”
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER”
Joshua Allen, a nurse practitioner at a small Kentucky hospital, snaked a rubber hose through a rack of pork ribs to practice inserting a chest tube to fix a collapsed lung.
It was 2020, and American Physician Partners was restructuring the ED where Mr. Allen worked, reducing shifts from two doctors to one. Once Mr. Allen had placed 10 tubes under a doctor’s supervision, he would be allowed to do it on his own.
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER,” he said. “If we do have a major trauma and multiple victims come in, there’s only one doctor there. ... We need to be prepared.”
Mr. Allen is one of many midlevel practitioners finding work in emergency departments. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants are among the fastest-growing occupations in the nation, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Generally, they have master’s degrees and receive several years of specialized schooling but have significantly less training than doctors. Many are permitted to diagnose patients and prescribe medication with little or no supervision from a doctor, although limitations vary by state.
The Neiman Institute found that the share of ED visits in which a midlevel practitioner was the main clinician increased by more than 172% between 2005 and 2020. Another study, in the Journal of Emergency Medicine, reported that if trends continue there may be equal numbers of midlevel practitioners and doctors in EDs by 2030.
There is little mystery as to why. Federal data shows emergency medicine doctors are paid about $310,000 a year on average, while nurse practitioners and physician assistants earn less than $120,000. Generally, hospitals can bill for care by a midlevel practitioner at 85% the rate of a doctor while paying them less than half as much.
Private equity can make millions in the gap.
For example, Envision once encouraged EDs to employ “the least expensive resource” and treat up to 35% of patients with midlevel practitioners, according to a 2017 PowerPoint presentation. The presentation drew scorn on social media and disappeared from Envision’s website.
Envision declined a request for a phone interview. In a written statement to KHN, spokesperson Aliese Polk said the company does not direct its physician leaders on how to care for patients and called the presentation a “concept guide” that does not represent current views.
American Physician Partners touted roughly the same staffing strategy in 2021 in response to the No Surprises Act, which threatened the company’s profits by outlawing surprise medical bills. In its confidential pitch to lenders, the company estimated it could cut almost $6 million by shifting more staffing from physicians to midlevel practitioners.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
She didn’t know much about miscarriage, but this seemed like one.
In the emergency department, she was examined then sent home, she said. She went back when her cramping became excruciating. Then home again. It ultimately took three trips to the ED on 3 consecutive days, generating three separate bills, before she saw a doctor who looked at her blood work and confirmed her fears.
“At the time I wasn’t thinking, ‘Oh, I need to see a doctor,’ ” Ms. Valle recalled. “But when you think about it, it’s like, ‘Well, dang – why didn’t I see a doctor?’ ” It’s unclear whether the repeat visits were due to delays in seeing a physician, but the experience worried her. And she’s still paying the bills.
The hospital declined to discuss Ms. Valle’s care, citing patient privacy. But 17 months before her 3-day ordeal, Tennova had outsourced its emergency departments to American Physician Partners, a medical staffing company owned by private equity investors. APP employs fewer doctors in its EDs as one of its cost-saving initiatives to increase earnings, according to a confidential company document obtained by KHN and NPR.
This staffing strategy has permeated hospitals, and particularly emergency departments, that seek to reduce their top expense: physician labor. While diagnosing and treating patients was once their domain, doctors are increasingly being replaced by nurse practitioners and physician assistants, collectively known as “midlevel practitioners,” who can perform many of the same duties and generate much of the same revenue for less than half of the pay.
“APP has numerous cost saving initiatives underway as part of the Company’s continual focus on cost optimization,” the document says, including a “shift of staffing” between doctors and midlevel practitioners.
In a statement to KHN, American Physician Partners said this strategy is a way to ensure all EDs remain fully staffed, calling it a “blended model” that allows doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants “to provide care to their fullest potential.”
Critics of this strategy say the quest to save money results in treatment meted out by someone with far less training than a physician, leaving patients vulnerable to misdiagnoses, higher medical bills, and inadequate care. And these fears are bolstered by evidence that suggests dropping doctors from EDs may not be good for patients.
A working paper, published in October by the National Bureau of Economic Research, analyzed roughly 1.1 million visits to 44 EDs throughout the Veterans Health Administration, where nurse practitioners can treat patients without oversight from doctors.
Researchers found that treatment by a nurse practitioner resulted on average in a 7% increase in cost of care and an 11% increase in length of stay, extending patients’ time in the ED by minutes for minor visits and hours for longer ones. These gaps widened among patients with more severe diagnoses, the study said, but could be somewhat mitigated by nurse practitioners with more experience.
The study also found that ED patients treated by a nurse practitioner were 20% more likely to be readmitted to the hospital for a preventable reason within 30 days, although the overall risk of readmission remained very small.
Yiqun Chen, PhD, who is an assistant professor of economics at the University of Illinois at Chicago and coauthored the study, said these findings are not an indictment of nurse practitioners in the ED. Instead, she said, she hopes the study will guide how to best deploy nurse practitioners: in treatment of simpler patients or circumstances when no doctor is available.
“It’s not just a simple question of if we can substitute physicians with nurse practitioners or not,” Dr. Chen said. “It depends on how we use them. If we just use them as independent providers, especially ... for relatively complicated patients, it doesn’t seem to be a very good use.”
Dr. Chen’s research echoes smaller studies, like one from The Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute that found nonphysician practitioners in EDs were associated with a 5.3% increase in imaging, which could unnecessarily increase bills for patients. Separately, a study at the Hattiesburg Clinic in Mississippi found that midlevel practitioners in primary care – not in the emergency department – increased the out-of-pocket costs to patients while also leading to worse performance on 9 of 10 quality-of-care metrics, including cancer screenings and vaccination rates.
But definitive evidence remains elusive that replacing ER doctors with nonphysicians has a negative impact on patients, said Cameron Gettel, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. Private equity investment and the use of midlevel practitioners rose in lockstep in the ED, Dr. Gettel said, and in the absence of game-changing research, the pattern will likely continue.
“Worse patient outcomes haven’t really been shown across the board,” he said. “And I think until that is shown, then they will continue to play an increasing role.”
For private equity, dropping ED docs is a “simple equation”
Private equity companies pool money from wealthy investors to buy their way into various industries, often slashing spending and seeking to flip businesses in 3 to 7 years. While this business model is a proven moneymaker on Wall Street, it raises concerns in health care, where critics worry the pressure to turn big profits will influence life-or-death decisions that were once left solely to medical professionals.
Nearly $1 trillion in private equity funds have gone into almost 8,000 health care transactions over the past decade, according to industry tracker PitchBook, including buying into medical staffing companies that many hospitals hire to manage their emergency departments.
Two firms dominate the ED staffing industry: TeamHealth, bought by private equity firm Blackstone in 2016, and Envision Healthcare, bought by KKR in 2018. Trying to undercut these staffing giants is American Physician Partners, a rapidly expanding company that runs EDs in at least 17 states and is 50% owned by private equity firm BBH Capital Partners.
These staffing companies have been among the most aggressive in replacing doctors to cut costs, said Robert McNamara, MD, a founder of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia.
“It’s a relatively simple equation,” Dr. McNamara said. “Their No. 1 expense is the board-certified emergency physician. So they are going to want to keep that expense as low as possible.”
Not everyone sees the trend of private equity in ED staffing in a negative light. Jennifer Orozco, president of the American Academy of Physician Associates, which represents physician assistants, said even if the change – to use more nonphysician providers – is driven by the staffing firms’ desire to make more money, patients are still well served by a team approach that includes nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
“Though I see that shift, it’s not about profits at the end of the day,” Ms. Orozco said. “It’s about the patient.”
The “shift” is nearly invisible to patients because hospitals rarely promote branding from their ED staffing firms and there is little public documentation of private equity investments.
Arthur Smolensky, MD, a Tennessee emergency medicine specialist attempting to measure private equity’s intrusion into EDs, said his review of hospital job postings and employment contracts in 14 major metropolitan areas found that 43% of ED patients were seen in EDs staffed by companies with nonphysician owners, nearly all of whom are private equity investors.
Dr. Smolensky hopes to publish his full study, expanding to 55 metro areas, later this year. But this research will merely quantify what many doctors already know: The ED has changed. Demoralized by an increased focus on profit, and wary of a looming surplus of emergency medicine residents because there are fewer jobs to fill, many experienced doctors are leaving the ED on their own, he said.
“Most of us didn’t go into medicine to supervise an army of people that are not as well trained as we are,” Dr. Smolensky said. “We want to take care of patients.”
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER”
Joshua Allen, a nurse practitioner at a small Kentucky hospital, snaked a rubber hose through a rack of pork ribs to practice inserting a chest tube to fix a collapsed lung.
It was 2020, and American Physician Partners was restructuring the ED where Mr. Allen worked, reducing shifts from two doctors to one. Once Mr. Allen had placed 10 tubes under a doctor’s supervision, he would be allowed to do it on his own.
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER,” he said. “If we do have a major trauma and multiple victims come in, there’s only one doctor there. ... We need to be prepared.”
Mr. Allen is one of many midlevel practitioners finding work in emergency departments. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants are among the fastest-growing occupations in the nation, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Generally, they have master’s degrees and receive several years of specialized schooling but have significantly less training than doctors. Many are permitted to diagnose patients and prescribe medication with little or no supervision from a doctor, although limitations vary by state.
