User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Hypertension medication adjustment less likely with polypill
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Repeat MRIs: Educating patients
In dementia workups, or even with more benign forms of cognitive impairment, a cranial imaging study is always needed. Like most neurologists I prefer MRIs, although I am willing to settle for a head CT when I have to.
These studies aren’t cheap, but as part of the workup, to exclude other causes, they are invaluable.
Generally one is all that is needed, although there are exceptions. But some patients and families seem to think MRIs need to be repeated often, anywhere from annually to every few months, “to make sure nothing has changed.”
You usually can’t talk them out of it either. There must be “some reason” why the patient keeps getting worse. Explaining that it’s a degenerative process that doesn’t show up on MRI gets me nowhere. They read something on the Internet about it, or heard a story about the uncle of a friend of a friend, or they focus on an incidental finding that must be the cause (like an 8-mm meningioma).
Generally I stand my ground. Obviously, there are times another imaging study is warranted, such as for a dramatic, acute neurological change, but in most cases all we’re really seeing is the sad progression of disease.
I’m not unsympathetic to these people. I feel bad that this has happened to them and that they’ve been given incorrect information. I take as much time as needed to explain the disease and why another study is not needed. It’s easy to write an order for the study to appease them, but it only leads to repeating it again in a few months. Every MRI I order costs time and money, and could take the same test away from a person who truly needs it.
Sometimes the patient and family will understand after we discuss it and the request is forgotten. Other times they leave my office upset, post a bad Yelp review about me refusing to treat their ailing parent, and change neurologists. Occasionally they’re able to get their internist to give in and order a repeat MRI, and when the repeat study hasn’t changed they call me wanting to know when the next one should be done.
Throwing more money at a problem, especially when you already know what the answer will be, is never a good idea. Not now, not ever ... in medicine or anything else.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
In dementia workups, or even with more benign forms of cognitive impairment, a cranial imaging study is always needed. Like most neurologists I prefer MRIs, although I am willing to settle for a head CT when I have to.
These studies aren’t cheap, but as part of the workup, to exclude other causes, they are invaluable.
Generally one is all that is needed, although there are exceptions. But some patients and families seem to think MRIs need to be repeated often, anywhere from annually to every few months, “to make sure nothing has changed.”
You usually can’t talk them out of it either. There must be “some reason” why the patient keeps getting worse. Explaining that it’s a degenerative process that doesn’t show up on MRI gets me nowhere. They read something on the Internet about it, or heard a story about the uncle of a friend of a friend, or they focus on an incidental finding that must be the cause (like an 8-mm meningioma).
Generally I stand my ground. Obviously, there are times another imaging study is warranted, such as for a dramatic, acute neurological change, but in most cases all we’re really seeing is the sad progression of disease.
I’m not unsympathetic to these people. I feel bad that this has happened to them and that they’ve been given incorrect information. I take as much time as needed to explain the disease and why another study is not needed. It’s easy to write an order for the study to appease them, but it only leads to repeating it again in a few months. Every MRI I order costs time and money, and could take the same test away from a person who truly needs it.
Sometimes the patient and family will understand after we discuss it and the request is forgotten. Other times they leave my office upset, post a bad Yelp review about me refusing to treat their ailing parent, and change neurologists. Occasionally they’re able to get their internist to give in and order a repeat MRI, and when the repeat study hasn’t changed they call me wanting to know when the next one should be done.
Throwing more money at a problem, especially when you already know what the answer will be, is never a good idea. Not now, not ever ... in medicine or anything else.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
In dementia workups, or even with more benign forms of cognitive impairment, a cranial imaging study is always needed. Like most neurologists I prefer MRIs, although I am willing to settle for a head CT when I have to.
These studies aren’t cheap, but as part of the workup, to exclude other causes, they are invaluable.
Generally one is all that is needed, although there are exceptions. But some patients and families seem to think MRIs need to be repeated often, anywhere from annually to every few months, “to make sure nothing has changed.”
You usually can’t talk them out of it either. There must be “some reason” why the patient keeps getting worse. Explaining that it’s a degenerative process that doesn’t show up on MRI gets me nowhere. They read something on the Internet about it, or heard a story about the uncle of a friend of a friend, or they focus on an incidental finding that must be the cause (like an 8-mm meningioma).
Generally I stand my ground. Obviously, there are times another imaging study is warranted, such as for a dramatic, acute neurological change, but in most cases all we’re really seeing is the sad progression of disease.
I’m not unsympathetic to these people. I feel bad that this has happened to them and that they’ve been given incorrect information. I take as much time as needed to explain the disease and why another study is not needed. It’s easy to write an order for the study to appease them, but it only leads to repeating it again in a few months. Every MRI I order costs time and money, and could take the same test away from a person who truly needs it.
Sometimes the patient and family will understand after we discuss it and the request is forgotten. Other times they leave my office upset, post a bad Yelp review about me refusing to treat their ailing parent, and change neurologists. Occasionally they’re able to get their internist to give in and order a repeat MRI, and when the repeat study hasn’t changed they call me wanting to know when the next one should be done.
Throwing more money at a problem, especially when you already know what the answer will be, is never a good idea. Not now, not ever ... in medicine or anything else.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Combination therapy quells COVID-19 cytokine storm
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone plus tocilizumab (Actemra, Genentech) as needed was associated with faster respiratory recovery, a lower likelihood of mechanical ventilation, and fewer in-hospital deaths compared with supportive care alone among people with COVID-19 experiencing a hyperinflammatory state known as a cytokine storm.
Compared with historic controls, participants in the treatment group were 79% more likely to achieve at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status, for example.
“COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome [CSS] is an important complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection in up to 25% of the patients,” lead author Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Furthermore, CSS often leads to death in this population, said Dr. Ramiro, a consultant rheumatologist and senior researcher at Leiden University Medical Center and Zuyderland Medical Center in Heerlen, the Netherlands.
Results of the COVID High-Intensity Immunosuppression in Cytokine Storm Syndrome (CHIC) study were published online July 20 in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Contrary to guidance?
The World Health Organization (WHO) cautions against administering corticosteroids to some critically ill patients with COVID-19. “WHO recommends against the routine use of systemic corticosteroids for treatment of viral pneumonia,” according to an interim guidance document on the clinical management of COVID-19 published May 27.
Dr. Ramiro and colleagues make a distinction, however, noting “the risk profile of such a short course of glucocorticoid for treatment of CSS needs to be separated from preexisting chronic use of glucocorticoid for conditions like rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.”
