User login
Tool predicts severe toxicity from chemo in older breast cancer patients
They devised and tested the tool, called the Cancer and Aging Research Group–Breast Cancer (CARG-BC) score, in two cohorts of patients aged 65 years or older with stage I-III breast cancer.
The area under the curve for predicting grade 3-5 toxicity was 0.75 in the development cohort and 0.69 in the validation cohort, for a combined AUC of 0.73.
The CARG-BC score outperformed both Karnofsky performance status (AUC, 0.50) and the Cancer and Aging Research Group Chemotherapy Toxicity Tool (AUC, 0.56).
CARG-BC risk groups were also associated with hospitalizations, dose modifications, and early termination of treatment.
Allison Magnuson, DO, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and colleagues described these results in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
About CARG-BC
To calculate a patient’s CARG-BC score, the researchers added up points assigned to eight independent predictors of grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity:
- Planned anthracycline use (1 point)
- Stage II or III disease (3 points)
- Planned treatment duration longer than 3 months (4 points)
- Abnormal liver function (3 points)
- Low hemoglobin level (3 points)
- A fall in the previous 6 months (4 points)
- Limited ability to walk more than 1 mile (3 points)
- Lack of social support (3 points)
Patients with scores of 0-5 have a low risk, those with scores of 6-11 have an intermediate risk, and those with scores of 12 or above have a high risk of grade 3-5 toxicity.
Patient characteristics and results
There were 283 patients in the development cohort and 190 in the validation cohort. There were no significant demographic, disease, or treatment differences between the cohorts.
All patients had a mean age of 70.5 years, 36.2% had stage I disease, 42.9% had stage II, and 20.9% had stage III disease. Three-quarters of patients were non-Hispanic White, and 99.4% were women. Roughly a third of patients had received an anthracycline-based regimen.
Overall, about a quarter of patients had an unplanned dose reduction (24%), dose delay (26%), stopped treatment early (24%), or were hospitalized during treatment (23%). All of these occurrences were more likely in intermediate- and high-risk patients versus low-risk patients (P < .001).
In the development cohort, 19% of low-risk patients, 54% of intermediate-risk patients, and 87% of high-risk patients developed grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity.
Compared with the 93 patients in the low-risk group, the odds of toxicity was almost 5 times greater for the 159 intermediate-risk subjects, and 28 times greater for the 30 high-risk subjects.
In the validation cohort, grade 3-5 toxicity rates were 27% in the low-risk group, 45% in the intermediate-risk group, and 76% in the high-risk group.
This study had its limitations, including that a majority of subjects (72.2%) had a college education, and the validation cohort was accrued from the same 16 institutions as the development cohort.
“Further validation in a more diverse population should be considered,” the investigators wrote.
A ‘useful’ tool for guiding therapy
The investigators noted that chemotherapy is a complex decision for older adults with stage I-III breast cancer. While it may be indicated, chemotherapy is underused often because of the higher risk of severe toxicity in older people.
“Unfortunately, older adults aged 65 and over, who comprise about half of all breast cancer diagnoses, are significantly less likely to be offered chemotherapy compared to younger patients – sometimes because their doctors fear they won’t be able to tolerate it,” investigator Mina Sedrak, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, Calif., said in a press release.
The CARG-BC score may be useful to direct therapy in older adults with early-stage breast cancer, the investigators wrote. They noted that intensifying supportive care and developing modified treatment regimens may be appropriate for patients at higher risk for toxicity.
“Although this score should not be used as the only factor in deciding whether to administer and/or alter the dose or schedule of chemotherapy, the CARG-BC score can be used to facilitate this complex decision-making process, along with clinical judgment and patient preferences,” they wrote.
“I think this is a great tool. [It] will be helpful to me to have a more accurate conversation with geriatric patients about the actual risk/benefit ratio for chemotherapy in early breast cancer,” said Amy Tiersten, MD, of Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, when asked for comment.
“If routinely implemented, it may help reduce age bias and also identify older patients who may look well but may be vulnerable and quickly decompensate while undergoing treatment,” said Lidia Schapira, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University. “Importantly, it can be used to guide conversations about trade-offs and to start a frank conversation about an older patient’s fears and concerns about treatment.”
This research was funded by the National Institute on Aging, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope. The investigators, Dr. Schapira, and Dr. Tiersten had no relevant disclosures.
They devised and tested the tool, called the Cancer and Aging Research Group–Breast Cancer (CARG-BC) score, in two cohorts of patients aged 65 years or older with stage I-III breast cancer.
The area under the curve for predicting grade 3-5 toxicity was 0.75 in the development cohort and 0.69 in the validation cohort, for a combined AUC of 0.73.
The CARG-BC score outperformed both Karnofsky performance status (AUC, 0.50) and the Cancer and Aging Research Group Chemotherapy Toxicity Tool (AUC, 0.56).
CARG-BC risk groups were also associated with hospitalizations, dose modifications, and early termination of treatment.
Allison Magnuson, DO, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and colleagues described these results in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
About CARG-BC
To calculate a patient’s CARG-BC score, the researchers added up points assigned to eight independent predictors of grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity:
- Planned anthracycline use (1 point)
- Stage II or III disease (3 points)
- Planned treatment duration longer than 3 months (4 points)
- Abnormal liver function (3 points)
- Low hemoglobin level (3 points)
- A fall in the previous 6 months (4 points)
- Limited ability to walk more than 1 mile (3 points)
- Lack of social support (3 points)
Patients with scores of 0-5 have a low risk, those with scores of 6-11 have an intermediate risk, and those with scores of 12 or above have a high risk of grade 3-5 toxicity.
Patient characteristics and results
There were 283 patients in the development cohort and 190 in the validation cohort. There were no significant demographic, disease, or treatment differences between the cohorts.
All patients had a mean age of 70.5 years, 36.2% had stage I disease, 42.9% had stage II, and 20.9% had stage III disease. Three-quarters of patients were non-Hispanic White, and 99.4% were women. Roughly a third of patients had received an anthracycline-based regimen.
Overall, about a quarter of patients had an unplanned dose reduction (24%), dose delay (26%), stopped treatment early (24%), or were hospitalized during treatment (23%). All of these occurrences were more likely in intermediate- and high-risk patients versus low-risk patients (P < .001).
In the development cohort, 19% of low-risk patients, 54% of intermediate-risk patients, and 87% of high-risk patients developed grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity.
Compared with the 93 patients in the low-risk group, the odds of toxicity was almost 5 times greater for the 159 intermediate-risk subjects, and 28 times greater for the 30 high-risk subjects.
In the validation cohort, grade 3-5 toxicity rates were 27% in the low-risk group, 45% in the intermediate-risk group, and 76% in the high-risk group.
This study had its limitations, including that a majority of subjects (72.2%) had a college education, and the validation cohort was accrued from the same 16 institutions as the development cohort.
“Further validation in a more diverse population should be considered,” the investigators wrote.
A ‘useful’ tool for guiding therapy
The investigators noted that chemotherapy is a complex decision for older adults with stage I-III breast cancer. While it may be indicated, chemotherapy is underused often because of the higher risk of severe toxicity in older people.
“Unfortunately, older adults aged 65 and over, who comprise about half of all breast cancer diagnoses, are significantly less likely to be offered chemotherapy compared to younger patients – sometimes because their doctors fear they won’t be able to tolerate it,” investigator Mina Sedrak, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, Calif., said in a press release.
The CARG-BC score may be useful to direct therapy in older adults with early-stage breast cancer, the investigators wrote. They noted that intensifying supportive care and developing modified treatment regimens may be appropriate for patients at higher risk for toxicity.
“Although this score should not be used as the only factor in deciding whether to administer and/or alter the dose or schedule of chemotherapy, the CARG-BC score can be used to facilitate this complex decision-making process, along with clinical judgment and patient preferences,” they wrote.
“I think this is a great tool. [It] will be helpful to me to have a more accurate conversation with geriatric patients about the actual risk/benefit ratio for chemotherapy in early breast cancer,” said Amy Tiersten, MD, of Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, when asked for comment.
“If routinely implemented, it may help reduce age bias and also identify older patients who may look well but may be vulnerable and quickly decompensate while undergoing treatment,” said Lidia Schapira, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University. “Importantly, it can be used to guide conversations about trade-offs and to start a frank conversation about an older patient’s fears and concerns about treatment.”
This research was funded by the National Institute on Aging, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope. The investigators, Dr. Schapira, and Dr. Tiersten had no relevant disclosures.
They devised and tested the tool, called the Cancer and Aging Research Group–Breast Cancer (CARG-BC) score, in two cohorts of patients aged 65 years or older with stage I-III breast cancer.
The area under the curve for predicting grade 3-5 toxicity was 0.75 in the development cohort and 0.69 in the validation cohort, for a combined AUC of 0.73.
The CARG-BC score outperformed both Karnofsky performance status (AUC, 0.50) and the Cancer and Aging Research Group Chemotherapy Toxicity Tool (AUC, 0.56).
CARG-BC risk groups were also associated with hospitalizations, dose modifications, and early termination of treatment.
Allison Magnuson, DO, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and colleagues described these results in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
About CARG-BC
To calculate a patient’s CARG-BC score, the researchers added up points assigned to eight independent predictors of grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity:
- Planned anthracycline use (1 point)
- Stage II or III disease (3 points)
- Planned treatment duration longer than 3 months (4 points)
- Abnormal liver function (3 points)
- Low hemoglobin level (3 points)
- A fall in the previous 6 months (4 points)
- Limited ability to walk more than 1 mile (3 points)
- Lack of social support (3 points)
Patients with scores of 0-5 have a low risk, those with scores of 6-11 have an intermediate risk, and those with scores of 12 or above have a high risk of grade 3-5 toxicity.
Patient characteristics and results
There were 283 patients in the development cohort and 190 in the validation cohort. There were no significant demographic, disease, or treatment differences between the cohorts.
All patients had a mean age of 70.5 years, 36.2% had stage I disease, 42.9% had stage II, and 20.9% had stage III disease. Three-quarters of patients were non-Hispanic White, and 99.4% were women. Roughly a third of patients had received an anthracycline-based regimen.
Overall, about a quarter of patients had an unplanned dose reduction (24%), dose delay (26%), stopped treatment early (24%), or were hospitalized during treatment (23%). All of these occurrences were more likely in intermediate- and high-risk patients versus low-risk patients (P < .001).
In the development cohort, 19% of low-risk patients, 54% of intermediate-risk patients, and 87% of high-risk patients developed grade 3-5 chemotherapy toxicity.
Compared with the 93 patients in the low-risk group, the odds of toxicity was almost 5 times greater for the 159 intermediate-risk subjects, and 28 times greater for the 30 high-risk subjects.
In the validation cohort, grade 3-5 toxicity rates were 27% in the low-risk group, 45% in the intermediate-risk group, and 76% in the high-risk group.
This study had its limitations, including that a majority of subjects (72.2%) had a college education, and the validation cohort was accrued from the same 16 institutions as the development cohort.
“Further validation in a more diverse population should be considered,” the investigators wrote.
A ‘useful’ tool for guiding therapy
The investigators noted that chemotherapy is a complex decision for older adults with stage I-III breast cancer. While it may be indicated, chemotherapy is underused often because of the higher risk of severe toxicity in older people.
“Unfortunately, older adults aged 65 and over, who comprise about half of all breast cancer diagnoses, are significantly less likely to be offered chemotherapy compared to younger patients – sometimes because their doctors fear they won’t be able to tolerate it,” investigator Mina Sedrak, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, Calif., said in a press release.