The Neiman Institute found that the share of ED visits in which a midlevel practitioner was the main clinician increased by more than 172% between 2005 and 2020. Another study, in the Journal of Emergency Medicine, reported that if trends continue there may be equal numbers of midlevel practitioners and doctors in EDs by 2030.
There is little mystery as to why. Federal data shows emergency medicine doctors are paid about $310,000 a year on average, while nurse practitioners and physician assistants earn less than $120,000. Generally, hospitals can bill for care by a midlevel practitioner at 85% the rate of a doctor while paying them less than half as much.
Private equity can make millions in the gap.
For example, Envision once encouraged EDs to employ “the least expensive resource” and treat up to 35% of patients with midlevel practitioners, according to a 2017 PowerPoint presentation. The presentation drew scorn on social media and disappeared from Envision’s website.
Envision declined a request for a phone interview. In a written statement to KHN, spokesperson Aliese Polk said the company does not direct its physician leaders on how to care for patients and called the presentation a “concept guide” that does not represent current views.
American Physician Partners touted roughly the same staffing strategy in 2021 in response to the No Surprises Act, which threatened the company’s profits by outlawing surprise medical bills. In its confidential pitch to lenders, the company estimated it could cut almost $6 million by shifting more staffing from physicians to midlevel practitioners.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
She didn’t know much about miscarriage, but this seemed like one.
In the emergency department, she was examined then sent home, she said. She went back when her cramping became excruciating. Then home again. It ultimately took three trips to the ED on 3 consecutive days, generating three separate bills, before she saw a doctor who looked at her blood work and confirmed her fears.
“At the time I wasn’t thinking, ‘Oh, I need to see a doctor,’ ” Ms. Valle recalled. “But when you think about it, it’s like, ‘Well, dang – why didn’t I see a doctor?’ ” It’s unclear whether the repeat visits were due to delays in seeing a physician, but the experience worried her. And she’s still paying the bills.
The hospital declined to discuss Ms. Valle’s care, citing patient privacy. But 17 months before her 3-day ordeal, Tennova had outsourced its emergency departments to American Physician Partners, a medical staffing company owned by private equity investors. APP employs fewer doctors in its EDs as one of its cost-saving initiatives to increase earnings, according to a confidential company document obtained by KHN and NPR.
This staffing strategy has permeated hospitals, and particularly emergency departments, that seek to reduce their top expense: physician labor. While diagnosing and treating patients was once their domain, doctors are increasingly being replaced by nurse practitioners and physician assistants, collectively known as “midlevel practitioners,” who can perform many of the same duties and generate much of the same revenue for less than half of the pay.
“APP has numerous cost saving initiatives underway as part of the Company’s continual focus on cost optimization,” the document says, including a “shift of staffing” between doctors and midlevel practitioners.
In a statement to KHN, American Physician Partners said this strategy is a way to ensure all EDs remain fully staffed, calling it a “blended model” that allows doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants “to provide care to their fullest potential.”
Critics of this strategy say the quest to save money results in treatment meted out by someone with far less training than a physician, leaving patients vulnerable to misdiagnoses, higher medical bills, and inadequate care. And these fears are bolstered by evidence that suggests dropping doctors from EDs may not be good for patients.
A working paper, published in October by the National Bureau of Economic Research, analyzed roughly 1.1 million visits to 44 EDs throughout the Veterans Health Administration, where nurse practitioners can treat patients without oversight from doctors.
Researchers found that treatment by a nurse practitioner resulted on average in a 7% increase in cost of care and an 11% increase in length of stay, extending patients’ time in the ED by minutes for minor visits and hours for longer ones. These gaps widened among patients with more severe diagnoses, the study said, but could be somewhat mitigated by nurse practitioners with more experience.
The study also found that ED patients treated by a nurse practitioner were 20% more likely to be readmitted to the hospital for a preventable reason within 30 days, although the overall risk of readmission remained very small.
Yiqun Chen, PhD, who is an assistant professor of economics at the University of Illinois at Chicago and coauthored the study, said these findings are not an indictment of nurse practitioners in the ED. Instead, she said, she hopes the study will guide how to best deploy nurse practitioners: in treatment of simpler patients or circumstances when no doctor is available.
“It’s not just a simple question of if we can substitute physicians with nurse practitioners or not,” Dr. Chen said. “It depends on how we use them. If we just use them as independent providers, especially ... for relatively complicated patients, it doesn’t seem to be a very good use.”
Dr. Chen’s research echoes smaller studies, like one from The Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute that found nonphysician practitioners in EDs were associated with a 5.3% increase in imaging, which could unnecessarily increase bills for patients. Separately, a study at the Hattiesburg Clinic in Mississippi found that midlevel practitioners in primary care – not in the emergency department – increased the out-of-pocket costs to patients while also leading to worse performance on 9 of 10 quality-of-care metrics, including cancer screenings and vaccination rates.
But definitive evidence remains elusive that replacing ER doctors with nonphysicians has a negative impact on patients, said Cameron Gettel, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. Private equity investment and the use of midlevel practitioners rose in lockstep in the ED, Dr. Gettel said, and in the absence of game-changing research, the pattern will likely continue.
“Worse patient outcomes haven’t really been shown across the board,” he said. “And I think until that is shown, then they will continue to play an increasing role.”
For private equity, dropping ED docs is a “simple equation”
Private equity companies pool money from wealthy investors to buy their way into various industries, often slashing spending and seeking to flip businesses in 3 to 7 years. While this business model is a proven moneymaker on Wall Street, it raises concerns in health care, where critics worry the pressure to turn big profits will influence life-or-death decisions that were once left solely to medical professionals.
Nearly $1 trillion in private equity funds have gone into almost 8,000 health care transactions over the past decade, according to industry tracker PitchBook, including buying into medical staffing companies that many hospitals hire to manage their emergency departments.
Two firms dominate the ED staffing industry: TeamHealth, bought by private equity firm Blackstone in 2016, and Envision Healthcare, bought by KKR in 2018. Trying to undercut these staffing giants is American Physician Partners, a rapidly expanding company that runs EDs in at least 17 states and is 50% owned by private equity firm BBH Capital Partners.
These staffing companies have been among the most aggressive in replacing doctors to cut costs, said Robert McNamara, MD, a founder of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia.
“It’s a relatively simple equation,” Dr. McNamara said. “Their No. 1 expense is the board-certified emergency physician. So they are going to want to keep that expense as low as possible.”
Not everyone sees the trend of private equity in ED staffing in a negative light. Jennifer Orozco, president of the American Academy of Physician Associates, which represents physician assistants, said even if the change – to use more nonphysician providers – is driven by the staffing firms’ desire to make more money, patients are still well served by a team approach that includes nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
“Though I see that shift, it’s not about profits at the end of the day,” Ms. Orozco said. “It’s about the patient.”
The “shift” is nearly invisible to patients because hospitals rarely promote branding from their ED staffing firms and there is little public documentation of private equity investments.
Arthur Smolensky, MD, a Tennessee emergency medicine specialist attempting to measure private equity’s intrusion into EDs, said his review of hospital job postings and employment contracts in 14 major metropolitan areas found that 43% of ED patients were seen in EDs staffed by companies with nonphysician owners, nearly all of whom are private equity investors.
Dr. Smolensky hopes to publish his full study, expanding to 55 metro areas, later this year. But this research will merely quantify what many doctors already know: The ED has changed. Demoralized by an increased focus on profit, and wary of a looming surplus of emergency medicine residents because there are fewer jobs to fill, many experienced doctors are leaving the ED on their own, he said.
“Most of us didn’t go into medicine to supervise an army of people that are not as well trained as we are,” Dr. Smolensky said. “We want to take care of patients.”
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER”
Joshua Allen, a nurse practitioner at a small Kentucky hospital, snaked a rubber hose through a rack of pork ribs to practice inserting a chest tube to fix a collapsed lung.
It was 2020, and American Physician Partners was restructuring the ED where Mr. Allen worked, reducing shifts from two doctors to one. Once Mr. Allen had placed 10 tubes under a doctor’s supervision, he would be allowed to do it on his own.
“I guess we’re the first guinea pigs for our ER,” he said. “If we do have a major trauma and multiple victims come in, there’s only one doctor there. ... We need to be prepared.”
Mr. Allen is one of many midlevel practitioners finding work in emergency departments. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants are among the fastest-growing occupations in the nation, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Generally, they have master’s degrees and receive several years of specialized schooling but have significantly less training than doctors. Many are permitted to diagnose patients and prescribe medication with little or no supervision from a doctor, although limitations vary by state.
The Neiman Institute found that the share of ED visits in which a midlevel practitioner was the main clinician increased by more than 172% between 2005 and 2020. Another study, in the Journal of Emergency Medicine, reported that if trends continue there may be equal numbers of midlevel practitioners and doctors in EDs by 2030.
There is little mystery as to why. Federal data shows emergency medicine doctors are paid about $310,000 a year on average, while nurse practitioners and physician assistants earn less than $120,000. Generally, hospitals can bill for care by a midlevel practitioner at 85% the rate of a doctor while paying them less than half as much.
Private equity can make millions in the gap.
