User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
FDA approves two JAK-1 inhibitors for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis
The available for this indication in the United States.
“It’s big news because a few years ago we didn’t have any systemic treatments that are safer than the classical immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and methotrexate,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, Waldman professor and system chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, told this news organization commenting on upadacitinib’s approval.
“The only oral approved drug for AD up to now was oral prednisone, which has terrible safety concerns. This is basically the first oral medication that we can provide our patients for long-term use.”
Upadacitinib
The approval of upadacitinib (Rinvoq), marketed by AbbVie, for moderate to severe AD in patients ages 12 and older, comes on the heels of findings from three pivotal phase 3 studies involving more than 2,500 adults and children 12 years of age and older with moderate to severe AD: Measure Up 1 and 2, led by Dr. Guttman-Yassky, which evaluated upadacitinib compared with placebo, and AD UP, which compared upadacitinib along with topical corticosteroids, compared with placebo.
Across the three studies, upadacitinib – both 15 mg and 30 mg once daily monotherapy – met all primary and secondary endpoints at week 16, with some patients achieving higher levels of skin clearance based on the Eczema Area and Severity Index 90 (EASI-90) and EASI-100.
“I always say that patients with AD need options,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “We need biologics. We need oral medications. Not everybody likes an injectable. The plus of the class of JAK inhibitors in general is the quick onset of action.” Many patients in her clinic are maintained on upadacitinib more than two years later “and are super happy,” she said. “Many of them failed cyclosporine and other immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and prednisone.”
She predicted that health insurance companies will find coverage cost-effective “because it sets a new bar for efficacy, and because many patients have failed other treatments.”
Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib (Cibinqo), marketed by Pfizer, was approved for adults with moderate to severe AD. The approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale clinical trial program of more than 1,600 patients. The recommended doses are 100 mg and 200 mg, with the 200 mg dose recommended for patients who are not responding to the 100 mg dose.
The labeling of abrocitinib and upadacitinib include a boxed warning for JAK inhibitors, regarding the risk of serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has served as a principal investigator for AbbVie and has received consulting fees from the company.
The available for this indication in the United States.
“It’s big news because a few years ago we didn’t have any systemic treatments that are safer than the classical immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and methotrexate,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, Waldman professor and system chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, told this news organization commenting on upadacitinib’s approval.
“The only oral approved drug for AD up to now was oral prednisone, which has terrible safety concerns. This is basically the first oral medication that we can provide our patients for long-term use.”
Upadacitinib
The approval of upadacitinib (Rinvoq), marketed by AbbVie, for moderate to severe AD in patients ages 12 and older, comes on the heels of findings from three pivotal phase 3 studies involving more than 2,500 adults and children 12 years of age and older with moderate to severe AD: Measure Up 1 and 2, led by Dr. Guttman-Yassky, which evaluated upadacitinib compared with placebo, and AD UP, which compared upadacitinib along with topical corticosteroids, compared with placebo.
Across the three studies, upadacitinib – both 15 mg and 30 mg once daily monotherapy – met all primary and secondary endpoints at week 16, with some patients achieving higher levels of skin clearance based on the Eczema Area and Severity Index 90 (EASI-90) and EASI-100.
“I always say that patients with AD need options,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “We need biologics. We need oral medications. Not everybody likes an injectable. The plus of the class of JAK inhibitors in general is the quick onset of action.” Many patients in her clinic are maintained on upadacitinib more than two years later “and are super happy,” she said. “Many of them failed cyclosporine and other immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and prednisone.”
She predicted that health insurance companies will find coverage cost-effective “because it sets a new bar for efficacy, and because many patients have failed other treatments.”
Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib (Cibinqo), marketed by Pfizer, was approved for adults with moderate to severe AD. The approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale clinical trial program of more than 1,600 patients. The recommended doses are 100 mg and 200 mg, with the 200 mg dose recommended for patients who are not responding to the 100 mg dose.
The labeling of abrocitinib and upadacitinib include a boxed warning for JAK inhibitors, regarding the risk of serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has served as a principal investigator for AbbVie and has received consulting fees from the company.
The available for this indication in the United States.
“It’s big news because a few years ago we didn’t have any systemic treatments that are safer than the classical immunosuppressants like cyclosporine and methotrexate,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, Waldman professor and system chair of dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, told this news organization commenting on upadacitinib’s approval.
“The only oral approved drug for AD up to now was oral prednisone, which has terrible safety concerns. This is basically the first oral medication that we can provide our patients for long-term use.”
Upadacitinib
The approval of upadacitinib (Rinvoq), marketed by AbbVie, for moderate to severe AD in patients ages 12 and older, comes on the heels of findings from three pivotal phase 3 studies involving more than 2,500 adults and children 12 years of age and older with moderate to severe AD: Measure Up 1 and 2, led by Dr. Guttman-Yassky, which evaluated upadacitinib compared with placebo, and AD UP, which compared upadacitinib along with topical corticosteroids, compared with placebo.
Across the three studies, upadacitinib – both 15 mg and 30 mg once daily monotherapy – met all primary and secondary endpoints at week 16, with some patients achieving higher levels of skin clearance based on the Eczema Area and Severity Index 90 (EASI-90) and EASI-100.
“I always say that patients with AD need options,” Dr. Guttman-Yassky said. “We need biologics. We need oral medications. Not everybody likes an injectable. The plus of the class of JAK inhibitors in general is the quick onset of action.” Many patients in her clinic are maintained on upadacitinib more than two years later “and are super happy,” she said. “Many of them failed cyclosporine and other immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and prednisone.”
She predicted that health insurance companies will find coverage cost-effective “because it sets a new bar for efficacy, and because many patients have failed other treatments.”
Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib (Cibinqo), marketed by Pfizer, was approved for adults with moderate to severe AD. The approval was based on results of five clinical trials from a large-scale clinical trial program of more than 1,600 patients. The recommended doses are 100 mg and 200 mg, with the 200 mg dose recommended for patients who are not responding to the 100 mg dose.
The labeling of abrocitinib and upadacitinib include a boxed warning for JAK inhibitors, regarding the risk of serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, and thrombosis.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has served as a principal investigator for AbbVie and has received consulting fees from the company.
FDA updates status of iPLEDGE access problems
The, one month after a modified program was launched, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Jan. 14.
The IPMG has “created a new tool within the system to help resolve account access for some user groups without using the call center. This tool is intended to allow prescribers and designees to send login links directly to their patients’ desired email address through the Manage Patients page of the iPLEDGE REMS portal,” the FDA statement said.
“Prescribers can also send login links to their designees still having difficulty accessing their iPLEDGE account,” and users should check their emails for messages from iPLEDGE, including spam folders, the FDA advises. The iPLEDGE strategy is designed to prevent fetal exposure to isotretinoin, which is highly teratogenic.
Days after the new, gender-neutral approach to the isotretinoin risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, the FDA convened an emergency meeting with representatives from the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to discuss the problematic rollout of the program, which was described as disastrous, chaotic, and a failure, with dermatologists on Twitter and elsewhere expressing anger and frustration over not being able to access the program or reach the call center.
A statement by the FDA on Dec. 23 followed, urging manufacturers to develop solutions for the website and to work with the AADA and pharmacy organizations to find solutions that would minimize treatment interruptions during the transition.
The modified REMS, launched on Dec. 13, is designed to make it more inclusive for transgender patients prescribed isotretinoin. Instead of three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males), patients who are prescribed isotretinoin for acne are assigned to one of two risk categories: those who can get pregnant and those who cannot get pregnant.
In the Jan. 14 statement, the FDA notes that the agency is continuing to work with the IPMG regarding the problems clinicians, pharmacists, and patients have had with accessing iPLEDGE over the last month.
