User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
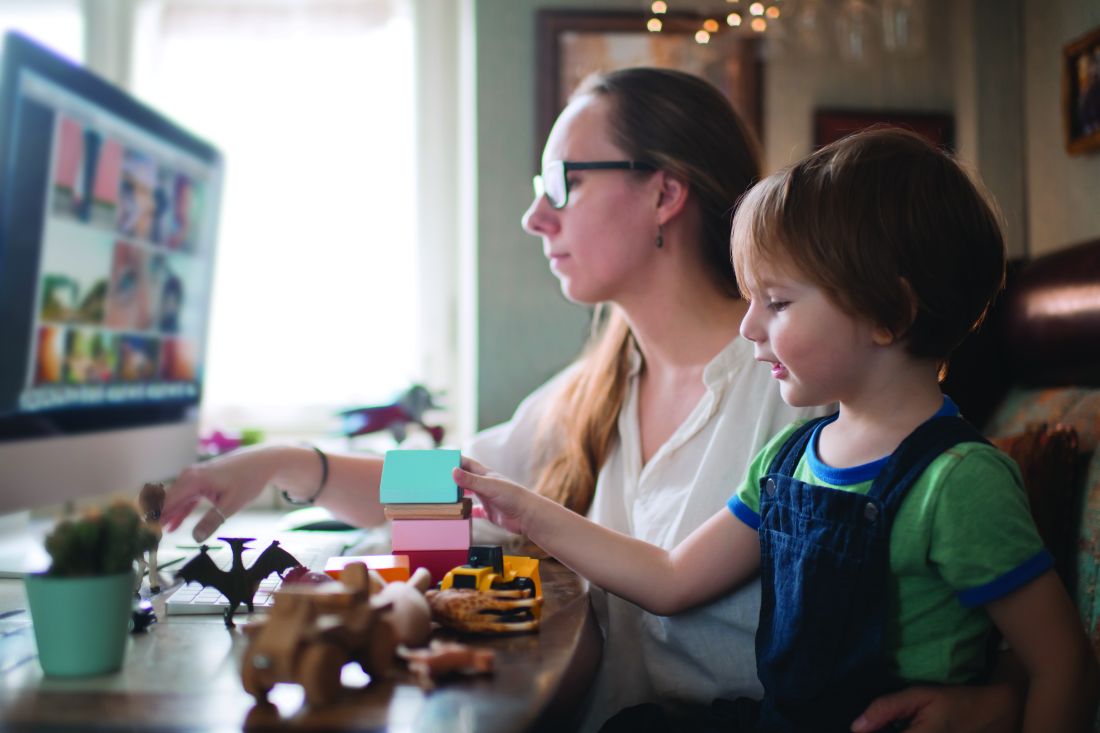
COVID-19 quarantine: Managing pediatric behavioral issues
We are living through unprecedented challenges, faced with profound uncertainties about the public health, the economy, the safety of our workplaces, the risks of gathering with friends and family, and even about the rhythm of the school year. Parents always have sought guidance from their pediatric providers when they are uncertain about their children’s health, behavior, and development. We want to share some guidance with you about several of the most common questions we have been hearing in the past few months, in the hope that it may prove useful in your conversations with patients and families.
What happens when we are so busy at home that our 2-year-old is ignored for much of the day?
If they are fortunate enough to be able to work from home, but have lost their child care, many parents are suddenly facing the sustained challenge of parenting while working. Even older children will have a tough time remembering that home is now a workplace, and they can’t interrupt their parents during a Zoom meeting. But older children will understand. Younger children (preschoolers) simply will not be able to understand that their parents are in sight but not fully available to them. They are exquisitely sensitive to their parents’ attention. If they are consistently ignored, behavioral problems can emerge. If both parents are at home, they should try to arrange a schedule taking turns so that one of them could turn their full attention to their kids if need be. If a working parent can be out of sight (i.e., in another room), it makes the situation easier for everyone.
If there is only one parent at home, that mom or dad should consider arranging a babysitter or sharing child care with a friend, with some reasonable safety provisions in place. The small risk of exposure to the virus is balanced by the risk of sustained invalidation in a developing child. Help parents set reasonable expectations for how productive they can be at home. If possible, they can manage their employer’s expectations, so that they do not find themselves in the impossible bind of choosing between a crying child and a crucial deadline. If they can work near the child (and be prepared for interruptions) when reading emails or writing, that may be enough availability for the child. And parents should not be discouraged when they have to repeatedly remind their children that they adore them, but also have to work while they are at home right now. Using age-appropriate screen time as a babysitter for a few hours each day is a perfectly acceptable part of a plan. Simply planning regular breaks when their children can have their attention will make the day easier for everyone at home.
What can I do about my 13-year-old who is lying around the house all day?
This is a time to pick your battles. If children can keep their regular sleep schedule, get their schoolwork done, and do some physical exercise every day, they are doing great. And if parents are continuously complaining that they are being lazy, it will probably cease to mean much to them. Instead, focus on clear, simple expectations, and parents should live by them, too. If parents can exercise with them, or try a new activity, that is a wonderful way to model self-care and trying new things. It is important to remember that the developmental task for a 13-year-old is to establish new avenues of independence that they will drive down further with each passing year. Give them some leeway to experiment and figure out their own way of handling this challenge, although it is bound to create some tension. Parents should always acknowledge how hard it is to stick with schoolwork without school, exercise without a team, practice music without a band, or do your work without an office!
What do we do about our 16-year-old who is staying up all night and sleeping until the late afternoon?
Adolescents naturally have their sleep cycle shift, so they are sleepy later and sleep longer. But staying up all night is usually about texting with friends or playing video games. The problem is that their sleep schedule can flip. They will not be able to participate in online class or enjoy exercise in the sun, and they rarely get enough sleep during the daytime, making them more irritable, anxious, inattentive, and tired. This will only make managing their schoolwork harder and increase the chances of conflict at home. So it is important to preserve rules around sleep. You might extend bedtime by an hour or so, but preserve rules and bedtime routines. Sleep is essential to health, well-being, and resilience, and all are critical during times of uncertainty and change.
We think our 17-year-old is using marijuana, and it might be a problem.
When parents think their children may have a problem with drugs, the children almost certainly do, as parents are typically the last to know about the extent of their use. Sheltering in place together may make their drug use much more apparent, and offer an opportunity for parents to respond. Talk with them about it. Let them know what you have noticed. See if they can tell you honestly about their drug use. Kids who are only experimenting socially are unlikely to be using drugs at home under quarantine. If you are truly calm and curious, they are more likely to be honest, and it could be a relief for them to discuss it with you. Find out what they think it helps, and what – if anything – they are worried about. Then share your concerns about marijuana use and the developing brain, and the risk of addiction. If they think it is “medical” use, remind them that anxiety or mood symptoms get better with therapy, whereas drugs (including marijuana) and alcohol actually worsen those problems. It is also a time to establish home rules, explain them, and enforce them. They will have your support while stopping and may learn that they are actually sleeping and feeling better after a few weeks without marijuana.
Parents should not hesitate to reach out to pediatric providers for guidance on local resources for assessment and treatment for substance abuse and addiction. These are medical problems, and they can become serious if untreated.
My 12-year-old perfectionist is very stressed about getting her work done well now that she is home schooling. How do I help her relax?
Some children, especially our anxious perfectionists, may respond to the switch to home school with great effort and organization. These kids usually are not the ones parents worry about. But they are very prone to expanding anxiety without the regular support and feedback of teachers. The school environment naturally encourages their taking chances and normalizes the setbacks and failures that are an essential part of learning something new. At home, parents are inclined to let these kids work independently. But they benefit from regular check-ins that are not focused on work completion or scores. Instead, ask about what they are doing that is hardest, and let them teach you about it. Model how you approach a new challenge, and how you regroup and try again when you don’t get it right. Finally, this is a good age to start discussing “reasonable expectations.” No one can “do their best” all the time; not parents, not professional athletes, not even machines can sustain long bursts of maximum speed without problems. Help them to start experimenting with different speeds and levels of effort, and see how it feels.
My 10-year-old is very anxious about catching coronavirus or one of us catching it. How do I help ease her anxiety when there is no certainty about how to prevent it?
Anxiety is a normal response to a situation with as much uncertainty as this one. But some are prone to more profound anxiety, and parents may find they are doing a lot of reassuring throughout the day. For especially anxious children (and adults), accommodating the anxiety by avoiding the stressful situation is a common response that provides temporary relief. But accommodation and avoidance actually fuel anxiety, and make it harder and harder to manage. It is important to talk about the “accommodations” we all are doing, how masks are recommended to protect others (not ourselves) and to slow down the spread of a new illness so our hospitals aren’t overwhelmed. It can seem counterintuitive, but rather than jumping to reassurance or dismissing their sense of risk, ask your children to play the full movie of what they are most worried about. What happens if they get sick? If you get sick? If they are worried about dying, go ahead and ask what they think happens then. You are demonstrating that you have confidence they can handle these feelings, and you are modeling curiosity – not avoidance – yourself. Correct any misunderstandings, check on facts together, acknowledge uncertainty. It also is very important for parents to assess whether their own anxiety level makes this task especially hard or may even be contributing to their children’s level of worry. Each of us is managing anxiety right now, and this moment presents an opportunity for all of us to learn about how we can face and bear it, learn to manage, and even master it.
We are all getting cabin fever at home and snapping at each other constantly. How do we keep the peace without just hiding in our rooms all day?
Cabin fever seems inevitable when a family is suddenly at home together all day every day with no end in sight. But if we establish some simple and realistic routines and preserve some structure without being rigid, it can go a long way to helping each member of a family to find their equilibrium in this new normal. Structure can be about preserving normal sleep and meal times. Ensuring everyone is getting adequate, restful sleep and is not hungry is probably the most powerful way to keep irritability and conflict low. It is also helpful to establish some new routines. These should be simple enough to be memorable and should be realistic. You might identify predictable blocks of time that are dedicated to school (or work), exercise, creative time, and family time. While much of the day may find each family member doing some independent activity, it helps when these “blocks” are the same for everybody. Try to consistently do one or two things together, like a walk after the family dinner or family game time. And also remember that everyone needs some alone time. Respect their need for this, and it will help you to explain when you need it. If someone wants to sit out the family Yahtzee tournament, don’t shame or punish them. Just invite them again the next night!
What are going to be the consequences of all this screen time?
The great majority of kids (and parents) will not suffer any adverse consequences from the increased amount of time spent in front of screens when these activities are varied and serve a useful purpose – including distraction, senseless fun, and social time. Beyond letter or email writing, screen and phone time are the only ways to stay socially connected while physically distant. But parents are the experts on their kids. Youth who are depressed and have in the past wanted to escape into long hours of video games or YouTube videos should not be allowed to do that now. Youth with attentional issues who have a hard time stopping video games will still have that difficulty. If they are getting adequate sleep and regular exercise, and are doing most of their school work and staying socially connected, screens are not dangerous. They are proving to be a wonderful tool to help us visit libraries and museums, take dance classes, learn new languages, follow the news, order groceries, or enjoy a movie together. If we stay connected to those we care about and to the world, then this time – although marked by profound suffering and loss – may prove to be a time when we were able to slow down and remember what truly matters in our lives.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
We are living through unprecedented challenges, faced with profound uncertainties about the public health, the economy, the safety of our workplaces, the risks of gathering with friends and family, and even about the rhythm of the school year. Parents always have sought guidance from their pediatric providers when they are uncertain about their children’s health, behavior, and development. We want to share some guidance with you about several of the most common questions we have been hearing in the past few months, in the hope that it may prove useful in your conversations with patients and families.
What happens when we are so busy at home that our 2-year-old is ignored for much of the day?
If they are fortunate enough to be able to work from home, but have lost their child care, many parents are suddenly facing the sustained challenge of parenting while working. Even older children will have a tough time remembering that home is now a workplace, and they can’t interrupt their parents during a Zoom meeting. But older children will understand. Younger children (preschoolers) simply will not be able to understand that their parents are in sight but not fully available to them. They are exquisitely sensitive to their parents’ attention. If they are consistently ignored, behavioral problems can emerge. If both parents are at home, they should try to arrange a schedule taking turns so that one of them could turn their full attention to their kids if need be. If a working parent can be out of sight (i.e., in another room), it makes the situation easier for everyone.
If there is only one parent at home, that mom or dad should consider arranging a babysitter or sharing child care with a friend, with some reasonable safety provisions in place. The small risk of exposure to the virus is balanced by the risk of sustained invalidation in a developing child. Help parents set reasonable expectations for how productive they can be at home. If possible, they can manage their employer’s expectations, so that they do not find themselves in the impossible bind of choosing between a crying child and a crucial deadline. If they can work near the child (and be prepared for interruptions) when reading emails or writing, that may be enough availability for the child. And parents should not be discouraged when they have to repeatedly remind their children that they adore them, but also have to work while they are at home right now. Using age-appropriate screen time as a babysitter for a few hours each day is a perfectly acceptable part of a plan. Simply planning regular breaks when their children can have their attention will make the day easier for everyone at home.
What can I do about my 13-year-old who is lying around the house all day?
This is a time to pick your battles. If children can keep their regular sleep schedule, get their schoolwork done, and do some physical exercise every day, they are doing great. And if parents are continuously complaining that they are being lazy, it will probably cease to mean much to them. Instead, focus on clear, simple expectations, and parents should live by them, too. If parents can exercise with them, or try a new activity, that is a wonderful way to model self-care and trying new things. It is important to remember that the developmental task for a 13-year-old is to establish new avenues of independence that they will drive down further with each passing year. Give them some leeway to experiment and figure out their own way of handling this challenge, although it is bound to create some tension. Parents should always acknowledge how hard it is to stick with schoolwork without school, exercise without a team, practice music without a band, or do your work without an office!
What do we do about our 16-year-old who is staying up all night and sleeping until the late afternoon?
Adolescents naturally have their sleep cycle shift, so they are sleepy later and sleep longer. But staying up all night is usually about texting with friends or playing video games. The problem is that their sleep schedule can flip. They will not be able to participate in online class or enjoy exercise in the sun, and they rarely get enough sleep during the daytime, making them more irritable, anxious, inattentive, and tired. This will only make managing their schoolwork harder and increase the chances of conflict at home. So it is important to preserve rules around sleep. You might extend bedtime by an hour or so, but preserve rules and bedtime routines. Sleep is essential to health, well-being, and resilience, and all are critical during times of uncertainty and change.
We think our 17-year-old is using marijuana, and it might be a problem.
When parents think their children may have a problem with drugs, the children almost certainly do, as parents are typically the last to know about the extent of their use. Sheltering in place together may make their drug use much more apparent, and offer an opportunity for parents to respond. Talk with them about it. Let them know what you have noticed. See if they can tell you honestly about their drug use. Kids who are only experimenting socially are unlikely to be using drugs at home under quarantine. If you are truly calm and curious, they are more likely to be honest, and it could be a relief for them to discuss it with you. Find out what they think it helps, and what – if anything – they are worried about. Then share your concerns about marijuana use and the developing brain, and the risk of addiction. If they think it is “medical” use, remind them that anxiety or mood symptoms get better with therapy, whereas drugs (including marijuana) and alcohol actually worsen those problems. It is also a time to establish home rules, explain them, and enforce them. They will have your support while stopping and may learn that they are actually sleeping and feeling better after a few weeks without marijuana.
Parents should not hesitate to reach out to pediatric providers for guidance on local resources for assessment and treatment for substance abuse and addiction. These are medical problems, and they can become serious if untreated.
My 12-year-old perfectionist is very stressed about getting her work done well now that she is home schooling. How do I help her relax?
Some children, especially our anxious perfectionists, may respond to the switch to home school with great effort and organization. These kids usually are not the ones parents worry about. But they are very prone to expanding anxiety without the regular support and feedback of teachers. The school environment naturally encourages their taking chances and normalizes the setbacks and failures that are an essential part of learning something new. At home, parents are inclined to let these kids work independently. But they benefit from regular check-ins that are not focused on work completion or scores. Instead, ask about what they are doing that is hardest, and let them teach you about it. Model how you approach a new challenge, and how you regroup and try again when you don’t get it right. Finally, this is a good age to start discussing “reasonable expectations.” No one can “do their best” all the time; not parents, not professional athletes, not even machines can sustain long bursts of maximum speed without problems. Help them to start experimenting with different speeds and levels of effort, and see how it feels.
My 10-year-old is very anxious about catching coronavirus or one of us catching it. How do I help ease her anxiety when there is no certainty about how to prevent it?
Anxiety is a normal response to a situation with as much uncertainty as this one. But some are prone to more profound anxiety, and parents may find they are doing a lot of reassuring throughout the day. For especially anxious children (and adults), accommodating the anxiety by avoiding the stressful situation is a common response that provides temporary relief. But accommodation and avoidance actually fuel anxiety, and make it harder and harder to manage. It is important to talk about the “accommodations” we all are doing, how masks are recommended to protect others (not ourselves) and to slow down the spread of a new illness so our hospitals aren’t overwhelmed. It can seem counterintuitive, but rather than jumping to reassurance or dismissing their sense of risk, ask your children to play the full movie of what they are most worried about. What happens if they get sick? If you get sick? If they are worried about dying, go ahead and ask what they think happens then. You are demonstrating that you have confidence they can handle these feelings, and you are modeling curiosity – not avoidance – yourself. Correct any misunderstandings, check on facts together, acknowledge uncertainty. It also is very important for parents to assess whether their own anxiety level makes this task especially hard or may even be contributing to their children’s level of worry. Each of us is managing anxiety right now, and this moment presents an opportunity for all of us to learn about how we can face and bear it, learn to manage, and even master it.
We are all getting cabin fever at home and snapping at each other constantly. How do we keep the peace without just hiding in our rooms all day?
Cabin fever seems inevitable when a family is suddenly at home together all day every day with no end in sight. But if we establish some simple and realistic routines and preserve some structure without being rigid, it can go a long way to helping each member of a family to find their equilibrium in this new normal. Structure can be about preserving normal sleep and meal times. Ensuring everyone is getting adequate, restful sleep and is not hungry is probably the most powerful way to keep irritability and conflict low. It is also helpful to establish some new routines. These should be simple enough to be memorable and should be realistic. You might identify predictable blocks of time that are dedicated to school (or work), exercise, creative time, and family time. While much of the day may find each family member doing some independent activity, it helps when these “blocks” are the same for everybody. Try to consistently do one or two things together, like a walk after the family dinner or family game time. And also remember that everyone needs some alone time. Respect their need for this, and it will help you to explain when you need it. If someone wants to sit out the family Yahtzee tournament, don’t shame or punish them. Just invite them again the next night!
What are going to be the consequences of all this screen time?
The great majority of kids (and parents) will not suffer any adverse consequences from the increased amount of time spent in front of screens when these activities are varied and serve a useful purpose – including distraction, senseless fun, and social time. Beyond letter or email writing, screen and phone time are the only ways to stay socially connected while physically distant. But parents are the experts on their kids. Youth who are depressed and have in the past wanted to escape into long hours of video games or YouTube videos should not be allowed to do that now. Youth with attentional issues who have a hard time stopping video games will still have that difficulty. If they are getting adequate sleep and regular exercise, and are doing most of their school work and staying socially connected, screens are not dangerous. They are proving to be a wonderful tool to help us visit libraries and museums, take dance classes, learn new languages, follow the news, order groceries, or enjoy a movie together. If we stay connected to those we care about and to the world, then this time – although marked by profound suffering and loss – may prove to be a time when we were able to slow down and remember what truly matters in our lives.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
We are living through unprecedented challenges, faced with profound uncertainties about the public health, the economy, the safety of our workplaces, the risks of gathering with friends and family, and even about the rhythm of the school year. Parents always have sought guidance from their pediatric providers when they are uncertain about their children’s health, behavior, and development. We want to share some guidance with you about several of the most common questions we have been hearing in the past few months, in the hope that it may prove useful in your conversations with patients and families.
What happens when we are so busy at home that our 2-year-old is ignored for much of the day?
If they are fortunate enough to be able to work from home, but have lost their child care, many parents are suddenly facing the sustained challenge of parenting while working. Even older children will have a tough time remembering that home is now a workplace, and they can’t interrupt their parents during a Zoom meeting. But older children will understand. Younger children (preschoolers) simply will not be able to understand that their parents are in sight but not fully available to them. They are exquisitely sensitive to their parents’ attention. If they are consistently ignored, behavioral problems can emerge. If both parents are at home, they should try to arrange a schedule taking turns so that one of them could turn their full attention to their kids if need be. If a working parent can be out of sight (i.e., in another room), it makes the situation easier for everyone.
If there is only one parent at home, that mom or dad should consider arranging a babysitter or sharing child care with a friend, with some reasonable safety provisions in place. The small risk of exposure to the virus is balanced by the risk of sustained invalidation in a developing child. Help parents set reasonable expectations for how productive they can be at home. If possible, they can manage their employer’s expectations, so that they do not find themselves in the impossible bind of choosing between a crying child and a crucial deadline. If they can work near the child (and be prepared for interruptions) when reading emails or writing, that may be enough availability for the child. And parents should not be discouraged when they have to repeatedly remind their children that they adore them, but also have to work while they are at home right now. Using age-appropriate screen time as a babysitter for a few hours each day is a perfectly acceptable part of a plan. Simply planning regular breaks when their children can have their attention will make the day easier for everyone at home.