For example, Envision once encouraged EDs to employ “the least expensive resource” and treat up to 35% of patients with midlevel practitioners, according to a 2017 PowerPoint presentation. The presentation drew scorn on social media and disappeared from Envision’s website.
Envision declined a request for a phone interview. In a written statement to KHN, spokesperson Aliese Polk said the company does not direct its physician leaders on how to care for patients and called the presentation a “concept guide” that does not represent current views.
American Physician Partners touted roughly the same staffing strategy in 2021 in response to the No Surprises Act, which threatened the company’s profits by outlawing surprise medical bills. In its confidential pitch to lenders, the company estimated it could cut almost $6 million by shifting more staffing from physicians to midlevel practitioners.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
USPSTF recommends against routine herpes screening for asymptomatic teens and adults
Asymptomatic adults, teens, and pregnant women with no known history or symptoms of herpes infection need not undergo routine screening, according to the latest recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The 2023 recommendation reaffirms the conclusion from 2016, wrote Carol M. Mangione, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and members of the task force.
“Currently, routine serologic screening for genital herpes is limited by the low predictive value of the widely available serologic screening tests and the expected high rate of false-positive results likely to occur with routine screening of asymptomatic persons in the U.S.,” the authors said.
In the recommendation, published in JAMA, the authors affirmed with moderate certainty and a grade D recommendation that the risks of routine screening for herpes simplex virus (HSV) in asymptomatic individuals outweigh the benefits.
The task force found no new evidence on the accuracy of serologic screening tests, the benefits of early detection and treatment, or on the harms of screening and treatment since the 2016 review of 17 studies in 19 publications, with data from more than 9,000 individuals.
Studies of the accuracy of serologic screening for herpes simplex virus-2 in the 2016 report mainly reflect populations with higher HSV-2 prevalence and are of limited applicability to the U.S. primary care population, the authors wrote. Evidence from the 2016 review also showed limited and inconsistent support for the early identification and treatment of HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, including those who were pregnant.
No new evidence has emerged since 2016 regarding harms of screening or treating genital herpes in asymptomatic individuals, the authors noted. “Based on previous evidence, the USPSTF estimated that using the widely available serologic tests for HSV-2, nearly 1 of every 2 diagnoses in the general U.S. primary care population could be false,” they said. The task force also concluded that the low accuracy of the current tests could prompt unnecessary treatment for individuals with false-positive diagnoses, as well as social and emotional harm for these individuals.
During a period of public comment from Aug. 16, 2022, to Sept. 12, 2022, individuals expressed concerns that the recommendation against routine screening showed a disinclination to take herpes seriously, and concerns that asymptomatic individuals could transmit the infection to sexual partners, the authors said. However, the estimated seroprevalence of HSV-1 and HSV-2 has declined in recent decades, and other comments supported the USPSTF’s analysis of the evidence and noted their consistency with current clinical practice.
The task force noted that research gaps remain and recognized the need to improve screening and treatment of genital herpes to prevent symptomatic episodes and transmission. Specifically, the USPSTF recommendation calls for more research to assess the accuracy of screening tests, to enroll more study participants from populations disproportionately affected by HSV, to examine the effect of behavioral counseling, and to clarify associations between HSV and pregnancy outcomes. In addition, the task force called for research to create an effective vaccine to prevent genital HSV infection and to develop a cure.
Targeted screening makes sense for now
“Given the frequency and severity of the range of diseases seen with HSV and the large proportion of persons who are asymptomatic, identifying carriers through type-specific serologic screening has long been considered a plausible strategy,” Mark D. Pearlman, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, accuracy of the currently available serology screening tests is low, and the adverse social and psychological effects and the impact on relationships for many asymptomatic individuals who test positive and may be incorrectly identified as infected remains a concern, said Dr. Pearlman.
Although some may be disagree about the value of routine serotesting for HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, other strategies can reduce the spread of infection and help those infected, he said.
Many experts continue to recommend targeted serotesting to high-risk populations, such as pregnant women whose nonpregnant partner is known to have genital or oral herpes and whose own infection status or serostatus is uncertain, said Dr. Pearlman. Other targeted strategies include screening individuals with recurrent or atypical genital symptoms and negative polymerase chain reaction assay or culture results, a clinical herpes diagnosis without laboratory confirmation, or those at increased risk because of a high number of sexual partners or a history of HIV infection, he said.
“Of note, the current CDC STI guidelines and ACOG both concur with the USPSTF that routine screening in the general population or routine screening during pregnancy are not recommended,” Dr. Pearlman said. Meanwhile, research efforts continue to help reduce the impact of HSV disease and development of a more effective testing methodology “might tip the balance in favor of routine screening” in the future, he emphasized.
The recommendations were supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The members of the task force received reimbursement for travel and an honorarium but had no other relevant financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Pearlman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Asymptomatic adults, teens, and pregnant women with no known history or symptoms of herpes infection need not undergo routine screening, according to the latest recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The 2023 recommendation reaffirms the conclusion from 2016, wrote Carol M. Mangione, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and members of the task force.
“Currently, routine serologic screening for genital herpes is limited by the low predictive value of the widely available serologic screening tests and the expected high rate of false-positive results likely to occur with routine screening of asymptomatic persons in the U.S.,” the authors said.
In the recommendation, published in JAMA, the authors affirmed with moderate certainty and a grade D recommendation that the risks of routine screening for herpes simplex virus (HSV) in asymptomatic individuals outweigh the benefits.
The task force found no new evidence on the accuracy of serologic screening tests, the benefits of early detection and treatment, or on the harms of screening and treatment since the 2016 review of 17 studies in 19 publications, with data from more than 9,000 individuals.
Studies of the accuracy of serologic screening for herpes simplex virus-2 in the 2016 report mainly reflect populations with higher HSV-2 prevalence and are of limited applicability to the U.S. primary care population, the authors wrote. Evidence from the 2016 review also showed limited and inconsistent support for the early identification and treatment of HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, including those who were pregnant.
No new evidence has emerged since 2016 regarding harms of screening or treating genital herpes in asymptomatic individuals, the authors noted. “Based on previous evidence, the USPSTF estimated that using the widely available serologic tests for HSV-2, nearly 1 of every 2 diagnoses in the general U.S. primary care population could be false,” they said. The task force also concluded that the low accuracy of the current tests could prompt unnecessary treatment for individuals with false-positive diagnoses, as well as social and emotional harm for these individuals.
During a period of public comment from Aug. 16, 2022, to Sept. 12, 2022, individuals expressed concerns that the recommendation against routine screening showed a disinclination to take herpes seriously, and concerns that asymptomatic individuals could transmit the infection to sexual partners, the authors said. However, the estimated seroprevalence of HSV-1 and HSV-2 has declined in recent decades, and other comments supported the USPSTF’s analysis of the evidence and noted their consistency with current clinical practice.
The task force noted that research gaps remain and recognized the need to improve screening and treatment of genital herpes to prevent symptomatic episodes and transmission. Specifically, the USPSTF recommendation calls for more research to assess the accuracy of screening tests, to enroll more study participants from populations disproportionately affected by HSV, to examine the effect of behavioral counseling, and to clarify associations between HSV and pregnancy outcomes. In addition, the task force called for research to create an effective vaccine to prevent genital HSV infection and to develop a cure.
Targeted screening makes sense for now
“Given the frequency and severity of the range of diseases seen with HSV and the large proportion of persons who are asymptomatic, identifying carriers through type-specific serologic screening has long been considered a plausible strategy,” Mark D. Pearlman, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, accuracy of the currently available serology screening tests is low, and the adverse social and psychological effects and the impact on relationships for many asymptomatic individuals who test positive and may be incorrectly identified as infected remains a concern, said Dr. Pearlman.
Although some may be disagree about the value of routine serotesting for HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, other strategies can reduce the spread of infection and help those infected, he said.
Many experts continue to recommend targeted serotesting to high-risk populations, such as pregnant women whose nonpregnant partner is known to have genital or oral herpes and whose own infection status or serostatus is uncertain, said Dr. Pearlman. Other targeted strategies include screening individuals with recurrent or atypical genital symptoms and negative polymerase chain reaction assay or culture results, a clinical herpes diagnosis without laboratory confirmation, or those at increased risk because of a high number of sexual partners or a history of HIV infection, he said.
“Of note, the current CDC STI guidelines and ACOG both concur with the USPSTF that routine screening in the general population or routine screening during pregnancy are not recommended,” Dr. Pearlman said. Meanwhile, research efforts continue to help reduce the impact of HSV disease and development of a more effective testing methodology “might tip the balance in favor of routine screening” in the future, he emphasized.
The recommendations were supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The members of the task force received reimbursement for travel and an honorarium but had no other relevant financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Pearlman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Asymptomatic adults, teens, and pregnant women with no known history or symptoms of herpes infection need not undergo routine screening, according to the latest recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The 2023 recommendation reaffirms the conclusion from 2016, wrote Carol M. Mangione, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and members of the task force.
“Currently, routine serologic screening for genital herpes is limited by the low predictive value of the widely available serologic screening tests and the expected high rate of false-positive results likely to occur with routine screening of asymptomatic persons in the U.S.,” the authors said.
