User login
The COVID-19 pandemic and changes in pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses
The COVID-19 pandemic upended the U.S. health care market and disrupted much of what was thought to be consistent and necessary hospital-based care for children. Early in the pandemic, clinics closed, elective surgeries were delayed, and well visits were postponed. Mitigation strategies were launched nationwide to limit the spread of SARS-CoV-2 including mask mandates, social distancing, shelter-in-place orders, and school closures. While these measures were enacted to target COVID-19, a potential off-target effect was reductions in transmission of other respiratory illness, and potentially nonrespiratory infectious illnesses and conditions exacerbated by acute infections.1 These measures have heavily impacted the pediatric population, wherein respiratory infections are common, and also because daycares and school can be hubs for disease transmission.2
To evaluate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric health care utilization, we performed a multicenter, cross-sectional study of 44 children’s hospitals using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database.3 Children aged 2 months to 18 years discharged from a PHIS hospital with nonsurgical diagnoses from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included in the study. The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, which was divided into three study periods: pre–COVID-19 (January–February 2020), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020). The primary outcomes were the observed-to-expected ratio of respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters of the study period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic. For these calculations, the expected encounters for each period was derived from the same calendar periods from prepandemic years (2017-2019).
A total of 9,051,980 pediatric encounters were included in the analyses: 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. We found a 42% reduction in overall encounters during the COVID-19 period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic, with a greater reduction in respiratory, compared with nonrespiratory illnesses, which decreased 62% and 38%, respectively. These reductions were consistent across geographic and encounter type (ED vs. hospitalization). The frequency of hospital-based encounters for common pediatric respiratory illnesses was substantially reduced, with reductions in asthma exacerbations (down 76%), pneumonia (down 81%), croup (down 84%), influenza (down 87%) and bronchiolitis (down 91%). Differences in both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses varied by age, with larger reductions found in children aged less than 12 years. While adolescent (children aged over 12 years) encounters diminished during the early COVID period for both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses, their encounters returned to previous levels faster than those from younger children. For respiratory illnesses, hospital-based adolescents encounters had returned to prepandemic levels by the end of the study period (September 2020).
These findings warrant consideration as relaxation of SARS-CoV-2 mitigation are contemplated. Encounters for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses declined less and recovered faster in adolescents, compared with younger children. The underlying contributors to this trend are likely multifactorial. For example, respiratory illnesses such as croup and bronchiolitis are more common in younger children and adolescents may be more likely to transmit SARS-CoV-2, compared with younger age groups.4,5 However, adolescents may have had less strict adherence to social distancing measures.6 Future efforts to halt transmission of SARS-CoV-2, as well as other respiratory pathogens, should inform mitigation efforts in the adolescent population with considerations of the intensity of social mixing in different pediatric age groups.
While reductions in encounters caused by respiratory illnesses were substantial, more modest but similar age-based trends were seen in nonrespiratory illnesses. Yet, reduced transmission of infectious agents may not fully explain these findings. For example, it is possible that families sought care for mild to moderate nonrespiratory illness in clinics or via telehealth rather than the EDs.7 Provided there were no unintended negative consequences, such transition of care to non-ED settings would suggest there was overutilization of hospital resources prior to the pandemic. Additional assessments would be helpful to examine this more closely and to clarify the long-term impact of those transitions.
It is also possible that the pandemic effects on financial, social, and family stress may have led to increases in some pediatric health care encounters, such as those for mental health conditions,8 nonaccidental trauma or inability to adhere to treatment because of lack of resources.9,10 Additional study on the evolution and distribution of social and stress-related illnesses is critical to maintain and improve the health of children and adolescents.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in rapid and marked changes to both communicable and noncommunicable illnesses and care-seeking behaviors. Some of these findings are encouraging, such as large reductions in respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses. However, other trends may be harbingers of negative health consequences of the pandemic, such as increases in health care utilization later in the pandemic. Further study of the evolving pandemic’s effects on disease and health care utilization is needed to benefit our children now and during the next pandemic.
Dr. Antoon is an assistant professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University and a pediatric hospitalist at the Monroe Carroll Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt, both in Nashville, Tenn.
References
1. Kenyon CC et al. Initial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric asthma emergency department utilization. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Sep;8(8):2774-6.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.05.045.
2. Luca G et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: A data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3.
3. Antoon JW et al. The COVID-19 Pandemic and changes in healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2021 Mar 8. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3608.
4. Park YJ et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;26(10):2465-8. doi: 10.3201/eid2610.201315.
5. Davies NG et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020 Aug;26(8):1205-11. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9.
6. Andrews JL et al. Peer influence in adolescence: Public health implications for COVID-19. Trends Cogn Sci. 2020;24(8):585-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.05.001.
7. Taquechel K et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Nov-Dec;8(10):3378-87.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057.
8. Hill RM et al. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. 2021;147(3):e2020029280. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-029280.
9. Sharma S et al. COVID-19: Differences in sentinel injury and child abuse reporting during a pandemic. Child Abuse Negl. 2020 Dec;110:104709. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104709.
10. Lauren BN et al. Predictors of households at risk for food insecurity in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. Public Health Nutr. 2021 Jan 27. doi: 10.1017/S1368980021000355.
The COVID-19 pandemic upended the U.S. health care market and disrupted much of what was thought to be consistent and necessary hospital-based care for children. Early in the pandemic, clinics closed, elective surgeries were delayed, and well visits were postponed. Mitigation strategies were launched nationwide to limit the spread of SARS-CoV-2 including mask mandates, social distancing, shelter-in-place orders, and school closures. While these measures were enacted to target COVID-19, a potential off-target effect was reductions in transmission of other respiratory illness, and potentially nonrespiratory infectious illnesses and conditions exacerbated by acute infections.1 These measures have heavily impacted the pediatric population, wherein respiratory infections are common, and also because daycares and school can be hubs for disease transmission.2
To evaluate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric health care utilization, we performed a multicenter, cross-sectional study of 44 children’s hospitals using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database.3 Children aged 2 months to 18 years discharged from a PHIS hospital with nonsurgical diagnoses from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included in the study. The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, which was divided into three study periods: pre–COVID-19 (January–February 2020), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020). The primary outcomes were the observed-to-expected ratio of respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters of the study period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic. For these calculations, the expected encounters for each period was derived from the same calendar periods from prepandemic years (2017-2019).
A total of 9,051,980 pediatric encounters were included in the analyses: 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. We found a 42% reduction in overall encounters during the COVID-19 period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic, with a greater reduction in respiratory, compared with nonrespiratory illnesses, which decreased 62% and 38%, respectively. These reductions were consistent across geographic and encounter type (ED vs. hospitalization). The frequency of hospital-based encounters for common pediatric respiratory illnesses was substantially reduced, with reductions in asthma exacerbations (down 76%), pneumonia (down 81%), croup (down 84%), influenza (down 87%) and bronchiolitis (down 91%). Differences in both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses varied by age, with larger reductions found in children aged less than 12 years. While adolescent (children aged over 12 years) encounters diminished during the early COVID period for both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses, their encounters returned to previous levels faster than those from younger children. For respiratory illnesses, hospital-based adolescents encounters had returned to prepandemic levels by the end of the study period (September 2020).
These findings warrant consideration as relaxation of SARS-CoV-2 mitigation are contemplated. Encounters for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses declined less and recovered faster in adolescents, compared with younger children. The underlying contributors to this trend are likely multifactorial. For example, respiratory illnesses such as croup and bronchiolitis are more common in younger children and adolescents may be more likely to transmit SARS-CoV-2, compared with younger age groups.4,5 However, adolescents may have had less strict adherence to social distancing measures.6 Future efforts to halt transmission of SARS-CoV-2, as well as other respiratory pathogens, should inform mitigation efforts in the adolescent population with considerations of the intensity of social mixing in different pediatric age groups.
While reductions in encounters caused by respiratory illnesses were substantial, more modest but similar age-based trends were seen in nonrespiratory illnesses. Yet, reduced transmission of infectious agents may not fully explain these findings. For example, it is possible that families sought care for mild to moderate nonrespiratory illness in clinics or via telehealth rather than the EDs.7 Provided there were no unintended negative consequences, such transition of care to non-ED settings would suggest there was overutilization of hospital resources prior to the pandemic. Additional assessments would be helpful to examine this more closely and to clarify the long-term impact of those transitions.
It is also possible that the pandemic effects on financial, social, and family stress may have led to increases in some pediatric health care encounters, such as those for mental health conditions,8 nonaccidental trauma or inability to adhere to treatment because of lack of resources.9,10 Additional study on the evolution and distribution of social and stress-related illnesses is critical to maintain and improve the health of children and adolescents.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in rapid and marked changes to both communicable and noncommunicable illnesses and care-seeking behaviors. Some of these findings are encouraging, such as large reductions in respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses. However, other trends may be harbingers of negative health consequences of the pandemic, such as increases in health care utilization later in the pandemic. Further study of the evolving pandemic’s effects on disease and health care utilization is needed to benefit our children now and during the next pandemic.
Dr. Antoon is an assistant professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University and a pediatric hospitalist at the Monroe Carroll Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt, both in Nashville, Tenn.
References
1. Kenyon CC et al. Initial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric asthma emergency department utilization. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Sep;8(8):2774-6.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.05.045.
2. Luca G et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: A data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3.
3. Antoon JW et al. The COVID-19 Pandemic and changes in healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2021 Mar 8. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3608.
4. Park YJ et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;26(10):2465-8. doi: 10.3201/eid2610.201315.
5. Davies NG et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020 Aug;26(8):1205-11. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9.
6. Andrews JL et al. Peer influence in adolescence: Public health implications for COVID-19. Trends Cogn Sci. 2020;24(8):585-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.05.001.
7. Taquechel K et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Nov-Dec;8(10):3378-87.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057.
8. Hill RM et al. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. 2021;147(3):e2020029280. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-029280.
9. Sharma S et al. COVID-19: Differences in sentinel injury and child abuse reporting during a pandemic. Child Abuse Negl. 2020 Dec;110:104709. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104709.
10. Lauren BN et al. Predictors of households at risk for food insecurity in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. Public Health Nutr. 2021 Jan 27. doi: 10.1017/S1368980021000355.
The COVID-19 pandemic upended the U.S. health care market and disrupted much of what was thought to be consistent and necessary hospital-based care for children. Early in the pandemic, clinics closed, elective surgeries were delayed, and well visits were postponed. Mitigation strategies were launched nationwide to limit the spread of SARS-CoV-2 including mask mandates, social distancing, shelter-in-place orders, and school closures. While these measures were enacted to target COVID-19, a potential off-target effect was reductions in transmission of other respiratory illness, and potentially nonrespiratory infectious illnesses and conditions exacerbated by acute infections.1 These measures have heavily impacted the pediatric population, wherein respiratory infections are common, and also because daycares and school can be hubs for disease transmission.2
To evaluate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric health care utilization, we performed a multicenter, cross-sectional study of 44 children’s hospitals using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database.3 Children aged 2 months to 18 years discharged from a PHIS hospital with nonsurgical diagnoses from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30 over a 4-year period (2017-2020) were included in the study. The primary exposure was the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, which was divided into three study periods: pre–COVID-19 (January–February 2020), early COVID-19 (March-April 2020), and COVID-19 (May-September 2020). The primary outcomes were the observed-to-expected ratio of respiratory and nonrespiratory illness encounters of the study period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic. For these calculations, the expected encounters for each period was derived from the same calendar periods from prepandemic years (2017-2019).
A total of 9,051,980 pediatric encounters were included in the analyses: 6,811,799 with nonrespiratory illnesses and 2,240,181 with respiratory illnesses. We found a 42% reduction in overall encounters during the COVID-19 period, compared with the 3 years prior to the pandemic, with a greater reduction in respiratory, compared with nonrespiratory illnesses, which decreased 62% and 38%, respectively. These reductions were consistent across geographic and encounter type (ED vs. hospitalization). The frequency of hospital-based encounters for common pediatric respiratory illnesses was substantially reduced, with reductions in asthma exacerbations (down 76%), pneumonia (down 81%), croup (down 84%), influenza (down 87%) and bronchiolitis (down 91%). Differences in both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses varied by age, with larger reductions found in children aged less than 12 years. While adolescent (children aged over 12 years) encounters diminished during the early COVID period for both respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses, their encounters returned to previous levels faster than those from younger children. For respiratory illnesses, hospital-based adolescents encounters had returned to prepandemic levels by the end of the study period (September 2020).
