User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Lifestyle coaching for obesity associated with improved cardiometabolic numbers in study
Patients who received intensive lifestyle training by coaches in the primary care setting experienced improvement in several indicators of cardiometabolic health in a 2-year trial.
The 803 trial participants comprised a racially diverse, low-income population with obesity. In this study, primary care clinics were randomly assigned to provide weight-loss coaching or usual care. Patients at the intensive training clinics lost significantly more weight than the other patients, as reported in a paper published in September in the New England Journal of Medicine on the PROmoting Successful Weight Loss in Primary CarE in Louisiana (PROPEL) trial. The patients who received weight loss coaching also had significantly more improvement in HDL cholesterol levels, total to HDL cholesterol ratios, and metabolic syndrome severity score, said researchers in the new paper on the PROPEL trial, which was published in Circulation on February 8 .
“We believe that one reason for success of the program was the use of a health coach [who] was embedded in the primary care office,” said lead author Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, associate executive director for population and public health sciences at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La. “This way, the patients could get their counseling in a familiar environment and did not have to go to a different setting. The coaches developed close relationships with the patients over the 2 years, and this helped develop a sense of responsibility in the patients as the coaches were helping the patients to set goals and kept them accountable.”
In the PROPEL study, 67% of patients were Black and had low health literacy scores that corresponded with less than a ninth-grade education level. The intensive lifestyle intervention program included weekly sessions with the trained health coaches over the first 6 months — 16 face-to-face and 6 over the phone — and then at least monthly for the last 18 months. The coaches had higher education degrees in nutrition, physical activity, or behavioral medicine. Before the program started, the coaches also received training in the management of obesity and related health issues, health literacy, and patient communication and education. The goal of the program was 10% weight loss, using personalized action plans on eating, dieting, and physical activity.
Those in the usual-care clinics continued receiving normal care and received newsletters on health topics, such as the importance of sleep and tips for limiting time spent sitting. The primary care physicians at those clinics also were given a presentation with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) information on intensive lifestyle interventions for obesity.
Cholesterol changes in intervention vs. control group
HDL cholesterol improved significantly among the coached patients, compared with the other patients, with a mean difference of 4.1 mg/dL at 1 year and 4.6 mg/dL at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). The total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio showed a similarly significant difference in decline, with a between-group difference of –0.29 at 1 year and –0.31 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). Also, the difference in the change in metabolic severity scores were –0.40 at 1 year and –0.21 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both).
Fasting blood glucose had declined after the 1st year by a significantly greater degree in the clinics with coaching, compared with the others, but not after the second year, researchers found.
There were no significant differences seen in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, or blood pressure. Dr. Katzmarzyk said the likely reason for no change in blood pressure was that it was already relatively well-controlled at baseline for all the patients.
Funding barriers to obesity treatment
The CMS currently cover intensive training for obesity if delivered directly by a primary care physician, according to the authors of the new paper. Dr. Katzmarzyk said he hopes that will change.
“We are hoping that the evidence provided in this study may change the way that CMS funds obesity treatment in the future by allowing an expansion of the care team,” he said.
John Flack, MD, chair of internal medicine at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, said that the main achievement of the study was that it showed that intensive weight-loss training in the primary-care setting could be accomplished in a racially diverse population with low health literacy.
“You can’t just automatically assume just because you’ve seen it in some other populations that you can replicate this in every population, so they’ve done a really good job,” he said.
That programs are eligible for reimbursement only if they’re run by primary-care physicians is an ongoing problem, he said.
“You don’t necessarily need to be a physician to do this,” Dr. Flack said.
For best results, payment for coaching should not be tied to office visits, Dr. Flack noted.
“If they’re de-tethered from the office visits and you’re paid for quality ... you’re going to build out your infrastructure differently to care for people,” he said.
Andrew Freeman, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Colorado, Denver, and cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s nutrition and lifestyle work group, said the findings dovetail with his experience.
“I’m a huge believer that when people need to make lifestyle changes, having someone hold their hand and guide them through the effort is incredibly rewarding and incredibly powerful,” said Dr. Freeman, who also oversees the intensive cardiac rehab program at National Jewish Health in Denver.
A program like this needs proper funding in order to work, Dr, Freeman noted. He added that, even with coaches being paid well, “if you are able to prevent just one readmission for, say, heart failure a month . . . you could be saving millions of dollars over just a couple of years.”
Dr. Katzmarzyk, Dr. Flack, and Dr. Freeman reported no relevant disclosures. Louisiana State University, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, and Montclair State University have interest in the intellectual property surrounding a weight graph used in the study. The other researchers reported grants and/or fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Takeda, Novo Nordisk, and other companies.
Patients who received intensive lifestyle training by coaches in the primary care setting experienced improvement in several indicators of cardiometabolic health in a 2-year trial.
The 803 trial participants comprised a racially diverse, low-income population with obesity. In this study, primary care clinics were randomly assigned to provide weight-loss coaching or usual care. Patients at the intensive training clinics lost significantly more weight than the other patients, as reported in a paper published in September in the New England Journal of Medicine on the PROmoting Successful Weight Loss in Primary CarE in Louisiana (PROPEL) trial. The patients who received weight loss coaching also had significantly more improvement in HDL cholesterol levels, total to HDL cholesterol ratios, and metabolic syndrome severity score, said researchers in the new paper on the PROPEL trial, which was published in Circulation on February 8 .
“We believe that one reason for success of the program was the use of a health coach [who] was embedded in the primary care office,” said lead author Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, associate executive director for population and public health sciences at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La. “This way, the patients could get their counseling in a familiar environment and did not have to go to a different setting. The coaches developed close relationships with the patients over the 2 years, and this helped develop a sense of responsibility in the patients as the coaches were helping the patients to set goals and kept them accountable.”
In the PROPEL study, 67% of patients were Black and had low health literacy scores that corresponded with less than a ninth-grade education level. The intensive lifestyle intervention program included weekly sessions with the trained health coaches over the first 6 months — 16 face-to-face and 6 over the phone — and then at least monthly for the last 18 months. The coaches had higher education degrees in nutrition, physical activity, or behavioral medicine. Before the program started, the coaches also received training in the management of obesity and related health issues, health literacy, and patient communication and education. The goal of the program was 10% weight loss, using personalized action plans on eating, dieting, and physical activity.
Those in the usual-care clinics continued receiving normal care and received newsletters on health topics, such as the importance of sleep and tips for limiting time spent sitting. The primary care physicians at those clinics also were given a presentation with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) information on intensive lifestyle interventions for obesity.
Cholesterol changes in intervention vs. control group
HDL cholesterol improved significantly among the coached patients, compared with the other patients, with a mean difference of 4.1 mg/dL at 1 year and 4.6 mg/dL at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). The total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio showed a similarly significant difference in decline, with a between-group difference of –0.29 at 1 year and –0.31 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). Also, the difference in the change in metabolic severity scores were –0.40 at 1 year and –0.21 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both).
Fasting blood glucose had declined after the 1st year by a significantly greater degree in the clinics with coaching, compared with the others, but not after the second year, researchers found.
There were no significant differences seen in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, or blood pressure. Dr. Katzmarzyk said the likely reason for no change in blood pressure was that it was already relatively well-controlled at baseline for all the patients.
Funding barriers to obesity treatment
The CMS currently cover intensive training for obesity if delivered directly by a primary care physician, according to the authors of the new paper. Dr. Katzmarzyk said he hopes that will change.
“We are hoping that the evidence provided in this study may change the way that CMS funds obesity treatment in the future by allowing an expansion of the care team,” he said.
John Flack, MD, chair of internal medicine at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, said that the main achievement of the study was that it showed that intensive weight-loss training in the primary-care setting could be accomplished in a racially diverse population with low health literacy.
“You can’t just automatically assume just because you’ve seen it in some other populations that you can replicate this in every population, so they’ve done a really good job,” he said.
That programs are eligible for reimbursement only if they’re run by primary-care physicians is an ongoing problem, he said.
“You don’t necessarily need to be a physician to do this,” Dr. Flack said.
For best results, payment for coaching should not be tied to office visits, Dr. Flack noted.
