User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Gout flares linked to transient jump in MI, stroke risk
There is evidence that gout and heart disease are mechanistically linked by inflammation and patients with gout are at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). But do gout flares, on their own, affect short-term risk for CV events? A new analysis based on records from British medical practices suggests that might be the case.
Risk for myocardial infarction or stroke climbed in the weeks after individual gout flare-ups in the study’s more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis. The jump in risk, significant but small in absolute terms, held for about 4 months in the case-control study before going away.
A sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who already had CVD when their gout was diagnosed yielded similar results.
The observational study isn’t able to show that gout flares themselves transiently raise the risk for MI or stroke, but it’s enough to send a cautionary message to physicians who care for patients with gout, rheumatologist Abhishek Abhishek, PhD, Nottingham (England) City Hospital, said in an interview.
In such patients who also have conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, or a history of heart disease, he said, it’s important “to manage risk factors really aggressively, knowing that when these patients have a gout flare, there’s a temporary increase in risk of a cardiovascular event.”
Managing their absolute CV risk – whether with drug therapy, lifestyle changes, or other interventions – should help limit the transient jump in risk for MI or stroke following a gout flare, proposed Dr. Abhishek, who is senior author on the study published in JAMA, with lead author Edoardo Cipolletta, MD, also from Nottingham City Hospital.
First robust evidence
The case-control study, which involved more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis, some who went on to have MI or stroke, looked at rates of such events at different time intervals after gout flares. Those who experienced such events showed a more than 90% increased likelihood of a gout flare-up in the preceding 60 days, a greater than 50% chance of a flare between 60 and 120 days before the event, but no increased likelihood prior to 120 days before the event.
Such a link between gout flares and CV events “has been suspected but never proven,” observed rheumatologist Hyon K. Choi, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not associated with the analysis. “This is the first time it has actually been shown in a robust way,” he said in an interview.
The study suggests a “likely causative relationship” between gout flares and CV events, but – as the published report noted – has limitations like any observational study, said Dr. Choi, who also directs the Gout & Crystal Arthropathy Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “Hopefully, this can be replicated in other cohorts.”
The analysis controlled for a number of relevant potential confounders, he noted, but couldn’t account for all issues that could argue against gout flares as a direct cause of the MIs and strokes.
Gout attacks are a complex experience with a range of potential indirect effects on CV risk, Dr. Choi observed. They can immobilize patients, possibly raising their risk for thrombotic events, for example. They can be exceptionally painful, which causes stress and can lead to frequent or chronic use of glucocorticoids or NSAIDs, all of which can exacerbate high blood pressure and possibly worsen CV risk.
A unique insight
The timing of gout flares relative to acute vascular events hasn’t been fully explored, observed an accompanying editorial. The current study’s “unique insight,” it stated, “is that disease activity from gout was associated with an incremental increase in risk for acute vascular events during the time period immediately following the gout flare.”
Although the study is observational, a “large body of evidence from animal and human research, mechanistic insights, and clinical interventions” support an association between flares and vascular events and “make a causal link eminently reasonable,” stated the editorialists, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, and Kirk U. Knowlton, MD, both with Intermountain Medical Center, Salt Lake City, Utah.
The findings, they wrote, “should alert clinicians and patients to the increased cardiovascular risk in the weeks beginning after a gout flare and should focus attention on optimizing preventive measures.” Those can include “lifestyle measures and standard risk-factor control including adherence to diet, statins, anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aspirin, colchicine), smoking cessation, diabetic and blood pressure control, and antithrombotic medications as indicated.”
Dr. Choi said the current results argue for more liberal use of colchicine, and for preferring colchicine over other anti-inflammatories, in patients with gout and traditional CV risk factors, given multiple randomized trials supporting the drug’s use in such cases. “If you use colchicine, you are covering their heart disease risk as well as their gout. It’s two birds with one stone.”
Nested case-control study
The investigators accessed electronic health records from 96,153 patients with recently diagnosed gout in England from 1997 to 2020; the cohort’s mean age was about 76 years, and 69% of participants were men. They matched 10,475 patients with at least one CV event to 52,099 others who didn’t have such an event by age, sex, and time from gout diagnosis. In each matched set of patients, those not experiencing a CV event were assigned a flare-to-event interval based on their matching with patients who did experience such an event.
Those with CV events, compared with patients without an event, had a greater than 90% increased likelihood of experiencing a gout flare-up in the 60 days preceding the event, a more than 50% greater chance of a flare-up 60-120 days before the CV event, but no increased likelihood more than 120 days before the event.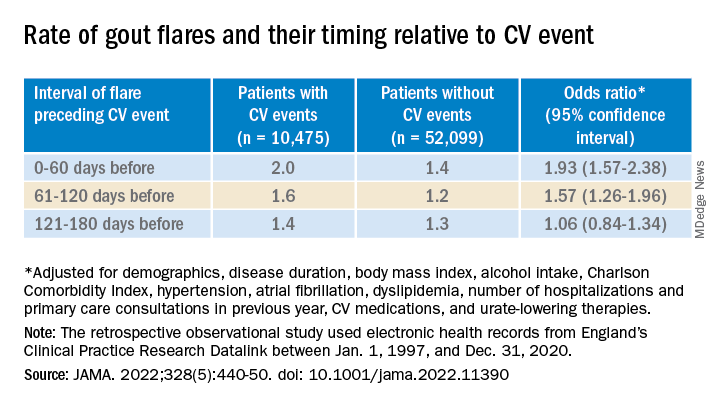
A self-controlled case series based on the same overall cohort with gout yielded similar results while sidestepping any potential for residual confounding, an inherent concern with any case–control analysis, the report notes. It involved 1,421 patients with one or more gout flare and at least one MI or stroke after the diagnosis of gout.
Among that cohort, the CV-event incidence rate ratio, adjusted for age and season of the year, by time interval after a gout flare, was 1.89 (95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.30) at 0-60 days, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.45-1.86) at 61-120 days, and1.29 (95% CI, 1.02-1.64) at 121-180 days.
Also similar, the report noted, were results of several sensitivity analyses, including one that excluded patients with confirmed CVD before their gout diagnosis; another that left out patients at low to moderate CV risk; and one that considered only gout flares treated with colchicine, corticosteroids, or NSAIDs.
The incremental CV event risks observed after flares in the study were small, which “has implications for both cost effectiveness and clinical relevance,” observed Dr. Anderson and Dr. Knowlton.
“An alternative to universal augmentation of cardiovascular risk prevention with therapies among patients with gout flares,” they wrote, would be “to further stratify risk by defining a group at highest near-term risk.” Such interventions could potentially be guided by markers of CV risk such as, for example, levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein or lipoprotein(a), or plaque burden on coronary-artery calcium scans.
Dr. Abhishek, Dr. Cipolletta, and the other authors reported no competing interests. Dr. Choi disclosed research support from Ironwood and Horizon; and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. Dr. Anderson disclosed receiving grants to his institution from Novartis and Milestone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is evidence that gout and heart disease are mechanistically linked by inflammation and patients with gout are at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). But do gout flares, on their own, affect short-term risk for CV events? A new analysis based on records from British medical practices suggests that might be the case.
Risk for myocardial infarction or stroke climbed in the weeks after individual gout flare-ups in the study’s more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis. The jump in risk, significant but small in absolute terms, held for about 4 months in the case-control study before going away.
A sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who already had CVD when their gout was diagnosed yielded similar results.
The observational study isn’t able to show that gout flares themselves transiently raise the risk for MI or stroke, but it’s enough to send a cautionary message to physicians who care for patients with gout, rheumatologist Abhishek Abhishek, PhD, Nottingham (England) City Hospital, said in an interview.
In such patients who also have conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, or a history of heart disease, he said, it’s important “to manage risk factors really aggressively, knowing that when these patients have a gout flare, there’s a temporary increase in risk of a cardiovascular event.”
Managing their absolute CV risk – whether with drug therapy, lifestyle changes, or other interventions – should help limit the transient jump in risk for MI or stroke following a gout flare, proposed Dr. Abhishek, who is senior author on the study published in JAMA, with lead author Edoardo Cipolletta, MD, also from Nottingham City Hospital.
First robust evidence
The case-control study, which involved more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis, some who went on to have MI or stroke, looked at rates of such events at different time intervals after gout flares. Those who experienced such events showed a more than 90% increased likelihood of a gout flare-up in the preceding 60 days, a greater than 50% chance of a flare between 60 and 120 days before the event, but no increased likelihood prior to 120 days before the event.
Such a link between gout flares and CV events “has been suspected but never proven,” observed rheumatologist Hyon K. Choi, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not associated with the analysis. “This is the first time it has actually been shown in a robust way,” he said in an interview.
The study suggests a “likely causative relationship” between gout flares and CV events, but – as the published report noted – has limitations like any observational study, said Dr. Choi, who also directs the Gout & Crystal Arthropathy Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “Hopefully, this can be replicated in other cohorts.”
The analysis controlled for a number of relevant potential confounders, he noted, but couldn’t account for all issues that could argue against gout flares as a direct cause of the MIs and strokes.
Gout attacks are a complex experience with a range of potential indirect effects on CV risk, Dr. Choi observed. They can immobilize patients, possibly raising their risk for thrombotic events, for example. They can be exceptionally painful, which causes stress and can lead to frequent or chronic use of glucocorticoids or NSAIDs, all of which can exacerbate high blood pressure and possibly worsen CV risk.
A unique insight
The timing of gout flares relative to acute vascular events hasn’t been fully explored, observed an accompanying editorial. The current study’s “unique insight,” it stated, “is that disease activity from gout was associated with an incremental increase in risk for acute vascular events during the time period immediately following the gout flare.”
Although the study is observational, a “large body of evidence from animal and human research, mechanistic insights, and clinical interventions” support an association between flares and vascular events and “make a causal link eminently reasonable,” stated the editorialists, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, and Kirk U. Knowlton, MD, both with Intermountain Medical Center, Salt Lake City, Utah.
The findings, they wrote, “should alert clinicians and patients to the increased cardiovascular risk in the weeks beginning after a gout flare and should focus attention on optimizing preventive measures.” Those can include “lifestyle measures and standard risk-factor control including adherence to diet, statins, anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aspirin, colchicine), smoking cessation, diabetic and blood pressure control, and antithrombotic medications as indicated.”
Dr. Choi said the current results argue for more liberal use of colchicine, and for preferring colchicine over other anti-inflammatories, in patients with gout and traditional CV risk factors, given multiple randomized trials supporting the drug’s use in such cases. “If you use colchicine, you are covering their heart disease risk as well as their gout. It’s two birds with one stone.”
Nested case-control study
The investigators accessed electronic health records from 96,153 patients with recently diagnosed gout in England from 1997 to 2020; the cohort’s mean age was about 76 years, and 69% of participants were men. They matched 10,475 patients with at least one CV event to 52,099 others who didn’t have such an event by age, sex, and time from gout diagnosis. In each matched set of patients, those not experiencing a CV event were assigned a flare-to-event interval based on their matching with patients who did experience such an event.
Those with CV events, compared with patients without an event, had a greater than 90% increased likelihood of experiencing a gout flare-up in the 60 days preceding the event, a more than 50% greater chance of a flare-up 60-120 days before the CV event, but no increased likelihood more than 120 days before the event.
A self-controlled case series based on the same overall cohort with gout yielded similar results while sidestepping any potential for residual confounding, an inherent concern with any case–control analysis, the report notes. It involved 1,421 patients with one or more gout flare and at least one MI or stroke after the diagnosis of gout.
Among that cohort, the CV-event incidence rate ratio, adjusted for age and season of the year, by time interval after a gout flare, was 1.89 (95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.30) at 0-60 days, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.45-1.86) at 61-120 days, and1.29 (95% CI, 1.02-1.64) at 121-180 days.
Also similar, the report noted, were results of several sensitivity analyses, including one that excluded patients with confirmed CVD before their gout diagnosis; another that left out patients at low to moderate CV risk; and one that considered only gout flares treated with colchicine, corticosteroids, or NSAIDs.
The incremental CV event risks observed after flares in the study were small, which “has implications for both cost effectiveness and clinical relevance,” observed Dr. Anderson and Dr. Knowlton.
“An alternative to universal augmentation of cardiovascular risk prevention with therapies among patients with gout flares,” they wrote, would be “to further stratify risk by defining a group at highest near-term risk.” Such interventions could potentially be guided by markers of CV risk such as, for example, levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein or lipoprotein(a), or plaque burden on coronary-artery calcium scans.
Dr. Abhishek, Dr. Cipolletta, and the other authors reported no competing interests. Dr. Choi disclosed research support from Ironwood and Horizon; and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. Dr. Anderson disclosed receiving grants to his institution from Novartis and Milestone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is evidence that gout and heart disease are mechanistically linked by inflammation and patients with gout are at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). But do gout flares, on their own, affect short-term risk for CV events? A new analysis based on records from British medical practices suggests that might be the case.
Risk for myocardial infarction or stroke climbed in the weeks after individual gout flare-ups in the study’s more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis. The jump in risk, significant but small in absolute terms, held for about 4 months in the case-control study before going away.
A sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who already had CVD when their gout was diagnosed yielded similar results.
The observational study isn’t able to show that gout flares themselves transiently raise the risk for MI or stroke, but it’s enough to send a cautionary message to physicians who care for patients with gout, rheumatologist Abhishek Abhishek, PhD, Nottingham (England) City Hospital, said in an interview.