“Although there has been progress, there is a significant amount of work still to be done,” the FDA acknowledged. “While we consider potential steps within the scope of FDA’s authorities, we will continue to meet with the IPMG for updates on the status of the problems with the iPLEDGE REMS and their progress towards having the system work as intended for all users.”
The, one month after a modified program was launched, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Jan. 14.
The IPMG has “created a new tool within the system to help resolve account access for some user groups without using the call center. This tool is intended to allow prescribers and designees to send login links directly to their patients’ desired email address through the Manage Patients page of the iPLEDGE REMS portal,” the FDA statement said.
“Prescribers can also send login links to their designees still having difficulty accessing their iPLEDGE account,” and users should check their emails for messages from iPLEDGE, including spam folders, the FDA advises. The iPLEDGE strategy is designed to prevent fetal exposure to isotretinoin, which is highly teratogenic.
Days after the new, gender-neutral approach to the isotretinoin risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, the FDA convened an emergency meeting with representatives from the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to discuss the problematic rollout of the program, which was described as disastrous, chaotic, and a failure, with dermatologists on Twitter and elsewhere expressing anger and frustration over not being able to access the program or reach the call center.
A statement by the FDA on Dec. 23 followed, urging manufacturers to develop solutions for the website and to work with the AADA and pharmacy organizations to find solutions that would minimize treatment interruptions during the transition.
The modified REMS, launched on Dec. 13, is designed to make it more inclusive for transgender patients prescribed isotretinoin. Instead of three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males), patients who are prescribed isotretinoin for acne are assigned to one of two risk categories: those who can get pregnant and those who cannot get pregnant.
In the Jan. 14 statement, the FDA notes that the agency is continuing to work with the IPMG regarding the problems clinicians, pharmacists, and patients have had with accessing iPLEDGE over the last month.
“Although there has been progress, there is a significant amount of work still to be done,” the FDA acknowledged. “While we consider potential steps within the scope of FDA’s authorities, we will continue to meet with the IPMG for updates on the status of the problems with the iPLEDGE REMS and their progress towards having the system work as intended for all users.”
The, one month after a modified program was launched, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Jan. 14.
The IPMG has “created a new tool within the system to help resolve account access for some user groups without using the call center. This tool is intended to allow prescribers and designees to send login links directly to their patients’ desired email address through the Manage Patients page of the iPLEDGE REMS portal,” the FDA statement said.
“Prescribers can also send login links to their designees still having difficulty accessing their iPLEDGE account,” and users should check their emails for messages from iPLEDGE, including spam folders, the FDA advises. The iPLEDGE strategy is designed to prevent fetal exposure to isotretinoin, which is highly teratogenic.
Days after the new, gender-neutral approach to the isotretinoin risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, the FDA convened an emergency meeting with representatives from the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) to discuss the problematic rollout of the program, which was described as disastrous, chaotic, and a failure, with dermatologists on Twitter and elsewhere expressing anger and frustration over not being able to access the program or reach the call center.
A statement by the FDA on Dec. 23 followed, urging manufacturers to develop solutions for the website and to work with the AADA and pharmacy organizations to find solutions that would minimize treatment interruptions during the transition.
The modified REMS, launched on Dec. 13, is designed to make it more inclusive for transgender patients prescribed isotretinoin. Instead of three risk categories (females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males), patients who are prescribed isotretinoin for acne are assigned to one of two risk categories: those who can get pregnant and those who cannot get pregnant.
In the Jan. 14 statement, the FDA notes that the agency is continuing to work with the IPMG regarding the problems clinicians, pharmacists, and patients have had with accessing iPLEDGE over the last month.
“Although there has been progress, there is a significant amount of work still to be done,” the FDA acknowledged. “While we consider potential steps within the scope of FDA’s authorities, we will continue to meet with the IPMG for updates on the status of the problems with the iPLEDGE REMS and their progress towards having the system work as intended for all users.”
NPs, PAs say stop attacks and support health care colleagues
This commentary was submitted as a rebuttal to “PA name change bad for patients and the profession.”
To the Editor:
At a time when COVID-19 cases are climbing and health care workers are struggling to meet the needs of our nation’s healthcare system, the commentary by Rebekah Bernard, MD, divides health care providers and demeans the education, experience, and value of physician associates (PA) and nurse practitioners (NP) in our opinion.
The ill timing of this negative message is equally matched by her mischaracterization of the PA title change and PA efforts to eliminate outdated administrative barriers, as well as her baseless attack on NP education and clinical training.
Let us be clear about one thing: What patients really want and deserve is access to high-quality care delivered by the health care provider of their choice. Patients deserve health care providers who are committed to modern, integrated, and coordinated health care delivery, led by professionals who are dedicated to ensuring that everyone is practicing to the full extent of their education, clinical experience, and scope of practice. Patients deserve health care providers who respect each other and work together to embrace solutions that will improve health care for the future.
Decades of research confirm the high quality of PA- and NP-delivered health care. The evidence is in, and it is irrefutable: PA- and NP-delivered care is associated with improved access to care, lower health care costs, and fewer avoidable emergency room visits.
With regard to the PA title change, the fact is this: Changing the profession’s title does not change what PAs do or affect a PA’s scope of practice. The new title – physician associate – directly addresses the common misperception that PAs merely “assist” physicians. It is in the best interest of patients and the health care system for PAs to hold a professional title that ensures clarity about the work that PAs do.
For the sake of patients, we urge Bernard and her organization to stop continuously attacking other professions and focus on what really matters – providing access to safe, effective, equitable, high-quality care to all patients.
We are committed to patient-centered, coordinated health care, and we continue to work with like-minded physicians and other colleagues to make this a reality.
Ms. Orozco is president and chair of the board of directors for the American Academy of Physician Associates. Dr. Kapu is president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This commentary was submitted as a rebuttal to “PA name change bad for patients and the profession.”
To the Editor:
At a time when COVID-19 cases are climbing and health care workers are struggling to meet the needs of our nation’s healthcare system, the commentary by Rebekah Bernard, MD, divides health care providers and demeans the education, experience, and value of physician associates (PA) and nurse practitioners (NP) in our opinion.
The ill timing of this negative message is equally matched by her mischaracterization of the PA title change and PA efforts to eliminate outdated administrative barriers, as well as her baseless attack on NP education and clinical training.
Let us be clear about one thing: What patients really want and deserve is access to high-quality care delivered by the health care provider of their choice. Patients deserve health care providers who are committed to modern, integrated, and coordinated health care delivery, led by professionals who are dedicated to ensuring that everyone is practicing to the full extent of their education, clinical experience, and scope of practice. Patients deserve health care providers who respect each other and work together to embrace solutions that will improve health care for the future.
Decades of research confirm the high quality of PA- and NP-delivered health care. The evidence is in, and it is irrefutable: PA- and NP-delivered care is associated with improved access to care, lower health care costs, and fewer avoidable emergency room visits.
With regard to the PA title change, the fact is this: Changing the profession’s title does not change what PAs do or affect a PA’s scope of practice. The new title – physician associate – directly addresses the common misperception that PAs merely “assist” physicians. It is in the best interest of patients and the health care system for PAs to hold a professional title that ensures clarity about the work that PAs do.
For the sake of patients, we urge Bernard and her organization to stop continuously attacking other professions and focus on what really matters – providing access to safe, effective, equitable, high-quality care to all patients.
We are committed to patient-centered, coordinated health care, and we continue to work with like-minded physicians and other colleagues to make this a reality.
Ms. Orozco is president and chair of the board of directors for the American Academy of Physician Associates. Dr. Kapu is president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This commentary was submitted as a rebuttal to “PA name change bad for patients and the profession.”
