User login
Excess Thrombotic Risk in RA Has No Clear Driving Factor
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — People with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a consistently higher risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) than the general population, but the reasons for this remain unclear, research presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR) reaffirmed.
Regardless of age, sex, body mass index (BMI), duration of disease, use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), people with RA are more likely to experience a pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis than those without RA.
However, “these are rare events,” James Galloway, MBChB, PhD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Centre for Rheumatic Diseases at King’s College London in England, said at the meeting.
In one analysis of data from 117,050 individuals living in England and Wales that are held within a large primary care practice database, Dr. Galloway and colleagues found that the unadjusted incidence of VTE in people diagnosed with RA (n = 23,410) was 0.44% vs 0.26% for matched controls within the general population (n = 93,640).
RA and VTE Risk
The overall risk for VTE was 46% higher among people with RA than among those without, although the absolute difference was small, Dr. Galloway reported.
“RA is associated with an increased risk of VTE; that’s been well described over the years,” Dr. Galloway told this news organization. Past research into why there is an elevated risk for VTE in patients with RA has often focused on the role of disease activity and inflammation.
“In the last few years, a new class of drugs, the JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors, have emerged in which we have seen a signal of increased VTE risk from a number of studies. And I think that puts a spotlight on our understanding of VTE risk,” Dr. Galloway said.
He added “JAK inhibitors are very powerful at controlling inflammation, but if you take away inflammation, there is still an excess risk. What else could be driving that?”
To examine the excess risk for VTE seen in people with RA, Dr. Galloway and colleagues performed three separate analyses using data collected between January 1999 and December 2018 by the Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Center.
One analysis looked at VTE risk according to age, sex, and BMI; another looked at the effect of the duration of RA; and a third analysis focused on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT.
For all three analyses, those with RA were matched in a 4:1 ratio to people from the general population without RA on the basis of current age, sex, calendar time, and years since registration at the primary care practice.
Observational Data Challenged
“These are observational data, so it’s important to weigh up the strengths and limitations,” Dr. Galloway acknowledged. Strengths are the large sample size and long follow-up provided by the database, which assesses and monitors more than 2000 primary care practices in England and Wales.
Confounding is still possible, despite adjusting for multiple factors that included sociodemographic factors; clinical features; and VTE risk factors such as smoking status, alcohol use, thrombophilia, reduced mobility, lower limb fracture, and a family history of VTE if data had been available. There wasn’t information on disease activity, for example, and disease duration was used as a surrogate marker for this.
Sitting in the audience, Marwan Bukhari, MBBS, PhD, challenged the population-matching process.
“Do you think maybe it was the matching that was the problem?” asked Dr. Bukhari, who is consultant rheumatologist at University Hospitals of Morecambe Bay NHS Foundation Trust and an honorary senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, both in England.
“They’re not entirely matched completely, correctly. Even if it is 4:1, there’s a difference between the populations,” he said.
Age, Sex, and Bodyweight
Over an average of 8.2 years’ follow-up, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) comparing VTE risk in women and men with and without RA were a respective 1.62 and 1.52. The corresponding aHRs for VTE according to different age groups were 2.13 for age 18-49 years, 1.57 for age 50-69 years, and 1.34 for age 70 years and older.
“The highest excess risk was in the youngest age group,” Dr. Galloway pointed out, “but all age groups showing a significant increased risk of venous thromboembolism.”
Similar findings were seen across different BMI categories, with the highest risk occurring in those in the lowest BMI group. The aHRs were 1.66, 1.60, and 1.41 for the BMI categories of less than 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, and more than 30 kg/m2, respectively.
Duration of RA
As for disease duration, nearly two thirds (63.9%) of the 23,410 adults with RA included in this analysis were included at or within 2 years of a diagnosis of RA, 7.8% within 2-5 years of diagnosis, 9.8% within 5-10 years of diagnosis, and 18.5% at 10 or more years after diagnosis.
The aHR for an increased relative risk for VTE in people with RA vs the control group ranged from 1.49 for 0-2 years of diagnosis up to 1.63 for more than 10 years since diagnosis.
“We could see no evidence that the VTE excess risk in rheumatoid arthritis was with a specific time since diagnosis,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. “It appears that the risk is increased in people with established RA, whether you’ve had the disease for 2 years or 10 years.”
Similar findings were also seen when they looked at aHRs for pulmonary embolism (1.46-2.02) and deep vein thrombosis (1.43-1.89) separately.
Oral Contraceptives and HRT
Data on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT were detailed in a virtual poster presentation. In this analysis, there were 16,664 women with and 65,448 without RA, and the average follow-up was 8.3 years.
“The number of people available for this analysis was small, and bigger studies are needed,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. Indeed, in the RA group, just 3.3% had used an estrogen-based oral contraceptive and 4.5% had used HRT compared with 3.9% and 3.8% in the control group, respectively.
The overall VTE risk was 52% higher in women with RA than in those without RA.
Risk for VTE was higher among women with RA regardless of the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or not (aHRs, 1.43 and 1.52, respectively) and regardless of the use of HRT or not (aHRs, 2.32 and 1.51).
Assess and Monitor
Together these data increase understanding of how age, gender, obesity, duration of disease, and estrogen-based contraception and HRT may make a difference to someone’s VTE risk.
“In all people with RA, we observe an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, and that is both relevant in a contemporary era when we think about prescribing and the different risks of drugs we use for therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Galloway said.
The overall take-home message, he said, is that VTE risk should be considered in everyone with RA and assessed and monitored accordingly. This includes those who may have traditionally been thought of as having a lower risk than others, such as men vs women, younger vs older individuals, and those who may have had RA for a few years.
The research was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Galloway reported receiving honoraria from Pfizer, AbbVie, Biovitrum, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Sobi, and UCB. Two coauthors of the work were employees of Pfizer. Dr. Bukhari had no conflicts of interest and was not involved in the research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — People with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a consistently higher risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) than the general population, but the reasons for this remain unclear, research presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR) reaffirmed.
Regardless of age, sex, body mass index (BMI), duration of disease, use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), people with RA are more likely to experience a pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis than those without RA.
However, “these are rare events,” James Galloway, MBChB, PhD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Centre for Rheumatic Diseases at King’s College London in England, said at the meeting.
In one analysis of data from 117,050 individuals living in England and Wales that are held within a large primary care practice database, Dr. Galloway and colleagues found that the unadjusted incidence of VTE in people diagnosed with RA (n = 23,410) was 0.44% vs 0.26% for matched controls within the general population (n = 93,640).
RA and VTE Risk
The overall risk for VTE was 46% higher among people with RA than among those without, although the absolute difference was small, Dr. Galloway reported.
“RA is associated with an increased risk of VTE; that’s been well described over the years,” Dr. Galloway told this news organization. Past research into why there is an elevated risk for VTE in patients with RA has often focused on the role of disease activity and inflammation.
“In the last few years, a new class of drugs, the JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors, have emerged in which we have seen a signal of increased VTE risk from a number of studies. And I think that puts a spotlight on our understanding of VTE risk,” Dr. Galloway said.
He added “JAK inhibitors are very powerful at controlling inflammation, but if you take away inflammation, there is still an excess risk. What else could be driving that?”
To examine the excess risk for VTE seen in people with RA, Dr. Galloway and colleagues performed three separate analyses using data collected between January 1999 and December 2018 by the Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Center.
One analysis looked at VTE risk according to age, sex, and BMI; another looked at the effect of the duration of RA; and a third analysis focused on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT.
For all three analyses, those with RA were matched in a 4:1 ratio to people from the general population without RA on the basis of current age, sex, calendar time, and years since registration at the primary care practice.
Observational Data Challenged
“These are observational data, so it’s important to weigh up the strengths and limitations,” Dr. Galloway acknowledged. Strengths are the large sample size and long follow-up provided by the database, which assesses and monitors more than 2000 primary care practices in England and Wales.
Confounding is still possible, despite adjusting for multiple factors that included sociodemographic factors; clinical features; and VTE risk factors such as smoking status, alcohol use, thrombophilia, reduced mobility, lower limb fracture, and a family history of VTE if data had been available. There wasn’t information on disease activity, for example, and disease duration was used as a surrogate marker for this.
Sitting in the audience, Marwan Bukhari, MBBS, PhD, challenged the population-matching process.
“Do you think maybe it was the matching that was the problem?” asked Dr. Bukhari, who is consultant rheumatologist at University Hospitals of Morecambe Bay NHS Foundation Trust and an honorary senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, both in England.
“They’re not entirely matched completely, correctly. Even if it is 4:1, there’s a difference between the populations,” he said.
Age, Sex, and Bodyweight
Over an average of 8.2 years’ follow-up, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) comparing VTE risk in women and men with and without RA were a respective 1.62 and 1.52. The corresponding aHRs for VTE according to different age groups were 2.13 for age 18-49 years, 1.57 for age 50-69 years, and 1.34 for age 70 years and older.
“The highest excess risk was in the youngest age group,” Dr. Galloway pointed out, “but all age groups showing a significant increased risk of venous thromboembolism.”
Similar findings were seen across different BMI categories, with the highest risk occurring in those in the lowest BMI group. The aHRs were 1.66, 1.60, and 1.41 for the BMI categories of less than 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, and more than 30 kg/m2, respectively.
Duration of RA
As for disease duration, nearly two thirds (63.9%) of the 23,410 adults with RA included in this analysis were included at or within 2 years of a diagnosis of RA, 7.8% within 2-5 years of diagnosis, 9.8% within 5-10 years of diagnosis, and 18.5% at 10 or more years after diagnosis.
The aHR for an increased relative risk for VTE in people with RA vs the control group ranged from 1.49 for 0-2 years of diagnosis up to 1.63 for more than 10 years since diagnosis.
“We could see no evidence that the VTE excess risk in rheumatoid arthritis was with a specific time since diagnosis,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. “It appears that the risk is increased in people with established RA, whether you’ve had the disease for 2 years or 10 years.”
Similar findings were also seen when they looked at aHRs for pulmonary embolism (1.46-2.02) and deep vein thrombosis (1.43-1.89) separately.
Oral Contraceptives and HRT
Data on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT were detailed in a virtual poster presentation. In this analysis, there were 16,664 women with and 65,448 without RA, and the average follow-up was 8.3 years.
“The number of people available for this analysis was small, and bigger studies are needed,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. Indeed, in the RA group, just 3.3% had used an estrogen-based oral contraceptive and 4.5% had used HRT compared with 3.9% and 3.8% in the control group, respectively.
The overall VTE risk was 52% higher in women with RA than in those without RA.
Risk for VTE was higher among women with RA regardless of the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or not (aHRs, 1.43 and 1.52, respectively) and regardless of the use of HRT or not (aHRs, 2.32 and 1.51).
Assess and Monitor
Together these data increase understanding of how age, gender, obesity, duration of disease, and estrogen-based contraception and HRT may make a difference to someone’s VTE risk.
“In all people with RA, we observe an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, and that is both relevant in a contemporary era when we think about prescribing and the different risks of drugs we use for therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Galloway said.
The overall take-home message, he said, is that VTE risk should be considered in everyone with RA and assessed and monitored accordingly. This includes those who may have traditionally been thought of as having a lower risk than others, such as men vs women, younger vs older individuals, and those who may have had RA for a few years.
The research was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Galloway reported receiving honoraria from Pfizer, AbbVie, Biovitrum, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Sobi, and UCB. Two coauthors of the work were employees of Pfizer. Dr. Bukhari had no conflicts of interest and was not involved in the research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL, ENGLAND — People with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a consistently higher risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE) than the general population, but the reasons for this remain unclear, research presented at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology (BSR) reaffirmed.
Regardless of age, sex, body mass index (BMI), duration of disease, use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), people with RA are more likely to experience a pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis than those without RA.
However, “these are rare events,” James Galloway, MBChB, PhD, professor of rheumatology and deputy head of the Centre for Rheumatic Diseases at King’s College London in England, said at the meeting.
In one analysis of data from 117,050 individuals living in England and Wales that are held within a large primary care practice database, Dr. Galloway and colleagues found that the unadjusted incidence of VTE in people diagnosed with RA (n = 23,410) was 0.44% vs 0.26% for matched controls within the general population (n = 93,640).
RA and VTE Risk
The overall risk for VTE was 46% higher among people with RA than among those without, although the absolute difference was small, Dr. Galloway reported.
“RA is associated with an increased risk of VTE; that’s been well described over the years,” Dr. Galloway told this news organization. Past research into why there is an elevated risk for VTE in patients with RA has often focused on the role of disease activity and inflammation.
“In the last few years, a new class of drugs, the JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitors, have emerged in which we have seen a signal of increased VTE risk from a number of studies. And I think that puts a spotlight on our understanding of VTE risk,” Dr. Galloway said.
He added “JAK inhibitors are very powerful at controlling inflammation, but if you take away inflammation, there is still an excess risk. What else could be driving that?”
To examine the excess risk for VTE seen in people with RA, Dr. Galloway and colleagues performed three separate analyses using data collected between January 1999 and December 2018 by the Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Center.
One analysis looked at VTE risk according to age, sex, and BMI; another looked at the effect of the duration of RA; and a third analysis focused on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT.
For all three analyses, those with RA were matched in a 4:1 ratio to people from the general population without RA on the basis of current age, sex, calendar time, and years since registration at the primary care practice.
Observational Data Challenged
“These are observational data, so it’s important to weigh up the strengths and limitations,” Dr. Galloway acknowledged. Strengths are the large sample size and long follow-up provided by the database, which assesses and monitors more than 2000 primary care practices in England and Wales.
Confounding is still possible, despite adjusting for multiple factors that included sociodemographic factors; clinical features; and VTE risk factors such as smoking status, alcohol use, thrombophilia, reduced mobility, lower limb fracture, and a family history of VTE if data had been available. There wasn’t information on disease activity, for example, and disease duration was used as a surrogate marker for this.
Sitting in the audience, Marwan Bukhari, MBBS, PhD, challenged the population-matching process.
“Do you think maybe it was the matching that was the problem?” asked Dr. Bukhari, who is consultant rheumatologist at University Hospitals of Morecambe Bay NHS Foundation Trust and an honorary senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, both in England.
“They’re not entirely matched completely, correctly. Even if it is 4:1, there’s a difference between the populations,” he said.
Age, Sex, and Bodyweight
Over an average of 8.2 years’ follow-up, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) comparing VTE risk in women and men with and without RA were a respective 1.62 and 1.52. The corresponding aHRs for VTE according to different age groups were 2.13 for age 18-49 years, 1.57 for age 50-69 years, and 1.34 for age 70 years and older.
“The highest excess risk was in the youngest age group,” Dr. Galloway pointed out, “but all age groups showing a significant increased risk of venous thromboembolism.”
Similar findings were seen across different BMI categories, with the highest risk occurring in those in the lowest BMI group. The aHRs were 1.66, 1.60, and 1.41 for the BMI categories of less than 25 kg/m2, 25-30 kg/m2, and more than 30 kg/m2, respectively.
Duration of RA
As for disease duration, nearly two thirds (63.9%) of the 23,410 adults with RA included in this analysis were included at or within 2 years of a diagnosis of RA, 7.8% within 2-5 years of diagnosis, 9.8% within 5-10 years of diagnosis, and 18.5% at 10 or more years after diagnosis.
The aHR for an increased relative risk for VTE in people with RA vs the control group ranged from 1.49 for 0-2 years of diagnosis up to 1.63 for more than 10 years since diagnosis.
“We could see no evidence that the VTE excess risk in rheumatoid arthritis was with a specific time since diagnosis,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. “It appears that the risk is increased in people with established RA, whether you’ve had the disease for 2 years or 10 years.”
Similar findings were also seen when they looked at aHRs for pulmonary embolism (1.46-2.02) and deep vein thrombosis (1.43-1.89) separately.
Oral Contraceptives and HRT
Data on the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or HRT were detailed in a virtual poster presentation. In this analysis, there were 16,664 women with and 65,448 without RA, and the average follow-up was 8.3 years.
“The number of people available for this analysis was small, and bigger studies are needed,” Dr. Galloway said in the interview. Indeed, in the RA group, just 3.3% had used an estrogen-based oral contraceptive and 4.5% had used HRT compared with 3.9% and 3.8% in the control group, respectively.
The overall VTE risk was 52% higher in women with RA than in those without RA.
Risk for VTE was higher among women with RA regardless of the use of estrogen-based oral contraceptives or not (aHRs, 1.43 and 1.52, respectively) and regardless of the use of HRT or not (aHRs, 2.32 and 1.51).
Assess and Monitor
Together these data increase understanding of how age, gender, obesity, duration of disease, and estrogen-based contraception and HRT may make a difference to someone’s VTE risk.
“In all people with RA, we observe an increased risk of venous thromboembolism, and that is both relevant in a contemporary era when we think about prescribing and the different risks of drugs we use for therapeutic strategies,” Dr. Galloway said.
The overall take-home message, he said, is that VTE risk should be considered in everyone with RA and assessed and monitored accordingly. This includes those who may have traditionally been thought of as having a lower risk than others, such as men vs women, younger vs older individuals, and those who may have had RA for a few years.
The research was funded by Pfizer. Dr. Galloway reported receiving honoraria from Pfizer, AbbVie, Biovitrum, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Chugai, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Sobi, and UCB. Two coauthors of the work were employees of Pfizer. Dr. Bukhari had no conflicts of interest and was not involved in the research.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BSR 2024
Clinical Manifestation of Degos Disease: Painful Penile Ulcers
To the Editor:
A 56-year-old man was referred to our Grand Rounds by another dermatologist in our health system for evaluation of a red scaly rash on the trunk that had been present for more than a year. More recently, over the course of approximately 9 months he experienced recurrent painful penile ulcers that lasted for approximately 4 weeks and then self-resolved. He had a medical history of central retinal vein occlusion, primary hyperparathyroidism, and nonspecific colitis. A family history was notable for lung cancer in the patient’s father and myelodysplastic syndrome and breast cancer in his mother; however, there was no family history of a similar rash. A bacterial culture of the penile ulcer was negative. Testing for antibodies against HIV and herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 was negative. Results of a serum VDRL test were nonreactive, which ruled out syphilis. The patient was treated by the referring dermatologist with azithromycin for possible chancroid without relief.
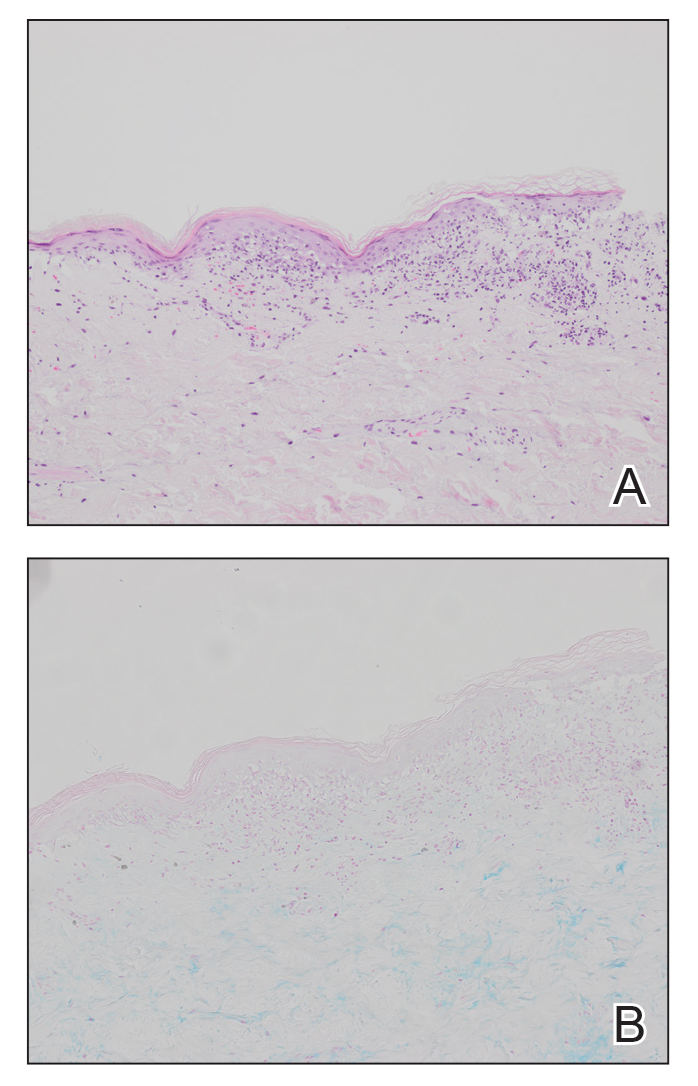
The patient was being followed by the referring dermatologist who initially was concerned for Degos disease based on clinical examination findings, prompting biopsy of a lesion on the back, which revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis, a sparse superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin—all highly suspicious for connective tissue disease (Figure 1). An antinuclear antibody test was positive, with a titer of 1:640. The patient was started on prednisone and referred to rheumatology; however, further evaluation by rheumatology for an autoimmune process—including anticardiolipin antibodies—was unremarkable. A few months prior to the current presentation, he also had mildly elevated liver function test results. A colonoscopy was performed, and a biopsy revealed nonspecific colitis. A biopsy of the penile ulcer also was nonspecific, showing only ulceration and acute and chronic inflammation. No epidermal interface change was seen. Results from a Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain, Treponema pallidum immunostain, and HSV polymerase chain reaction were negative for fungal organisms, spirochetes, and HSV, respectively. The differential diagnosis included trauma, aphthous ulceration, and Behçet disease. Behçet disease was suspected by the referring dermatologist, and the patient was treated with colchicine, prednisone, pimecrolimus cream, and topical lidocaine; however, the lesions persisted, and he was subsequently referred to our Grand Rounds for further evaluation.