These findings warrant consideration as relaxation of SARS-CoV-2 mitigation are contemplated. Encounters for respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses declined less and recovered faster in adolescents, compared with younger children. The underlying contributors to this trend are likely multifactorial. For example, respiratory illnesses such as croup and bronchiolitis are more common in younger children and adolescents may be more likely to transmit SARS-CoV-2, compared with younger age groups.4,5 However, adolescents may have had less strict adherence to social distancing measures.6 Future efforts to halt transmission of SARS-CoV-2, as well as other respiratory pathogens, should inform mitigation efforts in the adolescent population with considerations of the intensity of social mixing in different pediatric age groups.
While reductions in encounters caused by respiratory illnesses were substantial, more modest but similar age-based trends were seen in nonrespiratory illnesses. Yet, reduced transmission of infectious agents may not fully explain these findings. For example, it is possible that families sought care for mild to moderate nonrespiratory illness in clinics or via telehealth rather than the EDs.7 Provided there were no unintended negative consequences, such transition of care to non-ED settings would suggest there was overutilization of hospital resources prior to the pandemic. Additional assessments would be helpful to examine this more closely and to clarify the long-term impact of those transitions.
It is also possible that the pandemic effects on financial, social, and family stress may have led to increases in some pediatric health care encounters, such as those for mental health conditions,8 nonaccidental trauma or inability to adhere to treatment because of lack of resources.9,10 Additional study on the evolution and distribution of social and stress-related illnesses is critical to maintain and improve the health of children and adolescents.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in rapid and marked changes to both communicable and noncommunicable illnesses and care-seeking behaviors. Some of these findings are encouraging, such as large reductions in respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses. However, other trends may be harbingers of negative health consequences of the pandemic, such as increases in health care utilization later in the pandemic. Further study of the evolving pandemic’s effects on disease and health care utilization is needed to benefit our children now and during the next pandemic.
Dr. Antoon is an assistant professor of pediatrics at Vanderbilt University and a pediatric hospitalist at the Monroe Carroll Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt, both in Nashville, Tenn.
References
1. Kenyon CC et al. Initial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on pediatric asthma emergency department utilization. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Sep;8(8):2774-6.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.05.045.
2. Luca G et al. The impact of regular school closure on seasonal influenza epidemics: A data-driven spatial transmission model for Belgium. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2934-3.
3. Antoon JW et al. The COVID-19 Pandemic and changes in healthcare utilization for pediatric respiratory and nonrespiratory illnesses in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2021 Mar 8. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3608.
4. Park YJ et al. Contact tracing during coronavirus disease outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;26(10):2465-8. doi: 10.3201/eid2610.201315.
5. Davies NG et al. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat Med. 2020 Aug;26(8):1205-11. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9.
6. Andrews JL et al. Peer influence in adolescence: Public health implications for COVID-19. Trends Cogn Sci. 2020;24(8):585-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.05.001.
7. Taquechel K et al. Pediatric asthma healthcare utilization, viral testing, and air pollution changes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Nov-Dec;8(10):3378-87.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.07.057.
8. Hill RM et al. Suicide ideation and attempts in a pediatric emergency department before and during COVID-19. Pediatrics. 2021;147(3):e2020029280. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-029280.
9. Sharma S et al. COVID-19: Differences in sentinel injury and child abuse reporting during a pandemic. Child Abuse Negl. 2020 Dec;110:104709. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104709.
10. Lauren BN et al. Predictors of households at risk for food insecurity in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. Public Health Nutr. 2021 Jan 27. doi: 10.1017/S1368980021000355.
Severe IBS symptoms may have improved during COVID-19 lockdowns
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
Help your patients better understand IBS and symptoms by sharing AGA patient education at www.gastro.org/IBS.
This article was update May 27, 2021.
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
Help your patients better understand IBS and symptoms by sharing AGA patient education at www.gastro.org/IBS.
This article was update May 27, 2021.
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
Help your patients better understand IBS and symptoms by sharing AGA patient education at www.gastro.org/IBS.
This article was update May 27, 2021.
FROM DDW 2021
Pandemic colonoscopy restrictions may lead to worse CRC outcomes
For veterans, changes in colonoscopy screening caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased risks of delayed colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnosis and could lead to worse CRC outcomes, based on data from more than 33,000 patients in the Veterans Health Administration.
After COVID-19 screening policies were implemented, a significantly lower rate of veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC underwent colonoscopy, lead author Joshua Demb, PhD, a cancer epidemiologist at the University of California, San Diego, reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Veterans Health Administration enacted risk mitigation and management strategies in March 2020, including postponement of nearly all colonoscopies,” the investigators reported. “Notably, this included veterans with red flag signs or symptoms for CRC, among whom delays in workup could increase risk for later-stage and fatal CRC, if present.”
To measure the effects of this policy change, Dr. Demb and colleagues performed a cohort study involving 33,804 veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC, including hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, or abnormal guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT). Veterans were divided into two cohorts based on date of first red flag diagnosis: either before the COVID-19 policy was implemented (April to October 2019; n = 19,472) or after (April to October 2020; n = 14,332), with an intervening 6-month washout period.
Primary outcomes were proportion completing colonoscopy and time to colonoscopy completion. Multivariable logistic regression incorporated a number of demographic and medical covariates, including race/ethnicity, sex, age, number of red-flag signs/symptoms, first red-flag sign/symptom, and others.
Before the COVID-19 policy change, 44% of individuals with red-flag signs or symptoms received a colonoscopy, compared with 32% after the policy was introduced (P < .01). Adjusted models showed that veterans in the COVID policy group were 42% less likely to receive a diagnostic colonoscopy than those in the prepolicy group (odds ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.61). While these findings showed greater likelihood of receiving a screening before the pandemic, postpolicy colonoscopies were conducted sooner, with a median time to procedure of 41 days, compared with 65 days before the pandemic (P < .01). Similar differences in screening rates between pre- and postpandemic groups were observed across all types of red flag signs and symptoms.
“Lower colonoscopy uptake was observed among individuals with red-flag signs/symptoms for CRC post- versus preimplementation of COVID-19 policies, suggesting increased future risk for delayed CRC diagnosis and adverse CRC outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Prioritization may be needed to overcome backlog of colonoscopies
Jill Tinmouth, MD, PhD, lead scientist for ColonCancerCheck, Ontario’s organized colorectal cancer screening program, and a gastroenterologist and scientist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, shared similar concerns about delayed diagnoses.
“We might expect these cancers to present ... at a more advanced stage, and that, as a result, the outcomes from these cancers could be worse,” Dr. Tinmouth said in an interview.
She also noted the change in colonoscopy timing.
“A particularly interesting finding was that, when a colonoscopy occurred, the time to colonoscopy was shorter during the COVID era than in the pre-COVID era,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “The authors suggested that this might be as a result of Veterans Health Administration policies implemented as a result of the pandemic that led to prioritization of more urgent procedures.”
According to Dr. Tinmouth, similar prioritization may be needed to catch up with the backlog of colonoscopies created by pandemic-related policy changes. In a recent study comparing two backlog management techniques, Dr. Tinmouth and colleagues concluded that redirecting low-yield colonoscopies to FIT without increasing hospital colonoscopy capacity could reduce time to recovery by more than half.
Even so, screening programs may be facing a long road to recovery.
“Recovery of the colonoscopy backlog is going to be a challenge that will take a while – maybe even years – to resolve,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “Jurisdictions/institutions that have a strong centralized intake or triage will likely be most successful in resolving the backlog quickly as they will be able to prioritize the most urgent cases, such as persons with an abnormal FIT or with symptoms, and to redirect persons scheduled for a ‘low-yield’ colonoscopy to have a FIT instead.” Ontario defines low-yield colonoscopies as primary screening for average-risk individuals and follow-up colonoscopies for patients with low-risk adenomas at baseline.
When asked about strategies to address future pandemics, Dr. Tinmouth said, “I think that two key learnings for me from this [pandemic] are: one, not to let our guard down, and to remain vigilant and prepared – in terms of monitoring, supply chain, equipment, etc.] ... and two to create a nimble and agile health system so that we are able to assess the challenges that the next pandemic brings and address them as quickly as possible.”The investigators and Dr. Tinmouth reported no conflicts of interest.
For veterans, changes in colonoscopy screening caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased risks of delayed colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnosis and could lead to worse CRC outcomes, based on data from more than 33,000 patients in the Veterans Health Administration.
After COVID-19 screening policies were implemented, a significantly lower rate of veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC underwent colonoscopy, lead author Joshua Demb, PhD, a cancer epidemiologist at the University of California, San Diego, reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Veterans Health Administration enacted risk mitigation and management strategies in March 2020, including postponement of nearly all colonoscopies,” the investigators reported. “Notably, this included veterans with red flag signs or symptoms for CRC, among whom delays in workup could increase risk for later-stage and fatal CRC, if present.”
To measure the effects of this policy change, Dr. Demb and colleagues performed a cohort study involving 33,804 veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC, including hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, or abnormal guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT). Veterans were divided into two cohorts based on date of first red flag diagnosis: either before the COVID-19 policy was implemented (April to October 2019; n = 19,472) or after (April to October 2020; n = 14,332), with an intervening 6-month washout period.
Primary outcomes were proportion completing colonoscopy and time to colonoscopy completion. Multivariable logistic regression incorporated a number of demographic and medical covariates, including race/ethnicity, sex, age, number of red-flag signs/symptoms, first red-flag sign/symptom, and others.
Before the COVID-19 policy change, 44% of individuals with red-flag signs or symptoms received a colonoscopy, compared with 32% after the policy was introduced (P < .01). Adjusted models showed that veterans in the COVID policy group were 42% less likely to receive a diagnostic colonoscopy than those in the prepolicy group (odds ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.61). While these findings showed greater likelihood of receiving a screening before the pandemic, postpolicy colonoscopies were conducted sooner, with a median time to procedure of 41 days, compared with 65 days before the pandemic (P < .01). Similar differences in screening rates between pre- and postpandemic groups were observed across all types of red flag signs and symptoms.
“Lower colonoscopy uptake was observed among individuals with red-flag signs/symptoms for CRC post- versus preimplementation of COVID-19 policies, suggesting increased future risk for delayed CRC diagnosis and adverse CRC outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Prioritization may be needed to overcome backlog of colonoscopies
Jill Tinmouth, MD, PhD, lead scientist for ColonCancerCheck, Ontario’s organized colorectal cancer screening program, and a gastroenterologist and scientist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, shared similar concerns about delayed diagnoses.
“We might expect these cancers to present ... at a more advanced stage, and that, as a result, the outcomes from these cancers could be worse,” Dr. Tinmouth said in an interview.
She also noted the change in colonoscopy timing.
“A particularly interesting finding was that, when a colonoscopy occurred, the time to colonoscopy was shorter during the COVID era than in the pre-COVID era,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “The authors suggested that this might be as a result of Veterans Health Administration policies implemented as a result of the pandemic that led to prioritization of more urgent procedures.”
According to Dr. Tinmouth, similar prioritization may be needed to catch up with the backlog of colonoscopies created by pandemic-related policy changes. In a recent study comparing two backlog management techniques, Dr. Tinmouth and colleagues concluded that redirecting low-yield colonoscopies to FIT without increasing hospital colonoscopy capacity could reduce time to recovery by more than half.
Even so, screening programs may be facing a long road to recovery.
“Recovery of the colonoscopy backlog is going to be a challenge that will take a while – maybe even years – to resolve,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “Jurisdictions/institutions that have a strong centralized intake or triage will likely be most successful in resolving the backlog quickly as they will be able to prioritize the most urgent cases, such as persons with an abnormal FIT or with symptoms, and to redirect persons scheduled for a ‘low-yield’ colonoscopy to have a FIT instead.” Ontario defines low-yield colonoscopies as primary screening for average-risk individuals and follow-up colonoscopies for patients with low-risk adenomas at baseline.
When asked about strategies to address future pandemics, Dr. Tinmouth said, “I think that two key learnings for me from this [pandemic] are: one, not to let our guard down, and to remain vigilant and prepared – in terms of monitoring, supply chain, equipment, etc.] ... and two to create a nimble and agile health system so that we are able to assess the challenges that the next pandemic brings and address them as quickly as possible.”The investigators and Dr. Tinmouth reported no conflicts of interest.
For veterans, changes in colonoscopy screening caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased risks of delayed colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnosis and could lead to worse CRC outcomes, based on data from more than 33,000 patients in the Veterans Health Administration.
After COVID-19 screening policies were implemented, a significantly lower rate of veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC underwent colonoscopy, lead author Joshua Demb, PhD, a cancer epidemiologist at the University of California, San Diego, reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Veterans Health Administration enacted risk mitigation and management strategies in March 2020, including postponement of nearly all colonoscopies,” the investigators reported. “Notably, this included veterans with red flag signs or symptoms for CRC, among whom delays in workup could increase risk for later-stage and fatal CRC, if present.”