In such patients who also have conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia, or a history of heart disease, he said, it’s important “to manage risk factors really aggressively, knowing that when these patients have a gout flare, there’s a temporary increase in risk of a cardiovascular event.”
Managing their absolute CV risk – whether with drug therapy, lifestyle changes, or other interventions – should help limit the transient jump in risk for MI or stroke following a gout flare, proposed Dr. Abhishek, who is senior author on the study published in JAMA, with lead author Edoardo Cipolletta, MD, also from Nottingham City Hospital.
First robust evidence
The case-control study, which involved more than 60,000 patients with a recent gout diagnosis, some who went on to have MI or stroke, looked at rates of such events at different time intervals after gout flares. Those who experienced such events showed a more than 90% increased likelihood of a gout flare-up in the preceding 60 days, a greater than 50% chance of a flare between 60 and 120 days before the event, but no increased likelihood prior to 120 days before the event.
Such a link between gout flares and CV events “has been suspected but never proven,” observed rheumatologist Hyon K. Choi, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not associated with the analysis. “This is the first time it has actually been shown in a robust way,” he said in an interview.
The study suggests a “likely causative relationship” between gout flares and CV events, but – as the published report noted – has limitations like any observational study, said Dr. Choi, who also directs the Gout & Crystal Arthropathy Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “Hopefully, this can be replicated in other cohorts.”
The analysis controlled for a number of relevant potential confounders, he noted, but couldn’t account for all issues that could argue against gout flares as a direct cause of the MIs and strokes.
Gout attacks are a complex experience with a range of potential indirect effects on CV risk, Dr. Choi observed. They can immobilize patients, possibly raising their risk for thrombotic events, for example. They can be exceptionally painful, which causes stress and can lead to frequent or chronic use of glucocorticoids or NSAIDs, all of which can exacerbate high blood pressure and possibly worsen CV risk.
A unique insight
The timing of gout flares relative to acute vascular events hasn’t been fully explored, observed an accompanying editorial. The current study’s “unique insight,” it stated, “is that disease activity from gout was associated with an incremental increase in risk for acute vascular events during the time period immediately following the gout flare.”
Although the study is observational, a “large body of evidence from animal and human research, mechanistic insights, and clinical interventions” support an association between flares and vascular events and “make a causal link eminently reasonable,” stated the editorialists, Jeffrey L. Anderson, MD, and Kirk U. Knowlton, MD, both with Intermountain Medical Center, Salt Lake City, Utah.
The findings, they wrote, “should alert clinicians and patients to the increased cardiovascular risk in the weeks beginning after a gout flare and should focus attention on optimizing preventive measures.” Those can include “lifestyle measures and standard risk-factor control including adherence to diet, statins, anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aspirin, colchicine), smoking cessation, diabetic and blood pressure control, and antithrombotic medications as indicated.”
Dr. Choi said the current results argue for more liberal use of colchicine, and for preferring colchicine over other anti-inflammatories, in patients with gout and traditional CV risk factors, given multiple randomized trials supporting the drug’s use in such cases. “If you use colchicine, you are covering their heart disease risk as well as their gout. It’s two birds with one stone.”
Nested case-control study
The investigators accessed electronic health records from 96,153 patients with recently diagnosed gout in England from 1997 to 2020; the cohort’s mean age was about 76 years, and 69% of participants were men. They matched 10,475 patients with at least one CV event to 52,099 others who didn’t have such an event by age, sex, and time from gout diagnosis. In each matched set of patients, those not experiencing a CV event were assigned a flare-to-event interval based on their matching with patients who did experience such an event.
Those with CV events, compared with patients without an event, had a greater than 90% increased likelihood of experiencing a gout flare-up in the 60 days preceding the event, a more than 50% greater chance of a flare-up 60-120 days before the CV event, but no increased likelihood more than 120 days before the event.
A self-controlled case series based on the same overall cohort with gout yielded similar results while sidestepping any potential for residual confounding, an inherent concern with any case–control analysis, the report notes. It involved 1,421 patients with one or more gout flare and at least one MI or stroke after the diagnosis of gout.
Among that cohort, the CV-event incidence rate ratio, adjusted for age and season of the year, by time interval after a gout flare, was 1.89 (95% confidence interval, 1.54-2.30) at 0-60 days, 1.64 (95% CI, 1.45-1.86) at 61-120 days, and1.29 (95% CI, 1.02-1.64) at 121-180 days.
Also similar, the report noted, were results of several sensitivity analyses, including one that excluded patients with confirmed CVD before their gout diagnosis; another that left out patients at low to moderate CV risk; and one that considered only gout flares treated with colchicine, corticosteroids, or NSAIDs.
The incremental CV event risks observed after flares in the study were small, which “has implications for both cost effectiveness and clinical relevance,” observed Dr. Anderson and Dr. Knowlton.
“An alternative to universal augmentation of cardiovascular risk prevention with therapies among patients with gout flares,” they wrote, would be “to further stratify risk by defining a group at highest near-term risk.” Such interventions could potentially be guided by markers of CV risk such as, for example, levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein or lipoprotein(a), or plaque burden on coronary-artery calcium scans.
Dr. Abhishek, Dr. Cipolletta, and the other authors reported no competing interests. Dr. Choi disclosed research support from Ironwood and Horizon; and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. Dr. Anderson disclosed receiving grants to his institution from Novartis and Milestone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Ustekinumab becomes second biologic approved for PsA in kids
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the dual interleukin-12 and IL-23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara) for the treatment of juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) in patients aged 6 years and older, according to an Aug. 1 announcement from its manufacturer, Janssen.
The approval makes jPsA the sixth approved indication for ustekinumab, which include active psoriatic arthritis in adults, moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in both adults and children aged 6 years or older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults, and moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.
In addition, ustekinumab is now the second biologic to be approved for jPsA, following the agency’s December 2021 approval of secukinumab (Cosentyx) to treat jPsA in children and adolescents aged 2 years and older as well as enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 4 years and older.
In pediatric patients, ustekinumab is administered as a subcutaneous injection dosed four times per year after two starter doses.
Ustekinumab’s approval is based on “an extrapolation of the established data and existing safety profile” of ustekinumab in multiple phase 3 studies in adult and pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and adult patients with active PsA, according to Janssen.
“With the limited availability of pediatric patients for clinical trial inclusion, researchers can extrapolate data from trials with adults to determine the potential efficacy and tolerability of a treatment for a pediatric population,” according to the October 2021 announcement from the company that the Biologics License Application had been submitted to the FDA.
Juvenile arthritis occurs in an estimated 20-45 children per 100,000 in the United States, with about 5% of those children having jPsA, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation.
The prescribing information for ustekinumab includes specific warnings and areas of concern. The drug should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to ustekinumab. The drug may lower the ability of the immune system to fight infections and may increase risk of infections, sometimes serious, and a test for tuberculosis infection should be given before administration.
Patients taking ustekinumab should not be given a live vaccine, and their doctors should be informed if anyone in their household needs a live vaccine. They also should not receive the BCG vaccine during the 1 year before receiving the drug or 1 year after they stop taking it, according to Johnson & Johnson.
The most common adverse effects include nasal congestion, sore throat, runny nose, upper respiratory infections, fever, headache, tiredness, itching, nausea and vomiting, redness at the injection site, vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections, sinus infection, bronchitis, diarrhea, stomach pain, and joint pain.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Injectable HIV prevention better than pills in two trials
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – , according to new data from two HIV Prevention Trials Network (HPTN) studies reported at the International AIDS Society Conference.
Follow-up data from the HPTN 084 trial, which compared the two regimens in 3,224 sub-Saharan persons who were assigned female sex at birth, show that three new HIV infections occurred in the CAB LA group in the 12 months since the study was unblinded, versus 20 new infections among the TDF-FTC group. That translates to an 89% lower risk of infection in the CAB LA arm across both the blinded and unblinded phases of the trial, said lead investigator Sinead Delany-Moretlwe, MD, PhD, director of research, Wits Reproductive Health and HIV Institute, the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, during a press conference.
“The trial was designed with the assumption that both drugs were highly effective in preventing HIV infection but that, given the challenges with taking a pill a day, that injectable cabotegravir may offer an adherence advantage,” she said in an interview. “Our data appear to confirm this, as most of the participants in the TDF-FTC arm who became infected with HIV had evidence of poor or inconsistent use of PrEP.”
The study also found that pregnancy incidence increased “two- to threefold” between the blinded and the unblinded period, “and this emphasizes to us the desire of women to conceive safely, without the threat of HIV, and the importance of us continuing to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of cabotegravir in pregnant and breastfeeding women during open-label extension phase of HPTN 084, so that [they] are not excluded from access to this highly effective PrEP agent,” she said. To date, no congenital anomalies have been reported in babies born during the study.
In an update report from HPTN 083, which also showed superiority of CAB LA over TDF-FTC in cisgender men and transgender women (TGW), researchers reported the safety and efficacy of CAB LA use in TGW using gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT).
Among the 4,566 participants in HPTN 083, 570 were TGW, and of those, 58% used GAHT at baseline, reported Beatriz Grinsztejn, MD, PhD, head of the STD/AIDS Clinical Research Laboratory at the Instituto Nacional de Infectologicia/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
CAB LA drug concentrations measured in a subset of 53 TGW who received on-time CAB injections were comparable between those taking (n = 30) and those not taking GAHT (n = 23), “suggesting the lack of a gender-affirming hormone effect on CAB pharmacokinetics,” she said. “These are very promising results, as we all know that the use of gender-affirming hormone therapy is a major priority for our transgender women community, ... so the lack of drug-drug interaction is really a very important result.”
“Cabotegravir long-acting PrEP is now approved for all at-risk populations, including men who have sex with men, transgender women, and cisgender women, after the results of HPTN 083 and 084,” commented Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, an infectious disease physician, professor of medicine, and associate chief in the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).
Dr. Gandhi, who was not involved in either study, is also director of the UCSF Center for AIDS Research and medical director of the HIV Clinic (“Ward 86”) at San Francisco General Hospital. “The incredible efficacy of long-acting PrEP for cisgender women shown by HPTN 084 is game-changing for our practice, and we have already instituted CAB LA across a range of populations at Ward 86,” she said in an interview. “The durability of the 89% additional efficacy of CAB LA over oral TDF/FTC is thrilling and will lead to a greater use of long-acting options.”
She acknowledged that information on potential interactions of GAHT was needed from the HPTN 083 trial. “That cabotegravir levels did not change with the use of estradiol or spironolactone for gender-affirming therapy is important news for our practice and to reassure our TGW that they can safely and effectively use CAB LA for HIV prevention.”
The HPTN 084 and 083 trials were funded by the National Institutes for Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Delany-Moretlwe, Dr. Grinsztejn, and Dr. Gandhi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AIDS 2022
Children and COVID: Weekly cases top 95,000, admissions continue to rise
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.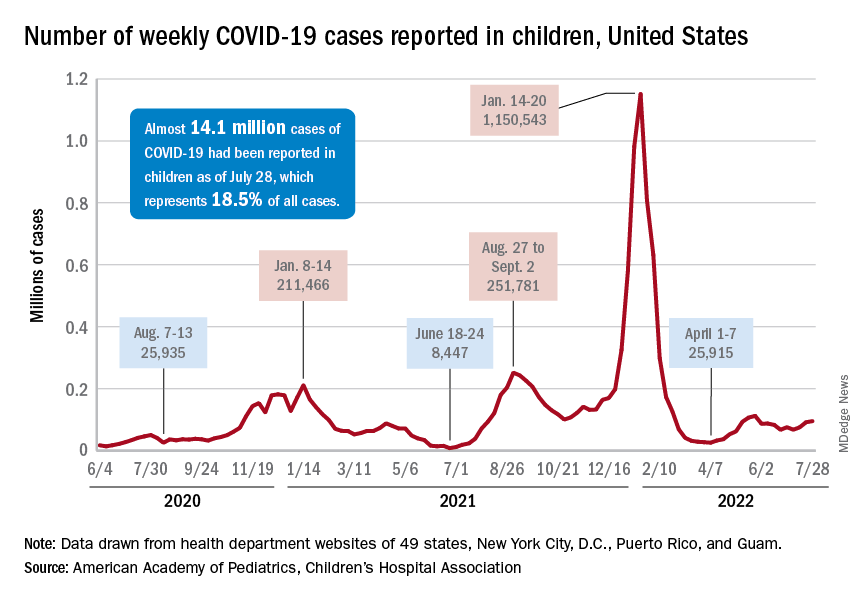
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.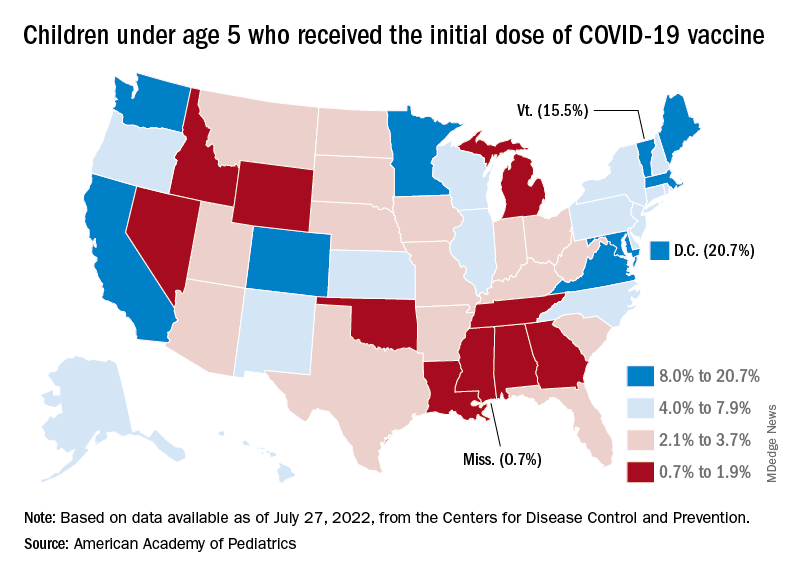
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
New pediatric COVID-19 cases increased for the third straight week as a substantial number of children under age 5 years started to receive their second doses of the vaccine.