What can I do about my 13-year-old who is lying around the house all day?
This is a time to pick your battles. If children can keep their regular sleep schedule, get their schoolwork done, and do some physical exercise every day, they are doing great. And if parents are continuously complaining that they are being lazy, it will probably cease to mean much to them. Instead, focus on clear, simple expectations, and parents should live by them, too. If parents can exercise with them, or try a new activity, that is a wonderful way to model self-care and trying new things. It is important to remember that the developmental task for a 13-year-old is to establish new avenues of independence that they will drive down further with each passing year. Give them some leeway to experiment and figure out their own way of handling this challenge, although it is bound to create some tension. Parents should always acknowledge how hard it is to stick with schoolwork without school, exercise without a team, practice music without a band, or do your work without an office!
What do we do about our 16-year-old who is staying up all night and sleeping until the late afternoon?
Adolescents naturally have their sleep cycle shift, so they are sleepy later and sleep longer. But staying up all night is usually about texting with friends or playing video games. The problem is that their sleep schedule can flip. They will not be able to participate in online class or enjoy exercise in the sun, and they rarely get enough sleep during the daytime, making them more irritable, anxious, inattentive, and tired. This will only make managing their schoolwork harder and increase the chances of conflict at home. So it is important to preserve rules around sleep. You might extend bedtime by an hour or so, but preserve rules and bedtime routines. Sleep is essential to health, well-being, and resilience, and all are critical during times of uncertainty and change.
We think our 17-year-old is using marijuana, and it might be a problem.
When parents think their children may have a problem with drugs, the children almost certainly do, as parents are typically the last to know about the extent of their use. Sheltering in place together may make their drug use much more apparent, and offer an opportunity for parents to respond. Talk with them about it. Let them know what you have noticed. See if they can tell you honestly about their drug use. Kids who are only experimenting socially are unlikely to be using drugs at home under quarantine. If you are truly calm and curious, they are more likely to be honest, and it could be a relief for them to discuss it with you. Find out what they think it helps, and what – if anything – they are worried about. Then share your concerns about marijuana use and the developing brain, and the risk of addiction. If they think it is “medical” use, remind them that anxiety or mood symptoms get better with therapy, whereas drugs (including marijuana) and alcohol actually worsen those problems. It is also a time to establish home rules, explain them, and enforce them. They will have your support while stopping and may learn that they are actually sleeping and feeling better after a few weeks without marijuana.
Parents should not hesitate to reach out to pediatric providers for guidance on local resources for assessment and treatment for substance abuse and addiction. These are medical problems, and they can become serious if untreated.
My 12-year-old perfectionist is very stressed about getting her work done well now that she is home schooling. How do I help her relax?
Some children, especially our anxious perfectionists, may respond to the switch to home school with great effort and organization. These kids usually are not the ones parents worry about. But they are very prone to expanding anxiety without the regular support and feedback of teachers. The school environment naturally encourages their taking chances and normalizes the setbacks and failures that are an essential part of learning something new. At home, parents are inclined to let these kids work independently. But they benefit from regular check-ins that are not focused on work completion or scores. Instead, ask about what they are doing that is hardest, and let them teach you about it. Model how you approach a new challenge, and how you regroup and try again when you don’t get it right. Finally, this is a good age to start discussing “reasonable expectations.” No one can “do their best” all the time; not parents, not professional athletes, not even machines can sustain long bursts of maximum speed without problems. Help them to start experimenting with different speeds and levels of effort, and see how it feels.
My 10-year-old is very anxious about catching coronavirus or one of us catching it. How do I help ease her anxiety when there is no certainty about how to prevent it?
Anxiety is a normal response to a situation with as much uncertainty as this one. But some are prone to more profound anxiety, and parents may find they are doing a lot of reassuring throughout the day. For especially anxious children (and adults), accommodating the anxiety by avoiding the stressful situation is a common response that provides temporary relief. But accommodation and avoidance actually fuel anxiety, and make it harder and harder to manage. It is important to talk about the “accommodations” we all are doing, how masks are recommended to protect others (not ourselves) and to slow down the spread of a new illness so our hospitals aren’t overwhelmed. It can seem counterintuitive, but rather than jumping to reassurance or dismissing their sense of risk, ask your children to play the full movie of what they are most worried about. What happens if they get sick? If you get sick? If they are worried about dying, go ahead and ask what they think happens then. You are demonstrating that you have confidence they can handle these feelings, and you are modeling curiosity – not avoidance – yourself. Correct any misunderstandings, check on facts together, acknowledge uncertainty. It also is very important for parents to assess whether their own anxiety level makes this task especially hard or may even be contributing to their children’s level of worry. Each of us is managing anxiety right now, and this moment presents an opportunity for all of us to learn about how we can face and bear it, learn to manage, and even master it.
We are all getting cabin fever at home and snapping at each other constantly. How do we keep the peace without just hiding in our rooms all day?
Cabin fever seems inevitable when a family is suddenly at home together all day every day with no end in sight. But if we establish some simple and realistic routines and preserve some structure without being rigid, it can go a long way to helping each member of a family to find their equilibrium in this new normal. Structure can be about preserving normal sleep and meal times. Ensuring everyone is getting adequate, restful sleep and is not hungry is probably the most powerful way to keep irritability and conflict low. It is also helpful to establish some new routines. These should be simple enough to be memorable and should be realistic. You might identify predictable blocks of time that are dedicated to school (or work), exercise, creative time, and family time. While much of the day may find each family member doing some independent activity, it helps when these “blocks” are the same for everybody. Try to consistently do one or two things together, like a walk after the family dinner or family game time. And also remember that everyone needs some alone time. Respect their need for this, and it will help you to explain when you need it. If someone wants to sit out the family Yahtzee tournament, don’t shame or punish them. Just invite them again the next night!
What are going to be the consequences of all this screen time?
The great majority of kids (and parents) will not suffer any adverse consequences from the increased amount of time spent in front of screens when these activities are varied and serve a useful purpose – including distraction, senseless fun, and social time. Beyond letter or email writing, screen and phone time are the only ways to stay socially connected while physically distant. But parents are the experts on their kids. Youth who are depressed and have in the past wanted to escape into long hours of video games or YouTube videos should not be allowed to do that now. Youth with attentional issues who have a hard time stopping video games will still have that difficulty. If they are getting adequate sleep and regular exercise, and are doing most of their school work and staying socially connected, screens are not dangerous. They are proving to be a wonderful tool to help us visit libraries and museums, take dance classes, learn new languages, follow the news, order groceries, or enjoy a movie together. If we stay connected to those we care about and to the world, then this time – although marked by profound suffering and loss – may prove to be a time when we were able to slow down and remember what truly matters in our lives.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
COVID-19 will likely change docs’ incentive targets, bonuses: Survey
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., told Medscape Medical News.
“This amounts to salary reductions of 10% to 30%,” he said.
The COVID-19 crisis dramatically reversed the consistent upward trajectory of physician compensation, according to a Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) survey, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
The survey, conducted April 7-8, found that practices have reported an average 55% drop in income. The report also found an average decrease in patient volume of 60%.
Before pandemic, salaries were rising
The pandemic interrupted a steady gain in compensation for this year compared to last, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020.
The report reflects data gathered from October 4, 2019, to February 10, 2020, and includes online survey responses from 17,000 physicians in more than 30 specialties.
Before the pandemic, primary care physician (PCP) pay was up 2.5%, to $243,000, from the previous year’s average of $237,000. Specialists saw a 1.5% increase, from $341,000 in 2019 to $346,000 this year.
Reported compensation for employed physicians included salary, bonus, and profit-sharing contributions. For those self-employed, compensation includes earnings after taxes and deductible business expenses before income tax.
This report reflects only full-time salaries. But most physicians work more than full time. The report notes that physicians overall spent 37.8 hours a week seeing patients. Add to that the 15.6 average hours spent on paperwork, and doctors are averaging 53.4 hours a week.
Administrative demands varied widely by specialty. Physicians in critical care, for example, spent the most hours on paperwork (19.1 per week), and ophthalmologists spent the least on those tasks, at 9.8.
Orthopedists top earners again
The top four specialties were the same this year as they were last year and were ranked in the same order: orthopedists made the most, at $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons, at $479,000, otolaryngologists, at $455,000, and cardiologists, at $438,000.
Pediatricians and public health/preventive medicine physicians made the least, at $232,000, followed by family physicians ($234,000) and diabetes/endocrinology specialists ($236,000).
Despite the low ranking, public health/preventive medicine providers had the biggest compensation increase of all physicians, up 11% from last year. Two specialties saw a decrease: otolaryngology salaries dropped 1%, and dermatology pay dropped 2%. Pay in gastroenterology and diabetes/endocrinology was virtually unchanged from last year.
Kentucky has highest pay
Ranked by state, physicians in Kentucky made the most on average ($346,000). Utah, Ohio, and North Carolina were new to the top 10 in physician pay this year, pushing out Connecticut, Arkansas, and Nevada.
More than half of all physicians receive incentive bonuses (58% of PCPs and 55% of specialists).
The average incentive bonus is 13% of salary, but that varies by specialty. Orthopedists got an average $96,000 bonus, whereas family physicians got $24,000.
According to the report, “Among physicians who have an incentive bonus, about a third of both PCPs and specialists say the prospect of an incentive bonus has encouraged them to work longer hours.”
Gender gap similar to previous year
Consistent with Medscape compensation reports over the past decade, this year’s report shows a large gender gap in pay. Among PCPs, men made 25% more than women ($264,000 vs. $212,000); among specialists, they made 31% more than their female colleagues ($375,000 vs. $286,000).
Some specialties report positive changes from growing awareness of the gap.
“Many organizations have been carefully analyzing their culture, transparency, and pay practices to make sure they aren’t unintentionally discriminating against any group of employees,” Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, pediatrician and CEO of MGMA, told Medscape Medical News.
She added that the growing physician shortage has given all physicians more leverage in salary demands and that increased recognition of the gender gap is giving women more confidence and more evidence to use in negotiations.
Three specialties have seen large increases in the past 5 years in the percentage of women physicians. Obstetrics/gynecology and pediatrics both saw increases from 50% in 2015 to 58% in 2020. Additionally, women now account for 54% of rheumatologists, up from 29% in 2015.
Would you choose your specialty again?
Of responding physicians who were asked if they would choose their specialty again, internists were least likely to say yes (66%), followed by nephrologists (69%) and family physicians (70%).
Orthopedists were most likely to say they would choose the same specialty (97%), followed by oncologists (96%) and ophthalmologists and dermatologists (both at 95%).
Most physicians overall (77%) said they would choose medicine again.
Despite aggravations and pressures, in this survey and in previous years, physicians have indicated that the top rewards are “gratitude/relationships with patients,” “being very good at what I do/finding answers, diagnoses,” and “knowing that I make the world a better place.” From 24% to 27% ranked those rewards most important.
“Making good money at a job I like” came in fourth, at 12%.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consider COVID-19–associated multisystem hyperinflammatory syndrome
A 21-year-old young adult presented to the ED with a 1-week history of high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. His mother was SARS-CoV-2 positive by polymerase chain reaction approximately 3 weeks prior; his PCR was negative for SARS-CoV-2.
Following admission, he became hypotensive and tachycardic with evidence of myocarditis. His chest x-ray was normal and his O2 saturation was 100% on room air. His clinical presentation was initially suggestive of toxic shock syndrome without a rash, but despite aggressive fluid resuscitation and broad-spectrum antibiotics, he continued to clinically deteriorate with persistent high fever and increasing cardiac stress. Echocardiography revealed biventricular dysfunction. His laboratory abnormalities included rising inflammatory markers and troponin I and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). A repeat PCR for SARS-CoV-2 was negative on day 2 of illness. He was diagnosed as likely having macrophage-activation syndrome (MAS) despite the atypical features (myocarditis), and he received Anakinra with no apparent response. He also was given intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for his myocarditis and subsequently high-dose steroids. He became afebrile, his blood pressure stabilized, his inflammatory markers declined, and over several days he returned to normal. His COVID-19 antibody test IgG was positive on day 4 of illness.
This case challenged us for several reasons. First, the PCR from his nasopharynx was negative on two occasions, which raises the issue of how sensitive and accurate these PCR tests are for SARS-CoV-2 or are patients with COVID-19–associated hyperinflammatory syndrome still PCR positive? Second, although we have seen many adult cases with a cytokine storm picture similar to this patient, nearly all of the prior cases had chest x-ray abnormalities and hypoxia. Third, the severity of the myocardial dysfunction and rising troponin and BNP also was unusual in our experience with COVID-19 infection. Lastly, the use of antibody detection to SARS-CoV-2 enabled us to confirm recent COIVD-19 disease and see his illness as part of the likely spectrum of clinical syndromes seen with this virus.
The Lancet reported eight children, aged 4-14 years, with a hyperinflammatory shock-like syndrome in early May.1 The cases had features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, KD shock syndrome, and toxic shock syndrome. Each case had high fever for multiple days; diarrhea and abdominal pain was present in even children; elevated ferritin, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, increased troponins, and ventricular dysfunction also was present in seven. Most patients had no pulmonary involvement, and most tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 despite four of the eight having direct contact with a COVID-positive family member. All received IVIg and antibiotics; six received aspirin. Seven of the eight made a full recovery; one child died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
Also in early May, the New York Times described a “mysterious” hyperinflammatory syndrome in children thought to be linked to COVID-19. A total of 76 suspected cases in children had been reported in New York state, three of whom died. The syndrome has been given the name pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome. The syndrome can resemble KD shock syndrome with rash; fever; conjunctivitis; hypotension; and redness in the lips, tongue and mucous membranes . It also can resemble toxic shock syndrome with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, the degree of cardiac inflammation and dysfunction is substantial in many cases and usually beyond that seen in KD or toxic shock.
The syndrome is not limited to the United States. The Royal College of Pediatrics and Child Health has created a case definition:2
- A child presenting with persistent fever, inflammation (elevated C-reactive protein, neutrophilia, and lymphopenia) and evidence of single or multiorgan dysfunction (shock, cardiac, respiratory, renal, gastrointestinal, or neurologic) with additional features.
- Exclusion of any other microbial causes such as bacterial sepsis or staphylococcal or streptococcal shock syndromes, infections known to be associated with myocarditis (such as enterovirus).
- SARS-CoV-2 testing may or may not be positive.
As with our young adult, treatment is supportive, nonspecific, and aimed at quieting the inflammatory response. The current thinking is the syndrome is seen as antibody to SARS-CoV-2 appears and frequently the nasopharyngeal PCR is negative. It is hypothesized that the syndrome occurs in genetically predisposed hosts and potentially is a late-onset inflammatory process or potentially an antibody-triggered inflammatory process. The negative PCR from nasopharyngeal specimens reflects that the onset is later in the course of disease; whether fecal samples would be COVID positive is unknown. As with our case, antibody testing for IgG against SARS-CoV-2 is appropriate to confirm COVID-19 disease and may be positive as early as day 7.
The approach needs to be team oriented and include cardiology, rheumatology, infectious diseases, and intensive care specialists working collaboratively. Such cases should be considered COVID positive despite negative PCR tests, and full personal protective equipment should be used as we do not as yet know if live virus could be found in stool. We initiated treatment with Anakinra (an interleukin-1 type-1 receptor inhibitor) as part of our treatment protocol for MAS; we did not appreciate a response. He then received IVIg and high-dose steroids, and he recovered over several days with improved cardiac function and stable blood pressure.
What is the pathogenesis? Is SARS-CoV-2 causative or just an associated finding? Who are the at-risk children, adolescents, and adults? Is there a genetic predisposition? What therapies work best? The eight cases described in London all received IVIg, as did our case, and all but one improved and survived. In adults we have seen substantial inflammation with elevated C-reactive protein (often as high as 300), ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides, fibrinogen, and d-dimers, but nearly all have extensive pulmonary disease, hypoxia, and are SARS-CoV-2 positive by PCR. Influenza is also associated with a cytokine storm syndrome in adolescents and young adults.3 The mechanisms influenza virus uses to initiate a cytokine storm and strategies for immunomodulatory treatment may provide insights into COVID-19–associated multisystem hyperinflammatory syndrome.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Dr. Camelo is a senior fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
2. Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health Guidance: Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19.
3. Liu Q et al.Cell Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;13(1):3-10.
A 21-year-old young adult presented to the ED with a 1-week history of high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. His mother was SARS-CoV-2 positive by polymerase chain reaction approximately 3 weeks prior; his PCR was negative for SARS-CoV-2.
Following admission, he became hypotensive and tachycardic with evidence of myocarditis. His chest x-ray was normal and his O2 saturation was 100% on room air. His clinical presentation was initially suggestive of toxic shock syndrome without a rash, but despite aggressive fluid resuscitation and broad-spectrum antibiotics, he continued to clinically deteriorate with persistent high fever and increasing cardiac stress. Echocardiography revealed biventricular dysfunction. His laboratory abnormalities included rising inflammatory markers and troponin I and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). A repeat PCR for SARS-CoV-2 was negative on day 2 of illness. He was diagnosed as likely having macrophage-activation syndrome (MAS) despite the atypical features (myocarditis), and he received Anakinra with no apparent response. He also was given intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for his myocarditis and subsequently high-dose steroids. He became afebrile, his blood pressure stabilized, his inflammatory markers declined, and over several days he returned to normal. His COVID-19 antibody test IgG was positive on day 4 of illness.
This case challenged us for several reasons. First, the PCR from his nasopharynx was negative on two occasions, which raises the issue of how sensitive and accurate these PCR tests are for SARS-CoV-2 or are patients with COVID-19–associated hyperinflammatory syndrome still PCR positive? Second, although we have seen many adult cases with a cytokine storm picture similar to this patient, nearly all of the prior cases had chest x-ray abnormalities and hypoxia. Third, the severity of the myocardial dysfunction and rising troponin and BNP also was unusual in our experience with COVID-19 infection. Lastly, the use of antibody detection to SARS-CoV-2 enabled us to confirm recent COIVD-19 disease and see his illness as part of the likely spectrum of clinical syndromes seen with this virus.
The Lancet reported eight children, aged 4-14 years, with a hyperinflammatory shock-like syndrome in early May.1 The cases had features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, KD shock syndrome, and toxic shock syndrome. Each case had high fever for multiple days; diarrhea and abdominal pain was present in even children; elevated ferritin, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, increased troponins, and ventricular dysfunction also was present in seven. Most patients had no pulmonary involvement, and most tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 despite four of the eight having direct contact with a COVID-positive family member. All received IVIg and antibiotics; six received aspirin. Seven of the eight made a full recovery; one child died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
Also in early May, the New York Times described a “mysterious” hyperinflammatory syndrome in children thought to be linked to COVID-19. A total of 76 suspected cases in children had been reported in New York state, three of whom died. The syndrome has been given the name pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome. The syndrome can resemble KD shock syndrome with rash; fever; conjunctivitis; hypotension; and redness in the lips, tongue and mucous membranes . It also can resemble toxic shock syndrome with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, the degree of cardiac inflammation and dysfunction is substantial in many cases and usually beyond that seen in KD or toxic shock.
The syndrome is not limited to the United States. The Royal College of Pediatrics and Child Health has created a case definition:2
- A child presenting with persistent fever, inflammation (elevated C-reactive protein, neutrophilia, and lymphopenia) and evidence of single or multiorgan dysfunction (shock, cardiac, respiratory, renal, gastrointestinal, or neurologic) with additional features.
- Exclusion of any other microbial causes such as bacterial sepsis or staphylococcal or streptococcal shock syndromes, infections known to be associated with myocarditis (such as enterovirus).
- SARS-CoV-2 testing may or may not be positive.
As with our young adult, treatment is supportive, nonspecific, and aimed at quieting the inflammatory response. The current thinking is the syndrome is seen as antibody to SARS-CoV-2 appears and frequently the nasopharyngeal PCR is negative. It is hypothesized that the syndrome occurs in genetically predisposed hosts and potentially is a late-onset inflammatory process or potentially an antibody-triggered inflammatory process. The negative PCR from nasopharyngeal specimens reflects that the onset is later in the course of disease; whether fecal samples would be COVID positive is unknown. As with our case, antibody testing for IgG against SARS-CoV-2 is appropriate to confirm COVID-19 disease and may be positive as early as day 7.
The approach needs to be team oriented and include cardiology, rheumatology, infectious diseases, and intensive care specialists working collaboratively. Such cases should be considered COVID positive despite negative PCR tests, and full personal protective equipment should be used as we do not as yet know if live virus could be found in stool. We initiated treatment with Anakinra (an interleukin-1 type-1 receptor inhibitor) as part of our treatment protocol for MAS; we did not appreciate a response. He then received IVIg and high-dose steroids, and he recovered over several days with improved cardiac function and stable blood pressure.