The CARG-BC score may be useful to direct therapy in older adults with early-stage breast cancer, the investigators wrote. They noted that intensifying supportive care and developing modified treatment regimens may be appropriate for patients at higher risk for toxicity.
“Although this score should not be used as the only factor in deciding whether to administer and/or alter the dose or schedule of chemotherapy, the CARG-BC score can be used to facilitate this complex decision-making process, along with clinical judgment and patient preferences,” they wrote.
“I think this is a great tool. [It] will be helpful to me to have a more accurate conversation with geriatric patients about the actual risk/benefit ratio for chemotherapy in early breast cancer,” said Amy Tiersten, MD, of Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, when asked for comment.
“If routinely implemented, it may help reduce age bias and also identify older patients who may look well but may be vulnerable and quickly decompensate while undergoing treatment,” said Lidia Schapira, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University. “Importantly, it can be used to guide conversations about trade-offs and to start a frank conversation about an older patient’s fears and concerns about treatment.”
This research was funded by the National Institute on Aging, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, and the Center for Cancer and Aging at City of Hope. The investigators, Dr. Schapira, and Dr. Tiersten had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Low-carb diets boost diabetes remission rates, at least short term
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Biden kicks off health agenda with COVID actions, WHO outreach
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
APA apologizes for past support of racism in psychiatry
The American Psychiatric Association has issued a formal apology for its past support of structural racism in psychiatry.
The apology, issued Jan. 18, coincided with the federal holiday honoring the life and work of civil rights activist Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
“We apologize for our role in perpetrating structural racism in this country, and we hope to begin to make amends for APA’s and psychiatry’s history of actions, intentional and not, that hurt Black, indigenous, and people of color,” APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
The apology was written and issued by the APA Board of Trustees. It acknowledges practices and events in psychiatry that contributed to racial inequality, and expresses the organization’s commitment to developing antiracist policies that promote equity in mental health for all.
“This apology is one important step we needed to take to move forward to a more equitable future. The board is issuing this document on Martin Luther King Jr. Day, because we hope that it honors his life’s work of reconciliation and equality. We do not take that legacy or his call to action lightly and will continue our important work,” said Dr. Geller.
One involved the Eastern State Hospital in Williamsburg, Va., the nation’s first psychiatric care facility, founded in 1773.
Eastern State, which for a time in the 1800s was called the Eastern Lunatic Asylum, was not segregated when founded. However, 70 years later, when the 13 founders of what is now the APA met to discuss improvements in mental health care delivery, the treatment system they created and the organization they founded aligned with that era’s racist social and political policies. In this system, Black patients received psychiatric care separately from White patients, the APA said.
The APA also acknowledged failing to act in Black Americans’ best interest at critical points in the United States’ sociopolitical evolution throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.
“This inactivity was notably evident while white supremacists lynched Black people during the Reconstruction Era as well as when Jim Crow segregation was in effect, which led to ‘separate but equal’ standards of care starting in 1896,” the APA said.
Later, the APA failed to declare support for Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka in 1954, along with further major civil rights legislation designed to improve social and psychological conditions for Black people, the organization admitted.
Throughout the decades that followed, psychiatric misdiagnosis among Black, indigenous, and people of color populations were also common, the APA acknowledged.
For example, late 20th century psychiatrists commonly attributed their minority patients’ frustrations to schizophrenia, while categorizing similar behaviors as “neuroticism” in White patients.
The APA pointed to one study which found that APA members diagnosed more Black than White patients with schizophrenia, even when both had otherwise identical clinical presentations.
“This reveals the basis for embedded discrimination within psychiatry that has contributed to reduced quality of care” for Black, indigenous, and people of color, and “perpetuation of dangerous stereotypes,” the APA said.
Saul Levin, MD, the APA’s medical director and CEO, said the Board of Trustees has taken “an important step in issuing this apology. The APA administration is committed to working toward inclusion, health equity, and fairness that everyone deserves.”
The APA Board of Trustees began drafting the apology late last year after it concluded that events and persistent inequities in health care and psychiatry had highlighted an organizational need for action.
The APA’s Presidential Task Force on Structural Racism is continuing with efforts to educate and engage members on the issue and implement changes within the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has issued a formal apology for its past support of structural racism in psychiatry.
The apology, issued Jan. 18, coincided with the federal holiday honoring the life and work of civil rights activist Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
“We apologize for our role in perpetrating structural racism in this country, and we hope to begin to make amends for APA’s and psychiatry’s history of actions, intentional and not, that hurt Black, indigenous, and people of color,” APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
The apology was written and issued by the APA Board of Trustees. It acknowledges practices and events in psychiatry that contributed to racial inequality, and expresses the organization’s commitment to developing antiracist policies that promote equity in mental health for all.
“This apology is one important step we needed to take to move forward to a more equitable future. The board is issuing this document on Martin Luther King Jr. Day, because we hope that it honors his life’s work of reconciliation and equality. We do not take that legacy or his call to action lightly and will continue our important work,” said Dr. Geller.
One involved the Eastern State Hospital in Williamsburg, Va., the nation’s first psychiatric care facility, founded in 1773.
Eastern State, which for a time in the 1800s was called the Eastern Lunatic Asylum, was not segregated when founded. However, 70 years later, when the 13 founders of what is now the APA met to discuss improvements in mental health care delivery, the treatment system they created and the organization they founded aligned with that era’s racist social and political policies. In this system, Black patients received psychiatric care separately from White patients, the APA said.
The APA also acknowledged failing to act in Black Americans’ best interest at critical points in the United States’ sociopolitical evolution throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.
“This inactivity was notably evident while white supremacists lynched Black people during the Reconstruction Era as well as when Jim Crow segregation was in effect, which led to ‘separate but equal’ standards of care starting in 1896,” the APA said.
Later, the APA failed to declare support for Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka in 1954, along with further major civil rights legislation designed to improve social and psychological conditions for Black people, the organization admitted.
Throughout the decades that followed, psychiatric misdiagnosis among Black, indigenous, and people of color populations were also common, the APA acknowledged.
For example, late 20th century psychiatrists commonly attributed their minority patients’ frustrations to schizophrenia, while categorizing similar behaviors as “neuroticism” in White patients.
The APA pointed to one study which found that APA members diagnosed more Black than White patients with schizophrenia, even when both had otherwise identical clinical presentations.
“This reveals the basis for embedded discrimination within psychiatry that has contributed to reduced quality of care” for Black, indigenous, and people of color, and “perpetuation of dangerous stereotypes,” the APA said.
Saul Levin, MD, the APA’s medical director and CEO, said the Board of Trustees has taken “an important step in issuing this apology. The APA administration is committed to working toward inclusion, health equity, and fairness that everyone deserves.”
The APA Board of Trustees began drafting the apology late last year after it concluded that events and persistent inequities in health care and psychiatry had highlighted an organizational need for action.
The APA’s Presidential Task Force on Structural Racism is continuing with efforts to educate and engage members on the issue and implement changes within the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association has issued a formal apology for its past support of structural racism in psychiatry.
The apology, issued Jan. 18, coincided with the federal holiday honoring the life and work of civil rights activist Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
“We apologize for our role in perpetrating structural racism in this country, and we hope to begin to make amends for APA’s and psychiatry’s history of actions, intentional and not, that hurt Black, indigenous, and people of color,” APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, MPH, said in a statement.
The apology was written and issued by the APA Board of Trustees. It acknowledges practices and events in psychiatry that contributed to racial inequality, and expresses the organization’s commitment to developing antiracist policies that promote equity in mental health for all.
“This apology is one important step we needed to take to move forward to a more equitable future. The board is issuing this document on Martin Luther King Jr. Day, because we hope that it honors his life’s work of reconciliation and equality. We do not take that legacy or his call to action lightly and will continue our important work,” said Dr. Geller.
One involved the Eastern State Hospital in Williamsburg, Va., the nation’s first psychiatric care facility, founded in 1773.
Eastern State, which for a time in the 1800s was called the Eastern Lunatic Asylum, was not segregated when founded. However, 70 years later, when the 13 founders of what is now the APA met to discuss improvements in mental health care delivery, the treatment system they created and the organization they founded aligned with that era’s racist social and political policies. In this system, Black patients received psychiatric care separately from White patients, the APA said.
The APA also acknowledged failing to act in Black Americans’ best interest at critical points in the United States’ sociopolitical evolution throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.
“This inactivity was notably evident while white supremacists lynched Black people during the Reconstruction Era as well as when Jim Crow segregation was in effect, which led to ‘separate but equal’ standards of care starting in 1896,” the APA said.
Later, the APA failed to declare support for Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka in 1954, along with further major civil rights legislation designed to improve social and psychological conditions for Black people, the organization admitted.
Throughout the decades that followed, psychiatric misdiagnosis among Black, indigenous, and people of color populations were also common, the APA acknowledged.
For example, late 20th century psychiatrists commonly attributed their minority patients’ frustrations to schizophrenia, while categorizing similar behaviors as “neuroticism” in White patients.
The APA pointed to one study which found that APA members diagnosed more Black than White patients with schizophrenia, even when both had otherwise identical clinical presentations.
“This reveals the basis for embedded discrimination within psychiatry that has contributed to reduced quality of care” for Black, indigenous, and people of color, and “perpetuation of dangerous stereotypes,” the APA said.
Saul Levin, MD, the APA’s medical director and CEO, said the Board of Trustees has taken “an important step in issuing this apology. The APA administration is committed to working toward inclusion, health equity, and fairness that everyone deserves.”
The APA Board of Trustees began drafting the apology late last year after it concluded that events and persistent inequities in health care and psychiatry had highlighted an organizational need for action.
The APA’s Presidential Task Force on Structural Racism is continuing with efforts to educate and engage members on the issue and implement changes within the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does screening for skin cancer result in melanoma overdiagnosis?
When the COVID-19 pandemic first hit, cancer screening in the United States came to an abrupt halt. That experience, coupled with the financial fallout of the pandemic, has led some doctors to reassess business as usual.
In particular, a trio has taken aim at skin cancer screening – arguing that it should stop – in a ‘sounding board’ commentary published online Jan. 7 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has functionally stopped skin cancer screening; what is important is not to restart it,” wrote the authors, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Welch has often raised questions about cancer screening and highlighted the issue of overdiagnosis.
In this latest essay, Dr. Welch teamed up with pathologist Benjamin Mazer, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who writes commentaries for this news organization, and dermatologist Adewole S. Adamson, MD, University of Texas, Austin, to argue that screening for skin cancer has led to an overdiagnosis of melanoma.
However, two melanoma experts pointed out flaws in some of their arguments, and said the issue is more nuanced than they present.
Arguing that melanoma is overdiagnosed
The incidence of melanoma is six times as high as it was 40 years ago, making it the third most common cancer in the United States, the investigators pointed out. However, while case rates have skyrocketed, death rates from melanoma have remained about the same, which points to overdiagnosis.
They described a cycle of increased diagnostic scrutiny that is driving overdiagnosis of melanoma. This includes heightened awareness (perhaps overly) among patients, widespread skin screenings, lower clinical thresholds for biopsy, and lower thresholds among pathologists for diagnosis of melanoma. Fear of missing cancer, legal concerns, and financial incentives may all contribute.
“We view the rise in the incidence of melanoma as a sentinel event, a warning that an epidemic of inspection, surveillance, and biopsy of pigmented skin lesions is permeating through the general population,” they wrote.
Furthermore, overdiagnosis could contribute to unnecessary intervention.