Participants in the current study tolerated immunosuppressive therapy well without evidence of impaired viral clearance or bacterial superinfection, they added.
Other experts disagree with recent recommendations to use corticosteroids to treat a hyperimmune response or suspected adrenal insufficiency in the setting of refractory shock in patients with COVID-19.
Information about immunosuppressive therapy and CSS linked to COVID-19 remains anecdotal, however, Dr. Ramiro and colleagues noted.
The researchers assessed outcomes of 86 individuals with COVID-19-associated CSS treated with high-dose methylprednisolone plus/minus tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody. They compared them with another 86 patients with COVID-19 treated with supportive care before initiation of the combination therapy protocol.
Participants with CSS had an oxygen saturation of 94% or lower at rest or tachypnea exceeding 30 breaths per minute.
They also had at least two of the following: C-reactive protein > 100 mg/L; serum ferritin > 900 mcg/L at one occasion or a twofold increase at admission within 48 hours; or D-dimer levels > 1,500 mcg/L.
The treatment group received methylprednisolone 250 mg intravenously on day 1, followed by 80 mg intravenously on days 2-5. Investigators permitted a 2-day extension if indicated.
Those who failed to clinically improve or experienced respiratory decline could also receive intravenous tocilizumab on day 2 or after. The agent was dosed at 8 mg/kg body weight during a single infusion from day 2-5 up to a maximum of 800 mg.
In all, 37 participants received tocilizumab, including two participants who received a second dose 5 days after initial treatment.
Except for one patient in the treatment group, all participants also received antibiotic treatment and nearly 80% received chloroquine.
Mechanical ventilation and mortality
The primary outcome of at least a two-stage improvement in respiratory status on a WHO scale associated with treatment yielded a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.79. The treatment group achieved this improvement a median 7 days earlier than controls.
Mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory deterioration was 71% less likely for the treatment group versus controls (HR, 0.29).
The treatment group were also 65% less likely to die in hospital (HR, 0.35) than were controls.
The researchers also reported a significant difference in the number of deaths at day 14 in the treatment vs. control group, at 10 vs. 33 patients (P < .0001).
Glucocorticoid sufficient for many
In a sensitivity analysis excluding patients who received tocilizumab, the benefits of treatment remained statistically significant, “suggesting that a clinically relevant treatment effect can be reached by high-dose glucocorticoids alone,” the researchers noted.
This finding suggests “that the timely administration of high-dose glucocorticoids alone may provide significant benefit in more than half of the patients, and that tocilizumab is only needed in those cases that had insufficient clinical improvement on methylprednisolone alone,” they added.
“This is an important finding given the limited availability of tocilizumab in many countries and tocilizumab’s high costs.”
Complications were fairly balanced between groups. For example, bacterial infections during hospitalization were diagnosed in eight patients in the treatment group versus seven in the control group.
In addition, cardiac arrhythmias occurred in both groups, but slightly less frequently in the treatment group (P = .265), and there was a trend towards more pulmonary embolisms in the treatment group (P = .059).
Strengths and limitations
“A treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids is a convenient choice since glucocorticoids are safe, widely available, and inexpensive,” the researchers noted. “Longer follow-up, however, is needed to give final resolution about the safety and efficacy of the strategy.”
A strength of the study was “meticulous selection of those patients more likely to benefit from immunosuppressive treatment, namely patients with a CSS,” she added.
The study featured a prospective, observational design for the treatment group and retrospective analysis of the historic controls. “Methodologically, the main limitation of the study is not being a randomized controlled trial,” she noted.
“Ethically it has shown to be very rewarding to consciously decide against a randomized control trial, as we are talking about a disease that if only treated with supportive care can lead to mortality up to almost 50% from COVID-19-associated CSS,” Dr. Ramiro said.
Going forward, Dr. Ramiro plans to continue monitoring patients who experienced CSS to assess their outcome post-COVID-19 infection. “We want to focus on cardiorespiratory, functional, and quality of life outcomes,” she said. “We will also compare the outcomes between patients that have received immunosuppression with those that haven’t.”
‘Quite interesting’ results
“We desperately need better evidence to guide the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19,” Nihar R. Desai, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the study, said in an interview.
“These data from the Netherlands are quite interesting and provide another signal to support the use of corticosteroids, with tocilizumab if needed, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to improve outcomes,” added Dr. Desai, associate professor of medicine and investigator at the Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
“While these data are not randomized and have a relatively small sample size, we had recently seen the results of the RECOVERY trial, a UK-based randomized trial demonstrating the benefit of steroids in COVID-19,” he said.
“Taken together, these studies seem to suggest that there is a benefit with steroid therapy.” Further validation of these results is warranted, he added.
“While not a randomized clinical trial, and thus susceptible to unmeasured bias, the study adds to mounting evidence that supports targeting the excessive inflammation found in some patients with COVID-19,” Jared Radbel, MD, a pulmonologist, critical care specialist, and assistant professor of medicine at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in an interview.
Dr. Radbel added that he is part of a multicenter group that has submitted a manuscript examining outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab.
Dr. Ramiro, Dr. Desai, and Dr. Radbel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
One-third of outpatients with COVID-19 are unwell weeks later
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to survey results in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD, for the CDC-COVID-19 Response Team, and colleagues conducted a multistate telephone survey of symptomatic adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The researchers found that 35% had not returned to their usual state of wellness when they were interviewed 2-3 weeks after testing.
Among the 270 of 274 people interviewed for whom there were data on return to health, 175 (65%) reported that they had returned to baseline health an average of 7 days from the date of testing.
Among the 274 symptomatic outpatients, the median number of symptoms was seven. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms.
Prolonged illness is well described in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19, especially among the older adult population, but little is known about other groups.
The proportion who had not returned to health differed by age: 26% of interviewees aged 18-34 years, 32% of those aged 35-49 years, and 47% of those at least 50 years old reported not having returned to their usual health (P = .010) within 14-21 days after receiving positive test results.
Among respondents aged 18-34 years who had no chronic medical condition, 19% (9 of 48) reported not having returned to their usual state of health during that time.
Public health messaging targeting younger adults, a group who might not be expected to be sick for weeks with mild disease, is particularly important, the authors wrote.
Kyle Annen, DO, medical director of transfusion services and patient blood management at Children’s Hospital Colorado and assistant professor of pathology at the University of Colorado, Denver, said in an interview that an important message is that delayed recovery (symptoms of fatigue, cough, and shortness of breath) was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization.
“This should impact the perception of this being a mild illness in the young adult population and encourage them to comply with recommendations of social distancing, masking, and hand washing,” she said.