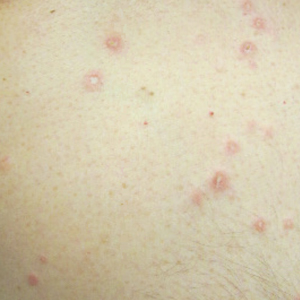
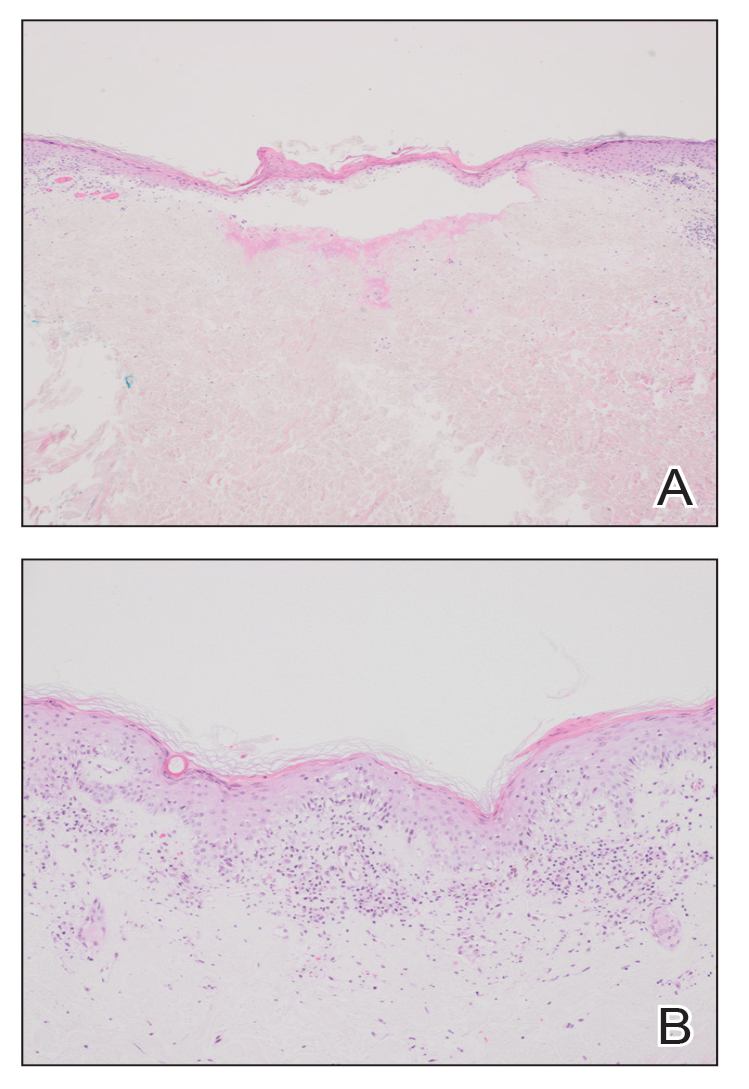
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed several small papules with white atrophic centers and erythematous rims on the trunk and extremities (Figure 2A). An ulceration was noted on the penile shaft (Figure 2B). Further evaluation for Behçet disease, including testing for pathergy and HLA-B51, was negative. Degos disease was strongly suspected clinically, and a repeat biopsy was performed of a lesion on the abdomen, which revealed central epidermal necrosis, atrophy, and parakeratosis with an underlying wedge-shaped dermal infarct surrounded by multiple small occluded dermal vessels, perivascular inflammation, and dermal edema (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was performed using antibodies against IgG, IgA, IgM, fibrinogen, albumin, and C3, which was negative. These findings from direct immunofluorescence and histopathology as well as the clinical presentation were considered compatible with Degos disease. The patient was started on aspirin and pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline 400 mg twice daily appeared to lessen some of the pain. Pain management specialists started the patient on gabapentin.

Approximately 4 months after the Grand Rounds evaluation, during which time he continued treatment with pentoxifylline, he was admitted to the hospital for intractable nausea and vomiting. His condition acutely declined due to bowel perforation, and he was started on eculizumab 1200 mg every 14 days. Because of an increased risk for meningococcal meningitis while on this medication, he also was given erythromycin 500 mg twice daily prophylactically. He was being followed by hematology for the vasculopathy, and they were planning to monitor for any disease changes with computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis every 3 months, as well as echocardiogram every 6 months for any development of pericardial or pleural fibrosis. Approximately 1 month later, the patient was admitted to the hospital again but died after 1 week from gastrointestinal complications (approximately 22 months after the onset of the rash).
Degos disease (atrophic papulosis) is a rare small vessel vasculopathy of unknown etiology, but complement-mediated endothelial injury plays a role.1,2 It typically occurs in the fourth decade of life, with a slight female predominance.3,4 The skin lesions are characteristic and described as 5- to 10-mm papules with atrophic white centers and erythematous telangiectatic rims, most commonly on the upper body and typically sparing the head, palms, and soles.1 Penile ulceration is an uncommon cutaneous feature, with only a few cases reported in the literature.5,6 Approximately one-third of patients will have only skin lesions, but two-thirds will develop systemic involvement 1 to 2 years after onset, with the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system most commonly involved. For those with systemic involvement, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 55%, and the most common causes of death are bowel perforation, peritonitis, and stroke.3,4 Because some patients appear to never develop systemic complications, Theodoridis et al4 proposed that the disease be classified as either malignant atrophic papulosis or benign atrophic papulosis to indicate the malignant systemic form and the benign cutaneous form, respectively.
The histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve.7 Early lesions show a superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate, possible interface dermatitis, and dermal mucin resembling lupus. The more fully developed lesions show a greater degree of inflammation and interface change as well as lymphocytic vasculitis. This stage also may have epidermal atrophy and early papillary dermal sclerosis resembling lichen sclerosus. The late-stage lesions, clinically observed as papules with atrophic white centers and surrounding erythema, show the classic pathology of wedge-shaped dermal sclerosis and central epidermal atrophy with surrounding hyperkeratosis. Interface dermatitis and dermal mucin can be seen in all stages, though mucin is diminished in the later stage.
Effective treatment options are limited; however, antithrombotics or compounds that facilitate blood perfusion, such as aspirin or pentoxifylline, initially can be used.1 Eculizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that prevents the cleavage of C5, has been used for salvage therapy,8 as in our case. Treprostinil, a prostacyclin analog that causes arterial vasodilation and inhibition of platelet aggregation, has been reported to improve bowel and cutaneous lesions, functional status, and neurologic symptoms.9
Our case highlights important features of Degos disease. First, it is important for both the clinician and the pathologist to recognize that the histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve. In our case, although the lesions were characteristic of Degos disease clinically, the initial biopsy was suspicious for connective tissue disease, which led to an autoimmune evaluation that ultimately was unremarkable. Recognizing that early lesions of Degos disease can resemble connective tissue disease histologically could have prevented this delay in diagnosis. However, Degos disease has been reported in association with autoimmune diseases.10 Second, although penile ulceration is uncommon, it can be a prominent cutaneous manifestation of the disease. Finally, eculizumab and treprostinil are therapeutic options that have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms and cutaneous lesions.8,9
- Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease)—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:10. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-10
- Magro CM, Poe JC, Kim C, et al. Degos disease: a C5b-9/interferon-α-mediated endotheliopathy syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135:599-610. doi:10.1309/AJCP66QIMFARLZKI
- Hu P, Mao Z, Liu C, et al. Malignant atrophic papulosis with motor aphasia and intestinal perforation: a case report and review of published works. J Dermatol. 2018;45:723-726. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14280
- Theodoridis A, Konstantinidou A, Makrantonaki E, et al. Malignant and benign forms of atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease): systemic involvement determines the prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:110-115. doi:10.1111/bjd.12642
- Thomson KF, Highet AS. Penile ulceration in fatal malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos’ disease). Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1320-1322. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03911.x
- Aydogan K, Alkan G, Karadogan Koran S, et al. Painful penile ulceration in a patient with malignant atrophic papulosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:612-616. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01227.x
- Harvell JD, Williford PL, White WL. Benign cutaneous Degos’ disease: a case report with emphasis on histopathology as papules chronologically evolve. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:116-123. doi:10.1097/00000372-200104000-00006
- Oliver B, Boehm M, Rosing DR, et al. Diffuse atrophic papules and plaques, intermittent abdominal pain, paresthesias, and cardiac abnormalities in a 55-year-old woman. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:1274-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.09.015
- Shapiro LS, Toledo-Garcia AE, Farrell JF. Effective treatment of malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease) with treprostinil—early experience. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:52. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-52
- Burgin S, Stone JH, Shenoy-Bhangle AS, et al. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 18-2014. A 32-year-old man with a rash, myalgia, and weakness. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2327-2337. doi:10.1056/NEJMcpc1304161
To the Editor:
A 56-year-old man was referred to our Grand Rounds by another dermatologist in our health system for evaluation of a red scaly rash on the trunk that had been present for more than a year. More recently, over the course of approximately 9 months he experienced recurrent painful penile ulcers that lasted for approximately 4 weeks and then self-resolved. He had a medical history of central retinal vein occlusion, primary hyperparathyroidism, and nonspecific colitis. A family history was notable for lung cancer in the patient’s father and myelodysplastic syndrome and breast cancer in his mother; however, there was no family history of a similar rash. A bacterial culture of the penile ulcer was negative. Testing for antibodies against HIV and herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 was negative. Results of a serum VDRL test were nonreactive, which ruled out syphilis. The patient was treated by the referring dermatologist with azithromycin for possible chancroid without relief.
The patient was being followed by the referring dermatologist who initially was concerned for Degos disease based on clinical examination findings, prompting biopsy of a lesion on the back, which revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis, a sparse superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin—all highly suspicious for connective tissue disease (Figure 1). An antinuclear antibody test was positive, with a titer of 1:640. The patient was started on prednisone and referred to rheumatology; however, further evaluation by rheumatology for an autoimmune process—including anticardiolipin antibodies—was unremarkable. A few months prior to the current presentation, he also had mildly elevated liver function test results. A colonoscopy was performed, and a biopsy revealed nonspecific colitis. A biopsy of the penile ulcer also was nonspecific, showing only ulceration and acute and chronic inflammation. No epidermal interface change was seen. Results from a Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain, Treponema pallidum immunostain, and HSV polymerase chain reaction were negative for fungal organisms, spirochetes, and HSV, respectively. The differential diagnosis included trauma, aphthous ulceration, and Behçet disease. Behçet disease was suspected by the referring dermatologist, and the patient was treated with colchicine, prednisone, pimecrolimus cream, and topical lidocaine; however, the lesions persisted, and he was subsequently referred to our Grand Rounds for further evaluation.

At the current presentation, physical examination revealed several small papules with white atrophic centers and erythematous rims on the trunk and extremities (Figure 2A). An ulceration was noted on the penile shaft (Figure 2B). Further evaluation for Behçet disease, including testing for pathergy and HLA-B51, was negative. Degos disease was strongly suspected clinically, and a repeat biopsy was performed of a lesion on the abdomen, which revealed central epidermal necrosis, atrophy, and parakeratosis with an underlying wedge-shaped dermal infarct surrounded by multiple small occluded dermal vessels, perivascular inflammation, and dermal edema (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was performed using antibodies against IgG, IgA, IgM, fibrinogen, albumin, and C3, which was negative. These findings from direct immunofluorescence and histopathology as well as the clinical presentation were considered compatible with Degos disease. The patient was started on aspirin and pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline 400 mg twice daily appeared to lessen some of the pain. Pain management specialists started the patient on gabapentin.

Approximately 4 months after the Grand Rounds evaluation, during which time he continued treatment with pentoxifylline, he was admitted to the hospital for intractable nausea and vomiting. His condition acutely declined due to bowel perforation, and he was started on eculizumab 1200 mg every 14 days. Because of an increased risk for meningococcal meningitis while on this medication, he also was given erythromycin 500 mg twice daily prophylactically. He was being followed by hematology for the vasculopathy, and they were planning to monitor for any disease changes with computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis every 3 months, as well as echocardiogram every 6 months for any development of pericardial or pleural fibrosis. Approximately 1 month later, the patient was admitted to the hospital again but died after 1 week from gastrointestinal complications (approximately 22 months after the onset of the rash).

Degos disease (atrophic papulosis) is a rare small vessel vasculopathy of unknown etiology, but complement-mediated endothelial injury plays a role.1,2 It typically occurs in the fourth decade of life, with a slight female predominance.3,4 The skin lesions are characteristic and described as 5- to 10-mm papules with atrophic white centers and erythematous telangiectatic rims, most commonly on the upper body and typically sparing the head, palms, and soles.1 Penile ulceration is an uncommon cutaneous feature, with only a few cases reported in the literature.5,6 Approximately one-third of patients will have only skin lesions, but two-thirds will develop systemic involvement 1 to 2 years after onset, with the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system most commonly involved. For those with systemic involvement, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 55%, and the most common causes of death are bowel perforation, peritonitis, and stroke.3,4 Because some patients appear to never develop systemic complications, Theodoridis et al4 proposed that the disease be classified as either malignant atrophic papulosis or benign atrophic papulosis to indicate the malignant systemic form and the benign cutaneous form, respectively.
The histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve.7 Early lesions show a superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate, possible interface dermatitis, and dermal mucin resembling lupus. The more fully developed lesions show a greater degree of inflammation and interface change as well as lymphocytic vasculitis. This stage also may have epidermal atrophy and early papillary dermal sclerosis resembling lichen sclerosus. The late-stage lesions, clinically observed as papules with atrophic white centers and surrounding erythema, show the classic pathology of wedge-shaped dermal sclerosis and central epidermal atrophy with surrounding hyperkeratosis. Interface dermatitis and dermal mucin can be seen in all stages, though mucin is diminished in the later stage.
Effective treatment options are limited; however, antithrombotics or compounds that facilitate blood perfusion, such as aspirin or pentoxifylline, initially can be used.1 Eculizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that prevents the cleavage of C5, has been used for salvage therapy,8 as in our case. Treprostinil, a prostacyclin analog that causes arterial vasodilation and inhibition of platelet aggregation, has been reported to improve bowel and cutaneous lesions, functional status, and neurologic symptoms.9
Our case highlights important features of Degos disease. First, it is important for both the clinician and the pathologist to recognize that the histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve. In our case, although the lesions were characteristic of Degos disease clinically, the initial biopsy was suspicious for connective tissue disease, which led to an autoimmune evaluation that ultimately was unremarkable. Recognizing that early lesions of Degos disease can resemble connective tissue disease histologically could have prevented this delay in diagnosis. However, Degos disease has been reported in association with autoimmune diseases.10 Second, although penile ulceration is uncommon, it can be a prominent cutaneous manifestation of the disease. Finally, eculizumab and treprostinil are therapeutic options that have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms and cutaneous lesions.8,9
To the Editor:
A 56-year-old man was referred to our Grand Rounds by another dermatologist in our health system for evaluation of a red scaly rash on the trunk that had been present for more than a year. More recently, over the course of approximately 9 months he experienced recurrent painful penile ulcers that lasted for approximately 4 weeks and then self-resolved. He had a medical history of central retinal vein occlusion, primary hyperparathyroidism, and nonspecific colitis. A family history was notable for lung cancer in the patient’s father and myelodysplastic syndrome and breast cancer in his mother; however, there was no family history of a similar rash. A bacterial culture of the penile ulcer was negative. Testing for antibodies against HIV and herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 was negative. Results of a serum VDRL test were nonreactive, which ruled out syphilis. The patient was treated by the referring dermatologist with azithromycin for possible chancroid without relief.
The patient was being followed by the referring dermatologist who initially was concerned for Degos disease based on clinical examination findings, prompting biopsy of a lesion on the back, which revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis, a sparse superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, and increased mucin—all highly suspicious for connective tissue disease (Figure 1). An antinuclear antibody test was positive, with a titer of 1:640. The patient was started on prednisone and referred to rheumatology; however, further evaluation by rheumatology for an autoimmune process—including anticardiolipin antibodies—was unremarkable. A few months prior to the current presentation, he also had mildly elevated liver function test results. A colonoscopy was performed, and a biopsy revealed nonspecific colitis. A biopsy of the penile ulcer also was nonspecific, showing only ulceration and acute and chronic inflammation. No epidermal interface change was seen. Results from a Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain, Treponema pallidum immunostain, and HSV polymerase chain reaction were negative for fungal organisms, spirochetes, and HSV, respectively. The differential diagnosis included trauma, aphthous ulceration, and Behçet disease. Behçet disease was suspected by the referring dermatologist, and the patient was treated with colchicine, prednisone, pimecrolimus cream, and topical lidocaine; however, the lesions persisted, and he was subsequently referred to our Grand Rounds for further evaluation.

At the current presentation, physical examination revealed several small papules with white atrophic centers and erythematous rims on the trunk and extremities (Figure 2A). An ulceration was noted on the penile shaft (Figure 2B). Further evaluation for Behçet disease, including testing for pathergy and HLA-B51, was negative. Degos disease was strongly suspected clinically, and a repeat biopsy was performed of a lesion on the abdomen, which revealed central epidermal necrosis, atrophy, and parakeratosis with an underlying wedge-shaped dermal infarct surrounded by multiple small occluded dermal vessels, perivascular inflammation, and dermal edema (Figure 3). Direct immunofluorescence was performed using antibodies against IgG, IgA, IgM, fibrinogen, albumin, and C3, which was negative. These findings from direct immunofluorescence and histopathology as well as the clinical presentation were considered compatible with Degos disease. The patient was started on aspirin and pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline 400 mg twice daily appeared to lessen some of the pain. Pain management specialists started the patient on gabapentin.

Approximately 4 months after the Grand Rounds evaluation, during which time he continued treatment with pentoxifylline, he was admitted to the hospital for intractable nausea and vomiting. His condition acutely declined due to bowel perforation, and he was started on eculizumab 1200 mg every 14 days. Because of an increased risk for meningococcal meningitis while on this medication, he also was given erythromycin 500 mg twice daily prophylactically. He was being followed by hematology for the vasculopathy, and they were planning to monitor for any disease changes with computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis every 3 months, as well as echocardiogram every 6 months for any development of pericardial or pleural fibrosis. Approximately 1 month later, the patient was admitted to the hospital again but died after 1 week from gastrointestinal complications (approximately 22 months after the onset of the rash).

Degos disease (atrophic papulosis) is a rare small vessel vasculopathy of unknown etiology, but complement-mediated endothelial injury plays a role.1,2 It typically occurs in the fourth decade of life, with a slight female predominance.3,4 The skin lesions are characteristic and described as 5- to 10-mm papules with atrophic white centers and erythematous telangiectatic rims, most commonly on the upper body and typically sparing the head, palms, and soles.1 Penile ulceration is an uncommon cutaneous feature, with only a few cases reported in the literature.5,6 Approximately one-third of patients will have only skin lesions, but two-thirds will develop systemic involvement 1 to 2 years after onset, with the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system most commonly involved. For those with systemic involvement, the 5-year survival rate is approximately 55%, and the most common causes of death are bowel perforation, peritonitis, and stroke.3,4 Because some patients appear to never develop systemic complications, Theodoridis et al4 proposed that the disease be classified as either malignant atrophic papulosis or benign atrophic papulosis to indicate the malignant systemic form and the benign cutaneous form, respectively.
The histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve.7 Early lesions show a superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrate, possible interface dermatitis, and dermal mucin resembling lupus. The more fully developed lesions show a greater degree of inflammation and interface change as well as lymphocytic vasculitis. This stage also may have epidermal atrophy and early papillary dermal sclerosis resembling lichen sclerosus. The late-stage lesions, clinically observed as papules with atrophic white centers and surrounding erythema, show the classic pathology of wedge-shaped dermal sclerosis and central epidermal atrophy with surrounding hyperkeratosis. Interface dermatitis and dermal mucin can be seen in all stages, though mucin is diminished in the later stage.