In the recommendation, published in JAMA, the authors affirmed with moderate certainty and a grade D recommendation that the risks of routine screening for herpes simplex virus (HSV) in asymptomatic individuals outweigh the benefits.
The task force found no new evidence on the accuracy of serologic screening tests, the benefits of early detection and treatment, or on the harms of screening and treatment since the 2016 review of 17 studies in 19 publications, with data from more than 9,000 individuals.
Studies of the accuracy of serologic screening for herpes simplex virus-2 in the 2016 report mainly reflect populations with higher HSV-2 prevalence and are of limited applicability to the U.S. primary care population, the authors wrote. Evidence from the 2016 review also showed limited and inconsistent support for the early identification and treatment of HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, including those who were pregnant.
No new evidence has emerged since 2016 regarding harms of screening or treating genital herpes in asymptomatic individuals, the authors noted. “Based on previous evidence, the USPSTF estimated that using the widely available serologic tests for HSV-2, nearly 1 of every 2 diagnoses in the general U.S. primary care population could be false,” they said. The task force also concluded that the low accuracy of the current tests could prompt unnecessary treatment for individuals with false-positive diagnoses, as well as social and emotional harm for these individuals.
During a period of public comment from Aug. 16, 2022, to Sept. 12, 2022, individuals expressed concerns that the recommendation against routine screening showed a disinclination to take herpes seriously, and concerns that asymptomatic individuals could transmit the infection to sexual partners, the authors said. However, the estimated seroprevalence of HSV-1 and HSV-2 has declined in recent decades, and other comments supported the USPSTF’s analysis of the evidence and noted their consistency with current clinical practice.
The task force noted that research gaps remain and recognized the need to improve screening and treatment of genital herpes to prevent symptomatic episodes and transmission. Specifically, the USPSTF recommendation calls for more research to assess the accuracy of screening tests, to enroll more study participants from populations disproportionately affected by HSV, to examine the effect of behavioral counseling, and to clarify associations between HSV and pregnancy outcomes. In addition, the task force called for research to create an effective vaccine to prevent genital HSV infection and to develop a cure.
Targeted screening makes sense for now
“Given the frequency and severity of the range of diseases seen with HSV and the large proportion of persons who are asymptomatic, identifying carriers through type-specific serologic screening has long been considered a plausible strategy,” Mark D. Pearlman, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, accuracy of the currently available serology screening tests is low, and the adverse social and psychological effects and the impact on relationships for many asymptomatic individuals who test positive and may be incorrectly identified as infected remains a concern, said Dr. Pearlman.
Although some may be disagree about the value of routine serotesting for HSV-2 in asymptomatic individuals, other strategies can reduce the spread of infection and help those infected, he said.
Many experts continue to recommend targeted serotesting to high-risk populations, such as pregnant women whose nonpregnant partner is known to have genital or oral herpes and whose own infection status or serostatus is uncertain, said Dr. Pearlman. Other targeted strategies include screening individuals with recurrent or atypical genital symptoms and negative polymerase chain reaction assay or culture results, a clinical herpes diagnosis without laboratory confirmation, or those at increased risk because of a high number of sexual partners or a history of HIV infection, he said.
“Of note, the current CDC STI guidelines and ACOG both concur with the USPSTF that routine screening in the general population or routine screening during pregnancy are not recommended,” Dr. Pearlman said. Meanwhile, research efforts continue to help reduce the impact of HSV disease and development of a more effective testing methodology “might tip the balance in favor of routine screening” in the future, he emphasized.
The recommendations were supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The members of the task force received reimbursement for travel and an honorarium but had no other relevant financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Pearlman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA
Antenatal corticosteroids: Fresh answers to old questions
Giving corticosteroids to pregnant women at risk for preterm birth before 34 weeks of gestational age has been the standard of care since the 1990s, but a few scenarios for their use remain up for debate. Two studies presented this week at the 2023 meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal–Fetal Medicine provided some fresh insight into the practice that could help clinicians better manage pregnant patients.
Neurodevelopmental outcomes in late preterm
First, should antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) be given to mothers who present with late preterm labor, defined as 34-36 weeks’ gestational age?
A landmark randomized clinical trial published in 2016 demonstrated that use of ACS in mothers in late preterm labor reduced severe respiratory complications. That practice has largely been adopted by clinicians. The only downside, according to the researchers, was that infants whose mothers received steroid therapy were more likely to develop hypoglycemia. The condition is self-limiting, but studies have raised concern about the potential long-term risk of neurocognitive or psychological outcomes in infants with hypoglycemia.
Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MSc, endowed chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, led the 2016 study. Her team was unable to secure funding for their originally planned follow-up study of the infants 2 years later. But once the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists endorsed the practice and more women received ACS in the late preterm period, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and her colleagues felt the need to “follow up the infants just to see what the outcomes are from a neurodevelopmental standpoint,” she said.
Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and colleagues recruited children older than age 6 from the original trial whose parents were willing to have them participate in a follow-up study. A total of 949 from the initial 2,831 cohort completed cognitive testing and received assessments for cerebral palsy, social impairment within the autism spectrum, and behavioral and emotional problems.
At the SMFM conference, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman reported no differences in the primary outcome of cognitive function between those whose mothers had received a single course of betamethasone and those who did not, or any differences in rates of the other outcomes.
Kathy Zhang-Rutledge, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist who practices with Obstetrix Maternal Fetal Medicine Group of Houston, part of Pediatrix Medical Group, said she was glad to see a study that addressed the potential long-term adverse events associated with ACS in the late preterm period.
“Having this pretty large study – with really good neurological testing results – should help reassure clinicians that this is something they should consider adopting in their practice,” Dr. Zhang-Rutledge said.
Are boosters better?
The second unresolved question was if a repeat course of ACS should be administered when a woman at risk for preterm birth receives a course of steroids but does not deliver in the following 7 days.
Any benefits to the initial course of ACS wear off after a week. As a result, clinicians often give booster courses 7 days after the first dose if the infant is likely to be delivered in the following week. A 2009 study showed this approach may protect infants from respiratory problems, but data on long-term outcomes have been weak.
ACOG guidelines say to “consider” a booster dose in women who are less than 34 weeks’ gestation at risk for preterm delivery within 7 days.
The exception is when the mother already has experienced preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM), because ACS may increase the risk for infection for both mother and child. ACOG doesn’t take a stand on use of booster doses for PPROM, citing a lack of data to show that potential benefits outweigh the potential risks of this approach.
A recent multicenter, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial attempted to fill that void in knowledge. Between 2016 and 2022, 194 women with PPROM and gestational age less than 32 weeks who had received an initial ACS course at least 7 days prior to randomization received a booster course of ACS or saline placebo.
“Our primary outcome was designed to be like the prior rescue study (in 2009) that we did with patients with intact membranes,” said Andrew Combs, MD, PhD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Pediatrix Medical Group in Sunrise, Fla., who participated in the earlier study. “It was a composite of neonatal morbidity that was any one of a variety of outcomes including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, and neonatal death.”
The primary outcome occurred in 64% of women who received booster ACS and 66% with placebo (odds ratio, 0.82; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-1.57), according to Dr. Combs, who presented the findings at SMFM.
Although the study was not powered to detect significant differences in specific outcomes, the rate of neonatal sepsis was not higher in the ACS group, suggesting that ACS may be safe if membranes have ruptured, the researchers reported. But because the booster course of ACS did not prevent respiratory morbidity, clinicians may wonder what to do with the findings.
Niraj Chavan, MD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and women’s health at Saint Louis University, said he was unsure how the study would affect clinical practice.
The relatively small sample number of patients prevented analysis of specific outcomes and subgroup analyses of important variables such as race, ethnicity, gestational age, and other comorbid conditions in the mothers, he said. So clinicians still must weigh potential risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis.
“You have to think about it in buckets,” he said, “One is conditions that would increase the risk for neonatal morbidity. The other is the risk for infection, both for the mom and the baby.”
But for Dr. Combs, the interpretation of the findings was simpler: “We concluded that there’s no indication to give a booster course of steroids after a week has elapsed in patients with ruptured membranes.”
The study presented by Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The study presented by Dr. Combs was funded by MEDNAX Center for Research, Education, and Quality, which in 2022 was renamed Pediatrix Center for Research, Education,and Quality. Dr. Combs is an employee of Pediatrix Medical Group but has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman, Dr. Zhang-Rutledge, and Dr. Chavan report no relevant financial relationships.
Ann Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist in Portland, Ore.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Giving corticosteroids to pregnant women at risk for preterm birth before 34 weeks of gestational age has been the standard of care since the 1990s, but a few scenarios for their use remain up for debate. Two studies presented this week at the 2023 meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal–Fetal Medicine provided some fresh insight into the practice that could help clinicians better manage pregnant patients.
Neurodevelopmental outcomes in late preterm
First, should antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) be given to mothers who present with late preterm labor, defined as 34-36 weeks’ gestational age?
A landmark randomized clinical trial published in 2016 demonstrated that use of ACS in mothers in late preterm labor reduced severe respiratory complications. That practice has largely been adopted by clinicians. The only downside, according to the researchers, was that infants whose mothers received steroid therapy were more likely to develop hypoglycemia. The condition is self-limiting, but studies have raised concern about the potential long-term risk of neurocognitive or psychological outcomes in infants with hypoglycemia.
Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MSc, endowed chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, led the 2016 study. Her team was unable to secure funding for their originally planned follow-up study of the infants 2 years later. But once the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists endorsed the practice and more women received ACS in the late preterm period, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and her colleagues felt the need to “follow up the infants just to see what the outcomes are from a neurodevelopmental standpoint,” she said.
Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and colleagues recruited children older than age 6 from the original trial whose parents were willing to have them participate in a follow-up study. A total of 949 from the initial 2,831 cohort completed cognitive testing and received assessments for cerebral palsy, social impairment within the autism spectrum, and behavioral and emotional problems.
At the SMFM conference, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman reported no differences in the primary outcome of cognitive function between those whose mothers had received a single course of betamethasone and those who did not, or any differences in rates of the other outcomes.
Kathy Zhang-Rutledge, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist who practices with Obstetrix Maternal Fetal Medicine Group of Houston, part of Pediatrix Medical Group, said she was glad to see a study that addressed the potential long-term adverse events associated with ACS in the late preterm period.
“Having this pretty large study – with really good neurological testing results – should help reassure clinicians that this is something they should consider adopting in their practice,” Dr. Zhang-Rutledge said.
Are boosters better?
The second unresolved question was if a repeat course of ACS should be administered when a woman at risk for preterm birth receives a course of steroids but does not deliver in the following 7 days.
Any benefits to the initial course of ACS wear off after a week. As a result, clinicians often give booster courses 7 days after the first dose if the infant is likely to be delivered in the following week. A 2009 study showed this approach may protect infants from respiratory problems, but data on long-term outcomes have been weak.
ACOG guidelines say to “consider” a booster dose in women who are less than 34 weeks’ gestation at risk for preterm delivery within 7 days.
The exception is when the mother already has experienced preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM), because ACS may increase the risk for infection for both mother and child. ACOG doesn’t take a stand on use of booster doses for PPROM, citing a lack of data to show that potential benefits outweigh the potential risks of this approach.
A recent multicenter, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial attempted to fill that void in knowledge. Between 2016 and 2022, 194 women with PPROM and gestational age less than 32 weeks who had received an initial ACS course at least 7 days prior to randomization received a booster course of ACS or saline placebo.
“Our primary outcome was designed to be like the prior rescue study (in 2009) that we did with patients with intact membranes,” said Andrew Combs, MD, PhD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Pediatrix Medical Group in Sunrise, Fla., who participated in the earlier study. “It was a composite of neonatal morbidity that was any one of a variety of outcomes including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, and neonatal death.”
The primary outcome occurred in 64% of women who received booster ACS and 66% with placebo (odds ratio, 0.82; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-1.57), according to Dr. Combs, who presented the findings at SMFM.
Although the study was not powered to detect significant differences in specific outcomes, the rate of neonatal sepsis was not higher in the ACS group, suggesting that ACS may be safe if membranes have ruptured, the researchers reported. But because the booster course of ACS did not prevent respiratory morbidity, clinicians may wonder what to do with the findings.
Niraj Chavan, MD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and women’s health at Saint Louis University, said he was unsure how the study would affect clinical practice.
The relatively small sample number of patients prevented analysis of specific outcomes and subgroup analyses of important variables such as race, ethnicity, gestational age, and other comorbid conditions in the mothers, he said. So clinicians still must weigh potential risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis.
“You have to think about it in buckets,” he said, “One is conditions that would increase the risk for neonatal morbidity. The other is the risk for infection, both for the mom and the baby.”
But for Dr. Combs, the interpretation of the findings was simpler: “We concluded that there’s no indication to give a booster course of steroids after a week has elapsed in patients with ruptured membranes.”
The study presented by Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The study presented by Dr. Combs was funded by MEDNAX Center for Research, Education, and Quality, which in 2022 was renamed Pediatrix Center for Research, Education,and Quality. Dr. Combs is an employee of Pediatrix Medical Group but has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman, Dr. Zhang-Rutledge, and Dr. Chavan report no relevant financial relationships.
Ann Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist in Portland, Ore.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Giving corticosteroids to pregnant women at risk for preterm birth before 34 weeks of gestational age has been the standard of care since the 1990s, but a few scenarios for their use remain up for debate. Two studies presented this week at the 2023 meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal–Fetal Medicine provided some fresh insight into the practice that could help clinicians better manage pregnant patients.
Neurodevelopmental outcomes in late preterm
First, should antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) be given to mothers who present with late preterm labor, defined as 34-36 weeks’ gestational age?
A landmark randomized clinical trial published in 2016 demonstrated that use of ACS in mothers in late preterm labor reduced severe respiratory complications. That practice has largely been adopted by clinicians. The only downside, according to the researchers, was that infants whose mothers received steroid therapy were more likely to develop hypoglycemia. The condition is self-limiting, but studies have raised concern about the potential long-term risk of neurocognitive or psychological outcomes in infants with hypoglycemia.
Cynthia Gyamfi-Bannerman, MD, MSc, endowed chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, led the 2016 study. Her team was unable to secure funding for their originally planned follow-up study of the infants 2 years later. But once the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists endorsed the practice and more women received ACS in the late preterm period, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and her colleagues felt the need to “follow up the infants just to see what the outcomes are from a neurodevelopmental standpoint,” she said.
Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman and colleagues recruited children older than age 6 from the original trial whose parents were willing to have them participate in a follow-up study. A total of 949 from the initial 2,831 cohort completed cognitive testing and received assessments for cerebral palsy, social impairment within the autism spectrum, and behavioral and emotional problems.
At the SMFM conference, Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman reported no differences in the primary outcome of cognitive function between those whose mothers had received a single course of betamethasone and those who did not, or any differences in rates of the other outcomes.
Kathy Zhang-Rutledge, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist who practices with Obstetrix Maternal Fetal Medicine Group of Houston, part of Pediatrix Medical Group, said she was glad to see a study that addressed the potential long-term adverse events associated with ACS in the late preterm period.
“Having this pretty large study – with really good neurological testing results – should help reassure clinicians that this is something they should consider adopting in their practice,” Dr. Zhang-Rutledge said.
Are boosters better?
The second unresolved question was if a repeat course of ACS should be administered when a woman at risk for preterm birth receives a course of steroids but does not deliver in the following 7 days.
Any benefits to the initial course of ACS wear off after a week. As a result, clinicians often give booster courses 7 days after the first dose if the infant is likely to be delivered in the following week. A 2009 study showed this approach may protect infants from respiratory problems, but data on long-term outcomes have been weak.
ACOG guidelines say to “consider” a booster dose in women who are less than 34 weeks’ gestation at risk for preterm delivery within 7 days.
The exception is when the mother already has experienced preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM), because ACS may increase the risk for infection for both mother and child. ACOG doesn’t take a stand on use of booster doses for PPROM, citing a lack of data to show that potential benefits outweigh the potential risks of this approach.
A recent multicenter, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial attempted to fill that void in knowledge. Between 2016 and 2022, 194 women with PPROM and gestational age less than 32 weeks who had received an initial ACS course at least 7 days prior to randomization received a booster course of ACS or saline placebo.
“Our primary outcome was designed to be like the prior rescue study (in 2009) that we did with patients with intact membranes,” said Andrew Combs, MD, PhD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Pediatrix Medical Group in Sunrise, Fla., who participated in the earlier study. “It was a composite of neonatal morbidity that was any one of a variety of outcomes including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, and neonatal death.”
The primary outcome occurred in 64% of women who received booster ACS and 66% with placebo (odds ratio, 0.82; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-1.57), according to Dr. Combs, who presented the findings at SMFM.
Although the study was not powered to detect significant differences in specific outcomes, the rate of neonatal sepsis was not higher in the ACS group, suggesting that ACS may be safe if membranes have ruptured, the researchers reported. But because the booster course of ACS did not prevent respiratory morbidity, clinicians may wonder what to do with the findings.
Niraj Chavan, MD, an associate professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and women’s health at Saint Louis University, said he was unsure how the study would affect clinical practice.
The relatively small sample number of patients prevented analysis of specific outcomes and subgroup analyses of important variables such as race, ethnicity, gestational age, and other comorbid conditions in the mothers, he said. So clinicians still must weigh potential risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis.
“You have to think about it in buckets,” he said, “One is conditions that would increase the risk for neonatal morbidity. The other is the risk for infection, both for the mom and the baby.”
But for Dr. Combs, the interpretation of the findings was simpler: “We concluded that there’s no indication to give a booster course of steroids after a week has elapsed in patients with ruptured membranes.”
The study presented by Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The study presented by Dr. Combs was funded by MEDNAX Center for Research, Education, and Quality, which in 2022 was renamed Pediatrix Center for Research, Education,and Quality. Dr. Combs is an employee of Pediatrix Medical Group but has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gyamfi-Bannerman, Dr. Zhang-Rutledge, and Dr. Chavan report no relevant financial relationships.
Ann Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist in Portland, Ore.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
NICU use up, birth weights down in babies of mothers with HCV
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
Infants born to women infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) faced twice the risk of stays in the neonatal ICU (NICU) and 2.7 times the risk of low birth weight, a new analysis finds, even when researchers adjusted their data to control for injectable drug use and maternal medical comorbidity.