Between 2004 and 2017, rates of biopsy among fee-for-service Medicare recipients almost doubled (from 5% to 8%), according to coding trends data cited in the article. Overdiagnosis and unnecessary intervention could cause psychological, financial, and physical harm to the patient, and the authors argued for interrupting the cycle.
“The most important step to break the cycle of melanoma overdiagnosis is to stop population-wide screening for skin cancer,” they wrote.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force currently states that there is insufficient evidence to weigh the balances versus the harms of skin cancer screening, leaving it open to interpretation.
“[T]he increase in melanoma diagnoses by a factor of 6, with at least an order of magnitude more persons undergoing a biopsy and no apparent effect on mortality, is more than enough to recommend against population-wide screening,” Dr. Welch and colleagues concluded.
But the issue may be more nuanced, argued a melanoma expert.
“Everyone agrees that screening high-risk groups has the greatest chance of reducing cancer mortality. In melanoma, the strongest risk factor is the number of moles and presence of clinically atypical moles,” David Polsky, MD, PhD, commented in an interview. Dr. Polsky is a professor of dermatologic oncology at the Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University Langone Health.
However, population-based studies have shown that at least half of melanoma patients are not considered high risk based on the appearance of the mole, he explained.
“Studies to identify genetic risk factors for melanoma have not yet progressed to the point where these can be tested in the clinic. We clearly have a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” he said.
Moreover, it’s not easy to predict which early melanomas will metastasize, said dermatologist Jennifer Stein, MD, PhD, who specializes in treating patients at high risk for melanoma at NYU Langone.
“This paper suggests that it may not be important to detect and treat melanoma in situ, and that the increase in diagnosis of melanoma in situ has led to more harms than good,” she said. “There is evidence that most melanomas do originate as in situ lesions. Unfortunately, we cannot predict which ones will become more aggressive. For this reason, we treat melanoma in situ.”
Taking issue with some of the arguments
Both Dr. Polsky and Dr. Stein took issue with several of the arguments put forward by Dr. Welch and colleagues.
For instance, Dr. Welch and colleagues cited research suggesting that UV light is a weak risk factor for melanoma, but Dr. Polsky disagreed. “There are many lines of evidence ranging from epidemiological, clinical, and biological studies that prove the causative association between ultraviolet light and melanoma, while acknowledging that other factors, such as genetic predisposition, play an important role,” he said. “Since ultraviolet light in the form of outdoor sunburns or indoor tanning exposure are modifiable risk factors, it is important that we continue with our current public messaging on their causal role in the development of melanoma.”
Furthermore, the 2012 study that the authors cited to support their argument that pathologists today are more likely to diagnose melanoma than in years past is flawed, according to Dr. Stein. The study was very small and included just nine contemporary pathologists. Unlike in real life, pathologists in the study could not diagnose lesions as “atypical,” and may have erred on the side of caution by calling them malignant.
“There were multiple limitations to this study that were acknowledged by its authors, who stated that it was a hypothesis-generating study and may not be generalizable,” Dr. Stein said.
In addition, Dr. Polsky took issue with the suggestion that awareness about melanoma among the general public is overly heightened.
“Reducing melanoma awareness would not be wise,” he said. “Studies have shown that awareness of melanoma is associated with the diagnosis of earlier-stage lesions that can be cured by simple skin surgery, without the need for more costly interventions utilized for more advanced melanomas.”
Dr. Mazer reported receiving travel compensation from Hillcrest Healthcare Systems, and is a commentator for this new organization. Dr. Welch has written three books on the subjects of overdiagnosis and testing for cancer. Dr. Adamson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the COVID-19 pandemic first hit, cancer screening in the United States came to an abrupt halt. That experience, coupled with the financial fallout of the pandemic, has led some doctors to reassess business as usual.
In particular, a trio has taken aim at skin cancer screening – arguing that it should stop – in a ‘sounding board’ commentary published online Jan. 7 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has functionally stopped skin cancer screening; what is important is not to restart it,” wrote the authors, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Welch has often raised questions about cancer screening and highlighted the issue of overdiagnosis.
In this latest essay, Dr. Welch teamed up with pathologist Benjamin Mazer, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who writes commentaries for this news organization, and dermatologist Adewole S. Adamson, MD, University of Texas, Austin, to argue that screening for skin cancer has led to an overdiagnosis of melanoma.
However, two melanoma experts pointed out flaws in some of their arguments, and said the issue is more nuanced than they present.
Arguing that melanoma is overdiagnosed
The incidence of melanoma is six times as high as it was 40 years ago, making it the third most common cancer in the United States, the investigators pointed out. However, while case rates have skyrocketed, death rates from melanoma have remained about the same, which points to overdiagnosis.
They described a cycle of increased diagnostic scrutiny that is driving overdiagnosis of melanoma. This includes heightened awareness (perhaps overly) among patients, widespread skin screenings, lower clinical thresholds for biopsy, and lower thresholds among pathologists for diagnosis of melanoma. Fear of missing cancer, legal concerns, and financial incentives may all contribute.
“We view the rise in the incidence of melanoma as a sentinel event, a warning that an epidemic of inspection, surveillance, and biopsy of pigmented skin lesions is permeating through the general population,” they wrote.
Furthermore, overdiagnosis could contribute to unnecessary intervention.
Between 2004 and 2017, rates of biopsy among fee-for-service Medicare recipients almost doubled (from 5% to 8%), according to coding trends data cited in the article. Overdiagnosis and unnecessary intervention could cause psychological, financial, and physical harm to the patient, and the authors argued for interrupting the cycle.
“The most important step to break the cycle of melanoma overdiagnosis is to stop population-wide screening for skin cancer,” they wrote.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force currently states that there is insufficient evidence to weigh the balances versus the harms of skin cancer screening, leaving it open to interpretation.
“[T]he increase in melanoma diagnoses by a factor of 6, with at least an order of magnitude more persons undergoing a biopsy and no apparent effect on mortality, is more than enough to recommend against population-wide screening,” Dr. Welch and colleagues concluded.
But the issue may be more nuanced, argued a melanoma expert.
“Everyone agrees that screening high-risk groups has the greatest chance of reducing cancer mortality. In melanoma, the strongest risk factor is the number of moles and presence of clinically atypical moles,” David Polsky, MD, PhD, commented in an interview. Dr. Polsky is a professor of dermatologic oncology at the Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University Langone Health.
However, population-based studies have shown that at least half of melanoma patients are not considered high risk based on the appearance of the mole, he explained.
“Studies to identify genetic risk factors for melanoma have not yet progressed to the point where these can be tested in the clinic. We clearly have a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” he said.
Moreover, it’s not easy to predict which early melanomas will metastasize, said dermatologist Jennifer Stein, MD, PhD, who specializes in treating patients at high risk for melanoma at NYU Langone.
“This paper suggests that it may not be important to detect and treat melanoma in situ, and that the increase in diagnosis of melanoma in situ has led to more harms than good,” she said. “There is evidence that most melanomas do originate as in situ lesions. Unfortunately, we cannot predict which ones will become more aggressive. For this reason, we treat melanoma in situ.”
Taking issue with some of the arguments
Both Dr. Polsky and Dr. Stein took issue with several of the arguments put forward by Dr. Welch and colleagues.
For instance, Dr. Welch and colleagues cited research suggesting that UV light is a weak risk factor for melanoma, but Dr. Polsky disagreed. “There are many lines of evidence ranging from epidemiological, clinical, and biological studies that prove the causative association between ultraviolet light and melanoma, while acknowledging that other factors, such as genetic predisposition, play an important role,” he said. “Since ultraviolet light in the form of outdoor sunburns or indoor tanning exposure are modifiable risk factors, it is important that we continue with our current public messaging on their causal role in the development of melanoma.”
Furthermore, the 2012 study that the authors cited to support their argument that pathologists today are more likely to diagnose melanoma than in years past is flawed, according to Dr. Stein. The study was very small and included just nine contemporary pathologists. Unlike in real life, pathologists in the study could not diagnose lesions as “atypical,” and may have erred on the side of caution by calling them malignant.
“There were multiple limitations to this study that were acknowledged by its authors, who stated that it was a hypothesis-generating study and may not be generalizable,” Dr. Stein said.
In addition, Dr. Polsky took issue with the suggestion that awareness about melanoma among the general public is overly heightened.
“Reducing melanoma awareness would not be wise,” he said. “Studies have shown that awareness of melanoma is associated with the diagnosis of earlier-stage lesions that can be cured by simple skin surgery, without the need for more costly interventions utilized for more advanced melanomas.”
Dr. Mazer reported receiving travel compensation from Hillcrest Healthcare Systems, and is a commentator for this new organization. Dr. Welch has written three books on the subjects of overdiagnosis and testing for cancer. Dr. Adamson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the COVID-19 pandemic first hit, cancer screening in the United States came to an abrupt halt. That experience, coupled with the financial fallout of the pandemic, has led some doctors to reassess business as usual.
In particular, a trio has taken aim at skin cancer screening – arguing that it should stop – in a ‘sounding board’ commentary published online Jan. 7 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has functionally stopped skin cancer screening; what is important is not to restart it,” wrote the authors, led by H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. Dr. Welch has often raised questions about cancer screening and highlighted the issue of overdiagnosis.
In this latest essay, Dr. Welch teamed up with pathologist Benjamin Mazer, MD, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who writes commentaries for this news organization, and dermatologist Adewole S. Adamson, MD, University of Texas, Austin, to argue that screening for skin cancer has led to an overdiagnosis of melanoma.
However, two melanoma experts pointed out flaws in some of their arguments, and said the issue is more nuanced than they present.
Arguing that melanoma is overdiagnosed
The incidence of melanoma is six times as high as it was 40 years ago, making it the third most common cancer in the United States, the investigators pointed out. However, while case rates have skyrocketed, death rates from melanoma have remained about the same, which points to overdiagnosis.
They described a cycle of increased diagnostic scrutiny that is driving overdiagnosis of melanoma. This includes heightened awareness (perhaps overly) among patients, widespread skin screenings, lower clinical thresholds for biopsy, and lower thresholds among pathologists for diagnosis of melanoma. Fear of missing cancer, legal concerns, and financial incentives may all contribute.
“We view the rise in the incidence of melanoma as a sentinel event, a warning that an epidemic of inspection, surveillance, and biopsy of pigmented skin lesions is permeating through the general population,” they wrote.
Furthermore, overdiagnosis could contribute to unnecessary intervention.
Between 2004 and 2017, rates of biopsy among fee-for-service Medicare recipients almost doubled (from 5% to 8%), according to coding trends data cited in the article. Overdiagnosis and unnecessary intervention could cause psychological, financial, and physical harm to the patient, and the authors argued for interrupting the cycle.
“The most important step to break the cycle of melanoma overdiagnosis is to stop population-wide screening for skin cancer,” they wrote.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force currently states that there is insufficient evidence to weigh the balances versus the harms of skin cancer screening, leaving it open to interpretation.
“[T]he increase in melanoma diagnoses by a factor of 6, with at least an order of magnitude more persons undergoing a biopsy and no apparent effect on mortality, is more than enough to recommend against population-wide screening,” Dr. Welch and colleagues concluded.
But the issue may be more nuanced, argued a melanoma expert.
“Everyone agrees that screening high-risk groups has the greatest chance of reducing cancer mortality. In melanoma, the strongest risk factor is the number of moles and presence of clinically atypical moles,” David Polsky, MD, PhD, commented in an interview. Dr. Polsky is a professor of dermatologic oncology at the Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University Langone Health.
However, population-based studies have shown that at least half of melanoma patients are not considered high risk based on the appearance of the mole, he explained.