Effective treatment options are limited; however, antithrombotics or compounds that facilitate blood perfusion, such as aspirin or pentoxifylline, initially can be used.1 Eculizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that prevents the cleavage of C5, has been used for salvage therapy,8 as in our case. Treprostinil, a prostacyclin analog that causes arterial vasodilation and inhibition of platelet aggregation, has been reported to improve bowel and cutaneous lesions, functional status, and neurologic symptoms.9
Our case highlights important features of Degos disease. First, it is important for both the clinician and the pathologist to recognize that the histopathology of Degos disease changes as the lesions evolve. In our case, although the lesions were characteristic of Degos disease clinically, the initial biopsy was suspicious for connective tissue disease, which led to an autoimmune evaluation that ultimately was unremarkable. Recognizing that early lesions of Degos disease can resemble connective tissue disease histologically could have prevented this delay in diagnosis. However, Degos disease has been reported in association with autoimmune diseases.10 Second, although penile ulceration is uncommon, it can be a prominent cutaneous manifestation of the disease. Finally, eculizumab and treprostinil are therapeutic options that have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms and cutaneous lesions.8,9
- Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease)—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:10. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-10
- Magro CM, Poe JC, Kim C, et al. Degos disease: a C5b-9/interferon-α-mediated endotheliopathy syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135:599-610. doi:10.1309/AJCP66QIMFARLZKI
- Hu P, Mao Z, Liu C, et al. Malignant atrophic papulosis with motor aphasia and intestinal perforation: a case report and review of published works. J Dermatol. 2018;45:723-726. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14280
- Theodoridis A, Konstantinidou A, Makrantonaki E, et al. Malignant and benign forms of atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease): systemic involvement determines the prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:110-115. doi:10.1111/bjd.12642
- Thomson KF, Highet AS. Penile ulceration in fatal malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos’ disease). Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1320-1322. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03911.x
- Aydogan K, Alkan G, Karadogan Koran S, et al. Painful penile ulceration in a patient with malignant atrophic papulosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:612-616. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01227.x
- Harvell JD, Williford PL, White WL. Benign cutaneous Degos’ disease: a case report with emphasis on histopathology as papules chronologically evolve. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:116-123. doi:10.1097/00000372-200104000-00006
- Oliver B, Boehm M, Rosing DR, et al. Diffuse atrophic papules and plaques, intermittent abdominal pain, paresthesias, and cardiac abnormalities in a 55-year-old woman. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:1274-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.09.015
- Shapiro LS, Toledo-Garcia AE, Farrell JF. Effective treatment of malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease) with treprostinil—early experience. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:52. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-52
- Burgin S, Stone JH, Shenoy-Bhangle AS, et al. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 18-2014. A 32-year-old man with a rash, myalgia, and weakness. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2327-2337. doi:10.1056/NEJMcpc1304161
- Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease)—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:10. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-10
- Magro CM, Poe JC, Kim C, et al. Degos disease: a C5b-9/interferon-α-mediated endotheliopathy syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;135:599-610. doi:10.1309/AJCP66QIMFARLZKI
- Hu P, Mao Z, Liu C, et al. Malignant atrophic papulosis with motor aphasia and intestinal perforation: a case report and review of published works. J Dermatol. 2018;45:723-726. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14280
- Theodoridis A, Konstantinidou A, Makrantonaki E, et al. Malignant and benign forms of atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease): systemic involvement determines the prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:110-115. doi:10.1111/bjd.12642
- Thomson KF, Highet AS. Penile ulceration in fatal malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos’ disease). Br J Dermatol. 2000;143:1320-1322. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03911.x
- Aydogan K, Alkan G, Karadogan Koran S, et al. Painful penile ulceration in a patient with malignant atrophic papulosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:612-616. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01227.x
- Harvell JD, Williford PL, White WL. Benign cutaneous Degos’ disease: a case report with emphasis on histopathology as papules chronologically evolve. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:116-123. doi:10.1097/00000372-200104000-00006
- Oliver B, Boehm M, Rosing DR, et al. Diffuse atrophic papules and plaques, intermittent abdominal pain, paresthesias, and cardiac abnormalities in a 55-year-old woman. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:1274-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.09.015
- Shapiro LS, Toledo-Garcia AE, Farrell JF. Effective treatment of malignant atrophic papulosis (Köhlmeier-Degos disease) with treprostinil—early experience. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:52. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-52
- Burgin S, Stone JH, Shenoy-Bhangle AS, et al. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 18-2014. A 32-year-old man with a rash, myalgia, and weakness. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2327-2337. doi:10.1056/NEJMcpc1304161
PRACTICE POINTS
- Papules with atrophic white centers and erythematous telangiectatic rims are the characteristic skin lesions found in Degos disease.
- A painful penile ulceration also may occur in Degos disease, though it is uncommon.
- The histopathology of skin lesions changes as the lesions evolve. Early lesions may resemble connective tissue disease. Late lesions show the classic pathology of wedge-shaped dermal sclerosis.
Mandatory DMV Reporting Tied to Dementia Underdiagnosis
, new research suggests.
Investigators found that primary care physicians (PCPs) in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 59% higher probability of underdiagnosing dementia compared with their counterparts in states that require patients to self-report or that have no reporting mandates.
“Our findings in this cross-sectional study raise concerns about potential adverse effects of mandatory clinician reporting for dementia diagnosis and underscore the need for careful consideration of the effect of such policies,” wrote the investigators, led by Soeren Mattke, MD, DSc, director of the USC Brain Health Observatory and research professor of economics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Lack of Guidance
As the US population ages, the number of older drivers is increasing, with 55.8 million drivers 65 years old or older. Approximately 7 million people in this age group have dementia — an estimate that is expected to increase to nearly 12 million by 2040.
The aging population raises a “critical policy question” about how to ensure road safety. Although the American Medical Association’s Code of Ethics outlines a physician’s obligation to identify drivers with medical impairments that impede safe driving, guidance restricting cognitively impaired drivers from driving is lacking.
In addition, evidence as to whether cognitive impairment indeed poses a threat to driving safety is mixed and has led to a lack of uniform policies with respect to reporting dementia.
Four states explicitly require clinicians to report dementia diagnoses to the DMV, which will then determine the patient’s fitness to drive, whereas 14 states require people with dementia to self-report. The remaining states have no explicit reporting requirements.
The issue of mandatory reporting is controversial, the researchers noted. On the one hand, physicians could protect patients and others by reporting potentially unsafe drivers.
On the other hand, evidence of an association with lower accident risks in patients with dementia is sparse and mandatory reporting may adversely affect physician-patient relationships. Empirical evidence for unintended consequences of reporting laws is lacking.
To examine the potential link between dementia underdiagnosis and mandatory reporting policies, the investigators analyzed the 100% data from the Medicare fee-for-service program and Medicare Advantage plans from 2017 to 2019, which included 223,036 PCPs with a panel of 25 or more Medicare patients.
The researchers examined dementia diagnosis rates in the patient panel of PCPs, rather than neurologists or gerontologists, regardless of who documented the diagnosis. Dr. Mattke said that it is possible that the diagnosis was established after referral to a specialist.
Each physician’s expected number of dementia cases was estimated using a predictive model based on patient characteristics. The researchers then compared the estimate with observed dementia diagnoses, thereby identifying clinicians who underdiagnosed dementia after sampling errors were accounted for.
‘Heavy-Handed Interference’
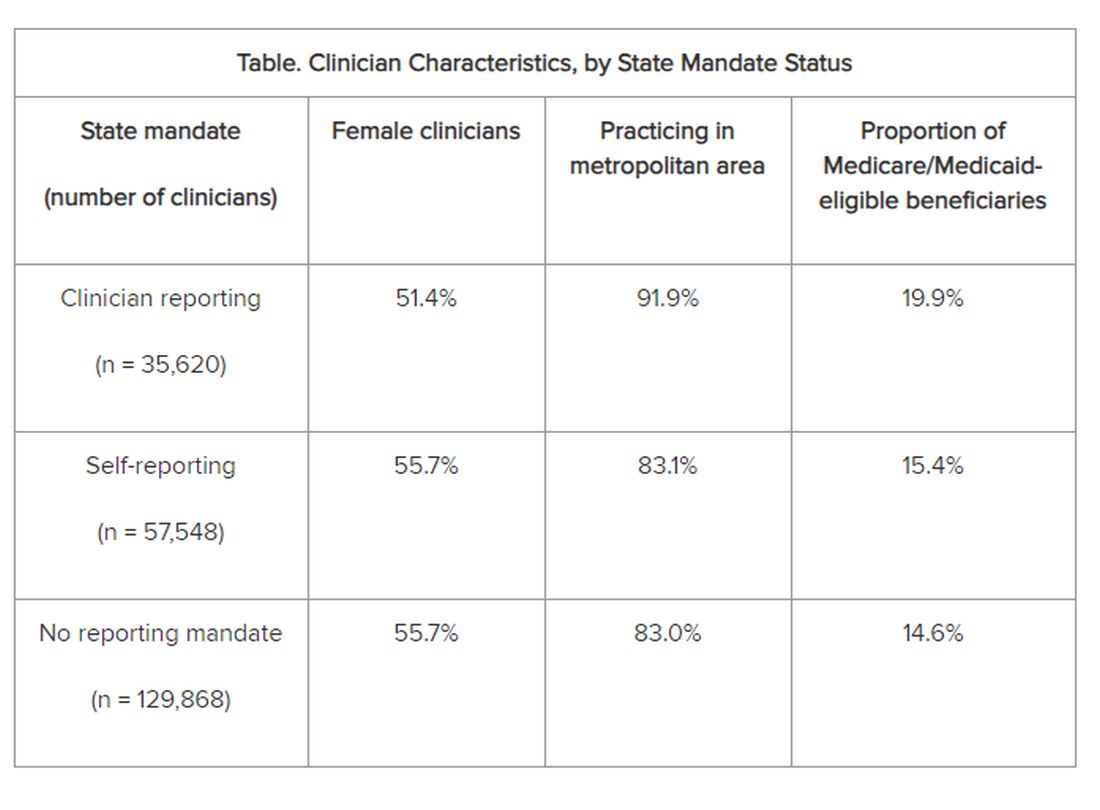
The researchers adjusted for several covariates potentially associated with a clinician’s probability of underdiagnosing dementia. These included sex, office location, practice specialty, racial/ethnic composition of the patient panel, and percentage of patients dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid. The table shows PCP characteristics.
Adjusted results showed that PCPs practicing in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 10.5%-14.2%) probability of underdiagnosing dementia versus 7.8% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.7%) in states with self-reporting and 7.7% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.4%) in states with no mandates, translating into a 4–percentage point difference (P < .001).
“Our study is the first to provide empirical evidence for the potential adverse effects of reporting policies,” the researchers noted. “Although we found that some clinicians underdiagnosed dementia regardless of state mandates, the key finding of this study reveals that primary care clinicians who practice in states with clinician reporting mandates were 59% more likely to do so…compared with those states with no reporting requirements…or driver self-reporting requirements.”
The investigators suggested that one potential explanation for underdiagnosis is patient resistance to cognitive testing. If patients were aware that the clinician was obligated by law to report their dementia diagnosis to the DMV, “they might be more inclined to conceal their symptoms or refuse further assessments, in addition to the general stigma and resistance to a formal assessment after a positive dementia screening result.”
“The findings suggest that policymakers might want to rethink those physician reporting mandates, since we also could not find conclusive evidence that they improve road safety,” Dr. Mattke said. “Maybe patients and their physicians can arrive at a sensible approach to determine driving fitness without such heavy-handed interference.”
However, he cautioned that the findings are not definitive and further study is needed before firm recommendations either for or against mandatory reporting.
In addition, the researchers noted several study limitations. One is that dementia underdiagnosis may also be associated with factors not captured in their model, including physician-patient relationships, health literacy, or language barriers.
However, Dr. Mattke noted, “ my sense is that those unobservable factors are not systematically related to state reporting policies and having omitted them would therefore not bias our results.”
Experts Weigh In
Commenting on the research, Morgan Daven, MA, the Alzheimer’s Association vice president of health systems, said that dementia is widely and significantly underdiagnosed, and not only in the states with dementia reporting mandates. Many factors may contribute to underdiagnosis, and although the study shows an association between reporting mandates and underdiagnosis, it does not demonstrate causation.
That said, Mr. Daven added, “fear and stigma related to dementia may inhibit the clinician, the patient, and their family from pursuing detection and diagnosis for dementia. As a society, we need to address dementia fear and stigma for all parties.”
He noted that useful tools include healthcare policies, workforce training, public awareness and education, and public policies to mitigate fear and stigma and their negative effects on diagnosis, care, support, and communication.
A potential study limitation is that it relied only on diagnoses by PCPs. Mr. Daven noted that the diagnosis of Alzheimer’ disease — the most common cause of dementia — is confirmation of amyloid buildup via a biomarker test, using PET or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
“Both of these tests are extremely limited in their use and accessibility in a primary care setting. Inclusion of diagnoses by dementia specialists would provide a more complete picture,” he said.
Mr. Daven added that the Alzheimer’s Association encourages families to proactively discuss driving and other disease-related safety concerns as soon as possible. The Alzheimer’s Association Dementia and Driving webpage offers tips and strategies to discuss driving concerns with a family member.
In an accompanying editorial, Donald Redelmeier, MD, MS(HSR), and Vidhi Bhatt, BSc, both of the Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, differentiate the mandate for physicians to warn patients with dementia about traffic safety from the mandate for reporting child maltreatment, gunshot victims, or communicable diseases. They noted that mandated warnings “are not easy, can engender patient dissatisfaction, and need to be handled with tact.”
Yet, they pointed out, “breaking bad news is what practicing medicine entails.” They emphasized that, regardless of government mandates, “counseling patients for more road safety is an essential skill for clinicians in diverse states who hope to help their patients avoid becoming more traffic statistics.”
Research reported in this publication was supported by Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, and a grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Mattke reported receiving grants from Genentech for a research contract with USC during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Eisai, Biogen, C2N, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Genentech; and serving on the Senscio Systems board of directors, ALZpath scientific advisory board, AiCure scientific advisory board, and Boston Millennia Partners scientific advisory board outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. The editorial was supported by the Canada Research Chair in Medical Decision Sciences, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Kimel-Schatzky Traumatic Brain Injury Research Fund, and the Graduate Diploma Program in Health Research at the University of Toronto. The editorial authors report no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Investigators found that primary care physicians (PCPs) in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 59% higher probability of underdiagnosing dementia compared with their counterparts in states that require patients to self-report or that have no reporting mandates.
“Our findings in this cross-sectional study raise concerns about potential adverse effects of mandatory clinician reporting for dementia diagnosis and underscore the need for careful consideration of the effect of such policies,” wrote the investigators, led by Soeren Mattke, MD, DSc, director of the USC Brain Health Observatory and research professor of economics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Lack of Guidance
As the US population ages, the number of older drivers is increasing, with 55.8 million drivers 65 years old or older. Approximately 7 million people in this age group have dementia — an estimate that is expected to increase to nearly 12 million by 2040.
The aging population raises a “critical policy question” about how to ensure road safety. Although the American Medical Association’s Code of Ethics outlines a physician’s obligation to identify drivers with medical impairments that impede safe driving, guidance restricting cognitively impaired drivers from driving is lacking.
In addition, evidence as to whether cognitive impairment indeed poses a threat to driving safety is mixed and has led to a lack of uniform policies with respect to reporting dementia.
Four states explicitly require clinicians to report dementia diagnoses to the DMV, which will then determine the patient’s fitness to drive, whereas 14 states require people with dementia to self-report. The remaining states have no explicit reporting requirements.
The issue of mandatory reporting is controversial, the researchers noted. On the one hand, physicians could protect patients and others by reporting potentially unsafe drivers.
On the other hand, evidence of an association with lower accident risks in patients with dementia is sparse and mandatory reporting may adversely affect physician-patient relationships. Empirical evidence for unintended consequences of reporting laws is lacking.
To examine the potential link between dementia underdiagnosis and mandatory reporting policies, the investigators analyzed the 100% data from the Medicare fee-for-service program and Medicare Advantage plans from 2017 to 2019, which included 223,036 PCPs with a panel of 25 or more Medicare patients.
The researchers examined dementia diagnosis rates in the patient panel of PCPs, rather than neurologists or gerontologists, regardless of who documented the diagnosis. Dr. Mattke said that it is possible that the diagnosis was established after referral to a specialist.
Each physician’s expected number of dementia cases was estimated using a predictive model based on patient characteristics. The researchers then compared the estimate with observed dementia diagnoses, thereby identifying clinicians who underdiagnosed dementia after sampling errors were accounted for.
‘Heavy-Handed Interference’
The researchers adjusted for several covariates potentially associated with a clinician’s probability of underdiagnosing dementia. These included sex, office location, practice specialty, racial/ethnic composition of the patient panel, and percentage of patients dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid. The table shows PCP characteristics.

Adjusted results showed that PCPs practicing in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 10.5%-14.2%) probability of underdiagnosing dementia versus 7.8% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.7%) in states with self-reporting and 7.7% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.4%) in states with no mandates, translating into a 4–percentage point difference (P < .001).
“Our study is the first to provide empirical evidence for the potential adverse effects of reporting policies,” the researchers noted. “Although we found that some clinicians underdiagnosed dementia regardless of state mandates, the key finding of this study reveals that primary care clinicians who practice in states with clinician reporting mandates were 59% more likely to do so…compared with those states with no reporting requirements…or driver self-reporting requirements.”
The investigators suggested that one potential explanation for underdiagnosis is patient resistance to cognitive testing. If patients were aware that the clinician was obligated by law to report their dementia diagnosis to the DMV, “they might be more inclined to conceal their symptoms or refuse further assessments, in addition to the general stigma and resistance to a formal assessment after a positive dementia screening result.”
“The findings suggest that policymakers might want to rethink those physician reporting mandates, since we also could not find conclusive evidence that they improve road safety,” Dr. Mattke said. “Maybe patients and their physicians can arrive at a sensible approach to determine driving fitness without such heavy-handed interference.”
However, he cautioned that the findings are not definitive and further study is needed before firm recommendations either for or against mandatory reporting.
In addition, the researchers noted several study limitations. One is that dementia underdiagnosis may also be associated with factors not captured in their model, including physician-patient relationships, health literacy, or language barriers.
However, Dr. Mattke noted, “ my sense is that those unobservable factors are not systematically related to state reporting policies and having omitted them would therefore not bias our results.”
Experts Weigh In
Commenting on the research, Morgan Daven, MA, the Alzheimer’s Association vice president of health systems, said that dementia is widely and significantly underdiagnosed, and not only in the states with dementia reporting mandates. Many factors may contribute to underdiagnosis, and although the study shows an association between reporting mandates and underdiagnosis, it does not demonstrate causation.
That said, Mr. Daven added, “fear and stigma related to dementia may inhibit the clinician, the patient, and their family from pursuing detection and diagnosis for dementia. As a society, we need to address dementia fear and stigma for all parties.”
He noted that useful tools include healthcare policies, workforce training, public awareness and education, and public policies to mitigate fear and stigma and their negative effects on diagnosis, care, support, and communication.
A potential study limitation is that it relied only on diagnoses by PCPs. Mr. Daven noted that the diagnosis of Alzheimer’ disease — the most common cause of dementia — is confirmation of amyloid buildup via a biomarker test, using PET or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
“Both of these tests are extremely limited in their use and accessibility in a primary care setting. Inclusion of diagnoses by dementia specialists would provide a more complete picture,” he said.
Mr. Daven added that the Alzheimer’s Association encourages families to proactively discuss driving and other disease-related safety concerns as soon as possible. The Alzheimer’s Association Dementia and Driving webpage offers tips and strategies to discuss driving concerns with a family member.
In an accompanying editorial, Donald Redelmeier, MD, MS(HSR), and Vidhi Bhatt, BSc, both of the Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, differentiate the mandate for physicians to warn patients with dementia about traffic safety from the mandate for reporting child maltreatment, gunshot victims, or communicable diseases. They noted that mandated warnings “are not easy, can engender patient dissatisfaction, and need to be handled with tact.”
Yet, they pointed out, “breaking bad news is what practicing medicine entails.” They emphasized that, regardless of government mandates, “counseling patients for more road safety is an essential skill for clinicians in diverse states who hope to help their patients avoid becoming more traffic statistics.”