Clinicians should be “aware that the infants of pregnant people with HCV may have a high rate of need for higher-level pediatric care,” said Brenna L. Hughes, MD, MSc, chief of maternal fetal medicine at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C. She spoke in an interview about the findings, which were presented at the meeting sponsored by the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
As Dr. Hughes noted, “HCV remains a serious problem in pregnancy because it often goes undiagnosed and/or untreated prior to pregnancy. It can be passed to infants, and this can cause significant health-related outcomes for children as they age.”
For the multicenter U.S. study, researchers identified 249 pregnant mothers with HCV from a 2012-2018 cohort and matched them by gestational age to controls (n = 486). The average age was 28; 71.1% of the cases were non-Hispanic White versus 41.6% of the controls; 8.4% of cases were non-Hispanic Black versus 32.1% of controls (P < .001 for race/ethnicity analysis); and 73% of cases were smokers versus 18% of controls (P < .001). More than 19% of cases reported injectable drug use during pregnancy versus 0.2% of controls (P < .001).
The researchers adjusted their findings for maternal age, body mass index, injectable drug use, and maternal comorbidity.
An earlier analysis of the study data found that 6% of pregnant women with HCV passed it on to their infants, especially those with high levels of virus in their systems. For the new study, researchers focused on various outcomes to test the assumption that “adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with HCV are related to prematurity or to ongoing use of injection drugs,” Dr. Hughes said.
There was no increase in rates of preterm birth or adverse maternal outcomes in the HCV cases. However, infants born to women with HCV were more likely than the controls to require a stay in the NICU (45% vs. 19%; adjusted relative risk, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.58). They were also more likely to have lower birth weights (small for gestational age < 5th percentile) (10.6% vs. 3.1%; ARR, 2.72; 95% CI, 1.38-5.34).
No difference in outcomes was seen when HCV cases with viremia (33%) were excluded.
“The most surprising finding was that the need for higher-level pediatric care was so high even though there wasn’t an increased risk of prematurity,” Dr. Hughes said.
She added it’s not clear why NICU stays and low birth weights were more common in infants of women with HCV. “It is possible that the higher risk of need for higher-level pediatric care was related to a need for observation or treatment due to use of opioid replacement therapies with opioid agonists.” As for lower birth weight, “there may be other unmeasured risk factors.”
Tatyana Kushner, MD, MSCE, of the division of liver diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview that the study adds to limited data about HCV in pregnancy. “These findings have been demonstrated in prior studies, and it would be important to tease apart whether [low birth weight] is related to the virus itself or more related to other confounding associated factors such as maternal substance use as well as other associated social determinants of health among women with HCV.”
As for the study’s message, Dr. Kushner said it makes it clear that “hepatitis C adversely impacts outcomes of pregnancy and it is important to identify women of childbearing age for treatment early, ideally prior to pregnancy, in order to improve their pregnancy outcomes. In addition, treatment of hepatitis C during pregnancy should be explored further to determine if treatment during pregnancy can improve outcomes.”
At the moment, she said, “there are ongoing studies to delineate the safety and efficacy of hepatitis C treatment during pregnancy. Given that we are screening for hepatitis C during pregnancy, we need clear recommendations on the use of direct-acting antivirals in people who screen positive.”
The study was funded by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The authors have no disclosures. Dr. Kushner disclosed research support (Gilead) and advisory board service (Gilead, AbbVie, Bausch, GlaxoSmithKline, and Eiger).
FROM THE PREGNANCY MEETING
‘Forever chemicals’ up type 2 diabetes risk in midlife White women
Middle-aged White women who had higher levels of some breakdown products of phthalates – a class of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or “forever chemicals,” that act as plasticizers – had a significantly greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes over a 6-year period compared with other similar women.
However, this association was not seen among Black or Asian middle-aged women.
These findings from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation – Multipollutant Study (SWAN-MPS), by Mia Q. Peng, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, have been published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
“Overall, our study has added some evidence to support the potential diabetogenic effects of phthalates, but it also highlights that much is still unknown about the metabolic effects of these chemicals,” the group noted.
“The apparent racial/ethnic differences in the associations between phthalates and incident diabetes should be investigated in future studies,” they cautioned.
Recruiting younger participants and observing them longer, they suggested, “will also help us understand the effects of phthalates on different stages of the diabetogenic process, including whether body fat gain is an important mediator.”
Phthalates are all around us
Low-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to personal care products, such as fragrance, nail polish, and some feminine hygiene products, as solvents, plasticizers, and fixatives, the researchers explained.
And high-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to polyvinyl chloride plastic products, such as plastic food packaging, clothing, and vinyl flooring, as plasticizers.
Phthalates have been hypothesized to contribute to the development of diabetes, but longitudinal evidence in humans was limited.
“Given widespread exposure to phthalates and the enormous costs of diabetes to individuals and societies, ongoing investments in the research on phthalates’ metabolic effects are warranted,” the researchers concluded.
Racial differences in phthalates and incident diabetes
“A new finding is that we observed some phthalates are associated with a higher risk of diabetes development, especially in White women [that] were not seen in Black or Asian women,” senior author Sung Kyun Park, ScD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization.
“We were surprised to see the racial/ethnic differences,” added Dr. Peng, formerly of the University of Michigan and now at Lifecourse Epidemiology of Adiposity and Diabetes Center, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
A possible explanation is that “compared to White women, Black women develop diabetes at a younger age and are exposed to higher levels of several phthalates,” and this study excluded women who already had diabetes by midlife, she noted.
“Although our study was conducted in a cohort of women,” Dr. Park stressed, “we hope that our findings are not interpreted that only women should be concerned of phthalates. Our findings add to the current literature that phthalates may be a potential risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
“Certain phthalates are prohibited in children’s toys and child care articles,” Dr. Peng noted, as explained by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. In addition, a bill has been introduced in Congress to ban phthalates in food contact substances.
“If phthalates are removed from plastics and other consumer products,” she cautioned, “we do have to be careful in the process to avoid replacing them with some other potentially harmful chemicals.”
A well-known example of this type of “regrettable substitution,” Dr. Park added, “is ‘BPA-free’ plastics that replaced bisphenol A with other bisphenols such as bisphenol-F (BPF) or bisphenol-S (BPS). The product has a label of ‘BPA-free’, but those replaced chemicals turned out to be equally toxic. Science is slow to determine if a new chemical introduced to the market is safe and can replace a regulated chemical.”
And studies have shown that a diet rich in meat, fat, and ultraprocessed foods is associated with increased exposures to some phthalates, especially when the foods are obtained away from home, such as fast foods, Dr. Peng observed. In addition, some phthalates are added to personal care products such as fragrance.
“As a first step,” she said, “I think reducing consumption of ultraprocessed foods packaged in plastics may help reduce phthalate exposure.”
A 2020 report from the Endocrine Society and the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), titled, “Plastics, EDCs, and Health,” summarizes research on bisphenol A, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), phthalates, and other EDCs that leach from plastics. The Endocrine Society website also has a link to a 2-page summary.
Levels of 12 phthalate metabolites
Previously, the researchers reported how another class of “forever chemicals,” PFAS, were associated with risk of hypertension in a 17-year follow-up of middle-aged women in the SWAN study.
In the current study, they analyzed data from 1,308 women in SWAN-MPS who had been recruited at five study sites (Oakland, Calif; Los Angeles; Detroit; Pittsburgh; and Boston).
The women were between ages 42 and 52 years in 1996-1997 and self-identified as White, Black, Chinese, or Japanese.
They did not have diabetes in 1999-2000 and had sufficient urine samples for phthalate assessment then and midway through a 6-year follow-up.
The women were a median age of 49 years in 1999-2000. About half were White, 20% were Black, 13% were Chinese, and 15% were Japanese.
Researchers analyzed levels of 12 metabolites, chosen because their parent phthalates have been widely used in industry and commerce, and exposure to these phthalates is a national biomonitoring priority.
The measured phthalates were:
Three metabolites of low-molecular-weight phthalates:
- mono-ethyl phthalate (MEP)
- mono-n-butyl phthalate (MnBP)
- mono-isobutyl phthalate (MiBP)
Four metabolites of the high-molecular-weight phthalate di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), which is of particular public health interest:
- mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate (MECPP)
Five metabolites of other high-molecular-weight phthalates:
- monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP)
- monoisononyl phthalate (MiNP)
- mono-carboxyoctyl phthalate (MCOP)
- mono-carboxy-isononyl phthalate (MCNP)
- mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP)
The researchers excluded MiNP from all analyses because it was detected in less than 1% of urine samples.
The different phthalate metabolites were detected in 84.8% of samples (MEHP) to 100% of samples (MnBP and MECPP).
Women who were younger, Black, current smokers, or obese generally had higher concentrations of phthalate metabolites.
Over 6 years, 61 women developed diabetes (an incidence rate of 8.1 per 1000 person-years).
Compared with other women, those with incident diabetes had significantly higher concentrations of all phthalate metabolites except DEHP metabolites and MCPP.
Phthalates were not associated with incident diabetes in Black or Asian women.
However, among White women, each doubling of the concentrations of MiBP, MBzP, MCOP, MCNP, and MCCP was associated with a 30% to 63% higher incidence of diabetes (HR 1.30 for MCNP; HR 1.63 for MiBP).