“Studies to identify genetic risk factors for melanoma have not yet progressed to the point where these can be tested in the clinic. We clearly have a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” he said.
Moreover, it’s not easy to predict which early melanomas will metastasize, said dermatologist Jennifer Stein, MD, PhD, who specializes in treating patients at high risk for melanoma at NYU Langone.
“This paper suggests that it may not be important to detect and treat melanoma in situ, and that the increase in diagnosis of melanoma in situ has led to more harms than good,” she said. “There is evidence that most melanomas do originate as in situ lesions. Unfortunately, we cannot predict which ones will become more aggressive. For this reason, we treat melanoma in situ.”
Taking issue with some of the arguments
Both Dr. Polsky and Dr. Stein took issue with several of the arguments put forward by Dr. Welch and colleagues.
For instance, Dr. Welch and colleagues cited research suggesting that UV light is a weak risk factor for melanoma, but Dr. Polsky disagreed. “There are many lines of evidence ranging from epidemiological, clinical, and biological studies that prove the causative association between ultraviolet light and melanoma, while acknowledging that other factors, such as genetic predisposition, play an important role,” he said. “Since ultraviolet light in the form of outdoor sunburns or indoor tanning exposure are modifiable risk factors, it is important that we continue with our current public messaging on their causal role in the development of melanoma.”
Furthermore, the 2012 study that the authors cited to support their argument that pathologists today are more likely to diagnose melanoma than in years past is flawed, according to Dr. Stein. The study was very small and included just nine contemporary pathologists. Unlike in real life, pathologists in the study could not diagnose lesions as “atypical,” and may have erred on the side of caution by calling them malignant.
“There were multiple limitations to this study that were acknowledged by its authors, who stated that it was a hypothesis-generating study and may not be generalizable,” Dr. Stein said.
In addition, Dr. Polsky took issue with the suggestion that awareness about melanoma among the general public is overly heightened.
“Reducing melanoma awareness would not be wise,” he said. “Studies have shown that awareness of melanoma is associated with the diagnosis of earlier-stage lesions that can be cured by simple skin surgery, without the need for more costly interventions utilized for more advanced melanomas.”
Dr. Mazer reported receiving travel compensation from Hillcrest Healthcare Systems, and is a commentator for this new organization. Dr. Welch has written three books on the subjects of overdiagnosis and testing for cancer. Dr. Adamson disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Global Ebola vaccine stockpile established
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
Longstanding rash
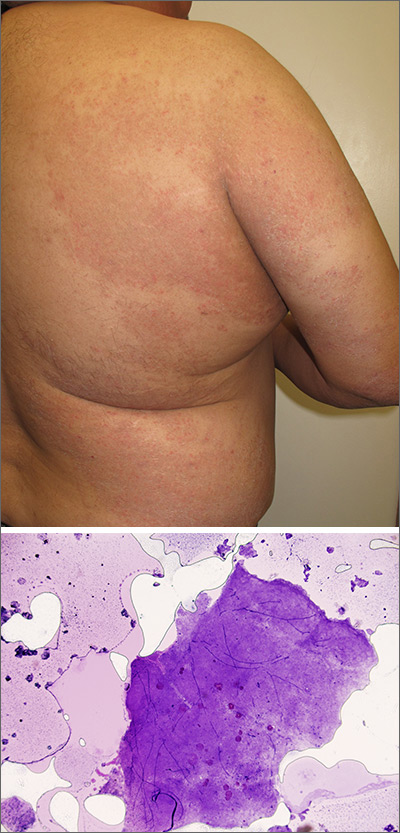
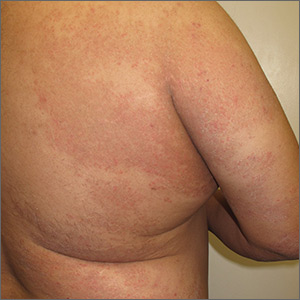
The patient was given a diagnosis of widespread tinea corporis. This diagnosis may not fit with the common paradigm of tinea as thin, scaly annular patches, often known as ringworm. However, a skin scraping was performed on the red scaly patches, and the diagnosis was confirmed.
A skin scraping is a simple procedure that takes minutes to yield actionable information. A scalpel blade is used in a scraping motion and skin flakes are caught on a slide as they fall from the skin. (Another glass slide can be used in place of the scalpel, which is slightly less frightening for children.) The sample is then covered with 1 to 2 drops of potassium hydroxide (KOH), in 1 of various available formulations, and covered with a coverslip. Gently heating the slide, or simply waiting a few minutes, will allow the KOH to begin dissolving some keratinocyte membranes and stain any fungal walls light purple.
Hyphae, which may be linear (see Figure) or branched, will cross multiple cell membranes and are themselves about the thickness of a cell membrane. A high-powered view of hyphae should reveal nuclei and septa.
Skin biopsy, culture, and a skin scraping sent to an outside lab are all alternatives to the aforementioned approach but take days or weeks to yield a result. Fungal polymerase chain reaction is a novel diagnostic approach that can be both sensitive and specific, but still requires several days for results and incurs additional cost to the patient.
In this case, the diagnosis was made at the patient’s bedside and terbinafine 250 mg/d for 3 weeks was chosen as systemic therapy because of the extent of disease. At the follow-up visit 2 months later, the patient’s rash had completely cleared.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Liu D, Coloe S, Baird R, et al. Application of PCR to the identification of dermatophyte fungi. J Med Microbiol. 2000;49:493-497.

The patient was given a diagnosis of widespread tinea corporis. This diagnosis may not fit with the common paradigm of tinea as thin, scaly annular patches, often known as ringworm. However, a skin scraping was performed on the red scaly patches, and the diagnosis was confirmed.
A skin scraping is a simple procedure that takes minutes to yield actionable information. A scalpel blade is used in a scraping motion and skin flakes are caught on a slide as they fall from the skin. (Another glass slide can be used in place of the scalpel, which is slightly less frightening for children.) The sample is then covered with 1 to 2 drops of potassium hydroxide (KOH), in 1 of various available formulations, and covered with a coverslip. Gently heating the slide, or simply waiting a few minutes, will allow the KOH to begin dissolving some keratinocyte membranes and stain any fungal walls light purple.
Hyphae, which may be linear (see Figure) or branched, will cross multiple cell membranes and are themselves about the thickness of a cell membrane. A high-powered view of hyphae should reveal nuclei and septa.
Skin biopsy, culture, and a skin scraping sent to an outside lab are all alternatives to the aforementioned approach but take days or weeks to yield a result. Fungal polymerase chain reaction is a novel diagnostic approach that can be both sensitive and specific, but still requires several days for results and incurs additional cost to the patient.
In this case, the diagnosis was made at the patient’s bedside and terbinafine 250 mg/d for 3 weeks was chosen as systemic therapy because of the extent of disease. At the follow-up visit 2 months later, the patient’s rash had completely cleared.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)

The patient was given a diagnosis of widespread tinea corporis. This diagnosis may not fit with the common paradigm of tinea as thin, scaly annular patches, often known as ringworm. However, a skin scraping was performed on the red scaly patches, and the diagnosis was confirmed.
A skin scraping is a simple procedure that takes minutes to yield actionable information. A scalpel blade is used in a scraping motion and skin flakes are caught on a slide as they fall from the skin. (Another glass slide can be used in place of the scalpel, which is slightly less frightening for children.) The sample is then covered with 1 to 2 drops of potassium hydroxide (KOH), in 1 of various available formulations, and covered with a coverslip. Gently heating the slide, or simply waiting a few minutes, will allow the KOH to begin dissolving some keratinocyte membranes and stain any fungal walls light purple.
Hyphae, which may be linear (see Figure) or branched, will cross multiple cell membranes and are themselves about the thickness of a cell membrane. A high-powered view of hyphae should reveal nuclei and septa.
Skin biopsy, culture, and a skin scraping sent to an outside lab are all alternatives to the aforementioned approach but take days or weeks to yield a result. Fungal polymerase chain reaction is a novel diagnostic approach that can be both sensitive and specific, but still requires several days for results and incurs additional cost to the patient.
In this case, the diagnosis was made at the patient’s bedside and terbinafine 250 mg/d for 3 weeks was chosen as systemic therapy because of the extent of disease. At the follow-up visit 2 months later, the patient’s rash had completely cleared.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Liu D, Coloe S, Baird R, et al. Application of PCR to the identification of dermatophyte fungi. J Med Microbiol. 2000;49:493-497.
Liu D, Coloe S, Baird R, et al. Application of PCR to the identification of dermatophyte fungi. J Med Microbiol. 2000;49:493-497.
Meta-analysis: No evidence that SNRIs relieve back pain
While some guidelines support serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) as treatments for back pain, a new systematic review and meta-analysis of existing research found no firm evidence of a benefit. Adverse effects, however, are common.
“Our review shows that, although these medicines are effective, the effect is small and unlikely to be considered clinically important by most patients,” wrote the authors of the review, which appeared Jan. 20 in the BMJ. “Our review also showed that about two-thirds of patients using SNRIs experience adverse events.”
However, the report hinted that certain classes of antidepressants may provide significant relief in knee OA and sciatica.
According to a 2018 review, 10 of 15 clinical guidelines from around the world – including those of the American College of Physicians – recommended antidepressants as treatments for low back pain, and 2 advised against them. “Evidence supporting the use of antidepressants is, however, uncertain,” wrote the authors of the new review, led by Giovanni E. Ferreira, PhD, of the University of Sydney. “Systematic reviews of antidepressants for back pain and osteoarthritis have either not included several published trials, considered only one type of antidepressant (e.g., duloxetine), or failed to assess the certainty of evidence.”
For the new review, the authors analyzed 33 randomized, controlled trials with a total of 5,318 subjects. Both published data and unpublished data from clinical trial registries were included.
Back pain trials
A total of 19 trials examined back pain, mostly lower back pain (16 trials), and none lasted more than 1 year. Fifteen examined SNRIs while others looked at other kinds of antidepressants.
The researchers found that “the effect of SNRIs was small [on back pain] and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance. ... Evidence ranging from low to very low certainty showed no benefit of a range of antidepressant classes, including SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], tetracyclic antidepressants, SARIs [serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors], and NDRIs [norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors] for pain and disability across follow-ups of 2 weeks or less, 3-13 weeks, and 3-12 months.”
Sciatica trials
Six trials examined antidepressants as treatments for sciatica. Very-low-certainty evidence suggested that SNRIs reduced pain at up to 2 weeks (1 trial, n = 50) but not at 3-13 weeks (3 trials, n = 96). The results of trials of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) were the opposite: low- to very-low-certainty evidence suggested the drugs didn’t reduce pain at up to 2 weeks (2 trials, n = 94) but did at 3-13 weeks (2 trials, n = 114) and 3-12 months (1 trial, n = 60).
“All sciatica trials were small, had imprecise estimates, and were at high risk of bias, which reduced the certainty of evidence to low and very low,” the authors cautioned. “This level of uncertainty indicates that the true estimate of effect of TCAs and SNRIs for sciatica is likely to be substantially different from what we estimated in our review.”
Knee OA trials
Eight trials examined SNRIs in knee OA. Moderate-certainty evidence linked the drugs to less pain at up to 2 weeks (four trials, n = 1,328) and low-certainty evidence linked them to less pain at 3-13 weeks (eight trials, n = 1,941). Low-certainty evidence also linked the drugs to less disability at 2 weeks or less (one trial, n = 353) and 3-13 weeks (seven trials, n = 1,810).
In knee OA, “the effect of SNRIs was small and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance,” the researchers wrote. “However, the lower limit of the confidence interval did contain clinically important effects for pain, but not for disability.”
