User login
How to Avoid Freaking Out About Kidney Function
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
Have Your Cake and Eat It, Too: Findings Based on Ingredients in Christmas Desserts From The Great British Bake Off
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m David Kerr, professor of cancer medicine at University of Oxford. As I become, sadly, older, I’ve become much more interested in the concept of cancer prevention than cancer treatment. Of course, I’m still a practicing cancer physician and researcher. That’s my daily bread and butter. But prevention is important.
There’s a really interesting article in the Christmas edition of The BMJ. This is an opportunity for us to take good science, but lighthearted science, to titillate and amuse our Christmas readers. This is a nice article from the States led by Joshua Wallach. As I say, this brings together good science in a sometimes absurd setting. I’ll read its title: “Association of Health Benefits and Harms of Christmas Dessert Ingredients in Recipes From The Great British Bake Off: Umbrella Review of Umbrella Reviews of Meta-analyses of Observational Studies.”
It’s obviously a very strong statistical underpinning from this group from Yale, predominantly — a half-decent university, as those of us from Oxford would have to admit. They used The Great British Bake Off website, Embase, Medline, and Scopus. They looked at the whole host of umbrella reviews and so on.
They were interested in looking at the relative balance of dangerous and protective ingredients that were recommended in Christmas desserts on this immensely popular television show called The Great British Bake Off. Some of you have watched it and have enjoyed watching the trials and tribulations of the various contestants.
They looked at 48 recipes for Christmas desserts, including cakes, biscuits, pastries, puddings, and conventional desserts. Of all these, there were 178 unique ingredients. Literature research then parsed whether these ingredients were good for you or bad for you.
It was very interesting that, when they put the summary together, the umbrella review of umbrella reviews of meta-analyses compressed together, it was good news for us all. Recipes for Christmas desserts, particularly from The Great British Bake Off — which should be enormously proud of this — tend to use ingredient groups that are associated with reductions rather than increases in the risk for disease. Hurrah!
This means that, clearly, Christmas is a time in which those of us who can, tend to overindulge in food. The granddad falling asleep with a full tummy, sitting with the family in front of a hot fire — all of us can remember and imagine all of that.
Perhaps the most important takeaway point from this observationally, critically important study is that, yes — at Christmas time, enjoy the dessert. You can have your cake and eat it, too. You heard it here. It’s philosophically true and statistically proven: You can have your cake and eat it.
Thanks for listening. I’d be very interested in your own recipes, and whether we think that the American Thanksgiving desserts correlate with British Christmas desserts in some way and are beneficial to your health.
Have a look at this article that is cleverly, wittily written. As always, Medscapers, for the time being, thanks for listening. Over and out.
Dr Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant); Genomic Health; Merck Serono, Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m David Kerr, professor of cancer medicine at University of Oxford. As I become, sadly, older, I’ve become much more interested in the concept of cancer prevention than cancer treatment. Of course, I’m still a practicing cancer physician and researcher. That’s my daily bread and butter. But prevention is important.
There’s a really interesting article in the Christmas edition of The BMJ. This is an opportunity for us to take good science, but lighthearted science, to titillate and amuse our Christmas readers. This is a nice article from the States led by Joshua Wallach. As I say, this brings together good science in a sometimes absurd setting. I’ll read its title: “Association of Health Benefits and Harms of Christmas Dessert Ingredients in Recipes From The Great British Bake Off: Umbrella Review of Umbrella Reviews of Meta-analyses of Observational Studies.”
It’s obviously a very strong statistical underpinning from this group from Yale, predominantly — a half-decent university, as those of us from Oxford would have to admit. They used The Great British Bake Off website, Embase, Medline, and Scopus. They looked at the whole host of umbrella reviews and so on.
They were interested in looking at the relative balance of dangerous and protective ingredients that were recommended in Christmas desserts on this immensely popular television show called The Great British Bake Off. Some of you have watched it and have enjoyed watching the trials and tribulations of the various contestants.
They looked at 48 recipes for Christmas desserts, including cakes, biscuits, pastries, puddings, and conventional desserts. Of all these, there were 178 unique ingredients. Literature research then parsed whether these ingredients were good for you or bad for you.
It was very interesting that, when they put the summary together, the umbrella review of umbrella reviews of meta-analyses compressed together, it was good news for us all. Recipes for Christmas desserts, particularly from The Great British Bake Off — which should be enormously proud of this — tend to use ingredient groups that are associated with reductions rather than increases in the risk for disease. Hurrah!
This means that, clearly, Christmas is a time in which those of us who can, tend to overindulge in food. The granddad falling asleep with a full tummy, sitting with the family in front of a hot fire — all of us can remember and imagine all of that.
Perhaps the most important takeaway point from this observationally, critically important study is that, yes — at Christmas time, enjoy the dessert. You can have your cake and eat it, too. You heard it here. It’s philosophically true and statistically proven: You can have your cake and eat it.
Thanks for listening. I’d be very interested in your own recipes, and whether we think that the American Thanksgiving desserts correlate with British Christmas desserts in some way and are beneficial to your health.
Have a look at this article that is cleverly, wittily written. As always, Medscapers, for the time being, thanks for listening. Over and out.
Dr Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant); Genomic Health; Merck Serono, Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m David Kerr, professor of cancer medicine at University of Oxford. As I become, sadly, older, I’ve become much more interested in the concept of cancer prevention than cancer treatment. Of course, I’m still a practicing cancer physician and researcher. That’s my daily bread and butter. But prevention is important.
There’s a really interesting article in the Christmas edition of The BMJ. This is an opportunity for us to take good science, but lighthearted science, to titillate and amuse our Christmas readers. This is a nice article from the States led by Joshua Wallach. As I say, this brings together good science in a sometimes absurd setting. I’ll read its title: “Association of Health Benefits and Harms of Christmas Dessert Ingredients in Recipes From The Great British Bake Off: Umbrella Review of Umbrella Reviews of Meta-analyses of Observational Studies.”
It’s obviously a very strong statistical underpinning from this group from Yale, predominantly — a half-decent university, as those of us from Oxford would have to admit. They used The Great British Bake Off website, Embase, Medline, and Scopus. They looked at the whole host of umbrella reviews and so on.
They were interested in looking at the relative balance of dangerous and protective ingredients that were recommended in Christmas desserts on this immensely popular television show called The Great British Bake Off. Some of you have watched it and have enjoyed watching the trials and tribulations of the various contestants.
They looked at 48 recipes for Christmas desserts, including cakes, biscuits, pastries, puddings, and conventional desserts. Of all these, there were 178 unique ingredients. Literature research then parsed whether these ingredients were good for you or bad for you.
It was very interesting that, when they put the summary together, the umbrella review of umbrella reviews of meta-analyses compressed together, it was good news for us all. Recipes for Christmas desserts, particularly from The Great British Bake Off — which should be enormously proud of this — tend to use ingredient groups that are associated with reductions rather than increases in the risk for disease. Hurrah!
This means that, clearly, Christmas is a time in which those of us who can, tend to overindulge in food. The granddad falling asleep with a full tummy, sitting with the family in front of a hot fire — all of us can remember and imagine all of that.
Perhaps the most important takeaway point from this observationally, critically important study is that, yes — at Christmas time, enjoy the dessert. You can have your cake and eat it, too. You heard it here. It’s philosophically true and statistically proven: You can have your cake and eat it.
Thanks for listening. I’d be very interested in your own recipes, and whether we think that the American Thanksgiving desserts correlate with British Christmas desserts in some way and are beneficial to your health.
Have a look at this article that is cleverly, wittily written. As always, Medscapers, for the time being, thanks for listening. Over and out.
Dr Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant); Genomic Health; Merck Serono, Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated Guidelines on Contraception Choice and Body Weight
As family doctors, we often provide contraception care for our patients and they ask many questions about what is the best choice for them. There are many factors that may contribute to our discussion with our patients, a patient’s body weight being just one of them.
We all know that some contraception methods have been shown to be less effective in patients with a body mass index (BMI) over 30. Additionally, many hormonal therapies are known to contribute to weight gain.
In August 2024, the Society of Family Planning set forth guidelines regarding contraception and body weight. The authors suggest that BMI may not be the best measure to use to reflect body size but suggest that it is the best we have. They state that we should refrain using the classification names contained within the BMI system: “healthy weight,” “obese,” etc. They caution against stigmatizing patients and bringing our own biases into the discussion.
It should be noted that no contraceptive method is contraindicated based on a patient’s body size. However, physicians should use evidence-based information to reach a shared decision with the patient. This should include risks based on body weight/size and its effect on contraception.
Although oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) affect the way steroid hormones are processed, efficacy is thought to be the same in all patients regardless of weight. Most contraception failures in patients taking OCPs are the result of incorrect use of the medication. It is important to note that in women with BMIs greater than 30 the risk of venous thromboembolism is increased with combined hormonal contraceptives.
It is suggested that women with BMIs greater than 30 avoid hormonal transdermal patches because of higher rates of contraception failure. Vaginal rings have not been adequately studied regarding their effectiveness in patients with BMIs greater than 30.
Contraceptive implants are another good choice for women with BMIs greater than 30. Despite the serum level of etonogestrel being lower than in women with BMIs under 30, most remained high enough to suppress ovulation. IUDs and depo medroxyprogesterone shots also appear to be effective in those with higher BMIs, although there is a slight increased risk of venous thromboembolism in those utilizing depo medroxyprogesterone shots.
It is important for us to be very familiar with all methods of contraception and we need to be comfortable discussing the options with our patients. If a patient desires contraception to avoid pregnancy, she must be informed when effectiveness may be reduced. We also need to be aware of the side effects and let our patients know what to expect. They need as much data as possible to make an informed decision about which method they choose. We may not agree with their decision, but if a patient is aware of what may happen, it is her choice to make.
Many women feel uncomfortable bringing up the discussion of contraception. We need to address this with women of child-bearing age. Often, broaching the topic will open the door to a whole host of concerns. Women with overweight may avoid seeking care because they were made uncomfortable in the medical setting or were made to feel stigmatized. We will never fix the obesity epidemic in the United States if our patients avoid coming into the office.