Recovery time of more than 2 weeks will affect work and school performance, especially prolonged fatigue, she noted. This was one of the prominent symptoms that were reported to be slow to dissipate.
“I think the most interesting point in this study is that of underlying conditions; psychiatric conditions were significantly correlated with prolonged recovery. I don’t think that many people think of depression and anxiety as an underlying medical condition in regards to COVID-19 risk. This could potentially have an impact, as depression and anxiety rates will likely increase as COVID-19 continues,” she said.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, said in an interview that it is “important to realize that the spectrum of disease with COVID is wide, including mild disease, severe disease, and prolonged disease. This report helps us understand some of the risk factors for those with prolonged symptoms and may allow us to refine even more clearly how we prioritize treatment and vaccine administration, once available.
“It also highlights the challenge of dealing with this virus. Not only do the symptoms vary widely, but so do the incubation period, the duration of symptoms, and the residual symptoms that sometimes occur. Clearly, there is much we still need to understand about this virus,” he said.
The interviews were conducted from April 15 to June 25 with a random sample of adults at least 18 years old who had received a first positive test result for SARS-CoV-2 at an outpatient visit at one of 14 US academic healthcare systems in 13 states.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Small NY study: Mother-baby transmission of COVID-19 not seen
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
according to a study out of New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
“It is suggested in the cumulative data that the virus does not confer additional risk to the fetus during labor or during the early postnatal period in both preterm and term infants,” concluded Jeffrey Perlman, MB ChB, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
But other experts suggest substantial gaps remain in our understanding of maternal transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
“Much more needs to be known,” Munish Gupta, MD, and colleagues from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an accompanying editorial.
The prospective study is the first to describe a cohort of U.S. COVID-19–related deliveries, with the prior neonatal impact of COVID-19 “almost exclusively” reported from China, noted the authors. They included a cohort of 326 women who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 on admission to labor and delivery at New York-Presbyterian Hospital between March 22 and April 15th, 2020. Of the 31 (10%) mothers who tested positive, 15 (48%) were asymptomatic and 16 (52%) were symptomatic.
Two babies were born prematurely (one by Cesarean) and were isolated in negative pressure rooms with continuous positive airway pressure. Both were moved out of isolation after two negative test results and “have exhibited an unremarkable clinical course,” the authors reported.
The other 29 term babies were cared for in their mothers’ rooms, with breastfeeding allowed, if desired. These babies and their mothers were discharged from the hospital between 24 and 48 hours after delivery.
“Visitor restriction for mothers who were positive for COVID-19 included 14 days of no visitation from the start of symptoms,” noted the team.
They added “since the prepublication release there have been a total of 47 mothers positive for COVID-19, resulting in 47 infants; 4 have been admitted to neonatal intensive care. In addition, 32 other infants have been tested for a variety of indications within the unit. All infants test results have been negative.”
The brief report outlined the institution’s checklist for delivery preparedness in either the operating room or labor delivery room, including personal protective equipment, resuscitation, transportation to the neonatal intensive care unit, and early postresuscitation care. “Suspected or confirmed COVID-19 alone in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy is not an indication for the resuscitation team or the neonatal fellow,” they noted, adding delivery room preparation and management should include contact precautions. “With scrupulous attention to infectious precautions, horizontal viral transmission should be minimized,” they advised.
Dr. Perlman and associates emphasized that rapid turnaround SARSCoV-2 testing is “crucial to minimize the likelihood of a provider becoming infected and/or infecting the infant.”
Although the findings are “clearly reassuring,” Dr. Gupta and colleagues have reservations. “To what extent does this report address concerns for infection risk with a rooming-in approach to care?” they asked in their accompanying editorial. “The answer is likely some, but not much.”
Many questions remain, they said, including: “What precautions were used to minimize infection risk during the postbirth hospital course? What was the approach to skin-to-skin care and direct mother-newborn contact? Were restrictions placed on family members? Were changes made to routine interventions such as hearing screens or circumcisions? What practices were in place around environmental cleaning? Most important, how did the newborns do after discharge?”
The current uncertainty around neonatal COVID-19 infection risk has led to “disparate” variations in care recommendations, they pointed out. Whereas China’s consensus guidelines recommend a 14-day separation of COVID-19–positive mothers from their healthy infants, a practice supported by the American Academy of Pediatrics “when possible,” the Italian Society of Neonatology, the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, and the Canadian Paediatric Society advise “rooming-in and breastfeeding with appropriate infection prevention measures.”
Dr. Gupta and colleagues pointed to the following as at least three “critical and time-sensitive needs for research around neonatal care and outcomes related to COVID-19”:
- Studies need to have much larger sample sizes and include diverse populations. This will allow for reliable measurement of outcomes.
- Descriptions of care practices must be in detail, especially about infection prevention; these should be presented in a way to compare the efficacy of different approaches.
- There needs to be follow-up information on outcomes of both the mother and the neonate after the birth hospitalization.
Asked to comment, Lillian Beard, MD, of George Washington University in Washington welcomed the data as “good news.”
“Although small, the study was done during a 3-week peak period at the hottest spot of the pandemic in the United States during that period. It illustrates how delivery room preparedness, adequate personal protective equipment, and carefully planned infection control precautions can positively impact outcomes even during a seemingly impossible period,” she said.
“Although there are many uncertainties about maternal COVID-19 transmission and neonatal infection risks ... in my opinion, during the after birth hospitalization, the inherent benefits of rooming in for breast feeding and the opportunities for the demonstration and teaching of infection prevention practices for the family home, far outweigh the risks of disease transmission,” said Dr. Beard, who was not involved with the study.
The study and the commentary emphasize the likely low risk of vertical transmission of the virus, with horizontal transmission being the greater risk. However, cases of transplacental transmission have been reported, and the lead investigator of one recent placental study cautions against complacency.
“Neonates can get infected in both ways. The majority of cases seem to be horizontal, but those who have been infected or highly suspected to be vertically infected are not a small percentage either,” said Daniele de Luca, MD, PhD, president-elect of the European Society for Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) and a neonatologist at Antoine Béclère Hospital in Clamart, France.
“Perlman’s data are interesting and consistent with other reports around the world. However, two things must be remembered,” he said in an interview. “First, newborn infants are at relatively low risk from SARS-CoV-2 infections, but this is very far from zero risk. Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections do exist and have been described around the world. While they have a mild course in the majority of cases, neonatologists should not forget them and should be prepared to offer the best care to these babies.”