To measure the effects of this policy change, Dr. Demb and colleagues performed a cohort study involving 33,804 veterans with red-flag signs or symptoms for CRC, including hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, or abnormal guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT). Veterans were divided into two cohorts based on date of first red flag diagnosis: either before the COVID-19 policy was implemented (April to October 2019; n = 19,472) or after (April to October 2020; n = 14,332), with an intervening 6-month washout period.
Primary outcomes were proportion completing colonoscopy and time to colonoscopy completion. Multivariable logistic regression incorporated a number of demographic and medical covariates, including race/ethnicity, sex, age, number of red-flag signs/symptoms, first red-flag sign/symptom, and others.
Before the COVID-19 policy change, 44% of individuals with red-flag signs or symptoms received a colonoscopy, compared with 32% after the policy was introduced (P < .01). Adjusted models showed that veterans in the COVID policy group were 42% less likely to receive a diagnostic colonoscopy than those in the prepolicy group (odds ratio, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.61). While these findings showed greater likelihood of receiving a screening before the pandemic, postpolicy colonoscopies were conducted sooner, with a median time to procedure of 41 days, compared with 65 days before the pandemic (P < .01). Similar differences in screening rates between pre- and postpandemic groups were observed across all types of red flag signs and symptoms.
“Lower colonoscopy uptake was observed among individuals with red-flag signs/symptoms for CRC post- versus preimplementation of COVID-19 policies, suggesting increased future risk for delayed CRC diagnosis and adverse CRC outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
Prioritization may be needed to overcome backlog of colonoscopies
Jill Tinmouth, MD, PhD, lead scientist for ColonCancerCheck, Ontario’s organized colorectal cancer screening program, and a gastroenterologist and scientist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, shared similar concerns about delayed diagnoses.
“We might expect these cancers to present ... at a more advanced stage, and that, as a result, the outcomes from these cancers could be worse,” Dr. Tinmouth said in an interview.
She also noted the change in colonoscopy timing.
“A particularly interesting finding was that, when a colonoscopy occurred, the time to colonoscopy was shorter during the COVID era than in the pre-COVID era,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “The authors suggested that this might be as a result of Veterans Health Administration policies implemented as a result of the pandemic that led to prioritization of more urgent procedures.”
According to Dr. Tinmouth, similar prioritization may be needed to catch up with the backlog of colonoscopies created by pandemic-related policy changes. In a recent study comparing two backlog management techniques, Dr. Tinmouth and colleagues concluded that redirecting low-yield colonoscopies to FIT without increasing hospital colonoscopy capacity could reduce time to recovery by more than half.
Even so, screening programs may be facing a long road to recovery.
“Recovery of the colonoscopy backlog is going to be a challenge that will take a while – maybe even years – to resolve,” Dr. Tinmouth said. “Jurisdictions/institutions that have a strong centralized intake or triage will likely be most successful in resolving the backlog quickly as they will be able to prioritize the most urgent cases, such as persons with an abnormal FIT or with symptoms, and to redirect persons scheduled for a ‘low-yield’ colonoscopy to have a FIT instead.” Ontario defines low-yield colonoscopies as primary screening for average-risk individuals and follow-up colonoscopies for patients with low-risk adenomas at baseline.
When asked about strategies to address future pandemics, Dr. Tinmouth said, “I think that two key learnings for me from this [pandemic] are: one, not to let our guard down, and to remain vigilant and prepared – in terms of monitoring, supply chain, equipment, etc.] ... and two to create a nimble and agile health system so that we are able to assess the challenges that the next pandemic brings and address them as quickly as possible.”The investigators and Dr. Tinmouth reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM DDW 2021
Severe IBS symptoms may improve during COVID-19 lockdowns
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms improved among patients who endured a prolonged COVID-19 lockdown in Argentina, a finding that was unexpected yet reaffirms the gut-brain connection in this gastrointestinal disorder, according to a coauthor of a study presented at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
These patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) reported improvements in disease severity and symptoms during the lockdown that were significant in comparison with the prepandemic period, according to Juan Pablo Stefanolo, MD, a lead author on the study.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from about 50% to 30%, accompanied by decreases in global and individual symptom scores, according to data presented at the meeting.
Investigators had assumed that IBS symptoms would worsen, fueled by new stresses and pressures related to a nationwide lockdown in Argentina that started in March 19, 2020, and didn’t fully end until November.
Now, the hypothesis has changed, according to Dr. Stefanolo, a physician in the neurogastroenterology and motility section at Hospital de Clínicas José de San Martín, Buenos Aires University.
“We think that probably just staying at home in a more relaxed way, and in a more controlled environment, could have improved those symptoms,” Dr. Stefanolo said in an interview.
Impact of lifestyle factors?
This reported decrease in overall severity and symptoms associated with IBS during the pandemic lockdown is an “interesting phenomenon” that deserves further study, said Purna C. Kashyap, MBBS, professor of medicine, physiology, and biomedical engineering at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors such as spending more time with family could be contributing to the improvement in symptoms, said Dr. Kashyap, who was not involved in the study.
“A follow-up survey which includes these additional factors could help ascertain why there was an improvement in symptoms and could help with developing effective treatment strategies,” Dr. Kashyap said.
A more detailed follow-up survey is definitely warranted, Dr. Stefanolo said, particularly as Argentina faces new and sweeping pandemic-related restrictions caused by a second-wave COVID-19 surge that now includes more than 30,000 new cases per day.
On May 21, Argentina entered a strict 9-day confinement period as President Alberto Fernández said the country was facing its “worst moment” of the pandemic to date.
Although the circumstances are very unfortunate, worsening pandemic conditions in Argentina are nonetheless a “perfect scenario” to explore in more detail how external stress burden impacts IBS symptoms, said Dr. Stefanolo.
Study results
To study the impact of the 2020 mandatory lockdown on gut-brain axis symptomatology in IBS patients, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors assessed a total of 129 patients with IBS-diarrhea or mixed bowel habits subtype. The mean age of participants was 54 years and 78% were female.
Patients were assessed by online survey or phone interview using the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scale (IBS-SS), Likert scales for IBS symptoms, and the Bristol Stool Scale, along with other measures of mood and comorbidities.
The proportion of patients with severe IBS dropped from 50% (65 patients) in the prepandemic period to 30% (39 patients) during the lockdown, Dr. Stefanolo and coauthors reported at the virtual DDW meeting. Similarly, mean IBS-SS scores dropped from 278.54 to 212.36 during lockdown, translating into a difference of 65.9 points.
Patients reported improvements in global IBS symptoms, pain, and distention. Stool consistency was also improved, with an average decrease on the Bristol scale of 2 points, according to the report.
Similar improvements from the prepandemic period were observed in anxiety and somatization scores, as well as in symptoms of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue.
By contrast, headache and pyrosis and/or regurgitation symptoms increased from the prepandemic period, possibly because of weight gain, according to Dr. Stefanolo who said that about 60% of patients reported weight gain during the lockdown.
Lifestyle advice
The patients in this study were being seen at a tertiary care center, so they tended to have more severe disease than what would be seen in general clinical practice, according to Dr. Stefanolo. Because of that, he advised caution in extrapolating these results to a broader patient population.
Nevertheless, this study does suggest the potential for lifestyle interventions that could make a difference for the average IBS patient, he said.
“It reinforces that outside stress has something to do with it, and that food maybe has something to do with it,” he said. “I think that giving that advice – try to be more relaxed, and maybe control the quality or the type of food you have – could be great to improve ... those symptoms, maybe.”
The study authors reported no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Kashyap reported relationships with Novome Biotechnologies, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and Pendulum.
FROM DDW 2021
Psychiatry is Neurology: White matter pathology permeates psychiatric disorders
Ask neurologists or psychiatrists to name a white matter (WM) brain disease and they are very likely to say multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating brain disorder caused by immune-mediated destruction of oligodendrocytes, the glial cells that manufacture myelin without which brain communications would come to a standstill.
MS is often associated with mood or psychotic disorders, yet it is regarded as a neurologic illness, not a psychiatric disorder.
Many neurologists and psychiatrists may not be aware that during the past few years, multiple diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies have revealed that many psychiatric disorders are associated with WM pathology.1
Most people think that the brain is composed mostly of neurons, but in fact the bulk of brain volume (60%) is comprised of WM and only 40% is gray matter, which includes both neurons and glial cells (astroglia, microglia, and oligodendroglia). WM includes >137,000 km of myelinated fibers, an extensive network that connects all brain regions and integrates its complex, multifaceted functions, culminating in a unified sense of self and agency.
The role of the corpus callosum
Early in my research career, I became interested in the corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric WM commissure connecting homologous areas across the 2 cerebral hemispheres. It is comprised of 200 million fibers of various diameters. Reasons for my fascination with the corpus callosum were:
The studies of Roger Sperry, the 1981 Nobel Laureate who led the team that was awarded the prize for split-brain research, which involved patients whose corpus callosum was cut to prevent the transfer of intractable epilepsy from 1 hemisphere to the other. Using a tachistoscope that he designed, Sperry discovered that the right and left hemispheres are 2 independent spheres of consciousness (ie, 2 individuals) with different skills.2 Cerebral dominance (laterality) fully integrates the 2 hemispheres via the corpus callosum, with a verbal hemisphere (the left, in 90% of people) dominating the other hemisphere and serving as the “spokesman self.” Thus, we all have 2 persons in our brain completely integrated into 1 “self.”2 This led me to wonder about the effects of an impaired corpus callosum on the “unified self.”
Postmortem and MRI studies conducted by our research group showed a significant difference in the thickness of the corpus callosum in a group of patients with schizophrenia vs healthy controls, which implied abnormal connectivity across the left and right hemispheres.3
Continue to: I then conducted a clinical study
I then conducted a clinical study examining patients with tumors impinging on the corpus callosum, which revealed that they developed psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations).4 This study suggested that disrupting the integrity of the callosal inter-hemispheric fibers can trigger fixed false beliefs and perceptual anomalies.4
A ‘dysconnection’ between hemispheres
I translated those observations about the corpus callosum into a published hypothesis5 in which I proposed that Schneider’s First-Rank Symptoms of schizophrenia of thought insertion, thought withdrawal, and thought broadcasting—as well as delusional experiences of “external control”—may be due to a neurobiologic abnormality in the corpus callosum that disrupts the flow of ongoing bits of information transmitted from the left to the right hemisphere, and vice versa. I proposed in my model that this disruption leads to the verbal left hemisphere of a psychotic patient to describe having thoughts inserted into it from an alien source, failing to recognize that the thoughts it is receiving are being transmitted from the disconnected right hemisphere, which is no longer part of the “self.” Similarly, impulses from the right hemispheric consciousness are now perceived by the patient’s verbal left hemisphere (which talks to the examining physician) as “external control.” Thus, I postulated that an abnormal corpus callosum structure would lead to a “dysconnection” (not “disconnection”) between the 2 hemispheres, and that anomalous dysconnectivity may generate both delusions and hallucinations. 6
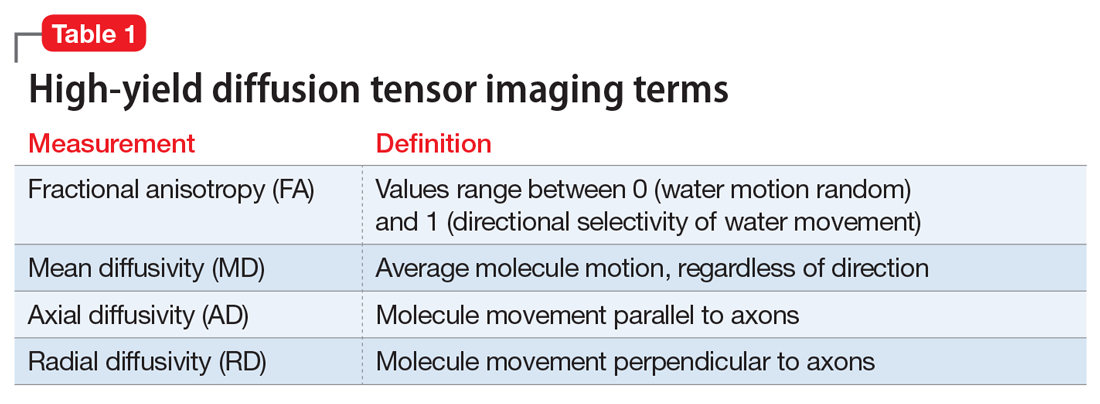
Two decades later, my assumptions were vindicated when DTI was invented, enabling the measurement of WM integrity, including the corpus callosum, the largest body of WM in the brain. Table 1 defines the main parameters of WM integrity, anisotropy and diffusivity, which measure water flow inside WM fibers.
During the past 15 years, many studies have confirmed the presence of significant abnormalities in the myelinated fibers of the corpus callosum in schizophrenia, which can be considered a validation of my hypothesis that the corpus callosum becomes a dysfunctional channel of communications between the right and left hemisphere. Subsequently, DTI studies have reported a spectrum of WM pathologies in various other cerebral bundles and not only in schizophrenia, but also in other major psychiatric disorders (Table 27-19).