Despite the 3-week trend, however, there are some positive signs. The new-case count for the latest reporting week (July 22-28) was over 95,000, but the 3.9% increase over the previous week’s 92,000 cases is much smaller than that week’s (July 15-21) corresponding jump of almost 22% over the July 8-14 total (75,000), according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
On the not-so-positive side is the trend in admissions among children aged 0-17 years, which continue to climb steadily and have nearly equaled the highest rate seen during the Delta surge in 2021. The rate on July 29 was 0.46 admissions per 100,000 population, and the highest rate over the course of the Delta surge was 0.47 per 100,000, but the all-time high from the Omicron surge – 1.25 per 100,000 in mid-January – is still a long way off, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A similar situation is occurring with emergency department visits, but there is differentiation by age group. Among those aged 0-11 years, visits with diagnosed COVID made up 6.5% of all their ED visits on July 25, which was well above the high (4.0%) during the Delta surge, the CDC said.
That is not the case, however, for the older children, for whom rates are rising more slowly. Those aged 12-15 have reached 3.4% so far this summer, as have the 16- to 17-years-olds, versus Delta highs last year of around 7%, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. As with admissions, though, current rates are well below the all-time Omicron high points, the CDC data show.
Joining the ranks of the fully vaccinated
Over the last 2 weeks, the first children to receive the COVID vaccine after its approval for those under age 5 years have been coming back for their second doses. Almost 50,000, about 0.3% of all those in that age group, had done so by July 27. Just over 662,000, about 3.4% of the total under-5 population, have received at least one dose, the CDC said.
Meanwhile, analysis of “data from the first several weeks following availability of the vaccine in this age group indicate high variability across states,” the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. In the District of Columbia, 20.7% of all children under age 5 have received an initial dose as of July 27, as have 15.5% of those in Vermont and 12.5% in Massachusetts. No other state was above 10%, but Mississippi, at 0.7%, was the only one below 1%.
The older children, obviously, have a head start, so their numbers are much higher. At the state level, Vermont has the highest initial dose rate, 69%, for those aged 5-11 years, while Alabama, Mississippi, and Wyoming, at 17%, are looking up at everyone else in the country. Among children aged 12-17 years, D.C. is the highest with 100% vaccination – Massachusetts and Rhode Island are at 98% – and Wyoming is the lowest with 40%, the AAP said.
Low calcium, potassium key risk factors for kidney stones
as well as their symptomatic recurrence, a population-based study of dietary factors shows.
“Our research is of particular importance as recommendations for preventing symptomatic recurrence of kidney stones has largely been based on dietary factors associated with the incidence rather than the recurrence of stone formation,” Api Chewcharat, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in a video discussing the study.
“We recommend a daily intake of calcium of approximately 1,200 mg and a diet that is high in potassium, especially high in fruits and vegetables, in order to prevent both incident and recurrent symptomatic kidney stone formation,” he stressed.
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Lower dietary calcium, potassium, and fluid associated with increased incidence
Some 411 patients with incident symptomatic kidney stone formation were recruited. Diets were compared between them and 384 controls. Patients were seen at the Mayo Clinic in either Minnesota or Florida between Jan. 1, 2009, and Aug. 31, 2018. “Dietary factors were based on a Viocare food frequency questionnaire administered during a baseline in-person study visit,” Dr. Chewcharat and colleagues observed.
During a median follow-up of 4.1 years, 73 patients experienced a symptomatic recurrence. In a fully adjusted analysis, a dietary calcium intake less than 1,200 mg/d was associated with incident stone formation. Similarly, among participants with a fluid intake less than 3,400 mL/d – about nine 12-oz glasses of fluid – was also associated with incident stone formation, as was a lower intake of dietary potassium, caffeine, and phytate. Phytate is an antioxidant found in whole grains, nuts, and other foods that can increase calcium absorption and urinary calcium excretion.
After excluding patients who were taking either a thiazide diuretic or a calcium supplement, lower dietary calcium and potassium, fluid, and phytate intake remained significantly associated with incident stone formation.
However, only lower dietary calcium intake was associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence, although a lower dietary potassium intake was also associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence in an analysis that adjusted for body mass index, fluid, and energy intake.
As the authors suggested, patients may be less keen to adjust their diet to prevent the development of incident kidney stones. On the other hand, they may be much more willing to adjust their diet to prevent their symptomatic recurrence. The Department of Agriculture currently recommends that individuals get approximately 1,200 mg/d of dietary calcium which, given the study results, appears to be justified for the prevention of symptomatic stone recurrence.
A higher-calcium diet is associated with a higher urinary pH, and citrate confers an alkali load which helps protect against the formation of calcium oxalate stones. Foods that are high in potassium also contain more fluid, citrate, and phytate, which, again, have been reported to be protective against kidney stones. “Changing your diet to prevent kidney stones can be very difficult,” Andrew Rule, MD, a nephrologist at the Mayo Clinic said in a statement.
“Thus, knowing the dietary factors that are most important for preventing kidney stone recurrence can help patients and providers know what to prioritize,” he added.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as well as their symptomatic recurrence, a population-based study of dietary factors shows.
“Our research is of particular importance as recommendations for preventing symptomatic recurrence of kidney stones has largely been based on dietary factors associated with the incidence rather than the recurrence of stone formation,” Api Chewcharat, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in a video discussing the study.
“We recommend a daily intake of calcium of approximately 1,200 mg and a diet that is high in potassium, especially high in fruits and vegetables, in order to prevent both incident and recurrent symptomatic kidney stone formation,” he stressed.
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Lower dietary calcium, potassium, and fluid associated with increased incidence
Some 411 patients with incident symptomatic kidney stone formation were recruited. Diets were compared between them and 384 controls. Patients were seen at the Mayo Clinic in either Minnesota or Florida between Jan. 1, 2009, and Aug. 31, 2018. “Dietary factors were based on a Viocare food frequency questionnaire administered during a baseline in-person study visit,” Dr. Chewcharat and colleagues observed.
During a median follow-up of 4.1 years, 73 patients experienced a symptomatic recurrence. In a fully adjusted analysis, a dietary calcium intake less than 1,200 mg/d was associated with incident stone formation. Similarly, among participants with a fluid intake less than 3,400 mL/d – about nine 12-oz glasses of fluid – was also associated with incident stone formation, as was a lower intake of dietary potassium, caffeine, and phytate. Phytate is an antioxidant found in whole grains, nuts, and other foods that can increase calcium absorption and urinary calcium excretion.
After excluding patients who were taking either a thiazide diuretic or a calcium supplement, lower dietary calcium and potassium, fluid, and phytate intake remained significantly associated with incident stone formation.
However, only lower dietary calcium intake was associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence, although a lower dietary potassium intake was also associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence in an analysis that adjusted for body mass index, fluid, and energy intake.
As the authors suggested, patients may be less keen to adjust their diet to prevent the development of incident kidney stones. On the other hand, they may be much more willing to adjust their diet to prevent their symptomatic recurrence. The Department of Agriculture currently recommends that individuals get approximately 1,200 mg/d of dietary calcium which, given the study results, appears to be justified for the prevention of symptomatic stone recurrence.
A higher-calcium diet is associated with a higher urinary pH, and citrate confers an alkali load which helps protect against the formation of calcium oxalate stones. Foods that are high in potassium also contain more fluid, citrate, and phytate, which, again, have been reported to be protective against kidney stones. “Changing your diet to prevent kidney stones can be very difficult,” Andrew Rule, MD, a nephrologist at the Mayo Clinic said in a statement.
“Thus, knowing the dietary factors that are most important for preventing kidney stone recurrence can help patients and providers know what to prioritize,” he added.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as well as their symptomatic recurrence, a population-based study of dietary factors shows.
“Our research is of particular importance as recommendations for preventing symptomatic recurrence of kidney stones has largely been based on dietary factors associated with the incidence rather than the recurrence of stone formation,” Api Chewcharat, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in a video discussing the study.
“We recommend a daily intake of calcium of approximately 1,200 mg and a diet that is high in potassium, especially high in fruits and vegetables, in order to prevent both incident and recurrent symptomatic kidney stone formation,” he stressed.
The study was published online in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Lower dietary calcium, potassium, and fluid associated with increased incidence
Some 411 patients with incident symptomatic kidney stone formation were recruited. Diets were compared between them and 384 controls. Patients were seen at the Mayo Clinic in either Minnesota or Florida between Jan. 1, 2009, and Aug. 31, 2018. “Dietary factors were based on a Viocare food frequency questionnaire administered during a baseline in-person study visit,” Dr. Chewcharat and colleagues observed.
During a median follow-up of 4.1 years, 73 patients experienced a symptomatic recurrence. In a fully adjusted analysis, a dietary calcium intake less than 1,200 mg/d was associated with incident stone formation. Similarly, among participants with a fluid intake less than 3,400 mL/d – about nine 12-oz glasses of fluid – was also associated with incident stone formation, as was a lower intake of dietary potassium, caffeine, and phytate. Phytate is an antioxidant found in whole grains, nuts, and other foods that can increase calcium absorption and urinary calcium excretion.
After excluding patients who were taking either a thiazide diuretic or a calcium supplement, lower dietary calcium and potassium, fluid, and phytate intake remained significantly associated with incident stone formation.
However, only lower dietary calcium intake was associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence, although a lower dietary potassium intake was also associated with a higher risk for symptomatic recurrence in an analysis that adjusted for body mass index, fluid, and energy intake.
As the authors suggested, patients may be less keen to adjust their diet to prevent the development of incident kidney stones. On the other hand, they may be much more willing to adjust their diet to prevent their symptomatic recurrence. The Department of Agriculture currently recommends that individuals get approximately 1,200 mg/d of dietary calcium which, given the study results, appears to be justified for the prevention of symptomatic stone recurrence.
A higher-calcium diet is associated with a higher urinary pH, and citrate confers an alkali load which helps protect against the formation of calcium oxalate stones. Foods that are high in potassium also contain more fluid, citrate, and phytate, which, again, have been reported to be protective against kidney stones. “Changing your diet to prevent kidney stones can be very difficult,” Andrew Rule, MD, a nephrologist at the Mayo Clinic said in a statement.
“Thus, knowing the dietary factors that are most important for preventing kidney stone recurrence can help patients and providers know what to prioritize,” he added.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PRECEEDINGS
COVID skin manifestations vary by type of variant, U.K. study finds
during the Omicron and Delta waves.
Among the key findings, the study shows that skin involvement during the Omicron wave was less frequent than during the Delta wave (11.4% vs. 17.6%), skin symptoms generally resolved more quickly, and that the risk for skin symptoms was similar whether patients had or had not been vaccinated, according to a team led by Alessia Visconti, PhD, a research fellow in the department of twin research and genetic epidemiology, King’s College, London.
These data are consistent with the experience of those dermatologists who have been following this area closely, according to Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
“Anecdotally, we thought we were seeing fewer skin symptoms with Omicron versus Delta and the ancestral strains, and now this study shows it is true,” said Dr. Freeman, who is also principal investigator of the American Academy of Dermatology’s International Dermatology COVID-19 Registry.
The data also confirm that the skin is less likely to be involved than in past waves of COVID-19 infections.
“Up to this point, it was hard to know if we were seeing fewer referrals for COVID-related skin rashes or if clinicians had just become more comfortable with these rashes and were not referring them as often,” added Dr. Freeman, who was among the study coauthors.
Data captured from 348,691 patients
The data from the study was generated by 348,691 users in the United Kingdom of the ZOE COVID study app, a smartphone-based tool introduced relatively early in the pandemic. It asked users to provide demographic data, information on COVID-19 symptoms, including those involving the skin, and treatments. Of 33 COVID-related symptoms included in the app, five related to the skin (acral rash, burning rash, erythematopapular rash, urticarial rash, and unusual hair loss).
While the focus of this study was to compare skin manifestations during the Omicron wave with the Delta wave of COVID-19, the investigators also had data on the experience in 2020 with wild-type COVID-19 that preceded both variants. Overall, this showed a stepwise decline in skin symptoms overall, as well in as skin symptoms that occurred in the absence of systemic symptoms.
“The shift in the skin manifestations makes sense when you think about the change that is also being seen in the systemic symptoms,” said Dr. Freeman, referring to lower rates of cough and loss of smell but higher rates of sore throat and fatigue. “Omicron is achieving immune escape, which is why there is a shift in involved tissues,” she said in an interview.
Previous data collected during the wild-type COVID-19 stage of the pandemic by the same group of investigators showed that 17% of patients reported skin rash as the first symptom of COVID-19 infection, and 21% reported skin rash as the only clinical sign of infection.