The guidelines also discuss contraception choices that may lead to weight gain. The medication alone may not be responsible but rather it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Along with the warning about weight gain, we should be counseling our patients regarding their lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise.
The authors of this guideline paper do a great job exploring each contraception method for women with BMI over 30. However, many factors go into deciding which choice is the best for an individual patient. A patient may do poorly at taking pills every day. Another may dislike the concept of inserting a vaginal ring. Each patient should be approached individually and all these factors need to be taken into consideration. Weight is an important factor to consider, but there are many others. If we fail to acknowledge the complexity of our patients, we can never do our best for them.
Dr. Girgis is a family medicine practitioner, South River, New Jersey, and clinical assistant professor of family medicine, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, New Jersey. She was paid by Pfizer as a consultant on Paxlovid and is the editor in chief of Physician’s Weekly.
As family doctors, we often provide contraception care for our patients and they ask many questions about what is the best choice for them. There are many factors that may contribute to our discussion with our patients, a patient’s body weight being just one of them.
We all know that some contraception methods have been shown to be less effective in patients with a body mass index (BMI) over 30. Additionally, many hormonal therapies are known to contribute to weight gain.
In August 2024, the Society of Family Planning set forth guidelines regarding contraception and body weight. The authors suggest that BMI may not be the best measure to use to reflect body size but suggest that it is the best we have. They state that we should refrain using the classification names contained within the BMI system: “healthy weight,” “obese,” etc. They caution against stigmatizing patients and bringing our own biases into the discussion.
It should be noted that no contraceptive method is contraindicated based on a patient’s body size. However, physicians should use evidence-based information to reach a shared decision with the patient. This should include risks based on body weight/size and its effect on contraception.
Although oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) affect the way steroid hormones are processed, efficacy is thought to be the same in all patients regardless of weight. Most contraception failures in patients taking OCPs are the result of incorrect use of the medication. It is important to note that in women with BMIs greater than 30 the risk of venous thromboembolism is increased with combined hormonal contraceptives.
It is suggested that women with BMIs greater than 30 avoid hormonal transdermal patches because of higher rates of contraception failure. Vaginal rings have not been adequately studied regarding their effectiveness in patients with BMIs greater than 30.
Contraceptive implants are another good choice for women with BMIs greater than 30. Despite the serum level of etonogestrel being lower than in women with BMIs under 30, most remained high enough to suppress ovulation. IUDs and depo medroxyprogesterone shots also appear to be effective in those with higher BMIs, although there is a slight increased risk of venous thromboembolism in those utilizing depo medroxyprogesterone shots.
It is important for us to be very familiar with all methods of contraception and we need to be comfortable discussing the options with our patients. If a patient desires contraception to avoid pregnancy, she must be informed when effectiveness may be reduced. We also need to be aware of the side effects and let our patients know what to expect. They need as much data as possible to make an informed decision about which method they choose. We may not agree with their decision, but if a patient is aware of what may happen, it is her choice to make.
Many women feel uncomfortable bringing up the discussion of contraception. We need to address this with women of child-bearing age. Often, broaching the topic will open the door to a whole host of concerns. Women with overweight may avoid seeking care because they were made uncomfortable in the medical setting or were made to feel stigmatized. We will never fix the obesity epidemic in the United States if our patients avoid coming into the office.
The guidelines also discuss contraception choices that may lead to weight gain. The medication alone may not be responsible but rather it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Along with the warning about weight gain, we should be counseling our patients regarding their lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise.
The authors of this guideline paper do a great job exploring each contraception method for women with BMI over 30. However, many factors go into deciding which choice is the best for an individual patient. A patient may do poorly at taking pills every day. Another may dislike the concept of inserting a vaginal ring. Each patient should be approached individually and all these factors need to be taken into consideration. Weight is an important factor to consider, but there are many others. If we fail to acknowledge the complexity of our patients, we can never do our best for them.
Dr. Girgis is a family medicine practitioner, South River, New Jersey, and clinical assistant professor of family medicine, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, New Jersey. She was paid by Pfizer as a consultant on Paxlovid and is the editor in chief of Physician’s Weekly.
As family doctors, we often provide contraception care for our patients and they ask many questions about what is the best choice for them. There are many factors that may contribute to our discussion with our patients, a patient’s body weight being just one of them.
We all know that some contraception methods have been shown to be less effective in patients with a body mass index (BMI) over 30. Additionally, many hormonal therapies are known to contribute to weight gain.
In August 2024, the Society of Family Planning set forth guidelines regarding contraception and body weight. The authors suggest that BMI may not be the best measure to use to reflect body size but suggest that it is the best we have. They state that we should refrain using the classification names contained within the BMI system: “healthy weight,” “obese,” etc. They caution against stigmatizing patients and bringing our own biases into the discussion.
It should be noted that no contraceptive method is contraindicated based on a patient’s body size. However, physicians should use evidence-based information to reach a shared decision with the patient. This should include risks based on body weight/size and its effect on contraception.
Although oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) affect the way steroid hormones are processed, efficacy is thought to be the same in all patients regardless of weight. Most contraception failures in patients taking OCPs are the result of incorrect use of the medication. It is important to note that in women with BMIs greater than 30 the risk of venous thromboembolism is increased with combined hormonal contraceptives.
It is suggested that women with BMIs greater than 30 avoid hormonal transdermal patches because of higher rates of contraception failure. Vaginal rings have not been adequately studied regarding their effectiveness in patients with BMIs greater than 30.
Contraceptive implants are another good choice for women with BMIs greater than 30. Despite the serum level of etonogestrel being lower than in women with BMIs under 30, most remained high enough to suppress ovulation. IUDs and depo medroxyprogesterone shots also appear to be effective in those with higher BMIs, although there is a slight increased risk of venous thromboembolism in those utilizing depo medroxyprogesterone shots.
It is important for us to be very familiar with all methods of contraception and we need to be comfortable discussing the options with our patients. If a patient desires contraception to avoid pregnancy, she must be informed when effectiveness may be reduced. We also need to be aware of the side effects and let our patients know what to expect. They need as much data as possible to make an informed decision about which method they choose. We may not agree with their decision, but if a patient is aware of what may happen, it is her choice to make.
Many women feel uncomfortable bringing up the discussion of contraception. We need to address this with women of child-bearing age. Often, broaching the topic will open the door to a whole host of concerns. Women with overweight may avoid seeking care because they were made uncomfortable in the medical setting or were made to feel stigmatized. We will never fix the obesity epidemic in the United States if our patients avoid coming into the office.
The guidelines also discuss contraception choices that may lead to weight gain. The medication alone may not be responsible but rather it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Along with the warning about weight gain, we should be counseling our patients regarding their lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise.
The authors of this guideline paper do a great job exploring each contraception method for women with BMI over 30. However, many factors go into deciding which choice is the best for an individual patient. A patient may do poorly at taking pills every day. Another may dislike the concept of inserting a vaginal ring. Each patient should be approached individually and all these factors need to be taken into consideration. Weight is an important factor to consider, but there are many others. If we fail to acknowledge the complexity of our patients, we can never do our best for them.
Dr. Girgis is a family medicine practitioner, South River, New Jersey, and clinical assistant professor of family medicine, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, New Jersey. She was paid by Pfizer as a consultant on Paxlovid and is the editor in chief of Physician’s Weekly.
Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Provocative Claims About Bacillus Lysate
Outrageous assertions with little evidence are not new. Even the famous statement “There’s a sucker born every minute,” long attributed to 1800s showman P.T. Barnum, lacks evidence that the circus founder uttered the remark. The message itself and the snippet of a story about the message may be pertinent, though, when we consider the touted benefits of Bacillus lysate for the skin. The focus of this column will be the foundation for the use of probiotics and prebiotics in skin care and then claims made about this skin care ingredient derived from a particular strain of Bacillus bacteria.
. Typically, this topic is broached in the context of the gut-skin axis and the skin and gut microbiomes.1-3 In 2014, Miyazaki et al. found that phenols produced by gut bacteria spurred skin disorders and that decreasing phenols with probiotics and/or prebiotics can restore or maintain cutaneous health.4
Probiotics have been associated with antioxidant activity, primarily because of the presence of antioxidant enzymes (eg, superoxide dismutase), the delivery of antioxidant substances (eg, glutathione), and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis.5-8 Further, probiotics are known to synthesize a cascade of substances with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and angiogenetic functions that can contribute to wound healing.9 The use of probiotics in skin health largely relies on applying inactivated beneficial bacteria.10 Prebiotics, which are non-digestible plant-based carbohydrates that aid digestion, inhibit pathogens, and support beneficial bacteria, are known to rebalance the skin microflora.10 In addition, prebiotics are considered a robust option to replace live bacteria in skin formulations.11 Bacterial cell lysates, which include bacterial metabolites, cell walls, and dead bacteria, are incorporated into skin care products as well.12
Probiotics and Wound Healing
In 2020, Ashoori et al. reported on their study of three formulations composed of probiotic supernatant (Lactobacillus reuteri, L. fermentum, and Bacillus subtilis sp. natto)-loaded chitosan nanogels prepared from cultures. They evaluated the effectiveness and dressing activity of the formulations by gauging wound closure and histological results in Sprague-Dawley rats. The researchers found that all probiotic lysate preparations conferred healing properties, with the Bacillus subtilis natto yielding the best wound healing quality. They concluded that probiotic lysate nanogels impart a range of benefits, such as favorable wound closure rates, improved appearance, and suitable histological results upon in vivo examination, supporting the potential use of such formulations to treat wounds.9
Probiotics and Treating Skin Disorders
A 2015 review by Roudsari et al. suggests that probiotics display the potential for preventing and treating various skin disorders, including acne, atopic dermatitis, allergic inflammation or hypersensitivity, eczema, photodamage, and wounds.8 They reported that in a US patent, Gueniche revealed ways to employ at least one probiotic microorganism (from Lactobacillus and/or Bifidobacterium) as an active agent to prevent or treat skin irritation.8,13 In addition, they noted that L. brevis was used successfully by DeSimone in 2003 to promote apoptosis and/or diminish inflammation, particularly in creams and ointments to alleviate inflammation.8
At around the same time, Miyazaki et al. reported that Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract stimulated the production of hyaluronic acid (HA) in organotypic cultures of human keratinocytes, cultures of human skin fibroblasts, and hairless mouse skin after 2 weeks of topical application and has the potential to promote HA synthesis in the epidermis and dermis and thus act as an anti-aging agent.14 In another study, Miyazaki et al. investigated the impact of Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract containing genistein and daidzein on the HA content of hairless mouse as well as human skin. After 6 weeks of topical application in mice, skin elasticity, viscoelasticity, hydration, and thickness improved, and HA content increased. In addition, after 3 months of topical application of a 10% Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract gel to the human forearm, decreases in skin elasticity were significantly mitigated.15More recently, in 2023, Xie et al. reviewed clinical and experimental data on the use of various species of Lactobacillus for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis (AD). They found evidence that multiple species (L. rhamnosus in animal and clinical experiments) appeared to be effective in preventing and treating AD, with L. acidophilus lessening symptoms and reported to be safe, L. plantarum improving symptoms through immunomodulatory activity, and L. sakei demonstrating anti-inflammatory and skin barrier protective activity. The authors also noted that L. paracasei exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on AD-like skin lesions, and L. reuteri supplementation prevented AD development. Overall, they called for more in vivo studies and randomized controlled clinical trials to fully elucidate the wide-ranging potential of Lactobacillus species in treating and preventing AD.16
The Darker Side of Using Prebiotic Species in Skin Care?