“If they’re de-tethered from the office visits and you’re paid for quality ... you’re going to build out your infrastructure differently to care for people,” he said.
Andrew Freeman, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Colorado, Denver, and cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s nutrition and lifestyle work group, said the findings dovetail with his experience.
“I’m a huge believer that when people need to make lifestyle changes, having someone hold their hand and guide them through the effort is incredibly rewarding and incredibly powerful,” said Dr. Freeman, who also oversees the intensive cardiac rehab program at National Jewish Health in Denver.
A program like this needs proper funding in order to work, Dr, Freeman noted. He added that, even with coaches being paid well, “if you are able to prevent just one readmission for, say, heart failure a month . . . you could be saving millions of dollars over just a couple of years.”
Dr. Katzmarzyk, Dr. Flack, and Dr. Freeman reported no relevant disclosures. Louisiana State University, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, and Montclair State University have interest in the intellectual property surrounding a weight graph used in the study. The other researchers reported grants and/or fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Takeda, Novo Nordisk, and other companies.
Patients who received intensive lifestyle training by coaches in the primary care setting experienced improvement in several indicators of cardiometabolic health in a 2-year trial.
The 803 trial participants comprised a racially diverse, low-income population with obesity. In this study, primary care clinics were randomly assigned to provide weight-loss coaching or usual care. Patients at the intensive training clinics lost significantly more weight than the other patients, as reported in a paper published in September in the New England Journal of Medicine on the PROmoting Successful Weight Loss in Primary CarE in Louisiana (PROPEL) trial. The patients who received weight loss coaching also had significantly more improvement in HDL cholesterol levels, total to HDL cholesterol ratios, and metabolic syndrome severity score, said researchers in the new paper on the PROPEL trial, which was published in Circulation on February 8 .
“We believe that one reason for success of the program was the use of a health coach [who] was embedded in the primary care office,” said lead author Peter Katzmarzyk, PhD, associate executive director for population and public health sciences at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, La. “This way, the patients could get their counseling in a familiar environment and did not have to go to a different setting. The coaches developed close relationships with the patients over the 2 years, and this helped develop a sense of responsibility in the patients as the coaches were helping the patients to set goals and kept them accountable.”
In the PROPEL study, 67% of patients were Black and had low health literacy scores that corresponded with less than a ninth-grade education level. The intensive lifestyle intervention program included weekly sessions with the trained health coaches over the first 6 months — 16 face-to-face and 6 over the phone — and then at least monthly for the last 18 months. The coaches had higher education degrees in nutrition, physical activity, or behavioral medicine. Before the program started, the coaches also received training in the management of obesity and related health issues, health literacy, and patient communication and education. The goal of the program was 10% weight loss, using personalized action plans on eating, dieting, and physical activity.
Those in the usual-care clinics continued receiving normal care and received newsletters on health topics, such as the importance of sleep and tips for limiting time spent sitting. The primary care physicians at those clinics also were given a presentation with Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) information on intensive lifestyle interventions for obesity.
Cholesterol changes in intervention vs. control group
HDL cholesterol improved significantly among the coached patients, compared with the other patients, with a mean difference of 4.1 mg/dL at 1 year and 4.6 mg/dL at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). The total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio showed a similarly significant difference in decline, with a between-group difference of –0.29 at 1 year and –0.31 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both). Also, the difference in the change in metabolic severity scores were –0.40 at 1 year and –0.21 at 2 years (P less than .01 for both).
Fasting blood glucose had declined after the 1st year by a significantly greater degree in the clinics with coaching, compared with the others, but not after the second year, researchers found.
There were no significant differences seen in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, or blood pressure. Dr. Katzmarzyk said the likely reason for no change in blood pressure was that it was already relatively well-controlled at baseline for all the patients.
Funding barriers to obesity treatment
The CMS currently cover intensive training for obesity if delivered directly by a primary care physician, according to the authors of the new paper. Dr. Katzmarzyk said he hopes that will change.
“We are hoping that the evidence provided in this study may change the way that CMS funds obesity treatment in the future by allowing an expansion of the care team,” he said.
John Flack, MD, chair of internal medicine at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, said that the main achievement of the study was that it showed that intensive weight-loss training in the primary-care setting could be accomplished in a racially diverse population with low health literacy.
“You can’t just automatically assume just because you’ve seen it in some other populations that you can replicate this in every population, so they’ve done a really good job,” he said.
That programs are eligible for reimbursement only if they’re run by primary-care physicians is an ongoing problem, he said.
“You don’t necessarily need to be a physician to do this,” Dr. Flack said.
For best results, payment for coaching should not be tied to office visits, Dr. Flack noted.
“If they’re de-tethered from the office visits and you’re paid for quality ... you’re going to build out your infrastructure differently to care for people,” he said.
Andrew Freeman, MD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Colorado, Denver, and cochair of the American College of Cardiology’s nutrition and lifestyle work group, said the findings dovetail with his experience.
“I’m a huge believer that when people need to make lifestyle changes, having someone hold their hand and guide them through the effort is incredibly rewarding and incredibly powerful,” said Dr. Freeman, who also oversees the intensive cardiac rehab program at National Jewish Health in Denver.
A program like this needs proper funding in order to work, Dr, Freeman noted. He added that, even with coaches being paid well, “if you are able to prevent just one readmission for, say, heart failure a month . . . you could be saving millions of dollars over just a couple of years.”
Dr. Katzmarzyk, Dr. Flack, and Dr. Freeman reported no relevant disclosures. Louisiana State University, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, and Montclair State University have interest in the intellectual property surrounding a weight graph used in the study. The other researchers reported grants and/or fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Takeda, Novo Nordisk, and other companies.
Expert calls for paradigm shift in lab monitoring of some dermatology drugs
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
FROM ODAC 2021
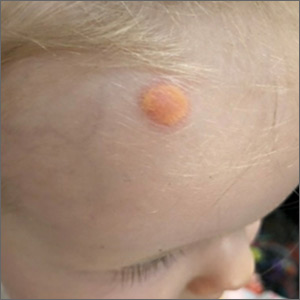
Child with yellow nodule
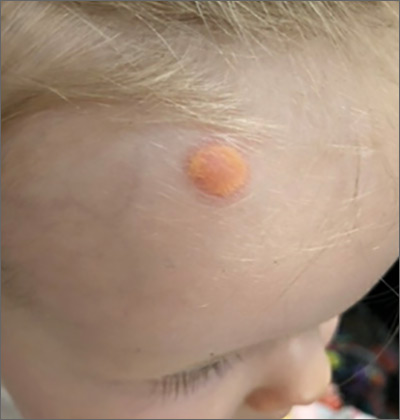
The characteristic orange-yellow color is the tip-off to the diagnosis of juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG). It manifests as asymptomatic solitary or scattered papules or nodules, congenitally, or most commonly during the first year of life.
JXG is an unusual non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that more commonly affects males. The etiology of JXG is unclear; it is presumed to be due to physical or infectious stimuli that produce a granulomatous histiocytic reaction. JXG typically manifests on the head, neck, upper extremities, and trunk. The appearance of JXG may be similar to that of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. If necessary, the diagnosis of JXG can be confirmed with a skin biopsy, which will reveal Touton-type giant cells and foamy histiocytes.
JXG is a benign and self-limiting disorder and spontaneously regresses within a few years. In rare cases, it can be systemic. If there are multiple lesions, relevant history, or physical exam features suggesting space-occupying lesions, imaging should be performed to rule out lesions in internal organs or structures. Treatment is indicated when there is systemic or symptomatic ocular involvement and may include surgical excision, radiotherapy, and/or systemic chemotherapy. In this case, the patient’s JXG management involved routine monitoring in anticipation of spontaneous resolution.
Image courtesy of John Durkin, MD, FAAD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. Text courtesy of Kerry Song, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile Xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan. Accessed January 29, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/#_NBK526103_pubdet

The characteristic orange-yellow color is the tip-off to the diagnosis of juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG). It manifests as asymptomatic solitary or scattered papules or nodules, congenitally, or most commonly during the first year of life.
JXG is an unusual non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that more commonly affects males. The etiology of JXG is unclear; it is presumed to be due to physical or infectious stimuli that produce a granulomatous histiocytic reaction. JXG typically manifests on the head, neck, upper extremities, and trunk. The appearance of JXG may be similar to that of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. If necessary, the diagnosis of JXG can be confirmed with a skin biopsy, which will reveal Touton-type giant cells and foamy histiocytes.
JXG is a benign and self-limiting disorder and spontaneously regresses within a few years. In rare cases, it can be systemic. If there are multiple lesions, relevant history, or physical exam features suggesting space-occupying lesions, imaging should be performed to rule out lesions in internal organs or structures. Treatment is indicated when there is systemic or symptomatic ocular involvement and may include surgical excision, radiotherapy, and/or systemic chemotherapy. In this case, the patient’s JXG management involved routine monitoring in anticipation of spontaneous resolution.
Image courtesy of John Durkin, MD, FAAD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. Text courtesy of Kerry Song, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The characteristic orange-yellow color is the tip-off to the diagnosis of juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG). It manifests as asymptomatic solitary or scattered papules or nodules, congenitally, or most commonly during the first year of life.
JXG is an unusual non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that more commonly affects males. The etiology of JXG is unclear; it is presumed to be due to physical or infectious stimuli that produce a granulomatous histiocytic reaction. JXG typically manifests on the head, neck, upper extremities, and trunk. The appearance of JXG may be similar to that of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. If necessary, the diagnosis of JXG can be confirmed with a skin biopsy, which will reveal Touton-type giant cells and foamy histiocytes.
JXG is a benign and self-limiting disorder and spontaneously regresses within a few years. In rare cases, it can be systemic. If there are multiple lesions, relevant history, or physical exam features suggesting space-occupying lesions, imaging should be performed to rule out lesions in internal organs or structures. Treatment is indicated when there is systemic or symptomatic ocular involvement and may include surgical excision, radiotherapy, and/or systemic chemotherapy. In this case, the patient’s JXG management involved routine monitoring in anticipation of spontaneous resolution.
Image courtesy of John Durkin, MD, FAAD, Department of Dermatology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. Text courtesy of Kerry Song, BS, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile Xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan. Accessed January 29, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/#_NBK526103_pubdet
Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile Xanthogranuloma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan. Accessed January 29, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/#_NBK526103_pubdet
Molecular insights suggest novel therapies for hidradenitis suppurativa
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
New approach to breast screening based on breast density at 40
The result would then be used to stratify further screening, with annual screening starting at age 40 for average-risk women who have dense breasts, and screening every 2 years starting at age 50 for women without dense breasts.
Such an approach would be cost effective and offers a more targeted risk-based strategy for the early detection of breast cancer when compared with current practices, say the authors, led by Tina Shih, PhD, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Their modeling study was published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, experts writing in an accompanying editorial are not persuaded. Karla Kerlikowske, MD, and Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, both from the University of California, San Francisco, point out that not all women with dense breasts are at increased risk for breast cancer. They caution against relying on breast density alone when determining screening strategies, and say age and other risk factors also need to be considered.
New approach proposed
Current recommendations from the United States Preventive Services Task Force suggest that women in their 40s can choose to undergo screening mammography based on their own personal preference, Dr. Shih explained in an interview.
However, these recommendations do not take into consideration the additional risk that breast density confers on breast cancer risk – and the only way women can know their breast density is to have a mammogram. “If you follow [current] guidelines, you would not know about your breast density until the age of 45 or 50,” she commented.
“But what if you knew about breast density earlier on and then acted on it –would that make a difference?” This was the question her team set out to explore.
For their study, the authors defined women with dense breasts as those with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) category C (heterogeneously dense breasts) and category D (extremely dense breasts).
The team used a computer model to compare seven different breast screening strategies:
- No screening.
- Triennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (T50).
- Biennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and triennial. screening from age 50 to 75 for women without dense breasts at the age of 50 (SA50T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and biennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breast at age 50 (SA50B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 49, and triennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 40, and biennial mammography for women from age 50 to 75 without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40B50).
Compared with a no-screening strategy, the average number of mammography sessions through a woman’s lifetime would increase from seven mammograms per lifetime for the least frequent screening (T50) to 22 mammograms per lifetime for the most intensive screening schedule, the team reports.
Compared with no screening, screening would reduce breast cancer deaths by 8.6 per 1,000 women (T50)–13.2 per 1,000 women (SA40B50).
A cost-effectiveness analysis showed that the proposed new approach (SA40B50) yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $36,200 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY), compared with the currently recommended biennial screening strategy. This is well within the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY that is generally accepted by society, the authors point out.
On the other hand, false-positive results and overdiagnosis would increase, the authors note.
The average number of false positives would increase from 141.2 per 1,000 women who underwent the least frequent triennial mammography screening schedule (T50) to 567.3 per 1,000 women with the new approach (SA40B50).
Rates of overdiagnosis would also increase from a low of 12.5% to a high of 18.6%, they add.
“With this study, we are not saying that everybody should start screening at the age of 40. We’re just saying, do a baseline mammography at 40, know your breast density status, and then we can try to modify the screening schedule based on individual risk,” Dr. Shih emphasized.
“Compared with other screening strategies examined in our study, this strategy is associated with the greatest reduction in breast cancer mortality and is cost effective, [although it] involves the most screening mammograms in a woman’s lifetime and higher rates of false-positive results and overdiagnosis,” the authors conclude.
Fundamental problem with this approach
The fundamental problem with this approach of stratifying risk on measurement of breast density – and on the basis of a single reading – is that not every woman with dense breasts is at increased risk for breast cancer, the editorialists comment.
Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo point out that, in fact, only about one-quarter of women with dense breasts are at high risk for a missed invasive cancer within 1 year of a negative mammogram, and these women can be identified by using the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium risk model.
“This observation means that most women with dense breasts can undergo biennial screening and need not consider annual screening or supplemental imaging,” the editorialists write.
“Thus, we caution against using breast density alone to determine if a woman is at elevated risk for breast cancer,” they emphasize.
An alternative option is to focus on overall risk to select screening strategies, they suggest. For example, most guidelines recommend screening from age 50 to 74, so identifying women in their 40s who have the same risk of a woman aged 50-59 is one way to determine who may benefit from earlier initiation of screening, the editorialists observe.
“Thus, women who have a first-degree relative with breast cancer or a history of breast biopsy could be offered screening in their 40s, and, if mammography shows dense breasts, they could continue biennial screening through their 40s,” the editorialists observe. “Such women with nondense breasts could resume biennial screening at age 50 years.”
Dr. Shih told this news organization that she did not disagree with the editorialists’ suggestion that physicians could focus on overall breast cancer risk to select an appropriate screening strategy for individual patients.
“What we are suggesting is, ‘Let’s just do a baseline assessment at the age of 40 so women know their breast density instead of waiting until they are older,’ “ she said.
“But what the editorialists are suggesting is a strategy that could be even more cost effective,” she acknowledged. Dr. Shih also said that Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo’s estimate that only one-quarter of women with dense breasts are actually at high risk for breast cancer likely reflects their limitation of breast density to only those women with BI-RADs category “D” – extremely dense breasts.
Yet as Dr. Shih notes, women with category C and category D breast densities are both at higher risk for breast cancer, so ignoring women with lesser degrees of breast density still doesn’t address the fact that they have a higher-than-average risk for breast cancer.
“It’s getting harder to make universal screening strategies work as we are learning more and more about breast cancer, so people are starting to talk about screening strategies based on a patient’s risk classification,” Dr. Shih noted.
“It’ll be harder to implement these kinds of strategies, but it seems like the right way to go,” she added.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Shih reports grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Pfizer and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Dr. Kerlikowske is an unpaid consultant for GRAIL for the STRIVE study. Dr. Bibbins-Domingo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The result would then be used to stratify further screening, with annual screening starting at age 40 for average-risk women who have dense breasts, and screening every 2 years starting at age 50 for women without dense breasts.