In the Delta and Omicron waves, skin rash was an isolated initial symptom in only 0.8% and 0.5% of patients, respectively. (The authors noted that, in the United Kingdom, the first documented samples of the Delta variant were detected in October 2020, and the first documented samples of the Omicron variant were detected in November 2021.)
During the early stages of wild-type COVID, an acral rash was characteristic, occurring in 3.1% of patients, according to the U.K. data. In the Delta wave, acral rashes, at an incidence of 1.1% remained positively correlated with a diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. In the Omicron wave, acral rashes were observed in only 0.7% of patients and were no longer statistically correlated with a positive COVID diagnosis.
Characteristic cutaneous symptoms are evolving
Early in the course of the COVID-19 epidemic, more than 30 types of rashes were observed in patients with COVID-19 infection. Cutaneous symptoms continue to be diverse, but some, such as acral rash, are being seen less frequently. For example, the odds ratio of a positive COVID-19 diagnosis among those with an erythematopapular rash fell from 1.76 to 1.08 between the Delta and Omicron waves.
While specific cutaneous symptoms are less predictive of a diagnosis of COVID-19, clinicians should not discount cutaneous symptoms as a sign of disease, according to Veronique Bataille, MD, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at King’s College.
“You need to keep an open mind” regarding cutaneous signs and a diagnosis of COVID-19, Dr. Bataille, one of the coauthors of the U.K. report, said in an interview. In general, she considers a low threshold of suspicion appropriate. “If the patient has no past history of skin disease and no other triggers for a rash, then, in a high prevalence area, COVID must be suspected.”
In most cases, the rash resolves on its own, but Dr. Bataille emphasized the need for individualized care. Even as the risk of life-threatening COVID-19 infections appears to be diminishing with current variants, cutaneous manifestations can be severe.
“There are cases of long COVID affecting the skin, such as urticaria or a lichenoid erythematopapular rash, both of which can be very pruritic and difficult to control,” she said.
Dr. Freeman echoed the importance of an individualized approach. She agreed that most cutaneous symptoms are self-limited, but there are exceptions and treatments vary for the different types of skin involvement. “I think another point to consider when examining skin lesions is monkey pox. The fact that these are overlapping outbreaks should not be ignored. You need to be alert for both.”
Dr. Visconti, Dr. Freeman, and Dr. Bataille reported no potential conflicts of interest.
during the Omicron and Delta waves.
Among the key findings, the study shows that skin involvement during the Omicron wave was less frequent than during the Delta wave (11.4% vs. 17.6%), skin symptoms generally resolved more quickly, and that the risk for skin symptoms was similar whether patients had or had not been vaccinated, according to a team led by Alessia Visconti, PhD, a research fellow in the department of twin research and genetic epidemiology, King’s College, London.
These data are consistent with the experience of those dermatologists who have been following this area closely, according to Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
“Anecdotally, we thought we were seeing fewer skin symptoms with Omicron versus Delta and the ancestral strains, and now this study shows it is true,” said Dr. Freeman, who is also principal investigator of the American Academy of Dermatology’s International Dermatology COVID-19 Registry.
The data also confirm that the skin is less likely to be involved than in past waves of COVID-19 infections.
“Up to this point, it was hard to know if we were seeing fewer referrals for COVID-related skin rashes or if clinicians had just become more comfortable with these rashes and were not referring them as often,” added Dr. Freeman, who was among the study coauthors.
Data captured from 348,691 patients
The data from the study was generated by 348,691 users in the United Kingdom of the ZOE COVID study app, a smartphone-based tool introduced relatively early in the pandemic. It asked users to provide demographic data, information on COVID-19 symptoms, including those involving the skin, and treatments. Of 33 COVID-related symptoms included in the app, five related to the skin (acral rash, burning rash, erythematopapular rash, urticarial rash, and unusual hair loss).
While the focus of this study was to compare skin manifestations during the Omicron wave with the Delta wave of COVID-19, the investigators also had data on the experience in 2020 with wild-type COVID-19 that preceded both variants. Overall, this showed a stepwise decline in skin symptoms overall, as well in as skin symptoms that occurred in the absence of systemic symptoms.
“The shift in the skin manifestations makes sense when you think about the change that is also being seen in the systemic symptoms,” said Dr. Freeman, referring to lower rates of cough and loss of smell but higher rates of sore throat and fatigue. “Omicron is achieving immune escape, which is why there is a shift in involved tissues,” she said in an interview.
Previous data collected during the wild-type COVID-19 stage of the pandemic by the same group of investigators showed that 17% of patients reported skin rash as the first symptom of COVID-19 infection, and 21% reported skin rash as the only clinical sign of infection.
In the Delta and Omicron waves, skin rash was an isolated initial symptom in only 0.8% and 0.5% of patients, respectively. (The authors noted that, in the United Kingdom, the first documented samples of the Delta variant were detected in October 2020, and the first documented samples of the Omicron variant were detected in November 2021.)
During the early stages of wild-type COVID, an acral rash was characteristic, occurring in 3.1% of patients, according to the U.K. data. In the Delta wave, acral rashes, at an incidence of 1.1% remained positively correlated with a diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. In the Omicron wave, acral rashes were observed in only 0.7% of patients and were no longer statistically correlated with a positive COVID diagnosis.
Characteristic cutaneous symptoms are evolving
Early in the course of the COVID-19 epidemic, more than 30 types of rashes were observed in patients with COVID-19 infection. Cutaneous symptoms continue to be diverse, but some, such as acral rash, are being seen less frequently. For example, the odds ratio of a positive COVID-19 diagnosis among those with an erythematopapular rash fell from 1.76 to 1.08 between the Delta and Omicron waves.
While specific cutaneous symptoms are less predictive of a diagnosis of COVID-19, clinicians should not discount cutaneous symptoms as a sign of disease, according to Veronique Bataille, MD, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at King’s College.
“You need to keep an open mind” regarding cutaneous signs and a diagnosis of COVID-19, Dr. Bataille, one of the coauthors of the U.K. report, said in an interview. In general, she considers a low threshold of suspicion appropriate. “If the patient has no past history of skin disease and no other triggers for a rash, then, in a high prevalence area, COVID must be suspected.”
In most cases, the rash resolves on its own, but Dr. Bataille emphasized the need for individualized care. Even as the risk of life-threatening COVID-19 infections appears to be diminishing with current variants, cutaneous manifestations can be severe.
“There are cases of long COVID affecting the skin, such as urticaria or a lichenoid erythematopapular rash, both of which can be very pruritic and difficult to control,” she said.
Dr. Freeman echoed the importance of an individualized approach. She agreed that most cutaneous symptoms are self-limited, but there are exceptions and treatments vary for the different types of skin involvement. “I think another point to consider when examining skin lesions is monkey pox. The fact that these are overlapping outbreaks should not be ignored. You need to be alert for both.”
Dr. Visconti, Dr. Freeman, and Dr. Bataille reported no potential conflicts of interest.
during the Omicron and Delta waves.
Among the key findings, the study shows that skin involvement during the Omicron wave was less frequent than during the Delta wave (11.4% vs. 17.6%), skin symptoms generally resolved more quickly, and that the risk for skin symptoms was similar whether patients had or had not been vaccinated, according to a team led by Alessia Visconti, PhD, a research fellow in the department of twin research and genetic epidemiology, King’s College, London.
These data are consistent with the experience of those dermatologists who have been following this area closely, according to Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of MGH Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
“Anecdotally, we thought we were seeing fewer skin symptoms with Omicron versus Delta and the ancestral strains, and now this study shows it is true,” said Dr. Freeman, who is also principal investigator of the American Academy of Dermatology’s International Dermatology COVID-19 Registry.
The data also confirm that the skin is less likely to be involved than in past waves of COVID-19 infections.
“Up to this point, it was hard to know if we were seeing fewer referrals for COVID-related skin rashes or if clinicians had just become more comfortable with these rashes and were not referring them as often,” added Dr. Freeman, who was among the study coauthors.
Data captured from 348,691 patients
The data from the study was generated by 348,691 users in the United Kingdom of the ZOE COVID study app, a smartphone-based tool introduced relatively early in the pandemic. It asked users to provide demographic data, information on COVID-19 symptoms, including those involving the skin, and treatments. Of 33 COVID-related symptoms included in the app, five related to the skin (acral rash, burning rash, erythematopapular rash, urticarial rash, and unusual hair loss).
While the focus of this study was to compare skin manifestations during the Omicron wave with the Delta wave of COVID-19, the investigators also had data on the experience in 2020 with wild-type COVID-19 that preceded both variants. Overall, this showed a stepwise decline in skin symptoms overall, as well in as skin symptoms that occurred in the absence of systemic symptoms.
“The shift in the skin manifestations makes sense when you think about the change that is also being seen in the systemic symptoms,” said Dr. Freeman, referring to lower rates of cough and loss of smell but higher rates of sore throat and fatigue. “Omicron is achieving immune escape, which is why there is a shift in involved tissues,” she said in an interview.
Previous data collected during the wild-type COVID-19 stage of the pandemic by the same group of investigators showed that 17% of patients reported skin rash as the first symptom of COVID-19 infection, and 21% reported skin rash as the only clinical sign of infection.
In the Delta and Omicron waves, skin rash was an isolated initial symptom in only 0.8% and 0.5% of patients, respectively. (The authors noted that, in the United Kingdom, the first documented samples of the Delta variant were detected in October 2020, and the first documented samples of the Omicron variant were detected in November 2021.)
During the early stages of wild-type COVID, an acral rash was characteristic, occurring in 3.1% of patients, according to the U.K. data. In the Delta wave, acral rashes, at an incidence of 1.1% remained positively correlated with a diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. In the Omicron wave, acral rashes were observed in only 0.7% of patients and were no longer statistically correlated with a positive COVID diagnosis.
Characteristic cutaneous symptoms are evolving
Early in the course of the COVID-19 epidemic, more than 30 types of rashes were observed in patients with COVID-19 infection. Cutaneous symptoms continue to be diverse, but some, such as acral rash, are being seen less frequently. For example, the odds ratio of a positive COVID-19 diagnosis among those with an erythematopapular rash fell from 1.76 to 1.08 between the Delta and Omicron waves.
While specific cutaneous symptoms are less predictive of a diagnosis of COVID-19, clinicians should not discount cutaneous symptoms as a sign of disease, according to Veronique Bataille, MD, PhD, a consultant dermatologist at King’s College.
“You need to keep an open mind” regarding cutaneous signs and a diagnosis of COVID-19, Dr. Bataille, one of the coauthors of the U.K. report, said in an interview. In general, she considers a low threshold of suspicion appropriate. “If the patient has no past history of skin disease and no other triggers for a rash, then, in a high prevalence area, COVID must be suspected.”
In most cases, the rash resolves on its own, but Dr. Bataille emphasized the need for individualized care. Even as the risk of life-threatening COVID-19 infections appears to be diminishing with current variants, cutaneous manifestations can be severe.
“There are cases of long COVID affecting the skin, such as urticaria or a lichenoid erythematopapular rash, both of which can be very pruritic and difficult to control,” she said.
Dr. Freeman echoed the importance of an individualized approach. She agreed that most cutaneous symptoms are self-limited, but there are exceptions and treatments vary for the different types of skin involvement. “I think another point to consider when examining skin lesions is monkey pox. The fact that these are overlapping outbreaks should not be ignored. You need to be alert for both.”
Dr. Visconti, Dr. Freeman, and Dr. Bataille reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Devices to detect skin cancer: FDA advisers offer mixed views
.
So far, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has cleared two devices. Both are computer-aided skin lesion classification devices meant to help clinicians assess cases of suspected melanoma.
Both were given a class III designation. That classification is intended for products that are considered to have a high risk of harm because of flawed design or implementation. Many such devices are under development, and there has been a proposal to include these devices in class II, which is less restrictive.
The FDA turned to one of its expert panels for advice. At a meeting held on Aug. 29, experts on the panel offered differing views and expressed concerns about the accuracy of these devices.
This was the second day of meetings of the general and plastic surgery devices panel of the FDA’s Medical Devices Advisory Committee. On the previous day, the panel held a wide-ranging discussion about expanding use of skin lesion analyzer devices.
The FDA sought the expert panel’s advice concerning a field that appears to be heating up quickly after relatively quiet times.
Two devices have been approved by the FDA so far, but only one is still being promoted – SciBase AB’s Nevisense. The Swedish company announced in May 2020 that it had received FDA approval for Nevisense 3.0, the third generation of their Nevisense system for early melanoma detection, an AI-based point-of-care system for the noninvasive evaluation of irregular moles.
The other device, known as MelaFind, was acquired by Strata Skin Sciences, but the company said in 2017 that it discontinued research and development, sales, and support activity related to the device, according to a filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
But there’s been a swell in recent years in the number of publications related to the use of AI and machine learning, which could give rise to new tools for aiding in the diagnosis of skin conditions, including cancer. Google is among the companies that are involved in these efforts.
So, the FDA asked the expert panel to discuss a series of questions related to how the agency should weigh the risks of computer-aided devices for melanoma diagnosis. The agency also asked the panel to provide feedback about how well risks associated with such devices and tools might be managed and to offer suggestions.
The discussion at the July 29 meeting spun beyond narrow questions about reclassification of the current class III devices to topics involving emerging technology, such as efforts to apply AI to dermatology.
“Innovation continues. Medical device developers are anxious to plan how they might be able to develop the level of evidence that would meet your expectations” for future products, Binita Ashar, MD, a senior official in FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, told the panel.
