User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Spectrum of dermatologic adverse events associated with amivantamab use
associated with EGFR inhibitors and atypical presentations. Toxic effects, however, were mitigated by dose interruptions, dAE management, and amivantamab dose reductions, allowing for cancer therapy continuation in all cases. Amivantamab doses were reduced in 5 out of 6 cases, according to a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology.
The EGFR exon 20 insertion–mutation portends insensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and poor prognosis. Amivantamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR and mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET) is Food and Drug Administration approved for this population. Acneiform eruptions and pruritus are the most common dAEs associated with EGFR inhibitors, with xerosis, fissures, and nail and hair changes occurring additionally. While no FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targets MET exclusively, capmatinib and tepotinib (both tyrosine kinase inhibitors) inhibit MET. They have been associated with photosensitivity, acneiform rash, paronychia, xerosis, pruritus, and mucositis.
The Belzer et al. letter reviewed six consecutive cases (mean age, 58) of dAEs associated with amivantamab at two academic health centers (treated June 2021 to August 2022) in order to describe dAEs associated with amivantamab use. “I suspect the rate of dAEs with amivantamab is similar to the rate of dAEs associated with first- and second-generation EGFR inhibitors, where the majority of patients, actually 75%-90%, develop cutaneous toxicity,” said Jonathan Leventhal, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., corresponding author for the Belzer et al. letter.
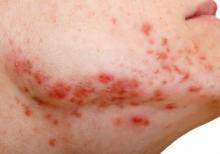
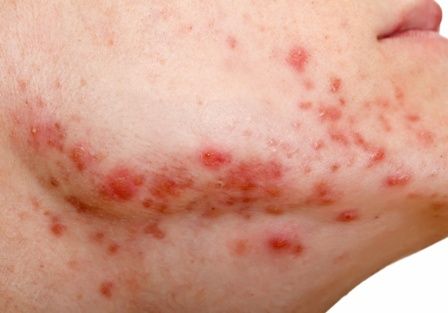
Time from treatment initiation with amivantamab to dAE ranged from less than 1 month to 4 months. All dAEs were grade 2 or 3 and all included acneiform eruptions. These were widespread in four cases and in another case complicated by impetiginization (culture results positive for methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus), and a further case was limited to the scalp, face, upper back, and upper chest. Others with widespread acneiform eruption included the face with hyperkeratotic crust of the scalp and dermatitis of the posterior neck. Fissuring of the palms and soles was noted in two cases with widespread acneiform eruptions. Paronychia with pyogenic granulomas was reported in four cases. Another case included onycholysis with suppurative paronychia.
In five cases amivantamab was stopped but successfully reinitiated at 67%-75% of the original dose. In one case amivantamab was continued at the original dose.
Doxycycline at 100 mg twice daily was included among all of the treatments for cutaneous dAEs. Silver nitrate cautery was applied for pyogenic granulomas in clinic. The case of grade 3 acneiform eruption of the scalp and face was treated with hydrogen peroxide soaks with debridement in clinic, doxycycline, aluminum acetate soaks, and triamcinolone ointment. All dermatologic cases resolved fully without scarring.
“It is very likely that this series highlights the more severe and unusual presentations of dAEs which were referred to oncodermatology. I suspect milder presentations were likely managed by oncologists,” Dr. Leventhal said in the interview.
“It is important for dermatologists and oncologists to be aware of the more severe and atypical dAEs associated with this novel FDA-approved targeted therapy.” Dr. Belzer said. “As amivantamab use increases, oncologists and dermatologists need to collaborate to ensure swift diagnosis and management of dAEs.”
One trial, the authors stated, revealed more than half of patients receiving EGFR inhibitors taking preemptive treatment with moisturizers, sunscreen, topical corticosteroids, and an oral tetracycline to have more than a 50% reduction in grade 2 or higher dAEs. Belzer et al. concluded that prophylactic treatment, including sun protection, should be considered before initiating treatment with amivantamab.
A limitation of the study, Belzer et al. acknowledged, was the small sample size.
Dr. Leventhal reported receiving personal fees from the advisory boards of Sanofi, Regeneron, and La Roche-Posay as well as clinical trial funding from Azitra and OnQuality Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work.
associated with EGFR inhibitors and atypical presentations. Toxic effects, however, were mitigated by dose interruptions, dAE management, and amivantamab dose reductions, allowing for cancer therapy continuation in all cases. Amivantamab doses were reduced in 5 out of 6 cases, according to a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology.
The EGFR exon 20 insertion–mutation portends insensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and poor prognosis. Amivantamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR and mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET) is Food and Drug Administration approved for this population. Acneiform eruptions and pruritus are the most common dAEs associated with EGFR inhibitors, with xerosis, fissures, and nail and hair changes occurring additionally. While no FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targets MET exclusively, capmatinib and tepotinib (both tyrosine kinase inhibitors) inhibit MET. They have been associated with photosensitivity, acneiform rash, paronychia, xerosis, pruritus, and mucositis.
The Belzer et al. letter reviewed six consecutive cases (mean age, 58) of dAEs associated with amivantamab at two academic health centers (treated June 2021 to August 2022) in order to describe dAEs associated with amivantamab use. “I suspect the rate of dAEs with amivantamab is similar to the rate of dAEs associated with first- and second-generation EGFR inhibitors, where the majority of patients, actually 75%-90%, develop cutaneous toxicity,” said Jonathan Leventhal, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., corresponding author for the Belzer et al. letter.
Time from treatment initiation with amivantamab to dAE ranged from less than 1 month to 4 months. All dAEs were grade 2 or 3 and all included acneiform eruptions. These were widespread in four cases and in another case complicated by impetiginization (culture results positive for methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus), and a further case was limited to the scalp, face, upper back, and upper chest. Others with widespread acneiform eruption included the face with hyperkeratotic crust of the scalp and dermatitis of the posterior neck. Fissuring of the palms and soles was noted in two cases with widespread acneiform eruptions. Paronychia with pyogenic granulomas was reported in four cases. Another case included onycholysis with suppurative paronychia.
In five cases amivantamab was stopped but successfully reinitiated at 67%-75% of the original dose. In one case amivantamab was continued at the original dose.
Doxycycline at 100 mg twice daily was included among all of the treatments for cutaneous dAEs. Silver nitrate cautery was applied for pyogenic granulomas in clinic. The case of grade 3 acneiform eruption of the scalp and face was treated with hydrogen peroxide soaks with debridement in clinic, doxycycline, aluminum acetate soaks, and triamcinolone ointment. All dermatologic cases resolved fully without scarring.
“It is very likely that this series highlights the more severe and unusual presentations of dAEs which were referred to oncodermatology. I suspect milder presentations were likely managed by oncologists,” Dr. Leventhal said in the interview.
“It is important for dermatologists and oncologists to be aware of the more severe and atypical dAEs associated with this novel FDA-approved targeted therapy.” Dr. Belzer said. “As amivantamab use increases, oncologists and dermatologists need to collaborate to ensure swift diagnosis and management of dAEs.”
One trial, the authors stated, revealed more than half of patients receiving EGFR inhibitors taking preemptive treatment with moisturizers, sunscreen, topical corticosteroids, and an oral tetracycline to have more than a 50% reduction in grade 2 or higher dAEs. Belzer et al. concluded that prophylactic treatment, including sun protection, should be considered before initiating treatment with amivantamab.
A limitation of the study, Belzer et al. acknowledged, was the small sample size.
Dr. Leventhal reported receiving personal fees from the advisory boards of Sanofi, Regeneron, and La Roche-Posay as well as clinical trial funding from Azitra and OnQuality Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work.
associated with EGFR inhibitors and atypical presentations. Toxic effects, however, were mitigated by dose interruptions, dAE management, and amivantamab dose reductions, allowing for cancer therapy continuation in all cases. Amivantamab doses were reduced in 5 out of 6 cases, according to a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology.
The EGFR exon 20 insertion–mutation portends insensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and poor prognosis. Amivantamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR and mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET) is Food and Drug Administration approved for this population. Acneiform eruptions and pruritus are the most common dAEs associated with EGFR inhibitors, with xerosis, fissures, and nail and hair changes occurring additionally. While no FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targets MET exclusively, capmatinib and tepotinib (both tyrosine kinase inhibitors) inhibit MET. They have been associated with photosensitivity, acneiform rash, paronychia, xerosis, pruritus, and mucositis.
The Belzer et al. letter reviewed six consecutive cases (mean age, 58) of dAEs associated with amivantamab at two academic health centers (treated June 2021 to August 2022) in order to describe dAEs associated with amivantamab use. “I suspect the rate of dAEs with amivantamab is similar to the rate of dAEs associated with first- and second-generation EGFR inhibitors, where the majority of patients, actually 75%-90%, develop cutaneous toxicity,” said Jonathan Leventhal, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., corresponding author for the Belzer et al. letter.
Time from treatment initiation with amivantamab to dAE ranged from less than 1 month to 4 months. All dAEs were grade 2 or 3 and all included acneiform eruptions. These were widespread in four cases and in another case complicated by impetiginization (culture results positive for methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus), and a further case was limited to the scalp, face, upper back, and upper chest. Others with widespread acneiform eruption included the face with hyperkeratotic crust of the scalp and dermatitis of the posterior neck. Fissuring of the palms and soles was noted in two cases with widespread acneiform eruptions. Paronychia with pyogenic granulomas was reported in four cases. Another case included onycholysis with suppurative paronychia.
In five cases amivantamab was stopped but successfully reinitiated at 67%-75% of the original dose. In one case amivantamab was continued at the original dose.
Doxycycline at 100 mg twice daily was included among all of the treatments for cutaneous dAEs. Silver nitrate cautery was applied for pyogenic granulomas in clinic. The case of grade 3 acneiform eruption of the scalp and face was treated with hydrogen peroxide soaks with debridement in clinic, doxycycline, aluminum acetate soaks, and triamcinolone ointment. All dermatologic cases resolved fully without scarring.
“It is very likely that this series highlights the more severe and unusual presentations of dAEs which were referred to oncodermatology. I suspect milder presentations were likely managed by oncologists,” Dr. Leventhal said in the interview.
“It is important for dermatologists and oncologists to be aware of the more severe and atypical dAEs associated with this novel FDA-approved targeted therapy.” Dr. Belzer said. “As amivantamab use increases, oncologists and dermatologists need to collaborate to ensure swift diagnosis and management of dAEs.”
One trial, the authors stated, revealed more than half of patients receiving EGFR inhibitors taking preemptive treatment with moisturizers, sunscreen, topical corticosteroids, and an oral tetracycline to have more than a 50% reduction in grade 2 or higher dAEs. Belzer et al. concluded that prophylactic treatment, including sun protection, should be considered before initiating treatment with amivantamab.