“Second, how this can be balanced with the need to promote breastfeeding and avoid overtreatment or separation from the mother is a question far from being answered. Gupta et al. in their commentary are right in saying that we have more questions than answers. While waiting for the results of large initiatives (such as the ESPNIC EPICENTRE Registry that they cite) to answer these open points, the best we can do is to provide a personalised case by case approach, transparent information to parents, and an open counselling informing clinical decisions.”
The study received no external funding. Dr. Perlman and associates had no financial disclosures. Dr. Gupta and colleagues had no relevant financial disclosures. Neither Dr. Beard nor Dr. de Luca had any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Perlman J et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(2):e20201567.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Men occupy most leadership roles in medicine
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Since the early 2000s, approximately half of medical students in the United States – and in many years, more than half – have been women, but according to an update provided at the virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
In pediatrics, a specialty in which approximately 70% of physicians are now women, there has been progress, but still less than 30% of pediatric department chairs are female, said Vincent Chiang, MD, chief medical officer of Boston Children’s Hospital, during a presentation at the virtual meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Citing published data and a survey he personally conducted of the top children’s hospitals identified by the U.S. News and World Report, Dr. Chiang said a minority of division chiefs, chief medical officers, chief financial officers, and other leaders are female. At his institution, only 2 of 16 division chiefs are female.
“No matter how you slice it, women are underrepresented in leadership positions,” he noted.
The problem is certainly not confined to medicine. Dr. Chiang cited data showing that women and men have reached “near parity” in workforce participation in the United States even though the 20% earnings gap has changed little over time.
According to 2020 data from the World Economic Forum, the United States ranked 51 for the gender gap calculated on the basis of economic, political, educational, and health attainment. Even if this places the United States in the top third of the rankings, it is far behind Iceland and the Scandinavian countries that lead the list.
Efforts to reduce structural biases are part of the fix, but Dr. Chiang cautioned that fundamental changes might never occur if the plan is to wait for an approach based on meritocracy. He said that existing structural biases are “slanted away from women,” who are not necessarily granted the opportunities that are readily available to men.
“A meritocracy only works if the initial playing field was level. Otherwise, it just perpetuates the inequalities,” he said.
The problem is not a shortage of women with the skills to lead. In a study by Zenger/Folkman, a consulting company that works on leadership skill development, women performed better than men in 16 of 18 leadership categories, according to Dr. Chiang.
“There is certainly no shortage of capable women,” he noted.
Of the many issues, Dr. Chiang highlighted two. The first is the challenge of placing women on leadership pathways. This is likely to require proactive strategies, such as fast-track advancement programs that guide female candidates toward leadership roles.
The second is more nuanced. According to Dr. Chiang, women who want to assume a leadership role should think more actively about how and who is making decisions at their institution so they can position themselves appropriately. This is nuanced because “there is a certain amount of gamesmanship,” he said. The rise to leadership “has never been a pure meritocracy.”
Importantly, many of the key decisions in any institution involve money, according to Dr. Chiang. As a result, he advised those seeking leadership roles to join audit committees or otherwise take on responsibility for profit-and-loss management. Even in a nonprofit institution, “you need to make the numbers work,” he said, citing the common catchphrase: “No margin, no mission.”
However, Dr. Chiang acknowledged the many obstacles that prevent women from working their way into positions of leadership. For example, networking is important, but women are not necessarily attracted or invited to some of the social engagements, such as golf outings, where strong relationships are created.
In a survey of 100,000 people working at Fortune 500 companies, “82% of women say they feel excluded at work and much of that comes from that informal networking,” Dr. Chiang said. “Whereas 92% of men think they are not excluding women in their daily work.”
There is no single solution, but Dr. Chiang believes that concrete structural changes are needed. Female doctors remain grossly underrepresented in leadership roles even as they now represent more than half of the workforce for many specialties. Based on the need for proactive approaches outlined by Dr. Chiang, it appears unlikely that gender inequality will ever resolve itself.
Lisa S. Rotenstein, MD, who has written on fixing the gender imbalance in health care, including for the Harvard Business Review, said she agreed during an interview that structural changes are critical.
“In order to address current disparities, leaders should be thinking about how to remove both the formal and informal obstacles that prevent women and minorities from getting into the rooms where these decisions are being made,” said Dr. Rotenstein, who is an instructor in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School in Boston.
“This will need to involve sponsorship that gets women invited to the right committees or in positions with responsibility for profit-and-loss management,” she added.
Dr. Rotenstein spoke about improving “access to the pipeline” that leads to leadership roles. The ways in which women are excluded from opportunities is often subtle and difficult to penetrate without fundamental changes, she explained.
“Institutions need to understand the processes that lead to leadership roles and make the changes that allow women and minorities to participate,” she said. It is not enough to recognize the problem, according to Dr. Rotenstein.
Like Dr. Chiang, she noted that changes are needed in the methods that move underrepresented groups into leadership roles.
Dr. Chiang reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
FROM PHM20
Migraine headache pearls
A 25-year-old woman presents to discuss treatment of her headaches. They occur two or three times a month and last for 4-6 hours. The headaches are disabling, have a pounding quality behind the patient’s right eye, and worsen with exercise. The patient’s neurologic exam is normal.
She has tried oral sumatriptan and naproxen, but neither drug provided her with any relief from the headaches. What treatment would you recommend?
A. Topiramate
B. Beta-blocker
C. Lasmiditan
D. Metoclopramide plus sumatriptan
E. Ubrogepant
It is common to see patients with migraine headaches and to see patients with migraines who have not responded to previous migraine therapies.
For this patient, I would try choice D first, giving metoclopramide with oral sumatriptan to see if it can improve response to sumatriptan. The two new classes of drugs for acute migraine therapy, the gepants and ditans, certainly have a role in patients unresponsive or intolerant of triptans/NSAIDS, but I would try several tricks with these less expensive medications first before entering into prior authorization hell trying to get a gepant or ditan.
When a patient has already used a triptan but experienced no benefit from it, often the next medication a patient tries is a different triptan. Dahlof reviewed four trials that looked at the efficacy of switching sumatriptan nonresponders to a different triptan and found that lack of response to sumatriptan did not predict lack of response to an alternative triptan.1 Unfortunately, acquiring insurance coverage for an alternate triptan can be difficult.
Other treatment options are nasal or injectable formulations of sumatriptan. Both of these are more costly than oral sumatriptan, and injectable sumatriptan has more side effects than oral triptans.