Research reported in this publication was supported by Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, and a grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Mattke reported receiving grants from Genentech for a research contract with USC during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Eisai, Biogen, C2N, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Genentech; and serving on the Senscio Systems board of directors, ALZpath scientific advisory board, AiCure scientific advisory board, and Boston Millennia Partners scientific advisory board outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. The editorial was supported by the Canada Research Chair in Medical Decision Sciences, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Kimel-Schatzky Traumatic Brain Injury Research Fund, and the Graduate Diploma Program in Health Research at the University of Toronto. The editorial authors report no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Investigators found that primary care physicians (PCPs) in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 59% higher probability of underdiagnosing dementia compared with their counterparts in states that require patients to self-report or that have no reporting mandates.
“Our findings in this cross-sectional study raise concerns about potential adverse effects of mandatory clinician reporting for dementia diagnosis and underscore the need for careful consideration of the effect of such policies,” wrote the investigators, led by Soeren Mattke, MD, DSc, director of the USC Brain Health Observatory and research professor of economics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Lack of Guidance
As the US population ages, the number of older drivers is increasing, with 55.8 million drivers 65 years old or older. Approximately 7 million people in this age group have dementia — an estimate that is expected to increase to nearly 12 million by 2040.
The aging population raises a “critical policy question” about how to ensure road safety. Although the American Medical Association’s Code of Ethics outlines a physician’s obligation to identify drivers with medical impairments that impede safe driving, guidance restricting cognitively impaired drivers from driving is lacking.
In addition, evidence as to whether cognitive impairment indeed poses a threat to driving safety is mixed and has led to a lack of uniform policies with respect to reporting dementia.
Four states explicitly require clinicians to report dementia diagnoses to the DMV, which will then determine the patient’s fitness to drive, whereas 14 states require people with dementia to self-report. The remaining states have no explicit reporting requirements.
The issue of mandatory reporting is controversial, the researchers noted. On the one hand, physicians could protect patients and others by reporting potentially unsafe drivers.
On the other hand, evidence of an association with lower accident risks in patients with dementia is sparse and mandatory reporting may adversely affect physician-patient relationships. Empirical evidence for unintended consequences of reporting laws is lacking.
To examine the potential link between dementia underdiagnosis and mandatory reporting policies, the investigators analyzed the 100% data from the Medicare fee-for-service program and Medicare Advantage plans from 2017 to 2019, which included 223,036 PCPs with a panel of 25 or more Medicare patients.
The researchers examined dementia diagnosis rates in the patient panel of PCPs, rather than neurologists or gerontologists, regardless of who documented the diagnosis. Dr. Mattke said that it is possible that the diagnosis was established after referral to a specialist.
Each physician’s expected number of dementia cases was estimated using a predictive model based on patient characteristics. The researchers then compared the estimate with observed dementia diagnoses, thereby identifying clinicians who underdiagnosed dementia after sampling errors were accounted for.
‘Heavy-Handed Interference’
The researchers adjusted for several covariates potentially associated with a clinician’s probability of underdiagnosing dementia. These included sex, office location, practice specialty, racial/ethnic composition of the patient panel, and percentage of patients dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid. The table shows PCP characteristics.

Adjusted results showed that PCPs practicing in states with clinician reporting mandates had a 12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 10.5%-14.2%) probability of underdiagnosing dementia versus 7.8% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.7%) in states with self-reporting and 7.7% (95% CI, 6.9%-8.4%) in states with no mandates, translating into a 4–percentage point difference (P < .001).
“Our study is the first to provide empirical evidence for the potential adverse effects of reporting policies,” the researchers noted. “Although we found that some clinicians underdiagnosed dementia regardless of state mandates, the key finding of this study reveals that primary care clinicians who practice in states with clinician reporting mandates were 59% more likely to do so…compared with those states with no reporting requirements…or driver self-reporting requirements.”
The investigators suggested that one potential explanation for underdiagnosis is patient resistance to cognitive testing. If patients were aware that the clinician was obligated by law to report their dementia diagnosis to the DMV, “they might be more inclined to conceal their symptoms or refuse further assessments, in addition to the general stigma and resistance to a formal assessment after a positive dementia screening result.”
“The findings suggest that policymakers might want to rethink those physician reporting mandates, since we also could not find conclusive evidence that they improve road safety,” Dr. Mattke said. “Maybe patients and their physicians can arrive at a sensible approach to determine driving fitness without such heavy-handed interference.”
However, he cautioned that the findings are not definitive and further study is needed before firm recommendations either for or against mandatory reporting.
In addition, the researchers noted several study limitations. One is that dementia underdiagnosis may also be associated with factors not captured in their model, including physician-patient relationships, health literacy, or language barriers.
However, Dr. Mattke noted, “ my sense is that those unobservable factors are not systematically related to state reporting policies and having omitted them would therefore not bias our results.”
Experts Weigh In
Commenting on the research, Morgan Daven, MA, the Alzheimer’s Association vice president of health systems, said that dementia is widely and significantly underdiagnosed, and not only in the states with dementia reporting mandates. Many factors may contribute to underdiagnosis, and although the study shows an association between reporting mandates and underdiagnosis, it does not demonstrate causation.
That said, Mr. Daven added, “fear and stigma related to dementia may inhibit the clinician, the patient, and their family from pursuing detection and diagnosis for dementia. As a society, we need to address dementia fear and stigma for all parties.”
He noted that useful tools include healthcare policies, workforce training, public awareness and education, and public policies to mitigate fear and stigma and their negative effects on diagnosis, care, support, and communication.
A potential study limitation is that it relied only on diagnoses by PCPs. Mr. Daven noted that the diagnosis of Alzheimer’ disease — the most common cause of dementia — is confirmation of amyloid buildup via a biomarker test, using PET or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
“Both of these tests are extremely limited in their use and accessibility in a primary care setting. Inclusion of diagnoses by dementia specialists would provide a more complete picture,” he said.
Mr. Daven added that the Alzheimer’s Association encourages families to proactively discuss driving and other disease-related safety concerns as soon as possible. The Alzheimer’s Association Dementia and Driving webpage offers tips and strategies to discuss driving concerns with a family member.
In an accompanying editorial, Donald Redelmeier, MD, MS(HSR), and Vidhi Bhatt, BSc, both of the Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, differentiate the mandate for physicians to warn patients with dementia about traffic safety from the mandate for reporting child maltreatment, gunshot victims, or communicable diseases. They noted that mandated warnings “are not easy, can engender patient dissatisfaction, and need to be handled with tact.”
Yet, they pointed out, “breaking bad news is what practicing medicine entails.” They emphasized that, regardless of government mandates, “counseling patients for more road safety is an essential skill for clinicians in diverse states who hope to help their patients avoid becoming more traffic statistics.”
Research reported in this publication was supported by Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, and a grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Mattke reported receiving grants from Genentech for a research contract with USC during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Eisai, Biogen, C2N, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Roche Genentech; and serving on the Senscio Systems board of directors, ALZpath scientific advisory board, AiCure scientific advisory board, and Boston Millennia Partners scientific advisory board outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. The editorial was supported by the Canada Research Chair in Medical Decision Sciences, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Kimel-Schatzky Traumatic Brain Injury Research Fund, and the Graduate Diploma Program in Health Research at the University of Toronto. The editorial authors report no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
From JAMA Network Open
Defining Your ‘Success’
Dear Friends,
The prevailing theme of this issue is “Success.” I have learned that “success” is personal and personalized. What “success” looked like 10, or even 5, years ago to me is very different from how I perceive it now; and I know it may be different 5 years from now. My definition of success should not look like another’s — that was the best advice I have gotten over the years and it has kept me constantly redefining what is important to me and placing value on where I want to allocate my time and efforts, at work and at home.
This issue of The New Gastroenterologist highlights topics from successful GIs within their own realms of expertise, offering insights on advancing in academic medicine, navigating financial wellness with a financial adviser, and becoming a future leader in GI.
In this issue’s clinically-focused articles, we spotlight two very nuanced and challenging topics. Dr. Sachin Srinivasan and Dr. Prateek Sharma review Barrett’s esophagus management for our “In Focus” section, with a particular emphasis on Barrett’s endoscopic therapy modalities for dysplasia and early neoplasia. Dr. Brooke Corning and team simplify their approach to pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD) in our “Short Clinical Reviews.” They suggest validated ways to assess patient history, pros and cons of various diagnostic tests, and stepwise management of PFD.
Navigating academic promotion can be overwhelming and may not be at the forefront with our early career GIs’ priorities. In our “Early Career” section, Dr. Vineet Rolston interviews two highly accomplished professors in academic medicine, Dr. Sophie Balzora and Dr. Mark Schattner, for their insights into the promotion process and recommendations for junior faculty.
Dr. Anjuli K. Luthra, a therapeutic endoscopist and founder of The Scope of Finance, emphasizes financial wellness for physicians. She breaks down the search for a financial adviser, including the different types, what to ask when searching for the right fit, and what to expect.
Lastly, this issue highlights an AGA program that invests in the development of leaders for the field — the Future Leaders Program (FLP). Dr. Parakkal Deepak and Dr. Edward L. Barnes, along with their mentor, Dr. Aasma Shaukat, describe their experience as a mentee-mentor triad of FLP and how this program has impacted their careers.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: Dr. C.G. Stockton was the first AGA president in 1897, a Professor of the Principles and Practice of Medicine and Clinical Medicine at the University of Buffalo in New York, and published on the relationship between GI/Hepatology and gout in the Journal of the American Medical Association the same year of his presidency.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
The prevailing theme of this issue is “Success.” I have learned that “success” is personal and personalized. What “success” looked like 10, or even 5, years ago to me is very different from how I perceive it now; and I know it may be different 5 years from now. My definition of success should not look like another’s — that was the best advice I have gotten over the years and it has kept me constantly redefining what is important to me and placing value on where I want to allocate my time and efforts, at work and at home.
This issue of The New Gastroenterologist highlights topics from successful GIs within their own realms of expertise, offering insights on advancing in academic medicine, navigating financial wellness with a financial adviser, and becoming a future leader in GI.
In this issue’s clinically-focused articles, we spotlight two very nuanced and challenging topics. Dr. Sachin Srinivasan and Dr. Prateek Sharma review Barrett’s esophagus management for our “In Focus” section, with a particular emphasis on Barrett’s endoscopic therapy modalities for dysplasia and early neoplasia. Dr. Brooke Corning and team simplify their approach to pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD) in our “Short Clinical Reviews.” They suggest validated ways to assess patient history, pros and cons of various diagnostic tests, and stepwise management of PFD.
Navigating academic promotion can be overwhelming and may not be at the forefront with our early career GIs’ priorities. In our “Early Career” section, Dr. Vineet Rolston interviews two highly accomplished professors in academic medicine, Dr. Sophie Balzora and Dr. Mark Schattner, for their insights into the promotion process and recommendations for junior faculty.
Dr. Anjuli K. Luthra, a therapeutic endoscopist and founder of The Scope of Finance, emphasizes financial wellness for physicians. She breaks down the search for a financial adviser, including the different types, what to ask when searching for the right fit, and what to expect.
Lastly, this issue highlights an AGA program that invests in the development of leaders for the field — the Future Leaders Program (FLP). Dr. Parakkal Deepak and Dr. Edward L. Barnes, along with their mentor, Dr. Aasma Shaukat, describe their experience as a mentee-mentor triad of FLP and how this program has impacted their careers.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: Dr. C.G. Stockton was the first AGA president in 1897, a Professor of the Principles and Practice of Medicine and Clinical Medicine at the University of Buffalo in New York, and published on the relationship between GI/Hepatology and gout in the Journal of the American Medical Association the same year of his presidency.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
The prevailing theme of this issue is “Success.” I have learned that “success” is personal and personalized. What “success” looked like 10, or even 5, years ago to me is very different from how I perceive it now; and I know it may be different 5 years from now. My definition of success should not look like another’s — that was the best advice I have gotten over the years and it has kept me constantly redefining what is important to me and placing value on where I want to allocate my time and efforts, at work and at home.
This issue of The New Gastroenterologist highlights topics from successful GIs within their own realms of expertise, offering insights on advancing in academic medicine, navigating financial wellness with a financial adviser, and becoming a future leader in GI.
In this issue’s clinically-focused articles, we spotlight two very nuanced and challenging topics. Dr. Sachin Srinivasan and Dr. Prateek Sharma review Barrett’s esophagus management for our “In Focus” section, with a particular emphasis on Barrett’s endoscopic therapy modalities for dysplasia and early neoplasia. Dr. Brooke Corning and team simplify their approach to pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD) in our “Short Clinical Reviews.” They suggest validated ways to assess patient history, pros and cons of various diagnostic tests, and stepwise management of PFD.
Navigating academic promotion can be overwhelming and may not be at the forefront with our early career GIs’ priorities. In our “Early Career” section, Dr. Vineet Rolston interviews two highly accomplished professors in academic medicine, Dr. Sophie Balzora and Dr. Mark Schattner, for their insights into the promotion process and recommendations for junior faculty.
Dr. Anjuli K. Luthra, a therapeutic endoscopist and founder of The Scope of Finance, emphasizes financial wellness for physicians. She breaks down the search for a financial adviser, including the different types, what to ask when searching for the right fit, and what to expect.
Lastly, this issue highlights an AGA program that invests in the development of leaders for the field — the Future Leaders Program (FLP). Dr. Parakkal Deepak and Dr. Edward L. Barnes, along with their mentor, Dr. Aasma Shaukat, describe their experience as a mentee-mentor triad of FLP and how this program has impacted their careers.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: Dr. C.G. Stockton was the first AGA president in 1897, a Professor of the Principles and Practice of Medicine and Clinical Medicine at the University of Buffalo in New York, and published on the relationship between GI/Hepatology and gout in the Journal of the American Medical Association the same year of his presidency.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
GI Doc Aims to Lift Barriers to CRC Screening for Black Patients
In gastroenterology, a good bedside manner is a vital attribute. Visiting with an anxious patient before a colonoscopy, Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, knew what to say to calm him down.
“I could tell he was really nervous about the procedure, even though he wasn’t letting on,” said Dr. Anyane-Yeboa, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. She put him at ease by cracking jokes and making him smile during the consent process. After it was over, he thanked her for making him feel more comfortable.
“I will have it done again, and I’ll come back to you next time,” said the patient.
GI doctors perform colonoscopies all day, every day, “so we sometimes forget how nervous people are. But it’s nice to be able to connect with people and put them at ease,” she said.
Interacting with patients gives her joy. Addressing health disparities is her long-term goal. Dr. Anyane-Yeboa’s research has focused on the barriers to colorectal cancer screening in the Black population, as well as disparities in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“I think there’s a lot that still needs to be done around colorectal cancer screening,” she said.
In an interview, she talks more in depth about her research and her ongoing work to increase public knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: When I got to residency, GI was the rotation that was the most fun. I was the most excited to read about it, the most excited to go to work the next day.
I remember people saying, “You should look at the people who are in the field and look at their personalities, and then think about which personalities match you best.” In residency I considered hematology, cardiology, and GI. The cardiologists were so serious, so intense, talking about research methods all the time. Whereas, the GI folks were joking, laughing, making fart jokes. I felt like these were my people, lighthearted and easy-going. And I genuinely enjoyed going to work every day and learning about the disorders of the GI tract. I still do to this day.
Q: Let’s discuss your research with IBD in Black populations and colorectal cancer screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: My two main areas of work are in IBD and minority populations, predominantly Black populations, and in colorectal cancer screening in minority populations, and again, mostly in historically marginalized populations.
With colon cancer, we know that there are disparities with incidence in mortality. Black individuals have had the second highest incidence in mortality from colorectal cancer. For me, being a Black female physician and seeing people who look like me, time and time again, being diagnosed with colorectal cancer and dying is really what drives me, because in GI, colon cancer screening is our bread and butter.
Some of the work that I’m doing now around colorectal cancer is in predominantly Black community health centers, working on increasing colorectal cancer screening rates in this population, and figuring out what the barriers are to screening and how we can address them, and what are some strategies that will work in a health center setting to get people screened.
Q: One study of yours surveyed unscreened Black individuals age ≥ 45 and found age-specific barriers to CRC screening in this population, as well as a lack of targeted messaging to incentivize screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: That mixed method study was done in partnership with the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable and American Cancer Society.
In that study, we found that the most common barrier to screening was self-procrastination or delay of screening, meaning, “I’m going to get screened, just not right now.” It’s not a priority. What was unique about this is we looked at it from age breakdown, so 45-49, 50-54, 55-plus. With the younger 45-49 group, we don’t know as much about how to get them screened. We also saw that healthcare providers weren’t starting conversations about screening with these younger newly eligible patients.
We also described effective messages to get people screened in that paper as well.
Q: What changes would you like to see going forward with screening? What still needs to happen?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: In some of the other work that I’ve done, particularly with the health centers and younger populations interviewed in focus groups, I’m seeing that those who are younger don’t really know much about colorectal cancer screening. Those who do know about it have seen commercials about popular stool-based testing brands, and that’s how they’ve learned about screening.
What I would like to see is ways to increase the knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening and colorectal cancer on a broad scale, on a more national, public-facing scale. Because I’m realizing that if they’re healthy young folks who aren’t going to the physician, who don’t have a primary care provider, then they might not even really hear about colorectal cancer screening. We need ways to educate the general public so individuals can advocate for themselves around screening.
I also want to see more providers discussing screening with all patients, starting from those 45-49, and younger if they have a family history. Providers should screen every single patient that they see. We know that every single person should be screened at 45 and older, and not all providers, surprisingly, are discussing it with their patients.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: Saturday morning is my favorite time of the week. I’m either catching up on my TV shows, or I might be on a walk with my dog, particularly in the afternoon. I live near an arboretum, so I usually walk through there on the weekend afternoons. I also might be trying out a new restaurant with my friends. I love traveling, so I might also be sightseeing in another country.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite junk food?
Cookies
Cat or dog person?
Both; love cats, have a dog
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Fashion boutique owner
Best place you’ve traveled to?
Morocco
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
Two
Favorite ice cream?
Don’t eat ice cream, only cookies
Favorite sport?
Tennis
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist (glass half full)
In gastroenterology, a good bedside manner is a vital attribute. Visiting with an anxious patient before a colonoscopy, Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, knew what to say to calm him down.
“I could tell he was really nervous about the procedure, even though he wasn’t letting on,” said Dr. Anyane-Yeboa, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. She put him at ease by cracking jokes and making him smile during the consent process. After it was over, he thanked her for making him feel more comfortable.
“I will have it done again, and I’ll come back to you next time,” said the patient.
GI doctors perform colonoscopies all day, every day, “so we sometimes forget how nervous people are. But it’s nice to be able to connect with people and put them at ease,” she said.
Interacting with patients gives her joy. Addressing health disparities is her long-term goal. Dr. Anyane-Yeboa’s research has focused on the barriers to colorectal cancer screening in the Black population, as well as disparities in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“I think there’s a lot that still needs to be done around colorectal cancer screening,” she said.
In an interview, she talks more in depth about her research and her ongoing work to increase public knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: When I got to residency, GI was the rotation that was the most fun. I was the most excited to read about it, the most excited to go to work the next day.
I remember people saying, “You should look at the people who are in the field and look at their personalities, and then think about which personalities match you best.” In residency I considered hematology, cardiology, and GI. The cardiologists were so serious, so intense, talking about research methods all the time. Whereas, the GI folks were joking, laughing, making fart jokes. I felt like these were my people, lighthearted and easy-going. And I genuinely enjoyed going to work every day and learning about the disorders of the GI tract. I still do to this day.
Q: Let’s discuss your research with IBD in Black populations and colorectal cancer screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: My two main areas of work are in IBD and minority populations, predominantly Black populations, and in colorectal cancer screening in minority populations, and again, mostly in historically marginalized populations.
With colon cancer, we know that there are disparities with incidence in mortality. Black individuals have had the second highest incidence in mortality from colorectal cancer. For me, being a Black female physician and seeing people who look like me, time and time again, being diagnosed with colorectal cancer and dying is really what drives me, because in GI, colon cancer screening is our bread and butter.
Some of the work that I’m doing now around colorectal cancer is in predominantly Black community health centers, working on increasing colorectal cancer screening rates in this population, and figuring out what the barriers are to screening and how we can address them, and what are some strategies that will work in a health center setting to get people screened.
Q: One study of yours surveyed unscreened Black individuals age ≥ 45 and found age-specific barriers to CRC screening in this population, as well as a lack of targeted messaging to incentivize screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: That mixed method study was done in partnership with the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable and American Cancer Society.
In that study, we found that the most common barrier to screening was self-procrastination or delay of screening, meaning, “I’m going to get screened, just not right now.” It’s not a priority. What was unique about this is we looked at it from age breakdown, so 45-49, 50-54, 55-plus. With the younger 45-49 group, we don’t know as much about how to get them screened. We also saw that healthcare providers weren’t starting conversations about screening with these younger newly eligible patients.
We also described effective messages to get people screened in that paper as well.
Q: What changes would you like to see going forward with screening? What still needs to happen?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: In some of the other work that I’ve done, particularly with the health centers and younger populations interviewed in focus groups, I’m seeing that those who are younger don’t really know much about colorectal cancer screening. Those who do know about it have seen commercials about popular stool-based testing brands, and that’s how they’ve learned about screening.
What I would like to see is ways to increase the knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening and colorectal cancer on a broad scale, on a more national, public-facing scale. Because I’m realizing that if they’re healthy young folks who aren’t going to the physician, who don’t have a primary care provider, then they might not even really hear about colorectal cancer screening. We need ways to educate the general public so individuals can advocate for themselves around screening.
I also want to see more providers discussing screening with all patients, starting from those 45-49, and younger if they have a family history. Providers should screen every single patient that they see. We know that every single person should be screened at 45 and older, and not all providers, surprisingly, are discussing it with their patients.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: Saturday morning is my favorite time of the week. I’m either catching up on my TV shows, or I might be on a walk with my dog, particularly in the afternoon. I live near an arboretum, so I usually walk through there on the weekend afternoons. I also might be trying out a new restaurant with my friends. I love traveling, so I might also be sightseeing in another country.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite junk food?
Cookies
Cat or dog person?
Both; love cats, have a dog
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Fashion boutique owner
Best place you’ve traveled to?
Morocco
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
Two
Favorite ice cream?
Don’t eat ice cream, only cookies
Favorite sport?
Tennis
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist (glass half full)
In gastroenterology, a good bedside manner is a vital attribute. Visiting with an anxious patient before a colonoscopy, Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, knew what to say to calm him down.
“I could tell he was really nervous about the procedure, even though he wasn’t letting on,” said Dr. Anyane-Yeboa, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. She put him at ease by cracking jokes and making him smile during the consent process. After it was over, he thanked her for making him feel more comfortable.
“I will have it done again, and I’ll come back to you next time,” said the patient.
GI doctors perform colonoscopies all day, every day, “so we sometimes forget how nervous people are. But it’s nice to be able to connect with people and put them at ease,” she said.
Interacting with patients gives her joy. Addressing health disparities is her long-term goal. Dr. Anyane-Yeboa’s research has focused on the barriers to colorectal cancer screening in the Black population, as well as disparities in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
“I think there’s a lot that still needs to be done around colorectal cancer screening,” she said.
In an interview, she talks more in depth about her research and her ongoing work to increase public knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening.
Q: Why did you choose GI?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: When I got to residency, GI was the rotation that was the most fun. I was the most excited to read about it, the most excited to go to work the next day.
I remember people saying, “You should look at the people who are in the field and look at their personalities, and then think about which personalities match you best.” In residency I considered hematology, cardiology, and GI. The cardiologists were so serious, so intense, talking about research methods all the time. Whereas, the GI folks were joking, laughing, making fart jokes. I felt like these were my people, lighthearted and easy-going. And I genuinely enjoyed going to work every day and learning about the disorders of the GI tract. I still do to this day.
Q: Let’s discuss your research with IBD in Black populations and colorectal cancer screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: My two main areas of work are in IBD and minority populations, predominantly Black populations, and in colorectal cancer screening in minority populations, and again, mostly in historically marginalized populations.
With colon cancer, we know that there are disparities with incidence in mortality. Black individuals have had the second highest incidence in mortality from colorectal cancer. For me, being a Black female physician and seeing people who look like me, time and time again, being diagnosed with colorectal cancer and dying is really what drives me, because in GI, colon cancer screening is our bread and butter.
Some of the work that I’m doing now around colorectal cancer is in predominantly Black community health centers, working on increasing colorectal cancer screening rates in this population, and figuring out what the barriers are to screening and how we can address them, and what are some strategies that will work in a health center setting to get people screened.
Q: One study of yours surveyed unscreened Black individuals age ≥ 45 and found age-specific barriers to CRC screening in this population, as well as a lack of targeted messaging to incentivize screening.
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: That mixed method study was done in partnership with the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable and American Cancer Society.
In that study, we found that the most common barrier to screening was self-procrastination or delay of screening, meaning, “I’m going to get screened, just not right now.” It’s not a priority. What was unique about this is we looked at it from age breakdown, so 45-49, 50-54, 55-plus. With the younger 45-49 group, we don’t know as much about how to get them screened. We also saw that healthcare providers weren’t starting conversations about screening with these younger newly eligible patients.
We also described effective messages to get people screened in that paper as well.
Q: What changes would you like to see going forward with screening? What still needs to happen?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: In some of the other work that I’ve done, particularly with the health centers and younger populations interviewed in focus groups, I’m seeing that those who are younger don’t really know much about colorectal cancer screening. Those who do know about it have seen commercials about popular stool-based testing brands, and that’s how they’ve learned about screening.
What I would like to see is ways to increase the knowledge and awareness about colorectal cancer screening and colorectal cancer on a broad scale, on a more national, public-facing scale. Because I’m realizing that if they’re healthy young folks who aren’t going to the physician, who don’t have a primary care provider, then they might not even really hear about colorectal cancer screening. We need ways to educate the general public so individuals can advocate for themselves around screening.
I also want to see more providers discussing screening with all patients, starting from those 45-49, and younger if they have a family history. Providers should screen every single patient that they see. We know that every single person should be screened at 45 and older, and not all providers, surprisingly, are discussing it with their patients.
Q: When you’re not being a GI, how do you spend your free weekend afternoons?
Dr. Anyane-Yeboa: Saturday morning is my favorite time of the week. I’m either catching up on my TV shows, or I might be on a walk with my dog, particularly in the afternoon. I live near an arboretum, so I usually walk through there on the weekend afternoons. I also might be trying out a new restaurant with my friends. I love traveling, so I might also be sightseeing in another country.
Lightning Round
Texting or talking?
Texting
Favorite junk food?
Cookies
Cat or dog person?
Both; love cats, have a dog
If you weren’t a gastroenterologist, what would you be?
Fashion boutique owner
Best place you’ve traveled to?
Morocco
How many cups of coffee do you drink per day?
Two
Favorite ice cream?
Don’t eat ice cream, only cookies
Favorite sport?
Tennis
Optimist or pessimist?
Optimist (glass half full)
Converging on Our Nation’s Capital
Release of our May issue coincides with our annual pilgrimage to Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), this year held in our nation’s capital of Washington, D.C.
As we peruse the preliminary program in planning our meeting coverage, I am always amazed at the breadth and depth of programming offered as part of a relatively brief, 4-day meeting — this is a testament to the hard work of the AGA Council and DDW organizing committees, who have the gargantuan task of ensuring an engaging, seamless meeting each year.
This year’s conference features over 400 original scientific sessions and 4,300 oral abstract and poster presentations, in addition to the always well-attended AGA Postgraduate Course. This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, which will feature a series of thought-provoking panel discussions on the future of GI healthcare and innovations in how we treat, disseminate, and teach, also is not to be missed. Beyond DDW, I hope you will join me in taking advantage of some of D.C.’s amazing cultural offerings, including the Smithsonian museums, National Gallery, Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, and many others.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we highlight an important AGA expert consensus commentary published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology examining the role of blood-based tests (“liquid biopsy”) in colorectal cancer screening. This guidance, which recognizes the promise of such tests but also urges caution in their adoption, is particularly important considering recently published data from the ECLIPSE study (also covered in this issue) evaluating the performance of Guardant’s ctDNA liquid biopsy compared to a screening colonoscopy. Also relevant to CRC screening, we highlight data on the performance of the “next gen” Cologuard test compared with FIT, which was recently published in NEJM. In our May Member Spotlight, we feature gastroenterologist Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, who shares her passion for addressing barriers to CRC screening for Black patients. Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo introduces our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting emerging applications of AI in GI endoscopy and hepatology. We hope you enjoy all the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Washington, D.C. (or virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Release of our May issue coincides with our annual pilgrimage to Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), this year held in our nation’s capital of Washington, D.C.
As we peruse the preliminary program in planning our meeting coverage, I am always amazed at the breadth and depth of programming offered as part of a relatively brief, 4-day meeting — this is a testament to the hard work of the AGA Council and DDW organizing committees, who have the gargantuan task of ensuring an engaging, seamless meeting each year.
This year’s conference features over 400 original scientific sessions and 4,300 oral abstract and poster presentations, in addition to the always well-attended AGA Postgraduate Course. This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, which will feature a series of thought-provoking panel discussions on the future of GI healthcare and innovations in how we treat, disseminate, and teach, also is not to be missed. Beyond DDW, I hope you will join me in taking advantage of some of D.C.’s amazing cultural offerings, including the Smithsonian museums, National Gallery, Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, and many others.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we highlight an important AGA expert consensus commentary published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology examining the role of blood-based tests (“liquid biopsy”) in colorectal cancer screening. This guidance, which recognizes the promise of such tests but also urges caution in their adoption, is particularly important considering recently published data from the ECLIPSE study (also covered in this issue) evaluating the performance of Guardant’s ctDNA liquid biopsy compared to a screening colonoscopy. Also relevant to CRC screening, we highlight data on the performance of the “next gen” Cologuard test compared with FIT, which was recently published in NEJM. In our May Member Spotlight, we feature gastroenterologist Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, who shares her passion for addressing barriers to CRC screening for Black patients. Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo introduces our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting emerging applications of AI in GI endoscopy and hepatology. We hope you enjoy all the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Washington, D.C. (or virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Release of our May issue coincides with our annual pilgrimage to Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), this year held in our nation’s capital of Washington, D.C.
As we peruse the preliminary program in planning our meeting coverage, I am always amazed at the breadth and depth of programming offered as part of a relatively brief, 4-day meeting — this is a testament to the hard work of the AGA Council and DDW organizing committees, who have the gargantuan task of ensuring an engaging, seamless meeting each year.
This year’s conference features over 400 original scientific sessions and 4,300 oral abstract and poster presentations, in addition to the always well-attended AGA Postgraduate Course. This year’s AGA Presidential Plenary, which will feature a series of thought-provoking panel discussions on the future of GI healthcare and innovations in how we treat, disseminate, and teach, also is not to be missed. Beyond DDW, I hope you will join me in taking advantage of some of D.C.’s amazing cultural offerings, including the Smithsonian museums, National Gallery, Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, and many others.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we highlight an important AGA expert consensus commentary published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology examining the role of blood-based tests (“liquid biopsy”) in colorectal cancer screening. This guidance, which recognizes the promise of such tests but also urges caution in their adoption, is particularly important considering recently published data from the ECLIPSE study (also covered in this issue) evaluating the performance of Guardant’s ctDNA liquid biopsy compared to a screening colonoscopy. Also relevant to CRC screening, we highlight data on the performance of the “next gen” Cologuard test compared with FIT, which was recently published in NEJM. In our May Member Spotlight, we feature gastroenterologist Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa, MD, MPH, who shares her passion for addressing barriers to CRC screening for Black patients. Finally, GIHN Associate Editor Dr. Avi Ketwaroo introduces our quarterly Perspectives column highlighting emerging applications of AI in GI endoscopy and hepatology. We hope you enjoy all the exciting content featured in this issue and look forward to seeing you in Washington, D.C. (or virtually) for DDW.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Commentary: Evaluating Recent BC Treatment Trials, May 2024
The class of CDK 4/6 inhibitors represents a significant advance in the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer. All three CDK 4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib) are approved in combination with endocrine therapy in the metastatic setting. As drugs show promise in later-stage disease, they are then often studied in the curative space. Presently, abemaciclib is the only CDK 4/6 inhibitor that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HR-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer, based on results from the monarchE trial, which demonstrated invasive disease-free survival benefit with the addition of 2 years of abemaciclib to endocrine therapy. At 4 years, the absolute difference in invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) between the groups was 6.4% (85.8% in the abemaciclib + endocrine therapy group vs 79.4% in the endocrine therapy–alone group).[3] In contrast, the PENELOPE-B and PALLAS trials did not show benefit with the addition of palbociclib to endocrine therapy in the adjuvant setting.[4,5] The phase 3 NATALEE trial randomly assigned patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer to ribociclib (400 mg daily for 3 weeks followed by 1 week off for 3 years) plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) or an NSAI alone. At the time of prespecified interim analysis, among 5101 patients, ribociclib + NSAI led to a significant improvement in IDFS compared with endocrine therapy alone (3-year IDFS was 90.4% vs 87.1%; hazard ratio 0.75; 95% CI 0.62-0.91; P = .003). It is certainly noteworthy that the trial design, endocrine therapies, and patient populations differed between these adjuvant studies; for example, NATALEE included a lower-risk population, and all patients received an NSAI (in monarchE approximately 30% received tamoxifen). The current results of NATALEE are encouraging; an absolute benefit of 3.3% should be considered and weighed against toxicities and cost, and longer follow-up is needed to further elucidate the role of ribociclib in the adjuvant space.
The meaningful impact of achieving a pathologic complete response (pCR) has been demonstrated in various prior studies. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy informs prognosis and helps tailor adjuvant therapy, the latter of which is particularly relevant for the HER2-positive subtype. Strategies to identify patients who are more likely to achieve pCR and predictors of early responders may aid in improving efficacy outcomes and limiting toxicities. TRAIN-3 is a single-arm, phase 2 study that included 235 and 232 patients with stage II/III HR-/HER2+ and HR+/HER2+ breast cancer, respectively, undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (weekly paclitaxel D1 and D8/carboplatin AUC 6 D1/trastuzumab D1/pertuzumab D1 every 3 weeks for up to nine cycles), and was designed to evaluate radiologic and pathologic response rates and event-free survival. Response was monitored by breast MRI every 3 cycles and lymph node biopsy. Among patients with HR-/HER2+ tumors, 84 (36%; 95% CI 30-43) achieved a radiologic complete response after one to three cycles, of whom the majority (88%; 95% CI 79-94) had pCR. Patients with HR+/HER2+ tumors did not show the same degree of benefit with an MRI-based monitoring strategy; among the 138 patients (59%; 95% CI 53-66) who had a complete radiologic response after one to nine cycles, 73 (53%; 95% CI 44-61) had pCR. Additional imaging-guided modalities being studied to tailor and optimize treatment include [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose-PET-CT and volumetric MRI, in the PHERGain and I-SPY trials, respectively.[6,7]
Additional References:
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470 Source
- Bartels SAL, Donker M, Poncet C, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer: 10-year results of the randomized controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:2159-2165. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01565 Source
- Johnston SRD, Toi M, O'Shaughnessy J, et al, on behalf of the monarchE Committee Members. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:77-90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00694-5 Source
- Loibl S, Marmé F, Martin M, et al. Palbociclib for residual high-risk invasive HR-positive and HER2-negative early breast cancer—The Penelope-B trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1518-1530. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03639 Source
- Gnant M, Dueck AC, Frantal S, et al, on behalf of the PALLAS groups and investigators. Adjuvant palbociclib for early breast cancer: The PALLAS trial results (ABCSG-42/AFT-05/BIG-14-03). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:282-293. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02554 Source
- Pérez-García JM, Cortés J, Ruiz-Borrego M, et al, on behalf of the PHERGain trial investigators. 3-year invasive disease-free survival with chemotherapy de-escalation using an 18F-FDG-PET-based, pathological complete response-adapted strategy in HER2-positive early breast cancer (PHERGain): A randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2024;403:1649-1659. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00054-0 Source
- Hylton NM, Gatsonis CA, Rosen MA, et al, for the ACRIN 6657 trial team and I-SPY 1 trial investigators. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Functional tumor volume by MR imaging predicts recurrence-free survival-results from the ACRIN 6657/CALGB 150007 I-SPY 1 trial. Radiology. 2016;279:44-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150013 Source
The class of CDK 4/6 inhibitors represents a significant advance in the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer. All three CDK 4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib) are approved in combination with endocrine therapy in the metastatic setting. As drugs show promise in later-stage disease, they are then often studied in the curative space. Presently, abemaciclib is the only CDK 4/6 inhibitor that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HR-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer, based on results from the monarchE trial, which demonstrated invasive disease-free survival benefit with the addition of 2 years of abemaciclib to endocrine therapy. At 4 years, the absolute difference in invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) between the groups was 6.4% (85.8% in the abemaciclib + endocrine therapy group vs 79.4% in the endocrine therapy–alone group).[3] In contrast, the PENELOPE-B and PALLAS trials did not show benefit with the addition of palbociclib to endocrine therapy in the adjuvant setting.[4,5] The phase 3 NATALEE trial randomly assigned patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer to ribociclib (400 mg daily for 3 weeks followed by 1 week off for 3 years) plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) or an NSAI alone. At the time of prespecified interim analysis, among 5101 patients, ribociclib + NSAI led to a significant improvement in IDFS compared with endocrine therapy alone (3-year IDFS was 90.4% vs 87.1%; hazard ratio 0.75; 95% CI 0.62-0.91; P = .003). It is certainly noteworthy that the trial design, endocrine therapies, and patient populations differed between these adjuvant studies; for example, NATALEE included a lower-risk population, and all patients received an NSAI (in monarchE approximately 30% received tamoxifen). The current results of NATALEE are encouraging; an absolute benefit of 3.3% should be considered and weighed against toxicities and cost, and longer follow-up is needed to further elucidate the role of ribociclib in the adjuvant space.
The meaningful impact of achieving a pathologic complete response (pCR) has been demonstrated in various prior studies. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy informs prognosis and helps tailor adjuvant therapy, the latter of which is particularly relevant for the HER2-positive subtype. Strategies to identify patients who are more likely to achieve pCR and predictors of early responders may aid in improving efficacy outcomes and limiting toxicities. TRAIN-3 is a single-arm, phase 2 study that included 235 and 232 patients with stage II/III HR-/HER2+ and HR+/HER2+ breast cancer, respectively, undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (weekly paclitaxel D1 and D8/carboplatin AUC 6 D1/trastuzumab D1/pertuzumab D1 every 3 weeks for up to nine cycles), and was designed to evaluate radiologic and pathologic response rates and event-free survival. Response was monitored by breast MRI every 3 cycles and lymph node biopsy. Among patients with HR-/HER2+ tumors, 84 (36%; 95% CI 30-43) achieved a radiologic complete response after one to three cycles, of whom the majority (88%; 95% CI 79-94) had pCR. Patients with HR+/HER2+ tumors did not show the same degree of benefit with an MRI-based monitoring strategy; among the 138 patients (59%; 95% CI 53-66) who had a complete radiologic response after one to nine cycles, 73 (53%; 95% CI 44-61) had pCR. Additional imaging-guided modalities being studied to tailor and optimize treatment include [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose-PET-CT and volumetric MRI, in the PHERGain and I-SPY trials, respectively.[6,7]
Additional References:
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470 Source
- Bartels SAL, Donker M, Poncet C, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer: 10-year results of the randomized controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:2159-2165. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01565 Source
- Johnston SRD, Toi M, O'Shaughnessy J, et al, on behalf of the monarchE Committee Members. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:77-90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00694-5 Source
- Loibl S, Marmé F, Martin M, et al. Palbociclib for residual high-risk invasive HR-positive and HER2-negative early breast cancer—The Penelope-B trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1518-1530. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03639 Source
- Gnant M, Dueck AC, Frantal S, et al, on behalf of the PALLAS groups and investigators. Adjuvant palbociclib for early breast cancer: The PALLAS trial results (ABCSG-42/AFT-05/BIG-14-03). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:282-293. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02554 Source
- Pérez-García JM, Cortés J, Ruiz-Borrego M, et al, on behalf of the PHERGain trial investigators. 3-year invasive disease-free survival with chemotherapy de-escalation using an 18F-FDG-PET-based, pathological complete response-adapted strategy in HER2-positive early breast cancer (PHERGain): A randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2024;403:1649-1659. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00054-0 Source
- Hylton NM, Gatsonis CA, Rosen MA, et al, for the ACRIN 6657 trial team and I-SPY 1 trial investigators. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Functional tumor volume by MR imaging predicts recurrence-free survival-results from the ACRIN 6657/CALGB 150007 I-SPY 1 trial. Radiology. 2016;279:44-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150013 Source
The class of CDK 4/6 inhibitors represents a significant advance in the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer. All three CDK 4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib) are approved in combination with endocrine therapy in the metastatic setting. As drugs show promise in later-stage disease, they are then often studied in the curative space. Presently, abemaciclib is the only CDK 4/6 inhibitor that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HR-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer, based on results from the monarchE trial, which demonstrated invasive disease-free survival benefit with the addition of 2 years of abemaciclib to endocrine therapy. At 4 years, the absolute difference in invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) between the groups was 6.4% (85.8% in the abemaciclib + endocrine therapy group vs 79.4% in the endocrine therapy–alone group).[3] In contrast, the PENELOPE-B and PALLAS trials did not show benefit with the addition of palbociclib to endocrine therapy in the adjuvant setting.[4,5] The phase 3 NATALEE trial randomly assigned patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer to ribociclib (400 mg daily for 3 weeks followed by 1 week off for 3 years) plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) or an NSAI alone. At the time of prespecified interim analysis, among 5101 patients, ribociclib + NSAI led to a significant improvement in IDFS compared with endocrine therapy alone (3-year IDFS was 90.4% vs 87.1%; hazard ratio 0.75; 95% CI 0.62-0.91; P = .003). It is certainly noteworthy that the trial design, endocrine therapies, and patient populations differed between these adjuvant studies; for example, NATALEE included a lower-risk population, and all patients received an NSAI (in monarchE approximately 30% received tamoxifen). The current results of NATALEE are encouraging; an absolute benefit of 3.3% should be considered and weighed against toxicities and cost, and longer follow-up is needed to further elucidate the role of ribociclib in the adjuvant space.
The meaningful impact of achieving a pathologic complete response (pCR) has been demonstrated in various prior studies. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy informs prognosis and helps tailor adjuvant therapy, the latter of which is particularly relevant for the HER2-positive subtype. Strategies to identify patients who are more likely to achieve pCR and predictors of early responders may aid in improving efficacy outcomes and limiting toxicities. TRAIN-3 is a single-arm, phase 2 study that included 235 and 232 patients with stage II/III HR-/HER2+ and HR+/HER2+ breast cancer, respectively, undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (weekly paclitaxel D1 and D8/carboplatin AUC 6 D1/trastuzumab D1/pertuzumab D1 every 3 weeks for up to nine cycles), and was designed to evaluate radiologic and pathologic response rates and event-free survival. Response was monitored by breast MRI every 3 cycles and lymph node biopsy. Among patients with HR-/HER2+ tumors, 84 (36%; 95% CI 30-43) achieved a radiologic complete response after one to three cycles, of whom the majority (88%; 95% CI 79-94) had pCR. Patients with HR+/HER2+ tumors did not show the same degree of benefit with an MRI-based monitoring strategy; among the 138 patients (59%; 95% CI 53-66) who had a complete radiologic response after one to nine cycles, 73 (53%; 95% CI 44-61) had pCR. Additional imaging-guided modalities being studied to tailor and optimize treatment include [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose-PET-CT and volumetric MRI, in the PHERGain and I-SPY trials, respectively.[6,7]
Additional References:
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:918-926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470 Source
- Bartels SAL, Donker M, Poncet C, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer: 10-year results of the randomized controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:2159-2165. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01565 Source
- Johnston SRD, Toi M, O'Shaughnessy J, et al, on behalf of the monarchE Committee Members. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:77-90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00694-5 Source
- Loibl S, Marmé F, Martin M, et al. Palbociclib for residual high-risk invasive HR-positive and HER2-negative early breast cancer—The Penelope-B trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1518-1530. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03639 Source
- Gnant M, Dueck AC, Frantal S, et al, on behalf of the PALLAS groups and investigators. Adjuvant palbociclib for early breast cancer: The PALLAS trial results (ABCSG-42/AFT-05/BIG-14-03). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:282-293. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02554 Source
- Pérez-García JM, Cortés J, Ruiz-Borrego M, et al, on behalf of the PHERGain trial investigators. 3-year invasive disease-free survival with chemotherapy de-escalation using an 18F-FDG-PET-based, pathological complete response-adapted strategy in HER2-positive early breast cancer (PHERGain): A randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2024;403:1649-1659. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00054-0 Source
- Hylton NM, Gatsonis CA, Rosen MA, et al, for the ACRIN 6657 trial team and I-SPY 1 trial investigators. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Functional tumor volume by MR imaging predicts recurrence-free survival-results from the ACRIN 6657/CALGB 150007 I-SPY 1 trial. Radiology. 2016;279:44-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150013 Source
Does ‘Brain Training’ Really Improve Cognition and Forestall Cognitive Decline?
The concept that cognitive health can be preserved or improved is often expressed as “use it or lose it.” Numerous modifiable risk factors are associated with “losing” cognitive abilities with age, and a cognitively active lifestyle may have a protective effect.
But what is a “cognitively active lifestyle” — do crosswords and Sudoku count?
One popular approach is “brain training.” While not a scientific term with an established definition, it “typically refers to tasks or drills that are designed to strengthen specific aspects of one’s cognitive function,” explained Yuko Hara, PhD, director of Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Manuel Montero-Odasso, MD, PhD, director of the Gait and Brain Lab, Parkwood Institute, London, Ontario, Canada, elaborated: “Cognitive training involves performing a definitive task or set of tasks where you increase attentional demands to improve focus and concentration and memory. You try to execute the new things that you’ve learned and to remember them.”
In a commentary published by this news organization in 2022, neuroscientist Michael Merzenich, PhD, professor emeritus at University of California San Francisco, said that growing a person’s cognitive reserve and actively managing brain health can play an important role in preventing or delaying Alzheimer’s disease. Important components of this include brain training and physical exercise.
Brain Training: Mechanism of Action
Dr. Montero-Odasso, team leader at the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging and team co-leader at the Ontario Neurodegenerative Research Initiative, explained that cognitive training creates new synapses in the brain, thus stimulating neuroplasticity.
“When we try to activate networks mainly in the frontal lobe, the prefrontal cortex, a key mechanism underlying this process is enhancement of the synaptic plasticity at excitatory synapses, which connect neurons into networks; in other words, we generate new synapses, and that’s how we enhance brain health and cognitive abilities.”
The more neural connections, the greater the processing speed of the brain, he continued. “Cognitive training creates an anatomical change in the brain.”
Executive functions, which include attention, inhibition, planning, and multitasking, are regulated predominantly by the prefrontal cortex. Damage in this region of the brain is also implicated in dementia. Alterations in the connectivity of this area are associated with cognitive impairment, independent of other structural pathological aberrations (eg, gray matter atrophy). These patterns may precede structural pathological changes associated with cognitive impairment and dementia.
Neuroplasticity changes have been corroborated through neuroimaging, which has demonstrated that after cognitive training, there is more activation in the prefrontal cortex that correlates with new synapses, Dr. Montero-Odasso said.
Henry Mahncke, PhD, CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ, explained that early research was conducted on rodents and monkeys, with Dr. Merzenich as one of the leading pioneers in developing the concept of brain plasticity. Dr. Merzenich cofounded Posit Science and is currently its chief scientific officer.
Dr. Mahncke recounted that as a graduate student, he had worked with Dr. Merzenich researching brain plasticity. When Dr. Merzenich founded Posit Science, he asked Dr. Mahncke to join the company to help develop approaches to enhance brain plasticity — building the brain-training exercises and running the clinical trials.
“It’s now well understood that the brain can rewire itself at any age and in almost any condition,” Dr. Mahncke said. “In kids and in younger and older adults, whether with healthy or unhealthy brains, the fundamental way the brain works is by continually rewiring and rebuilding itself, based on what we ask it to do.”
Dr. Mahncke said.
Unsubstantiated Claims and Controversy
Brain training is not without controversy, Dr. Hara pointed out. “Some manufacturers of brain games have been criticized and even fined for making unsubstantiated claims,” she said.
A 2016 review found that brain-training interventions do improve performance on specific trained tasks, but there is less evidence that they improve performance on closely related tasks and little evidence that training improves everyday cognitive performance. A 2017 review reached similar conclusions, calling evidence regarding prevention or delay of cognitive decline or dementia through brain games “insufficient,” although cognitive training could “improve cognition in the domain trained.”
“The general consensus is that for most brain-training programs, people may get better at specific tasks through practice, but these improvements don’t necessarily translate into improvement in other tasks that require other cognitive domains or prevention of dementia or age-related cognitive decline,” Dr. Hara said.
She noted that most brain-training programs “have not been rigorously tested in clinical trials” — although some, such as those featured in the ACTIVE trial, did show evidence of effectiveness.
Dr. Mahncke agreed. “Asking whether brain training works is like asking whether small molecules improve health,” he said noting that some brain-training programs are nonsense and not evidence based. He believes that his company’s product, BrainHQ, and some others are “backed by robust evidence in their ability to stave off, slow, or even reverse cognitive changes.”
BrainHQ is a web-based brain game suite that can be used independently as an app or in group settings (classes and webinars) and is covered by some Medicare Advantage insurance plans. It encompasses “dozens of individual brain-training exercises, linked by a common thread. Each one is intensively designed to make the brain faster and more accurate,” said Dr. Mahncke.
He explained that human brains “get noisy as people get older, like a radio which is wearing out, so there’s static in the background. This makes the music hard to hear, and in the case of the human brain, it makes it difficult to pay attention.” The exercises are “designed to tamp down the ‘noise,’ speed up the brain, and make information processing more accurate.”
Dr. Mahncke called this a “bottom-up” approach, in contrast to many previous cognitive-training approaches that come from the brain injury rehabilitation field. They teach “top-down” skills and strategies designed to compensate for deficits in specific domains, such as reading, concentration, or fine motor skills.
By contrast, the approach of BrainHQ is “to improve the overall processing system of the brain with speed, attention, working memory, and executive function, which will in turn impact all skills and activities.”
Supporting Evidence
Dr. Mahncke cited several supporting studies. For example, the IMPACT study randomized 487 adults (aged ≥ 65 years) to receive either a brain plasticity–based computerized cognitive training program (BrainHQ) or a novelty- and intensity-matched general cognitive stimulation treatment program (intervention and control group, respectively) for an 8-week period.
Those who underwent brain training showed significantly greater improvement in the repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS Auditory Memory/Attention) compared with those in the control group (3.9 vs 1.8, respectively; P =.02). The intervention group also showed significant improvements on multiple secondary measures of attention and memory. The magnitude of the effect sizes suggests that the results are clinically significant, according to the authors.
The ACTIVE study tested the effects of different cognitive training programs on cognitive function and time to dementia. The researchers randomized 2802 healthy older adults (mean age, 74 years) to a control group with no cognitive training or one of three brain-training groups comprising:
1. In-person training on verbal memory skills
2. In-person training on reasoning and problem-solving
3. Computer-based speed-of-processing training on visual attention
Participants in the training groups completed 10 sessions, each lasting 60-75 minutes, over a 5- to 6-week period. A random subsample of each training group was selected to receive “booster” sessions, with four-session booster training delivered at 11 and 35 months. All study participants completed follow-up tests of cognition and function after 1, 2, 3, 5, and 10 years.
At the end of 10 years, those assigned to the speed-of-processing training, now part of BrainHQ, had a 29% lower risk for dementia than those in the control group who received no training. No reduction was found in the memory or reasoning training groups. Participants who completed the “booster” sessions had an even greater reduction: Each additional booster session was associated with a 10% lower risk for dementia.
Dr. Montero-Odasso was involved in the SYNERGIC study that randomized 175 participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI; average age, 73 years) to one of five study arms:
1. Multidomain intervention with exercise, cognitive training, and vitamin D
2. Exercise, cognitive training, and placebo
3. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and vitamin D
4. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
5. Control group with balance-toning exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
“Sham” cognitive training consisted of alternating between two tasks (touristic search and video watching) performed on a tablet, with the same time exposure as the intervention training.
The researchers found that after 6 months of interventions, all active arms with aerobic-resistance exercise showed improvement in the ADAS-Cog-13, an established outcome to evaluate dementia treatments, when compared with the control group — regardless of the addition of cognitive training or vitamin D.
Compared with exercise alone (arms 3 and 4), those who did exercise plus cognitive training (arms 1 and 2) showed greater improvements in their ADAS-Cog-13l score, with a mean difference of −1.45 points (P = .02). The greatest improvement was seen in those who underwent the multidomain intervention in arm 1.
The authors noted that the mean 2.64-point improvement seen in the ADAS-Cog-13 for the multidomain intervention is actually larger than changes seen in previous pharmaceutical trials among individuals with MCI or mild dementia and “approaches” the three points considered clinically meaningful.
“We found that older adults with MCI who received aerobic-resistance exercise with sequential computerized cognitive training significantly improved cognition,” Dr. Montero-Odasso said. “The cognitive training we used was called Neuropeak, a multidomain lifestyle training delivered through a web-based platform developed by our co-leader Louis Bherer at Université de Montréal.”
He explained that the purpose “is to challenge your brain to the point where you need to make an effort to remember things, pay attention, and later to execute tasks. The evidence from clinical trials, including ours, shows this type of brain challenge is effective in slowing and even reversing cognitive decline.”
A follow-up study, SYNERGIC 2.0, is ongoing.
Puzzles, Board Games, and New Challenges
Formal brain-training programs aren’t the only way to improve brain plasticity, Dr. Hara said. Observational studies suggested an association between improved cognitive performance and/or lower dementia risk and engaging in number and word puzzles, such as crosswords, cards, or board games.
Some studies suggested that older adults who use technology might also protect their cognitive reserve. Dr. Hara cited a US longitudinal study of more than 18,000 older adults suggesting that regular Internet users had roughly half the risk for dementia compared to nonregular Internet users. Estimates of daily Internet use suggested a U-shaped relationship with dementia with 0.1-2.0 hours daily (excluding time spent watching television or movies online) associated with the lowest risk. Similar associations between Internet use and a lower risk for cognitive decline have been reported in the United Kingdom and Europe.
“Engaging in mentally stimulating activities can increase ‘cognitive reserve’ — meaning, capacity of the brain to resist the effects of age-related changes or disease-related pathology, such that one can maintain cognitive function for longer,” Dr. Hara said. “Cognitively stimulating activities, regardless of the type, may help delay the onset of cognitive decline.”
She listed several examples of activities that are stimulating to the brain, including learning a new game or puzzle, a new language, or a new dance, and learning how to play a musical instrument.
Dr. Montero-Odasso emphasized that the “newness” is key to increasing and preserving cognitive reserve. “Just surfing the Internet, playing word or board games, or doing crossword puzzles won’t be enough if you’ve been doing these things all your life,” he said. “It won’t hurt, of course, but it won’t necessarily increase your cognitive abilities.
“For example, a person who regularly engages in public speaking may not improve cognition by taking a public-speaking course, but someone who has never spoken before an audience might show cognitive improvements as a result of learning a new skill,” he said. “Or someone who knows several languages already might gain from learning a brand-new language.”
He cited research supporting the benefits of dancing, which he called “an ideal activity because it’s physical, so it provides the exercise that’s been associated with improved cognition. But it also requires learning new steps and moves, which builds the synapses in the brain. And the socialization of dance classes adds another component that can improve cognition.”
Dr. Mahncke hopes that beyond engaging in day-to-day new activities, seniors will participate in computerized brain training. “There’s no reason that evidence-based training can’t be offered in senior and community centers, as yoga and swimming are,” he said. “It doesn’t have to be simply something people do on their own virtually.”
Zoom classes and Medicare reimbursements are “good steps in the right direction, but it’s time to expand this potentially life-transformative intervention so that it reaches the ever-expanding population of seniors in the United States and beyond.”
Dr. Hara reported having no disclosures. Dr. Montero-Odasso reported having no commercial or financial interest related to this topic. He serves as the president of the Canadian Geriatrics Société and is team leader in the Canadian Consortium of Neurodegeneration in Aging. Dr. Mahncke is CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The concept that cognitive health can be preserved or improved is often expressed as “use it or lose it.” Numerous modifiable risk factors are associated with “losing” cognitive abilities with age, and a cognitively active lifestyle may have a protective effect.
But what is a “cognitively active lifestyle” — do crosswords and Sudoku count?
One popular approach is “brain training.” While not a scientific term with an established definition, it “typically refers to tasks or drills that are designed to strengthen specific aspects of one’s cognitive function,” explained Yuko Hara, PhD, director of Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Manuel Montero-Odasso, MD, PhD, director of the Gait and Brain Lab, Parkwood Institute, London, Ontario, Canada, elaborated: “Cognitive training involves performing a definitive task or set of tasks where you increase attentional demands to improve focus and concentration and memory. You try to execute the new things that you’ve learned and to remember them.”
In a commentary published by this news organization in 2022, neuroscientist Michael Merzenich, PhD, professor emeritus at University of California San Francisco, said that growing a person’s cognitive reserve and actively managing brain health can play an important role in preventing or delaying Alzheimer’s disease. Important components of this include brain training and physical exercise.
Brain Training: Mechanism of Action
Dr. Montero-Odasso, team leader at the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging and team co-leader at the Ontario Neurodegenerative Research Initiative, explained that cognitive training creates new synapses in the brain, thus stimulating neuroplasticity.
“When we try to activate networks mainly in the frontal lobe, the prefrontal cortex, a key mechanism underlying this process is enhancement of the synaptic plasticity at excitatory synapses, which connect neurons into networks; in other words, we generate new synapses, and that’s how we enhance brain health and cognitive abilities.”
The more neural connections, the greater the processing speed of the brain, he continued. “Cognitive training creates an anatomical change in the brain.”
Executive functions, which include attention, inhibition, planning, and multitasking, are regulated predominantly by the prefrontal cortex. Damage in this region of the brain is also implicated in dementia. Alterations in the connectivity of this area are associated with cognitive impairment, independent of other structural pathological aberrations (eg, gray matter atrophy). These patterns may precede structural pathological changes associated with cognitive impairment and dementia.
Neuroplasticity changes have been corroborated through neuroimaging, which has demonstrated that after cognitive training, there is more activation in the prefrontal cortex that correlates with new synapses, Dr. Montero-Odasso said.
Henry Mahncke, PhD, CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ, explained that early research was conducted on rodents and monkeys, with Dr. Merzenich as one of the leading pioneers in developing the concept of brain plasticity. Dr. Merzenich cofounded Posit Science and is currently its chief scientific officer.
Dr. Mahncke recounted that as a graduate student, he had worked with Dr. Merzenich researching brain plasticity. When Dr. Merzenich founded Posit Science, he asked Dr. Mahncke to join the company to help develop approaches to enhance brain plasticity — building the brain-training exercises and running the clinical trials.
“It’s now well understood that the brain can rewire itself at any age and in almost any condition,” Dr. Mahncke said. “In kids and in younger and older adults, whether with healthy or unhealthy brains, the fundamental way the brain works is by continually rewiring and rebuilding itself, based on what we ask it to do.”
Dr. Mahncke said.
Unsubstantiated Claims and Controversy
Brain training is not without controversy, Dr. Hara pointed out. “Some manufacturers of brain games have been criticized and even fined for making unsubstantiated claims,” she said.
A 2016 review found that brain-training interventions do improve performance on specific trained tasks, but there is less evidence that they improve performance on closely related tasks and little evidence that training improves everyday cognitive performance. A 2017 review reached similar conclusions, calling evidence regarding prevention or delay of cognitive decline or dementia through brain games “insufficient,” although cognitive training could “improve cognition in the domain trained.”
“The general consensus is that for most brain-training programs, people may get better at specific tasks through practice, but these improvements don’t necessarily translate into improvement in other tasks that require other cognitive domains or prevention of dementia or age-related cognitive decline,” Dr. Hara said.
She noted that most brain-training programs “have not been rigorously tested in clinical trials” — although some, such as those featured in the ACTIVE trial, did show evidence of effectiveness.
Dr. Mahncke agreed. “Asking whether brain training works is like asking whether small molecules improve health,” he said noting that some brain-training programs are nonsense and not evidence based. He believes that his company’s product, BrainHQ, and some others are “backed by robust evidence in their ability to stave off, slow, or even reverse cognitive changes.”
BrainHQ is a web-based brain game suite that can be used independently as an app or in group settings (classes and webinars) and is covered by some Medicare Advantage insurance plans. It encompasses “dozens of individual brain-training exercises, linked by a common thread. Each one is intensively designed to make the brain faster and more accurate,” said Dr. Mahncke.
He explained that human brains “get noisy as people get older, like a radio which is wearing out, so there’s static in the background. This makes the music hard to hear, and in the case of the human brain, it makes it difficult to pay attention.” The exercises are “designed to tamp down the ‘noise,’ speed up the brain, and make information processing more accurate.”
Dr. Mahncke called this a “bottom-up” approach, in contrast to many previous cognitive-training approaches that come from the brain injury rehabilitation field. They teach “top-down” skills and strategies designed to compensate for deficits in specific domains, such as reading, concentration, or fine motor skills.
By contrast, the approach of BrainHQ is “to improve the overall processing system of the brain with speed, attention, working memory, and executive function, which will in turn impact all skills and activities.”