A limitation of the study, Belzer et al. acknowledged, was the small sample size.
Dr. Leventhal reported receiving personal fees from the advisory boards of Sanofi, Regeneron, and La Roche-Posay as well as clinical trial funding from Azitra and OnQuality Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Little evidence to support lasers for ‘vaginal rejuvenation’
Laser devices licensed in Canada to treat genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) are often marketed for vaginal rejuvenation with claims that they will tighten the vagina and improve sexual function, despite lack of evidence, a new commentary reveals.
Vaginal lasers heat the vaginal epithelium and cause thermal necrosis. This intervention induces collagen remodeling and synthesis, neovascularization, and elastin formation and may result in improved vaginal elasticity and restoration of premenopausal epithelial function, according to coauthors Blayne Welk, MD, MSc, an associate professor of urologic surgery at Western University, London, Ont., and Erin Kelly, MD, a lecturer in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
Their patients’ questions and experiences with the laser devices prompted the commentary, they told this news organization.
“A large part of my practice involves addressing GSM and urinary incontinence,” said Dr. Kelly. “Many women present to the clinic having heard of vaginal laser procedures, having had vaginal laser procedures, or having been told they need vaginal laser procedures. My impression has been that these procedures are being marketed to women … without rigorous study.”
“Many women are reluctant to have mesh slings for stress incontinence due to some of the potential risks,” and they are looking for less invasive options, said Dr. Welk. Over the past few years, he has had increasing questions from patients about the use of lasers to improve this condition.
The commentary was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Transparency needed
The first vaginal energy device was licensed by Health Canada in 2015 to treat GSM. That meant the device was deemed to have met basic safety, effectiveness, and quality criteria. But no controlled studies are required for regulatory approval of such devices, and after licensing, some providers rebranded the device indication from GSM to vaginal rejuvenation, said Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk.
Vaginal laser therapies are offered throughout Canada, with at least one provider of vaginal rejuvenation procedures in the 10 most populous cities. Under the current system, the number of patients who pay for these procedures and the amount that they pay cannot be tracked. Nor can the number of vaginal laser systems active in Canada be tracked. Patients can refer themselves for the service, and providers’ publicly quoted costs (on websites, for example) are thousands of dollars for treatment.
The rebranding for vaginal rejuvenation “represents a difference between the licensing of a medical device by Health Canada and the way that these devices are used and marketed,” according to the commentary. “A procedure with limited high-quality evidence supporting its efficacy and a potential financial conflict of interest for providers may not be serving the best interests of people in Canada, even if the risk of adverse events is low.”
Updates to Canada’s medical devices action plan, including mandatory reporting of serious incidents and the ability to compel manufacturers to provide information on safety and effectiveness, “represent important progress,” according to Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk. However, problems persist, including lack of a requirement for peer-reviewed, controlled studies.
Furthermore, women who undergo laser treatment for GSM, urinary incontinence, or vaginal rejuvenation may not receive a proper medical evaluation and standard treatments, the authors noted.
“I would like to see more transparency and public-facing information available on approved medical devices,” said Dr. Welk. “Health Canada has an online database of approved devices, but no information around the evidence submitted during the approval process is available, nor are the indications for the various devices.”
In addition, he said, many devices in the registry are listed by a serial number rather than the name that would be familiar to the public, “making it hard to match up information.”
Dr. Kelly added the “encouraging” news that the Canadian Society for Pelvic Medicine is working with Health Canada to “improve knowledge translation when it comes to transparency regarding medical devices.”
Medicine before marketing
“The commentary provides an accurate and evidence-based assessment of the use of vaginal laser treatments,” Jason Abbott, B Med (Hons), PhD, professor of gynecology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization. “The marketing of this device is a case of putting the cart before the horse. It is essential that strong, scientific, and reproducible studies be available on efficacy and safety before there is a direct-to-consumer marketing approach.”
Clinicians should advise patients when the treatment effect is likely to be minimal or risky, especially when there is a financial incentive to the clinician, he said. “Governments, regulators, and medical societies have a duty of care to the public to make sure that the medicine comes before the marketing. Otherwise, we are no better than snake oil sellers.
“Given the size of studies to date, the improvement in symptoms following treatment may be less than a few percent,” he noted. “That may be acceptable to some women. We don’t know.”
Dr. Abbott’s team is conducting research to define what women would want as a minimal level of improvement, the maximum cost, and the maximum risk from the laser procedure.
“In cancer … the benefit of a new treatment may only be a few percent for survival,” he said. “That may be completely acceptable for some or even many patients. What we cannot do, however, is extrapolate those same expectations to a treatment for a benign condition where quality of life is compromised.”
Echoing Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk, Dr. Abbott said, “It is important that there be transparency in the clinical communication. Patients should be told that the best scientific studies that are judged based on their quality show there is no benefit to laser treatment for GSM or urinary incontinence.”
Although the medical risks may be low, he added, “financial risk also needs to be discussed. Patients should be encouraged to participate in clinical trials where there is no cost to them to gain the information first, before wholesale uptake of the treatment. … Should patients still wish to undergo the procedure once the risks and an honest account of the evidence is given to them, that of course is their choice.” Dr. Kelly, Dr. Welk, and Dr. Abbott had no commercial funding or relevant financial relationships to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Laser devices licensed in Canada to treat genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) are often marketed for vaginal rejuvenation with claims that they will tighten the vagina and improve sexual function, despite lack of evidence, a new commentary reveals.
Vaginal lasers heat the vaginal epithelium and cause thermal necrosis. This intervention induces collagen remodeling and synthesis, neovascularization, and elastin formation and may result in improved vaginal elasticity and restoration of premenopausal epithelial function, according to coauthors Blayne Welk, MD, MSc, an associate professor of urologic surgery at Western University, London, Ont., and Erin Kelly, MD, a lecturer in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
Their patients’ questions and experiences with the laser devices prompted the commentary, they told this news organization.
“A large part of my practice involves addressing GSM and urinary incontinence,” said Dr. Kelly. “Many women present to the clinic having heard of vaginal laser procedures, having had vaginal laser procedures, or having been told they need vaginal laser procedures. My impression has been that these procedures are being marketed to women … without rigorous study.”
“Many women are reluctant to have mesh slings for stress incontinence due to some of the potential risks,” and they are looking for less invasive options, said Dr. Welk. Over the past few years, he has had increasing questions from patients about the use of lasers to improve this condition.
The commentary was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Transparency needed
The first vaginal energy device was licensed by Health Canada in 2015 to treat GSM. That meant the device was deemed to have met basic safety, effectiveness, and quality criteria. But no controlled studies are required for regulatory approval of such devices, and after licensing, some providers rebranded the device indication from GSM to vaginal rejuvenation, said Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk.
Vaginal laser therapies are offered throughout Canada, with at least one provider of vaginal rejuvenation procedures in the 10 most populous cities. Under the current system, the number of patients who pay for these procedures and the amount that they pay cannot be tracked. Nor can the number of vaginal laser systems active in Canada be tracked. Patients can refer themselves for the service, and providers’ publicly quoted costs (on websites, for example) are thousands of dollars for treatment.
The rebranding for vaginal rejuvenation “represents a difference between the licensing of a medical device by Health Canada and the way that these devices are used and marketed,” according to the commentary. “A procedure with limited high-quality evidence supporting its efficacy and a potential financial conflict of interest for providers may not be serving the best interests of people in Canada, even if the risk of adverse events is low.”
Updates to Canada’s medical devices action plan, including mandatory reporting of serious incidents and the ability to compel manufacturers to provide information on safety and effectiveness, “represent important progress,” according to Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk. However, problems persist, including lack of a requirement for peer-reviewed, controlled studies.
Furthermore, women who undergo laser treatment for GSM, urinary incontinence, or vaginal rejuvenation may not receive a proper medical evaluation and standard treatments, the authors noted.
“I would like to see more transparency and public-facing information available on approved medical devices,” said Dr. Welk. “Health Canada has an online database of approved devices, but no information around the evidence submitted during the approval process is available, nor are the indications for the various devices.”
In addition, he said, many devices in the registry are listed by a serial number rather than the name that would be familiar to the public, “making it hard to match up information.”
Dr. Kelly added the “encouraging” news that the Canadian Society for Pelvic Medicine is working with Health Canada to “improve knowledge translation when it comes to transparency regarding medical devices.”
Medicine before marketing
“The commentary provides an accurate and evidence-based assessment of the use of vaginal laser treatments,” Jason Abbott, B Med (Hons), PhD, professor of gynecology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization. “The marketing of this device is a case of putting the cart before the horse. It is essential that strong, scientific, and reproducible studies be available on efficacy and safety before there is a direct-to-consumer marketing approach.”
Clinicians should advise patients when the treatment effect is likely to be minimal or risky, especially when there is a financial incentive to the clinician, he said. “Governments, regulators, and medical societies have a duty of care to the public to make sure that the medicine comes before the marketing. Otherwise, we are no better than snake oil sellers.
“Given the size of studies to date, the improvement in symptoms following treatment may be less than a few percent,” he noted. “That may be acceptable to some women. We don’t know.”
Dr. Abbott’s team is conducting research to define what women would want as a minimal level of improvement, the maximum cost, and the maximum risk from the laser procedure.
“In cancer … the benefit of a new treatment may only be a few percent for survival,” he said. “That may be completely acceptable for some or even many patients. What we cannot do, however, is extrapolate those same expectations to a treatment for a benign condition where quality of life is compromised.”
Echoing Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk, Dr. Abbott said, “It is important that there be transparency in the clinical communication. Patients should be told that the best scientific studies that are judged based on their quality show there is no benefit to laser treatment for GSM or urinary incontinence.”
Although the medical risks may be low, he added, “financial risk also needs to be discussed. Patients should be encouraged to participate in clinical trials where there is no cost to them to gain the information first, before wholesale uptake of the treatment. … Should patients still wish to undergo the procedure once the risks and an honest account of the evidence is given to them, that of course is their choice.” Dr. Kelly, Dr. Welk, and Dr. Abbott had no commercial funding or relevant financial relationships to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Laser devices licensed in Canada to treat genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) are often marketed for vaginal rejuvenation with claims that they will tighten the vagina and improve sexual function, despite lack of evidence, a new commentary reveals.
Vaginal lasers heat the vaginal epithelium and cause thermal necrosis. This intervention induces collagen remodeling and synthesis, neovascularization, and elastin formation and may result in improved vaginal elasticity and restoration of premenopausal epithelial function, according to coauthors Blayne Welk, MD, MSc, an associate professor of urologic surgery at Western University, London, Ont., and Erin Kelly, MD, a lecturer in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
Their patients’ questions and experiences with the laser devices prompted the commentary, they told this news organization.