To the Editor:
At a time when COVID-19 cases are climbing and health care workers are struggling to meet the needs of our nation’s healthcare system, the commentary by Rebekah Bernard, MD, divides health care providers and demeans the education, experience, and value of physician associates (PA) and nurse practitioners (NP) in our opinion.
The ill timing of this negative message is equally matched by her mischaracterization of the PA title change and PA efforts to eliminate outdated administrative barriers, as well as her baseless attack on NP education and clinical training.
Let us be clear about one thing: What patients really want and deserve is access to high-quality care delivered by the health care provider of their choice. Patients deserve health care providers who are committed to modern, integrated, and coordinated health care delivery, led by professionals who are dedicated to ensuring that everyone is practicing to the full extent of their education, clinical experience, and scope of practice. Patients deserve health care providers who respect each other and work together to embrace solutions that will improve health care for the future.
Decades of research confirm the high quality of PA- and NP-delivered health care. The evidence is in, and it is irrefutable: PA- and NP-delivered care is associated with improved access to care, lower health care costs, and fewer avoidable emergency room visits.
With regard to the PA title change, the fact is this: Changing the profession’s title does not change what PAs do or affect a PA’s scope of practice. The new title – physician associate – directly addresses the common misperception that PAs merely “assist” physicians. It is in the best interest of patients and the health care system for PAs to hold a professional title that ensures clarity about the work that PAs do.
For the sake of patients, we urge Bernard and her organization to stop continuously attacking other professions and focus on what really matters – providing access to safe, effective, equitable, high-quality care to all patients.
We are committed to patient-centered, coordinated health care, and we continue to work with like-minded physicians and other colleagues to make this a reality.
Ms. Orozco is president and chair of the board of directors for the American Academy of Physician Associates. Dr. Kapu is president of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sometimes You Can’t Blame the Sun
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “e”).
DISCUSSION
Most cases of dermatomyositis, which the patient’s presentation and lab results suggested, require nerve conduction studies, a check of serum aldolase levels, and skin and muscle biopsies to complete the work-up. However, the arrival at a diagnosis is only the first step.
Patients with dermatomyositis, particularly those older than 60, require evaluation for occult malignancy. There is evidence that the body’s immune response to the cancer is what drives the disease process. Hence the need for the studies listed, looking for breast, lung, and gastrointestinal cancers especially.
Dermatomyositis is thought to be an inflammatory myopathy, possibly driven by autoimmune factors. It is rare (about 1 to 22 per 100,000) and affects women more than men.
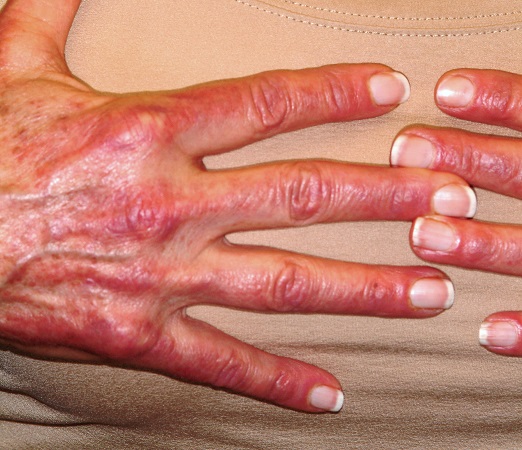
The “sunburn” rash is typical, especially on the face, chest, and dorsal hands, and usually clears completely when the cancer is found and cured. Other common findings include elevated creatine kinase, hand rashes (known as Gottron’s papules), and dystrophic calcification in skin and/or joints.
TREATMENT
Aside from addressing a possible malignancy, treatment of dermatomyositis usually starts with glucocorticoids, eventually tapered and replaced by steroid-sparing agents such as azathioprine or cyclosporine. These drugs have dramatically increased the chances of survival and eventual cure.
It’s common for the photosensitivity to persist long after the myositis has resolved, which is why sunscreen and other sun-protective measures are advised.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “e”).
DISCUSSION
Most cases of dermatomyositis, which the patient’s presentation and lab results suggested, require nerve conduction studies, a check of serum aldolase levels, and skin and muscle biopsies to complete the work-up. However, the arrival at a diagnosis is only the first step.
Patients with dermatomyositis, particularly those older than 60, require evaluation for occult malignancy. There is evidence that the body’s immune response to the cancer is what drives the disease process. Hence the need for the studies listed, looking for breast, lung, and gastrointestinal cancers especially.
Dermatomyositis is thought to be an inflammatory myopathy, possibly driven by autoimmune factors. It is rare (about 1 to 22 per 100,000) and affects women more than men.
The “sunburn” rash is typical, especially on the face, chest, and dorsal hands, and usually clears completely when the cancer is found and cured. Other common findings include elevated creatine kinase, hand rashes (known as Gottron’s papules), and dystrophic calcification in skin and/or joints.
TREATMENT
Aside from addressing a possible malignancy, treatment of dermatomyositis usually starts with glucocorticoids, eventually tapered and replaced by steroid-sparing agents such as azathioprine or cyclosporine. These drugs have dramatically increased the chances of survival and eventual cure.
It’s common for the photosensitivity to persist long after the myositis has resolved, which is why sunscreen and other sun-protective measures are advised.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “e”).
DISCUSSION
Most cases of dermatomyositis, which the patient’s presentation and lab results suggested, require nerve conduction studies, a check of serum aldolase levels, and skin and muscle biopsies to complete the work-up. However, the arrival at a diagnosis is only the first step.
Patients with dermatomyositis, particularly those older than 60, require evaluation for occult malignancy. There is evidence that the body’s immune response to the cancer is what drives the disease process. Hence the need for the studies listed, looking for breast, lung, and gastrointestinal cancers especially.
Dermatomyositis is thought to be an inflammatory myopathy, possibly driven by autoimmune factors. It is rare (about 1 to 22 per 100,000) and affects women more than men.
The “sunburn” rash is typical, especially on the face, chest, and dorsal hands, and usually clears completely when the cancer is found and cured. Other common findings include elevated creatine kinase, hand rashes (known as Gottron’s papules), and dystrophic calcification in skin and/or joints.
TREATMENT
Aside from addressing a possible malignancy, treatment of dermatomyositis usually starts with glucocorticoids, eventually tapered and replaced by steroid-sparing agents such as azathioprine or cyclosporine. These drugs have dramatically increased the chances of survival and eventual cure.
It’s common for the photosensitivity to persist long after the myositis has resolved, which is why sunscreen and other sun-protective measures are advised.
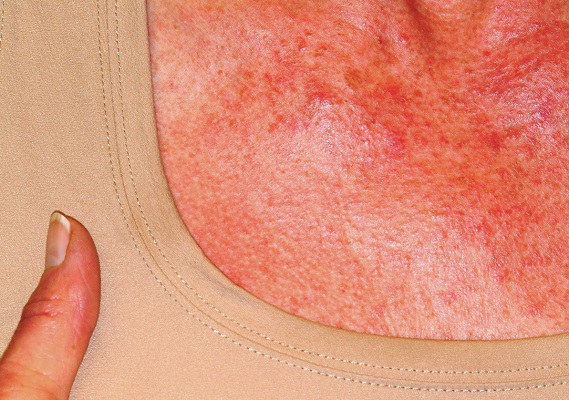
A 60-year-old woman was referred to dermatology for evaluation of “sunburn.” The rash was painful and unrelieved by topical medications, including class IV steroid creams. The redness was tender and warm to touch.
The rash had been present for months. During this period, the patient also had grown increasingly weak, leading her to quit her job. In the clinic, she was unable to stand from a seated position without difficulty. She reported no other health concerns and had quit smoking 5 years previously, after 30 years.