Supporting Evidence
Dr. Mahncke cited several supporting studies. For example, the IMPACT study randomized 487 adults (aged ≥ 65 years) to receive either a brain plasticity–based computerized cognitive training program (BrainHQ) or a novelty- and intensity-matched general cognitive stimulation treatment program (intervention and control group, respectively) for an 8-week period.
Those who underwent brain training showed significantly greater improvement in the repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS Auditory Memory/Attention) compared with those in the control group (3.9 vs 1.8, respectively; P =.02). The intervention group also showed significant improvements on multiple secondary measures of attention and memory. The magnitude of the effect sizes suggests that the results are clinically significant, according to the authors.
The ACTIVE study tested the effects of different cognitive training programs on cognitive function and time to dementia. The researchers randomized 2802 healthy older adults (mean age, 74 years) to a control group with no cognitive training or one of three brain-training groups comprising:
1. In-person training on verbal memory skills
2. In-person training on reasoning and problem-solving
3. Computer-based speed-of-processing training on visual attention
Participants in the training groups completed 10 sessions, each lasting 60-75 minutes, over a 5- to 6-week period. A random subsample of each training group was selected to receive “booster” sessions, with four-session booster training delivered at 11 and 35 months. All study participants completed follow-up tests of cognition and function after 1, 2, 3, 5, and 10 years.
At the end of 10 years, those assigned to the speed-of-processing training, now part of BrainHQ, had a 29% lower risk for dementia than those in the control group who received no training. No reduction was found in the memory or reasoning training groups. Participants who completed the “booster” sessions had an even greater reduction: Each additional booster session was associated with a 10% lower risk for dementia.
Dr. Montero-Odasso was involved in the SYNERGIC study that randomized 175 participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI; average age, 73 years) to one of five study arms:
1. Multidomain intervention with exercise, cognitive training, and vitamin D
2. Exercise, cognitive training, and placebo
3. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and vitamin D
4. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
5. Control group with balance-toning exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
“Sham” cognitive training consisted of alternating between two tasks (touristic search and video watching) performed on a tablet, with the same time exposure as the intervention training.
The researchers found that after 6 months of interventions, all active arms with aerobic-resistance exercise showed improvement in the ADAS-Cog-13, an established outcome to evaluate dementia treatments, when compared with the control group — regardless of the addition of cognitive training or vitamin D.
Compared with exercise alone (arms 3 and 4), those who did exercise plus cognitive training (arms 1 and 2) showed greater improvements in their ADAS-Cog-13l score, with a mean difference of −1.45 points (P = .02). The greatest improvement was seen in those who underwent the multidomain intervention in arm 1.
The authors noted that the mean 2.64-point improvement seen in the ADAS-Cog-13 for the multidomain intervention is actually larger than changes seen in previous pharmaceutical trials among individuals with MCI or mild dementia and “approaches” the three points considered clinically meaningful.
“We found that older adults with MCI who received aerobic-resistance exercise with sequential computerized cognitive training significantly improved cognition,” Dr. Montero-Odasso said. “The cognitive training we used was called Neuropeak, a multidomain lifestyle training delivered through a web-based platform developed by our co-leader Louis Bherer at Université de Montréal.”
He explained that the purpose “is to challenge your brain to the point where you need to make an effort to remember things, pay attention, and later to execute tasks. The evidence from clinical trials, including ours, shows this type of brain challenge is effective in slowing and even reversing cognitive decline.”
A follow-up study, SYNERGIC 2.0, is ongoing.
Puzzles, Board Games, and New Challenges
Formal brain-training programs aren’t the only way to improve brain plasticity, Dr. Hara said. Observational studies suggested an association between improved cognitive performance and/or lower dementia risk and engaging in number and word puzzles, such as crosswords, cards, or board games.
Some studies suggested that older adults who use technology might also protect their cognitive reserve. Dr. Hara cited a US longitudinal study of more than 18,000 older adults suggesting that regular Internet users had roughly half the risk for dementia compared to nonregular Internet users. Estimates of daily Internet use suggested a U-shaped relationship with dementia with 0.1-2.0 hours daily (excluding time spent watching television or movies online) associated with the lowest risk. Similar associations between Internet use and a lower risk for cognitive decline have been reported in the United Kingdom and Europe.
“Engaging in mentally stimulating activities can increase ‘cognitive reserve’ — meaning, capacity of the brain to resist the effects of age-related changes or disease-related pathology, such that one can maintain cognitive function for longer,” Dr. Hara said. “Cognitively stimulating activities, regardless of the type, may help delay the onset of cognitive decline.”
She listed several examples of activities that are stimulating to the brain, including learning a new game or puzzle, a new language, or a new dance, and learning how to play a musical instrument.
Dr. Montero-Odasso emphasized that the “newness” is key to increasing and preserving cognitive reserve. “Just surfing the Internet, playing word or board games, or doing crossword puzzles won’t be enough if you’ve been doing these things all your life,” he said. “It won’t hurt, of course, but it won’t necessarily increase your cognitive abilities.
“For example, a person who regularly engages in public speaking may not improve cognition by taking a public-speaking course, but someone who has never spoken before an audience might show cognitive improvements as a result of learning a new skill,” he said. “Or someone who knows several languages already might gain from learning a brand-new language.”
He cited research supporting the benefits of dancing, which he called “an ideal activity because it’s physical, so it provides the exercise that’s been associated with improved cognition. But it also requires learning new steps and moves, which builds the synapses in the brain. And the socialization of dance classes adds another component that can improve cognition.”
Dr. Mahncke hopes that beyond engaging in day-to-day new activities, seniors will participate in computerized brain training. “There’s no reason that evidence-based training can’t be offered in senior and community centers, as yoga and swimming are,” he said. “It doesn’t have to be simply something people do on their own virtually.”
Zoom classes and Medicare reimbursements are “good steps in the right direction, but it’s time to expand this potentially life-transformative intervention so that it reaches the ever-expanding population of seniors in the United States and beyond.”
Dr. Hara reported having no disclosures. Dr. Montero-Odasso reported having no commercial or financial interest related to this topic. He serves as the president of the Canadian Geriatrics Société and is team leader in the Canadian Consortium of Neurodegeneration in Aging. Dr. Mahncke is CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The concept that cognitive health can be preserved or improved is often expressed as “use it or lose it.” Numerous modifiable risk factors are associated with “losing” cognitive abilities with age, and a cognitively active lifestyle may have a protective effect.
But what is a “cognitively active lifestyle” — do crosswords and Sudoku count?
One popular approach is “brain training.” While not a scientific term with an established definition, it “typically refers to tasks or drills that are designed to strengthen specific aspects of one’s cognitive function,” explained Yuko Hara, PhD, director of Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Manuel Montero-Odasso, MD, PhD, director of the Gait and Brain Lab, Parkwood Institute, London, Ontario, Canada, elaborated: “Cognitive training involves performing a definitive task or set of tasks where you increase attentional demands to improve focus and concentration and memory. You try to execute the new things that you’ve learned and to remember them.”
In a commentary published by this news organization in 2022, neuroscientist Michael Merzenich, PhD, professor emeritus at University of California San Francisco, said that growing a person’s cognitive reserve and actively managing brain health can play an important role in preventing or delaying Alzheimer’s disease. Important components of this include brain training and physical exercise.
Brain Training: Mechanism of Action
Dr. Montero-Odasso, team leader at the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging and team co-leader at the Ontario Neurodegenerative Research Initiative, explained that cognitive training creates new synapses in the brain, thus stimulating neuroplasticity.
“When we try to activate networks mainly in the frontal lobe, the prefrontal cortex, a key mechanism underlying this process is enhancement of the synaptic plasticity at excitatory synapses, which connect neurons into networks; in other words, we generate new synapses, and that’s how we enhance brain health and cognitive abilities.”
The more neural connections, the greater the processing speed of the brain, he continued. “Cognitive training creates an anatomical change in the brain.”
Executive functions, which include attention, inhibition, planning, and multitasking, are regulated predominantly by the prefrontal cortex. Damage in this region of the brain is also implicated in dementia. Alterations in the connectivity of this area are associated with cognitive impairment, independent of other structural pathological aberrations (eg, gray matter atrophy). These patterns may precede structural pathological changes associated with cognitive impairment and dementia.
Neuroplasticity changes have been corroborated through neuroimaging, which has demonstrated that after cognitive training, there is more activation in the prefrontal cortex that correlates with new synapses, Dr. Montero-Odasso said.
Henry Mahncke, PhD, CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ, explained that early research was conducted on rodents and monkeys, with Dr. Merzenich as one of the leading pioneers in developing the concept of brain plasticity. Dr. Merzenich cofounded Posit Science and is currently its chief scientific officer.
Dr. Mahncke recounted that as a graduate student, he had worked with Dr. Merzenich researching brain plasticity. When Dr. Merzenich founded Posit Science, he asked Dr. Mahncke to join the company to help develop approaches to enhance brain plasticity — building the brain-training exercises and running the clinical trials.
“It’s now well understood that the brain can rewire itself at any age and in almost any condition,” Dr. Mahncke said. “In kids and in younger and older adults, whether with healthy or unhealthy brains, the fundamental way the brain works is by continually rewiring and rebuilding itself, based on what we ask it to do.”
Dr. Mahncke said.
Unsubstantiated Claims and Controversy
Brain training is not without controversy, Dr. Hara pointed out. “Some manufacturers of brain games have been criticized and even fined for making unsubstantiated claims,” she said.
A 2016 review found that brain-training interventions do improve performance on specific trained tasks, but there is less evidence that they improve performance on closely related tasks and little evidence that training improves everyday cognitive performance. A 2017 review reached similar conclusions, calling evidence regarding prevention or delay of cognitive decline or dementia through brain games “insufficient,” although cognitive training could “improve cognition in the domain trained.”
“The general consensus is that for most brain-training programs, people may get better at specific tasks through practice, but these improvements don’t necessarily translate into improvement in other tasks that require other cognitive domains or prevention of dementia or age-related cognitive decline,” Dr. Hara said.
She noted that most brain-training programs “have not been rigorously tested in clinical trials” — although some, such as those featured in the ACTIVE trial, did show evidence of effectiveness.
Dr. Mahncke agreed. “Asking whether brain training works is like asking whether small molecules improve health,” he said noting that some brain-training programs are nonsense and not evidence based. He believes that his company’s product, BrainHQ, and some others are “backed by robust evidence in their ability to stave off, slow, or even reverse cognitive changes.”
BrainHQ is a web-based brain game suite that can be used independently as an app or in group settings (classes and webinars) and is covered by some Medicare Advantage insurance plans. It encompasses “dozens of individual brain-training exercises, linked by a common thread. Each one is intensively designed to make the brain faster and more accurate,” said Dr. Mahncke.
He explained that human brains “get noisy as people get older, like a radio which is wearing out, so there’s static in the background. This makes the music hard to hear, and in the case of the human brain, it makes it difficult to pay attention.” The exercises are “designed to tamp down the ‘noise,’ speed up the brain, and make information processing more accurate.”
Dr. Mahncke called this a “bottom-up” approach, in contrast to many previous cognitive-training approaches that come from the brain injury rehabilitation field. They teach “top-down” skills and strategies designed to compensate for deficits in specific domains, such as reading, concentration, or fine motor skills.
By contrast, the approach of BrainHQ is “to improve the overall processing system of the brain with speed, attention, working memory, and executive function, which will in turn impact all skills and activities.”
Supporting Evidence
Dr. Mahncke cited several supporting studies. For example, the IMPACT study randomized 487 adults (aged ≥ 65 years) to receive either a brain plasticity–based computerized cognitive training program (BrainHQ) or a novelty- and intensity-matched general cognitive stimulation treatment program (intervention and control group, respectively) for an 8-week period.
Those who underwent brain training showed significantly greater improvement in the repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS Auditory Memory/Attention) compared with those in the control group (3.9 vs 1.8, respectively; P =.02). The intervention group also showed significant improvements on multiple secondary measures of attention and memory. The magnitude of the effect sizes suggests that the results are clinically significant, according to the authors.
The ACTIVE study tested the effects of different cognitive training programs on cognitive function and time to dementia. The researchers randomized 2802 healthy older adults (mean age, 74 years) to a control group with no cognitive training or one of three brain-training groups comprising:
1. In-person training on verbal memory skills
2. In-person training on reasoning and problem-solving
3. Computer-based speed-of-processing training on visual attention
Participants in the training groups completed 10 sessions, each lasting 60-75 minutes, over a 5- to 6-week period. A random subsample of each training group was selected to receive “booster” sessions, with four-session booster training delivered at 11 and 35 months. All study participants completed follow-up tests of cognition and function after 1, 2, 3, 5, and 10 years.
At the end of 10 years, those assigned to the speed-of-processing training, now part of BrainHQ, had a 29% lower risk for dementia than those in the control group who received no training. No reduction was found in the memory or reasoning training groups. Participants who completed the “booster” sessions had an even greater reduction: Each additional booster session was associated with a 10% lower risk for dementia.
Dr. Montero-Odasso was involved in the SYNERGIC study that randomized 175 participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI; average age, 73 years) to one of five study arms:
1. Multidomain intervention with exercise, cognitive training, and vitamin D
2. Exercise, cognitive training, and placebo
3. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and vitamin D
4. Exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
5. Control group with balance-toning exercise, sham cognitive training, and placebo
“Sham” cognitive training consisted of alternating between two tasks (touristic search and video watching) performed on a tablet, with the same time exposure as the intervention training.
The researchers found that after 6 months of interventions, all active arms with aerobic-resistance exercise showed improvement in the ADAS-Cog-13, an established outcome to evaluate dementia treatments, when compared with the control group — regardless of the addition of cognitive training or vitamin D.
Compared with exercise alone (arms 3 and 4), those who did exercise plus cognitive training (arms 1 and 2) showed greater improvements in their ADAS-Cog-13l score, with a mean difference of −1.45 points (P = .02). The greatest improvement was seen in those who underwent the multidomain intervention in arm 1.
The authors noted that the mean 2.64-point improvement seen in the ADAS-Cog-13 for the multidomain intervention is actually larger than changes seen in previous pharmaceutical trials among individuals with MCI or mild dementia and “approaches” the three points considered clinically meaningful.
“We found that older adults with MCI who received aerobic-resistance exercise with sequential computerized cognitive training significantly improved cognition,” Dr. Montero-Odasso said. “The cognitive training we used was called Neuropeak, a multidomain lifestyle training delivered through a web-based platform developed by our co-leader Louis Bherer at Université de Montréal.”
He explained that the purpose “is to challenge your brain to the point where you need to make an effort to remember things, pay attention, and later to execute tasks. The evidence from clinical trials, including ours, shows this type of brain challenge is effective in slowing and even reversing cognitive decline.”
A follow-up study, SYNERGIC 2.0, is ongoing.
Puzzles, Board Games, and New Challenges
Formal brain-training programs aren’t the only way to improve brain plasticity, Dr. Hara said. Observational studies suggested an association between improved cognitive performance and/or lower dementia risk and engaging in number and word puzzles, such as crosswords, cards, or board games.
Some studies suggested that older adults who use technology might also protect their cognitive reserve. Dr. Hara cited a US longitudinal study of more than 18,000 older adults suggesting that regular Internet users had roughly half the risk for dementia compared to nonregular Internet users. Estimates of daily Internet use suggested a U-shaped relationship with dementia with 0.1-2.0 hours daily (excluding time spent watching television or movies online) associated with the lowest risk. Similar associations between Internet use and a lower risk for cognitive decline have been reported in the United Kingdom and Europe.
“Engaging in mentally stimulating activities can increase ‘cognitive reserve’ — meaning, capacity of the brain to resist the effects of age-related changes or disease-related pathology, such that one can maintain cognitive function for longer,” Dr. Hara said. “Cognitively stimulating activities, regardless of the type, may help delay the onset of cognitive decline.”
She listed several examples of activities that are stimulating to the brain, including learning a new game or puzzle, a new language, or a new dance, and learning how to play a musical instrument.
Dr. Montero-Odasso emphasized that the “newness” is key to increasing and preserving cognitive reserve. “Just surfing the Internet, playing word or board games, or doing crossword puzzles won’t be enough if you’ve been doing these things all your life,” he said. “It won’t hurt, of course, but it won’t necessarily increase your cognitive abilities.
“For example, a person who regularly engages in public speaking may not improve cognition by taking a public-speaking course, but someone who has never spoken before an audience might show cognitive improvements as a result of learning a new skill,” he said. “Or someone who knows several languages already might gain from learning a brand-new language.”
He cited research supporting the benefits of dancing, which he called “an ideal activity because it’s physical, so it provides the exercise that’s been associated with improved cognition. But it also requires learning new steps and moves, which builds the synapses in the brain. And the socialization of dance classes adds another component that can improve cognition.”
Dr. Mahncke hopes that beyond engaging in day-to-day new activities, seniors will participate in computerized brain training. “There’s no reason that evidence-based training can’t be offered in senior and community centers, as yoga and swimming are,” he said. “It doesn’t have to be simply something people do on their own virtually.”
Zoom classes and Medicare reimbursements are “good steps in the right direction, but it’s time to expand this potentially life-transformative intervention so that it reaches the ever-expanding population of seniors in the United States and beyond.”
Dr. Hara reported having no disclosures. Dr. Montero-Odasso reported having no commercial or financial interest related to this topic. He serves as the president of the Canadian Geriatrics Société and is team leader in the Canadian Consortium of Neurodegeneration in Aging. Dr. Mahncke is CEO of the brain training company Posit Science/BrainHQ.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Highlights in Atherosclerosis and Lipid Management From ACC 2024
Lipid highlights from the 2024 American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions included positive outcomes for bempedoic acid in statin-intolerant patients and a inclisiran-first strategy for patients with atherosclerosis. The presentations are reported by Dr Erin Michos, associate director of preventive cardiology, Johns Hopkins University. Dr Michos begins with an update of the CLEAR Outcomes trial, which examined bempedoic acid, a nonstatin inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, in patients who had cardiovascular disease or were at high risk of developing it. The trial found that bempedoic acid safely reduced cardiovascular events by 13% compared with placebo — findings of particular value for patients unable or unwilling to take guideline-recommended doses of statins. Commendably, the trial enrolled 48% women and 17% Hispanic/Latinx persons. Dr Michos also reports on a trial investigating an inclisiran-first strategy vs usual care in patients with atherosclerosis. The reduction in LDL cholesterol was 60% for patients in the inclisiran upfront arm vs only 7% for patients provided with usual care. In closing, Dr Michos discusses the TACTIC trial, which was an evaluation of a technology-assisted web application used to qualify patients for nonprescription statin administration.
--
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; Director of Women's Cardiovascular Health Research, Associate Director of Preventive Cardiology, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Boehringer Ingelheim; Edwards Lifesciences; Esperion; Merck; Medtronic; New Amsterdam; Novo Nordisk; Novartis; Pfizer
Lipid highlights from the 2024 American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions included positive outcomes for bempedoic acid in statin-intolerant patients and a inclisiran-first strategy for patients with atherosclerosis. The presentations are reported by Dr Erin Michos, associate director of preventive cardiology, Johns Hopkins University. Dr Michos begins with an update of the CLEAR Outcomes trial, which examined bempedoic acid, a nonstatin inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, in patients who had cardiovascular disease or were at high risk of developing it. The trial found that bempedoic acid safely reduced cardiovascular events by 13% compared with placebo — findings of particular value for patients unable or unwilling to take guideline-recommended doses of statins. Commendably, the trial enrolled 48% women and 17% Hispanic/Latinx persons. Dr Michos also reports on a trial investigating an inclisiran-first strategy vs usual care in patients with atherosclerosis. The reduction in LDL cholesterol was 60% for patients in the inclisiran upfront arm vs only 7% for patients provided with usual care. In closing, Dr Michos discusses the TACTIC trial, which was an evaluation of a technology-assisted web application used to qualify patients for nonprescription statin administration.
--
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; Director of Women's Cardiovascular Health Research, Associate Director of Preventive Cardiology, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Boehringer Ingelheim; Edwards Lifesciences; Esperion; Merck; Medtronic; New Amsterdam; Novo Nordisk; Novartis; Pfizer
Lipid highlights from the 2024 American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions included positive outcomes for bempedoic acid in statin-intolerant patients and a inclisiran-first strategy for patients with atherosclerosis. The presentations are reported by Dr Erin Michos, associate director of preventive cardiology, Johns Hopkins University. Dr Michos begins with an update of the CLEAR Outcomes trial, which examined bempedoic acid, a nonstatin inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, in patients who had cardiovascular disease or were at high risk of developing it. The trial found that bempedoic acid safely reduced cardiovascular events by 13% compared with placebo — findings of particular value for patients unable or unwilling to take guideline-recommended doses of statins. Commendably, the trial enrolled 48% women and 17% Hispanic/Latinx persons. Dr Michos also reports on a trial investigating an inclisiran-first strategy vs usual care in patients with atherosclerosis. The reduction in LDL cholesterol was 60% for patients in the inclisiran upfront arm vs only 7% for patients provided with usual care. In closing, Dr Michos discusses the TACTIC trial, which was an evaluation of a technology-assisted web application used to qualify patients for nonprescription statin administration.