The SWAN study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Department of Health & Human Services, National Institute on Aging, National Institute of Nursing Research, NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health, and SWAN Repository. The current study was supported by the National Center for Research Resources, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, NIH, National Institute of Environmental Health, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Dr. Peng was supported by an Interdisciplinary Research Training on Health and Aging grant from the NIA. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Middle-aged White women who had higher levels of some breakdown products of phthalates – a class of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or “forever chemicals,” that act as plasticizers – had a significantly greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes over a 6-year period compared with other similar women.
However, this association was not seen among Black or Asian middle-aged women.
These findings from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation – Multipollutant Study (SWAN-MPS), by Mia Q. Peng, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, have been published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
“Overall, our study has added some evidence to support the potential diabetogenic effects of phthalates, but it also highlights that much is still unknown about the metabolic effects of these chemicals,” the group noted.
“The apparent racial/ethnic differences in the associations between phthalates and incident diabetes should be investigated in future studies,” they cautioned.
Recruiting younger participants and observing them longer, they suggested, “will also help us understand the effects of phthalates on different stages of the diabetogenic process, including whether body fat gain is an important mediator.”
Phthalates are all around us
Low-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to personal care products, such as fragrance, nail polish, and some feminine hygiene products, as solvents, plasticizers, and fixatives, the researchers explained.
And high-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to polyvinyl chloride plastic products, such as plastic food packaging, clothing, and vinyl flooring, as plasticizers.
Phthalates have been hypothesized to contribute to the development of diabetes, but longitudinal evidence in humans was limited.
“Given widespread exposure to phthalates and the enormous costs of diabetes to individuals and societies, ongoing investments in the research on phthalates’ metabolic effects are warranted,” the researchers concluded.
Racial differences in phthalates and incident diabetes
“A new finding is that we observed some phthalates are associated with a higher risk of diabetes development, especially in White women [that] were not seen in Black or Asian women,” senior author Sung Kyun Park, ScD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization.
“We were surprised to see the racial/ethnic differences,” added Dr. Peng, formerly of the University of Michigan and now at Lifecourse Epidemiology of Adiposity and Diabetes Center, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
A possible explanation is that “compared to White women, Black women develop diabetes at a younger age and are exposed to higher levels of several phthalates,” and this study excluded women who already had diabetes by midlife, she noted.
“Although our study was conducted in a cohort of women,” Dr. Park stressed, “we hope that our findings are not interpreted that only women should be concerned of phthalates. Our findings add to the current literature that phthalates may be a potential risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
“Certain phthalates are prohibited in children’s toys and child care articles,” Dr. Peng noted, as explained by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. In addition, a bill has been introduced in Congress to ban phthalates in food contact substances.
“If phthalates are removed from plastics and other consumer products,” she cautioned, “we do have to be careful in the process to avoid replacing them with some other potentially harmful chemicals.”
A well-known example of this type of “regrettable substitution,” Dr. Park added, “is ‘BPA-free’ plastics that replaced bisphenol A with other bisphenols such as bisphenol-F (BPF) or bisphenol-S (BPS). The product has a label of ‘BPA-free’, but those replaced chemicals turned out to be equally toxic. Science is slow to determine if a new chemical introduced to the market is safe and can replace a regulated chemical.”
And studies have shown that a diet rich in meat, fat, and ultraprocessed foods is associated with increased exposures to some phthalates, especially when the foods are obtained away from home, such as fast foods, Dr. Peng observed. In addition, some phthalates are added to personal care products such as fragrance.
“As a first step,” she said, “I think reducing consumption of ultraprocessed foods packaged in plastics may help reduce phthalate exposure.”
A 2020 report from the Endocrine Society and the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), titled, “Plastics, EDCs, and Health,” summarizes research on bisphenol A, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), phthalates, and other EDCs that leach from plastics. The Endocrine Society website also has a link to a 2-page summary.
Levels of 12 phthalate metabolites
Previously, the researchers reported how another class of “forever chemicals,” PFAS, were associated with risk of hypertension in a 17-year follow-up of middle-aged women in the SWAN study.
In the current study, they analyzed data from 1,308 women in SWAN-MPS who had been recruited at five study sites (Oakland, Calif; Los Angeles; Detroit; Pittsburgh; and Boston).
The women were between ages 42 and 52 years in 1996-1997 and self-identified as White, Black, Chinese, or Japanese.
They did not have diabetes in 1999-2000 and had sufficient urine samples for phthalate assessment then and midway through a 6-year follow-up.
The women were a median age of 49 years in 1999-2000. About half were White, 20% were Black, 13% were Chinese, and 15% were Japanese.
Researchers analyzed levels of 12 metabolites, chosen because their parent phthalates have been widely used in industry and commerce, and exposure to these phthalates is a national biomonitoring priority.
The measured phthalates were:
Three metabolites of low-molecular-weight phthalates:
- mono-ethyl phthalate (MEP)
- mono-n-butyl phthalate (MnBP)
- mono-isobutyl phthalate (MiBP)
Four metabolites of the high-molecular-weight phthalate di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), which is of particular public health interest:
- mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate (MECPP)
Five metabolites of other high-molecular-weight phthalates:
- monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP)
- monoisononyl phthalate (MiNP)
- mono-carboxyoctyl phthalate (MCOP)
- mono-carboxy-isononyl phthalate (MCNP)
- mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP)
The researchers excluded MiNP from all analyses because it was detected in less than 1% of urine samples.
The different phthalate metabolites were detected in 84.8% of samples (MEHP) to 100% of samples (MnBP and MECPP).
Women who were younger, Black, current smokers, or obese generally had higher concentrations of phthalate metabolites.
Over 6 years, 61 women developed diabetes (an incidence rate of 8.1 per 1000 person-years).
Compared with other women, those with incident diabetes had significantly higher concentrations of all phthalate metabolites except DEHP metabolites and MCPP.
Phthalates were not associated with incident diabetes in Black or Asian women.
However, among White women, each doubling of the concentrations of MiBP, MBzP, MCOP, MCNP, and MCCP was associated with a 30% to 63% higher incidence of diabetes (HR 1.30 for MCNP; HR 1.63 for MiBP).
The SWAN study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Department of Health & Human Services, National Institute on Aging, National Institute of Nursing Research, NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health, and SWAN Repository. The current study was supported by the National Center for Research Resources, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, NIH, National Institute of Environmental Health, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Dr. Peng was supported by an Interdisciplinary Research Training on Health and Aging grant from the NIA. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Middle-aged White women who had higher levels of some breakdown products of phthalates – a class of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or “forever chemicals,” that act as plasticizers – had a significantly greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes over a 6-year period compared with other similar women.
However, this association was not seen among Black or Asian middle-aged women.
These findings from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation – Multipollutant Study (SWAN-MPS), by Mia Q. Peng, PhD, MPH, and colleagues, have been published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
“Overall, our study has added some evidence to support the potential diabetogenic effects of phthalates, but it also highlights that much is still unknown about the metabolic effects of these chemicals,” the group noted.
“The apparent racial/ethnic differences in the associations between phthalates and incident diabetes should be investigated in future studies,” they cautioned.
Recruiting younger participants and observing them longer, they suggested, “will also help us understand the effects of phthalates on different stages of the diabetogenic process, including whether body fat gain is an important mediator.”
Phthalates are all around us
Low-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to personal care products, such as fragrance, nail polish, and some feminine hygiene products, as solvents, plasticizers, and fixatives, the researchers explained.
And high-molecular-weight phthalates are frequently added to polyvinyl chloride plastic products, such as plastic food packaging, clothing, and vinyl flooring, as plasticizers.
Phthalates have been hypothesized to contribute to the development of diabetes, but longitudinal evidence in humans was limited.
“Given widespread exposure to phthalates and the enormous costs of diabetes to individuals and societies, ongoing investments in the research on phthalates’ metabolic effects are warranted,” the researchers concluded.
Racial differences in phthalates and incident diabetes
“A new finding is that we observed some phthalates are associated with a higher risk of diabetes development, especially in White women [that] were not seen in Black or Asian women,” senior author Sung Kyun Park, ScD, MPH, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, told this news organization.
“We were surprised to see the racial/ethnic differences,” added Dr. Peng, formerly of the University of Michigan and now at Lifecourse Epidemiology of Adiposity and Diabetes Center, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
A possible explanation is that “compared to White women, Black women develop diabetes at a younger age and are exposed to higher levels of several phthalates,” and this study excluded women who already had diabetes by midlife, she noted.
“Although our study was conducted in a cohort of women,” Dr. Park stressed, “we hope that our findings are not interpreted that only women should be concerned of phthalates. Our findings add to the current literature that phthalates may be a potential risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
“Certain phthalates are prohibited in children’s toys and child care articles,” Dr. Peng noted, as explained by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. In addition, a bill has been introduced in Congress to ban phthalates in food contact substances.
“If phthalates are removed from plastics and other consumer products,” she cautioned, “we do have to be careful in the process to avoid replacing them with some other potentially harmful chemicals.”