Combining treatment with metoclopramide can be helpful. In a study by Schulman and Dermott looking at patients who had previously been triptan nonresponders, 63% of those who took metoclopramide with sumatriptan had meaningful pain relief, compared with 31% of those who received sumatriptan and placebo.2
In a different study, Tfelt-Hansen et al. compared treatment with the combination of lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide versus treatment with 100 mg of sumatriptan.3 There was no difference in outcomes between the two treatment groups, with the lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide patients having a 57% success rate for first treated migraine compared with 53% of the sumatriptan-treated patients.
Treating with the combination of naproxen plus sumatriptan is superior to treating with either medication alone. Brandes et al. reported on two studies involving the use of the sumatriptan/naproxen combination, compared with using sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo.4 In both, taking the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to taking sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo (P < .001).
In a study of patients with poor prior response to triptans, Mathew et al. found that the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to placebo for both 2- and 24-hour headache relief (P < .001).5
Pearl
Try several options before abandoning triptans in previous triptan nonresponders, including trying a different triptan, adding metoclopramide, orcombining with an NSAID.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Dahlöf CG. Infrequent or nonresponse to oral sumatriptan does not predict response to other triptans – review of four trials. Cephalalgia. 2006 Feb;26(2):98-106.
2. Schulman EA, Dermott KF. Sumatriptan plus metoclopramide in triptan-nonresponsive migraineurs. Headache. 2003 Jul-Aug;43(7):729-33.
3. Tfelt-Hansen P et al. The effectiveness of combined oral lysine acetylsalicylate and metoclopramide compared with oral sumatriptan for migraine. Lancet. 1995 Oct 7;346(8980):923-6.
4. Brandes JL et al. Sumatriptan‐naproxen for acute treatment of migraine: A randomized trial. JAMA. 2007;297:1443‐54.
5. Mathew NT, Landy S, Stark S, et al. Fixed‐dose sumatriptan and naproxen in poor responders to triptans with a short half‐life. Headache. 2009;49:971‐82.
A 25-year-old woman presents to discuss treatment of her headaches. They occur two or three times a month and last for 4-6 hours. The headaches are disabling, have a pounding quality behind the patient’s right eye, and worsen with exercise. The patient’s neurologic exam is normal.
She has tried oral sumatriptan and naproxen, but neither drug provided her with any relief from the headaches. What treatment would you recommend?
A. Topiramate
B. Beta-blocker
C. Lasmiditan
D. Metoclopramide plus sumatriptan
E. Ubrogepant
It is common to see patients with migraine headaches and to see patients with migraines who have not responded to previous migraine therapies.
For this patient, I would try choice D first, giving metoclopramide with oral sumatriptan to see if it can improve response to sumatriptan. The two new classes of drugs for acute migraine therapy, the gepants and ditans, certainly have a role in patients unresponsive or intolerant of triptans/NSAIDS, but I would try several tricks with these less expensive medications first before entering into prior authorization hell trying to get a gepant or ditan.
When a patient has already used a triptan but experienced no benefit from it, often the next medication a patient tries is a different triptan. Dahlof reviewed four trials that looked at the efficacy of switching sumatriptan nonresponders to a different triptan and found that lack of response to sumatriptan did not predict lack of response to an alternative triptan.1 Unfortunately, acquiring insurance coverage for an alternate triptan can be difficult.
Other treatment options are nasal or injectable formulations of sumatriptan. Both of these are more costly than oral sumatriptan, and injectable sumatriptan has more side effects than oral triptans.
Combining treatment with metoclopramide can be helpful. In a study by Schulman and Dermott looking at patients who had previously been triptan nonresponders, 63% of those who took metoclopramide with sumatriptan had meaningful pain relief, compared with 31% of those who received sumatriptan and placebo.2
In a different study, Tfelt-Hansen et al. compared treatment with the combination of lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide versus treatment with 100 mg of sumatriptan.3 There was no difference in outcomes between the two treatment groups, with the lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide patients having a 57% success rate for first treated migraine compared with 53% of the sumatriptan-treated patients.
Treating with the combination of naproxen plus sumatriptan is superior to treating with either medication alone. Brandes et al. reported on two studies involving the use of the sumatriptan/naproxen combination, compared with using sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo.4 In both, taking the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to taking sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo (P < .001).
In a study of patients with poor prior response to triptans, Mathew et al. found that the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to placebo for both 2- and 24-hour headache relief (P < .001).5
Pearl
Try several options before abandoning triptans in previous triptan nonresponders, including trying a different triptan, adding metoclopramide, orcombining with an NSAID.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Dahlöf CG. Infrequent or nonresponse to oral sumatriptan does not predict response to other triptans – review of four trials. Cephalalgia. 2006 Feb;26(2):98-106.
2. Schulman EA, Dermott KF. Sumatriptan plus metoclopramide in triptan-nonresponsive migraineurs. Headache. 2003 Jul-Aug;43(7):729-33.
3. Tfelt-Hansen P et al. The effectiveness of combined oral lysine acetylsalicylate and metoclopramide compared with oral sumatriptan for migraine. Lancet. 1995 Oct 7;346(8980):923-6.
4. Brandes JL et al. Sumatriptan‐naproxen for acute treatment of migraine: A randomized trial. JAMA. 2007;297:1443‐54.
5. Mathew NT, Landy S, Stark S, et al. Fixed‐dose sumatriptan and naproxen in poor responders to triptans with a short half‐life. Headache. 2009;49:971‐82.
A 25-year-old woman presents to discuss treatment of her headaches. They occur two or three times a month and last for 4-6 hours. The headaches are disabling, have a pounding quality behind the patient’s right eye, and worsen with exercise. The patient’s neurologic exam is normal.
She has tried oral sumatriptan and naproxen, but neither drug provided her with any relief from the headaches. What treatment would you recommend?
A. Topiramate
B. Beta-blocker
C. Lasmiditan
D. Metoclopramide plus sumatriptan
E. Ubrogepant
It is common to see patients with migraine headaches and to see patients with migraines who have not responded to previous migraine therapies.
For this patient, I would try choice D first, giving metoclopramide with oral sumatriptan to see if it can improve response to sumatriptan. The two new classes of drugs for acute migraine therapy, the gepants and ditans, certainly have a role in patients unresponsive or intolerant of triptans/NSAIDS, but I would try several tricks with these less expensive medications first before entering into prior authorization hell trying to get a gepant or ditan.
When a patient has already used a triptan but experienced no benefit from it, often the next medication a patient tries is a different triptan. Dahlof reviewed four trials that looked at the efficacy of switching sumatriptan nonresponders to a different triptan and found that lack of response to sumatriptan did not predict lack of response to an alternative triptan.1 Unfortunately, acquiring insurance coverage for an alternate triptan can be difficult.