--
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; Director of Women's Cardiovascular Health Research, Associate Director of Preventive Cardiology, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Boehringer Ingelheim; Edwards Lifesciences; Esperion; Merck; Medtronic; New Amsterdam; Novo Nordisk; Novartis; Pfizer

Primary Care Shortage Reshaping How Patients Seek Care
By February of 2022, Ella, a 25-year-old behavioral interventionist in Colorado Springs, Colorado, was sick with strep-like symptoms for the third time in 3 months. She didn’t bother to call her doctor.
The first two times she had strep throat, she’d tried to schedule an appointment with her newest primary care doctor but couldn’t get in. They only had available appointments 5 and even 10 days out, but she’d already had symptoms for 3 days.
Until she graduated college, Ella had only known easy-access primary care. Her childhood family doctor and the nurse practitioners at her college clinic knew her. They anticipated her yearly allergies and knew about her predisposition for strep throat. Appointments were easy to schedule, and providers responded to her messages. But since entering the workforce and leaving her parent’s insurance, the kind of primary care she’d come to rely on was nearly impossible to find.
“I went to urgent care, and that became my primary care,” she told this news organization.
Patients Can’t Get Appointments
Primary care is in crisis. A growing number of Americans, like Ella, can’t access care when they need it. According to a 2024 report, 29% of adults and 14% of children don’t have a regular source of care. Those looking for a new primary care provider face extensive research and 6- to 9-month waits for a new patient appointment — if they can get in at all.
But even those with a primary care provider face long wait times: Days to weeks for a sick visit and months for a wellness checkup. Over one third of Medicare beneficiaries wait more than a month to see a doctor. Accessing primary care is more difficult than access to surgery, physical therapy, or rehabilitative care, according to a survey of Medicare beneficiaries by the Commonwealth Fund.
“Shortages tend to be in rural and urban underserved areas, but now, you’re hearing about primary care shortages in Boston, which is a mecca of healthcare,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Coalition.
While retail clinics, urgent care, and telehealth help close the gap in acute needs, they miss one of primary care’s most critical benefits: A doctor who knows you. There’s strong evidence that ongoing treatment from a primary care physician (PCP) who knows your history, family, and context results in better long-term outcomes and fewer hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
If patients continue to find it too hard to break into primary care or set up an appointment, experts are concerned that they’ll stop pursuing primary care altogether.
Doctors’ Hands Are Tied
“I want to highlight that this is not an issue of primary care doctors not wanting to be accessible,” said Lisa Rotenstein, MD, MBA, a PCP and medical director of Ambulatory Quality and Safety at the University of California San Francisco Health. “These access issues are symptoms of the design of primary care in the United States.”
Across the United States, there’s a dearth of family medicine doctors, pediatricians, and internists. And without significantly more primary care providers, there’s simply no way for all Americans to get optimal primary care. The Health Resources and Services administration estimates a current shortage of 13,000 primary care providers. And that shortage will skyrocket to 68,000 by 2036 as the number of Americans needing care balloons and existing PCPs retire with too few trainees to fill their shoes.
The American Association of Medical Colleges predicts a slightly lower shortage in 2036 — between 20,000 and 40,000 primary care physicians — only if more residency positions are funded nationwide.
However, even with more positions, medical trainees see little incentive to pursue primary care. Young doctors are avoiding primary care because of the pressures, Dr. Rotenstein said. There’s incredible pressure to get reimbursement for primary care doctors. And the added administrative burden makes “the work life of these specialties not really manageable,” she said.
Continued Shortages of PCPs
“We know there’s a documented pajama time,” Ms. Greiner said. For every 1 hour spent with a patient, primary care must spend nearly 2 additional hours on electronic health records and desk work, according to a study by the American Medical Association. Even with all those additional hours devoted to getting paid, primary care doctors make an average of $103,000 less annually compared with their counterparts in surgery and oncology.
It’s not an attractive combination for a new doctor with medical debt. This year, Ms. Greiner said that residency positions in internal medicine and pediatrics went unfilled. Of those trainees who do go into a primary care specialty, many won’t last. Only half of primary care residents practice in primary care 3-5 years later. The rest choose to subspecialize or become hospitalists.
These untenable demands on a primary care provider don’t go unnoticed by patients. In Ella’s attempts to invest in a new primary care relationship, she often doesn’t feel heard and can tell the doctor is rushed. “[Urgent care is] probably not the best care because they don’t know me, but it does seem like they are able to listen to me better,” Ella said.
Patients Want to Invest in Primary Care
Primary care should work like putting money in a bank account, Dr. Rotenstein said. Young patients invest in the relationship and reap the benefits of a doctor who knows them later in life when they need more complex care. But if seeing a doctor is so difficult, many young people may stop investing in their PCP relationship.
“One thing ... that I worry about in this kind of situation where patients really have to put in a lot of work to get the care they need is in inequities of care,” Dr. Rotenstein said. “We know some of our patients are more able to undertake that work.”
Alternatively, the primary care shortage could be reshaping how patients seek care. A 2023 study showed the proportion of primary care preventative visits increased over 20 years. Policies under the Affordable Care Act were the driving force. But it’s also true that sick visits are being diverted to urgent care.
Ella told this news organization she doesn’t even consider primary care for sick visits at this point. “I can’t wait 5 days or a week and a half. Unless I have bigger issues, like I need tests, I’m not even going to go to primary care.” It’s possible that other patients also see primary care as a place for testing and wellness checks and leave sick visits to retail and urgent care.
The Road Ahead
There’s no single fix for primary care, but experts agree that the fee-for-service model is a core issue for the specialty. In a 2021 report, the National Association of Engineering and Medicine said that primary care reform needs to include higher reimbursement rates for primary care and that US primary care should be restructured so that payers “pay primary care teams to care for people, not doctors to deliver services.”
In the current model, the doctor-patient clinic time is the only income-generating part of a primary care practice. A better model would consider the communication, administration, teams, and support doctors have to fund to provide the best primary care.
“We need to change how we pay and how much we pay, so [primary care doctors] are properly incentivized to build out a team to provide the comprehensive care you need,” Ms. Greiner said.
In the meantime, primary care doctors are adapting. Some drop down to part-time to account for the additional administrative workload. Others are transitioning to concierge services to offer the quality of care they want while getting the income they need. Still, others specialize their practice, offering primary care to a subset of the population, like older adults.
Employers are also looking to improve care access for their employees, hiring in-house doctors to provide primary care on site. Ms. Greiner recently met with a group of chief medical officers from major companies to discuss expanding primary care access via the workplace.
The efforts to adapt amid a broken system are admirable, Dr. Rotenstein said. And whatever a PCP has to do to keep practicing in primary care is laudable. The only problem with these adaptations is they largely limit a doctor’s patient pool and, therefore, limit access, she said. More significant reforms that adequately reimburse primary care and incentivize new doctors are still needed.
As for Ella, she got married. Her wife is in the military, so now she has Tricare, which comes with a more streamlined process to access primary care. However, doctor shortages are just as evident in that system. The couple called to schedule new patient appointments after their recent move to Virginia. The first available ones were 6 weeks out.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
By February of 2022, Ella, a 25-year-old behavioral interventionist in Colorado Springs, Colorado, was sick with strep-like symptoms for the third time in 3 months. She didn’t bother to call her doctor.
The first two times she had strep throat, she’d tried to schedule an appointment with her newest primary care doctor but couldn’t get in. They only had available appointments 5 and even 10 days out, but she’d already had symptoms for 3 days.
Until she graduated college, Ella had only known easy-access primary care. Her childhood family doctor and the nurse practitioners at her college clinic knew her. They anticipated her yearly allergies and knew about her predisposition for strep throat. Appointments were easy to schedule, and providers responded to her messages. But since entering the workforce and leaving her parent’s insurance, the kind of primary care she’d come to rely on was nearly impossible to find.
“I went to urgent care, and that became my primary care,” she told this news organization.
Patients Can’t Get Appointments
Primary care is in crisis. A growing number of Americans, like Ella, can’t access care when they need it. According to a 2024 report, 29% of adults and 14% of children don’t have a regular source of care. Those looking for a new primary care provider face extensive research and 6- to 9-month waits for a new patient appointment — if they can get in at all.
But even those with a primary care provider face long wait times: Days to weeks for a sick visit and months for a wellness checkup. Over one third of Medicare beneficiaries wait more than a month to see a doctor. Accessing primary care is more difficult than access to surgery, physical therapy, or rehabilitative care, according to a survey of Medicare beneficiaries by the Commonwealth Fund.
“Shortages tend to be in rural and urban underserved areas, but now, you’re hearing about primary care shortages in Boston, which is a mecca of healthcare,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Coalition.
While retail clinics, urgent care, and telehealth help close the gap in acute needs, they miss one of primary care’s most critical benefits: A doctor who knows you. There’s strong evidence that ongoing treatment from a primary care physician (PCP) who knows your history, family, and context results in better long-term outcomes and fewer hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
If patients continue to find it too hard to break into primary care or set up an appointment, experts are concerned that they’ll stop pursuing primary care altogether.
Doctors’ Hands Are Tied
“I want to highlight that this is not an issue of primary care doctors not wanting to be accessible,” said Lisa Rotenstein, MD, MBA, a PCP and medical director of Ambulatory Quality and Safety at the University of California San Francisco Health. “These access issues are symptoms of the design of primary care in the United States.”
Across the United States, there’s a dearth of family medicine doctors, pediatricians, and internists. And without significantly more primary care providers, there’s simply no way for all Americans to get optimal primary care. The Health Resources and Services administration estimates a current shortage of 13,000 primary care providers. And that shortage will skyrocket to 68,000 by 2036 as the number of Americans needing care balloons and existing PCPs retire with too few trainees to fill their shoes.
The American Association of Medical Colleges predicts a slightly lower shortage in 2036 — between 20,000 and 40,000 primary care physicians — only if more residency positions are funded nationwide.
However, even with more positions, medical trainees see little incentive to pursue primary care. Young doctors are avoiding primary care because of the pressures, Dr. Rotenstein said. There’s incredible pressure to get reimbursement for primary care doctors. And the added administrative burden makes “the work life of these specialties not really manageable,” she said.
Continued Shortages of PCPs
“We know there’s a documented pajama time,” Ms. Greiner said. For every 1 hour spent with a patient, primary care must spend nearly 2 additional hours on electronic health records and desk work, according to a study by the American Medical Association. Even with all those additional hours devoted to getting paid, primary care doctors make an average of $103,000 less annually compared with their counterparts in surgery and oncology.
It’s not an attractive combination for a new doctor with medical debt. This year, Ms. Greiner said that residency positions in internal medicine and pediatrics went unfilled. Of those trainees who do go into a primary care specialty, many won’t last. Only half of primary care residents practice in primary care 3-5 years later. The rest choose to subspecialize or become hospitalists.
These untenable demands on a primary care provider don’t go unnoticed by patients. In Ella’s attempts to invest in a new primary care relationship, she often doesn’t feel heard and can tell the doctor is rushed. “[Urgent care is] probably not the best care because they don’t know me, but it does seem like they are able to listen to me better,” Ella said.
Patients Want to Invest in Primary Care
Primary care should work like putting money in a bank account, Dr. Rotenstein said. Young patients invest in the relationship and reap the benefits of a doctor who knows them later in life when they need more complex care. But if seeing a doctor is so difficult, many young people may stop investing in their PCP relationship.
“One thing ... that I worry about in this kind of situation where patients really have to put in a lot of work to get the care they need is in inequities of care,” Dr. Rotenstein said. “We know some of our patients are more able to undertake that work.”
Alternatively, the primary care shortage could be reshaping how patients seek care. A 2023 study showed the proportion of primary care preventative visits increased over 20 years. Policies under the Affordable Care Act were the driving force. But it’s also true that sick visits are being diverted to urgent care.
Ella told this news organization she doesn’t even consider primary care for sick visits at this point. “I can’t wait 5 days or a week and a half. Unless I have bigger issues, like I need tests, I’m not even going to go to primary care.” It’s possible that other patients also see primary care as a place for testing and wellness checks and leave sick visits to retail and urgent care.
The Road Ahead
There’s no single fix for primary care, but experts agree that the fee-for-service model is a core issue for the specialty. In a 2021 report, the National Association of Engineering and Medicine said that primary care reform needs to include higher reimbursement rates for primary care and that US primary care should be restructured so that payers “pay primary care teams to care for people, not doctors to deliver services.”
In the current model, the doctor-patient clinic time is the only income-generating part of a primary care practice. A better model would consider the communication, administration, teams, and support doctors have to fund to provide the best primary care.
“We need to change how we pay and how much we pay, so [primary care doctors] are properly incentivized to build out a team to provide the comprehensive care you need,” Ms. Greiner said.
In the meantime, primary care doctors are adapting. Some drop down to part-time to account for the additional administrative workload. Others are transitioning to concierge services to offer the quality of care they want while getting the income they need. Still, others specialize their practice, offering primary care to a subset of the population, like older adults.
Employers are also looking to improve care access for their employees, hiring in-house doctors to provide primary care on site. Ms. Greiner recently met with a group of chief medical officers from major companies to discuss expanding primary care access via the workplace.
The efforts to adapt amid a broken system are admirable, Dr. Rotenstein said. And whatever a PCP has to do to keep practicing in primary care is laudable. The only problem with these adaptations is they largely limit a doctor’s patient pool and, therefore, limit access, she said. More significant reforms that adequately reimburse primary care and incentivize new doctors are still needed.
As for Ella, she got married. Her wife is in the military, so now she has Tricare, which comes with a more streamlined process to access primary care. However, doctor shortages are just as evident in that system. The couple called to schedule new patient appointments after their recent move to Virginia. The first available ones were 6 weeks out.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
By February of 2022, Ella, a 25-year-old behavioral interventionist in Colorado Springs, Colorado, was sick with strep-like symptoms for the third time in 3 months. She didn’t bother to call her doctor.
The first two times she had strep throat, she’d tried to schedule an appointment with her newest primary care doctor but couldn’t get in. They only had available appointments 5 and even 10 days out, but she’d already had symptoms for 3 days.
Until she graduated college, Ella had only known easy-access primary care. Her childhood family doctor and the nurse practitioners at her college clinic knew her. They anticipated her yearly allergies and knew about her predisposition for strep throat. Appointments were easy to schedule, and providers responded to her messages. But since entering the workforce and leaving her parent’s insurance, the kind of primary care she’d come to rely on was nearly impossible to find.
“I went to urgent care, and that became my primary care,” she told this news organization.
Patients Can’t Get Appointments
Primary care is in crisis. A growing number of Americans, like Ella, can’t access care when they need it. According to a 2024 report, 29% of adults and 14% of children don’t have a regular source of care. Those looking for a new primary care provider face extensive research and 6- to 9-month waits for a new patient appointment — if they can get in at all.
But even those with a primary care provider face long wait times: Days to weeks for a sick visit and months for a wellness checkup. Over one third of Medicare beneficiaries wait more than a month to see a doctor. Accessing primary care is more difficult than access to surgery, physical therapy, or rehabilitative care, according to a survey of Medicare beneficiaries by the Commonwealth Fund.
“Shortages tend to be in rural and urban underserved areas, but now, you’re hearing about primary care shortages in Boston, which is a mecca of healthcare,” said Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Coalition.
While retail clinics, urgent care, and telehealth help close the gap in acute needs, they miss one of primary care’s most critical benefits: A doctor who knows you. There’s strong evidence that ongoing treatment from a primary care physician (PCP) who knows your history, family, and context results in better long-term outcomes and fewer hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
If patients continue to find it too hard to break into primary care or set up an appointment, experts are concerned that they’ll stop pursuing primary care altogether.
Doctors’ Hands Are Tied
“I want to highlight that this is not an issue of primary care doctors not wanting to be accessible,” said Lisa Rotenstein, MD, MBA, a PCP and medical director of Ambulatory Quality and Safety at the University of California San Francisco Health. “These access issues are symptoms of the design of primary care in the United States.”
Across the United States, there’s a dearth of family medicine doctors, pediatricians, and internists. And without significantly more primary care providers, there’s simply no way for all Americans to get optimal primary care. The Health Resources and Services administration estimates a current shortage of 13,000 primary care providers. And that shortage will skyrocket to 68,000 by 2036 as the number of Americans needing care balloons and existing PCPs retire with too few trainees to fill their shoes.
The American Association of Medical Colleges predicts a slightly lower shortage in 2036 — between 20,000 and 40,000 primary care physicians — only if more residency positions are funded nationwide.
However, even with more positions, medical trainees see little incentive to pursue primary care. Young doctors are avoiding primary care because of the pressures, Dr. Rotenstein said. There’s incredible pressure to get reimbursement for primary care doctors. And the added administrative burden makes “the work life of these specialties not really manageable,” she said.
Continued Shortages of PCPs
“We know there’s a documented pajama time,” Ms. Greiner said. For every 1 hour spent with a patient, primary care must spend nearly 2 additional hours on electronic health records and desk work, according to a study by the American Medical Association. Even with all those additional hours devoted to getting paid, primary care doctors make an average of $103,000 less annually compared with their counterparts in surgery and oncology.
It’s not an attractive combination for a new doctor with medical debt. This year, Ms. Greiner said that residency positions in internal medicine and pediatrics went unfilled. Of those trainees who do go into a primary care specialty, many won’t last. Only half of primary care residents practice in primary care 3-5 years later. The rest choose to subspecialize or become hospitalists.
These untenable demands on a primary care provider don’t go unnoticed by patients. In Ella’s attempts to invest in a new primary care relationship, she often doesn’t feel heard and can tell the doctor is rushed. “[Urgent care is] probably not the best care because they don’t know me, but it does seem like they are able to listen to me better,” Ella said.
Patients Want to Invest in Primary Care
Primary care should work like putting money in a bank account, Dr. Rotenstein said. Young patients invest in the relationship and reap the benefits of a doctor who knows them later in life when they need more complex care. But if seeing a doctor is so difficult, many young people may stop investing in their PCP relationship.
“One thing ... that I worry about in this kind of situation where patients really have to put in a lot of work to get the care they need is in inequities of care,” Dr. Rotenstein said. “We know some of our patients are more able to undertake that work.”
Alternatively, the primary care shortage could be reshaping how patients seek care. A 2023 study showed the proportion of primary care preventative visits increased over 20 years. Policies under the Affordable Care Act were the driving force. But it’s also true that sick visits are being diverted to urgent care.
Ella told this news organization she doesn’t even consider primary care for sick visits at this point. “I can’t wait 5 days or a week and a half. Unless I have bigger issues, like I need tests, I’m not even going to go to primary care.” It’s possible that other patients also see primary care as a place for testing and wellness checks and leave sick visits to retail and urgent care.
The Road Ahead
There’s no single fix for primary care, but experts agree that the fee-for-service model is a core issue for the specialty. In a 2021 report, the National Association of Engineering and Medicine said that primary care reform needs to include higher reimbursement rates for primary care and that US primary care should be restructured so that payers “pay primary care teams to care for people, not doctors to deliver services.”
In the current model, the doctor-patient clinic time is the only income-generating part of a primary care practice. A better model would consider the communication, administration, teams, and support doctors have to fund to provide the best primary care.
“We need to change how we pay and how much we pay, so [primary care doctors] are properly incentivized to build out a team to provide the comprehensive care you need,” Ms. Greiner said.
In the meantime, primary care doctors are adapting. Some drop down to part-time to account for the additional administrative workload. Others are transitioning to concierge services to offer the quality of care they want while getting the income they need. Still, others specialize their practice, offering primary care to a subset of the population, like older adults.
Employers are also looking to improve care access for their employees, hiring in-house doctors to provide primary care on site. Ms. Greiner recently met with a group of chief medical officers from major companies to discuss expanding primary care access via the workplace.
The efforts to adapt amid a broken system are admirable, Dr. Rotenstein said. And whatever a PCP has to do to keep practicing in primary care is laudable. The only problem with these adaptations is they largely limit a doctor’s patient pool and, therefore, limit access, she said. More significant reforms that adequately reimburse primary care and incentivize new doctors are still needed.
As for Ella, she got married. Her wife is in the military, so now she has Tricare, which comes with a more streamlined process to access primary care. However, doctor shortages are just as evident in that system. The couple called to schedule new patient appointments after their recent move to Virginia. The first available ones were 6 weeks out.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.