Antidepressant side effects in trials
A total of 21 trials (n = 4,107) looked at side effects when antidepressants were studied as treatments for back pain and OA. Low-certainty evidence in 13 SNRI trials (n = 3,447) suggested a higher risk of any adverse events in antidepressant versus placebo (62.5% vs. 49.7%; relative risk, 1.23, 95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.30), but there was no significantly higher risk of serious adverse events in 10 SNRI trials with 3,309 subjects (1.6% vs. 1.3%; RR, 1.12, 95% CI, 0.61-2.07).
As for adverse effects of non-SNRIs, “the number of studies evaluating the safety of other antidepressant classes was small, trials were underpowered to detect harm, and the certainty of evidence ranged from low to very low,” the researchers wrote.
Going forward, the authors said that “large, definitive randomized trials that are free of industry ties are urgently needed to resolve uncertainties about the efficacy of antidepressants for sciatica and osteoarthritis highlighted by this review.”
‘Largely ineffective’ drug treatments
In an accompanying commentary, Martin Underwood, of the University of Warwick in Coventry, England, and Colin Tysall, of the University Hospitals of Coventry and Warwickshire, also in Coventry, noted that “drug treatments are largely ineffective for back pain and osteoarthritis and have the potential for serious harm. We need to work harder to help people with these disorders to live better with their pain without recourse to the prescription pad.”
However, they noted that SNRIs may still be helpful for patients with back pain or OA. “Absolute effect sizes for physical treatments for low-back pain are of similar magnitudes to those reported here and translate into numbers needed to treat of between five and nine. If the same were true for SNRIs, some people might choose to a try that option for a 1 in 10 chance of a worthwhile reduction in pain after 3 months. They can easily stop if treatment is ineffective or does not suit them.”
The research received no specific funding. The review authors disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline (postgraduate scholarship), Pfizer (investigational product for two trials), and Flexeze (provision of heat wraps for a trial). Mr. Underwood reported being a director and shareholder of Clinvivo. Mr. Tysall reported no disclosures.
While some guidelines support serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) as treatments for back pain, a new systematic review and meta-analysis of existing research found no firm evidence of a benefit. Adverse effects, however, are common.
“Our review shows that, although these medicines are effective, the effect is small and unlikely to be considered clinically important by most patients,” wrote the authors of the review, which appeared Jan. 20 in the BMJ. “Our review also showed that about two-thirds of patients using SNRIs experience adverse events.”
However, the report hinted that certain classes of antidepressants may provide significant relief in knee OA and sciatica.
According to a 2018 review, 10 of 15 clinical guidelines from around the world – including those of the American College of Physicians – recommended antidepressants as treatments for low back pain, and 2 advised against them. “Evidence supporting the use of antidepressants is, however, uncertain,” wrote the authors of the new review, led by Giovanni E. Ferreira, PhD, of the University of Sydney. “Systematic reviews of antidepressants for back pain and osteoarthritis have either not included several published trials, considered only one type of antidepressant (e.g., duloxetine), or failed to assess the certainty of evidence.”
For the new review, the authors analyzed 33 randomized, controlled trials with a total of 5,318 subjects. Both published data and unpublished data from clinical trial registries were included.
Back pain trials
A total of 19 trials examined back pain, mostly lower back pain (16 trials), and none lasted more than 1 year. Fifteen examined SNRIs while others looked at other kinds of antidepressants.
The researchers found that “the effect of SNRIs was small [on back pain] and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance. ... Evidence ranging from low to very low certainty showed no benefit of a range of antidepressant classes, including SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], tetracyclic antidepressants, SARIs [serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors], and NDRIs [norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors] for pain and disability across follow-ups of 2 weeks or less, 3-13 weeks, and 3-12 months.”
Sciatica trials
Six trials examined antidepressants as treatments for sciatica. Very-low-certainty evidence suggested that SNRIs reduced pain at up to 2 weeks (1 trial, n = 50) but not at 3-13 weeks (3 trials, n = 96). The results of trials of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) were the opposite: low- to very-low-certainty evidence suggested the drugs didn’t reduce pain at up to 2 weeks (2 trials, n = 94) but did at 3-13 weeks (2 trials, n = 114) and 3-12 months (1 trial, n = 60).
“All sciatica trials were small, had imprecise estimates, and were at high risk of bias, which reduced the certainty of evidence to low and very low,” the authors cautioned. “This level of uncertainty indicates that the true estimate of effect of TCAs and SNRIs for sciatica is likely to be substantially different from what we estimated in our review.”
Knee OA trials
Eight trials examined SNRIs in knee OA. Moderate-certainty evidence linked the drugs to less pain at up to 2 weeks (four trials, n = 1,328) and low-certainty evidence linked them to less pain at 3-13 weeks (eight trials, n = 1,941). Low-certainty evidence also linked the drugs to less disability at 2 weeks or less (one trial, n = 353) and 3-13 weeks (seven trials, n = 1,810).
In knee OA, “the effect of SNRIs was small and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance,” the researchers wrote. “However, the lower limit of the confidence interval did contain clinically important effects for pain, but not for disability.”
Antidepressant side effects in trials
A total of 21 trials (n = 4,107) looked at side effects when antidepressants were studied as treatments for back pain and OA. Low-certainty evidence in 13 SNRI trials (n = 3,447) suggested a higher risk of any adverse events in antidepressant versus placebo (62.5% vs. 49.7%; relative risk, 1.23, 95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.30), but there was no significantly higher risk of serious adverse events in 10 SNRI trials with 3,309 subjects (1.6% vs. 1.3%; RR, 1.12, 95% CI, 0.61-2.07).
As for adverse effects of non-SNRIs, “the number of studies evaluating the safety of other antidepressant classes was small, trials were underpowered to detect harm, and the certainty of evidence ranged from low to very low,” the researchers wrote.
Going forward, the authors said that “large, definitive randomized trials that are free of industry ties are urgently needed to resolve uncertainties about the efficacy of antidepressants for sciatica and osteoarthritis highlighted by this review.”
‘Largely ineffective’ drug treatments
In an accompanying commentary, Martin Underwood, of the University of Warwick in Coventry, England, and Colin Tysall, of the University Hospitals of Coventry and Warwickshire, also in Coventry, noted that “drug treatments are largely ineffective for back pain and osteoarthritis and have the potential for serious harm. We need to work harder to help people with these disorders to live better with their pain without recourse to the prescription pad.”
However, they noted that SNRIs may still be helpful for patients with back pain or OA. “Absolute effect sizes for physical treatments for low-back pain are of similar magnitudes to those reported here and translate into numbers needed to treat of between five and nine. If the same were true for SNRIs, some people might choose to a try that option for a 1 in 10 chance of a worthwhile reduction in pain after 3 months. They can easily stop if treatment is ineffective or does not suit them.”
The research received no specific funding. The review authors disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline (postgraduate scholarship), Pfizer (investigational product for two trials), and Flexeze (provision of heat wraps for a trial). Mr. Underwood reported being a director and shareholder of Clinvivo. Mr. Tysall reported no disclosures.
While some guidelines support serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) as treatments for back pain, a new systematic review and meta-analysis of existing research found no firm evidence of a benefit. Adverse effects, however, are common.
“Our review shows that, although these medicines are effective, the effect is small and unlikely to be considered clinically important by most patients,” wrote the authors of the review, which appeared Jan. 20 in the BMJ. “Our review also showed that about two-thirds of patients using SNRIs experience adverse events.”
However, the report hinted that certain classes of antidepressants may provide significant relief in knee OA and sciatica.
According to a 2018 review, 10 of 15 clinical guidelines from around the world – including those of the American College of Physicians – recommended antidepressants as treatments for low back pain, and 2 advised against them. “Evidence supporting the use of antidepressants is, however, uncertain,” wrote the authors of the new review, led by Giovanni E. Ferreira, PhD, of the University of Sydney. “Systematic reviews of antidepressants for back pain and osteoarthritis have either not included several published trials, considered only one type of antidepressant (e.g., duloxetine), or failed to assess the certainty of evidence.”
For the new review, the authors analyzed 33 randomized, controlled trials with a total of 5,318 subjects. Both published data and unpublished data from clinical trial registries were included.
Back pain trials
A total of 19 trials examined back pain, mostly lower back pain (16 trials), and none lasted more than 1 year. Fifteen examined SNRIs while others looked at other kinds of antidepressants.
The researchers found that “the effect of SNRIs was small [on back pain] and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance. ... Evidence ranging from low to very low certainty showed no benefit of a range of antidepressant classes, including SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], tetracyclic antidepressants, SARIs [serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors], and NDRIs [norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors] for pain and disability across follow-ups of 2 weeks or less, 3-13 weeks, and 3-12 months.”
Sciatica trials
Six trials examined antidepressants as treatments for sciatica. Very-low-certainty evidence suggested that SNRIs reduced pain at up to 2 weeks (1 trial, n = 50) but not at 3-13 weeks (3 trials, n = 96). The results of trials of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) were the opposite: low- to very-low-certainty evidence suggested the drugs didn’t reduce pain at up to 2 weeks (2 trials, n = 94) but did at 3-13 weeks (2 trials, n = 114) and 3-12 months (1 trial, n = 60).
“All sciatica trials were small, had imprecise estimates, and were at high risk of bias, which reduced the certainty of evidence to low and very low,” the authors cautioned. “This level of uncertainty indicates that the true estimate of effect of TCAs and SNRIs for sciatica is likely to be substantially different from what we estimated in our review.”
Knee OA trials
Eight trials examined SNRIs in knee OA. Moderate-certainty evidence linked the drugs to less pain at up to 2 weeks (four trials, n = 1,328) and low-certainty evidence linked them to less pain at 3-13 weeks (eight trials, n = 1,941). Low-certainty evidence also linked the drugs to less disability at 2 weeks or less (one trial, n = 353) and 3-13 weeks (seven trials, n = 1,810).
In knee OA, “the effect of SNRIs was small and below this review’s predetermined threshold of clinical importance,” the researchers wrote. “However, the lower limit of the confidence interval did contain clinically important effects for pain, but not for disability.”
Antidepressant side effects in trials
A total of 21 trials (n = 4,107) looked at side effects when antidepressants were studied as treatments for back pain and OA. Low-certainty evidence in 13 SNRI trials (n = 3,447) suggested a higher risk of any adverse events in antidepressant versus placebo (62.5% vs. 49.7%; relative risk, 1.23, 95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.30), but there was no significantly higher risk of serious adverse events in 10 SNRI trials with 3,309 subjects (1.6% vs. 1.3%; RR, 1.12, 95% CI, 0.61-2.07).
As for adverse effects of non-SNRIs, “the number of studies evaluating the safety of other antidepressant classes was small, trials were underpowered to detect harm, and the certainty of evidence ranged from low to very low,” the researchers wrote.
Going forward, the authors said that “large, definitive randomized trials that are free of industry ties are urgently needed to resolve uncertainties about the efficacy of antidepressants for sciatica and osteoarthritis highlighted by this review.”
‘Largely ineffective’ drug treatments
In an accompanying commentary, Martin Underwood, of the University of Warwick in Coventry, England, and Colin Tysall, of the University Hospitals of Coventry and Warwickshire, also in Coventry, noted that “drug treatments are largely ineffective for back pain and osteoarthritis and have the potential for serious harm. We need to work harder to help people with these disorders to live better with their pain without recourse to the prescription pad.”