On examination, diffuse blanchable macular erythema on the patient’s face and chest was immediately observed. There was also an odd rash, composed of hundreds of tiny confluent papules, concentrated over the interphalangeal joints and dorsal hands. These too were warm and tender to touch. Most of her cuticles were peeling off; closer examination under magnification revealed tortuous capillaries on the distal cuticles of several fingers.
Bloodwork revealed a creatine kinase level slightly greater than 1000 U/L, and a positive antinuclear antibody, dilution unknown.
Cardiac inflammation can be present after mild COVID infection
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More vitamin D not better for reducing cancer or CVD incidence
according to a new randomized controlled study.
In the cohort of nearly 2,500 healthy individuals, the researchers found no differences in cancer or CVD incidence over 5 years between the groups randomly assigned to vitamin D supplementation and to placebo.
The findings, published online Jan. 4, 2022, in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, may be influenced by the fact that most participants had sufficient vitamin D levels at baseline, and thus received higher than recommended doses of vitamin D during the study.
“Vitamin D3 supplementation with 1600 or 3200 IU/day for 5 years did not reduce the incidence of major CVD events, any invasive cancer, or mortality among generally healthy and mostly vitamin D sufficient older adults in Finland,” write the authors, led by Jyrki Virtanen, RD, PhD, associate professor of nutrition and public health at University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio.
“The low number of subjects with low vitamin D concentrations was a bit of a surprise for us also, but it likely reflects the quite successful food fortification policy in Finland,” Dr. Virtanen told this news organization.
Prior research has found that vitamin D insufficiency is associated with a higher risk of nearly all diseases. Although the evidence on the benefits of vitamin D supplementation remains more limited, a meta-analysis reported a consistent and significant 13% reduction in cancer mortality in those who received vitamin D supplements.
In this study, Dr. Virtanen and colleagues investigated the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer and CVD incidence in a cohort of 2,495 healthy participants.
Men 60 years or older and women 65 years or older were randomly assigned to one of three groups: placebo, 40 mcg (1,600 IU) of daily vitamin D3, or 80 mcg (3,200 IU) of daily vitamin D3.
Data collected at baseline and throughout the trial included serum 25(OH)D concentrations, nutrition, sun exposure, medication use, mental health, and other factors that could affect the risk of disease.
The study’s primary endpoints were incident of major CVD and invasive cancer. Secondary endpoints included incidence of myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD mortality as well as site-specific cancers and cancer death.
Follow-up occurred via annual study questionnaires and national registry data. A representative subcohort of 551 participants had more detailed in-person evaluations. In the sub-cohort, mean serum 25(OH)D concentration was 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL) at baseline; 9.1% had concentrations less than 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) and 50.0% had concentrations of at least 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL).
The authors identified no major differences between the three arms at baseline, but noted that, compared with the overall study population, those in the subcohort were younger, more likely to use their own vitamin D supplements, and more likely to rate their health as good or excellent.
Among 503 participants that had complete data from baseline, the mean increase in serum 25(OH)D in participants receiving 1,600 IU/day vitamin D3 was 23.4 nmol/L (9.4 ng/mL) and 43.6 nmol/L (17.4 ng/mL) in the arm receiving 3,200 IU/day between baseline and 6 months. The authors observed a small additional increase in levels between the 6-month and 12-month visits, but few changes in vitamin D3 levels in the placebo arm.
At the 5-year follow-up, major CVD events occurred in 4.9% of participants in the placebo arm, 5% in those in the 1,600 IU/d arm (hazard ratio, 0.97), and 4.3% of those in the 3,200 IU/d arm (HR, 0.84; P = .44). Invasive cancer at follow-up was diagnosed in 4.9% of placebo recipients, 5.8% of those on 1,600 IU/d supplementation (HR, 1.14; P = .55), and 4.8% in the 3,200 IU/d group (HR, 0.95; P = .81). No significant differences were observed in the secondary endpoints or in total mortality.
The authors did not conduct a subanalysis in participants who had low 25(OH)D concentrations levels at baseline because “there were too few participants to do any meaningful analyses,” said Dr. Virtanen, who noted that blood samples were available for a representative subgroup of 550 subjects, and only 9% of them had low 25(OH)D concentrations at baseline.
Dr. Virtanen noted that future vitamin D supplementation trials should focus on recruiting participants with low vitamin D status.
The study was supported by funding from the Academy of Finland, University of Eastern Finland, Juho Vainio Foundation, Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa, Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research, Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation, and Finnish Cultural Foundation. Dr. Virtanen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new randomized controlled study.
In the cohort of nearly 2,500 healthy individuals, the researchers found no differences in cancer or CVD incidence over 5 years between the groups randomly assigned to vitamin D supplementation and to placebo.
The findings, published online Jan. 4, 2022, in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, may be influenced by the fact that most participants had sufficient vitamin D levels at baseline, and thus received higher than recommended doses of vitamin D during the study.
“Vitamin D3 supplementation with 1600 or 3200 IU/day for 5 years did not reduce the incidence of major CVD events, any invasive cancer, or mortality among generally healthy and mostly vitamin D sufficient older adults in Finland,” write the authors, led by Jyrki Virtanen, RD, PhD, associate professor of nutrition and public health at University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio.
“The low number of subjects with low vitamin D concentrations was a bit of a surprise for us also, but it likely reflects the quite successful food fortification policy in Finland,” Dr. Virtanen told this news organization.
Prior research has found that vitamin D insufficiency is associated with a higher risk of nearly all diseases. Although the evidence on the benefits of vitamin D supplementation remains more limited, a meta-analysis reported a consistent and significant 13% reduction in cancer mortality in those who received vitamin D supplements.
In this study, Dr. Virtanen and colleagues investigated the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer and CVD incidence in a cohort of 2,495 healthy participants.
Men 60 years or older and women 65 years or older were randomly assigned to one of three groups: placebo, 40 mcg (1,600 IU) of daily vitamin D3, or 80 mcg (3,200 IU) of daily vitamin D3.
Data collected at baseline and throughout the trial included serum 25(OH)D concentrations, nutrition, sun exposure, medication use, mental health, and other factors that could affect the risk of disease.
The study’s primary endpoints were incident of major CVD and invasive cancer. Secondary endpoints included incidence of myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD mortality as well as site-specific cancers and cancer death.
Follow-up occurred via annual study questionnaires and national registry data. A representative subcohort of 551 participants had more detailed in-person evaluations. In the sub-cohort, mean serum 25(OH)D concentration was 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL) at baseline; 9.1% had concentrations less than 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) and 50.0% had concentrations of at least 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL).
The authors identified no major differences between the three arms at baseline, but noted that, compared with the overall study population, those in the subcohort were younger, more likely to use their own vitamin D supplements, and more likely to rate their health as good or excellent.
Among 503 participants that had complete data from baseline, the mean increase in serum 25(OH)D in participants receiving 1,600 IU/day vitamin D3 was 23.4 nmol/L (9.4 ng/mL) and 43.6 nmol/L (17.4 ng/mL) in the arm receiving 3,200 IU/day between baseline and 6 months. The authors observed a small additional increase in levels between the 6-month and 12-month visits, but few changes in vitamin D3 levels in the placebo arm.
At the 5-year follow-up, major CVD events occurred in 4.9% of participants in the placebo arm, 5% in those in the 1,600 IU/d arm (hazard ratio, 0.97), and 4.3% of those in the 3,200 IU/d arm (HR, 0.84; P = .44). Invasive cancer at follow-up was diagnosed in 4.9% of placebo recipients, 5.8% of those on 1,600 IU/d supplementation (HR, 1.14; P = .55), and 4.8% in the 3,200 IU/d group (HR, 0.95; P = .81). No significant differences were observed in the secondary endpoints or in total mortality.
