User login
Federal Health Care Data Trends 2024
Federal Health Care Data Trends is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, showcasing the latest research in health care for veterans and active-duty military members via compelling infographics. Click below to view highlights from the issue:
Federal Health Care Data Trends is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, showcasing the latest research in health care for veterans and active-duty military members via compelling infographics. Click below to view highlights from the issue:
Federal Health Care Data Trends is a special supplement to Federal Practitioner, showcasing the latest research in health care for veterans and active-duty military members via compelling infographics. Click below to view highlights from the issue:
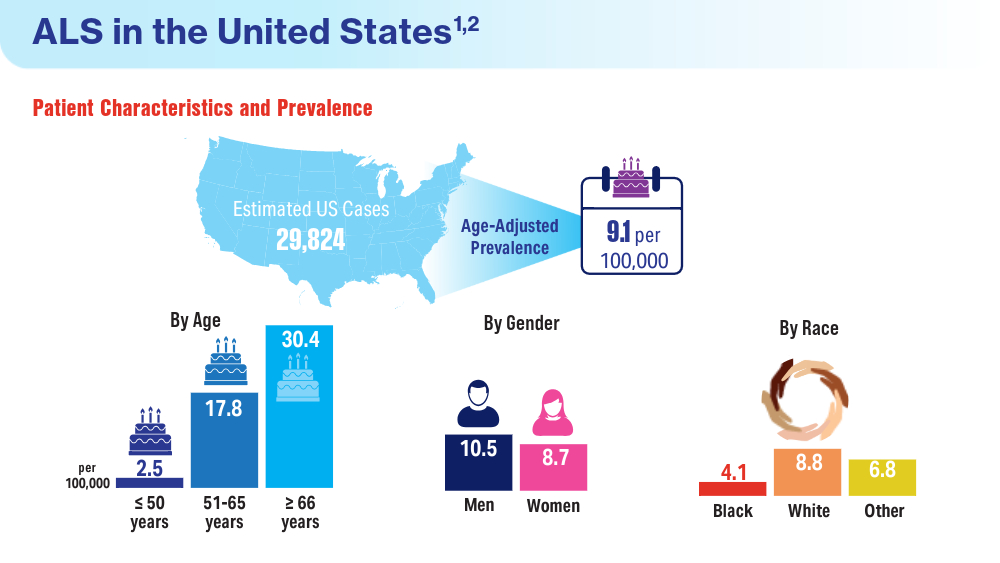
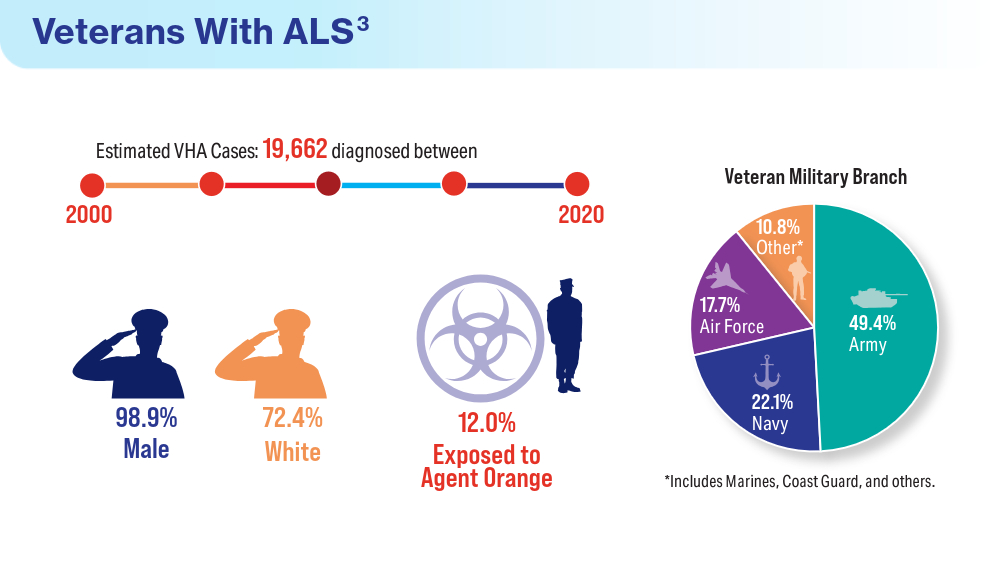
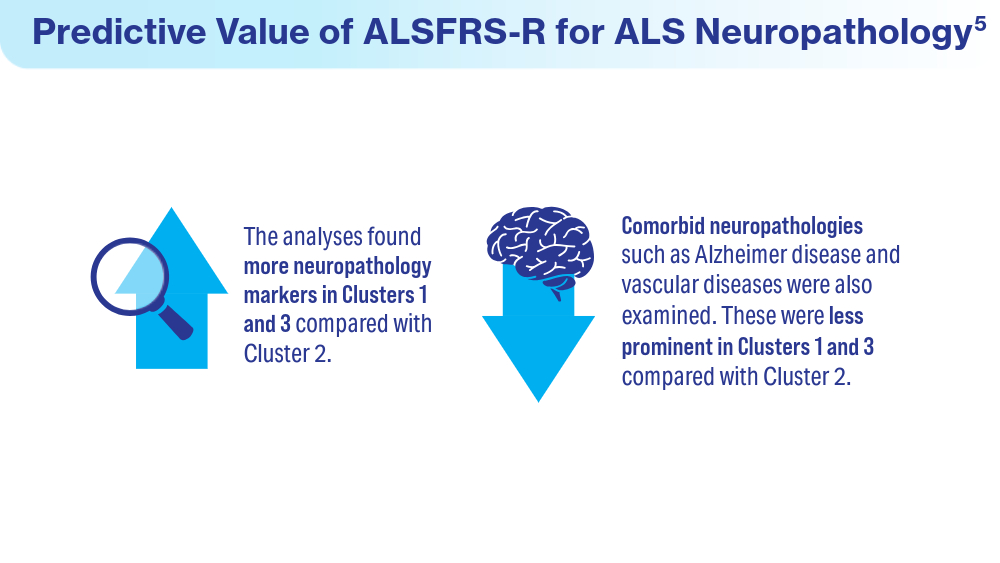
Data Trends 2024: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Mehta P, Raymond J, Zhang Y, et al. Prevalence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the United States, 2018. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 21, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2245858
- What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/als/WhatisAmyotrophiclateralsclerosis.html
- Reimer RJ, Goncalves A, Soper B, et al. An electronic health record cohort of veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 9, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2239300
- Kudritzki V, Howard IM. Telehealth-based exercise in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1238916. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1238916
- Colvin LE, Foster ZW, Stein TD, et al. Utility of the ALSFRS-R for predicting ALS and comorbid disease neuropathology: the Veterans Affairs Biorepository Brain Bank. Muscle Nerve. 2022;66(2):167-174. doi:10.1002/mus.27635
- Rabadi MH, Russell KC, Xu C. Predictors of mortality in veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: respiratory status and speech disorder at presentation. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e943288. doi:10.12659/MSM.943288
- Mehta P, Raymond J, Zhang Y, et al. Prevalence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the United States, 2018. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 21, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2245858
- What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/als/WhatisAmyotrophiclateralsclerosis.html
- Reimer RJ, Goncalves A, Soper B, et al. An electronic health record cohort of veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 9, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2239300
- Kudritzki V, Howard IM. Telehealth-based exercise in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1238916. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1238916
- Colvin LE, Foster ZW, Stein TD, et al. Utility of the ALSFRS-R for predicting ALS and comorbid disease neuropathology: the Veterans Affairs Biorepository Brain Bank. Muscle Nerve. 2022;66(2):167-174. doi:10.1002/mus.27635
- Rabadi MH, Russell KC, Xu C. Predictors of mortality in veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: respiratory status and speech disorder at presentation. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e943288. doi:10.12659/MSM.943288
- Mehta P, Raymond J, Zhang Y, et al. Prevalence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the United States, 2018. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 21, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2245858
- What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated May 13, 2022. Accessed April 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/als/WhatisAmyotrophiclateralsclerosis.html
- Reimer RJ, Goncalves A, Soper B, et al. An electronic health record cohort of veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. Published online August 9, 2023. doi:10.1080/21678421.2023.2239300
- Kudritzki V, Howard IM. Telehealth-based exercise in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1238916. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1238916
- Colvin LE, Foster ZW, Stein TD, et al. Utility of the ALSFRS-R for predicting ALS and comorbid disease neuropathology: the Veterans Affairs Biorepository Brain Bank. Muscle Nerve. 2022;66(2):167-174. doi:10.1002/mus.27635
- Rabadi MH, Russell KC, Xu C. Predictors of mortality in veterans with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: respiratory status and speech disorder at presentation. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e943288. doi:10.12659/MSM.943288
Data Trends 2024: Arthritis
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Overview of VA research on arthritis. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/arthritis.cfm
- Fallon EA, Boring MA, Foster AL, Stowe EW, Lites TD, Allen KD. Arthritis prevalence among veterans — United States, 2017–2021. MMWR Recomm Reports. 2023;72(45):1209-1216. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7245a1
- Huffman KF, Ambrose KR, Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Callahan LF. The critical role of physical activity and weight management in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a narrative review. J Rheumatol. 2023;51(3):224-233. doi:10.3899/ jrheum.2023-0819
- Lo GH. Successfully treating patients with osteoarthritis: how encouragement of physical activity can generate the best outcomes. A physician’s perspective. J Rheumatol. 2023:jrheum.2023-0899. doi:10.3899/jrheum.2023-0899
- Overton C, Nelson AE, Neogi T. Osteoarthritis treatment guidelines from six professional societies: similarities and differences. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48(3):637-657. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2022.03.009
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Overview of VA research on arthritis. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/arthritis.cfm
- Fallon EA, Boring MA, Foster AL, Stowe EW, Lites TD, Allen KD. Arthritis prevalence among veterans — United States, 2017–2021. MMWR Recomm Reports. 2023;72(45):1209-1216. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7245a1
- Huffman KF, Ambrose KR, Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Callahan LF. The critical role of physical activity and weight management in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a narrative review. J Rheumatol. 2023;51(3):224-233. doi:10.3899/ jrheum.2023-0819
- Lo GH. Successfully treating patients with osteoarthritis: how encouragement of physical activity can generate the best outcomes. A physician’s perspective. J Rheumatol. 2023:jrheum.2023-0899. doi:10.3899/jrheum.2023-0899
- Overton C, Nelson AE, Neogi T. Osteoarthritis treatment guidelines from six professional societies: similarities and differences. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48(3):637-657. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2022.03.009
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Overview of VA research on arthritis. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/arthritis.cfm
- Fallon EA, Boring MA, Foster AL, Stowe EW, Lites TD, Allen KD. Arthritis prevalence among veterans — United States, 2017–2021. MMWR Recomm Reports. 2023;72(45):1209-1216. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7245a1
- Huffman KF, Ambrose KR, Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Callahan LF. The critical role of physical activity and weight management in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a narrative review. J Rheumatol. 2023;51(3):224-233. doi:10.3899/ jrheum.2023-0819
- Lo GH. Successfully treating patients with osteoarthritis: how encouragement of physical activity can generate the best outcomes. A physician’s perspective. J Rheumatol. 2023:jrheum.2023-0899. doi:10.3899/jrheum.2023-0899
- Overton C, Nelson AE, Neogi T. Osteoarthritis treatment guidelines from six professional societies: similarities and differences. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48(3):637-657. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2022.03.009
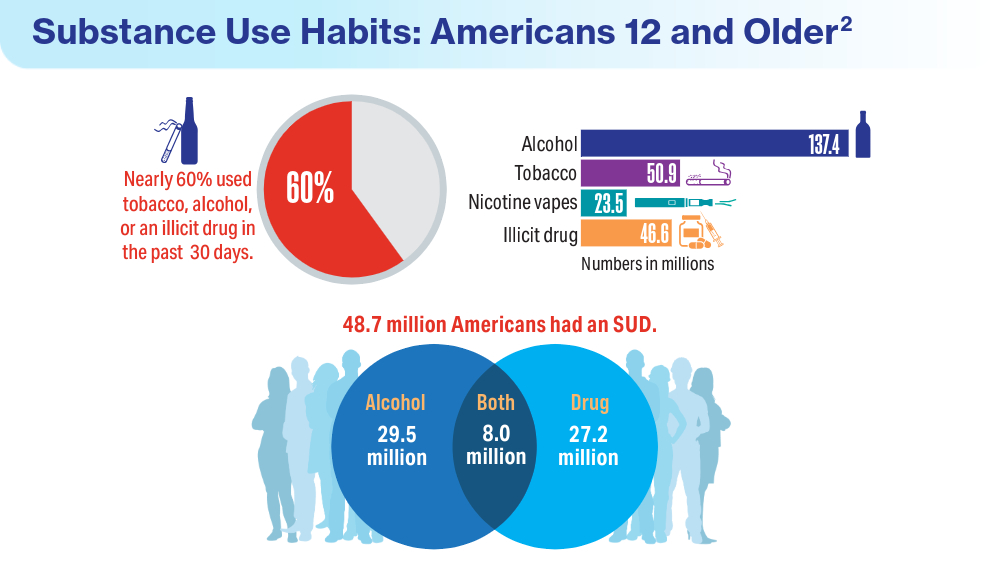
Data Trends 2024: Substance Use Disorder
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
- Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77. doi:10.2147/sar.s116720
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: a companion infographic. SAMHSA publication no. PEP23-07-01-007. November 13, 2023. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42730/2022-nsduh-infographic-report.pdf
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Among the Veteran Population Aged 18 or Older. Accessed March 25, 2024. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt44472/2022-nsduh-pop-slides-veterans.pdf
- Cypel YS, DePhilippis D, Davey VJ. Substance use in U.S. Vietnam War era veterans and nonveterans: results from the Vietnam Era Health Retrospective Observational Study. Subst Use Misuse. 2023;58(7):858-870. doi:10.1080/10826084.2023.2188427
- Otufowora A, Liu Y, Okusanya A, Ogidan A, Okusanya A, Cottler LB. The effect of veteran status and chronic pain on past 30-day sedative use among community-dwelling adult males. J Am Board Fam Med. 2024;37(1):118-128. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2023.230226R2
Data Trends 2024: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA research on traumatic brain injury. Updated July 2020. Accessed April 19, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/pubs/docs/va_factsheets/tbi.pdf
- Miles SR, Sayer NA, Belanger HG, et al. Comparing outcomes of the Veterans Health Administration's traumatic brain injury and mental health screening programs: types and frequency of specialty services used. J Neurotrauma. 2023;40(1-2):102-111. doi:10.1089/neu.2022.0176
- Pogoda TK, Adams RS, Carlson KF, Dismuke-Greer CE, Amuan M, Pugh MJ. Risk of adverse outcomes among veterans who screen positive for traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration but do not complete a comprehensive evaluation: a LIMBIC-CENC study. J Head Trauma Rehabil. Published online June 19, 2023. doi:10.1097/HTR.0000000000000881
- Kinney AR, Yan XD, Schneider AL, et al. Unmet need for outpatient occupational therapy services among veterans with mild traumatic brain injury in the Veterans Health Administration: the role of facility characteristics. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;104(11):1802-1811. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.030
- Clark JMR, Ozturk ED, Chanfreau-Coffinier C, Merritt VC; VA Million Veteran Program. Evaluation of clinical outcomes and employment status in veterans with dual diagnosis of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Qual Life Res. 2024;33(1):229-239. doi:10.1007/s11136-023-03518-7
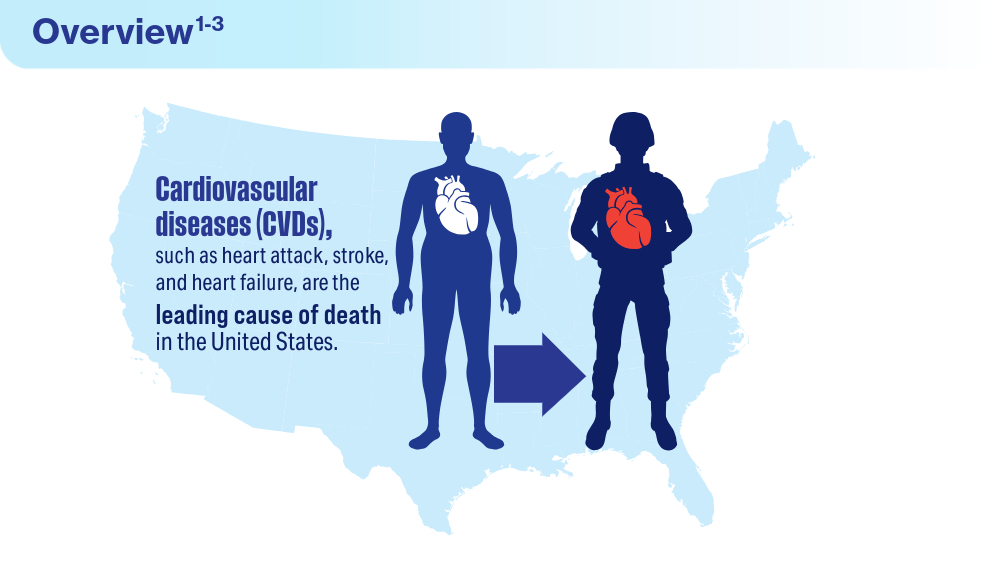
Data Trends 2024: Cardiology
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
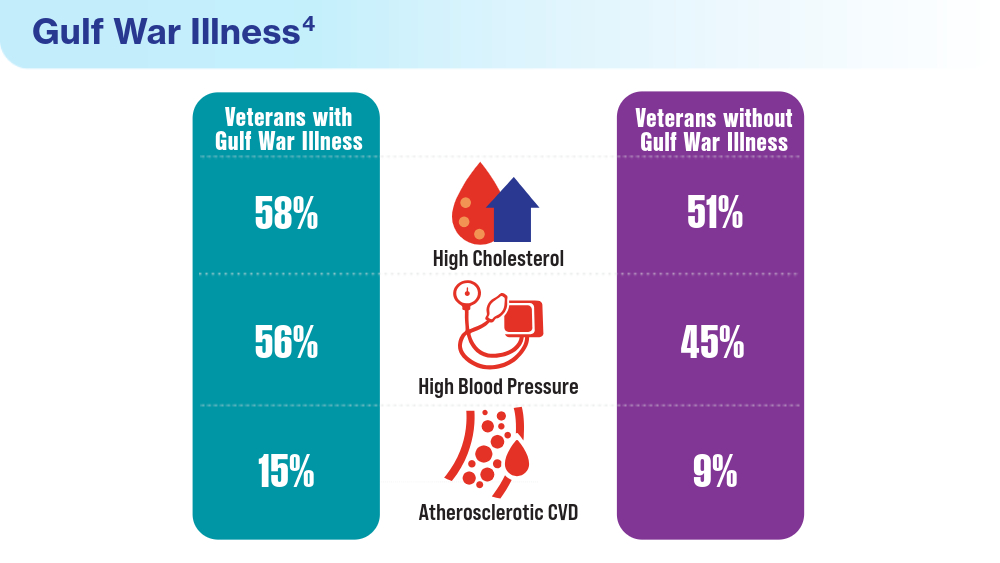
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
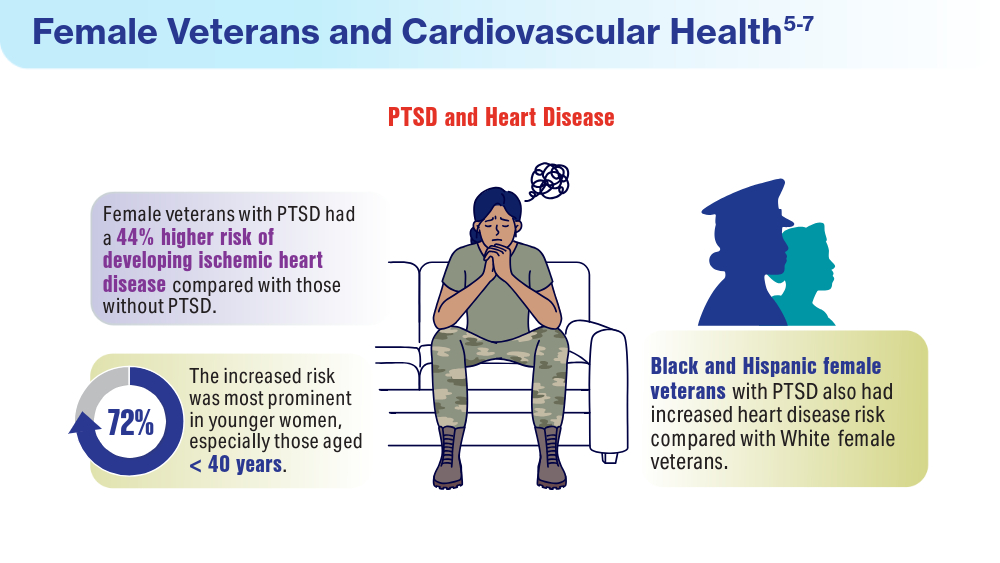
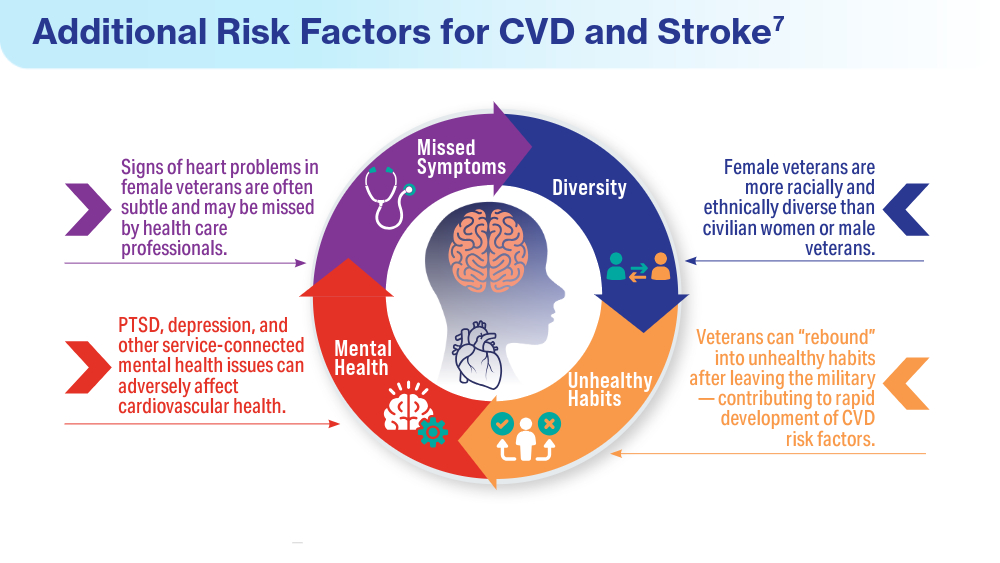
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
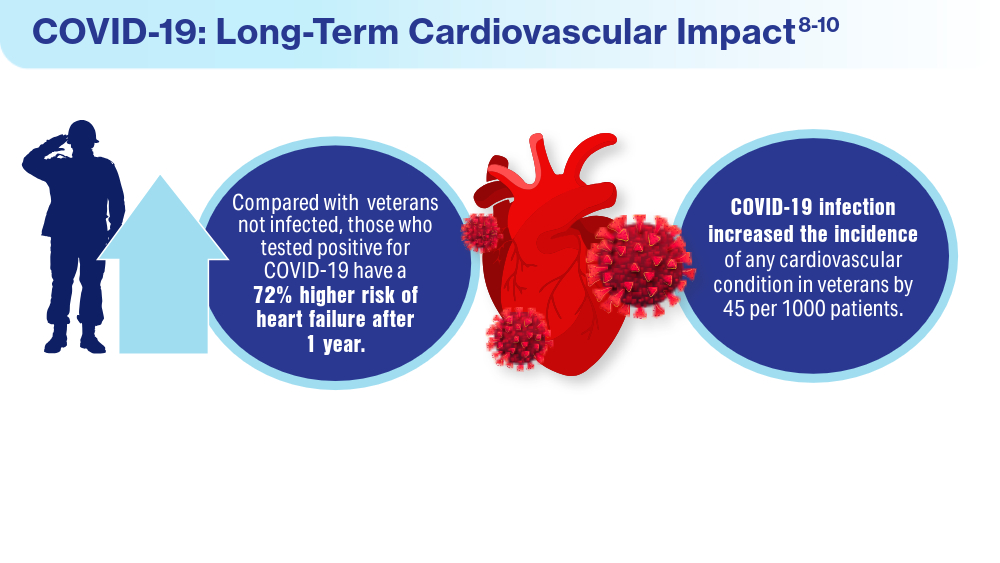
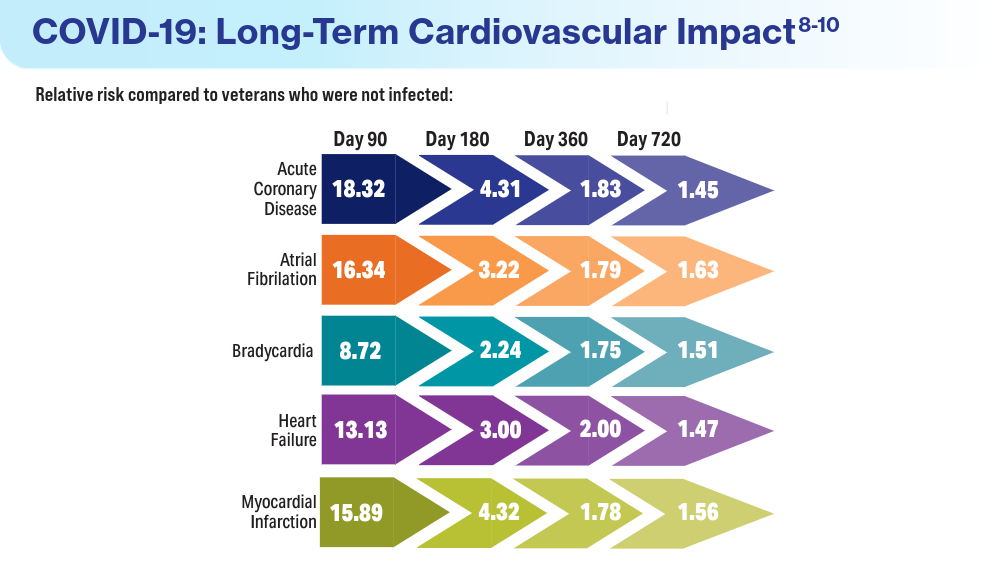
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
- Boersma P, Cohen RA, Zelaya CE, Moy E. Multiple chronic conditions among veterans and nonveterans: United States, 2015–2018. Natl Health Stat Rep. 2021;(153):1-13. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr153-508.pdf
- Army troops have worse heart health than civilian population, study says. American Heart Association News. June 5, 2019. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2019/06/05/army-troops-have-worse-heart-health-than-civilian-population-study-says
- Haira RS, Kataruka A, Akeroyd JM, et al. Association of Body Mass Index with Risk Factor Optimization and Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in US Veterans with Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12:e004817 doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.004817
- Merschel M. Gulf War illness may increase risk for heart disease or stroke. American Heart Association News. September 29, 2023. Accessed March 15, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/news/2023/09/29/gulf-war-illness-may-increase-risk-for-heart-disease-or-stroke
- Women veterans and heart health. American Heart Association: Go Red for Women. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.goredforwomen.org/en/about-heart-disease-in-women/facts/women-veterans-and-heart-health
- Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2023 Update. American Heart Association Professional Heart Daily. January 25, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://professional.heart.org/en/science-news/heart-disease-and-stroke-statistics-2023-update
- Ebrahimi R. Sumner J, Lynch K, et al. Women veterans with PTSD have higher rate of heart disease. American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2020, Presentation 314 - P12702. American Heart Association News. November 9, 2020. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/women-veterans-with-ptsd-have-higher-rate-of-heart-disease
- Wadman M. COVID-19 takes serious toll on heart health—a full year after recovery. Science. Updated February 13, 2022. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-takes-serious-toll-heart-health-full-year-after-recovery
- Bowe B, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Postacute sequale of COVID-19 at 2 years. Nature Medicine. 2023;29:2347-2357. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02521-2
- Offord C. COVID-19 boosts risks of health problems 2 years later, giant study of veterans says. Science. August 21, 2023. Accessed March 13, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/covid-19-boosts-risks-health-problems-2-years-later-giant-study-veterans-says
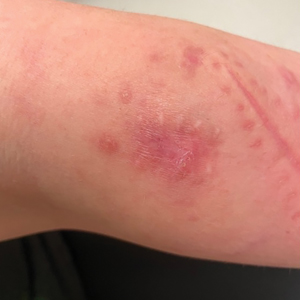
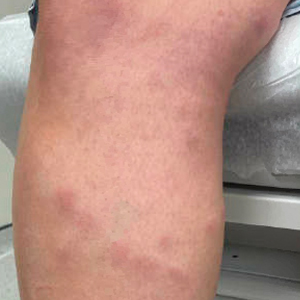
Scarring Head Wound
The Diagnosis: Brunsting-Perry Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Physical examination and histopathology are paramount in diagnosing Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid (BPCP). In our patient, histopathology showed subepidermal blistering with a mixed superficial dermal inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for linear IgG and C3 antibodies along the basement membrane. The scarring erosions on the scalp combined with the autoantibody findings on direct immunofluorescence were consistent with BPCP. He was started on dapsone 100 mg daily and demonstrated complete resolution of symptoms after 10 months, with the exception of persistent scarring hair loss (Figure).

Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid is a rare dermatologic condition. It was first defined in 1957 when Brunsting and Perry1 examined 7 patients with cicatricial pemphigoid that predominantly affected the head and neck region, with occasional mucous membrane involvement but no mucosal scarring. Characteristically, BPCP manifests as scarring herpetiform plaques with varied blisters, erosions, crusts, and scarring.1 It primarily affects middle-aged men.2
Historically, BPCP has been considered a variant of cicatricial pemphigoid (now known as mucous membrane pemphigoid), bullous pemphigoid, or epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.3 The antigen target has not been established clearly; however, autoantibodies against laminin 332, collagen VII, and BP180 and BP230 have been proposed.2,4,5 Jacoby et al6 described BPCP on a spectrum with bullous pemphigoid and cicatricial pemphigoid, with primarily circulating autoantibodies on one end and tissue-fixed autoantibodies on the other.
The differential for BPCP also includes anti-p200 pemphigoid and anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid. Anti-p200 pemphigoid also is known as bullous pemphigoid with antibodies against the 200-kDa protein.7 It may clinically manifest similar to bullous pemphigoid and other subepidermal autoimmune blistering diseases; thus, immunopathologic differentiation can be helpful. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid (also known as anti–laminin gamma-1 pemphigoid) is characterized by autoantibodies targeting the laminin 332 protein in the basement membrane zone, resulting in blistering and erosions.8 Similar to BPCP and epidermolysis bullosa aquisita, anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid may affect cephalic regions and mucous membrane surfaces, resulting in scarring and cicatricial changes. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid also has been associated with internal malignancy.8 The use of the salt-split skin technique can be utilized to differentiate these entities based on their autoantibody-binding patterns in relation to the lamina densa.
Treatment options for mild BPCP include potent topical or intralesional steroids and dapsone, while more severe cases may require systemic therapy with rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or cyclophosphamide.4
This case highlights the importance of histopathologic examination of skin lesions with an unusual history or clinical presentation. Dermatologists should consider BPCP when presented with erosions, ulcerations, or blisters of the head and neck in middle-aged male patients.
- Brunsting LA, Perry HO. Benign pemphigoid? a report of seven cases with chronic, scarring, herpetiform plaques about the head and neck. AMA Arch Derm. 1957;75:489-501. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1957.01550160015002
- Jedlickova H, Neidermeier A, Zgažarová S, et al. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid of the scalp with antibodies against laminin 332. Dermatology. 2011;222:193-195. doi:10.1159/000322842
- Eichhoff G. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid as differential diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Cureus. 2019;11:E5400. doi:10.7759/cureus.5400
- Asfour L, Chong H, Mee J, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid variant) localized to the face and diagnosed with antigen identification using skin deficient in type VII collagen. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:e90-e96. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000000829
- Zhou S, Zou Y, Pan M. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid transitioning from previous bullous pemphigoid. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:192-194. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.018
- Jacoby WD Jr, Bartholome CW, Ramchand SC, et al. Cicatricial pemphigoid (Brunsting-Perry type). case report and immunofluorescence findings. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:779-781. doi:10.1001/archderm.1978.01640170079018
- Kridin K, Ahmed AR. Anti-p200 pemphigoid: a systematic review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2466. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02466
- Shi L, Li X, Qian H. Anti-laminin 332-type mucous membrane pemphigoid. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1461. doi:10.3390/biom12101461
The Diagnosis: Brunsting-Perry Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Physical examination and histopathology are paramount in diagnosing Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid (BPCP). In our patient, histopathology showed subepidermal blistering with a mixed superficial dermal inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for linear IgG and C3 antibodies along the basement membrane. The scarring erosions on the scalp combined with the autoantibody findings on direct immunofluorescence were consistent with BPCP. He was started on dapsone 100 mg daily and demonstrated complete resolution of symptoms after 10 months, with the exception of persistent scarring hair loss (Figure).

Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid is a rare dermatologic condition. It was first defined in 1957 when Brunsting and Perry1 examined 7 patients with cicatricial pemphigoid that predominantly affected the head and neck region, with occasional mucous membrane involvement but no mucosal scarring. Characteristically, BPCP manifests as scarring herpetiform plaques with varied blisters, erosions, crusts, and scarring.1 It primarily affects middle-aged men.2
Historically, BPCP has been considered a variant of cicatricial pemphigoid (now known as mucous membrane pemphigoid), bullous pemphigoid, or epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.3 The antigen target has not been established clearly; however, autoantibodies against laminin 332, collagen VII, and BP180 and BP230 have been proposed.2,4,5 Jacoby et al6 described BPCP on a spectrum with bullous pemphigoid and cicatricial pemphigoid, with primarily circulating autoantibodies on one end and tissue-fixed autoantibodies on the other.
The differential for BPCP also includes anti-p200 pemphigoid and anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid. Anti-p200 pemphigoid also is known as bullous pemphigoid with antibodies against the 200-kDa protein.7 It may clinically manifest similar to bullous pemphigoid and other subepidermal autoimmune blistering diseases; thus, immunopathologic differentiation can be helpful. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid (also known as anti–laminin gamma-1 pemphigoid) is characterized by autoantibodies targeting the laminin 332 protein in the basement membrane zone, resulting in blistering and erosions.8 Similar to BPCP and epidermolysis bullosa aquisita, anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid may affect cephalic regions and mucous membrane surfaces, resulting in scarring and cicatricial changes. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid also has been associated with internal malignancy.8 The use of the salt-split skin technique can be utilized to differentiate these entities based on their autoantibody-binding patterns in relation to the lamina densa.
Treatment options for mild BPCP include potent topical or intralesional steroids and dapsone, while more severe cases may require systemic therapy with rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or cyclophosphamide.4
This case highlights the importance of histopathologic examination of skin lesions with an unusual history or clinical presentation. Dermatologists should consider BPCP when presented with erosions, ulcerations, or blisters of the head and neck in middle-aged male patients.
The Diagnosis: Brunsting-Perry Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Physical examination and histopathology are paramount in diagnosing Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid (BPCP). In our patient, histopathology showed subepidermal blistering with a mixed superficial dermal inflammatory cell infiltrate. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for linear IgG and C3 antibodies along the basement membrane. The scarring erosions on the scalp combined with the autoantibody findings on direct immunofluorescence were consistent with BPCP. He was started on dapsone 100 mg daily and demonstrated complete resolution of symptoms after 10 months, with the exception of persistent scarring hair loss (Figure).

Brunsting-Perry cicatricial pemphigoid is a rare dermatologic condition. It was first defined in 1957 when Brunsting and Perry1 examined 7 patients with cicatricial pemphigoid that predominantly affected the head and neck region, with occasional mucous membrane involvement but no mucosal scarring. Characteristically, BPCP manifests as scarring herpetiform plaques with varied blisters, erosions, crusts, and scarring.1 It primarily affects middle-aged men.2
Historically, BPCP has been considered a variant of cicatricial pemphigoid (now known as mucous membrane pemphigoid), bullous pemphigoid, or epidermolysis bullosa acquisita.3 The antigen target has not been established clearly; however, autoantibodies against laminin 332, collagen VII, and BP180 and BP230 have been proposed.2,4,5 Jacoby et al6 described BPCP on a spectrum with bullous pemphigoid and cicatricial pemphigoid, with primarily circulating autoantibodies on one end and tissue-fixed autoantibodies on the other.
The differential for BPCP also includes anti-p200 pemphigoid and anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid. Anti-p200 pemphigoid also is known as bullous pemphigoid with antibodies against the 200-kDa protein.7 It may clinically manifest similar to bullous pemphigoid and other subepidermal autoimmune blistering diseases; thus, immunopathologic differentiation can be helpful. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid (also known as anti–laminin gamma-1 pemphigoid) is characterized by autoantibodies targeting the laminin 332 protein in the basement membrane zone, resulting in blistering and erosions.8 Similar to BPCP and epidermolysis bullosa aquisita, anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid may affect cephalic regions and mucous membrane surfaces, resulting in scarring and cicatricial changes. Anti–laminin 332 pemphigoid also has been associated with internal malignancy.8 The use of the salt-split skin technique can be utilized to differentiate these entities based on their autoantibody-binding patterns in relation to the lamina densa.
Treatment options for mild BPCP include potent topical or intralesional steroids and dapsone, while more severe cases may require systemic therapy with rituximab, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, or cyclophosphamide.4
This case highlights the importance of histopathologic examination of skin lesions with an unusual history or clinical presentation. Dermatologists should consider BPCP when presented with erosions, ulcerations, or blisters of the head and neck in middle-aged male patients.
- Brunsting LA, Perry HO. Benign pemphigoid? a report of seven cases with chronic, scarring, herpetiform plaques about the head and neck. AMA Arch Derm. 1957;75:489-501. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1957.01550160015002
- Jedlickova H, Neidermeier A, Zgažarová S, et al. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid of the scalp with antibodies against laminin 332. Dermatology. 2011;222:193-195. doi:10.1159/000322842
- Eichhoff G. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid as differential diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Cureus. 2019;11:E5400. doi:10.7759/cureus.5400
- Asfour L, Chong H, Mee J, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid variant) localized to the face and diagnosed with antigen identification using skin deficient in type VII collagen. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:e90-e96. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000000829
- Zhou S, Zou Y, Pan M. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid transitioning from previous bullous pemphigoid. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:192-194. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.018
- Jacoby WD Jr, Bartholome CW, Ramchand SC, et al. Cicatricial pemphigoid (Brunsting-Perry type). case report and immunofluorescence findings. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:779-781. doi:10.1001/archderm.1978.01640170079018
- Kridin K, Ahmed AR. Anti-p200 pemphigoid: a systematic review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2466. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02466
- Shi L, Li X, Qian H. Anti-laminin 332-type mucous membrane pemphigoid. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1461. doi:10.3390/biom12101461
- Brunsting LA, Perry HO. Benign pemphigoid? a report of seven cases with chronic, scarring, herpetiform plaques about the head and neck. AMA Arch Derm. 1957;75:489-501. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1957.01550160015002
- Jedlickova H, Neidermeier A, Zgažarová S, et al. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid of the scalp with antibodies against laminin 332. Dermatology. 2011;222:193-195. doi:10.1159/000322842
- Eichhoff G. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid as differential diagnosis of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Cureus. 2019;11:E5400. doi:10.7759/cureus.5400
- Asfour L, Chong H, Mee J, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid variant) localized to the face and diagnosed with antigen identification using skin deficient in type VII collagen. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:e90-e96. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000000829
- Zhou S, Zou Y, Pan M. Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid transitioning from previous bullous pemphigoid. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:192-194. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.12.018
- Jacoby WD Jr, Bartholome CW, Ramchand SC, et al. Cicatricial pemphigoid (Brunsting-Perry type). case report and immunofluorescence findings. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:779-781. doi:10.1001/archderm.1978.01640170079018
- Kridin K, Ahmed AR. Anti-p200 pemphigoid: a systematic review. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2466. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02466
- Shi L, Li X, Qian H. Anti-laminin 332-type mucous membrane pemphigoid. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1461. doi:10.3390/biom12101461
A 60-year-old man presented to a dermatology clinic with a wound on the scalp that had persisted for 11 months. The lesion started as a small erosion that eventually progressed to involve the entire parietal scalp. He had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and Graves disease. Physical examination demonstrated a large scar over the vertex scalp with central erosion, overlying crust, peripheral scalp atrophy, hypopigmentation at the periphery, and exaggerated superficial vasculature. Some oral erosions also were observed. A review of systems was negative for any constitutional symptoms. A month prior, the patient had been started on dapsone 50 mg with a prednisone taper by an outside dermatologist and noticed some improvement.

Association Between Pruritus and Fibromyalgia: Results of a Population-Based, Cross-Sectional Study
Pruritus, which is defined as an itching sensation that elicits a desire to scratch, is the most common cutaneous condition. Pruritus is considered chronic when it lasts for more than 6 weeks.1 Etiologies implicated in chronic pruritus include but are not limited to primary skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, systemic causes, neuropathic disorders, and psychogenic reasons.2 In approximately 8% to 35% of patients, the cause of pruritus remains elusive despite intensive investigation.3 The mechanisms of itch are multifaceted and include complex neural pathways.4 Although itch and pain share many similarities, they have distinct pathways based on their spinal connections.5 Nevertheless, both conditions show a wide overlap of receptors on peripheral nerve endings and activated brain parts.6,7 Fibromyalgia, the third most common musculoskeletal condition, affects 2% to 3% of the population worldwide and is at least 7 times more common in females.8,9 Its pathogenesis is not entirely clear but is thought to involve neurogenic inflammation, aberrations in peripheral nerves, and central pain mechanisms. Fibromyalgia is characterized by a plethora of symptoms including chronic widespread pain, autonomic disturbances, persistent fatigue and sleep disturbances, and hyperalgesia, as well as somatic and psychiatric symptoms.10
Fibromyalgia is accompanied by altered skin features including increased counts of mast cells and excessive degranulation,11 neurogenic inflammation with elevated cytokine expression,12 disrupted collagen metabolism,13 and microcirculation abnormalities.14 There has been limited research exploring the dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. One retrospective study that included 845 patients with fibromyalgia reported increased occurrence of “neurodermatoses,” including pruritus, neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodules, and lichen simplex chronicus (LSC), among other cutaneous comorbidities.15 Another small study demonstrated an increased incidence of xerosis and neurotic excoriations in females with fibromyalgia.16 A paucity of large epidemiologic studies demonstrating the fibromyalgia-pruritus connection may lead to misdiagnosis, misinterpretation, and undertreatment of these patients.
Up to 49% of fibromyalgia patients experience small-fiber neuropathy.17 Electrophysiologic measurements, quantitative sensory testing, pain-related evoked potentials, and skin biopsies showed that patients with fibromyalgia have compromised small-fiber function, impaired pathways carrying fiber pain signals, and reduced skin innervation and regenerating fibers.18,19 Accordingly, pruritus that has been reported in fibromyalgia is believed to be of neuropathic origin.15 Overall, it is suspected that the same mechanism that causes hypersensitivity and pain in fibromyalgia patients also predisposes them to pruritus. Similar systemic treatments (eg, analgesics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants) prescribed for both conditions support this theory.20-25
Our large cross-sectional study sought to establish the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as related pruritic conditions.
Methods
Study Design and Setting—We conducted a cross-sectional retrospective study using data-mining techniques to access information from the Clalit Health Services (CHS) database. Clalit Health Services is the largest health maintenance organization in Israel. It encompasses an extensive database with continuous real-time input from medical, administrative, and pharmaceutical computerized operating systems, which helps facilitate data collection for epidemiologic studies. A chronic disease register is gathered from these data sources and continuously updated and validated through logistic checks. The current study was approved by the institutional review board of the CHS (approval #0212-17-com2). Informed consent was not required because the data were de-identified and this was a noninterventional observational study.
Study Population and Covariates—Medical records of CHS enrollees were screened for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia, and data on prevalent cases of fibromyalgia were retrieved. The diagnosis of fibromyalgia was based on the documentation of a fibromyalgia-specific diagnostic code registered by a board-certified rheumatologist. A control group of individuals without fibromyalgia was selected through 1:2 matching based on age, sex, and primary care clinic. The control group was randomly selected from the list of CHS members frequency-matched to cases, excluding case patients with fibromyalgia. Age matching was grounded on the exact year of birth (1-year strata).
Other covariates in the analysis included pruritus-related skin disorders, including prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC. There were 3 socioeconomic status categories according to patients' poverty index: low, intermediate, and high.26
Statistical Analysis—The distribution of sociodemographic and clinical features was compared between patients with fibromyalgia and controls using the χ2 test for sex and socioeconomic status and the t test for age. Conditional logistic regression then was used to calculate adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI to compare patients with fibromyalgia and controls with respect to the presence of pruritic comorbidities. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 26). P<.05 was considered statistically significant in all tests.
Results
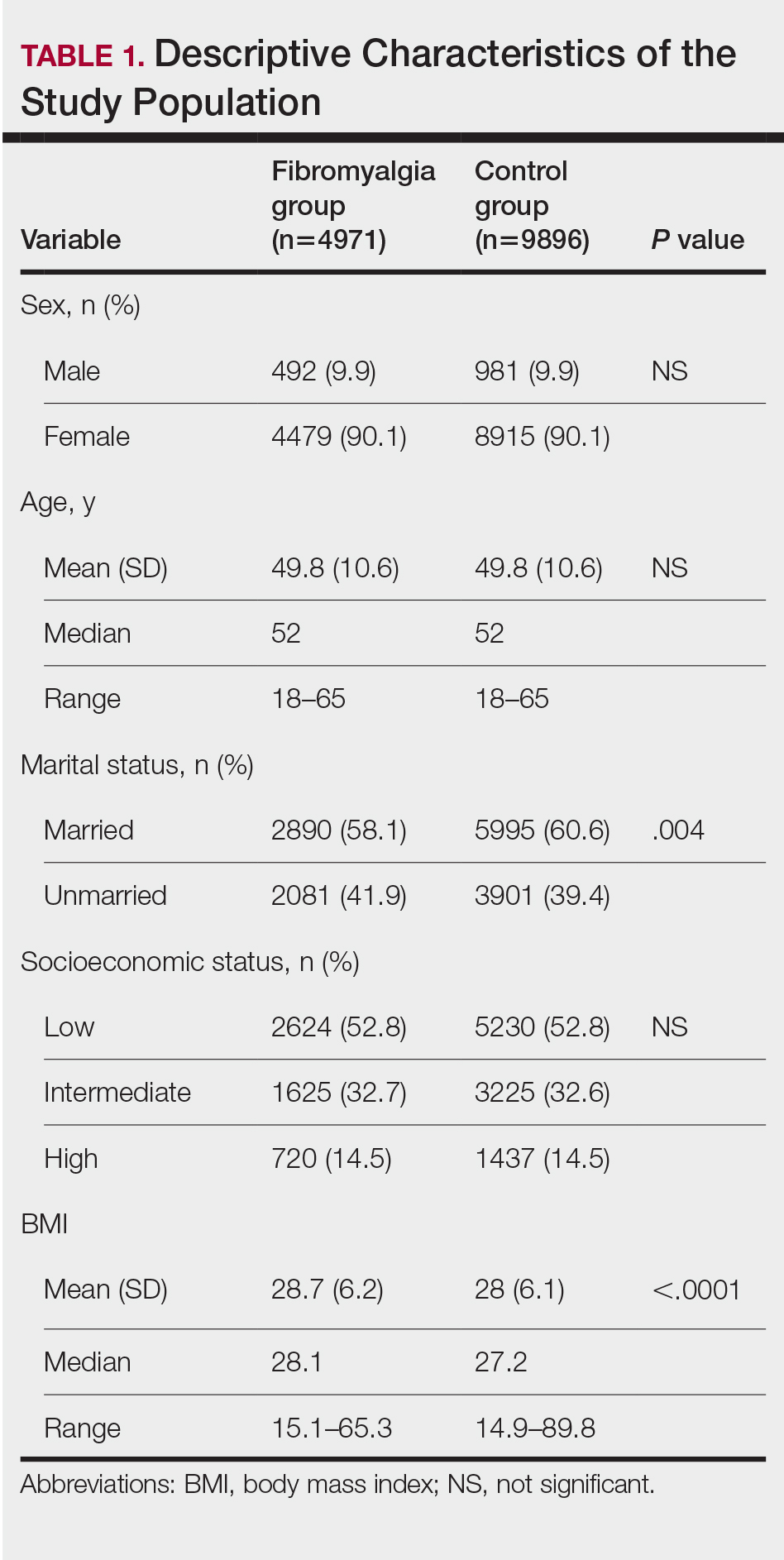
Our study population comprised 4971 patients with fibromyalgia and 9896 age- and sex-matched controls. Proportional to the reported female predominance among patients with fibromyalgia,27 4479 (90.1%) patients with fibromyalgia were females and a similar proportion was documented among controls (P=.99). There was a slightly higher proportion of unmarried patients among those with fibromyalgia compared with controls (41.9% vs 39.4%; P=.004). Socioeconomic status was matched between patients and controls (P=.99). Descriptive characteristics of the study population are presented in Table 1.
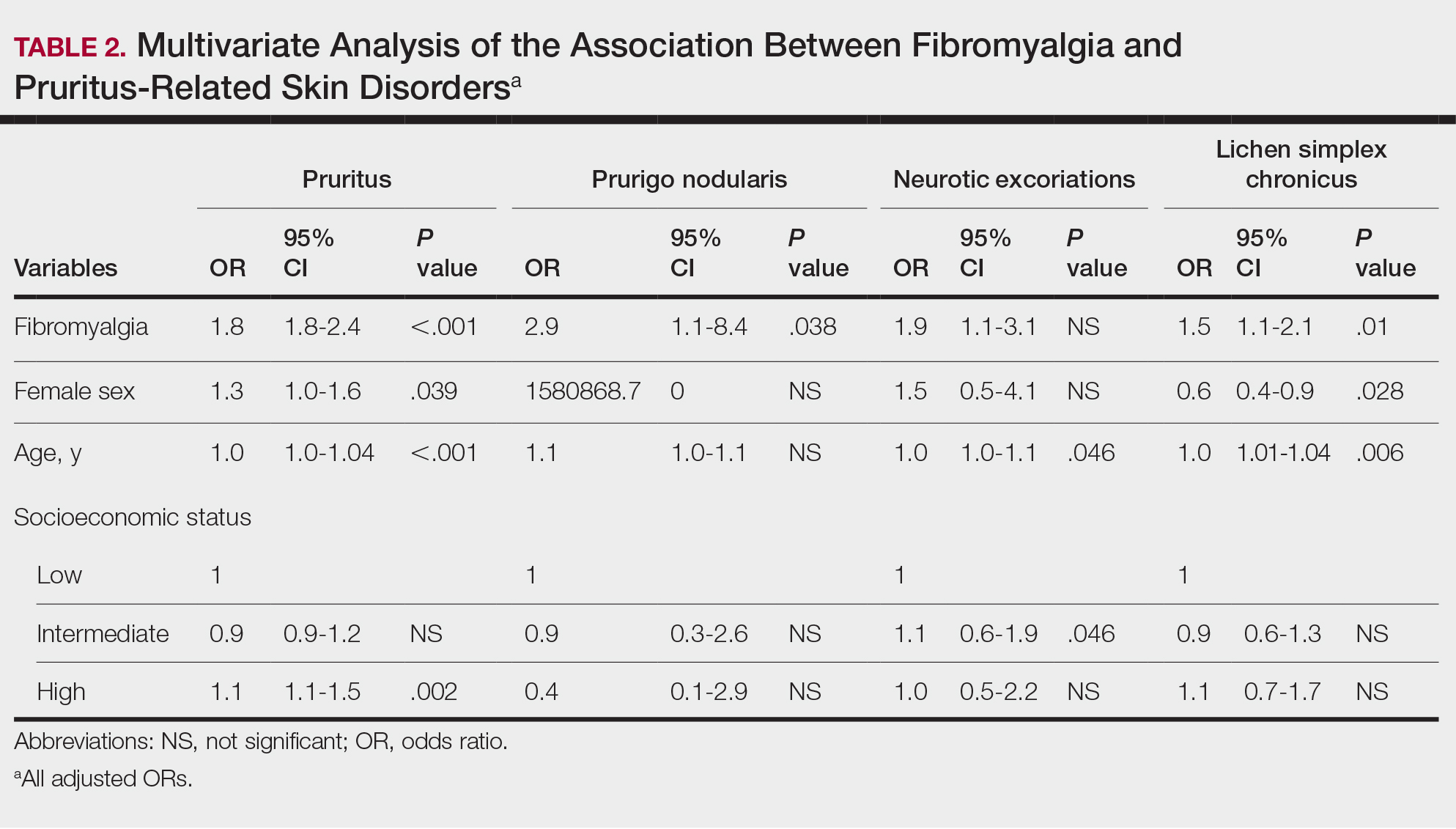
We assessed the presence of pruritus as well as 3 other pruritus-related skin disorders—prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC—among patients with fibromyalgia and controls. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the independent association between fibromyalgia and pruritus. Table 2 presents the results of multivariate logistic regression models and summarizes the adjusted ORs for pruritic conditions in patients with fibromyalgia and different demographic features across the entire study sample. Fibromyalgia demonstrated strong independent associations with pruritus (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.8-2.4; P<.001), prurigo nodularis (OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.038), and LSC (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01); the association with neurotic excoriations was not significant. Female sex significantly increased the risk for pruritus (OR 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6; P=.039), while age slightly increased the odds for pruritus (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.04; P<.001), neurotic excoriations (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.1; P=.046), and LSC (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.01-1.04; P=.006). Finally, socioeconomic status was inversely correlated with pruritus (OR, 1.1; 95% CI, 1.1-1.5; P=.002).
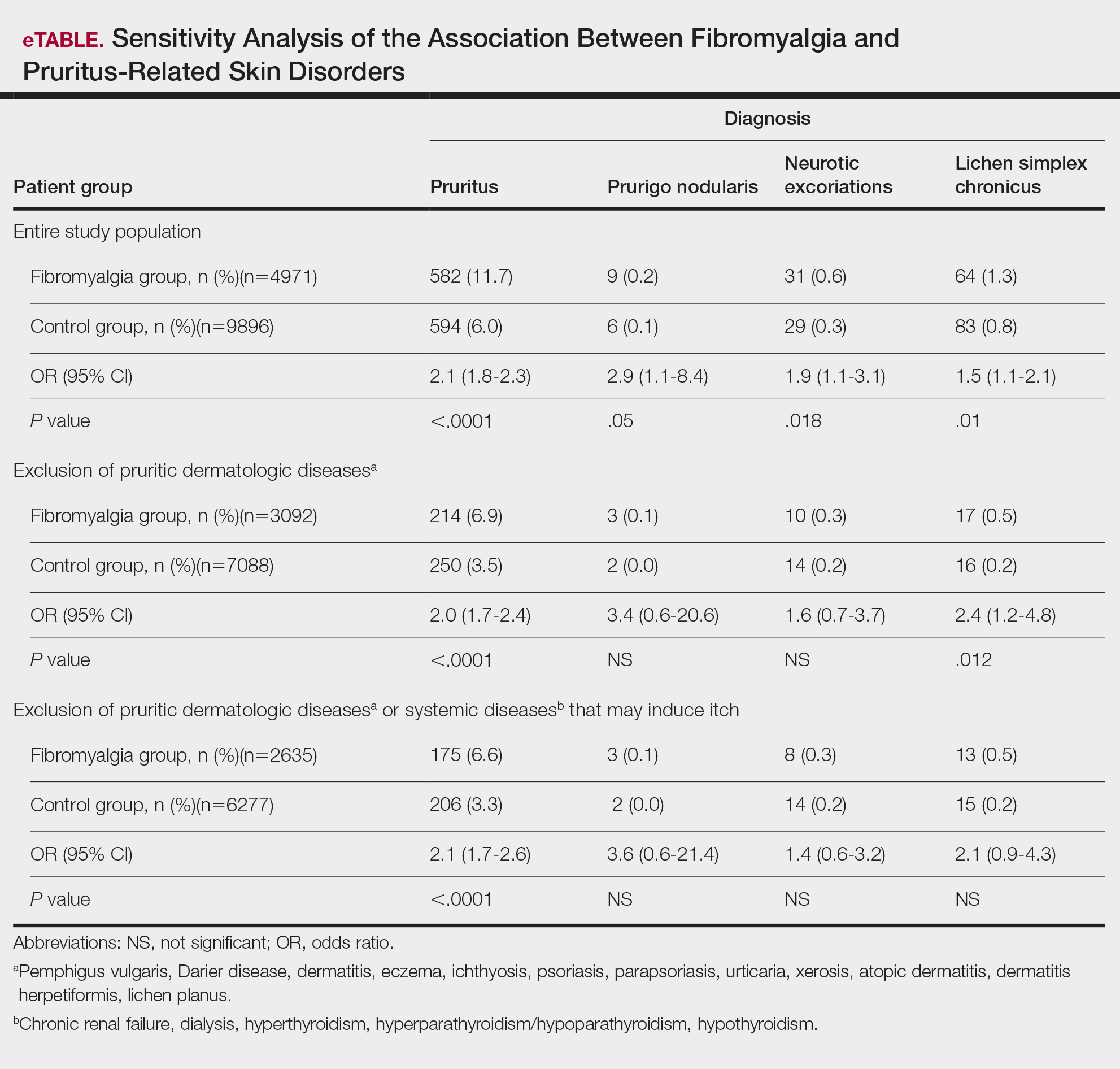
Frequencies and ORs for the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus with associated pruritic disorders stratified by exclusion of pruritic dermatologic and/or systemic diseases that may induce itch are presented in the eTable. Analyzing the entire study cohort, significant increases were observed in the odds of all 4 pruritic disorders analyzed. The frequency of pruritus was almost double in patients with fibromyalgia compared with controls (11.7% vs 6.0%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.8-2.3; P<.0001). Prurigo nodularis (0.2% vs 0.1%; OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.05), neurotic excoriations (0.6% vs 0.3%; OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.1; P=.018), and LSC (1.3% vs 0.8%; OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01) frequencies were all higher in patients with fibromyalgia than controls. When primary skin disorders that may cause itch (eg, pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, dermatitis, eczema, ichthyosis, psoriasis, parapsoriasis, urticaria, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, lichen planus) were excluded, the prevalence of pruritus in patients with fibromyalgia was still 1.97 times greater than in the controls (6.9% vs. 3.5%; OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4; P<.0001). These results remained unchanged even when excluding pruritic dermatologic disorders as well as systemic diseases associated with pruritus (eg, chronic renal failure, dialysis, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism/hypoparathyroidism, hypothyroidism). Patients with fibromyalgia still displayed a significantly higher prevalence of pruritus compared with the control group (6.6% vs 3.3%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.7-2.6; P<.0001).
Comment
A wide range of skin manifestations have been associated with fibromyalgia, but the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Nevertheless, it is conceivable that autonomic nervous system dysfunction,28-31 amplified cutaneous opioid receptor activity,32 and an elevated presence of cutaneous mast cells with excessive degranulation may partially explain the frequent occurrence of pruritus and related skin disorders such as neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodularis, and LSC in individuals with fibromyalgia.15,16 In line with these findings, our study—which was based on data from the largest health maintenance organization in Israel—demonstrated an increased prevalence of pruritus and related pruritic disorders among individuals diagnosed with fibromyalgia.
This cross-sectional study links pruritus with fibromyalgia. Few preliminary epidemiologic studies have shown an increased occurrence of cutaneous manifestations in patients with fibromyalgia. One chart review that looked at skin findings in patients with fibromyalgia revealed 32 distinct cutaneous manifestations, and pruritus was the major concern in 3.3% of 845 patients.15
A focused cross-sectional study involving only women (66 with fibromyalgia and 79 healthy controls) discovered 14 skin conditions that were more common in those with fibromyalgia. Notably, xerosis and neurotic excoriations were more prevalent compared to the control group.16
The brain and the skin—both derivatives of the embryonic ectoderm33,34—are linked by pruritus. Although itch has its dedicated neurons, there is a wide-ranging overlap of brain-activated areas between pain and itch,6 and the neural anatomy of pain and itch are closely related in both the peripheral and central nervous systems35-37; for example, diseases of the central nervous system are accompanied by pruritus in as many as 15% of cases, while postherpetic neuralgia can result in chronic pain, itching, or a combination of both.38,39 Other instances include notalgia paresthetica and brachioradial pruritus.38 Additionally, there is a noteworthy psychologic impact associated with both itch and pain,40,41 with both psychosomatic and psychologic factors implicated in chronic pruritus and in fibromyalgia.42 Lastly, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system are altered in both fibromyalgia and pruritus.43-45
Tey et al45 characterized the itch experienced in fibromyalgia as functional, which is described as pruritus associated with a somatoform disorder. In our study, we found a higher prevalence of pruritus among patients with fibromyalgia, and this association remained significant (P<.05) even when excluding other pruritic skin conditions and systemic diseases that can trigger itching. In addition, our logistic regression analyses revealed independent associations between fibromyalgia and pruritus, prurigo nodularis, and LSC.
According to Twycross et al,46 there are 4 clinical categories of itch, which may coexist7: pruritoceptive (originating in the skin), neuropathic (originating in pathology located along the afferent pathway), neurogenic (central origin but lacks a neural pathology), and psychogenic.47 Skin biopsy findings in patients with fibromyalgia include increased mast cell counts11 and degranulation,48 increased expression of δ and κ opioid receptors,32 vasoconstriction within tender points,49 and elevated IL-1β, IL-6, or tumor necrosis factor α by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.12 A case recently was presented by Görg et al50 involving a female patient with fibromyalgia who had been experiencing chronic pruritus, which the authors attributed to small-fiber neuropathy based on evidence from a skin biopsy indicating a reduced number of intraepidermal nerves and the fact that the itching originated around tender points. Altogether, the observed alterations may work together to make patients with fibromyalgia more susceptible to various skin-related comorbidities in general, especially those related to pruritus. Eventually, it might be the case that several itch categories and related pathomechanisms are involved in the pruritus phenotype of patients with fibromyalgia.
Age-related alterations in nerve fibers, lower immune function, xerosis, polypharmacy, and increased frequency of systemic diseases with age are just a few of the factors that may predispose older individuals to pruritus.51,52 Indeed, our logistic regression model showed that age was significantly and independently associated with pruritus (P<.001), neurotic excoriations (P=.046), and LSC (P=.006). Female sex also was significantly linked with pruritus (P=.039). Intriguingly, high socioeconomic status was significantly associated with the diagnosis of pruritus (P=.002), possibly due to easier access to medical care.
There is a considerable overlap between the therapeutic approaches used in pruritus, pruritus-related skin disorders, and fibromyalgia. Antidepressants, anxiolytics, analgesics, and antiepileptics have been used to address both conditions.45 The association between these conditions advocates for a multidisciplinary approach in patients with fibromyalgia and potentially supports the rationale for unified therapeutics for both conditions.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate an association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as associated pruritic skin disorders. Given the convoluted and largely undiscovered mechanisms underlying fibromyalgia, managing patients with this condition may present substantial challenges.53 The data presented here support the implementation of a multidisciplinary treatment approach for patients with fibromyalgia. This approach should focus on managing fibromyalgia pain as well as addressing its concurrent skin-related conditions. It is advisable to consider treatments such as antiepileptics (eg, pregabalin, gabapentin) that specifically target neuropathic disorders in affected patients. These treatments may hold promise for alleviating fibromyalgia-related pain54 and mitigating its related cutaneous comorbidities, especially pruritus.
- Stander S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:291-294.
- Yosipovitch G, Bernhard JD. Clinical practice. chronic pruritus. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1625-1634.
- Song J, Xian D, Yang L, et al. Pruritus: progress toward pathogenesis and treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:9625936.
- Potenzieri C, Undem BJ. Basic mechanisms of itch. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012;42:8-19.
- McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M. Itching for an explanation. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15:497-501.
- Drzezga A, Darsow U, Treede RD, et al. Central activation by histamine-induced itch: analogies to pain processing: a correlational analysis of O-15 H2O positron emission tomography studies. Pain. 2001; 92:295-305.
- Yosipovitch G, Greaves MW, Schmelz M. Itch. Lancet. 2003;361:690-694.
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:15-25.
- Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:26-35.
- Sarzi-Puttini P, Giorgi V, Marotto D, et al. Fibromyalgia: an update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:645-660.
- Blanco I, Beritze N, Arguelles M, et al. Abnormal overexpression of mastocytes in skin biopsies of fibromyalgia patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:1403-1412.
- Salemi S, Rethage J, Wollina U, et al. Detection of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in skin of patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:146-150.
- Sprott H, Muller A, Heine H. Collagen cross-links in fibromyalgia syndrome. Z Rheumatol. 1998;57(suppl 2):52-55.
- Morf S, Amann-Vesti B, Forster A, et al. Microcirculation abnormalities in patients with fibromyalgia—measured by capillary microscopy and laser fluxmetry. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R209-R216.
- Laniosz V, Wetter DA, Godar DA. Dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:1009-1013.
- Dogramaci AC, Yalcinkaya EY. Skin problems in fibromyalgia. Nobel Med. 2009;5:50-52.
- Grayston R, Czanner G, Elhadd K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia: implications for a new paradigm in fibromyalgia etiopathogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48:933-940.
- Uceyler N, Zeller D, Kahn AK, et al. Small fibre pathology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Brain. 2013;136:1857-1867.
- Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008; 131:1912- 1925.
- Reed C, Birnbaum HG, Ivanova JI, et al. Real-world role of tricyclic antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:533-540.
- Moret C, Briley M. Antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006;2:537-548.
- Arnold LM, Keck PE Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. a meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics. 2000;41:104-113.
- Moore A, Wiffen P, Kalso E. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. JAMA. 2014;312:182-183.
- Shevchenko A, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Yosipovitch G. Causes, pathophysiology, and treatment of pruritus in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:140-151.
- Scheinfeld N. The role of gabapentin in treating diseases with cutaneous manifestations and pain. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:491-495.
- Points Location Intelligence. Accessed July 30, 2024. https://points.co.il/en/points-location-intelligence/
- Yunus MB. The role of gender in fibromyalgia syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001;3:128-134.
- Cakir T, Evcik D, Dundar U, et al. Evaluation of sympathetic skin response and f wave in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. Turk J Rheumatol. 2011;26:38-43.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Koklukaya E. The correlation of laboratory tests and sympathetic skin response parameters by using artificial neural networks in fibromyalgia patients. J Med Syst. 2012;36:1841-1848.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Arslan E, et al. A study on the effects of sympathetic skin response parameters in diagnosis of fibromyalgia using artificial neural networks. J Med Syst. 2016;40:54.
- Ulas UH, Unlu E, Hamamcioglu K, et al. Dysautonomia in fibromyalgia syndrome: sympathetic skin responses and RR interval analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:383-387.
- Salemi S, Aeschlimann A, Wollina U, et al. Up-regulation of delta-opioid receptors and kappa-opioid receptors in the skin of fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2464-2466.
- Elshazzly M, Lopez MJ, Reddy V, et al. Central nervous system. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Hu MS, Borrelli MR, Hong WX, et al. Embryonic skin development and repair. Organogenesis. 2018;14:46-63.
- Davidson S, Zhang X, Yoon CH, et al. The itch-producing agents histamine and cowhage activate separate populations of primate spinothalamic tract neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10007-10014.
- Sikand P, Shimada SG, Green BG, et al. Similar itch and nociceptive sensations evoked by punctate cutaneous application of capsaicin, histamine and cowhage. Pain. 2009;144:66-75.
- Davidson S, Giesler GJ. The multiple pathways for itch and their interactions with pain. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:550-558.
- Dhand A, Aminoff MJ. The neurology of itch. Brain. 2014;137:313-322.
- Binder A, Koroschetz J, Baron R. Disease mechanisms in neuropathic itch. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008;4:329-337.
- Fjellner B, Arnetz BB. Psychological predictors of pruritus during mental stress. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65:504-508.
- Papoiu AD, Wang H, Coghill RC, et al. Contagious itch in humans: a study of visual ‘transmission’ of itch in atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1299-1303.
- Stumpf A, Schneider G, Stander S. Psychosomatic and psychiatric disorders and psychologic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:704-708.
- Herman JP, McKlveen JM, Ghosal S, et al. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr Physiol. 2016;6:603-621.
- Brown ED, Micozzi MS, Craft NE, et al. Plasma carotenoids in normal men after a single ingestion of vegetables or purified beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49:1258-1265.
- Tey HL, Wallengren J, Yosipovitch G. Psychosomatic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:31-40.
- Twycross R, Greaves MW, Handwerker H, et al. Itch: scratching more than the surface. QJM. 2003;96:7-26.
- Bernhard JD. Itch and pruritus: what are they, and how should itches be classified? Dermatol Ther. 2005;18:288-291.
- Enestrom S, Bengtsson A, Frodin T. Dermal IgG deposits and increase of mast cells in patients with fibromyalgia—relevant findings or epiphenomena? Scand J Rheumatol. 1997;26:308-313.
- Jeschonneck M, Grohmann G, Hein G, et al. Abnormal microcirculation and temperature in skin above tender points in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39:917-921.
- Görg M, Zeidler C, Pereira MP, et al. Generalized chronic pruritus with fibromyalgia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:909-911.
- Garibyan L, Chiou AS, Elmariah SB. Advanced aging skin and itch: addressing an unmet need. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:92-103.
- Cohen KR, Frank J, Salbu RL, et al. Pruritus in the elderly: clinical approaches to the improvement of quality of life. P T. 2012;37:227-239.
- Tzadok R, Ablin JN. Current and emerging pharmacotherapy for fibromyalgia. Pain Res Manag. 2020; 2020:6541798.
- Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia—an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD010567.
Pruritus, which is defined as an itching sensation that elicits a desire to scratch, is the most common cutaneous condition. Pruritus is considered chronic when it lasts for more than 6 weeks.1 Etiologies implicated in chronic pruritus include but are not limited to primary skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, systemic causes, neuropathic disorders, and psychogenic reasons.2 In approximately 8% to 35% of patients, the cause of pruritus remains elusive despite intensive investigation.3 The mechanisms of itch are multifaceted and include complex neural pathways.4 Although itch and pain share many similarities, they have distinct pathways based on their spinal connections.5 Nevertheless, both conditions show a wide overlap of receptors on peripheral nerve endings and activated brain parts.6,7 Fibromyalgia, the third most common musculoskeletal condition, affects 2% to 3% of the population worldwide and is at least 7 times more common in females.8,9 Its pathogenesis is not entirely clear but is thought to involve neurogenic inflammation, aberrations in peripheral nerves, and central pain mechanisms. Fibromyalgia is characterized by a plethora of symptoms including chronic widespread pain, autonomic disturbances, persistent fatigue and sleep disturbances, and hyperalgesia, as well as somatic and psychiatric symptoms.10
Fibromyalgia is accompanied by altered skin features including increased counts of mast cells and excessive degranulation,11 neurogenic inflammation with elevated cytokine expression,12 disrupted collagen metabolism,13 and microcirculation abnormalities.14 There has been limited research exploring the dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. One retrospective study that included 845 patients with fibromyalgia reported increased occurrence of “neurodermatoses,” including pruritus, neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodules, and lichen simplex chronicus (LSC), among other cutaneous comorbidities.15 Another small study demonstrated an increased incidence of xerosis and neurotic excoriations in females with fibromyalgia.16 A paucity of large epidemiologic studies demonstrating the fibromyalgia-pruritus connection may lead to misdiagnosis, misinterpretation, and undertreatment of these patients.
Up to 49% of fibromyalgia patients experience small-fiber neuropathy.17 Electrophysiologic measurements, quantitative sensory testing, pain-related evoked potentials, and skin biopsies showed that patients with fibromyalgia have compromised small-fiber function, impaired pathways carrying fiber pain signals, and reduced skin innervation and regenerating fibers.18,19 Accordingly, pruritus that has been reported in fibromyalgia is believed to be of neuropathic origin.15 Overall, it is suspected that the same mechanism that causes hypersensitivity and pain in fibromyalgia patients also predisposes them to pruritus. Similar systemic treatments (eg, analgesics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants) prescribed for both conditions support this theory.20-25
Our large cross-sectional study sought to establish the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as related pruritic conditions.
Methods
Study Design and Setting—We conducted a cross-sectional retrospective study using data-mining techniques to access information from the Clalit Health Services (CHS) database. Clalit Health Services is the largest health maintenance organization in Israel. It encompasses an extensive database with continuous real-time input from medical, administrative, and pharmaceutical computerized operating systems, which helps facilitate data collection for epidemiologic studies. A chronic disease register is gathered from these data sources and continuously updated and validated through logistic checks. The current study was approved by the institutional review board of the CHS (approval #0212-17-com2). Informed consent was not required because the data were de-identified and this was a noninterventional observational study.
Study Population and Covariates—Medical records of CHS enrollees were screened for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia, and data on prevalent cases of fibromyalgia were retrieved. The diagnosis of fibromyalgia was based on the documentation of a fibromyalgia-specific diagnostic code registered by a board-certified rheumatologist. A control group of individuals without fibromyalgia was selected through 1:2 matching based on age, sex, and primary care clinic. The control group was randomly selected from the list of CHS members frequency-matched to cases, excluding case patients with fibromyalgia. Age matching was grounded on the exact year of birth (1-year strata).
Other covariates in the analysis included pruritus-related skin disorders, including prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC. There were 3 socioeconomic status categories according to patients' poverty index: low, intermediate, and high.26
Statistical Analysis—The distribution of sociodemographic and clinical features was compared between patients with fibromyalgia and controls using the χ2 test for sex and socioeconomic status and the t test for age. Conditional logistic regression then was used to calculate adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI to compare patients with fibromyalgia and controls with respect to the presence of pruritic comorbidities. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 26). P<.05 was considered statistically significant in all tests.
Results
Our study population comprised 4971 patients with fibromyalgia and 9896 age- and sex-matched controls. Proportional to the reported female predominance among patients with fibromyalgia,27 4479 (90.1%) patients with fibromyalgia were females and a similar proportion was documented among controls (P=.99). There was a slightly higher proportion of unmarried patients among those with fibromyalgia compared with controls (41.9% vs 39.4%; P=.004). Socioeconomic status was matched between patients and controls (P=.99). Descriptive characteristics of the study population are presented in Table 1.

We assessed the presence of pruritus as well as 3 other pruritus-related skin disorders—prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC—among patients with fibromyalgia and controls. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the independent association between fibromyalgia and pruritus. Table 2 presents the results of multivariate logistic regression models and summarizes the adjusted ORs for pruritic conditions in patients with fibromyalgia and different demographic features across the entire study sample. Fibromyalgia demonstrated strong independent associations with pruritus (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.8-2.4; P<.001), prurigo nodularis (OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.038), and LSC (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01); the association with neurotic excoriations was not significant. Female sex significantly increased the risk for pruritus (OR 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6; P=.039), while age slightly increased the odds for pruritus (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.04; P<.001), neurotic excoriations (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.1; P=.046), and LSC (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.01-1.04; P=.006). Finally, socioeconomic status was inversely correlated with pruritus (OR, 1.1; 95% CI, 1.1-1.5; P=.002).

Frequencies and ORs for the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus with associated pruritic disorders stratified by exclusion of pruritic dermatologic and/or systemic diseases that may induce itch are presented in the eTable. Analyzing the entire study cohort, significant increases were observed in the odds of all 4 pruritic disorders analyzed. The frequency of pruritus was almost double in patients with fibromyalgia compared with controls (11.7% vs 6.0%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.8-2.3; P<.0001). Prurigo nodularis (0.2% vs 0.1%; OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.05), neurotic excoriations (0.6% vs 0.3%; OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.1; P=.018), and LSC (1.3% vs 0.8%; OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01) frequencies were all higher in patients with fibromyalgia than controls. When primary skin disorders that may cause itch (eg, pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, dermatitis, eczema, ichthyosis, psoriasis, parapsoriasis, urticaria, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, lichen planus) were excluded, the prevalence of pruritus in patients with fibromyalgia was still 1.97 times greater than in the controls (6.9% vs. 3.5%; OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4; P<.0001). These results remained unchanged even when excluding pruritic dermatologic disorders as well as systemic diseases associated with pruritus (eg, chronic renal failure, dialysis, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism/hypoparathyroidism, hypothyroidism). Patients with fibromyalgia still displayed a significantly higher prevalence of pruritus compared with the control group (6.6% vs 3.3%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.7-2.6; P<.0001).

Comment
A wide range of skin manifestations have been associated with fibromyalgia, but the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Nevertheless, it is conceivable that autonomic nervous system dysfunction,28-31 amplified cutaneous opioid receptor activity,32 and an elevated presence of cutaneous mast cells with excessive degranulation may partially explain the frequent occurrence of pruritus and related skin disorders such as neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodularis, and LSC in individuals with fibromyalgia.15,16 In line with these findings, our study—which was based on data from the largest health maintenance organization in Israel—demonstrated an increased prevalence of pruritus and related pruritic disorders among individuals diagnosed with fibromyalgia.
This cross-sectional study links pruritus with fibromyalgia. Few preliminary epidemiologic studies have shown an increased occurrence of cutaneous manifestations in patients with fibromyalgia. One chart review that looked at skin findings in patients with fibromyalgia revealed 32 distinct cutaneous manifestations, and pruritus was the major concern in 3.3% of 845 patients.15
A focused cross-sectional study involving only women (66 with fibromyalgia and 79 healthy controls) discovered 14 skin conditions that were more common in those with fibromyalgia. Notably, xerosis and neurotic excoriations were more prevalent compared to the control group.16
The brain and the skin—both derivatives of the embryonic ectoderm33,34—are linked by pruritus. Although itch has its dedicated neurons, there is a wide-ranging overlap of brain-activated areas between pain and itch,6 and the neural anatomy of pain and itch are closely related in both the peripheral and central nervous systems35-37; for example, diseases of the central nervous system are accompanied by pruritus in as many as 15% of cases, while postherpetic neuralgia can result in chronic pain, itching, or a combination of both.38,39 Other instances include notalgia paresthetica and brachioradial pruritus.38 Additionally, there is a noteworthy psychologic impact associated with both itch and pain,40,41 with both psychosomatic and psychologic factors implicated in chronic pruritus and in fibromyalgia.42 Lastly, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system are altered in both fibromyalgia and pruritus.43-45
Tey et al45 characterized the itch experienced in fibromyalgia as functional, which is described as pruritus associated with a somatoform disorder. In our study, we found a higher prevalence of pruritus among patients with fibromyalgia, and this association remained significant (P<.05) even when excluding other pruritic skin conditions and systemic diseases that can trigger itching. In addition, our logistic regression analyses revealed independent associations between fibromyalgia and pruritus, prurigo nodularis, and LSC.
According to Twycross et al,46 there are 4 clinical categories of itch, which may coexist7: pruritoceptive (originating in the skin), neuropathic (originating in pathology located along the afferent pathway), neurogenic (central origin but lacks a neural pathology), and psychogenic.47 Skin biopsy findings in patients with fibromyalgia include increased mast cell counts11 and degranulation,48 increased expression of δ and κ opioid receptors,32 vasoconstriction within tender points,49 and elevated IL-1β, IL-6, or tumor necrosis factor α by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.12 A case recently was presented by Görg et al50 involving a female patient with fibromyalgia who had been experiencing chronic pruritus, which the authors attributed to small-fiber neuropathy based on evidence from a skin biopsy indicating a reduced number of intraepidermal nerves and the fact that the itching originated around tender points. Altogether, the observed alterations may work together to make patients with fibromyalgia more susceptible to various skin-related comorbidities in general, especially those related to pruritus. Eventually, it might be the case that several itch categories and related pathomechanisms are involved in the pruritus phenotype of patients with fibromyalgia.
Age-related alterations in nerve fibers, lower immune function, xerosis, polypharmacy, and increased frequency of systemic diseases with age are just a few of the factors that may predispose older individuals to pruritus.51,52 Indeed, our logistic regression model showed that age was significantly and independently associated with pruritus (P<.001), neurotic excoriations (P=.046), and LSC (P=.006). Female sex also was significantly linked with pruritus (P=.039). Intriguingly, high socioeconomic status was significantly associated with the diagnosis of pruritus (P=.002), possibly due to easier access to medical care.
There is a considerable overlap between the therapeutic approaches used in pruritus, pruritus-related skin disorders, and fibromyalgia. Antidepressants, anxiolytics, analgesics, and antiepileptics have been used to address both conditions.45 The association between these conditions advocates for a multidisciplinary approach in patients with fibromyalgia and potentially supports the rationale for unified therapeutics for both conditions.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate an association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as associated pruritic skin disorders. Given the convoluted and largely undiscovered mechanisms underlying fibromyalgia, managing patients with this condition may present substantial challenges.53 The data presented here support the implementation of a multidisciplinary treatment approach for patients with fibromyalgia. This approach should focus on managing fibromyalgia pain as well as addressing its concurrent skin-related conditions. It is advisable to consider treatments such as antiepileptics (eg, pregabalin, gabapentin) that specifically target neuropathic disorders in affected patients. These treatments may hold promise for alleviating fibromyalgia-related pain54 and mitigating its related cutaneous comorbidities, especially pruritus.
Pruritus, which is defined as an itching sensation that elicits a desire to scratch, is the most common cutaneous condition. Pruritus is considered chronic when it lasts for more than 6 weeks.1 Etiologies implicated in chronic pruritus include but are not limited to primary skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, systemic causes, neuropathic disorders, and psychogenic reasons.2 In approximately 8% to 35% of patients, the cause of pruritus remains elusive despite intensive investigation.3 The mechanisms of itch are multifaceted and include complex neural pathways.4 Although itch and pain share many similarities, they have distinct pathways based on their spinal connections.5 Nevertheless, both conditions show a wide overlap of receptors on peripheral nerve endings and activated brain parts.6,7 Fibromyalgia, the third most common musculoskeletal condition, affects 2% to 3% of the population worldwide and is at least 7 times more common in females.8,9 Its pathogenesis is not entirely clear but is thought to involve neurogenic inflammation, aberrations in peripheral nerves, and central pain mechanisms. Fibromyalgia is characterized by a plethora of symptoms including chronic widespread pain, autonomic disturbances, persistent fatigue and sleep disturbances, and hyperalgesia, as well as somatic and psychiatric symptoms.10
Fibromyalgia is accompanied by altered skin features including increased counts of mast cells and excessive degranulation,11 neurogenic inflammation with elevated cytokine expression,12 disrupted collagen metabolism,13 and microcirculation abnormalities.14 There has been limited research exploring the dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. One retrospective study that included 845 patients with fibromyalgia reported increased occurrence of “neurodermatoses,” including pruritus, neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodules, and lichen simplex chronicus (LSC), among other cutaneous comorbidities.15 Another small study demonstrated an increased incidence of xerosis and neurotic excoriations in females with fibromyalgia.16 A paucity of large epidemiologic studies demonstrating the fibromyalgia-pruritus connection may lead to misdiagnosis, misinterpretation, and undertreatment of these patients.
Up to 49% of fibromyalgia patients experience small-fiber neuropathy.17 Electrophysiologic measurements, quantitative sensory testing, pain-related evoked potentials, and skin biopsies showed that patients with fibromyalgia have compromised small-fiber function, impaired pathways carrying fiber pain signals, and reduced skin innervation and regenerating fibers.18,19 Accordingly, pruritus that has been reported in fibromyalgia is believed to be of neuropathic origin.15 Overall, it is suspected that the same mechanism that causes hypersensitivity and pain in fibromyalgia patients also predisposes them to pruritus. Similar systemic treatments (eg, analgesics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants) prescribed for both conditions support this theory.20-25
Our large cross-sectional study sought to establish the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as related pruritic conditions.
Methods
Study Design and Setting—We conducted a cross-sectional retrospective study using data-mining techniques to access information from the Clalit Health Services (CHS) database. Clalit Health Services is the largest health maintenance organization in Israel. It encompasses an extensive database with continuous real-time input from medical, administrative, and pharmaceutical computerized operating systems, which helps facilitate data collection for epidemiologic studies. A chronic disease register is gathered from these data sources and continuously updated and validated through logistic checks. The current study was approved by the institutional review board of the CHS (approval #0212-17-com2). Informed consent was not required because the data were de-identified and this was a noninterventional observational study.
Study Population and Covariates—Medical records of CHS enrollees were screened for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia, and data on prevalent cases of fibromyalgia were retrieved. The diagnosis of fibromyalgia was based on the documentation of a fibromyalgia-specific diagnostic code registered by a board-certified rheumatologist. A control group of individuals without fibromyalgia was selected through 1:2 matching based on age, sex, and primary care clinic. The control group was randomly selected from the list of CHS members frequency-matched to cases, excluding case patients with fibromyalgia. Age matching was grounded on the exact year of birth (1-year strata).
Other covariates in the analysis included pruritus-related skin disorders, including prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC. There were 3 socioeconomic status categories according to patients' poverty index: low, intermediate, and high.26
Statistical Analysis—The distribution of sociodemographic and clinical features was compared between patients with fibromyalgia and controls using the χ2 test for sex and socioeconomic status and the t test for age. Conditional logistic regression then was used to calculate adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI to compare patients with fibromyalgia and controls with respect to the presence of pruritic comorbidities. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 26). P<.05 was considered statistically significant in all tests.
Results
Our study population comprised 4971 patients with fibromyalgia and 9896 age- and sex-matched controls. Proportional to the reported female predominance among patients with fibromyalgia,27 4479 (90.1%) patients with fibromyalgia were females and a similar proportion was documented among controls (P=.99). There was a slightly higher proportion of unmarried patients among those with fibromyalgia compared with controls (41.9% vs 39.4%; P=.004). Socioeconomic status was matched between patients and controls (P=.99). Descriptive characteristics of the study population are presented in Table 1.

We assessed the presence of pruritus as well as 3 other pruritus-related skin disorders—prurigo nodularis, neurotic excoriations, and LSC—among patients with fibromyalgia and controls. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the independent association between fibromyalgia and pruritus. Table 2 presents the results of multivariate logistic regression models and summarizes the adjusted ORs for pruritic conditions in patients with fibromyalgia and different demographic features across the entire study sample. Fibromyalgia demonstrated strong independent associations with pruritus (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.8-2.4; P<.001), prurigo nodularis (OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.038), and LSC (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01); the association with neurotic excoriations was not significant. Female sex significantly increased the risk for pruritus (OR 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6; P=.039), while age slightly increased the odds for pruritus (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.04; P<.001), neurotic excoriations (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.0-1.1; P=.046), and LSC (OR, 1.0; 95% CI, 1.01-1.04; P=.006). Finally, socioeconomic status was inversely correlated with pruritus (OR, 1.1; 95% CI, 1.1-1.5; P=.002).

Frequencies and ORs for the association between fibromyalgia and pruritus with associated pruritic disorders stratified by exclusion of pruritic dermatologic and/or systemic diseases that may induce itch are presented in the eTable. Analyzing the entire study cohort, significant increases were observed in the odds of all 4 pruritic disorders analyzed. The frequency of pruritus was almost double in patients with fibromyalgia compared with controls (11.7% vs 6.0%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.8-2.3; P<.0001). Prurigo nodularis (0.2% vs 0.1%; OR, 2.9; 95% CI, 1.1-8.4; P=.05), neurotic excoriations (0.6% vs 0.3%; OR, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.1-3.1; P=.018), and LSC (1.3% vs 0.8%; OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1; P=.01) frequencies were all higher in patients with fibromyalgia than controls. When primary skin disorders that may cause itch (eg, pemphigus vulgaris, Darier disease, dermatitis, eczema, ichthyosis, psoriasis, parapsoriasis, urticaria, xerosis, atopic dermatitis, dermatitis herpetiformis, lichen planus) were excluded, the prevalence of pruritus in patients with fibromyalgia was still 1.97 times greater than in the controls (6.9% vs. 3.5%; OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.7-2.4; P<.0001). These results remained unchanged even when excluding pruritic dermatologic disorders as well as systemic diseases associated with pruritus (eg, chronic renal failure, dialysis, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism/hypoparathyroidism, hypothyroidism). Patients with fibromyalgia still displayed a significantly higher prevalence of pruritus compared with the control group (6.6% vs 3.3%; OR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.7-2.6; P<.0001).

Comment
A wide range of skin manifestations have been associated with fibromyalgia, but the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Nevertheless, it is conceivable that autonomic nervous system dysfunction,28-31 amplified cutaneous opioid receptor activity,32 and an elevated presence of cutaneous mast cells with excessive degranulation may partially explain the frequent occurrence of pruritus and related skin disorders such as neurotic excoriations, prurigo nodularis, and LSC in individuals with fibromyalgia.15,16 In line with these findings, our study—which was based on data from the largest health maintenance organization in Israel—demonstrated an increased prevalence of pruritus and related pruritic disorders among individuals diagnosed with fibromyalgia.
This cross-sectional study links pruritus with fibromyalgia. Few preliminary epidemiologic studies have shown an increased occurrence of cutaneous manifestations in patients with fibromyalgia. One chart review that looked at skin findings in patients with fibromyalgia revealed 32 distinct cutaneous manifestations, and pruritus was the major concern in 3.3% of 845 patients.15
A focused cross-sectional study involving only women (66 with fibromyalgia and 79 healthy controls) discovered 14 skin conditions that were more common in those with fibromyalgia. Notably, xerosis and neurotic excoriations were more prevalent compared to the control group.16
The brain and the skin—both derivatives of the embryonic ectoderm33,34—are linked by pruritus. Although itch has its dedicated neurons, there is a wide-ranging overlap of brain-activated areas between pain and itch,6 and the neural anatomy of pain and itch are closely related in both the peripheral and central nervous systems35-37; for example, diseases of the central nervous system are accompanied by pruritus in as many as 15% of cases, while postherpetic neuralgia can result in chronic pain, itching, or a combination of both.38,39 Other instances include notalgia paresthetica and brachioradial pruritus.38 Additionally, there is a noteworthy psychologic impact associated with both itch and pain,40,41 with both psychosomatic and psychologic factors implicated in chronic pruritus and in fibromyalgia.42 Lastly, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system are altered in both fibromyalgia and pruritus.43-45
Tey et al45 characterized the itch experienced in fibromyalgia as functional, which is described as pruritus associated with a somatoform disorder. In our study, we found a higher prevalence of pruritus among patients with fibromyalgia, and this association remained significant (P<.05) even when excluding other pruritic skin conditions and systemic diseases that can trigger itching. In addition, our logistic regression analyses revealed independent associations between fibromyalgia and pruritus, prurigo nodularis, and LSC.
According to Twycross et al,46 there are 4 clinical categories of itch, which may coexist7: pruritoceptive (originating in the skin), neuropathic (originating in pathology located along the afferent pathway), neurogenic (central origin but lacks a neural pathology), and psychogenic.47 Skin biopsy findings in patients with fibromyalgia include increased mast cell counts11 and degranulation,48 increased expression of δ and κ opioid receptors,32 vasoconstriction within tender points,49 and elevated IL-1β, IL-6, or tumor necrosis factor α by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.12 A case recently was presented by Görg et al50 involving a female patient with fibromyalgia who had been experiencing chronic pruritus, which the authors attributed to small-fiber neuropathy based on evidence from a skin biopsy indicating a reduced number of intraepidermal nerves and the fact that the itching originated around tender points. Altogether, the observed alterations may work together to make patients with fibromyalgia more susceptible to various skin-related comorbidities in general, especially those related to pruritus. Eventually, it might be the case that several itch categories and related pathomechanisms are involved in the pruritus phenotype of patients with fibromyalgia.
Age-related alterations in nerve fibers, lower immune function, xerosis, polypharmacy, and increased frequency of systemic diseases with age are just a few of the factors that may predispose older individuals to pruritus.51,52 Indeed, our logistic regression model showed that age was significantly and independently associated with pruritus (P<.001), neurotic excoriations (P=.046), and LSC (P=.006). Female sex also was significantly linked with pruritus (P=.039). Intriguingly, high socioeconomic status was significantly associated with the diagnosis of pruritus (P=.002), possibly due to easier access to medical care.
There is a considerable overlap between the therapeutic approaches used in pruritus, pruritus-related skin disorders, and fibromyalgia. Antidepressants, anxiolytics, analgesics, and antiepileptics have been used to address both conditions.45 The association between these conditions advocates for a multidisciplinary approach in patients with fibromyalgia and potentially supports the rationale for unified therapeutics for both conditions.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate an association between fibromyalgia and pruritus as well as associated pruritic skin disorders. Given the convoluted and largely undiscovered mechanisms underlying fibromyalgia, managing patients with this condition may present substantial challenges.53 The data presented here support the implementation of a multidisciplinary treatment approach for patients with fibromyalgia. This approach should focus on managing fibromyalgia pain as well as addressing its concurrent skin-related conditions. It is advisable to consider treatments such as antiepileptics (eg, pregabalin, gabapentin) that specifically target neuropathic disorders in affected patients. These treatments may hold promise for alleviating fibromyalgia-related pain54 and mitigating its related cutaneous comorbidities, especially pruritus.
- Stander S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:291-294.
- Yosipovitch G, Bernhard JD. Clinical practice. chronic pruritus. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1625-1634.
- Song J, Xian D, Yang L, et al. Pruritus: progress toward pathogenesis and treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:9625936.
- Potenzieri C, Undem BJ. Basic mechanisms of itch. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012;42:8-19.
- McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M. Itching for an explanation. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15:497-501.
- Drzezga A, Darsow U, Treede RD, et al. Central activation by histamine-induced itch: analogies to pain processing: a correlational analysis of O-15 H2O positron emission tomography studies. Pain. 2001; 92:295-305.
- Yosipovitch G, Greaves MW, Schmelz M. Itch. Lancet. 2003;361:690-694.
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:15-25.
- Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:26-35.
- Sarzi-Puttini P, Giorgi V, Marotto D, et al. Fibromyalgia: an update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:645-660.
- Blanco I, Beritze N, Arguelles M, et al. Abnormal overexpression of mastocytes in skin biopsies of fibromyalgia patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:1403-1412.
- Salemi S, Rethage J, Wollina U, et al. Detection of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in skin of patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:146-150.
- Sprott H, Muller A, Heine H. Collagen cross-links in fibromyalgia syndrome. Z Rheumatol. 1998;57(suppl 2):52-55.
- Morf S, Amann-Vesti B, Forster A, et al. Microcirculation abnormalities in patients with fibromyalgia—measured by capillary microscopy and laser fluxmetry. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R209-R216.
- Laniosz V, Wetter DA, Godar DA. Dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:1009-1013.
- Dogramaci AC, Yalcinkaya EY. Skin problems in fibromyalgia. Nobel Med. 2009;5:50-52.
- Grayston R, Czanner G, Elhadd K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia: implications for a new paradigm in fibromyalgia etiopathogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48:933-940.
- Uceyler N, Zeller D, Kahn AK, et al. Small fibre pathology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Brain. 2013;136:1857-1867.
- Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008; 131:1912- 1925.
- Reed C, Birnbaum HG, Ivanova JI, et al. Real-world role of tricyclic antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:533-540.
- Moret C, Briley M. Antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006;2:537-548.
- Arnold LM, Keck PE Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. a meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics. 2000;41:104-113.
- Moore A, Wiffen P, Kalso E. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. JAMA. 2014;312:182-183.
- Shevchenko A, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Yosipovitch G. Causes, pathophysiology, and treatment of pruritus in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:140-151.
- Scheinfeld N. The role of gabapentin in treating diseases with cutaneous manifestations and pain. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:491-495.
- Points Location Intelligence. Accessed July 30, 2024. https://points.co.il/en/points-location-intelligence/
- Yunus MB. The role of gender in fibromyalgia syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001;3:128-134.
- Cakir T, Evcik D, Dundar U, et al. Evaluation of sympathetic skin response and f wave in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. Turk J Rheumatol. 2011;26:38-43.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Koklukaya E. The correlation of laboratory tests and sympathetic skin response parameters by using artificial neural networks in fibromyalgia patients. J Med Syst. 2012;36:1841-1848.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Arslan E, et al. A study on the effects of sympathetic skin response parameters in diagnosis of fibromyalgia using artificial neural networks. J Med Syst. 2016;40:54.
- Ulas UH, Unlu E, Hamamcioglu K, et al. Dysautonomia in fibromyalgia syndrome: sympathetic skin responses and RR interval analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:383-387.
- Salemi S, Aeschlimann A, Wollina U, et al. Up-regulation of delta-opioid receptors and kappa-opioid receptors in the skin of fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2464-2466.
- Elshazzly M, Lopez MJ, Reddy V, et al. Central nervous system. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Hu MS, Borrelli MR, Hong WX, et al. Embryonic skin development and repair. Organogenesis. 2018;14:46-63.
- Davidson S, Zhang X, Yoon CH, et al. The itch-producing agents histamine and cowhage activate separate populations of primate spinothalamic tract neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10007-10014.
- Sikand P, Shimada SG, Green BG, et al. Similar itch and nociceptive sensations evoked by punctate cutaneous application of capsaicin, histamine and cowhage. Pain. 2009;144:66-75.
- Davidson S, Giesler GJ. The multiple pathways for itch and their interactions with pain. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:550-558.
- Dhand A, Aminoff MJ. The neurology of itch. Brain. 2014;137:313-322.
- Binder A, Koroschetz J, Baron R. Disease mechanisms in neuropathic itch. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008;4:329-337.
- Fjellner B, Arnetz BB. Psychological predictors of pruritus during mental stress. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65:504-508.
- Papoiu AD, Wang H, Coghill RC, et al. Contagious itch in humans: a study of visual ‘transmission’ of itch in atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1299-1303.
- Stumpf A, Schneider G, Stander S. Psychosomatic and psychiatric disorders and psychologic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:704-708.
- Herman JP, McKlveen JM, Ghosal S, et al. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr Physiol. 2016;6:603-621.
- Brown ED, Micozzi MS, Craft NE, et al. Plasma carotenoids in normal men after a single ingestion of vegetables or purified beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49:1258-1265.
- Tey HL, Wallengren J, Yosipovitch G. Psychosomatic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:31-40.
- Twycross R, Greaves MW, Handwerker H, et al. Itch: scratching more than the surface. QJM. 2003;96:7-26.
- Bernhard JD. Itch and pruritus: what are they, and how should itches be classified? Dermatol Ther. 2005;18:288-291.
- Enestrom S, Bengtsson A, Frodin T. Dermal IgG deposits and increase of mast cells in patients with fibromyalgia—relevant findings or epiphenomena? Scand J Rheumatol. 1997;26:308-313.
- Jeschonneck M, Grohmann G, Hein G, et al. Abnormal microcirculation and temperature in skin above tender points in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39:917-921.
- Görg M, Zeidler C, Pereira MP, et al. Generalized chronic pruritus with fibromyalgia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:909-911.
- Garibyan L, Chiou AS, Elmariah SB. Advanced aging skin and itch: addressing an unmet need. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:92-103.
- Cohen KR, Frank J, Salbu RL, et al. Pruritus in the elderly: clinical approaches to the improvement of quality of life. P T. 2012;37:227-239.
- Tzadok R, Ablin JN. Current and emerging pharmacotherapy for fibromyalgia. Pain Res Manag. 2020; 2020:6541798.
- Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia—an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD010567.
- Stander S, Weisshaar E, Mettang T, et al. Clinical classification of itch: a position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:291-294.
- Yosipovitch G, Bernhard JD. Clinical practice. chronic pruritus. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1625-1634.
- Song J, Xian D, Yang L, et al. Pruritus: progress toward pathogenesis and treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:9625936.
- Potenzieri C, Undem BJ. Basic mechanisms of itch. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012;42:8-19.
- McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M. Itching for an explanation. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15:497-501.
- Drzezga A, Darsow U, Treede RD, et al. Central activation by histamine-induced itch: analogies to pain processing: a correlational analysis of O-15 H2O positron emission tomography studies. Pain. 2001; 92:295-305.
- Yosipovitch G, Greaves MW, Schmelz M. Itch. Lancet. 2003;361:690-694.
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:15-25.
- Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:26-35.
- Sarzi-Puttini P, Giorgi V, Marotto D, et al. Fibromyalgia: an update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:645-660.
- Blanco I, Beritze N, Arguelles M, et al. Abnormal overexpression of mastocytes in skin biopsies of fibromyalgia patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:1403-1412.
- Salemi S, Rethage J, Wollina U, et al. Detection of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in skin of patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:146-150.
- Sprott H, Muller A, Heine H. Collagen cross-links in fibromyalgia syndrome. Z Rheumatol. 1998;57(suppl 2):52-55.
- Morf S, Amann-Vesti B, Forster A, et al. Microcirculation abnormalities in patients with fibromyalgia—measured by capillary microscopy and laser fluxmetry. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R209-R216.
- Laniosz V, Wetter DA, Godar DA. Dermatologic manifestations of fibromyalgia. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:1009-1013.
- Dogramaci AC, Yalcinkaya EY. Skin problems in fibromyalgia. Nobel Med. 2009;5:50-52.
- Grayston R, Czanner G, Elhadd K, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia: implications for a new paradigm in fibromyalgia etiopathogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48:933-940.
- Uceyler N, Zeller D, Kahn AK, et al. Small fibre pathology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Brain. 2013;136:1857-1867.
- Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008; 131:1912- 1925.
- Reed C, Birnbaum HG, Ivanova JI, et al. Real-world role of tricyclic antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:533-540.
- Moret C, Briley M. Antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006;2:537-548.
- Arnold LM, Keck PE Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. a meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics. 2000;41:104-113.
- Moore A, Wiffen P, Kalso E. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. JAMA. 2014;312:182-183.
- Shevchenko A, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Yosipovitch G. Causes, pathophysiology, and treatment of pruritus in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:140-151.
- Scheinfeld N. The role of gabapentin in treating diseases with cutaneous manifestations and pain. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:491-495.
- Points Location Intelligence. Accessed July 30, 2024. https://points.co.il/en/points-location-intelligence/
- Yunus MB. The role of gender in fibromyalgia syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001;3:128-134.
- Cakir T, Evcik D, Dundar U, et al. Evaluation of sympathetic skin response and f wave in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. Turk J Rheumatol. 2011;26:38-43.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Koklukaya E. The correlation of laboratory tests and sympathetic skin response parameters by using artificial neural networks in fibromyalgia patients. J Med Syst. 2012;36:1841-1848.
- Ozkan O, Yildiz M, Arslan E, et al. A study on the effects of sympathetic skin response parameters in diagnosis of fibromyalgia using artificial neural networks. J Med Syst. 2016;40:54.
- Ulas UH, Unlu E, Hamamcioglu K, et al. Dysautonomia in fibromyalgia syndrome: sympathetic skin responses and RR interval analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:383-387.
- Salemi S, Aeschlimann A, Wollina U, et al. Up-regulation of delta-opioid receptors and kappa-opioid receptors in the skin of fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2464-2466.
- Elshazzly M, Lopez MJ, Reddy V, et al. Central nervous system. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Hu MS, Borrelli MR, Hong WX, et al. Embryonic skin development and repair. Organogenesis. 2018;14:46-63.
- Davidson S, Zhang X, Yoon CH, et al. The itch-producing agents histamine and cowhage activate separate populations of primate spinothalamic tract neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10007-10014.
- Sikand P, Shimada SG, Green BG, et al. Similar itch and nociceptive sensations evoked by punctate cutaneous application of capsaicin, histamine and cowhage. Pain. 2009;144:66-75.
- Davidson S, Giesler GJ. The multiple pathways for itch and their interactions with pain. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:550-558.
- Dhand A, Aminoff MJ. The neurology of itch. Brain. 2014;137:313-322.
- Binder A, Koroschetz J, Baron R. Disease mechanisms in neuropathic itch. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008;4:329-337.
- Fjellner B, Arnetz BB. Psychological predictors of pruritus during mental stress. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65:504-508.
- Papoiu AD, Wang H, Coghill RC, et al. Contagious itch in humans: a study of visual ‘transmission’ of itch in atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1299-1303.
- Stumpf A, Schneider G, Stander S. Psychosomatic and psychiatric disorders and psychologic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:704-708.
- Herman JP, McKlveen JM, Ghosal S, et al. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr Physiol. 2016;6:603-621.
- Brown ED, Micozzi MS, Craft NE, et al. Plasma carotenoids in normal men after a single ingestion of vegetables or purified beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49:1258-1265.
- Tey HL, Wallengren J, Yosipovitch G. Psychosomatic factors in pruritus. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:31-40.
- Twycross R, Greaves MW, Handwerker H, et al. Itch: scratching more than the surface. QJM. 2003;96:7-26.
- Bernhard JD. Itch and pruritus: what are they, and how should itches be classified? Dermatol Ther. 2005;18:288-291.
- Enestrom S, Bengtsson A, Frodin T. Dermal IgG deposits and increase of mast cells in patients with fibromyalgia—relevant findings or epiphenomena? Scand J Rheumatol. 1997;26:308-313.
- Jeschonneck M, Grohmann G, Hein G, et al. Abnormal microcirculation and temperature in skin above tender points in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39:917-921.
- Görg M, Zeidler C, Pereira MP, et al. Generalized chronic pruritus with fibromyalgia. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:909-911.
- Garibyan L, Chiou AS, Elmariah SB. Advanced aging skin and itch: addressing an unmet need. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:92-103.
- Cohen KR, Frank J, Salbu RL, et al. Pruritus in the elderly: clinical approaches to the improvement of quality of life. P T. 2012;37:227-239.
- Tzadok R, Ablin JN. Current and emerging pharmacotherapy for fibromyalgia. Pain Res Manag. 2020; 2020:6541798.
- Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Antiepileptic drugs for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia—an overview of Cochrane reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD010567.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware of the connection between fibromyalgia, pruritus, and related conditions to improve patient care.
- The association between fibromyalgia and pruritus underscores the importance of employing multidisciplinary treatment strategies for managing these conditions.
Painful Plaque on the Forearm
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium marinum Infection
A repeat excisional biopsy showed suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with negative stains for infectious organisms; however, tissue culture grew Mycobacterium marinum. The patient had a history of exposure to fish tanks, which are a potential habitat for nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria can enter the body through a minor laceration or cut in the skin, which was likely due to her occupation and pet care activities.1 Her fish tank exposure combined with the cutaneous findings of a long-standing indurated plaque with proximal nodular lymphangitis made M marinum infection the most likely diagnosis.2
Due to the limited specificity and sensitivity of patient symptoms, histologic staining, and direct microscopy, the gold standard for diagnosing acid-fast bacilli is tissue culture. 3 Tissue polymerase chain reaction testing is most useful in identifying the species of mycobacteria when histologic stains identify acid-fast bacilli but repeated tissue cultures are negative.4 With M marinum, a high clinical suspicion is needed to acquire a positive tissue culture because it needs to be grown for several weeks and at a temperature of 30 °C.5 Therefore, the physician should inform the laboratory if there is any suspicion for M marinum to increase the likelihood of obtaining a positive culture.
The differential diagnosis for M marinum infection includes other skin diseases that can cause nodular lymphangitis (also known as sporotrichoid spread) such as sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and certain bacterial and fungal infections. Although cat scratch disease, which is caused by Bartonella henselae, can appear similar to M marinum on histopathology, it clinically manifests with a single papulovesicular lesion at the site of inoculation that then forms a central eschar and resolves within a few weeks. Cat scratch disease typically causes painful lymphadenopathy, but it does not cause nodular lymphangitis or sporotrichoid spread.6 Sporotrichosis can have a similar clinical and histologic manifestation to M marinum infection, but the patient history typically includes exposure to Sporothrix schenckii through gardening or other contact with thorns, plants, or soil.2 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a similar clinical appearance to M marinum infection, but nodular lymphangitis does not occur and histopathology would demonstrate noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas.7 Lastly, although vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum can have some of the same histologic findings as M marinum, it typically also demonstrates sinus tract formation, which was not present in our case. Additionally, vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum manifests with a verrucous and pustular plaque that would not have lymphocutaneous spread.8
Treatment of cutaneous M marinum infection is guided by antibiotic susceptibility testing. One regimen is clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily9) plus ethambutol. 10 Treatment often entails a multidrug combination due to the high rates of antibiotic resistance. Other antibiotics that potentially can be used include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, minocycline, and quinolones. The treatment duration typically is more than 3 months, and therapy is continued for 4 to 6 weeks after the skin lesions resolve.11 Excision of the lesion is reserved for patients with M marinum infection that fails to respond to antibiotic therapy.5
- Wayne LG, Sramek HA. Agents of newly recognized or infrequently encountered mycobacterial diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992;5:1-25. doi:10.1128/CMR.5.1.1
- Tobin EH, Jih WW. Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections: etiology, diagnosis and therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63:326-332.
- van Ingen J. Diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;34:103-109. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1333569
- Williamson H, Phillips R, Sarfo S, et al. Genetic diversity of PCR-positive, culture-negative and culture-positive Mycobacterium ulcerans isolated from Buruli ulcer patients in Ghana. PLoS One. 2014;9:E88007. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088007
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Baranowski K, Huang B. Cat scratch disease. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 12, 2023. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK482139/
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.006
- Borg Grech S, Vella Baldacchino A, Corso R, et al. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021;8:002656. doi:10.12890/2021_002656
- Krooks J, Weatherall A, Markowitz S. Complete resolution of Mycobacterium marinum infection with clarithromycin and ethambutol: a case report and a review of the literature. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:48-51.
- Medel-Plaza M., Esteban J. Current treatment options for Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2023;24:1113-1123. doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2211258
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Bonifaz A. Nodular lymphangitis (sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections): clues to differential diagnosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:56. doi:10.3390/jof4020056
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium marinum Infection
A repeat excisional biopsy showed suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with negative stains for infectious organisms; however, tissue culture grew Mycobacterium marinum. The patient had a history of exposure to fish tanks, which are a potential habitat for nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria can enter the body through a minor laceration or cut in the skin, which was likely due to her occupation and pet care activities.1 Her fish tank exposure combined with the cutaneous findings of a long-standing indurated plaque with proximal nodular lymphangitis made M marinum infection the most likely diagnosis.2
Due to the limited specificity and sensitivity of patient symptoms, histologic staining, and direct microscopy, the gold standard for diagnosing acid-fast bacilli is tissue culture. 3 Tissue polymerase chain reaction testing is most useful in identifying the species of mycobacteria when histologic stains identify acid-fast bacilli but repeated tissue cultures are negative.4 With M marinum, a high clinical suspicion is needed to acquire a positive tissue culture because it needs to be grown for several weeks and at a temperature of 30 °C.5 Therefore, the physician should inform the laboratory if there is any suspicion for M marinum to increase the likelihood of obtaining a positive culture.
The differential diagnosis for M marinum infection includes other skin diseases that can cause nodular lymphangitis (also known as sporotrichoid spread) such as sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and certain bacterial and fungal infections. Although cat scratch disease, which is caused by Bartonella henselae, can appear similar to M marinum on histopathology, it clinically manifests with a single papulovesicular lesion at the site of inoculation that then forms a central eschar and resolves within a few weeks. Cat scratch disease typically causes painful lymphadenopathy, but it does not cause nodular lymphangitis or sporotrichoid spread.6 Sporotrichosis can have a similar clinical and histologic manifestation to M marinum infection, but the patient history typically includes exposure to Sporothrix schenckii through gardening or other contact with thorns, plants, or soil.2 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a similar clinical appearance to M marinum infection, but nodular lymphangitis does not occur and histopathology would demonstrate noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas.7 Lastly, although vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum can have some of the same histologic findings as M marinum, it typically also demonstrates sinus tract formation, which was not present in our case. Additionally, vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum manifests with a verrucous and pustular plaque that would not have lymphocutaneous spread.8
Treatment of cutaneous M marinum infection is guided by antibiotic susceptibility testing. One regimen is clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily9) plus ethambutol. 10 Treatment often entails a multidrug combination due to the high rates of antibiotic resistance. Other antibiotics that potentially can be used include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, minocycline, and quinolones. The treatment duration typically is more than 3 months, and therapy is continued for 4 to 6 weeks after the skin lesions resolve.11 Excision of the lesion is reserved for patients with M marinum infection that fails to respond to antibiotic therapy.5
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium marinum Infection
A repeat excisional biopsy showed suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with negative stains for infectious organisms; however, tissue culture grew Mycobacterium marinum. The patient had a history of exposure to fish tanks, which are a potential habitat for nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria can enter the body through a minor laceration or cut in the skin, which was likely due to her occupation and pet care activities.1 Her fish tank exposure combined with the cutaneous findings of a long-standing indurated plaque with proximal nodular lymphangitis made M marinum infection the most likely diagnosis.2
Due to the limited specificity and sensitivity of patient symptoms, histologic staining, and direct microscopy, the gold standard for diagnosing acid-fast bacilli is tissue culture. 3 Tissue polymerase chain reaction testing is most useful in identifying the species of mycobacteria when histologic stains identify acid-fast bacilli but repeated tissue cultures are negative.4 With M marinum, a high clinical suspicion is needed to acquire a positive tissue culture because it needs to be grown for several weeks and at a temperature of 30 °C.5 Therefore, the physician should inform the laboratory if there is any suspicion for M marinum to increase the likelihood of obtaining a positive culture.
The differential diagnosis for M marinum infection includes other skin diseases that can cause nodular lymphangitis (also known as sporotrichoid spread) such as sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and certain bacterial and fungal infections. Although cat scratch disease, which is caused by Bartonella henselae, can appear similar to M marinum on histopathology, it clinically manifests with a single papulovesicular lesion at the site of inoculation that then forms a central eschar and resolves within a few weeks. Cat scratch disease typically causes painful lymphadenopathy, but it does not cause nodular lymphangitis or sporotrichoid spread.6 Sporotrichosis can have a similar clinical and histologic manifestation to M marinum infection, but the patient history typically includes exposure to Sporothrix schenckii through gardening or other contact with thorns, plants, or soil.2 Cutaneous sarcoidosis can have a similar clinical appearance to M marinum infection, but nodular lymphangitis does not occur and histopathology would demonstrate noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas.7 Lastly, although vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum can have some of the same histologic findings as M marinum, it typically also demonstrates sinus tract formation, which was not present in our case. Additionally, vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum manifests with a verrucous and pustular plaque that would not have lymphocutaneous spread.8
Treatment of cutaneous M marinum infection is guided by antibiotic susceptibility testing. One regimen is clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily9) plus ethambutol. 10 Treatment often entails a multidrug combination due to the high rates of antibiotic resistance. Other antibiotics that potentially can be used include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, minocycline, and quinolones. The treatment duration typically is more than 3 months, and therapy is continued for 4 to 6 weeks after the skin lesions resolve.11 Excision of the lesion is reserved for patients with M marinum infection that fails to respond to antibiotic therapy.5
- Wayne LG, Sramek HA. Agents of newly recognized or infrequently encountered mycobacterial diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992;5:1-25. doi:10.1128/CMR.5.1.1
- Tobin EH, Jih WW. Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections: etiology, diagnosis and therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63:326-332.
- van Ingen J. Diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;34:103-109. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1333569
- Williamson H, Phillips R, Sarfo S, et al. Genetic diversity of PCR-positive, culture-negative and culture-positive Mycobacterium ulcerans isolated from Buruli ulcer patients in Ghana. PLoS One. 2014;9:E88007. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088007
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Baranowski K, Huang B. Cat scratch disease. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 12, 2023. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK482139/
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.006
- Borg Grech S, Vella Baldacchino A, Corso R, et al. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021;8:002656. doi:10.12890/2021_002656
- Krooks J, Weatherall A, Markowitz S. Complete resolution of Mycobacterium marinum infection with clarithromycin and ethambutol: a case report and a review of the literature. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:48-51.
- Medel-Plaza M., Esteban J. Current treatment options for Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2023;24:1113-1123. doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2211258
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Bonifaz A. Nodular lymphangitis (sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections): clues to differential diagnosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:56. doi:10.3390/jof4020056
- Wayne LG, Sramek HA. Agents of newly recognized or infrequently encountered mycobacterial diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992;5:1-25. doi:10.1128/CMR.5.1.1
- Tobin EH, Jih WW. Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections: etiology, diagnosis and therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63:326-332.
- van Ingen J. Diagnosis of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;34:103-109. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1333569
- Williamson H, Phillips R, Sarfo S, et al. Genetic diversity of PCR-positive, culture-negative and culture-positive Mycobacterium ulcerans isolated from Buruli ulcer patients in Ghana. PLoS One. 2014;9:E88007. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088007
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Baranowski K, Huang B. Cat scratch disease. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 12, 2023. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/books/NBK482139/
- Sanchez M, Haimovic A, Prystowsky S. Sarcoidosis. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:389-416. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.006
- Borg Grech S, Vella Baldacchino A, Corso R, et al. Superficial granulomatous pyoderma successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2021;8:002656. doi:10.12890/2021_002656
- Krooks J, Weatherall A, Markowitz S. Complete resolution of Mycobacterium marinum infection with clarithromycin and ethambutol: a case report and a review of the literature. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:48-51.
- Medel-Plaza M., Esteban J. Current treatment options for Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2023;24:1113-1123. doi:10.1080/14656566.2023.2211258
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Bonifaz A. Nodular lymphangitis (sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections): clues to differential diagnosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:56. doi:10.3390/jof4020056
A 30-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with lesions on the right forearm of 2 years’ duration. Her medical history was unremarkable. She reported working as a chef and caring for multiple pets in her home, including 3 cats, 6 fish tanks, 3 dogs, and 3 lizards. Physical examination revealed a painful, indurated, red-violaceous plaque on the right forearm with satellite pink nodules that had been slowly migrating proximally up the forearm. An outside excisional biopsy performed 1 year prior had shown suppurative granulomatous dermatitis with negative stains for infectious organisms and negative tissue cultures. At that time, the patient was diagnosed with ruptured folliculitis; however, a subsequent lack of clinical improvement prompted her to seek a second opinion at our clinic.
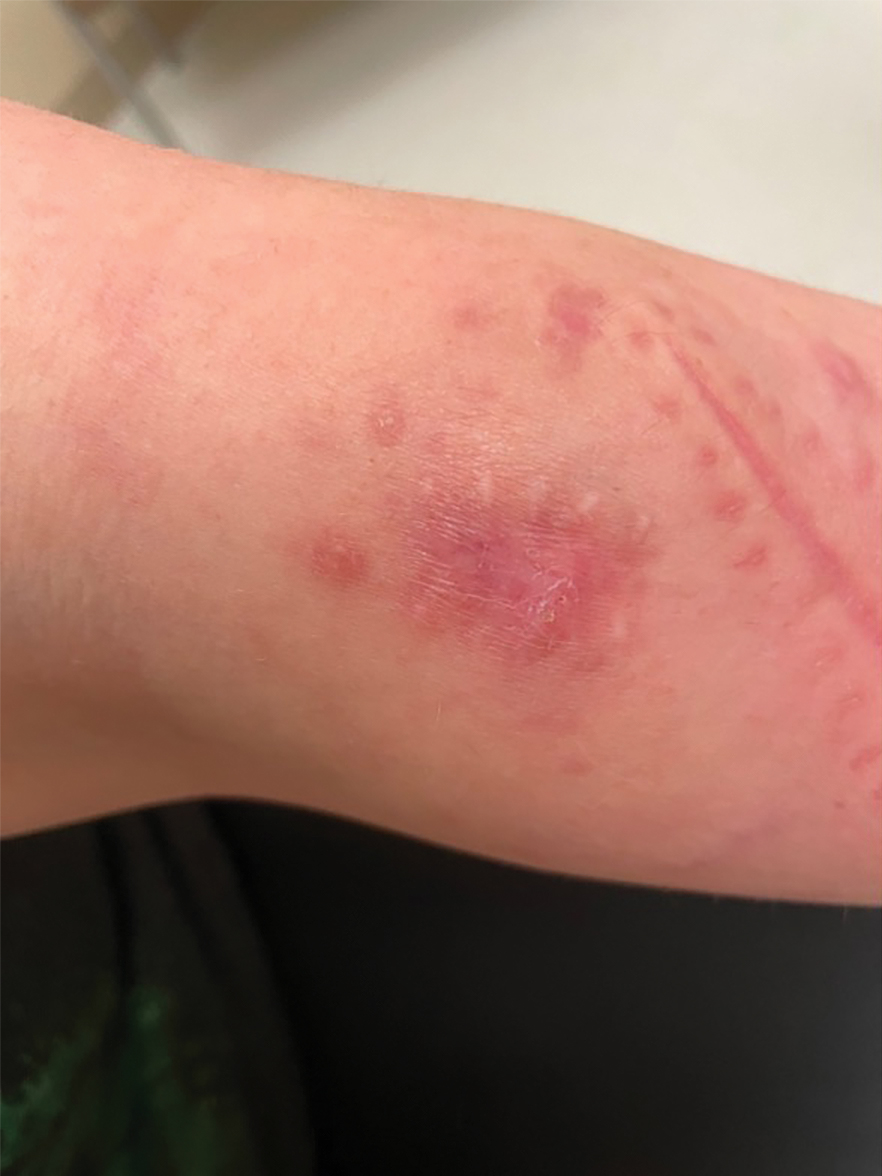
Erythema Nodosum Triggered by a Bite From a Copperhead Snake
The clinical manifestations of snakebites vary based on the species of snake, bite location, and amount and strength of the venom injected. Locally acting toxins in snake venom predominantly consist of enzymes, such as phospholipase A2, that cause local tissue destruction and can result in pain, swelling, blistering, ecchymosis, and tissue necrosis at the site of the bite within hours to days after the bite.1 Systemically acting toxins can target a wide variety of tissues and cause severe systemic complications including paralysis, rhabdomyolysis secondary to muscle damage, coagulopathy, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory failure.2
Although pain and swelling following snakebites typically resolve by 1 month after envenomation, copperhead snakes—a type of pit viper—may cause residual symptoms of pain and swelling lasting for a year or more.3 Additional cutaneous manifestations of copperhead snakebites include wound infections at the bite site, such as cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis. More devastating complications that have been described following snake envenomation include tissue injury of an entire extremity and development of compartment syndrome, which requires urgent fasciotomy to prevent potential loss of the affected limb.4
Physicians should be aware of the potential complications of snakebites to properly manage and counsel their patients. We describe a 42-year-old woman with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules persisting for 4 months following a copperhead snakebite. A biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of snakebite-associated erythema nodosum (EN).
Case Report
A 42-year-old woman presented to our clinic with progressive tender, pruritic, deep-seated, erythematous nodules in multiple locations on the legs after sustaining a bite by a copperhead snake on the left foot 4 months prior. The lesions tended to fluctuate in intensity. In the days following the bite, she initially developed painful red bumps on the left foot just proximal to the bite site with associated pain and swelling extending up to just below the left knee. She reported no other notable symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, fatigue, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms. Physical examination revealed bilateral pitting edema, which was worse in the left leg, along with multiple deep, palpable, tender subcutaneous nodules with erythematous surface change (Figure 1).
Workup performed by an outside provider over the previous month included 2 venous duplex ultrasounds of the left leg, which showed no signs of deep vein thrombosis. Additionally, the patient underwent lateral and anteroposterior radiographs of the left foot, tibia, and fibula, which showed no evidence of fracture.
Given the morphology and distribution of the lesions (Figure 2), EN was strongly favored as the cause of the symptoms, and a biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. All immunohistochemical stains including auramine-rhodamine for acid-fast bacilli, Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver for fungal organisms, and Brown and Brenn were negative. Given the waxing and waning course of the lesions, which suggested an active neutrophilic rather than purely chronic granulomatous phase of EN, the patient was treated with colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for 1 month.
Causes of EN and Clinical Manifestations
Erythema nodosum is a common form of septal panniculitis that can be precipitated by inflammatory conditions, infection, or medications (commonly oral contraceptive pills) but often is idiopathic.5 The acute phase is neutrophilic, with evolution over time to a granulomatous phase. Common etiologies include sarcoidosis; inflammatory bowel disease; and bacterial or fungal infections such as Streptococcus (especially common in children), histoplasmosis, and coccidioidomycosis. The patient was otherwise healthy and was not taking any medications that are known triggers of EN. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE in the English-language literature using the terms copperhead snake bite, erythema nodosum snake, and copperhead snake erythema nodosum revealed no reports of EN following a bite from a copperhead snake; however, in one case, an adder bite led to erysipelas, likely due to disturbed blood and lymphatic flow, which then triggered EN.6 Additionally, EN has been reported as a delayed reaction to jellyfish stings.7
Clinical features of EN include the development of tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules and plaques most frequently over the pretibial region. Lesions typically evolve from raised, deep-seated nodules into flat indurated plaques over a span of weeks. Occasionally, there is a slight prodromal phase marked by nonspecific symptoms such as fever and arthralgia lasting for 3 to 6 days. Erythema nodosum typically results in spontaneous resolution after 4 to 8 weeks, and management involves treatment of any underlying condition with symptomatic care. Interestingly, our patient experienced persistent symptoms over the course of 4 months, with development of new nodular lesions throughout this time period. The most frequently used drugs for the management of symptomatic EN include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, and potassium iodide.8 A characteristic histologic finding of the granulomatous phase is the Miescher radial granuloma, which is a septal collection of histiocytes surrounding a cleft.9
Snakebite Reactions
Snakebites can result in a wide range of local and systemic manifestations, as snake venom may contain 20 or more toxins.10 Local complications of pit viper bites include pain, swelling, and fang marks; when examining fang marks, the presence of 2 distinct puncture wounds often indicates envenomation with a poisonous snake, whereas nonvenomous snakebites often result in smaller puncture wounds arranged in an arc. Following bites, pain can develop immediately and spread proximally up the affected limb, which occurred in our patient in the days following the bite. Intense local reactions can occur, as bites often result in intense edema of the affected limb spreading to the trunk in the days to weeks after the bite, occasionally accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy. Some bites can result in local necrosis and secondary bacterial infection caused by organisms in the oral cavity of the culprit snake.
Although they were not present in our patient, snakebites can result in a wide range of systemic toxicities ranging from clotting defects and hemolysis to neurotoxicity, myotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity.10 In severe cases, snake venom can result in disseminated intravascular coagulation, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory collapse.
The eastern copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) is a species of venomous snake that is endemic to eastern North America. Copperheads are members of the subfamily Crotalinae in the family Viperidae.11 Reported reactions to copperhead bites include cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, compartment syndrome, and tissue necrosis of an entire affected extremity.12,13 Our patient displayed no systemic symptoms to suggest envenomation.
Management of Snakebites
Treatment of snakebites varies based on the constellation and severity of symptoms as well as how recently the envenomation occurred. In urgent cases, antivenom may be administered to prevent further toxicity. In cases of progressive compartment syndrome, emergent surgical procedures such as fasciotomy or amputation are required to prevent further complications. When a superimposed bacterial infection is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics are required. Because our patient presented 4 months following the initial bite with isolated cutaneous manifestations, she was treated symptomatically with colchicine for EN.1,2
Final Thoughts
Our patient presented with EN following a bite from a copperhead snake. Physicians should be aware of possible etiologies of EN to evaluate patients who present with new-onset tender subcutaneous nodules. Additionally, physicians should be aware of venomous snakes endemic to their region and also understand the various complications that can result following a snakebite, with the potential for lingering cutaneous manifestations weeks to months following the initial bite.
- Warrell DA. Snake bite. Lancet. 2010;375:77-88. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61754-2
- White J. Overview of venomous snakes of the world. In: Dart RC, eds. Medical Toxicology. 3rd ed. Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2004:1543
- Spiller HA, Bosse GM. Prospective study of morbidity associated with snakebite envenomation. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:125-130. doi:10.1081/clt-120019127
- Scharman EJ, Noffsinger VD. Copperhead snakebites: clinical severity of local effects. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38:55-61. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.116148
- Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema nodosum. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; November 28, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470369/
- Nowowiejska J, Baran A, Flisiak I. Rare coexistence of unilateral erythema nodosum with erysipelas in the area of previous adder bite. Przegl Epidemiol. 2020;74:355-361. doi:10.32394/pe.74.28
- Auerbach PS, Hays JT. Erythema nodosum following a jellyfish sting. J Emerg Med. 1987;5:487-491. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(87)90211-3
- Gilchrist H, Patterson JW. Erythema nodosum and erythema induratum (nodular vasculitis): diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:320-327. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01332.x
- Sánchez Yus E, Sanz Vico MD, de Diego V. Miescher’s radial granuloma. a characteristic marker of erythema nodosum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;11:434-442. doi:10.1097/00000372-198910000-00005
- Mehta SR, Sashindran VK. Clinical features and management of snake bite. Med J Armed Forces India. 2002;58:247-249. doi:10.1016/S0377-1237(02)80140-X
- Brys AK, Gandolfi BM, Levinson H, et al. Copperhead envenomation resulting in a rare case of hand compartment syndrome and subsequent fasciotomy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E396. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000367
- Clark RF, Selden BS, Furbee B. The incidence of wound infection following crotalid envenomation. J Emerg Med. 1993;11:583-586. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(93)90313-v
- Buchanan JT, Thurman J. Crotalidae envenomation. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; October 3, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551615/
The clinical manifestations of snakebites vary based on the species of snake, bite location, and amount and strength of the venom injected. Locally acting toxins in snake venom predominantly consist of enzymes, such as phospholipase A2, that cause local tissue destruction and can result in pain, swelling, blistering, ecchymosis, and tissue necrosis at the site of the bite within hours to days after the bite.1 Systemically acting toxins can target a wide variety of tissues and cause severe systemic complications including paralysis, rhabdomyolysis secondary to muscle damage, coagulopathy, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory failure.2
Although pain and swelling following snakebites typically resolve by 1 month after envenomation, copperhead snakes—a type of pit viper—may cause residual symptoms of pain and swelling lasting for a year or more.3 Additional cutaneous manifestations of copperhead snakebites include wound infections at the bite site, such as cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis. More devastating complications that have been described following snake envenomation include tissue injury of an entire extremity and development of compartment syndrome, which requires urgent fasciotomy to prevent potential loss of the affected limb.4
Physicians should be aware of the potential complications of snakebites to properly manage and counsel their patients. We describe a 42-year-old woman with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules persisting for 4 months following a copperhead snakebite. A biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of snakebite-associated erythema nodosum (EN).
Case Report
A 42-year-old woman presented to our clinic with progressive tender, pruritic, deep-seated, erythematous nodules in multiple locations on the legs after sustaining a bite by a copperhead snake on the left foot 4 months prior. The lesions tended to fluctuate in intensity. In the days following the bite, she initially developed painful red bumps on the left foot just proximal to the bite site with associated pain and swelling extending up to just below the left knee. She reported no other notable symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, fatigue, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms. Physical examination revealed bilateral pitting edema, which was worse in the left leg, along with multiple deep, palpable, tender subcutaneous nodules with erythematous surface change (Figure 1).

Workup performed by an outside provider over the previous month included 2 venous duplex ultrasounds of the left leg, which showed no signs of deep vein thrombosis. Additionally, the patient underwent lateral and anteroposterior radiographs of the left foot, tibia, and fibula, which showed no evidence of fracture.
Given the morphology and distribution of the lesions (Figure 2), EN was strongly favored as the cause of the symptoms, and a biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. All immunohistochemical stains including auramine-rhodamine for acid-fast bacilli, Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver for fungal organisms, and Brown and Brenn were negative. Given the waxing and waning course of the lesions, which suggested an active neutrophilic rather than purely chronic granulomatous phase of EN, the patient was treated with colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for 1 month.

Causes of EN and Clinical Manifestations
Erythema nodosum is a common form of septal panniculitis that can be precipitated by inflammatory conditions, infection, or medications (commonly oral contraceptive pills) but often is idiopathic.5 The acute phase is neutrophilic, with evolution over time to a granulomatous phase. Common etiologies include sarcoidosis; inflammatory bowel disease; and bacterial or fungal infections such as Streptococcus (especially common in children), histoplasmosis, and coccidioidomycosis. The patient was otherwise healthy and was not taking any medications that are known triggers of EN. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE in the English-language literature using the terms copperhead snake bite, erythema nodosum snake, and copperhead snake erythema nodosum revealed no reports of EN following a bite from a copperhead snake; however, in one case, an adder bite led to erysipelas, likely due to disturbed blood and lymphatic flow, which then triggered EN.6 Additionally, EN has been reported as a delayed reaction to jellyfish stings.7
Clinical features of EN include the development of tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules and plaques most frequently over the pretibial region. Lesions typically evolve from raised, deep-seated nodules into flat indurated plaques over a span of weeks. Occasionally, there is a slight prodromal phase marked by nonspecific symptoms such as fever and arthralgia lasting for 3 to 6 days. Erythema nodosum typically results in spontaneous resolution after 4 to 8 weeks, and management involves treatment of any underlying condition with symptomatic care. Interestingly, our patient experienced persistent symptoms over the course of 4 months, with development of new nodular lesions throughout this time period. The most frequently used drugs for the management of symptomatic EN include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, and potassium iodide.8 A characteristic histologic finding of the granulomatous phase is the Miescher radial granuloma, which is a septal collection of histiocytes surrounding a cleft.9
Snakebite Reactions
Snakebites can result in a wide range of local and systemic manifestations, as snake venom may contain 20 or more toxins.10 Local complications of pit viper bites include pain, swelling, and fang marks; when examining fang marks, the presence of 2 distinct puncture wounds often indicates envenomation with a poisonous snake, whereas nonvenomous snakebites often result in smaller puncture wounds arranged in an arc. Following bites, pain can develop immediately and spread proximally up the affected limb, which occurred in our patient in the days following the bite. Intense local reactions can occur, as bites often result in intense edema of the affected limb spreading to the trunk in the days to weeks after the bite, occasionally accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy. Some bites can result in local necrosis and secondary bacterial infection caused by organisms in the oral cavity of the culprit snake.
Although they were not present in our patient, snakebites can result in a wide range of systemic toxicities ranging from clotting defects and hemolysis to neurotoxicity, myotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity.10 In severe cases, snake venom can result in disseminated intravascular coagulation, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory collapse.
The eastern copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) is a species of venomous snake that is endemic to eastern North America. Copperheads are members of the subfamily Crotalinae in the family Viperidae.11 Reported reactions to copperhead bites include cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, compartment syndrome, and tissue necrosis of an entire affected extremity.12,13 Our patient displayed no systemic symptoms to suggest envenomation.
Management of Snakebites
Treatment of snakebites varies based on the constellation and severity of symptoms as well as how recently the envenomation occurred. In urgent cases, antivenom may be administered to prevent further toxicity. In cases of progressive compartment syndrome, emergent surgical procedures such as fasciotomy or amputation are required to prevent further complications. When a superimposed bacterial infection is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics are required. Because our patient presented 4 months following the initial bite with isolated cutaneous manifestations, she was treated symptomatically with colchicine for EN.1,2
Final Thoughts
Our patient presented with EN following a bite from a copperhead snake. Physicians should be aware of possible etiologies of EN to evaluate patients who present with new-onset tender subcutaneous nodules. Additionally, physicians should be aware of venomous snakes endemic to their region and also understand the various complications that can result following a snakebite, with the potential for lingering cutaneous manifestations weeks to months following the initial bite.
The clinical manifestations of snakebites vary based on the species of snake, bite location, and amount and strength of the venom injected. Locally acting toxins in snake venom predominantly consist of enzymes, such as phospholipase A2, that cause local tissue destruction and can result in pain, swelling, blistering, ecchymosis, and tissue necrosis at the site of the bite within hours to days after the bite.1 Systemically acting toxins can target a wide variety of tissues and cause severe systemic complications including paralysis, rhabdomyolysis secondary to muscle damage, coagulopathy, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory failure.2
Although pain and swelling following snakebites typically resolve by 1 month after envenomation, copperhead snakes—a type of pit viper—may cause residual symptoms of pain and swelling lasting for a year or more.3 Additional cutaneous manifestations of copperhead snakebites include wound infections at the bite site, such as cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis. More devastating complications that have been described following snake envenomation include tissue injury of an entire extremity and development of compartment syndrome, which requires urgent fasciotomy to prevent potential loss of the affected limb.4
Physicians should be aware of the potential complications of snakebites to properly manage and counsel their patients. We describe a 42-year-old woman with tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules persisting for 4 months following a copperhead snakebite. A biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of snakebite-associated erythema nodosum (EN).
Case Report
A 42-year-old woman presented to our clinic with progressive tender, pruritic, deep-seated, erythematous nodules in multiple locations on the legs after sustaining a bite by a copperhead snake on the left foot 4 months prior. The lesions tended to fluctuate in intensity. In the days following the bite, she initially developed painful red bumps on the left foot just proximal to the bite site with associated pain and swelling extending up to just below the left knee. She reported no other notable symptoms such as fever, arthralgia, fatigue, or gastrointestinal tract symptoms. Physical examination revealed bilateral pitting edema, which was worse in the left leg, along with multiple deep, palpable, tender subcutaneous nodules with erythematous surface change (Figure 1).

Workup performed by an outside provider over the previous month included 2 venous duplex ultrasounds of the left leg, which showed no signs of deep vein thrombosis. Additionally, the patient underwent lateral and anteroposterior radiographs of the left foot, tibia, and fibula, which showed no evidence of fracture.
Given the morphology and distribution of the lesions (Figure 2), EN was strongly favored as the cause of the symptoms, and a biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. All immunohistochemical stains including auramine-rhodamine for acid-fast bacilli, Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver for fungal organisms, and Brown and Brenn were negative. Given the waxing and waning course of the lesions, which suggested an active neutrophilic rather than purely chronic granulomatous phase of EN, the patient was treated with colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for 1 month.

Causes of EN and Clinical Manifestations
Erythema nodosum is a common form of septal panniculitis that can be precipitated by inflammatory conditions, infection, or medications (commonly oral contraceptive pills) but often is idiopathic.5 The acute phase is neutrophilic, with evolution over time to a granulomatous phase. Common etiologies include sarcoidosis; inflammatory bowel disease; and bacterial or fungal infections such as Streptococcus (especially common in children), histoplasmosis, and coccidioidomycosis. The patient was otherwise healthy and was not taking any medications that are known triggers of EN. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE in the English-language literature using the terms copperhead snake bite, erythema nodosum snake, and copperhead snake erythema nodosum revealed no reports of EN following a bite from a copperhead snake; however, in one case, an adder bite led to erysipelas, likely due to disturbed blood and lymphatic flow, which then triggered EN.6 Additionally, EN has been reported as a delayed reaction to jellyfish stings.7
Clinical features of EN include the development of tender, erythematous, subcutaneous nodules and plaques most frequently over the pretibial region. Lesions typically evolve from raised, deep-seated nodules into flat indurated plaques over a span of weeks. Occasionally, there is a slight prodromal phase marked by nonspecific symptoms such as fever and arthralgia lasting for 3 to 6 days. Erythema nodosum typically results in spontaneous resolution after 4 to 8 weeks, and management involves treatment of any underlying condition with symptomatic care. Interestingly, our patient experienced persistent symptoms over the course of 4 months, with development of new nodular lesions throughout this time period. The most frequently used drugs for the management of symptomatic EN include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, and potassium iodide.8 A characteristic histologic finding of the granulomatous phase is the Miescher radial granuloma, which is a septal collection of histiocytes surrounding a cleft.9
Snakebite Reactions
Snakebites can result in a wide range of local and systemic manifestations, as snake venom may contain 20 or more toxins.10 Local complications of pit viper bites include pain, swelling, and fang marks; when examining fang marks, the presence of 2 distinct puncture wounds often indicates envenomation with a poisonous snake, whereas nonvenomous snakebites often result in smaller puncture wounds arranged in an arc. Following bites, pain can develop immediately and spread proximally up the affected limb, which occurred in our patient in the days following the bite. Intense local reactions can occur, as bites often result in intense edema of the affected limb spreading to the trunk in the days to weeks after the bite, occasionally accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy. Some bites can result in local necrosis and secondary bacterial infection caused by organisms in the oral cavity of the culprit snake.
Although they were not present in our patient, snakebites can result in a wide range of systemic toxicities ranging from clotting defects and hemolysis to neurotoxicity, myotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity.10 In severe cases, snake venom can result in disseminated intravascular coagulation, sepsis, and cardiorespiratory collapse.
The eastern copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) is a species of venomous snake that is endemic to eastern North America. Copperheads are members of the subfamily Crotalinae in the family Viperidae.11 Reported reactions to copperhead bites include cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis, compartment syndrome, and tissue necrosis of an entire affected extremity.12,13 Our patient displayed no systemic symptoms to suggest envenomation.
Management of Snakebites
Treatment of snakebites varies based on the constellation and severity of symptoms as well as how recently the envenomation occurred. In urgent cases, antivenom may be administered to prevent further toxicity. In cases of progressive compartment syndrome, emergent surgical procedures such as fasciotomy or amputation are required to prevent further complications. When a superimposed bacterial infection is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics are required. Because our patient presented 4 months following the initial bite with isolated cutaneous manifestations, she was treated symptomatically with colchicine for EN.1,2
Final Thoughts
Our patient presented with EN following a bite from a copperhead snake. Physicians should be aware of possible etiologies of EN to evaluate patients who present with new-onset tender subcutaneous nodules. Additionally, physicians should be aware of venomous snakes endemic to their region and also understand the various complications that can result following a snakebite, with the potential for lingering cutaneous manifestations weeks to months following the initial bite.
- Warrell DA. Snake bite. Lancet. 2010;375:77-88. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61754-2
- White J. Overview of venomous snakes of the world. In: Dart RC, eds. Medical Toxicology. 3rd ed. Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2004:1543
- Spiller HA, Bosse GM. Prospective study of morbidity associated with snakebite envenomation. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:125-130. doi:10.1081/clt-120019127
- Scharman EJ, Noffsinger VD. Copperhead snakebites: clinical severity of local effects. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38:55-61. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.116148
- Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema nodosum. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; November 28, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470369/
- Nowowiejska J, Baran A, Flisiak I. Rare coexistence of unilateral erythema nodosum with erysipelas in the area of previous adder bite. Przegl Epidemiol. 2020;74:355-361. doi:10.32394/pe.74.28
- Auerbach PS, Hays JT. Erythema nodosum following a jellyfish sting. J Emerg Med. 1987;5:487-491. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(87)90211-3
- Gilchrist H, Patterson JW. Erythema nodosum and erythema induratum (nodular vasculitis): diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:320-327. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01332.x
- Sánchez Yus E, Sanz Vico MD, de Diego V. Miescher’s radial granuloma. a characteristic marker of erythema nodosum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;11:434-442. doi:10.1097/00000372-198910000-00005
- Mehta SR, Sashindran VK. Clinical features and management of snake bite. Med J Armed Forces India. 2002;58:247-249. doi:10.1016/S0377-1237(02)80140-X
- Brys AK, Gandolfi BM, Levinson H, et al. Copperhead envenomation resulting in a rare case of hand compartment syndrome and subsequent fasciotomy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E396. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000367
- Clark RF, Selden BS, Furbee B. The incidence of wound infection following crotalid envenomation. J Emerg Med. 1993;11:583-586. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(93)90313-v
- Buchanan JT, Thurman J. Crotalidae envenomation. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; October 3, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551615/
- Warrell DA. Snake bite. Lancet. 2010;375:77-88. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61754-2
- White J. Overview of venomous snakes of the world. In: Dart RC, eds. Medical Toxicology. 3rd ed. Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2004:1543
- Spiller HA, Bosse GM. Prospective study of morbidity associated with snakebite envenomation. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:125-130. doi:10.1081/clt-120019127
- Scharman EJ, Noffsinger VD. Copperhead snakebites: clinical severity of local effects. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38:55-61. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.116148
- Hafsi W, Badri T. Erythema nodosum. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; November 28, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470369/
- Nowowiejska J, Baran A, Flisiak I. Rare coexistence of unilateral erythema nodosum with erysipelas in the area of previous adder bite. Przegl Epidemiol. 2020;74:355-361. doi:10.32394/pe.74.28
- Auerbach PS, Hays JT. Erythema nodosum following a jellyfish sting. J Emerg Med. 1987;5:487-491. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(87)90211-3
- Gilchrist H, Patterson JW. Erythema nodosum and erythema induratum (nodular vasculitis): diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:320-327. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01332.x
- Sánchez Yus E, Sanz Vico MD, de Diego V. Miescher’s radial granuloma. a characteristic marker of erythema nodosum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;11:434-442. doi:10.1097/00000372-198910000-00005
- Mehta SR, Sashindran VK. Clinical features and management of snake bite. Med J Armed Forces India. 2002;58:247-249. doi:10.1016/S0377-1237(02)80140-X
- Brys AK, Gandolfi BM, Levinson H, et al. Copperhead envenomation resulting in a rare case of hand compartment syndrome and subsequent fasciotomy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E396. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000367
- Clark RF, Selden BS, Furbee B. The incidence of wound infection following crotalid envenomation. J Emerg Med. 1993;11:583-586. doi:10.1016/0736-4679(93)90313-v
- Buchanan JT, Thurman J. Crotalidae envenomation. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; October 3, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551615/
Practice Points
- Erythema nodosum (EN) can occur following snakebites from pit vipers such as the eastern copperhead.
- The acute phase of EN is neutrophilic and responds to colchicine. The chronic phase of EN is granulomatous and responds best to rest and elevation as well as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and iodides.