The pathophysiology of WM pathology in many psychiatric disorders may include neurodevelopmental aberrations (genetic, environmental, or both, which may alter WM structure and/or myelination), neuroinflammation, or oxidative stress (free radicals), which can cause disintegration of the vital myelin sheaths, leading to disruption of brain connectivity.6,7 Researchers now consider the brain’s WM network dysconnectivity as generating a variety of psychiatric symptoms, including psychosis, depression, mania, anxiety, autism, aggression, impulsivity, psychopathy, and cognitive impairments.
It is not surprising that WM repair has become a therapeutic target in psychiatry and neurology. Among the strategies being investigated are inhibiting the Nogo-A signaling pathways20 or modulating the Lingo-1 signaling.21 However, the most well-established myelin repair pathway is prolactin, a neuroprotective hormone with several beneficial effects on the brain (Table 322,23), including the proliferation of oligodendroglia, the main source of myelin (and the number of which declines in schizophrenia). Antipsychotics that increase prolactin have been shown to increase WM volume.24,25 It has even been proposed that a decline in oligodendrocytes and low myelin synthesis may be one of the neurobiologic pathologies in schizophrenia.26 One of the 24 neuroprotective properties of the second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) is the restoration of WM integrity.27 It’s worth noting that WM pathology has been found to be present at the onset of schizophrenia before treatment, and that SGAs have been reported to correct it.28

Continue to: In conclusion...
In conclusion, psychiatric disorders, usually referred to as “mental illnesses,” are unquestionably neurologic disorders. Similarly, all neurologic disorders are associated with psychiatric manifestations. WM pathology is only 1 of numerous structural brain abnormalities that have been documented across psychiatric disorders, which proves that psychiatry is a clinical neuroscience, just like neurology. I strongly advocate that psychiatry and neurology reunite into a single medical specialty. Both focus on disorders of brain structure and/or function, and these disorders also share much more than WM pathology.29
1. Sagarwala R and Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology is shared across multiple psychiatric brain disorders: Is abnormal diffusivity a transdiagnostic biomarker for psychopathology? Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry. 2020;2:00010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bionps.2019.100010
2. Pearce JMS; FRCP. The “split brain” and Roger Wolcott Sperry (1913-1994). Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175(4):217-220.
3. Nasrallah HA, Andreasen NC, Coffman JA, et al. A controlled magnetic resonance imaging study of corpus callosum thickness in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1986;21(3):274-282.
4. Nasrallah HA, McChesney CM. Psychopathology of corpus callosum tumors. Biol Psychiatry. 1981;16(7):663-669.
5. Nasrallah HA. The unintegrated right cerebral hemispheric consciousness as alien intruder: a possible mechanism for Schneiderian delusions in schizophrenia. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(3):273-282.
6. Friston K, Brown HR, Siemerkus J, et al. The dysconnection hypothesis (2016). Schizophr Res. 2016;176(2-3):83-94.
7. Najjar S, Pearlman DM. Neuroinflammation and white matter pathology in schizophrenia: systematic review. Schizophr Res. 2015;161(1):102-112.
8. Benedetti F, Bollettini I. Recent findings on the role of white matter pathology in bipolar disorder. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2014;22(6):338-341.
9. Zheng H, Bergamino M, Ford BN, et al; Tulsa 1000 Investigators. Replicable association between human cytomegalovirus infection and reduced white matter fractional anisotropy in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021;46(5):928-938.
10. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in drug-naïve OCD patients before and after pharmacotherapy. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(1):42-47.
11. Lee KS, Lee SH. White matter-based structural brain network of anxiety. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:61-70.
12. Swanson MR, Hazlett HC. White matter as a monitoring biomarker for neurodevelopmental disorder intervention studies. J Neurodev Disord. 2019;11(1):33.
13. Hampton WH, Hanik IM, Olson IR. Substance abuse and white matter: findings, limitations, and future of diffusion tensor imaging research. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:288-298.
14. Waller R, Dotterer HL, Murray L, et al. White-matter tract abnormalities and antisocial behavior: a systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies across development. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;14:201-215.
15. Wolf RC, Pujara MS, Motzkin JC, et al. Interpersonal traits of psychopathy linked to reduced integrity of the uncinate fasciculus. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(10):4202-4209.
16. Puzzo I, Seunarine K, Sully K, et al. Altered white-matter microstructure in conduct disorder is specifically associated with elevated callous-unemotional traits. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018;46(7):1451-1466.
17. Finger EC, Marsh A, Blair KS, et al. Impaired functional but preserved structural connectivity in limbic white matter tracts in youth with conduct disorder or oppositional defiant disorder plus psychopathic traits. Psychiatry Res. 2012;202(3):239-244.
18. Li C, Dong M, Womer FY, et al. Transdiagnostic time-varying dysconnectivity across major psychiatric disorders. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(4):1182-1196.
19. Khanbabaei M, Hughes E, Ellegood J, et al. Precocious myelination in a mouse model of autism. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):251.
20. Petratos S, Theotokis P, Kim MJ, et al. That’s a wrap! Molecular drivers governing neuronal nogo receptor-dependent myelin plasticity and integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:227
21. Fernandez-Enright F, Andrews JL, Newell KA, et al. Novel implications of Lingo-1 and its signaling partners in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2014;4(1):e348. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.121
22. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Stewart SB, et al. In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009;113(2-3):322-331.
23. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Amar CP, et al. Long acting injection versus oral risperidone in first-episode schizophrenia: differential impact on white matter myelination trajectory. Schizophr Res. 2011 Oct;132(1):35-41
24. Tishler TA, Bartzokis G, Lu PH, et al. Abnormal trajectory of intracortical myelination in schizophrenia implicates white matter in disease pathophysiology and the therapeutic mechanism of action of antipsychotics. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2018;3(5):454-462.
25. Ren Y, Wang H, Xiao L. Improving myelin/oligodendrocyte-related dysfunction: a new mechanism of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia? Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;16(3):691-700.
26. Dietz AG, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Glial cells in schizophrenia: a unified hypothesis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7(3):272-281.
27. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7
28. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. (In press.) The effect of antipsychotic medications on white matter integrity in first-episode drug naïve patients with psychosis. Asian Journal of Psychiatry.
29. Nasrallah HA. Let’s tear down the silos and reunify psychiatry and neurology. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(8):9-10.
Ask neurologists or psychiatrists to name a white matter (WM) brain disease and they are very likely to say multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating brain disorder caused by immune-mediated destruction of oligodendrocytes, the glial cells that manufacture myelin without which brain communications would come to a standstill.
MS is often associated with mood or psychotic disorders, yet it is regarded as a neurologic illness, not a psychiatric disorder.
Many neurologists and psychiatrists may not be aware that during the past few years, multiple diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies have revealed that many psychiatric disorders are associated with WM pathology.1
Most people think that the brain is composed mostly of neurons, but in fact the bulk of brain volume (60%) is comprised of WM and only 40% is gray matter, which includes both neurons and glial cells (astroglia, microglia, and oligodendroglia). WM includes >137,000 km of myelinated fibers, an extensive network that connects all brain regions and integrates its complex, multifaceted functions, culminating in a unified sense of self and agency.
The role of the corpus callosum
Early in my research career, I became interested in the corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric WM commissure connecting homologous areas across the 2 cerebral hemispheres. It is comprised of 200 million fibers of various diameters. Reasons for my fascination with the corpus callosum were:
The studies of Roger Sperry, the 1981 Nobel Laureate who led the team that was awarded the prize for split-brain research, which involved patients whose corpus callosum was cut to prevent the transfer of intractable epilepsy from 1 hemisphere to the other. Using a tachistoscope that he designed, Sperry discovered that the right and left hemispheres are 2 independent spheres of consciousness (ie, 2 individuals) with different skills.2 Cerebral dominance (laterality) fully integrates the 2 hemispheres via the corpus callosum, with a verbal hemisphere (the left, in 90% of people) dominating the other hemisphere and serving as the “spokesman self.” Thus, we all have 2 persons in our brain completely integrated into 1 “self.”2 This led me to wonder about the effects of an impaired corpus callosum on the “unified self.”
Postmortem and MRI studies conducted by our research group showed a significant difference in the thickness of the corpus callosum in a group of patients with schizophrenia vs healthy controls, which implied abnormal connectivity across the left and right hemispheres.3
Continue to: I then conducted a clinical study
I then conducted a clinical study examining patients with tumors impinging on the corpus callosum, which revealed that they developed psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations).4 This study suggested that disrupting the integrity of the callosal inter-hemispheric fibers can trigger fixed false beliefs and perceptual anomalies.4
A ‘dysconnection’ between hemispheres
I translated those observations about the corpus callosum into a published hypothesis5 in which I proposed that Schneider’s First-Rank Symptoms of schizophrenia of thought insertion, thought withdrawal, and thought broadcasting—as well as delusional experiences of “external control”—may be due to a neurobiologic abnormality in the corpus callosum that disrupts the flow of ongoing bits of information transmitted from the left to the right hemisphere, and vice versa. I proposed in my model that this disruption leads to the verbal left hemisphere of a psychotic patient to describe having thoughts inserted into it from an alien source, failing to recognize that the thoughts it is receiving are being transmitted from the disconnected right hemisphere, which is no longer part of the “self.” Similarly, impulses from the right hemispheric consciousness are now perceived by the patient’s verbal left hemisphere (which talks to the examining physician) as “external control.” Thus, I postulated that an abnormal corpus callosum structure would lead to a “dysconnection” (not “disconnection”) between the 2 hemispheres, and that anomalous dysconnectivity may generate both delusions and hallucinations. 6
Two decades later, my assumptions were vindicated when DTI was invented, enabling the measurement of WM integrity, including the corpus callosum, the largest body of WM in the brain. Table 1 defines the main parameters of WM integrity, anisotropy and diffusivity, which measure water flow inside WM fibers.

During the past 15 years, many studies have confirmed the presence of significant abnormalities in the myelinated fibers of the corpus callosum in schizophrenia, which can be considered a validation of my hypothesis that the corpus callosum becomes a dysfunctional channel of communications between the right and left hemisphere. Subsequently, DTI studies have reported a spectrum of WM pathologies in various other cerebral bundles and not only in schizophrenia, but also in other major psychiatric disorders (Table 27-19).
The pathophysiology of WM pathology in many psychiatric disorders may include neurodevelopmental aberrations (genetic, environmental, or both, which may alter WM structure and/or myelination), neuroinflammation, or oxidative stress (free radicals), which can cause disintegration of the vital myelin sheaths, leading to disruption of brain connectivity.6,7 Researchers now consider the brain’s WM network dysconnectivity as generating a variety of psychiatric symptoms, including psychosis, depression, mania, anxiety, autism, aggression, impulsivity, psychopathy, and cognitive impairments.
It is not surprising that WM repair has become a therapeutic target in psychiatry and neurology. Among the strategies being investigated are inhibiting the Nogo-A signaling pathways20 or modulating the Lingo-1 signaling.21 However, the most well-established myelin repair pathway is prolactin, a neuroprotective hormone with several beneficial effects on the brain (Table 322,23), including the proliferation of oligodendroglia, the main source of myelin (and the number of which declines in schizophrenia). Antipsychotics that increase prolactin have been shown to increase WM volume.24,25 It has even been proposed that a decline in oligodendrocytes and low myelin synthesis may be one of the neurobiologic pathologies in schizophrenia.26 One of the 24 neuroprotective properties of the second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) is the restoration of WM integrity.27 It’s worth noting that WM pathology has been found to be present at the onset of schizophrenia before treatment, and that SGAs have been reported to correct it.28

Continue to: In conclusion...
In conclusion, psychiatric disorders, usually referred to as “mental illnesses,” are unquestionably neurologic disorders. Similarly, all neurologic disorders are associated with psychiatric manifestations. WM pathology is only 1 of numerous structural brain abnormalities that have been documented across psychiatric disorders, which proves that psychiatry is a clinical neuroscience, just like neurology. I strongly advocate that psychiatry and neurology reunite into a single medical specialty. Both focus on disorders of brain structure and/or function, and these disorders also share much more than WM pathology.29
Ask neurologists or psychiatrists to name a white matter (WM) brain disease and they are very likely to say multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating brain disorder caused by immune-mediated destruction of oligodendrocytes, the glial cells that manufacture myelin without which brain communications would come to a standstill.
MS is often associated with mood or psychotic disorders, yet it is regarded as a neurologic illness, not a psychiatric disorder.
Many neurologists and psychiatrists may not be aware that during the past few years, multiple diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies have revealed that many psychiatric disorders are associated with WM pathology.1
Most people think that the brain is composed mostly of neurons, but in fact the bulk of brain volume (60%) is comprised of WM and only 40% is gray matter, which includes both neurons and glial cells (astroglia, microglia, and oligodendroglia). WM includes >137,000 km of myelinated fibers, an extensive network that connects all brain regions and integrates its complex, multifaceted functions, culminating in a unified sense of self and agency.