The authors did not conduct a subanalysis in participants who had low 25(OH)D concentrations levels at baseline because “there were too few participants to do any meaningful analyses,” said Dr. Virtanen, who noted that blood samples were available for a representative subgroup of 550 subjects, and only 9% of them had low 25(OH)D concentrations at baseline.
Dr. Virtanen noted that future vitamin D supplementation trials should focus on recruiting participants with low vitamin D status.
The study was supported by funding from the Academy of Finland, University of Eastern Finland, Juho Vainio Foundation, Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa, Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research, Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation, and Finnish Cultural Foundation. Dr. Virtanen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new randomized controlled study.
In the cohort of nearly 2,500 healthy individuals, the researchers found no differences in cancer or CVD incidence over 5 years between the groups randomly assigned to vitamin D supplementation and to placebo.
The findings, published online Jan. 4, 2022, in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, may be influenced by the fact that most participants had sufficient vitamin D levels at baseline, and thus received higher than recommended doses of vitamin D during the study.
“Vitamin D3 supplementation with 1600 or 3200 IU/day for 5 years did not reduce the incidence of major CVD events, any invasive cancer, or mortality among generally healthy and mostly vitamin D sufficient older adults in Finland,” write the authors, led by Jyrki Virtanen, RD, PhD, associate professor of nutrition and public health at University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio.
“The low number of subjects with low vitamin D concentrations was a bit of a surprise for us also, but it likely reflects the quite successful food fortification policy in Finland,” Dr. Virtanen told this news organization.
Prior research has found that vitamin D insufficiency is associated with a higher risk of nearly all diseases. Although the evidence on the benefits of vitamin D supplementation remains more limited, a meta-analysis reported a consistent and significant 13% reduction in cancer mortality in those who received vitamin D supplements.
In this study, Dr. Virtanen and colleagues investigated the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer and CVD incidence in a cohort of 2,495 healthy participants.
Men 60 years or older and women 65 years or older were randomly assigned to one of three groups: placebo, 40 mcg (1,600 IU) of daily vitamin D3, or 80 mcg (3,200 IU) of daily vitamin D3.
Data collected at baseline and throughout the trial included serum 25(OH)D concentrations, nutrition, sun exposure, medication use, mental health, and other factors that could affect the risk of disease.
The study’s primary endpoints were incident of major CVD and invasive cancer. Secondary endpoints included incidence of myocardial infarction, stroke, and CVD mortality as well as site-specific cancers and cancer death.
Follow-up occurred via annual study questionnaires and national registry data. A representative subcohort of 551 participants had more detailed in-person evaluations. In the sub-cohort, mean serum 25(OH)D concentration was 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL) at baseline; 9.1% had concentrations less than 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL) and 50.0% had concentrations of at least 75 nmol/L (30 ng/mL).
The authors identified no major differences between the three arms at baseline, but noted that, compared with the overall study population, those in the subcohort were younger, more likely to use their own vitamin D supplements, and more likely to rate their health as good or excellent.
Among 503 participants that had complete data from baseline, the mean increase in serum 25(OH)D in participants receiving 1,600 IU/day vitamin D3 was 23.4 nmol/L (9.4 ng/mL) and 43.6 nmol/L (17.4 ng/mL) in the arm receiving 3,200 IU/day between baseline and 6 months. The authors observed a small additional increase in levels between the 6-month and 12-month visits, but few changes in vitamin D3 levels in the placebo arm.
At the 5-year follow-up, major CVD events occurred in 4.9% of participants in the placebo arm, 5% in those in the 1,600 IU/d arm (hazard ratio, 0.97), and 4.3% of those in the 3,200 IU/d arm (HR, 0.84; P = .44). Invasive cancer at follow-up was diagnosed in 4.9% of placebo recipients, 5.8% of those on 1,600 IU/d supplementation (HR, 1.14; P = .55), and 4.8% in the 3,200 IU/d group (HR, 0.95; P = .81). No significant differences were observed in the secondary endpoints or in total mortality.
The authors did not conduct a subanalysis in participants who had low 25(OH)D concentrations levels at baseline because “there were too few participants to do any meaningful analyses,” said Dr. Virtanen, who noted that blood samples were available for a representative subgroup of 550 subjects, and only 9% of them had low 25(OH)D concentrations at baseline.
Dr. Virtanen noted that future vitamin D supplementation trials should focus on recruiting participants with low vitamin D status.
The study was supported by funding from the Academy of Finland, University of Eastern Finland, Juho Vainio Foundation, Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa, Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research, Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation, and Finnish Cultural Foundation. Dr. Virtanen disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NUTRITION
ACIP releases new dengue vaccine recommendations
The vaccine is only to be used for children aged 9-16 who live in endemic areas and who have evidence with a specific diagnostic test of prior dengue infection.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne virus found throughout the world, primarily in tropical or subtropical climates. Cases had steadily been increasing to 5.2 million in 2019, and the geographic distribution of cases is broadening with climate change and urbanization. About half of the world’s population is now at risk.
The dengue virus has four serotypes. The first infection may be mild or asymptomatic, but the second one can be life-threatening because of a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
The lead author of the new recommendations is Gabriela Paz-Bailey, MD, PhD, division of vector-borne diseases, dengue branch, CDC. She told this news organization that, during the second infection, when there are “low levels of antibodies from that first infection, the antibodies help the virus get inside the cells. There the virus is not killed, and that results in increased viral load, and then that can result in more severe disease and the plasma leakage” syndrome, which can lead to shock, severe bleeding, and organ failure. The death rate for severe dengue is up to 13%.
Previous infection with Zika virus, common in the same areas where dengue is endemic, can also increase the risk for symptomatic and severe dengue for subsequent infections.
In the United States, Puerto Rico is the main focus of control efforts because 95% of domestic dengue cases originate there – almost 30,000 cases between 2010 and 2020, with 11,000 cases and 4,000 hospitalizations occurring in children between the ages of 10 and 19.
Because Aedes aegypti, the primary mosquito vector transmitting dengue, is resistant to all commonly used insecticides in Puerto Rico, preventive efforts have shifted from insecticides to vaccination.
Antibody tests prevaccination
The main concern with the Sanofi’s dengue vaccine is that it could act as an asymptomatic primary dengue infection, in effect priming the body for a severe reaction from antibody-dependent enhancement with a subsequent infection. That is why it’s critical that the vaccine only be given to children with evidence of prior disease.
Dr. Paz-Bailey said: “The CDC came up with recommendations of what the performance of the test used for prevaccination screening should be. And it was 98% specificity and 75% sensitivity. ... But no test by itself was found to have a specificity of 98%, and this is why we’re recommending the two-test algorithm,” in which two different assays are run off the same blood sample, drawn at a prevaccination visit.
If the child has evidence of prior dengue, they can proceed with vaccination to protect against recurrent infection. Dengvaxia is given as a series of three shots over 6 months. Vaccine efficacy is 82% – so not everyone is protected, and additionally, that protection declines over time.
There is concern that it will be difficult to achieve compliance with such a complex regimen. Dr. Paz-Bailey said, “But I think that the trust in vaccines that is highly prevalent for [Puerto] Rico and trusting the health care system, and sort of the importance that is assigned to dengue by providers and by parents because of previous outbreaks and previous experiences is going to help us.” She added, “I think that the COVID experience has been very revealing. And what we have learned is that Puerto Rico has a very strong health care system, a very strong network of vaccine providers. ... Coverage for COVID vaccine is higher than in other parts of the U.S.”
One of the interesting things about dengue is that the first infection can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening. The second infection is generally worse because of this antibody-dependent enhancement phenomenon. Eng Eong Ooi, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology, National University of Singapore, told this news organization, “After you have two infections, you seem to be protected quite well against the remaining two [serotypes]. The vaccine serves as another episode of infection in those who had prior dengue, so then any natural infections after the vaccination in the seropositive become like the outcome of a third or fourth infection.”