According to manufacturer Delavie Sciences, its Aeonia product line was based on research conducted on the International Space Station, which allowed for its patented microorganism to be exposed to the conditions of outer space. This cornerstone ingredient, Bacillus lysate, once returned to Earth, reportedly exhibited anti-aging and UV-protective characteristics. The product line has been described as a prebiotic that contributes to a healthy skin barrier.17
In a September 2023 interview in CosmeticsDesign, the president of Delavie Sciences clarified that its Bacillus lysate contains no live bacteria and that it is not a probiotic, but rather, the certified prebiotic lysate is a Bacillus extract that has been used to strengthen the SPF potency of skin care formulations.18 Because of the research performed on the International Space Station, the manufacturers are claiming these ingredients could be “out-of-this-world” as a way to promote results that have, as yet, not been verified by peer review.
Conclusion
Probiotics and prebiotics continue to be the focus of multiple lines of research for their applications and further potential in skin care. In the case of the Bacillus lysate prebiotic compound, there is a kernel of an interesting idea here, at the very least. But proprietary research limits our ability to render a comprehensive evaluation at this time. Such bold and outrageous claims spur more skepticism than optimism. However, lysates are the latest thing in skin care — so we need to keep watch on the developments to stay current. But that’s what you have me for, I’ll help keep you current on new ingredient findings. If you are on LinkedIn, come connect with me. I post breaking ingredient news and skin care trends there to help you answer patient questions. When you are asked if these lysates work, the answer is: All the data we have on bacillus extract are from computer analysis of the ingredient properties and not on the actual formulations or products. Stay tuned.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Mahmud MR et al. Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2096995. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995.
2. Sinha S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2021 Sep-Oct;39(5):829-839. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.021.
3. Gao T et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jul 13;15(14):3123. doi: 10.3390/nu15143123.
4. Miyazaki K et al. Benef Microbes. 2014 Jun 1;5(2):121-128. doi: 10.3920/BM2012.0066.
5. Shen Q et al. Anaerobe. 2010 Aug;16(4):380-386. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.06.006.
6. Peran L et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006 Dec;21(8):737-746. doi: 10.1007/s00384-005-0773-y.
7. Kodali VP, Sen R. Biotechnol J. 2008 Feb;3(2):245-251. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700208.
8. Roudsari MR et al. Health effects of probiotics on the skin. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(9):1219-40. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.680078.
9. Ashoori Y et al. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 28;2020:8868618. doi: 10.1155/2020/8868618.
10. Simmering R, Breves R. Hautarzt. 2009 Oct;60(10):809-814. doi: 10.1007/s00105-009-1759-4.
11. Bockmuhl D. IFSSC Mag. 2006 Sep 30;9[3]:1-5.
12. Lew LC, Liong MT. J Appl Microbiol. 2013 May;114(5):1241-1253. doi: 10.1111/jam.12137.
13. Gueniche A. US Patent, US 20100226892. 2010.
14. Miyazaki K et al. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2003 Mar-Apr;16(2):108-116. doi: 10.1159/000069031.
15. Miyazaki et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2004 Sep-Oct;55(5):473-479.16. Xie A et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 16;13:1137275. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1137275.
17. Delavie Sciences. Skincare Science: Aeonia. Skincare from the Stars.
. Accessed December 12, 2024.
18. Stern C. CosmeticsDesign USA. September 7, 2023.
Outrageous assertions with little evidence are not new. Even the famous statement “There’s a sucker born every minute,” long attributed to 1800s showman P.T. Barnum, lacks evidence that the circus founder uttered the remark. The message itself and the snippet of a story about the message may be pertinent, though, when we consider the touted benefits of Bacillus lysate for the skin. The focus of this column will be the foundation for the use of probiotics and prebiotics in skin care and then claims made about this skin care ingredient derived from a particular strain of Bacillus bacteria.
. Typically, this topic is broached in the context of the gut-skin axis and the skin and gut microbiomes.1-3 In 2014, Miyazaki et al. found that phenols produced by gut bacteria spurred skin disorders and that decreasing phenols with probiotics and/or prebiotics can restore or maintain cutaneous health.4
Probiotics have been associated with antioxidant activity, primarily because of the presence of antioxidant enzymes (eg, superoxide dismutase), the delivery of antioxidant substances (eg, glutathione), and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis.5-8 Further, probiotics are known to synthesize a cascade of substances with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and angiogenetic functions that can contribute to wound healing.9 The use of probiotics in skin health largely relies on applying inactivated beneficial bacteria.10 Prebiotics, which are non-digestible plant-based carbohydrates that aid digestion, inhibit pathogens, and support beneficial bacteria, are known to rebalance the skin microflora.10 In addition, prebiotics are considered a robust option to replace live bacteria in skin formulations.11 Bacterial cell lysates, which include bacterial metabolites, cell walls, and dead bacteria, are incorporated into skin care products as well.12
Probiotics and Wound Healing
In 2020, Ashoori et al. reported on their study of three formulations composed of probiotic supernatant (Lactobacillus reuteri, L. fermentum, and Bacillus subtilis sp. natto)-loaded chitosan nanogels prepared from cultures. They evaluated the effectiveness and dressing activity of the formulations by gauging wound closure and histological results in Sprague-Dawley rats. The researchers found that all probiotic lysate preparations conferred healing properties, with the Bacillus subtilis natto yielding the best wound healing quality. They concluded that probiotic lysate nanogels impart a range of benefits, such as favorable wound closure rates, improved appearance, and suitable histological results upon in vivo examination, supporting the potential use of such formulations to treat wounds.9
Probiotics and Treating Skin Disorders
A 2015 review by Roudsari et al. suggests that probiotics display the potential for preventing and treating various skin disorders, including acne, atopic dermatitis, allergic inflammation or hypersensitivity, eczema, photodamage, and wounds.8 They reported that in a US patent, Gueniche revealed ways to employ at least one probiotic microorganism (from Lactobacillus and/or Bifidobacterium) as an active agent to prevent or treat skin irritation.8,13 In addition, they noted that L. brevis was used successfully by DeSimone in 2003 to promote apoptosis and/or diminish inflammation, particularly in creams and ointments to alleviate inflammation.8
At around the same time, Miyazaki et al. reported that Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract stimulated the production of hyaluronic acid (HA) in organotypic cultures of human keratinocytes, cultures of human skin fibroblasts, and hairless mouse skin after 2 weeks of topical application and has the potential to promote HA synthesis in the epidermis and dermis and thus act as an anti-aging agent.14 In another study, Miyazaki et al. investigated the impact of Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract containing genistein and daidzein on the HA content of hairless mouse as well as human skin. After 6 weeks of topical application in mice, skin elasticity, viscoelasticity, hydration, and thickness improved, and HA content increased. In addition, after 3 months of topical application of a 10% Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract gel to the human forearm, decreases in skin elasticity were significantly mitigated.15More recently, in 2023, Xie et al. reviewed clinical and experimental data on the use of various species of Lactobacillus for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis (AD). They found evidence that multiple species (L. rhamnosus in animal and clinical experiments) appeared to be effective in preventing and treating AD, with L. acidophilus lessening symptoms and reported to be safe, L. plantarum improving symptoms through immunomodulatory activity, and L. sakei demonstrating anti-inflammatory and skin barrier protective activity. The authors also noted that L. paracasei exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on AD-like skin lesions, and L. reuteri supplementation prevented AD development. Overall, they called for more in vivo studies and randomized controlled clinical trials to fully elucidate the wide-ranging potential of Lactobacillus species in treating and preventing AD.16
The Darker Side of Using Prebiotic Species in Skin Care?
According to manufacturer Delavie Sciences, its Aeonia product line was based on research conducted on the International Space Station, which allowed for its patented microorganism to be exposed to the conditions of outer space. This cornerstone ingredient, Bacillus lysate, once returned to Earth, reportedly exhibited anti-aging and UV-protective characteristics. The product line has been described as a prebiotic that contributes to a healthy skin barrier.17
In a September 2023 interview in CosmeticsDesign, the president of Delavie Sciences clarified that its Bacillus lysate contains no live bacteria and that it is not a probiotic, but rather, the certified prebiotic lysate is a Bacillus extract that has been used to strengthen the SPF potency of skin care formulations.18 Because of the research performed on the International Space Station, the manufacturers are claiming these ingredients could be “out-of-this-world” as a way to promote results that have, as yet, not been verified by peer review.