Company CEO backs tougher regulation
Simon Grant, the chief executive of SciBase, which markets Nevisense, the first and only skin cancer–detecting device currently on the U.S. market, sought to make a case for sticking with the tougher class III regulations.
Speaking during the public comment session, Mr. Grant said switching to class II designations would weaken the standards used in clearing products that analyze skin lesions so as to put patients at risk.
Under the FDA’s rules, the agency designates as class III devices that present potential unreasonable risk of illness or injury. Only about 10% of devices fall into this category. Such devices include implantable pacemakers and breast implants, as well as SciBase’s Nevisense.
About 43% of medical devices fall into the class II category, which includes powered wheelchairs and some pregnancy test kits, the FDA website says.
Class I medical devices pose minimal potential for harm and tend to be simpler in design. These include enema kits and elastic bandages, the FDA says.
Mr. Grant told the meeting that in his career he has worked on two class III products and about 20 class II products. (He had previously worked at medical startups Synectics Medical and Neoventa, as well as established multinationals such as Medtronic.)
“I can tell you that – practically – the FDA has many fewer sticks and much less control when it comes to class II devices,” he said. He offered an example of a manufacturer of a class II device having more latitude in making small changes to products without notifying the FDA.
In his hypothetical example, such a change could have unintended consequences, and “with AI systems, small changes can result in large and nonlinear or even random effects,” Mr. Grant said. “But it’s too late if the product is on the market and the harm has already occurred,” he said.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association also protested the reclassifying of approved computer-aided melanoma detection class III devices.
In a statement posted on the FDA website as part of the materials for the meeting, the ASDSA raised a series of concerns about the prospects of expanded U.S. use of tools for assisting in diagnosing melanoma, including ones that would be marketed to consumers.
“To the extent that algorithms and devices for patient self-diagnosis of skin lesions are already widely available, they should be required to include detailed disclaimers that include that they are for entertainment and educational purposes and not a diagnostic device, that they are not approved by dermatologists or a recognized medical regulatory authority for self-diagnosis,” the ASDSA said.
Devices and algorithms in screening tools “are not highly regulated and remain unproven. They may result in wrong diagnoses, missed diagnoses, or over- or underdiagnosis,” the ASDSA added. “Both patients at low risk and those at high risk are better served by scheduling an in-person examination with a board-certified dermatologist, who can also help them determine the appropriate future skin screening schedule that is most appropriate for them.”
‘Stepping stone’
However, there is strong consumer demand for better information about skin conditions, and many patients face hurdles in going to dermatologists.
Google research has shown that consumers are seeking “a stepping stone” between the information they can easily find online and what they could get from a medical professional, said Lily Peng, MD, PhD, a director of product management for the health AI team at Google. Dr. Peng was a scheduled presenter at the July 29 meeting.
Consumers often are looking for more information on common conditions such as acne and poison ivy, and they sometimes face challenges in getting access to clinicians, she said.
“There are many unmet needs for consumers experiencing skin issues, many of which are lower-acuity conditions. There’s a big opportunity to increase accessibility and relevance of health journeys for consumers,” Dr. Peng said. “We have heard from consumers that they would like to have a self-help tool for nonserious conditions so they can decide when to seek medical attention.”
Dr. Peng’s presentation was not directly related to the question of class II or class III designation for existing products. Instead, her talk served as a glimpse into the work already underway in creating apps and tools for consumers.
Google researchers have published a number of studies in recent years about the use of AI to improve dermatology diagnosis.
A 2020 article reported on Google’s test of a form of AI known as deep learning system (DLS) to provide a differential diagnosis of skin conditions. On 963 validation cases, where a rotating panel of three board-certified dermatologists defined the reference standard, the DLS was noninferior to six other dermatologists and was superior to six primary care physicians (PCPs) and six nurse practitioners (NPs), according to a summary of the article.
A 2021 report published in JAMA Network Open said that use of an AI tool was associated with a higher agreement rate with dermatologists’ reference diagnoses for both PCPs and NPs.
In a 2021 blog post, Google scientists wrote that their AI model that powers a tool for checking skin conditions had earned European clearance, known as a CE mark, as a class I medical device.
SkinVision has an app that the company says “is available worldwide (with the exception of the USA and Canada).” The firm’s website includes a link where people in the United States and Canada can sign up for notifications about when SkinVision will be available in these nations.
‘Not ready for prime time’
The FDA panel did not cast formal votes at the July 29 meeting. Rather, the members engaged in broad discussions about risks and potential benefits of new tools for aiding in the detection of skin cancer.
Among the key issues discussed was a question of whether the FDA could impose requirements and restrictions, known as special controls, to provide “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness” for computer-aided devices that provide adjunctive diagnostic information to dermatologists about lesions suspicious for melanoma.
Among the potential special controls would be clinical performance testing in regards to rates of the sensitivity (true-positive rate) and specificity (true-negative rate).
The FDA could also look at requirements on software validation and verification and cybersecurity testing, as well as directions on labeling so as to mitigate risk.
Dermatologists serving on the panel called for caution in proceeding with steps that would make it easier for companies to market tools for aiding in melanoma diagnosis than it would be within the class III framework used for MelaFind and Nevisense.
Many expressed concerns about the need to design studies that would answer questions about how well new tools could accurately identify concerning lesions.
The phrase “not ready for prime time” was used at least three times during the discussion.
FDA panelist Maral Skelsey, MD, a skin cancer specialist from Chevy Chase, Maryland, said that over the years, she had used both Nevisense and MelaFind.
She said she had found MelaFind “unusable,” owing in large part to the high number of false positives it generated. The device also was limited as to where on patients’ bodies it could be used.
However, she spoke with enthusiasm about the prospects for better devices to aid in diagnosis of skin lesions. “It’s an area where we’re on the verge, and we really need these devices. There’s a need for patients to be able to examine themselves, for nondermatologists to be able to assess lesions,” Dr. Skelsey said.
But this field is “just not ready for prime time” yet, even with special controls, Dr. Skelsey said. To loosen approval standards too quickly could be a “detriment to what’s coming down the pipeline,” she said.
“It’s harmful to things that are likely to be around the corner,” she said.
FDA panelist Renata Block, PA-C, who works in a Chicago dermatology practice, pressed for maintaining a class III designation. “We are not ready for prime time yet, though the data that is coming down the pipeline on what we have is quite exciting,” Ms. Block said.
FDA panelist Karla V. Ballman, PhD, a statistician from Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said there would need to be a clear standard for clinical performance before proceeding toward reclassification of devices for aid in detecting melanoma. “I just don’t think it’s ready for prime time at this point and should remain in class III,” she said.
But there was support from some panelists for the idea of a lower bar for clearance, combined with special controls to ensure patient safety.
In expressing her view, FDA panelist Katalin Roth, MD, JD, professor of medicine, George Washington University, Washington, said she was an outlier in her support for the agency’s view that these risks could be managed and that future tools could allow more patients to take a step on the pathway toward critical diagnoses.
“I deal with a lot of people with cancer as a palliative care physician,” Dr. Roth said. “I think what we’re missing here is the issue of time. Melanoma is a terrible disease, and missing the diagnosis is a terrible thing, but I think special controls would be sufficient to counter the concerns of my colleagues on the committee.”
The FDA’s Dr. Ashar ended the meeting with questions posed to one panelist, Veronica Rotemberg, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Rotemberg has for years been working in the field of research on developing AI and other computer-based tools for detecting and diagnosing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
She has been publicly skeptical of the performance of commercial apps that scan moles and other lesions and that claim to identify which are cancerous. A May blog post on the Memorial Sloan Kettering website highlighted a recent British Journal of Dermatology article in which Dr. Rotemberg and coauthors reported on their evaluations of commercial apps. They judged them to be on average only 59% accurate, the blog post said.
However, during an earlier discussion at the meeting, she had spoken more positively about the prospects for using special controls in the near term to mitigate risk, although she said she would have a “very long list” of these requirements.
In the closing exchange with Dr. Ashar, Dr. Rotemberg outlined steps that could potentially ensure the safe use of tools to aid in melanoma screening. These included a need for postmarketing surveillance, which would require evaluation over time of algorithms used in tools meant to detect skin cancer.
“We need to have a mechanism for sampling,” Dr. Rotemberg said. “Most of our data is electronic now anyway, so comparing an algorithm and performance with biopsy results should not be that challenging.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
So far, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has cleared two devices. Both are computer-aided skin lesion classification devices meant to help clinicians assess cases of suspected melanoma.
Both were given a class III designation. That classification is intended for products that are considered to have a high risk of harm because of flawed design or implementation. Many such devices are under development, and there has been a proposal to include these devices in class II, which is less restrictive.
The FDA turned to one of its expert panels for advice. At a meeting held on Aug. 29, experts on the panel offered differing views and expressed concerns about the accuracy of these devices.
This was the second day of meetings of the general and plastic surgery devices panel of the FDA’s Medical Devices Advisory Committee. On the previous day, the panel held a wide-ranging discussion about expanding use of skin lesion analyzer devices.
The FDA sought the expert panel’s advice concerning a field that appears to be heating up quickly after relatively quiet times.
Two devices have been approved by the FDA so far, but only one is still being promoted – SciBase AB’s Nevisense. The Swedish company announced in May 2020 that it had received FDA approval for Nevisense 3.0, the third generation of their Nevisense system for early melanoma detection, an AI-based point-of-care system for the noninvasive evaluation of irregular moles.
The other device, known as MelaFind, was acquired by Strata Skin Sciences, but the company said in 2017 that it discontinued research and development, sales, and support activity related to the device, according to a filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
But there’s been a swell in recent years in the number of publications related to the use of AI and machine learning, which could give rise to new tools for aiding in the diagnosis of skin conditions, including cancer. Google is among the companies that are involved in these efforts.
So, the FDA asked the expert panel to discuss a series of questions related to how the agency should weigh the risks of computer-aided devices for melanoma diagnosis. The agency also asked the panel to provide feedback about how well risks associated with such devices and tools might be managed and to offer suggestions.
The discussion at the July 29 meeting spun beyond narrow questions about reclassification of the current class III devices to topics involving emerging technology, such as efforts to apply AI to dermatology.
“Innovation continues. Medical device developers are anxious to plan how they might be able to develop the level of evidence that would meet your expectations” for future products, Binita Ashar, MD, a senior official in FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, told the panel.
Company CEO backs tougher regulation
Simon Grant, the chief executive of SciBase, which markets Nevisense, the first and only skin cancer–detecting device currently on the U.S. market, sought to make a case for sticking with the tougher class III regulations.
Speaking during the public comment session, Mr. Grant said switching to class II designations would weaken the standards used in clearing products that analyze skin lesions so as to put patients at risk.
Under the FDA’s rules, the agency designates as class III devices that present potential unreasonable risk of illness or injury. Only about 10% of devices fall into this category. Such devices include implantable pacemakers and breast implants, as well as SciBase’s Nevisense.
About 43% of medical devices fall into the class II category, which includes powered wheelchairs and some pregnancy test kits, the FDA website says.
Class I medical devices pose minimal potential for harm and tend to be simpler in design. These include enema kits and elastic bandages, the FDA says.
Mr. Grant told the meeting that in his career he has worked on two class III products and about 20 class II products. (He had previously worked at medical startups Synectics Medical and Neoventa, as well as established multinationals such as Medtronic.)
“I can tell you that – practically – the FDA has many fewer sticks and much less control when it comes to class II devices,” he said. He offered an example of a manufacturer of a class II device having more latitude in making small changes to products without notifying the FDA.
In his hypothetical example, such a change could have unintended consequences, and “with AI systems, small changes can result in large and nonlinear or even random effects,” Mr. Grant said. “But it’s too late if the product is on the market and the harm has already occurred,” he said.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association also protested the reclassifying of approved computer-aided melanoma detection class III devices.
In a statement posted on the FDA website as part of the materials for the meeting, the ASDSA raised a series of concerns about the prospects of expanded U.S. use of tools for assisting in diagnosing melanoma, including ones that would be marketed to consumers.
“To the extent that algorithms and devices for patient self-diagnosis of skin lesions are already widely available, they should be required to include detailed disclaimers that include that they are for entertainment and educational purposes and not a diagnostic device, that they are not approved by dermatologists or a recognized medical regulatory authority for self-diagnosis,” the ASDSA said.
Devices and algorithms in screening tools “are not highly regulated and remain unproven. They may result in wrong diagnoses, missed diagnoses, or over- or underdiagnosis,” the ASDSA added. “Both patients at low risk and those at high risk are better served by scheduling an in-person examination with a board-certified dermatologist, who can also help them determine the appropriate future skin screening schedule that is most appropriate for them.”
‘Stepping stone’
However, there is strong consumer demand for better information about skin conditions, and many patients face hurdles in going to dermatologists.
Google research has shown that consumers are seeking “a stepping stone” between the information they can easily find online and what they could get from a medical professional, said Lily Peng, MD, PhD, a director of product management for the health AI team at Google. Dr. Peng was a scheduled presenter at the July 29 meeting.
Consumers often are looking for more information on common conditions such as acne and poison ivy, and they sometimes face challenges in getting access to clinicians, she said.
“There are many unmet needs for consumers experiencing skin issues, many of which are lower-acuity conditions. There’s a big opportunity to increase accessibility and relevance of health journeys for consumers,” Dr. Peng said. “We have heard from consumers that they would like to have a self-help tool for nonserious conditions so they can decide when to seek medical attention.”
Dr. Peng’s presentation was not directly related to the question of class II or class III designation for existing products. Instead, her talk served as a glimpse into the work already underway in creating apps and tools for consumers.
Google researchers have published a number of studies in recent years about the use of AI to improve dermatology diagnosis.
A 2020 article reported on Google’s test of a form of AI known as deep learning system (DLS) to provide a differential diagnosis of skin conditions. On 963 validation cases, where a rotating panel of three board-certified dermatologists defined the reference standard, the DLS was noninferior to six other dermatologists and was superior to six primary care physicians (PCPs) and six nurse practitioners (NPs), according to a summary of the article.
A 2021 report published in JAMA Network Open said that use of an AI tool was associated with a higher agreement rate with dermatologists’ reference diagnoses for both PCPs and NPs.
In a 2021 blog post, Google scientists wrote that their AI model that powers a tool for checking skin conditions had earned European clearance, known as a CE mark, as a class I medical device.
SkinVision has an app that the company says “is available worldwide (with the exception of the USA and Canada).” The firm’s website includes a link where people in the United States and Canada can sign up for notifications about when SkinVision will be available in these nations.
‘Not ready for prime time’
The FDA panel did not cast formal votes at the July 29 meeting. Rather, the members engaged in broad discussions about risks and potential benefits of new tools for aiding in the detection of skin cancer.
Among the key issues discussed was a question of whether the FDA could impose requirements and restrictions, known as special controls, to provide “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness” for computer-aided devices that provide adjunctive diagnostic information to dermatologists about lesions suspicious for melanoma.
Among the potential special controls would be clinical performance testing in regards to rates of the sensitivity (true-positive rate) and specificity (true-negative rate).
The FDA could also look at requirements on software validation and verification and cybersecurity testing, as well as directions on labeling so as to mitigate risk.
Dermatologists serving on the panel called for caution in proceeding with steps that would make it easier for companies to market tools for aiding in melanoma diagnosis than it would be within the class III framework used for MelaFind and Nevisense.
Many expressed concerns about the need to design studies that would answer questions about how well new tools could accurately identify concerning lesions.
The phrase “not ready for prime time” was used at least three times during the discussion.
FDA panelist Maral Skelsey, MD, a skin cancer specialist from Chevy Chase, Maryland, said that over the years, she had used both Nevisense and MelaFind.
She said she had found MelaFind “unusable,” owing in large part to the high number of false positives it generated. The device also was limited as to where on patients’ bodies it could be used.
However, she spoke with enthusiasm about the prospects for better devices to aid in diagnosis of skin lesions. “It’s an area where we’re on the verge, and we really need these devices. There’s a need for patients to be able to examine themselves, for nondermatologists to be able to assess lesions,” Dr. Skelsey said.
But this field is “just not ready for prime time” yet, even with special controls, Dr. Skelsey said. To loosen approval standards too quickly could be a “detriment to what’s coming down the pipeline,” she said.
“It’s harmful to things that are likely to be around the corner,” she said.
FDA panelist Renata Block, PA-C, who works in a Chicago dermatology practice, pressed for maintaining a class III designation. “We are not ready for prime time yet, though the data that is coming down the pipeline on what we have is quite exciting,” Ms. Block said.
FDA panelist Karla V. Ballman, PhD, a statistician from Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said there would need to be a clear standard for clinical performance before proceeding toward reclassification of devices for aid in detecting melanoma. “I just don’t think it’s ready for prime time at this point and should remain in class III,” she said.
But there was support from some panelists for the idea of a lower bar for clearance, combined with special controls to ensure patient safety.
In expressing her view, FDA panelist Katalin Roth, MD, JD, professor of medicine, George Washington University, Washington, said she was an outlier in her support for the agency’s view that these risks could be managed and that future tools could allow more patients to take a step on the pathway toward critical diagnoses.
“I deal with a lot of people with cancer as a palliative care physician,” Dr. Roth said. “I think what we’re missing here is the issue of time. Melanoma is a terrible disease, and missing the diagnosis is a terrible thing, but I think special controls would be sufficient to counter the concerns of my colleagues on the committee.”
The FDA’s Dr. Ashar ended the meeting with questions posed to one panelist, Veronica Rotemberg, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Rotemberg has for years been working in the field of research on developing AI and other computer-based tools for detecting and diagnosing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
She has been publicly skeptical of the performance of commercial apps that scan moles and other lesions and that claim to identify which are cancerous. A May blog post on the Memorial Sloan Kettering website highlighted a recent British Journal of Dermatology article in which Dr. Rotemberg and coauthors reported on their evaluations of commercial apps. They judged them to be on average only 59% accurate, the blog post said.
However, during an earlier discussion at the meeting, she had spoken more positively about the prospects for using special controls in the near term to mitigate risk, although she said she would have a “very long list” of these requirements.
In the closing exchange with Dr. Ashar, Dr. Rotemberg outlined steps that could potentially ensure the safe use of tools to aid in melanoma screening. These included a need for postmarketing surveillance, which would require evaluation over time of algorithms used in tools meant to detect skin cancer.
“We need to have a mechanism for sampling,” Dr. Rotemberg said. “Most of our data is electronic now anyway, so comparing an algorithm and performance with biopsy results should not be that challenging.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
So far, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has cleared two devices. Both are computer-aided skin lesion classification devices meant to help clinicians assess cases of suspected melanoma.
Both were given a class III designation. That classification is intended for products that are considered to have a high risk of harm because of flawed design or implementation. Many such devices are under development, and there has been a proposal to include these devices in class II, which is less restrictive.
The FDA turned to one of its expert panels for advice. At a meeting held on Aug. 29, experts on the panel offered differing views and expressed concerns about the accuracy of these devices.
This was the second day of meetings of the general and plastic surgery devices panel of the FDA’s Medical Devices Advisory Committee. On the previous day, the panel held a wide-ranging discussion about expanding use of skin lesion analyzer devices.
The FDA sought the expert panel’s advice concerning a field that appears to be heating up quickly after relatively quiet times.
Two devices have been approved by the FDA so far, but only one is still being promoted – SciBase AB’s Nevisense. The Swedish company announced in May 2020 that it had received FDA approval for Nevisense 3.0, the third generation of their Nevisense system for early melanoma detection, an AI-based point-of-care system for the noninvasive evaluation of irregular moles.
The other device, known as MelaFind, was acquired by Strata Skin Sciences, but the company said in 2017 that it discontinued research and development, sales, and support activity related to the device, according to a filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
But there’s been a swell in recent years in the number of publications related to the use of AI and machine learning, which could give rise to new tools for aiding in the diagnosis of skin conditions, including cancer. Google is among the companies that are involved in these efforts.
So, the FDA asked the expert panel to discuss a series of questions related to how the agency should weigh the risks of computer-aided devices for melanoma diagnosis. The agency also asked the panel to provide feedback about how well risks associated with such devices and tools might be managed and to offer suggestions.
The discussion at the July 29 meeting spun beyond narrow questions about reclassification of the current class III devices to topics involving emerging technology, such as efforts to apply AI to dermatology.
“Innovation continues. Medical device developers are anxious to plan how they might be able to develop the level of evidence that would meet your expectations” for future products, Binita Ashar, MD, a senior official in FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, told the panel.
Company CEO backs tougher regulation
Simon Grant, the chief executive of SciBase, which markets Nevisense, the first and only skin cancer–detecting device currently on the U.S. market, sought to make a case for sticking with the tougher class III regulations.
Speaking during the public comment session, Mr. Grant said switching to class II designations would weaken the standards used in clearing products that analyze skin lesions so as to put patients at risk.
Under the FDA’s rules, the agency designates as class III devices that present potential unreasonable risk of illness or injury. Only about 10% of devices fall into this category. Such devices include implantable pacemakers and breast implants, as well as SciBase’s Nevisense.
About 43% of medical devices fall into the class II category, which includes powered wheelchairs and some pregnancy test kits, the FDA website says.
Class I medical devices pose minimal potential for harm and tend to be simpler in design. These include enema kits and elastic bandages, the FDA says.
Mr. Grant told the meeting that in his career he has worked on two class III products and about 20 class II products. (He had previously worked at medical startups Synectics Medical and Neoventa, as well as established multinationals such as Medtronic.)
“I can tell you that – practically – the FDA has many fewer sticks and much less control when it comes to class II devices,” he said. He offered an example of a manufacturer of a class II device having more latitude in making small changes to products without notifying the FDA.
In his hypothetical example, such a change could have unintended consequences, and “with AI systems, small changes can result in large and nonlinear or even random effects,” Mr. Grant said. “But it’s too late if the product is on the market and the harm has already occurred,” he said.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association also protested the reclassifying of approved computer-aided melanoma detection class III devices.
In a statement posted on the FDA website as part of the materials for the meeting, the ASDSA raised a series of concerns about the prospects of expanded U.S. use of tools for assisting in diagnosing melanoma, including ones that would be marketed to consumers.
“To the extent that algorithms and devices for patient self-diagnosis of skin lesions are already widely available, they should be required to include detailed disclaimers that include that they are for entertainment and educational purposes and not a diagnostic device, that they are not approved by dermatologists or a recognized medical regulatory authority for self-diagnosis,” the ASDSA said.
Devices and algorithms in screening tools “are not highly regulated and remain unproven. They may result in wrong diagnoses, missed diagnoses, or over- or underdiagnosis,” the ASDSA added. “Both patients at low risk and those at high risk are better served by scheduling an in-person examination with a board-certified dermatologist, who can also help them determine the appropriate future skin screening schedule that is most appropriate for them.”
‘Stepping stone’
However, there is strong consumer demand for better information about skin conditions, and many patients face hurdles in going to dermatologists.
Google research has shown that consumers are seeking “a stepping stone” between the information they can easily find online and what they could get from a medical professional, said Lily Peng, MD, PhD, a director of product management for the health AI team at Google. Dr. Peng was a scheduled presenter at the July 29 meeting.
Consumers often are looking for more information on common conditions such as acne and poison ivy, and they sometimes face challenges in getting access to clinicians, she said.
“There are many unmet needs for consumers experiencing skin issues, many of which are lower-acuity conditions. There’s a big opportunity to increase accessibility and relevance of health journeys for consumers,” Dr. Peng said. “We have heard from consumers that they would like to have a self-help tool for nonserious conditions so they can decide when to seek medical attention.”
Dr. Peng’s presentation was not directly related to the question of class II or class III designation for existing products. Instead, her talk served as a glimpse into the work already underway in creating apps and tools for consumers.
Google researchers have published a number of studies in recent years about the use of AI to improve dermatology diagnosis.
A 2020 article reported on Google’s test of a form of AI known as deep learning system (DLS) to provide a differential diagnosis of skin conditions. On 963 validation cases, where a rotating panel of three board-certified dermatologists defined the reference standard, the DLS was noninferior to six other dermatologists and was superior to six primary care physicians (PCPs) and six nurse practitioners (NPs), according to a summary of the article.
A 2021 report published in JAMA Network Open said that use of an AI tool was associated with a higher agreement rate with dermatologists’ reference diagnoses for both PCPs and NPs.
In a 2021 blog post, Google scientists wrote that their AI model that powers a tool for checking skin conditions had earned European clearance, known as a CE mark, as a class I medical device.
SkinVision has an app that the company says “is available worldwide (with the exception of the USA and Canada).” The firm’s website includes a link where people in the United States and Canada can sign up for notifications about when SkinVision will be available in these nations.
‘Not ready for prime time’
The FDA panel did not cast formal votes at the July 29 meeting. Rather, the members engaged in broad discussions about risks and potential benefits of new tools for aiding in the detection of skin cancer.
Among the key issues discussed was a question of whether the FDA could impose requirements and restrictions, known as special controls, to provide “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness” for computer-aided devices that provide adjunctive diagnostic information to dermatologists about lesions suspicious for melanoma.
Among the potential special controls would be clinical performance testing in regards to rates of the sensitivity (true-positive rate) and specificity (true-negative rate).
The FDA could also look at requirements on software validation and verification and cybersecurity testing, as well as directions on labeling so as to mitigate risk.
Dermatologists serving on the panel called for caution in proceeding with steps that would make it easier for companies to market tools for aiding in melanoma diagnosis than it would be within the class III framework used for MelaFind and Nevisense.
Many expressed concerns about the need to design studies that would answer questions about how well new tools could accurately identify concerning lesions.
The phrase “not ready for prime time” was used at least three times during the discussion.
FDA panelist Maral Skelsey, MD, a skin cancer specialist from Chevy Chase, Maryland, said that over the years, she had used both Nevisense and MelaFind.
She said she had found MelaFind “unusable,” owing in large part to the high number of false positives it generated. The device also was limited as to where on patients’ bodies it could be used.
However, she spoke with enthusiasm about the prospects for better devices to aid in diagnosis of skin lesions. “It’s an area where we’re on the verge, and we really need these devices. There’s a need for patients to be able to examine themselves, for nondermatologists to be able to assess lesions,” Dr. Skelsey said.
But this field is “just not ready for prime time” yet, even with special controls, Dr. Skelsey said. To loosen approval standards too quickly could be a “detriment to what’s coming down the pipeline,” she said.
“It’s harmful to things that are likely to be around the corner,” she said.
FDA panelist Renata Block, PA-C, who works in a Chicago dermatology practice, pressed for maintaining a class III designation. “We are not ready for prime time yet, though the data that is coming down the pipeline on what we have is quite exciting,” Ms. Block said.
FDA panelist Karla V. Ballman, PhD, a statistician from Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said there would need to be a clear standard for clinical performance before proceeding toward reclassification of devices for aid in detecting melanoma. “I just don’t think it’s ready for prime time at this point and should remain in class III,” she said.
But there was support from some panelists for the idea of a lower bar for clearance, combined with special controls to ensure patient safety.
In expressing her view, FDA panelist Katalin Roth, MD, JD, professor of medicine, George Washington University, Washington, said she was an outlier in her support for the agency’s view that these risks could be managed and that future tools could allow more patients to take a step on the pathway toward critical diagnoses.
“I deal with a lot of people with cancer as a palliative care physician,” Dr. Roth said. “I think what we’re missing here is the issue of time. Melanoma is a terrible disease, and missing the diagnosis is a terrible thing, but I think special controls would be sufficient to counter the concerns of my colleagues on the committee.”
The FDA’s Dr. Ashar ended the meeting with questions posed to one panelist, Veronica Rotemberg, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Dr. Rotemberg has for years been working in the field of research on developing AI and other computer-based tools for detecting and diagnosing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
She has been publicly skeptical of the performance of commercial apps that scan moles and other lesions and that claim to identify which are cancerous. A May blog post on the Memorial Sloan Kettering website highlighted a recent British Journal of Dermatology article in which Dr. Rotemberg and coauthors reported on their evaluations of commercial apps. They judged them to be on average only 59% accurate, the blog post said.
However, during an earlier discussion at the meeting, she had spoken more positively about the prospects for using special controls in the near term to mitigate risk, although she said she would have a “very long list” of these requirements.
In the closing exchange with Dr. Ashar, Dr. Rotemberg outlined steps that could potentially ensure the safe use of tools to aid in melanoma screening. These included a need for postmarketing surveillance, which would require evaluation over time of algorithms used in tools meant to detect skin cancer.
“We need to have a mechanism for sampling,” Dr. Rotemberg said. “Most of our data is electronic now anyway, so comparing an algorithm and performance with biopsy results should not be that challenging.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Landmark ALLIANCE results offer tenofovir guidance in HIV/HBV coinfection
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MONTREAL – Interim results of ALLIANCE, the first head-to-head trial comparing two different tenofovir-containing antiretroviral regimens for the treatment of HIV and hepatitis B (HBV) coinfection, demonstrate the superiority of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) over dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + F/TDF), researchers reported at a meeting of the International AIDS Society.
, with more HBV DNA suppression and significantly more seroconversion, reported lead investigator Anchalee Avihingsanon, MD, PhD, at a press conference during the meeting. Dr. Avihingsanon heads the medical department of the HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration (HIV-NAT) at the Thai Red Cross AIDS Research Centre, Bangkok.
The ongoing phase 3, multicountry study has 48-week results for 243 participants, who were HIV/HBV coinfected and treatment naive. All subjects received three pills of ART per day, with blinded randomization to (active B/F/TAF + placebo DTG + placebo TDF/FTC or placebo B/F/TAF + active DTG + active TDF/FTC). The primary endpoints at 48 weeks were proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL and plasma HBV DNA less than 29 IU/mL.
For the HIV endpoint, results showed both the B/F/TAF and DTG + F/TDF arms had high rates of suppression (95% and 91%, respectively, P = .21), but the B/F/TAF group had significantly higher rates of HBV DNA suppression (63% vs 43.4%, P = .0023) and HBeAg seroconversion (23.3% vs. 11.3%), with numerically higher, but not statistically significant differences in HBsAg loss/seroconversion (12.6% vs. 5.8% and 8.4% vs. 3.3%), HBeAg loss (25.6% vs 14.4%), and ALT normalization (73.3% vs 55.3%).
No participant developed treatment-emergent HIV-1 drug resistance while on B/F/TAF, and there were few study-drug–related AEs or discontinuations, she reported.
“There is hardly any good reason to give the two-pill DTG regimen over single-tablet BTG/TAF/FTC in HBV-coinfected people living with HIV [PLWH],” commented Babafemi Taiwo, MD, chief of infectious diseases and professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., who was not involved in the research. “This gives me confidence to prescribe bictegravir/TAF/FTC, which has the added advantage of being a single-tablet formulation, to HBV coinfected PLWH,” he said in an interview. However, he added, the results “call for some head-scratching since TAF is not known to be better than TDF for HBV treatment in persons without HIV.”
“The lower response rate of the TDF group is still poorly understood,” agreed Dr. Avihingsanon, emphasizing that “HBV and HIV/HBV are not the same, and TDF and TAF are also different. TAF has slightly more drug-drug interactions than TDF. I guess its end product in the liver might be higher. What is exciting to me is that there was such a high rate of HBsAg loss and HBs seroconversion in HIV/HBV coinfection, which is totally different from HBV monoinfection [< 1% at 48 weeks]. For me as an investigator, this important finding has additional benefit to further explore the immunologic outcome for possible HBV cure strategy.” She said the study remains blinded until week 96, at which time further data may shed light on this question.
“Perhaps a larger study would help clarify impact of TAF versus TDF on measures that did not achieve statistical significance in this study. Long-term follow up to better understand the clinical implications of these results could be helpful as well,” Dr. Taiwo added.
The study was funded by Gilead. Dr. Avihingsanon reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Taiwo disclosed that he has served as consultant to ViiV/GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck, and consulted for Gilead on COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AIDS 2022
Ongoing debate whether COVID links to new diabetes in kids
compared with the pre-pandemic rate, in new research.
This contrasts with findings from a U.S. study and a German study, but this is “not the final word” about this possible association, lead author Rayzel Shulman, MD, admits, since the study may have been underpowered.
The population-based, cross-sectional study was published recently as a research letter in JAMA Open.
The researchers found a nonsignificant increase in the monthly rate of new diabetes during the first 18 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, compared with the 3 prior years (relative risk 1.09, 95% confidence interval).
New study contrasts with previous reports
This differs from a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in which COVID-19 infection was associated with a significant increase in new onset of diabetes in children during March 2020 through June 2021, “although some experts have criticized the study methods and conclusion validity,” Dr. Shulman and colleagues write.
Another study, from Germany, reported a significant 1.15-fold increase in type 1 diabetes in children during the pandemic, they note.
The current study may have been underpowered and too small to show a significant association between COVID-19 and new diabetes, the researchers acknowledge.
And the 1.30 upper limit of the confidence interval shows that it “cannot rule out a possible 1.3-fold increase” in relative risk of a diagnosis of diabetes related to COVID, Dr. Shulman explained to this news organization.
It will be important to see how the rates have changed since September 2021 (the end of the current study), added Dr. Shulman, an adjunct scientist at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and a physician and scientist at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto.
The current study did find a decreased (delayed) rate of diagnosis of new diabetes during the first months of the pandemic when there were lockdowns, followed by a “catch-up” increase in rates later on, as has been reported earlier.
“Our study is definitely not the final word on this,” Dr. Shulman summarized in a statement from ICES. “However, our findings call into question whether a direct association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes in children exists.”
COVID-diabetes link?
The researchers analyzed health administrative data from January 2017 to September 2021.
They identified 2,700,178 children and youth in Ontario who were under age 18 in 2021, who had a mean age of 9.2, and about half were girls.
Between November 2020 and April 2021, an estimated 3.3% of children in Ontario had a SARS-COV-2 infection.
New diagnoses of diabetes in this age group are mostly type 1 diabetes, based on previous studies.
The rate of incident diabetes was 15%-32% lower during the first 3 months of the pandemic, March-May 2020 (1.67-2.34 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic monthly rate during 2017, 2018, and 2019 (2.54-2.59 cases per 100,000).
The rate of incident diabetes was 33%-50% higher during February to July 2021 (3.48-4.18 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic rate.
The pre-pandemic and pandemic monthly rates of incident diabetes were similar during the other months.
The group concludes: “The lack of both an observable increase in overall diabetes incidence among children during the 18-month pandemic restrictions [in this Ontario study] and a plausible biological mechanism call into question an association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes.”
More research is needed. “Given the variability in monthly [relative risks], additional population-based, longer-term data are needed to examine the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 and diabetes risk among children,” the authors write.
This study was supported by ICES (which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health) and by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Shulman reported receiving fees from Dexcom outside the submitted work, and she and three other authors reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
compared with the pre-pandemic rate, in new research.
This contrasts with findings from a U.S. study and a German study, but this is “not the final word” about this possible association, lead author Rayzel Shulman, MD, admits, since the study may have been underpowered.
The population-based, cross-sectional study was published recently as a research letter in JAMA Open.
The researchers found a nonsignificant increase in the monthly rate of new diabetes during the first 18 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, compared with the 3 prior years (relative risk 1.09, 95% confidence interval).
New study contrasts with previous reports
This differs from a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in which COVID-19 infection was associated with a significant increase in new onset of diabetes in children during March 2020 through June 2021, “although some experts have criticized the study methods and conclusion validity,” Dr. Shulman and colleagues write.
Another study, from Germany, reported a significant 1.15-fold increase in type 1 diabetes in children during the pandemic, they note.
The current study may have been underpowered and too small to show a significant association between COVID-19 and new diabetes, the researchers acknowledge.
And the 1.30 upper limit of the confidence interval shows that it “cannot rule out a possible 1.3-fold increase” in relative risk of a diagnosis of diabetes related to COVID, Dr. Shulman explained to this news organization.
It will be important to see how the rates have changed since September 2021 (the end of the current study), added Dr. Shulman, an adjunct scientist at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and a physician and scientist at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto.
The current study did find a decreased (delayed) rate of diagnosis of new diabetes during the first months of the pandemic when there were lockdowns, followed by a “catch-up” increase in rates later on, as has been reported earlier.
“Our study is definitely not the final word on this,” Dr. Shulman summarized in a statement from ICES. “However, our findings call into question whether a direct association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes in children exists.”
COVID-diabetes link?
The researchers analyzed health administrative data from January 2017 to September 2021.
They identified 2,700,178 children and youth in Ontario who were under age 18 in 2021, who had a mean age of 9.2, and about half were girls.
Between November 2020 and April 2021, an estimated 3.3% of children in Ontario had a SARS-COV-2 infection.
New diagnoses of diabetes in this age group are mostly type 1 diabetes, based on previous studies.
The rate of incident diabetes was 15%-32% lower during the first 3 months of the pandemic, March-May 2020 (1.67-2.34 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic monthly rate during 2017, 2018, and 2019 (2.54-2.59 cases per 100,000).
The rate of incident diabetes was 33%-50% higher during February to July 2021 (3.48-4.18 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic rate.
The pre-pandemic and pandemic monthly rates of incident diabetes were similar during the other months.
The group concludes: “The lack of both an observable increase in overall diabetes incidence among children during the 18-month pandemic restrictions [in this Ontario study] and a plausible biological mechanism call into question an association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes.”
More research is needed. “Given the variability in monthly [relative risks], additional population-based, longer-term data are needed to examine the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 and diabetes risk among children,” the authors write.
This study was supported by ICES (which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health) and by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Shulman reported receiving fees from Dexcom outside the submitted work, and she and three other authors reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
compared with the pre-pandemic rate, in new research.
This contrasts with findings from a U.S. study and a German study, but this is “not the final word” about this possible association, lead author Rayzel Shulman, MD, admits, since the study may have been underpowered.
The population-based, cross-sectional study was published recently as a research letter in JAMA Open.
The researchers found a nonsignificant increase in the monthly rate of new diabetes during the first 18 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, compared with the 3 prior years (relative risk 1.09, 95% confidence interval).
New study contrasts with previous reports
This differs from a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in which COVID-19 infection was associated with a significant increase in new onset of diabetes in children during March 2020 through June 2021, “although some experts have criticized the study methods and conclusion validity,” Dr. Shulman and colleagues write.
Another study, from Germany, reported a significant 1.15-fold increase in type 1 diabetes in children during the pandemic, they note.
The current study may have been underpowered and too small to show a significant association between COVID-19 and new diabetes, the researchers acknowledge.
And the 1.30 upper limit of the confidence interval shows that it “cannot rule out a possible 1.3-fold increase” in relative risk of a diagnosis of diabetes related to COVID, Dr. Shulman explained to this news organization.
It will be important to see how the rates have changed since September 2021 (the end of the current study), added Dr. Shulman, an adjunct scientist at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and a physician and scientist at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto.
The current study did find a decreased (delayed) rate of diagnosis of new diabetes during the first months of the pandemic when there were lockdowns, followed by a “catch-up” increase in rates later on, as has been reported earlier.
“Our study is definitely not the final word on this,” Dr. Shulman summarized in a statement from ICES. “However, our findings call into question whether a direct association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes in children exists.”
COVID-diabetes link?
The researchers analyzed health administrative data from January 2017 to September 2021.
They identified 2,700,178 children and youth in Ontario who were under age 18 in 2021, who had a mean age of 9.2, and about half were girls.
Between November 2020 and April 2021, an estimated 3.3% of children in Ontario had a SARS-COV-2 infection.
New diagnoses of diabetes in this age group are mostly type 1 diabetes, based on previous studies.
The rate of incident diabetes was 15%-32% lower during the first 3 months of the pandemic, March-May 2020 (1.67-2.34 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic monthly rate during 2017, 2018, and 2019 (2.54-2.59 cases per 100,000).
The rate of incident diabetes was 33%-50% higher during February to July 2021 (3.48-4.18 cases per 100,000), compared with the pre-pandemic rate.
The pre-pandemic and pandemic monthly rates of incident diabetes were similar during the other months.