What is the pathogenesis? Is SARS-CoV-2 causative or just an associated finding? Who are the at-risk children, adolescents, and adults? Is there a genetic predisposition? What therapies work best? The eight cases described in London all received IVIg, as did our case, and all but one improved and survived. In adults we have seen substantial inflammation with elevated C-reactive protein (often as high as 300), ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides, fibrinogen, and d-dimers, but nearly all have extensive pulmonary disease, hypoxia, and are SARS-CoV-2 positive by PCR. Influenza is also associated with a cytokine storm syndrome in adolescents and young adults.3 The mechanisms influenza virus uses to initiate a cytokine storm and strategies for immunomodulatory treatment may provide insights into COVID-19–associated multisystem hyperinflammatory syndrome.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Dr. Camelo is a senior fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
2. Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health Guidance: Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19.
3. Liu Q et al.Cell Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;13(1):3-10.
A 21-year-old young adult presented to the ED with a 1-week history of high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. His mother was SARS-CoV-2 positive by polymerase chain reaction approximately 3 weeks prior; his PCR was negative for SARS-CoV-2.
Following admission, he became hypotensive and tachycardic with evidence of myocarditis. His chest x-ray was normal and his O2 saturation was 100% on room air. His clinical presentation was initially suggestive of toxic shock syndrome without a rash, but despite aggressive fluid resuscitation and broad-spectrum antibiotics, he continued to clinically deteriorate with persistent high fever and increasing cardiac stress. Echocardiography revealed biventricular dysfunction. His laboratory abnormalities included rising inflammatory markers and troponin I and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). A repeat PCR for SARS-CoV-2 was negative on day 2 of illness. He was diagnosed as likely having macrophage-activation syndrome (MAS) despite the atypical features (myocarditis), and he received Anakinra with no apparent response. He also was given intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for his myocarditis and subsequently high-dose steroids. He became afebrile, his blood pressure stabilized, his inflammatory markers declined, and over several days he returned to normal. His COVID-19 antibody test IgG was positive on day 4 of illness.
This case challenged us for several reasons. First, the PCR from his nasopharynx was negative on two occasions, which raises the issue of how sensitive and accurate these PCR tests are for SARS-CoV-2 or are patients with COVID-19–associated hyperinflammatory syndrome still PCR positive? Second, although we have seen many adult cases with a cytokine storm picture similar to this patient, nearly all of the prior cases had chest x-ray abnormalities and hypoxia. Third, the severity of the myocardial dysfunction and rising troponin and BNP also was unusual in our experience with COVID-19 infection. Lastly, the use of antibody detection to SARS-CoV-2 enabled us to confirm recent COIVD-19 disease and see his illness as part of the likely spectrum of clinical syndromes seen with this virus.
The Lancet reported eight children, aged 4-14 years, with a hyperinflammatory shock-like syndrome in early May.1 The cases had features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, KD shock syndrome, and toxic shock syndrome. Each case had high fever for multiple days; diarrhea and abdominal pain was present in even children; elevated ferritin, C-reactive protein, d-dimer, increased troponins, and ventricular dysfunction also was present in seven. Most patients had no pulmonary involvement, and most tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 despite four of the eight having direct contact with a COVID-positive family member. All received IVIg and antibiotics; six received aspirin. Seven of the eight made a full recovery; one child died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
Also in early May, the New York Times described a “mysterious” hyperinflammatory syndrome in children thought to be linked to COVID-19. A total of 76 suspected cases in children had been reported in New York state, three of whom died. The syndrome has been given the name pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome. The syndrome can resemble KD shock syndrome with rash; fever; conjunctivitis; hypotension; and redness in the lips, tongue and mucous membranes . It also can resemble toxic shock syndrome with abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, the degree of cardiac inflammation and dysfunction is substantial in many cases and usually beyond that seen in KD or toxic shock.
The syndrome is not limited to the United States. The Royal College of Pediatrics and Child Health has created a case definition:2
- A child presenting with persistent fever, inflammation (elevated C-reactive protein, neutrophilia, and lymphopenia) and evidence of single or multiorgan dysfunction (shock, cardiac, respiratory, renal, gastrointestinal, or neurologic) with additional features.
- Exclusion of any other microbial causes such as bacterial sepsis or staphylococcal or streptococcal shock syndromes, infections known to be associated with myocarditis (such as enterovirus).
- SARS-CoV-2 testing may or may not be positive.
As with our young adult, treatment is supportive, nonspecific, and aimed at quieting the inflammatory response. The current thinking is the syndrome is seen as antibody to SARS-CoV-2 appears and frequently the nasopharyngeal PCR is negative. It is hypothesized that the syndrome occurs in genetically predisposed hosts and potentially is a late-onset inflammatory process or potentially an antibody-triggered inflammatory process. The negative PCR from nasopharyngeal specimens reflects that the onset is later in the course of disease; whether fecal samples would be COVID positive is unknown. As with our case, antibody testing for IgG against SARS-CoV-2 is appropriate to confirm COVID-19 disease and may be positive as early as day 7.
The approach needs to be team oriented and include cardiology, rheumatology, infectious diseases, and intensive care specialists working collaboratively. Such cases should be considered COVID positive despite negative PCR tests, and full personal protective equipment should be used as we do not as yet know if live virus could be found in stool. We initiated treatment with Anakinra (an interleukin-1 type-1 receptor inhibitor) as part of our treatment protocol for MAS; we did not appreciate a response. He then received IVIg and high-dose steroids, and he recovered over several days with improved cardiac function and stable blood pressure.
What is the pathogenesis? Is SARS-CoV-2 causative or just an associated finding? Who are the at-risk children, adolescents, and adults? Is there a genetic predisposition? What therapies work best? The eight cases described in London all received IVIg, as did our case, and all but one improved and survived. In adults we have seen substantial inflammation with elevated C-reactive protein (often as high as 300), ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase, triglycerides, fibrinogen, and d-dimers, but nearly all have extensive pulmonary disease, hypoxia, and are SARS-CoV-2 positive by PCR. Influenza is also associated with a cytokine storm syndrome in adolescents and young adults.3 The mechanisms influenza virus uses to initiate a cytokine storm and strategies for immunomodulatory treatment may provide insights into COVID-19–associated multisystem hyperinflammatory syndrome.
Dr. Pelton is professor of pediatrics and epidemiology at Boston University and public health and senior attending physician in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. Dr. Camelo is a senior fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at Boston Medical Center. They have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
2. Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health Guidance: Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19.
3. Liu Q et al.Cell Mol Immunol. 2016 Jan;13(1):3-10.
COVID-19 fears tied to dangerous drop in child vaccinations
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The social distancing and sheltering in place mandated because of the COVID-19 pandemic are keeping parents and kids out of their doctors’ offices, and that has prompted a steep decline in recommended routine vaccinations for U.S. children, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers.
Pediatric vaccinations dropped sharply after the national emergency was declared on March 13, suggesting that some children may be at increased risk for other serious infectious diseases, such as measles.
The researchers compared weekly orders for federally funded vaccines from Jan. 6 to April 19, 2020, with those during the same period in 2019.
They noted that, by the end of the study period, there was a cumulative COVID-19–related decline of 2.5 million doses in orders for routine noninfluenza pediatric childhood vaccines recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, as well as a cumulative decline in orders of 250,000 doses of measles vaccines.
Although the overall decrease in vaccinations during the study period was larger, according to CDC spokesperson Richard Quartarone, the above figures represent declines clearly associated with the pandemic.
The weekly number of measles vaccines ordered for children aged 24 months or older fell dramatically to about 500 during the week beginning March 16, 2020, and fell further to approximately 250 during the week beginning March 23. It stayed at that level until the week beginning April 13. By comparison, more than 2,500 were ordered during the week starting March 2, before the emergency was declared.
The decline was notably less for children younger than 2 years. For those children, orders dropped to about 750 during the week starting March 23 and climbed slightly for 3 weeks. By comparison, during the week of March 2, about 2,000 vaccines were ordered.
The findings, which were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, stem from an analysis of ordering data from the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, as well as from vaccine administration data from the CDC’s Vaccine Tracking System and the collaborative Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD).
The VFC provides federally purchased vaccines at no cost to about half of persons aged 18 years or younger. The VSD collaborates on vaccine coverage with the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office and eight large health care organizations across the country. Vaccination coverage is the usual metric for assessing vaccine usage; providers’ orders and the number of doses administered are two proxy measures, the authors explained.
“The substantial reduction in VFC-funded pediatric vaccine ordering after the COVID-19 emergency declaration is consistent with changes in vaccine administration among children in the VSD population receiving care through eight large U.S. health care organizations,” wrote Jeanne M. Santoli, MD, and colleagues, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. “The smaller decline in measles-containing vaccine administration among children aged ≤24 months suggests that system-level strategies to prioritize well child care and immunization for this age group are being implemented.”
Dr. Santoli, who is an Atlanta-based pediatrician, and associates stressed the importance of maintaining regular vaccinations during the pandemic. “The identified declines in routine pediatric vaccine ordering and doses administered might indicate that U.S. children and their communities face increased risks for outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases,” they wrote. “Parental concerns about potentially exposing their children to COVID-19 during well child visits might contribute to the declines observed.” Parents should therefore be reminded of the necessity of protecting their children against vaccine-preventable diseases.
In 2019, a Gallup survey reported that overall support for vaccination continued to decline in the United States.
The researchers predicted that, as social distancing relaxes, unvaccinated children will be more susceptible to other serious diseases. “In response, continued coordinated efforts between health care providers and public health officials at the local, state, and federal levels will be necessary to achieve rapid catch-up vaccination,” they concluded.
The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: What will happen to physician income this year?
“At a combined system and hospital board meeting yesterday, there was a financial presentation,” said a cardiologist in Minnesota, who declined to be named. “We have ‘salary support’ through May 16, which means we will be receiving base pay at our 2019 level. After May 16, I think it’s fairly certain salaries will be decreased.”
A general internist in the same area added: “The system has decided to pay physicians and other employees for 8 weeks, until May 15, and they are borrowing about $150 million to do this. We don’t know what will happen after May 15, but we are supposed to have an update in early May.”
Physician income is of huge interest, and many aspects of it are discussed in Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2020, just released.
The worst may be yet to come
Of all the categories of physicians, “I am worried about private practices the most,” said Travis Singleton, senior vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm. “They don’t have a financial cushion, and will start seeing big drops in revenue at the end of May.”
“A lot of the A/R [accounts receivables] for practices come within 30 days, and very little comes in after 90 days,” said Terrence R. McWilliams, MD, chief clinical consultant at HSG Advisors, a consultancy for not-for-profit hospitals and their employed physician networks around the country. “So private practices are reaching the point where prior A/R will start to dwindle and they will start feeling the decline in new claims submissions.”
Large practices may have a bigger financial cushion, but in many cases, they also have more liabilities. “We don’t know the financial loss yet, but I think it’s been devastating,” said Paul M. Yonover, MD, a urologist at UroPartners, a large single-specialty practice in Chicago with 62 urologists. “In fact, the financial loss may well be larger than our loss in volume, because we have to support our own surgery center, pathology lab, radiation center, and other in-house services.”
Employed physicians in limbo
In contrast to physicians in private practices, many employed physicians at hospitals and health systems have been shielded from the impact of COVID-19 – at least for now.
“The experiences of employed physicians are very mixed,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins. “Some health systems have reduced physicians’ pay by 20%, but other systems have been putting off any reductions.”
Hospitals and health systems are struggling. “Stopping elective surgeries deeply affected hospitals,” said Ryan Inman, founder of Physician Wealth Services in San Diego. “With fewer elective surgeries, they have much less income coming in. Some big hospitals that are pillars of their community are under great financial stress.”
“Hospitals’ patient volumes have fallen by 50%-90%,” Mr. McWilliams reported. “Lower volume means lower pay for employed physicians, who are paid by straight productivity or other models that require high volumes. However, some health systems have intervened to make sure these physicians get some money.”
Base pay is often safe for now, but quarterly bonuses are on the chopping block. “Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., a state mecca for physician employment. “They’ve been told that they will continue to get their base salary but forget about the quarterly bonuses. This amounts to salary reductions of 10%-30%.”
Ensuring payment for these doctors means lowering their productivity benchmarks, but the benchmarks might still be too high for these times. An internist at a large health system in Minneapolis–St. Paul reports that, at a lunch meeting, employed doctors learned that payment benchmarks will be reduced to 70% of their 2019 monthly average.
“I am seeing nowhere near 70% of what I was seeing last year,” he said in an interview, asking that his name not be used. “Given how slow things have been, I am probably closer to 30%, but have not been given any data on this, so I am guessing at this point.”
Adapting to a brave new world
Even as they face a dark financial future, physicians have had to completely revamp the way they practice medicine – a cumbersome process that, in itself, incurred some financial losses. They had to obtain masks and other PPE, reposition or even close down their waiting rooms, cut back on unneeded staff, and adapt to telemedicine.
“It’s been an incredibly challenging time,” said Dr. Yonover, the Chicago urologist. “As a doctor. I cannot avoid contact, and it’s not totally clear yet how the virus spreads. But I don’t have the option of closing the door. As a practice owner, you’re responsible for the health and well-being of employees, patients, and the business.”
“A practice’s daily routine is somewhat slower and costlier,” said David N. Gans, MSHA, senior fellow at the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents group practices. “Between each patient, you have to clean a lot more than previously, and you have to stock up on PPE such as masks and gowns. PPE used to be limited to infectious patients, but now it’s universal.”
At PA Clinical Network, a clinically integrated network in Pennsylvania, volume fell 40%-50% and income fell 30%-50% from late March to late April, according to Jaan Sidorov, MD, an internist who is CEO of the network, which has 158 physicians in a variety of specialties working in 54 practices around the state.
“Revenue went down but it didn’t crash,” he said. “And our physicians pivoted very quickly. They adapted to telehealth and applied for the federal loan programs. They didn’t use waiting rooms. In some cases, staff was out in the parking lot, putting stethoscopes through patients’ windows.”
“None of the practices closed, not even temporarily,” Dr. Sidorov said. “But clearly this cannot go forever without having serious consequences.”
How much can telemedicine help?
Telemedicine has been a lifeline for many struggling practices. “As much as 20%-40% of a practice’s losses can be recouped through telemedicine, depending on variables like patients’ attitudes,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins.
The rise in telemedicine was made possible by a temporary relaxation of the limits on telemedicine payments by Medicare and many private payers. Medicare is currently paying the same rates for telemedicine as it does for in-office visits.
In a recent MGMA Stat survey, 97% of practices reported that they had taken up telemedicine, according to Mr. Gans. He estimates that 80% of primary care could be converted to telemedicine, including medication refills, ongoing care of chronic patients, and recording patients’ vital signs from home.
Some primary care physicians are now using telemedicine for 100% of their visits. “I voluntarily closed my practice weeks ago except for virtual visits due to the risk of exposure for my patients,” a doctor in South Carolina told the Primary Care Collaborative in mid-April. “I continue to pay my staff out of pocket but have reduced hours and am not receiving any income myself.”
However, Mr. Inman of Physician Wealth Services said family medicine clients using telemedicine for all of their patients are earning less per visit, even though the Medicare reimbursement is the same as for an office visit. “They earn less because they cannot charge for any ancillaries, such as labs or imaging,” he said.
“Telemedicine has its limits,” Mr. Singleton said. It cannot replace elective surgeries, and even in primary care practices, “there is a lot of work for which patients have to come in, such as physicals or providing vaccines,” he said. “I know of one doctor who has refrigerator full of vaccines to give out. That pays his bills.”
In many cases, “telemedicine” simply means using the phone, with no video. Many patients can only use the phone, and Medicare now reimburses for some kinds of phone visits. In a mid-April survey of primary care providers, 44% were using the telephone for the majority of their visits, and 14% were not using video at all. Medicare recently decided to pay physicians the same amount for telephone visits as in-person visits.
Financial boosts will run out soon
Many private practices are surviving only because they have managed to tap into new federal programs that can finance them for the short-term. Here are the main examples:
Receiving advance Medicare payments. Through the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payment Program, physicians can be paid up to 3 months of their average Medicare reimbursement in advance. However, repayment starts 120 days after receiving the money and must be completed within 210 days.
Obtaining a federal loan. Under the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), which is available to all kinds of small businesses, practices can apply for up to 2.5 times their average monthly payroll costs.
PPP money can be used for payroll, rent, mortgage interest, or utility payments for up to 8 weeks. The loan will be entirely forgiven as long as the rules are followed. For example, three quarters of the money must go to payroll, and laid-off employees must be rehired by June 30.
There was such a rush for the first round of PPP loans that many physicians failed to get the loan. “Many of my physician clients applied for the loan as soon as they could, but none of them got it,” said Mr. Inman, the San Diego financial adviser. “We are hoping that the next round of funding will provide them some relief.” The second round started on April 27.
Physicians who have already obtained the PPP loan are very relieved. “This loan made it possible for us to pay our employees,” said George W. Monks, MD, a dermatologist in Tulsa, Okla., and president of the Oklahoma Medical Association.
Staff benefiting from higher unemployment payments. Many practices and hospitals are laying off their staff so that they can collect unemployment benefits. This is a good time to do that because the federal government has boosted unemployment payments by $600 a week, creating a total benefit that is greater than many people earned at their regular jobs.
This extra boost ends in July, but practices with PPP loans will have to rehire their laid-off workers a month before that. Getting laid-off staffers to come back in is going to be critical, and some practices are already having a hard time convincing them to come back, said Michael La Penna, a physician practice manager in Grand Rapids, Mich.
“They are finding that those people don’t want to come back in yet,” he said. “In many cases they have to care for children at home or have been getting generous unemployment checks.”
The problem with all these temporary financial boosts is that they will disappear within weeks or months from now. Mr. La Penna is concerned that the sudden loss of this support could send some practices spinning into bankruptcy. “Unless volume gets better very soon, time is running out for a lot of practices,” he said.
Hospitals, which also have been depending on federal assistance, may run out of money, too. Daniel Wrenne, a financial planner for physicians in Lexington, Ky., said smaller hospitals are particularly vulnerable because they lack the capital. He said a friend who is an attorney for hospitals predicted that 25% of small regional hospitals “won’t make it through this.”
Such financial turmoil might prompt many physicians to retire or find a new job, said Gary Price, MD, a plastic surgeon in New Haven, Conn., and president of the Physicians Foundation, an advocacy group for the profession. In a survey of doctors by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins, released on April 21, 18% planned to retire, temporarily close their practices, or opt out of patient care, and another 14%, presumably employed physicians, planned to change jobs.
Is recovery around the corner?
In early May, practices in many parts of the country were seeing the possibility of a return to normal business – or at least what could pass for normal in these unusual times.
“From mid-March to mid-April, hospitals and practices were in panic mode,” said MGMA’s Mr. Gans. “They were focusing on the here and now. But from mid-April to mid-May, they could begin looking at the big picture and decide how they will get back into business.”
Surgeons devastated by bans on elective surgeries might see a bounce in cases, as the backlog of patients comes back in. By late April, 10 states reinstituted elective surgeries, including California, Arizona, Georgia, Indiana, Colorado, and Oklahoma, and New York has reinstituted elective surgeries for some counties.
Dr. Price said he hopes to reopen his plastic surgery practice by the end of June. “If it takes longer than that, I’m not sure that the practice will survive.” His PPP loan would have run out and he would have to lay off his staff. “At that point, ongoing viability of practice would become a real question.”
Dr. Monks said he hopes a lot more patients will come to his dermatology practice. As of the end of April, “we’re starting to see an uptick in the number of patients wanting to come in,” he said. “They seem to be more comfortable with the new world we’re living in.
“Viewing the backlog of cases that haven’t been attended to,” Dr. Monks added, “I think we’ll be really busy for a while.”
But Mr. La Penna said he thinks the expected backlog of elective patients will be more like a trickle than a flood. “Many patients aren’t going to want to return that fast,” he said. “They may have a condition that makes exposure to COVID-19 more risky, like diabetes or high blood pressure, or they’re elderly, or they live in a household with one of these risk groups.”
Andrew Musbach, cofounder of MD Wealth Management in Chelsea, Mich., said he expects a slow recovery for primary care physicians as well. “Even when the lockdowns are over, not everyone is going to feel comfortable coming to a hospital or visiting a doctor’s office unless it’s absolutely necessary,” he said.
Getting back to normal patient volumes will involve finding better ways to protect patients and staff from COVID-19, Dr. Yonover said. At his urology practice, “we take all the usual precautions, but nothing yet has made it dramatically easier to protect patients and staff,” he said. “Rapid, accurate testing for COVID-19 would change the landscape, but I have no idea when that will come.”
Mr. Wrenne advises his physician clients that a financial recovery will take months. “I tell them to plan for 6 months, until October, before income returns to pre–COVID-19 levels. Reimbursement lags appointments by as much as 3 months, plus it will probably take the economy 2-3 months more to get back to normal.”