Such an approach would be cost effective and offers a more targeted risk-based strategy for the early detection of breast cancer when compared with current practices, say the authors, led by Tina Shih, PhD, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Their modeling study was published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, experts writing in an accompanying editorial are not persuaded. Karla Kerlikowske, MD, and Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, both from the University of California, San Francisco, point out that not all women with dense breasts are at increased risk for breast cancer. They caution against relying on breast density alone when determining screening strategies, and say age and other risk factors also need to be considered.
New approach proposed
Current recommendations from the United States Preventive Services Task Force suggest that women in their 40s can choose to undergo screening mammography based on their own personal preference, Dr. Shih explained in an interview.
However, these recommendations do not take into consideration the additional risk that breast density confers on breast cancer risk – and the only way women can know their breast density is to have a mammogram. “If you follow [current] guidelines, you would not know about your breast density until the age of 45 or 50,” she commented.
“But what if you knew about breast density earlier on and then acted on it –would that make a difference?” This was the question her team set out to explore.
For their study, the authors defined women with dense breasts as those with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) category C (heterogeneously dense breasts) and category D (extremely dense breasts).
The team used a computer model to compare seven different breast screening strategies:
- No screening.
- Triennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (T50).
- Biennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and triennial. screening from age 50 to 75 for women without dense breasts at the age of 50 (SA50T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and biennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breast at age 50 (SA50B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 49, and triennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 40, and biennial mammography for women from age 50 to 75 without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40B50).
Compared with a no-screening strategy, the average number of mammography sessions through a woman’s lifetime would increase from seven mammograms per lifetime for the least frequent screening (T50) to 22 mammograms per lifetime for the most intensive screening schedule, the team reports.
Compared with no screening, screening would reduce breast cancer deaths by 8.6 per 1,000 women (T50)–13.2 per 1,000 women (SA40B50).
A cost-effectiveness analysis showed that the proposed new approach (SA40B50) yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $36,200 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY), compared with the currently recommended biennial screening strategy. This is well within the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY that is generally accepted by society, the authors point out.
On the other hand, false-positive results and overdiagnosis would increase, the authors note.
The average number of false positives would increase from 141.2 per 1,000 women who underwent the least frequent triennial mammography screening schedule (T50) to 567.3 per 1,000 women with the new approach (SA40B50).
Rates of overdiagnosis would also increase from a low of 12.5% to a high of 18.6%, they add.
“With this study, we are not saying that everybody should start screening at the age of 40. We’re just saying, do a baseline mammography at 40, know your breast density status, and then we can try to modify the screening schedule based on individual risk,” Dr. Shih emphasized.
“Compared with other screening strategies examined in our study, this strategy is associated with the greatest reduction in breast cancer mortality and is cost effective, [although it] involves the most screening mammograms in a woman’s lifetime and higher rates of false-positive results and overdiagnosis,” the authors conclude.
Fundamental problem with this approach
The fundamental problem with this approach of stratifying risk on measurement of breast density – and on the basis of a single reading – is that not every woman with dense breasts is at increased risk for breast cancer, the editorialists comment.
Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo point out that, in fact, only about one-quarter of women with dense breasts are at high risk for a missed invasive cancer within 1 year of a negative mammogram, and these women can be identified by using the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium risk model.
“This observation means that most women with dense breasts can undergo biennial screening and need not consider annual screening or supplemental imaging,” the editorialists write.
“Thus, we caution against using breast density alone to determine if a woman is at elevated risk for breast cancer,” they emphasize.
An alternative option is to focus on overall risk to select screening strategies, they suggest. For example, most guidelines recommend screening from age 50 to 74, so identifying women in their 40s who have the same risk of a woman aged 50-59 is one way to determine who may benefit from earlier initiation of screening, the editorialists observe.
“Thus, women who have a first-degree relative with breast cancer or a history of breast biopsy could be offered screening in their 40s, and, if mammography shows dense breasts, they could continue biennial screening through their 40s,” the editorialists observe. “Such women with nondense breasts could resume biennial screening at age 50 years.”
Dr. Shih told this news organization that she did not disagree with the editorialists’ suggestion that physicians could focus on overall breast cancer risk to select an appropriate screening strategy for individual patients.
“What we are suggesting is, ‘Let’s just do a baseline assessment at the age of 40 so women know their breast density instead of waiting until they are older,’ “ she said.
“But what the editorialists are suggesting is a strategy that could be even more cost effective,” she acknowledged. Dr. Shih also said that Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo’s estimate that only one-quarter of women with dense breasts are actually at high risk for breast cancer likely reflects their limitation of breast density to only those women with BI-RADs category “D” – extremely dense breasts.
Yet as Dr. Shih notes, women with category C and category D breast densities are both at higher risk for breast cancer, so ignoring women with lesser degrees of breast density still doesn’t address the fact that they have a higher-than-average risk for breast cancer.
“It’s getting harder to make universal screening strategies work as we are learning more and more about breast cancer, so people are starting to talk about screening strategies based on a patient’s risk classification,” Dr. Shih noted.
“It’ll be harder to implement these kinds of strategies, but it seems like the right way to go,” she added.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Shih reports grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Pfizer and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Dr. Kerlikowske is an unpaid consultant for GRAIL for the STRIVE study. Dr. Bibbins-Domingo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The result would then be used to stratify further screening, with annual screening starting at age 40 for average-risk women who have dense breasts, and screening every 2 years starting at age 50 for women without dense breasts.
Such an approach would be cost effective and offers a more targeted risk-based strategy for the early detection of breast cancer when compared with current practices, say the authors, led by Tina Shih, PhD, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Their modeling study was published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, experts writing in an accompanying editorial are not persuaded. Karla Kerlikowske, MD, and Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, MD, PhD, both from the University of California, San Francisco, point out that not all women with dense breasts are at increased risk for breast cancer. They caution against relying on breast density alone when determining screening strategies, and say age and other risk factors also need to be considered.
New approach proposed
Current recommendations from the United States Preventive Services Task Force suggest that women in their 40s can choose to undergo screening mammography based on their own personal preference, Dr. Shih explained in an interview.
However, these recommendations do not take into consideration the additional risk that breast density confers on breast cancer risk – and the only way women can know their breast density is to have a mammogram. “If you follow [current] guidelines, you would not know about your breast density until the age of 45 or 50,” she commented.
“But what if you knew about breast density earlier on and then acted on it –would that make a difference?” This was the question her team set out to explore.
For their study, the authors defined women with dense breasts as those with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) category C (heterogeneously dense breasts) and category D (extremely dense breasts).
The team used a computer model to compare seven different breast screening strategies:
- No screening.
- Triennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (T50).
- Biennial mammography from age 50 to 75 years (B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and triennial. screening from age 50 to 75 for women without dense breasts at the age of 50 (SA50T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 50 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 50, and biennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breast at age 50 (SA50B50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 49, and triennial screening from age 50 to 75 for those without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40T50).
- Stratified annual mammography from age 40 to 75 for women with dense breasts at age 40, and biennial mammography for women from age 50 to 75 without dense breasts at age 40 (SA40B50).
Compared with a no-screening strategy, the average number of mammography sessions through a woman’s lifetime would increase from seven mammograms per lifetime for the least frequent screening (T50) to 22 mammograms per lifetime for the most intensive screening schedule, the team reports.
Compared with no screening, screening would reduce breast cancer deaths by 8.6 per 1,000 women (T50)–13.2 per 1,000 women (SA40B50).
A cost-effectiveness analysis showed that the proposed new approach (SA40B50) yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $36,200 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY), compared with the currently recommended biennial screening strategy. This is well within the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY that is generally accepted by society, the authors point out.
On the other hand, false-positive results and overdiagnosis would increase, the authors note.
The average number of false positives would increase from 141.2 per 1,000 women who underwent the least frequent triennial mammography screening schedule (T50) to 567.3 per 1,000 women with the new approach (SA40B50).
Rates of overdiagnosis would also increase from a low of 12.5% to a high of 18.6%, they add.
“With this study, we are not saying that everybody should start screening at the age of 40. We’re just saying, do a baseline mammography at 40, know your breast density status, and then we can try to modify the screening schedule based on individual risk,” Dr. Shih emphasized.
“Compared with other screening strategies examined in our study, this strategy is associated with the greatest reduction in breast cancer mortality and is cost effective, [although it] involves the most screening mammograms in a woman’s lifetime and higher rates of false-positive results and overdiagnosis,” the authors conclude.