Other treatment options are nasal or injectable formulations of sumatriptan. Both of these are more costly than oral sumatriptan, and injectable sumatriptan has more side effects than oral triptans.
Combining treatment with metoclopramide can be helpful. In a study by Schulman and Dermott looking at patients who had previously been triptan nonresponders, 63% of those who took metoclopramide with sumatriptan had meaningful pain relief, compared with 31% of those who received sumatriptan and placebo.2
In a different study, Tfelt-Hansen et al. compared treatment with the combination of lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide versus treatment with 100 mg of sumatriptan.3 There was no difference in outcomes between the two treatment groups, with the lysine acetylsalicylate plus metoclopramide patients having a 57% success rate for first treated migraine compared with 53% of the sumatriptan-treated patients.
Treating with the combination of naproxen plus sumatriptan is superior to treating with either medication alone. Brandes et al. reported on two studies involving the use of the sumatriptan/naproxen combination, compared with using sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo.4 In both, taking the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to taking sumatriptan, naproxen, or placebo (P < .001).
In a study of patients with poor prior response to triptans, Mathew et al. found that the sumatriptan/naproxen combination was superior to placebo for both 2- and 24-hour headache relief (P < .001).5
Pearl
Try several options before abandoning triptans in previous triptan nonresponders, including trying a different triptan, adding metoclopramide, orcombining with an NSAID.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Dahlöf CG. Infrequent or nonresponse to oral sumatriptan does not predict response to other triptans – review of four trials. Cephalalgia. 2006 Feb;26(2):98-106.
2. Schulman EA, Dermott KF. Sumatriptan plus metoclopramide in triptan-nonresponsive migraineurs. Headache. 2003 Jul-Aug;43(7):729-33.
3. Tfelt-Hansen P et al. The effectiveness of combined oral lysine acetylsalicylate and metoclopramide compared with oral sumatriptan for migraine. Lancet. 1995 Oct 7;346(8980):923-6.
4. Brandes JL et al. Sumatriptan‐naproxen for acute treatment of migraine: A randomized trial. JAMA. 2007;297:1443‐54.
5. Mathew NT, Landy S, Stark S, et al. Fixed‐dose sumatriptan and naproxen in poor responders to triptans with a short half‐life. Headache. 2009;49:971‐82.
Rapid drop of antibodies seen in those with mild COVID-19
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The research was conducted by F. Javier Ibarrondo, PhD, and colleagues and was published online on July 21 in a letter to the editor of the New England Journal of Medicine. Ibarrondo is associate researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. (The original letter incorrectly calculated the half-life at 73 days.)
Coauthor Otto Yang, MD, professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at UCLA, told Medscape Medical News that the rapidity in the antibody drop at 5 weeks “is striking compared to other infections.”
The phenomenon has been suspected and has been observed before but had not been quantified.
“Our paper is the first to put firm numbers on the dropping of antibodies after early infection,” he said.
The researchers evaluated 34 people (average age, 43 years) who had recovered from mild COVID-19 and had referred themselves to UCLA for observational research.
Previous report also found a quick fade
As Medscape Medical News reported, a previous study from China that was published in Nature Medicine also found that the antibodies fade quickly.
Interpreting the meaning of the current research comes with a few caveats, Dr. Yang said.
“One is that we don’t know for sure that antibodies are what protect people from getting infected,” he said. Although it’s a reasonable assumption, he said, that’s not always the case.
Another caveat is that even if antibodies do protect, the tests being used to measure them – including the test that was used in this study – may not measure them the right way, and it is not yet known how many antibodies are needed for protection, he explained.
The UCLA researchers used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor–binding domain immunoglobulin G concentrations.
“No reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically”
The study provides further proof that “[t]here’s no reason for anybody to be getting an antibody test medically right now,” Dr. Yang said.
Additionally, “FDA-approved tests are not approved for quantitative measures, only qualitative,” he continued. He noted that the findings may have implications with respect to herd immunity.
“Herd immunity depends on a lot of people having immunity to the infection all at the same time. If infection is followed by only brief protection from infection, the natural infection is not going to reach herd immunity,” he explained.
Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program in Nashville, Tenn., pointed out that antibodies “are just part of the story.”
“When we make an immune response to any germ,” he said, “we not only make an immune response for the time being but for the future. The next time we’re exposed, we can call into action B cells and T cells who have been there and done that.”
So even though the antibodies fade over time, other arms of the immune system are being trained for future action, he said.
Herd immunity does not require that populations have a huge level of antibodies that remains forever, he explained.
“It requires that in general, we’re not going to get infected as easily, and we’re not going to have disease as easily, and we’re not going to transmit the virus for as long,” he said.
Dr. Creech said he and others researching COVID-19 find that studies that show that antibodies fade quickly provide more proof “that this coronavirus is going to be here to stay unless we can take care of it through very effective treatments to take it from potentially fatal disease to one that is nothing more than a cold” or until a vaccine is developed.
He noted there are four other coronaviruses in widespread circulation every year that “amount to about 25% of the common cold.”
This study may help narrow the window as to when convalescent plasma – plasma that is taken from people who have recovered from COVID-19 and that is used to help people who are acutely ill with the disease – will be most effective, Dr. Creech explained. He said the results suggest that it is important that plasma be collected within the first couple of months after recovery so as to capture the most antibodies.
This study is important as another snapshot “so we understand the differences between severe and mild disease, so we can study it over time, so we have all the tools we need as we start these pivotal vaccine studies to make sure we’re making the right immune response for the right duration of time so we can put an end to this pandemic,” Dr. Creech concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the James B. Pendleton Charitable Trust, and the McCarthy Family Foundation. A coauthor reports receiving grants from Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr. Creech has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is the presence of enanthem a clue for COVID-19?
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
Larger studies should explore and confirm this association, the study’s authors and other experts suggested.
Dermatologists are already aware of the connection between enanthem and viral etiology. “As seen with other viral infections, we wondered if COVID-19 could produce enanthem in addition to skin rash exanthem,” one of the study author’s, Juan Jiménez-Cauhe, MD, a dermatologist with Hospital Universitario Ramon y Cajal, Madrid, said in an interview. He and his colleagues summarized their findings in a research letter in JAMA Dermatology.
They examined the oral cavity of 21 COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care hospital who also had a skin rash from March 30 to April 8. They classified enanthems into four categories: petechial, macular, macular with petechiae, or erythematovesicular. Six of the patients presented with oral lesions, all of them located in the palate; in one patient, the enanthem was macular, it was petechial in two patients and was macular with petechiae in three patients. The six patients ranged between the ages of 40 and 69 years; four were women.