A well-known example of this type of “regrettable substitution,” Dr. Park added, “is ‘BPA-free’ plastics that replaced bisphenol A with other bisphenols such as bisphenol-F (BPF) or bisphenol-S (BPS). The product has a label of ‘BPA-free’, but those replaced chemicals turned out to be equally toxic. Science is slow to determine if a new chemical introduced to the market is safe and can replace a regulated chemical.”
And studies have shown that a diet rich in meat, fat, and ultraprocessed foods is associated with increased exposures to some phthalates, especially when the foods are obtained away from home, such as fast foods, Dr. Peng observed. In addition, some phthalates are added to personal care products such as fragrance.
“As a first step,” she said, “I think reducing consumption of ultraprocessed foods packaged in plastics may help reduce phthalate exposure.”
A 2020 report from the Endocrine Society and the International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN), titled, “Plastics, EDCs, and Health,” summarizes research on bisphenol A, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), phthalates, and other EDCs that leach from plastics. The Endocrine Society website also has a link to a 2-page summary.
Levels of 12 phthalate metabolites
Previously, the researchers reported how another class of “forever chemicals,” PFAS, were associated with risk of hypertension in a 17-year follow-up of middle-aged women in the SWAN study.
In the current study, they analyzed data from 1,308 women in SWAN-MPS who had been recruited at five study sites (Oakland, Calif; Los Angeles; Detroit; Pittsburgh; and Boston).
The women were between ages 42 and 52 years in 1996-1997 and self-identified as White, Black, Chinese, or Japanese.
They did not have diabetes in 1999-2000 and had sufficient urine samples for phthalate assessment then and midway through a 6-year follow-up.
The women were a median age of 49 years in 1999-2000. About half were White, 20% were Black, 13% were Chinese, and 15% were Japanese.
Researchers analyzed levels of 12 metabolites, chosen because their parent phthalates have been widely used in industry and commerce, and exposure to these phthalates is a national biomonitoring priority.
The measured phthalates were:
Three metabolites of low-molecular-weight phthalates:
- mono-ethyl phthalate (MEP)
- mono-n-butyl phthalate (MnBP)
- mono-isobutyl phthalate (MiBP)
Four metabolites of the high-molecular-weight phthalate di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), which is of particular public health interest:
- mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP)
- mono(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate (MECPP)
Five metabolites of other high-molecular-weight phthalates:
- monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP)
- monoisononyl phthalate (MiNP)
- mono-carboxyoctyl phthalate (MCOP)
- mono-carboxy-isononyl phthalate (MCNP)
- mono(3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP)
The researchers excluded MiNP from all analyses because it was detected in less than 1% of urine samples.
The different phthalate metabolites were detected in 84.8% of samples (MEHP) to 100% of samples (MnBP and MECPP).
Women who were younger, Black, current smokers, or obese generally had higher concentrations of phthalate metabolites.
Over 6 years, 61 women developed diabetes (an incidence rate of 8.1 per 1000 person-years).
Compared with other women, those with incident diabetes had significantly higher concentrations of all phthalate metabolites except DEHP metabolites and MCPP.
Phthalates were not associated with incident diabetes in Black or Asian women.
However, among White women, each doubling of the concentrations of MiBP, MBzP, MCOP, MCNP, and MCCP was associated with a 30% to 63% higher incidence of diabetes (HR 1.30 for MCNP; HR 1.63 for MiBP).
The SWAN study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Department of Health & Human Services, National Institute on Aging, National Institute of Nursing Research, NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health, and SWAN Repository. The current study was supported by the National Center for Research Resources, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, NIH, National Institute of Environmental Health, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Dr. Peng was supported by an Interdisciplinary Research Training on Health and Aging grant from the NIA. The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Valid option’ for partial breast irradiation in breast cancer
The study covered in this summary was published on researchsquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- According to numerous guidelines, partial breast irradiation after lumpectomy is a sound approach for early-stage breast cancer, but there is a lack of consensus about treatment schedules.
- The investigators suggest that 30 Gy in five daily fractions is a “valid option” for these patients in a field that lacks consensus.
Study design
- The team reviewed 381 women with early breast cancer treated with this approach (30 Gy in five daily fractions) at their center from 2013 to 2022.
- Half of patients had left-sided tumors, 94.5% had invasive ductal carcinomas, 96.6% had grade 1 or grade 2 disease, and tumors were luminal like in 99.2% of patients.
- Following lumpectomy, women underwent partial breast irradiation to the tumor bed plus 15 mm of isometric expansion beyond it.
- Follow-up was a median of 28 months.
Key results
- Seven patients (2%) had a local recurrence, of which two were in the treatment field.
- Three-year local control, disease-free survival, and overall survival were high (97.5%, 95.7%, and 96.9%, respectively).
- Nearly 90% of patients and 97% of physicians reported good or excellent cosmesis.
- Ten patients (2.9%) had grade 2 late toxicities, including edema, asthenia, and fibrosis; there were no grade 3 or higher adverse events.
- Five patients (1.5%) had late cardiac major events, four of whom were treated on the right breast; three patients (0.9%) had late pulmonary fibrosis.
- The safety and efficacy outcomes are in line with previous reports, including those that used different dosage and/or fractionation schedules.
Limitations
- The study was retrospective, with a relatively short follow-up.
- Quality of life was not assessed.
- There was no objective baseline measure of cosmesis against which to compare cosmetic results.
Disclosures
- There was no funding for the study, and the investigators didn’t have any conflicts of interest to report.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “One-Week External Beam Partial Breast Irradiation: Survival and Toxicity Outcomes,” led by Riccardo Ray Colciago from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan. The study has not been peer reviewed. The full text can be found at researchsquare.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on researchsquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- According to numerous guidelines, partial breast irradiation after lumpectomy is a sound approach for early-stage breast cancer, but there is a lack of consensus about treatment schedules.
- The investigators suggest that 30 Gy in five daily fractions is a “valid option” for these patients in a field that lacks consensus.
Study design
- The team reviewed 381 women with early breast cancer treated with this approach (30 Gy in five daily fractions) at their center from 2013 to 2022.
- Half of patients had left-sided tumors, 94.5% had invasive ductal carcinomas, 96.6% had grade 1 or grade 2 disease, and tumors were luminal like in 99.2% of patients.
- Following lumpectomy, women underwent partial breast irradiation to the tumor bed plus 15 mm of isometric expansion beyond it.
- Follow-up was a median of 28 months.
Key results
- Seven patients (2%) had a local recurrence, of which two were in the treatment field.
- Three-year local control, disease-free survival, and overall survival were high (97.5%, 95.7%, and 96.9%, respectively).
- Nearly 90% of patients and 97% of physicians reported good or excellent cosmesis.
- Ten patients (2.9%) had grade 2 late toxicities, including edema, asthenia, and fibrosis; there were no grade 3 or higher adverse events.
- Five patients (1.5%) had late cardiac major events, four of whom were treated on the right breast; three patients (0.9%) had late pulmonary fibrosis.
- The safety and efficacy outcomes are in line with previous reports, including those that used different dosage and/or fractionation schedules.
Limitations
- The study was retrospective, with a relatively short follow-up.
- Quality of life was not assessed.
- There was no objective baseline measure of cosmesis against which to compare cosmetic results.
Disclosures
- There was no funding for the study, and the investigators didn’t have any conflicts of interest to report.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “One-Week External Beam Partial Breast Irradiation: Survival and Toxicity Outcomes,” led by Riccardo Ray Colciago from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan. The study has not been peer reviewed. The full text can be found at researchsquare.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on researchsquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- According to numerous guidelines, partial breast irradiation after lumpectomy is a sound approach for early-stage breast cancer, but there is a lack of consensus about treatment schedules.
- The investigators suggest that 30 Gy in five daily fractions is a “valid option” for these patients in a field that lacks consensus.
Study design
- The team reviewed 381 women with early breast cancer treated with this approach (30 Gy in five daily fractions) at their center from 2013 to 2022.
- Half of patients had left-sided tumors, 94.5% had invasive ductal carcinomas, 96.6% had grade 1 or grade 2 disease, and tumors were luminal like in 99.2% of patients.
- Following lumpectomy, women underwent partial breast irradiation to the tumor bed plus 15 mm of isometric expansion beyond it.
- Follow-up was a median of 28 months.
Key results
- Seven patients (2%) had a local recurrence, of which two were in the treatment field.
- Three-year local control, disease-free survival, and overall survival were high (97.5%, 95.7%, and 96.9%, respectively).
- Nearly 90% of patients and 97% of physicians reported good or excellent cosmesis.
- Ten patients (2.9%) had grade 2 late toxicities, including edema, asthenia, and fibrosis; there were no grade 3 or higher adverse events.
- Five patients (1.5%) had late cardiac major events, four of whom were treated on the right breast; three patients (0.9%) had late pulmonary fibrosis.
- The safety and efficacy outcomes are in line with previous reports, including those that used different dosage and/or fractionation schedules.
Limitations
- The study was retrospective, with a relatively short follow-up.
- Quality of life was not assessed.
- There was no objective baseline measure of cosmesis against which to compare cosmetic results.
Disclosures
- There was no funding for the study, and the investigators didn’t have any conflicts of interest to report.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “One-Week External Beam Partial Breast Irradiation: Survival and Toxicity Outcomes,” led by Riccardo Ray Colciago from the Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan. The study has not been peer reviewed. The full text can be found at researchsquare.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.