Conclusion
Probiotics and prebiotics continue to be the focus of multiple lines of research for their applications and further potential in skin care. In the case of the Bacillus lysate prebiotic compound, there is a kernel of an interesting idea here, at the very least. But proprietary research limits our ability to render a comprehensive evaluation at this time. Such bold and outrageous claims spur more skepticism than optimism. However, lysates are the latest thing in skin care — so we need to keep watch on the developments to stay current. But that’s what you have me for, I’ll help keep you current on new ingredient findings. If you are on LinkedIn, come connect with me. I post breaking ingredient news and skin care trends there to help you answer patient questions. When you are asked if these lysates work, the answer is: All the data we have on bacillus extract are from computer analysis of the ingredient properties and not on the actual formulations or products. Stay tuned.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Mahmud MR et al. Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2096995. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995.
2. Sinha S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2021 Sep-Oct;39(5):829-839. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.021.
3. Gao T et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jul 13;15(14):3123. doi: 10.3390/nu15143123.
4. Miyazaki K et al. Benef Microbes. 2014 Jun 1;5(2):121-128. doi: 10.3920/BM2012.0066.
5. Shen Q et al. Anaerobe. 2010 Aug;16(4):380-386. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.06.006.
6. Peran L et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006 Dec;21(8):737-746. doi: 10.1007/s00384-005-0773-y.
7. Kodali VP, Sen R. Biotechnol J. 2008 Feb;3(2):245-251. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700208.
8. Roudsari MR et al. Health effects of probiotics on the skin. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(9):1219-40. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.680078.
9. Ashoori Y et al. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 28;2020:8868618. doi: 10.1155/2020/8868618.
10. Simmering R, Breves R. Hautarzt. 2009 Oct;60(10):809-814. doi: 10.1007/s00105-009-1759-4.
11. Bockmuhl D. IFSSC Mag. 2006 Sep 30;9[3]:1-5.
12. Lew LC, Liong MT. J Appl Microbiol. 2013 May;114(5):1241-1253. doi: 10.1111/jam.12137.
13. Gueniche A. US Patent, US 20100226892. 2010.
14. Miyazaki K et al. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2003 Mar-Apr;16(2):108-116. doi: 10.1159/000069031.
15. Miyazaki et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2004 Sep-Oct;55(5):473-479.16. Xie A et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 16;13:1137275. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1137275.
17. Delavie Sciences. Skincare Science: Aeonia. Skincare from the Stars.
. Accessed December 12, 2024.
18. Stern C. CosmeticsDesign USA. September 7, 2023.
Outrageous assertions with little evidence are not new. Even the famous statement “There’s a sucker born every minute,” long attributed to 1800s showman P.T. Barnum, lacks evidence that the circus founder uttered the remark. The message itself and the snippet of a story about the message may be pertinent, though, when we consider the touted benefits of Bacillus lysate for the skin. The focus of this column will be the foundation for the use of probiotics and prebiotics in skin care and then claims made about this skin care ingredient derived from a particular strain of Bacillus bacteria.
. Typically, this topic is broached in the context of the gut-skin axis and the skin and gut microbiomes.1-3 In 2014, Miyazaki et al. found that phenols produced by gut bacteria spurred skin disorders and that decreasing phenols with probiotics and/or prebiotics can restore or maintain cutaneous health.4
Probiotics have been associated with antioxidant activity, primarily because of the presence of antioxidant enzymes (eg, superoxide dismutase), the delivery of antioxidant substances (eg, glutathione), and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis.5-8 Further, probiotics are known to synthesize a cascade of substances with anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and angiogenetic functions that can contribute to wound healing.9 The use of probiotics in skin health largely relies on applying inactivated beneficial bacteria.10 Prebiotics, which are non-digestible plant-based carbohydrates that aid digestion, inhibit pathogens, and support beneficial bacteria, are known to rebalance the skin microflora.10 In addition, prebiotics are considered a robust option to replace live bacteria in skin formulations.11 Bacterial cell lysates, which include bacterial metabolites, cell walls, and dead bacteria, are incorporated into skin care products as well.12
Probiotics and Wound Healing
In 2020, Ashoori et al. reported on their study of three formulations composed of probiotic supernatant (Lactobacillus reuteri, L. fermentum, and Bacillus subtilis sp. natto)-loaded chitosan nanogels prepared from cultures. They evaluated the effectiveness and dressing activity of the formulations by gauging wound closure and histological results in Sprague-Dawley rats. The researchers found that all probiotic lysate preparations conferred healing properties, with the Bacillus subtilis natto yielding the best wound healing quality. They concluded that probiotic lysate nanogels impart a range of benefits, such as favorable wound closure rates, improved appearance, and suitable histological results upon in vivo examination, supporting the potential use of such formulations to treat wounds.9
Probiotics and Treating Skin Disorders
A 2015 review by Roudsari et al. suggests that probiotics display the potential for preventing and treating various skin disorders, including acne, atopic dermatitis, allergic inflammation or hypersensitivity, eczema, photodamage, and wounds.8 They reported that in a US patent, Gueniche revealed ways to employ at least one probiotic microorganism (from Lactobacillus and/or Bifidobacterium) as an active agent to prevent or treat skin irritation.8,13 In addition, they noted that L. brevis was used successfully by DeSimone in 2003 to promote apoptosis and/or diminish inflammation, particularly in creams and ointments to alleviate inflammation.8
At around the same time, Miyazaki et al. reported that Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract stimulated the production of hyaluronic acid (HA) in organotypic cultures of human keratinocytes, cultures of human skin fibroblasts, and hairless mouse skin after 2 weeks of topical application and has the potential to promote HA synthesis in the epidermis and dermis and thus act as an anti-aging agent.14 In another study, Miyazaki et al. investigated the impact of Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract containing genistein and daidzein on the HA content of hairless mouse as well as human skin. After 6 weeks of topical application in mice, skin elasticity, viscoelasticity, hydration, and thickness improved, and HA content increased. In addition, after 3 months of topical application of a 10% Bifidobacterium-fermented soy milk extract gel to the human forearm, decreases in skin elasticity were significantly mitigated.15More recently, in 2023, Xie et al. reviewed clinical and experimental data on the use of various species of Lactobacillus for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis (AD). They found evidence that multiple species (L. rhamnosus in animal and clinical experiments) appeared to be effective in preventing and treating AD, with L. acidophilus lessening symptoms and reported to be safe, L. plantarum improving symptoms through immunomodulatory activity, and L. sakei demonstrating anti-inflammatory and skin barrier protective activity. The authors also noted that L. paracasei exhibited anti-inflammatory effects on AD-like skin lesions, and L. reuteri supplementation prevented AD development. Overall, they called for more in vivo studies and randomized controlled clinical trials to fully elucidate the wide-ranging potential of Lactobacillus species in treating and preventing AD.16
The Darker Side of Using Prebiotic Species in Skin Care?
According to manufacturer Delavie Sciences, its Aeonia product line was based on research conducted on the International Space Station, which allowed for its patented microorganism to be exposed to the conditions of outer space. This cornerstone ingredient, Bacillus lysate, once returned to Earth, reportedly exhibited anti-aging and UV-protective characteristics. The product line has been described as a prebiotic that contributes to a healthy skin barrier.17
In a September 2023 interview in CosmeticsDesign, the president of Delavie Sciences clarified that its Bacillus lysate contains no live bacteria and that it is not a probiotic, but rather, the certified prebiotic lysate is a Bacillus extract that has been used to strengthen the SPF potency of skin care formulations.18 Because of the research performed on the International Space Station, the manufacturers are claiming these ingredients could be “out-of-this-world” as a way to promote results that have, as yet, not been verified by peer review.
Conclusion
Probiotics and prebiotics continue to be the focus of multiple lines of research for their applications and further potential in skin care. In the case of the Bacillus lysate prebiotic compound, there is a kernel of an interesting idea here, at the very least. But proprietary research limits our ability to render a comprehensive evaluation at this time. Such bold and outrageous claims spur more skepticism than optimism. However, lysates are the latest thing in skin care — so we need to keep watch on the developments to stay current. But that’s what you have me for, I’ll help keep you current on new ingredient findings. If you are on LinkedIn, come connect with me. I post breaking ingredient news and skin care trends there to help you answer patient questions. When you are asked if these lysates work, the answer is: All the data we have on bacillus extract are from computer analysis of the ingredient properties and not on the actual formulations or products. Stay tuned.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions Inc., a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Mahmud MR et al. Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2096995. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2096995.
2. Sinha S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2021 Sep-Oct;39(5):829-839. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.021.
3. Gao T et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jul 13;15(14):3123. doi: 10.3390/nu15143123.
4. Miyazaki K et al. Benef Microbes. 2014 Jun 1;5(2):121-128. doi: 10.3920/BM2012.0066.
5. Shen Q et al. Anaerobe. 2010 Aug;16(4):380-386. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.06.006.
6. Peran L et al. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006 Dec;21(8):737-746. doi: 10.1007/s00384-005-0773-y.
7. Kodali VP, Sen R. Biotechnol J. 2008 Feb;3(2):245-251. doi: 10.1002/biot.200700208.
8. Roudsari MR et al. Health effects of probiotics on the skin. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2015;55(9):1219-40. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.680078.
9. Ashoori Y et al. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 28;2020:8868618. doi: 10.1155/2020/8868618.
10. Simmering R, Breves R. Hautarzt. 2009 Oct;60(10):809-814. doi: 10.1007/s00105-009-1759-4.
11. Bockmuhl D. IFSSC Mag. 2006 Sep 30;9[3]:1-5.
12. Lew LC, Liong MT. J Appl Microbiol. 2013 May;114(5):1241-1253. doi: 10.1111/jam.12137.
13. Gueniche A. US Patent, US 20100226892. 2010.
14. Miyazaki K et al. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2003 Mar-Apr;16(2):108-116. doi: 10.1159/000069031.
15. Miyazaki et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2004 Sep-Oct;55(5):473-479.16. Xie A et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 16;13:1137275. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1137275.
17. Delavie Sciences. Skincare Science: Aeonia. Skincare from the Stars.
. Accessed December 12, 2024.