The role of the corpus callosum
Early in my research career, I became interested in the corpus callosum, the largest interhemispheric WM commissure connecting homologous areas across the 2 cerebral hemispheres. It is comprised of 200 million fibers of various diameters. Reasons for my fascination with the corpus callosum were:
The studies of Roger Sperry, the 1981 Nobel Laureate who led the team that was awarded the prize for split-brain research, which involved patients whose corpus callosum was cut to prevent the transfer of intractable epilepsy from 1 hemisphere to the other. Using a tachistoscope that he designed, Sperry discovered that the right and left hemispheres are 2 independent spheres of consciousness (ie, 2 individuals) with different skills.2 Cerebral dominance (laterality) fully integrates the 2 hemispheres via the corpus callosum, with a verbal hemisphere (the left, in 90% of people) dominating the other hemisphere and serving as the “spokesman self.” Thus, we all have 2 persons in our brain completely integrated into 1 “self.”2 This led me to wonder about the effects of an impaired corpus callosum on the “unified self.”
Postmortem and MRI studies conducted by our research group showed a significant difference in the thickness of the corpus callosum in a group of patients with schizophrenia vs healthy controls, which implied abnormal connectivity across the left and right hemispheres.3
Continue to: I then conducted a clinical study
I then conducted a clinical study examining patients with tumors impinging on the corpus callosum, which revealed that they developed psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations).4 This study suggested that disrupting the integrity of the callosal inter-hemispheric fibers can trigger fixed false beliefs and perceptual anomalies.4
A ‘dysconnection’ between hemispheres
I translated those observations about the corpus callosum into a published hypothesis5 in which I proposed that Schneider’s First-Rank Symptoms of schizophrenia of thought insertion, thought withdrawal, and thought broadcasting—as well as delusional experiences of “external control”—may be due to a neurobiologic abnormality in the corpus callosum that disrupts the flow of ongoing bits of information transmitted from the left to the right hemisphere, and vice versa. I proposed in my model that this disruption leads to the verbal left hemisphere of a psychotic patient to describe having thoughts inserted into it from an alien source, failing to recognize that the thoughts it is receiving are being transmitted from the disconnected right hemisphere, which is no longer part of the “self.” Similarly, impulses from the right hemispheric consciousness are now perceived by the patient’s verbal left hemisphere (which talks to the examining physician) as “external control.” Thus, I postulated that an abnormal corpus callosum structure would lead to a “dysconnection” (not “disconnection”) between the 2 hemispheres, and that anomalous dysconnectivity may generate both delusions and hallucinations. 6
Two decades later, my assumptions were vindicated when DTI was invented, enabling the measurement of WM integrity, including the corpus callosum, the largest body of WM in the brain. Table 1 defines the main parameters of WM integrity, anisotropy and diffusivity, which measure water flow inside WM fibers.

During the past 15 years, many studies have confirmed the presence of significant abnormalities in the myelinated fibers of the corpus callosum in schizophrenia, which can be considered a validation of my hypothesis that the corpus callosum becomes a dysfunctional channel of communications between the right and left hemisphere. Subsequently, DTI studies have reported a spectrum of WM pathologies in various other cerebral bundles and not only in schizophrenia, but also in other major psychiatric disorders (Table 27-19).
The pathophysiology of WM pathology in many psychiatric disorders may include neurodevelopmental aberrations (genetic, environmental, or both, which may alter WM structure and/or myelination), neuroinflammation, or oxidative stress (free radicals), which can cause disintegration of the vital myelin sheaths, leading to disruption of brain connectivity.6,7 Researchers now consider the brain’s WM network dysconnectivity as generating a variety of psychiatric symptoms, including psychosis, depression, mania, anxiety, autism, aggression, impulsivity, psychopathy, and cognitive impairments.
It is not surprising that WM repair has become a therapeutic target in psychiatry and neurology. Among the strategies being investigated are inhibiting the Nogo-A signaling pathways20 or modulating the Lingo-1 signaling.21 However, the most well-established myelin repair pathway is prolactin, a neuroprotective hormone with several beneficial effects on the brain (Table 322,23), including the proliferation of oligodendroglia, the main source of myelin (and the number of which declines in schizophrenia). Antipsychotics that increase prolactin have been shown to increase WM volume.24,25 It has even been proposed that a decline in oligodendrocytes and low myelin synthesis may be one of the neurobiologic pathologies in schizophrenia.26 One of the 24 neuroprotective properties of the second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) is the restoration of WM integrity.27 It’s worth noting that WM pathology has been found to be present at the onset of schizophrenia before treatment, and that SGAs have been reported to correct it.28

Continue to: In conclusion...
In conclusion, psychiatric disorders, usually referred to as “mental illnesses,” are unquestionably neurologic disorders. Similarly, all neurologic disorders are associated with psychiatric manifestations. WM pathology is only 1 of numerous structural brain abnormalities that have been documented across psychiatric disorders, which proves that psychiatry is a clinical neuroscience, just like neurology. I strongly advocate that psychiatry and neurology reunite into a single medical specialty. Both focus on disorders of brain structure and/or function, and these disorders also share much more than WM pathology.29
1. Sagarwala R and Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology is shared across multiple psychiatric brain disorders: Is abnormal diffusivity a transdiagnostic biomarker for psychopathology? Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry. 2020;2:00010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bionps.2019.100010
2. Pearce JMS; FRCP. The “split brain” and Roger Wolcott Sperry (1913-1994). Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175(4):217-220.
3. Nasrallah HA, Andreasen NC, Coffman JA, et al. A controlled magnetic resonance imaging study of corpus callosum thickness in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1986;21(3):274-282.
4. Nasrallah HA, McChesney CM. Psychopathology of corpus callosum tumors. Biol Psychiatry. 1981;16(7):663-669.
5. Nasrallah HA. The unintegrated right cerebral hemispheric consciousness as alien intruder: a possible mechanism for Schneiderian delusions in schizophrenia. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(3):273-282.
6. Friston K, Brown HR, Siemerkus J, et al. The dysconnection hypothesis (2016). Schizophr Res. 2016;176(2-3):83-94.
7. Najjar S, Pearlman DM. Neuroinflammation and white matter pathology in schizophrenia: systematic review. Schizophr Res. 2015;161(1):102-112.
8. Benedetti F, Bollettini I. Recent findings on the role of white matter pathology in bipolar disorder. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2014;22(6):338-341.
9. Zheng H, Bergamino M, Ford BN, et al; Tulsa 1000 Investigators. Replicable association between human cytomegalovirus infection and reduced white matter fractional anisotropy in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021;46(5):928-938.
10. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in drug-naïve OCD patients before and after pharmacotherapy. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(1):42-47.
11. Lee KS, Lee SH. White matter-based structural brain network of anxiety. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:61-70.
12. Swanson MR, Hazlett HC. White matter as a monitoring biomarker for neurodevelopmental disorder intervention studies. J Neurodev Disord. 2019;11(1):33.
13. Hampton WH, Hanik IM, Olson IR. Substance abuse and white matter: findings, limitations, and future of diffusion tensor imaging research. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:288-298.
14. Waller R, Dotterer HL, Murray L, et al. White-matter tract abnormalities and antisocial behavior: a systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies across development. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;14:201-215.
15. Wolf RC, Pujara MS, Motzkin JC, et al. Interpersonal traits of psychopathy linked to reduced integrity of the uncinate fasciculus. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(10):4202-4209.
16. Puzzo I, Seunarine K, Sully K, et al. Altered white-matter microstructure in conduct disorder is specifically associated with elevated callous-unemotional traits. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018;46(7):1451-1466.
17. Finger EC, Marsh A, Blair KS, et al. Impaired functional but preserved structural connectivity in limbic white matter tracts in youth with conduct disorder or oppositional defiant disorder plus psychopathic traits. Psychiatry Res. 2012;202(3):239-244.
18. Li C, Dong M, Womer FY, et al. Transdiagnostic time-varying dysconnectivity across major psychiatric disorders. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(4):1182-1196.
19. Khanbabaei M, Hughes E, Ellegood J, et al. Precocious myelination in a mouse model of autism. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):251.
20. Petratos S, Theotokis P, Kim MJ, et al. That’s a wrap! Molecular drivers governing neuronal nogo receptor-dependent myelin plasticity and integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:227
21. Fernandez-Enright F, Andrews JL, Newell KA, et al. Novel implications of Lingo-1 and its signaling partners in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2014;4(1):e348. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.121
22. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Stewart SB, et al. In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009;113(2-3):322-331.
23. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Amar CP, et al. Long acting injection versus oral risperidone in first-episode schizophrenia: differential impact on white matter myelination trajectory. Schizophr Res. 2011 Oct;132(1):35-41
24. Tishler TA, Bartzokis G, Lu PH, et al. Abnormal trajectory of intracortical myelination in schizophrenia implicates white matter in disease pathophysiology and the therapeutic mechanism of action of antipsychotics. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2018;3(5):454-462.
25. Ren Y, Wang H, Xiao L. Improving myelin/oligodendrocyte-related dysfunction: a new mechanism of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia? Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;16(3):691-700.
26. Dietz AG, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Glial cells in schizophrenia: a unified hypothesis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7(3):272-281.
27. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7
28. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. (In press.) The effect of antipsychotic medications on white matter integrity in first-episode drug naïve patients with psychosis. Asian Journal of Psychiatry.
29. Nasrallah HA. Let’s tear down the silos and reunify psychiatry and neurology. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(8):9-10.
1. Sagarwala R and Nasrallah HA. White matter pathology is shared across multiple psychiatric brain disorders: Is abnormal diffusivity a transdiagnostic biomarker for psychopathology? Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry. 2020;2:00010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bionps.2019.100010
2. Pearce JMS; FRCP. The “split brain” and Roger Wolcott Sperry (1913-1994). Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175(4):217-220.
3. Nasrallah HA, Andreasen NC, Coffman JA, et al. A controlled magnetic resonance imaging study of corpus callosum thickness in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1986;21(3):274-282.
4. Nasrallah HA, McChesney CM. Psychopathology of corpus callosum tumors. Biol Psychiatry. 1981;16(7):663-669.
5. Nasrallah HA. The unintegrated right cerebral hemispheric consciousness as alien intruder: a possible mechanism for Schneiderian delusions in schizophrenia. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(3):273-282.
6. Friston K, Brown HR, Siemerkus J, et al. The dysconnection hypothesis (2016). Schizophr Res. 2016;176(2-3):83-94.
7. Najjar S, Pearlman DM. Neuroinflammation and white matter pathology in schizophrenia: systematic review. Schizophr Res. 2015;161(1):102-112.
8. Benedetti F, Bollettini I. Recent findings on the role of white matter pathology in bipolar disorder. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2014;22(6):338-341.
9. Zheng H, Bergamino M, Ford BN, et al; Tulsa 1000 Investigators. Replicable association between human cytomegalovirus infection and reduced white matter fractional anisotropy in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021;46(5):928-938.
10. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in drug-naïve OCD patients before and after pharmacotherapy. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020;32(1):42-47.
11. Lee KS, Lee SH. White matter-based structural brain network of anxiety. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:61-70.
12. Swanson MR, Hazlett HC. White matter as a monitoring biomarker for neurodevelopmental disorder intervention studies. J Neurodev Disord. 2019;11(1):33.
13. Hampton WH, Hanik IM, Olson IR. Substance abuse and white matter: findings, limitations, and future of diffusion tensor imaging research. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;197:288-298.
14. Waller R, Dotterer HL, Murray L, et al. White-matter tract abnormalities and antisocial behavior: a systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies across development. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;14:201-215.
15. Wolf RC, Pujara MS, Motzkin JC, et al. Interpersonal traits of psychopathy linked to reduced integrity of the uncinate fasciculus. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(10):4202-4209.
16. Puzzo I, Seunarine K, Sully K, et al. Altered white-matter microstructure in conduct disorder is specifically associated with elevated callous-unemotional traits. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018;46(7):1451-1466.
17. Finger EC, Marsh A, Blair KS, et al. Impaired functional but preserved structural connectivity in limbic white matter tracts in youth with conduct disorder or oppositional defiant disorder plus psychopathic traits. Psychiatry Res. 2012;202(3):239-244.
18. Li C, Dong M, Womer FY, et al. Transdiagnostic time-varying dysconnectivity across major psychiatric disorders. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(4):1182-1196.
19. Khanbabaei M, Hughes E, Ellegood J, et al. Precocious myelination in a mouse model of autism. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):251.
20. Petratos S, Theotokis P, Kim MJ, et al. That’s a wrap! Molecular drivers governing neuronal nogo receptor-dependent myelin plasticity and integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:227
21. Fernandez-Enright F, Andrews JL, Newell KA, et al. Novel implications of Lingo-1 and its signaling partners in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2014;4(1):e348. doi: 10.1038/tp.2013.121
22. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Stewart SB, et al. In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009;113(2-3):322-331.
23. Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Amar CP, et al. Long acting injection versus oral risperidone in first-episode schizophrenia: differential impact on white matter myelination trajectory. Schizophr Res. 2011 Oct;132(1):35-41
24. Tishler TA, Bartzokis G, Lu PH, et al. Abnormal trajectory of intracortical myelination in schizophrenia implicates white matter in disease pathophysiology and the therapeutic mechanism of action of antipsychotics. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2018;3(5):454-462.
25. Ren Y, Wang H, Xiao L. Improving myelin/oligodendrocyte-related dysfunction: a new mechanism of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia? Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013;16(3):691-700.
26. Dietz AG, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M. Glial cells in schizophrenia: a unified hypothesis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020;7(3):272-281.
27. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7
28. Sagarwala R, Nasrallah HA. (In press.) The effect of antipsychotic medications on white matter integrity in first-episode drug naïve patients with psychosis. Asian Journal of Psychiatry.
29. Nasrallah HA. Let’s tear down the silos and reunify psychiatry and neurology. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(8):9-10.
Daily cup of coffee cuts type 2 diabetes risk by about 5%
Drinking one cup of coffee each day lowered individual risk for developing type 2 diabetes 4%-6%, according to data from a pair of large, population-based cohorts.
Coffee had previously been associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, said Carolina Ochoa-Rosales, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. However, the potential impact of coffee consumption on the subclinical inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes has not been well studied, she said.
In a study presented at the American Heart Association’s virtual Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales and colleagues reviewed information for men and women who were enrolled in the UK Biobank Study (145,368) and in the Rotterdam Study (7,172).
Coffee consumption assessment was based on interviews, while diabetes incidence was based on fasting glucose measures, general medical records, and pharmacy records of type 2 diabetes drugs.
The researchers used a Cox proportional hazard model to determine the association between coffee and type 2 diabetes, controlling for sociodemographic, health, and lifestyle factors.
Overall, an increase of one coffee cup a day was associated with a 4%-6% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes (hazard ratios, 0.94 for the Rotterdam Study and 0.96 for the UK Biobank study). The effects appeared strongest in drinkers of filtered or ground coffee vs. those who reported drinking mainly instant coffee, she added.
Also, an increase in coffee consumption of one cup a day was linked to lower levels of longitudinally assessed homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), with lower C reactive protein (CRP) and higher levels of adiponectin, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said.
Levels of CRP and adiponectin may contribute to the association between coffee consumption and diabetes risk, she said. In a mediation analysis, CRP levels mediated roughly 3%-9% of the effect of coffee on type 2 diabetes risk; some effect was observed for adiponectin, but did not reach statistical significance, she added.
The study findings were limited by the lack of control for all potential confounding variables, and the results must be interpreted cautiously, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that coffee’s beneficial effects on lowering type 2 diabetes risk are partially mediated by improvements in systemic inflammation, she concluded. “Other mediators that we did not investigate may also play a role,” she said.
Large cohort adds credibility
Although the associations between coffee and type 2 diabetes have been previously reported, “this study offers important findings due to the carefully standardized analyses on these two major data sources,” Linda Van Horn, PhD, RD, said in an interview.
But what makes this study different is that “these investigators hypothesized that this association could be due to an anti-inflammatory benefit,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is that drinking moderate amounts of filtered coffee offers a potentially reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Van Horn, of Northwestern University, Chicago. However, additional research is needed to account for the total amount of coffee per day, and whether additions such as cream or sugar or other additives make a difference in outcomes, she added.
“Also, the risk vs. benefit of drinking coffee over the life course, including childhood, pregnancy, and older age, with possible adverse drug-nutrient interactions, remain unexplored,” she noted.
Dr. Ochoa-Rosales disclosed study funding from the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee but had no other financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Van Horn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Drinking one cup of coffee each day lowered individual risk for developing type 2 diabetes 4%-6%, according to data from a pair of large, population-based cohorts.
Coffee had previously been associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, said Carolina Ochoa-Rosales, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. However, the potential impact of coffee consumption on the subclinical inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes has not been well studied, she said.
In a study presented at the American Heart Association’s virtual Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales and colleagues reviewed information for men and women who were enrolled in the UK Biobank Study (145,368) and in the Rotterdam Study (7,172).
Coffee consumption assessment was based on interviews, while diabetes incidence was based on fasting glucose measures, general medical records, and pharmacy records of type 2 diabetes drugs.
The researchers used a Cox proportional hazard model to determine the association between coffee and type 2 diabetes, controlling for sociodemographic, health, and lifestyle factors.
Overall, an increase of one coffee cup a day was associated with a 4%-6% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes (hazard ratios, 0.94 for the Rotterdam Study and 0.96 for the UK Biobank study). The effects appeared strongest in drinkers of filtered or ground coffee vs. those who reported drinking mainly instant coffee, she added.
Also, an increase in coffee consumption of one cup a day was linked to lower levels of longitudinally assessed homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), with lower C reactive protein (CRP) and higher levels of adiponectin, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said.
Levels of CRP and adiponectin may contribute to the association between coffee consumption and diabetes risk, she said. In a mediation analysis, CRP levels mediated roughly 3%-9% of the effect of coffee on type 2 diabetes risk; some effect was observed for adiponectin, but did not reach statistical significance, she added.
The study findings were limited by the lack of control for all potential confounding variables, and the results must be interpreted cautiously, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that coffee’s beneficial effects on lowering type 2 diabetes risk are partially mediated by improvements in systemic inflammation, she concluded. “Other mediators that we did not investigate may also play a role,” she said.
Large cohort adds credibility
Although the associations between coffee and type 2 diabetes have been previously reported, “this study offers important findings due to the carefully standardized analyses on these two major data sources,” Linda Van Horn, PhD, RD, said in an interview.
But what makes this study different is that “these investigators hypothesized that this association could be due to an anti-inflammatory benefit,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is that drinking moderate amounts of filtered coffee offers a potentially reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Van Horn, of Northwestern University, Chicago. However, additional research is needed to account for the total amount of coffee per day, and whether additions such as cream or sugar or other additives make a difference in outcomes, she added.
“Also, the risk vs. benefit of drinking coffee over the life course, including childhood, pregnancy, and older age, with possible adverse drug-nutrient interactions, remain unexplored,” she noted.
Dr. Ochoa-Rosales disclosed study funding from the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee but had no other financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Van Horn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Drinking one cup of coffee each day lowered individual risk for developing type 2 diabetes 4%-6%, according to data from a pair of large, population-based cohorts.
Coffee had previously been associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, said Carolina Ochoa-Rosales, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. However, the potential impact of coffee consumption on the subclinical inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes has not been well studied, she said.
In a study presented at the American Heart Association’s virtual Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle & Cardiometabolic Health meeting, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales and colleagues reviewed information for men and women who were enrolled in the UK Biobank Study (145,368) and in the Rotterdam Study (7,172).
Coffee consumption assessment was based on interviews, while diabetes incidence was based on fasting glucose measures, general medical records, and pharmacy records of type 2 diabetes drugs.
The researchers used a Cox proportional hazard model to determine the association between coffee and type 2 diabetes, controlling for sociodemographic, health, and lifestyle factors.
Overall, an increase of one coffee cup a day was associated with a 4%-6% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes (hazard ratios, 0.94 for the Rotterdam Study and 0.96 for the UK Biobank study). The effects appeared strongest in drinkers of filtered or ground coffee vs. those who reported drinking mainly instant coffee, she added.
Also, an increase in coffee consumption of one cup a day was linked to lower levels of longitudinally assessed homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), with lower C reactive protein (CRP) and higher levels of adiponectin, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said.
Levels of CRP and adiponectin may contribute to the association between coffee consumption and diabetes risk, she said. In a mediation analysis, CRP levels mediated roughly 3%-9% of the effect of coffee on type 2 diabetes risk; some effect was observed for adiponectin, but did not reach statistical significance, she added.
The study findings were limited by the lack of control for all potential confounding variables, and the results must be interpreted cautiously, Dr. Ochoa-Rosales said. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and suggest that coffee’s beneficial effects on lowering type 2 diabetes risk are partially mediated by improvements in systemic inflammation, she concluded. “Other mediators that we did not investigate may also play a role,” she said.
Large cohort adds credibility
Although the associations between coffee and type 2 diabetes have been previously reported, “this study offers important findings due to the carefully standardized analyses on these two major data sources,” Linda Van Horn, PhD, RD, said in an interview.
But what makes this study different is that “these investigators hypothesized that this association could be due to an anti-inflammatory benefit,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is that drinking moderate amounts of filtered coffee offers a potentially reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Van Horn, of Northwestern University, Chicago. However, additional research is needed to account for the total amount of coffee per day, and whether additions such as cream or sugar or other additives make a difference in outcomes, she added.
“Also, the risk vs. benefit of drinking coffee over the life course, including childhood, pregnancy, and older age, with possible adverse drug-nutrient interactions, remain unexplored,” she noted.
Dr. Ochoa-Rosales disclosed study funding from the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee but had no other financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Van Horn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM EPI/LIFESTYLE 2021
USPSTF final recommendation on CRC screening: 45 is the new 50
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) should now begin at the age of 45 and not 50 for average-risk individuals in the United States, notes the final recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendation finalizes draft guidelines issued in October 2020 and mandates insurance coverage to ensure equal access to CRC screening regardless of a patient’s insurance status.
The USPSTF’s final recommendations also now align with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of CRC screening to 45 years in 2018.
“New statistics project an alarming rise in the incidence of young-onset colorectal cancer, projected to be the leading cause of cancer death in patients aged 20-49 by 2040,” commented Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, director, Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and lead author of a JAMA editorial about the new guideline.
“We must take bold steps to translate the lowered age of beginning screening into meaningful decreases in CRC incidence and mortality,” she emphasized.
The USPSTF recommendations and substantial evidence supporting them were published online May 18, 2021, in JAMA.
Risk factors for CRC
As the USPSTF authors noted, age is one of the most important risk factors for CRC, with nearly 94% of all new cases of CRC occurring in adults 45 years of age and older. Justification for the lower age of CRC screening initiation was based on simulation models showing that initiation of screening at the age of 45 was associated with an estimated additional 22-27 life-years gained, compared with starting at the age of 50.
The USPSTF continues to recommend screening for CRC in all adults aged between 50 and 75 years, lowering the age for screening to 45 years in recognition of the fact that, in 2020, 11% of colon cancers and 15% of rectal cancers occurred in patients under the age of 50.
The USPSTF also continues to conclude that there is a “small net benefit” of screening for CRC in adults aged between 76 and 85 years who have been previously screened.
However, the decision to screen patients in this age group should be based on individual risk factors for CRC, a patient’s overall health status, and personal preference. Perhaps self-evidently, adults in this age group who have never been screened for CRC are more likely to benefit from CRC screening than those who have been previously screened.
Similar to the previous guidelines released in 2016, the updated USPSTF recommendations continue to offer a menu of screening strategies, although the frequency of screening for each of the screening strategies varies. Recommended screening strategies include:
- High-sensitivity guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year
- Stool DNA-FIT every 1-3 years
- CT colonography every 5 years
- every 5 years
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 10 years plus annual FIT
- screening every 10 years
“Based on the evidence, there are many tests available that can effectively screen for colorectal cancer and the right test is the one that gets done,” USPSTF member Martha Kubik, PhD, RN, said in a statement.
“To encourage screening and help patients select the best test for them, we urge primary care clinicians to talk about the pros and cons of the various recommended options with their patients,” she added.
An accompanying review of the effectiveness, accuracy, and potential harms of CRC screening methods underscores how different screening tests have different levels of evidence demonstrating their ability to detect cancer, precursor lesions, or both, as well as their ability to reduce mortality from cancer.
Eligible patients
Currently, fewer than 70% of eligible patients in the United States undergo CRC screening, Dr. Ng pointed out in the editorial. In addition, CRC disproportionately affects African American patients, who are about 20% more likely to get CRC and about 40% more likely to die from it, compared with other patient groups. Modeling studies published along with the USPSTF recommendations showed equal benefit for screening regardless of race and gender, underscoring the importance of screening adherence, especially in patient populations disproportionately affected by CRC.
“Far too many people in the U.S. are not receiving this lifesaving preventive service,” USPSTF vice chair Michael Barry, MD, said in a statement.
“We hope that this new recommendation to screen people ages 45-49, coupled with our long-standing recommendation to screen people 50-75, will prevent more people from dying from colorectal cancer,” he added.