“A large part of my practice involves addressing GSM and urinary incontinence,” said Dr. Kelly. “Many women present to the clinic having heard of vaginal laser procedures, having had vaginal laser procedures, or having been told they need vaginal laser procedures. My impression has been that these procedures are being marketed to women … without rigorous study.”
“Many women are reluctant to have mesh slings for stress incontinence due to some of the potential risks,” and they are looking for less invasive options, said Dr. Welk. Over the past few years, he has had increasing questions from patients about the use of lasers to improve this condition.
The commentary was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Transparency needed
The first vaginal energy device was licensed by Health Canada in 2015 to treat GSM. That meant the device was deemed to have met basic safety, effectiveness, and quality criteria. But no controlled studies are required for regulatory approval of such devices, and after licensing, some providers rebranded the device indication from GSM to vaginal rejuvenation, said Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk.
Vaginal laser therapies are offered throughout Canada, with at least one provider of vaginal rejuvenation procedures in the 10 most populous cities. Under the current system, the number of patients who pay for these procedures and the amount that they pay cannot be tracked. Nor can the number of vaginal laser systems active in Canada be tracked. Patients can refer themselves for the service, and providers’ publicly quoted costs (on websites, for example) are thousands of dollars for treatment.
The rebranding for vaginal rejuvenation “represents a difference between the licensing of a medical device by Health Canada and the way that these devices are used and marketed,” according to the commentary. “A procedure with limited high-quality evidence supporting its efficacy and a potential financial conflict of interest for providers may not be serving the best interests of people in Canada, even if the risk of adverse events is low.”
Updates to Canada’s medical devices action plan, including mandatory reporting of serious incidents and the ability to compel manufacturers to provide information on safety and effectiveness, “represent important progress,” according to Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk. However, problems persist, including lack of a requirement for peer-reviewed, controlled studies.
Furthermore, women who undergo laser treatment for GSM, urinary incontinence, or vaginal rejuvenation may not receive a proper medical evaluation and standard treatments, the authors noted.
“I would like to see more transparency and public-facing information available on approved medical devices,” said Dr. Welk. “Health Canada has an online database of approved devices, but no information around the evidence submitted during the approval process is available, nor are the indications for the various devices.”
In addition, he said, many devices in the registry are listed by a serial number rather than the name that would be familiar to the public, “making it hard to match up information.”
Dr. Kelly added the “encouraging” news that the Canadian Society for Pelvic Medicine is working with Health Canada to “improve knowledge translation when it comes to transparency regarding medical devices.”
Medicine before marketing
“The commentary provides an accurate and evidence-based assessment of the use of vaginal laser treatments,” Jason Abbott, B Med (Hons), PhD, professor of gynecology at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, told this news organization. “The marketing of this device is a case of putting the cart before the horse. It is essential that strong, scientific, and reproducible studies be available on efficacy and safety before there is a direct-to-consumer marketing approach.”
Clinicians should advise patients when the treatment effect is likely to be minimal or risky, especially when there is a financial incentive to the clinician, he said. “Governments, regulators, and medical societies have a duty of care to the public to make sure that the medicine comes before the marketing. Otherwise, we are no better than snake oil sellers.
“Given the size of studies to date, the improvement in symptoms following treatment may be less than a few percent,” he noted. “That may be acceptable to some women. We don’t know.”
Dr. Abbott’s team is conducting research to define what women would want as a minimal level of improvement, the maximum cost, and the maximum risk from the laser procedure.
“In cancer … the benefit of a new treatment may only be a few percent for survival,” he said. “That may be completely acceptable for some or even many patients. What we cannot do, however, is extrapolate those same expectations to a treatment for a benign condition where quality of life is compromised.”
Echoing Dr. Kelly and Dr. Welk, Dr. Abbott said, “It is important that there be transparency in the clinical communication. Patients should be told that the best scientific studies that are judged based on their quality show there is no benefit to laser treatment for GSM or urinary incontinence.”
Although the medical risks may be low, he added, “financial risk also needs to be discussed. Patients should be encouraged to participate in clinical trials where there is no cost to them to gain the information first, before wholesale uptake of the treatment. … Should patients still wish to undergo the procedure once the risks and an honest account of the evidence is given to them, that of course is their choice.” Dr. Kelly, Dr. Welk, and Dr. Abbott had no commercial funding or relevant financial relationships to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Systemic sclerosis antibodies show link to interstitial lung disease in RA
Adults with rheumatoid arthritis or primary Sjogren’s syndrome plus interstitial lung disease had higher levels of systemic sclerosis–specific antibodies than those without lung disease, based on data from 101 individuals.
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) has been associated with the development of interstitial lung disease (ILD), but the prevalence of SSc autoantibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and primary Sjogren’s syndrome (SS) has not been explored, wrote Vasilike Koulouri, MD, of Kapodistrian University of Athens, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, the researchers reviewed serum data from patients with RA and SS using immunoblot assays to determine the prevalence of SSc-specific and anti-Ro52 autoantibodies, both of which have been associated with ILD in SSc patients.
The study population included 28 RA patients with ILD, 32 RA patients without ILD, 9 primary SS patients with ILD, and 32 primary SS patients with no ILD. The mean age of the RA participants was 63.4 years, 70% were women, and the mean age at RA diagnosis was 50.2 years. The mean age of the primary SS group was 60.3 years, 87.8% were female, and the mean age at diagnosis was 52.7 years.
Overall, SSc-specific antibodies across all titers were detected more frequently in RA patients with ILD compared with those with no ILD, though not statistically significant (42.9% vs. 21.9%, P = .08). However, “This trend was mainly attributed to the statistically significant difference between the two groups at strong titers (25% vs. 3.1%, P = .01),” the researchers wrote. Notably, they added.
No significant differences appeared in the prevalence of SSc-specific or Ro52 autoantibodies between primary SS patients with and without ILD, which might be attributable in part to the increased prevalence of anticentromere antibodies in primary SS, the researchers said.
RA patients who were positive for SSc-specific antibodies at strong titers were significantly more likely to have respiratory abnormalities than those who were negative (87.5% vs. 47.2%, P = .04), but no such differences appeared in primary SS patients.
“Early detection of SSc antibodies could be important in clinical practice as it may mandate further diagnostic (for example, screening for pulmonary hypertension) and therapeutic approaches of these patients,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, mainly the small sample size, but also the potential for false-positive results on antibody titers, lack of data on the clinical significance of medium autoantibody titers, and the lack of long-term follow-up data, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that many seropositive RA patients with evidence of ILD “may evolve to a clinically evident overlap of RA and SSc” that would benefit from targeted treatment, they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from Novartis AG and by the Molecular Immunology and Clinical Applications Unit, Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with rheumatoid arthritis or primary Sjogren’s syndrome plus interstitial lung disease had higher levels of systemic sclerosis–specific antibodies than those without lung disease, based on data from 101 individuals.
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) has been associated with the development of interstitial lung disease (ILD), but the prevalence of SSc autoantibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and primary Sjogren’s syndrome (SS) has not been explored, wrote Vasilike Koulouri, MD, of Kapodistrian University of Athens, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, the researchers reviewed serum data from patients with RA and SS using immunoblot assays to determine the prevalence of SSc-specific and anti-Ro52 autoantibodies, both of which have been associated with ILD in SSc patients.
The study population included 28 RA patients with ILD, 32 RA patients without ILD, 9 primary SS patients with ILD, and 32 primary SS patients with no ILD. The mean age of the RA participants was 63.4 years, 70% were women, and the mean age at RA diagnosis was 50.2 years. The mean age of the primary SS group was 60.3 years, 87.8% were female, and the mean age at diagnosis was 52.7 years.
Overall, SSc-specific antibodies across all titers were detected more frequently in RA patients with ILD compared with those with no ILD, though not statistically significant (42.9% vs. 21.9%, P = .08). However, “This trend was mainly attributed to the statistically significant difference between the two groups at strong titers (25% vs. 3.1%, P = .01),” the researchers wrote. Notably, they added.
No significant differences appeared in the prevalence of SSc-specific or Ro52 autoantibodies between primary SS patients with and without ILD, which might be attributable in part to the increased prevalence of anticentromere antibodies in primary SS, the researchers said.
RA patients who were positive for SSc-specific antibodies at strong titers were significantly more likely to have respiratory abnormalities than those who were negative (87.5% vs. 47.2%, P = .04), but no such differences appeared in primary SS patients.
“Early detection of SSc antibodies could be important in clinical practice as it may mandate further diagnostic (for example, screening for pulmonary hypertension) and therapeutic approaches of these patients,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, mainly the small sample size, but also the potential for false-positive results on antibody titers, lack of data on the clinical significance of medium autoantibody titers, and the lack of long-term follow-up data, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that many seropositive RA patients with evidence of ILD “may evolve to a clinically evident overlap of RA and SSc” that would benefit from targeted treatment, they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from Novartis AG and by the Molecular Immunology and Clinical Applications Unit, Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with rheumatoid arthritis or primary Sjogren’s syndrome plus interstitial lung disease had higher levels of systemic sclerosis–specific antibodies than those without lung disease, based on data from 101 individuals.
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) has been associated with the development of interstitial lung disease (ILD), but the prevalence of SSc autoantibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and primary Sjogren’s syndrome (SS) has not been explored, wrote Vasilike Koulouri, MD, of Kapodistrian University of Athens, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, the researchers reviewed serum data from patients with RA and SS using immunoblot assays to determine the prevalence of SSc-specific and anti-Ro52 autoantibodies, both of which have been associated with ILD in SSc patients.
The study population included 28 RA patients with ILD, 32 RA patients without ILD, 9 primary SS patients with ILD, and 32 primary SS patients with no ILD. The mean age of the RA participants was 63.4 years, 70% were women, and the mean age at RA diagnosis was 50.2 years. The mean age of the primary SS group was 60.3 years, 87.8% were female, and the mean age at diagnosis was 52.7 years.
Overall, SSc-specific antibodies across all titers were detected more frequently in RA patients with ILD compared with those with no ILD, though not statistically significant (42.9% vs. 21.9%, P = .08). However, “This trend was mainly attributed to the statistically significant difference between the two groups at strong titers (25% vs. 3.1%, P = .01),” the researchers wrote. Notably, they added.
No significant differences appeared in the prevalence of SSc-specific or Ro52 autoantibodies between primary SS patients with and without ILD, which might be attributable in part to the increased prevalence of anticentromere antibodies in primary SS, the researchers said.
