User login
Fifth COVID shot recommended for patients with cancer
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has recommended a fifth COVID-19 mRNA shot for people who are immunocompromised, including many with cancer or a history of cancer.
A fifth shot of an mRNA vaccine represents a second booster, the group explained, because the primary mRNA immunization series for immunocompromised individuals involves three doses of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine.
The update, issued today, comes from the NCCN’s Advisory Committee on COVID-19 Vaccination and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis, which released its first vaccine guidelines for patients with cancer in January 2021. The NCCN has issued numerous updates since then as information about the virus and vaccines has evolved.
“We know a lot more about COVID-19 and the vaccines now, and we can use that knowledge to minimize the confusion and enhance the protection we can offer to our immunocompromised patients,” said advisory committee co-leader Lindsey Baden, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
The latest iteration of the NCCN’s COVID guidelines includes an update for patients who initially received Johnson & Johnson’s single-shot vaccine, including a recommendation that patients receive an mRNA vaccine for both the first and second booster.
The group also updated dosing recommendations for pre-exposure prevention with tixagevimab plus cilgavimab (Evusheld, AstraZeneca), suggesting 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody instead of 150 mg, based on in vitro activity against Omicron variants.
The group noted that the Moderna and Pfizer shots can be used interchangeably for boosters.
“The NCCN Committee considers both homologous and heterologous boosters to be appropriate options,” the experts wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has recommended a fifth COVID-19 mRNA shot for people who are immunocompromised, including many with cancer or a history of cancer.
A fifth shot of an mRNA vaccine represents a second booster, the group explained, because the primary mRNA immunization series for immunocompromised individuals involves three doses of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine.
The update, issued today, comes from the NCCN’s Advisory Committee on COVID-19 Vaccination and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis, which released its first vaccine guidelines for patients with cancer in January 2021. The NCCN has issued numerous updates since then as information about the virus and vaccines has evolved.
“We know a lot more about COVID-19 and the vaccines now, and we can use that knowledge to minimize the confusion and enhance the protection we can offer to our immunocompromised patients,” said advisory committee co-leader Lindsey Baden, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
The latest iteration of the NCCN’s COVID guidelines includes an update for patients who initially received Johnson & Johnson’s single-shot vaccine, including a recommendation that patients receive an mRNA vaccine for both the first and second booster.
The group also updated dosing recommendations for pre-exposure prevention with tixagevimab plus cilgavimab (Evusheld, AstraZeneca), suggesting 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody instead of 150 mg, based on in vitro activity against Omicron variants.
The group noted that the Moderna and Pfizer shots can be used interchangeably for boosters.
“The NCCN Committee considers both homologous and heterologous boosters to be appropriate options,” the experts wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has recommended a fifth COVID-19 mRNA shot for people who are immunocompromised, including many with cancer or a history of cancer.
A fifth shot of an mRNA vaccine represents a second booster, the group explained, because the primary mRNA immunization series for immunocompromised individuals involves three doses of either the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine.
The update, issued today, comes from the NCCN’s Advisory Committee on COVID-19 Vaccination and Pre-exposure Prophylaxis, which released its first vaccine guidelines for patients with cancer in January 2021. The NCCN has issued numerous updates since then as information about the virus and vaccines has evolved.
“We know a lot more about COVID-19 and the vaccines now, and we can use that knowledge to minimize the confusion and enhance the protection we can offer to our immunocompromised patients,” said advisory committee co-leader Lindsey Baden, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
The latest iteration of the NCCN’s COVID guidelines includes an update for patients who initially received Johnson & Johnson’s single-shot vaccine, including a recommendation that patients receive an mRNA vaccine for both the first and second booster.
The group also updated dosing recommendations for pre-exposure prevention with tixagevimab plus cilgavimab (Evusheld, AstraZeneca), suggesting 300 mg of each monoclonal antibody instead of 150 mg, based on in vitro activity against Omicron variants.
The group noted that the Moderna and Pfizer shots can be used interchangeably for boosters.
“The NCCN Committee considers both homologous and heterologous boosters to be appropriate options,” the experts wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Career pivots: A new perspective on psychiatry
Psychiatrists practice a field of medicine that relies on one’s clinical perspective to interpret observable behaviors originating from the brains of others. In this manner, psychiatry and photography are similar. And digital technology has changed them both.
In photography, there are many technical aspects for one to master when framing and capturing a shot. The length of exposure. The amount of light needed. The speed of the film, which is its sensitivity to light. The aperture that controls how much light falls on the film. The movement of the subject across the film during the exposure. Despite the fact that physical film has mostly yielded to electronic sensors over the past couple decades, these basic aspects of photography remain.
But perspective is the critical ingredient. This is what brings the greatest impact to photography. The composition, or the subject of the photograph and how its elements – foreground, background, shapes, patterns, texture, shadow, motion, leading lines, and focal points – are arranged. The most powerful way to improve the composition – more powerful than fancy camera bells and whistles – is to move. One step to the left or right, one step forward or back. Stand on your toes, or crouch to your knees. Pivot this way or that. A simple change in perspective dramatically changes the nature and the energy of the captured image.
In fact, many physicians are changing what they actually do for a living. Pivoting their clinical perspectives. And applying those perspectives to other areas. The latest catalyst fueling these career pivots, these changes in perspectives, has been the incredible global impact of the tiny little coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2. The COVID-19 pandemic that began two years ago has disrupted the entire planet. The virus has caused us all to change our perspective, to see our world differently, and our place in it.
The virus has exposed defects in our health care delivery system. And physicians have necessarily reacted, injecting changes in what they do and how they do it. Many of these changes rely on digital technology, building upon the groundwork laid over the past couple of decades to convert our paper processes into electronic processes, and our manual work flows into digital work flows. This groundwork is no small thing, as it relies on conventions and standards, such as DICOM, LOINC, AES, CDA, UMLS, FHIR, ICD, NDC, USCDI, and SNOMED-CT. Establishing, maintaining, and evolving health care standards requires organized groups of people to come together to share their diverse perspectives. This is but one of many places where physicians are using their unique clinical perspective to share what they see with others.
This column will focus on these professional pivots that physicians make when they take a step to the left or right to change their perspective and share their viewpoints in different settings with diverse groups of people. Some of these pivots are small, while others are career changing. But the theme that knits them together is about taking what one has learned while helping others achieve better health, and using that perspective to make a difference.
Dr. Daviss is chief medical officer for Optum Maryland and immediate past president of the Maryland-DC Society of Addiction Medicine, and former medical director and senior medical advisor at SAMHSA. He is coauthor of the 2011 book, Shrink Rap: Three Psychiatrists Explain Their Work. Psychiatrists and other physicians may share their own experience with pivots they have made with Dr. Daviss via email ([email protected]) or Twitter (@HITshrink). The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of his employer or organizations with which he is associated.
Psychiatrists practice a field of medicine that relies on one’s clinical perspective to interpret observable behaviors originating from the brains of others. In this manner, psychiatry and photography are similar. And digital technology has changed them both.
In photography, there are many technical aspects for one to master when framing and capturing a shot. The length of exposure. The amount of light needed. The speed of the film, which is its sensitivity to light. The aperture that controls how much light falls on the film. The movement of the subject across the film during the exposure. Despite the fact that physical film has mostly yielded to electronic sensors over the past couple decades, these basic aspects of photography remain.
But perspective is the critical ingredient. This is what brings the greatest impact to photography. The composition, or the subject of the photograph and how its elements – foreground, background, shapes, patterns, texture, shadow, motion, leading lines, and focal points – are arranged. The most powerful way to improve the composition – more powerful than fancy camera bells and whistles – is to move. One step to the left or right, one step forward or back. Stand on your toes, or crouch to your knees. Pivot this way or that. A simple change in perspective dramatically changes the nature and the energy of the captured image.
In fact, many physicians are changing what they actually do for a living. Pivoting their clinical perspectives. And applying those perspectives to other areas. The latest catalyst fueling these career pivots, these changes in perspectives, has been the incredible global impact of the tiny little coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2. The COVID-19 pandemic that began two years ago has disrupted the entire planet. The virus has caused us all to change our perspective, to see our world differently, and our place in it.
The virus has exposed defects in our health care delivery system. And physicians have necessarily reacted, injecting changes in what they do and how they do it. Many of these changes rely on digital technology, building upon the groundwork laid over the past couple of decades to convert our paper processes into electronic processes, and our manual work flows into digital work flows. This groundwork is no small thing, as it relies on conventions and standards, such as DICOM, LOINC, AES, CDA, UMLS, FHIR, ICD, NDC, USCDI, and SNOMED-CT. Establishing, maintaining, and evolving health care standards requires organized groups of people to come together to share their diverse perspectives. This is but one of many places where physicians are using their unique clinical perspective to share what they see with others.
This column will focus on these professional pivots that physicians make when they take a step to the left or right to change their perspective and share their viewpoints in different settings with diverse groups of people. Some of these pivots are small, while others are career changing. But the theme that knits them together is about taking what one has learned while helping others achieve better health, and using that perspective to make a difference.
Dr. Daviss is chief medical officer for Optum Maryland and immediate past president of the Maryland-DC Society of Addiction Medicine, and former medical director and senior medical advisor at SAMHSA. He is coauthor of the 2011 book, Shrink Rap: Three Psychiatrists Explain Their Work. Psychiatrists and other physicians may share their own experience with pivots they have made with Dr. Daviss via email ([email protected]) or Twitter (@HITshrink). The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of his employer or organizations with which he is associated.
Psychiatrists practice a field of medicine that relies on one’s clinical perspective to interpret observable behaviors originating from the brains of others. In this manner, psychiatry and photography are similar. And digital technology has changed them both.
In photography, there are many technical aspects for one to master when framing and capturing a shot. The length of exposure. The amount of light needed. The speed of the film, which is its sensitivity to light. The aperture that controls how much light falls on the film. The movement of the subject across the film during the exposure. Despite the fact that physical film has mostly yielded to electronic sensors over the past couple decades, these basic aspects of photography remain.
But perspective is the critical ingredient. This is what brings the greatest impact to photography. The composition, or the subject of the photograph and how its elements – foreground, background, shapes, patterns, texture, shadow, motion, leading lines, and focal points – are arranged. The most powerful way to improve the composition – more powerful than fancy camera bells and whistles – is to move. One step to the left or right, one step forward or back. Stand on your toes, or crouch to your knees. Pivot this way or that. A simple change in perspective dramatically changes the nature and the energy of the captured image.
In fact, many physicians are changing what they actually do for a living. Pivoting their clinical perspectives. And applying those perspectives to other areas. The latest catalyst fueling these career pivots, these changes in perspectives, has been the incredible global impact of the tiny little coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2. The COVID-19 pandemic that began two years ago has disrupted the entire planet. The virus has caused us all to change our perspective, to see our world differently, and our place in it.
The virus has exposed defects in our health care delivery system. And physicians have necessarily reacted, injecting changes in what they do and how they do it. Many of these changes rely on digital technology, building upon the groundwork laid over the past couple of decades to convert our paper processes into electronic processes, and our manual work flows into digital work flows. This groundwork is no small thing, as it relies on conventions and standards, such as DICOM, LOINC, AES, CDA, UMLS, FHIR, ICD, NDC, USCDI, and SNOMED-CT. Establishing, maintaining, and evolving health care standards requires organized groups of people to come together to share their diverse perspectives. This is but one of many places where physicians are using their unique clinical perspective to share what they see with others.
This column will focus on these professional pivots that physicians make when they take a step to the left or right to change their perspective and share their viewpoints in different settings with diverse groups of people. Some of these pivots are small, while others are career changing. But the theme that knits them together is about taking what one has learned while helping others achieve better health, and using that perspective to make a difference.
Dr. Daviss is chief medical officer for Optum Maryland and immediate past president of the Maryland-DC Society of Addiction Medicine, and former medical director and senior medical advisor at SAMHSA. He is coauthor of the 2011 book, Shrink Rap: Three Psychiatrists Explain Their Work. Psychiatrists and other physicians may share their own experience with pivots they have made with Dr. Daviss via email ([email protected]) or Twitter (@HITshrink). The opinions expressed are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of his employer or organizations with which he is associated.
Screening for anxiety in young children
On April 12, 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force released the draft of a recommendation statement titled Screening for Anxiety in Children and Adolescents. Based on their observation that 7.8% of children and adolescents have a current anxiety disorder and their analysis of the magnitude of the net benefit, the Task Force plans on recommending that children ages 8-18 years be screened for the condition. However, the group could not find evidence to support screening for children 7 years and younger.
Over more than 4 decades of general pediatric practice, it became obvious to me that anxiety was driving a high percentage of my office visits. Most often in young children it was parental anxiety that was prompting the phone call or office visit. In older childhood and adolescence it was patient anxiety that began to play a larger role.
Over the last 2 decades the level of anxiety in all age groups has seemed to increase. How large a role the events of Sept. 11, 2001, and other terrorist attacks were playing in this phenomenon is unclear to me. However, I suspect they were significant. More recently the pandemic and the failure of both political parties to forge a working arrangement have fueled even more anxiety in many demographic segments. It may be safe to say that everyone is anxious to one degree or another.
Broad-based anxiety in the general population and the incidence of anxiety disorders severe enough to disrupt a child’s life are certainly two different kettles of fish. However, the factors that have raised the level of anxiety across all age groups certainly hasn’t made things any easier for the child who has inherited or developed an anxiety disorder.
Glancing at the 600-page evidence synthesis that accompanies the task force’s report it is clear that they have taken their challenge seriously. However, I wonder whether looking at the 7-and-under age group with a different lens might have resulted in the inclusion of younger children in their recommendation.
I understand that to support their recommendations the U.S. Preventive Services Task Forces must rely on data from peer-reviewed studies that have looked at quantifiable outcomes. However, I suspect the task force would agree that its recommendations shouldn’t prevent the rest of us from using our own observations and intuition when deciding whether to selectively screen our younger patients for anxiety disorders.
Although it may not generate a measurable data point, providing the parents of a 5-year-old whose troubling behavior is in part the result of an anxiety disorder is invaluable. Do we need to screen all 5-year-olds? The task force says probably not given the current state of our knowledge and I agree. But, the fact that almost 8% of the pediatric population carries the diagnosis and my anecdotal observations suggest that as pediatricians we should be learning more about anxiety disorders and their wide variety of presentations. Then we should selectively screen more of our patients. In fact, I suspect we might help our patients and ourselves by questioning more parents about their own mental health histories even before we have any inkling that their child has a problem. While the degree to which anxiety disorders are inheritable and the exact mechanism is far from clear, I think this history might be a valuable piece of information to learn as early as the prenatal get-acquainted visit. A simple question to a new or expecting parent about what worries them most about becoming a parent would be a good opener. Your reassurance that you expect parents to be worried and welcome hearing about their concerns should be a step in building a strong foundation for a family-provider relationship.
Anxiety happens and unfortunately so do anxiety disorders. We need to be doing a better job of acknowledging and responding to these two realities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
*This column was updated on 5/4/2022.
On April 12, 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force released the draft of a recommendation statement titled Screening for Anxiety in Children and Adolescents. Based on their observation that 7.8% of children and adolescents have a current anxiety disorder and their analysis of the magnitude of the net benefit, the Task Force plans on recommending that children ages 8-18 years be screened for the condition. However, the group could not find evidence to support screening for children 7 years and younger.
Over more than 4 decades of general pediatric practice, it became obvious to me that anxiety was driving a high percentage of my office visits. Most often in young children it was parental anxiety that was prompting the phone call or office visit. In older childhood and adolescence it was patient anxiety that began to play a larger role.
Over the last 2 decades the level of anxiety in all age groups has seemed to increase. How large a role the events of Sept. 11, 2001, and other terrorist attacks were playing in this phenomenon is unclear to me. However, I suspect they were significant. More recently the pandemic and the failure of both political parties to forge a working arrangement have fueled even more anxiety in many demographic segments. It may be safe to say that everyone is anxious to one degree or another.
Broad-based anxiety in the general population and the incidence of anxiety disorders severe enough to disrupt a child’s life are certainly two different kettles of fish. However, the factors that have raised the level of anxiety across all age groups certainly hasn’t made things any easier for the child who has inherited or developed an anxiety disorder.
Glancing at the 600-page evidence synthesis that accompanies the task force’s report it is clear that they have taken their challenge seriously. However, I wonder whether looking at the 7-and-under age group with a different lens might have resulted in the inclusion of younger children in their recommendation.
I understand that to support their recommendations the U.S. Preventive Services Task Forces must rely on data from peer-reviewed studies that have looked at quantifiable outcomes. However, I suspect the task force would agree that its recommendations shouldn’t prevent the rest of us from using our own observations and intuition when deciding whether to selectively screen our younger patients for anxiety disorders.
Although it may not generate a measurable data point, providing the parents of a 5-year-old whose troubling behavior is in part the result of an anxiety disorder is invaluable. Do we need to screen all 5-year-olds? The task force says probably not given the current state of our knowledge and I agree. But, the fact that almost 8% of the pediatric population carries the diagnosis and my anecdotal observations suggest that as pediatricians we should be learning more about anxiety disorders and their wide variety of presentations. Then we should selectively screen more of our patients. In fact, I suspect we might help our patients and ourselves by questioning more parents about their own mental health histories even before we have any inkling that their child has a problem. While the degree to which anxiety disorders are inheritable and the exact mechanism is far from clear, I think this history might be a valuable piece of information to learn as early as the prenatal get-acquainted visit. A simple question to a new or expecting parent about what worries them most about becoming a parent would be a good opener. Your reassurance that you expect parents to be worried and welcome hearing about their concerns should be a step in building a strong foundation for a family-provider relationship.
Anxiety happens and unfortunately so do anxiety disorders. We need to be doing a better job of acknowledging and responding to these two realities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
*This column was updated on 5/4/2022.
On April 12, 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force released the draft of a recommendation statement titled Screening for Anxiety in Children and Adolescents. Based on their observation that 7.8% of children and adolescents have a current anxiety disorder and their analysis of the magnitude of the net benefit, the Task Force plans on recommending that children ages 8-18 years be screened for the condition. However, the group could not find evidence to support screening for children 7 years and younger.
Over more than 4 decades of general pediatric practice, it became obvious to me that anxiety was driving a high percentage of my office visits. Most often in young children it was parental anxiety that was prompting the phone call or office visit. In older childhood and adolescence it was patient anxiety that began to play a larger role.
Over the last 2 decades the level of anxiety in all age groups has seemed to increase. How large a role the events of Sept. 11, 2001, and other terrorist attacks were playing in this phenomenon is unclear to me. However, I suspect they were significant. More recently the pandemic and the failure of both political parties to forge a working arrangement have fueled even more anxiety in many demographic segments. It may be safe to say that everyone is anxious to one degree or another.
Broad-based anxiety in the general population and the incidence of anxiety disorders severe enough to disrupt a child’s life are certainly two different kettles of fish. However, the factors that have raised the level of anxiety across all age groups certainly hasn’t made things any easier for the child who has inherited or developed an anxiety disorder.
Glancing at the 600-page evidence synthesis that accompanies the task force’s report it is clear that they have taken their challenge seriously. However, I wonder whether looking at the 7-and-under age group with a different lens might have resulted in the inclusion of younger children in their recommendation.
I understand that to support their recommendations the U.S. Preventive Services Task Forces must rely on data from peer-reviewed studies that have looked at quantifiable outcomes. However, I suspect the task force would agree that its recommendations shouldn’t prevent the rest of us from using our own observations and intuition when deciding whether to selectively screen our younger patients for anxiety disorders.
Although it may not generate a measurable data point, providing the parents of a 5-year-old whose troubling behavior is in part the result of an anxiety disorder is invaluable. Do we need to screen all 5-year-olds? The task force says probably not given the current state of our knowledge and I agree. But, the fact that almost 8% of the pediatric population carries the diagnosis and my anecdotal observations suggest that as pediatricians we should be learning more about anxiety disorders and their wide variety of presentations. Then we should selectively screen more of our patients. In fact, I suspect we might help our patients and ourselves by questioning more parents about their own mental health histories even before we have any inkling that their child has a problem. While the degree to which anxiety disorders are inheritable and the exact mechanism is far from clear, I think this history might be a valuable piece of information to learn as early as the prenatal get-acquainted visit. A simple question to a new or expecting parent about what worries them most about becoming a parent would be a good opener. Your reassurance that you expect parents to be worried and welcome hearing about their concerns should be a step in building a strong foundation for a family-provider relationship.
