User login
Yellow Papules and Plaques on a Child
The Diagnosis: Tuberous Xanthoma
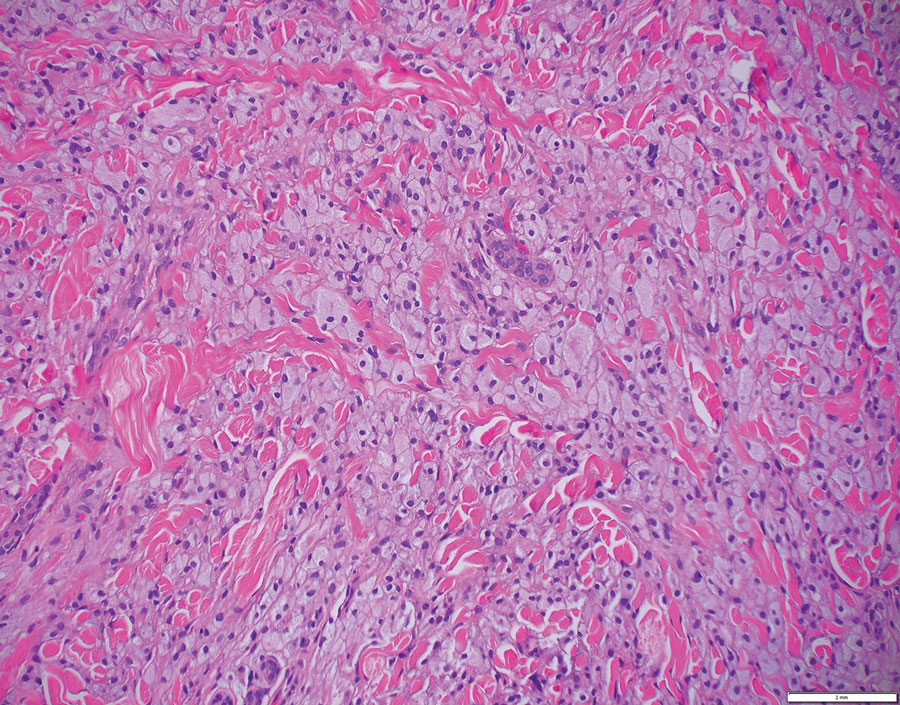
The skin biopsy revealed a nodular collection of foam cells (quiz image [bottom]). Tuberous xanthoma was the most likely diagnosis based on the patient’s history as well as the clinical and histologic findings. Tuberous xanthomas are flat or elevated nodules in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, commonly occurring on the skin over the joints.1 Smaller nodules and papules often are referred to as tuberoeruptive xanthomas and exist on a continuum with the larger tuberous xanthomas. All xanthomas appear histologically similar, with collections of foam cells present within the dermis.2 Foam cells form when serum lipoproteins diffuse through capillary walls, deposit in the skin or tendons, and are scavenged by monocytes.3 Tuberous xanthomas, along with tendinous, eruptive, and planar xanthomas, are the most likely to be associated with hyperlipidemia.4 They may indicate an underlying disorder of lipid metabolism, such as familial hypercholesterolemia.1,3 This is the most common cause of inheritable cardiovascular disease, with a prevalence of approximately 1:250.2 Premature cardiovascular disease risk increases 2 to 4 times in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia and tendinous xanthomas,1 illustrating that recognition of cutaneous lesions can lead to earlier diagnosis and prevention of patient morbidity and mortality.
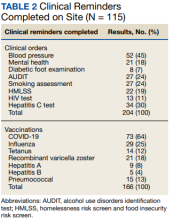
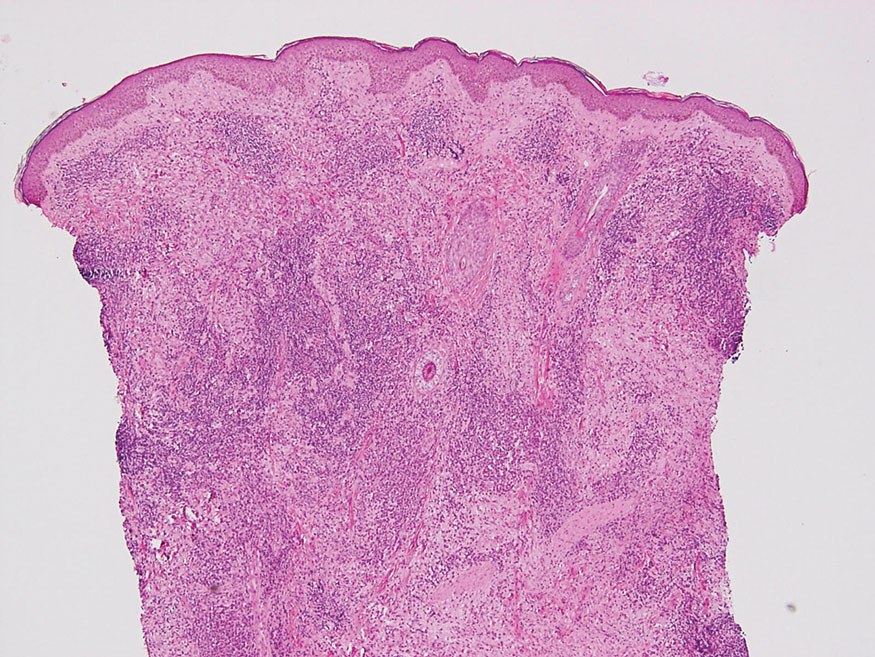
Juvenile xanthogranuloma typically presents as smooth yellow papules or nodules on the head and neck, with a characteristic “setting-sun” appearance (ie, yellow center with an erythematous halo) on dermoscopy.5 Histologically, juvenile xanthogranulomas are composed of foam cells and a mixed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with eosinophils within the dermis. Giant cells with a ring of nuclei surrounded by cytoplasm containing lipid vacuoles (called Touton giant cells) are characteristic (Figure 1). In contrast to tuberous xanthomas, juvenile xanthogranulomas often present within the first year of life.6
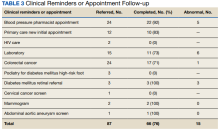
Keloid scars are more prevalent in patients with skin of color. They are characterized by eosinophilic keloidal collagen with a whorled proliferation of fibroblasts on histology (Figure 2).7 They occur spontaneously or at sites of injury and present as bluish-red or flesh-colored firm papules or nodules.8 In our patient, keloid scars were an unlikely diagnosis due to the lack of trauma and the absence of keloidal collagen on histology.
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum typically presents as an erythematous, yellow-brown, circular plaque on the anterior lower leg in patients with diabetes mellitus; it rarely occurs in children.9 Microscopy shows palisaded granulomas surrounding necrobiotic collagen arranged horizontally in a layer cake–like fashion (Figure 3).9,10 The etiology of necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum currently is unknown, though immune complex deposition may contribute to its pathology. It has been associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus, though severity of the lesions is not associated with extent of glycemic control.10
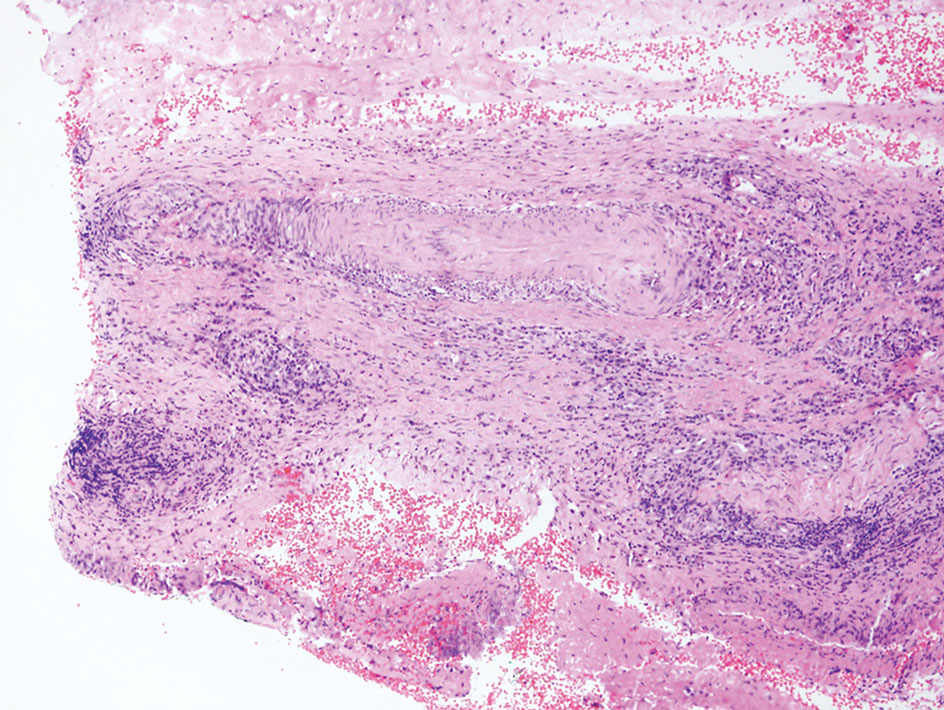
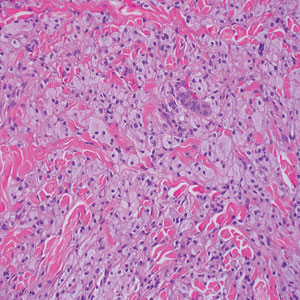
Rosai-Dorfman disease is an uncommon disorder characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes that most often presents as bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy in children and young adults but rarely can present with cutaneous lesions when extranodal involvement is present.11,12 The cutaneous form most commonly presents as red papules or nodules. On histology, the lesions exhibit a nodular dermal proliferation of histiocytes and smaller lymphocytoid cells with a marbled or starry sky–like appearance on low power (Figure 4). On higher magnification, the characteristic finding of emperipolesis can be seen.11 On immunohistochemistry, the histiocytes stain positively for CD68 and S-100. Although the pathogenesis currently is unknown, evidence of clonality indicates the disease may be related to a neoplastic process.12
- Zak A, Zeman M, Slaby A, et al. Xanthomas: clinical and pathophysiological relations. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158:181-188. doi:10.5507/bp.2014.016
- Ison HE, Clarke SL, Knowles JW. Familial hypercholesterolemia. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK174884/
- Sathiyakumar V, Jones SR, Martin SS. Xanthomas and lipoprotein disorders. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Massangale WT. Xanthomas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018:1634-1643.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/
- Hernández-San Martín MJ, Vargas-Mora P, Aranibar L. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: an entity with a wide clinical spectrum. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:725-733. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.07.004
- Lee JY, Yang C, Chao S, et al. Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathology. 2004;26:379-384.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al. Benign neoplasms and hyperplasias. In: Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw Hill; 2017:141-188.
- Bonura C, Frontino G, Rigamonti A, et al. Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum: a pediatric case report. Dermatoendocrinol. 2014;6:E27790. doi:10.4161/derm.27790
- Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy.kumc.edu/books/NBK459318/
- Parrent T, Clark T, Hall D. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Cutis. 2012;90:237-238.