The group concludes: “The lack of both an observable increase in overall diabetes incidence among children during the 18-month pandemic restrictions [in this Ontario study] and a plausible biological mechanism call into question an association between COVID-19 and new-onset diabetes.”
More research is needed. “Given the variability in monthly [relative risks], additional population-based, longer-term data are needed to examine the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 and diabetes risk among children,” the authors write.
This study was supported by ICES (which is funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health) and by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Shulman reported receiving fees from Dexcom outside the submitted work, and she and three other authors reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA OPEN
Skin-picking, hair-pulling disorders: Diagnostic criteria, prevalence, and treatment
INDIANAPOLIS –
And while both body-focused repetitive behavior disorders affect a greater proportion of females than males, “we have no current information that is useful about what hormonal influences may or may not play in terms of picking and pulling behaviors,” Jon E. Grant, MD, JD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “On a cognitive level, affected children and adolescents often have impaired inhibitory control but they are often 1-2 standard deviations above average IQ. They have Type A personalities [and are] very driven young kids. They also do not tolerate any down time or boredom. They need to be doing something all the time.”
According to the DSM-5, the diagnostic criteria for skin picking includes recurrent skin picking that results in skin lesions and is not attributable to another medical condition or substance. It also involves repeated attempts to decrease or stop the behavior and causes clinically significant distress or impairment.
“The other medical condition that we are interested in is the misuse of or dependence upon amphetamines or other prescription-based or illicit stimulants,” Dr. Grant said. “I saw a young man who was using about 600 mg of Ritalin a day, and he was picking all over the place. He did not have a primary skin disorder.”
The lifetime prevalence of skin picking disorder ranges between 1.4% and 5.4% of the general population. However, about 63% of people in a community sample endorsed some form of skin picking, and in a study of 105 college students, almost 40% said they picked their skin and had noticeable tissue damage as a result.
“Skin picking is not the same as self-injury,” Dr. Grant said. “It is also not simply an anxiety disorder. Anxiety will make people who pick worse, so people will say that they pick when they’re under stress. I can give them benzodiazepines and they’re still going to pick.”
Animal and human studies demonstrate that skin picking and hair pulling primarily affect females. “You will encounter young boys that pick and pull, but it largely affects females, and it tends to start around puberty,” he said. “Picking can have an onset after the age of 30, which is quite uncommon.”
From a cognitive standpoint, pathological skin pickers demonstrate impaired inhibitory control, impaired stop signal reaction time, increased rates of negative urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to negative emotions), and increased rates of positive urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to exciting or pleasurable emotions).
Trichotillomania
The lifetime prevalence of trichotillomania ranges between 0.6% and 3.9%. The onset is typically from ages 10-13 years, and the mean duration of illness is 22 years.
The DSM-5 criteria for trichotillomania are similar to that of skin-picking disorder, “although we don’t really worry about the substance use issue with people who pull their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “It doesn’t seem to have a correlation.” In addition, sometimes, children “will worsen pulling or picking when they have co-occurring ADHD and they’ve been started on a stimulant, even at a typical dose. For kids who have those issues, we prefer to try nonstimulant options for their ADHD such as bupropion or atomoxetine.”
Individuals with trichotillomania also tend to have low self-esteem and increased social anxiety, he added, and about one-third report low or very low quality of life. “When you notice alopecia, particularly in young girls who often have longer hair, up to 20% will eat their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “We don’t know why. It’s not related to vitamin deficiencies; it’s not a pica type of iron deficiency. There seems to be a shame piece about eating one’s own hair, but it’s important to assess that. Ask about constipation or overflow incontinence because they can get a bezoar, which can rupture” and can be fatal.
Skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania co-occur in up to 20% of cases. “When they do it tends to be a more difficult problem,” he said. These patients often come for mental health care because of depression, and most, he added, say “I don’t think I would be depressed if I wasn’t covered with excoriations or missing most of my hair.”
Treatment for both conditions
According to Dr. Grant, the treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is a specific psychotherapy known as “habit reversal therapy,” which involves helping the patient gain better self-control. The drawback is that it’s difficult to find someone trained in habit reversal therapy, “who know anything about skin picking and hair pulling,” he said. “That has been a huge challenge in the field.”
In his experience, the medical treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is N-acetylcysteine, an over-the-counter amino acid and antioxidant, which has been shown to be helpful at a dose of 2,400 mg per day. “Patients report to me that some of the excoriations clear up a little quicker as they’re taking it,” Dr. Grant said.
There may also be a role for antipsychotic therapy, he said, “but because of the associated weight gain with most antipsychotics we prefer not to use them.”
The opioid antagonist naltrexone has been shown to be effective in the subset of patients with skin-picking or hair-pulling disorders whose parents have a substance use disorder, Dr. Grant said. “The thought is that there’s something addictive about this behavior in some kids. These kids will look forward to picking and find it rewarding and exciting.”
Dr. Grant reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
INDIANAPOLIS –
And while both body-focused repetitive behavior disorders affect a greater proportion of females than males, “we have no current information that is useful about what hormonal influences may or may not play in terms of picking and pulling behaviors,” Jon E. Grant, MD, JD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “On a cognitive level, affected children and adolescents often have impaired inhibitory control but they are often 1-2 standard deviations above average IQ. They have Type A personalities [and are] very driven young kids. They also do not tolerate any down time or boredom. They need to be doing something all the time.”
According to the DSM-5, the diagnostic criteria for skin picking includes recurrent skin picking that results in skin lesions and is not attributable to another medical condition or substance. It also involves repeated attempts to decrease or stop the behavior and causes clinically significant distress or impairment.
“The other medical condition that we are interested in is the misuse of or dependence upon amphetamines or other prescription-based or illicit stimulants,” Dr. Grant said. “I saw a young man who was using about 600 mg of Ritalin a day, and he was picking all over the place. He did not have a primary skin disorder.”
The lifetime prevalence of skin picking disorder ranges between 1.4% and 5.4% of the general population. However, about 63% of people in a community sample endorsed some form of skin picking, and in a study of 105 college students, almost 40% said they picked their skin and had noticeable tissue damage as a result.
“Skin picking is not the same as self-injury,” Dr. Grant said. “It is also not simply an anxiety disorder. Anxiety will make people who pick worse, so people will say that they pick when they’re under stress. I can give them benzodiazepines and they’re still going to pick.”
Animal and human studies demonstrate that skin picking and hair pulling primarily affect females. “You will encounter young boys that pick and pull, but it largely affects females, and it tends to start around puberty,” he said. “Picking can have an onset after the age of 30, which is quite uncommon.”
From a cognitive standpoint, pathological skin pickers demonstrate impaired inhibitory control, impaired stop signal reaction time, increased rates of negative urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to negative emotions), and increased rates of positive urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to exciting or pleasurable emotions).
Trichotillomania
The lifetime prevalence of trichotillomania ranges between 0.6% and 3.9%. The onset is typically from ages 10-13 years, and the mean duration of illness is 22 years.
The DSM-5 criteria for trichotillomania are similar to that of skin-picking disorder, “although we don’t really worry about the substance use issue with people who pull their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “It doesn’t seem to have a correlation.” In addition, sometimes, children “will worsen pulling or picking when they have co-occurring ADHD and they’ve been started on a stimulant, even at a typical dose. For kids who have those issues, we prefer to try nonstimulant options for their ADHD such as bupropion or atomoxetine.”
Individuals with trichotillomania also tend to have low self-esteem and increased social anxiety, he added, and about one-third report low or very low quality of life. “When you notice alopecia, particularly in young girls who often have longer hair, up to 20% will eat their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “We don’t know why. It’s not related to vitamin deficiencies; it’s not a pica type of iron deficiency. There seems to be a shame piece about eating one’s own hair, but it’s important to assess that. Ask about constipation or overflow incontinence because they can get a bezoar, which can rupture” and can be fatal.
Skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania co-occur in up to 20% of cases. “When they do it tends to be a more difficult problem,” he said. These patients often come for mental health care because of depression, and most, he added, say “I don’t think I would be depressed if I wasn’t covered with excoriations or missing most of my hair.”
Treatment for both conditions
According to Dr. Grant, the treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is a specific psychotherapy known as “habit reversal therapy,” which involves helping the patient gain better self-control. The drawback is that it’s difficult to find someone trained in habit reversal therapy, “who know anything about skin picking and hair pulling,” he said. “That has been a huge challenge in the field.”
In his experience, the medical treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is N-acetylcysteine, an over-the-counter amino acid and antioxidant, which has been shown to be helpful at a dose of 2,400 mg per day. “Patients report to me that some of the excoriations clear up a little quicker as they’re taking it,” Dr. Grant said.
There may also be a role for antipsychotic therapy, he said, “but because of the associated weight gain with most antipsychotics we prefer not to use them.”
The opioid antagonist naltrexone has been shown to be effective in the subset of patients with skin-picking or hair-pulling disorders whose parents have a substance use disorder, Dr. Grant said. “The thought is that there’s something addictive about this behavior in some kids. These kids will look forward to picking and find it rewarding and exciting.”
Dr. Grant reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
INDIANAPOLIS –
And while both body-focused repetitive behavior disorders affect a greater proportion of females than males, “we have no current information that is useful about what hormonal influences may or may not play in terms of picking and pulling behaviors,” Jon E. Grant, MD, JD, MPH, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “On a cognitive level, affected children and adolescents often have impaired inhibitory control but they are often 1-2 standard deviations above average IQ. They have Type A personalities [and are] very driven young kids. They also do not tolerate any down time or boredom. They need to be doing something all the time.”
According to the DSM-5, the diagnostic criteria for skin picking includes recurrent skin picking that results in skin lesions and is not attributable to another medical condition or substance. It also involves repeated attempts to decrease or stop the behavior and causes clinically significant distress or impairment.
“The other medical condition that we are interested in is the misuse of or dependence upon amphetamines or other prescription-based or illicit stimulants,” Dr. Grant said. “I saw a young man who was using about 600 mg of Ritalin a day, and he was picking all over the place. He did not have a primary skin disorder.”
The lifetime prevalence of skin picking disorder ranges between 1.4% and 5.4% of the general population. However, about 63% of people in a community sample endorsed some form of skin picking, and in a study of 105 college students, almost 40% said they picked their skin and had noticeable tissue damage as a result.
“Skin picking is not the same as self-injury,” Dr. Grant said. “It is also not simply an anxiety disorder. Anxiety will make people who pick worse, so people will say that they pick when they’re under stress. I can give them benzodiazepines and they’re still going to pick.”
Animal and human studies demonstrate that skin picking and hair pulling primarily affect females. “You will encounter young boys that pick and pull, but it largely affects females, and it tends to start around puberty,” he said. “Picking can have an onset after the age of 30, which is quite uncommon.”
From a cognitive standpoint, pathological skin pickers demonstrate impaired inhibitory control, impaired stop signal reaction time, increased rates of negative urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to negative emotions), and increased rates of positive urgency (a tendency to act impulsively in response to exciting or pleasurable emotions).
Trichotillomania
The lifetime prevalence of trichotillomania ranges between 0.6% and 3.9%. The onset is typically from ages 10-13 years, and the mean duration of illness is 22 years.
The DSM-5 criteria for trichotillomania are similar to that of skin-picking disorder, “although we don’t really worry about the substance use issue with people who pull their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “It doesn’t seem to have a correlation.” In addition, sometimes, children “will worsen pulling or picking when they have co-occurring ADHD and they’ve been started on a stimulant, even at a typical dose. For kids who have those issues, we prefer to try nonstimulant options for their ADHD such as bupropion or atomoxetine.”
Individuals with trichotillomania also tend to have low self-esteem and increased social anxiety, he added, and about one-third report low or very low quality of life. “When you notice alopecia, particularly in young girls who often have longer hair, up to 20% will eat their hair,” Dr. Grant said. “We don’t know why. It’s not related to vitamin deficiencies; it’s not a pica type of iron deficiency. There seems to be a shame piece about eating one’s own hair, but it’s important to assess that. Ask about constipation or overflow incontinence because they can get a bezoar, which can rupture” and can be fatal.
Skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania co-occur in up to 20% of cases. “When they do it tends to be a more difficult problem,” he said. These patients often come for mental health care because of depression, and most, he added, say “I don’t think I would be depressed if I wasn’t covered with excoriations or missing most of my hair.”
Treatment for both conditions
According to Dr. Grant, the treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is a specific psychotherapy known as “habit reversal therapy,” which involves helping the patient gain better self-control. The drawback is that it’s difficult to find someone trained in habit reversal therapy, “who know anything about skin picking and hair pulling,” he said. “That has been a huge challenge in the field.”
In his experience, the medical treatment of choice for skin-picking disorder and trichotillomania is N-acetylcysteine, an over-the-counter amino acid and antioxidant, which has been shown to be helpful at a dose of 2,400 mg per day. “Patients report to me that some of the excoriations clear up a little quicker as they’re taking it,” Dr. Grant said.
There may also be a role for antipsychotic therapy, he said, “but because of the associated weight gain with most antipsychotics we prefer not to use them.”
The opioid antagonist naltrexone has been shown to be effective in the subset of patients with skin-picking or hair-pulling disorders whose parents have a substance use disorder, Dr. Grant said. “The thought is that there’s something addictive about this behavior in some kids. These kids will look forward to picking and find it rewarding and exciting.”
Dr. Grant reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT SPD 2022