However, they noted that SNRIs may still be helpful for patients with back pain or OA. “Absolute effect sizes for physical treatments for low-back pain are of similar magnitudes to those reported here and translate into numbers needed to treat of between five and nine. If the same were true for SNRIs, some people might choose to a try that option for a 1 in 10 chance of a worthwhile reduction in pain after 3 months. They can easily stop if treatment is ineffective or does not suit them.”
The research received no specific funding. The review authors disclosed relationships with GlaxoSmithKline (postgraduate scholarship), Pfizer (investigational product for two trials), and Flexeze (provision of heat wraps for a trial). Mr. Underwood reported being a director and shareholder of Clinvivo. Mr. Tysall reported no disclosures.
FROM THE BMJ
Give women's mental health a seat at the health care table
Why it’s time for women’s mental health to be recognized as the subspecialty it already is
It wasn’t until I (Dr. Leistikow) finished my psychiatry residency that I realized the training I had received in women’s mental health was unusual. It was simply a required experience for PGY-3 residents at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
All of us, regardless of interest, spent 1 afternoon a week over 6 months caring for patients in a specialty psychiatric clinic for women (run by Dr. Payne and Dr. Osborne). We discussed cases and received didactics on such topics as risk factors for postpartum depression; the risks of untreated mental illness in pregnancy, compared with the risks of various psychiatric medications; how to choose and dose medications for bipolar disorder as blood levels change across pregnancy; which resources to consult to determine the amounts and risks of various medications passed on in breast milk; and how to diagnose and treat premenstrual dysphoric disorder, to name a few lecture subjects.
By the time we were done, all residents had received more than 20 hours of teaching about how to treat mental illness in women across the reproductive life cycle. This was 20 hours more than is currently required by the American College of Graduate Medical Education, the accrediting body for all residencies, including psychiatry.1 It is time for that to change.
Women’s need for psychiatric treatment that addresses reproductive transitions is not new; it is as old as time. Not only do women who previously needed psychiatric treatment continue to need treatment when they get pregnant or are breastfeeding, but it is now well recognized that times of reproductive transition or flux – whether premenstrual, post partum, or perimenopausal – confer increased risk for both new-onset and exacerbations of prior mental illnesses.
What has changed is psychiatry’s ability to finally meet that need. Previously, despite the fact that women make up the majority of patients presenting for treatment, that nearly all women will menstruate and go through menopause, and that more than 80% of American women will have at least one pregnancy during their lifetime,psychiatrists practice as if these reproductive transitions were unfortunate blips getting in the doctor’s way.2 We mostly threw up our hands when our patients became pregnant, reflexively stopped all medications, and expected women to suffer for the sake of their babies.
with a large and growing research base, with both agreed-upon best practices and evolving standards of care informed by and responsive to the scientific literature. We now know that untreated maternal psychiatric illness carries its own risks for infants both before and after delivery; that many maternal pharmacologic treatments are lower risk for infants than previously thought; that protecting and treating women’s mental health in pregnancy has benefits for women, their babies, and the families that depend on them; and that there is now a growing evidence base informing both new and older treatments and enabling women and their doctors to make complex decisions balancing risk and benefit across the life cycle.
Many psychiatrists-in-training are hungry for this knowledge. At last count, in the United States alone, there were 16 women’s mental health fellowships available, up from just 3 in 2008.3 The problem is that none of them are accredited or funded by the ACGME, because reproductive psychiatry (here used interchangeably with the term women’s mental health) has not been officially recognized as a subspecialty. This means that current funding frequently rests on philanthropy, which often cannot be sustained, and clinical billing, which gives fellows in some programs such heavy clinical responsibilities that little time is left for scholarly work. Lack of subspecialty status also blocks numerous important downstream effects that would flow from this recognition.
Reproductive psychiatry clearly already meets criteria laid out by the American Board of Medical Specialties for defining a subspecialty field. As argued elsewhere, it has a distinct patient population with definable care needs and a standalone body of scientific medical knowledge as well as a national (and international) community of experts that has already done much to improve women’s access to care they desperately need.4 It also meets the ACGME’s criteria for a new subspecialty except for approval by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.5 Finally, it also meets the requirements of the ABPN except for having 25 fellowship programs with 50 fellowship positions and 50 trainees per year completing fellowships, a challenging Catch-22 without the necessary funding that would accrue from accreditation.6
Despite growing awareness and demand, there remains a shortage of psychiatrists trained to treat women during times of reproductive transition and to pass their recommendations and knowledge on to their primary care and ob.gyn. colleagues. What official recognition would bring, in addition to funding for fellowships post residency, is a guaranteed seat at the table in psychiatry residencies, in terms of a required number of hours devoted to these topics for trainees, ensuring that all graduating psychiatrists have at least some exposure to the knowledge and practices so material to their patients.
It isn’t enough to wait for residencies to see the writing on the wall and voluntarily carve out a slice of pie devoted to women’s mental health from the limited time and resources available to train residents. A 2017 survey of psychiatry residency program training directors found that 23%, or almost a quarter of programs that responded, offered no reproductive psychiatry training at all, that 49% required 5 hours or less across all 4 years of training, and that 75% of programs had no required clinical exposure to reproductive psychiatry patients.7 Despite the fact that 87% of training directors surveyed agreed either that reproductive psychiatry was “an important area of education” or a subject general residents should be competent in, ACGME-recognized specialties take precedence.
A system so patchy and insufficient won’t do. It’s not good enough for the trainees who frequently have to look outside of their own institutions for the training they know they need. It’s not good enough for the pregnant or postpartum patient looking for evidence-based advice, who is currently left on her own to determine, prior to booking an appointment, whether a specific psychiatrist has received any training relevant to treating her. Adding reproductive psychiatry to the topics a graduating psychiatrist must have some proficiency in also signals to recent graduates and experienced attendings, as well as the relevant examining boards and producers of continuing medical education content, that women’s mental health is no longer a fringe topic but rather foundational to all practicing psychiatrists.
The oil needed to prime this pump is official recognition of the subspecialty that reproductive psychiatry already is. The women’s mental health community is ready. The research base is well established and growing exponentially. The number of women’s mental health fellowships is healthy and would increase significantly with ACGME funding. Psychiatry residency training programs can turn to recent graduates of these fellowships as well as their own faculty with reproductive psychiatry experience to teach trainees. In addition, the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry, over the last 4 years, has created a repository of free online modules dedicated to facilitating this type of training, with case discussions across numerous topics for use by both educators and trainees. The American Psychiatric Association recently formed the Committee on Women’s Mental Health in 2020 and will be publishing a textbook based on work done by the NCRP within the coming year.
Imagine the changed world that would open to all psychiatrists if reproductive psychiatry were given the credentials it deserves. When writing prescriptions, we would view pregnancy as the potential outcome it is in any woman of reproductive age, given that 50% of pregnancies are unplanned, and let women know ahead of time how to think about possible fetal effects rather than waiting for their panicked phone messages or hearing that they have stopped their medications abruptly. We would work to identify our patient’s individual risk factors for postpartum depression predelivery to reduce that risk and prevent or limit illness. We would plan ahead for close follow-up post partum during the window of greatest risk, rather than expecting women to drop out of care while taking care of their infants or languish on scheduling waiting lists. We would feel confident in giving evidence-based advice to our patients around times of reproductive transition across the life cycle, but especially in pregnancy and lactation, empowering women to make healthy decisions for themselves and their families, no longer abandoning them just when they need us most.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Psychiatry. Accreditation Counsel for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1.
2. Livingston G. “They’re waiting longer, but U.S. women today more likely to have children than a decade ago.” Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. pewsocialtrends.org. 2018 Jan 18.
3. Nagle-Yang S et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):202-6.
4. Payne JL. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2019 May;31(3):207-9.
5. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Policies and Procedures. 2020 Sep 26.
6. American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology. Requirements for Subspecialty Recognition, Attachment A. 2008.
7. Osborne LM et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):197-201.
Dr. Leistikow is a reproductive psychiatrist and clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, where she sees patients and helps train residents and fellows. She is on the education committee of the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry (NCRPtraining.org) and has written about women’s mental health for textbooks, scientific journals and on her private practice blog at www.womenspsychiatrybaltimore.com. Dr. Leistikow has no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Payne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the Women’s Mood Disorders Center at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. In addition to providing outstanding clinical care for women with mood disorders, she conducts research into the genetic, biological, and environmental factors involved in postpartum depression. She and her colleagues have recently identified two epigenetic biomarkers of postpartum depression and are working hard to replicate this work with National Institutes of Health funding. Most recently, she was appointed to the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on women’s mental health and is serving as president-elect for both the Marcé of North America and the International Marcé Perinatal Mental Health Societies. She disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Sage Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. Osborne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and of gynecology and obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University, where she directs a postdoctoral fellowship program in reproductive psychiatry. She is an expert on the diagnosis and treatment of mood and anxiety disorders during pregnancy, the post partum, the premenstrual period, and perimenopause. Her work is supported by the Brain and Behavior Foundation, the Doris Duke Foundation, the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, and the National Institute of Mental Health. She has no conflicts of interest.
Why it’s time for women’s mental health to be recognized as the subspecialty it already is
Why it’s time for women’s mental health to be recognized as the subspecialty it already is
It wasn’t until I (Dr. Leistikow) finished my psychiatry residency that I realized the training I had received in women’s mental health was unusual. It was simply a required experience for PGY-3 residents at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
All of us, regardless of interest, spent 1 afternoon a week over 6 months caring for patients in a specialty psychiatric clinic for women (run by Dr. Payne and Dr. Osborne). We discussed cases and received didactics on such topics as risk factors for postpartum depression; the risks of untreated mental illness in pregnancy, compared with the risks of various psychiatric medications; how to choose and dose medications for bipolar disorder as blood levels change across pregnancy; which resources to consult to determine the amounts and risks of various medications passed on in breast milk; and how to diagnose and treat premenstrual dysphoric disorder, to name a few lecture subjects.
By the time we were done, all residents had received more than 20 hours of teaching about how to treat mental illness in women across the reproductive life cycle. This was 20 hours more than is currently required by the American College of Graduate Medical Education, the accrediting body for all residencies, including psychiatry.1 It is time for that to change.
Women’s need for psychiatric treatment that addresses reproductive transitions is not new; it is as old as time. Not only do women who previously needed psychiatric treatment continue to need treatment when they get pregnant or are breastfeeding, but it is now well recognized that times of reproductive transition or flux – whether premenstrual, post partum, or perimenopausal – confer increased risk for both new-onset and exacerbations of prior mental illnesses.
What has changed is psychiatry’s ability to finally meet that need. Previously, despite the fact that women make up the majority of patients presenting for treatment, that nearly all women will menstruate and go through menopause, and that more than 80% of American women will have at least one pregnancy during their lifetime,psychiatrists practice as if these reproductive transitions were unfortunate blips getting in the doctor’s way.2 We mostly threw up our hands when our patients became pregnant, reflexively stopped all medications, and expected women to suffer for the sake of their babies.
with a large and growing research base, with both agreed-upon best practices and evolving standards of care informed by and responsive to the scientific literature. We now know that untreated maternal psychiatric illness carries its own risks for infants both before and after delivery; that many maternal pharmacologic treatments are lower risk for infants than previously thought; that protecting and treating women’s mental health in pregnancy has benefits for women, their babies, and the families that depend on them; and that there is now a growing evidence base informing both new and older treatments and enabling women and their doctors to make complex decisions balancing risk and benefit across the life cycle.