- Bruce-Brand C, Schneider JW, Schubert P. Rosai-Dorfman disease: an overview. J Clin Pathol. 2020;73:697-705. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206733
The Diagnosis: Tuberous Xanthoma
The skin biopsy revealed a nodular collection of foam cells (quiz image [bottom]). Tuberous xanthoma was the most likely diagnosis based on the patient’s history as well as the clinical and histologic findings. Tuberous xanthomas are flat or elevated nodules in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, commonly occurring on the skin over the joints.1 Smaller nodules and papules often are referred to as tuberoeruptive xanthomas and exist on a continuum with the larger tuberous xanthomas. All xanthomas appear histologically similar, with collections of foam cells present within the dermis.2 Foam cells form when serum lipoproteins diffuse through capillary walls, deposit in the skin or tendons, and are scavenged by monocytes.3 Tuberous xanthomas, along with tendinous, eruptive, and planar xanthomas, are the most likely to be associated with hyperlipidemia.4 They may indicate an underlying disorder of lipid metabolism, such as familial hypercholesterolemia.1,3 This is the most common cause of inheritable cardiovascular disease, with a prevalence of approximately 1:250.2 Premature cardiovascular disease risk increases 2 to 4 times in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia and tendinous xanthomas,1 illustrating that recognition of cutaneous lesions can lead to earlier diagnosis and prevention of patient morbidity and mortality.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma typically presents as smooth yellow papules or nodules on the head and neck, with a characteristic “setting-sun” appearance (ie, yellow center with an erythematous halo) on dermoscopy.5 Histologically, juvenile xanthogranulomas are composed of foam cells and a mixed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with eosinophils within the dermis. Giant cells with a ring of nuclei surrounded by cytoplasm containing lipid vacuoles (called Touton giant cells) are characteristic (Figure 1). In contrast to tuberous xanthomas, juvenile xanthogranulomas often present within the first year of life.6

Keloid scars are more prevalent in patients with skin of color. They are characterized by eosinophilic keloidal collagen with a whorled proliferation of fibroblasts on histology (Figure 2).7 They occur spontaneously or at sites of injury and present as bluish-red or flesh-colored firm papules or nodules.8 In our patient, keloid scars were an unlikely diagnosis due to the lack of trauma and the absence of keloidal collagen on histology.

Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum typically presents as an erythematous, yellow-brown, circular plaque on the anterior lower leg in patients with diabetes mellitus; it rarely occurs in children.9 Microscopy shows palisaded granulomas surrounding necrobiotic collagen arranged horizontally in a layer cake–like fashion (Figure 3).9,10 The etiology of necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum currently is unknown, though immune complex deposition may contribute to its pathology. It has been associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus, though severity of the lesions is not associated with extent of glycemic control.10

Rosai-Dorfman disease is an uncommon disorder characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes that most often presents as bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy in children and young adults but rarely can present with cutaneous lesions when extranodal involvement is present.11,12 The cutaneous form most commonly presents as red papules or nodules. On histology, the lesions exhibit a nodular dermal proliferation of histiocytes and smaller lymphocytoid cells with a marbled or starry sky–like appearance on low power (Figure 4). On higher magnification, the characteristic finding of emperipolesis can be seen.11 On immunohistochemistry, the histiocytes stain positively for CD68 and S-100. Although the pathogenesis currently is unknown, evidence of clonality indicates the disease may be related to a neoplastic process.12

The Diagnosis: Tuberous Xanthoma
The skin biopsy revealed a nodular collection of foam cells (quiz image [bottom]). Tuberous xanthoma was the most likely diagnosis based on the patient’s history as well as the clinical and histologic findings. Tuberous xanthomas are flat or elevated nodules in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, commonly occurring on the skin over the joints.1 Smaller nodules and papules often are referred to as tuberoeruptive xanthomas and exist on a continuum with the larger tuberous xanthomas. All xanthomas appear histologically similar, with collections of foam cells present within the dermis.2 Foam cells form when serum lipoproteins diffuse through capillary walls, deposit in the skin or tendons, and are scavenged by monocytes.3 Tuberous xanthomas, along with tendinous, eruptive, and planar xanthomas, are the most likely to be associated with hyperlipidemia.4 They may indicate an underlying disorder of lipid metabolism, such as familial hypercholesterolemia.1,3 This is the most common cause of inheritable cardiovascular disease, with a prevalence of approximately 1:250.2 Premature cardiovascular disease risk increases 2 to 4 times in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia and tendinous xanthomas,1 illustrating that recognition of cutaneous lesions can lead to earlier diagnosis and prevention of patient morbidity and mortality.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma typically presents as smooth yellow papules or nodules on the head and neck, with a characteristic “setting-sun” appearance (ie, yellow center with an erythematous halo) on dermoscopy.5 Histologically, juvenile xanthogranulomas are composed of foam cells and a mixed lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with eosinophils within the dermis. Giant cells with a ring of nuclei surrounded by cytoplasm containing lipid vacuoles (called Touton giant cells) are characteristic (Figure 1). In contrast to tuberous xanthomas, juvenile xanthogranulomas often present within the first year of life.6

Keloid scars are more prevalent in patients with skin of color. They are characterized by eosinophilic keloidal collagen with a whorled proliferation of fibroblasts on histology (Figure 2).7 They occur spontaneously or at sites of injury and present as bluish-red or flesh-colored firm papules or nodules.8 In our patient, keloid scars were an unlikely diagnosis due to the lack of trauma and the absence of keloidal collagen on histology.

Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum typically presents as an erythematous, yellow-brown, circular plaque on the anterior lower leg in patients with diabetes mellitus; it rarely occurs in children.9 Microscopy shows palisaded granulomas surrounding necrobiotic collagen arranged horizontally in a layer cake–like fashion (Figure 3).9,10 The etiology of necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum currently is unknown, though immune complex deposition may contribute to its pathology. It has been associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus, though severity of the lesions is not associated with extent of glycemic control.10

Rosai-Dorfman disease is an uncommon disorder characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes that most often presents as bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy in children and young adults but rarely can present with cutaneous lesions when extranodal involvement is present.11,12 The cutaneous form most commonly presents as red papules or nodules. On histology, the lesions exhibit a nodular dermal proliferation of histiocytes and smaller lymphocytoid cells with a marbled or starry sky–like appearance on low power (Figure 4). On higher magnification, the characteristic finding of emperipolesis can be seen.11 On immunohistochemistry, the histiocytes stain positively for CD68 and S-100. Although the pathogenesis currently is unknown, evidence of clonality indicates the disease may be related to a neoplastic process.12

- Zak A, Zeman M, Slaby A, et al. Xanthomas: clinical and pathophysiological relations. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158:181-188. doi:10.5507/bp.2014.016
- Ison HE, Clarke SL, Knowles JW. Familial hypercholesterolemia. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK174884/
- Sathiyakumar V, Jones SR, Martin SS. Xanthomas and lipoprotein disorders. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Massangale WT. Xanthomas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018:1634-1643.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/
- Hernández-San Martín MJ, Vargas-Mora P, Aranibar L. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: an entity with a wide clinical spectrum. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:725-733. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.07.004
- Lee JY, Yang C, Chao S, et al. Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathology. 2004;26:379-384.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al. Benign neoplasms and hyperplasias. In: Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw Hill; 2017:141-188.
- Bonura C, Frontino G, Rigamonti A, et al. Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum: a pediatric case report. Dermatoendocrinol. 2014;6:E27790. doi:10.4161/derm.27790
- Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy.kumc.edu/books/NBK459318/
- Parrent T, Clark T, Hall D. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Cutis. 2012;90:237-238.
- Bruce-Brand C, Schneider JW, Schubert P. Rosai-Dorfman disease: an overview. J Clin Pathol. 2020;73:697-705. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206733
- Zak A, Zeman M, Slaby A, et al. Xanthomas: clinical and pathophysiological relations. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158:181-188. doi:10.5507/bp.2014.016
- Ison HE, Clarke SL, Knowles JW. Familial hypercholesterolemia. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK174884/
- Sathiyakumar V, Jones SR, Martin SS. Xanthomas and lipoprotein disorders. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Massangale WT. Xanthomas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018:1634-1643.
- Collie JS, Harper CD, Fillman EP. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526103/
- Hernández-San Martín MJ, Vargas-Mora P, Aranibar L. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: an entity with a wide clinical spectrum. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020;111:725-733. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.07.004
- Lee JY, Yang C, Chao S, et al. Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathology. 2004;26:379-384.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al. Benign neoplasms and hyperplasias. In: Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 8th ed. McGraw Hill; 2017:141-188.
- Bonura C, Frontino G, Rigamonti A, et al. Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum: a pediatric case report. Dermatoendocrinol. 2014;6:E27790. doi:10.4161/derm.27790
- Lepe K, Riley CA, Salazar FJ. Necrobiosis lipoidica. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy.kumc.edu/books/NBK459318/
- Parrent T, Clark T, Hall D. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Cutis. 2012;90:237-238.