Vaccination alone will not solve dengue. Dr. Ooi said, “There’s not one method that would fully control dengue. You need both vaccines as well as control measures, whether it’s Wolbachia or something else. At the same time, I think we need antiviral drugs, because hitting this virus in just one part of its life cycle wouldn’t make a huge, lasting impact.” Dr. Ooi added that as “the spread of the virus and the population immunity drops, you’re actually now more vulnerable to dengue outbreaks when they do get introduced. So, suppressing transmission alone isn’t the answer. You also have to keep herd immunity levels high. So if we can reduce the virus transmission by controlling either mosquito population or transmission and at the same time vaccinate to keep the immunity levels high, then I think we have a chance of controlling dengue.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey concluded: “I do want to emphasize that we are excited about having these tools, because for years and years, we have had really limited options to prevent and control dengue. It’s an important addition to have the vaccine be approved to be used within the U.S., and it’s going to pave the road for future vaccines.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey and Dr. Ooi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vaccine is only to be used for children aged 9-16 who live in endemic areas and who have evidence with a specific diagnostic test of prior dengue infection.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne virus found throughout the world, primarily in tropical or subtropical climates. Cases had steadily been increasing to 5.2 million in 2019, and the geographic distribution of cases is broadening with climate change and urbanization. About half of the world’s population is now at risk.
The dengue virus has four serotypes. The first infection may be mild or asymptomatic, but the second one can be life-threatening because of a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
The lead author of the new recommendations is Gabriela Paz-Bailey, MD, PhD, division of vector-borne diseases, dengue branch, CDC. She told this news organization that, during the second infection, when there are “low levels of antibodies from that first infection, the antibodies help the virus get inside the cells. There the virus is not killed, and that results in increased viral load, and then that can result in more severe disease and the plasma leakage” syndrome, which can lead to shock, severe bleeding, and organ failure. The death rate for severe dengue is up to 13%.
Previous infection with Zika virus, common in the same areas where dengue is endemic, can also increase the risk for symptomatic and severe dengue for subsequent infections.
In the United States, Puerto Rico is the main focus of control efforts because 95% of domestic dengue cases originate there – almost 30,000 cases between 2010 and 2020, with 11,000 cases and 4,000 hospitalizations occurring in children between the ages of 10 and 19.
Because Aedes aegypti, the primary mosquito vector transmitting dengue, is resistant to all commonly used insecticides in Puerto Rico, preventive efforts have shifted from insecticides to vaccination.
Antibody tests prevaccination
The main concern with the Sanofi’s dengue vaccine is that it could act as an asymptomatic primary dengue infection, in effect priming the body for a severe reaction from antibody-dependent enhancement with a subsequent infection. That is why it’s critical that the vaccine only be given to children with evidence of prior disease.
Dr. Paz-Bailey said: “The CDC came up with recommendations of what the performance of the test used for prevaccination screening should be. And it was 98% specificity and 75% sensitivity. ... But no test by itself was found to have a specificity of 98%, and this is why we’re recommending the two-test algorithm,” in which two different assays are run off the same blood sample, drawn at a prevaccination visit.
If the child has evidence of prior dengue, they can proceed with vaccination to protect against recurrent infection. Dengvaxia is given as a series of three shots over 6 months. Vaccine efficacy is 82% – so not everyone is protected, and additionally, that protection declines over time.
There is concern that it will be difficult to achieve compliance with such a complex regimen. Dr. Paz-Bailey said, “But I think that the trust in vaccines that is highly prevalent for [Puerto] Rico and trusting the health care system, and sort of the importance that is assigned to dengue by providers and by parents because of previous outbreaks and previous experiences is going to help us.” She added, “I think that the COVID experience has been very revealing. And what we have learned is that Puerto Rico has a very strong health care system, a very strong network of vaccine providers. ... Coverage for COVID vaccine is higher than in other parts of the U.S.”
One of the interesting things about dengue is that the first infection can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening. The second infection is generally worse because of this antibody-dependent enhancement phenomenon. Eng Eong Ooi, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology, National University of Singapore, told this news organization, “After you have two infections, you seem to be protected quite well against the remaining two [serotypes]. The vaccine serves as another episode of infection in those who had prior dengue, so then any natural infections after the vaccination in the seropositive become like the outcome of a third or fourth infection.”
Vaccination alone will not solve dengue. Dr. Ooi said, “There’s not one method that would fully control dengue. You need both vaccines as well as control measures, whether it’s Wolbachia or something else. At the same time, I think we need antiviral drugs, because hitting this virus in just one part of its life cycle wouldn’t make a huge, lasting impact.” Dr. Ooi added that as “the spread of the virus and the population immunity drops, you’re actually now more vulnerable to dengue outbreaks when they do get introduced. So, suppressing transmission alone isn’t the answer. You also have to keep herd immunity levels high. So if we can reduce the virus transmission by controlling either mosquito population or transmission and at the same time vaccinate to keep the immunity levels high, then I think we have a chance of controlling dengue.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey concluded: “I do want to emphasize that we are excited about having these tools, because for years and years, we have had really limited options to prevent and control dengue. It’s an important addition to have the vaccine be approved to be used within the U.S., and it’s going to pave the road for future vaccines.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey and Dr. Ooi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vaccine is only to be used for children aged 9-16 who live in endemic areas and who have evidence with a specific diagnostic test of prior dengue infection.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne virus found throughout the world, primarily in tropical or subtropical climates. Cases had steadily been increasing to 5.2 million in 2019, and the geographic distribution of cases is broadening with climate change and urbanization. About half of the world’s population is now at risk.
The dengue virus has four serotypes. The first infection may be mild or asymptomatic, but the second one can be life-threatening because of a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
The lead author of the new recommendations is Gabriela Paz-Bailey, MD, PhD, division of vector-borne diseases, dengue branch, CDC. She told this news organization that, during the second infection, when there are “low levels of antibodies from that first infection, the antibodies help the virus get inside the cells. There the virus is not killed, and that results in increased viral load, and then that can result in more severe disease and the plasma leakage” syndrome, which can lead to shock, severe bleeding, and organ failure. The death rate for severe dengue is up to 13%.
Previous infection with Zika virus, common in the same areas where dengue is endemic, can also increase the risk for symptomatic and severe dengue for subsequent infections.
In the United States, Puerto Rico is the main focus of control efforts because 95% of domestic dengue cases originate there – almost 30,000 cases between 2010 and 2020, with 11,000 cases and 4,000 hospitalizations occurring in children between the ages of 10 and 19.
Because Aedes aegypti, the primary mosquito vector transmitting dengue, is resistant to all commonly used insecticides in Puerto Rico, preventive efforts have shifted from insecticides to vaccination.
Antibody tests prevaccination
The main concern with the Sanofi’s dengue vaccine is that it could act as an asymptomatic primary dengue infection, in effect priming the body for a severe reaction from antibody-dependent enhancement with a subsequent infection. That is why it’s critical that the vaccine only be given to children with evidence of prior disease.
Dr. Paz-Bailey said: “The CDC came up with recommendations of what the performance of the test used for prevaccination screening should be. And it was 98% specificity and 75% sensitivity. ... But no test by itself was found to have a specificity of 98%, and this is why we’re recommending the two-test algorithm,” in which two different assays are run off the same blood sample, drawn at a prevaccination visit.
If the child has evidence of prior dengue, they can proceed with vaccination to protect against recurrent infection. Dengvaxia is given as a series of three shots over 6 months. Vaccine efficacy is 82% – so not everyone is protected, and additionally, that protection declines over time.
There is concern that it will be difficult to achieve compliance with such a complex regimen. Dr. Paz-Bailey said, “But I think that the trust in vaccines that is highly prevalent for [Puerto] Rico and trusting the health care system, and sort of the importance that is assigned to dengue by providers and by parents because of previous outbreaks and previous experiences is going to help us.” She added, “I think that the COVID experience has been very revealing. And what we have learned is that Puerto Rico has a very strong health care system, a very strong network of vaccine providers. ... Coverage for COVID vaccine is higher than in other parts of the U.S.”
One of the interesting things about dengue is that the first infection can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening. The second infection is generally worse because of this antibody-dependent enhancement phenomenon. Eng Eong Ooi, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology, National University of Singapore, told this news organization, “After you have two infections, you seem to be protected quite well against the remaining two [serotypes]. The vaccine serves as another episode of infection in those who had prior dengue, so then any natural infections after the vaccination in the seropositive become like the outcome of a third or fourth infection.”
Vaccination alone will not solve dengue. Dr. Ooi said, “There’s not one method that would fully control dengue. You need both vaccines as well as control measures, whether it’s Wolbachia or something else. At the same time, I think we need antiviral drugs, because hitting this virus in just one part of its life cycle wouldn’t make a huge, lasting impact.” Dr. Ooi added that as “the spread of the virus and the population immunity drops, you’re actually now more vulnerable to dengue outbreaks when they do get introduced. So, suppressing transmission alone isn’t the answer. You also have to keep herd immunity levels high. So if we can reduce the virus transmission by controlling either mosquito population or transmission and at the same time vaccinate to keep the immunity levels high, then I think we have a chance of controlling dengue.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey concluded: “I do want to emphasize that we are excited about having these tools, because for years and years, we have had really limited options to prevent and control dengue. It’s an important addition to have the vaccine be approved to be used within the U.S., and it’s going to pave the road for future vaccines.”
Dr. Paz-Bailey and Dr. Ooi reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MMWR RECOMMENDATIONS AND REPORTS
Swallowable intragastric balloon shows significant weight loss
results from a meta-analysis show.
“We believe this analysis to be the most comprehensive review [of the Allurion balloon],” reported first author Daryl Ramai, MD, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues in the research, published in the November/December 2021 issue of the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
“Our study showed that the Allurion balloon reduces waist circumference and triglyceride levels and [is] associated with less adverse events when compared with other intragastric balloons,” the authors concluded.
Unlike other balloons, the Allurion gastric balloon is compressed into a small capsule that is connected to a thin catheter and, once swallowed, it is then inflated with 550 mL of liquid through the catheter to create a feeling of fullness and help control hunger.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis in approximately 20 minutes, potentially avoiding the burden and extra costs of surgery or endoscopic placement and removal. After approximately 4 months, the balloon is designed to empty through a valve that spontaneously opens, and the balloon is then passed in the stool.
Though currently used around the world, the balloon does not yet have approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Meta-analysis shows 12.2% average weight loss across studies
To assess the balloon’s performance, the authors identified 7 out of 273 published studies that met the analysis criteria. The studies included 2,152 patients, ranging in age from 18 to 65 years, with a mean baseline body mass index of 32.1-38.6 kg/m2.
All of the studies were prospective, with reported outcomes at 3-4 months, when the Allurion balloon typically deflates. Three of the studies were multicenter, while four were single center.
In terms of improvements in BMI, the results showed the pooled mean difference from baseline through to the end of the studies was 0.88 (P = .001), and the weighted average percentage of total body weight loss during treatment across the studies was 12.2%.
The mean excess body weight loss across the Allurion studies was 49.1%.
The analysis was not designed to directly compare outcomes with other balloons, but the authors note, for instance, that the ReShape Duo intragastric balloon (an FDA-approved dual-balloon system) has been reported in a previous study to be associated with a percentage of total body weight loss of 7.6% at 6 months, compared with 3.6% observed among those with lifestyle modifications.
However, a separate meta-analysis showed the pooled percentage of total body weight loss with the FDA-approved Orbera balloon to be about the same as the current Allurion analysis, at 12.3% at 3 months after implantation (followed by 13.2% at 6 months and 11.3% at 12 months). The analysis further showed excess body weight loss with the Orbera balloon at 12 months to be 25.4%.
In other outcomes, the current meta-analysis also showed significant improvements with the Allurion balloon in waist circumference of 0.89 (P = .001) and in triglyceride levels of 0.66 (P = .004) versus baseline.
Previous research involving the FDA-approved Obalon intragastric balloon, which is inflated with gas rather than liquid, showed a significant reduction in waist circumference from 109 cm (±12.3) to 99 cm (±10.5) (P < .05), and another study showed that 37.5% of patients receiving the Orbera balloon had normalized triglyceride levels after 4 months, without concomitant medical therapy.
Adverse events appear lower vs. other balloons
Potential risks associated with the Allurion balloon include the potential for early deflation; however, the pooled rate of early balloon deflation observed in the meta-analysis was relatively low at 1.8%.
Other adverse events reported with the Allurion balloon were abdominal pain (37.5%), vomiting (29.6%), diarrhea (15.4%), and small bowel obstruction (0.5%).
The corresponding rates of abdominal pain with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported at 54.5% and 57.5%, respectively, with the effects possibly caused by overinflation, the authors noted.
And rates of vomiting with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported as much higher, at 86.7% and 86.8%, respectively.
Of note, there were no deaths or cases of acute pancreatitis reported in the meta-analysis studies of Allurion.
As reported by this news organization, such concerns have been raised in previous FDA alerts regarding the Orbera and ReShape Duo liquid-filled intragastric balloons.
In the most recent update, issued in April 2020, the FDA described receiving reports of 18 deaths that had occurred worldwide since the approvals of the Orbera and ReShape balloons, including eight in the United States.
Dr. Ramai noted that the concern about the issues is warranted.
“These concerns are valid,” he told this news organization. “Theoretically, since the Allurion balloon is placed for a shorter time span, it is conceivable that there may be less adverse events. However, comparative trials are needed to confirm this.”
Although the balloons show efficacy in patients struggling with weight loss, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease, “the type and duration of intragastric balloons should be tailored to the patient,” Dr. Ramai said.
“Clinicians should thoroughly discuss with their patients the benefits and risks of using an intragastric balloon,” he added. “Furthermore, placement of intragastric balloons should only be attempted by clinicians with expertise in bariatric endoscopy.”
The study received no financial support. Dr. Ramai reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com,
results from a meta-analysis show.
“We believe this analysis to be the most comprehensive review [of the Allurion balloon],” reported first author Daryl Ramai, MD, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues in the research, published in the November/December 2021 issue of the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
“Our study showed that the Allurion balloon reduces waist circumference and triglyceride levels and [is] associated with less adverse events when compared with other intragastric balloons,” the authors concluded.
Unlike other balloons, the Allurion gastric balloon is compressed into a small capsule that is connected to a thin catheter and, once swallowed, it is then inflated with 550 mL of liquid through the catheter to create a feeling of fullness and help control hunger.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis in approximately 20 minutes, potentially avoiding the burden and extra costs of surgery or endoscopic placement and removal. After approximately 4 months, the balloon is designed to empty through a valve that spontaneously opens, and the balloon is then passed in the stool.
Though currently used around the world, the balloon does not yet have approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Meta-analysis shows 12.2% average weight loss across studies
To assess the balloon’s performance, the authors identified 7 out of 273 published studies that met the analysis criteria. The studies included 2,152 patients, ranging in age from 18 to 65 years, with a mean baseline body mass index of 32.1-38.6 kg/m2.
All of the studies were prospective, with reported outcomes at 3-4 months, when the Allurion balloon typically deflates. Three of the studies were multicenter, while four were single center.
In terms of improvements in BMI, the results showed the pooled mean difference from baseline through to the end of the studies was 0.88 (P = .001), and the weighted average percentage of total body weight loss during treatment across the studies was 12.2%.
The mean excess body weight loss across the Allurion studies was 49.1%.
The analysis was not designed to directly compare outcomes with other balloons, but the authors note, for instance, that the ReShape Duo intragastric balloon (an FDA-approved dual-balloon system) has been reported in a previous study to be associated with a percentage of total body weight loss of 7.6% at 6 months, compared with 3.6% observed among those with lifestyle modifications.
However, a separate meta-analysis showed the pooled percentage of total body weight loss with the FDA-approved Orbera balloon to be about the same as the current Allurion analysis, at 12.3% at 3 months after implantation (followed by 13.2% at 6 months and 11.3% at 12 months). The analysis further showed excess body weight loss with the Orbera balloon at 12 months to be 25.4%.
In other outcomes, the current meta-analysis also showed significant improvements with the Allurion balloon in waist circumference of 0.89 (P = .001) and in triglyceride levels of 0.66 (P = .004) versus baseline.
Previous research involving the FDA-approved Obalon intragastric balloon, which is inflated with gas rather than liquid, showed a significant reduction in waist circumference from 109 cm (±12.3) to 99 cm (±10.5) (P < .05), and another study showed that 37.5% of patients receiving the Orbera balloon had normalized triglyceride levels after 4 months, without concomitant medical therapy.
Adverse events appear lower vs. other balloons
Potential risks associated with the Allurion balloon include the potential for early deflation; however, the pooled rate of early balloon deflation observed in the meta-analysis was relatively low at 1.8%.
Other adverse events reported with the Allurion balloon were abdominal pain (37.5%), vomiting (29.6%), diarrhea (15.4%), and small bowel obstruction (0.5%).
The corresponding rates of abdominal pain with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported at 54.5% and 57.5%, respectively, with the effects possibly caused by overinflation, the authors noted.
And rates of vomiting with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported as much higher, at 86.7% and 86.8%, respectively.
Of note, there were no deaths or cases of acute pancreatitis reported in the meta-analysis studies of Allurion.
As reported by this news organization, such concerns have been raised in previous FDA alerts regarding the Orbera and ReShape Duo liquid-filled intragastric balloons.
In the most recent update, issued in April 2020, the FDA described receiving reports of 18 deaths that had occurred worldwide since the approvals of the Orbera and ReShape balloons, including eight in the United States.
Dr. Ramai noted that the concern about the issues is warranted.
“These concerns are valid,” he told this news organization. “Theoretically, since the Allurion balloon is placed for a shorter time span, it is conceivable that there may be less adverse events. However, comparative trials are needed to confirm this.”
Although the balloons show efficacy in patients struggling with weight loss, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease, “the type and duration of intragastric balloons should be tailored to the patient,” Dr. Ramai said.
“Clinicians should thoroughly discuss with their patients the benefits and risks of using an intragastric balloon,” he added. “Furthermore, placement of intragastric balloons should only be attempted by clinicians with expertise in bariatric endoscopy.”
The study received no financial support. Dr. Ramai reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com,
results from a meta-analysis show.
“We believe this analysis to be the most comprehensive review [of the Allurion balloon],” reported first author Daryl Ramai, MD, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues in the research, published in the November/December 2021 issue of the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
“Our study showed that the Allurion balloon reduces waist circumference and triglyceride levels and [is] associated with less adverse events when compared with other intragastric balloons,” the authors concluded.
Unlike other balloons, the Allurion gastric balloon is compressed into a small capsule that is connected to a thin catheter and, once swallowed, it is then inflated with 550 mL of liquid through the catheter to create a feeling of fullness and help control hunger.
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis in approximately 20 minutes, potentially avoiding the burden and extra costs of surgery or endoscopic placement and removal. After approximately 4 months, the balloon is designed to empty through a valve that spontaneously opens, and the balloon is then passed in the stool.
Though currently used around the world, the balloon does not yet have approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Meta-analysis shows 12.2% average weight loss across studies
To assess the balloon’s performance, the authors identified 7 out of 273 published studies that met the analysis criteria. The studies included 2,152 patients, ranging in age from 18 to 65 years, with a mean baseline body mass index of 32.1-38.6 kg/m2.
All of the studies were prospective, with reported outcomes at 3-4 months, when the Allurion balloon typically deflates. Three of the studies were multicenter, while four were single center.
In terms of improvements in BMI, the results showed the pooled mean difference from baseline through to the end of the studies was 0.88 (P = .001), and the weighted average percentage of total body weight loss during treatment across the studies was 12.2%.
The mean excess body weight loss across the Allurion studies was 49.1%.
The analysis was not designed to directly compare outcomes with other balloons, but the authors note, for instance, that the ReShape Duo intragastric balloon (an FDA-approved dual-balloon system) has been reported in a previous study to be associated with a percentage of total body weight loss of 7.6% at 6 months, compared with 3.6% observed among those with lifestyle modifications.
However, a separate meta-analysis showed the pooled percentage of total body weight loss with the FDA-approved Orbera balloon to be about the same as the current Allurion analysis, at 12.3% at 3 months after implantation (followed by 13.2% at 6 months and 11.3% at 12 months). The analysis further showed excess body weight loss with the Orbera balloon at 12 months to be 25.4%.
In other outcomes, the current meta-analysis also showed significant improvements with the Allurion balloon in waist circumference of 0.89 (P = .001) and in triglyceride levels of 0.66 (P = .004) versus baseline.
Previous research involving the FDA-approved Obalon intragastric balloon, which is inflated with gas rather than liquid, showed a significant reduction in waist circumference from 109 cm (±12.3) to 99 cm (±10.5) (P < .05), and another study showed that 37.5% of patients receiving the Orbera balloon had normalized triglyceride levels after 4 months, without concomitant medical therapy.
Adverse events appear lower vs. other balloons
Potential risks associated with the Allurion balloon include the potential for early deflation; however, the pooled rate of early balloon deflation observed in the meta-analysis was relatively low at 1.8%.
Other adverse events reported with the Allurion balloon were abdominal pain (37.5%), vomiting (29.6%), diarrhea (15.4%), and small bowel obstruction (0.5%).
The corresponding rates of abdominal pain with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported at 54.5% and 57.5%, respectively, with the effects possibly caused by overinflation, the authors noted.
And rates of vomiting with the ReShape Duo and Orbera balloons have been reported as much higher, at 86.7% and 86.8%, respectively.
Of note, there were no deaths or cases of acute pancreatitis reported in the meta-analysis studies of Allurion.
As reported by this news organization, such concerns have been raised in previous FDA alerts regarding the Orbera and ReShape Duo liquid-filled intragastric balloons.
In the most recent update, issued in April 2020, the FDA described receiving reports of 18 deaths that had occurred worldwide since the approvals of the Orbera and ReShape balloons, including eight in the United States.
Dr. Ramai noted that the concern about the issues is warranted.
“These concerns are valid,” he told this news organization. “Theoretically, since the Allurion balloon is placed for a shorter time span, it is conceivable that there may be less adverse events. However, comparative trials are needed to confirm this.”
Although the balloons show efficacy in patients struggling with weight loss, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease, “the type and duration of intragastric balloons should be tailored to the patient,” Dr. Ramai said.
“Clinicians should thoroughly discuss with their patients the benefits and risks of using an intragastric balloon,” he added. “Furthermore, placement of intragastric balloons should only be attempted by clinicians with expertise in bariatric endoscopy.”
The study received no financial support. Dr. Ramai reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com,
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
Quebec plans to fine unvaccinated adults
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC to update mask recommendations as Omicron spreads
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.