Anxiety happens and unfortunately so do anxiety disorders. We need to be doing a better job of acknowledging and responding to these two realities.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
*This column was updated on 5/4/2022.
Virtual reality an ‘exciting opportunity’ for geriatric psychiatry
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers are increasingly turning their attention to virtual reality (VR) for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in older adults.
Recent studies have highlighted the usefulness of VR in treating depression and loneliness in older patients who may be socially isolated because of their age, comorbidities, or the COVID-19 pandemic.
“The unique capability of virtual reality to create an immersive and engaging setting is an exciting opportunity for geriatric psychiatry,” Harmehr Sekhon, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow, Lady Davis Institute/Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, and McLean Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
, Dr. Sekhon said.
One novel approach involves using VR to administer a mindfulness intervention in older adults. Dr. Sekhon shared information on her own mindfulness study and on other developments in VR and telemedicine at the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting.
Potential bridging tool
As the population ages, the prevalence of mental health disorders increases. Telemedicine has proved to be a potential “bridge” to address the health care needs of older adults, Dr. Sekhon noted.
She cited her systematic review of telemedicine for older adults with dementia during COVID-19. Results showed that telemedicine was a “beneficial approach” to assisting these individuals and that it increased accessibility, said Dr. Sekhon.
In addition, a survey published last year showed that 87% of Americans in general want to continue using telehealth services after the pandemic. Most respondents agreed that telehealth had made it easier to get the care they needed. They also reported having received the same level of care via telehealth as with in-person care.
A growing body of research shows that VR has “positive influences on mood and well-being, cognition, pain management, [and] treatment of phobias in younger adults,” Dr. Sekhon said. She added that there is evidence that VR is feasible for older adults, with applications in cognitive disorders.
She cited a recent systematic review of 55 studies that assessed the impact of different types of VR on mental health in older adults. The results showed that VR could be helpful in screening for cognitive impairment – and it was comparable to some paper-based assessment. It was also useful as a training tool for those with cognitive impairment.
Examples of VR interventions that can be used to treat cognitive impairment include “virtual cities, kitchens, supermarkets,” Dr. Sekhon noted.
The technology is increasingly being used as a tool to deliver psychotherapy, in which patient engagement is “a key determinant” of outcomes, she added. “Virtual reality is a cutting-edge, engaging, and immersive technique to administer psychotherapy,” she said.
Such VR approaches are proving successful in older patients. Dr. Sekhon highlighted the case of an 85-year-old woman who engaged in ten sessions of psychodynamic psychotherapy that targeted persistent dysthymia and negativistic mood. The case was part of a proof-of-concept study published in the May issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Dr. Sekhon noted the intervention was well tolerated and was associated with minimal side effects.
VR-based meditation
Dr. Sekhon and her colleagues are now conducting a randomized controlled trial of VR meditation in older adults. VR-based meditation has been shown to increase relaxation and to decrease anxiety, sadness, and anger in younger adults. However, it has not been studied in the geriatric population.
The pilot study is assessing the feasibility and tolerability of VR meditation for older adults and its effects on stress, anxiety, depression, sleep, and quality of life. The study involves 30 adults aged 60 years and older.
Participants receive either 15-minute VR mindfulness meditation sessions twice a week for 4 weeks or are on a control wait list. The meditation sessions are user friendly and focus on breath meditation and body scans, Dr. Sekhon reported.
Because participants are older and balance is a concern, safety steps are incorporated into the sessions. “We ensure they’re doing this in a seated position, in a chair with arm rests, so that they’re very stable and there’s no risk of falls,” said Dr. Sekhon.
Another concern with VR is motion sickness, she noted. “It’s pretty minimal, but the best way we found so far is giving older adults time to adapt and feel comfortable with the VR,” she said. From the first session, participants learn how to put on the device and are checked to make sure they are comfortable with the process. To help them get used to everything, video and audio are not included during the first session.
Dr. Sekhon noted that results from the study are expected later this year.
In addition to mindfulness, researchers are using VR to deliver other established interventions, such as exposure therapy – and are implementing these approaches in varied environments, including long-term and palliative care settings.
VR-related technology is constantly improving and is becoming easier to use and more affordable, said Dr. Sekhon. She noted that the simplest devices that rely on smartphones cost as little as $15.
Although VR in older adults is promising, there are barriers to its adoption and use in research, she noted. For example, older adults may have cognitive, visual, or hearing impairments. They may have limited digital literacy, and/or they may not have access to the required technology.
These barriers can be overcome through workarounds, including providing instructional videos and digital literacy assistance via Zoom and working with community partners to facilitate study recruitment of older patients, Dr. Sekhon said.
Dr. Sekhon’s research is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherche du Quebec Sante.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAGP 2022
Smartphone diagnosis in infant seizures could be highly effective
This video transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: Welcome to Medscape. I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting from the American Epilepsy Society meeting.
Today, I have the pleasure of speaking with Dr. Chethan Rao, a child and adolescent neurology resident from the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. Dr. Rao has a particular interest in pediatric epilepsy. Welcome, Dr. Rao.
Chethan Rao, DO: Thank you, Dr. Wilner. It’s a pleasure to be here, and thanks for taking the time to highlight our work.
Dr. Wilner: You had a very interesting paper at the meeting that I wanted to talk about, focused on infantile spasms and smartphone video. Before we dive into the paper, tell us: What are infantile spasms, and why is it important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Infantile spasms, also known as epileptic spasms, are 1- to 2-second seizures, and they typically consist of sudden stiffening of the body with brief bending forward or backward of the arms, legs, and head. They usually happen around age 3-8 months, and they typically occur in clusters, most often after awakening from sleep.
The incidence is about 1 in 2,000-3,000 children. Many kids with spasms go on to develop seizures that are very difficult to treat, like Lennox-Gastaut epilepsy, and many go on to have developmental delays as well.
Dr. Wilner: Are these subtle? In other words, could a parent have a child like that and not really recognize that this is something abnormal? Or are they so dramatic that parents say: “We’re going to the emergency room?”
Dr. Rao: One of the problems that we encounter often is that in this age group of infants, they have benign sleep myoclonus; they have Sandifer syndrome related to reflux. Those can be very difficult mimics of spasms. They’re not the most clear-cut, but they look usually different enough from normal baby movements that they get parents to seek medical attention.
Dr. Wilner: You mentioned that the infantile spasms really are a type of epilepsy and symptomatic, usually, of some underlying neurologic condition. Why is it so important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Great question. Many studies have looked at developmental outcomes based on when spasms were diagnosed and treated, and all of them have replicated time over time that the earlier you get to treatment for the spasms, the better the outcomes are for seizure control and for development.
For this reason, infantile spasm is considered a neurologic urgency in our world. Like I said, accurate diagnosis is often complicated by these potential mimics. Prompt EEG is one of the most important things for confirmation of diagnosis.
Dr. Wilner: But to get that EEG, it has to get all the way to the neurologist, right? It’s not something they’re going to do in the ER. I saw a statistic: There are millions, if not billions, of smartphones out there. Where does the smartphone come in?
Dr. Rao: Absolutely. One of the things that we have on our side these days is that almost everyone has a smartphone at their disposal. One of the recent polls in 2021 showed that more than 95% of adults of childbearing age have smartphones with video access. As some other studies have shown in the adult world, we all really have an epilepsy monitoring unit minus the EEG in our own pockets.
It’s definitely a useful tool, as that first screening video can be used in adjunct to history and physical. There have been many of studies on the adult epilepsy side showing the predictive value of smartphone video for differentiating things like epileptic seizures and nonepileptic spells. What we wanted to do is use smartphone video to pin the diagnosis early of infantile spasms and get it treated as quickly as possible.
Dr. Wilner: I’m a fan. Every now and then, I do have a patient who brings in a video of some spell. I’m an adult neurologist. The patient had a spell, and you ask them – of course they don’t remember – and you ask the witness, who usually is not a trained observer. There have been one or two occasions where I thought: “Well, I don’t know if that was really a seizure.” Then they show me the video and it’s like, “Wow, that is definitely a convulsion.” A picture definitely can be worth a thousand words.
You studied this systematically for your poster. Tell me about what you did.
Dr. Rao: Since the poster, we’ve actually expanded the study, so I’ll give you the updated version. We looked at 101 infants retrospectively at two large children’s health care centers: Nemours Children’s, associated with Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. We narrowed it down to 80 patients whom we included. Of these, 43 had smartphone video capture when they first presented and 37 had no video when they first presented.
We found a 17-day difference by median in the time to diagnosis and treatment. In other words, the video group was diagnosed and treated 17 days by median, compared with the no-video group. Although 17 days may not sound like a big number, in this context it can make a huge difference. That’s been shown by one of these key studies in our field called the UK Infantile Spasms Study. The 2-week difference made about a 10-point difference on the developmental scale that they use – so pretty significant.
Dr. Wilner: Let me think about this for a minute. Was that because the parents brought the child in with their video and the doctor said, “Hey, that’s infantile spasms. Here’s your shot of ACTH [or whatever they’re using these days].” Or was it because the parents who were attentive enough to use video brought their kids in sooner?
Or was this the time from when they brought the child in to treatment? Is that the time you looked at? So it wasn’t just that these were more attentive parents and more likely to use the video – you’re looking at the time from presentation with or without video until treatment, is that right?
Dr. Rao: We looked to the time from the start of the spasms, as reported by the parents, to the time of diagnosis and then the start of spasms to the time of treatment. What you asked was a fantastic question. We wanted to know who these parents are who are taking videos versus the ones that are not.
We looked at the race/ethnicity data and socioeconomic status data. There were no significant differences between the video and nonvideo group. That would not explain the difference in our results here.
Dr. Wilner: Do you have plans to follow these approximately 40 children 5 years from now and see who’s riding a bicycle and who’s still stuck in the stroller? Is there going to be a difference?
Dr. Rao: Because time to diagnosis and time to treatment were our primary outcomes, long-term follow-up may not really help as much in this study. We did have a couple of other ideas for future studies. One that we wanted to look at was kids who have risk factors for developing spasms, such as trisomy 21, tuberous sclerosis, and congenital cortical malformations; those kids are at a much higher risk for developing spasms around 3-8 months of life.
In giving targeted counseling to those families about how they can use smartphone video to minimize the time to diagnosis and treatment, we think we may be able to learn more and maybe do that prospectively.
The other interesting idea is using artificial intelligence technology for spasm detection in some of these smartphone videos. They’re already using it for different seizure types. It could be an efficient first pass when we get a whole bunch of smartphone videos to determine which ones we need to pursue further steps – to see whether we need to get long-term EEG monitoring or not.
Dr. Wilner: As an epileptologist, I was going to say that we have smartphone EKG. All we need now is smartphone EEG, and then you’ll have all the information you need on day one. It may be a ways away.
As a bottom line, would it be fair to say that parents should not hesitate to take a video of any suspiciously abnormal behavior and bring it to their family doctor or pediatric neurologist?
Dr. Rao: Yes. I was happy to see the Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance put out a promotional video that had some steps for when parents see things that are suspicious for spasms, and they do recommend using smartphone video and promptly showing it to their doctors. I think the difference that we hope to provide in this study is that we can now quantify the effect of having that smartphone video when they first present.
My takeaway from this study that I would like to show is encouraging the use of smartphone video as an adjunct tool and for providers to ask for the videos, but also for these pediatric centers to develop an infrastructure – either a secure, monitored email address like we have at our center or a patient portal – where parents can submit video concerning for spasms.
Dr. Wilner: Save the trip to the doctor. Get that video out there first.
Dr. Rao: Especially in the pandemic world, right?
Dr. Wilner: Yes. I understand that you are a neurology resident. To wrap up, what’s the next step for you?
Dr. Rao: I’m finishing up my child neurology residency this year, and I’m moving out to Stanford for pediatric epilepsy fellowship. We’re preparing this project we’re talking about for submission soon, and we’re working on another project, which is a systematic review of genetic testing and the presurgical workup for pediatric drug-resistant focal epilepsy.
Dr. Wilner: Excellent. That’s pretty exciting. Good luck to you. I want to thank you very much for telling us about your research.
Dr. Rao: It was a pleasure speaking with you, and I look forward to the next time.
Dr. Wilner: I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting for Medscape. Thanks for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This video transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: Welcome to Medscape. I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting from the American Epilepsy Society meeting.
Today, I have the pleasure of speaking with Dr. Chethan Rao, a child and adolescent neurology resident from the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. Dr. Rao has a particular interest in pediatric epilepsy. Welcome, Dr. Rao.
Chethan Rao, DO: Thank you, Dr. Wilner. It’s a pleasure to be here, and thanks for taking the time to highlight our work.
Dr. Wilner: You had a very interesting paper at the meeting that I wanted to talk about, focused on infantile spasms and smartphone video. Before we dive into the paper, tell us: What are infantile spasms, and why is it important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Infantile spasms, also known as epileptic spasms, are 1- to 2-second seizures, and they typically consist of sudden stiffening of the body with brief bending forward or backward of the arms, legs, and head. They usually happen around age 3-8 months, and they typically occur in clusters, most often after awakening from sleep.
The incidence is about 1 in 2,000-3,000 children. Many kids with spasms go on to develop seizures that are very difficult to treat, like Lennox-Gastaut epilepsy, and many go on to have developmental delays as well.
Dr. Wilner: Are these subtle? In other words, could a parent have a child like that and not really recognize that this is something abnormal? Or are they so dramatic that parents say: “We’re going to the emergency room?”
Dr. Rao: One of the problems that we encounter often is that in this age group of infants, they have benign sleep myoclonus; they have Sandifer syndrome related to reflux. Those can be very difficult mimics of spasms. They’re not the most clear-cut, but they look usually different enough from normal baby movements that they get parents to seek medical attention.
Dr. Wilner: You mentioned that the infantile spasms really are a type of epilepsy and symptomatic, usually, of some underlying neurologic condition. Why is it so important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Great question. Many studies have looked at developmental outcomes based on when spasms were diagnosed and treated, and all of them have replicated time over time that the earlier you get to treatment for the spasms, the better the outcomes are for seizure control and for development.
For this reason, infantile spasm is considered a neurologic urgency in our world. Like I said, accurate diagnosis is often complicated by these potential mimics. Prompt EEG is one of the most important things for confirmation of diagnosis.
Dr. Wilner: But to get that EEG, it has to get all the way to the neurologist, right? It’s not something they’re going to do in the ER. I saw a statistic: There are millions, if not billions, of smartphones out there. Where does the smartphone come in?
Dr. Rao: Absolutely. One of the things that we have on our side these days is that almost everyone has a smartphone at their disposal. One of the recent polls in 2021 showed that more than 95% of adults of childbearing age have smartphones with video access. As some other studies have shown in the adult world, we all really have an epilepsy monitoring unit minus the EEG in our own pockets.
It’s definitely a useful tool, as that first screening video can be used in adjunct to history and physical. There have been many of studies on the adult epilepsy side showing the predictive value of smartphone video for differentiating things like epileptic seizures and nonepileptic spells. What we wanted to do is use smartphone video to pin the diagnosis early of infantile spasms and get it treated as quickly as possible.
Dr. Wilner: I’m a fan. Every now and then, I do have a patient who brings in a video of some spell. I’m an adult neurologist. The patient had a spell, and you ask them – of course they don’t remember – and you ask the witness, who usually is not a trained observer. There have been one or two occasions where I thought: “Well, I don’t know if that was really a seizure.” Then they show me the video and it’s like, “Wow, that is definitely a convulsion.” A picture definitely can be worth a thousand words.
You studied this systematically for your poster. Tell me about what you did.
Dr. Rao: Since the poster, we’ve actually expanded the study, so I’ll give you the updated version. We looked at 101 infants retrospectively at two large children’s health care centers: Nemours Children’s, associated with Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. We narrowed it down to 80 patients whom we included. Of these, 43 had smartphone video capture when they first presented and 37 had no video when they first presented.
We found a 17-day difference by median in the time to diagnosis and treatment. In other words, the video group was diagnosed and treated 17 days by median, compared with the no-video group. Although 17 days may not sound like a big number, in this context it can make a huge difference. That’s been shown by one of these key studies in our field called the UK Infantile Spasms Study. The 2-week difference made about a 10-point difference on the developmental scale that they use – so pretty significant.
Dr. Wilner: Let me think about this for a minute. Was that because the parents brought the child in with their video and the doctor said, “Hey, that’s infantile spasms. Here’s your shot of ACTH [or whatever they’re using these days].” Or was it because the parents who were attentive enough to use video brought their kids in sooner?
Or was this the time from when they brought the child in to treatment? Is that the time you looked at? So it wasn’t just that these were more attentive parents and more likely to use the video – you’re looking at the time from presentation with or without video until treatment, is that right?
Dr. Rao: We looked to the time from the start of the spasms, as reported by the parents, to the time of diagnosis and then the start of spasms to the time of treatment. What you asked was a fantastic question. We wanted to know who these parents are who are taking videos versus the ones that are not.
We looked at the race/ethnicity data and socioeconomic status data. There were no significant differences between the video and nonvideo group. That would not explain the difference in our results here.
Dr. Wilner: Do you have plans to follow these approximately 40 children 5 years from now and see who’s riding a bicycle and who’s still stuck in the stroller? Is there going to be a difference?
Dr. Rao: Because time to diagnosis and time to treatment were our primary outcomes, long-term follow-up may not really help as much in this study. We did have a couple of other ideas for future studies. One that we wanted to look at was kids who have risk factors for developing spasms, such as trisomy 21, tuberous sclerosis, and congenital cortical malformations; those kids are at a much higher risk for developing spasms around 3-8 months of life.
In giving targeted counseling to those families about how they can use smartphone video to minimize the time to diagnosis and treatment, we think we may be able to learn more and maybe do that prospectively.
The other interesting idea is using artificial intelligence technology for spasm detection in some of these smartphone videos. They’re already using it for different seizure types. It could be an efficient first pass when we get a whole bunch of smartphone videos to determine which ones we need to pursue further steps – to see whether we need to get long-term EEG monitoring or not.
Dr. Wilner: As an epileptologist, I was going to say that we have smartphone EKG. All we need now is smartphone EEG, and then you’ll have all the information you need on day one. It may be a ways away.
As a bottom line, would it be fair to say that parents should not hesitate to take a video of any suspiciously abnormal behavior and bring it to their family doctor or pediatric neurologist?
Dr. Rao: Yes. I was happy to see the Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance put out a promotional video that had some steps for when parents see things that are suspicious for spasms, and they do recommend using smartphone video and promptly showing it to their doctors. I think the difference that we hope to provide in this study is that we can now quantify the effect of having that smartphone video when they first present.
My takeaway from this study that I would like to show is encouraging the use of smartphone video as an adjunct tool and for providers to ask for the videos, but also for these pediatric centers to develop an infrastructure – either a secure, monitored email address like we have at our center or a patient portal – where parents can submit video concerning for spasms.
Dr. Wilner: Save the trip to the doctor. Get that video out there first.
Dr. Rao: Especially in the pandemic world, right?
Dr. Wilner: Yes. I understand that you are a neurology resident. To wrap up, what’s the next step for you?
Dr. Rao: I’m finishing up my child neurology residency this year, and I’m moving out to Stanford for pediatric epilepsy fellowship. We’re preparing this project we’re talking about for submission soon, and we’re working on another project, which is a systematic review of genetic testing and the presurgical workup for pediatric drug-resistant focal epilepsy.
Dr. Wilner: Excellent. That’s pretty exciting. Good luck to you. I want to thank you very much for telling us about your research.
Dr. Rao: It was a pleasure speaking with you, and I look forward to the next time.
Dr. Wilner: I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting for Medscape. Thanks for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This video transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: Welcome to Medscape. I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting from the American Epilepsy Society meeting.