Dr. Ng echoed this sentiment in her editorial: “The USPSTF recommendation for beginning colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults at age 45 years has moved the field one step forward and indicates that ‘45 is the new 50,’ ” she observed.
“Lowering the recommended age to initiate screening will make colorectal cancer screening available to millions more people in the United States and, hopefully, many more lives will be saved by catching colorectal cancer earlier as well as by preventing colorectal cancer,” Dr. Ng affirmed.
“AGA fully supports the decision of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to reduce the age at which to initiate screening among individuals at average risk for development of colorectal cancer to 45 years,” said John Inadomi, MD, AGAF, AGA Institute President. “This decision harmonizes the recommendations between the major U.S. screening guidelines including the American Cancer Society and American College of Physicians. Furthermore, we expect the U.S. Multi-Society Task force, of which the AGA is a member, to also reduce the age at which we recommend initiation screening to 45 years. We expect this important change to save lives and improve the health of the U.S. population.” Read more at https://gastro.org/news/aga-gi-societies-support-lowering-crc-screening-age/.
All members of the USPSTF received travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings.
Dr. Ng reported receiving nonfinancial support from Pharmavite as well as grants from the Evergrande Group, Janssen, Revolution Medicines, Genentech, and Gilead Sciences. She has also reported receiving personal fees from Seattle Genetics, Array Biopharma, BiomX, and X-Biotix Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) should now begin at the age of 45 and not 50 for average-risk individuals in the United States, notes the final recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendation finalizes draft guidelines issued in October 2020 and mandates insurance coverage to ensure equal access to CRC screening regardless of a patient’s insurance status.
The USPSTF’s final recommendations also now align with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of CRC screening to 45 years in 2018.
“New statistics project an alarming rise in the incidence of young-onset colorectal cancer, projected to be the leading cause of cancer death in patients aged 20-49 by 2040,” commented Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, director, Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and lead author of a JAMA editorial about the new guideline.
“We must take bold steps to translate the lowered age of beginning screening into meaningful decreases in CRC incidence and mortality,” she emphasized.
The USPSTF recommendations and substantial evidence supporting them were published online May 18, 2021, in JAMA.
Risk factors for CRC
As the USPSTF authors noted, age is one of the most important risk factors for CRC, with nearly 94% of all new cases of CRC occurring in adults 45 years of age and older. Justification for the lower age of CRC screening initiation was based on simulation models showing that initiation of screening at the age of 45 was associated with an estimated additional 22-27 life-years gained, compared with starting at the age of 50.
The USPSTF continues to recommend screening for CRC in all adults aged between 50 and 75 years, lowering the age for screening to 45 years in recognition of the fact that, in 2020, 11% of colon cancers and 15% of rectal cancers occurred in patients under the age of 50.
The USPSTF also continues to conclude that there is a “small net benefit” of screening for CRC in adults aged between 76 and 85 years who have been previously screened.
However, the decision to screen patients in this age group should be based on individual risk factors for CRC, a patient’s overall health status, and personal preference. Perhaps self-evidently, adults in this age group who have never been screened for CRC are more likely to benefit from CRC screening than those who have been previously screened.
Similar to the previous guidelines released in 2016, the updated USPSTF recommendations continue to offer a menu of screening strategies, although the frequency of screening for each of the screening strategies varies. Recommended screening strategies include:
- High-sensitivity guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year
- Stool DNA-FIT every 1-3 years
- CT colonography every 5 years
- every 5 years
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 10 years plus annual FIT
- screening every 10 years
“Based on the evidence, there are many tests available that can effectively screen for colorectal cancer and the right test is the one that gets done,” USPSTF member Martha Kubik, PhD, RN, said in a statement.
“To encourage screening and help patients select the best test for them, we urge primary care clinicians to talk about the pros and cons of the various recommended options with their patients,” she added.
An accompanying review of the effectiveness, accuracy, and potential harms of CRC screening methods underscores how different screening tests have different levels of evidence demonstrating their ability to detect cancer, precursor lesions, or both, as well as their ability to reduce mortality from cancer.
Eligible patients
Currently, fewer than 70% of eligible patients in the United States undergo CRC screening, Dr. Ng pointed out in the editorial. In addition, CRC disproportionately affects African American patients, who are about 20% more likely to get CRC and about 40% more likely to die from it, compared with other patient groups. Modeling studies published along with the USPSTF recommendations showed equal benefit for screening regardless of race and gender, underscoring the importance of screening adherence, especially in patient populations disproportionately affected by CRC.
“Far too many people in the U.S. are not receiving this lifesaving preventive service,” USPSTF vice chair Michael Barry, MD, said in a statement.
“We hope that this new recommendation to screen people ages 45-49, coupled with our long-standing recommendation to screen people 50-75, will prevent more people from dying from colorectal cancer,” he added.
Dr. Ng echoed this sentiment in her editorial: “The USPSTF recommendation for beginning colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults at age 45 years has moved the field one step forward and indicates that ‘45 is the new 50,’ ” she observed.
“Lowering the recommended age to initiate screening will make colorectal cancer screening available to millions more people in the United States and, hopefully, many more lives will be saved by catching colorectal cancer earlier as well as by preventing colorectal cancer,” Dr. Ng affirmed.
“AGA fully supports the decision of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to reduce the age at which to initiate screening among individuals at average risk for development of colorectal cancer to 45 years,” said John Inadomi, MD, AGAF, AGA Institute President. “This decision harmonizes the recommendations between the major U.S. screening guidelines including the American Cancer Society and American College of Physicians. Furthermore, we expect the U.S. Multi-Society Task force, of which the AGA is a member, to also reduce the age at which we recommend initiation screening to 45 years. We expect this important change to save lives and improve the health of the U.S. population.” Read more at https://gastro.org/news/aga-gi-societies-support-lowering-crc-screening-age/.
All members of the USPSTF received travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings.
Dr. Ng reported receiving nonfinancial support from Pharmavite as well as grants from the Evergrande Group, Janssen, Revolution Medicines, Genentech, and Gilead Sciences. She has also reported receiving personal fees from Seattle Genetics, Array Biopharma, BiomX, and X-Biotix Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) should now begin at the age of 45 and not 50 for average-risk individuals in the United States, notes the final recommendation from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.
The recommendation finalizes draft guidelines issued in October 2020 and mandates insurance coverage to ensure equal access to CRC screening regardless of a patient’s insurance status.
The USPSTF’s final recommendations also now align with those of the American Cancer Society, which lowered the age for initiation of CRC screening to 45 years in 2018.
“New statistics project an alarming rise in the incidence of young-onset colorectal cancer, projected to be the leading cause of cancer death in patients aged 20-49 by 2040,” commented Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, director, Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, and lead author of a JAMA editorial about the new guideline.
“We must take bold steps to translate the lowered age of beginning screening into meaningful decreases in CRC incidence and mortality,” she emphasized.
The USPSTF recommendations and substantial evidence supporting them were published online May 18, 2021, in JAMA.
Risk factors for CRC
As the USPSTF authors noted, age is one of the most important risk factors for CRC, with nearly 94% of all new cases of CRC occurring in adults 45 years of age and older. Justification for the lower age of CRC screening initiation was based on simulation models showing that initiation of screening at the age of 45 was associated with an estimated additional 22-27 life-years gained, compared with starting at the age of 50.
The USPSTF continues to recommend screening for CRC in all adults aged between 50 and 75 years, lowering the age for screening to 45 years in recognition of the fact that, in 2020, 11% of colon cancers and 15% of rectal cancers occurred in patients under the age of 50.
The USPSTF also continues to conclude that there is a “small net benefit” of screening for CRC in adults aged between 76 and 85 years who have been previously screened.
However, the decision to screen patients in this age group should be based on individual risk factors for CRC, a patient’s overall health status, and personal preference. Perhaps self-evidently, adults in this age group who have never been screened for CRC are more likely to benefit from CRC screening than those who have been previously screened.
Similar to the previous guidelines released in 2016, the updated USPSTF recommendations continue to offer a menu of screening strategies, although the frequency of screening for each of the screening strategies varies. Recommended screening strategies include:
- High-sensitivity guaiac fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year
- Stool DNA-FIT every 1-3 years
- CT colonography every 5 years
- every 5 years
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 10 years plus annual FIT
- screening every 10 years
“Based on the evidence, there are many tests available that can effectively screen for colorectal cancer and the right test is the one that gets done,” USPSTF member Martha Kubik, PhD, RN, said in a statement.
“To encourage screening and help patients select the best test for them, we urge primary care clinicians to talk about the pros and cons of the various recommended options with their patients,” she added.
An accompanying review of the effectiveness, accuracy, and potential harms of CRC screening methods underscores how different screening tests have different levels of evidence demonstrating their ability to detect cancer, precursor lesions, or both, as well as their ability to reduce mortality from cancer.
Eligible patients
Currently, fewer than 70% of eligible patients in the United States undergo CRC screening, Dr. Ng pointed out in the editorial. In addition, CRC disproportionately affects African American patients, who are about 20% more likely to get CRC and about 40% more likely to die from it, compared with other patient groups. Modeling studies published along with the USPSTF recommendations showed equal benefit for screening regardless of race and gender, underscoring the importance of screening adherence, especially in patient populations disproportionately affected by CRC.
“Far too many people in the U.S. are not receiving this lifesaving preventive service,” USPSTF vice chair Michael Barry, MD, said in a statement.
“We hope that this new recommendation to screen people ages 45-49, coupled with our long-standing recommendation to screen people 50-75, will prevent more people from dying from colorectal cancer,” he added.
Dr. Ng echoed this sentiment in her editorial: “The USPSTF recommendation for beginning colorectal cancer screening for average-risk adults at age 45 years has moved the field one step forward and indicates that ‘45 is the new 50,’ ” she observed.
“Lowering the recommended age to initiate screening will make colorectal cancer screening available to millions more people in the United States and, hopefully, many more lives will be saved by catching colorectal cancer earlier as well as by preventing colorectal cancer,” Dr. Ng affirmed.
“AGA fully supports the decision of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to reduce the age at which to initiate screening among individuals at average risk for development of colorectal cancer to 45 years,” said John Inadomi, MD, AGAF, AGA Institute President. “This decision harmonizes the recommendations between the major U.S. screening guidelines including the American Cancer Society and American College of Physicians. Furthermore, we expect the U.S. Multi-Society Task force, of which the AGA is a member, to also reduce the age at which we recommend initiation screening to 45 years. We expect this important change to save lives and improve the health of the U.S. population.” Read more at https://gastro.org/news/aga-gi-societies-support-lowering-crc-screening-age/.
All members of the USPSTF received travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings.
Dr. Ng reported receiving nonfinancial support from Pharmavite as well as grants from the Evergrande Group, Janssen, Revolution Medicines, Genentech, and Gilead Sciences. She has also reported receiving personal fees from Seattle Genetics, Array Biopharma, BiomX, and X-Biotix Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
OSA: Heart rate change may signal CPAP benefit
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ATS 2021
Liver, gastric cancer disparities consistent across race and ethnicity
While colorectal cancer may be the most common and deadly gastrointestinal malignancy, liver and gastric cancers account for some of the most consistent racial and ethnic disparities, a recent retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of U.S. data suggested.
Liver and gastric cancer incidence and mortality were significantly higher for all racial and ethnic minority groups in the study, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to the analysis. Notably, however, non-Hispanic Blacks represented the only group to also have elevated incidence and mortality for pancreatic and colorectal, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to investigator Aileen Bui, MD, with the University of California, Los Angeles Health.
These study results highlights the need to address modifiable cancer risk factors and overcome barriers to cancer prevention and care in medically underserved minority populations, Dr. Bui said in a virtual presentation of the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“While we cannot infer causation or determine risk factors for certain malignancies from the results of our study, there’s little data to support a strong role of biological or genetic differences between racial and ethnic groups to account for the observed disparities in incidence and mortality for GI cancers,” she said in her presentation.
Setting out to explore disparities
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality remain on the rise, despite significant progress in some areas, including colorectal cancer screening and the introduction of effective treatments for hepatitis C virus, Dr. Bui said.
Incidence and mortality from gastrointestinal cancers are set to increase by 34% and 43%, respectively, by the year 2040, and will remain a significant contributor to cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, according to the researcher.
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality are known to vary by race and ethnicity, so Dr. Bui and colleagues sought to assess the extent of racial and ethnic disparities for individual gastrointestinal cancer types. They identified more than 140,000 incident cases of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, esophageal, and gastric cancers in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 2013 to 2017. They also incorporated nearly 185,000 mortality cases for those same types of malignancy from National Center for Health Statistics data from the years 2014 to 2018.
Breaking down the numbers
Overall, the incidence of colorectal cancer was highest, at 36.9 (cases per 100,000), followed by pancreatic cancer at 11.0, gastric cancer at 7.1, esophageal cancer at 4.1, and liver cancer at 3.0, Dr. Bui’s data show. The mortality rate was again highest for colorectal cancer, followed by pancreatic, liver, esophageal and gastric cancer.