- Bruce-Brand C, Schneider JW, Schubert P. Rosai-Dorfman disease: an overview. J Clin Pathol. 2020;73:697-705. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206733
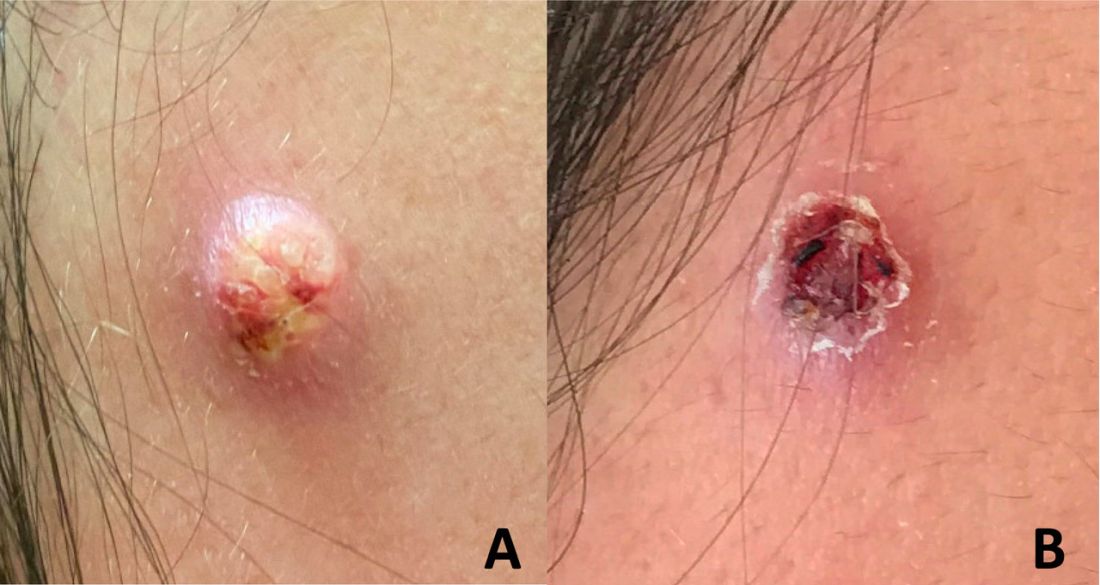
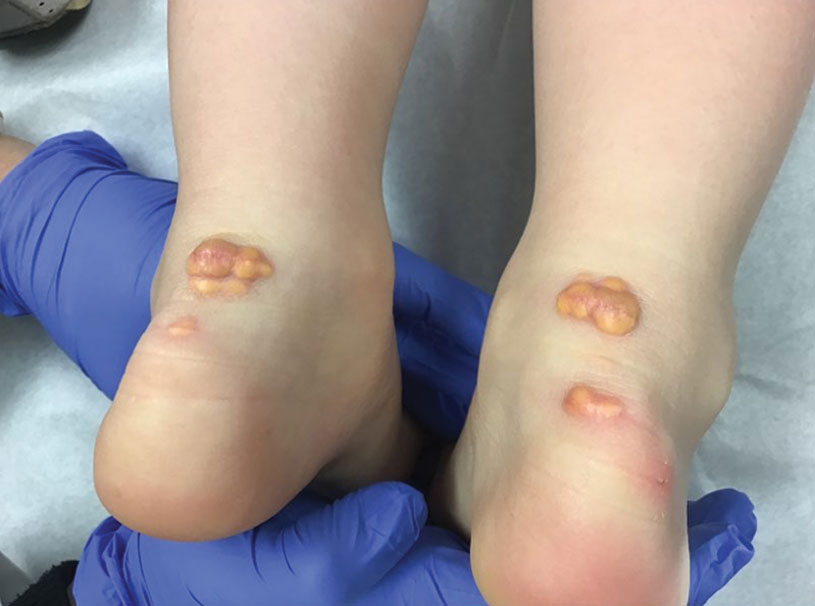
A 3-year-old girl presented with raised, firm, enlarging, asymptomatic, well-defined, subcutaneous papules, plaques, and nodules on the hands, knees, and posterior ankles of 1 year’s duration. The patient’s mother stated that the lesions began on the ankles (top), and she initially believed them to be due to friction from the child’s shoes until the more recent involvement of the knees and hands. The patient’s father, paternal grandfather, and paternal great-grandfather had a history of elevated cholesterol levels. A shave biopsy was performed (bottom).
Novel co-admin of CAR T cells achieves 99% remission in leukemia
In this trial, the largest study to date of a CAR T-cell therapy for such patients, the researchers co-administered two CAR T-cell therapies, one targeting CD19 and the other targeting CD22.
The results showed that 192 of 194 patients (99%) achieved a complete remission.
The combined overall 12-month event-free survival was 73.5%.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
These results are better than what has been reported for CAR T cells that are already on the market. These products, which target CD19, have achieved complete remission in 85.5% of cases and a 12-month event-free survival of 52.4% in children with B-ALL.
“We do believe [this approach] will become standard of care,” said study author Ching-Hon Pui, MD, of the departments of oncology, pathology, and global pediatric medicine, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis.
He noted that this work builds on the huge success that has already been achieved in this field with CAR T-cell products directed at CD19. The first of these products to reach the market was tisagenlecleucel-T (Novartis).
“To put this study in context, the first child who received CAR T-cell therapy for B-ALL after multiple relapses has recently celebrated her 10-year cancer-free survival milestone, and we hope that our finding will result in many more such milestones,” he said.
These new results are very impressive, said Stephen P. Hunger, MD, an expert commenting for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which highlighted the research in a press release. “They were also able to treat almost 200 patients in a relatively short time.”
Hunger pointed out that dual administration and targeting is not a new idea and is one of the strategies that is currently under investigation. But it is too early to consider this to be the standard of care, he said. “We want to see it replicated in other centers and to see longer follow-up,” said Dr. Hunger, who is Distinguished Chair in Pediatrics and director of the center for childhood cancer research at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “We can establish this as a first step down the road, and we will see if others will achieve similar results.”
Strategy of dual targeting
Despite the success CAR T-cell therapy in childhood leukemia, the currently available products have limitations, Dr. Pui and colleagues note.
About half of patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells experience relapse within 1 year, owing either to loss of CAR T-cell persistence or to loss of CD19 antigen because of splice variants, acquired genetic mutations, or lineage switch.
With further treatment with CAR T cells directed against CD22, 70%-80% of patients who failed CD19 CAR T will achieve into complete remission. However, most will experience relapse.
Recent efforts in the field have turned to exploring the safety and feasibility of CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results were not superior to those of the CD19 CAR T-cell therapy given alone, although sequential treatment has yielded promising response rates, the authors note.
They hypothesized that co-administration of CD19- and CD22-targeted CAR T cells would improve efficacy, as it could forestall the development of drug resistance.
Achieved 99% remission
Dr. Pui and colleagues conducted a phase 2 trial that included 225 evaluable patients aged 20 years or younger who were being treated at five urban hospitals in and near Shanghai, China. Of this group, 194 had refractory disease or hematologic relapse, and 31 patients had isolated extramedullary relapse.
A safety run-in stage to determine the recommended dose was initially conducted. An interim analysis of the first 30 patients who were treated (27 at the recommended dose) showed that the approach was safe and effective. Additional patients were then enrolled.
The 192 patients (of 194) who achieved complete remission attained negative minimal residual disease status.
At a median follow-up of 11 months, 43 patients experienced relapse (24 with CD191/CD221 relapse, 16 with CD19– /CD221, one with CD19– /CD22– , and two unknown), for a cumulative risk of 22.2%.
Transplant and relapse options
In an interview, Dr. Pui noted that various treatment options were available for the children who experienced relapse. “For patients who were in good clinical condition, we will treat them with molecular therapeutics, allogeneic CAR T cells from donor, or even repeated humanized CD19 and/or CD22 CAR T cells with or without CD20 CAR T cells in an attempt to induce a remission for allogeneic transplantation,” he said.
The site-specific 12-month event-free survival rate in the trial was 69.2% for patients who did not receive a transplant, 95% for those children who had an isolated relapse to the testicles, and 68.6% for those who had an isolated central nervous system relapse.
After censoring 78 patients for consolidative transplantation, the 12-month overall survival was 87.7%.
Consolidative transplantation was performed in 24 of the 37 patients with KMT2A-rearranged or ZNF384-rearranged ALL and in 54 patients because of parental request. The reason for this was that patients with these two genetic subtypes of leukemia (KMT2A-rearranged and ZNF384-rearranged), under the pressure of phenotype-specific treatment (such as CAR T cells or blinatumomab) are at risk of lineage switch and development of secondary acute myeloid leukemia, explained Dr. Pui. “That is an even more resistant form of leukemia, and up to 5%-10% of the patients have been reported to develop this complication.
“We performed consolidation transplantation in these patients to avoid the risk of lineage switch but would accept the parental request not to perform allogeneic transplant after they were clearly informed of the risk,” he told this news organization.
He also suggested that this approach of co-administration of two types of CAR T cells would be especially suitable for “patients with extramedullary involvement, because most of them will be spared of local irradiation so that they can preserve their neurocognitive function and fertility and avoid radiation-induced second cancer, such as brain tumor,” he said.
Lower toxicity
With regard to toxicity, the majority of patients (n = 98, 88%) developed cytokine release syndrome, which was grade ≥3 in 64 (28.4%) patients and fatal in one. Neurotoxicity occurred in 47 (20.9%) patients, was of grade ≥3 in 9 (4.0%) patients, and was fatal in 2 patients who received 12 x 106 and 5.6 x 106 CAR T cells/kg.
In addition, grade 3 or 4 seizure developed in 14.2% of the patients; it was more common in those who had presented with isolated or combined CNS leukemia. Grade 3 or 4 hypotension occurred in 40.9% of the patients. About three-quarters of the patients were treated with tocilizumab (n = 67, 74.2%), and 79 (35.1%) were treated with corticosteroids.
“In general, CD19 and CD22 CAR T cells were less toxic than CD19 CAR T cells, the historical controls, in our experience,” said Dr. Pui. “There were three fatal complications, a rate not excessive considering a large number of patients were treated.”
Future studies needed
The researchers note that in this trial, the CD22 CAR T cells did not expand as robustly or persist as long as did the CD19 CAR T cells, and they hope that future studies will elucidate whether enhancing CD22 CAR T-cell persistence and activity would further improve outcomes.
The study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Translational Medicine, the Research Programs of Shanghai Science, the Technology Commission Foundation, the U.S. National Cancer Institute, the VIVA China Children’s Cancer Foundation, and the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this trial, the largest study to date of a CAR T-cell therapy for such patients, the researchers co-administered two CAR T-cell therapies, one targeting CD19 and the other targeting CD22.
The results showed that 192 of 194 patients (99%) achieved a complete remission.
The combined overall 12-month event-free survival was 73.5%.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
These results are better than what has been reported for CAR T cells that are already on the market. These products, which target CD19, have achieved complete remission in 85.5% of cases and a 12-month event-free survival of 52.4% in children with B-ALL.
“We do believe [this approach] will become standard of care,” said study author Ching-Hon Pui, MD, of the departments of oncology, pathology, and global pediatric medicine, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis.
He noted that this work builds on the huge success that has already been achieved in this field with CAR T-cell products directed at CD19. The first of these products to reach the market was tisagenlecleucel-T (Novartis).
“To put this study in context, the first child who received CAR T-cell therapy for B-ALL after multiple relapses has recently celebrated her 10-year cancer-free survival milestone, and we hope that our finding will result in many more such milestones,” he said.
These new results are very impressive, said Stephen P. Hunger, MD, an expert commenting for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which highlighted the research in a press release. “They were also able to treat almost 200 patients in a relatively short time.”
Hunger pointed out that dual administration and targeting is not a new idea and is one of the strategies that is currently under investigation. But it is too early to consider this to be the standard of care, he said. “We want to see it replicated in other centers and to see longer follow-up,” said Dr. Hunger, who is Distinguished Chair in Pediatrics and director of the center for childhood cancer research at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “We can establish this as a first step down the road, and we will see if others will achieve similar results.”
Strategy of dual targeting
Despite the success CAR T-cell therapy in childhood leukemia, the currently available products have limitations, Dr. Pui and colleagues note.
About half of patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells experience relapse within 1 year, owing either to loss of CAR T-cell persistence or to loss of CD19 antigen because of splice variants, acquired genetic mutations, or lineage switch.
With further treatment with CAR T cells directed against CD22, 70%-80% of patients who failed CD19 CAR T will achieve into complete remission. However, most will experience relapse.
Recent efforts in the field have turned to exploring the safety and feasibility of CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results were not superior to those of the CD19 CAR T-cell therapy given alone, although sequential treatment has yielded promising response rates, the authors note.
They hypothesized that co-administration of CD19- and CD22-targeted CAR T cells would improve efficacy, as it could forestall the development of drug resistance.
Achieved 99% remission
Dr. Pui and colleagues conducted a phase 2 trial that included 225 evaluable patients aged 20 years or younger who were being treated at five urban hospitals in and near Shanghai, China. Of this group, 194 had refractory disease or hematologic relapse, and 31 patients had isolated extramedullary relapse.
A safety run-in stage to determine the recommended dose was initially conducted. An interim analysis of the first 30 patients who were treated (27 at the recommended dose) showed that the approach was safe and effective. Additional patients were then enrolled.
The 192 patients (of 194) who achieved complete remission attained negative minimal residual disease status.
At a median follow-up of 11 months, 43 patients experienced relapse (24 with CD191/CD221 relapse, 16 with CD19– /CD221, one with CD19– /CD22– , and two unknown), for a cumulative risk of 22.2%.
Transplant and relapse options
In an interview, Dr. Pui noted that various treatment options were available for the children who experienced relapse. “For patients who were in good clinical condition, we will treat them with molecular therapeutics, allogeneic CAR T cells from donor, or even repeated humanized CD19 and/or CD22 CAR T cells with or without CD20 CAR T cells in an attempt to induce a remission for allogeneic transplantation,” he said.
The site-specific 12-month event-free survival rate in the trial was 69.2% for patients who did not receive a transplant, 95% for those children who had an isolated relapse to the testicles, and 68.6% for those who had an isolated central nervous system relapse.
After censoring 78 patients for consolidative transplantation, the 12-month overall survival was 87.7%.
Consolidative transplantation was performed in 24 of the 37 patients with KMT2A-rearranged or ZNF384-rearranged ALL and in 54 patients because of parental request. The reason for this was that patients with these two genetic subtypes of leukemia (KMT2A-rearranged and ZNF384-rearranged), under the pressure of phenotype-specific treatment (such as CAR T cells or blinatumomab) are at risk of lineage switch and development of secondary acute myeloid leukemia, explained Dr. Pui. “That is an even more resistant form of leukemia, and up to 5%-10% of the patients have been reported to develop this complication.
“We performed consolidation transplantation in these patients to avoid the risk of lineage switch but would accept the parental request not to perform allogeneic transplant after they were clearly informed of the risk,” he told this news organization.
He also suggested that this approach of co-administration of two types of CAR T cells would be especially suitable for “patients with extramedullary involvement, because most of them will be spared of local irradiation so that they can preserve their neurocognitive function and fertility and avoid radiation-induced second cancer, such as brain tumor,” he said.
Lower toxicity
With regard to toxicity, the majority of patients (n = 98, 88%) developed cytokine release syndrome, which was grade ≥3 in 64 (28.4%) patients and fatal in one. Neurotoxicity occurred in 47 (20.9%) patients, was of grade ≥3 in 9 (4.0%) patients, and was fatal in 2 patients who received 12 x 106 and 5.6 x 106 CAR T cells/kg.
In addition, grade 3 or 4 seizure developed in 14.2% of the patients; it was more common in those who had presented with isolated or combined CNS leukemia. Grade 3 or 4 hypotension occurred in 40.9% of the patients. About three-quarters of the patients were treated with tocilizumab (n = 67, 74.2%), and 79 (35.1%) were treated with corticosteroids.
“In general, CD19 and CD22 CAR T cells were less toxic than CD19 CAR T cells, the historical controls, in our experience,” said Dr. Pui. “There were three fatal complications, a rate not excessive considering a large number of patients were treated.”
Future studies needed
The researchers note that in this trial, the CD22 CAR T cells did not expand as robustly or persist as long as did the CD19 CAR T cells, and they hope that future studies will elucidate whether enhancing CD22 CAR T-cell persistence and activity would further improve outcomes.
The study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Translational Medicine, the Research Programs of Shanghai Science, the Technology Commission Foundation, the U.S. National Cancer Institute, the VIVA China Children’s Cancer Foundation, and the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this trial, the largest study to date of a CAR T-cell therapy for such patients, the researchers co-administered two CAR T-cell therapies, one targeting CD19 and the other targeting CD22.
The results showed that 192 of 194 patients (99%) achieved a complete remission.
The combined overall 12-month event-free survival was 73.5%.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
These results are better than what has been reported for CAR T cells that are already on the market. These products, which target CD19, have achieved complete remission in 85.5% of cases and a 12-month event-free survival of 52.4% in children with B-ALL.
“We do believe [this approach] will become standard of care,” said study author Ching-Hon Pui, MD, of the departments of oncology, pathology, and global pediatric medicine, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis.
He noted that this work builds on the huge success that has already been achieved in this field with CAR T-cell products directed at CD19. The first of these products to reach the market was tisagenlecleucel-T (Novartis).
“To put this study in context, the first child who received CAR T-cell therapy for B-ALL after multiple relapses has recently celebrated her 10-year cancer-free survival milestone, and we hope that our finding will result in many more such milestones,” he said.
These new results are very impressive, said Stephen P. Hunger, MD, an expert commenting for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which highlighted the research in a press release. “They were also able to treat almost 200 patients in a relatively short time.”
Hunger pointed out that dual administration and targeting is not a new idea and is one of the strategies that is currently under investigation. But it is too early to consider this to be the standard of care, he said. “We want to see it replicated in other centers and to see longer follow-up,” said Dr. Hunger, who is Distinguished Chair in Pediatrics and director of the center for childhood cancer research at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “We can establish this as a first step down the road, and we will see if others will achieve similar results.”
Strategy of dual targeting
Despite the success CAR T-cell therapy in childhood leukemia, the currently available products have limitations, Dr. Pui and colleagues note.
About half of patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells experience relapse within 1 year, owing either to loss of CAR T-cell persistence or to loss of CD19 antigen because of splice variants, acquired genetic mutations, or lineage switch.
With further treatment with CAR T cells directed against CD22, 70%-80% of patients who failed CD19 CAR T will achieve into complete remission. However, most will experience relapse.
Recent efforts in the field have turned to exploring the safety and feasibility of CAR T cells that target both CD19 and CD22. The results were not superior to those of the CD19 CAR T-cell therapy given alone, although sequential treatment has yielded promising response rates, the authors note.
They hypothesized that co-administration of CD19- and CD22-targeted CAR T cells would improve efficacy, as it could forestall the development of drug resistance.
Achieved 99% remission
Dr. Pui and colleagues conducted a phase 2 trial that included 225 evaluable patients aged 20 years or younger who were being treated at five urban hospitals in and near Shanghai, China. Of this group, 194 had refractory disease or hematologic relapse, and 31 patients had isolated extramedullary relapse.
A safety run-in stage to determine the recommended dose was initially conducted. An interim analysis of the first 30 patients who were treated (27 at the recommended dose) showed that the approach was safe and effective. Additional patients were then enrolled.
The 192 patients (of 194) who achieved complete remission attained negative minimal residual disease status.
At a median follow-up of 11 months, 43 patients experienced relapse (24 with CD191/CD221 relapse, 16 with CD19– /CD221, one with CD19– /CD22– , and two unknown), for a cumulative risk of 22.2%.
Transplant and relapse options
In an interview, Dr. Pui noted that various treatment options were available for the children who experienced relapse. “For patients who were in good clinical condition, we will treat them with molecular therapeutics, allogeneic CAR T cells from donor, or even repeated humanized CD19 and/or CD22 CAR T cells with or without CD20 CAR T cells in an attempt to induce a remission for allogeneic transplantation,” he said.
The site-specific 12-month event-free survival rate in the trial was 69.2% for patients who did not receive a transplant, 95% for those children who had an isolated relapse to the testicles, and 68.6% for those who had an isolated central nervous system relapse.
After censoring 78 patients for consolidative transplantation, the 12-month overall survival was 87.7%.
Consolidative transplantation was performed in 24 of the 37 patients with KMT2A-rearranged or ZNF384-rearranged ALL and in 54 patients because of parental request. The reason for this was that patients with these two genetic subtypes of leukemia (KMT2A-rearranged and ZNF384-rearranged), under the pressure of phenotype-specific treatment (such as CAR T cells or blinatumomab) are at risk of lineage switch and development of secondary acute myeloid leukemia, explained Dr. Pui. “That is an even more resistant form of leukemia, and up to 5%-10% of the patients have been reported to develop this complication.
“We performed consolidation transplantation in these patients to avoid the risk of lineage switch but would accept the parental request not to perform allogeneic transplant after they were clearly informed of the risk,” he told this news organization.
He also suggested that this approach of co-administration of two types of CAR T cells would be especially suitable for “patients with extramedullary involvement, because most of them will be spared of local irradiation so that they can preserve their neurocognitive function and fertility and avoid radiation-induced second cancer, such as brain tumor,” he said.
Lower toxicity
With regard to toxicity, the majority of patients (n = 98, 88%) developed cytokine release syndrome, which was grade ≥3 in 64 (28.4%) patients and fatal in one. Neurotoxicity occurred in 47 (20.9%) patients, was of grade ≥3 in 9 (4.0%) patients, and was fatal in 2 patients who received 12 x 106 and 5.6 x 106 CAR T cells/kg.
In addition, grade 3 or 4 seizure developed in 14.2% of the patients; it was more common in those who had presented with isolated or combined CNS leukemia. Grade 3 or 4 hypotension occurred in 40.9% of the patients. About three-quarters of the patients were treated with tocilizumab (n = 67, 74.2%), and 79 (35.1%) were treated with corticosteroids.
“In general, CD19 and CD22 CAR T cells were less toxic than CD19 CAR T cells, the historical controls, in our experience,” said Dr. Pui. “There were three fatal complications, a rate not excessive considering a large number of patients were treated.”
Future studies needed
The researchers note that in this trial, the CD22 CAR T cells did not expand as robustly or persist as long as did the CD19 CAR T cells, and they hope that future studies will elucidate whether enhancing CD22 CAR T-cell persistence and activity would further improve outcomes.