Many psychiatrists-in-training are hungry for this knowledge. At last count, in the United States alone, there were 16 women’s mental health fellowships available, up from just 3 in 2008.3 The problem is that none of them are accredited or funded by the ACGME, because reproductive psychiatry (here used interchangeably with the term women’s mental health) has not been officially recognized as a subspecialty. This means that current funding frequently rests on philanthropy, which often cannot be sustained, and clinical billing, which gives fellows in some programs such heavy clinical responsibilities that little time is left for scholarly work. Lack of subspecialty status also blocks numerous important downstream effects that would flow from this recognition.
Reproductive psychiatry clearly already meets criteria laid out by the American Board of Medical Specialties for defining a subspecialty field. As argued elsewhere, it has a distinct patient population with definable care needs and a standalone body of scientific medical knowledge as well as a national (and international) community of experts that has already done much to improve women’s access to care they desperately need.4 It also meets the ACGME’s criteria for a new subspecialty except for approval by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.5 Finally, it also meets the requirements of the ABPN except for having 25 fellowship programs with 50 fellowship positions and 50 trainees per year completing fellowships, a challenging Catch-22 without the necessary funding that would accrue from accreditation.6
Despite growing awareness and demand, there remains a shortage of psychiatrists trained to treat women during times of reproductive transition and to pass their recommendations and knowledge on to their primary care and ob.gyn. colleagues. What official recognition would bring, in addition to funding for fellowships post residency, is a guaranteed seat at the table in psychiatry residencies, in terms of a required number of hours devoted to these topics for trainees, ensuring that all graduating psychiatrists have at least some exposure to the knowledge and practices so material to their patients.
It isn’t enough to wait for residencies to see the writing on the wall and voluntarily carve out a slice of pie devoted to women’s mental health from the limited time and resources available to train residents. A 2017 survey of psychiatry residency program training directors found that 23%, or almost a quarter of programs that responded, offered no reproductive psychiatry training at all, that 49% required 5 hours or less across all 4 years of training, and that 75% of programs had no required clinical exposure to reproductive psychiatry patients.7 Despite the fact that 87% of training directors surveyed agreed either that reproductive psychiatry was “an important area of education” or a subject general residents should be competent in, ACGME-recognized specialties take precedence.
A system so patchy and insufficient won’t do. It’s not good enough for the trainees who frequently have to look outside of their own institutions for the training they know they need. It’s not good enough for the pregnant or postpartum patient looking for evidence-based advice, who is currently left on her own to determine, prior to booking an appointment, whether a specific psychiatrist has received any training relevant to treating her. Adding reproductive psychiatry to the topics a graduating psychiatrist must have some proficiency in also signals to recent graduates and experienced attendings, as well as the relevant examining boards and producers of continuing medical education content, that women’s mental health is no longer a fringe topic but rather foundational to all practicing psychiatrists.
The oil needed to prime this pump is official recognition of the subspecialty that reproductive psychiatry already is. The women’s mental health community is ready. The research base is well established and growing exponentially. The number of women’s mental health fellowships is healthy and would increase significantly with ACGME funding. Psychiatry residency training programs can turn to recent graduates of these fellowships as well as their own faculty with reproductive psychiatry experience to teach trainees. In addition, the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry, over the last 4 years, has created a repository of free online modules dedicated to facilitating this type of training, with case discussions across numerous topics for use by both educators and trainees. The American Psychiatric Association recently formed the Committee on Women’s Mental Health in 2020 and will be publishing a textbook based on work done by the NCRP within the coming year.
Imagine the changed world that would open to all psychiatrists if reproductive psychiatry were given the credentials it deserves. When writing prescriptions, we would view pregnancy as the potential outcome it is in any woman of reproductive age, given that 50% of pregnancies are unplanned, and let women know ahead of time how to think about possible fetal effects rather than waiting for their panicked phone messages or hearing that they have stopped their medications abruptly. We would work to identify our patient’s individual risk factors for postpartum depression predelivery to reduce that risk and prevent or limit illness. We would plan ahead for close follow-up post partum during the window of greatest risk, rather than expecting women to drop out of care while taking care of their infants or languish on scheduling waiting lists. We would feel confident in giving evidence-based advice to our patients around times of reproductive transition across the life cycle, but especially in pregnancy and lactation, empowering women to make healthy decisions for themselves and their families, no longer abandoning them just when they need us most.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Psychiatry. Accreditation Counsel for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1.
2. Livingston G. “They’re waiting longer, but U.S. women today more likely to have children than a decade ago.” Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. pewsocialtrends.org. 2018 Jan 18.
3. Nagle-Yang S et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):202-6.
4. Payne JL. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2019 May;31(3):207-9.
5. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Policies and Procedures. 2020 Sep 26.
6. American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology. Requirements for Subspecialty Recognition, Attachment A. 2008.
7. Osborne LM et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):197-201.
Dr. Leistikow is a reproductive psychiatrist and clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, where she sees patients and helps train residents and fellows. She is on the education committee of the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry (NCRPtraining.org) and has written about women’s mental health for textbooks, scientific journals and on her private practice blog at www.womenspsychiatrybaltimore.com. Dr. Leistikow has no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Payne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the Women’s Mood Disorders Center at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. In addition to providing outstanding clinical care for women with mood disorders, she conducts research into the genetic, biological, and environmental factors involved in postpartum depression. She and her colleagues have recently identified two epigenetic biomarkers of postpartum depression and are working hard to replicate this work with National Institutes of Health funding. Most recently, she was appointed to the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on women’s mental health and is serving as president-elect for both the Marcé of North America and the International Marcé Perinatal Mental Health Societies. She disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Sage Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. Osborne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and of gynecology and obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University, where she directs a postdoctoral fellowship program in reproductive psychiatry. She is an expert on the diagnosis and treatment of mood and anxiety disorders during pregnancy, the post partum, the premenstrual period, and perimenopause. Her work is supported by the Brain and Behavior Foundation, the Doris Duke Foundation, the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, and the National Institute of Mental Health. She has no conflicts of interest.
It wasn’t until I (Dr. Leistikow) finished my psychiatry residency that I realized the training I had received in women’s mental health was unusual. It was simply a required experience for PGY-3 residents at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
All of us, regardless of interest, spent 1 afternoon a week over 6 months caring for patients in a specialty psychiatric clinic for women (run by Dr. Payne and Dr. Osborne). We discussed cases and received didactics on such topics as risk factors for postpartum depression; the risks of untreated mental illness in pregnancy, compared with the risks of various psychiatric medications; how to choose and dose medications for bipolar disorder as blood levels change across pregnancy; which resources to consult to determine the amounts and risks of various medications passed on in breast milk; and how to diagnose and treat premenstrual dysphoric disorder, to name a few lecture subjects.
By the time we were done, all residents had received more than 20 hours of teaching about how to treat mental illness in women across the reproductive life cycle. This was 20 hours more than is currently required by the American College of Graduate Medical Education, the accrediting body for all residencies, including psychiatry.1 It is time for that to change.
Women’s need for psychiatric treatment that addresses reproductive transitions is not new; it is as old as time. Not only do women who previously needed psychiatric treatment continue to need treatment when they get pregnant or are breastfeeding, but it is now well recognized that times of reproductive transition or flux – whether premenstrual, post partum, or perimenopausal – confer increased risk for both new-onset and exacerbations of prior mental illnesses.
What has changed is psychiatry’s ability to finally meet that need. Previously, despite the fact that women make up the majority of patients presenting for treatment, that nearly all women will menstruate and go through menopause, and that more than 80% of American women will have at least one pregnancy during their lifetime,psychiatrists practice as if these reproductive transitions were unfortunate blips getting in the doctor’s way.2 We mostly threw up our hands when our patients became pregnant, reflexively stopped all medications, and expected women to suffer for the sake of their babies.
with a large and growing research base, with both agreed-upon best practices and evolving standards of care informed by and responsive to the scientific literature. We now know that untreated maternal psychiatric illness carries its own risks for infants both before and after delivery; that many maternal pharmacologic treatments are lower risk for infants than previously thought; that protecting and treating women’s mental health in pregnancy has benefits for women, their babies, and the families that depend on them; and that there is now a growing evidence base informing both new and older treatments and enabling women and their doctors to make complex decisions balancing risk and benefit across the life cycle.
Many psychiatrists-in-training are hungry for this knowledge. At last count, in the United States alone, there were 16 women’s mental health fellowships available, up from just 3 in 2008.3 The problem is that none of them are accredited or funded by the ACGME, because reproductive psychiatry (here used interchangeably with the term women’s mental health) has not been officially recognized as a subspecialty. This means that current funding frequently rests on philanthropy, which often cannot be sustained, and clinical billing, which gives fellows in some programs such heavy clinical responsibilities that little time is left for scholarly work. Lack of subspecialty status also blocks numerous important downstream effects that would flow from this recognition.
Reproductive psychiatry clearly already meets criteria laid out by the American Board of Medical Specialties for defining a subspecialty field. As argued elsewhere, it has a distinct patient population with definable care needs and a standalone body of scientific medical knowledge as well as a national (and international) community of experts that has already done much to improve women’s access to care they desperately need.4 It also meets the ACGME’s criteria for a new subspecialty except for approval by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology.5 Finally, it also meets the requirements of the ABPN except for having 25 fellowship programs with 50 fellowship positions and 50 trainees per year completing fellowships, a challenging Catch-22 without the necessary funding that would accrue from accreditation.6
Despite growing awareness and demand, there remains a shortage of psychiatrists trained to treat women during times of reproductive transition and to pass their recommendations and knowledge on to their primary care and ob.gyn. colleagues. What official recognition would bring, in addition to funding for fellowships post residency, is a guaranteed seat at the table in psychiatry residencies, in terms of a required number of hours devoted to these topics for trainees, ensuring that all graduating psychiatrists have at least some exposure to the knowledge and practices so material to their patients.
It isn’t enough to wait for residencies to see the writing on the wall and voluntarily carve out a slice of pie devoted to women’s mental health from the limited time and resources available to train residents. A 2017 survey of psychiatry residency program training directors found that 23%, or almost a quarter of programs that responded, offered no reproductive psychiatry training at all, that 49% required 5 hours or less across all 4 years of training, and that 75% of programs had no required clinical exposure to reproductive psychiatry patients.7 Despite the fact that 87% of training directors surveyed agreed either that reproductive psychiatry was “an important area of education” or a subject general residents should be competent in, ACGME-recognized specialties take precedence.
A system so patchy and insufficient won’t do. It’s not good enough for the trainees who frequently have to look outside of their own institutions for the training they know they need. It’s not good enough for the pregnant or postpartum patient looking for evidence-based advice, who is currently left on her own to determine, prior to booking an appointment, whether a specific psychiatrist has received any training relevant to treating her. Adding reproductive psychiatry to the topics a graduating psychiatrist must have some proficiency in also signals to recent graduates and experienced attendings, as well as the relevant examining boards and producers of continuing medical education content, that women’s mental health is no longer a fringe topic but rather foundational to all practicing psychiatrists.
The oil needed to prime this pump is official recognition of the subspecialty that reproductive psychiatry already is. The women’s mental health community is ready. The research base is well established and growing exponentially. The number of women’s mental health fellowships is healthy and would increase significantly with ACGME funding. Psychiatry residency training programs can turn to recent graduates of these fellowships as well as their own faculty with reproductive psychiatry experience to teach trainees. In addition, the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry, over the last 4 years, has created a repository of free online modules dedicated to facilitating this type of training, with case discussions across numerous topics for use by both educators and trainees. The American Psychiatric Association recently formed the Committee on Women’s Mental Health in 2020 and will be publishing a textbook based on work done by the NCRP within the coming year.