18. Stern C. CosmeticsDesign USA. September 7, 2023.
Freezing the Pain: A New Way to Treat Rib Fractures
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Noise and Artificial Light
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The Cause of All That Stress: Tonsillectomy?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
You know those times in your life when you’re just feeling ... stressed? You’re on the edge; you have no chill; everything just sort of gets to you. If you can step away from the anxiety for a moment, you might ask yourself where it’s all coming from. Is it really the stuff in your inbox at work or is it money issues at home? Is it something with your relationship, or maybe it’s your sleep quality or your diet? One thing you probably won’t blame for those acute stress reactions is the tonsillectomy you had as a kid. But according to new research, maybe you should.
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are among the most common surgical procedures young people in the United States undergo, with about 300,000 cases a year, according to recent numbers. That’s down a bit from numbers a decade or so ago, but suffice it to say, a good chunk of the population is walking around right now without their tonsils.
The data supporting tonsillectomy have never been great. The two big indications for the surgery are recurrent sore throat — data show that tonsillectomy reduces this by about 0.7 sore throats per year— and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The data for improvement of OSA are a bit better than the data for sore throats.
Also, tonsillectomy is a relatively quick, relatively well-reimbursed surgery with indications that are — let’s be honest — somewhat subjective, and so variation is high. One study found that in a single Vermont town, nearly 60% of the population had had their tonsils removed by the time they turned 18. A few towns over, the rate was 20%.
A few factors have led to the decline of tonsillectomy in recent years. Reimbursement rates have gone down a bit. Additionally, better data collection and statistical analysis have shown that the benefits of the procedure are relatively modest.
And then there is a body of medical literature that at first struck me as surprising and almost bizarre: data linking tonsillectomy to subsequent physical and psychiatric disorders.
I teach a course on interpretation of the medical literature, and one of the first things I teach my students is to check their gut when they see the conclusion of a study.
Basically, even before you read the data, have a sense in your own mind if the hypothesis seems reasonable. If a paper is going to conclude that smoking leads to increased risk for bone cancer, I’d say that seems like a reasonable thing to study. If a paper purports to show a link between eating poultry and bone cancer, I’m going to be reading it with quite a bit more skepticism.
The technical term for that process is assessing “biologic plausibility.” If we’re talking tonsils, we have to ask ourselves: Is it plausible that removing someone’s tonsils when they are young should lead to major problems in the future?
At first blush, it didn’t seem very plausible to me.
But the truth is, there are quite a few studies out there demonstrating links like this: links between tonsillectomy and irritable bowel syndrome; links between tonsillectomy and cancer; links between tonsillectomy and depression.
And this week, appearing in JAMA Network Open, is a study linking tonsillectomy with stress disorders.
Researchers leveraged Sweden’s health database, which contains longitudinal data on basically every person who has lived in Sweden since 1981. This database let them know who had a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy, and when, and what happened to them later in life.
I think the best way to present these data is to show you what they found, and then challenge that finding, and then show you what they did in anticipation of the challenges we would have to their findings. It’s a pretty thorough study.
So, topline results here. The researchers first identified 83,957 individuals who had their tonsils removed. They matched each of them with 10 controls who did not have their tonsils removed but were the same age and sex.
Over around 30 years of follow-up, those people who had their tonsils removed were 43% more likely to develop a stress-related disorder. Among the specific disorders, the risk for PTSD was substantially higher: 55% higher in the tonsillectomy group.
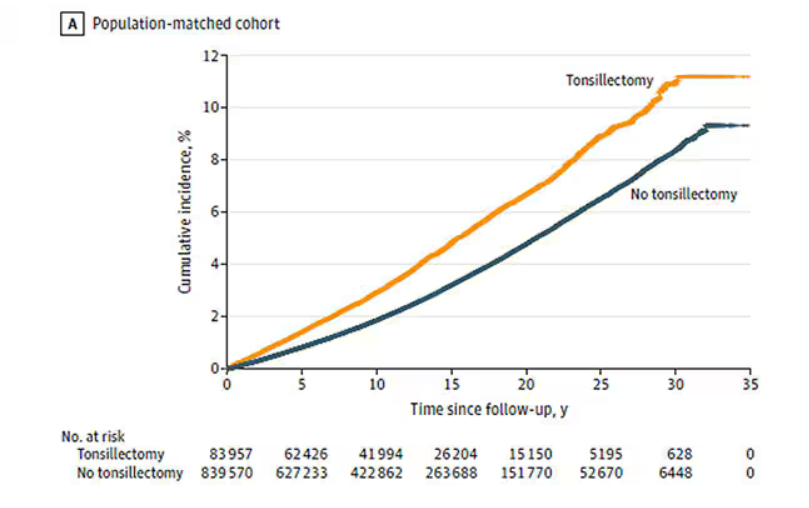
That’s pretty surprising, but I bet you already want to push back against this. Sure, the control group was the same age and sex, but other factors might be different between the two groups. You’d be right to think so. People who got their tonsils out were more likely to have parents with a history of stress-related disorders and who had lower educational attainment. But the primary results were adjusted for those factors.
There’s more to a family than parental educational attainment, of course. To account for household factors that might be harder to measure, the researchers created a second control group, this one comprising the siblings of people who had their tonsils removed but who hadn’t themselves had their tonsils removed.
The relationship between tonsillectomy and stress disorders in this population was not quite as robust but still present: a 34% increase in any stress disorder and a 41% increase in the risk for PTSD.
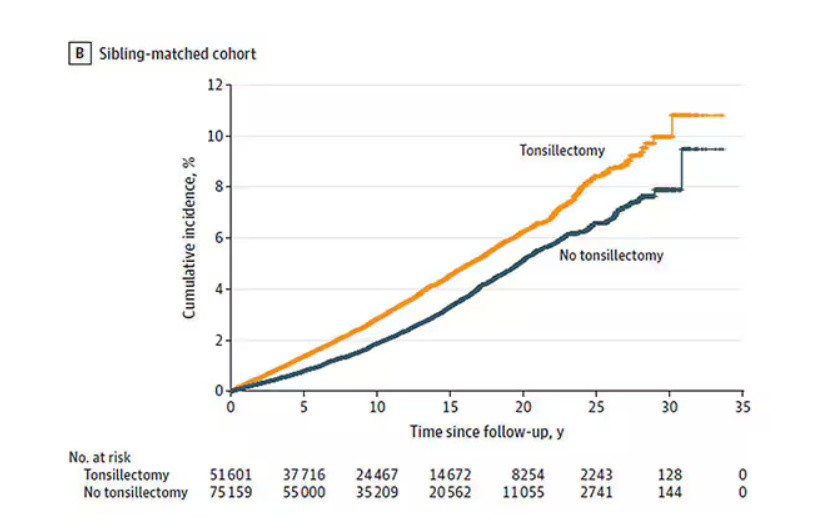
Maybe kids who get their tonsils out are just followed more closely thereafter, so doctors might notice a stress disorder and document it in the medical record; whereas with other kids it might go unnoticed. This is known as ascertainment bias. The researchers addressed this in a sensitivity analysis where they excluded new diagnoses of stress disorders that occurred in the first 3 years after tonsillectomy. The results were largely unchanged.
So how do we explain these data? We observe a correlation between tonsillectomy in youth and stress disorders in later life. But correlation is not causation. One possibility, perhaps even the most likely possibility, is that tonsillectomy is a marker of some other problem. Maybe these kids are more prone to infections and are therefore more likely to need their tonsils removed. Then, after a lifetime of more infections than average, their stress responses are higher. Or maybe kids with a higher BMI are more likely to have their tonsils removed due to sleep apnea concerns, and it’s that elevated BMI that leads to higher stress in later life.
Or maybe this is causal. Maybe there actually is biological plausibility here. The authors suggest that removal of tonsils might lead to broader changes in the immune system; after all, tonsillar tissue is on the front line of our defense against pathogens that might enter our bodies through our mouths or noses. Immunologic changes lead to greater inflammation over time, and there is decent evidence to link chronic inflammation to a variety of physical and psychological disorders.
In support of this, the authors show that the kids with tonsillectomy were more likely to be hospitalized for an infectious disease in the future as well, in magnitudes similar to the increased risk for stress. But they don’t actually show that the relationship between tonsillectomy and stress is mediated by that increased risk for infectious disease.
In the end, I find these data really intriguing. Before I dug into the literature, it seemed highly unlikely that removal of these small lumps of tissue would have much of an effect on anything. Now I’m not so sure. A few things can be removed from the human body without any consequences, but it can be hard to know exactly what those consequences are.
That said, given the rather marginal benefits of tonsillectomy and the growing number of studies expanding on the risks, I expect that we’ll see the rates of the surgery decline even further in the future.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Connecticut. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
You know those times in your life when you’re just feeling ... stressed? You’re on the edge; you have no chill; everything just sort of gets to you. If you can step away from the anxiety for a moment, you might ask yourself where it’s all coming from. Is it really the stuff in your inbox at work or is it money issues at home? Is it something with your relationship, or maybe it’s your sleep quality or your diet? One thing you probably won’t blame for those acute stress reactions is the tonsillectomy you had as a kid. But according to new research, maybe you should.
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are among the most common surgical procedures young people in the United States undergo, with about 300,000 cases a year, according to recent numbers. That’s down a bit from numbers a decade or so ago, but suffice it to say, a good chunk of the population is walking around right now without their tonsils.
The data supporting tonsillectomy have never been great. The two big indications for the surgery are recurrent sore throat — data show that tonsillectomy reduces this by about 0.7 sore throats per year— and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The data for improvement of OSA are a bit better than the data for sore throats.
Also, tonsillectomy is a relatively quick, relatively well-reimbursed surgery with indications that are — let’s be honest — somewhat subjective, and so variation is high. One study found that in a single Vermont town, nearly 60% of the population had had their tonsils removed by the time they turned 18. A few towns over, the rate was 20%.
A few factors have led to the decline of tonsillectomy in recent years. Reimbursement rates have gone down a bit. Additionally, better data collection and statistical analysis have shown that the benefits of the procedure are relatively modest.
And then there is a body of medical literature that at first struck me as surprising and almost bizarre: data linking tonsillectomy to subsequent physical and psychiatric disorders.
I teach a course on interpretation of the medical literature, and one of the first things I teach my students is to check their gut when they see the conclusion of a study.
Basically, even before you read the data, have a sense in your own mind if the hypothesis seems reasonable. If a paper is going to conclude that smoking leads to increased risk for bone cancer, I’d say that seems like a reasonable thing to study. If a paper purports to show a link between eating poultry and bone cancer, I’m going to be reading it with quite a bit more skepticism.
The technical term for that process is assessing “biologic plausibility.” If we’re talking tonsils, we have to ask ourselves: Is it plausible that removing someone’s tonsils when they are young should lead to major problems in the future?
At first blush, it didn’t seem very plausible to me.
But the truth is, there are quite a few studies out there demonstrating links like this: links between tonsillectomy and irritable bowel syndrome; links between tonsillectomy and cancer; links between tonsillectomy and depression.
And this week, appearing in JAMA Network Open, is a study linking tonsillectomy with stress disorders.
Researchers leveraged Sweden’s health database, which contains longitudinal data on basically every person who has lived in Sweden since 1981. This database let them know who had a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy, and when, and what happened to them later in life.
I think the best way to present these data is to show you what they found, and then challenge that finding, and then show you what they did in anticipation of the challenges we would have to their findings. It’s a pretty thorough study.
So, topline results here. The researchers first identified 83,957 individuals who had their tonsils removed. They matched each of them with 10 controls who did not have their tonsils removed but were the same age and sex.
Over around 30 years of follow-up, those people who had their tonsils removed were 43% more likely to develop a stress-related disorder. Among the specific disorders, the risk for PTSD was substantially higher: 55% higher in the tonsillectomy group.

That’s pretty surprising, but I bet you already want to push back against this. Sure, the control group was the same age and sex, but other factors might be different between the two groups. You’d be right to think so. People who got their tonsils out were more likely to have parents with a history of stress-related disorders and who had lower educational attainment. But the primary results were adjusted for those factors.
There’s more to a family than parental educational attainment, of course. To account for household factors that might be harder to measure, the researchers created a second control group, this one comprising the siblings of people who had their tonsils removed but who hadn’t themselves had their tonsils removed.
The relationship between tonsillectomy and stress disorders in this population was not quite as robust but still present: a 34% increase in any stress disorder and a 41% increase in the risk for PTSD.

Maybe kids who get their tonsils out are just followed more closely thereafter, so doctors might notice a stress disorder and document it in the medical record; whereas with other kids it might go unnoticed. This is known as ascertainment bias. The researchers addressed this in a sensitivity analysis where they excluded new diagnoses of stress disorders that occurred in the first 3 years after tonsillectomy. The results were largely unchanged.
So how do we explain these data? We observe a correlation between tonsillectomy in youth and stress disorders in later life. But correlation is not causation. One possibility, perhaps even the most likely possibility, is that tonsillectomy is a marker of some other problem. Maybe these kids are more prone to infections and are therefore more likely to need their tonsils removed. Then, after a lifetime of more infections than average, their stress responses are higher. Or maybe kids with a higher BMI are more likely to have their tonsils removed due to sleep apnea concerns, and it’s that elevated BMI that leads to higher stress in later life.
Or maybe this is causal. Maybe there actually is biological plausibility here. The authors suggest that removal of tonsils might lead to broader changes in the immune system; after all, tonsillar tissue is on the front line of our defense against pathogens that might enter our bodies through our mouths or noses. Immunologic changes lead to greater inflammation over time, and there is decent evidence to link chronic inflammation to a variety of physical and psychological disorders.
In support of this, the authors show that the kids with tonsillectomy were more likely to be hospitalized for an infectious disease in the future as well, in magnitudes similar to the increased risk for stress. But they don’t actually show that the relationship between tonsillectomy and stress is mediated by that increased risk for infectious disease.
In the end, I find these data really intriguing. Before I dug into the literature, it seemed highly unlikely that removal of these small lumps of tissue would have much of an effect on anything. Now I’m not so sure. A few things can be removed from the human body without any consequences, but it can be hard to know exactly what those consequences are.
That said, given the rather marginal benefits of tonsillectomy and the growing number of studies expanding on the risks, I expect that we’ll see the rates of the surgery decline even further in the future.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Connecticut. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
You know those times in your life when you’re just feeling ... stressed? You’re on the edge; you have no chill; everything just sort of gets to you. If you can step away from the anxiety for a moment, you might ask yourself where it’s all coming from. Is it really the stuff in your inbox at work or is it money issues at home? Is it something with your relationship, or maybe it’s your sleep quality or your diet? One thing you probably won’t blame for those acute stress reactions is the tonsillectomy you had as a kid. But according to new research, maybe you should.
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are among the most common surgical procedures young people in the United States undergo, with about 300,000 cases a year, according to recent numbers. That’s down a bit from numbers a decade or so ago, but suffice it to say, a good chunk of the population is walking around right now without their tonsils.
The data supporting tonsillectomy have never been great. The two big indications for the surgery are recurrent sore throat — data show that tonsillectomy reduces this by about 0.7 sore throats per year— and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The data for improvement of OSA are a bit better than the data for sore throats.
Also, tonsillectomy is a relatively quick, relatively well-reimbursed surgery with indications that are — let’s be honest — somewhat subjective, and so variation is high. One study found that in a single Vermont town, nearly 60% of the population had had their tonsils removed by the time they turned 18. A few towns over, the rate was 20%.
A few factors have led to the decline of tonsillectomy in recent years. Reimbursement rates have gone down a bit. Additionally, better data collection and statistical analysis have shown that the benefits of the procedure are relatively modest.
And then there is a body of medical literature that at first struck me as surprising and almost bizarre: data linking tonsillectomy to subsequent physical and psychiatric disorders.
I teach a course on interpretation of the medical literature, and one of the first things I teach my students is to check their gut when they see the conclusion of a study.
Basically, even before you read the data, have a sense in your own mind if the hypothesis seems reasonable. If a paper is going to conclude that smoking leads to increased risk for bone cancer, I’d say that seems like a reasonable thing to study. If a paper purports to show a link between eating poultry and bone cancer, I’m going to be reading it with quite a bit more skepticism.
The technical term for that process is assessing “biologic plausibility.” If we’re talking tonsils, we have to ask ourselves: Is it plausible that removing someone’s tonsils when they are young should lead to major problems in the future?
At first blush, it didn’t seem very plausible to me.
But the truth is, there are quite a few studies out there demonstrating links like this: links between tonsillectomy and irritable bowel syndrome; links between tonsillectomy and cancer; links between tonsillectomy and depression.
And this week, appearing in JAMA Network Open, is a study linking tonsillectomy with stress disorders.
Researchers leveraged Sweden’s health database, which contains longitudinal data on basically every person who has lived in Sweden since 1981. This database let them know who had a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy, and when, and what happened to them later in life.
I think the best way to present these data is to show you what they found, and then challenge that finding, and then show you what they did in anticipation of the challenges we would have to their findings. It’s a pretty thorough study.
So, topline results here. The researchers first identified 83,957 individuals who had their tonsils removed. They matched each of them with 10 controls who did not have their tonsils removed but were the same age and sex.
Over around 30 years of follow-up, those people who had their tonsils removed were 43% more likely to develop a stress-related disorder. Among the specific disorders, the risk for PTSD was substantially higher: 55% higher in the tonsillectomy group.

That’s pretty surprising, but I bet you already want to push back against this. Sure, the control group was the same age and sex, but other factors might be different between the two groups. You’d be right to think so. People who got their tonsils out were more likely to have parents with a history of stress-related disorders and who had lower educational attainment. But the primary results were adjusted for those factors.
There’s more to a family than parental educational attainment, of course. To account for household factors that might be harder to measure, the researchers created a second control group, this one comprising the siblings of people who had their tonsils removed but who hadn’t themselves had their tonsils removed.
The relationship between tonsillectomy and stress disorders in this population was not quite as robust but still present: a 34% increase in any stress disorder and a 41% increase in the risk for PTSD.

Maybe kids who get their tonsils out are just followed more closely thereafter, so doctors might notice a stress disorder and document it in the medical record; whereas with other kids it might go unnoticed. This is known as ascertainment bias. The researchers addressed this in a sensitivity analysis where they excluded new diagnoses of stress disorders that occurred in the first 3 years after tonsillectomy. The results were largely unchanged.
So how do we explain these data? We observe a correlation between tonsillectomy in youth and stress disorders in later life. But correlation is not causation. One possibility, perhaps even the most likely possibility, is that tonsillectomy is a marker of some other problem. Maybe these kids are more prone to infections and are therefore more likely to need their tonsils removed. Then, after a lifetime of more infections than average, their stress responses are higher. Or maybe kids with a higher BMI are more likely to have their tonsils removed due to sleep apnea concerns, and it’s that elevated BMI that leads to higher stress in later life.
Or maybe this is causal. Maybe there actually is biological plausibility here. The authors suggest that removal of tonsils might lead to broader changes in the immune system; after all, tonsillar tissue is on the front line of our defense against pathogens that might enter our bodies through our mouths or noses. Immunologic changes lead to greater inflammation over time, and there is decent evidence to link chronic inflammation to a variety of physical and psychological disorders.
In support of this, the authors show that the kids with tonsillectomy were more likely to be hospitalized for an infectious disease in the future as well, in magnitudes similar to the increased risk for stress. But they don’t actually show that the relationship between tonsillectomy and stress is mediated by that increased risk for infectious disease.
In the end, I find these data really intriguing. Before I dug into the literature, it seemed highly unlikely that removal of these small lumps of tissue would have much of an effect on anything. Now I’m not so sure. A few things can be removed from the human body without any consequences, but it can be hard to know exactly what those consequences are.
That said, given the rather marginal benefits of tonsillectomy and the growing number of studies expanding on the risks, I expect that we’ll see the rates of the surgery decline even further in the future.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Connecticut. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transdermal Beats Oral Estrogen for CVD Safety of Hormone Therapy
I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) on different forms of contemporary menopausal hormone therapy and risks for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
This is a very large-scale and comprehensive study from Sweden that looked at more than 900,000 women, including more than 77,000 users of hormone therapy. The women were aged 50-58 years and the study leveraged the nationwide register system, where they have information on prescription medications as well as health outcomes that can be linked.
This study looked at the different forms of hormone therapy: oral vs transdermal, estrogen with and without a progestogen, and also tibolone (which is not available in the United States). The endpoints included myocardial infarction (MI), total ischemic heart disease, stroke, a composite of CVD, as well as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
They found that tibolone was associated with the greatest increased risk for CVD; there was actually an increase in both ischemic heart disease and stroke as well as composite CVD. They did not see an increased risk for VTE. This may be related to the unique pharmacologic profile of tibolone, which has estrogenic, progestogenic, and androgenic properties.
The estrogens tested in the estrogen plus progestin and estrogen alone formulations were not conjugated equine estrogen as tested in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and HERS trials, but mostly oral or transdermal estradiol. With combination estrogen plus progestin, they saw a small (about 20%) increase in ischemic heart disease, similar to what was seen in the WHI. And they saw about a doubling in the risk for VTE, also similar to what was seen in the WHI. With estrogen alone there was no increase in ischemic heart disease or MI, but there was about a 50% increase in VTE — again, similar to the WHI findings.
With transdermal estradiol (transdermal forms of estrogen), in contrast, there was no clear increase in any of these CVD outcomes. In fact, there was a borderline reduction in both MI and composite CVD.
So overall, this study suggests greater cardiovascular safety with transdermal compared with oral estrogen. This would be expected, given the first-pass metabolism and increased clotting associated with oral estrogens.
On the basis of a large body of evidence, we know that for women in early menopause who have bothersome vasomotor symptoms, if they’re healthy, oral or transdermal estrogen could be used according to the preference of the woman. But this study suggests that, especially in women who do have cardiovascular risk factors, it may be very reasonable to lean toward the use of transdermal over oral estrogen among those who are choosing to use hormone therapy.
We certainly need more research on transdermal estradiol, micronized progesterone, and these contemporary formulations that are being used. But in the meantime, this study in the BMJ does provide very useful information for women and their clinicians.
Dr Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts; Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) on different forms of contemporary menopausal hormone therapy and risks for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
This is a very large-scale and comprehensive study from Sweden that looked at more than 900,000 women, including more than 77,000 users of hormone therapy. The women were aged 50-58 years and the study leveraged the nationwide register system, where they have information on prescription medications as well as health outcomes that can be linked.
This study looked at the different forms of hormone therapy: oral vs transdermal, estrogen with and without a progestogen, and also tibolone (which is not available in the United States). The endpoints included myocardial infarction (MI), total ischemic heart disease, stroke, a composite of CVD, as well as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
They found that tibolone was associated with the greatest increased risk for CVD; there was actually an increase in both ischemic heart disease and stroke as well as composite CVD. They did not see an increased risk for VTE. This may be related to the unique pharmacologic profile of tibolone, which has estrogenic, progestogenic, and androgenic properties.
The estrogens tested in the estrogen plus progestin and estrogen alone formulations were not conjugated equine estrogen as tested in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and HERS trials, but mostly oral or transdermal estradiol. With combination estrogen plus progestin, they saw a small (about 20%) increase in ischemic heart disease, similar to what was seen in the WHI. And they saw about a doubling in the risk for VTE, also similar to what was seen in the WHI. With estrogen alone there was no increase in ischemic heart disease or MI, but there was about a 50% increase in VTE — again, similar to the WHI findings.
With transdermal estradiol (transdermal forms of estrogen), in contrast, there was no clear increase in any of these CVD outcomes. In fact, there was a borderline reduction in both MI and composite CVD.
So overall, this study suggests greater cardiovascular safety with transdermal compared with oral estrogen. This would be expected, given the first-pass metabolism and increased clotting associated with oral estrogens.
On the basis of a large body of evidence, we know that for women in early menopause who have bothersome vasomotor symptoms, if they’re healthy, oral or transdermal estrogen could be used according to the preference of the woman. But this study suggests that, especially in women who do have cardiovascular risk factors, it may be very reasonable to lean toward the use of transdermal over oral estrogen among those who are choosing to use hormone therapy.
We certainly need more research on transdermal estradiol, micronized progesterone, and these contemporary formulations that are being used. But in the meantime, this study in the BMJ does provide very useful information for women and their clinicians.
Dr Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts; Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I’d like to talk with you about a recent report in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) on different forms of contemporary menopausal hormone therapy and risks for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
This is a very large-scale and comprehensive study from Sweden that looked at more than 900,000 women, including more than 77,000 users of hormone therapy. The women were aged 50-58 years and the study leveraged the nationwide register system, where they have information on prescription medications as well as health outcomes that can be linked.
This study looked at the different forms of hormone therapy: oral vs transdermal, estrogen with and without a progestogen, and also tibolone (which is not available in the United States). The endpoints included myocardial infarction (MI), total ischemic heart disease, stroke, a composite of CVD, as well as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
They found that tibolone was associated with the greatest increased risk for CVD; there was actually an increase in both ischemic heart disease and stroke as well as composite CVD. They did not see an increased risk for VTE. This may be related to the unique pharmacologic profile of tibolone, which has estrogenic, progestogenic, and androgenic properties.
The estrogens tested in the estrogen plus progestin and estrogen alone formulations were not conjugated equine estrogen as tested in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and HERS trials, but mostly oral or transdermal estradiol. With combination estrogen plus progestin, they saw a small (about 20%) increase in ischemic heart disease, similar to what was seen in the WHI. And they saw about a doubling in the risk for VTE, also similar to what was seen in the WHI. With estrogen alone there was no increase in ischemic heart disease or MI, but there was about a 50% increase in VTE — again, similar to the WHI findings.
With transdermal estradiol (transdermal forms of estrogen), in contrast, there was no clear increase in any of these CVD outcomes. In fact, there was a borderline reduction in both MI and composite CVD.
So overall, this study suggests greater cardiovascular safety with transdermal compared with oral estrogen. This would be expected, given the first-pass metabolism and increased clotting associated with oral estrogens.
On the basis of a large body of evidence, we know that for women in early menopause who have bothersome vasomotor symptoms, if they’re healthy, oral or transdermal estrogen could be used according to the preference of the woman. But this study suggests that, especially in women who do have cardiovascular risk factors, it may be very reasonable to lean toward the use of transdermal over oral estrogen among those who are choosing to use hormone therapy.
We certainly need more research on transdermal estradiol, micronized progesterone, and these contemporary formulations that are being used. But in the meantime, this study in the BMJ does provide very useful information for women and their clinicians.
Dr Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts; Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Vitamin E Beneficial for Bone Health?
Vitamin E may be best known for boosting skin and eye health as well as immune function. In recent years, researchers have explored the potential benefits of vitamin E on bone loss, especially in women with menopause-related osteoporosis. While data are beginning to roll in from these studies, evidence supporting a positive impact of vitamin E on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains elusive.
For osteoporosis, the rationale for using vitamin E is based on its antioxidant activity, which can scavenge potentially damaging free radicals. Researchers have asked whether vitamin E can help maintain the integrity of bone matrix and stimulate bone formation while minimizing bone resorption, particularly in trabecular (spongy) bone, the bone compartment preferentially affected in perimenopausal bone loss.
Vitamin E mostly consists of two isomers: alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol. Alpha-tocopherol has higher antioxidant activity and is found in nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, and vitamin E supplements. Gamma-tocopherol is known for its superior anti-inflammatory properties and accounts for about 70% of the total vitamin E intake in a typical American diet, largely sourced from soybean and other vegetable oils.
Benefits and Risks in Bone Loss Studies
Perimenopausal bone loss is caused, to a great extent, by the decrease in sex hormones. Studies of vitamin E in ovariectomized rats have yielded mixed results. This animal model lacks sex hormones and has similar bone changes to those of postmenopausal women. Some animal studies have suggested a positive effect of vitamin E on bone while others have reported no effect.
Studies in humans also have produced conflicting reports of positive, neutral, and negative associations of vitamin E with bone health. For example, the Women’s Health Initiative examined the relationship between vitamin and mineral antioxidants and bone health in postmenopausal women and found no significant association between antioxidants and bone mineral density.
Another study examining data from children and adolescents enrolled in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database found an inverse association between alpha-tocopherol and lumbar spine bone density, suggesting a deleterious effect on bone. Inverse associations also have been reported in certain studies of postmenopausal women.
High doses of alpha-tocopherol have been linked to a risk for impaired bone health through a variety of mechanisms, such as interference with vitamin K metabolism; competitive binding for alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, inhibiting the entry of beneficial vitamin E isomers, including gamma-tocopherol; and pro-oxidant effects that harm bone. Thus, postmenopausal women taking vitamin E supplements primarily as high doses of alpha-tocopherol might be hindering their bone health.
Data for gamma-tocopherol are more promising. Some studies hypothesize that gamma-tocopherol might uncouple bone turnover, leading to increased bone formation without affecting bone resorption. Further, a randomized controlled study of mixed tocopherols (rather than alpha-tocopherol) vs placebo reported a protective effect of this preparation on bone outcomes by suppressing bone resorption. This raises the importance of considering the specific forms of vitamin E when evaluating its role in bone health.
Limitations of Current Studies
Researchers acknowledge several limitations in studies to date. For example, there are very few randomized controlled trials assessing the impact of vitamin E on bone health. Most studies are cross-sectional or observational, even when longitudinal. Cross-sectional and observational designs prevent us from establishing a causal relationship between vitamin E and bone endpoints.
Such designs also run the risk of additional confounders that may affect associations between vitamin E and bone, or the lack thereof. These could include both known and unknown confounders. Of note, gamma-tocopherol intake data were not available for certain NHANES studies.
Further, people often consume multiple nutrients and supplements, complicating the identification of specific nutrient-disease associations. Most human studies estimate tocopherol intake by dietary questionnaires or measure serum tocopherol levels, which reflect short-term dietary intake, while bone mineral density is probably influenced by long-term dietary patterns.
Too Soon to Prescribe Vitamin E for Bone Health
Some nutrition experts advocate for vitamin E supplements containing mixed tocopherols, specifically suggesting a ratio of 50-100 IU of gamma-tocopherol per 400 IU of D-alpha-tocopherol. Additional research is essential to confirm and further clarify the role of gamma-tocopherol in bone formation and resorption. In fact, it is also important to explore the influence of other compounds in the vitamin E family on skeletal health.
Until more data are available, we would recommend following the Institute of Medicine’s guidelines for the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin E. This is age dependent, ranging from 4 to 11 mg/d between the ages of 0 and 13 years, and 15 mg/d thereafter.
Overall, evidence of vitamin E’s impact on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains inconclusive. Although some observational and interventional studies suggest potential benefits, more interventional studies, particularly randomized controlled trials, are necessary to explore the risks and benefits of vitamin E supplementation and serum vitamin E levels on bone density and fracture risk more thoroughly.
Dr. Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, both in Charlottesville, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia, and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin E may be best known for boosting skin and eye health as well as immune function. In recent years, researchers have explored the potential benefits of vitamin E on bone loss, especially in women with menopause-related osteoporosis. While data are beginning to roll in from these studies, evidence supporting a positive impact of vitamin E on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains elusive.
For osteoporosis, the rationale for using vitamin E is based on its antioxidant activity, which can scavenge potentially damaging free radicals. Researchers have asked whether vitamin E can help maintain the integrity of bone matrix and stimulate bone formation while minimizing bone resorption, particularly in trabecular (spongy) bone, the bone compartment preferentially affected in perimenopausal bone loss.
Vitamin E mostly consists of two isomers: alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol. Alpha-tocopherol has higher antioxidant activity and is found in nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, and vitamin E supplements. Gamma-tocopherol is known for its superior anti-inflammatory properties and accounts for about 70% of the total vitamin E intake in a typical American diet, largely sourced from soybean and other vegetable oils.
Benefits and Risks in Bone Loss Studies
Perimenopausal bone loss is caused, to a great extent, by the decrease in sex hormones. Studies of vitamin E in ovariectomized rats have yielded mixed results. This animal model lacks sex hormones and has similar bone changes to those of postmenopausal women. Some animal studies have suggested a positive effect of vitamin E on bone while others have reported no effect.
Studies in humans also have produced conflicting reports of positive, neutral, and negative associations of vitamin E with bone health. For example, the Women’s Health Initiative examined the relationship between vitamin and mineral antioxidants and bone health in postmenopausal women and found no significant association between antioxidants and bone mineral density.
Another study examining data from children and adolescents enrolled in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database found an inverse association between alpha-tocopherol and lumbar spine bone density, suggesting a deleterious effect on bone. Inverse associations also have been reported in certain studies of postmenopausal women.
High doses of alpha-tocopherol have been linked to a risk for impaired bone health through a variety of mechanisms, such as interference with vitamin K metabolism; competitive binding for alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, inhibiting the entry of beneficial vitamin E isomers, including gamma-tocopherol; and pro-oxidant effects that harm bone. Thus, postmenopausal women taking vitamin E supplements primarily as high doses of alpha-tocopherol might be hindering their bone health.
Data for gamma-tocopherol are more promising. Some studies hypothesize that gamma-tocopherol might uncouple bone turnover, leading to increased bone formation without affecting bone resorption. Further, a randomized controlled study of mixed tocopherols (rather than alpha-tocopherol) vs placebo reported a protective effect of this preparation on bone outcomes by suppressing bone resorption. This raises the importance of considering the specific forms of vitamin E when evaluating its role in bone health.
Limitations of Current Studies
Researchers acknowledge several limitations in studies to date. For example, there are very few randomized controlled trials assessing the impact of vitamin E on bone health. Most studies are cross-sectional or observational, even when longitudinal. Cross-sectional and observational designs prevent us from establishing a causal relationship between vitamin E and bone endpoints.
Such designs also run the risk of additional confounders that may affect associations between vitamin E and bone, or the lack thereof. These could include both known and unknown confounders. Of note, gamma-tocopherol intake data were not available for certain NHANES studies.
Further, people often consume multiple nutrients and supplements, complicating the identification of specific nutrient-disease associations. Most human studies estimate tocopherol intake by dietary questionnaires or measure serum tocopherol levels, which reflect short-term dietary intake, while bone mineral density is probably influenced by long-term dietary patterns.
Too Soon to Prescribe Vitamin E for Bone Health
Some nutrition experts advocate for vitamin E supplements containing mixed tocopherols, specifically suggesting a ratio of 50-100 IU of gamma-tocopherol per 400 IU of D-alpha-tocopherol. Additional research is essential to confirm and further clarify the role of gamma-tocopherol in bone formation and resorption. In fact, it is also important to explore the influence of other compounds in the vitamin E family on skeletal health.
Until more data are available, we would recommend following the Institute of Medicine’s guidelines for the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin E. This is age dependent, ranging from 4 to 11 mg/d between the ages of 0 and 13 years, and 15 mg/d thereafter.
Overall, evidence of vitamin E’s impact on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains inconclusive. Although some observational and interventional studies suggest potential benefits, more interventional studies, particularly randomized controlled trials, are necessary to explore the risks and benefits of vitamin E supplementation and serum vitamin E levels on bone density and fracture risk more thoroughly.
Dr. Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, both in Charlottesville, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia, and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin E may be best known for boosting skin and eye health as well as immune function. In recent years, researchers have explored the potential benefits of vitamin E on bone loss, especially in women with menopause-related osteoporosis. While data are beginning to roll in from these studies, evidence supporting a positive impact of vitamin E on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains elusive.
For osteoporosis, the rationale for using vitamin E is based on its antioxidant activity, which can scavenge potentially damaging free radicals. Researchers have asked whether vitamin E can help maintain the integrity of bone matrix and stimulate bone formation while minimizing bone resorption, particularly in trabecular (spongy) bone, the bone compartment preferentially affected in perimenopausal bone loss.
Vitamin E mostly consists of two isomers: alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol. Alpha-tocopherol has higher antioxidant activity and is found in nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, and vitamin E supplements. Gamma-tocopherol is known for its superior anti-inflammatory properties and accounts for about 70% of the total vitamin E intake in a typical American diet, largely sourced from soybean and other vegetable oils.
Benefits and Risks in Bone Loss Studies
Perimenopausal bone loss is caused, to a great extent, by the decrease in sex hormones. Studies of vitamin E in ovariectomized rats have yielded mixed results. This animal model lacks sex hormones and has similar bone changes to those of postmenopausal women. Some animal studies have suggested a positive effect of vitamin E on bone while others have reported no effect.
Studies in humans also have produced conflicting reports of positive, neutral, and negative associations of vitamin E with bone health. For example, the Women’s Health Initiative examined the relationship between vitamin and mineral antioxidants and bone health in postmenopausal women and found no significant association between antioxidants and bone mineral density.
Another study examining data from children and adolescents enrolled in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database found an inverse association between alpha-tocopherol and lumbar spine bone density, suggesting a deleterious effect on bone. Inverse associations also have been reported in certain studies of postmenopausal women.
High doses of alpha-tocopherol have been linked to a risk for impaired bone health through a variety of mechanisms, such as interference with vitamin K metabolism; competitive binding for alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, inhibiting the entry of beneficial vitamin E isomers, including gamma-tocopherol; and pro-oxidant effects that harm bone. Thus, postmenopausal women taking vitamin E supplements primarily as high doses of alpha-tocopherol might be hindering their bone health.
Data for gamma-tocopherol are more promising. Some studies hypothesize that gamma-tocopherol might uncouple bone turnover, leading to increased bone formation without affecting bone resorption. Further, a randomized controlled study of mixed tocopherols (rather than alpha-tocopherol) vs placebo reported a protective effect of this preparation on bone outcomes by suppressing bone resorption. This raises the importance of considering the specific forms of vitamin E when evaluating its role in bone health.
Limitations of Current Studies
Researchers acknowledge several limitations in studies to date. For example, there are very few randomized controlled trials assessing the impact of vitamin E on bone health. Most studies are cross-sectional or observational, even when longitudinal. Cross-sectional and observational designs prevent us from establishing a causal relationship between vitamin E and bone endpoints.
Such designs also run the risk of additional confounders that may affect associations between vitamin E and bone, or the lack thereof. These could include both known and unknown confounders. Of note, gamma-tocopherol intake data were not available for certain NHANES studies.
Further, people often consume multiple nutrients and supplements, complicating the identification of specific nutrient-disease associations. Most human studies estimate tocopherol intake by dietary questionnaires or measure serum tocopherol levels, which reflect short-term dietary intake, while bone mineral density is probably influenced by long-term dietary patterns.
Too Soon to Prescribe Vitamin E for Bone Health
Some nutrition experts advocate for vitamin E supplements containing mixed tocopherols, specifically suggesting a ratio of 50-100 IU of gamma-tocopherol per 400 IU of D-alpha-tocopherol. Additional research is essential to confirm and further clarify the role of gamma-tocopherol in bone formation and resorption. In fact, it is also important to explore the influence of other compounds in the vitamin E family on skeletal health.
Until more data are available, we would recommend following the Institute of Medicine’s guidelines for the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin E. This is age dependent, ranging from 4 to 11 mg/d between the ages of 0 and 13 years, and 15 mg/d thereafter.
Overall, evidence of vitamin E’s impact on osteoporosis and hip fracture risk in perimenopausal women remains inconclusive. Although some observational and interventional studies suggest potential benefits, more interventional studies, particularly randomized controlled trials, are necessary to explore the risks and benefits of vitamin E supplementation and serum vitamin E levels on bone density and fracture risk more thoroughly.
Dr. Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, both in Charlottesville, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia, and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Diet and Gut Bacteria Be Fueling Early CRC?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.