Today, I have the pleasure of speaking with Dr. Chethan Rao, a child and adolescent neurology resident from the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla. Dr. Rao has a particular interest in pediatric epilepsy. Welcome, Dr. Rao.
Chethan Rao, DO: Thank you, Dr. Wilner. It’s a pleasure to be here, and thanks for taking the time to highlight our work.
Dr. Wilner: You had a very interesting paper at the meeting that I wanted to talk about, focused on infantile spasms and smartphone video. Before we dive into the paper, tell us: What are infantile spasms, and why is it important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Infantile spasms, also known as epileptic spasms, are 1- to 2-second seizures, and they typically consist of sudden stiffening of the body with brief bending forward or backward of the arms, legs, and head. They usually happen around age 3-8 months, and they typically occur in clusters, most often after awakening from sleep.
The incidence is about 1 in 2,000-3,000 children. Many kids with spasms go on to develop seizures that are very difficult to treat, like Lennox-Gastaut epilepsy, and many go on to have developmental delays as well.
Dr. Wilner: Are these subtle? In other words, could a parent have a child like that and not really recognize that this is something abnormal? Or are they so dramatic that parents say: “We’re going to the emergency room?”
Dr. Rao: One of the problems that we encounter often is that in this age group of infants, they have benign sleep myoclonus; they have Sandifer syndrome related to reflux. Those can be very difficult mimics of spasms. They’re not the most clear-cut, but they look usually different enough from normal baby movements that they get parents to seek medical attention.
Dr. Wilner: You mentioned that the infantile spasms really are a type of epilepsy and symptomatic, usually, of some underlying neurologic condition. Why is it so important to diagnose them early?
Dr. Rao: Great question. Many studies have looked at developmental outcomes based on when spasms were diagnosed and treated, and all of them have replicated time over time that the earlier you get to treatment for the spasms, the better the outcomes are for seizure control and for development.
For this reason, infantile spasm is considered a neurologic urgency in our world. Like I said, accurate diagnosis is often complicated by these potential mimics. Prompt EEG is one of the most important things for confirmation of diagnosis.
Dr. Wilner: But to get that EEG, it has to get all the way to the neurologist, right? It’s not something they’re going to do in the ER. I saw a statistic: There are millions, if not billions, of smartphones out there. Where does the smartphone come in?
Dr. Rao: Absolutely. One of the things that we have on our side these days is that almost everyone has a smartphone at their disposal. One of the recent polls in 2021 showed that more than 95% of adults of childbearing age have smartphones with video access. As some other studies have shown in the adult world, we all really have an epilepsy monitoring unit minus the EEG in our own pockets.
It’s definitely a useful tool, as that first screening video can be used in adjunct to history and physical. There have been many of studies on the adult epilepsy side showing the predictive value of smartphone video for differentiating things like epileptic seizures and nonepileptic spells. What we wanted to do is use smartphone video to pin the diagnosis early of infantile spasms and get it treated as quickly as possible.
Dr. Wilner: I’m a fan. Every now and then, I do have a patient who brings in a video of some spell. I’m an adult neurologist. The patient had a spell, and you ask them – of course they don’t remember – and you ask the witness, who usually is not a trained observer. There have been one or two occasions where I thought: “Well, I don’t know if that was really a seizure.” Then they show me the video and it’s like, “Wow, that is definitely a convulsion.” A picture definitely can be worth a thousand words.
You studied this systematically for your poster. Tell me about what you did.
Dr. Rao: Since the poster, we’ve actually expanded the study, so I’ll give you the updated version. We looked at 101 infants retrospectively at two large children’s health care centers: Nemours Children’s, associated with Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., and Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. We narrowed it down to 80 patients whom we included. Of these, 43 had smartphone video capture when they first presented and 37 had no video when they first presented.
We found a 17-day difference by median in the time to diagnosis and treatment. In other words, the video group was diagnosed and treated 17 days by median, compared with the no-video group. Although 17 days may not sound like a big number, in this context it can make a huge difference. That’s been shown by one of these key studies in our field called the UK Infantile Spasms Study. The 2-week difference made about a 10-point difference on the developmental scale that they use – so pretty significant.
Dr. Wilner: Let me think about this for a minute. Was that because the parents brought the child in with their video and the doctor said, “Hey, that’s infantile spasms. Here’s your shot of ACTH [or whatever they’re using these days].” Or was it because the parents who were attentive enough to use video brought their kids in sooner?
Or was this the time from when they brought the child in to treatment? Is that the time you looked at? So it wasn’t just that these were more attentive parents and more likely to use the video – you’re looking at the time from presentation with or without video until treatment, is that right?
Dr. Rao: We looked to the time from the start of the spasms, as reported by the parents, to the time of diagnosis and then the start of spasms to the time of treatment. What you asked was a fantastic question. We wanted to know who these parents are who are taking videos versus the ones that are not.
We looked at the race/ethnicity data and socioeconomic status data. There were no significant differences between the video and nonvideo group. That would not explain the difference in our results here.
Dr. Wilner: Do you have plans to follow these approximately 40 children 5 years from now and see who’s riding a bicycle and who’s still stuck in the stroller? Is there going to be a difference?
Dr. Rao: Because time to diagnosis and time to treatment were our primary outcomes, long-term follow-up may not really help as much in this study. We did have a couple of other ideas for future studies. One that we wanted to look at was kids who have risk factors for developing spasms, such as trisomy 21, tuberous sclerosis, and congenital cortical malformations; those kids are at a much higher risk for developing spasms around 3-8 months of life.
In giving targeted counseling to those families about how they can use smartphone video to minimize the time to diagnosis and treatment, we think we may be able to learn more and maybe do that prospectively.
The other interesting idea is using artificial intelligence technology for spasm detection in some of these smartphone videos. They’re already using it for different seizure types. It could be an efficient first pass when we get a whole bunch of smartphone videos to determine which ones we need to pursue further steps – to see whether we need to get long-term EEG monitoring or not.
Dr. Wilner: As an epileptologist, I was going to say that we have smartphone EKG. All we need now is smartphone EEG, and then you’ll have all the information you need on day one. It may be a ways away.
As a bottom line, would it be fair to say that parents should not hesitate to take a video of any suspiciously abnormal behavior and bring it to their family doctor or pediatric neurologist?
Dr. Rao: Yes. I was happy to see the Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance put out a promotional video that had some steps for when parents see things that are suspicious for spasms, and they do recommend using smartphone video and promptly showing it to their doctors. I think the difference that we hope to provide in this study is that we can now quantify the effect of having that smartphone video when they first present.
My takeaway from this study that I would like to show is encouraging the use of smartphone video as an adjunct tool and for providers to ask for the videos, but also for these pediatric centers to develop an infrastructure – either a secure, monitored email address like we have at our center or a patient portal – where parents can submit video concerning for spasms.
Dr. Wilner: Save the trip to the doctor. Get that video out there first.
Dr. Rao: Especially in the pandemic world, right?
Dr. Wilner: Yes. I understand that you are a neurology resident. To wrap up, what’s the next step for you?
Dr. Rao: I’m finishing up my child neurology residency this year, and I’m moving out to Stanford for pediatric epilepsy fellowship. We’re preparing this project we’re talking about for submission soon, and we’re working on another project, which is a systematic review of genetic testing and the presurgical workup for pediatric drug-resistant focal epilepsy.
Dr. Wilner: Excellent. That’s pretty exciting. Good luck to you. I want to thank you very much for telling us about your research.
Dr. Rao: It was a pleasure speaking with you, and I look forward to the next time.
Dr. Wilner: I’m Dr Andrew Wilner, reporting for Medscape. Thanks for watching.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Implant may alleviate sleep apnea in teens with Down syndrome
Upper airway hypoglossal nerve stimulation is safe and effective in adolescents with Down syndrome and severe persistent obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurring after adenotonsillectomy and who couldn’t tolerate positive airway pressure, early research suggests.
In a phase I study, 42 adolescents received a surgically implanted device that moves the tongue forward during sleep. Results at 1-year follow-up showed 66% “responded well” to treatment and showed a drop in apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of at least 50%.
“Parents came back to us and said not only is the sleep better but my child seems to be doing better during the day,” lead investigator Christopher Hartnick, MD, director of the Division of Pediatric Otolaryngology and the Pediatric Airway, Voice, and Swallowing Center at Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Boston, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery.
Limited options
Upper airway simulation has been shown previously to be effective for adults with OSA, but up until now, the process has not been evaluated in children.
The device used in the current study “stimulates the hypoglossal nerve to protrude the tongue and open the airway on inspiration during sleep,” the investigators note.
“Hypoglossal nerve stimulation may be a particularly suitable therapy for patients with Down syndrome because it can augment neuromuscular airway tone and reduce anatomical obstruction at the base of the tongue, a common site of residual obstruction in children with Down syndrome,” they add.
“This study was born out of the frustration of not having an effective treatment option for children with Down syndrome who struggle with sleep apnea,” Dr. Hartnick said in a news release.
A total of 42 adolescents (67% male; mean age, 15 years) with Down syndrome and persistent severe OSA after adenotonsillectomy were implanted with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator. All were followed for 12 months.
The surgery was safe, with the most common adverse event being temporary tongue discomfort in five patients (12%). This typically resolved in weeks, the researchers note.
High response, adherence rates
Results showed response rates and adherence to therapy was high. The mean duration of nightly therapy was 9 hours, with 40 children (95.2%) using the device at least 4 hours every night.
The implant was also effective, with a mean decrease in AHI of 12.9 events per hour (95% confidence interval, –17.0 to –8.7 events per hour).
Nearly two-thirds of the children had at least a 50% reduction in their AHI, while roughly three-fourths had a 12-month follow-up AHI of less than 10 events per hour.
There were also significant improvements in polysomnographic and parent-reported quality of life outcomes 12 months after the implant, including improvement in sleep and daily functioning, behavior, and language.
“Sleep apnea remains one of the most common conditions that I grapple with working with patients with Down syndrome and their families,” co-investigator Brian Skotko, MD, Emma Campbell endowed chair on Down syndrome at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“Until now, so many of our patients had run out of treatment options, and their health and well-being were declining. Now, with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator treatment, we may have an effective and safe way to treat apnea and maximize brain health for people with Down syndrome,” Dr. Skotko added.
Dr. Hartnick and Dr. Skotko have received a $4 million, 5-year grant from the National Institutes of Health to assess whether upper airway stimulation might help cognition in children with Down syndrome.
Landmark investigation
Co-authors of an invited commentary said they “applaud” the researchers for their “landmark” investigation, which demonstrated a response to upper airway stimulation in children with Down syndrome and OSA that is on par with what has been achieved in adults with OSA.
“They have established the safety of the procedure; however, future research is necessary to optimize the results of implant,” write Norman Friedman, MD, and Katherine Green, MD, both from the department of otolaryngology – head and neck surgery, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
“Further assessment regarding patient selection and the systematic preoperative identification of potential barriers that might affect successful use of therapy will be beneficial to improve longitudinal outcomes and success in this population that is uniquely different from the adult cohorts that have received implants to date,” they add.
The study was funded by Inspire Medical Systems, which provided eight devices for the study but otherwise did not have a role in its design and conduct. The LuMind IDSC Down Syndrome Foundation also provided funding for the study. Dr. Hartnick and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of disclosures for the other investigators is available in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Upper airway hypoglossal nerve stimulation is safe and effective in adolescents with Down syndrome and severe persistent obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurring after adenotonsillectomy and who couldn’t tolerate positive airway pressure, early research suggests.
In a phase I study, 42 adolescents received a surgically implanted device that moves the tongue forward during sleep. Results at 1-year follow-up showed 66% “responded well” to treatment and showed a drop in apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of at least 50%.
“Parents came back to us and said not only is the sleep better but my child seems to be doing better during the day,” lead investigator Christopher Hartnick, MD, director of the Division of Pediatric Otolaryngology and the Pediatric Airway, Voice, and Swallowing Center at Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Boston, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery.
Limited options
Upper airway simulation has been shown previously to be effective for adults with OSA, but up until now, the process has not been evaluated in children.
The device used in the current study “stimulates the hypoglossal nerve to protrude the tongue and open the airway on inspiration during sleep,” the investigators note.
“Hypoglossal nerve stimulation may be a particularly suitable therapy for patients with Down syndrome because it can augment neuromuscular airway tone and reduce anatomical obstruction at the base of the tongue, a common site of residual obstruction in children with Down syndrome,” they add.
“This study was born out of the frustration of not having an effective treatment option for children with Down syndrome who struggle with sleep apnea,” Dr. Hartnick said in a news release.
A total of 42 adolescents (67% male; mean age, 15 years) with Down syndrome and persistent severe OSA after adenotonsillectomy were implanted with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator. All were followed for 12 months.
The surgery was safe, with the most common adverse event being temporary tongue discomfort in five patients (12%). This typically resolved in weeks, the researchers note.
High response, adherence rates
Results showed response rates and adherence to therapy was high. The mean duration of nightly therapy was 9 hours, with 40 children (95.2%) using the device at least 4 hours every night.
The implant was also effective, with a mean decrease in AHI of 12.9 events per hour (95% confidence interval, –17.0 to –8.7 events per hour).
Nearly two-thirds of the children had at least a 50% reduction in their AHI, while roughly three-fourths had a 12-month follow-up AHI of less than 10 events per hour.
There were also significant improvements in polysomnographic and parent-reported quality of life outcomes 12 months after the implant, including improvement in sleep and daily functioning, behavior, and language.
“Sleep apnea remains one of the most common conditions that I grapple with working with patients with Down syndrome and their families,” co-investigator Brian Skotko, MD, Emma Campbell endowed chair on Down syndrome at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“Until now, so many of our patients had run out of treatment options, and their health and well-being were declining. Now, with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator treatment, we may have an effective and safe way to treat apnea and maximize brain health for people with Down syndrome,” Dr. Skotko added.
Dr. Hartnick and Dr. Skotko have received a $4 million, 5-year grant from the National Institutes of Health to assess whether upper airway stimulation might help cognition in children with Down syndrome.
Landmark investigation
Co-authors of an invited commentary said they “applaud” the researchers for their “landmark” investigation, which demonstrated a response to upper airway stimulation in children with Down syndrome and OSA that is on par with what has been achieved in adults with OSA.
“They have established the safety of the procedure; however, future research is necessary to optimize the results of implant,” write Norman Friedman, MD, and Katherine Green, MD, both from the department of otolaryngology – head and neck surgery, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
“Further assessment regarding patient selection and the systematic preoperative identification of potential barriers that might affect successful use of therapy will be beneficial to improve longitudinal outcomes and success in this population that is uniquely different from the adult cohorts that have received implants to date,” they add.
The study was funded by Inspire Medical Systems, which provided eight devices for the study but otherwise did not have a role in its design and conduct. The LuMind IDSC Down Syndrome Foundation also provided funding for the study. Dr. Hartnick and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of disclosures for the other investigators is available in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Upper airway hypoglossal nerve stimulation is safe and effective in adolescents with Down syndrome and severe persistent obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurring after adenotonsillectomy and who couldn’t tolerate positive airway pressure, early research suggests.
In a phase I study, 42 adolescents received a surgically implanted device that moves the tongue forward during sleep. Results at 1-year follow-up showed 66% “responded well” to treatment and showed a drop in apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of at least 50%.
“Parents came back to us and said not only is the sleep better but my child seems to be doing better during the day,” lead investigator Christopher Hartnick, MD, director of the Division of Pediatric Otolaryngology and the Pediatric Airway, Voice, and Swallowing Center at Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Boston, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery.
Limited options
Upper airway simulation has been shown previously to be effective for adults with OSA, but up until now, the process has not been evaluated in children.
The device used in the current study “stimulates the hypoglossal nerve to protrude the tongue and open the airway on inspiration during sleep,” the investigators note.
“Hypoglossal nerve stimulation may be a particularly suitable therapy for patients with Down syndrome because it can augment neuromuscular airway tone and reduce anatomical obstruction at the base of the tongue, a common site of residual obstruction in children with Down syndrome,” they add.
“This study was born out of the frustration of not having an effective treatment option for children with Down syndrome who struggle with sleep apnea,” Dr. Hartnick said in a news release.
A total of 42 adolescents (67% male; mean age, 15 years) with Down syndrome and persistent severe OSA after adenotonsillectomy were implanted with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator. All were followed for 12 months.
The surgery was safe, with the most common adverse event being temporary tongue discomfort in five patients (12%). This typically resolved in weeks, the researchers note.
High response, adherence rates
Results showed response rates and adherence to therapy was high. The mean duration of nightly therapy was 9 hours, with 40 children (95.2%) using the device at least 4 hours every night.
The implant was also effective, with a mean decrease in AHI of 12.9 events per hour (95% confidence interval, –17.0 to –8.7 events per hour).
Nearly two-thirds of the children had at least a 50% reduction in their AHI, while roughly three-fourths had a 12-month follow-up AHI of less than 10 events per hour.
There were also significant improvements in polysomnographic and parent-reported quality of life outcomes 12 months after the implant, including improvement in sleep and daily functioning, behavior, and language.
“Sleep apnea remains one of the most common conditions that I grapple with working with patients with Down syndrome and their families,” co-investigator Brian Skotko, MD, Emma Campbell endowed chair on Down syndrome at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in the release.
“Until now, so many of our patients had run out of treatment options, and their health and well-being were declining. Now, with the hypoglossal nerve stimulator treatment, we may have an effective and safe way to treat apnea and maximize brain health for people with Down syndrome,” Dr. Skotko added.
Dr. Hartnick and Dr. Skotko have received a $4 million, 5-year grant from the National Institutes of Health to assess whether upper airway stimulation might help cognition in children with Down syndrome.
Landmark investigation
Co-authors of an invited commentary said they “applaud” the researchers for their “landmark” investigation, which demonstrated a response to upper airway stimulation in children with Down syndrome and OSA that is on par with what has been achieved in adults with OSA.
“They have established the safety of the procedure; however, future research is necessary to optimize the results of implant,” write Norman Friedman, MD, and Katherine Green, MD, both from the department of otolaryngology – head and neck surgery, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
“Further assessment regarding patient selection and the systematic preoperative identification of potential barriers that might affect successful use of therapy will be beneficial to improve longitudinal outcomes and success in this population that is uniquely different from the adult cohorts that have received implants to date,” they add.
The study was funded by Inspire Medical Systems, which provided eight devices for the study but otherwise did not have a role in its design and conduct. The LuMind IDSC Down Syndrome Foundation also provided funding for the study. Dr. Hartnick and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of disclosures for the other investigators is available in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How old is too old to work as a doctor?
Air traffic controllers face mandatory retirement at age 56, with exceptions up to 61. Commercial airline pilots must bow out at 65; same for foreign service employees. Physicians, however, have no age limit, regardless of specialty.
As the profession rapidly ages – some 30% of the physician workforce is currently a senior, according to the American Medical Association – the topic of whether or not there should be a standard measure or age for retirement is front and center. The AMA’s Council on Medical Education formed a workgroup to look into the issue in 2015 and 2018, and in 2021, delegates adopted a set of guidelines for screening and assessing physicians, but stopped short of a mandate.
Mark Katlic, MD, chair of surgery at Lifebridge Health System, Baltimore, has devoted a decade to studying this topic. “I’m a bit of an outlier looking into this,” he says. “The public is unaware and seemingly unconcerned about the issue. Even among the medical profession, there’s been a series of fits and starts to develop a cohesive approach.”
One of the reasons guidelines – mandatory or otherwise – have been tough to come by is that aging brings with it a huge degree of variability. “If you look at a group of 80-year-olds, there will be much more variability than within a group of 40-year-olds,” Dr. Katlic pointed out.
Indeed, some 80-year-olds can easily continue to teach college courses, keep up in 10K running races, or perform delicate surgeries. Yet others in their peer group might struggle to properly button a shirt, walk a flight of stairs, or remember yesterday’s meals. Functional age is not the same as chronological age.
Frank Stockdale, MD, PhD, an 86-year-old practicing oncologist at Stanford (Calif.) University Health, counts himself in the camp opposed to age-based assessments. “It’s age discrimination,” he says. “Physicians receive assessments throughout their careers as part of the accreditation process – there’s no need to change that as doctors reach a certain age.”