When compared with non-Hispanic Whites, all racial ethnic minority groups had significantly higher incidence of both liver and gastric cancers, according to Dr. Bui.
The researchers calculated rate ratios for gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality, with ratios above 1 indicating a higher incidence relative to non-Hispanic Whites.
Among Hispanics, the incidence rate ratios were 1.83 for both liver and gastric cancers, according to the analysis. Similarly, non-Hispanic Asian Pacific Islanders had IRRs of 2.00 for liver cancer and 1.9 for gastric cancer. Non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives had IRRs of 2.09 for liver cancer and 1.51 for gastric cancer.
By contrast, non-Hispanic Blacks had significantly higher IRRs not only for liver and gastric cancers, at 1.64 and 1.8, respectively, but also for pancreatic cancer, at 1.18, and colorectal cancer at 1.17, Dr. Bui said.
Similar trends were seen in mortality in the presented data, with all racial and ethnic groups exhibiting significantly increased mortality RRs for liver and gastric cancer, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, but with non-Hispanic Blacks showing significantly increases in RRs for liver (1.66), gastric (2.36), pancreatic (1.22), and colorectal (1.36) cancers.
Esophageal cancer rates of incidence and mortality were both lower in racial and ethnic minority groups, compared with non-Hispanic whites, according to Dr. Bui.
Increasing screening and surveillance
While the esophageal cancer data is encouraging, these data otherwise clearly highlight the need to step up efforts to help level gastrointestinal cancer disparities, according to Byron Cryer, MD, professor of internal medicine and associate dean for the office of faculty diversity and development at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Clearly more work needs to be done for the other four cancers,” Dr. Cryer said in an interview.
Screening and surveillance may be key to addressing those disparities, not only for colorectal cancer, but for the liver and gastric cancers for which disparities were seen throughout racial and ethnic groups in this study.
“We know that if we get rid of hepatitis C virus early, you can prevent those downstream complications such as cancer,” Dr. Cryer said. “It’s same thing with the gastric cancer – if we get rid of Helicobacter pylori early on in the infection, we decrease the burden of cancer down downstream years later.”
Dr. Bui provided no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Cryer has nothing to disclose.
While colorectal cancer may be the most common and deadly gastrointestinal malignancy, liver and gastric cancers account for some of the most consistent racial and ethnic disparities, a recent retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of U.S. data suggested.
Liver and gastric cancer incidence and mortality were significantly higher for all racial and ethnic minority groups in the study, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to the analysis. Notably, however, non-Hispanic Blacks represented the only group to also have elevated incidence and mortality for pancreatic and colorectal, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to investigator Aileen Bui, MD, with the University of California, Los Angeles Health.
These study results highlights the need to address modifiable cancer risk factors and overcome barriers to cancer prevention and care in medically underserved minority populations, Dr. Bui said in a virtual presentation of the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“While we cannot infer causation or determine risk factors for certain malignancies from the results of our study, there’s little data to support a strong role of biological or genetic differences between racial and ethnic groups to account for the observed disparities in incidence and mortality for GI cancers,” she said in her presentation.
Setting out to explore disparities
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality remain on the rise, despite significant progress in some areas, including colorectal cancer screening and the introduction of effective treatments for hepatitis C virus, Dr. Bui said.
Incidence and mortality from gastrointestinal cancers are set to increase by 34% and 43%, respectively, by the year 2040, and will remain a significant contributor to cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, according to the researcher.
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality are known to vary by race and ethnicity, so Dr. Bui and colleagues sought to assess the extent of racial and ethnic disparities for individual gastrointestinal cancer types. They identified more than 140,000 incident cases of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, esophageal, and gastric cancers in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 2013 to 2017. They also incorporated nearly 185,000 mortality cases for those same types of malignancy from National Center for Health Statistics data from the years 2014 to 2018.
Breaking down the numbers
Overall, the incidence of colorectal cancer was highest, at 36.9 (cases per 100,000), followed by pancreatic cancer at 11.0, gastric cancer at 7.1, esophageal cancer at 4.1, and liver cancer at 3.0, Dr. Bui’s data show. The mortality rate was again highest for colorectal cancer, followed by pancreatic, liver, esophageal and gastric cancer.
When compared with non-Hispanic Whites, all racial ethnic minority groups had significantly higher incidence of both liver and gastric cancers, according to Dr. Bui.
The researchers calculated rate ratios for gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality, with ratios above 1 indicating a higher incidence relative to non-Hispanic Whites.
Among Hispanics, the incidence rate ratios were 1.83 for both liver and gastric cancers, according to the analysis. Similarly, non-Hispanic Asian Pacific Islanders had IRRs of 2.00 for liver cancer and 1.9 for gastric cancer. Non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives had IRRs of 2.09 for liver cancer and 1.51 for gastric cancer.
By contrast, non-Hispanic Blacks had significantly higher IRRs not only for liver and gastric cancers, at 1.64 and 1.8, respectively, but also for pancreatic cancer, at 1.18, and colorectal cancer at 1.17, Dr. Bui said.
Similar trends were seen in mortality in the presented data, with all racial and ethnic groups exhibiting significantly increased mortality RRs for liver and gastric cancer, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, but with non-Hispanic Blacks showing significantly increases in RRs for liver (1.66), gastric (2.36), pancreatic (1.22), and colorectal (1.36) cancers.
Esophageal cancer rates of incidence and mortality were both lower in racial and ethnic minority groups, compared with non-Hispanic whites, according to Dr. Bui.
Increasing screening and surveillance
While the esophageal cancer data is encouraging, these data otherwise clearly highlight the need to step up efforts to help level gastrointestinal cancer disparities, according to Byron Cryer, MD, professor of internal medicine and associate dean for the office of faculty diversity and development at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Clearly more work needs to be done for the other four cancers,” Dr. Cryer said in an interview.
Screening and surveillance may be key to addressing those disparities, not only for colorectal cancer, but for the liver and gastric cancers for which disparities were seen throughout racial and ethnic groups in this study.
“We know that if we get rid of hepatitis C virus early, you can prevent those downstream complications such as cancer,” Dr. Cryer said. “It’s same thing with the gastric cancer – if we get rid of Helicobacter pylori early on in the infection, we decrease the burden of cancer down downstream years later.”
Dr. Bui provided no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Cryer has nothing to disclose.
While colorectal cancer may be the most common and deadly gastrointestinal malignancy, liver and gastric cancers account for some of the most consistent racial and ethnic disparities, a recent retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of U.S. data suggested.
Liver and gastric cancer incidence and mortality were significantly higher for all racial and ethnic minority groups in the study, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to the analysis. Notably, however, non-Hispanic Blacks represented the only group to also have elevated incidence and mortality for pancreatic and colorectal, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, according to investigator Aileen Bui, MD, with the University of California, Los Angeles Health.
These study results highlights the need to address modifiable cancer risk factors and overcome barriers to cancer prevention and care in medically underserved minority populations, Dr. Bui said in a virtual presentation of the results at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
“While we cannot infer causation or determine risk factors for certain malignancies from the results of our study, there’s little data to support a strong role of biological or genetic differences between racial and ethnic groups to account for the observed disparities in incidence and mortality for GI cancers,” she said in her presentation.
Setting out to explore disparities
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality remain on the rise, despite significant progress in some areas, including colorectal cancer screening and the introduction of effective treatments for hepatitis C virus, Dr. Bui said.
Incidence and mortality from gastrointestinal cancers are set to increase by 34% and 43%, respectively, by the year 2040, and will remain a significant contributor to cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, according to the researcher.
Gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality are known to vary by race and ethnicity, so Dr. Bui and colleagues sought to assess the extent of racial and ethnic disparities for individual gastrointestinal cancer types. They identified more than 140,000 incident cases of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, esophageal, and gastric cancers in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 2013 to 2017. They also incorporated nearly 185,000 mortality cases for those same types of malignancy from National Center for Health Statistics data from the years 2014 to 2018.
Breaking down the numbers
Overall, the incidence of colorectal cancer was highest, at 36.9 (cases per 100,000), followed by pancreatic cancer at 11.0, gastric cancer at 7.1, esophageal cancer at 4.1, and liver cancer at 3.0, Dr. Bui’s data show. The mortality rate was again highest for colorectal cancer, followed by pancreatic, liver, esophageal and gastric cancer.
When compared with non-Hispanic Whites, all racial ethnic minority groups had significantly higher incidence of both liver and gastric cancers, according to Dr. Bui.
The researchers calculated rate ratios for gastrointestinal cancer incidence and mortality, with ratios above 1 indicating a higher incidence relative to non-Hispanic Whites.
Among Hispanics, the incidence rate ratios were 1.83 for both liver and gastric cancers, according to the analysis. Similarly, non-Hispanic Asian Pacific Islanders had IRRs of 2.00 for liver cancer and 1.9 for gastric cancer. Non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives had IRRs of 2.09 for liver cancer and 1.51 for gastric cancer.
By contrast, non-Hispanic Blacks had significantly higher IRRs not only for liver and gastric cancers, at 1.64 and 1.8, respectively, but also for pancreatic cancer, at 1.18, and colorectal cancer at 1.17, Dr. Bui said.
Similar trends were seen in mortality in the presented data, with all racial and ethnic groups exhibiting significantly increased mortality RRs for liver and gastric cancer, compared with non-Hispanic Whites, but with non-Hispanic Blacks showing significantly increases in RRs for liver (1.66), gastric (2.36), pancreatic (1.22), and colorectal (1.36) cancers.
Esophageal cancer rates of incidence and mortality were both lower in racial and ethnic minority groups, compared with non-Hispanic whites, according to Dr. Bui.
Increasing screening and surveillance
While the esophageal cancer data is encouraging, these data otherwise clearly highlight the need to step up efforts to help level gastrointestinal cancer disparities, according to Byron Cryer, MD, professor of internal medicine and associate dean for the office of faculty diversity and development at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Clearly more work needs to be done for the other four cancers,” Dr. Cryer said in an interview.
Screening and surveillance may be key to addressing those disparities, not only for colorectal cancer, but for the liver and gastric cancers for which disparities were seen throughout racial and ethnic groups in this study.
“We know that if we get rid of hepatitis C virus early, you can prevent those downstream complications such as cancer,” Dr. Cryer said. “It’s same thing with the gastric cancer – if we get rid of Helicobacter pylori early on in the infection, we decrease the burden of cancer down downstream years later.”
Dr. Bui provided no financial disclosures related to the research. Dr. Cryer has nothing to disclose.
FROM DDW 2021
Scaly patches on hand and feet
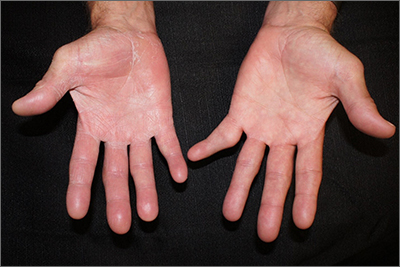
A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578

A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)

A potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount of skin scrapings from the patient’s feet and hand confirmed a diagnosis of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis—the so-called 2-foot, 1-hand syndrome. Additionally, nail clippings from the patient’s right hand confirmed onychomycosis.
Tinea is common and caused by various dermatophytes that are ubiquitous in soil. Often there is a history of atopic dermatitis or xerosis leading to skin barrier dysfunction. Immunosuppression and diabetes mellitus are also predisposing factors. Trichophyton rubrum is a commonly isolated cause.
On the hands, tinea may be challenging to distinguish from irritant dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. A KOH prep test should be considered for any red, scaly rash, especially on the hands and feet. Curiously, the incidence of unilateral tinea manuum and bilateral tinea pedis occurs relatively frequently and can affect either the dominant or nondominant hand. The cause of this asymmetry is speculative.
Topical therapy with various antifungals—terbinafine, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox—can be effective, but challenging to apply to affected areas. For the treatment of nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine or itraconazole is usually indicated (6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks for toenails). Terbinafine is generally tolerated very well for both 6- and 12-week courses. Some clinicians consider lab monitoring unnecessary because the risk of hepatic injury from terbinafine is uncertain; others consider it worthwhile to check liver function test results prior to initiation of terbinafine and after 6 weeks of therapy, with either a 6- or 12-week course.1
Since the patient in this case had skin and nail disease, oral therapy with terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks was prescribed. His skin cleared within 3 weeks and his nails cleared after 6 months. It is important to counsel patients with nail disease that treatment will end before they see a clinical improvement. Fingernails typically require 6 months to see clearance and toenails require 18 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578
1. Stolmeier DA, Stratman HB, McIntee TJ, et al. Utility of laboratory test result monitoring in patients taking oral terbinafine or griseofulvin for dermatophyte infections. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1409-1416. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3578