RA patients who were positive for SSc-specific antibodies at strong titers were significantly more likely to have respiratory abnormalities than those who were negative (87.5% vs. 47.2%, P = .04), but no such differences appeared in primary SS patients.
“Early detection of SSc antibodies could be important in clinical practice as it may mandate further diagnostic (for example, screening for pulmonary hypertension) and therapeutic approaches of these patients,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, mainly the small sample size, but also the potential for false-positive results on antibody titers, lack of data on the clinical significance of medium autoantibody titers, and the lack of long-term follow-up data, the researchers noted.
However, the results suggest that many seropositive RA patients with evidence of ILD “may evolve to a clinically evident overlap of RA and SSc” that would benefit from targeted treatment, they concluded.
The study was supported by a grant from Novartis AG and by the Molecular Immunology and Clinical Applications Unit, Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF TRANSLATIONAL AUTOIMMUNITY
Large cohort study finds isotretinoin not associated with IBD
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.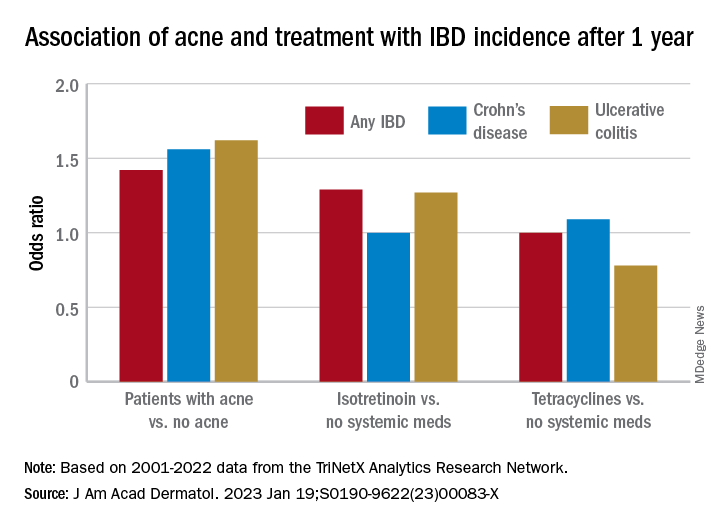
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Periorbital Orange Spots
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
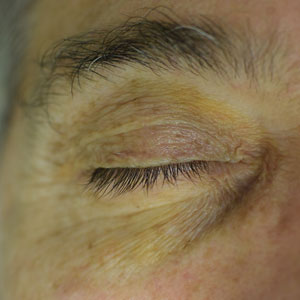
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
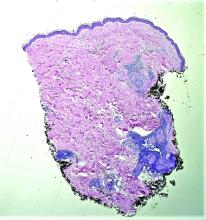
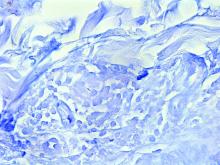
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
A 63-year-old White man with a history of melanoma presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of gradually worsening yellow discoloration around the eyes of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination revealed periorbital yellow-orange patches (top). The discolorations were nonelevated and nonpalpable. Dermoscopy revealed yellow blotches with sparing of the hair follicles (bottom). The remainder of the skin examination was unremarkable.
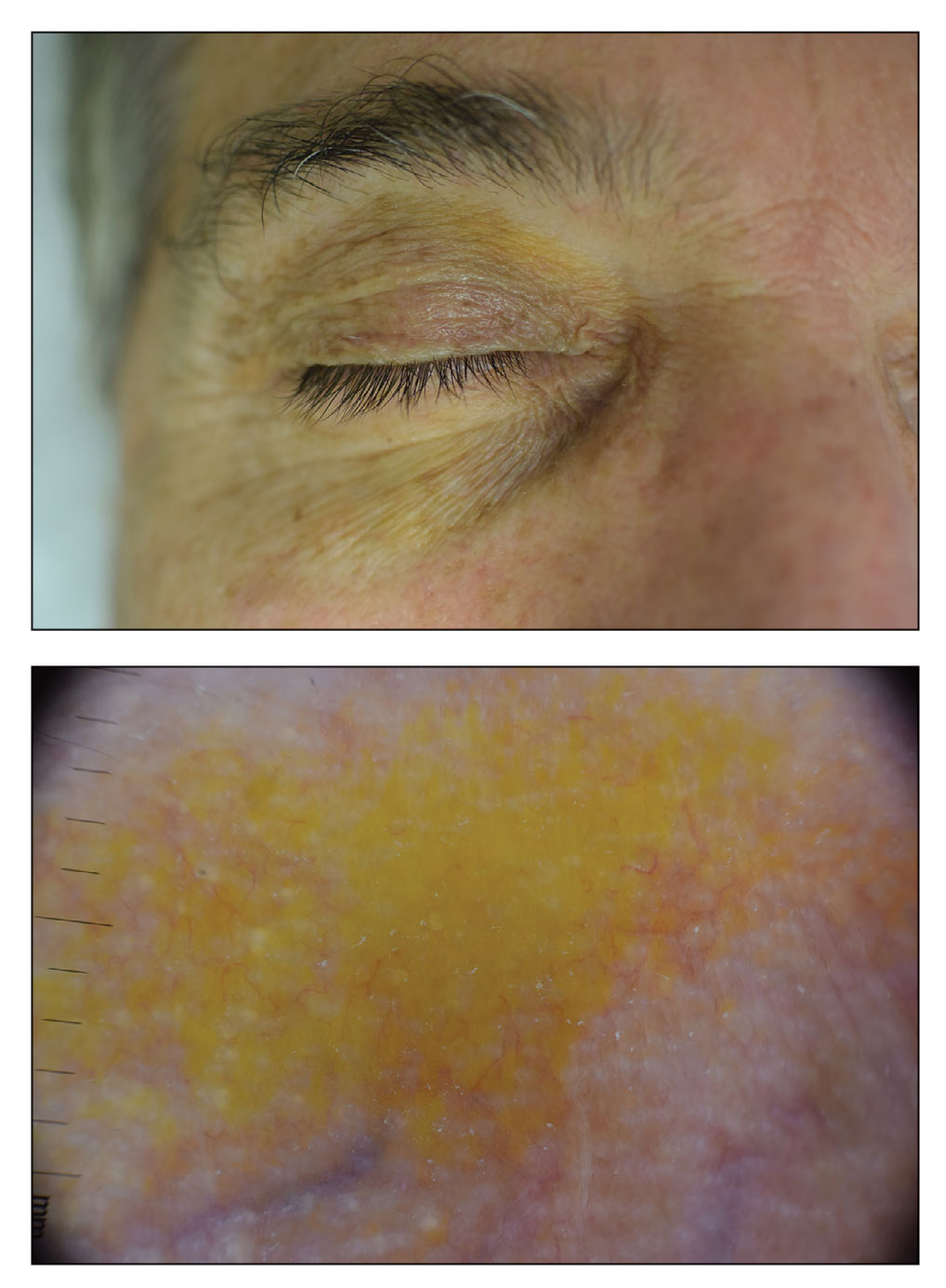
A White male presented with a 1½-year history of a progressive hypoesthetic annular, hyperpigmented plaque on the upper arm
Paucibacillary tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by few anesthetic hypo- or hyperpigmented lesions and can be accompanied by palpable peripheral nerve enlargements.
Tuberculoid leprosy presents histologically with epithelioid histiocytes with lymphocytes and Langhans giant cells. Neurotropic granulomas are also characteristic of tuberculoid leprosy. Fite staining allows for the identification of the acid-fast bacilli of M. leprae, which in some cases are quite few in number. The standard mycobacterium stain, Ziehl-Neelsen, is a good option for M. tuberculosis, but because of the relative weak mycolic acid coat of M. leprae, the Fite stain is more appropriate for identifying M. leprae.
Clinically, other than the presence of fewer than five hypoesthetic lesions that are either hypopigmented or erythematous, tuberculoid leprosy often presents with additional peripheral nerve involvement that manifests as numbness and tingling in hands and feet.1 This patient denied any tingling, weakness, or numbness, outside of the anesthetic lesion on his posterior upper arm.
The patient, born in the United States, had a remote history of military travel to Iraq, Kuwait, and the Philippines, but had not traveled internationally within the last 15 years, apart from a cruise to the Bahamas. He denied any known contact with individuals with similar lesions. He denied a history of contact with armadillos, but acknowledged that they are native to where he resides in central Florida, and that he had seen them in his yard.
Histopathological examination revealed an unremarkable epidermis with a superficial and deep perivascular, periadnexal, and perineural lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Fite stain revealed rare rod-shaped organisms (Figure 2). These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of paucibacillary, tuberculoid leprosy.
The patient’s travel history to highly endemic areas (Middle East), as well as possible environmental contact with armadillos – including contact with soil that the armadillos occupied – could explain plausible modes of transmission. Following consultation with our infectious disease department and the National Hansen’s Disease Program, our patient began a planned course of therapy with 18 months of minocycline, rifampin, and moxifloxacin.
Human-to-human transmission of HD has been well documented; however, zoonotic transmission – specifically via the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) – serves as another suggested means of transmission, especially in the Southeastern United States.2-6 Travel to highly-endemic areas increases the risk of contracting HD, which may take up to 20 years following contact with the bacteria to manifest clinically.
While central Florida was previously thought to be a nonendemic area of disease, the incidence of the disease in this region has increased in recent years.7 Human-to-human transmission, which remains a concern with immigration from highly-endemic regions, occurs via long-term contact with nasal droplets of an infected person.8,9
Many patients in regions with very few cases of leprosy deny travel to other endemic regions and contact with infected people. Thus, zoonotic transmission remains a legitimate concern in the Southeastern United States – accounting, at least in part, for many of the non–human-transmitted cases of leprosy.2,10 We encourage clinicians to maintain a high level of clinical suspicion for leprosy when evaluating patients presenting with hypoesthetic cutaneous lesions and to obtain a travel history and to ask about armadillo exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Smith, from the University of South Florida, Tampa; Dr. Hatch and Dr. Sarriera-Lazaro, from the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of South Florida; and Dr. Turner and Dr. Beachkofsky, from the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital, Tampa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited this case. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease), in: “Goldman’s Cecil Medicine,” 24th ed. (Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2012: pp. 1950-4.
2. Sharma R et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;21(12):2127-34.
3. Lane JE et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):714-6.
4. Clark BM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008 Jun;78(6):962-7.
5. Bruce S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Aug;43(2 Pt 1):223-8.
6. Loughry WJ et al. J Wildl Dis. 2009 Jan;45(1):144-52.
7. FDo H. Florida charts: Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy). Health FDo. 2019. https://www.flhealthcharts.gov/ChartsReports/rdPage.aspx?rdReport=NonVitalIndNoGrpCounts.DataViewer&cid=174.
8. Maymone MBC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul;83(1):1-14.
9. Scollard DM et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):338-81.
10. Domozych R et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2016 May 12;2(3):189-92.
Paucibacillary tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by few anesthetic hypo- or hyperpigmented lesions and can be accompanied by palpable peripheral nerve enlargements.
Tuberculoid leprosy presents histologically with epithelioid histiocytes with lymphocytes and Langhans giant cells. Neurotropic granulomas are also characteristic of tuberculoid leprosy. Fite staining allows for the identification of the acid-fast bacilli of M. leprae, which in some cases are quite few in number. The standard mycobacterium stain, Ziehl-Neelsen, is a good option for M. tuberculosis, but because of the relative weak mycolic acid coat of M. leprae, the Fite stain is more appropriate for identifying M. leprae.
Clinically, other than the presence of fewer than five hypoesthetic lesions that are either hypopigmented or erythematous, tuberculoid leprosy often presents with additional peripheral nerve involvement that manifests as numbness and tingling in hands and feet.1 This patient denied any tingling, weakness, or numbness, outside of the anesthetic lesion on his posterior upper arm.
The patient, born in the United States, had a remote history of military travel to Iraq, Kuwait, and the Philippines, but had not traveled internationally within the last 15 years, apart from a cruise to the Bahamas. He denied any known contact with individuals with similar lesions. He denied a history of contact with armadillos, but acknowledged that they are native to where he resides in central Florida, and that he had seen them in his yard.
Histopathological examination revealed an unremarkable epidermis with a superficial and deep perivascular, periadnexal, and perineural lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Fite stain revealed rare rod-shaped organisms (Figure 2). These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of paucibacillary, tuberculoid leprosy.
The patient’s travel history to highly endemic areas (Middle East), as well as possible environmental contact with armadillos – including contact with soil that the armadillos occupied – could explain plausible modes of transmission. Following consultation with our infectious disease department and the National Hansen’s Disease Program, our patient began a planned course of therapy with 18 months of minocycline, rifampin, and moxifloxacin.
Human-to-human transmission of HD has been well documented; however, zoonotic transmission – specifically via the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) – serves as another suggested means of transmission, especially in the Southeastern United States.2-6 Travel to highly-endemic areas increases the risk of contracting HD, which may take up to 20 years following contact with the bacteria to manifest clinically.
While central Florida was previously thought to be a nonendemic area of disease, the incidence of the disease in this region has increased in recent years.7 Human-to-human transmission, which remains a concern with immigration from highly-endemic regions, occurs via long-term contact with nasal droplets of an infected person.8,9
Many patients in regions with very few cases of leprosy deny travel to other endemic regions and contact with infected people. Thus, zoonotic transmission remains a legitimate concern in the Southeastern United States – accounting, at least in part, for many of the non–human-transmitted cases of leprosy.2,10 We encourage clinicians to maintain a high level of clinical suspicion for leprosy when evaluating patients presenting with hypoesthetic cutaneous lesions and to obtain a travel history and to ask about armadillo exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Smith, from the University of South Florida, Tampa; Dr. Hatch and Dr. Sarriera-Lazaro, from the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of South Florida; and Dr. Turner and Dr. Beachkofsky, from the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital, Tampa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited this case. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease), in: “Goldman’s Cecil Medicine,” 24th ed. (Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2012: pp. 1950-4.
2. Sharma R et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;21(12):2127-34.
3. Lane JE et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):714-6.
4. Clark BM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008 Jun;78(6):962-7.
5. Bruce S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Aug;43(2 Pt 1):223-8.
6. Loughry WJ et al. J Wildl Dis. 2009 Jan;45(1):144-52.
7. FDo H. Florida charts: Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy). Health FDo. 2019. https://www.flhealthcharts.gov/ChartsReports/rdPage.aspx?rdReport=NonVitalIndNoGrpCounts.DataViewer&cid=174.
8. Maymone MBC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul;83(1):1-14.
9. Scollard DM et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):338-81.
10. Domozych R et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2016 May 12;2(3):189-92.
Paucibacillary tuberculoid leprosy is characterized by few anesthetic hypo- or hyperpigmented lesions and can be accompanied by palpable peripheral nerve enlargements.
Tuberculoid leprosy presents histologically with epithelioid histiocytes with lymphocytes and Langhans giant cells. Neurotropic granulomas are also characteristic of tuberculoid leprosy. Fite staining allows for the identification of the acid-fast bacilli of M. leprae, which in some cases are quite few in number. The standard mycobacterium stain, Ziehl-Neelsen, is a good option for M. tuberculosis, but because of the relative weak mycolic acid coat of M. leprae, the Fite stain is more appropriate for identifying M. leprae.
Clinically, other than the presence of fewer than five hypoesthetic lesions that are either hypopigmented or erythematous, tuberculoid leprosy often presents with additional peripheral nerve involvement that manifests as numbness and tingling in hands and feet.1 This patient denied any tingling, weakness, or numbness, outside of the anesthetic lesion on his posterior upper arm.
The patient, born in the United States, had a remote history of military travel to Iraq, Kuwait, and the Philippines, but had not traveled internationally within the last 15 years, apart from a cruise to the Bahamas. He denied any known contact with individuals with similar lesions. He denied a history of contact with armadillos, but acknowledged that they are native to where he resides in central Florida, and that he had seen them in his yard.
Histopathological examination revealed an unremarkable epidermis with a superficial and deep perivascular, periadnexal, and perineural lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Fite stain revealed rare rod-shaped organisms (Figure 2). These findings are consistent with a diagnosis of paucibacillary, tuberculoid leprosy.
The patient’s travel history to highly endemic areas (Middle East), as well as possible environmental contact with armadillos – including contact with soil that the armadillos occupied – could explain plausible modes of transmission. Following consultation with our infectious disease department and the National Hansen’s Disease Program, our patient began a planned course of therapy with 18 months of minocycline, rifampin, and moxifloxacin.
Human-to-human transmission of HD has been well documented; however, zoonotic transmission – specifically via the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) – serves as another suggested means of transmission, especially in the Southeastern United States.2-6 Travel to highly-endemic areas increases the risk of contracting HD, which may take up to 20 years following contact with the bacteria to manifest clinically.
While central Florida was previously thought to be a nonendemic area of disease, the incidence of the disease in this region has increased in recent years.7 Human-to-human transmission, which remains a concern with immigration from highly-endemic regions, occurs via long-term contact with nasal droplets of an infected person.8,9
Many patients in regions with very few cases of leprosy deny travel to other endemic regions and contact with infected people. Thus, zoonotic transmission remains a legitimate concern in the Southeastern United States – accounting, at least in part, for many of the non–human-transmitted cases of leprosy.2,10 We encourage clinicians to maintain a high level of clinical suspicion for leprosy when evaluating patients presenting with hypoesthetic cutaneous lesions and to obtain a travel history and to ask about armadillo exposure.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Smith, from the University of South Florida, Tampa; Dr. Hatch and Dr. Sarriera-Lazaro, from the department of dermatology and cutaneous surgery, University of South Florida; and Dr. Turner and Dr. Beachkofsky, from the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital, Tampa. Dr. Bilu Martin edited this case. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease), in: “Goldman’s Cecil Medicine,” 24th ed. (Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2012: pp. 1950-4.
2. Sharma R et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;21(12):2127-34.
3. Lane JE et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):714-6.
4. Clark BM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008 Jun;78(6):962-7.
5. Bruce S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Aug;43(2 Pt 1):223-8.
6. Loughry WJ et al. J Wildl Dis. 2009 Jan;45(1):144-52.
7. FDo H. Florida charts: Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy). Health FDo. 2019. https://www.flhealthcharts.gov/ChartsReports/rdPage.aspx?rdReport=NonVitalIndNoGrpCounts.DataViewer&cid=174.
8. Maymone MBC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul;83(1):1-14.
9. Scollard DM et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):338-81.
10. Domozych R et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2016 May 12;2(3):189-92.
A 44-year-old White male presented with a 1½-year history of a progressive hypoesthetic annular, mildly hyperpigmented plaque on the left posterior upper arm.
He denied pruritus, pain, or systemic symptoms including weight loss, visual changes, cough, dyspnea, and abdominal pain. He also denied any paresthesia or weakness. On physical examination, there is a subtle, solitary 4-cm annular skin-colored thin plaque on the patient's left posterior upper arm (Figure 1).
Punch biopsy of the lesion was performed, and the histopathological findings are illustrated in Figure 2.
Bacterial vaginosis linked with persistent HPV infections
Montrouge, France – Four in five women will be infected by one or more human papillomavirus (HPV) strains during their lifetimes. For most of these women, the HPV will be cleared from the body, but 5% of them will develop precancerous lesions in the cervix.
At a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases Society, Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, took the opportunity to discuss the importance of vaginal flora and the need to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis.
Striking a balance
Essential for reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections, a healthy vaginal flora is made up of millions of microorganisms, mainly lactobacilli, as well as other bacteria (Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Prevotella, streptococcus, gonococcus), HPV, and fungi.
Lactobacilli produce lactic acid, which reduces the vagina’s pH, as well as hydrogen peroxide, which is toxic to the other bacteria.
Different factors, such as alcohol, a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and sugar, and especially smoking, can lead to an imbalance of the bacteria in the vaginal flora and thus result in vaginosis. What occurs is an abnormal multiplication of different types of anaerobic bacteria that are normally present in much lower numbers. There is a relative reduction in lactobacilli, which results in an increased vaginal pH, a greater risk of contracting an STI, and reduced clearance of the HPV infection. “Women who smoke probably experience persistent HPV infections due to an imbalance in vaginal flora,” said Dr. Maruani.
Vaginosis and HPV
When there are fewer lactobacilli than there should be, these bacteria can no longer protect the vaginal mucosa, which is disrupted by other bacteria. “HPV then has access to the basal cells,” said Dr. Maruani, acknowledging that the relationship between bacterial vaginosis and persistent HPV infections has been the subject of numerous research studies over the past decade or so. “For years, I would see this same link in my patients. Those with persistent vaginosis were also the ones with persistent HPV. And I’m not the only one to notice this. Studies have also been carried out investigating this exact correlation,” she added.
These studies have shown that HPV infections persist in cases of vaginosis, resulting in the appearance of epithelial lesions. Additionally, the lesions are more severe when dysbiosis is more severe.
What about probiotics? Can they treat dysbiosis and an HPV infection at the same time? “Probiotics work very well for vaginosis, provided they are used for a long time. We know that they lessen HPV infections and low-grade lesions,” said Dr. Maruani, although no randomized studies support this conclusion. “It’s not a one size fits all. We aren’t about to treat patients with precancerous lesions with probiotics.” There are currently no data concerning the efficacy of probiotics on high-grade lesions. These days, Dr. Maruani has been thinking about a new issue: the benefit of diagnosing cases of asymptomatic vaginosis – because treating them would reduce the risk of persistent HPV infection.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Montrouge, France – Four in five women will be infected by one or more human papillomavirus (HPV) strains during their lifetimes. For most of these women, the HPV will be cleared from the body, but 5% of them will develop precancerous lesions in the cervix.
At a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases Society, Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, took the opportunity to discuss the importance of vaginal flora and the need to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis.
Striking a balance
Essential for reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections, a healthy vaginal flora is made up of millions of microorganisms, mainly lactobacilli, as well as other bacteria (Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Prevotella, streptococcus, gonococcus), HPV, and fungi.
Lactobacilli produce lactic acid, which reduces the vagina’s pH, as well as hydrogen peroxide, which is toxic to the other bacteria.
Different factors, such as alcohol, a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and sugar, and especially smoking, can lead to an imbalance of the bacteria in the vaginal flora and thus result in vaginosis. What occurs is an abnormal multiplication of different types of anaerobic bacteria that are normally present in much lower numbers. There is a relative reduction in lactobacilli, which results in an increased vaginal pH, a greater risk of contracting an STI, and reduced clearance of the HPV infection. “Women who smoke probably experience persistent HPV infections due to an imbalance in vaginal flora,” said Dr. Maruani.
Vaginosis and HPV
When there are fewer lactobacilli than there should be, these bacteria can no longer protect the vaginal mucosa, which is disrupted by other bacteria. “HPV then has access to the basal cells,” said Dr. Maruani, acknowledging that the relationship between bacterial vaginosis and persistent HPV infections has been the subject of numerous research studies over the past decade or so. “For years, I would see this same link in my patients. Those with persistent vaginosis were also the ones with persistent HPV. And I’m not the only one to notice this. Studies have also been carried out investigating this exact correlation,” she added.
These studies have shown that HPV infections persist in cases of vaginosis, resulting in the appearance of epithelial lesions. Additionally, the lesions are more severe when dysbiosis is more severe.
What about probiotics? Can they treat dysbiosis and an HPV infection at the same time? “Probiotics work very well for vaginosis, provided they are used for a long time. We know that they lessen HPV infections and low-grade lesions,” said Dr. Maruani, although no randomized studies support this conclusion. “It’s not a one size fits all. We aren’t about to treat patients with precancerous lesions with probiotics.” There are currently no data concerning the efficacy of probiotics on high-grade lesions. These days, Dr. Maruani has been thinking about a new issue: the benefit of diagnosing cases of asymptomatic vaginosis – because treating them would reduce the risk of persistent HPV infection.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Montrouge, France – Four in five women will be infected by one or more human papillomavirus (HPV) strains during their lifetimes. For most of these women, the HPV will be cleared from the body, but 5% of them will develop precancerous lesions in the cervix.
At a press conference ahead of the 46th meeting of the French Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases Society, Julia Maruani, MD, a medical gynecologist in Marseille, France, took the opportunity to discuss the importance of vaginal flora and the need to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis.
Striking a balance
Essential for reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections, a healthy vaginal flora is made up of millions of microorganisms, mainly lactobacilli, as well as other bacteria (Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Prevotella, streptococcus, gonococcus), HPV, and fungi.
Lactobacilli produce lactic acid, which reduces the vagina’s pH, as well as hydrogen peroxide, which is toxic to the other bacteria.
Different factors, such as alcohol, a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and sugar, and especially smoking, can lead to an imbalance of the bacteria in the vaginal flora and thus result in vaginosis. What occurs is an abnormal multiplication of different types of anaerobic bacteria that are normally present in much lower numbers. There is a relative reduction in lactobacilli, which results in an increased vaginal pH, a greater risk of contracting an STI, and reduced clearance of the HPV infection. “Women who smoke probably experience persistent HPV infections due to an imbalance in vaginal flora,” said Dr. Maruani.
Vaginosis and HPV
When there are fewer lactobacilli than there should be, these bacteria can no longer protect the vaginal mucosa, which is disrupted by other bacteria. “HPV then has access to the basal cells,” said Dr. Maruani, acknowledging that the relationship between bacterial vaginosis and persistent HPV infections has been the subject of numerous research studies over the past decade or so. “For years, I would see this same link in my patients. Those with persistent vaginosis were also the ones with persistent HPV. And I’m not the only one to notice this. Studies have also been carried out investigating this exact correlation,” she added.
These studies have shown that HPV infections persist in cases of vaginosis, resulting in the appearance of epithelial lesions. Additionally, the lesions are more severe when dysbiosis is more severe.
What about probiotics? Can they treat dysbiosis and an HPV infection at the same time? “Probiotics work very well for vaginosis, provided they are used for a long time. We know that they lessen HPV infections and low-grade lesions,” said Dr. Maruani, although no randomized studies support this conclusion. “It’s not a one size fits all. We aren’t about to treat patients with precancerous lesions with probiotics.” There are currently no data concerning the efficacy of probiotics on high-grade lesions. These days, Dr. Maruani has been thinking about a new issue: the benefit of diagnosing cases of asymptomatic vaginosis – because treating them would reduce the risk of persistent HPV infection.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Ozempic face’: Accepting wrinkles for improved health
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 12% of PsA patients need musculoskeletal surgery
Among adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 11.8% required at least one musculoskeletal surgery related to their disease, based on data from more than 1,500 individuals at the University of Toronto’s Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
“Despite optimal medical therapy to control systemic inflammation and preserve joint function, a subset of patients with PsA still require musculoskeletal (MSK) surgery for disease-related morbidity,” but data on the prevalence of MSK surgeries and the associated risk factors are lacking, wrote Timothy S.H. Kwok, MD, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
In a study published in The Journal of Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed data from a longitudinal cohort of 1,574 adults aged 18 years and older with PsA established at the Toronto clinic during 1978-2019.
Overall, 185 patients had 379 MSK surgeries related to PsA during the study period for a prevalence of 11.8%.
The most common procedures were arthrodesis and arthroplasty (27% for both). More than half (59%) of the surgeries were joint sacrificing, and 41% were joint retaining, and 57 procedures were revisions related to the primary surgery.
Among 1,018 patients with data complete enough for a multivariate analysis, including 71 PsA surgeries, factors significantly associated with an increased risk for surgery were a higher number of damaged joints (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; P < .001), tender or swollen joints (HR, 1.04; P = .01), and the presence of nail lesions (HR, 2.08; P < .01). Other predictors of surgery were higher scores on the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HR, 2.01; P < .001), elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (HR, 2.37; P = .02), and HLA-B27 positivity (HR, 2.22; P = .048).
However, a higher score on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index was significantly associated with lower risk of surgery (HR, 0.88; P < .002) The use of biologics had no significant impact on MSK surgery, the researchers noted.
The high percentage of joint sacrificing surgeries suggests a high burden of MSK surgery in patients with PsA, the researchers wrote in their discussion. The current study supports findings from previous studies and highlights the potential limitations and need for improvement in the current medical treatment paradigm for PsA, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for referral bias of complex cases to the center, which might have caused overestimation of the number of surgeries. The similarity in surgeries specifically related to PsA and degenerative arthritis also makes overestimation of surgeries possible, the researchers noted.
However, the study is one of the largest known to evaluate the prevalence of risk factors for MSK surgery in PsA patients over a long period of time, and identified surgeries directly attributable to PsA, they said. The study ended prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which increased the external validity of the findings, they added.
The study was supported by the Krembil Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Among adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 11.8% required at least one musculoskeletal surgery related to their disease, based on data from more than 1,500 individuals at the University of Toronto’s Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
“Despite optimal medical therapy to control systemic inflammation and preserve joint function, a subset of patients with PsA still require musculoskeletal (MSK) surgery for disease-related morbidity,” but data on the prevalence of MSK surgeries and the associated risk factors are lacking, wrote Timothy S.H. Kwok, MD, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
In a study published in The Journal of Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed data from a longitudinal cohort of 1,574 adults aged 18 years and older with PsA established at the Toronto clinic during 1978-2019.
Overall, 185 patients had 379 MSK surgeries related to PsA during the study period for a prevalence of 11.8%.
The most common procedures were arthrodesis and arthroplasty (27% for both). More than half (59%) of the surgeries were joint sacrificing, and 41% were joint retaining, and 57 procedures were revisions related to the primary surgery.
Among 1,018 patients with data complete enough for a multivariate analysis, including 71 PsA surgeries, factors significantly associated with an increased risk for surgery were a higher number of damaged joints (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; P < .001), tender or swollen joints (HR, 1.04; P = .01), and the presence of nail lesions (HR, 2.08; P < .01). Other predictors of surgery were higher scores on the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HR, 2.01; P < .001), elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (HR, 2.37; P = .02), and HLA-B27 positivity (HR, 2.22; P = .048).
However, a higher score on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index was significantly associated with lower risk of surgery (HR, 0.88; P < .002) The use of biologics had no significant impact on MSK surgery, the researchers noted.
The high percentage of joint sacrificing surgeries suggests a high burden of MSK surgery in patients with PsA, the researchers wrote in their discussion. The current study supports findings from previous studies and highlights the potential limitations and need for improvement in the current medical treatment paradigm for PsA, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for referral bias of complex cases to the center, which might have caused overestimation of the number of surgeries. The similarity in surgeries specifically related to PsA and degenerative arthritis also makes overestimation of surgeries possible, the researchers noted.
However, the study is one of the largest known to evaluate the prevalence of risk factors for MSK surgery in PsA patients over a long period of time, and identified surgeries directly attributable to PsA, they said. The study ended prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which increased the external validity of the findings, they added.
The study was supported by the Krembil Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Among adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), 11.8% required at least one musculoskeletal surgery related to their disease, based on data from more than 1,500 individuals at the University of Toronto’s Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
“Despite optimal medical therapy to control systemic inflammation and preserve joint function, a subset of patients with PsA still require musculoskeletal (MSK) surgery for disease-related morbidity,” but data on the prevalence of MSK surgeries and the associated risk factors are lacking, wrote Timothy S.H. Kwok, MD, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
In a study published in The Journal of Rheumatology, the researchers reviewed data from a longitudinal cohort of 1,574 adults aged 18 years and older with PsA established at the Toronto clinic during 1978-2019.
Overall, 185 patients had 379 MSK surgeries related to PsA during the study period for a prevalence of 11.8%.
The most common procedures were arthrodesis and arthroplasty (27% for both). More than half (59%) of the surgeries were joint sacrificing, and 41% were joint retaining, and 57 procedures were revisions related to the primary surgery.
Among 1,018 patients with data complete enough for a multivariate analysis, including 71 PsA surgeries, factors significantly associated with an increased risk for surgery were a higher number of damaged joints (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; P < .001), tender or swollen joints (HR, 1.04; P = .01), and the presence of nail lesions (HR, 2.08; P < .01). Other predictors of surgery were higher scores on the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HR, 2.01; P < .001), elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (HR, 2.37; P = .02), and HLA-B27 positivity (HR, 2.22; P = .048).
However, a higher score on the Psoriasis Area Severity Index was significantly associated with lower risk of surgery (HR, 0.88; P < .002) The use of biologics had no significant impact on MSK surgery, the researchers noted.
The high percentage of joint sacrificing surgeries suggests a high burden of MSK surgery in patients with PsA, the researchers wrote in their discussion. The current study supports findings from previous studies and highlights the potential limitations and need for improvement in the current medical treatment paradigm for PsA, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for referral bias of complex cases to the center, which might have caused overestimation of the number of surgeries. The similarity in surgeries specifically related to PsA and degenerative arthritis also makes overestimation of surgeries possible, the researchers noted.
However, the study is one of the largest known to evaluate the prevalence of risk factors for MSK surgery in PsA patients over a long period of time, and identified surgeries directly attributable to PsA, they said. The study ended prior to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which increased the external validity of the findings, they added.
The study was supported by the Krembil Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF RHEUMATOLOGY
A Dermatology Hospitalist Team’s Response to the Inpatient Consult Flowchart
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Cutis article by Dobkin et al1 (Cutis. 2022;109:218-220) regarding guidelines for inpatient and emergency department dermatology consultations. We agree with the authors that dermatology training is lacking in other medical specialties, which makes it challenging for teams to assess the appropriateness of a dermatology consultation in the inpatient setting. Inpatient dermatology consultation can be utilized in a hospital system to aid in rapid and accurate diagnosis, avoid inappropriate therapies, and decrease length of stay2 and readmission rates3 while providing education to the primary teams. This is precisely why in many instances the availability of inpatient dermatology consultation is so important because nondermatologists often are unable to determine whether a rash is life-threatening, benign, or something in between. From the perspective of dermatology hospitalists, there is room for improvement in the flowchart Dobkin et al1 presented to guide inpatient dermatology consultation.
To have a productive relationship with our internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, psychiatry, and other hospital-based colleagues, we must keep an open mind when a consultation is received. We feel that the flowchart proposed by Dobkin et al1 presents too narrow a viewpoint on the utility of inpatient dermatology. It rests on assertions that other teams will be able to determine the appropriate dermatologic diagnosis without involving a dermatologist, which often is not the case.
We disagree with several recommendations in the flowchart, the first being the assertion that patients who are “hemodynamically unstable due to [a] nondermatologic problem (eg, intubated on pressors, febrile, and hypotensive)” are not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation.1 Although dermatologists do not commonly encounter patients with critical illness in the outpatient clinic, dermatology consultation can be extremely helpful and even lifesaving in the inpatient setting. It is unrealistic to expect the primary teams to know whether cutaneous manifestations potentially could be related to the patient’s overall clinical picture. On the contrary, we would encourage the primary team in charge of a hemodynamically unstable patient to consult dermatology at the first sign of an unexplained rash. Take for example an acutely ill patient who develops retiform purpura. There are well-established dermatology guidelines for the workup of retiform purpura,4 including prompt biopsy and assessment of broad, potentially life-threatening differential diagnoses from calciphylaxis to angioinvasive fungal infection. In this scenario, the dermatology consultant may render the correct diagnosis and recommend immediate treatment that could be lifesaving.
Secondly, we do not agree with the recommendation that a patient in hospice care is not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation. Patients receiving hospice or palliative care have high rates of potentially symptomatic cutaneous diseases,5 including intertrigo and dermatitis—comprising stasis, seborrheic, and contact dermatitis.6 Although aggressive intervention for asymptomatic benign or malignant skin conditions may not be in line with their goals of care, an inpatient dermatology consultation can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. This population also is one that is unlikely to be able to attend an outpatient dermatology clinic appointment and therefore are good candidates for inpatient consultation.
Lastly, we want to highlight the difference between a stable chronic dermatologic disease and an acute flare that may occur while a patient is hospitalized, regardless of whether it is the reason for admission. For example, a patient with psoriasis affecting limited body surface area who is hospitalized for a myocardial infarction is not appropriate for a dermatology consultation. However, if that same patient develops erythroderma while they are hospitalized for cardiac monitoring, it would certainly be appropriate for dermatology to be consulted. Additionally, there are times when a chronic skin disease is the reason for hospitalization; dermatology, although technically a consulting service, would be the primary decision-maker for the patient’s care in this situation. In these scenarios, it is important for the patient to be able to establish care for long-term outpatient management of their condition; however, it is prudent to involve dermatology while the patient is acutely hospitalized to guide their treatment plan until they are able to see a dermatologist after discharge.
In conclusion, we believe that hospital dermatology is a valuable tool that can be utilized in many different scenarios. Although there are certainly situations more appropriate for outpatient dermatology referral, we would caution against overly simplified algorithms that could discourage valuable inpatient dermatology consultations. It often is worth a conversation with your dermatology consultant (when available at an institution) to determine the best course of action for each patient. Additionally, we recognize the need for more formalized guidelines on when to pursue inpatient dermatology consultation. We are members of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists and encourage readers to reference their website, which provides additional resources on inpatient dermatology (https://societydermatologyhospitalists.com/inpatient-dermatology-literature/).
Authors’ Response
We appreciate the letter in response to our commentary on the appropriateness of inpatient dermatology consultations. It is the continued refining and re-evaluation of concepts such as these that allow our field to grow and improve knowledge and patient care.
We sought to provide a nonpatronizing yet simple consultation flowchart that would help guide triage of patients in need or not in need of dermatologic evaluation by the inpatient teams. Understandably, the impressions of our flowchart have been variable based on different readers’ medical backgrounds and experiences. It is certainly possible that our flowchart lacked certain exceptions and oversimplified certain concepts, and we welcome further refining of this flowchart to better guide inpatient dermatology consultations.
We do, however, disagree that the primary team would not know whether a patient is intubated in the intensive care unit for a dermatology reason. If the patient is in such a status, it would be pertinent for the primary team to conduct a timely workup that could include consultations until a diagnosis is made. We were not implying that every dermatology consultation in the intensive care unit is unwarranted, especially if it can lead to a primary dermatologic diagnosis. We do believe that a thorough history could elicit an allergy or other chronic skin condition that could save resources and spending within a hospital. Likewise, psoriasis comes in many different presentations, and although we do not believe a consultation for chronic psoriatic plaques is appropriate in the hospital, it is absolutely appropriate for a patient who is erythrodermic from any cause.
Our flowchart was intended to be the first step to providing education on when consultations are appropriate, and further refinement will be necessary.
Hershel Dobkin, MD; Timothy Blackwell, BS; Robin Ashinoff, MD
Drs. Dobkin and Ashinoff are from Hackensack University Medical Center, New Jersey. Mr. Blackwell is from the Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, Stratford, New Jersey.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Hershel Dobkin, MD, Hackensack University Medical Center, 30 Prospect Ave, Hackensack, NJ 07601 ([email protected]).
- Dobkin H, Blackwell T, Ashinoff R. When are inpatient and emergency dermatologic consultations appropriate? Cutis. 2022;109:218-220. doi:10.12788/cutis.0492
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Hu L, Haynes H, Ferrazza D, et al. Impact of specialist consultations on inpatient admissions for dermatology-specific and related DRGs. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28:1477-1482. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2440-2
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.07.112
- Pisano C, Paladichuk H, Keeling B. Dermatology in palliative medicine [published online October 14, 2021]. BMJ Support Palliat Care. doi:10.1136/bmjspcare-2021-003342
- Barnabé C, Daeninck P. “Beauty is only skin deep”: prevalence of dermatologic disease on a palliative care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005;29:419-422. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.08.009
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Cutis article by Dobkin et al1 (Cutis. 2022;109:218-220) regarding guidelines for inpatient and emergency department dermatology consultations. We agree with the authors that dermatology training is lacking in other medical specialties, which makes it challenging for teams to assess the appropriateness of a dermatology consultation in the inpatient setting. Inpatient dermatology consultation can be utilized in a hospital system to aid in rapid and accurate diagnosis, avoid inappropriate therapies, and decrease length of stay2 and readmission rates3 while providing education to the primary teams. This is precisely why in many instances the availability of inpatient dermatology consultation is so important because nondermatologists often are unable to determine whether a rash is life-threatening, benign, or something in between. From the perspective of dermatology hospitalists, there is room for improvement in the flowchart Dobkin et al1 presented to guide inpatient dermatology consultation.
To have a productive relationship with our internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, psychiatry, and other hospital-based colleagues, we must keep an open mind when a consultation is received. We feel that the flowchart proposed by Dobkin et al1 presents too narrow a viewpoint on the utility of inpatient dermatology. It rests on assertions that other teams will be able to determine the appropriate dermatologic diagnosis without involving a dermatologist, which often is not the case.
We disagree with several recommendations in the flowchart, the first being the assertion that patients who are “hemodynamically unstable due to [a] nondermatologic problem (eg, intubated on pressors, febrile, and hypotensive)” are not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation.1 Although dermatologists do not commonly encounter patients with critical illness in the outpatient clinic, dermatology consultation can be extremely helpful and even lifesaving in the inpatient setting. It is unrealistic to expect the primary teams to know whether cutaneous manifestations potentially could be related to the patient’s overall clinical picture. On the contrary, we would encourage the primary team in charge of a hemodynamically unstable patient to consult dermatology at the first sign of an unexplained rash. Take for example an acutely ill patient who develops retiform purpura. There are well-established dermatology guidelines for the workup of retiform purpura,4 including prompt biopsy and assessment of broad, potentially life-threatening differential diagnoses from calciphylaxis to angioinvasive fungal infection. In this scenario, the dermatology consultant may render the correct diagnosis and recommend immediate treatment that could be lifesaving.
Secondly, we do not agree with the recommendation that a patient in hospice care is not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation. Patients receiving hospice or palliative care have high rates of potentially symptomatic cutaneous diseases,5 including intertrigo and dermatitis—comprising stasis, seborrheic, and contact dermatitis.6 Although aggressive intervention for asymptomatic benign or malignant skin conditions may not be in line with their goals of care, an inpatient dermatology consultation can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. This population also is one that is unlikely to be able to attend an outpatient dermatology clinic appointment and therefore are good candidates for inpatient consultation.
Lastly, we want to highlight the difference between a stable chronic dermatologic disease and an acute flare that may occur while a patient is hospitalized, regardless of whether it is the reason for admission. For example, a patient with psoriasis affecting limited body surface area who is hospitalized for a myocardial infarction is not appropriate for a dermatology consultation. However, if that same patient develops erythroderma while they are hospitalized for cardiac monitoring, it would certainly be appropriate for dermatology to be consulted. Additionally, there are times when a chronic skin disease is the reason for hospitalization; dermatology, although technically a consulting service, would be the primary decision-maker for the patient’s care in this situation. In these scenarios, it is important for the patient to be able to establish care for long-term outpatient management of their condition; however, it is prudent to involve dermatology while the patient is acutely hospitalized to guide their treatment plan until they are able to see a dermatologist after discharge.
In conclusion, we believe that hospital dermatology is a valuable tool that can be utilized in many different scenarios. Although there are certainly situations more appropriate for outpatient dermatology referral, we would caution against overly simplified algorithms that could discourage valuable inpatient dermatology consultations. It often is worth a conversation with your dermatology consultant (when available at an institution) to determine the best course of action for each patient. Additionally, we recognize the need for more formalized guidelines on when to pursue inpatient dermatology consultation. We are members of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists and encourage readers to reference their website, which provides additional resources on inpatient dermatology (https://societydermatologyhospitalists.com/inpatient-dermatology-literature/).
Authors’ Response
We appreciate the letter in response to our commentary on the appropriateness of inpatient dermatology consultations. It is the continued refining and re-evaluation of concepts such as these that allow our field to grow and improve knowledge and patient care.
We sought to provide a nonpatronizing yet simple consultation flowchart that would help guide triage of patients in need or not in need of dermatologic evaluation by the inpatient teams. Understandably, the impressions of our flowchart have been variable based on different readers’ medical backgrounds and experiences. It is certainly possible that our flowchart lacked certain exceptions and oversimplified certain concepts, and we welcome further refining of this flowchart to better guide inpatient dermatology consultations.
We do, however, disagree that the primary team would not know whether a patient is intubated in the intensive care unit for a dermatology reason. If the patient is in such a status, it would be pertinent for the primary team to conduct a timely workup that could include consultations until a diagnosis is made. We were not implying that every dermatology consultation in the intensive care unit is unwarranted, especially if it can lead to a primary dermatologic diagnosis. We do believe that a thorough history could elicit an allergy or other chronic skin condition that could save resources and spending within a hospital. Likewise, psoriasis comes in many different presentations, and although we do not believe a consultation for chronic psoriatic plaques is appropriate in the hospital, it is absolutely appropriate for a patient who is erythrodermic from any cause.
Our flowchart was intended to be the first step to providing education on when consultations are appropriate, and further refinement will be necessary.
Hershel Dobkin, MD; Timothy Blackwell, BS; Robin Ashinoff, MD
Drs. Dobkin and Ashinoff are from Hackensack University Medical Center, New Jersey. Mr. Blackwell is from the Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, Stratford, New Jersey.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Hershel Dobkin, MD, Hackensack University Medical Center, 30 Prospect Ave, Hackensack, NJ 07601 ([email protected]).
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Cutis article by Dobkin et al1 (Cutis. 2022;109:218-220) regarding guidelines for inpatient and emergency department dermatology consultations. We agree with the authors that dermatology training is lacking in other medical specialties, which makes it challenging for teams to assess the appropriateness of a dermatology consultation in the inpatient setting. Inpatient dermatology consultation can be utilized in a hospital system to aid in rapid and accurate diagnosis, avoid inappropriate therapies, and decrease length of stay2 and readmission rates3 while providing education to the primary teams. This is precisely why in many instances the availability of inpatient dermatology consultation is so important because nondermatologists often are unable to determine whether a rash is life-threatening, benign, or something in between. From the perspective of dermatology hospitalists, there is room for improvement in the flowchart Dobkin et al1 presented to guide inpatient dermatology consultation.
To have a productive relationship with our internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, psychiatry, and other hospital-based colleagues, we must keep an open mind when a consultation is received. We feel that the flowchart proposed by Dobkin et al1 presents too narrow a viewpoint on the utility of inpatient dermatology. It rests on assertions that other teams will be able to determine the appropriate dermatologic diagnosis without involving a dermatologist, which often is not the case.
We disagree with several recommendations in the flowchart, the first being the assertion that patients who are “hemodynamically unstable due to [a] nondermatologic problem (eg, intubated on pressors, febrile, and hypotensive)” are not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation.1 Although dermatologists do not commonly encounter patients with critical illness in the outpatient clinic, dermatology consultation can be extremely helpful and even lifesaving in the inpatient setting. It is unrealistic to expect the primary teams to know whether cutaneous manifestations potentially could be related to the patient’s overall clinical picture. On the contrary, we would encourage the primary team in charge of a hemodynamically unstable patient to consult dermatology at the first sign of an unexplained rash. Take for example an acutely ill patient who develops retiform purpura. There are well-established dermatology guidelines for the workup of retiform purpura,4 including prompt biopsy and assessment of broad, potentially life-threatening differential diagnoses from calciphylaxis to angioinvasive fungal infection. In this scenario, the dermatology consultant may render the correct diagnosis and recommend immediate treatment that could be lifesaving.
Secondly, we do not agree with the recommendation that a patient in hospice care is not appropriate for inpatient dermatology consultation. Patients receiving hospice or palliative care have high rates of potentially symptomatic cutaneous diseases,5 including intertrigo and dermatitis—comprising stasis, seborrheic, and contact dermatitis.6 Although aggressive intervention for asymptomatic benign or malignant skin conditions may not be in line with their goals of care, an inpatient dermatology consultation can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. This population also is one that is unlikely to be able to attend an outpatient dermatology clinic appointment and therefore are good candidates for inpatient consultation.
Lastly, we want to highlight the difference between a stable chronic dermatologic disease and an acute flare that may occur while a patient is hospitalized, regardless of whether it is the reason for admission. For example, a patient with psoriasis affecting limited body surface area who is hospitalized for a myocardial infarction is not appropriate for a dermatology consultation. However, if that same patient develops erythroderma while they are hospitalized for cardiac monitoring, it would certainly be appropriate for dermatology to be consulted. Additionally, there are times when a chronic skin disease is the reason for hospitalization; dermatology, although technically a consulting service, would be the primary decision-maker for the patient’s care in this situation. In these scenarios, it is important for the patient to be able to establish care for long-term outpatient management of their condition; however, it is prudent to involve dermatology while the patient is acutely hospitalized to guide their treatment plan until they are able to see a dermatologist after discharge.
In conclusion, we believe that hospital dermatology is a valuable tool that can be utilized in many different scenarios. Although there are certainly situations more appropriate for outpatient dermatology referral, we would caution against overly simplified algorithms that could discourage valuable inpatient dermatology consultations. It often is worth a conversation with your dermatology consultant (when available at an institution) to determine the best course of action for each patient. Additionally, we recognize the need for more formalized guidelines on when to pursue inpatient dermatology consultation. We are members of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists and encourage readers to reference their website, which provides additional resources on inpatient dermatology (https://societydermatologyhospitalists.com/inpatient-dermatology-literature/).
Authors’ Response
We appreciate the letter in response to our commentary on the appropriateness of inpatient dermatology consultations. It is the continued refining and re-evaluation of concepts such as these that allow our field to grow and improve knowledge and patient care.
We sought to provide a nonpatronizing yet simple consultation flowchart that would help guide triage of patients in need or not in need of dermatologic evaluation by the inpatient teams. Understandably, the impressions of our flowchart have been variable based on different readers’ medical backgrounds and experiences. It is certainly possible that our flowchart lacked certain exceptions and oversimplified certain concepts, and we welcome further refining of this flowchart to better guide inpatient dermatology consultations.
We do, however, disagree that the primary team would not know whether a patient is intubated in the intensive care unit for a dermatology reason. If the patient is in such a status, it would be pertinent for the primary team to conduct a timely workup that could include consultations until a diagnosis is made. We were not implying that every dermatology consultation in the intensive care unit is unwarranted, especially if it can lead to a primary dermatologic diagnosis. We do believe that a thorough history could elicit an allergy or other chronic skin condition that could save resources and spending within a hospital. Likewise, psoriasis comes in many different presentations, and although we do not believe a consultation for chronic psoriatic plaques is appropriate in the hospital, it is absolutely appropriate for a patient who is erythrodermic from any cause.
Our flowchart was intended to be the first step to providing education on when consultations are appropriate, and further refinement will be necessary.
Hershel Dobkin, MD; Timothy Blackwell, BS; Robin Ashinoff, MD
Drs. Dobkin and Ashinoff are from Hackensack University Medical Center, New Jersey. Mr. Blackwell is from the Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, Stratford, New Jersey.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Hershel Dobkin, MD, Hackensack University Medical Center, 30 Prospect Ave, Hackensack, NJ 07601 ([email protected]).
- Dobkin H, Blackwell T, Ashinoff R. When are inpatient and emergency dermatologic consultations appropriate? Cutis. 2022;109:218-220. doi:10.12788/cutis.0492
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Hu L, Haynes H, Ferrazza D, et al. Impact of specialist consultations on inpatient admissions for dermatology-specific and related DRGs. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28:1477-1482. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2440-2
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.07.112
- Pisano C, Paladichuk H, Keeling B. Dermatology in palliative medicine [published online October 14, 2021]. BMJ Support Palliat Care. doi:10.1136/bmjspcare-2021-003342
- Barnabé C, Daeninck P. “Beauty is only skin deep”: prevalence of dermatologic disease on a palliative care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005;29:419-422. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.08.009
- Dobkin H, Blackwell T, Ashinoff R. When are inpatient and emergency dermatologic consultations appropriate? Cutis. 2022;109:218-220. doi:10.12788/cutis.0492
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.6196
- Hu L, Haynes H, Ferrazza D, et al. Impact of specialist consultations on inpatient admissions for dermatology-specific and related DRGs. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28:1477-1482. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2440-2
- Georgesen C, Fox LP, Harp J. Retiform purpura: a diagnostic approach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:783-796. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.07.112
- Pisano C, Paladichuk H, Keeling B. Dermatology in palliative medicine [published online October 14, 2021]. BMJ Support Palliat Care. doi:10.1136/bmjspcare-2021-003342
- Barnabé C, Daeninck P. “Beauty is only skin deep”: prevalence of dermatologic disease on a palliative care unit. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005;29:419-422. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.08.009