Dr. Stockdale suggests that in many cases, malpractice suits are filed against mid-career doctors, not those of advanced age. “If you’re using the argument that there is an accumulation of deficits with age, the fact is that those deficits begin well before your 70s,” he said. “It’s better to have a uniform screening policy and begin at a much younger age.”
At Stanford, in fact, there was a former assessment policy that included cognitive testing, but physicians were successful in seeing that portion of testing eliminated. “It is a physical examination, by a physician of choice, certifying that for the privileges requested there is no physical or mental reason the candidate cannot safely perform them,” Dr. Stockdale explained.
In some cases, medical staffs have filed lawsuits to fight age-related testing. In New Haven, Conn., for instance, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) filed a suit in 2020 on behalf of the Yale New Haven Hospital staff, alleging a discriminatory “late career practitioner policy.”
A similar case in Minnesota reached a settlement in 2021, providing monetary relief to staff impacted by out-of-pocket costs for the assessment, in addition to requiring that the hospital in question report to the EEOC any complaints related to age discrimination.
James Ellison, MD, MPH, chair in Memory Care and Geriatrics with ChristianaCare in Wilmington, Del., points out that aging can bring benefits for practicing physicians. “Age is very individualized and there are good and bad consequences,” he said. “Experience can build knowledge and confidence and expertise, and it does improve diagnostic accuracy.”
On the flip side, however, age-related brain changes include loss of volume and lower levels of some neurotransmitters, resulting in cognitive changes. “Functional changes occur too,” Dr. Ellison said.
“Just as some aging athletes may lose a degree of speed, strength, and flexibility, and some aging scientists may lose a part of their former cognitive speed, flexibility, and mental strength, aging health care providers can lose some of the physical coordination, strength, and visual acuity necessary to perform demanding surgical operations. They can also lose some of the processing speed, working memory, and executive function that allows them to excel in cognitive professional tasks.”
An estimated 5.8 million Americans age 65 and older have Alzheimer’s dementia, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Picking an arbitrary age for mandatory retirement isn’t the right approach for physicians, said Dr. Katlic. Rather, he said, the answer is to establish late-practitioner screening programs. “Very few hospitals have them, however,” he pointed out. “We do [at Lifebridge Health], and so do a few dozen others, but that’s out of hundreds.”
Instead, what typically plays out is that hospital staff might begin to notice a decline in a colleague. Things like a disheveled appearance or lack of hygiene, or trouble with memory, such as getting lost en route back to his or her office. Even dangerous behaviors such as nodding off during a procedure are not unheard of.
There are many examples of physician decline that fly under the radar. “Unfortunately, it’s unusual for cognitively impaired health care providers to recognize and report their own difficulties,” said Dr. Ellison. “Although peers are expected to report cognitively impaired colleagues, they often fail to do so. In some other countries, age-based assessment is an accepted policy. In the U.S., this is not a uniform policy.”
Sometimes physicians can remain on the job in spite of decline thanks to certain “props,” according to Dr. Ellison. “Good procedures, efficient supports, and various workarounds compensate,” he said, “but often are not sufficient to maintain high-quality practice.”
Most often, these situations play out slowly, until the problem becomes glaringly obvious and potentially dangerous, and someone in a position of power must step in.
“Often, it’s hearsay from a nurse or another staff member, and then a hospital president or chief of staff must make a career-affecting decision for the doctor in question,” said Dr. Katlic.
Because there is little self- or colleague policing – and barring official or binding guidelines on the aging physician issue – both Dr. Katlic and Dr. Ellison are proponents of late-career screening.
How screening can help
As it stands, Dr. Katlic maintains that the profession isn’t doing enough to ensure public safety. “We have peer review and recertification processes, but when you get down to it, we don’t police ourselves well,” he said. “All physicians are assessed throughout their careers as part of the hospital accreditation process, which is fair and adequate.”
Dr. Katlic said that there are three main benchmarks that physicians should be able to meet at an agreed upon age: a physical exam, a neurocognitive screening, and an eye exam. “At some reasonable age, I personally believe these exams should take place,” he said. “We can allow doctors to pick their own practitioners for the eye and physical exams, but the neurocognitive exam should be completed by a PhD neuropsychologist.”
At Lifebridge, for instance, these screenings begin at age 75 and take place every 2 years, during the recredentialing process. It applies to all specialties, not just surgeons. “Surgery is a little different in that it requires fine motor skills in addition to the others we test, but you want any physician to be cognitively intact,” Dr. Katlic pointed out. “All doctors need the ability to make decisions quickly, often under noisy, distracting conditions.”
Dr. Ellison supports applying the screenings to all specialties. “Let’s not forget that all physicians must be alert to the many ways in which their patients reveal what needs attention, evaluation, and treatment,” he said. “Some health care tasks could be performed without visual input; for example, perhaps psychotherapy could be provided competently by a clinician who lacks visual acuity. Auditory input might not be necessary for reading x-rays – but the information a health care provider gets from their eyes and ears is important, not just for surgeons.”
University of California San Diego has established what it calls its Physician Assessment and Clinical Education (PACE) program. One of the nation’s oldest and largest such programs, the hospital founded PACE in 1996. Most physicians taking part arrive as a requirement of disciplinary action from the state medical board, but a small percentage self-refers.
PACE involves two phases. The first is a 2-day set of tests and measures core competency knowledge. Phase 2 is more comprehensive and lasts 5 days. Here, within their specialty, physicians participate in the activities of the corresponding residency program. Faculty evaluates the physician, and a multidisciplinary team meets to review all the findings of the combined phases.
Depending on the results, doctors may face remediation steps that range from programs to address performance deficiencies to residency-level clinical experiences. According to a paper on the program published by the institution, “most physicians referred to the PACE program are found to have mild to moderate performance dyscompetence.”
In the case of the 2021 guidelines adopted by AMA delegates, there are nine principles for assessment. They should be evidence-based, ethical, relevant, accountable, fair and equitable, transparent, supportive, and nonburdensome, and should afford physicians due process protections.
Looking ahead
Even Dr. Katlic worries about the possibility of Congress intervening to establish federal-level, mandatory retirement age. “This just doesn’t make sense for our profession given the great variability we see,” he said. “My biggest hope is that more individual hospitals will institute these screenings.”
As the physician population ages – and the influx of new doctors shrinks – the slope becomes even more slippery. The AMA is predicting a physician shortage of nearly 40,000 by the year 2034. This strengthens arguments to keep existing physicians practicing for as long as possible and might make institutions less likely to screen.
It’s all a delicate balancing act and a continuing work in progress, said Dr. Ellison. “Ultimately, I believe we need to find a way to understand and address the possible implications for public safety, while at the same time protecting the privacy and dignity of our valued older physicians and other health care providers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Air traffic controllers face mandatory retirement at age 56, with exceptions up to 61. Commercial airline pilots must bow out at 65; same for foreign service employees. Physicians, however, have no age limit, regardless of specialty.
As the profession rapidly ages – some 30% of the physician workforce is currently a senior, according to the American Medical Association – the topic of whether or not there should be a standard measure or age for retirement is front and center. The AMA’s Council on Medical Education formed a workgroup to look into the issue in 2015 and 2018, and in 2021, delegates adopted a set of guidelines for screening and assessing physicians, but stopped short of a mandate.
Mark Katlic, MD, chair of surgery at Lifebridge Health System, Baltimore, has devoted a decade to studying this topic. “I’m a bit of an outlier looking into this,” he says. “The public is unaware and seemingly unconcerned about the issue. Even among the medical profession, there’s been a series of fits and starts to develop a cohesive approach.”
One of the reasons guidelines – mandatory or otherwise – have been tough to come by is that aging brings with it a huge degree of variability. “If you look at a group of 80-year-olds, there will be much more variability than within a group of 40-year-olds,” Dr. Katlic pointed out.
Indeed, some 80-year-olds can easily continue to teach college courses, keep up in 10K running races, or perform delicate surgeries. Yet others in their peer group might struggle to properly button a shirt, walk a flight of stairs, or remember yesterday’s meals. Functional age is not the same as chronological age.
Frank Stockdale, MD, PhD, an 86-year-old practicing oncologist at Stanford (Calif.) University Health, counts himself in the camp opposed to age-based assessments. “It’s age discrimination,” he says. “Physicians receive assessments throughout their careers as part of the accreditation process – there’s no need to change that as doctors reach a certain age.”
Dr. Stockdale suggests that in many cases, malpractice suits are filed against mid-career doctors, not those of advanced age. “If you’re using the argument that there is an accumulation of deficits with age, the fact is that those deficits begin well before your 70s,” he said. “It’s better to have a uniform screening policy and begin at a much younger age.”
At Stanford, in fact, there was a former assessment policy that included cognitive testing, but physicians were successful in seeing that portion of testing eliminated. “It is a physical examination, by a physician of choice, certifying that for the privileges requested there is no physical or mental reason the candidate cannot safely perform them,” Dr. Stockdale explained.
In some cases, medical staffs have filed lawsuits to fight age-related testing. In New Haven, Conn., for instance, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) filed a suit in 2020 on behalf of the Yale New Haven Hospital staff, alleging a discriminatory “late career practitioner policy.”
A similar case in Minnesota reached a settlement in 2021, providing monetary relief to staff impacted by out-of-pocket costs for the assessment, in addition to requiring that the hospital in question report to the EEOC any complaints related to age discrimination.
James Ellison, MD, MPH, chair in Memory Care and Geriatrics with ChristianaCare in Wilmington, Del., points out that aging can bring benefits for practicing physicians. “Age is very individualized and there are good and bad consequences,” he said. “Experience can build knowledge and confidence and expertise, and it does improve diagnostic accuracy.”
On the flip side, however, age-related brain changes include loss of volume and lower levels of some neurotransmitters, resulting in cognitive changes. “Functional changes occur too,” Dr. Ellison said.
“Just as some aging athletes may lose a degree of speed, strength, and flexibility, and some aging scientists may lose a part of their former cognitive speed, flexibility, and mental strength, aging health care providers can lose some of the physical coordination, strength, and visual acuity necessary to perform demanding surgical operations. They can also lose some of the processing speed, working memory, and executive function that allows them to excel in cognitive professional tasks.”
An estimated 5.8 million Americans age 65 and older have Alzheimer’s dementia, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Picking an arbitrary age for mandatory retirement isn’t the right approach for physicians, said Dr. Katlic. Rather, he said, the answer is to establish late-practitioner screening programs. “Very few hospitals have them, however,” he pointed out. “We do [at Lifebridge Health], and so do a few dozen others, but that’s out of hundreds.”
Instead, what typically plays out is that hospital staff might begin to notice a decline in a colleague. Things like a disheveled appearance or lack of hygiene, or trouble with memory, such as getting lost en route back to his or her office. Even dangerous behaviors such as nodding off during a procedure are not unheard of.
There are many examples of physician decline that fly under the radar. “Unfortunately, it’s unusual for cognitively impaired health care providers to recognize and report their own difficulties,” said Dr. Ellison. “Although peers are expected to report cognitively impaired colleagues, they often fail to do so. In some other countries, age-based assessment is an accepted policy. In the U.S., this is not a uniform policy.”
Sometimes physicians can remain on the job in spite of decline thanks to certain “props,” according to Dr. Ellison. “Good procedures, efficient supports, and various workarounds compensate,” he said, “but often are not sufficient to maintain high-quality practice.”
Most often, these situations play out slowly, until the problem becomes glaringly obvious and potentially dangerous, and someone in a position of power must step in.
“Often, it’s hearsay from a nurse or another staff member, and then a hospital president or chief of staff must make a career-affecting decision for the doctor in question,” said Dr. Katlic.
Because there is little self- or colleague policing – and barring official or binding guidelines on the aging physician issue – both Dr. Katlic and Dr. Ellison are proponents of late-career screening.
How screening can help
As it stands, Dr. Katlic maintains that the profession isn’t doing enough to ensure public safety. “We have peer review and recertification processes, but when you get down to it, we don’t police ourselves well,” he said. “All physicians are assessed throughout their careers as part of the hospital accreditation process, which is fair and adequate.”
Dr. Katlic said that there are three main benchmarks that physicians should be able to meet at an agreed upon age: a physical exam, a neurocognitive screening, and an eye exam. “At some reasonable age, I personally believe these exams should take place,” he said. “We can allow doctors to pick their own practitioners for the eye and physical exams, but the neurocognitive exam should be completed by a PhD neuropsychologist.”
At Lifebridge, for instance, these screenings begin at age 75 and take place every 2 years, during the recredentialing process. It applies to all specialties, not just surgeons. “Surgery is a little different in that it requires fine motor skills in addition to the others we test, but you want any physician to be cognitively intact,” Dr. Katlic pointed out. “All doctors need the ability to make decisions quickly, often under noisy, distracting conditions.”
Dr. Ellison supports applying the screenings to all specialties. “Let’s not forget that all physicians must be alert to the many ways in which their patients reveal what needs attention, evaluation, and treatment,” he said. “Some health care tasks could be performed without visual input; for example, perhaps psychotherapy could be provided competently by a clinician who lacks visual acuity. Auditory input might not be necessary for reading x-rays – but the information a health care provider gets from their eyes and ears is important, not just for surgeons.”
University of California San Diego has established what it calls its Physician Assessment and Clinical Education (PACE) program. One of the nation’s oldest and largest such programs, the hospital founded PACE in 1996. Most physicians taking part arrive as a requirement of disciplinary action from the state medical board, but a small percentage self-refers.
PACE involves two phases. The first is a 2-day set of tests and measures core competency knowledge. Phase 2 is more comprehensive and lasts 5 days. Here, within their specialty, physicians participate in the activities of the corresponding residency program. Faculty evaluates the physician, and a multidisciplinary team meets to review all the findings of the combined phases.
Depending on the results, doctors may face remediation steps that range from programs to address performance deficiencies to residency-level clinical experiences. According to a paper on the program published by the institution, “most physicians referred to the PACE program are found to have mild to moderate performance dyscompetence.”
In the case of the 2021 guidelines adopted by AMA delegates, there are nine principles for assessment. They should be evidence-based, ethical, relevant, accountable, fair and equitable, transparent, supportive, and nonburdensome, and should afford physicians due process protections.
Looking ahead
Even Dr. Katlic worries about the possibility of Congress intervening to establish federal-level, mandatory retirement age. “This just doesn’t make sense for our profession given the great variability we see,” he said. “My biggest hope is that more individual hospitals will institute these screenings.”
As the physician population ages – and the influx of new doctors shrinks – the slope becomes even more slippery. The AMA is predicting a physician shortage of nearly 40,000 by the year 2034. This strengthens arguments to keep existing physicians practicing for as long as possible and might make institutions less likely to screen.
It’s all a delicate balancing act and a continuing work in progress, said Dr. Ellison. “Ultimately, I believe we need to find a way to understand and address the possible implications for public safety, while at the same time protecting the privacy and dignity of our valued older physicians and other health care providers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Air traffic controllers face mandatory retirement at age 56, with exceptions up to 61. Commercial airline pilots must bow out at 65; same for foreign service employees. Physicians, however, have no age limit, regardless of specialty.
As the profession rapidly ages – some 30% of the physician workforce is currently a senior, according to the American Medical Association – the topic of whether or not there should be a standard measure or age for retirement is front and center. The AMA’s Council on Medical Education formed a workgroup to look into the issue in 2015 and 2018, and in 2021, delegates adopted a set of guidelines for screening and assessing physicians, but stopped short of a mandate.
Mark Katlic, MD, chair of surgery at Lifebridge Health System, Baltimore, has devoted a decade to studying this topic. “I’m a bit of an outlier looking into this,” he says. “The public is unaware and seemingly unconcerned about the issue. Even among the medical profession, there’s been a series of fits and starts to develop a cohesive approach.”
One of the reasons guidelines – mandatory or otherwise – have been tough to come by is that aging brings with it a huge degree of variability. “If you look at a group of 80-year-olds, there will be much more variability than within a group of 40-year-olds,” Dr. Katlic pointed out.
Indeed, some 80-year-olds can easily continue to teach college courses, keep up in 10K running races, or perform delicate surgeries. Yet others in their peer group might struggle to properly button a shirt, walk a flight of stairs, or remember yesterday’s meals. Functional age is not the same as chronological age.
Frank Stockdale, MD, PhD, an 86-year-old practicing oncologist at Stanford (Calif.) University Health, counts himself in the camp opposed to age-based assessments. “It’s age discrimination,” he says. “Physicians receive assessments throughout their careers as part of the accreditation process – there’s no need to change that as doctors reach a certain age.”
Dr. Stockdale suggests that in many cases, malpractice suits are filed against mid-career doctors, not those of advanced age. “If you’re using the argument that there is an accumulation of deficits with age, the fact is that those deficits begin well before your 70s,” he said. “It’s better to have a uniform screening policy and begin at a much younger age.”
At Stanford, in fact, there was a former assessment policy that included cognitive testing, but physicians were successful in seeing that portion of testing eliminated. “It is a physical examination, by a physician of choice, certifying that for the privileges requested there is no physical or mental reason the candidate cannot safely perform them,” Dr. Stockdale explained.
In some cases, medical staffs have filed lawsuits to fight age-related testing. In New Haven, Conn., for instance, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) filed a suit in 2020 on behalf of the Yale New Haven Hospital staff, alleging a discriminatory “late career practitioner policy.”
A similar case in Minnesota reached a settlement in 2021, providing monetary relief to staff impacted by out-of-pocket costs for the assessment, in addition to requiring that the hospital in question report to the EEOC any complaints related to age discrimination.
James Ellison, MD, MPH, chair in Memory Care and Geriatrics with ChristianaCare in Wilmington, Del., points out that aging can bring benefits for practicing physicians. “Age is very individualized and there are good and bad consequences,” he said. “Experience can build knowledge and confidence and expertise, and it does improve diagnostic accuracy.”
On the flip side, however, age-related brain changes include loss of volume and lower levels of some neurotransmitters, resulting in cognitive changes. “Functional changes occur too,” Dr. Ellison said.
“Just as some aging athletes may lose a degree of speed, strength, and flexibility, and some aging scientists may lose a part of their former cognitive speed, flexibility, and mental strength, aging health care providers can lose some of the physical coordination, strength, and visual acuity necessary to perform demanding surgical operations. They can also lose some of the processing speed, working memory, and executive function that allows them to excel in cognitive professional tasks.”
An estimated 5.8 million Americans age 65 and older have Alzheimer’s dementia, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Picking an arbitrary age for mandatory retirement isn’t the right approach for physicians, said Dr. Katlic. Rather, he said, the answer is to establish late-practitioner screening programs. “Very few hospitals have them, however,” he pointed out. “We do [at Lifebridge Health], and so do a few dozen others, but that’s out of hundreds.”
Instead, what typically plays out is that hospital staff might begin to notice a decline in a colleague. Things like a disheveled appearance or lack of hygiene, or trouble with memory, such as getting lost en route back to his or her office. Even dangerous behaviors such as nodding off during a procedure are not unheard of.
There are many examples of physician decline that fly under the radar. “Unfortunately, it’s unusual for cognitively impaired health care providers to recognize and report their own difficulties,” said Dr. Ellison. “Although peers are expected to report cognitively impaired colleagues, they often fail to do so. In some other countries, age-based assessment is an accepted policy. In the U.S., this is not a uniform policy.”
Sometimes physicians can remain on the job in spite of decline thanks to certain “props,” according to Dr. Ellison. “Good procedures, efficient supports, and various workarounds compensate,” he said, “but often are not sufficient to maintain high-quality practice.”
Most often, these situations play out slowly, until the problem becomes glaringly obvious and potentially dangerous, and someone in a position of power must step in.
“Often, it’s hearsay from a nurse or another staff member, and then a hospital president or chief of staff must make a career-affecting decision for the doctor in question,” said Dr. Katlic.
Because there is little self- or colleague policing – and barring official or binding guidelines on the aging physician issue – both Dr. Katlic and Dr. Ellison are proponents of late-career screening.
How screening can help
As it stands, Dr. Katlic maintains that the profession isn’t doing enough to ensure public safety. “We have peer review and recertification processes, but when you get down to it, we don’t police ourselves well,” he said. “All physicians are assessed throughout their careers as part of the hospital accreditation process, which is fair and adequate.”
Dr. Katlic said that there are three main benchmarks that physicians should be able to meet at an agreed upon age: a physical exam, a neurocognitive screening, and an eye exam. “At some reasonable age, I personally believe these exams should take place,” he said. “We can allow doctors to pick their own practitioners for the eye and physical exams, but the neurocognitive exam should be completed by a PhD neuropsychologist.”
At Lifebridge, for instance, these screenings begin at age 75 and take place every 2 years, during the recredentialing process. It applies to all specialties, not just surgeons. “Surgery is a little different in that it requires fine motor skills in addition to the others we test, but you want any physician to be cognitively intact,” Dr. Katlic pointed out. “All doctors need the ability to make decisions quickly, often under noisy, distracting conditions.”
Dr. Ellison supports applying the screenings to all specialties. “Let’s not forget that all physicians must be alert to the many ways in which their patients reveal what needs attention, evaluation, and treatment,” he said. “Some health care tasks could be performed without visual input; for example, perhaps psychotherapy could be provided competently by a clinician who lacks visual acuity. Auditory input might not be necessary for reading x-rays – but the information a health care provider gets from their eyes and ears is important, not just for surgeons.”
University of California San Diego has established what it calls its Physician Assessment and Clinical Education (PACE) program. One of the nation’s oldest and largest such programs, the hospital founded PACE in 1996. Most physicians taking part arrive as a requirement of disciplinary action from the state medical board, but a small percentage self-refers.
PACE involves two phases. The first is a 2-day set of tests and measures core competency knowledge. Phase 2 is more comprehensive and lasts 5 days. Here, within their specialty, physicians participate in the activities of the corresponding residency program. Faculty evaluates the physician, and a multidisciplinary team meets to review all the findings of the combined phases.
Depending on the results, doctors may face remediation steps that range from programs to address performance deficiencies to residency-level clinical experiences. According to a paper on the program published by the institution, “most physicians referred to the PACE program are found to have mild to moderate performance dyscompetence.”
In the case of the 2021 guidelines adopted by AMA delegates, there are nine principles for assessment. They should be evidence-based, ethical, relevant, accountable, fair and equitable, transparent, supportive, and nonburdensome, and should afford physicians due process protections.
Looking ahead
Even Dr. Katlic worries about the possibility of Congress intervening to establish federal-level, mandatory retirement age. “This just doesn’t make sense for our profession given the great variability we see,” he said. “My biggest hope is that more individual hospitals will institute these screenings.”
As the physician population ages – and the influx of new doctors shrinks – the slope becomes even more slippery. The AMA is predicting a physician shortage of nearly 40,000 by the year 2034. This strengthens arguments to keep existing physicians practicing for as long as possible and might make institutions less likely to screen.
It’s all a delicate balancing act and a continuing work in progress, said Dr. Ellison. “Ultimately, I believe we need to find a way to understand and address the possible implications for public safety, while at the same time protecting the privacy and dignity of our valued older physicians and other health care providers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis (Part 1)
It is unfortunate that, in some clinical areas, medical conditions are still treated by name and not based on the underlying pathological process. It would be odd in 2022 to treat “dropsy” instead of heart or kidney disease (2 very different causes of edema). Similarly, if the FDA had been approving drugs 150 years ago, we would have medications on label for “dementia praecox,” not schizophrenia or Alzheimer disease. With the help of DSM-5, psychiatry still resides in the descriptive symptomatic world of disorders.
In the United States, thanks to Freud, psychiatric symptoms became separated from medical symptoms, which made it more difficult to associate psychiatric manifestations with the underlying pathophysiology. Though the physical manifestations that parallel emotional symptoms—such as the dry mouth of anxiety, the tremor and leg weakness of fear, the constipation and blurry vision of depression, the breathing difficulty of anger, the abdominal pain of stress, the blushing of shyness, the palpitations of flashbacks, and endless others—are well known, the present classification of psychiatric disorders is blind to it. Neurochemical causes of gastrointestinal spasm or muscle tension are better researched than underlying central neurochemistry, though the same neurotransmitters drive them.
Can the biochemistry of psychiatric symptoms be judged on the basis of peripheral symptoms? Can the mental manifestations be connected to biological causation, and vice versa? Would psychiatrists be better off selecting treatments by recognizing involved neurotransmitters instead of addressing descriptive “depression, anxiety, and psychosis”? Each of these clinical syndromes may be caused by entirely different underlying neuronal mechanisms. Such mechanisms could be suggested if medical symptoms (which are measurable and objective) would become part of the psychiatric diagnosis. Is treating the “cough” sufficient, or would recognition that tuberculosis caused the cough guide better treatment? Is it time to abandon descriptive conditions and replace them with a specific “mechanism-based” viewpoint?
Ample research has shown that serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, endorphins, glutamate, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) are the neurotransmitters most responsible in the process of both psychiatric disorders and chronic pain. These neurotransmitters are involved in much more than emotions (including the feeling of pain). An abundance of medical symptom clusters point toward which neurotransmitter dysfunction may be leading in specific cases of distinct types of depression, psychosis, anxiety, or “chronic pain.” Even presently, there are medications available (both for FDA-approved indications and off-label) that can be used to regulate these neurotransmitters, allowing practitioners to target the possible biological underlining of psychiatric or pain pathology. Hopefully, in the not-so-distant future, there will be specific medications for serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenergic depression as well as for GABAergic anxiety, endorphin psychosis, noradrenergic insomnia, and similar conditions.
Numerous neurotransmitters may be connected to both depression and pain in all their forms. These include (but are not limited to) prostaglandins, bradykinins, substance P, potassium, magnesium, calcium, histamine, adenosine triphosphate, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), nitric oxide (NO), cholecystokinin 7 (CCK7), neurotrophic growth factor (NGF), neurotensin, acetylcholine (Ach), oxytocin, cannabinoids, and others. These have not been researched sufficiently to identify their clinical presentation of excessive or insufficient availability at the sites of neurotransmission. It is difficult to draw conclusions about what kind of clinical symptoms they may cause (outside of pain), and therefore, they are not addressed in this article.
Both high and low levels of certain neurotransmitters may be associated with psychiatric conditions and chronic pain. Too much is as bad as too little.1 This applies to both quantity of neurotransmitters as well as quality of the corresponding receptor activity. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation. Reading indirect signs of bodily functions is a basic clinical skill that should not be forgotten, even in the time of advanced technology.
A different way of viewing psychiatric disorders
In this article, we present 4 hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. In no way do these descriptions reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known or suspected, and extensive research is required to confirm or disprove what we describe here.
Continue to: There are no well-recognized...
There are no well-recognized, well-established, reliable, or validated syndromes described in our work. Our goal is to suggest an alternative way of looking at psychiatric disorders by viewing syndromal presentation through the lens of specific neurotransmitters. The collection of symptoms associated with various neurotransmitters as presented in this hypothesis is not complete. We have assembled what is described in the literature as a suggestion for specific future research. We simplified these clinical presentations by omitting scenarios in which a specific neurotransmitter increases in one area but not another. For example, all the symptoms of dopamine excess we describe would not have to occur concurrently in the same patient, but they may develop in certain patients depending on which dopaminergic pathway is exhibiting excess activity. Such distinctions may be established only by exhaustive research not yet conducted.
Our proposal may seem radical, but it truly is not. For example, if we know that dopamine excess may cause seizures, psychosis, and blood pressure elevation, why not consider dopamine excess as an underlying cause in a patient with depression who exhibits these symptoms simultaneously? And why not call it “dopamine excess syndrome”? We already have “serotonin syndrome” for a patient experiencing a serotonin storm. However, using the same logic, it should be called “serotonin excess syndrome.” And if we know of “serotonin excess syndrome,” why not consider “serotonin deficiency syndrome”?
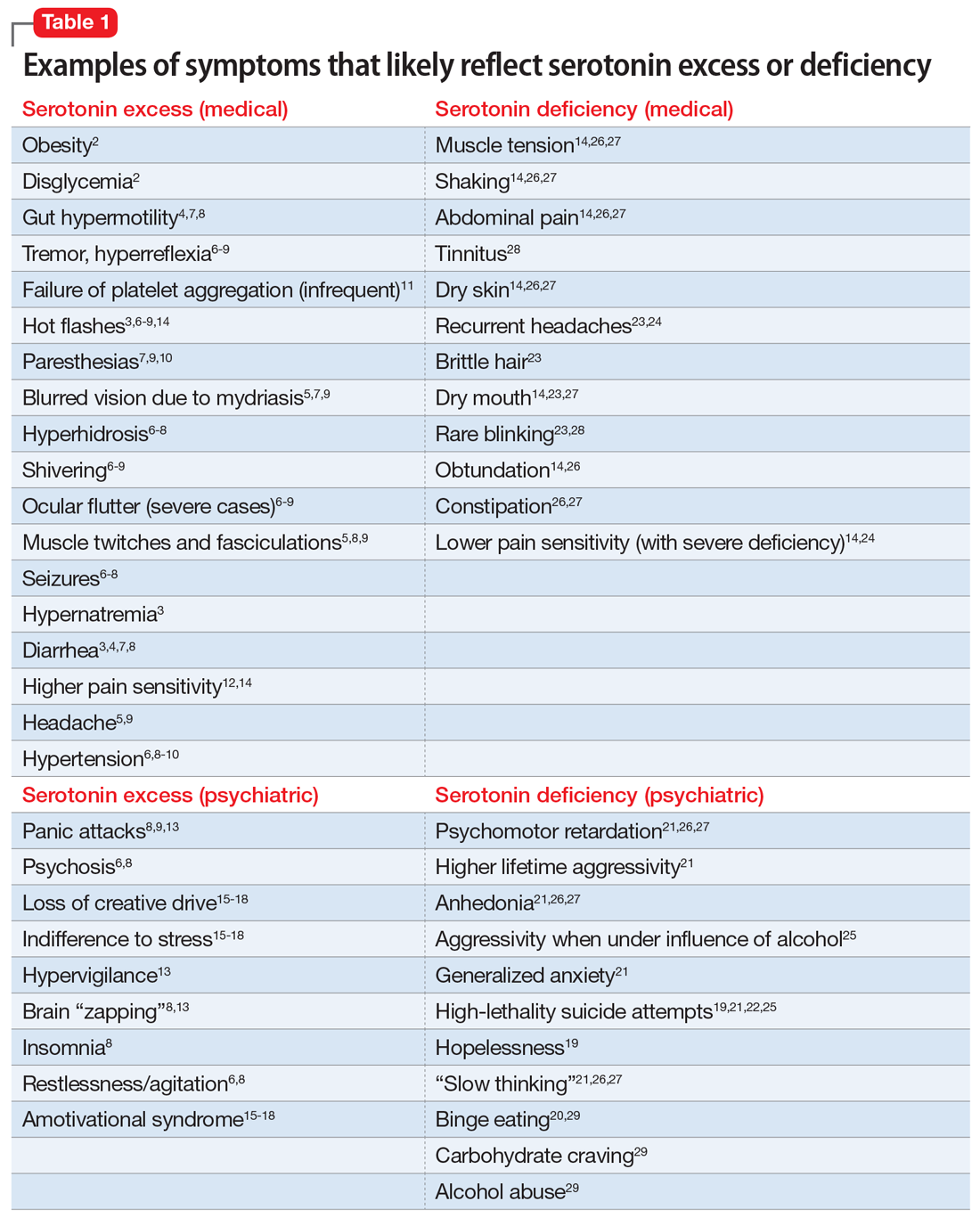
In Part 1 of this article, we discuss serotonin and dopamine. Table 1 outlines medical and psychiatric symptoms that likely reflect serotonin excess2-18 and deficiency,14,19-29 and Table 2 lists symptoms that likely reflect dopamine excess14,30-41 and deficiency.4,14,20,38,40-43 In Part 2 we will touch on endorphins and norepinephrine, and in Part 3 we will conclude by looking at GABA and glutamate.
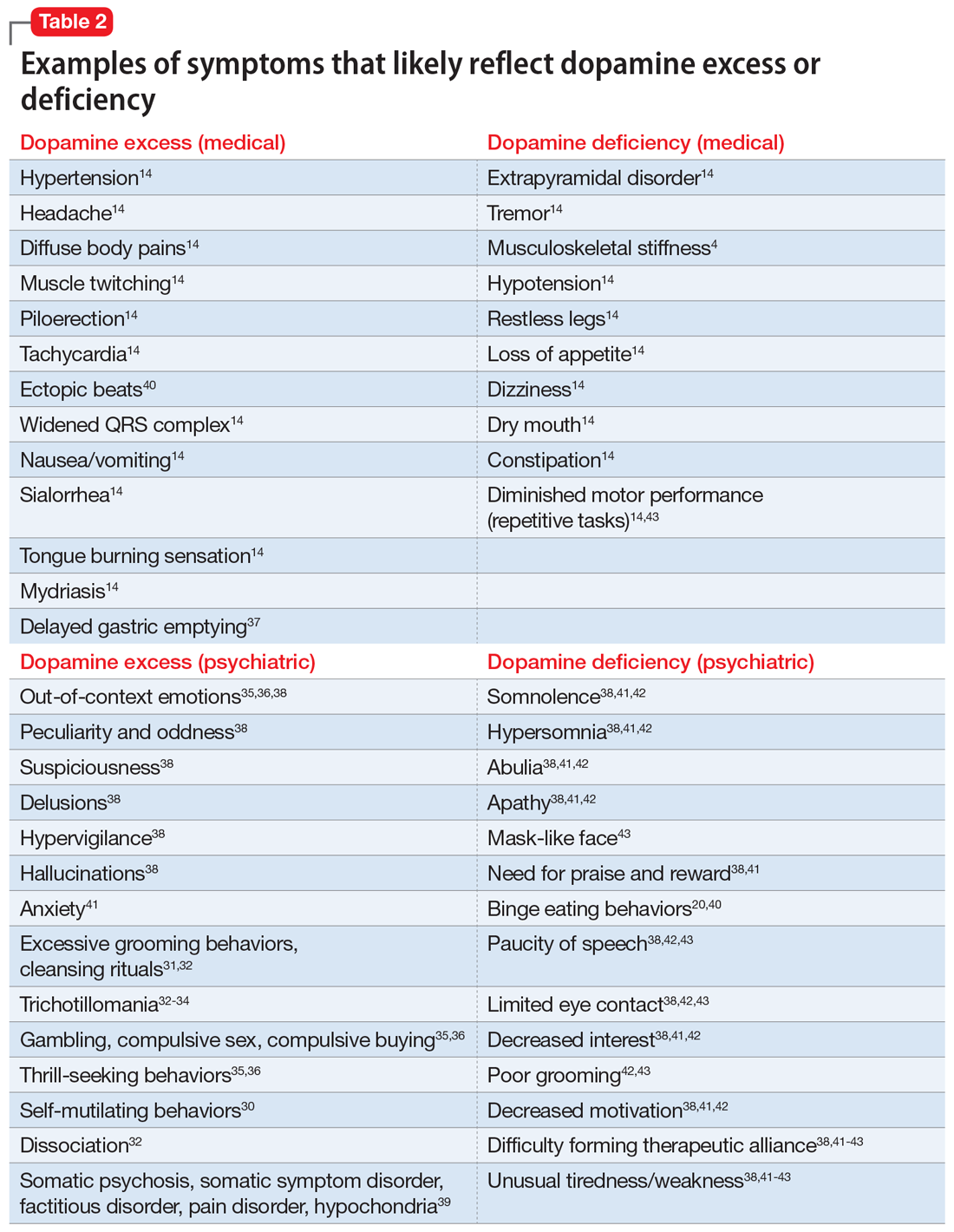
Serotonin excess (Table 12-18)
On a recent office visit, Ms. H reports that most of the time she does not feel much of anything, but she still experiences panic attacks8,9,13,15 and is easily agitated.6,8 Her mother died recently, and Ms. H is concerned that she did not grieve.15-18 She failed her last semester in college and was indifferent to her failure.18 She sleeps poorly,8 is failing her creative classes, and wonders why she has lost her artistic inclination.16-18 Ms. H has difficulty with amotivation, planning, social interactions, and speech.16,17 All of those symptoms worsened after she was prescribed fluoxetine approximately 1 year ago for her “blues.” Ms. H is obese and continues to gain weight,2 though she frequently has diarrhea,3,4,7,8 loud peristalsis, and abdominal cramps.4,7,8 She sweats easily6-8 and her heart frequently races.8,9 Additionally, Ms. H’s primary care physician told her that she has “borderline diabetes.”2 She is prone to frequent bruising11 and is easy to shake, even when she is experiencing minimal anxiety.6-9 Ms. H had consulted with a neurologist because of unusual electrical “zapping” in her brain and muscle twitches.5,8,9,13 She had experienced a seizure as a child, but this was possibly related to hypernatremia,2 and she has not taken any anticonvulsant medication for several years.8 She exhibits hyperactive deep tendon reflexes and tremors5,7,9 and blinks frequently.6,9 She experiences hot flashes,3,6-8,14 does not tolerate heat, and prefers cooler weather.8,9 Her pains and aches,12,14 to which she has been prone all of her life, have recently become much worse, and she was diagnosed with fibromyalgia in part because she frequently feels stiff all over.10 She complains of strange tingling and prickling sensations in her hands and feet, especially when anxious.7,9,10 Her headaches also worsened and may be precipitated by bright light, as her pupils are usually dilated.5,7,9 Her hypertension is fairly controlled with medication.6,8-10 Ms. H says she experienced a psychotic episode when she was in her mid-teens,6,8 but reassures you that “she is not that bad now,” although she remains hypervigilant.13 Also while in her teens, Ms. H was treated with paroxetine and experienced restlessness, agitation, delirium, tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, diaphoresis, diarrhea, and neuromuscular excitation, which prompted discontinuation of the antidepressant.5-7,9,10
Impression. Ms. H exhibits symptoms associated with serotonin hyperactivity. Discontinuing and avoiding selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) would be prudent; prescribing an anticonvulsant would be reasonable. Using a GABAergic medication to suppress serotonin (eg, baclofen) is likely to help. Avoiding dopaminergic medications is a must. Antidepressive antipsychotics would be logical to use. The use of serotonin-suppressing medications may be considered. One may argue for the use of beta-blockers in such a patient.
Continue to: Serotonin deficiency
Serotonin deficiency (Table 114,19-29)
Mr. A is chronically depressed, hopeless,19 and easily angered.21 He does not believe anyone can help him.19 You are concerned for his safety because he had attempted to end his life by shooting himself in the chest.19,21,22,25 Even when he’s not particularly depressed, Mr. A does not enjoy much of anything.21,26,27 He becomes particularly agitated when he drinks alcohol,25 which unfortunately is common for him.29 He engages in binge eating to feel better; he knows this is not healthy but he cannot control his behavior.20,29 Mr. A is poorly compliant with his medications, even with a blood thinner, which he was prescribed due to an episode of deep vein thrombosis. He complains of chronic daily headaches and episodic migraines.23,24 He rarely blinks,23,28 his skin is dry and cool, his hair is brittle,23 his mouth is dry,14,23,27 and he constantly licks his chapped lips.14,26,27 Mr. A frequently has general body pain26,31 but is dismissive of his body aches and completely stops reporting pain when his depression gets particularly severe. When depressed, he is slow in movement and thinking.14,21,26,27 He is more concerned with anxiety than depression.21 Mr. A is plagued by constipation, abdominal pain, muscle tension, and episodes of shaking.14,26,27 He also frequently complains about chronic tinnitus.28
Impression. Mr. A shows symptoms associated with serotonin hypoactivity. SSRIs and any other antidepressants with serotonin activity would be an obvious choice for treatment. A mood-stabilizing antipsychotic with serotonin activity would be welcome in treatment. Thyroid hormone supplementation may be of value, especially if thyroid stimulating hormone level is high. Light therapy, a diet with food that contains tryptophan, psychotherapy, and exercise are desirable. Avoiding benzodiazepines would be a good idea.
Dopamine excess (Table 214,30-41)
Ms. L presents with complaints of “fibromyalgia” and “daily headaches,”14 and also dissociation (finding herself in places when she does not know how she got there) and “out-of-body experiences.”32 She is odd, and states that people do not understand her and that she is “different.”38 Her friend, who is present at the appointment, elaborates on Ms. L’s bizarreness and oddness in behavior, out-of-context emotions, suspiciousness, paranoia, and possible hallucinations.35,36,38 Ms. L discloses frequent diffuse body pains, headaches, nausea, excessive salivation, and tongue burning, as well as muscle twitching.14 Sex worsens her headaches and body pain. She reports seizures that are not registered on EEG. In the office, she is suspicious, exhibits odd posturing, tends to misinterpret your words, and makes you feel uncomfortable. Anxiety38 and multiple obsessive-compulsive symptoms, especially excessive cleaning and grooming, complicate Ms. L’s life.31,32,34 On examination, she is hypertensive, and she has scars caused by self-cutting and skin picking on her arms.30-32 An electrocardiogram shows an elevated heart rate, widened QRS complex, and ectopic heartbeats.14 Ms. L has experienced trichotillomania since adolescence32-34 and her fingernails are bitten to the skin.34 She has difficulty with impulse control, and thrill-seeking is a prominent part of her life, mainly via gambling, compulsive sex, and compulsive buying.35,36 She also says she experiences indigestion and delayed gastric emptying.37
Impression. Ms. L exhibits multiple symptoms associated with dopamine excess. Dopamine antagonists should be considered and may help not only with her psychiatric symptoms but also with her pain symptoms. Bupropion (as a dopamine agonist), caffeine, and stimulants should be avoided.
Excessive dopamine is, in extreme cases, associated with somatic psychosis, somatic symptom disorder, factitious disorder, pain disorder, and hypochondria.39 It may come with odd and bizarre/peculiar symptoms out of proportion with objectively identified pathology. These symptoms are common in chronic pain and headache patients, and need to be addressed by appropriate use of dopamine antagonizing medications.39
Continue to: Dopamine deficiency
Dopamine deficiency (Table 24,14,20,38,40-43)
Mr. W experiences widespread pain, including chronic back pain, headaches, and abdominal pain. He also has substantial anhedonia, lack of interest, procrastination, and hypersomnia.41,42 He is apathetic and has difficulty getting up in the morning.41,42 Unusual tiredness and weakness drive him to overuse caffeine; he states that 5 Mountain Dews and 4 cups of regular coffee a day make his headaches bearable.38,41-43 Sex also improves his headaches. Since childhood, he has taken stimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. He reports that occasional use of cocaine helps ease his pain and depression. Mr. W’s wife is concerned with her husband’s low sexual drive and alcohol consumption, and discloses that he has periodic trouble with gambling. Mr. W was forced into psychotherapy but never was able to work productively with his therapist.38,41-43 He loves eating and cannot control his weight.40 This contrasts with episodic anorexia he experienced when he was younger.20 His face is usually emotionless.43 Mr. W is prone to constipation.14 His restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder are so bad that his wife refuses to share a bed with him.14 He is clumsy and has a problem with repetitive motor tasks.43 A paucity of speech, limited eye contact, poor grooming, and difficulty forming therapeutic alliances have long been part of Mr. W’s history.38,42,43 On physical examination, he has a dry mouth; he is stiff, tremulous, and hypotensive.14
Impression. Mr. W shows multiple symptoms associated with dopamine deficiency. Bupropion may be reasonable to consider. Dopamine augmentation via the use of stimulants is warranted in such patients, especially if stimulants had not been tried before (lisdexamfetamine would be a good choice to minimize addictive potential). For a patient with dopamine deficiency, levodopa may improve more than just restless legs. Amantadine may improve dopaminergic signaling through the accelerated dopamine release and decrease in presynaptic uptake, so this medication may be carefully tried.44 Pain treatment would not be successful for Mr. W without simultaneous treatment for his substance use.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of serotonin and dopamine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Abell SR, El-Mallakh RS. Serotonin-mediated anxiety: How to recognize and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):37-40. doi:10.12788/cp.0168
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Baclofen • Ozobax
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisdexamfetamine • Vyvanse
Paroxetine • Paxil
1. Stahl SM. Dazzled by the dominions of dopamine: clinical roles of D3, D2, and D1 receptors. CNS Spectr. 2017;22(4):305-311.
2. Young RL, Lumsden AL, Martin AM, et al. Augmented capacity for peripheral serotonin release in human obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(11):1880-1889.
3. Ahlman H. Serotonin and carcinoid tumors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7(Suppl 7):S79-S85.
4. Terry N, Margolis KG. Serotonergic mechanisms regulating the GI tract: experimental evidence and therapeutic relevance. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;239:319-342.
5. Prakash S, Belani P, Trivedi A. Headache as a presenting feature in patients with serotonin syndrome: a case series. Cephalalgia. 2014;34(2):148-153.
6. van Ewijk CE, Jacobs GE, Girbes ARJ. Unsuspected serotonin toxicity in the ICU. Ann Intensive Care. 2016;6(1):85.
7. Pedavally S, Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA. Serotonin syndrome in the intensive care unit: clinical presentations and precipitating medications. Neurocrit Care. 2014;21(1):108-113.
8. Nguyen H, Pan A, Smollin C, et al. An 11-year retrospective review of cyproheptadine use in serotonin syndrome cases reported to the California Poison Control System. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2019;44(2):327-334.
9. Ansari H, Kouti L. Drug interaction and serotonin toxicity with opioid use: another reason to avoid opioids in headache and migraine treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(8):50.
10. Ott M, Mannchen JK, Jamshidi F, et al. Management of severe arterial hypertension associated with serotonin syndrome: a case report analysis based on systematic review techniques. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019;9:2045125318818814. doi:10.1177/2045125318818814
11. Cerrito F, Lazzaro MP, Gaudio E, et al. 5HT2-receptors and serotonin release: their role in human platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 1993;53(3):209-215.
12. Ohayon MM. Pain sensitivity, depression, and sleep deprivation: links with serotoninergic dysfunction. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43(16):1243-1245.
13. Maron E, Shlik J. Serotonin function in panic disorder: important, but why? Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(1):1-11.
14. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:120,199,201-204,730-740.
15. Garland EJ, Baerg EA. Amotivational syndrome associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001;11(2):181-186.
16. George MS, Trimble MR. A fluvoxamine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in a patient with comorbid Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome and obsessive compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 1992;53(10):379-380.
17. Hoehn-Saric R, Harris GJ, Pearlson GD, et al. A fluoxetine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in an obsessive compulsive patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 1991;52(3):131-133.
18. Hoehn-Saric R, Lipsey JR, McLeod DR. Apathy and indifference in patients on fluvoxamine and fluoxetine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10(5):343-345.
19. Samuelsson M, Jokinen J, Nordström AL, et al. CSF 5-HIAA, suicide intent and hopelessness in the prediction of early suicide in male high-risk suicide attempters. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006;113(1):44-47.
20. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
21. Mann JJ, Oquendo M, Underwood MD, et al. The neurobiology of suicide risk: a review for the clinician. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 2:7-116.
22. Mann JJ, Malone KM. Cerebrospinal fluid amines and higher-lethality suicide attempts in depressed inpatients. Biol Psychiatry. 1997;41(2):162-171.
23. Joseph R, Welch KM, D’Andrea G. Serotonergic hypofunction in migraine: a synthesis of evidence based on platelet dense body dysfunction. Cephalalgia. 1989;9(4):293-299.
24. Pakalnis A, Splaingard M, Splaingard D, et al. Serotonin effects on sleep and emotional disorders in adolescent migraine. Headache. 2009;49(10):1486-1492.
25. Virkkunen M, Goldman D, Nielsen DA, et al. Low brain serotonin turnover rate (low CSF 5-HIAA) and impulsive violence. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1995;20(4):271-275.
26. Liu Y, Zhao J, Fan X, et al. Dysfunction in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems and somatic symptoms in psychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:286.
27. Ginsburg GS, Riddle MA, Davies M. Somatic symptoms in children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006;45(10):1179-1187.
28. O’Malley PG, Jackson JL, Santoro J, et al. Antidepressant therapy for unexplained symptoms and symptom syndromes. J Fam Pract. 1999;48(12):980-990.
29. Fortuna JL. Sweet preference, sugar addiction and the familial history of alcohol dependence: shared neural pathways and genes. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2010;42(2):147-151.
30. Stanley B, Sher L, Wilson S, et al. Non-suicidal self-injurious behavior, endogenous opioids and monoamine neurotransmitters. J Affect Disord. 2010;124(1-2):134-140.
31. Graybiel AM, Saka E. A genetic basis for obsessive grooming. Neuron. 2002;33(1):1-2.
32. Tse W, Hälbig TD. Skin picking in Parkinson’s disease: a behavioral side-effect of dopaminergic treatment? Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64(2):214.
33. Ayaydın H. Probable emergence of symptoms of trichotillomania by atomoxetine: a case report. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2019;29(2)220-222.
34. Paholpak P, Mendez MF. Trichotillomania as a manifestation of dementia. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2016;2016:9782702. doi:10.1155/2016/9782702
35. Clark CA, Dagher A. The role of dopamine in risk taking: a specific look at Parkinson’s disease and gambling. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:196.
36. Norbury A, Husain M. Sensation-seeking: dopaminergic modulation and risk for psychopathology. Behav Brain Res. 2015;288:79-93.
37. Chen TS, Chang FY. Elevated serum dopamine increases while coffee consumption decreases the occurrence of reddish streaks in the intact stomach. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(12):1810-1814.
38. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st edition. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:420-429.
39. Arbuck DM. Antipsychotics, dopamine, and pain. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(1):25-29,31.
40. Bello NT, Hajnal A. Dopamine and binge eating behaviors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010;97(1):25-33.
41. Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, Sajatovic M, et al; Expert Consensus Panel on Adherence Problems in Serious and Persistent Mental Illness. The expert consensus guideline series: adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70 Suppl 4:1-46.
42. Milev P, Ho BC, Arndt S, et al. Predictive values of neurocognition and negative symptoms on functional outcome in schizophrenia: a longitudinal first-episode study with 7-year follow-up. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(3):495-506.
43. Gepshtein S, Li X, Snider J, et al. Dopamine function and the efficiency of human movement. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(3):645-657.
44. Scarff JR. The ABCDs of treating tardive dyskinesia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):21,55.
It is unfortunate that, in some clinical areas, medical conditions are still treated by name and not based on the underlying pathological process. It would be odd in 2022 to treat “dropsy” instead of heart or kidney disease (2 very different causes of edema). Similarly, if the FDA had been approving drugs 150 years ago, we would have medications on label for “dementia praecox,” not schizophrenia or Alzheimer disease. With the help of DSM-5, psychiatry still resides in the descriptive symptomatic world of disorders.
In the United States, thanks to Freud, psychiatric symptoms became separated from medical symptoms, which made it more difficult to associate psychiatric manifestations with the underlying pathophysiology. Though the physical manifestations that parallel emotional symptoms—such as the dry mouth of anxiety, the tremor and leg weakness of fear, the constipation and blurry vision of depression, the breathing difficulty of anger, the abdominal pain of stress, the blushing of shyness, the palpitations of flashbacks, and endless others—are well known, the present classification of psychiatric disorders is blind to it. Neurochemical causes of gastrointestinal spasm or muscle tension are better researched than underlying central neurochemistry, though the same neurotransmitters drive them.
Can the biochemistry of psychiatric symptoms be judged on the basis of peripheral symptoms? Can the mental manifestations be connected to biological causation, and vice versa? Would psychiatrists be better off selecting treatments by recognizing involved neurotransmitters instead of addressing descriptive “depression, anxiety, and psychosis”? Each of these clinical syndromes may be caused by entirely different underlying neuronal mechanisms. Such mechanisms could be suggested if medical symptoms (which are measurable and objective) would become part of the psychiatric diagnosis. Is treating the “cough” sufficient, or would recognition that tuberculosis caused the cough guide better treatment? Is it time to abandon descriptive conditions and replace them with a specific “mechanism-based” viewpoint?
Ample research has shown that serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, endorphins, glutamate, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) are the neurotransmitters most responsible in the process of both psychiatric disorders and chronic pain. These neurotransmitters are involved in much more than emotions (including the feeling of pain). An abundance of medical symptom clusters point toward which neurotransmitter dysfunction may be leading in specific cases of distinct types of depression, psychosis, anxiety, or “chronic pain.” Even presently, there are medications available (both for FDA-approved indications and off-label) that can be used to regulate these neurotransmitters, allowing practitioners to target the possible biological underlining of psychiatric or pain pathology. Hopefully, in the not-so-distant future, there will be specific medications for serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenergic depression as well as for GABAergic anxiety, endorphin psychosis, noradrenergic insomnia, and similar conditions.
Numerous neurotransmitters may be connected to both depression and pain in all their forms. These include (but are not limited to) prostaglandins, bradykinins, substance P, potassium, magnesium, calcium, histamine, adenosine triphosphate, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), nitric oxide (NO), cholecystokinin 7 (CCK7), neurotrophic growth factor (NGF), neurotensin, acetylcholine (Ach), oxytocin, cannabinoids, and others. These have not been researched sufficiently to identify their clinical presentation of excessive or insufficient availability at the sites of neurotransmission. It is difficult to draw conclusions about what kind of clinical symptoms they may cause (outside of pain), and therefore, they are not addressed in this article.
Both high and low levels of certain neurotransmitters may be associated with psychiatric conditions and chronic pain. Too much is as bad as too little.1 This applies to both quantity of neurotransmitters as well as quality of the corresponding receptor activity. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation. Reading indirect signs of bodily functions is a basic clinical skill that should not be forgotten, even in the time of advanced technology.
A different way of viewing psychiatric disorders
In this article, we present 4 hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. In no way do these descriptions reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known or suspected, and extensive research is required to confirm or disprove what we describe here.
Continue to: There are no well-recognized...
There are no well-recognized, well-established, reliable, or validated syndromes described in our work. Our goal is to suggest an alternative way of looking at psychiatric disorders by viewing syndromal presentation through the lens of specific neurotransmitters. The collection of symptoms associated with various neurotransmitters as presented in this hypothesis is not complete. We have assembled what is described in the literature as a suggestion for specific future research. We simplified these clinical presentations by omitting scenarios in which a specific neurotransmitter increases in one area but not another. For example, all the symptoms of dopamine excess we describe would not have to occur concurrently in the same patient, but they may develop in certain patients depending on which dopaminergic pathway is exhibiting excess activity. Such distinctions may be established only by exhaustive research not yet conducted.
Our proposal may seem radical, but it truly is not. For example, if we know that dopamine excess may cause seizures, psychosis, and blood pressure elevation, why not consider dopamine excess as an underlying cause in a patient with depression who exhibits these symptoms simultaneously? And why not call it “dopamine excess syndrome”? We already have “serotonin syndrome” for a patient experiencing a serotonin storm. However, using the same logic, it should be called “serotonin excess syndrome.” And if we know of “serotonin excess syndrome,” why not consider “serotonin deficiency syndrome”?

In Part 1 of this article, we discuss serotonin and dopamine. Table 1 outlines medical and psychiatric symptoms that likely reflect serotonin excess2-18 and deficiency,14,19-29 and Table 2 lists symptoms that likely reflect dopamine excess14,30-41 and deficiency.4,14,20,38,40-43 In Part 2 we will touch on endorphins and norepinephrine, and in Part 3 we will conclude by looking at GABA and glutamate.

Serotonin excess (Table 12-18)
On a recent office visit, Ms. H reports that most of the time she does not feel much of anything, but she still experiences panic attacks8,9,13,15 and is easily agitated.6,8 Her mother died recently, and Ms. H is concerned that she did not grieve.15-18 She failed her last semester in college and was indifferent to her failure.18 She sleeps poorly,8 is failing her creative classes, and wonders why she has lost her artistic inclination.16-18 Ms. H has difficulty with amotivation, planning, social interactions, and speech.16,17 All of those symptoms worsened after she was prescribed fluoxetine approximately 1 year ago for her “blues.” Ms. H is obese and continues to gain weight,2 though she frequently has diarrhea,3,4,7,8 loud peristalsis, and abdominal cramps.4,7,8 She sweats easily6-8 and her heart frequently races.8,9 Additionally, Ms. H’s primary care physician told her that she has “borderline diabetes.”2 She is prone to frequent bruising11 and is easy to shake, even when she is experiencing minimal anxiety.6-9 Ms. H had consulted with a neurologist because of unusual electrical “zapping” in her brain and muscle twitches.5,8,9,13 She had experienced a seizure as a child, but this was possibly related to hypernatremia,2 and she has not taken any anticonvulsant medication for several years.8 She exhibits hyperactive deep tendon reflexes and tremors5,7,9 and blinks frequently.6,9 She experiences hot flashes,3,6-8,14 does not tolerate heat, and prefers cooler weather.8,9 Her pains and aches,12,14 to which she has been prone all of her life, have recently become much worse, and she was diagnosed with fibromyalgia in part because she frequently feels stiff all over.10 She complains of strange tingling and prickling sensations in her hands and feet, especially when anxious.7,9,10 Her headaches also worsened and may be precipitated by bright light, as her pupils are usually dilated.5,7,9 Her hypertension is fairly controlled with medication.6,8-10 Ms. H says she experienced a psychotic episode when she was in her mid-teens,6,8 but reassures you that “she is not that bad now,” although she remains hypervigilant.13 Also while in her teens, Ms. H was treated with paroxetine and experienced restlessness, agitation, delirium, tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, diaphoresis, diarrhea, and neuromuscular excitation, which prompted discontinuation of the antidepressant.5-7,9,10
Impression. Ms. H exhibits symptoms associated with serotonin hyperactivity. Discontinuing and avoiding selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) would be prudent; prescribing an anticonvulsant would be reasonable. Using a GABAergic medication to suppress serotonin (eg, baclofen) is likely to help. Avoiding dopaminergic medications is a must. Antidepressive antipsychotics would be logical to use. The use of serotonin-suppressing medications may be considered. One may argue for the use of beta-blockers in such a patient.
Continue to: Serotonin deficiency
Serotonin deficiency (Table 114,19-29)
Mr. A is chronically depressed, hopeless,19 and easily angered.21 He does not believe anyone can help him.19 You are concerned for his safety because he had attempted to end his life by shooting himself in the chest.19,21,22,25 Even when he’s not particularly depressed, Mr. A does not enjoy much of anything.21,26,27 He becomes particularly agitated when he drinks alcohol,25 which unfortunately is common for him.29 He engages in binge eating to feel better; he knows this is not healthy but he cannot control his behavior.20,29 Mr. A is poorly compliant with his medications, even with a blood thinner, which he was prescribed due to an episode of deep vein thrombosis. He complains of chronic daily headaches and episodic migraines.23,24 He rarely blinks,23,28 his skin is dry and cool, his hair is brittle,23 his mouth is dry,14,23,27 and he constantly licks his chapped lips.14,26,27 Mr. A frequently has general body pain26,31 but is dismissive of his body aches and completely stops reporting pain when his depression gets particularly severe. When depressed, he is slow in movement and thinking.14,21,26,27 He is more concerned with anxiety than depression.21 Mr. A is plagued by constipation, abdominal pain, muscle tension, and episodes of shaking.14,26,27 He also frequently complains about chronic tinnitus.28
Impression. Mr. A shows symptoms associated with serotonin hypoactivity. SSRIs and any other antidepressants with serotonin activity would be an obvious choice for treatment. A mood-stabilizing antipsychotic with serotonin activity would be welcome in treatment. Thyroid hormone supplementation may be of value, especially if thyroid stimulating hormone level is high. Light therapy, a diet with food that contains tryptophan, psychotherapy, and exercise are desirable. Avoiding benzodiazepines would be a good idea.
Dopamine excess (Table 214,30-41)
Ms. L presents with complaints of “fibromyalgia” and “daily headaches,”14 and also dissociation (finding herself in places when she does not know how she got there) and “out-of-body experiences.”32 She is odd, and states that people do not understand her and that she is “different.”38 Her friend, who is present at the appointment, elaborates on Ms. L’s bizarreness and oddness in behavior, out-of-context emotions, suspiciousness, paranoia, and possible hallucinations.35,36,38 Ms. L discloses frequent diffuse body pains, headaches, nausea, excessive salivation, and tongue burning, as well as muscle twitching.14 Sex worsens her headaches and body pain. She reports seizures that are not registered on EEG. In the office, she is suspicious, exhibits odd posturing, tends to misinterpret your words, and makes you feel uncomfortable. Anxiety38 and multiple obsessive-compulsive symptoms, especially excessive cleaning and grooming, complicate Ms. L’s life.31,32,34 On examination, she is hypertensive, and she has scars caused by self-cutting and skin picking on her arms.30-32 An electrocardiogram shows an elevated heart rate, widened QRS complex, and ectopic heartbeats.14 Ms. L has experienced trichotillomania since adolescence32-34 and her fingernails are bitten to the skin.34 She has difficulty with impulse control, and thrill-seeking is a prominent part of her life, mainly via gambling, compulsive sex, and compulsive buying.35,36 She also says she experiences indigestion and delayed gastric emptying.37
Impression. Ms. L exhibits multiple symptoms associated with dopamine excess. Dopamine antagonists should be considered and may help not only with her psychiatric symptoms but also with her pain symptoms. Bupropion (as a dopamine agonist), caffeine, and stimulants should be avoided.
Excessive dopamine is, in extreme cases, associated with somatic psychosis, somatic symptom disorder, factitious disorder, pain disorder, and hypochondria.39 It may come with odd and bizarre/peculiar symptoms out of proportion with objectively identified pathology. These symptoms are common in chronic pain and headache patients, and need to be addressed by appropriate use of dopamine antagonizing medications.39
Continue to: Dopamine deficiency
Dopamine deficiency (Table 24,14,20,38,40-43)
Mr. W experiences widespread pain, including chronic back pain, headaches, and abdominal pain. He also has substantial anhedonia, lack of interest, procrastination, and hypersomnia.41,42 He is apathetic and has difficulty getting up in the morning.41,42 Unusual tiredness and weakness drive him to overuse caffeine; he states that 5 Mountain Dews and 4 cups of regular coffee a day make his headaches bearable.38,41-43 Sex also improves his headaches. Since childhood, he has taken stimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. He reports that occasional use of cocaine helps ease his pain and depression. Mr. W’s wife is concerned with her husband’s low sexual drive and alcohol consumption, and discloses that he has periodic trouble with gambling. Mr. W was forced into psychotherapy but never was able to work productively with his therapist.38,41-43 He loves eating and cannot control his weight.40 This contrasts with episodic anorexia he experienced when he was younger.20 His face is usually emotionless.43 Mr. W is prone to constipation.14 His restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder are so bad that his wife refuses to share a bed with him.14 He is clumsy and has a problem with repetitive motor tasks.43 A paucity of speech, limited eye contact, poor grooming, and difficulty forming therapeutic alliances have long been part of Mr. W’s history.38,42,43 On physical examination, he has a dry mouth; he is stiff, tremulous, and hypotensive.14
Impression. Mr. W shows multiple symptoms associated with dopamine deficiency. Bupropion may be reasonable to consider. Dopamine augmentation via the use of stimulants is warranted in such patients, especially if stimulants had not been tried before (lisdexamfetamine would be a good choice to minimize addictive potential). For a patient with dopamine deficiency, levodopa may improve more than just restless legs. Amantadine may improve dopaminergic signaling through the accelerated dopamine release and decrease in presynaptic uptake, so this medication may be carefully tried.44 Pain treatment would not be successful for Mr. W without simultaneous treatment for his substance use.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of serotonin and dopamine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Abell SR, El-Mallakh RS. Serotonin-mediated anxiety: How to recognize and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):37-40. doi:10.12788/cp.0168
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Baclofen • Ozobax
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisdexamfetamine • Vyvanse
Paroxetine • Paxil
It is unfortunate that, in some clinical areas, medical conditions are still treated by name and not based on the underlying pathological process. It would be odd in 2022 to treat “dropsy” instead of heart or kidney disease (2 very different causes of edema). Similarly, if the FDA had been approving drugs 150 years ago, we would have medications on label for “dementia praecox,” not schizophrenia or Alzheimer disease. With the help of DSM-5, psychiatry still resides in the descriptive symptomatic world of disorders.
In the United States, thanks to Freud, psychiatric symptoms became separated from medical symptoms, which made it more difficult to associate psychiatric manifestations with the underlying pathophysiology. Though the physical manifestations that parallel emotional symptoms—such as the dry mouth of anxiety, the tremor and leg weakness of fear, the constipation and blurry vision of depression, the breathing difficulty of anger, the abdominal pain of stress, the blushing of shyness, the palpitations of flashbacks, and endless others—are well known, the present classification of psychiatric disorders is blind to it. Neurochemical causes of gastrointestinal spasm or muscle tension are better researched than underlying central neurochemistry, though the same neurotransmitters drive them.
Can the biochemistry of psychiatric symptoms be judged on the basis of peripheral symptoms? Can the mental manifestations be connected to biological causation, and vice versa? Would psychiatrists be better off selecting treatments by recognizing involved neurotransmitters instead of addressing descriptive “depression, anxiety, and psychosis”? Each of these clinical syndromes may be caused by entirely different underlying neuronal mechanisms. Such mechanisms could be suggested if medical symptoms (which are measurable and objective) would become part of the psychiatric diagnosis. Is treating the “cough” sufficient, or would recognition that tuberculosis caused the cough guide better treatment? Is it time to abandon descriptive conditions and replace them with a specific “mechanism-based” viewpoint?
Ample research has shown that serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, endorphins, glutamate, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) are the neurotransmitters most responsible in the process of both psychiatric disorders and chronic pain. These neurotransmitters are involved in much more than emotions (including the feeling of pain). An abundance of medical symptom clusters point toward which neurotransmitter dysfunction may be leading in specific cases of distinct types of depression, psychosis, anxiety, or “chronic pain.” Even presently, there are medications available (both for FDA-approved indications and off-label) that can be used to regulate these neurotransmitters, allowing practitioners to target the possible biological underlining of psychiatric or pain pathology. Hopefully, in the not-so-distant future, there will be specific medications for serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenergic depression as well as for GABAergic anxiety, endorphin psychosis, noradrenergic insomnia, and similar conditions.
Numerous neurotransmitters may be connected to both depression and pain in all their forms. These include (but are not limited to) prostaglandins, bradykinins, substance P, potassium, magnesium, calcium, histamine, adenosine triphosphate, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), nitric oxide (NO), cholecystokinin 7 (CCK7), neurotrophic growth factor (NGF), neurotensin, acetylcholine (Ach), oxytocin, cannabinoids, and others. These have not been researched sufficiently to identify their clinical presentation of excessive or insufficient availability at the sites of neurotransmission. It is difficult to draw conclusions about what kind of clinical symptoms they may cause (outside of pain), and therefore, they are not addressed in this article.
Both high and low levels of certain neurotransmitters may be associated with psychiatric conditions and chronic pain. Too much is as bad as too little.1 This applies to both quantity of neurotransmitters as well as quality of the corresponding receptor activity. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation. Reading indirect signs of bodily functions is a basic clinical skill that should not be forgotten, even in the time of advanced technology.
A different way of viewing psychiatric disorders
In this article, we present 4 hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. In no way do these descriptions reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known or suspected, and extensive research is required to confirm or disprove what we describe here.
Continue to: There are no well-recognized...
There are no well-recognized, well-established, reliable, or validated syndromes described in our work. Our goal is to suggest an alternative way of looking at psychiatric disorders by viewing syndromal presentation through the lens of specific neurotransmitters. The collection of symptoms associated with various neurotransmitters as presented in this hypothesis is not complete. We have assembled what is described in the literature as a suggestion for specific future research. We simplified these clinical presentations by omitting scenarios in which a specific neurotransmitter increases in one area but not another. For example, all the symptoms of dopamine excess we describe would not have to occur concurrently in the same patient, but they may develop in certain patients depending on which dopaminergic pathway is exhibiting excess activity. Such distinctions may be established only by exhaustive research not yet conducted.
Our proposal may seem radical, but it truly is not. For example, if we know that dopamine excess may cause seizures, psychosis, and blood pressure elevation, why not consider dopamine excess as an underlying cause in a patient with depression who exhibits these symptoms simultaneously? And why not call it “dopamine excess syndrome”? We already have “serotonin syndrome” for a patient experiencing a serotonin storm. However, using the same logic, it should be called “serotonin excess syndrome.” And if we know of “serotonin excess syndrome,” why not consider “serotonin deficiency syndrome”?

In Part 1 of this article, we discuss serotonin and dopamine. Table 1 outlines medical and psychiatric symptoms that likely reflect serotonin excess2-18 and deficiency,14,19-29 and Table 2 lists symptoms that likely reflect dopamine excess14,30-41 and deficiency.4,14,20,38,40-43 In Part 2 we will touch on endorphins and norepinephrine, and in Part 3 we will conclude by looking at GABA and glutamate.

Serotonin excess (Table 12-18)
On a recent office visit, Ms. H reports that most of the time she does not feel much of anything, but she still experiences panic attacks8,9,13,15 and is easily agitated.6,8 Her mother died recently, and Ms. H is concerned that she did not grieve.15-18 She failed her last semester in college and was indifferent to her failure.18 She sleeps poorly,8 is failing her creative classes, and wonders why she has lost her artistic inclination.16-18 Ms. H has difficulty with amotivation, planning, social interactions, and speech.16,17 All of those symptoms worsened after she was prescribed fluoxetine approximately 1 year ago for her “blues.” Ms. H is obese and continues to gain weight,2 though she frequently has diarrhea,3,4,7,8 loud peristalsis, and abdominal cramps.4,7,8 She sweats easily6-8 and her heart frequently races.8,9 Additionally, Ms. H’s primary care physician told her that she has “borderline diabetes.”2 She is prone to frequent bruising11 and is easy to shake, even when she is experiencing minimal anxiety.6-9 Ms. H had consulted with a neurologist because of unusual electrical “zapping” in her brain and muscle twitches.5,8,9,13 She had experienced a seizure as a child, but this was possibly related to hypernatremia,2 and she has not taken any anticonvulsant medication for several years.8 She exhibits hyperactive deep tendon reflexes and tremors5,7,9 and blinks frequently.6,9 She experiences hot flashes,3,6-8,14 does not tolerate heat, and prefers cooler weather.8,9 Her pains and aches,12,14 to which she has been prone all of her life, have recently become much worse, and she was diagnosed with fibromyalgia in part because she frequently feels stiff all over.10 She complains of strange tingling and prickling sensations in her hands and feet, especially when anxious.7,9,10 Her headaches also worsened and may be precipitated by bright light, as her pupils are usually dilated.5,7,9 Her hypertension is fairly controlled with medication.6,8-10 Ms. H says she experienced a psychotic episode when she was in her mid-teens,6,8 but reassures you that “she is not that bad now,” although she remains hypervigilant.13 Also while in her teens, Ms. H was treated with paroxetine and experienced restlessness, agitation, delirium, tachycardia, fluctuating blood pressure, diaphoresis, diarrhea, and neuromuscular excitation, which prompted discontinuation of the antidepressant.5-7,9,10
Impression. Ms. H exhibits symptoms associated with serotonin hyperactivity. Discontinuing and avoiding selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) would be prudent; prescribing an anticonvulsant would be reasonable. Using a GABAergic medication to suppress serotonin (eg, baclofen) is likely to help. Avoiding dopaminergic medications is a must. Antidepressive antipsychotics would be logical to use. The use of serotonin-suppressing medications may be considered. One may argue for the use of beta-blockers in such a patient.
Continue to: Serotonin deficiency
Serotonin deficiency (Table 114,19-29)
Mr. A is chronically depressed, hopeless,19 and easily angered.21 He does not believe anyone can help him.19 You are concerned for his safety because he had attempted to end his life by shooting himself in the chest.19,21,22,25 Even when he’s not particularly depressed, Mr. A does not enjoy much of anything.21,26,27 He becomes particularly agitated when he drinks alcohol,25 which unfortunately is common for him.29 He engages in binge eating to feel better; he knows this is not healthy but he cannot control his behavior.20,29 Mr. A is poorly compliant with his medications, even with a blood thinner, which he was prescribed due to an episode of deep vein thrombosis. He complains of chronic daily headaches and episodic migraines.23,24 He rarely blinks,23,28 his skin is dry and cool, his hair is brittle,23 his mouth is dry,14,23,27 and he constantly licks his chapped lips.14,26,27 Mr. A frequently has general body pain26,31 but is dismissive of his body aches and completely stops reporting pain when his depression gets particularly severe. When depressed, he is slow in movement and thinking.14,21,26,27 He is more concerned with anxiety than depression.21 Mr. A is plagued by constipation, abdominal pain, muscle tension, and episodes of shaking.14,26,27 He also frequently complains about chronic tinnitus.28
Impression. Mr. A shows symptoms associated with serotonin hypoactivity. SSRIs and any other antidepressants with serotonin activity would be an obvious choice for treatment. A mood-stabilizing antipsychotic with serotonin activity would be welcome in treatment. Thyroid hormone supplementation may be of value, especially if thyroid stimulating hormone level is high. Light therapy, a diet with food that contains tryptophan, psychotherapy, and exercise are desirable. Avoiding benzodiazepines would be a good idea.
Dopamine excess (Table 214,30-41)
Ms. L presents with complaints of “fibromyalgia” and “daily headaches,”14 and also dissociation (finding herself in places when she does not know how she got there) and “out-of-body experiences.”32 She is odd, and states that people do not understand her and that she is “different.”38 Her friend, who is present at the appointment, elaborates on Ms. L’s bizarreness and oddness in behavior, out-of-context emotions, suspiciousness, paranoia, and possible hallucinations.35,36,38 Ms. L discloses frequent diffuse body pains, headaches, nausea, excessive salivation, and tongue burning, as well as muscle twitching.14 Sex worsens her headaches and body pain. She reports seizures that are not registered on EEG. In the office, she is suspicious, exhibits odd posturing, tends to misinterpret your words, and makes you feel uncomfortable. Anxiety38 and multiple obsessive-compulsive symptoms, especially excessive cleaning and grooming, complicate Ms. L’s life.31,32,34 On examination, she is hypertensive, and she has scars caused by self-cutting and skin picking on her arms.30-32 An electrocardiogram shows an elevated heart rate, widened QRS complex, and ectopic heartbeats.14 Ms. L has experienced trichotillomania since adolescence32-34 and her fingernails are bitten to the skin.34 She has difficulty with impulse control, and thrill-seeking is a prominent part of her life, mainly via gambling, compulsive sex, and compulsive buying.35,36 She also says she experiences indigestion and delayed gastric emptying.37
Impression. Ms. L exhibits multiple symptoms associated with dopamine excess. Dopamine antagonists should be considered and may help not only with her psychiatric symptoms but also with her pain symptoms. Bupropion (as a dopamine agonist), caffeine, and stimulants should be avoided.
Excessive dopamine is, in extreme cases, associated with somatic psychosis, somatic symptom disorder, factitious disorder, pain disorder, and hypochondria.39 It may come with odd and bizarre/peculiar symptoms out of proportion with objectively identified pathology. These symptoms are common in chronic pain and headache patients, and need to be addressed by appropriate use of dopamine antagonizing medications.39
Continue to: Dopamine deficiency
Dopamine deficiency (Table 24,14,20,38,40-43)
Mr. W experiences widespread pain, including chronic back pain, headaches, and abdominal pain. He also has substantial anhedonia, lack of interest, procrastination, and hypersomnia.41,42 He is apathetic and has difficulty getting up in the morning.41,42 Unusual tiredness and weakness drive him to overuse caffeine; he states that 5 Mountain Dews and 4 cups of regular coffee a day make his headaches bearable.38,41-43 Sex also improves his headaches. Since childhood, he has taken stimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. He reports that occasional use of cocaine helps ease his pain and depression. Mr. W’s wife is concerned with her husband’s low sexual drive and alcohol consumption, and discloses that he has periodic trouble with gambling. Mr. W was forced into psychotherapy but never was able to work productively with his therapist.38,41-43 He loves eating and cannot control his weight.40 This contrasts with episodic anorexia he experienced when he was younger.20 His face is usually emotionless.43 Mr. W is prone to constipation.14 His restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder are so bad that his wife refuses to share a bed with him.14 He is clumsy and has a problem with repetitive motor tasks.43 A paucity of speech, limited eye contact, poor grooming, and difficulty forming therapeutic alliances have long been part of Mr. W’s history.38,42,43 On physical examination, he has a dry mouth; he is stiff, tremulous, and hypotensive.14
Impression. Mr. W shows multiple symptoms associated with dopamine deficiency. Bupropion may be reasonable to consider. Dopamine augmentation via the use of stimulants is warranted in such patients, especially if stimulants had not been tried before (lisdexamfetamine would be a good choice to minimize addictive potential). For a patient with dopamine deficiency, levodopa may improve more than just restless legs. Amantadine may improve dopaminergic signaling through the accelerated dopamine release and decrease in presynaptic uptake, so this medication may be carefully tried.44 Pain treatment would not be successful for Mr. W without simultaneous treatment for his substance use.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of serotonin and dopamine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Abell SR, El-Mallakh RS. Serotonin-mediated anxiety: How to recognize and treat it. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(11):37-40. doi:10.12788/cp.0168
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Baclofen • Ozobax
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Lisdexamfetamine • Vyvanse
Paroxetine • Paxil
1. Stahl SM. Dazzled by the dominions of dopamine: clinical roles of D3, D2, and D1 receptors. CNS Spectr. 2017;22(4):305-311.
2. Young RL, Lumsden AL, Martin AM, et al. Augmented capacity for peripheral serotonin release in human obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(11):1880-1889.
3. Ahlman H. Serotonin and carcinoid tumors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7(Suppl 7):S79-S85.
4. Terry N, Margolis KG. Serotonergic mechanisms regulating the GI tract: experimental evidence and therapeutic relevance. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;239:319-342.
5. Prakash S, Belani P, Trivedi A. Headache as a presenting feature in patients with serotonin syndrome: a case series. Cephalalgia. 2014;34(2):148-153.
6. van Ewijk CE, Jacobs GE, Girbes ARJ. Unsuspected serotonin toxicity in the ICU. Ann Intensive Care. 2016;6(1):85.
7. Pedavally S, Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA. Serotonin syndrome in the intensive care unit: clinical presentations and precipitating medications. Neurocrit Care. 2014;21(1):108-113.
8. Nguyen H, Pan A, Smollin C, et al. An 11-year retrospective review of cyproheptadine use in serotonin syndrome cases reported to the California Poison Control System. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2019;44(2):327-334.
9. Ansari H, Kouti L. Drug interaction and serotonin toxicity with opioid use: another reason to avoid opioids in headache and migraine treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(8):50.
10. Ott M, Mannchen JK, Jamshidi F, et al. Management of severe arterial hypertension associated with serotonin syndrome: a case report analysis based on systematic review techniques. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019;9:2045125318818814. doi:10.1177/2045125318818814
11. Cerrito F, Lazzaro MP, Gaudio E, et al. 5HT2-receptors and serotonin release: their role in human platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 1993;53(3):209-215.
12. Ohayon MM. Pain sensitivity, depression, and sleep deprivation: links with serotoninergic dysfunction. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43(16):1243-1245.
13. Maron E, Shlik J. Serotonin function in panic disorder: important, but why? Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(1):1-11.
14. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:120,199,201-204,730-740.
15. Garland EJ, Baerg EA. Amotivational syndrome associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001;11(2):181-186.
16. George MS, Trimble MR. A fluvoxamine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in a patient with comorbid Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome and obsessive compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 1992;53(10):379-380.
17. Hoehn-Saric R, Harris GJ, Pearlson GD, et al. A fluoxetine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in an obsessive compulsive patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 1991;52(3):131-133.
18. Hoehn-Saric R, Lipsey JR, McLeod DR. Apathy and indifference in patients on fluvoxamine and fluoxetine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10(5):343-345.
19. Samuelsson M, Jokinen J, Nordström AL, et al. CSF 5-HIAA, suicide intent and hopelessness in the prediction of early suicide in male high-risk suicide attempters. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006;113(1):44-47.
20. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
21. Mann JJ, Oquendo M, Underwood MD, et al. The neurobiology of suicide risk: a review for the clinician. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 2:7-116.
22. Mann JJ, Malone KM. Cerebrospinal fluid amines and higher-lethality suicide attempts in depressed inpatients. Biol Psychiatry. 1997;41(2):162-171.
23. Joseph R, Welch KM, D’Andrea G. Serotonergic hypofunction in migraine: a synthesis of evidence based on platelet dense body dysfunction. Cephalalgia. 1989;9(4):293-299.
24. Pakalnis A, Splaingard M, Splaingard D, et al. Serotonin effects on sleep and emotional disorders in adolescent migraine. Headache. 2009;49(10):1486-1492.
25. Virkkunen M, Goldman D, Nielsen DA, et al. Low brain serotonin turnover rate (low CSF 5-HIAA) and impulsive violence. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1995;20(4):271-275.
26. Liu Y, Zhao J, Fan X, et al. Dysfunction in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems and somatic symptoms in psychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:286.
27. Ginsburg GS, Riddle MA, Davies M. Somatic symptoms in children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006;45(10):1179-1187.
28. O’Malley PG, Jackson JL, Santoro J, et al. Antidepressant therapy for unexplained symptoms and symptom syndromes. J Fam Pract. 1999;48(12):980-990.
29. Fortuna JL. Sweet preference, sugar addiction and the familial history of alcohol dependence: shared neural pathways and genes. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2010;42(2):147-151.
30. Stanley B, Sher L, Wilson S, et al. Non-suicidal self-injurious behavior, endogenous opioids and monoamine neurotransmitters. J Affect Disord. 2010;124(1-2):134-140.
31. Graybiel AM, Saka E. A genetic basis for obsessive grooming. Neuron. 2002;33(1):1-2.
32. Tse W, Hälbig TD. Skin picking in Parkinson’s disease: a behavioral side-effect of dopaminergic treatment? Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64(2):214.
33. Ayaydın H. Probable emergence of symptoms of trichotillomania by atomoxetine: a case report. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2019;29(2)220-222.
34. Paholpak P, Mendez MF. Trichotillomania as a manifestation of dementia. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2016;2016:9782702. doi:10.1155/2016/9782702
35. Clark CA, Dagher A. The role of dopamine in risk taking: a specific look at Parkinson’s disease and gambling. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:196.
36. Norbury A, Husain M. Sensation-seeking: dopaminergic modulation and risk for psychopathology. Behav Brain Res. 2015;288:79-93.
37. Chen TS, Chang FY. Elevated serum dopamine increases while coffee consumption decreases the occurrence of reddish streaks in the intact stomach. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(12):1810-1814.
38. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st edition. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:420-429.
39. Arbuck DM. Antipsychotics, dopamine, and pain. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(1):25-29,31.
40. Bello NT, Hajnal A. Dopamine and binge eating behaviors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010;97(1):25-33.
41. Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, Sajatovic M, et al; Expert Consensus Panel on Adherence Problems in Serious and Persistent Mental Illness. The expert consensus guideline series: adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70 Suppl 4:1-46.
42. Milev P, Ho BC, Arndt S, et al. Predictive values of neurocognition and negative symptoms on functional outcome in schizophrenia: a longitudinal first-episode study with 7-year follow-up. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(3):495-506.
43. Gepshtein S, Li X, Snider J, et al. Dopamine function and the efficiency of human movement. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(3):645-657.
44. Scarff JR. The ABCDs of treating tardive dyskinesia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):21,55.
1. Stahl SM. Dazzled by the dominions of dopamine: clinical roles of D3, D2, and D1 receptors. CNS Spectr. 2017;22(4):305-311.
2. Young RL, Lumsden AL, Martin AM, et al. Augmented capacity for peripheral serotonin release in human obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(11):1880-1889.
3. Ahlman H. Serotonin and carcinoid tumors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7(Suppl 7):S79-S85.
4. Terry N, Margolis KG. Serotonergic mechanisms regulating the GI tract: experimental evidence and therapeutic relevance. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;239:319-342.
5. Prakash S, Belani P, Trivedi A. Headache as a presenting feature in patients with serotonin syndrome: a case series. Cephalalgia. 2014;34(2):148-153.
6. van Ewijk CE, Jacobs GE, Girbes ARJ. Unsuspected serotonin toxicity in the ICU. Ann Intensive Care. 2016;6(1):85.
7. Pedavally S, Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA. Serotonin syndrome in the intensive care unit: clinical presentations and precipitating medications. Neurocrit Care. 2014;21(1):108-113.
8. Nguyen H, Pan A, Smollin C, et al. An 11-year retrospective review of cyproheptadine use in serotonin syndrome cases reported to the California Poison Control System. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2019;44(2):327-334.
9. Ansari H, Kouti L. Drug interaction and serotonin toxicity with opioid use: another reason to avoid opioids in headache and migraine treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016;20(8):50.
10. Ott M, Mannchen JK, Jamshidi F, et al. Management of severe arterial hypertension associated with serotonin syndrome: a case report analysis based on systematic review techniques. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019;9:2045125318818814. doi:10.1177/2045125318818814
11. Cerrito F, Lazzaro MP, Gaudio E, et al. 5HT2-receptors and serotonin release: their role in human platelet aggregation. Life Sci. 1993;53(3):209-215.
12. Ohayon MM. Pain sensitivity, depression, and sleep deprivation: links with serotoninergic dysfunction. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43(16):1243-1245.
13. Maron E, Shlik J. Serotonin function in panic disorder: important, but why? Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(1):1-11.
14. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:120,199,201-204,730-740.
15. Garland EJ, Baerg EA. Amotivational syndrome associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in children and adolescents. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2001;11(2):181-186.
16. George MS, Trimble MR. A fluvoxamine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in a patient with comorbid Gilles de la Tourette’s syndrome and obsessive compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 1992;53(10):379-380.
17. Hoehn-Saric R, Harris GJ, Pearlson GD, et al. A fluoxetine-induced frontal lobe syndrome in an obsessive compulsive patient. J Clin Psychiatry. 1991;52(3):131-133.
18. Hoehn-Saric R, Lipsey JR, McLeod DR. Apathy and indifference in patients on fluvoxamine and fluoxetine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10(5):343-345.
19. Samuelsson M, Jokinen J, Nordström AL, et al. CSF 5-HIAA, suicide intent and hopelessness in the prediction of early suicide in male high-risk suicide attempters. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006;113(1):44-47.
20. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
21. Mann JJ, Oquendo M, Underwood MD, et al. The neurobiology of suicide risk: a review for the clinician. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60 Suppl 2:7-116.
22. Mann JJ, Malone KM. Cerebrospinal fluid amines and higher-lethality suicide attempts in depressed inpatients. Biol Psychiatry. 1997;41(2):162-171.
23. Joseph R, Welch KM, D’Andrea G. Serotonergic hypofunction in migraine: a synthesis of evidence based on platelet dense body dysfunction. Cephalalgia. 1989;9(4):293-299.
24. Pakalnis A, Splaingard M, Splaingard D, et al. Serotonin effects on sleep and emotional disorders in adolescent migraine. Headache. 2009;49(10):1486-1492.
25. Virkkunen M, Goldman D, Nielsen DA, et al. Low brain serotonin turnover rate (low CSF 5-HIAA) and impulsive violence. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1995;20(4):271-275.
26. Liu Y, Zhao J, Fan X, et al. Dysfunction in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems and somatic symptoms in psychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:286.
27. Ginsburg GS, Riddle MA, Davies M. Somatic symptoms in children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006;45(10):1179-1187.
28. O’Malley PG, Jackson JL, Santoro J, et al. Antidepressant therapy for unexplained symptoms and symptom syndromes. J Fam Pract. 1999;48(12):980-990.
29. Fortuna JL. Sweet preference, sugar addiction and the familial history of alcohol dependence: shared neural pathways and genes. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2010;42(2):147-151.
30. Stanley B, Sher L, Wilson S, et al. Non-suicidal self-injurious behavior, endogenous opioids and monoamine neurotransmitters. J Affect Disord. 2010;124(1-2):134-140.
31. Graybiel AM, Saka E. A genetic basis for obsessive grooming. Neuron. 2002;33(1):1-2.
32. Tse W, Hälbig TD. Skin picking in Parkinson’s disease: a behavioral side-effect of dopaminergic treatment? Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64(2):214.
33. Ayaydın H. Probable emergence of symptoms of trichotillomania by atomoxetine: a case report. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2019;29(2)220-222.
34. Paholpak P, Mendez MF. Trichotillomania as a manifestation of dementia. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2016;2016:9782702. doi:10.1155/2016/9782702
35. Clark CA, Dagher A. The role of dopamine in risk taking: a specific look at Parkinson’s disease and gambling. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:196.
36. Norbury A, Husain M. Sensation-seeking: dopaminergic modulation and risk for psychopathology. Behav Brain Res. 2015;288:79-93.
37. Chen TS, Chang FY. Elevated serum dopamine increases while coffee consumption decreases the occurrence of reddish streaks in the intact stomach. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(12):1810-1814.
38. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st edition. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:420-429.
39. Arbuck DM. Antipsychotics, dopamine, and pain. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(1):25-29,31.
40. Bello NT, Hajnal A. Dopamine and binge eating behaviors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010;97(1):25-33.
41. Velligan DI, Weiden PJ, Sajatovic M, et al; Expert Consensus Panel on Adherence Problems in Serious and Persistent Mental Illness. The expert consensus guideline series: adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70 Suppl 4:1-46.
42. Milev P, Ho BC, Arndt S, et al. Predictive values of neurocognition and negative symptoms on functional outcome in schizophrenia: a longitudinal first-episode study with 7-year follow-up. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(3):495-506.
43. Gepshtein S, Li X, Snider J, et al. Dopamine function and the efficiency of human movement. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(3):645-657.
44. Scarff JR. The ABCDs of treating tardive dyskinesia. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):21,55.
30 years of fake nursing ends with 7-year prison sentence
A Canadian woman who officials allege faked being a registered nurse for some 30 years in Canada and the United States is scheduled to appear in court next month after being sentenced to 7 years in prison.
She was previously sentenced April 22 in an Ontario court after she pled guilty in January to seven offenses, including impersonation, assault with a weapon, and assault, according to CBC Radio-Canada.
Ms. Cleroux, who uses several aliases, had a long history of deception in three provinces in Canada, as well as in Colorado and Florida. The sentencing in Ontario stemmed from incidents at a medical and dental clinic in Ottawa last year, which included administration of medications to patients through needle injections, Ottawa Police reported in a press statement obtained by this news organization.
Authorities charged Ms. Cleroux in September with assault with a weapon and criminal negligence causing bodily harm, along with “personation to gain advantage,” obtaining by false pretense, and using a forged document, this news organization reported.
Ms. Cleroux has been in custody since her arrest by Ottawa Police in August.
The Vancouver Police Department (VPD) charged Ms. Cleroux last year with fraud of over $5,000 and personation with intent. VPD investigated claims that an employee at BC Women’s Hospital fraudulently identified herself as a nurse while working there between June 2020 and June 2021, according to a VPD press release.
Nursing colleges in British Columbia and Ontario issued warnings that she had used aliases and purported to be a registered nurse to gain employment. The aliases included Melanie Thompson, Melanie Smith, and Melanie Cleroux.
Ms. Cleroux was believed to be a student in a nursing school in Colorado, but she only completed 2 years of a 4-year nursing course and was never certified as a nurse, according to CBC. Her criminal record dates back 30 years and includes 67 adult convictions and other convictions in her youth, CBC reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Canadian woman who officials allege faked being a registered nurse for some 30 years in Canada and the United States is scheduled to appear in court next month after being sentenced to 7 years in prison.
She was previously sentenced April 22 in an Ontario court after she pled guilty in January to seven offenses, including impersonation, assault with a weapon, and assault, according to CBC Radio-Canada.
Ms. Cleroux, who uses several aliases, had a long history of deception in three provinces in Canada, as well as in Colorado and Florida. The sentencing in Ontario stemmed from incidents at a medical and dental clinic in Ottawa last year, which included administration of medications to patients through needle injections, Ottawa Police reported in a press statement obtained by this news organization.
Authorities charged Ms. Cleroux in September with assault with a weapon and criminal negligence causing bodily harm, along with “personation to gain advantage,” obtaining by false pretense, and using a forged document, this news organization reported.
Ms. Cleroux has been in custody since her arrest by Ottawa Police in August.
The Vancouver Police Department (VPD) charged Ms. Cleroux last year with fraud of over $5,000 and personation with intent. VPD investigated claims that an employee at BC Women’s Hospital fraudulently identified herself as a nurse while working there between June 2020 and June 2021, according to a VPD press release.
Nursing colleges in British Columbia and Ontario issued warnings that she had used aliases and purported to be a registered nurse to gain employment. The aliases included Melanie Thompson, Melanie Smith, and Melanie Cleroux.
Ms. Cleroux was believed to be a student in a nursing school in Colorado, but she only completed 2 years of a 4-year nursing course and was never certified as a nurse, according to CBC. Her criminal record dates back 30 years and includes 67 adult convictions and other convictions in her youth, CBC reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Canadian woman who officials allege faked being a registered nurse for some 30 years in Canada and the United States is scheduled to appear in court next month after being sentenced to 7 years in prison.
She was previously sentenced April 22 in an Ontario court after she pled guilty in January to seven offenses, including impersonation, assault with a weapon, and assault, according to CBC Radio-Canada.
Ms. Cleroux, who uses several aliases, had a long history of deception in three provinces in Canada, as well as in Colorado and Florida. The sentencing in Ontario stemmed from incidents at a medical and dental clinic in Ottawa last year, which included administration of medications to patients through needle injections, Ottawa Police reported in a press statement obtained by this news organization.
Authorities charged Ms. Cleroux in September with assault with a weapon and criminal negligence causing bodily harm, along with “personation to gain advantage,” obtaining by false pretense, and using a forged document, this news organization reported.
Ms. Cleroux has been in custody since her arrest by Ottawa Police in August.
The Vancouver Police Department (VPD) charged Ms. Cleroux last year with fraud of over $5,000 and personation with intent. VPD investigated claims that an employee at BC Women’s Hospital fraudulently identified herself as a nurse while working there between June 2020 and June 2021, according to a VPD press release.
Nursing colleges in British Columbia and Ontario issued warnings that she had used aliases and purported to be a registered nurse to gain employment. The aliases included Melanie Thompson, Melanie Smith, and Melanie Cleroux.
Ms. Cleroux was believed to be a student in a nursing school in Colorado, but she only completed 2 years of a 4-year nursing course and was never certified as a nurse, according to CBC. Her criminal record dates back 30 years and includes 67 adult convictions and other convictions in her youth, CBC reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves oteseconazole for chronic yeast infections
The Food and Drug Administration has approved oteseconazole capsules (Vivjoa), an azole antifungal agent, for the prevention of recurrent yeast infections in women who are not of reproductive potential.
Oteseconazole inhibits CYP51, an enzyme fungi require to preserve the integrity of their cell walls and to grow properly, according to Mycovia, the drug’s manufacturer. It is the first FDA-approved product for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC).
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, or chronic yeast infection, affects an estimated 138 million women worldwide annually. The condition is defined as three or more symptomatic acute episodes of yeast infection within a 12-month period. The primary symptoms of RVVC include vaginal itching, burning, irritation, and inflammation. Some patients may also experience abnormal vaginal discharge and pain during sex or urination.
“A medicine with Vivjoa’s sustained efficacy combined with the clinical safety profile has been long needed, as until now, physicians and their patients have had no FDA-approved medications for RVVC,” Stephen Brand, PhD, chief development officer of Mycovia, said in a statement. “We are excited to be the first to offer a medication designed specifically for RVVC, a challenging and chronic condition that is expected to increase in prevalence over the next decade.”
Approval for oteseconazole was based on results of three phase 3 trials involving 875 patients at 232 sites across 11 countries. In the U.S.-only ultraVIOLET trial, 89.7% of women with RVVC who received oteseconazole cleared their initial yeast infection and did not experience a recurrence during the 50-week maintenance period, compared with 57.1% of those who received fluconazole (Diflucan) followed by placebo (P < .001), according to Mycovia.
The most common side effects reported in phase 3 clinical studies were headache (7.4%) and nausea (3.6%), the company said. Patients with a hypersensitivity to oteseconazole should not take the drug, nor should those who are of reproductive potential, pregnant, or lactating.
Mycovia said it plans to launch the drug in the second quarter of 2022.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved oteseconazole capsules (Vivjoa), an azole antifungal agent, for the prevention of recurrent yeast infections in women who are not of reproductive potential.
Oteseconazole inhibits CYP51, an enzyme fungi require to preserve the integrity of their cell walls and to grow properly, according to Mycovia, the drug’s manufacturer. It is the first FDA-approved product for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC).
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, or chronic yeast infection, affects an estimated 138 million women worldwide annually. The condition is defined as three or more symptomatic acute episodes of yeast infection within a 12-month period. The primary symptoms of RVVC include vaginal itching, burning, irritation, and inflammation. Some patients may also experience abnormal vaginal discharge and pain during sex or urination.
“A medicine with Vivjoa’s sustained efficacy combined with the clinical safety profile has been long needed, as until now, physicians and their patients have had no FDA-approved medications for RVVC,” Stephen Brand, PhD, chief development officer of Mycovia, said in a statement. “We are excited to be the first to offer a medication designed specifically for RVVC, a challenging and chronic condition that is expected to increase in prevalence over the next decade.”
Approval for oteseconazole was based on results of three phase 3 trials involving 875 patients at 232 sites across 11 countries. In the U.S.-only ultraVIOLET trial, 89.7% of women with RVVC who received oteseconazole cleared their initial yeast infection and did not experience a recurrence during the 50-week maintenance period, compared with 57.1% of those who received fluconazole (Diflucan) followed by placebo (P < .001), according to Mycovia.
The most common side effects reported in phase 3 clinical studies were headache (7.4%) and nausea (3.6%), the company said. Patients with a hypersensitivity to oteseconazole should not take the drug, nor should those who are of reproductive potential, pregnant, or lactating.
Mycovia said it plans to launch the drug in the second quarter of 2022.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved oteseconazole capsules (Vivjoa), an azole antifungal agent, for the prevention of recurrent yeast infections in women who are not of reproductive potential.
Oteseconazole inhibits CYP51, an enzyme fungi require to preserve the integrity of their cell walls and to grow properly, according to Mycovia, the drug’s manufacturer. It is the first FDA-approved product for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC).
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, or chronic yeast infection, affects an estimated 138 million women worldwide annually. The condition is defined as three or more symptomatic acute episodes of yeast infection within a 12-month period. The primary symptoms of RVVC include vaginal itching, burning, irritation, and inflammation. Some patients may also experience abnormal vaginal discharge and pain during sex or urination.
“A medicine with Vivjoa’s sustained efficacy combined with the clinical safety profile has been long needed, as until now, physicians and their patients have had no FDA-approved medications for RVVC,” Stephen Brand, PhD, chief development officer of Mycovia, said in a statement. “We are excited to be the first to offer a medication designed specifically for RVVC, a challenging and chronic condition that is expected to increase in prevalence over the next decade.”
Approval for oteseconazole was based on results of three phase 3 trials involving 875 patients at 232 sites across 11 countries. In the U.S.-only ultraVIOLET trial, 89.7% of women with RVVC who received oteseconazole cleared their initial yeast infection and did not experience a recurrence during the 50-week maintenance period, compared with 57.1% of those who received fluconazole (Diflucan) followed by placebo (P < .001), according to Mycovia.
The most common side effects reported in phase 3 clinical studies were headache (7.4%) and nausea (3.6%), the company said. Patients with a hypersensitivity to oteseconazole should not take the drug, nor should those who are of reproductive potential, pregnant, or lactating.
Mycovia said it plans to launch the drug in the second quarter of 2022.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.