“We are facing a recession, and how long it will last is anyone’s guess,” said Alex Kilian, a physician wealth manager at Aldrich Wealth in San Diego. “The federal government’s efforts to stimulate the economy is keeping it from crashing, but there are no real signs that it will actually pick up. It may take years for the travel and entertainment industries to come back.”
A recession means patients will have less spending power, and health care sectors like laser eye surgery may be damaged for years to come, said John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “[That kind of surgery] is purely elective and relatively costly,” he said. “When people get back to work, they are going to be building up their savings and avoiding new debt. They won’t be having [laser eye surgery].”
“There won’t be any quick return to normal for me,” said Dr. Price, the Connecticut plastic surgeon. “The damage this time will probably be worse than in the Great Recession. Back then, plastic surgery was off by 20%, but this time you have the extra problem of patients reluctant to come into medical offices.”
“To get patients to come in, facilities are going to have to convince patients that they are safe,” Mr. Singleton said. “That may mean undertaking some marketing and promotion, and hospitals tend to be much better at that than practices.”
What a new wave of COVID-19 would mean
Some states have begun reopening public places, which could signal patients to return to doctors’ offices even though doctors’ offices were never officially closed. Oklahoma, for example, reopened restaurants, movie theaters, and sports venues on May 1.
Dr. Monks, president of the Oklahoma Medical Association, said his group opposes states reopening. “The governor’s order is too hasty and overly ambitious,” he said. “Oklahoma has seen an ongoing growth in the number of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the past week alone [in late April].”
The concern is that opening up public places too soon would create a new wave of COVID-19, which would not only be a public health disaster, but also a financial disaster for physicians. Doctors would be back where they were in March, but unlike in March, they would not benefit from revenues from previously busy times.
Mr. Pinto said the number of COVID-19 cases will rise and fall in the next 2 years, forcing states to reenact new bans on public gatherings and on elective surgeries until the numbers subside again.
Mr. Pinto said authorities in Singapore have successfully handled such waves of the disease through short bans that are tantamount to tapping the brakes of a car. “As the car gathers speed down the hill, you tap the brake,” he said. “I suspect we’ll be seeing a lot of brake-tapping until a vaccine can be developed and distributed.”
Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, recalled the worldwide Spanish Flu pandemic a century ago. “People were allowed out of their houses after 2 months, and the flu spiked up again,” he said. “I hope we don’t make that mistake this time.”
Dr. LeRoy said it’s not possible to predict how the COVID-19 crisis will play out. “What will the future be like? I don’t know the answer,” he said. “The information we learn in next hours, days, or months will probably change everything.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“At a combined system and hospital board meeting yesterday, there was a financial presentation,” said a cardiologist in Minnesota, who declined to be named. “We have ‘salary support’ through May 16, which means we will be receiving base pay at our 2019 level. After May 16, I think it’s fairly certain salaries will be decreased.”
A general internist in the same area added: “The system has decided to pay physicians and other employees for 8 weeks, until May 15, and they are borrowing about $150 million to do this. We don’t know what will happen after May 15, but we are supposed to have an update in early May.”
Physician income is of huge interest, and many aspects of it are discussed in Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2020, just released.
The worst may be yet to come
Of all the categories of physicians, “I am worried about private practices the most,” said Travis Singleton, senior vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm. “They don’t have a financial cushion, and will start seeing big drops in revenue at the end of May.”
“A lot of the A/R [accounts receivables] for practices come within 30 days, and very little comes in after 90 days,” said Terrence R. McWilliams, MD, chief clinical consultant at HSG Advisors, a consultancy for not-for-profit hospitals and their employed physician networks around the country. “So private practices are reaching the point where prior A/R will start to dwindle and they will start feeling the decline in new claims submissions.”
Large practices may have a bigger financial cushion, but in many cases, they also have more liabilities. “We don’t know the financial loss yet, but I think it’s been devastating,” said Paul M. Yonover, MD, a urologist at UroPartners, a large single-specialty practice in Chicago with 62 urologists. “In fact, the financial loss may well be larger than our loss in volume, because we have to support our own surgery center, pathology lab, radiation center, and other in-house services.”
Employed physicians in limbo
In contrast to physicians in private practices, many employed physicians at hospitals and health systems have been shielded from the impact of COVID-19 – at least for now.
“The experiences of employed physicians are very mixed,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins. “Some health systems have reduced physicians’ pay by 20%, but other systems have been putting off any reductions.”
Hospitals and health systems are struggling. “Stopping elective surgeries deeply affected hospitals,” said Ryan Inman, founder of Physician Wealth Services in San Diego. “With fewer elective surgeries, they have much less income coming in. Some big hospitals that are pillars of their community are under great financial stress.”
“Hospitals’ patient volumes have fallen by 50%-90%,” Mr. McWilliams reported. “Lower volume means lower pay for employed physicians, who are paid by straight productivity or other models that require high volumes. However, some health systems have intervened to make sure these physicians get some money.”
Base pay is often safe for now, but quarterly bonuses are on the chopping block. “Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., a state mecca for physician employment. “They’ve been told that they will continue to get their base salary but forget about the quarterly bonuses. This amounts to salary reductions of 10%-30%.”
Ensuring payment for these doctors means lowering their productivity benchmarks, but the benchmarks might still be too high for these times. An internist at a large health system in Minneapolis–St. Paul reports that, at a lunch meeting, employed doctors learned that payment benchmarks will be reduced to 70% of their 2019 monthly average.
“I am seeing nowhere near 70% of what I was seeing last year,” he said in an interview, asking that his name not be used. “Given how slow things have been, I am probably closer to 30%, but have not been given any data on this, so I am guessing at this point.”
Adapting to a brave new world
Even as they face a dark financial future, physicians have had to completely revamp the way they practice medicine – a cumbersome process that, in itself, incurred some financial losses. They had to obtain masks and other PPE, reposition or even close down their waiting rooms, cut back on unneeded staff, and adapt to telemedicine.
“It’s been an incredibly challenging time,” said Dr. Yonover, the Chicago urologist. “As a doctor. I cannot avoid contact, and it’s not totally clear yet how the virus spreads. But I don’t have the option of closing the door. As a practice owner, you’re responsible for the health and well-being of employees, patients, and the business.”
“A practice’s daily routine is somewhat slower and costlier,” said David N. Gans, MSHA, senior fellow at the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents group practices. “Between each patient, you have to clean a lot more than previously, and you have to stock up on PPE such as masks and gowns. PPE used to be limited to infectious patients, but now it’s universal.”
At PA Clinical Network, a clinically integrated network in Pennsylvania, volume fell 40%-50% and income fell 30%-50% from late March to late April, according to Jaan Sidorov, MD, an internist who is CEO of the network, which has 158 physicians in a variety of specialties working in 54 practices around the state.
“Revenue went down but it didn’t crash,” he said. “And our physicians pivoted very quickly. They adapted to telehealth and applied for the federal loan programs. They didn’t use waiting rooms. In some cases, staff was out in the parking lot, putting stethoscopes through patients’ windows.”
“None of the practices closed, not even temporarily,” Dr. Sidorov said. “But clearly this cannot go forever without having serious consequences.”
How much can telemedicine help?
Telemedicine has been a lifeline for many struggling practices. “As much as 20%-40% of a practice’s losses can be recouped through telemedicine, depending on variables like patients’ attitudes,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins.
The rise in telemedicine was made possible by a temporary relaxation of the limits on telemedicine payments by Medicare and many private payers. Medicare is currently paying the same rates for telemedicine as it does for in-office visits.
In a recent MGMA Stat survey, 97% of practices reported that they had taken up telemedicine, according to Mr. Gans. He estimates that 80% of primary care could be converted to telemedicine, including medication refills, ongoing care of chronic patients, and recording patients’ vital signs from home.
Some primary care physicians are now using telemedicine for 100% of their visits. “I voluntarily closed my practice weeks ago except for virtual visits due to the risk of exposure for my patients,” a doctor in South Carolina told the Primary Care Collaborative in mid-April. “I continue to pay my staff out of pocket but have reduced hours and am not receiving any income myself.”
However, Mr. Inman of Physician Wealth Services said family medicine clients using telemedicine for all of their patients are earning less per visit, even though the Medicare reimbursement is the same as for an office visit. “They earn less because they cannot charge for any ancillaries, such as labs or imaging,” he said.
“Telemedicine has its limits,” Mr. Singleton said. It cannot replace elective surgeries, and even in primary care practices, “there is a lot of work for which patients have to come in, such as physicals or providing vaccines,” he said. “I know of one doctor who has refrigerator full of vaccines to give out. That pays his bills.”
In many cases, “telemedicine” simply means using the phone, with no video. Many patients can only use the phone, and Medicare now reimburses for some kinds of phone visits. In a mid-April survey of primary care providers, 44% were using the telephone for the majority of their visits, and 14% were not using video at all. Medicare recently decided to pay physicians the same amount for telephone visits as in-person visits.
Financial boosts will run out soon
Many private practices are surviving only because they have managed to tap into new federal programs that can finance them for the short-term. Here are the main examples:
Receiving advance Medicare payments. Through the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payment Program, physicians can be paid up to 3 months of their average Medicare reimbursement in advance. However, repayment starts 120 days after receiving the money and must be completed within 210 days.
Obtaining a federal loan. Under the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), which is available to all kinds of small businesses, practices can apply for up to 2.5 times their average monthly payroll costs.
PPP money can be used for payroll, rent, mortgage interest, or utility payments for up to 8 weeks. The loan will be entirely forgiven as long as the rules are followed. For example, three quarters of the money must go to payroll, and laid-off employees must be rehired by June 30.
There was such a rush for the first round of PPP loans that many physicians failed to get the loan. “Many of my physician clients applied for the loan as soon as they could, but none of them got it,” said Mr. Inman, the San Diego financial adviser. “We are hoping that the next round of funding will provide them some relief.” The second round started on April 27.
Physicians who have already obtained the PPP loan are very relieved. “This loan made it possible for us to pay our employees,” said George W. Monks, MD, a dermatologist in Tulsa, Okla., and president of the Oklahoma Medical Association.
Staff benefiting from higher unemployment payments. Many practices and hospitals are laying off their staff so that they can collect unemployment benefits. This is a good time to do that because the federal government has boosted unemployment payments by $600 a week, creating a total benefit that is greater than many people earned at their regular jobs.
This extra boost ends in July, but practices with PPP loans will have to rehire their laid-off workers a month before that. Getting laid-off staffers to come back in is going to be critical, and some practices are already having a hard time convincing them to come back, said Michael La Penna, a physician practice manager in Grand Rapids, Mich.
“They are finding that those people don’t want to come back in yet,” he said. “In many cases they have to care for children at home or have been getting generous unemployment checks.”
The problem with all these temporary financial boosts is that they will disappear within weeks or months from now. Mr. La Penna is concerned that the sudden loss of this support could send some practices spinning into bankruptcy. “Unless volume gets better very soon, time is running out for a lot of practices,” he said.
Hospitals, which also have been depending on federal assistance, may run out of money, too. Daniel Wrenne, a financial planner for physicians in Lexington, Ky., said smaller hospitals are particularly vulnerable because they lack the capital. He said a friend who is an attorney for hospitals predicted that 25% of small regional hospitals “won’t make it through this.”
Such financial turmoil might prompt many physicians to retire or find a new job, said Gary Price, MD, a plastic surgeon in New Haven, Conn., and president of the Physicians Foundation, an advocacy group for the profession. In a survey of doctors by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins, released on April 21, 18% planned to retire, temporarily close their practices, or opt out of patient care, and another 14%, presumably employed physicians, planned to change jobs.
Is recovery around the corner?
In early May, practices in many parts of the country were seeing the possibility of a return to normal business – or at least what could pass for normal in these unusual times.
“From mid-March to mid-April, hospitals and practices were in panic mode,” said MGMA’s Mr. Gans. “They were focusing on the here and now. But from mid-April to mid-May, they could begin looking at the big picture and decide how they will get back into business.”
Surgeons devastated by bans on elective surgeries might see a bounce in cases, as the backlog of patients comes back in. By late April, 10 states reinstituted elective surgeries, including California, Arizona, Georgia, Indiana, Colorado, and Oklahoma, and New York has reinstituted elective surgeries for some counties.
Dr. Price said he hopes to reopen his plastic surgery practice by the end of June. “If it takes longer than that, I’m not sure that the practice will survive.” His PPP loan would have run out and he would have to lay off his staff. “At that point, ongoing viability of practice would become a real question.”
Dr. Monks said he hopes a lot more patients will come to his dermatology practice. As of the end of April, “we’re starting to see an uptick in the number of patients wanting to come in,” he said. “They seem to be more comfortable with the new world we’re living in.
“Viewing the backlog of cases that haven’t been attended to,” Dr. Monks added, “I think we’ll be really busy for a while.”
But Mr. La Penna said he thinks the expected backlog of elective patients will be more like a trickle than a flood. “Many patients aren’t going to want to return that fast,” he said. “They may have a condition that makes exposure to COVID-19 more risky, like diabetes or high blood pressure, or they’re elderly, or they live in a household with one of these risk groups.”
Andrew Musbach, cofounder of MD Wealth Management in Chelsea, Mich., said he expects a slow recovery for primary care physicians as well. “Even when the lockdowns are over, not everyone is going to feel comfortable coming to a hospital or visiting a doctor’s office unless it’s absolutely necessary,” he said.
Getting back to normal patient volumes will involve finding better ways to protect patients and staff from COVID-19, Dr. Yonover said. At his urology practice, “we take all the usual precautions, but nothing yet has made it dramatically easier to protect patients and staff,” he said. “Rapid, accurate testing for COVID-19 would change the landscape, but I have no idea when that will come.”
Mr. Wrenne advises his physician clients that a financial recovery will take months. “I tell them to plan for 6 months, until October, before income returns to pre–COVID-19 levels. Reimbursement lags appointments by as much as 3 months, plus it will probably take the economy 2-3 months more to get back to normal.”
“We are facing a recession, and how long it will last is anyone’s guess,” said Alex Kilian, a physician wealth manager at Aldrich Wealth in San Diego. “The federal government’s efforts to stimulate the economy is keeping it from crashing, but there are no real signs that it will actually pick up. It may take years for the travel and entertainment industries to come back.”
A recession means patients will have less spending power, and health care sectors like laser eye surgery may be damaged for years to come, said John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “[That kind of surgery] is purely elective and relatively costly,” he said. “When people get back to work, they are going to be building up their savings and avoiding new debt. They won’t be having [laser eye surgery].”
“There won’t be any quick return to normal for me,” said Dr. Price, the Connecticut plastic surgeon. “The damage this time will probably be worse than in the Great Recession. Back then, plastic surgery was off by 20%, but this time you have the extra problem of patients reluctant to come into medical offices.”
“To get patients to come in, facilities are going to have to convince patients that they are safe,” Mr. Singleton said. “That may mean undertaking some marketing and promotion, and hospitals tend to be much better at that than practices.”
What a new wave of COVID-19 would mean
Some states have begun reopening public places, which could signal patients to return to doctors’ offices even though doctors’ offices were never officially closed. Oklahoma, for example, reopened restaurants, movie theaters, and sports venues on May 1.
Dr. Monks, president of the Oklahoma Medical Association, said his group opposes states reopening. “The governor’s order is too hasty and overly ambitious,” he said. “Oklahoma has seen an ongoing growth in the number of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the past week alone [in late April].”
The concern is that opening up public places too soon would create a new wave of COVID-19, which would not only be a public health disaster, but also a financial disaster for physicians. Doctors would be back where they were in March, but unlike in March, they would not benefit from revenues from previously busy times.
Mr. Pinto said the number of COVID-19 cases will rise and fall in the next 2 years, forcing states to reenact new bans on public gatherings and on elective surgeries until the numbers subside again.
Mr. Pinto said authorities in Singapore have successfully handled such waves of the disease through short bans that are tantamount to tapping the brakes of a car. “As the car gathers speed down the hill, you tap the brake,” he said. “I suspect we’ll be seeing a lot of brake-tapping until a vaccine can be developed and distributed.”
Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, recalled the worldwide Spanish Flu pandemic a century ago. “People were allowed out of their houses after 2 months, and the flu spiked up again,” he said. “I hope we don’t make that mistake this time.”
Dr. LeRoy said it’s not possible to predict how the COVID-19 crisis will play out. “What will the future be like? I don’t know the answer,” he said. “The information we learn in next hours, days, or months will probably change everything.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“At a combined system and hospital board meeting yesterday, there was a financial presentation,” said a cardiologist in Minnesota, who declined to be named. “We have ‘salary support’ through May 16, which means we will be receiving base pay at our 2019 level. After May 16, I think it’s fairly certain salaries will be decreased.”
A general internist in the same area added: “The system has decided to pay physicians and other employees for 8 weeks, until May 15, and they are borrowing about $150 million to do this. We don’t know what will happen after May 15, but we are supposed to have an update in early May.”
Physician income is of huge interest, and many aspects of it are discussed in Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2020, just released.
The worst may be yet to come
Of all the categories of physicians, “I am worried about private practices the most,” said Travis Singleton, senior vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm. “They don’t have a financial cushion, and will start seeing big drops in revenue at the end of May.”
“A lot of the A/R [accounts receivables] for practices come within 30 days, and very little comes in after 90 days,” said Terrence R. McWilliams, MD, chief clinical consultant at HSG Advisors, a consultancy for not-for-profit hospitals and their employed physician networks around the country. “So private practices are reaching the point where prior A/R will start to dwindle and they will start feeling the decline in new claims submissions.”
Large practices may have a bigger financial cushion, but in many cases, they also have more liabilities. “We don’t know the financial loss yet, but I think it’s been devastating,” said Paul M. Yonover, MD, a urologist at UroPartners, a large single-specialty practice in Chicago with 62 urologists. “In fact, the financial loss may well be larger than our loss in volume, because we have to support our own surgery center, pathology lab, radiation center, and other in-house services.”
Employed physicians in limbo
In contrast to physicians in private practices, many employed physicians at hospitals and health systems have been shielded from the impact of COVID-19 – at least for now.
“The experiences of employed physicians are very mixed,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins. “Some health systems have reduced physicians’ pay by 20%, but other systems have been putting off any reductions.”
Hospitals and health systems are struggling. “Stopping elective surgeries deeply affected hospitals,” said Ryan Inman, founder of Physician Wealth Services in San Diego. “With fewer elective surgeries, they have much less income coming in. Some big hospitals that are pillars of their community are under great financial stress.”
“Hospitals’ patient volumes have fallen by 50%-90%,” Mr. McWilliams reported. “Lower volume means lower pay for employed physicians, who are paid by straight productivity or other models that require high volumes. However, some health systems have intervened to make sure these physicians get some money.”
Base pay is often safe for now, but quarterly bonuses are on the chopping block. “Employed physicians are often getting a guaranteed salary for a month or two, but no bonuses or extra distributions,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a financial adviser for physicians in St. Louis Park, Minn., a state mecca for physician employment. “They’ve been told that they will continue to get their base salary but forget about the quarterly bonuses. This amounts to salary reductions of 10%-30%.”
Ensuring payment for these doctors means lowering their productivity benchmarks, but the benchmarks might still be too high for these times. An internist at a large health system in Minneapolis–St. Paul reports that, at a lunch meeting, employed doctors learned that payment benchmarks will be reduced to 70% of their 2019 monthly average.
“I am seeing nowhere near 70% of what I was seeing last year,” he said in an interview, asking that his name not be used. “Given how slow things have been, I am probably closer to 30%, but have not been given any data on this, so I am guessing at this point.”
Adapting to a brave new world
Even as they face a dark financial future, physicians have had to completely revamp the way they practice medicine – a cumbersome process that, in itself, incurred some financial losses. They had to obtain masks and other PPE, reposition or even close down their waiting rooms, cut back on unneeded staff, and adapt to telemedicine.
“It’s been an incredibly challenging time,” said Dr. Yonover, the Chicago urologist. “As a doctor. I cannot avoid contact, and it’s not totally clear yet how the virus spreads. But I don’t have the option of closing the door. As a practice owner, you’re responsible for the health and well-being of employees, patients, and the business.”
“A practice’s daily routine is somewhat slower and costlier,” said David N. Gans, MSHA, senior fellow at the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents group practices. “Between each patient, you have to clean a lot more than previously, and you have to stock up on PPE such as masks and gowns. PPE used to be limited to infectious patients, but now it’s universal.”
At PA Clinical Network, a clinically integrated network in Pennsylvania, volume fell 40%-50% and income fell 30%-50% from late March to late April, according to Jaan Sidorov, MD, an internist who is CEO of the network, which has 158 physicians in a variety of specialties working in 54 practices around the state.
“Revenue went down but it didn’t crash,” he said. “And our physicians pivoted very quickly. They adapted to telehealth and applied for the federal loan programs. They didn’t use waiting rooms. In some cases, staff was out in the parking lot, putting stethoscopes through patients’ windows.”
“None of the practices closed, not even temporarily,” Dr. Sidorov said. “But clearly this cannot go forever without having serious consequences.”
How much can telemedicine help?
Telemedicine has been a lifeline for many struggling practices. “As much as 20%-40% of a practice’s losses can be recouped through telemedicine, depending on variables like patients’ attitudes,” said Mr. Singleton at Merritt Hawkins.
The rise in telemedicine was made possible by a temporary relaxation of the limits on telemedicine payments by Medicare and many private payers. Medicare is currently paying the same rates for telemedicine as it does for in-office visits.
In a recent MGMA Stat survey, 97% of practices reported that they had taken up telemedicine, according to Mr. Gans. He estimates that 80% of primary care could be converted to telemedicine, including medication refills, ongoing care of chronic patients, and recording patients’ vital signs from home.
Some primary care physicians are now using telemedicine for 100% of their visits. “I voluntarily closed my practice weeks ago except for virtual visits due to the risk of exposure for my patients,” a doctor in South Carolina told the Primary Care Collaborative in mid-April. “I continue to pay my staff out of pocket but have reduced hours and am not receiving any income myself.”
However, Mr. Inman of Physician Wealth Services said family medicine clients using telemedicine for all of their patients are earning less per visit, even though the Medicare reimbursement is the same as for an office visit. “They earn less because they cannot charge for any ancillaries, such as labs or imaging,” he said.
“Telemedicine has its limits,” Mr. Singleton said. It cannot replace elective surgeries, and even in primary care practices, “there is a lot of work for which patients have to come in, such as physicals or providing vaccines,” he said. “I know of one doctor who has refrigerator full of vaccines to give out. That pays his bills.”
In many cases, “telemedicine” simply means using the phone, with no video. Many patients can only use the phone, and Medicare now reimburses for some kinds of phone visits. In a mid-April survey of primary care providers, 44% were using the telephone for the majority of their visits, and 14% were not using video at all. Medicare recently decided to pay physicians the same amount for telephone visits as in-person visits.
Financial boosts will run out soon
Many private practices are surviving only because they have managed to tap into new federal programs that can finance them for the short-term. Here are the main examples:
Receiving advance Medicare payments. Through the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payment Program, physicians can be paid up to 3 months of their average Medicare reimbursement in advance. However, repayment starts 120 days after receiving the money and must be completed within 210 days.
Obtaining a federal loan. Under the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), which is available to all kinds of small businesses, practices can apply for up to 2.5 times their average monthly payroll costs.
PPP money can be used for payroll, rent, mortgage interest, or utility payments for up to 8 weeks. The loan will be entirely forgiven as long as the rules are followed. For example, three quarters of the money must go to payroll, and laid-off employees must be rehired by June 30.
There was such a rush for the first round of PPP loans that many physicians failed to get the loan. “Many of my physician clients applied for the loan as soon as they could, but none of them got it,” said Mr. Inman, the San Diego financial adviser. “We are hoping that the next round of funding will provide them some relief.” The second round started on April 27.
Physicians who have already obtained the PPP loan are very relieved. “This loan made it possible for us to pay our employees,” said George W. Monks, MD, a dermatologist in Tulsa, Okla., and president of the Oklahoma Medical Association.
Staff benefiting from higher unemployment payments. Many practices and hospitals are laying off their staff so that they can collect unemployment benefits. This is a good time to do that because the federal government has boosted unemployment payments by $600 a week, creating a total benefit that is greater than many people earned at their regular jobs.
This extra boost ends in July, but practices with PPP loans will have to rehire their laid-off workers a month before that. Getting laid-off staffers to come back in is going to be critical, and some practices are already having a hard time convincing them to come back, said Michael La Penna, a physician practice manager in Grand Rapids, Mich.
“They are finding that those people don’t want to come back in yet,” he said. “In many cases they have to care for children at home or have been getting generous unemployment checks.”
The problem with all these temporary financial boosts is that they will disappear within weeks or months from now. Mr. La Penna is concerned that the sudden loss of this support could send some practices spinning into bankruptcy. “Unless volume gets better very soon, time is running out for a lot of practices,” he said.
Hospitals, which also have been depending on federal assistance, may run out of money, too. Daniel Wrenne, a financial planner for physicians in Lexington, Ky., said smaller hospitals are particularly vulnerable because they lack the capital. He said a friend who is an attorney for hospitals predicted that 25% of small regional hospitals “won’t make it through this.”
Such financial turmoil might prompt many physicians to retire or find a new job, said Gary Price, MD, a plastic surgeon in New Haven, Conn., and president of the Physicians Foundation, an advocacy group for the profession. In a survey of doctors by the Physicians Foundation and Merritt Hawkins, released on April 21, 18% planned to retire, temporarily close their practices, or opt out of patient care, and another 14%, presumably employed physicians, planned to change jobs.
Is recovery around the corner?
In early May, practices in many parts of the country were seeing the possibility of a return to normal business – or at least what could pass for normal in these unusual times.
“From mid-March to mid-April, hospitals and practices were in panic mode,” said MGMA’s Mr. Gans. “They were focusing on the here and now. But from mid-April to mid-May, they could begin looking at the big picture and decide how they will get back into business.”
Surgeons devastated by bans on elective surgeries might see a bounce in cases, as the backlog of patients comes back in. By late April, 10 states reinstituted elective surgeries, including California, Arizona, Georgia, Indiana, Colorado, and Oklahoma, and New York has reinstituted elective surgeries for some counties.
Dr. Price said he hopes to reopen his plastic surgery practice by the end of June. “If it takes longer than that, I’m not sure that the practice will survive.” His PPP loan would have run out and he would have to lay off his staff. “At that point, ongoing viability of practice would become a real question.”
Dr. Monks said he hopes a lot more patients will come to his dermatology practice. As of the end of April, “we’re starting to see an uptick in the number of patients wanting to come in,” he said. “They seem to be more comfortable with the new world we’re living in.
“Viewing the backlog of cases that haven’t been attended to,” Dr. Monks added, “I think we’ll be really busy for a while.”
But Mr. La Penna said he thinks the expected backlog of elective patients will be more like a trickle than a flood. “Many patients aren’t going to want to return that fast,” he said. “They may have a condition that makes exposure to COVID-19 more risky, like diabetes or high blood pressure, or they’re elderly, or they live in a household with one of these risk groups.”
Andrew Musbach, cofounder of MD Wealth Management in Chelsea, Mich., said he expects a slow recovery for primary care physicians as well. “Even when the lockdowns are over, not everyone is going to feel comfortable coming to a hospital or visiting a doctor’s office unless it’s absolutely necessary,” he said.
Getting back to normal patient volumes will involve finding better ways to protect patients and staff from COVID-19, Dr. Yonover said. At his urology practice, “we take all the usual precautions, but nothing yet has made it dramatically easier to protect patients and staff,” he said. “Rapid, accurate testing for COVID-19 would change the landscape, but I have no idea when that will come.”
Mr. Wrenne advises his physician clients that a financial recovery will take months. “I tell them to plan for 6 months, until October, before income returns to pre–COVID-19 levels. Reimbursement lags appointments by as much as 3 months, plus it will probably take the economy 2-3 months more to get back to normal.”
“We are facing a recession, and how long it will last is anyone’s guess,” said Alex Kilian, a physician wealth manager at Aldrich Wealth in San Diego. “The federal government’s efforts to stimulate the economy is keeping it from crashing, but there are no real signs that it will actually pick up. It may take years for the travel and entertainment industries to come back.”
A recession means patients will have less spending power, and health care sectors like laser eye surgery may be damaged for years to come, said John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “[That kind of surgery] is purely elective and relatively costly,” he said. “When people get back to work, they are going to be building up their savings and avoiding new debt. They won’t be having [laser eye surgery].”
“There won’t be any quick return to normal for me,” said Dr. Price, the Connecticut plastic surgeon. “The damage this time will probably be worse than in the Great Recession. Back then, plastic surgery was off by 20%, but this time you have the extra problem of patients reluctant to come into medical offices.”
“To get patients to come in, facilities are going to have to convince patients that they are safe,” Mr. Singleton said. “That may mean undertaking some marketing and promotion, and hospitals tend to be much better at that than practices.”
What a new wave of COVID-19 would mean
Some states have begun reopening public places, which could signal patients to return to doctors’ offices even though doctors’ offices were never officially closed. Oklahoma, for example, reopened restaurants, movie theaters, and sports venues on May 1.
Dr. Monks, president of the Oklahoma Medical Association, said his group opposes states reopening. “The governor’s order is too hasty and overly ambitious,” he said. “Oklahoma has seen an ongoing growth in the number of cases, hospitalizations, and deaths in the past week alone [in late April].”
The concern is that opening up public places too soon would create a new wave of COVID-19, which would not only be a public health disaster, but also a financial disaster for physicians. Doctors would be back where they were in March, but unlike in March, they would not benefit from revenues from previously busy times.
Mr. Pinto said the number of COVID-19 cases will rise and fall in the next 2 years, forcing states to reenact new bans on public gatherings and on elective surgeries until the numbers subside again.
Mr. Pinto said authorities in Singapore have successfully handled such waves of the disease through short bans that are tantamount to tapping the brakes of a car. “As the car gathers speed down the hill, you tap the brake,” he said. “I suspect we’ll be seeing a lot of brake-tapping until a vaccine can be developed and distributed.”
Gary LeRoy, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, recalled the worldwide Spanish Flu pandemic a century ago. “People were allowed out of their houses after 2 months, and the flu spiked up again,” he said. “I hope we don’t make that mistake this time.”
Dr. LeRoy said it’s not possible to predict how the COVID-19 crisis will play out. “What will the future be like? I don’t know the answer,” he said. “The information we learn in next hours, days, or months will probably change everything.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts recommend slow, steady approach to reopening laser and cosmetic surgery practices
“People talk about reinventing the wheel,” Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., said during an hour-long webinar on May 5 sponsored by the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “In this case, we’re inventing the wheel; no one’s ever done this before – not in our lifetimes. The last pandemic was over 100 years ago, when there wasn’t aesthetic medicine.”
Dr. Dover joined a panel of four other experts from around the country to discuss how to reopen practices safely and effectively. Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Houston Cosmetic Dermatology & Laser Center, moderated the event.
In Florida, which reopened certain businesses on May 4, 2020, Jill S. Waibel, MD, plans to start at 25% capacity at Miami Dermatology and Laser Institute, and build from there. “We’re trying to take care of skin cancer patients first,” said Dr. Waibel, a dermatologist who owns the practice. “Then we’re going to start doing less aggressive cosmetic procedures like injectables, nonablative procedures. We’ll move into the more aggressive procedures as we ease back into it. We really want to see what’s going to happen 2-3 weeks down the line now that things are starting to open up.”
In Maryland, where state officials announced on May 6 that guidelines would be issued to allow for nonmedical procedures, Elizabeth L. Tanzi, MD, founder and director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, expects things to “look very different” once her practice reopens. “We are taking it very slowly,” she said. “Teledermatology for acne and other follow-ups is not something we did before, but it is certainly something that we’ll continue.”
The way she sees it, having the proper personal protective equipment is a key part of any reopening discussion. “I am not going near anyone’s face without an N95 mask that fits well, and without a face shield,” she said. “If you’re delegating these procedures to people that you don’t trust to be wearing the PPE correctly, then you shouldn’t be delegating them, because a key is the PPE. You have to assume that everyone has the virus at every time.”
In Ardmore, Pa., the Main Line Center for Laser Surgery remains closed because of current state regulations. When practice director Eric F. Bernstein, MD, gets the green light to reopen, patients will undergo a consultation by phone or videoconference and pay their bill before they set foot in the office. “We’re on the second floor, so patients can take a stairwell and avoid the elevator,” Dr. Bernstein said. “They’ll come in, not check in at the desk; go right to the room. There will be one treater and one assistant. If the patient doesn’t come in with a mask, we’ll supply one. It’s going to be a very different process. People are setting their hours longer because they’re going to be seeing fewer people. There will be no sitting in the waiting room.”
In the COVID-19 epicenter, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, director of the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, has been performing Mohs procedures and treating children with vascular malformations, but everything else is on hold. “Once the governor [Andrew Cuomo] lifts the stay-at-home restrictions, we’ll ease into things,” he said. “The issue of performing more invasive procedures – like ablative fractional resurfacing – is something that we are concerned about. I’m concerned about any laser that has environmental plume. For example, with our tattoo-removal procedures, I intend to treat every patient through a gel for the short term, and perhaps even for the long term. One can do that safely, and that eliminates the plume altogether.”
At the center, Dr. Geronemus added, “we do a fair amount of ablative fractional resurfacing and some fully ablative resurfacing. I intend to use large facial shields with these patients. We do use vacuum in each room as it stands right now, not only with electrosurgery, but we’ll be adding that to laser procedures as well. That will be helpful.”
In Chestnut Hill, Mass., Dr. Dover and his colleagues plan to practice what he termed “universal COVID precaution” by wearing a face mask, goggles, or a face shield, gloves, and protective clothing when necessary. “We are not going to do any ablative procedures, no procedures with plume, and we’re going to try and eliminate risk as much as we can,” he said. “We will have no waiting room; the patients will walk right to an exam room. They’ll be prescreened on the phone. The only thing they’ll have done when they first come in is to have their temperature taken, and they’ll be checked in and out with the doctor and the nurse in the room, and that’s it. There will be no other extraneous people to help to eliminate risk. We’re cutting our schedules down by 75% so that we can socially distance within our practice,” Dr. Dover said.
Dr. Dover served as lead author on “A path to resume aesthetic care: Executive summary of Project AesCert guidance supplement – practical considerations for aesthetic medicine professionals supporting clinic preparedness in response to the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak,” which was published online in Facial Plastic Surgery & Aesthetic Medicine (2002 May 5. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2020.0239). His coauthors included a facial plastic surgeon and three infectious disease experts.
Dr. Dover said, “We took the advice of these experts in infectious diseases, who said, ‘we don’t know all the right answers [to resuming aesthetic care]. We can mitigate risk, but we cannot eliminate risk. You have to treat every patient in your office as if they’re COVID-19 positive. If you do that, you’ll have a safe office. It’ll be the safest place in your world, safer than a grocery store, where you have no idea who you’re standing beside.’ ”
“The problem with this virus, compared to, say, SARS-CoV-1, is that these patients are positive and shedding virus 2-3 days before they get a fever,” he added. “With SARS-CoV-1, they had a fever first and then they shed virus. What I learned was, treat everybody with universal precautions.” The document includes tips for communicating with patient about expectations for office visits, clinic schedule management, cleaning procedures, PPE, treatment room set-up, and employee health screening and training.
During the webinar, an ASLMS member posed a question to the panelists about their comfort level in performing mechanical microneedling and radiofrequency (RF) microneedling procedures as aesthetic practices begin to reopen. “Generally, there’s no plume with microneedling with or without RF,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Depending upon the procedure that you’re doing, some of the microneedling procedures are very bloody; that may carry a risk unto itself. Other procedures where you’re using a thermal component have less bleeding. I’m more inclined to proceed with an RF with microneedling procedure and less inclined to proceed with a bloody, more aggressive microneedling procedure.”
Dr. Waibel emphasized the importance of disinfecting the microneedling device between uses. “If you have disposable needle cartridges, I think it’s a lot safer than if you have to clean [them],” she said. “We know that COVID-19 can live up to 3 hours, at least in a lab scenario, so you don’t want to transmit it from patient to patient. If someone has COVID-19 on their nose, and you microneedle over it, and that’s not completely disinfected, you could spread it to the next patient. We have really amped up our cleaning in between rooms. We have a whole crew that cleans every surface with [disinfectant wipes] and 90% alcohol.”
With reported shortages of N95 in many health care settings, some panelists said that they plan to reuse masks until the supply chain improves. Dr. Dover said that one option is to “use a mask, label it, number it, drop it in into a paper bag or into a [sealed plastic food container] upside down without touching the front of it,” he said. “If it sits for a week and you see patients 5 days a week, that mask will be dried out and highly effective a week later. That’s what we’re going to do until there is a big supply of them.”
The pandemic has also thrown a monkey wrench into aesthetic and medical dermatology clinical research efforts. According to Dr. Dover, many aesthetic studies have been shut down, “and most companies are giving us little guidance,” he said. “As they figure things out, they ask us to do things over and over again. So, I hope that clinical research will improve because of COVID-19 in the long term, but in the short term, it’s been a bit of a nightmare.”
Dr. Geronemus added that, in order to fulfill criteria for most studies, clinicians are required to see patients in a certain number of days. “We’re out of protocol in many different studies, so we’re requesting that protocols be amended and that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] and the sponsors will consider opportunities to make those changes,” he said. “We’ll do as much as we can virtually, but if you’re studying an acne scar, you really need to see the patient [in person].”
Strict social distancing measures are also disrupting agreements that dermatologists may have had with trainees and fellows before the pandemic hit. “We’ve had to send letters and e-mails to people who were planning visits and preceptorships,” Dr. Dover said. “Even with our fellows, we’re going to have to figure out a way to practice so as not to complicate the issue in the room. The more people in the room, the more risk there is for transmitting disease. It’s really an issue.”
Dr. Tanzi limits everyone in the room during procedures. “We’re screening patients beforehand and telling them no family members, unless there’s a disability; no kids, unless it’s a kid coming in for acne treatment and they have to bring their parent; no drivers – they can wait outside,” she said.
Another ASLMS member asked the panelists if they plan to incorporate an informed consent form for COVID-19 risk into their practices, similar to the one developed by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “That’s a tough one,” Dr. Waibel said. “Before patients enter our practice, we take their temperature and ask them several COVID-related symptoms and contact questions – which they validate as true.”
Dr. Geronemus said that he will consider the idea. “The downside is logistical,” he said. “Patients sign so many forms already; they’re complaining that it takes so long to get into see me, and my hand is tired from signing so many forms.’”
Dr. Dover said that he and his colleagues are planning to use a COVID-19 risk consent form. “I’d err on the side of yes rather than on the side of no, because you’re better off overdoing it than underdoing it,” he said. “This is not the time for shortcuts.”
[email protected]

“People talk about reinventing the wheel,” Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., said during an hour-long webinar on May 5 sponsored by the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “In this case, we’re inventing the wheel; no one’s ever done this before – not in our lifetimes. The last pandemic was over 100 years ago, when there wasn’t aesthetic medicine.”
Dr. Dover joined a panel of four other experts from around the country to discuss how to reopen practices safely and effectively. Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Houston Cosmetic Dermatology & Laser Center, moderated the event.
In Florida, which reopened certain businesses on May 4, 2020, Jill S. Waibel, MD, plans to start at 25% capacity at Miami Dermatology and Laser Institute, and build from there. “We’re trying to take care of skin cancer patients first,” said Dr. Waibel, a dermatologist who owns the practice. “Then we’re going to start doing less aggressive cosmetic procedures like injectables, nonablative procedures. We’ll move into the more aggressive procedures as we ease back into it. We really want to see what’s going to happen 2-3 weeks down the line now that things are starting to open up.”
In Maryland, where state officials announced on May 6 that guidelines would be issued to allow for nonmedical procedures, Elizabeth L. Tanzi, MD, founder and director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, expects things to “look very different” once her practice reopens. “We are taking it very slowly,” she said. “Teledermatology for acne and other follow-ups is not something we did before, but it is certainly something that we’ll continue.”
The way she sees it, having the proper personal protective equipment is a key part of any reopening discussion. “I am not going near anyone’s face without an N95 mask that fits well, and without a face shield,” she said. “If you’re delegating these procedures to people that you don’t trust to be wearing the PPE correctly, then you shouldn’t be delegating them, because a key is the PPE. You have to assume that everyone has the virus at every time.”
In Ardmore, Pa., the Main Line Center for Laser Surgery remains closed because of current state regulations. When practice director Eric F. Bernstein, MD, gets the green light to reopen, patients will undergo a consultation by phone or videoconference and pay their bill before they set foot in the office. “We’re on the second floor, so patients can take a stairwell and avoid the elevator,” Dr. Bernstein said. “They’ll come in, not check in at the desk; go right to the room. There will be one treater and one assistant. If the patient doesn’t come in with a mask, we’ll supply one. It’s going to be a very different process. People are setting their hours longer because they’re going to be seeing fewer people. There will be no sitting in the waiting room.”
In the COVID-19 epicenter, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, director of the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, has been performing Mohs procedures and treating children with vascular malformations, but everything else is on hold. “Once the governor [Andrew Cuomo] lifts the stay-at-home restrictions, we’ll ease into things,” he said. “The issue of performing more invasive procedures – like ablative fractional resurfacing – is something that we are concerned about. I’m concerned about any laser that has environmental plume. For example, with our tattoo-removal procedures, I intend to treat every patient through a gel for the short term, and perhaps even for the long term. One can do that safely, and that eliminates the plume altogether.”
At the center, Dr. Geronemus added, “we do a fair amount of ablative fractional resurfacing and some fully ablative resurfacing. I intend to use large facial shields with these patients. We do use vacuum in each room as it stands right now, not only with electrosurgery, but we’ll be adding that to laser procedures as well. That will be helpful.”
In Chestnut Hill, Mass., Dr. Dover and his colleagues plan to practice what he termed “universal COVID precaution” by wearing a face mask, goggles, or a face shield, gloves, and protective clothing when necessary. “We are not going to do any ablative procedures, no procedures with plume, and we’re going to try and eliminate risk as much as we can,” he said. “We will have no waiting room; the patients will walk right to an exam room. They’ll be prescreened on the phone. The only thing they’ll have done when they first come in is to have their temperature taken, and they’ll be checked in and out with the doctor and the nurse in the room, and that’s it. There will be no other extraneous people to help to eliminate risk. We’re cutting our schedules down by 75% so that we can socially distance within our practice,” Dr. Dover said.
Dr. Dover served as lead author on “A path to resume aesthetic care: Executive summary of Project AesCert guidance supplement – practical considerations for aesthetic medicine professionals supporting clinic preparedness in response to the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak,” which was published online in Facial Plastic Surgery & Aesthetic Medicine (2002 May 5. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2020.0239). His coauthors included a facial plastic surgeon and three infectious disease experts.
Dr. Dover said, “We took the advice of these experts in infectious diseases, who said, ‘we don’t know all the right answers [to resuming aesthetic care]. We can mitigate risk, but we cannot eliminate risk. You have to treat every patient in your office as if they’re COVID-19 positive. If you do that, you’ll have a safe office. It’ll be the safest place in your world, safer than a grocery store, where you have no idea who you’re standing beside.’ ”
“The problem with this virus, compared to, say, SARS-CoV-1, is that these patients are positive and shedding virus 2-3 days before they get a fever,” he added. “With SARS-CoV-1, they had a fever first and then they shed virus. What I learned was, treat everybody with universal precautions.” The document includes tips for communicating with patient about expectations for office visits, clinic schedule management, cleaning procedures, PPE, treatment room set-up, and employee health screening and training.
During the webinar, an ASLMS member posed a question to the panelists about their comfort level in performing mechanical microneedling and radiofrequency (RF) microneedling procedures as aesthetic practices begin to reopen. “Generally, there’s no plume with microneedling with or without RF,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Depending upon the procedure that you’re doing, some of the microneedling procedures are very bloody; that may carry a risk unto itself. Other procedures where you’re using a thermal component have less bleeding. I’m more inclined to proceed with an RF with microneedling procedure and less inclined to proceed with a bloody, more aggressive microneedling procedure.”
Dr. Waibel emphasized the importance of disinfecting the microneedling device between uses. “If you have disposable needle cartridges, I think it’s a lot safer than if you have to clean [them],” she said. “We know that COVID-19 can live up to 3 hours, at least in a lab scenario, so you don’t want to transmit it from patient to patient. If someone has COVID-19 on their nose, and you microneedle over it, and that’s not completely disinfected, you could spread it to the next patient. We have really amped up our cleaning in between rooms. We have a whole crew that cleans every surface with [disinfectant wipes] and 90% alcohol.”
With reported shortages of N95 in many health care settings, some panelists said that they plan to reuse masks until the supply chain improves. Dr. Dover said that one option is to “use a mask, label it, number it, drop it in into a paper bag or into a [sealed plastic food container] upside down without touching the front of it,” he said. “If it sits for a week and you see patients 5 days a week, that mask will be dried out and highly effective a week later. That’s what we’re going to do until there is a big supply of them.”
The pandemic has also thrown a monkey wrench into aesthetic and medical dermatology clinical research efforts. According to Dr. Dover, many aesthetic studies have been shut down, “and most companies are giving us little guidance,” he said. “As they figure things out, they ask us to do things over and over again. So, I hope that clinical research will improve because of COVID-19 in the long term, but in the short term, it’s been a bit of a nightmare.”
Dr. Geronemus added that, in order to fulfill criteria for most studies, clinicians are required to see patients in a certain number of days. “We’re out of protocol in many different studies, so we’re requesting that protocols be amended and that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] and the sponsors will consider opportunities to make those changes,” he said. “We’ll do as much as we can virtually, but if you’re studying an acne scar, you really need to see the patient [in person].”
Strict social distancing measures are also disrupting agreements that dermatologists may have had with trainees and fellows before the pandemic hit. “We’ve had to send letters and e-mails to people who were planning visits and preceptorships,” Dr. Dover said. “Even with our fellows, we’re going to have to figure out a way to practice so as not to complicate the issue in the room. The more people in the room, the more risk there is for transmitting disease. It’s really an issue.”
Dr. Tanzi limits everyone in the room during procedures. “We’re screening patients beforehand and telling them no family members, unless there’s a disability; no kids, unless it’s a kid coming in for acne treatment and they have to bring their parent; no drivers – they can wait outside,” she said.
Another ASLMS member asked the panelists if they plan to incorporate an informed consent form for COVID-19 risk into their practices, similar to the one developed by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “That’s a tough one,” Dr. Waibel said. “Before patients enter our practice, we take their temperature and ask them several COVID-related symptoms and contact questions – which they validate as true.”
Dr. Geronemus said that he will consider the idea. “The downside is logistical,” he said. “Patients sign so many forms already; they’re complaining that it takes so long to get into see me, and my hand is tired from signing so many forms.’”
Dr. Dover said that he and his colleagues are planning to use a COVID-19 risk consent form. “I’d err on the side of yes rather than on the side of no, because you’re better off overdoing it than underdoing it,” he said. “This is not the time for shortcuts.”
[email protected]

“People talk about reinventing the wheel,” Jeffrey S. Dover, MD, codirector of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Mass., said during an hour-long webinar on May 5 sponsored by the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “In this case, we’re inventing the wheel; no one’s ever done this before – not in our lifetimes. The last pandemic was over 100 years ago, when there wasn’t aesthetic medicine.”
Dr. Dover joined a panel of four other experts from around the country to discuss how to reopen practices safely and effectively. Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Houston Cosmetic Dermatology & Laser Center, moderated the event.
In Florida, which reopened certain businesses on May 4, 2020, Jill S. Waibel, MD, plans to start at 25% capacity at Miami Dermatology and Laser Institute, and build from there. “We’re trying to take care of skin cancer patients first,” said Dr. Waibel, a dermatologist who owns the practice. “Then we’re going to start doing less aggressive cosmetic procedures like injectables, nonablative procedures. We’ll move into the more aggressive procedures as we ease back into it. We really want to see what’s going to happen 2-3 weeks down the line now that things are starting to open up.”
In Maryland, where state officials announced on May 6 that guidelines would be issued to allow for nonmedical procedures, Elizabeth L. Tanzi, MD, founder and director of Capital Laser & Skin Care in Chevy Chase, expects things to “look very different” once her practice reopens. “We are taking it very slowly,” she said. “Teledermatology for acne and other follow-ups is not something we did before, but it is certainly something that we’ll continue.”
The way she sees it, having the proper personal protective equipment is a key part of any reopening discussion. “I am not going near anyone’s face without an N95 mask that fits well, and without a face shield,” she said. “If you’re delegating these procedures to people that you don’t trust to be wearing the PPE correctly, then you shouldn’t be delegating them, because a key is the PPE. You have to assume that everyone has the virus at every time.”
In Ardmore, Pa., the Main Line Center for Laser Surgery remains closed because of current state regulations. When practice director Eric F. Bernstein, MD, gets the green light to reopen, patients will undergo a consultation by phone or videoconference and pay their bill before they set foot in the office. “We’re on the second floor, so patients can take a stairwell and avoid the elevator,” Dr. Bernstein said. “They’ll come in, not check in at the desk; go right to the room. There will be one treater and one assistant. If the patient doesn’t come in with a mask, we’ll supply one. It’s going to be a very different process. People are setting their hours longer because they’re going to be seeing fewer people. There will be no sitting in the waiting room.”
In the COVID-19 epicenter, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, director of the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, has been performing Mohs procedures and treating children with vascular malformations, but everything else is on hold. “Once the governor [Andrew Cuomo] lifts the stay-at-home restrictions, we’ll ease into things,” he said. “The issue of performing more invasive procedures – like ablative fractional resurfacing – is something that we are concerned about. I’m concerned about any laser that has environmental plume. For example, with our tattoo-removal procedures, I intend to treat every patient through a gel for the short term, and perhaps even for the long term. One can do that safely, and that eliminates the plume altogether.”
At the center, Dr. Geronemus added, “we do a fair amount of ablative fractional resurfacing and some fully ablative resurfacing. I intend to use large facial shields with these patients. We do use vacuum in each room as it stands right now, not only with electrosurgery, but we’ll be adding that to laser procedures as well. That will be helpful.”
In Chestnut Hill, Mass., Dr. Dover and his colleagues plan to practice what he termed “universal COVID precaution” by wearing a face mask, goggles, or a face shield, gloves, and protective clothing when necessary. “We are not going to do any ablative procedures, no procedures with plume, and we’re going to try and eliminate risk as much as we can,” he said. “We will have no waiting room; the patients will walk right to an exam room. They’ll be prescreened on the phone. The only thing they’ll have done when they first come in is to have their temperature taken, and they’ll be checked in and out with the doctor and the nurse in the room, and that’s it. There will be no other extraneous people to help to eliminate risk. We’re cutting our schedules down by 75% so that we can socially distance within our practice,” Dr. Dover said.
Dr. Dover served as lead author on “A path to resume aesthetic care: Executive summary of Project AesCert guidance supplement – practical considerations for aesthetic medicine professionals supporting clinic preparedness in response to the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak,” which was published online in Facial Plastic Surgery & Aesthetic Medicine (2002 May 5. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2020.0239). His coauthors included a facial plastic surgeon and three infectious disease experts.
Dr. Dover said, “We took the advice of these experts in infectious diseases, who said, ‘we don’t know all the right answers [to resuming aesthetic care]. We can mitigate risk, but we cannot eliminate risk. You have to treat every patient in your office as if they’re COVID-19 positive. If you do that, you’ll have a safe office. It’ll be the safest place in your world, safer than a grocery store, where you have no idea who you’re standing beside.’ ”
“The problem with this virus, compared to, say, SARS-CoV-1, is that these patients are positive and shedding virus 2-3 days before they get a fever,” he added. “With SARS-CoV-1, they had a fever first and then they shed virus. What I learned was, treat everybody with universal precautions.” The document includes tips for communicating with patient about expectations for office visits, clinic schedule management, cleaning procedures, PPE, treatment room set-up, and employee health screening and training.
During the webinar, an ASLMS member posed a question to the panelists about their comfort level in performing mechanical microneedling and radiofrequency (RF) microneedling procedures as aesthetic practices begin to reopen. “Generally, there’s no plume with microneedling with or without RF,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Depending upon the procedure that you’re doing, some of the microneedling procedures are very bloody; that may carry a risk unto itself. Other procedures where you’re using a thermal component have less bleeding. I’m more inclined to proceed with an RF with microneedling procedure and less inclined to proceed with a bloody, more aggressive microneedling procedure.”
Dr. Waibel emphasized the importance of disinfecting the microneedling device between uses. “If you have disposable needle cartridges, I think it’s a lot safer than if you have to clean [them],” she said. “We know that COVID-19 can live up to 3 hours, at least in a lab scenario, so you don’t want to transmit it from patient to patient. If someone has COVID-19 on their nose, and you microneedle over it, and that’s not completely disinfected, you could spread it to the next patient. We have really amped up our cleaning in between rooms. We have a whole crew that cleans every surface with [disinfectant wipes] and 90% alcohol.”
With reported shortages of N95 in many health care settings, some panelists said that they plan to reuse masks until the supply chain improves. Dr. Dover said that one option is to “use a mask, label it, number it, drop it in into a paper bag or into a [sealed plastic food container] upside down without touching the front of it,” he said. “If it sits for a week and you see patients 5 days a week, that mask will be dried out and highly effective a week later. That’s what we’re going to do until there is a big supply of them.”
The pandemic has also thrown a monkey wrench into aesthetic and medical dermatology clinical research efforts. According to Dr. Dover, many aesthetic studies have been shut down, “and most companies are giving us little guidance,” he said. “As they figure things out, they ask us to do things over and over again. So, I hope that clinical research will improve because of COVID-19 in the long term, but in the short term, it’s been a bit of a nightmare.”
Dr. Geronemus added that, in order to fulfill criteria for most studies, clinicians are required to see patients in a certain number of days. “We’re out of protocol in many different studies, so we’re requesting that protocols be amended and that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] and the sponsors will consider opportunities to make those changes,” he said. “We’ll do as much as we can virtually, but if you’re studying an acne scar, you really need to see the patient [in person].”
Strict social distancing measures are also disrupting agreements that dermatologists may have had with trainees and fellows before the pandemic hit. “We’ve had to send letters and e-mails to people who were planning visits and preceptorships,” Dr. Dover said. “Even with our fellows, we’re going to have to figure out a way to practice so as not to complicate the issue in the room. The more people in the room, the more risk there is for transmitting disease. It’s really an issue.”
Dr. Tanzi limits everyone in the room during procedures. “We’re screening patients beforehand and telling them no family members, unless there’s a disability; no kids, unless it’s a kid coming in for acne treatment and they have to bring their parent; no drivers – they can wait outside,” she said.
Another ASLMS member asked the panelists if they plan to incorporate an informed consent form for COVID-19 risk into their practices, similar to the one developed by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons. “That’s a tough one,” Dr. Waibel said. “Before patients enter our practice, we take their temperature and ask them several COVID-related symptoms and contact questions – which they validate as true.”
Dr. Geronemus said that he will consider the idea. “The downside is logistical,” he said. “Patients sign so many forms already; they’re complaining that it takes so long to get into see me, and my hand is tired from signing so many forms.’”
Dr. Dover said that he and his colleagues are planning to use a COVID-19 risk consent form. “I’d err on the side of yes rather than on the side of no, because you’re better off overdoing it than underdoing it,” he said. “This is not the time for shortcuts.”
[email protected]
The third surge: Are we prepared for the non-COVID crisis?
Over the last several weeks, hospitals and health systems have focused on the COVID-19 epidemic, preparing and expanding bed capacities for the surge of admissions both in intensive care and medical units. An indirect impact of this has been the reduction in outpatient staffing and resources, with the shifting of staff for inpatient care. Many areas seem to have passed the peak in the number of cases and are now seeing a plateau or downward trend in the admissions to acute care facilities.
During this period, there has been a noticeable downtrend in patients being evaluated in the ED, or admitted for decompensation of chronic conditions like heart failure, COPD and diabetes mellitus, or such acute conditions as stroke and MI. Studies from Italy and Spain, and closer to home from Atlanta and Boston, point to a significant decrease in numbers of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) admissions.1 Duke Health saw a decrease in stroke admissions in their hospitals by 34%.2
One could argue that these patients are in fact presenting with COVID-19 or similar symptoms as is evidenced by the studies linking the severity of SARS-Co-V2 infection to chronic conditions like diabetes mellitus and obesity.2 On the other hand, the message of social isolation and avoidance of nonurgent visits could lead to delays in care resulting in patients presenting sicker and in advanced stages.3 Also, this has not been limited to the adult population. For example, reports indicate that visits to WakeMed’s pediatric emergency rooms in Wake County, N.C., were down by 60%.2
We could well be seeing a calm before the storm. While it is anticipated that there may be a second surge of COVID-19 cases, health systems would do well to be prepared for the “third surge,” consisting of patients coming in with chronic medical conditions for which they have been, so far, avoiding follow-up and managing at home, and acute medical conditions with delayed diagnoses. The impact could likely be more in the subset of patients with limited access to health care, including medications and follow-up, resulting in a disproportionate burden on safety-net hospitals.
Compounding this issue would be the economic impact of the current crisis on health systems, their staffing, and resources. Several major organizations have already proposed budget cuts and reduction of the workforce, raising significant concerns about the future of health care workers who put their lives at risk during this pandemic.4 There is no guarantee that the federal funding provided by the stimulus packages will save jobs in the health care industry. This problem needs new leadership thinking, and every organization that puts employees over profits margins will have a long-term impact on communities.
Another area of concern is a shift in resources and workflow from ambulatory to inpatient settings for the COVID-19 pandemic, and the need for revamping the ambulatory services with reshifting the workforce. As COVID-19 cases plateau, the resurgence of non-COVID–related admissions will require additional help in inpatient settings. Prioritizing the ambulatory services based on financial benefits versus patient outcomes is also a major challenge to leadership.5
Lastly, the current health care crisis has led to significant stress, both emotional and physical, among frontline caregivers, increasing the risk of burnout.6 How leadership helps health care workers to cope with these stressors, and the resources they provide, is going to play a key role in long term retention of their talent, and will reflect on the organizational culture. Though it might seem trivial, posttraumatic stress disorder related to this is already obvious, and health care leadership needs to put every effort in providing the resources to help prevent burnout, in partnership with national organizations like the Society of Hospital Medicine and the American College of Physicians.
The expansion of telemedicine has provided a unique opportunity to address several of these issues while maintaining the nonpharmacologic interventions to fight the epidemic, and keeping the cost curve as low as possible.7 Extension of these services to all ambulatory service lines, including home health and therapy, is the next big step in the new health care era. Virtual check-ins by physicians, advance practice clinicians, and home care nurses could help alleviate the concerns regarding delays in care of patients with chronic conditions, and help identify those at risk. This would also be of help with staffing shortages, and possibly provide much needed support to frontline providers.
Dr. Prasad is currently medical director of care management and a hospitalist at Advocate Aurora Health in Milwaukee. He was previously quality and utilization officer and chief of the medical staff at Aurora Sinai Medical Center. Dr. Prasad is cochair of SHM’s IT Special Interest Group, sits on the HQPS Committee, and is president of SHM’s Wisconsin Chapter. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Wood S. TCTMD. 2020 Apr 2. “The mystery of the missing STEMIs during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
2. Stradling R. The News & Observer. 2020 Apr 21. “Fewer people are going to Triangle [N.C.] emergency rooms, and that could be a bad thing.”
3. Kasanagottu K. USA Today. 2020 Apr 15. “Don’t delay care for chronic illness over coronavirus. It’s bad for you and for hospitals.”
4. Snowbeck C. The Star Tribune. 2020 Apr 11. “Mayo Clinic cutting pay for more than 20,000 workers.”
5. LaPointe J. RevCycle Intelligence. 2020 Mar 31. “How much will the COVID-19 pandemic cost hospitals?”
6. Gavidia M. AJMC. 2020 Mar 31. “Sleep, physician burnout linked amid COVID-19 pandemic.”
7. Hollander JE and Carr BG. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 30;382(18):1679-81. “Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for COVID-19.”
Over the last several weeks, hospitals and health systems have focused on the COVID-19 epidemic, preparing and expanding bed capacities for the surge of admissions both in intensive care and medical units. An indirect impact of this has been the reduction in outpatient staffing and resources, with the shifting of staff for inpatient care. Many areas seem to have passed the peak in the number of cases and are now seeing a plateau or downward trend in the admissions to acute care facilities.
During this period, there has been a noticeable downtrend in patients being evaluated in the ED, or admitted for decompensation of chronic conditions like heart failure, COPD and diabetes mellitus, or such acute conditions as stroke and MI. Studies from Italy and Spain, and closer to home from Atlanta and Boston, point to a significant decrease in numbers of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) admissions.1 Duke Health saw a decrease in stroke admissions in their hospitals by 34%.2
One could argue that these patients are in fact presenting with COVID-19 or similar symptoms as is evidenced by the studies linking the severity of SARS-Co-V2 infection to chronic conditions like diabetes mellitus and obesity.2 On the other hand, the message of social isolation and avoidance of nonurgent visits could lead to delays in care resulting in patients presenting sicker and in advanced stages.3 Also, this has not been limited to the adult population. For example, reports indicate that visits to WakeMed’s pediatric emergency rooms in Wake County, N.C., were down by 60%.2
We could well be seeing a calm before the storm. While it is anticipated that there may be a second surge of COVID-19 cases, health systems would do well to be prepared for the “third surge,” consisting of patients coming in with chronic medical conditions for which they have been, so far, avoiding follow-up and managing at home, and acute medical conditions with delayed diagnoses. The impact could likely be more in the subset of patients with limited access to health care, including medications and follow-up, resulting in a disproportionate burden on safety-net hospitals.
Compounding this issue would be the economic impact of the current crisis on health systems, their staffing, and resources. Several major organizations have already proposed budget cuts and reduction of the workforce, raising significant concerns about the future of health care workers who put their lives at risk during this pandemic.4 There is no guarantee that the federal funding provided by the stimulus packages will save jobs in the health care industry. This problem needs new leadership thinking, and every organization that puts employees over profits margins will have a long-term impact on communities.
Another area of concern is a shift in resources and workflow from ambulatory to inpatient settings for the COVID-19 pandemic, and the need for revamping the ambulatory services with reshifting the workforce. As COVID-19 cases plateau, the resurgence of non-COVID–related admissions will require additional help in inpatient settings. Prioritizing the ambulatory services based on financial benefits versus patient outcomes is also a major challenge to leadership.5
Lastly, the current health care crisis has led to significant stress, both emotional and physical, among frontline caregivers, increasing the risk of burnout.6 How leadership helps health care workers to cope with these stressors, and the resources they provide, is going to play a key role in long term retention of their talent, and will reflect on the organizational culture. Though it might seem trivial, posttraumatic stress disorder related to this is already obvious, and health care leadership needs to put every effort in providing the resources to help prevent burnout, in partnership with national organizations like the Society of Hospital Medicine and the American College of Physicians.
The expansion of telemedicine has provided a unique opportunity to address several of these issues while maintaining the nonpharmacologic interventions to fight the epidemic, and keeping the cost curve as low as possible.7 Extension of these services to all ambulatory service lines, including home health and therapy, is the next big step in the new health care era. Virtual check-ins by physicians, advance practice clinicians, and home care nurses could help alleviate the concerns regarding delays in care of patients with chronic conditions, and help identify those at risk. This would also be of help with staffing shortages, and possibly provide much needed support to frontline providers.
Dr. Prasad is currently medical director of care management and a hospitalist at Advocate Aurora Health in Milwaukee. He was previously quality and utilization officer and chief of the medical staff at Aurora Sinai Medical Center. Dr. Prasad is cochair of SHM’s IT Special Interest Group, sits on the HQPS Committee, and is president of SHM’s Wisconsin Chapter. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Wood S. TCTMD. 2020 Apr 2. “The mystery of the missing STEMIs during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
2. Stradling R. The News & Observer. 2020 Apr 21. “Fewer people are going to Triangle [N.C.] emergency rooms, and that could be a bad thing.”
3. Kasanagottu K. USA Today. 2020 Apr 15. “Don’t delay care for chronic illness over coronavirus. It’s bad for you and for hospitals.”
4. Snowbeck C. The Star Tribune. 2020 Apr 11. “Mayo Clinic cutting pay for more than 20,000 workers.”
5. LaPointe J. RevCycle Intelligence. 2020 Mar 31. “How much will the COVID-19 pandemic cost hospitals?”
6. Gavidia M. AJMC. 2020 Mar 31. “Sleep, physician burnout linked amid COVID-19 pandemic.”
7. Hollander JE and Carr BG. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 30;382(18):1679-81. “Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for COVID-19.”
Over the last several weeks, hospitals and health systems have focused on the COVID-19 epidemic, preparing and expanding bed capacities for the surge of admissions both in intensive care and medical units. An indirect impact of this has been the reduction in outpatient staffing and resources, with the shifting of staff for inpatient care. Many areas seem to have passed the peak in the number of cases and are now seeing a plateau or downward trend in the admissions to acute care facilities.
During this period, there has been a noticeable downtrend in patients being evaluated in the ED, or admitted for decompensation of chronic conditions like heart failure, COPD and diabetes mellitus, or such acute conditions as stroke and MI. Studies from Italy and Spain, and closer to home from Atlanta and Boston, point to a significant decrease in numbers of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) admissions.1 Duke Health saw a decrease in stroke admissions in their hospitals by 34%.2
One could argue that these patients are in fact presenting with COVID-19 or similar symptoms as is evidenced by the studies linking the severity of SARS-Co-V2 infection to chronic conditions like diabetes mellitus and obesity.2 On the other hand, the message of social isolation and avoidance of nonurgent visits could lead to delays in care resulting in patients presenting sicker and in advanced stages.3 Also, this has not been limited to the adult population. For example, reports indicate that visits to WakeMed’s pediatric emergency rooms in Wake County, N.C., were down by 60%.2
We could well be seeing a calm before the storm. While it is anticipated that there may be a second surge of COVID-19 cases, health systems would do well to be prepared for the “third surge,” consisting of patients coming in with chronic medical conditions for which they have been, so far, avoiding follow-up and managing at home, and acute medical conditions with delayed diagnoses. The impact could likely be more in the subset of patients with limited access to health care, including medications and follow-up, resulting in a disproportionate burden on safety-net hospitals.
Compounding this issue would be the economic impact of the current crisis on health systems, their staffing, and resources. Several major organizations have already proposed budget cuts and reduction of the workforce, raising significant concerns about the future of health care workers who put their lives at risk during this pandemic.4 There is no guarantee that the federal funding provided by the stimulus packages will save jobs in the health care industry. This problem needs new leadership thinking, and every organization that puts employees over profits margins will have a long-term impact on communities.
Another area of concern is a shift in resources and workflow from ambulatory to inpatient settings for the COVID-19 pandemic, and the need for revamping the ambulatory services with reshifting the workforce. As COVID-19 cases plateau, the resurgence of non-COVID–related admissions will require additional help in inpatient settings. Prioritizing the ambulatory services based on financial benefits versus patient outcomes is also a major challenge to leadership.5
Lastly, the current health care crisis has led to significant stress, both emotional and physical, among frontline caregivers, increasing the risk of burnout.6 How leadership helps health care workers to cope with these stressors, and the resources they provide, is going to play a key role in long term retention of their talent, and will reflect on the organizational culture. Though it might seem trivial, posttraumatic stress disorder related to this is already obvious, and health care leadership needs to put every effort in providing the resources to help prevent burnout, in partnership with national organizations like the Society of Hospital Medicine and the American College of Physicians.
The expansion of telemedicine has provided a unique opportunity to address several of these issues while maintaining the nonpharmacologic interventions to fight the epidemic, and keeping the cost curve as low as possible.7 Extension of these services to all ambulatory service lines, including home health and therapy, is the next big step in the new health care era. Virtual check-ins by physicians, advance practice clinicians, and home care nurses could help alleviate the concerns regarding delays in care of patients with chronic conditions, and help identify those at risk. This would also be of help with staffing shortages, and possibly provide much needed support to frontline providers.
Dr. Prasad is currently medical director of care management and a hospitalist at Advocate Aurora Health in Milwaukee. He was previously quality and utilization officer and chief of the medical staff at Aurora Sinai Medical Center. Dr. Prasad is cochair of SHM’s IT Special Interest Group, sits on the HQPS Committee, and is president of SHM’s Wisconsin Chapter. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Wood S. TCTMD. 2020 Apr 2. “The mystery of the missing STEMIs during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
2. Stradling R. The News & Observer. 2020 Apr 21. “Fewer people are going to Triangle [N.C.] emergency rooms, and that could be a bad thing.”
3. Kasanagottu K. USA Today. 2020 Apr 15. “Don’t delay care for chronic illness over coronavirus. It’s bad for you and for hospitals.”
4. Snowbeck C. The Star Tribune. 2020 Apr 11. “Mayo Clinic cutting pay for more than 20,000 workers.”
5. LaPointe J. RevCycle Intelligence. 2020 Mar 31. “How much will the COVID-19 pandemic cost hospitals?”
6. Gavidia M. AJMC. 2020 Mar 31. “Sleep, physician burnout linked amid COVID-19 pandemic.”
7. Hollander JE and Carr BG. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 30;382(18):1679-81. “Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for COVID-19.”
COVID-19 experiences from the pediatrician front line
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the United States, several members of the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board shared how practices have been adapting to the pandemic, especially in terms of immunization.
Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a member of a four-pediatrician private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview that “we have been seeing only children under age 2 years for their well visits to keep them up to date on their vaccinations” as recommended by infectious disease departments at nearby hospitals such as Connecticut Children’s Medical Center. “We also are seeing the 4- and 5-year-old children for vaccinations.”
Dr. Kinsella explained that, in case parents don’t want to bring their children into the office, her staff is offering to give the vaccinations in the parking lot. But most families are coming into the office.
“We are only seeing well babies and take the parent and child back to a room as soon as they come in the office to avoid having patients sit in the waiting room. At this point, both parents and office staff are wearing masks; we are cleaning the rooms between patients,” Dr. Kinsella said.
“Most of our patients are coming in for their vaccines, so I don’t anticipate a lot of kids being behind. However, we will have a surge of all the physicals that need to be done prior to school in the fall. We have thought about opening up for the weekends for physicals to accommodate this. We also may need to start the day earlier and end later. I have heard some schools may be postponing the date the physicals are due.”
Because of a lack of full personal protective equipment, the practice has not been seeing sick visits in the office, but they have been doing a lot of telehealth visits. “We have been using doxy.me for that, which is free, incredibly easy to use, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)–compliant,” she said. “I am finding some visits, such as ADHD follow-ups and mental health follow-ups, very amenable to telehealth.”
“The hardest part – as I am sure is for most pediatricians – is the financial strain to a small business,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “We are down about 70% in revenue from this time last year. We have had to lay-off half our staff, and those who are working have much-reduced hours. We did not get the first round of funding for the paycheck protection program loan from the government and are waiting on the second round. We are trying to recoup some business by doing telehealth, but [the insurance companies] are only paying about 75%-80%. We also are charging for phone calls over 5 minutes. It will take a long time once we are up and running to recoup the losses.
“When this is all over, I’m hoping that we will be able to continue to incorporate telehealth into our schedules as I think it is convenient for families. I also am hoping that pediatricians continue to bill for phone calls as we have been giving out a lot of free care prior to this. I hope the American Academy of Pediatrics and all pediatricians work together to advocate for payment of these modalities,” she said.
J. Howard Smart, MD, who is chairman of the department of pediatrics at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said in an interview, “We have been bringing all of the infants and toddlers in for checkups and vaccines up to age 18 months.” These visits are scheduled in the morning, and sick patients are scheduled in the afternoon. “Well-child visits for older ages are being done by video, and the kindergarten and adolescent vaccines can be done by quick nurse visits. We will have some catching up to do once restrictions are lifted.”
“A fair amount of discussion went into these decisions. Is a video checkup better than no checkup? There is no clear-cut answer. Important things can be addressed by video: lifestyle, diet, exercise, family coping with stay-at-home orders, maintaining healthy childhood relationships, Internet use, ongoing education, among others. We know that we may miss things that can only be picked up by physical examination: hypertension, heart murmurs, abnormal growth, sexual development, abdominal masses, subtle strabismus. This is why we need to bring these children back for the physical exam later,” Dr. Smart emphasized.
“One possible negative result of doing the ‘well-child check’ by video would be if the parent assumed that the ‘checkup’ was done, never brought the child back for the exam, and something was missed that needed intervention. It will be important to get the message across that the return visit is needed. The American Academy of Pediatrics made this a part of their recommendations. It is going to be important for payers to realize that we need to do both visits – and to pay accordingly,” he concluded.
Francis E. Rushton Jr., MD, of Birmingham, Ala., described in an interview how the pediatricians in his former practice are looking for new ways to encourage shot administration in a timely manner during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as exploring ways to partner with home visitors in encouraging timely infant and toddler vaccinations.
At South Carolina’s Beaufort Pediatrics, Joseph Floyd, MD, described a multipronged initiative. The practice’s well-child visit reminder system is being reprogrammed to check for lapses in vaccinations rather than just well-child visit attendance. For the most part, Dr. Floyd stated parents appreciate the reminders and accept the need for vaccination: “In the absence of immunizations for coronavirus, families seem to be more cognizant of the value of the vaccines we do have.” Beaufort Pediatrics is also partnering with their local hospital on a publicity campaign stressing the importance of staying up to date with currently available and recommended vaccines.
Other child-service organizations are concerned as well. Dr. Francis E. Rushton Jr., as faculty with the Education Development Center’s Health Resources and Services Administration–funded home-visiting quality improvement collaborative (HV CoIIN 2.0), described efforts with home visitors in Alabama and other states. “Home visitors understand the importance of immunizations to the health and welfare of the infants they care for. They’re looking for opportunities to improve compliance with vaccination regimens.” Some of these home-visiting agencies are employing quality improvement technique to improve compliance. One idea they are working on is documenting annual training on updated vaccines for the home visitors. They are working on protocols for linking their clients with primary health care providers, referral relations, and relationship development with local pediatric offices. Motivational interviewing techniques for home visitors focused on immunizations are being considered. For families who are hesitant, home visitors are considering accompanying the family when they come to the doctor’s office while paying attention to COVID-19 social distancing policies at medical facilities.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the United States, several members of the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board shared how practices have been adapting to the pandemic, especially in terms of immunization.
Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a member of a four-pediatrician private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview that “we have been seeing only children under age 2 years for their well visits to keep them up to date on their vaccinations” as recommended by infectious disease departments at nearby hospitals such as Connecticut Children’s Medical Center. “We also are seeing the 4- and 5-year-old children for vaccinations.”
Dr. Kinsella explained that, in case parents don’t want to bring their children into the office, her staff is offering to give the vaccinations in the parking lot. But most families are coming into the office.
“We are only seeing well babies and take the parent and child back to a room as soon as they come in the office to avoid having patients sit in the waiting room. At this point, both parents and office staff are wearing masks; we are cleaning the rooms between patients,” Dr. Kinsella said.
“Most of our patients are coming in for their vaccines, so I don’t anticipate a lot of kids being behind. However, we will have a surge of all the physicals that need to be done prior to school in the fall. We have thought about opening up for the weekends for physicals to accommodate this. We also may need to start the day earlier and end later. I have heard some schools may be postponing the date the physicals are due.”
Because of a lack of full personal protective equipment, the practice has not been seeing sick visits in the office, but they have been doing a lot of telehealth visits. “We have been using doxy.me for that, which is free, incredibly easy to use, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)–compliant,” she said. “I am finding some visits, such as ADHD follow-ups and mental health follow-ups, very amenable to telehealth.”
“The hardest part – as I am sure is for most pediatricians – is the financial strain to a small business,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “We are down about 70% in revenue from this time last year. We have had to lay-off half our staff, and those who are working have much-reduced hours. We did not get the first round of funding for the paycheck protection program loan from the government and are waiting on the second round. We are trying to recoup some business by doing telehealth, but [the insurance companies] are only paying about 75%-80%. We also are charging for phone calls over 5 minutes. It will take a long time once we are up and running to recoup the losses.
“When this is all over, I’m hoping that we will be able to continue to incorporate telehealth into our schedules as I think it is convenient for families. I also am hoping that pediatricians continue to bill for phone calls as we have been giving out a lot of free care prior to this. I hope the American Academy of Pediatrics and all pediatricians work together to advocate for payment of these modalities,” she said.
J. Howard Smart, MD, who is chairman of the department of pediatrics at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said in an interview, “We have been bringing all of the infants and toddlers in for checkups and vaccines up to age 18 months.” These visits are scheduled in the morning, and sick patients are scheduled in the afternoon. “Well-child visits for older ages are being done by video, and the kindergarten and adolescent vaccines can be done by quick nurse visits. We will have some catching up to do once restrictions are lifted.”
“A fair amount of discussion went into these decisions. Is a video checkup better than no checkup? There is no clear-cut answer. Important things can be addressed by video: lifestyle, diet, exercise, family coping with stay-at-home orders, maintaining healthy childhood relationships, Internet use, ongoing education, among others. We know that we may miss things that can only be picked up by physical examination: hypertension, heart murmurs, abnormal growth, sexual development, abdominal masses, subtle strabismus. This is why we need to bring these children back for the physical exam later,” Dr. Smart emphasized.
“One possible negative result of doing the ‘well-child check’ by video would be if the parent assumed that the ‘checkup’ was done, never brought the child back for the exam, and something was missed that needed intervention. It will be important to get the message across that the return visit is needed. The American Academy of Pediatrics made this a part of their recommendations. It is going to be important for payers to realize that we need to do both visits – and to pay accordingly,” he concluded.
Francis E. Rushton Jr., MD, of Birmingham, Ala., described in an interview how the pediatricians in his former practice are looking for new ways to encourage shot administration in a timely manner during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as exploring ways to partner with home visitors in encouraging timely infant and toddler vaccinations.
At South Carolina’s Beaufort Pediatrics, Joseph Floyd, MD, described a multipronged initiative. The practice’s well-child visit reminder system is being reprogrammed to check for lapses in vaccinations rather than just well-child visit attendance. For the most part, Dr. Floyd stated parents appreciate the reminders and accept the need for vaccination: “In the absence of immunizations for coronavirus, families seem to be more cognizant of the value of the vaccines we do have.” Beaufort Pediatrics is also partnering with their local hospital on a publicity campaign stressing the importance of staying up to date with currently available and recommended vaccines.
Other child-service organizations are concerned as well. Dr. Francis E. Rushton Jr., as faculty with the Education Development Center’s Health Resources and Services Administration–funded home-visiting quality improvement collaborative (HV CoIIN 2.0), described efforts with home visitors in Alabama and other states. “Home visitors understand the importance of immunizations to the health and welfare of the infants they care for. They’re looking for opportunities to improve compliance with vaccination regimens.” Some of these home-visiting agencies are employing quality improvement technique to improve compliance. One idea they are working on is documenting annual training on updated vaccines for the home visitors. They are working on protocols for linking their clients with primary health care providers, referral relations, and relationship development with local pediatric offices. Motivational interviewing techniques for home visitors focused on immunizations are being considered. For families who are hesitant, home visitors are considering accompanying the family when they come to the doctor’s office while paying attention to COVID-19 social distancing policies at medical facilities.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the United States, several members of the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board shared how practices have been adapting to the pandemic, especially in terms of immunization.
Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a member of a four-pediatrician private practice in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview that “we have been seeing only children under age 2 years for their well visits to keep them up to date on their vaccinations” as recommended by infectious disease departments at nearby hospitals such as Connecticut Children’s Medical Center. “We also are seeing the 4- and 5-year-old children for vaccinations.”
Dr. Kinsella explained that, in case parents don’t want to bring their children into the office, her staff is offering to give the vaccinations in the parking lot. But most families are coming into the office.
“We are only seeing well babies and take the parent and child back to a room as soon as they come in the office to avoid having patients sit in the waiting room. At this point, both parents and office staff are wearing masks; we are cleaning the rooms between patients,” Dr. Kinsella said.
“Most of our patients are coming in for their vaccines, so I don’t anticipate a lot of kids being behind. However, we will have a surge of all the physicals that need to be done prior to school in the fall. We have thought about opening up for the weekends for physicals to accommodate this. We also may need to start the day earlier and end later. I have heard some schools may be postponing the date the physicals are due.”
Because of a lack of full personal protective equipment, the practice has not been seeing sick visits in the office, but they have been doing a lot of telehealth visits. “We have been using doxy.me for that, which is free, incredibly easy to use, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)–compliant,” she said. “I am finding some visits, such as ADHD follow-ups and mental health follow-ups, very amenable to telehealth.”
“The hardest part – as I am sure is for most pediatricians – is the financial strain to a small business,” Dr. Kinsella noted. “We are down about 70% in revenue from this time last year. We have had to lay-off half our staff, and those who are working have much-reduced hours. We did not get the first round of funding for the paycheck protection program loan from the government and are waiting on the second round. We are trying to recoup some business by doing telehealth, but [the insurance companies] are only paying about 75%-80%. We also are charging for phone calls over 5 minutes. It will take a long time once we are up and running to recoup the losses.
“When this is all over, I’m hoping that we will be able to continue to incorporate telehealth into our schedules as I think it is convenient for families. I also am hoping that pediatricians continue to bill for phone calls as we have been giving out a lot of free care prior to this. I hope the American Academy of Pediatrics and all pediatricians work together to advocate for payment of these modalities,” she said.
J. Howard Smart, MD, who is chairman of the department of pediatrics at Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group in San Diego, said in an interview, “We have been bringing all of the infants and toddlers in for checkups and vaccines up to age 18 months.” These visits are scheduled in the morning, and sick patients are scheduled in the afternoon. “Well-child visits for older ages are being done by video, and the kindergarten and adolescent vaccines can be done by quick nurse visits. We will have some catching up to do once restrictions are lifted.”
“A fair amount of discussion went into these decisions. Is a video checkup better than no checkup? There is no clear-cut answer. Important things can be addressed by video: lifestyle, diet, exercise, family coping with stay-at-home orders, maintaining healthy childhood relationships, Internet use, ongoing education, among others. We know that we may miss things that can only be picked up by physical examination: hypertension, heart murmurs, abnormal growth, sexual development, abdominal masses, subtle strabismus. This is why we need to bring these children back for the physical exam later,” Dr. Smart emphasized.
“One possible negative result of doing the ‘well-child check’ by video would be if the parent assumed that the ‘checkup’ was done, never brought the child back for the exam, and something was missed that needed intervention. It will be important to get the message across that the return visit is needed. The American Academy of Pediatrics made this a part of their recommendations. It is going to be important for payers to realize that we need to do both visits – and to pay accordingly,” he concluded.
Francis E. Rushton Jr., MD, of Birmingham, Ala., described in an interview how the pediatricians in his former practice are looking for new ways to encourage shot administration in a timely manner during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as exploring ways to partner with home visitors in encouraging timely infant and toddler vaccinations.
At South Carolina’s Beaufort Pediatrics, Joseph Floyd, MD, described a multipronged initiative. The practice’s well-child visit reminder system is being reprogrammed to check for lapses in vaccinations rather than just well-child visit attendance. For the most part, Dr. Floyd stated parents appreciate the reminders and accept the need for vaccination: “In the absence of immunizations for coronavirus, families seem to be more cognizant of the value of the vaccines we do have.” Beaufort Pediatrics is also partnering with their local hospital on a publicity campaign stressing the importance of staying up to date with currently available and recommended vaccines.
Other child-service organizations are concerned as well. Dr. Francis E. Rushton Jr., as faculty with the Education Development Center’s Health Resources and Services Administration–funded home-visiting quality improvement collaborative (HV CoIIN 2.0), described efforts with home visitors in Alabama and other states. “Home visitors understand the importance of immunizations to the health and welfare of the infants they care for. They’re looking for opportunities to improve compliance with vaccination regimens.” Some of these home-visiting agencies are employing quality improvement technique to improve compliance. One idea they are working on is documenting annual training on updated vaccines for the home visitors. They are working on protocols for linking their clients with primary health care providers, referral relations, and relationship development with local pediatric offices. Motivational interviewing techniques for home visitors focused on immunizations are being considered. For families who are hesitant, home visitors are considering accompanying the family when they come to the doctor’s office while paying attention to COVID-19 social distancing policies at medical facilities.
Inhaled nitric oxide explored for COVID-19 oxygenation
The successful treatment of a patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension who contracted COVID-19 with self-administered inhaled nitrous oxide from a tankless device at home has caught the imagination of researchers investigating treatments for other patients.
It is not clear whether the team was treating the COVID or “some manifestation of her pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” said Roham Zamanian, MD, a pulmonologist at Stanford Health in Palo Alto, California.
This is why a clinical trial is needed, he told Medscape Medical News.
“In this case, the COVID-19 respiratory infection led to a pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” he explained. And the 34-year-old woman, who is also a physician, had demonstrated a response to nitric oxide before contracting the COVID-19 virus.
Zamanian and his colleagues describe the case in a letter published online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care. It will be discussed at the upcoming American Thoracic Society 2020 International Conference.
COVID-19 was confirmed in the patient, who had stable vasoreactive idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, after she returned from a trip to Egypt. She did not want to travel the 350 miles from her home to the hospital for treatment, potentially infecting others, unless it was absolutely necessary.
“We had to make sure we were doing the right thing treating her at home, and we had to do it quickly,” Zamanian said. The patient was put on a remote routine – with vital monitoring in place – that included 6-minute walk tests twice daily and video conferencing. She also completed the EmPHasis-10 questionnaire, which is used to assess the status of patients with pulmonary hypertension.
The care team filed an Emergency Investigational New Drug application for the off-label at-home use of the tankless inhaled nitric oxide system (GENOSYL DS, VERO Biotech), which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The system has so far been approved only for the treatment of newborns with persistent pulmonary hypertension.
Off-label inhaled nitric oxide has never been used in an outpatient setting. “That’s where this case is unique,” Zamanian explained.
“This case was very specific. We knew she was vasoreactive, and she knew how to use the device,” he said. “And we know nitric oxide is a quick-acting medication when it works, showing results in minutes, if not seconds.”
Within 24 hours of approval, the tankless system arrived at her home.
The patient’s therapy consisted of nitric oxide at a dose of 20 ppm plus supplemental oxygen delivered by nasal cannula at a dose of 2 L/min for 12 to 14 hours a day. After symptomatic improvement, a stepwise reduction in nitric oxide was implemented from day 13 to 17, with the dose dropping to 10 ppm, 5 ppm, and then 0 ppm.
“We quickly knew she was responding and feeling better. Without the medication, she would very likely have needed to be hospitalized,” Zamanian said.
“The real novelty of this case is demonstrating use in an outpatient system,” he pointed out. “My perspective is that this particular case was very specific, in a person who had been formally evaluated and known to be responsive to this treatment.”
The team is now preparing to launch a clinical trial of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients without pulmonary hypertension, Zamanian reported.
Treating other patients
Nitric oxide could be useful for patients who come in with pulmonary hypertension, but “we have to test and figure that out. It could also be that patients with other underlying lung diseases could be helped with nitric oxide as well,” Zamanian said.
To treat on an outpatient basis, “we would need to make sure patients have established and reliable communications with an investigator or physician.” In addition, a protocol will have to be established that outlines how to administer the nitric oxide treatment and how to connect the nasal cannula.
“We envision patients being prescribed a certain dose and then working with either their healthcare provider or respiratory therapist to follow the standards we set,” he explained.
Although it is not a cure, nitric oxide could improve oxygenation for COIVD-19 patients in respiratory distress who have a component of abnormal pulmonary vascular function “largely driven” by ventilation perfusion – or V/Q – mismatch, he explained.
It is widely known that the gas, because it is a selective pulmonary vasodilator, can be used as rescue therapy in patients with refractory hypoxemia due to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
“There is justification for studying it in both pulmonary hypertension and nonpulmonary hypertension patients,” Zamanian added. “The idea is that there is a component of pulmonary function and constriction with COVID-19 that may be at play here, which is not typical of regular ARDS.”
Several trials underway
In early April, an investigation into the use of high-dose nitric oxide therapy for the treatment of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 who suffer lung complications was approved by the Therapeutic Products Directorate of Health Canada.
The NONTM – Inhaled Gaseous Nitric Oxide Antimicrobial Treatment of Difficult Bacterial and Viral Lung (COVID-19) Infections – trial will test the use of Thiolanox, a high-concentration, 5000 ppm nitric oxide canister (Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals) administered with the INODD delivery device (Novoteris), at Vancouver Coastal Health Authority facilities. The open-label safety study will look at whether nitric oxide can reduce the bacterial load in the lungs of adults and adolescents.
Last week, two randomized multicenter clinical trials — also focused on the potential therapeutic benefits of nitric oxide in patients with COVID-19 in a hospital setting — were launched by teams at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The NoCovid trial will look at nitric oxide for mild to moderate COVID-19 in 240 patients treated with a noninvasive CPAP system or a nonrebreathing mask system.
The NOSARSCOVID trial will look at the use of the INOmax (Mallinckrodt) nitric oxide inhalation system in 200 COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome.
“Data suggest that inhaled nitric oxide may have an important role in helping patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) to achieve normal oxygen levels in the blood,” Lorenzo Berra, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, said in a news release from Mallinckrodt announcing NOSARSCOVID.
“The trial we are conducting will help us gain critical insights into the potential effectiveness of INOmax in treating ARDS in critically ill COVID-19 patients,” Berra explains.
INOmax has already been used to treat COVID-19 patients in more than 170 hospitals in the United States, according to the news release.
Still, for COVID-19 treatment, “it’s still all hypothetical, as it hasn’t been proven,” said Alex Stenzler, founder and president of Novoteris.
We’ve demonstrated that we are able to get more oxygen to the blood and that there are some pro- and anti-inflammatory properties, “but there’s no randomized evidence, and the numbers are small,” he told Medscape Medical News.
And if there is a response or benefit, “we won’t know the reason for that benefit – if it’s anti-inflammatory, antiviral, or a vascular effect,” he pointed out.
“Nitric oxide is one of the most important signaling molecules in the human body. Our own body uses it to kill organisms and cells, heal wounds,” he explained, but “we’re a long way off from knowing” whether it can help ARDS patients.
COVID-19 Ventilation Clinical Practice Guidelines, issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Society of Critical Care, warn that “in patients with ARDS who are on mechanical ventilation, routine use of inhaled nitric oxide is not recommended,” as reported by Medscape.
Antimicrobial, antiviral properties
Previous studies of nitric oxide have shown that it has antiviral and antimicrobial properties.
Nitric oxide was shown to reduce H1N1 in vitro in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells in a 2013 study conducted by Chris Miller, PhD, from the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, and colleagues. Miller is currently involved in the NONTM trial.
This could be an added benefit of treatment. “Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral properties,” Zamanian said. “We need to investigate it further to see how it can help us avoid negative outcomes.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The successful treatment of a patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension who contracted COVID-19 with self-administered inhaled nitrous oxide from a tankless device at home has caught the imagination of researchers investigating treatments for other patients.
It is not clear whether the team was treating the COVID or “some manifestation of her pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” said Roham Zamanian, MD, a pulmonologist at Stanford Health in Palo Alto, California.
This is why a clinical trial is needed, he told Medscape Medical News.
“In this case, the COVID-19 respiratory infection led to a pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” he explained. And the 34-year-old woman, who is also a physician, had demonstrated a response to nitric oxide before contracting the COVID-19 virus.
Zamanian and his colleagues describe the case in a letter published online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care. It will be discussed at the upcoming American Thoracic Society 2020 International Conference.
COVID-19 was confirmed in the patient, who had stable vasoreactive idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, after she returned from a trip to Egypt. She did not want to travel the 350 miles from her home to the hospital for treatment, potentially infecting others, unless it was absolutely necessary.
“We had to make sure we were doing the right thing treating her at home, and we had to do it quickly,” Zamanian said. The patient was put on a remote routine – with vital monitoring in place – that included 6-minute walk tests twice daily and video conferencing. She also completed the EmPHasis-10 questionnaire, which is used to assess the status of patients with pulmonary hypertension.
The care team filed an Emergency Investigational New Drug application for the off-label at-home use of the tankless inhaled nitric oxide system (GENOSYL DS, VERO Biotech), which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The system has so far been approved only for the treatment of newborns with persistent pulmonary hypertension.
Off-label inhaled nitric oxide has never been used in an outpatient setting. “That’s where this case is unique,” Zamanian explained.
“This case was very specific. We knew she was vasoreactive, and she knew how to use the device,” he said. “And we know nitric oxide is a quick-acting medication when it works, showing results in minutes, if not seconds.”
Within 24 hours of approval, the tankless system arrived at her home.
The patient’s therapy consisted of nitric oxide at a dose of 20 ppm plus supplemental oxygen delivered by nasal cannula at a dose of 2 L/min for 12 to 14 hours a day. After symptomatic improvement, a stepwise reduction in nitric oxide was implemented from day 13 to 17, with the dose dropping to 10 ppm, 5 ppm, and then 0 ppm.
“We quickly knew she was responding and feeling better. Without the medication, she would very likely have needed to be hospitalized,” Zamanian said.
“The real novelty of this case is demonstrating use in an outpatient system,” he pointed out. “My perspective is that this particular case was very specific, in a person who had been formally evaluated and known to be responsive to this treatment.”
The team is now preparing to launch a clinical trial of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients without pulmonary hypertension, Zamanian reported.
Treating other patients
Nitric oxide could be useful for patients who come in with pulmonary hypertension, but “we have to test and figure that out. It could also be that patients with other underlying lung diseases could be helped with nitric oxide as well,” Zamanian said.
To treat on an outpatient basis, “we would need to make sure patients have established and reliable communications with an investigator or physician.” In addition, a protocol will have to be established that outlines how to administer the nitric oxide treatment and how to connect the nasal cannula.
“We envision patients being prescribed a certain dose and then working with either their healthcare provider or respiratory therapist to follow the standards we set,” he explained.
Although it is not a cure, nitric oxide could improve oxygenation for COIVD-19 patients in respiratory distress who have a component of abnormal pulmonary vascular function “largely driven” by ventilation perfusion – or V/Q – mismatch, he explained.
It is widely known that the gas, because it is a selective pulmonary vasodilator, can be used as rescue therapy in patients with refractory hypoxemia due to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
“There is justification for studying it in both pulmonary hypertension and nonpulmonary hypertension patients,” Zamanian added. “The idea is that there is a component of pulmonary function and constriction with COVID-19 that may be at play here, which is not typical of regular ARDS.”
Several trials underway
In early April, an investigation into the use of high-dose nitric oxide therapy for the treatment of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 who suffer lung complications was approved by the Therapeutic Products Directorate of Health Canada.
The NONTM – Inhaled Gaseous Nitric Oxide Antimicrobial Treatment of Difficult Bacterial and Viral Lung (COVID-19) Infections – trial will test the use of Thiolanox, a high-concentration, 5000 ppm nitric oxide canister (Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals) administered with the INODD delivery device (Novoteris), at Vancouver Coastal Health Authority facilities. The open-label safety study will look at whether nitric oxide can reduce the bacterial load in the lungs of adults and adolescents.
Last week, two randomized multicenter clinical trials — also focused on the potential therapeutic benefits of nitric oxide in patients with COVID-19 in a hospital setting — were launched by teams at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The NoCovid trial will look at nitric oxide for mild to moderate COVID-19 in 240 patients treated with a noninvasive CPAP system or a nonrebreathing mask system.
The NOSARSCOVID trial will look at the use of the INOmax (Mallinckrodt) nitric oxide inhalation system in 200 COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome.
“Data suggest that inhaled nitric oxide may have an important role in helping patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) to achieve normal oxygen levels in the blood,” Lorenzo Berra, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, said in a news release from Mallinckrodt announcing NOSARSCOVID.
“The trial we are conducting will help us gain critical insights into the potential effectiveness of INOmax in treating ARDS in critically ill COVID-19 patients,” Berra explains.
INOmax has already been used to treat COVID-19 patients in more than 170 hospitals in the United States, according to the news release.
Still, for COVID-19 treatment, “it’s still all hypothetical, as it hasn’t been proven,” said Alex Stenzler, founder and president of Novoteris.
We’ve demonstrated that we are able to get more oxygen to the blood and that there are some pro- and anti-inflammatory properties, “but there’s no randomized evidence, and the numbers are small,” he told Medscape Medical News.
And if there is a response or benefit, “we won’t know the reason for that benefit – if it’s anti-inflammatory, antiviral, or a vascular effect,” he pointed out.
“Nitric oxide is one of the most important signaling molecules in the human body. Our own body uses it to kill organisms and cells, heal wounds,” he explained, but “we’re a long way off from knowing” whether it can help ARDS patients.
COVID-19 Ventilation Clinical Practice Guidelines, issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Society of Critical Care, warn that “in patients with ARDS who are on mechanical ventilation, routine use of inhaled nitric oxide is not recommended,” as reported by Medscape.
Antimicrobial, antiviral properties
Previous studies of nitric oxide have shown that it has antiviral and antimicrobial properties.
Nitric oxide was shown to reduce H1N1 in vitro in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells in a 2013 study conducted by Chris Miller, PhD, from the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, and colleagues. Miller is currently involved in the NONTM trial.
This could be an added benefit of treatment. “Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral properties,” Zamanian said. “We need to investigate it further to see how it can help us avoid negative outcomes.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The successful treatment of a patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension who contracted COVID-19 with self-administered inhaled nitrous oxide from a tankless device at home has caught the imagination of researchers investigating treatments for other patients.
It is not clear whether the team was treating the COVID or “some manifestation of her pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” said Roham Zamanian, MD, a pulmonologist at Stanford Health in Palo Alto, California.
This is why a clinical trial is needed, he told Medscape Medical News.
“In this case, the COVID-19 respiratory infection led to a pulmonary hypertension exacerbation,” he explained. And the 34-year-old woman, who is also a physician, had demonstrated a response to nitric oxide before contracting the COVID-19 virus.
Zamanian and his colleagues describe the case in a letter published online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care. It will be discussed at the upcoming American Thoracic Society 2020 International Conference.
COVID-19 was confirmed in the patient, who had stable vasoreactive idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, after she returned from a trip to Egypt. She did not want to travel the 350 miles from her home to the hospital for treatment, potentially infecting others, unless it was absolutely necessary.
“We had to make sure we were doing the right thing treating her at home, and we had to do it quickly,” Zamanian said. The patient was put on a remote routine – with vital monitoring in place – that included 6-minute walk tests twice daily and video conferencing. She also completed the EmPHasis-10 questionnaire, which is used to assess the status of patients with pulmonary hypertension.
The care team filed an Emergency Investigational New Drug application for the off-label at-home use of the tankless inhaled nitric oxide system (GENOSYL DS, VERO Biotech), which was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The system has so far been approved only for the treatment of newborns with persistent pulmonary hypertension.
Off-label inhaled nitric oxide has never been used in an outpatient setting. “That’s where this case is unique,” Zamanian explained.
“This case was very specific. We knew she was vasoreactive, and she knew how to use the device,” he said. “And we know nitric oxide is a quick-acting medication when it works, showing results in minutes, if not seconds.”
Within 24 hours of approval, the tankless system arrived at her home.
The patient’s therapy consisted of nitric oxide at a dose of 20 ppm plus supplemental oxygen delivered by nasal cannula at a dose of 2 L/min for 12 to 14 hours a day. After symptomatic improvement, a stepwise reduction in nitric oxide was implemented from day 13 to 17, with the dose dropping to 10 ppm, 5 ppm, and then 0 ppm.
“We quickly knew she was responding and feeling better. Without the medication, she would very likely have needed to be hospitalized,” Zamanian said.
“The real novelty of this case is demonstrating use in an outpatient system,” he pointed out. “My perspective is that this particular case was very specific, in a person who had been formally evaluated and known to be responsive to this treatment.”
The team is now preparing to launch a clinical trial of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients without pulmonary hypertension, Zamanian reported.
Treating other patients
Nitric oxide could be useful for patients who come in with pulmonary hypertension, but “we have to test and figure that out. It could also be that patients with other underlying lung diseases could be helped with nitric oxide as well,” Zamanian said.
To treat on an outpatient basis, “we would need to make sure patients have established and reliable communications with an investigator or physician.” In addition, a protocol will have to be established that outlines how to administer the nitric oxide treatment and how to connect the nasal cannula.
“We envision patients being prescribed a certain dose and then working with either their healthcare provider or respiratory therapist to follow the standards we set,” he explained.
Although it is not a cure, nitric oxide could improve oxygenation for COIVD-19 patients in respiratory distress who have a component of abnormal pulmonary vascular function “largely driven” by ventilation perfusion – or V/Q – mismatch, he explained.
It is widely known that the gas, because it is a selective pulmonary vasodilator, can be used as rescue therapy in patients with refractory hypoxemia due to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
“There is justification for studying it in both pulmonary hypertension and nonpulmonary hypertension patients,” Zamanian added. “The idea is that there is a component of pulmonary function and constriction with COVID-19 that may be at play here, which is not typical of regular ARDS.”
Several trials underway
In early April, an investigation into the use of high-dose nitric oxide therapy for the treatment of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 who suffer lung complications was approved by the Therapeutic Products Directorate of Health Canada.
The NONTM – Inhaled Gaseous Nitric Oxide Antimicrobial Treatment of Difficult Bacterial and Viral Lung (COVID-19) Infections – trial will test the use of Thiolanox, a high-concentration, 5000 ppm nitric oxide canister (Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals) administered with the INODD delivery device (Novoteris), at Vancouver Coastal Health Authority facilities. The open-label safety study will look at whether nitric oxide can reduce the bacterial load in the lungs of adults and adolescents.
Last week, two randomized multicenter clinical trials — also focused on the potential therapeutic benefits of nitric oxide in patients with COVID-19 in a hospital setting — were launched by teams at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The NoCovid trial will look at nitric oxide for mild to moderate COVID-19 in 240 patients treated with a noninvasive CPAP system or a nonrebreathing mask system.
The NOSARSCOVID trial will look at the use of the INOmax (Mallinckrodt) nitric oxide inhalation system in 200 COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome.
“Data suggest that inhaled nitric oxide may have an important role in helping patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) to achieve normal oxygen levels in the blood,” Lorenzo Berra, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, said in a news release from Mallinckrodt announcing NOSARSCOVID.
“The trial we are conducting will help us gain critical insights into the potential effectiveness of INOmax in treating ARDS in critically ill COVID-19 patients,” Berra explains.
INOmax has already been used to treat COVID-19 patients in more than 170 hospitals in the United States, according to the news release.
Still, for COVID-19 treatment, “it’s still all hypothetical, as it hasn’t been proven,” said Alex Stenzler, founder and president of Novoteris.
We’ve demonstrated that we are able to get more oxygen to the blood and that there are some pro- and anti-inflammatory properties, “but there’s no randomized evidence, and the numbers are small,” he told Medscape Medical News.
And if there is a response or benefit, “we won’t know the reason for that benefit – if it’s anti-inflammatory, antiviral, or a vascular effect,” he pointed out.
“Nitric oxide is one of the most important signaling molecules in the human body. Our own body uses it to kill organisms and cells, heal wounds,” he explained, but “we’re a long way off from knowing” whether it can help ARDS patients.
COVID-19 Ventilation Clinical Practice Guidelines, issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine and the Society of Critical Care, warn that “in patients with ARDS who are on mechanical ventilation, routine use of inhaled nitric oxide is not recommended,” as reported by Medscape.
Antimicrobial, antiviral properties
Previous studies of nitric oxide have shown that it has antiviral and antimicrobial properties.
Nitric oxide was shown to reduce H1N1 in vitro in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells in a 2013 study conducted by Chris Miller, PhD, from the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, and colleagues. Miller is currently involved in the NONTM trial.
This could be an added benefit of treatment. “Nitric oxide has been shown to have antiviral properties,” Zamanian said. “We need to investigate it further to see how it can help us avoid negative outcomes.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advice on treating rheumatic diseases from a COVID-19 epicenter
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.




