Fundamental problem with this approach
The fundamental problem with this approach of stratifying risk on measurement of breast density – and on the basis of a single reading – is that not every woman with dense breasts is at increased risk for breast cancer, the editorialists comment.
Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo point out that, in fact, only about one-quarter of women with dense breasts are at high risk for a missed invasive cancer within 1 year of a negative mammogram, and these women can be identified by using the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium risk model.
“This observation means that most women with dense breasts can undergo biennial screening and need not consider annual screening or supplemental imaging,” the editorialists write.
“Thus, we caution against using breast density alone to determine if a woman is at elevated risk for breast cancer,” they emphasize.
An alternative option is to focus on overall risk to select screening strategies, they suggest. For example, most guidelines recommend screening from age 50 to 74, so identifying women in their 40s who have the same risk of a woman aged 50-59 is one way to determine who may benefit from earlier initiation of screening, the editorialists observe.
“Thus, women who have a first-degree relative with breast cancer or a history of breast biopsy could be offered screening in their 40s, and, if mammography shows dense breasts, they could continue biennial screening through their 40s,” the editorialists observe. “Such women with nondense breasts could resume biennial screening at age 50 years.”
Dr. Shih told this news organization that she did not disagree with the editorialists’ suggestion that physicians could focus on overall breast cancer risk to select an appropriate screening strategy for individual patients.
“What we are suggesting is, ‘Let’s just do a baseline assessment at the age of 40 so women know their breast density instead of waiting until they are older,’ “ she said.
“But what the editorialists are suggesting is a strategy that could be even more cost effective,” she acknowledged. Dr. Shih also said that Dr. Kerlikowske and Dr. Bibbins-Domingo’s estimate that only one-quarter of women with dense breasts are actually at high risk for breast cancer likely reflects their limitation of breast density to only those women with BI-RADs category “D” – extremely dense breasts.
Yet as Dr. Shih notes, women with category C and category D breast densities are both at higher risk for breast cancer, so ignoring women with lesser degrees of breast density still doesn’t address the fact that they have a higher-than-average risk for breast cancer.
“It’s getting harder to make universal screening strategies work as we are learning more and more about breast cancer, so people are starting to talk about screening strategies based on a patient’s risk classification,” Dr. Shih noted.
“It’ll be harder to implement these kinds of strategies, but it seems like the right way to go,” she added.
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Shih reports grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Pfizer and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Dr. Kerlikowske is an unpaid consultant for GRAIL for the STRIVE study. Dr. Bibbins-Domingo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I Spy, Near the Corner of My Eye
ANSWER
The correct answer—the false statement—is that SA has no pathologic implications (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
SAs are usually benign and occur in 10% to 15% of the population (particularly in children). But they can sometimes be a sign of serious disease such as liver failure, with related esophageal varices, especially if > 3 lesions are present.
SAs are caused by a failure in the sphincter muscle surrounding a dilated cutaneous arteriole, which in turn is caused by increased estrogen levels in the blood. This increase can be related to the estrogen in birth control medications or to pregnancy.
A diseased liver, unable to metabolize estrogen properly, can contribute to increased blood levels of estrogen. For example, about one-third of patients with cirrhosis will develop multiple SAs.
SAs are seen only in the distribution of the superior vena cava. This means that—in addition to manifesting on the face—they can also appear on the arms, hands, trunk, and fingers.
Momentarily fading completely when central pressure is applied is a peculiar trait of SAs and is therefore diagnostic.
TREATMENT
While these lesions do, in fact, usually resolve on their own, treatment attempts are usually highly satisfactory. In my experience, destruction by laser ablation is superior to electrodessication, though recurrences are common. At the time of this presentation, the patient and her mother were still pondering the treatment options.
ANSWER
The correct answer—the false statement—is that SA has no pathologic implications (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
SAs are usually benign and occur in 10% to 15% of the population (particularly in children). But they can sometimes be a sign of serious disease such as liver failure, with related esophageal varices, especially if > 3 lesions are present.
SAs are caused by a failure in the sphincter muscle surrounding a dilated cutaneous arteriole, which in turn is caused by increased estrogen levels in the blood. This increase can be related to the estrogen in birth control medications or to pregnancy.
A diseased liver, unable to metabolize estrogen properly, can contribute to increased blood levels of estrogen. For example, about one-third of patients with cirrhosis will develop multiple SAs.
SAs are seen only in the distribution of the superior vena cava. This means that—in addition to manifesting on the face—they can also appear on the arms, hands, trunk, and fingers.
Momentarily fading completely when central pressure is applied is a peculiar trait of SAs and is therefore diagnostic.
TREATMENT
While these lesions do, in fact, usually resolve on their own, treatment attempts are usually highly satisfactory. In my experience, destruction by laser ablation is superior to electrodessication, though recurrences are common. At the time of this presentation, the patient and her mother were still pondering the treatment options.
ANSWER
The correct answer—the false statement—is that SA has no pathologic implications (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
SAs are usually benign and occur in 10% to 15% of the population (particularly in children). But they can sometimes be a sign of serious disease such as liver failure, with related esophageal varices, especially if > 3 lesions are present.
SAs are caused by a failure in the sphincter muscle surrounding a dilated cutaneous arteriole, which in turn is caused by increased estrogen levels in the blood. This increase can be related to the estrogen in birth control medications or to pregnancy.
A diseased liver, unable to metabolize estrogen properly, can contribute to increased blood levels of estrogen. For example, about one-third of patients with cirrhosis will develop multiple SAs.
SAs are seen only in the distribution of the superior vena cava. This means that—in addition to manifesting on the face—they can also appear on the arms, hands, trunk, and fingers.
Momentarily fading completely when central pressure is applied is a peculiar trait of SAs and is therefore diagnostic.
TREATMENT
While these lesions do, in fact, usually resolve on their own, treatment attempts are usually highly satisfactory. In my experience, destruction by laser ablation is superior to electrodessication, though recurrences are common. At the time of this presentation, the patient and her mother were still pondering the treatment options.
About 3 years ago, an asymptomatic lesion appeared on an 8-year-old girl’s right cheek. Because the spot made her feel self-conscious, the child’s mother had tried covering it up with makeup—but the makeup was even more obvious than the spot.
Their primary care provider (PCP) advised them to do nothing, noting that such lesions usually resolve on their own. The PCP did not believe the lesion was indicative of any related health problems. Dissatisfied with this instruction, the mother brings her daughter to dermatology for evaluation.
The girl is in otherwise good health. The lesion in question is a curious, bright red macule consisting of a tiny pinpoint red dot with very narrow “legs” (tiny, slender, red, vascular lines) emanating from the periphery. It is about 7 mm, and the center red dot is about 1 mm in diameter.
Using a dull pencil to create gentle pinpoint pressure causes the whole lesion to instantly and completely fade, only to return fully after pressure is released. The lesion is diagnosed as a typical spider angioma (SA; also known as spider nevi).
Inhaled hyaluronan may bring sigh of relief to COPD patients
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
(COPD), findings of a new study suggest.
HMW-HA was associated with a significantly shorter duration of noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation (NIPPV), lower systemic inflammatory markers, and lower measured peak airway pressure, compared with placebo, reported lead author Flavia Galdi, MD, of Campus Bio-Medico University Hospital, Rome, and colleagues.
“HMW-HA is a naturally occurring sugar that is abundant in the extracellular matrix, including in the lung,” the investigators wrote in Respiratory Research. “[It] has been used routinely, together with hypertonic saline, in cystic fibrosis patients [for several years] with no reported side effects; rather, it improves tolerability and decreases the need for bronchodilators in these patients.”
According to Robert A. Sandhaus, MD, PhD, FCCP, of National Jewish Health, Denver, the role of hyaluronan in lung disease was first recognized decades ago.
“Data stretching back into the 1970s has identified decreases in hyaluronan content in emphysematous lung tissue, protection of lung connective tissue from proteolysis by hyaluronan, and potential therapeutic roles for hyaluronan in a variety of disease, especially of the lungs,” he said in an interview.
For patients with COPD, treatment with HMW-HA may provide benefit by counteracting an imbalance in diseased lung tissue, wrote Dr. Galdi and colleagues.
“Emerging evidence suggests that imbalance between declining HMW-HA levels, and increasing smaller fragments of hyaluronan may contribute to chronic airway disease pathogenesis,” they wrote. “This has led to the hypothesis that exogenous supplementation of HMW-HA may restore hyaluronan homeostasis in favor of undegraded molecules, inhibit inflammation and loss of lung function, and ameliorate COPD progression.”
To test this hypothesis, the investigators screened 44 patients with a history of acute exacerbations of COPD necessitating NIPPV, ultimately excluding 3 patients because of heart failure. Following 1:1 randomization, 20 patients received HMW-HA while 21 received placebo, each twice daily, in conjunction with NIPPV and standard medical therapy. Treatment continued until NIPPV failure or liberation from NIPPV. Most patients received NIPPV in the hospital; however, home/chronic NIPPV was given to four patients in the placebo group and three patients in the HMW-HA group.
The primary outcome was duration of NIPPV. Secondary outcomes included markers of systemic inflammation associated with acute exacerbations of COPD and respiratory physiology parameters. Adverse events were also reported.
Results showed that patients treated with HMW-HA were liberated sooner from NIPPV than were those who received placebo (mean, 5.2 vs 6.4 days; P < .037). Similarly, patients in the HMW-HA group had significantly shorter hospital stay, on average, than those in the placebo group (mean, 7.2 vs 10.2 days; P = .039). Median values followed a similar pattern.
“These data suggest that HMW-HA shortened the duration of acute respiratory failure, need for NIPPV and, consequently, hospital length of stay in these patients,” the investigators wrote.
Secondary outcomes further supported these therapeutic benefits. Compared with placebo, HMW-HA was associated with significantly lower peak pressure and greater improvements in both pCO2/FiO2 ratio and inflammatory markers. No adverse events were reported.
Further analyses involving human bronchial epithelial cell cultures offered some mechanistic insight. Using micro-optical coherence tomography imaging, the investigators found that HMW-HA treatment was associated with “a prominent effect on mucociliary transport” in cell cultures derived from COPD patients and in healthy nonsmoker cell cultures exposed to cigarette smoke extract.
“Our study shows for the first time the therapeutic potential of an extracellular matrix molecule in acute exacerbation of human lung disease,” the investigators concluded, noting a “clinically meaningful salutary effect” on duration of NIPPV.
Dr. Galdi and colleagues went on to predict that benefits in a real-world patient population could be even more meaningful.
“Since the serum samples were collected at the end of NIPPV, HMW-HA–treated patients were on average sampled a day earlier than placebo-treated patients (because they were liberated from NIPPV a day earlier on average),” the investigators wrote. “Thus, HMW-HA treatment effects may have been underestimated in our study.”
According to Dr. Sandhaus, “The current report, while a relatively small single-center study, is well controlled and the results suggest that inhaled hyaluronan decreased time on noninvasive ventilation, decreased hospital stay duration, and decreased some mediators of inflammation.”
He also suggested that HMW-HA may have a role in the prophylactic setting.
“The limitations of this pilot study are appropriately explored by the authors but do not dampen the exciting possibility that this therapeutic approach may hold promise not only in severe exacerbations of COPD but potentially for the prevention of such exacerbations,” Dr. Sandhaus said.
Jerome O. Cantor, MD, FCCP, of St. John’s University, New York, who previously conducted a pilot study for using lower molecular weight hyaluronan in COPD and published a review on the subject, said that more studies are necessary.
“Further clinical trials are needed to better determine the role of hyaluronan as an adjunct to existing therapies for COPD exacerbations,” he said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The investigators and Dr. Sandhaus declared no conflicts of interest. Dr. Cantor disclosed a relationship with MatRx Therapeutics.
FROM RESPIRATORY RESEARCH
COVID-19 in children: New cases down for third straight week
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
New COVID-19 cases in children dropped for the third consecutive week, even as children continue to make up a larger share of all cases, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

New child cases totaled almost 118,000 for the week of Jan. 29-Feb. 4, continuing the decline that began right after the United States topped 200,000 cases for the only time Jan. 8-14, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For the latest week, however, children represented 16.0% of all new COVID-19 cases, continuing a 5-week increase that began in early December 2020, after the proportion had dropped to 12.6%, based on data collected from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. During the week of Sept. 11-17, children made up 16.9% of all cases, the highest level seen during the pandemic.
The 2.93 million cases that have been reported in children make up 12.9% of all cases since the pandemic began, and the overall rate of pediatric coronavirus infection is 3,899 cases per 100,000 children in the population. Taking a step down from the national level, 30 states are above that rate and 18 are below it, along with D.C., New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam (New York and Texas are excluded), the AAP and CHA reported.
There were 12 new COVID-19–related child deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, bringing the total to 227. Nationally, 0.06% of all deaths have occurred in children, with rates ranging from 0.00% (11 states) to 0.26% (Nebraska) in the 45 jurisdictions, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Child hospitalizations rose to 1.9% of all hospitalizations after holding at 1.8% since mid-November in 25 reporting jurisdictions (24 states and New York City), but the hospitalization rate among children with COVID held at 0.8%, where it has been for the last 4 weeks. Hospitalization rates as high as 3.8% were recorded early in the pandemic, the AAP and CHA noted.
Coffee lowers heart failure risk in unique study
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
Higher coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of heart failure, according to a machine learning–based algorithm that analyzed data from three large observational trials.
“Coffee consumption actually was predictive on top of known risk factors originally identified from those three trials.” The study is significant because it underscores the potential of big data for individualizing patient management, lead investigator David Kao, MD, said in an interview. “We in fact adjusted for the scores that are commonly used to predict heart disease, and coffee consumption remained a predictor even on top of that.”
The study used supervised machine learning to analyze data on diet and other variables from three well-known observational studies: Framingham Heart Study (FHS), Cardiovascular Heart Study (CHS), and ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). The goal of the study, published online on Feb. 9, 2021*, was to identify potential novel risk factors for incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
“The main difference of the relationship between coffee and heart disease, compared with prior analyses, is that we’re able to find it in these well-known and well-accepted studies that have helped us find risk factors before,” Dr. Kao said
The study included 2,732 FHS participants aged 30-62 years, 3,704 CHS patients aged 65 and older, and 14,925 ARIC subjects aged 45-64, all of whom had no history of cardiovascular disease events when they enrolled. Primary outcomes for the machine-learning study were times to incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
Mathematics, not hypotheses
To compensate for variations in methodologies between the three observational trials, the study used 204 data measurements collected at the first FHS exam, including 16 dietary variables and for which similar data were collected for the other two studies.
The machine-learning model used what’s known as a random forest analysis to identify the leading potential risk factors from among the 204 variables. To confirm findings between studies, the authors used a technique called “data harmonization” to smooth variations in the methodologies of the trials, not only with participant age and duration and date of the trials, but also in how data on coffee consumption were gathered. For example, FHS collected that data as cups per day, whereas CHS and ARIC collected that as monthly, weekly, and daily consumption. The study converted the coffee consumption data from CHS and ARIC to cups per day to conform to FHS data.
Random forest analysis is a type of machine learning that randomly creates a cluster of decision trees – the “forest” – to determine which variables, such as dietary factors, are important in predicting a result. The analysis uses mathematics, not hypotheses, to identify important variables.
Heart failure and risk reduced
In this study, the analysis determined that each cup of caffeinated coffee daily was linked with a 5% reduction in the risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.95; P = .02) and 6% reduction in stroke risk (HR, 0.94; P = .02), but had no significant impact on risk for coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease.
When the data were adjusted for the FHS CVD risk score, increasing coffee consumption remained significantly associated with an identical lower risk of heart failure (P = .03) but not stroke (P = .33).
While the study supports an association between coffee consumption and heart failure risk, it doesn’t establish causation, noted Alice H. Lichtenstein, DSc, director and senior scientist at the Cardiovascular Nutrition Laboratory at Tufts University, Boston. “The authors could not rule out the possibility that caffeinated coffee intake was a proxy for other heart-healthy lifestyle behaviors,” Dr. Lichtenstein said. “Perhaps the best message from the study is that there appears to be no adverse effects of drinking moderate amounts of caffeinated coffee, and there may be benefits.”
She added a note of caution. “This result does not suggest coffee intake should be increased, nor does it give license to increasing coffee drinks with a lot of added cream and sugar.”
Machine learning mines observational trials
Dr. Kao explained the rationale for applying a machine-learning algorithm to the three observational trials. “When these trials were designed in general, they had an idea of what they were looking for in terms of what might be a risk factor,” said Dr. Kao, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “What we were interested in doing was to look for risk factors that nobody really thought about ahead of time and let the data show us what might be a predictor without any bias of what we imagined to be true.”
He described the role of machine learning in extracting and “filtering” data from the trials. “Machine learning allows us to look at a very large number of factors or variables and identify the most important ones in predicting a specific outcome,” he said. This study evaluated the 204 variables and focused on dietary factors because they’re modifiable.
“We looked at them in these different studies where we could, and coffee was the one that was reproducible in all of them,” he said. “Machine learning helped filter down these very large numbers of variables in ways you can’t do with traditional statistics. It’s useful in studies like this because they gather thousands and thousands of variables that generally nobody uses, but these methods allow you to actually do something with them – to determine which ones are most important.”
He added: “These methods I think will take us toward personalized medicine where you’re really individualizing a plan for keeping a patient healthy. We still have a lot of work to do, but there’s a lot of promise for really helping each of us to figure out the ways we can become the healthiest that we can be.”
The study was supported with funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the American Heart Association. Dr. Kao and coauthors, as well as Dr. Lichtenstein, had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
*Correction, 2/10/21: An earlier version of this article misstated the study's publication date.
FROM CIRCULATION: HEART FAILURE
A third discontinuing levothyroxine have normal thyroid levels
Approximately a third of patients treated for hypothyroidism continue to maintain normal thyroid levels after discontinuing thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Those who were treated for overt hypothyroidism were less likely to maintain normal hormone levels than those with subclinical disease, the new meta-analysis shows.
“This analysis is the first to summarize the limited evidence regarding successful thyroid hormone discontinuation, but unfortunately more research is needed to develop an evidenced-based strategy for deprescribing thyroid hormone replacement,” Nydia Burgos, MD, and colleagues write in their article published online in Thyroid.
Nevertheless, the main findings were somewhat surprising, Dr. Burgos of the division of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism, University of Puerto Rico, told this news organization.
“I expected that a considerable portion of patients would remain euthyroid, but up to a third of patients was an impressive number,” she said.
The finding could be an indicator of people who may not have had much benefit from the treatment in the first place, she noted.
“The truth of the matter is that levothyroxine (LT4) is among the top-prescribed drugs in the United States, and every day in clinics we encounter patients that were started on thyroid hormone replacement therapy for unclear reasons, as a therapeutic trial that was never reassessed, or as treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism without having convincing criteria for treatment,” she observed.
Meta-analysis of 17 studies examining LT4 discontinuation
Known to be highly effective in the treatment of overt hypothyroidism, LT4 is often prescribed long term; however, it is also commonly prescribed for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism, despite research suggesting no benefits in these patients.
With a guideline panel underscoring the lack of evidence and issuing a “strong recommendation” in May 2019 against treatment with thyroid hormones in adults with subclinical hypothyroidism (elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] levels and normal free T4 levels), clinicians may increasingly be considering discontinuation strategies.
To examine the evidence to date on the clinical outcomes of discontinuing LT4, Dr. Burgos and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis in which they identified 17 observational studies that met the inclusion criteria. Of a total of 1,103 patients in the studies, 86% were women. Most studies included only adults.
With a median follow-up of 5 years, the pooled estimate of patients maintaining euthyroidism after treatment discontinuation was 37.2%.
The estimated rate of remaining euthyroid was significantly lower among those with overt hypothyroidism (11.8%) compared with those with subclinical hypothyroidism (35.6%).
Meanwhile, as many as 65.8% of patients ended up restarting thyroid hormone treatment during the follow-up period, according to pooled estimates, and the rate was as high as 87.2% in patients with overt hypothyroidism. The mean increase in TSH from time of LT4 discontinuation to follow-up was 9.4 mIU/L.
Among specific factors shown to be linked to a lower likelihood of euthyroidism at follow-up were inconsistent echogenicity on thyroid ultrasound, elevated TSH (8-9 mIU/L), and the presence of thyroid antibodies.
Only a few of the studies evaluated thyroid hormones other than synthetic LT4 (such as the commonly used desiccated thyroid), and so the analysis did not compare differences between therapies, Dr. Burgos noted.
Despite the lack of evidence of benefits of LT4 treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism, the finding that, even among those patients, approximately two-thirds were not euthyroid at follow-up was not unexpected, she added.
“I am not surprised that, even in the subclinical hypothyroidism group about two-thirds of participants were not euthyroid, because when looking at the natural history of subclinical hypothyroidism in other studies, only a fifth had normalized thyroid hormone tests, while the majority continue with mild subclinical hypothyroidism and a fifth progress to overt hypothyroidism,” she explained.
More work needed to determine best way to taper down LT4
The specific regimens for discontinuing LT4 were detailed in only three studies and reflected varying approaches, ranging from tapering down the dose over 2 weeks to reducing the dose over several more weeks, or even months, Dr. Burgos noted
“We need more studies to figure out which tapering regimen will promote a more favorable outcome,” she said.
“The ideal regimen will be one in which patients can comply with follow-up visits and have thyroid function testing done before symptoms of hypothyroidism develop.”
In addition to likely offering no benefit to people with subclinical hypothyroidism, other reasons for discontinuing LT4 in patients who are considered appropriate candidates include concerns about side effects in older patients.
The authors say there is evidence indicating that as many as 50% of patients older than 65 who take thyroid hormones develop iatrogenic hyperthyroidism, which can have detrimental effects including an increased risk for cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, bone loss, and fractures.
Collaborative approach to ‘deprescribing’ suggested
To get patients off LT4, the authors suggest a collaborative approach of “deprescribing,” whereby the health care professional supervises with a goal of managing polypharmacy and improving outcomes.
“This systematic process starts with an accurate evaluation of the medication list, followed by identification of potentially inappropriate medications, collaboration between patients and clinicians to decide whether deprescribing would be appropriate, and establishing a supportive plan to safely deprescribe the medication,” they write.
When decision-making is shared, patients are more likely to consider discontinuation if they understand why the medication is inappropriate, have their concerns related to the discontinuation addressed, understand the process, and feel that they have the support of the clinical team, the authors conclude.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately a third of patients treated for hypothyroidism continue to maintain normal thyroid levels after discontinuing thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Those who were treated for overt hypothyroidism were less likely to maintain normal hormone levels than those with subclinical disease, the new meta-analysis shows.
“This analysis is the first to summarize the limited evidence regarding successful thyroid hormone discontinuation, but unfortunately more research is needed to develop an evidenced-based strategy for deprescribing thyroid hormone replacement,” Nydia Burgos, MD, and colleagues write in their article published online in Thyroid.
Nevertheless, the main findings were somewhat surprising, Dr. Burgos of the division of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism, University of Puerto Rico, told this news organization.
“I expected that a considerable portion of patients would remain euthyroid, but up to a third of patients was an impressive number,” she said.
The finding could be an indicator of people who may not have had much benefit from the treatment in the first place, she noted.
“The truth of the matter is that levothyroxine (LT4) is among the top-prescribed drugs in the United States, and every day in clinics we encounter patients that were started on thyroid hormone replacement therapy for unclear reasons, as a therapeutic trial that was never reassessed, or as treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism without having convincing criteria for treatment,” she observed.
Meta-analysis of 17 studies examining LT4 discontinuation
Known to be highly effective in the treatment of overt hypothyroidism, LT4 is often prescribed long term; however, it is also commonly prescribed for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism, despite research suggesting no benefits in these patients.
With a guideline panel underscoring the lack of evidence and issuing a “strong recommendation” in May 2019 against treatment with thyroid hormones in adults with subclinical hypothyroidism (elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] levels and normal free T4 levels), clinicians may increasingly be considering discontinuation strategies.
To examine the evidence to date on the clinical outcomes of discontinuing LT4, Dr. Burgos and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis in which they identified 17 observational studies that met the inclusion criteria. Of a total of 1,103 patients in the studies, 86% were women. Most studies included only adults.
With a median follow-up of 5 years, the pooled estimate of patients maintaining euthyroidism after treatment discontinuation was 37.2%.
The estimated rate of remaining euthyroid was significantly lower among those with overt hypothyroidism (11.8%) compared with those with subclinical hypothyroidism (35.6%).
Meanwhile, as many as 65.8% of patients ended up restarting thyroid hormone treatment during the follow-up period, according to pooled estimates, and the rate was as high as 87.2% in patients with overt hypothyroidism. The mean increase in TSH from time of LT4 discontinuation to follow-up was 9.4 mIU/L.
Among specific factors shown to be linked to a lower likelihood of euthyroidism at follow-up were inconsistent echogenicity on thyroid ultrasound, elevated TSH (8-9 mIU/L), and the presence of thyroid antibodies.
Only a few of the studies evaluated thyroid hormones other than synthetic LT4 (such as the commonly used desiccated thyroid), and so the analysis did not compare differences between therapies, Dr. Burgos noted.
Despite the lack of evidence of benefits of LT4 treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism, the finding that, even among those patients, approximately two-thirds were not euthyroid at follow-up was not unexpected, she added.
“I am not surprised that, even in the subclinical hypothyroidism group about two-thirds of participants were not euthyroid, because when looking at the natural history of subclinical hypothyroidism in other studies, only a fifth had normalized thyroid hormone tests, while the majority continue with mild subclinical hypothyroidism and a fifth progress to overt hypothyroidism,” she explained.
More work needed to determine best way to taper down LT4
The specific regimens for discontinuing LT4 were detailed in only three studies and reflected varying approaches, ranging from tapering down the dose over 2 weeks to reducing the dose over several more weeks, or even months, Dr. Burgos noted
“We need more studies to figure out which tapering regimen will promote a more favorable outcome,” she said.
“The ideal regimen will be one in which patients can comply with follow-up visits and have thyroid function testing done before symptoms of hypothyroidism develop.”
In addition to likely offering no benefit to people with subclinical hypothyroidism, other reasons for discontinuing LT4 in patients who are considered appropriate candidates include concerns about side effects in older patients.
The authors say there is evidence indicating that as many as 50% of patients older than 65 who take thyroid hormones develop iatrogenic hyperthyroidism, which can have detrimental effects including an increased risk for cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, bone loss, and fractures.
Collaborative approach to ‘deprescribing’ suggested
To get patients off LT4, the authors suggest a collaborative approach of “deprescribing,” whereby the health care professional supervises with a goal of managing polypharmacy and improving outcomes.
“This systematic process starts with an accurate evaluation of the medication list, followed by identification of potentially inappropriate medications, collaboration between patients and clinicians to decide whether deprescribing would be appropriate, and establishing a supportive plan to safely deprescribe the medication,” they write.
When decision-making is shared, patients are more likely to consider discontinuation if they understand why the medication is inappropriate, have their concerns related to the discontinuation addressed, understand the process, and feel that they have the support of the clinical team, the authors conclude.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately a third of patients treated for hypothyroidism continue to maintain normal thyroid levels after discontinuing thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Those who were treated for overt hypothyroidism were less likely to maintain normal hormone levels than those with subclinical disease, the new meta-analysis shows.
“This analysis is the first to summarize the limited evidence regarding successful thyroid hormone discontinuation, but unfortunately more research is needed to develop an evidenced-based strategy for deprescribing thyroid hormone replacement,” Nydia Burgos, MD, and colleagues write in their article published online in Thyroid.
Nevertheless, the main findings were somewhat surprising, Dr. Burgos of the division of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism, University of Puerto Rico, told this news organization.
“I expected that a considerable portion of patients would remain euthyroid, but up to a third of patients was an impressive number,” she said.
The finding could be an indicator of people who may not have had much benefit from the treatment in the first place, she noted.
“The truth of the matter is that levothyroxine (LT4) is among the top-prescribed drugs in the United States, and every day in clinics we encounter patients that were started on thyroid hormone replacement therapy for unclear reasons, as a therapeutic trial that was never reassessed, or as treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism without having convincing criteria for treatment,” she observed.
Meta-analysis of 17 studies examining LT4 discontinuation
Known to be highly effective in the treatment of overt hypothyroidism, LT4 is often prescribed long term; however, it is also commonly prescribed for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism, despite research suggesting no benefits in these patients.
With a guideline panel underscoring the lack of evidence and issuing a “strong recommendation” in May 2019 against treatment with thyroid hormones in adults with subclinical hypothyroidism (elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] levels and normal free T4 levels), clinicians may increasingly be considering discontinuation strategies.
To examine the evidence to date on the clinical outcomes of discontinuing LT4, Dr. Burgos and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis in which they identified 17 observational studies that met the inclusion criteria. Of a total of 1,103 patients in the studies, 86% were women. Most studies included only adults.
With a median follow-up of 5 years, the pooled estimate of patients maintaining euthyroidism after treatment discontinuation was 37.2%.
The estimated rate of remaining euthyroid was significantly lower among those with overt hypothyroidism (11.8%) compared with those with subclinical hypothyroidism (35.6%).
Meanwhile, as many as 65.8% of patients ended up restarting thyroid hormone treatment during the follow-up period, according to pooled estimates, and the rate was as high as 87.2% in patients with overt hypothyroidism. The mean increase in TSH from time of LT4 discontinuation to follow-up was 9.4 mIU/L.
Among specific factors shown to be linked to a lower likelihood of euthyroidism at follow-up were inconsistent echogenicity on thyroid ultrasound, elevated TSH (8-9 mIU/L), and the presence of thyroid antibodies.
Only a few of the studies evaluated thyroid hormones other than synthetic LT4 (such as the commonly used desiccated thyroid), and so the analysis did not compare differences between therapies, Dr. Burgos noted.
Despite the lack of evidence of benefits of LT4 treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism, the finding that, even among those patients, approximately two-thirds were not euthyroid at follow-up was not unexpected, she added.
“I am not surprised that, even in the subclinical hypothyroidism group about two-thirds of participants were not euthyroid, because when looking at the natural history of subclinical hypothyroidism in other studies, only a fifth had normalized thyroid hormone tests, while the majority continue with mild subclinical hypothyroidism and a fifth progress to overt hypothyroidism,” she explained.
More work needed to determine best way to taper down LT4
The specific regimens for discontinuing LT4 were detailed in only three studies and reflected varying approaches, ranging from tapering down the dose over 2 weeks to reducing the dose over several more weeks, or even months, Dr. Burgos noted
“We need more studies to figure out which tapering regimen will promote a more favorable outcome,” she said.
“The ideal regimen will be one in which patients can comply with follow-up visits and have thyroid function testing done before symptoms of hypothyroidism develop.”
In addition to likely offering no benefit to people with subclinical hypothyroidism, other reasons for discontinuing LT4 in patients who are considered appropriate candidates include concerns about side effects in older patients.
The authors say there is evidence indicating that as many as 50% of patients older than 65 who take thyroid hormones develop iatrogenic hyperthyroidism, which can have detrimental effects including an increased risk for cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, bone loss, and fractures.
Collaborative approach to ‘deprescribing’ suggested
To get patients off LT4, the authors suggest a collaborative approach of “deprescribing,” whereby the health care professional supervises with a goal of managing polypharmacy and improving outcomes.
“This systematic process starts with an accurate evaluation of the medication list, followed by identification of potentially inappropriate medications, collaboration between patients and clinicians to decide whether deprescribing would be appropriate, and establishing a supportive plan to safely deprescribe the medication,” they write.
When decision-making is shared, patients are more likely to consider discontinuation if they understand why the medication is inappropriate, have their concerns related to the discontinuation addressed, understand the process, and feel that they have the support of the clinical team, the authors conclude.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.