The study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Translational Medicine, the Research Programs of Shanghai Science, the Technology Commission Foundation, the U.S. National Cancer Institute, the VIVA China Children’s Cancer Foundation, and the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
An adolescent male presents with an eroded bump on the temple
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
The clitoris steps into the spotlight with major scientific discovery
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More Than a Health Fair: Preventive Health Care During COVID-19 Vaccine Events
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
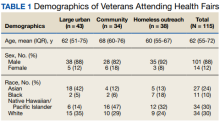
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
Shortly into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, warned of a coming tsunami of chronic diseases, exacerbated by missed care during the pandemic.1 According to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) survey, more than 30% of adults reported delaying or avoiding routine medical care in the first 6 months of 2020. This rate was highest in people with comorbidities.2 Multiple studies demonstrated declines in hypertension care, hemoglobin A1c testing, mammography, and colon cancer screening.3-5 There has been a resultant increase in colon cancer complications, wounds, and amputations.6,7 The United Kingdom is expected to have a 7.9% to 16.6% increase in future deaths due to breast and colorectal cancer (CRC).8 The World Health Organization estimates an excess 14.9 million people died in 2020 and 2021, either directly from or indirectly related to COVID-19.9
Due to the large-scale conversion from face-to-face care to telehealth modalities, COVID-19 vaccination events offered a unique opportunity to perform preventive health care that requires in-person visits, since most US adults have sought vaccination. However, vaccine events may not reach people most at risk for COVID-19 or chronic disease. Groups of Americans with lower vaccination rates were concerned about driving times and missing work to get the vaccine.10
Distance and travel time may be a particular challenge in Hawaii. Oahu is considered rural by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA); some communities are 80 minutes away from the VA Pacific Islands Health Care System (VAPIHCS) main facility. Oahu has approximately 150 veterans experiencing homelessness who may not have transportation to vaccine events. Additionally, VAPIHCS serves veterans that may be at higher risk of not receiving COVID-19 vaccination. Racial and ethnic minority residents have lower vaccination rates, yet are at a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and complications, and through the pandemic, this vaccination gap worsened.11,12 More than 10% of the population of Hawaii is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and this population is at elevated risk for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and COVID-19 mortality.13-16
Health Fair Program
The VA provides clinical reminders in its electronic health record (EHR) that are specified by age, gender assigned at birth, and comorbidities. The clinical reminder program is intended to provide clinically relevant reminders for preventive care at the point of care. Veterans with overdue clinical reminders can be identified by name and address, allowing for the creation of health fair events that were directed towards communities with veterans with clinical reminders, including COVID-19 vaccination need. A team of health care professionals from VAPIHCS conceived of a health fair program to increase the reach of vaccine events and include preventive care in partnership with the VAPIHCS Vet Center Program, local communities, U.S.VETS, and the Hawaii Institute of Health Services (HIHS). We sought to determine which services could be offered in community settings; large vaccine events; and at homeless emergency, transitional, or permanent housing. We tracked veterans who received care in the different locations of the directed health fair.
This project was determined to be a quality improvement initiative by the VAPIHCS Office of Research and Development. It was jointly planned by the VAPIHCS pharmacy, infectious diseases, Vet Center Program, and homeless team to make the COVID-19 vaccines available to more rural and to veterans experiencing homelessness, and in response to a decline in facility face-to-face visits. Monthly meetings were held to select sites within zip codes with higher numbers of open clinical reminders and lower vaccination uptake. Informatics developed a list of clinical reminders by zip code for care performed at face-to-face visits.
Partners
The Vet Center Program, suicide prevention coordinator, and the homeless outreach team have a mandate to perform outreach events.17,18 These services collaborate with community partners to locate sites for events. The team was able to leverage these contacts to set up sites for events. The Vet Center Program readjustment counselor and the suicide prevention coordinator provide mental health counseling. The Vet Center counsels on veteran benefits. They supplied a mobile van with WiFi, counseling and examination spaces, and refrigeration, which became the mobile clinic for the preventive care offered at events. The homeless program works with multiple community partners. They contract with HIHS and U.S.VETS to provide emergency and permanent housing for veterans. Each event is reviewed with HIHS and U.S.VETS staff for permission to be on site. The suicide prevention coordinator or the Vet Center readjustment counselor and the homeless team became regular attendees of events. The homeless team provided resources for housing or food insecurity.
Preventive Health Measures
The VA clinical reminder system supports caregivers for both preventive health care and chronic condition management.19 Clinical reminders appear as due in the EHR, and reminder reports can be run by clinical informatics to determine groups of patients who have not had a reminder completed. The following reminders were completed: vaccinations (including COVID-19), CRC screening, diabetic foot check and teaching of foot care, diabetic retinal consultations, laboratory studies (lipids, hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin), mammogram and pap smear referrals, mental health reminders, homeless and food insecurity screening, HIV and hepatitis C testing, and blood pressure (BP) measurement. Health records were reviewed 3 months after each event to determine whether they were completed by the veteran. Additionally, we determined whether BP was controlled (< 130/80 mm Hg).
Settings
Large urban event. The first setting for the health fair was a large vaccination event near the VAPIHCS center in April 2021. Attendance was solicited by VEText, phone calls, and social media advertisements. At check-in, veterans with relevant open clinical reminders were invited to receive preventive health care during the 15-minute monitoring period after the COVID-19 vaccine. The Vet Center Program stationed the mobile van outside the vaccination event, where a physician and a clinical pharmacy specialist (CPS) did assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests for about 4 hours. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Community Settings. Nine events occurred at least monthly between March and September 2021 at 4 different sites in Oahu. Texts and phone calls were used to solicit attendance; there was no prior publicity on social media. Community events required scheduling resources; this required about 30 hours of medical staff assistant time. Seven sites were visited for about 3 hours each. A physician, pharmacy technician, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans who had never signed up for VA health care.
Homeless veteran outreach. Five events occurred at 2 homeless veteran housing sites between August 2021 and January 2022. These sites were emergency housing sites (2 events) and transitional and permanent housing (2 events). U.S.VETS and HIHS contacted veterans living in those settings to promote the event. A physician, registered nurse, licensed practical nurse, and CPS conducted assessments, completed reminders, and entered follow-up requests. A medical support assistant registered veterans that had never signed up for VA health care. Each event lasted approximate 3 hours.
Process Quality Improvement
After the CDC changed recommendations to allow concurrent vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine, we added other vaccinations to the events. This occurred during the course of community events. In June of 2021, there was a health advisory concerning hepatitis A among people experiencing homelessness in Oahu, so hepatitis vaccinations were added for events for veterans.20
Veterans Served
The EHR was used to determine demographics, open clinical reminders, and attendance at follow-up. Simple descriptive statistics were performed in Microsoft Excel. A total of 115 veterans were seen for preventive health visits, and 404 clinical reminders were completed. Seven hundred veterans attended the large centrally located vaccine event and 43 agreed to have a preventive health visit. Thirty-eight veterans had a preventive health visit at homeless outreach events and 34 veterans had a preventive health visit at the community events. Veterans at community
Of the 166 vaccines given, 73 were for COVID-19. Besides vaccination,
Veteran follow-up or completion
Discussion
This program provided evidence that adding preventive screenings to vaccine events may help reach veterans who may have missed important preventive care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The involvement of clinical informatics service allowed the outreach to be targeted to communities with incomplete clinical reminders. Interventions that could not be completed at the event had high levels of follow-up by veterans with important findings. The presence of a physician or nurse and a CPS allowed for point-of-care testing, as well as entering orders for medication, laboratory tests, and consultations. The attendance by representatives from the Vet Center, suicide prevention, and homeless services allowed counseling regarding benefits, and mental health follow-up. We believe that we were able to reach communities of veterans with unmet preventive needs and had higher risk of severe COVID-19, given the high numbers with open clinical reminders, the number of vaccines provided, and the high percentage of racial and ethnic minority veterans at events in the community. Our program experience provides some evidence that mobile and pop-up vaccination clinics may be beneficial for screening and managing chronic diseases, as proposed elsewhere.21-24
Strengths of this intervention include that we were able to show a high level of follow-up for recommended medical care as well as the results of our interventions. We have found no similar articles that provide data on completion of follow-up appointments after a health fair. A prior study showed only 23% to 63% of participants at a health fair reported having a recommended follow-up discussion with doctors, but the study reported no outcome of completed cancer screenings.25
Limitations
Weaknesses include the fact that health fair events may reach only healthy people, since attendees generally report better health and better health behaviors than nonattendees.26,27 We felt this was more problematic for the large-scale urban event and that offering rural events and events in homeless housing improved the reach. Future efforts will involve the use of social media and mailings to solicit attendance. To improve follow-up, future work will include adding to the events: phlebotomy or expanded point-of-care testing; specialty care telehealth capability; cervical cancer screen self-collection; and tele-retinal services.
Conclusions
This program provided evidence that directed, preventive screening can be performed in outreach settings paired with vaccine events. These vaccination events in rural and homeless settings reached communities with demonstrable COVID-19 vaccination and other preventive care needs. This approach could be used to help veterans catch up on needed preventive care.
Acknowledgments
Veterans Affairs Pacific Islands Health Care System: Anthony Chance, LCSW; Nicholas Chang, PharmD; Andrew Dahlburg, LCSW; Wilminia G. Ellorimo-Gil, RN; Paul Guillory, RN; Wendy D. Joy; Arthur Minor, LCSW; Avalua Smith; Jessica Spurrier, RN. Veterans Health Administration Vet Center Program: Rolly O. Alvarado; Edmond G. DeGuzman; Richard T. Teel. Hawaii Institute for Human Services. U.S.VETS.
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
1. Califf RM. Avoiding the coming tsunami of common, chronic disease: What the lessons of the COVID-19 pandemic can teach us. Circulation. 2021;143(19):1831-1834. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053461
2. Czeisler MÉ, Marynak K, Clarke KEN, et al. Delay or avoidance of medical care because of COVID-19-related concerns - United States, June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1250-1257. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6936a4
3. European Society of Hypertension Corona-virus Disease 19 Task Force. The corona-virus disease 2019 pandemic compromised routine care for hypertension: a survey conducted among excellence centers of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):190-195. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000002703
4. Whaley CM, Pera MF, Cantor J, et al. Changes in health services use among commercially insured US populations during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2024984. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.24984
5. Song H, Bergman A, Chen AT, et al. Disruptions in preventive care: mammograms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Serv Res. 2021;56(1):95-101. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13596
6. Shinkwin M, Silva L, Vogel I, et al. COVID-19 and the emergency presentation of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2021;23(8):2014-2019. doi:10.1111/codi.15662
7. Rogers LC, Snyder RJ, Joseph WS. Diabetes-related amputations: a pandemic within a pandemic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;20-248. doi:10.7547/20-248
8. Maringe C, Spicer J, Morris M, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(8):1023-1034. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30388-0
9. World Health Organization. 14.9 million excess deaths associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. May 5, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-covid-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021
10. Padamsee TJ, Bond RM, Dixon GN, et al. Changes in COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Black and White individuals in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(1):e2144470. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44470
11. Barry V, Dasgupta S, Weller DL, et al. Patterns in COVID-19 vaccination coverage, by social vulnerability and urbanicity - United States, December 14, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(22):818-824. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7022e1
12. Baack BN, Abad N, Yankey D, et al. COVID-19 vaccination coverage and intent among adults aged 18-39 years - United States, March-May 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(25):928-933. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7025e2
13. United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts Hawaii. July 7, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/HI
14. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. Diabetes - Adult. November 23, 2021. Updated July 31, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXDiabetesAA.html
15. Hawaii Health Data Warehouse. High Blood Pressure, Adult. November 23, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://hhdw.org/report/indicator/summary/DXBPHighAA.html
16. Penaia CS, Morey BN, Thomas KB, et al. Disparities in Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander COVID-19 mortality: a community-driven data response. Am J Public Health. 2021;111(S2):S49-S52. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2021.306370
17. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1500.02 Readjustment Counseling Services (RCS) Vet Center Program. January 26, 2021. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9168
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1162.08 Health Care for Veterans Homeless Outreach Services. February 18, 2022. Accessed September 7, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=9673
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical Reminders Version 2.0. Clinician Guide. October 2006. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vdl/documents/clinical/cprs-clinical_reminders/pxrm_2_4_um.pdf
20. Hawaii Department of Health. Hepatitis A Cases on Oahu and Maui. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2021/06/Medical-Advisory-HepA-June-21-2021.pdf
21. Hamel L, Lopes L, Sparks G, et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: January 2022. January 28, 2022. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/poll-finding/kff-covid-19-vaccine-monitor-january-2022
22. Mast C, Munoz del Rio A. Delayed cancer screenings—a second look. Epic Research Network. July 17, 2020. Accessed August 31, 2022. https://epicresearch.org/articles/delayed-cancer-screenings-a-second-look
23. Shaukat A, Church T. Colorectal cancer screening in the USA in the wake of COVID-19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(8):726-727. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30191-6
24. Crespo J, Lazarus JV, Iruzubieta P, García F, García-Samaniego J; Alliance for the elimination of viral hepatitis in Spain. Let’s leverage SARS-CoV2 vaccination to screen for hepatitis C in Spain, in Europe, around the world. J Hepatol. 2021;75(1):224-226. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.009
25. Escoffery C, Liang S, Rodgers K, et al. Process evaluation of health fairs promoting cancer screenings. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):865. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3867-3
26. Waller PR, Crow C, Sands D, Becker H. Health related attitudes and health promoting behaviors: differences between health fair attenders and a community group. Am J Health Promot. 1988;3(1):17-32. doi:10.4278/0890-1171-3.1.17
27. Price JH, O’Connell J, Kukulka G. Preventive health behaviors related to the ten leading causes of mortality of health-fair attenders and nonattenders. Psychol Rep. 1985;56(1):131-135. doi:10.2466/pr0.1985.56.1.131
Thoracic Oncology & Chest Imaging Network
Ultrasound & Chest Imaging Section
VExUS scan: The missing piece of hemodynamic puzzle?
Volume status and tailoring the correct level of fluid resuscitation is challenging for the intensivist. Determining “fluid overload,” especially in the setting of acute kidney injury, can be difficult. While a Swan-Ganz catheter, central venous pressure, or inferior vena cava (IVC) ultrasound measurement can suggest elevated right atrial pressure, the effect on organ level hemodynamics is unknown.
Abdominal venous Doppler is a method to view the effects of venous pressure on abdominal organ venous flow. An application of this is the Venous Excess Ultrasound Score (VExUS) (Rola, et al. Ultrasound J. 2021;13[1]:32). VExUS uses IVC diameter and pulse wave doppler waveforms from the hepatic, portal, and renal veins to grade venous congestion from none to severe. Studies demonstrate an association between venous congestion and renal dysfunction in cardiac surgery (Beaubien-Souligny, et al. Ultrasound J. 2020;12[1]:16) and general ICU patients (Spiegel, et al. Crit Care. 2020;24[1]:615).
This practice of identifying venous congestion and avoiding over-resuscitation could improve patient care. However, acquiring quality images and waveforms may prove to be difficult, and interpretation may be confounded by other disease states such as cirrhosis. Though it is postulated that removing fluid could be beneficial to patients with high VExUS scores, this has yet to be proven and may be difficult to prove. While the score estimates volume status well, the source of venous congestion is not identified such that it should be used as a clinical supplement to other data.
VExUS has a strong physiologic basis, and early clinical experience indicates a strong role in improving assessment of venous congestion, an important aspect of volume status. This is an area of ongoing research to ensure appropriate and effective use.
Kyle Swartz, DO
Steven Fox, MD
John Levasseur, DO
Ultrasound & Chest Imaging Section
VExUS scan: The missing piece of hemodynamic puzzle?
Volume status and tailoring the correct level of fluid resuscitation is challenging for the intensivist. Determining “fluid overload,” especially in the setting of acute kidney injury, can be difficult. While a Swan-Ganz catheter, central venous pressure, or inferior vena cava (IVC) ultrasound measurement can suggest elevated right atrial pressure, the effect on organ level hemodynamics is unknown.
Abdominal venous Doppler is a method to view the effects of venous pressure on abdominal organ venous flow. An application of this is the Venous Excess Ultrasound Score (VExUS) (Rola, et al. Ultrasound J. 2021;13[1]:32). VExUS uses IVC diameter and pulse wave doppler waveforms from the hepatic, portal, and renal veins to grade venous congestion from none to severe. Studies demonstrate an association between venous congestion and renal dysfunction in cardiac surgery (Beaubien-Souligny, et al. Ultrasound J. 2020;12[1]:16) and general ICU patients (Spiegel, et al. Crit Care. 2020;24[1]:615).
This practice of identifying venous congestion and avoiding over-resuscitation could improve patient care. However, acquiring quality images and waveforms may prove to be difficult, and interpretation may be confounded by other disease states such as cirrhosis. Though it is postulated that removing fluid could be beneficial to patients with high VExUS scores, this has yet to be proven and may be difficult to prove. While the score estimates volume status well, the source of venous congestion is not identified such that it should be used as a clinical supplement to other data.
VExUS has a strong physiologic basis, and early clinical experience indicates a strong role in improving assessment of venous congestion, an important aspect of volume status. This is an area of ongoing research to ensure appropriate and effective use.
Kyle Swartz, DO
Steven Fox, MD
John Levasseur, DO
Ultrasound & Chest Imaging Section
VExUS scan: The missing piece of hemodynamic puzzle?
Volume status and tailoring the correct level of fluid resuscitation is challenging for the intensivist. Determining “fluid overload,” especially in the setting of acute kidney injury, can be difficult. While a Swan-Ganz catheter, central venous pressure, or inferior vena cava (IVC) ultrasound measurement can suggest elevated right atrial pressure, the effect on organ level hemodynamics is unknown.
Abdominal venous Doppler is a method to view the effects of venous pressure on abdominal organ venous flow. An application of this is the Venous Excess Ultrasound Score (VExUS) (Rola, et al. Ultrasound J. 2021;13[1]:32). VExUS uses IVC diameter and pulse wave doppler waveforms from the hepatic, portal, and renal veins to grade venous congestion from none to severe. Studies demonstrate an association between venous congestion and renal dysfunction in cardiac surgery (Beaubien-Souligny, et al. Ultrasound J. 2020;12[1]:16) and general ICU patients (Spiegel, et al. Crit Care. 2020;24[1]:615).
This practice of identifying venous congestion and avoiding over-resuscitation could improve patient care. However, acquiring quality images and waveforms may prove to be difficult, and interpretation may be confounded by other disease states such as cirrhosis. Though it is postulated that removing fluid could be beneficial to patients with high VExUS scores, this has yet to be proven and may be difficult to prove. While the score estimates volume status well, the source of venous congestion is not identified such that it should be used as a clinical supplement to other data.
VExUS has a strong physiologic basis, and early clinical experience indicates a strong role in improving assessment of venous congestion, an important aspect of volume status. This is an area of ongoing research to ensure appropriate and effective use.
Kyle Swartz, DO
Steven Fox, MD
John Levasseur, DO
Critical Care Network
Sepsis/Shock Section
Fluid Resuscitation – Back to BaSICS
The age-old debate regarding the appropriate timing, volume, and type of fluid resuscitation for patients in septic shock rages on – or does it? In October 2021, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign published updated guidelines for the management of sepsis. One of the biggest changes from prior versions was downgrading the recommendation for an initial 30mL/kg bolus of IV crystalloid for the initial resuscitation of a patient in septic shock to a suggestion, based on dynamic measures to assess individual patients’ fluid balance (Evans, et al. Crit Care Med. 2021;49[11]:e1063-e1143).
Traditionally, 0.9% saline had been the resuscitative fluid of choice in sepsis. But it has a propensity to cause physiologic derangements such as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, renal afferent vasoconstriction, and reduced glomerular filtration rate – not to mention, can be a signal for possibly increased mortality, as seen in the SMART trial (Semler, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378[9]:829-839). Normal saline had subsequently fallen from grace in favor of balanced crystalloids such as Lactated Ringer’s and Plasma-Lyte. However, the recent PLUS and BaSICS trials showed no significant difference in 90-day mortality or secondary outcomes of acute kidney injury, need for renal replacement therapy, or ICU mortality (Finfer, et al. N Engl J Med. 2022;386[9]:815-826; Zampieri, et al. JAMA. 2021;326[9]:818-829). While these are large randomized controlled trials, a major weakness is the administration of uncontrolled resuscitative fluids prior to randomization and even postenrollment, which may have biased results.
Ultimately, does the choice between salt water or balanced crystalloids matter? Despite the limitations in the newest trials, probably less than the timely administration of antibiotics and pressors, unless your patient also has a traumatic TBI – then go with the saline. But, in the everlasting quest for medical excellence, choosing the balanced fluid that causes the least physiologic derangement seems to make the most sense.
LCDR Meredith Olsen, MD, USN
Ankita Agarwal, MD
The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
Sepsis/Shock Section
Fluid Resuscitation – Back to BaSICS
The age-old debate regarding the appropriate timing, volume, and type of fluid resuscitation for patients in septic shock rages on – or does it? In October 2021, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign published updated guidelines for the management of sepsis. One of the biggest changes from prior versions was downgrading the recommendation for an initial 30mL/kg bolus of IV crystalloid for the initial resuscitation of a patient in septic shock to a suggestion, based on dynamic measures to assess individual patients’ fluid balance (Evans, et al. Crit Care Med. 2021;49[11]:e1063-e1143).
Traditionally, 0.9% saline had been the resuscitative fluid of choice in sepsis. But it has a propensity to cause physiologic derangements such as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, renal afferent vasoconstriction, and reduced glomerular filtration rate – not to mention, can be a signal for possibly increased mortality, as seen in the SMART trial (Semler, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378[9]:829-839). Normal saline had subsequently fallen from grace in favor of balanced crystalloids such as Lactated Ringer’s and Plasma-Lyte. However, the recent PLUS and BaSICS trials showed no significant difference in 90-day mortality or secondary outcomes of acute kidney injury, need for renal replacement therapy, or ICU mortality (Finfer, et al. N Engl J Med. 2022;386[9]:815-826; Zampieri, et al. JAMA. 2021;326[9]:818-829). While these are large randomized controlled trials, a major weakness is the administration of uncontrolled resuscitative fluids prior to randomization and even postenrollment, which may have biased results.
Ultimately, does the choice between salt water or balanced crystalloids matter? Despite the limitations in the newest trials, probably less than the timely administration of antibiotics and pressors, unless your patient also has a traumatic TBI – then go with the saline. But, in the everlasting quest for medical excellence, choosing the balanced fluid that causes the least physiologic derangement seems to make the most sense.
LCDR Meredith Olsen, MD, USN
Ankita Agarwal, MD
The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
Sepsis/Shock Section
Fluid Resuscitation – Back to BaSICS
The age-old debate regarding the appropriate timing, volume, and type of fluid resuscitation for patients in septic shock rages on – or does it? In October 2021, the Surviving Sepsis Campaign published updated guidelines for the management of sepsis. One of the biggest changes from prior versions was downgrading the recommendation for an initial 30mL/kg bolus of IV crystalloid for the initial resuscitation of a patient in septic shock to a suggestion, based on dynamic measures to assess individual patients’ fluid balance (Evans, et al. Crit Care Med. 2021;49[11]:e1063-e1143).
Traditionally, 0.9% saline had been the resuscitative fluid of choice in sepsis. But it has a propensity to cause physiologic derangements such as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, renal afferent vasoconstriction, and reduced glomerular filtration rate – not to mention, can be a signal for possibly increased mortality, as seen in the SMART trial (Semler, et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;378[9]:829-839). Normal saline had subsequently fallen from grace in favor of balanced crystalloids such as Lactated Ringer’s and Plasma-Lyte. However, the recent PLUS and BaSICS trials showed no significant difference in 90-day mortality or secondary outcomes of acute kidney injury, need for renal replacement therapy, or ICU mortality (Finfer, et al. N Engl J Med. 2022;386[9]:815-826; Zampieri, et al. JAMA. 2021;326[9]:818-829). While these are large randomized controlled trials, a major weakness is the administration of uncontrolled resuscitative fluids prior to randomization and even postenrollment, which may have biased results.
Ultimately, does the choice between salt water or balanced crystalloids matter? Despite the limitations in the newest trials, probably less than the timely administration of antibiotics and pressors, unless your patient also has a traumatic TBI – then go with the saline. But, in the everlasting quest for medical excellence, choosing the balanced fluid that causes the least physiologic derangement seems to make the most sense.
LCDR Meredith Olsen, MD, USN
Ankita Agarwal, MD
The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government.
Breaking the itch-scratch cycle with mindfulness
Apple A. Bodemer, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, teaches patients how to breathe mindfully. So does Kathy Farah, MD, an integrative family physician who practices in Roberts, Wis.
, they said at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“As with any integrative modality, if it’s safe and effective, then let’s use it,” Dr. Farah said in a presentation on the mind-body approach to pain and itch.
“A breathwork session can literally take 1 minute,” said Dr. Bodemer, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin and director of an integrative dermatology clinic. Dr. Bodemer, who completed a fellowship in integrative medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona and sits on the American Board of Integrative Medicine, spoke on a mindfulness panel at the meeting.
Her favorite breathing practice is the “4-7-8” breath taught by Andrew Weil, MD, founder and director of the center. This involves inhaling through the nose for a count of 4, holding for 7, and exhaling through the mouth for a count of 8. “It doesn’t matter how slow or fast, it’s the tempo that matters ... On exhale, squeeze your abs in to engage your core and get air out of your lungs as much as you can,” she said, advising a cycle of three at a time.
A technique known as “square breathing” (breath in 4, hold for 4, breath out for 4, hold for 4) is another helpful technique to “reset the nervous system” said Dr. Farah, who worked for many years in a children’s hospital. With children, she said, “I often do five finger breathing.”
For five finger breathing, the children spread their fingers apart in front of them or on the ground and use the pointer finger of the opposite hand to trace each finger, inhaling while tracing upward, and exhaling while tracing down.
Dr. Farah, associate clinical director of The Center for Mind-Body Medicine in Washington, DC, said her commitment to mindfulness was influenced by a “seminal” study published over 20 years ago showing that patients with moderate to severe psoriasis who used a meditation-based, audiotape-guided stress reduction intervention during phototherapy sessions had more rapid resolution of psoriatic lesions than did patients who didn’t use the mindfulness exercise.
Among more recent findings: A cross-sectional study of 120 adult dermatology patients, published in the British Journal of Dermatology in 2016, assessed skin shame, social anxiety, anxiety, depression, dermatological quality of life, and levels of mindfulness, and found that higher levels of mindfulness were associated with lower levels of psychosocial distress.
Another cross-sectional questionnaire study looked at mindfulness and “itch catastrophizing” in 155 adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Higher levels of a specific facet of mindfulness termed “acting with awareness” were associated with lower levels of itch catastrophizing, the researchers found. “Catastrophizing is a negative way of thinking, this itching will never stop,” Dr. Farah explained. The study shows that “mindfulness can actually help reduce some of the automatic scratching and response to itch. So it’s a great adjunct to pharmaceuticals.”
Affirmations – phrases and statements that are repeated to oneself to help challenge negative thoughts – can also help reverse itch catastrophizing. Statements such as “I can breathe through this feeling of itching,” or “I can move to feel comfortable and relaxed” encourage positive change, she said.
“I teach [mindfulness skills like breathing] a lot, without any expectations. I’ll say ‘give it a try and see what you think.’ If patients feel even a micron better, then they’re invested” and can then find numerous tools online, Dr. Farah said. “Can I do this [in a busy schedule] with every patient? Absolutely not. But can I do it with every 10th patient? Maybe.”
Dr. Bodemer’s experience has shown her that “breathing with your patient builds rapport,” she said. “There’s something very powerful in that in terms of building trust. ... I’ll just do it [during a visit, to show them] and almost always, patients start breathing with me, with an invitation or without.”
For her own health, 4-7-8 breathing has “been a gateway to meditation and deeper practices,” she said. “But even without going very deep, it has a long history of being able to modulate the stress response. It’s the parasympathetic-sympathetic rebalancing I’m interested in.”
Mindful breathing and other mind-body practices also can be helpful for parents of children with eczema, she and Dr. Farah said.
Dr. Bodemer and Dr. Farah reported no financial relationships to disclose.
Apple A. Bodemer, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, teaches patients how to breathe mindfully. So does Kathy Farah, MD, an integrative family physician who practices in Roberts, Wis.
, they said at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“As with any integrative modality, if it’s safe and effective, then let’s use it,” Dr. Farah said in a presentation on the mind-body approach to pain and itch.
“A breathwork session can literally take 1 minute,” said Dr. Bodemer, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin and director of an integrative dermatology clinic. Dr. Bodemer, who completed a fellowship in integrative medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona and sits on the American Board of Integrative Medicine, spoke on a mindfulness panel at the meeting.
Her favorite breathing practice is the “4-7-8” breath taught by Andrew Weil, MD, founder and director of the center. This involves inhaling through the nose for a count of 4, holding for 7, and exhaling through the mouth for a count of 8. “It doesn’t matter how slow or fast, it’s the tempo that matters ... On exhale, squeeze your abs in to engage your core and get air out of your lungs as much as you can,” she said, advising a cycle of three at a time.
A technique known as “square breathing” (breath in 4, hold for 4, breath out for 4, hold for 4) is another helpful technique to “reset the nervous system” said Dr. Farah, who worked for many years in a children’s hospital. With children, she said, “I often do five finger breathing.”
For five finger breathing, the children spread their fingers apart in front of them or on the ground and use the pointer finger of the opposite hand to trace each finger, inhaling while tracing upward, and exhaling while tracing down.
Dr. Farah, associate clinical director of The Center for Mind-Body Medicine in Washington, DC, said her commitment to mindfulness was influenced by a “seminal” study published over 20 years ago showing that patients with moderate to severe psoriasis who used a meditation-based, audiotape-guided stress reduction intervention during phototherapy sessions had more rapid resolution of psoriatic lesions than did patients who didn’t use the mindfulness exercise.
Among more recent findings: A cross-sectional study of 120 adult dermatology patients, published in the British Journal of Dermatology in 2016, assessed skin shame, social anxiety, anxiety, depression, dermatological quality of life, and levels of mindfulness, and found that higher levels of mindfulness were associated with lower levels of psychosocial distress.
Another cross-sectional questionnaire study looked at mindfulness and “itch catastrophizing” in 155 adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Higher levels of a specific facet of mindfulness termed “acting with awareness” were associated with lower levels of itch catastrophizing, the researchers found. “Catastrophizing is a negative way of thinking, this itching will never stop,” Dr. Farah explained. The study shows that “mindfulness can actually help reduce some of the automatic scratching and response to itch. So it’s a great adjunct to pharmaceuticals.”
Affirmations – phrases and statements that are repeated to oneself to help challenge negative thoughts – can also help reverse itch catastrophizing. Statements such as “I can breathe through this feeling of itching,” or “I can move to feel comfortable and relaxed” encourage positive change, she said.
“I teach [mindfulness skills like breathing] a lot, without any expectations. I’ll say ‘give it a try and see what you think.’ If patients feel even a micron better, then they’re invested” and can then find numerous tools online, Dr. Farah said. “Can I do this [in a busy schedule] with every patient? Absolutely not. But can I do it with every 10th patient? Maybe.”
Dr. Bodemer’s experience has shown her that “breathing with your patient builds rapport,” she said. “There’s something very powerful in that in terms of building trust. ... I’ll just do it [during a visit, to show them] and almost always, patients start breathing with me, with an invitation or without.”
For her own health, 4-7-8 breathing has “been a gateway to meditation and deeper practices,” she said. “But even without going very deep, it has a long history of being able to modulate the stress response. It’s the parasympathetic-sympathetic rebalancing I’m interested in.”
Mindful breathing and other mind-body practices also can be helpful for parents of children with eczema, she and Dr. Farah said.
Dr. Bodemer and Dr. Farah reported no financial relationships to disclose.
Apple A. Bodemer, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, teaches patients how to breathe mindfully. So does Kathy Farah, MD, an integrative family physician who practices in Roberts, Wis.
, they said at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“As with any integrative modality, if it’s safe and effective, then let’s use it,” Dr. Farah said in a presentation on the mind-body approach to pain and itch.
“A breathwork session can literally take 1 minute,” said Dr. Bodemer, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin and director of an integrative dermatology clinic. Dr. Bodemer, who completed a fellowship in integrative medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona and sits on the American Board of Integrative Medicine, spoke on a mindfulness panel at the meeting.
Her favorite breathing practice is the “4-7-8” breath taught by Andrew Weil, MD, founder and director of the center. This involves inhaling through the nose for a count of 4, holding for 7, and exhaling through the mouth for a count of 8. “It doesn’t matter how slow or fast, it’s the tempo that matters ... On exhale, squeeze your abs in to engage your core and get air out of your lungs as much as you can,” she said, advising a cycle of three at a time.
A technique known as “square breathing” (breath in 4, hold for 4, breath out for 4, hold for 4) is another helpful technique to “reset the nervous system” said Dr. Farah, who worked for many years in a children’s hospital. With children, she said, “I often do five finger breathing.”
For five finger breathing, the children spread their fingers apart in front of them or on the ground and use the pointer finger of the opposite hand to trace each finger, inhaling while tracing upward, and exhaling while tracing down.
Dr. Farah, associate clinical director of The Center for Mind-Body Medicine in Washington, DC, said her commitment to mindfulness was influenced by a “seminal” study published over 20 years ago showing that patients with moderate to severe psoriasis who used a meditation-based, audiotape-guided stress reduction intervention during phototherapy sessions had more rapid resolution of psoriatic lesions than did patients who didn’t use the mindfulness exercise.
Among more recent findings: A cross-sectional study of 120 adult dermatology patients, published in the British Journal of Dermatology in 2016, assessed skin shame, social anxiety, anxiety, depression, dermatological quality of life, and levels of mindfulness, and found that higher levels of mindfulness were associated with lower levels of psychosocial distress.
Another cross-sectional questionnaire study looked at mindfulness and “itch catastrophizing” in 155 adult patients with atopic dermatitis. Higher levels of a specific facet of mindfulness termed “acting with awareness” were associated with lower levels of itch catastrophizing, the researchers found. “Catastrophizing is a negative way of thinking, this itching will never stop,” Dr. Farah explained. The study shows that “mindfulness can actually help reduce some of the automatic scratching and response to itch. So it’s a great adjunct to pharmaceuticals.”
Affirmations – phrases and statements that are repeated to oneself to help challenge negative thoughts – can also help reverse itch catastrophizing. Statements such as “I can breathe through this feeling of itching,” or “I can move to feel comfortable and relaxed” encourage positive change, she said.
“I teach [mindfulness skills like breathing] a lot, without any expectations. I’ll say ‘give it a try and see what you think.’ If patients feel even a micron better, then they’re invested” and can then find numerous tools online, Dr. Farah said. “Can I do this [in a busy schedule] with every patient? Absolutely not. But can I do it with every 10th patient? Maybe.”
Dr. Bodemer’s experience has shown her that “breathing with your patient builds rapport,” she said. “There’s something very powerful in that in terms of building trust. ... I’ll just do it [during a visit, to show them] and almost always, patients start breathing with me, with an invitation or without.”
For her own health, 4-7-8 breathing has “been a gateway to meditation and deeper practices,” she said. “But even without going very deep, it has a long history of being able to modulate the stress response. It’s the parasympathetic-sympathetic rebalancing I’m interested in.”
Mindful breathing and other mind-body practices also can be helpful for parents of children with eczema, she and Dr. Farah said.
Dr. Bodemer and Dr. Farah reported no financial relationships to disclose.
FROM IDS 2022
Test strips ID fetal tissue in vaginal blood
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Treating deadly disease in utero called ‘revolutionary’ advance
The successful treatment of Pompe disease in utero for the first time may be the start of a new chapter for fetal therapy, researchers said.
A report published online in the New England Journal of Medicine describes in utero enzyme-replacement therapy (ERT) for infantile-onset Pompe disease.
The patient, now a toddler, is thriving, according to the researchers. Her parents previously had children with the same disorder who died.
“This treatment expands the repertoire of fetal therapies in a new direction,” Tippi MacKenzie, MD, a pediatric surgeon with University of California, San Francisco, Benioff Children’s Hospitals and a coauthor of the report, said in a news release. “As new treatments become available for children with genetic conditions, we are developing protocols to apply them before birth.”
Dr. MacKenzie codirects the University of California, San Francisco’s center for maternal-fetal precision medicine and directs the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research.
Pompe disease is caused by mutations in a gene that makes acid alpha-glucosidase. With limited amounts of this enzyme, dangerous amounts of glycogen accumulate in the body. Babies with infantile-onset disease typically have enlarged hearts and die by age 2 years.
The condition, which occurs in an estimated 1 in 40,000 births, is one of several early-onset lysosomal storage disorders. Patients with these diseases “are ideal candidates for prenatal therapy because organ damage starts in utero,” the researchers said.
Newborn screening can lead to early initiation of treatment with recombinant enzymes, “but this strategy does not completely prevent irreversible organ damage,” the authors said.
The patient in the new report received six prenatal ERT treatments at the Ottawa Hospital and is receiving postnatal enzyme therapy at CHEO, a pediatric hospital and research center in Ottawa.
Investigators administered alglucosidase alfa through the umbilical vein. They delivered the first infusion to the fetus at 24 weeks 5 days of gestation. They continued providing infusions at 2-week intervals through 34 weeks 5 days of gestation.
She is doing well at age 16 months, with normal cardiac and motor function, and is meeting developmental milestones, according to the news release.
The successful treatment involved collaboration among the University of California, San Francisco, where researchers are conducting a clinical trial of this treatment approach; CHEO and the Ottawa Hospital; and Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Under normal circumstances, the patient’s family would have traveled to Benioff Children’s Hospitals fetal treatment center to participate in the clinical trial, but COVID-19 restrictions led the researchers to deliver the therapy to Ottawa as part of the trial.
The University of California, San Francisco, has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval to treat Pompe disease and several other lysosomal storage disorders in utero as part of a phase 1 clinical trial with 10 patients. The other diseases are mucopolysaccharidosis types 1, 2, 4a, 6, and 7; Gaucher disease types 2 and 3; and Wolman disease.
Patients with Pompe disease might typically be diagnosed clinically at age 3-6 months, said study coauthor Paul Harmatz, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco. With newborn screening, the disease might be diagnosed at 1 week. But intervening before birth may be optimal, Dr. Harmatz said.
Fetal treatment appears to be “revolutionary at this point,” Dr. Harmatz said.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Sanofi Genzyme provided the enzyme for the patient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The successful treatment of Pompe disease in utero for the first time may be the start of a new chapter for fetal therapy, researchers said.
A report published online in the New England Journal of Medicine describes in utero enzyme-replacement therapy (ERT) for infantile-onset Pompe disease.
The patient, now a toddler, is thriving, according to the researchers. Her parents previously had children with the same disorder who died.
“This treatment expands the repertoire of fetal therapies in a new direction,” Tippi MacKenzie, MD, a pediatric surgeon with University of California, San Francisco, Benioff Children’s Hospitals and a coauthor of the report, said in a news release. “As new treatments become available for children with genetic conditions, we are developing protocols to apply them before birth.”
Dr. MacKenzie codirects the University of California, San Francisco’s center for maternal-fetal precision medicine and directs the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research.
Pompe disease is caused by mutations in a gene that makes acid alpha-glucosidase. With limited amounts of this enzyme, dangerous amounts of glycogen accumulate in the body. Babies with infantile-onset disease typically have enlarged hearts and die by age 2 years.
The condition, which occurs in an estimated 1 in 40,000 births, is one of several early-onset lysosomal storage disorders. Patients with these diseases “are ideal candidates for prenatal therapy because organ damage starts in utero,” the researchers said.
Newborn screening can lead to early initiation of treatment with recombinant enzymes, “but this strategy does not completely prevent irreversible organ damage,” the authors said.
The patient in the new report received six prenatal ERT treatments at the Ottawa Hospital and is receiving postnatal enzyme therapy at CHEO, a pediatric hospital and research center in Ottawa.
Investigators administered alglucosidase alfa through the umbilical vein. They delivered the first infusion to the fetus at 24 weeks 5 days of gestation. They continued providing infusions at 2-week intervals through 34 weeks 5 days of gestation.
She is doing well at age 16 months, with normal cardiac and motor function, and is meeting developmental milestones, according to the news release.
The successful treatment involved collaboration among the University of California, San Francisco, where researchers are conducting a clinical trial of this treatment approach; CHEO and the Ottawa Hospital; and Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Under normal circumstances, the patient’s family would have traveled to Benioff Children’s Hospitals fetal treatment center to participate in the clinical trial, but COVID-19 restrictions led the researchers to deliver the therapy to Ottawa as part of the trial.
The University of California, San Francisco, has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval to treat Pompe disease and several other lysosomal storage disorders in utero as part of a phase 1 clinical trial with 10 patients. The other diseases are mucopolysaccharidosis types 1, 2, 4a, 6, and 7; Gaucher disease types 2 and 3; and Wolman disease.
Patients with Pompe disease might typically be diagnosed clinically at age 3-6 months, said study coauthor Paul Harmatz, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco. With newborn screening, the disease might be diagnosed at 1 week. But intervening before birth may be optimal, Dr. Harmatz said.
Fetal treatment appears to be “revolutionary at this point,” Dr. Harmatz said.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Sanofi Genzyme provided the enzyme for the patient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The successful treatment of Pompe disease in utero for the first time may be the start of a new chapter for fetal therapy, researchers said.
A report published online in the New England Journal of Medicine describes in utero enzyme-replacement therapy (ERT) for infantile-onset Pompe disease.
The patient, now a toddler, is thriving, according to the researchers. Her parents previously had children with the same disorder who died.
“This treatment expands the repertoire of fetal therapies in a new direction,” Tippi MacKenzie, MD, a pediatric surgeon with University of California, San Francisco, Benioff Children’s Hospitals and a coauthor of the report, said in a news release. “As new treatments become available for children with genetic conditions, we are developing protocols to apply them before birth.”
Dr. MacKenzie codirects the University of California, San Francisco’s center for maternal-fetal precision medicine and directs the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research.
Pompe disease is caused by mutations in a gene that makes acid alpha-glucosidase. With limited amounts of this enzyme, dangerous amounts of glycogen accumulate in the body. Babies with infantile-onset disease typically have enlarged hearts and die by age 2 years.
The condition, which occurs in an estimated 1 in 40,000 births, is one of several early-onset lysosomal storage disorders. Patients with these diseases “are ideal candidates for prenatal therapy because organ damage starts in utero,” the researchers said.
Newborn screening can lead to early initiation of treatment with recombinant enzymes, “but this strategy does not completely prevent irreversible organ damage,” the authors said.
The patient in the new report received six prenatal ERT treatments at the Ottawa Hospital and is receiving postnatal enzyme therapy at CHEO, a pediatric hospital and research center in Ottawa.
Investigators administered alglucosidase alfa through the umbilical vein. They delivered the first infusion to the fetus at 24 weeks 5 days of gestation. They continued providing infusions at 2-week intervals through 34 weeks 5 days of gestation.
She is doing well at age 16 months, with normal cardiac and motor function, and is meeting developmental milestones, according to the news release.
The successful treatment involved collaboration among the University of California, San Francisco, where researchers are conducting a clinical trial of this treatment approach; CHEO and the Ottawa Hospital; and Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Under normal circumstances, the patient’s family would have traveled to Benioff Children’s Hospitals fetal treatment center to participate in the clinical trial, but COVID-19 restrictions led the researchers to deliver the therapy to Ottawa as part of the trial.
The University of California, San Francisco, has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval to treat Pompe disease and several other lysosomal storage disorders in utero as part of a phase 1 clinical trial with 10 patients. The other diseases are mucopolysaccharidosis types 1, 2, 4a, 6, and 7; Gaucher disease types 2 and 3; and Wolman disease.
Patients with Pompe disease might typically be diagnosed clinically at age 3-6 months, said study coauthor Paul Harmatz, MD, with the University of California, San Francisco. With newborn screening, the disease might be diagnosed at 1 week. But intervening before birth may be optimal, Dr. Harmatz said.
Fetal treatment appears to be “revolutionary at this point,” Dr. Harmatz said.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health. Sanofi Genzyme provided the enzyme for the patient.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.