Petechial or vesicular patterns are often associated with viral infections. In this particular study, the investigators did not observe vesicular lesions.
On average, mucocutaneous lesions appeared about 12 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. “Interestingly, this latency was shorter in patients with petechial enanthem, compared with those with a macular lesion with petechiae appearance,” the authors wrote.
This shorter time might suggest an association for SARS-CoV-2, said Dr. Jiménez-Cauhe. Strong cough may have also caused petechial lesions on the palate, but it’s unlikely, as they appeared close in time to COVID-19 symptoms. It’s also unlikely that any drugs caused the lesions, as drug rashes can take 2-3 weeks to appear.
This fits in line with other evidence of broader skin manifestations appearing at the same time or after COVID-19, Esther Freeman, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Freeman, director of global health dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, is the principal investigator of the COVID-19 Dermatology Registry, a collaboration of the American Academy of Dermatology and International League of Dermatological Societies.
The study’s small cohort made it difficult to establish a solid association between the oral lesions and SARS-CoV-2. “However, the presence of enanthem in a patient with a skin rash is a useful finding that suggests a viral etiology rather than a drug reaction. This is particularly useful in COVID-19 patients, who were receiving many drugs as part of the treatment,” Dr. Jimenez-Cauhe said. Future studies should assess whether the presence of enanthem and exanthem lead physicians to consider SARS-CoV-2 as possible agents, ruling out infection with a blood or nasopharyngeal test.
This study adds to the growing body of knowledge on cutaneous and mucocutaneous findings associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Jules Lipoff, MD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “One challenge in evaluating these findings is that these findings are nonspecific, and medication reactions can often cause similar rashes, such as morbilliform eruptions that can be associated with both viruses and medications.”
Enanthems, as the study authors noted, are more specific to viral infections and are less commonly associated with medication reactions. “So, even though this is a small case series with significant limitations, it does add more evidence that COVID-19 is directly responsible for findings in the skin and mucous membranes,” said Dr. Lipoff.
Dr. Freeman noted that the study may also encourage clinicians to look in a patient’s mouth when assessing for SARS-CoV-2. Additional research should examine these data in a larger population.
Several studies by Dr. Freeman, Dr. Lipoff, and others strongly suggest that SARS-CoV-2 has a spectrum of associated dermatologic manifestations. One evaluated perniolike skin lesions (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug; 83[2]:486-92). The other was a case series from the COVID-19 registry that examined 716 cases of new-onset dermatologic symptoms in patients from 31 countries with confirmed/suspected SARS-CoV-2 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jul 2;S0190-9622[20]32126-5.).
The authors of the report had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jimenez-Cauhe J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jul 15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2550.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Most neurologists live within their means, are savers
An important caveat, however, is that data for this year’s report were collected prior to Feb. 11, 2020, as part of the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020. The financial picture has changed for many physicians since then because of COVID-19’s impact on medical practices.
While it will be some time before medical practices become accustomed to a new version of normal, the report data provide a picture of the debt load and net worth of neurologists.
Below the middle earners
According to the Medscape Neurologist Compensation Report 2020, neurologists are below the middle earners of all physicians, earning $280,000 on average this year. That’s up from $267,000 last year. More than half of neurologists (58%) report a net worth (total assets minus total liabilities) of less than $1 million (52% men, 70% women), while 36% have a net worth between $1 and $5 million (40% men, 29% women), and 6% top $5 million in net worth (8% men, 1% women).
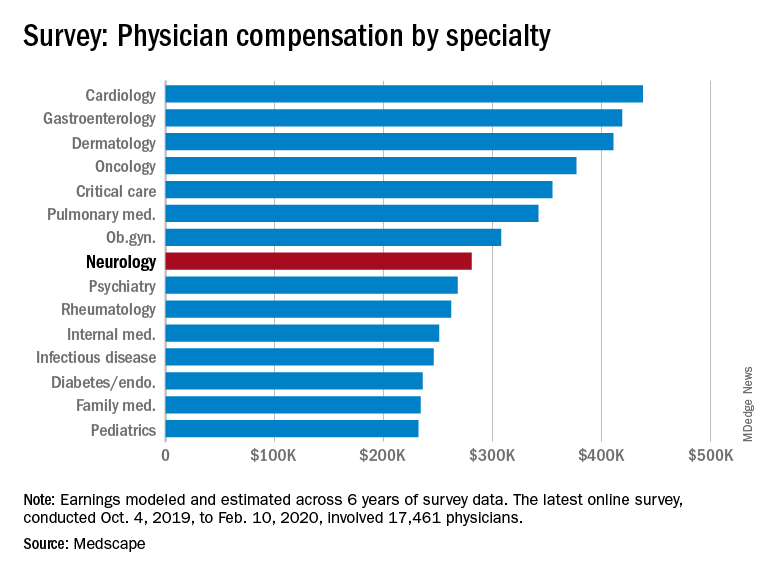
Among specialists, orthopedists are most likely to top the $5 million level (at 19%), followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%), according to the Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Conversely, about two in five neurologists (41%) have a net worth under $500,000, just below family medicine physicians (46%) and pediatricians (44%).
For roughly two thirds of neurologists (64%), their major expense is mortgage payment on their primary residence. Around one third of neurologists have a mortgage of $300,000 or less, 28% have no mortgage or a mortgage that is paid off, and 17% have a mortgage topping $500,000. Six in 10 neurologists live in a house that is 3000 square feet or smaller.
Mortgage aside, other top ongoing expenses for neurologists are car payments (35%), credit card debt (28%), school loans (25%), and childcare (19%). At 25%, neurologists are in the middle of the list when it comes to physicians still paying off loans for education.
Spender or saver?
The average American has four credit cards, according to the credit reporting agency Experian. Among neurologists, more than half said they have four or fewer credit cards, including 37% with three to four cards, 16% with one to two cards, and 1% with no cards. A little more than a quarter of neurologists (28%) have five to six credit cards and 18% have more than seven at their disposal.
Only a small percentage of neurologists (7%) say they live above their means; 57% live at their means and 35% live below their means.
More than half (59%) of neurologists contribute $1,000 or more to a tax-deferred retirement or college savings account each month, while 12% do not do this on a regular basis. About two thirds of neurologists make contributions to a taxable savings account, a tool many use when tax-deferred contributions have reached their limit.
Nearly half of neurologists (48%) rely on a “mental budget” for personal expenses, while 18% rely on a written budget or use software or an app for budgeting; 34% do not have a budget for personal expenses.
Nearly three quarters of neurologists did not experience a financial loss in 2019. Of those that did, the main causes were bad investments (10%) and practice-related issues (9%), followed by legal fees (5%), real estate loss (4%), and divorce (1%).
Among neurologists with joint finances with a spouse or partner, 62% pool their income to pay household expenses. For 12%, the person who earns more pays more of the bills and/or expenses. Only a small percentage divide bills and expenses equally (4%).
Forty-three percent of neurologists said they currently work with a financial planner or had in the past, 38% never did, and 19% met with a financial planner but did not pursue working with that person.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An important caveat, however, is that data for this year’s report were collected prior to Feb. 11, 2020, as part of the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020. The financial picture has changed for many physicians since then because of COVID-19’s impact on medical practices.
While it will be some time before medical practices become accustomed to a new version of normal, the report data provide a picture of the debt load and net worth of neurologists.
Below the middle earners
According to the Medscape Neurologist Compensation Report 2020, neurologists are below the middle earners of all physicians, earning $280,000 on average this year. That’s up from $267,000 last year. More than half of neurologists (58%) report a net worth (total assets minus total liabilities) of less than $1 million (52% men, 70% women), while 36% have a net worth between $1 and $5 million (40% men, 29% women), and 6% top $5 million in net worth (8% men, 1% women).

Among specialists, orthopedists are most likely to top the $5 million level (at 19%), followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%), according to the Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Conversely, about two in five neurologists (41%) have a net worth under $500,000, just below family medicine physicians (46%) and pediatricians (44%).
For roughly two thirds of neurologists (64%), their major expense is mortgage payment on their primary residence. Around one third of neurologists have a mortgage of $300,000 or less, 28% have no mortgage or a mortgage that is paid off, and 17% have a mortgage topping $500,000. Six in 10 neurologists live in a house that is 3000 square feet or smaller.
Mortgage aside, other top ongoing expenses for neurologists are car payments (35%), credit card debt (28%), school loans (25%), and childcare (19%). At 25%, neurologists are in the middle of the list when it comes to physicians still paying off loans for education.
Spender or saver?
The average American has four credit cards, according to the credit reporting agency Experian. Among neurologists, more than half said they have four or fewer credit cards, including 37% with three to four cards, 16% with one to two cards, and 1% with no cards. A little more than a quarter of neurologists (28%) have five to six credit cards and 18% have more than seven at their disposal.
Only a small percentage of neurologists (7%) say they live above their means; 57% live at their means and 35% live below their means.
More than half (59%) of neurologists contribute $1,000 or more to a tax-deferred retirement or college savings account each month, while 12% do not do this on a regular basis. About two thirds of neurologists make contributions to a taxable savings account, a tool many use when tax-deferred contributions have reached their limit.
Nearly half of neurologists (48%) rely on a “mental budget” for personal expenses, while 18% rely on a written budget or use software or an app for budgeting; 34% do not have a budget for personal expenses.
Nearly three quarters of neurologists did not experience a financial loss in 2019. Of those that did, the main causes were bad investments (10%) and practice-related issues (9%), followed by legal fees (5%), real estate loss (4%), and divorce (1%).
Among neurologists with joint finances with a spouse or partner, 62% pool their income to pay household expenses. For 12%, the person who earns more pays more of the bills and/or expenses. Only a small percentage divide bills and expenses equally (4%).
Forty-three percent of neurologists said they currently work with a financial planner or had in the past, 38% never did, and 19% met with a financial planner but did not pursue working with that person.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An important caveat, however, is that data for this year’s report were collected prior to Feb. 11, 2020, as part of the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2020. The financial picture has changed for many physicians since then because of COVID-19’s impact on medical practices.
While it will be some time before medical practices become accustomed to a new version of normal, the report data provide a picture of the debt load and net worth of neurologists.
Below the middle earners
According to the Medscape Neurologist Compensation Report 2020, neurologists are below the middle earners of all physicians, earning $280,000 on average this year. That’s up from $267,000 last year. More than half of neurologists (58%) report a net worth (total assets minus total liabilities) of less than $1 million (52% men, 70% women), while 36% have a net worth between $1 and $5 million (40% men, 29% women), and 6% top $5 million in net worth (8% men, 1% women).

Among specialists, orthopedists are most likely to top the $5 million level (at 19%), followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%), according to the Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Conversely, about two in five neurologists (41%) have a net worth under $500,000, just below family medicine physicians (46%) and pediatricians (44%).
For roughly two thirds of neurologists (64%), their major expense is mortgage payment on their primary residence. Around one third of neurologists have a mortgage of $300,000 or less, 28% have no mortgage or a mortgage that is paid off, and 17% have a mortgage topping $500,000. Six in 10 neurologists live in a house that is 3000 square feet or smaller.
Mortgage aside, other top ongoing expenses for neurologists are car payments (35%), credit card debt (28%), school loans (25%), and childcare (19%). At 25%, neurologists are in the middle of the list when it comes to physicians still paying off loans for education.
Spender or saver?
The average American has four credit cards, according to the credit reporting agency Experian. Among neurologists, more than half said they have four or fewer credit cards, including 37% with three to four cards, 16% with one to two cards, and 1% with no cards. A little more than a quarter of neurologists (28%) have five to six credit cards and 18% have more than seven at their disposal.
Only a small percentage of neurologists (7%) say they live above their means; 57% live at their means and 35% live below their means.
More than half (59%) of neurologists contribute $1,000 or more to a tax-deferred retirement or college savings account each month, while 12% do not do this on a regular basis. About two thirds of neurologists make contributions to a taxable savings account, a tool many use when tax-deferred contributions have reached their limit.
Nearly half of neurologists (48%) rely on a “mental budget” for personal expenses, while 18% rely on a written budget or use software or an app for budgeting; 34% do not have a budget for personal expenses.
Nearly three quarters of neurologists did not experience a financial loss in 2019. Of those that did, the main causes were bad investments (10%) and practice-related issues (9%), followed by legal fees (5%), real estate loss (4%), and divorce (1%).
Among neurologists with joint finances with a spouse or partner, 62% pool their income to pay household expenses. For 12%, the person who earns more pays more of the bills and/or expenses. Only a small percentage divide bills and expenses equally (4%).
Forty-three percent of neurologists said they currently work with a financial planner or had in the past, 38% never did, and 19% met with a financial planner but did not pursue working with that person.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

