Imagine the changed world that would open to all psychiatrists if reproductive psychiatry were given the credentials it deserves. When writing prescriptions, we would view pregnancy as the potential outcome it is in any woman of reproductive age, given that 50% of pregnancies are unplanned, and let women know ahead of time how to think about possible fetal effects rather than waiting for their panicked phone messages or hearing that they have stopped their medications abruptly. We would work to identify our patient’s individual risk factors for postpartum depression predelivery to reduce that risk and prevent or limit illness. We would plan ahead for close follow-up post partum during the window of greatest risk, rather than expecting women to drop out of care while taking care of their infants or languish on scheduling waiting lists. We would feel confident in giving evidence-based advice to our patients around times of reproductive transition across the life cycle, but especially in pregnancy and lactation, empowering women to make healthy decisions for themselves and their families, no longer abandoning them just when they need us most.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Psychiatry. Accreditation Counsel for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1.
2. Livingston G. “They’re waiting longer, but U.S. women today more likely to have children than a decade ago.” Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. pewsocialtrends.org. 2018 Jan 18.
3. Nagle-Yang S et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):202-6.
4. Payne JL. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2019 May;31(3):207-9.
5. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Policies and Procedures. 2020 Sep 26.
6. American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology. Requirements for Subspecialty Recognition, Attachment A. 2008.
7. Osborne LM et al. Acad Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;42(2):197-201.
Dr. Leistikow is a reproductive psychiatrist and clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, where she sees patients and helps train residents and fellows. She is on the education committee of the National Curriculum in Reproductive Psychiatry (NCRPtraining.org) and has written about women’s mental health for textbooks, scientific journals and on her private practice blog at www.womenspsychiatrybaltimore.com. Dr. Leistikow has no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Payne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the Women’s Mood Disorders Center at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. In addition to providing outstanding clinical care for women with mood disorders, she conducts research into the genetic, biological, and environmental factors involved in postpartum depression. She and her colleagues have recently identified two epigenetic biomarkers of postpartum depression and are working hard to replicate this work with National Institutes of Health funding. Most recently, she was appointed to the American Psychiatric Association’s committee on women’s mental health and is serving as president-elect for both the Marcé of North America and the International Marcé Perinatal Mental Health Societies. She disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Sage Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Dr. Osborne is associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and of gynecology and obstetrics at Johns Hopkins University, where she directs a postdoctoral fellowship program in reproductive psychiatry. She is an expert on the diagnosis and treatment of mood and anxiety disorders during pregnancy, the post partum, the premenstrual period, and perimenopause. Her work is supported by the Brain and Behavior Foundation, the Doris Duke Foundation, the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, and the National Institute of Mental Health. She has no conflicts of interest.
Face masks can aggravate rosacea
The “maskne” phenomenon – that is, new onset or exacerbation of preexisting acne due to prolonged wearing of protective face masks – has become commonplace during the COVID-19 pandemic. Less well appreciated is that rosacea often markedly worsens, too, Giovanni Damiani, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“This is particularly interesting because two inflammatory dermatoses with different pathogenesis are both mechanically and microbiologically triggered by mask use,” observed Dr. Damiani, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
He presented . These patients – 23 with papulopustular and 13 with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea – were wearing face masks for at least 6 hours per day during quarantine. Most were using what Dr. Damiani termed “community masks,” meaning they weren’t approved by the European regulatory agency as personal protective equipment.
Every yardstick Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators employed to characterize the patients’ rosacea demonstrated that the dermatosis was significantly worse during the prolonged mask-wearing period. For example, the average prequarantine score on the Global Flushing Severity Scale was 2.56, jumping to 3.97 after a month of masked quarantine. The flushing score climbed from 1.83 to 2.78 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea, and from 3.85 to 6.08 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Scores on the Clinician’s Erythema Assessment rose from 1.09 to 1.7 in the papulopustular rosacea patients, and from 2.46 to 3.54 in those with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea.
Scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index climbed from 7.35 prequarantine to 10.65 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea and from 5.15 to 8.69 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Investigator Global Assessment and Patient’s Self-Assessment scores also deteriorated significantly after a month in masked quarantine.
Clinically, the mask-aggravated rosacea, or “maskacea,” was mainly localized to the dorsal lower third of the nose as well as the cheeks. The ocular and perioral areas and the chin were least affected.
Dr. Damiani advised his colleagues to intensify therapy promptly when patients report any worsening of their preexisting rosacea in connection with use of face masks. He has found this condition is often relatively treatment resistant so long as affected patients continue to wear face masks as an essential tool in preventing transmission of COVID-19.
The dermatologist noted that not all face masks are equal offenders when it comes to aggravating common facial dermatoses. During the spring 2020 pandemic quarantine in Milan, 11.6% of 318 mask wearers, none health care professionals, presented to Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators for treatment of facial dermatoses. The facial dermatosis rate was 5.4% among 168 users of masks bearing the European Union CE mark signifying the devices met relevant safety and performance standards, compared with 18.7% in 150 users of community masks with no CE mark. The rate of irritant contact dermatitis was zero with the CE mark masks and 4.7% with the community masks.
During quarantine, however, these patients wore their protective face masks for only a limited time, since for the most part they were restricted to home. In contrast, during the first week after the quarantine was lifted in early May and the daily hours of mask use increased, facial dermatoses were diagnosed in 8.7% of 23 users of CE-approved masks, compared with 45% of 71 wearers of community masks. Dr. Damiani and colleagues diagnosed irritant contact dermatitis in 16% of the community mask wearers post quarantine, but in not a single user of a mask bearing the CE mark.
The National Rosacea Society has issued patient guidance on avoiding rosacea flare-ups during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Dr. Damiani reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
The “maskne” phenomenon – that is, new onset or exacerbation of preexisting acne due to prolonged wearing of protective face masks – has become commonplace during the COVID-19 pandemic. Less well appreciated is that rosacea often markedly worsens, too, Giovanni Damiani, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“This is particularly interesting because two inflammatory dermatoses with different pathogenesis are both mechanically and microbiologically triggered by mask use,” observed Dr. Damiani, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
He presented . These patients – 23 with papulopustular and 13 with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea – were wearing face masks for at least 6 hours per day during quarantine. Most were using what Dr. Damiani termed “community masks,” meaning they weren’t approved by the European regulatory agency as personal protective equipment.
Every yardstick Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators employed to characterize the patients’ rosacea demonstrated that the dermatosis was significantly worse during the prolonged mask-wearing period. For example, the average prequarantine score on the Global Flushing Severity Scale was 2.56, jumping to 3.97 after a month of masked quarantine. The flushing score climbed from 1.83 to 2.78 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea, and from 3.85 to 6.08 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Scores on the Clinician’s Erythema Assessment rose from 1.09 to 1.7 in the papulopustular rosacea patients, and from 2.46 to 3.54 in those with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea.
Scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index climbed from 7.35 prequarantine to 10.65 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea and from 5.15 to 8.69 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Investigator Global Assessment and Patient’s Self-Assessment scores also deteriorated significantly after a month in masked quarantine.
Clinically, the mask-aggravated rosacea, or “maskacea,” was mainly localized to the dorsal lower third of the nose as well as the cheeks. The ocular and perioral areas and the chin were least affected.
Dr. Damiani advised his colleagues to intensify therapy promptly when patients report any worsening of their preexisting rosacea in connection with use of face masks. He has found this condition is often relatively treatment resistant so long as affected patients continue to wear face masks as an essential tool in preventing transmission of COVID-19.
The dermatologist noted that not all face masks are equal offenders when it comes to aggravating common facial dermatoses. During the spring 2020 pandemic quarantine in Milan, 11.6% of 318 mask wearers, none health care professionals, presented to Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators for treatment of facial dermatoses. The facial dermatosis rate was 5.4% among 168 users of masks bearing the European Union CE mark signifying the devices met relevant safety and performance standards, compared with 18.7% in 150 users of community masks with no CE mark. The rate of irritant contact dermatitis was zero with the CE mark masks and 4.7% with the community masks.
During quarantine, however, these patients wore their protective face masks for only a limited time, since for the most part they were restricted to home. In contrast, during the first week after the quarantine was lifted in early May and the daily hours of mask use increased, facial dermatoses were diagnosed in 8.7% of 23 users of CE-approved masks, compared with 45% of 71 wearers of community masks. Dr. Damiani and colleagues diagnosed irritant contact dermatitis in 16% of the community mask wearers post quarantine, but in not a single user of a mask bearing the CE mark.
The National Rosacea Society has issued patient guidance on avoiding rosacea flare-ups during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Dr. Damiani reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
The “maskne” phenomenon – that is, new onset or exacerbation of preexisting acne due to prolonged wearing of protective face masks – has become commonplace during the COVID-19 pandemic. Less well appreciated is that rosacea often markedly worsens, too, Giovanni Damiani, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“This is particularly interesting because two inflammatory dermatoses with different pathogenesis are both mechanically and microbiologically triggered by mask use,” observed Dr. Damiani, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
He presented . These patients – 23 with papulopustular and 13 with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea – were wearing face masks for at least 6 hours per day during quarantine. Most were using what Dr. Damiani termed “community masks,” meaning they weren’t approved by the European regulatory agency as personal protective equipment.
Every yardstick Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators employed to characterize the patients’ rosacea demonstrated that the dermatosis was significantly worse during the prolonged mask-wearing period. For example, the average prequarantine score on the Global Flushing Severity Scale was 2.56, jumping to 3.97 after a month of masked quarantine. The flushing score climbed from 1.83 to 2.78 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea, and from 3.85 to 6.08 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Scores on the Clinician’s Erythema Assessment rose from 1.09 to 1.7 in the papulopustular rosacea patients, and from 2.46 to 3.54 in those with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea.
Scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index climbed from 7.35 prequarantine to 10.65 in the subgroup with papulopustular rosacea and from 5.15 to 8.69 in patients with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. Investigator Global Assessment and Patient’s Self-Assessment scores also deteriorated significantly after a month in masked quarantine.
Clinically, the mask-aggravated rosacea, or “maskacea,” was mainly localized to the dorsal lower third of the nose as well as the cheeks. The ocular and perioral areas and the chin were least affected.
Dr. Damiani advised his colleagues to intensify therapy promptly when patients report any worsening of their preexisting rosacea in connection with use of face masks. He has found this condition is often relatively treatment resistant so long as affected patients continue to wear face masks as an essential tool in preventing transmission of COVID-19.
The dermatologist noted that not all face masks are equal offenders when it comes to aggravating common facial dermatoses. During the spring 2020 pandemic quarantine in Milan, 11.6% of 318 mask wearers, none health care professionals, presented to Dr. Damiani and coinvestigators for treatment of facial dermatoses. The facial dermatosis rate was 5.4% among 168 users of masks bearing the European Union CE mark signifying the devices met relevant safety and performance standards, compared with 18.7% in 150 users of community masks with no CE mark. The rate of irritant contact dermatitis was zero with the CE mark masks and 4.7% with the community masks.
During quarantine, however, these patients wore their protective face masks for only a limited time, since for the most part they were restricted to home. In contrast, during the first week after the quarantine was lifted in early May and the daily hours of mask use increased, facial dermatoses were diagnosed in 8.7% of 23 users of CE-approved masks, compared with 45% of 71 wearers of community masks. Dr. Damiani and colleagues diagnosed irritant contact dermatitis in 16% of the community mask wearers post quarantine, but in not a single user of a mask bearing the CE mark.
The National Rosacea Society has issued patient guidance on avoiding rosacea flare-ups during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Dr. Damiani reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS