User login
PEGPH20 strikeout raises doubts about stroma-targeting agents in pancreatic cancer
The median overall survival was 11.2 months with PEGPH20 plus AG and 11.5 months with placebo plus AG. The median progression-free survival was 7.1 months in both treatment arms.
Eric Van Cutsem, MD, PhD, of University Hospitals Gasthuisberg Leuven and KU Leuven in Belgium, and colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The authors explained that, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “a dense fibrotic stroma (i.e., desmoplasia) surrounds the growing tumor mass, which can compress tumor vasculature within the microenvironment and increase interstitial pressure, impeding perfusion and delivery of systemic agents.”
PEGPH20 is an enzyme that degrades hyaluronan, a major component of the stroma. The researchers’ hypothesis was that PEGPH20 would weaken the stromal barrier and facilitate greater penetration of the AG combination into the tumor.
However, PEGPH20 failed to improve upon results with AG in this trial, which led Halozyme Therapeutics to halt further development of PEGPH20.
The negative findings in this trial, as well as the failure of other stroma-remodeling agents in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “collectively indicates the need to reevaluate this treatment strategy,” Dr. Van Cutsem and colleagues wrote.
“More preclinical and retrospective analyses are needed to better understand the failures of tumor stroma remodeling and whether and how it should continue to be pursued,” the authors added.
Phase 3 results
The intent-to-treat analysis included 492 adults with previously untreated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. All patients expressed high hyaluronan levels, as defined by at least 50% hyaluronan staining in the extracellular matrix from tumor samples.
There were 165 subjects randomized to receive placebo plus AG and 327 randomized to receive PEGPH20 plus AG. Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms.
The overall response rate was 47% with PEGPH20-AG and 36% with placebo-AG. The median duration of response was 6.1 months and 7.4 months, respectively.
The overall survival analysis was performed after 330 deaths. There were no significant differences between the PEGPH20 and placebo arms with regard to median overall survival (11.2 months and 11.5 months, respectively; hazard ratio, 1.00, P = .97) or progression-free survival (7.1 months in both arms; HR, 0.97).
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (AE). The most common AEs of any grade that were more frequent in the PEGPH20 arm than in the placebo arm (≥ 2%) were peripheral edema (61.8% vs. 33.3%), muscle spasms (51.4% vs. 9.6%), myalgia (28.9% vs. 14.7%), and arthralgia (19.4% vs. 11.5%).
Grade 3 or higher AEs that were more common with PEGPH20 (≥ 2%) included fatigue (16.0% vs. 9.6%), muscle spasms (6.5% vs. 0.6%), and hyponatremia (8.0% vs. 3.8%).
“[T]here were no apparent safety signals that affected study treatment exposure or survival,” the investigators noted.
Two failed trials
“We now have two failed clinical trials for PEGPH20. Could it be perhaps that our theory of targeting the desmoplastic response is simply not enough?” Nausheen Hakim, DO, of Northwell Health Cancer Institute in New York, and colleagues wrote in a commentary shortly after Halozyme released topline results from the phase 3 trial (Pancreas [Fairfax]. 2019;3[1]:e1-e4. doi: 10.17140/POJ-3-e010).
The second study the editorialists were referring to is a phase 1b/2 trial of PEGPH20 added to fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 1;37[13]:1062-9).
In this trial, the median overall survival was worse with PEGPH20 than without it, at 7.7 months and 14.4 months, respectively. The difference was probably due to the increased toxicity with the PEGPH20 regimen, which led to subjects receiving only half the number of chemotherapy cycles as the control group, Dr. Hakim and colleagues wrote.
“Perhaps it is not solely the desmoplastic reaction that is the cause of chemoresistance of pancreatic cells but additional intrinsic factors at play,” the editorialists wrote. “It may indeed be a combination of stroma-modifying agents as well as other strategies to overcome chemoresistance to better fight pancreatic cancer. Further studies in molecular biology to better characterize the complex interaction between the microenvironment and cancer cells are warranted.”
The phase 3 study was funded by Halozyme Therapeutics. The authors disclosed relationships with Halozyme and many other companies. The editorialists disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Van Cutsem E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul 24;JCO2000590. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00590.
The median overall survival was 11.2 months with PEGPH20 plus AG and 11.5 months with placebo plus AG. The median progression-free survival was 7.1 months in both treatment arms.
Eric Van Cutsem, MD, PhD, of University Hospitals Gasthuisberg Leuven and KU Leuven in Belgium, and colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The authors explained that, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “a dense fibrotic stroma (i.e., desmoplasia) surrounds the growing tumor mass, which can compress tumor vasculature within the microenvironment and increase interstitial pressure, impeding perfusion and delivery of systemic agents.”
PEGPH20 is an enzyme that degrades hyaluronan, a major component of the stroma. The researchers’ hypothesis was that PEGPH20 would weaken the stromal barrier and facilitate greater penetration of the AG combination into the tumor.
However, PEGPH20 failed to improve upon results with AG in this trial, which led Halozyme Therapeutics to halt further development of PEGPH20.
The negative findings in this trial, as well as the failure of other stroma-remodeling agents in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “collectively indicates the need to reevaluate this treatment strategy,” Dr. Van Cutsem and colleagues wrote.
“More preclinical and retrospective analyses are needed to better understand the failures of tumor stroma remodeling and whether and how it should continue to be pursued,” the authors added.
Phase 3 results
The intent-to-treat analysis included 492 adults with previously untreated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. All patients expressed high hyaluronan levels, as defined by at least 50% hyaluronan staining in the extracellular matrix from tumor samples.
There were 165 subjects randomized to receive placebo plus AG and 327 randomized to receive PEGPH20 plus AG. Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms.
The overall response rate was 47% with PEGPH20-AG and 36% with placebo-AG. The median duration of response was 6.1 months and 7.4 months, respectively.
The overall survival analysis was performed after 330 deaths. There were no significant differences between the PEGPH20 and placebo arms with regard to median overall survival (11.2 months and 11.5 months, respectively; hazard ratio, 1.00, P = .97) or progression-free survival (7.1 months in both arms; HR, 0.97).
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (AE). The most common AEs of any grade that were more frequent in the PEGPH20 arm than in the placebo arm (≥ 2%) were peripheral edema (61.8% vs. 33.3%), muscle spasms (51.4% vs. 9.6%), myalgia (28.9% vs. 14.7%), and arthralgia (19.4% vs. 11.5%).
Grade 3 or higher AEs that were more common with PEGPH20 (≥ 2%) included fatigue (16.0% vs. 9.6%), muscle spasms (6.5% vs. 0.6%), and hyponatremia (8.0% vs. 3.8%).
“[T]here were no apparent safety signals that affected study treatment exposure or survival,” the investigators noted.
Two failed trials
“We now have two failed clinical trials for PEGPH20. Could it be perhaps that our theory of targeting the desmoplastic response is simply not enough?” Nausheen Hakim, DO, of Northwell Health Cancer Institute in New York, and colleagues wrote in a commentary shortly after Halozyme released topline results from the phase 3 trial (Pancreas [Fairfax]. 2019;3[1]:e1-e4. doi: 10.17140/POJ-3-e010).
The second study the editorialists were referring to is a phase 1b/2 trial of PEGPH20 added to fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 1;37[13]:1062-9).
In this trial, the median overall survival was worse with PEGPH20 than without it, at 7.7 months and 14.4 months, respectively. The difference was probably due to the increased toxicity with the PEGPH20 regimen, which led to subjects receiving only half the number of chemotherapy cycles as the control group, Dr. Hakim and colleagues wrote.
“Perhaps it is not solely the desmoplastic reaction that is the cause of chemoresistance of pancreatic cells but additional intrinsic factors at play,” the editorialists wrote. “It may indeed be a combination of stroma-modifying agents as well as other strategies to overcome chemoresistance to better fight pancreatic cancer. Further studies in molecular biology to better characterize the complex interaction between the microenvironment and cancer cells are warranted.”
The phase 3 study was funded by Halozyme Therapeutics. The authors disclosed relationships with Halozyme and many other companies. The editorialists disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Van Cutsem E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul 24;JCO2000590. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00590.
The median overall survival was 11.2 months with PEGPH20 plus AG and 11.5 months with placebo plus AG. The median progression-free survival was 7.1 months in both treatment arms.
Eric Van Cutsem, MD, PhD, of University Hospitals Gasthuisberg Leuven and KU Leuven in Belgium, and colleagues reported these findings in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The authors explained that, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “a dense fibrotic stroma (i.e., desmoplasia) surrounds the growing tumor mass, which can compress tumor vasculature within the microenvironment and increase interstitial pressure, impeding perfusion and delivery of systemic agents.”
PEGPH20 is an enzyme that degrades hyaluronan, a major component of the stroma. The researchers’ hypothesis was that PEGPH20 would weaken the stromal barrier and facilitate greater penetration of the AG combination into the tumor.
However, PEGPH20 failed to improve upon results with AG in this trial, which led Halozyme Therapeutics to halt further development of PEGPH20.
The negative findings in this trial, as well as the failure of other stroma-remodeling agents in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, “collectively indicates the need to reevaluate this treatment strategy,” Dr. Van Cutsem and colleagues wrote.
“More preclinical and retrospective analyses are needed to better understand the failures of tumor stroma remodeling and whether and how it should continue to be pursued,” the authors added.
Phase 3 results
The intent-to-treat analysis included 492 adults with previously untreated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. All patients expressed high hyaluronan levels, as defined by at least 50% hyaluronan staining in the extracellular matrix from tumor samples.
There were 165 subjects randomized to receive placebo plus AG and 327 randomized to receive PEGPH20 plus AG. Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms.
The overall response rate was 47% with PEGPH20-AG and 36% with placebo-AG. The median duration of response was 6.1 months and 7.4 months, respectively.
The overall survival analysis was performed after 330 deaths. There were no significant differences between the PEGPH20 and placebo arms with regard to median overall survival (11.2 months and 11.5 months, respectively; hazard ratio, 1.00, P = .97) or progression-free survival (7.1 months in both arms; HR, 0.97).
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (AE). The most common AEs of any grade that were more frequent in the PEGPH20 arm than in the placebo arm (≥ 2%) were peripheral edema (61.8% vs. 33.3%), muscle spasms (51.4% vs. 9.6%), myalgia (28.9% vs. 14.7%), and arthralgia (19.4% vs. 11.5%).
Grade 3 or higher AEs that were more common with PEGPH20 (≥ 2%) included fatigue (16.0% vs. 9.6%), muscle spasms (6.5% vs. 0.6%), and hyponatremia (8.0% vs. 3.8%).
“[T]here were no apparent safety signals that affected study treatment exposure or survival,” the investigators noted.
Two failed trials
“We now have two failed clinical trials for PEGPH20. Could it be perhaps that our theory of targeting the desmoplastic response is simply not enough?” Nausheen Hakim, DO, of Northwell Health Cancer Institute in New York, and colleagues wrote in a commentary shortly after Halozyme released topline results from the phase 3 trial (Pancreas [Fairfax]. 2019;3[1]:e1-e4. doi: 10.17140/POJ-3-e010).
The second study the editorialists were referring to is a phase 1b/2 trial of PEGPH20 added to fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 1;37[13]:1062-9).
In this trial, the median overall survival was worse with PEGPH20 than without it, at 7.7 months and 14.4 months, respectively. The difference was probably due to the increased toxicity with the PEGPH20 regimen, which led to subjects receiving only half the number of chemotherapy cycles as the control group, Dr. Hakim and colleagues wrote.
“Perhaps it is not solely the desmoplastic reaction that is the cause of chemoresistance of pancreatic cells but additional intrinsic factors at play,” the editorialists wrote. “It may indeed be a combination of stroma-modifying agents as well as other strategies to overcome chemoresistance to better fight pancreatic cancer. Further studies in molecular biology to better characterize the complex interaction between the microenvironment and cancer cells are warranted.”
The phase 3 study was funded by Halozyme Therapeutics. The authors disclosed relationships with Halozyme and many other companies. The editorialists disclosed no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Van Cutsem E et al. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul 24;JCO2000590. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00590.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
COVID-19 taking financial toll on people in U.S. with diabetes
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
No rise in major hemorrhagic events with antiplatelet therapy after ICH
Background: Antiplatelet agents reduce the risk of major vascular events in patient with established vaso-occlusive disease, but they may increase the risk of ICH. Patients with prior ICH are at risk for both vaso-occlusive and hemorrhagic events. Clarification of the relative risk and benefit of antiplatelet agent use in this clinical scenario would serve to guide therapy.
Study design: Prospective, open-label, randomized parallel group trial.
Setting: 122 hospitals located in the United Kingdom.
Synopsis: The study included 537 adult patients with imaging-confirmed, nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage who were previously prescribed antithrombotic medications were randomized in 1:1 fashion to either start or avoid antiplatelet therapy. Participants were followed up on an annual basis with postal questionnaires both to the participants and their primary care providers. No significant difference was identified in rates of recurrent ICH (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-1.03), major hemorrhagic events (aHR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.39-1.30), or major occlusive vascular events (aHR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.65-1.60) between groups.
Hospitalists should be aware that these data suggest that the risk assessment for resumption of antiplatelet agents should not be affected by a history of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage when weighed against the benefit of these medications in patients with occlusive vascular disease.
Bottom line: Resumption of antiplatelet agents following intracerebral hemorrhage showed no evidence of increased risk of recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage or major hemorrhagic events.
Citation: RESTART Collaboration. Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): A randomized, open-label trial. Lancet. 2019. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30840-2.
Dr. Deitelzweig is system department chair of hospital medicine at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
Background: Antiplatelet agents reduce the risk of major vascular events in patient with established vaso-occlusive disease, but they may increase the risk of ICH. Patients with prior ICH are at risk for both vaso-occlusive and hemorrhagic events. Clarification of the relative risk and benefit of antiplatelet agent use in this clinical scenario would serve to guide therapy.
Study design: Prospective, open-label, randomized parallel group trial.
Setting: 122 hospitals located in the United Kingdom.
Synopsis: The study included 537 adult patients with imaging-confirmed, nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage who were previously prescribed antithrombotic medications were randomized in 1:1 fashion to either start or avoid antiplatelet therapy. Participants were followed up on an annual basis with postal questionnaires both to the participants and their primary care providers. No significant difference was identified in rates of recurrent ICH (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-1.03), major hemorrhagic events (aHR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.39-1.30), or major occlusive vascular events (aHR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.65-1.60) between groups.
Hospitalists should be aware that these data suggest that the risk assessment for resumption of antiplatelet agents should not be affected by a history of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage when weighed against the benefit of these medications in patients with occlusive vascular disease.
Bottom line: Resumption of antiplatelet agents following intracerebral hemorrhage showed no evidence of increased risk of recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage or major hemorrhagic events.
Citation: RESTART Collaboration. Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): A randomized, open-label trial. Lancet. 2019. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30840-2.
Dr. Deitelzweig is system department chair of hospital medicine at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
Background: Antiplatelet agents reduce the risk of major vascular events in patient with established vaso-occlusive disease, but they may increase the risk of ICH. Patients with prior ICH are at risk for both vaso-occlusive and hemorrhagic events. Clarification of the relative risk and benefit of antiplatelet agent use in this clinical scenario would serve to guide therapy.
Study design: Prospective, open-label, randomized parallel group trial.
Setting: 122 hospitals located in the United Kingdom.
Synopsis: The study included 537 adult patients with imaging-confirmed, nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage who were previously prescribed antithrombotic medications were randomized in 1:1 fashion to either start or avoid antiplatelet therapy. Participants were followed up on an annual basis with postal questionnaires both to the participants and their primary care providers. No significant difference was identified in rates of recurrent ICH (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-1.03), major hemorrhagic events (aHR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.39-1.30), or major occlusive vascular events (aHR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.65-1.60) between groups.
Hospitalists should be aware that these data suggest that the risk assessment for resumption of antiplatelet agents should not be affected by a history of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage when weighed against the benefit of these medications in patients with occlusive vascular disease.
Bottom line: Resumption of antiplatelet agents following intracerebral hemorrhage showed no evidence of increased risk of recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage or major hemorrhagic events.
Citation: RESTART Collaboration. Effects of antiplatelet therapy after stroke due to intracerebral haemorrhage (RESTART): A randomized, open-label trial. Lancet. 2019. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30840-2.
Dr. Deitelzweig is system department chair of hospital medicine at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
Infection ups mortality risk in patients with dementia
Infection increases mortality risk among patients with dementia, new research suggests. A large, registry-based cohort study showed that
“This is the first study to our knowledge to show that increased mortality is observed across all infection types in people with dementia and that increased mortality is seen both short and long term,” said coinvestigator Janet Janbek, a PhD student at the Danish Dementia Research Center, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Large Danish cohort
The investigators analyzed data from Danish national health registries for nearly 1.5 million individuals aged 65 years and older who had visited the hospital with an infection. There were 575,260 deaths during more than 12.7 million person-years of follow-up.
Patients with dementia who also had a hospital visit for infection died at a 6.5 times higher rate than participants without dementia or an infection. Those with either dementia alone or infection-related contacts alone had a threefold increased rate of death.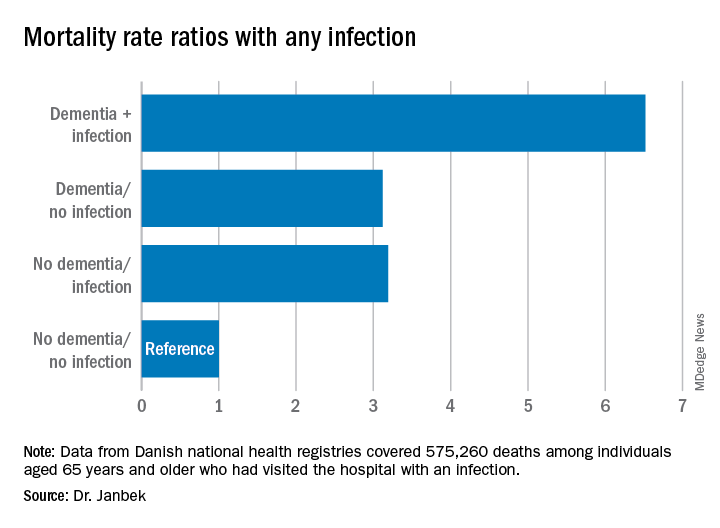
The mortality rate was highest within the first 30 days following the hospital visit for infection. However, the rate remained elevated for 10 years after the initial infection-related hospital visit.
Mortality rates from all infections, including major infections, such as sepsis, down to minor ear infections were elevated in patients with dementia, compared with people who did not have dementia or an infection-related hospital visit.
Ms. Janbek said there are several possible explanations for the association of infection and increased mortality risk in those with dementia. “After a hospital contact with a severe infection, people with dementia may become more reliant on external care, become more frail, and have declined functional levels, which might explain the observed association.”
It might also be that patients with dementia have more severe infections than those without dementia at the time of hospital contact, possibly because of delayed diagnosis, which could explain the higher mortality rates, said Ms. Janbek.
“It is also plausible that infections play a role in worsening dementia and subsequently lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
“Clinicians and health care personnel need to pay closer attention to infections of all types in people with dementia, and steps toward better clinical management and improved posthospital care need to be explored and undertaken. We need to identify possible preventive measures and targeted interventions in people with dementia and infections,” Ms. Janbek said.
‘Interesting observation’
Commenting on the study, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said it presents “an interesting observation.” However, “we can’t make any direct assumptions from this research per se about infections and dementia and whether they are causative in any way,” noted Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved with the study.
Instead, the study highlighted the importance of “taking care of our overall health and making sure that individuals that might be vulnerable to infection, like those who are already living with dementia, are getting the best care possible,” she said.
Ms. Janbek and Dr. Edelmayer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Infection increases mortality risk among patients with dementia, new research suggests. A large, registry-based cohort study showed that
“This is the first study to our knowledge to show that increased mortality is observed across all infection types in people with dementia and that increased mortality is seen both short and long term,” said coinvestigator Janet Janbek, a PhD student at the Danish Dementia Research Center, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Large Danish cohort
The investigators analyzed data from Danish national health registries for nearly 1.5 million individuals aged 65 years and older who had visited the hospital with an infection. There were 575,260 deaths during more than 12.7 million person-years of follow-up.
Patients with dementia who also had a hospital visit for infection died at a 6.5 times higher rate than participants without dementia or an infection. Those with either dementia alone or infection-related contacts alone had a threefold increased rate of death.
The mortality rate was highest within the first 30 days following the hospital visit for infection. However, the rate remained elevated for 10 years after the initial infection-related hospital visit.
Mortality rates from all infections, including major infections, such as sepsis, down to minor ear infections were elevated in patients with dementia, compared with people who did not have dementia or an infection-related hospital visit.
Ms. Janbek said there are several possible explanations for the association of infection and increased mortality risk in those with dementia. “After a hospital contact with a severe infection, people with dementia may become more reliant on external care, become more frail, and have declined functional levels, which might explain the observed association.”
It might also be that patients with dementia have more severe infections than those without dementia at the time of hospital contact, possibly because of delayed diagnosis, which could explain the higher mortality rates, said Ms. Janbek.
“It is also plausible that infections play a role in worsening dementia and subsequently lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
“Clinicians and health care personnel need to pay closer attention to infections of all types in people with dementia, and steps toward better clinical management and improved posthospital care need to be explored and undertaken. We need to identify possible preventive measures and targeted interventions in people with dementia and infections,” Ms. Janbek said.
‘Interesting observation’
Commenting on the study, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said it presents “an interesting observation.” However, “we can’t make any direct assumptions from this research per se about infections and dementia and whether they are causative in any way,” noted Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved with the study.
Instead, the study highlighted the importance of “taking care of our overall health and making sure that individuals that might be vulnerable to infection, like those who are already living with dementia, are getting the best care possible,” she said.
Ms. Janbek and Dr. Edelmayer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Infection increases mortality risk among patients with dementia, new research suggests. A large, registry-based cohort study showed that
“This is the first study to our knowledge to show that increased mortality is observed across all infection types in people with dementia and that increased mortality is seen both short and long term,” said coinvestigator Janet Janbek, a PhD student at the Danish Dementia Research Center, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Large Danish cohort
The investigators analyzed data from Danish national health registries for nearly 1.5 million individuals aged 65 years and older who had visited the hospital with an infection. There were 575,260 deaths during more than 12.7 million person-years of follow-up.
Patients with dementia who also had a hospital visit for infection died at a 6.5 times higher rate than participants without dementia or an infection. Those with either dementia alone or infection-related contacts alone had a threefold increased rate of death.
The mortality rate was highest within the first 30 days following the hospital visit for infection. However, the rate remained elevated for 10 years after the initial infection-related hospital visit.
Mortality rates from all infections, including major infections, such as sepsis, down to minor ear infections were elevated in patients with dementia, compared with people who did not have dementia or an infection-related hospital visit.
Ms. Janbek said there are several possible explanations for the association of infection and increased mortality risk in those with dementia. “After a hospital contact with a severe infection, people with dementia may become more reliant on external care, become more frail, and have declined functional levels, which might explain the observed association.”
It might also be that patients with dementia have more severe infections than those without dementia at the time of hospital contact, possibly because of delayed diagnosis, which could explain the higher mortality rates, said Ms. Janbek.
“It is also plausible that infections play a role in worsening dementia and subsequently lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
“Clinicians and health care personnel need to pay closer attention to infections of all types in people with dementia, and steps toward better clinical management and improved posthospital care need to be explored and undertaken. We need to identify possible preventive measures and targeted interventions in people with dementia and infections,” Ms. Janbek said.
‘Interesting observation’
Commenting on the study, Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, said it presents “an interesting observation.” However, “we can’t make any direct assumptions from this research per se about infections and dementia and whether they are causative in any way,” noted Dr. Edelmayer, who was not involved with the study.
Instead, the study highlighted the importance of “taking care of our overall health and making sure that individuals that might be vulnerable to infection, like those who are already living with dementia, are getting the best care possible,” she said.
Ms. Janbek and Dr. Edelmayer have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2020
Why are we still talking about hydroxychloroquine?
This is getting pretty ridiculous. The number of well-done, evidence-based trials of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 showing minimal-to-no benefit is increasing. There are still studies that show benefit in certain cases, but many of them are small-scale or even anecdotal.
How long is this going to go on? If the evidence supporting its use were to be put through the standard Food and Drug Administration approval panels it wouldn’t have a chance.
Yet, because it’s become a political football (like masks), science and rational research are tossed out the window. At the end of July we were all treated to videos of Dr. Stella Immanuel claiming the drug is a cure. Dr. Immanuel may have medical credentials, but she also supports beliefs that space aliens and the Illuminati are involved in running governments, and that multiple gynecologic disorders are caused by sexual relations with demons and witches during dreams.
Even so, her hydroxychloroquine statements were given heavy play during a news cycle, then endorsed by the president and his supporters, all with very little immediate background provided for other claims she’s made in the past.
Medicine is a science. Politics shouldn’t be. Continuing to give it to sick people, despite the growing evidence against it, violates the “do-no-harm” tenet of our field.
There was no shame in trying it and failing. This is the process through which all treatments are tested. If they work (such as with penicillin, for example) that’s wonderful. If they fail (such as with countless Alzheimer’s trials) we learn what doesn’t work and move on.
But to keep claiming success where there isn’t any moves beyond science and into things that whiff of a hoax, such as 1989’s cold fusion or recurrent claims of capturing Bigfoot.
With an implacable enemy such as COVID-19 at the door, money and effort need to be focused on finding what works, not on putting stale milk back in the refrigerator and hoping it comes out fresh.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
This is getting pretty ridiculous. The number of well-done, evidence-based trials of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 showing minimal-to-no benefit is increasing. There are still studies that show benefit in certain cases, but many of them are small-scale or even anecdotal.
How long is this going to go on? If the evidence supporting its use were to be put through the standard Food and Drug Administration approval panels it wouldn’t have a chance.
Yet, because it’s become a political football (like masks), science and rational research are tossed out the window. At the end of July we were all treated to videos of Dr. Stella Immanuel claiming the drug is a cure. Dr. Immanuel may have medical credentials, but she also supports beliefs that space aliens and the Illuminati are involved in running governments, and that multiple gynecologic disorders are caused by sexual relations with demons and witches during dreams.
Even so, her hydroxychloroquine statements were given heavy play during a news cycle, then endorsed by the president and his supporters, all with very little immediate background provided for other claims she’s made in the past.
Medicine is a science. Politics shouldn’t be. Continuing to give it to sick people, despite the growing evidence against it, violates the “do-no-harm” tenet of our field.
There was no shame in trying it and failing. This is the process through which all treatments are tested. If they work (such as with penicillin, for example) that’s wonderful. If they fail (such as with countless Alzheimer’s trials) we learn what doesn’t work and move on.
But to keep claiming success where there isn’t any moves beyond science and into things that whiff of a hoax, such as 1989’s cold fusion or recurrent claims of capturing Bigfoot.
With an implacable enemy such as COVID-19 at the door, money and effort need to be focused on finding what works, not on putting stale milk back in the refrigerator and hoping it comes out fresh.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
This is getting pretty ridiculous. The number of well-done, evidence-based trials of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 showing minimal-to-no benefit is increasing. There are still studies that show benefit in certain cases, but many of them are small-scale or even anecdotal.
How long is this going to go on? If the evidence supporting its use were to be put through the standard Food and Drug Administration approval panels it wouldn’t have a chance.
Yet, because it’s become a political football (like masks), science and rational research are tossed out the window. At the end of July we were all treated to videos of Dr. Stella Immanuel claiming the drug is a cure. Dr. Immanuel may have medical credentials, but she also supports beliefs that space aliens and the Illuminati are involved in running governments, and that multiple gynecologic disorders are caused by sexual relations with demons and witches during dreams.
Even so, her hydroxychloroquine statements were given heavy play during a news cycle, then endorsed by the president and his supporters, all with very little immediate background provided for other claims she’s made in the past.
Medicine is a science. Politics shouldn’t be. Continuing to give it to sick people, despite the growing evidence against it, violates the “do-no-harm” tenet of our field.
There was no shame in trying it and failing. This is the process through which all treatments are tested. If they work (such as with penicillin, for example) that’s wonderful. If they fail (such as with countless Alzheimer’s trials) we learn what doesn’t work and move on.
But to keep claiming success where there isn’t any moves beyond science and into things that whiff of a hoax, such as 1989’s cold fusion or recurrent claims of capturing Bigfoot.
With an implacable enemy such as COVID-19 at the door, money and effort need to be focused on finding what works, not on putting stale milk back in the refrigerator and hoping it comes out fresh.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Early palliative care fails to improve QOL in advanced heart failure
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
ACS disagrees with CDC on HPV vaccination in adults
The ACS has endorsed two recommendations made by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, but the ACS does not agree with a third recommendation for older adults.
The ACIP recommends shared clinical decision-making regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in some adults aged 27-45 years who are not adequately vaccinated. The ACS does not endorse this recommendation “because of the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians, and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” wrote Debbie Saslow, PhD, of the ACS’s section on human papillomavirus and gynecologic cancers, and colleagues.
Dr. Saslow and colleagues detailed the ACS recommendations in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The HPV vaccine protects against the virus that can cause cervical, oropharyngeal, anal, vaginal, vulvar, and penile cancers. For younger people, the ACIP recommends routine HPV vaccination of boys and girls aged 9-12 years and catch-up vaccination in everyone up to age 26 who has not been fully immunized against HPV.
The ACS endorses both of these recommendations. It also advises clinicians to tell patients aged 22-26 years who haven’t received the HPV vaccine or completed the series that the vaccine is less effective at reducing the risk of cancer at older ages.
After the Food and Drug Administration approved the HPV vaccine for adults aged 27-45 years, the ACIP updated its recommendations to state that routine catch-up vaccination is not recommended for anyone aged over 26 years. However, the ACIP recommended that these older adults talk with their providers about the risks and benefits of the vaccine to determine whether to get it.
The ACS subsequently conducted a methodological review of the ACIP’s recommendations and published its own adapted guidance, stating that the ACS does not endorse the shared decision-making. Administering the HPV vaccine to adults aged over 26 years would only prevent an estimated 0.5% of additional cancer cases, 0.4% additional cases of cervical precancer, and 0.3% additional cases of genital warts over the next 100 years, compared with vaccination under age 26.
“In addition to the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, other considerations included the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” according to the guidance. The ACS also expressed concern that these provider-patient discussions could interfere with the public health goal of increasing HPV vaccination in younger people.
HPV vaccination rates have lagged substantially behind other routinely recommended childhood vaccinations. Just over half (51%) of U.S. teens aged 13-17 years were up to date with HPV vaccination, and 68% had received one dose of the vaccine in 2018, according to the National Immunization Survey.
It’s very uncommon for a professional medical organization to not endorse recommendations from the CDC, particularly with vaccines, according to Robert A. Bednarczyk, PhD, an assistant professor of public health at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in HPV vaccination research but was not involved with the ACS statement or the ACIP recommendations.
“Often, for vaccination recommendations, there is a harmonization between health care provider organizations, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians, etc., when new vaccination schedules are released,” Dr. Bednarczyk said.
He acknowledged the ACS’s reasons for not endorsing the ACIP’s HPV recommendations in older adults: the burden of shared decision-making given the communication issues, the vaccine’s lower effectiveness in this population, and the ongoing HPV vaccine shortage.
But Dr. Bednarczyk also pointed out that the ACIP’s recommendation opens the door to these discussions when they may actually be needed, such as in adults at greater risk for HPV. He cited data suggesting that, in 2015, divorces occurred in 24 out of 1,000 married people aged 25-39 years and 21 out of 1,000 people aged 40-49.
“When you consider these marriages that end, in addition to marriages that end when one spouse dies, there is a potential for individuals who previously had a low risk of HPV acquisition now entering into new potential sexual relationships,” Dr. Bednarczyk said. “Additionally, it has been estimated that approximately 4% of the U.S. population are in open or consensually nonmonogamous relationships, where exposure to more sexual partners may increase their risk for HPV. These are just some examples of where conversations with health care providers, and shared clinical decision-making, can help with a targeted reduction of HPV risk.”
The ACIP recommendation regarding adults aged 27-45 years also provides people in this age group with insurance coverage for the HPV vaccine if they choose to get it, Dr. Bednarczyk pointed out. Insurance companies may not be required to cover HPV vaccination in people aged over 26 years without the CDC’s recommendation, even if it’s not for routine immunization.
Dr. Bednarczyk agreed, however, with how the ACS adapted the CDC’s recommendation for routine vaccination in youth. The CDC’s routine recommendation is at ages 11-12 but can begin at 9 years, according to the ACIP. The ACS guidance qualifies this statement to place more emphasis on encouraging the vaccine earlier.
“Routine HPV vaccination between ages 9-12 is expected to achieve higher on-time vaccination rates, resulting in increased numbers of cancers prevented,” according to the ACS. “Health care providers are encouraged to start offering the HPV vaccine at age 9 or 10.”
Dr. Bednarczyk pointed to some of his past research finding low proportions of teens fully vaccinated against HPV by age 13 years (J Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 31;220[5]:730-4). Therefore, “any efforts to encourage vaccination, including starting the series at ages 9-10 years may help,” he said.
He also agreed that there may be diminished effectiveness with vaccinating adults aged 22-26, “but this should also be considered relative to an individual’s risk of acquiring HPV.”
While an HPV vaccine shortage is a major concern and HPV vaccination efforts should remain most focused on young teens, adults should not necessarily be neglected, Dr. Bednarczyk noted.
“Given how common HPV infection is in the population, open discussion between patients and health care providers can help identify those adults for whom HPV vaccination can be effective,” he said.
The development of the ACS guideline was supported by ACS operational funds. The ACS has received an independent educational grant from Merck Sharp & Dohme for a project intended to increase HPV vaccination rates. Dr. Saslow is the principal investigator for a cooperative agreement between the ACS and the CDC to support the National HPV Vaccination Roundtable and is coprincipal investigator of a cooperative agreement between the ACS and CDC to support initiatives to increase HPV vaccination. The remaining authors and Dr. Bednarczyk reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Saslow D et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul 8. doi: 10.3322/caac.21616.
The ACS has endorsed two recommendations made by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, but the ACS does not agree with a third recommendation for older adults.
The ACIP recommends shared clinical decision-making regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in some adults aged 27-45 years who are not adequately vaccinated. The ACS does not endorse this recommendation “because of the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians, and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” wrote Debbie Saslow, PhD, of the ACS’s section on human papillomavirus and gynecologic cancers, and colleagues.
Dr. Saslow and colleagues detailed the ACS recommendations in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The HPV vaccine protects against the virus that can cause cervical, oropharyngeal, anal, vaginal, vulvar, and penile cancers. For younger people, the ACIP recommends routine HPV vaccination of boys and girls aged 9-12 years and catch-up vaccination in everyone up to age 26 who has not been fully immunized against HPV.
The ACS endorses both of these recommendations. It also advises clinicians to tell patients aged 22-26 years who haven’t received the HPV vaccine or completed the series that the vaccine is less effective at reducing the risk of cancer at older ages.
After the Food and Drug Administration approved the HPV vaccine for adults aged 27-45 years, the ACIP updated its recommendations to state that routine catch-up vaccination is not recommended for anyone aged over 26 years. However, the ACIP recommended that these older adults talk with their providers about the risks and benefits of the vaccine to determine whether to get it.
The ACS subsequently conducted a methodological review of the ACIP’s recommendations and published its own adapted guidance, stating that the ACS does not endorse the shared decision-making. Administering the HPV vaccine to adults aged over 26 years would only prevent an estimated 0.5% of additional cancer cases, 0.4% additional cases of cervical precancer, and 0.3% additional cases of genital warts over the next 100 years, compared with vaccination under age 26.
“In addition to the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, other considerations included the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” according to the guidance. The ACS also expressed concern that these provider-patient discussions could interfere with the public health goal of increasing HPV vaccination in younger people.
HPV vaccination rates have lagged substantially behind other routinely recommended childhood vaccinations. Just over half (51%) of U.S. teens aged 13-17 years were up to date with HPV vaccination, and 68% had received one dose of the vaccine in 2018, according to the National Immunization Survey.
It’s very uncommon for a professional medical organization to not endorse recommendations from the CDC, particularly with vaccines, according to Robert A. Bednarczyk, PhD, an assistant professor of public health at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in HPV vaccination research but was not involved with the ACS statement or the ACIP recommendations.
“Often, for vaccination recommendations, there is a harmonization between health care provider organizations, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians, etc., when new vaccination schedules are released,” Dr. Bednarczyk said.
He acknowledged the ACS’s reasons for not endorsing the ACIP’s HPV recommendations in older adults: the burden of shared decision-making given the communication issues, the vaccine’s lower effectiveness in this population, and the ongoing HPV vaccine shortage.
But Dr. Bednarczyk also pointed out that the ACIP’s recommendation opens the door to these discussions when they may actually be needed, such as in adults at greater risk for HPV. He cited data suggesting that, in 2015, divorces occurred in 24 out of 1,000 married people aged 25-39 years and 21 out of 1,000 people aged 40-49.
“When you consider these marriages that end, in addition to marriages that end when one spouse dies, there is a potential for individuals who previously had a low risk of HPV acquisition now entering into new potential sexual relationships,” Dr. Bednarczyk said. “Additionally, it has been estimated that approximately 4% of the U.S. population are in open or consensually nonmonogamous relationships, where exposure to more sexual partners may increase their risk for HPV. These are just some examples of where conversations with health care providers, and shared clinical decision-making, can help with a targeted reduction of HPV risk.”
The ACIP recommendation regarding adults aged 27-45 years also provides people in this age group with insurance coverage for the HPV vaccine if they choose to get it, Dr. Bednarczyk pointed out. Insurance companies may not be required to cover HPV vaccination in people aged over 26 years without the CDC’s recommendation, even if it’s not for routine immunization.
Dr. Bednarczyk agreed, however, with how the ACS adapted the CDC’s recommendation for routine vaccination in youth. The CDC’s routine recommendation is at ages 11-12 but can begin at 9 years, according to the ACIP. The ACS guidance qualifies this statement to place more emphasis on encouraging the vaccine earlier.
“Routine HPV vaccination between ages 9-12 is expected to achieve higher on-time vaccination rates, resulting in increased numbers of cancers prevented,” according to the ACS. “Health care providers are encouraged to start offering the HPV vaccine at age 9 or 10.”
Dr. Bednarczyk pointed to some of his past research finding low proportions of teens fully vaccinated against HPV by age 13 years (J Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 31;220[5]:730-4). Therefore, “any efforts to encourage vaccination, including starting the series at ages 9-10 years may help,” he said.
He also agreed that there may be diminished effectiveness with vaccinating adults aged 22-26, “but this should also be considered relative to an individual’s risk of acquiring HPV.”
While an HPV vaccine shortage is a major concern and HPV vaccination efforts should remain most focused on young teens, adults should not necessarily be neglected, Dr. Bednarczyk noted.
“Given how common HPV infection is in the population, open discussion between patients and health care providers can help identify those adults for whom HPV vaccination can be effective,” he said.
The development of the ACS guideline was supported by ACS operational funds. The ACS has received an independent educational grant from Merck Sharp & Dohme for a project intended to increase HPV vaccination rates. Dr. Saslow is the principal investigator for a cooperative agreement between the ACS and the CDC to support the National HPV Vaccination Roundtable and is coprincipal investigator of a cooperative agreement between the ACS and CDC to support initiatives to increase HPV vaccination. The remaining authors and Dr. Bednarczyk reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Saslow D et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul 8. doi: 10.3322/caac.21616.
The ACS has endorsed two recommendations made by the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, but the ACS does not agree with a third recommendation for older adults.
The ACIP recommends shared clinical decision-making regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in some adults aged 27-45 years who are not adequately vaccinated. The ACS does not endorse this recommendation “because of the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians, and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” wrote Debbie Saslow, PhD, of the ACS’s section on human papillomavirus and gynecologic cancers, and colleagues.
Dr. Saslow and colleagues detailed the ACS recommendations in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
The HPV vaccine protects against the virus that can cause cervical, oropharyngeal, anal, vaginal, vulvar, and penile cancers. For younger people, the ACIP recommends routine HPV vaccination of boys and girls aged 9-12 years and catch-up vaccination in everyone up to age 26 who has not been fully immunized against HPV.
The ACS endorses both of these recommendations. It also advises clinicians to tell patients aged 22-26 years who haven’t received the HPV vaccine or completed the series that the vaccine is less effective at reducing the risk of cancer at older ages.
After the Food and Drug Administration approved the HPV vaccine for adults aged 27-45 years, the ACIP updated its recommendations to state that routine catch-up vaccination is not recommended for anyone aged over 26 years. However, the ACIP recommended that these older adults talk with their providers about the risks and benefits of the vaccine to determine whether to get it.
The ACS subsequently conducted a methodological review of the ACIP’s recommendations and published its own adapted guidance, stating that the ACS does not endorse the shared decision-making. Administering the HPV vaccine to adults aged over 26 years would only prevent an estimated 0.5% of additional cancer cases, 0.4% additional cases of cervical precancer, and 0.3% additional cases of genital warts over the next 100 years, compared with vaccination under age 26.
“In addition to the low effectiveness and low cancer prevention potential of vaccination in this age group, other considerations included the burden of decision-making on patients and clinicians and the lack of sufficient guidance on the selection of individuals who might benefit,” according to the guidance. The ACS also expressed concern that these provider-patient discussions could interfere with the public health goal of increasing HPV vaccination in younger people.
HPV vaccination rates have lagged substantially behind other routinely recommended childhood vaccinations. Just over half (51%) of U.S. teens aged 13-17 years were up to date with HPV vaccination, and 68% had received one dose of the vaccine in 2018, according to the National Immunization Survey.
It’s very uncommon for a professional medical organization to not endorse recommendations from the CDC, particularly with vaccines, according to Robert A. Bednarczyk, PhD, an assistant professor of public health at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in HPV vaccination research but was not involved with the ACS statement or the ACIP recommendations.
“Often, for vaccination recommendations, there is a harmonization between health care provider organizations, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians, etc., when new vaccination schedules are released,” Dr. Bednarczyk said.
He acknowledged the ACS’s reasons for not endorsing the ACIP’s HPV recommendations in older adults: the burden of shared decision-making given the communication issues, the vaccine’s lower effectiveness in this population, and the ongoing HPV vaccine shortage.
But Dr. Bednarczyk also pointed out that the ACIP’s recommendation opens the door to these discussions when they may actually be needed, such as in adults at greater risk for HPV. He cited data suggesting that, in 2015, divorces occurred in 24 out of 1,000 married people aged 25-39 years and 21 out of 1,000 people aged 40-49.
“When you consider these marriages that end, in addition to marriages that end when one spouse dies, there is a potential for individuals who previously had a low risk of HPV acquisition now entering into new potential sexual relationships,” Dr. Bednarczyk said. “Additionally, it has been estimated that approximately 4% of the U.S. population are in open or consensually nonmonogamous relationships, where exposure to more sexual partners may increase their risk for HPV. These are just some examples of where conversations with health care providers, and shared clinical decision-making, can help with a targeted reduction of HPV risk.”
The ACIP recommendation regarding adults aged 27-45 years also provides people in this age group with insurance coverage for the HPV vaccine if they choose to get it, Dr. Bednarczyk pointed out. Insurance companies may not be required to cover HPV vaccination in people aged over 26 years without the CDC’s recommendation, even if it’s not for routine immunization.
Dr. Bednarczyk agreed, however, with how the ACS adapted the CDC’s recommendation for routine vaccination in youth. The CDC’s routine recommendation is at ages 11-12 but can begin at 9 years, according to the ACIP. The ACS guidance qualifies this statement to place more emphasis on encouraging the vaccine earlier.
“Routine HPV vaccination between ages 9-12 is expected to achieve higher on-time vaccination rates, resulting in increased numbers of cancers prevented,” according to the ACS. “Health care providers are encouraged to start offering the HPV vaccine at age 9 or 10.”
Dr. Bednarczyk pointed to some of his past research finding low proportions of teens fully vaccinated against HPV by age 13 years (J Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 31;220[5]:730-4). Therefore, “any efforts to encourage vaccination, including starting the series at ages 9-10 years may help,” he said.
He also agreed that there may be diminished effectiveness with vaccinating adults aged 22-26, “but this should also be considered relative to an individual’s risk of acquiring HPV.”
While an HPV vaccine shortage is a major concern and HPV vaccination efforts should remain most focused on young teens, adults should not necessarily be neglected, Dr. Bednarczyk noted.
“Given how common HPV infection is in the population, open discussion between patients and health care providers can help identify those adults for whom HPV vaccination can be effective,” he said.
The development of the ACS guideline was supported by ACS operational funds. The ACS has received an independent educational grant from Merck Sharp & Dohme for a project intended to increase HPV vaccination rates. Dr. Saslow is the principal investigator for a cooperative agreement between the ACS and the CDC to support the National HPV Vaccination Roundtable and is coprincipal investigator of a cooperative agreement between the ACS and CDC to support initiatives to increase HPV vaccination. The remaining authors and Dr. Bednarczyk reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Saslow D et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul 8. doi: 10.3322/caac.21616.
FROM CA: A CANCER JOURNAL FOR CLINICIANS
P-tau217 differentiates Alzheimer’s disease from other neurodegenerative conditions
new research suggests.
Results from a large multinational study showed that the level of P-tau217 in blood collected during life was an accurate predictor of tau brain changes seen in brain tissue after death. In addition, increasing blood P-tau217 levels can be detected in some individuals up to 20 years before the average age of onset of the early cognitive decline that signals Alzheimer’s disease, researchers reported.
“While there is still more work to be done, this biomarker has the potential to have a transformational impact on research, treatment, prevention, and therapy development, and in the clinical setting,” said senior author Eric M. Reiman, MD, executive director of Banner Alzheimer’s Institute in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and simultaneously published online July 28 in JAMA.
Three cohorts
The international team of researchers evaluated the P-tau217 blood test in 1,402 adults from three cohorts. The first cohort was made up of 81 individuals in the Arizona (Banner Sun Health Research Institute) Brain Donation program and included clinical, blood, and neuropathologic data. The second cohort included 699 individuals in the Swedish BioFINDER-2 study and provided clinical, brain imaging, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and blood data. The third cohort was made up of 522 participants from the Columbian autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease kindred, including 365 PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers and 257 mutation noncarriers.
In the Arizona cohort, plasma P-tau217 discriminated neuropathologically defined Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s disease (area under the curve, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81-0.97) with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181 and neurofilament light chain (NfL) (AUC range, 0.50-0.72; P < .05).
In the Swedish BioFINDER-2 cohort, the discriminative accuracy of plasma P-tau217 for clinical Alzheimer’s disease dementia versus other neurodegenerative diseases was 96% (AUC, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).
This was significantly higher than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, and MRI measures (AUC range, 0.50-0.81; P < .001), but was not significantly different than CSF P-tau217, CSF P-tau181, and tau-PET (AUC range, 0.90-0.99; P > .15).
In the Colombian cohort, plasma P-tau217 levels were significantly greater among PSEN1 mutation carriers than noncarriers starting at around age 25 years, which is 20 years prior to the estimated onset of mild cognitive impairment among mutation carriers.
Additionally, plasma P-tau217 levels correlated with cerebral tau tangles, and discriminated abnormal versus normal tau-PET scans with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, CSF P-tau181, CSF Abeta42:Abeta40 ratio, and MRI measures.
The blood test “opens the possibility of early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease before the dementia stage, which is very important for clinical trials evaluating novel therapies that might stop or slow down the disease process,” presenting author Oskar Hansson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, said in a statement.
Further research is now needed to optimize the P-tau217 blood test, validate the findings in unselected and diverse populations, and determine its potential role in the clinic, the investigators noted.
Potential game changer?
Commenting on the study, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, noted his enthusiasm for the test. “This tau blood test will be a real game changer, advancing clinical care and research,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved in the research.
“This is a real breakthrough: a simple and accessible blood test that can diagnose Alzheimer’s disease better than the more costly and invasive methods currently available like PET scans and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers,” he said.
The P-tau217 blood test “is like the equivalent of the cholesterol test for heart disease, but for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Fillit added.
As previously reported, another study presented at AAIC 2020 compared P-tau217 with P-tau181 to determine which could best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Results showed that, although the two biomarkers were similar overall, P-tau217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy.
The study by Reiman et al. was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, and the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation. Dr. Hansson reported receiving grants from Roche, Biogen, and Pfizer, and receiving nonfinancial support from GE Healthcare, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, and Euroimmun. Dr. Reiman has received grants from Roche/Roche Diagnostics and received personal fees from Alkahest, Alzheon, Aural Analytics, Denali, Green Valley, MagQ, Takeda/Zinfandel, and United Neuroscience. He is also a cofounder of AlzPath, which aims to further develop P-tau217 and fluid biomarkers; holds a patent owned by Banner Health for a strategy to use biomarkers to accelerate evaluation of Alzheimer prevention therapies; and is a principal investigator of prevention trials that include research agreements with Genentech/Roche and Novartis/Amgen, PET studies that include research agreements with Avid/Lilly, and several National Institute of Health–supported research studies. Dr. Fillit reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a large multinational study showed that the level of P-tau217 in blood collected during life was an accurate predictor of tau brain changes seen in brain tissue after death. In addition, increasing blood P-tau217 levels can be detected in some individuals up to 20 years before the average age of onset of the early cognitive decline that signals Alzheimer’s disease, researchers reported.
“While there is still more work to be done, this biomarker has the potential to have a transformational impact on research, treatment, prevention, and therapy development, and in the clinical setting,” said senior author Eric M. Reiman, MD, executive director of Banner Alzheimer’s Institute in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and simultaneously published online July 28 in JAMA.
Three cohorts
The international team of researchers evaluated the P-tau217 blood test in 1,402 adults from three cohorts. The first cohort was made up of 81 individuals in the Arizona (Banner Sun Health Research Institute) Brain Donation program and included clinical, blood, and neuropathologic data. The second cohort included 699 individuals in the Swedish BioFINDER-2 study and provided clinical, brain imaging, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and blood data. The third cohort was made up of 522 participants from the Columbian autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease kindred, including 365 PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers and 257 mutation noncarriers.
In the Arizona cohort, plasma P-tau217 discriminated neuropathologically defined Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s disease (area under the curve, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81-0.97) with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181 and neurofilament light chain (NfL) (AUC range, 0.50-0.72; P < .05).
In the Swedish BioFINDER-2 cohort, the discriminative accuracy of plasma P-tau217 for clinical Alzheimer’s disease dementia versus other neurodegenerative diseases was 96% (AUC, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).
This was significantly higher than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, and MRI measures (AUC range, 0.50-0.81; P < .001), but was not significantly different than CSF P-tau217, CSF P-tau181, and tau-PET (AUC range, 0.90-0.99; P > .15).
In the Colombian cohort, plasma P-tau217 levels were significantly greater among PSEN1 mutation carriers than noncarriers starting at around age 25 years, which is 20 years prior to the estimated onset of mild cognitive impairment among mutation carriers.
Additionally, plasma P-tau217 levels correlated with cerebral tau tangles, and discriminated abnormal versus normal tau-PET scans with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, CSF P-tau181, CSF Abeta42:Abeta40 ratio, and MRI measures.
The blood test “opens the possibility of early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease before the dementia stage, which is very important for clinical trials evaluating novel therapies that might stop or slow down the disease process,” presenting author Oskar Hansson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, said in a statement.
Further research is now needed to optimize the P-tau217 blood test, validate the findings in unselected and diverse populations, and determine its potential role in the clinic, the investigators noted.
Potential game changer?
Commenting on the study, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, noted his enthusiasm for the test. “This tau blood test will be a real game changer, advancing clinical care and research,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved in the research.
“This is a real breakthrough: a simple and accessible blood test that can diagnose Alzheimer’s disease better than the more costly and invasive methods currently available like PET scans and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers,” he said.
The P-tau217 blood test “is like the equivalent of the cholesterol test for heart disease, but for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Fillit added.
As previously reported, another study presented at AAIC 2020 compared P-tau217 with P-tau181 to determine which could best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Results showed that, although the two biomarkers were similar overall, P-tau217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy.
The study by Reiman et al. was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, and the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation. Dr. Hansson reported receiving grants from Roche, Biogen, and Pfizer, and receiving nonfinancial support from GE Healthcare, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, and Euroimmun. Dr. Reiman has received grants from Roche/Roche Diagnostics and received personal fees from Alkahest, Alzheon, Aural Analytics, Denali, Green Valley, MagQ, Takeda/Zinfandel, and United Neuroscience. He is also a cofounder of AlzPath, which aims to further develop P-tau217 and fluid biomarkers; holds a patent owned by Banner Health for a strategy to use biomarkers to accelerate evaluation of Alzheimer prevention therapies; and is a principal investigator of prevention trials that include research agreements with Genentech/Roche and Novartis/Amgen, PET studies that include research agreements with Avid/Lilly, and several National Institute of Health–supported research studies. Dr. Fillit reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a large multinational study showed that the level of P-tau217 in blood collected during life was an accurate predictor of tau brain changes seen in brain tissue after death. In addition, increasing blood P-tau217 levels can be detected in some individuals up to 20 years before the average age of onset of the early cognitive decline that signals Alzheimer’s disease, researchers reported.
“While there is still more work to be done, this biomarker has the potential to have a transformational impact on research, treatment, prevention, and therapy development, and in the clinical setting,” said senior author Eric M. Reiman, MD, executive director of Banner Alzheimer’s Institute in Phoenix.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and simultaneously published online July 28 in JAMA.
Three cohorts
The international team of researchers evaluated the P-tau217 blood test in 1,402 adults from three cohorts. The first cohort was made up of 81 individuals in the Arizona (Banner Sun Health Research Institute) Brain Donation program and included clinical, blood, and neuropathologic data. The second cohort included 699 individuals in the Swedish BioFINDER-2 study and provided clinical, brain imaging, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and blood data. The third cohort was made up of 522 participants from the Columbian autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease kindred, including 365 PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers and 257 mutation noncarriers.
In the Arizona cohort, plasma P-tau217 discriminated neuropathologically defined Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s disease (area under the curve, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.81-0.97) with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181 and neurofilament light chain (NfL) (AUC range, 0.50-0.72; P < .05).
In the Swedish BioFINDER-2 cohort, the discriminative accuracy of plasma P-tau217 for clinical Alzheimer’s disease dementia versus other neurodegenerative diseases was 96% (AUC, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.93-0.98).
This was significantly higher than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, and MRI measures (AUC range, 0.50-0.81; P < .001), but was not significantly different than CSF P-tau217, CSF P-tau181, and tau-PET (AUC range, 0.90-0.99; P > .15).
In the Colombian cohort, plasma P-tau217 levels were significantly greater among PSEN1 mutation carriers than noncarriers starting at around age 25 years, which is 20 years prior to the estimated onset of mild cognitive impairment among mutation carriers.
Additionally, plasma P-tau217 levels correlated with cerebral tau tangles, and discriminated abnormal versus normal tau-PET scans with significantly higher accuracy than plasma P-tau181, plasma NfL, CSF P-tau181, CSF Abeta42:Abeta40 ratio, and MRI measures.
The blood test “opens the possibility of early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease before the dementia stage, which is very important for clinical trials evaluating novel therapies that might stop or slow down the disease process,” presenting author Oskar Hansson, MD, PhD, of Lund (Sweden) University, said in a statement.
Further research is now needed to optimize the P-tau217 blood test, validate the findings in unselected and diverse populations, and determine its potential role in the clinic, the investigators noted.
Potential game changer?
Commenting on the study, Howard Fillit, MD, founding executive director and chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, noted his enthusiasm for the test. “This tau blood test will be a real game changer, advancing clinical care and research,” said Dr. Fillit, who was not involved in the research.
“This is a real breakthrough: a simple and accessible blood test that can diagnose Alzheimer’s disease better than the more costly and invasive methods currently available like PET scans and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers,” he said.
The P-tau217 blood test “is like the equivalent of the cholesterol test for heart disease, but for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Fillit added.
As previously reported, another study presented at AAIC 2020 compared P-tau217 with P-tau181 to determine which could best identify individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Results showed that, although the two biomarkers were similar overall, P-tau217 had a slight edge in terms of accuracy.
The study by Reiman et al. was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, and the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation. Dr. Hansson reported receiving grants from Roche, Biogen, and Pfizer, and receiving nonfinancial support from GE Healthcare, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, and Euroimmun. Dr. Reiman has received grants from Roche/Roche Diagnostics and received personal fees from Alkahest, Alzheon, Aural Analytics, Denali, Green Valley, MagQ, Takeda/Zinfandel, and United Neuroscience. He is also a cofounder of AlzPath, which aims to further develop P-tau217 and fluid biomarkers; holds a patent owned by Banner Health for a strategy to use biomarkers to accelerate evaluation of Alzheimer prevention therapies; and is a principal investigator of prevention trials that include research agreements with Genentech/Roche and Novartis/Amgen, PET studies that include research agreements with Avid/Lilly, and several National Institute of Health–supported research studies. Dr. Fillit reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2020
Urine screen as part of triple test improves ID of adrenal cancer
A strategy that includes a urine steroid test along with imaging characteristics and tumor size criteria can significantly improve the challenging diagnosis of adrenocortical cancer, helping to avoid unnecessary, and often unsuccessful, further imaging and even surgery, new research shows.
“A triple-test strategy of tumor diameter, imaging characteristics, and urine steroid metabolomics improves detection of adrenocortical carcinoma, which could shorten time to surgery for patients with ... carcinoma and help to avoid unnecessary surgery in patients with benign tumors,” the authors say in research published online July 23 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The triple-test strategy can be expected to make its way into international guidelines, notes joint lead author Irina Bancos, MD, an associate professor of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in a press statement issued by the University of Birmingham (England), which also had a number of researchers involved in the study.
“The findings of this study will feed into the next international guidelines on the management of adrenal tumors and the implementation of the new test will hopefully improve the overall outlook for patients diagnosed with adrenal tumors,” Dr. Bancos emphasized.
More imaging has led to detection of more adrenal tumors
Advances in CT and MRI imaging have increased the ability to detect adrenal incidentalomas, which are now picked up on about 5% of scans, and the widespread use of imaging has compounded the prevalence of such findings, particularly in older people.
Adrenocortical carcinomas represent only about 2%-12% of adrenal incidentalomas, but the prognosis is very poor, and early detection and surgery can improve outcomes, so findings of any adrenal tumor typically trigger additional multimodal imaging to rule out malignancy.
Evidence is lacking on the accuracy of imaging in determining whether such masses are truly cancerous, or benign, and such procedures add costs, as well as expose patients to radiation that may ultimately have no benefit. However, a previous proof-of-concept study from the same authors did show that the presence of excess adrenal steroid hormones in the urine is a key indicator of adrenal tumors, and other research has supported the findings.
All three tests together give best predictive value: EURINE-ACT
To further validate this work, the authors conducted the EURINE-ACT trial, a prospective 14-center study that is the first of its kind to evaluate the efficacy of a screening strategy for adrenocortical carcinoma that combines urine steroid profiling with tumor size and imaging characteristics.
The study of 2,017 participants with newly diagnosed adrenal masses, recruited from January 2011 to July 2016 from specialist centers in 11 different countries, assessed the diagnostic accuracy of three components: maximum tumor diameter (≥4 cm vs. <4 cm), imaging characteristics (positive vs. negative), and urine steroid metabolomics (low, medium, or high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma), separately and in combination.
Of the patients, 98 (4.9%) had adrenocortical carcinoma confirmed clinically, histopathologically, or biochemically.
Tumors with diameters of 4 cm or larger were identified in 488 patients (24.2%) and were observed in the vast majority of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma (96 of 98), for a positive predictive value (PPV) of 19.7%.
Likewise, the PPV for imaging characteristics was 19.7%. However, increasing the unenhanced CT tumor attenuation threshold to 20 Hounsfield units (HU) from the recommended 10 HU increased specificity for adrenocortical carcinoma (80.0% vs. 64.0%) while maintaining sensitivity (99.0% vs. 100.0%).
Comparatively, a urine steroid metabolomics result suggesting a high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma had a PPV of 34.6%.
A total of 106 patients (5.3%) met the criteria for all three measures, and the PPV for all three was 76.4%.
Using the criteria, 70 patients (3.5%) were classified as being at moderate risk of adrenocortical carcinoma and 1,841 (91.3%) at low risk, for a negative predictive value (NPV) of 99.7%.
“Use of radiation-free, noninvasive urine steroid metabolomics has a higher PPV than two standard imaging tests, and best performance was seen with the combination of all three tests,” the authors state.
Limit urine test to patients with larger tumors
They note that the use of the combined diagnostic strategy would have led to additional imaging in only 488 (24.2%) of the study’s 2,017 patients, compared with the 2,737 scans that were actually conducted before reaching a diagnostic decision.
“Implementation of urine steroid metabolomics in the routine diagnostic assessment of newly discovered adrenal masses could reduce the number of imaging procedures required to diagnose adrenocortical carcinoma and avoid unnecessary surgery of benign adrenal tumors, potentially yielding beneficial effects with respect to patient burden and health care costs,” they stress.
And regarding imaging parameters, “we also showed that using a cutoff of 20 HU for unenhanced CT tumor attenuation increases the accuracy of imaging characteristic assessment for exclusion of adrenocortical carcinoma, compared with the currently recommended cutoff of 10 HU, which has immediate implications for clinical practice,” they emphasize.
In an accompanying editorial, Adina F. Turcu, MD, of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Axel K. Walch, MD, of the Helmholtz Zentrum München–German Research Centre for Environmental Health, agree. “The introduction of urine steroid metabolomics into routine clinical practice would provide major advantages,” they state.
However, they point out that, although the overall negative predictive value of the test was excellent, the specificity was weak.
“Thus, urine steroid metabolomics should be limited to patients who have adrenal nodules larger than 4 cm and have qualitative imaging characteristics suggestive of malignancy,” say Dr. Turcu and Dr. Walch.
The EURINE-ACT study results suggest this subgroup would represent roughly only 12% of all patients with adrenal incidentalomas, they add.
Issues that remain to be addressed with regard to the implementation of the screening strategy include how to best respond to patients who are classified as having intermediate or moderate risk of malignancy, and whether the diagnostic value of steroid metabolomics could be refined by adding analytes or parameters, the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Commission, U.K. Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, U.K. National Institute for Health Research, U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Claire Khan Trust Fund at University Hospitals Birmingham Charities, and the Mayo Clinic Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A strategy that includes a urine steroid test along with imaging characteristics and tumor size criteria can significantly improve the challenging diagnosis of adrenocortical cancer, helping to avoid unnecessary, and often unsuccessful, further imaging and even surgery, new research shows.
“A triple-test strategy of tumor diameter, imaging characteristics, and urine steroid metabolomics improves detection of adrenocortical carcinoma, which could shorten time to surgery for patients with ... carcinoma and help to avoid unnecessary surgery in patients with benign tumors,” the authors say in research published online July 23 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The triple-test strategy can be expected to make its way into international guidelines, notes joint lead author Irina Bancos, MD, an associate professor of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in a press statement issued by the University of Birmingham (England), which also had a number of researchers involved in the study.
“The findings of this study will feed into the next international guidelines on the management of adrenal tumors and the implementation of the new test will hopefully improve the overall outlook for patients diagnosed with adrenal tumors,” Dr. Bancos emphasized.
More imaging has led to detection of more adrenal tumors
Advances in CT and MRI imaging have increased the ability to detect adrenal incidentalomas, which are now picked up on about 5% of scans, and the widespread use of imaging has compounded the prevalence of such findings, particularly in older people.
Adrenocortical carcinomas represent only about 2%-12% of adrenal incidentalomas, but the prognosis is very poor, and early detection and surgery can improve outcomes, so findings of any adrenal tumor typically trigger additional multimodal imaging to rule out malignancy.
Evidence is lacking on the accuracy of imaging in determining whether such masses are truly cancerous, or benign, and such procedures add costs, as well as expose patients to radiation that may ultimately have no benefit. However, a previous proof-of-concept study from the same authors did show that the presence of excess adrenal steroid hormones in the urine is a key indicator of adrenal tumors, and other research has supported the findings.
All three tests together give best predictive value: EURINE-ACT
To further validate this work, the authors conducted the EURINE-ACT trial, a prospective 14-center study that is the first of its kind to evaluate the efficacy of a screening strategy for adrenocortical carcinoma that combines urine steroid profiling with tumor size and imaging characteristics.
The study of 2,017 participants with newly diagnosed adrenal masses, recruited from January 2011 to July 2016 from specialist centers in 11 different countries, assessed the diagnostic accuracy of three components: maximum tumor diameter (≥4 cm vs. <4 cm), imaging characteristics (positive vs. negative), and urine steroid metabolomics (low, medium, or high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma), separately and in combination.
Of the patients, 98 (4.9%) had adrenocortical carcinoma confirmed clinically, histopathologically, or biochemically.
Tumors with diameters of 4 cm or larger were identified in 488 patients (24.2%) and were observed in the vast majority of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma (96 of 98), for a positive predictive value (PPV) of 19.7%.
Likewise, the PPV for imaging characteristics was 19.7%. However, increasing the unenhanced CT tumor attenuation threshold to 20 Hounsfield units (HU) from the recommended 10 HU increased specificity for adrenocortical carcinoma (80.0% vs. 64.0%) while maintaining sensitivity (99.0% vs. 100.0%).
Comparatively, a urine steroid metabolomics result suggesting a high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma had a PPV of 34.6%.
A total of 106 patients (5.3%) met the criteria for all three measures, and the PPV for all three was 76.4%.
Using the criteria, 70 patients (3.5%) were classified as being at moderate risk of adrenocortical carcinoma and 1,841 (91.3%) at low risk, for a negative predictive value (NPV) of 99.7%.
“Use of radiation-free, noninvasive urine steroid metabolomics has a higher PPV than two standard imaging tests, and best performance was seen with the combination of all three tests,” the authors state.
Limit urine test to patients with larger tumors
They note that the use of the combined diagnostic strategy would have led to additional imaging in only 488 (24.2%) of the study’s 2,017 patients, compared with the 2,737 scans that were actually conducted before reaching a diagnostic decision.
“Implementation of urine steroid metabolomics in the routine diagnostic assessment of newly discovered adrenal masses could reduce the number of imaging procedures required to diagnose adrenocortical carcinoma and avoid unnecessary surgery of benign adrenal tumors, potentially yielding beneficial effects with respect to patient burden and health care costs,” they stress.
And regarding imaging parameters, “we also showed that using a cutoff of 20 HU for unenhanced CT tumor attenuation increases the accuracy of imaging characteristic assessment for exclusion of adrenocortical carcinoma, compared with the currently recommended cutoff of 10 HU, which has immediate implications for clinical practice,” they emphasize.
In an accompanying editorial, Adina F. Turcu, MD, of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Axel K. Walch, MD, of the Helmholtz Zentrum München–German Research Centre for Environmental Health, agree. “The introduction of urine steroid metabolomics into routine clinical practice would provide major advantages,” they state.
However, they point out that, although the overall negative predictive value of the test was excellent, the specificity was weak.
“Thus, urine steroid metabolomics should be limited to patients who have adrenal nodules larger than 4 cm and have qualitative imaging characteristics suggestive of malignancy,” say Dr. Turcu and Dr. Walch.
The EURINE-ACT study results suggest this subgroup would represent roughly only 12% of all patients with adrenal incidentalomas, they add.
Issues that remain to be addressed with regard to the implementation of the screening strategy include how to best respond to patients who are classified as having intermediate or moderate risk of malignancy, and whether the diagnostic value of steroid metabolomics could be refined by adding analytes or parameters, the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Commission, U.K. Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, U.K. National Institute for Health Research, U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Claire Khan Trust Fund at University Hospitals Birmingham Charities, and the Mayo Clinic Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A strategy that includes a urine steroid test along with imaging characteristics and tumor size criteria can significantly improve the challenging diagnosis of adrenocortical cancer, helping to avoid unnecessary, and often unsuccessful, further imaging and even surgery, new research shows.
“A triple-test strategy of tumor diameter, imaging characteristics, and urine steroid metabolomics improves detection of adrenocortical carcinoma, which could shorten time to surgery for patients with ... carcinoma and help to avoid unnecessary surgery in patients with benign tumors,” the authors say in research published online July 23 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The triple-test strategy can be expected to make its way into international guidelines, notes joint lead author Irina Bancos, MD, an associate professor of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in a press statement issued by the University of Birmingham (England), which also had a number of researchers involved in the study.
“The findings of this study will feed into the next international guidelines on the management of adrenal tumors and the implementation of the new test will hopefully improve the overall outlook for patients diagnosed with adrenal tumors,” Dr. Bancos emphasized.
More imaging has led to detection of more adrenal tumors
Advances in CT and MRI imaging have increased the ability to detect adrenal incidentalomas, which are now picked up on about 5% of scans, and the widespread use of imaging has compounded the prevalence of such findings, particularly in older people.
Adrenocortical carcinomas represent only about 2%-12% of adrenal incidentalomas, but the prognosis is very poor, and early detection and surgery can improve outcomes, so findings of any adrenal tumor typically trigger additional multimodal imaging to rule out malignancy.
Evidence is lacking on the accuracy of imaging in determining whether such masses are truly cancerous, or benign, and such procedures add costs, as well as expose patients to radiation that may ultimately have no benefit. However, a previous proof-of-concept study from the same authors did show that the presence of excess adrenal steroid hormones in the urine is a key indicator of adrenal tumors, and other research has supported the findings.
All three tests together give best predictive value: EURINE-ACT
To further validate this work, the authors conducted the EURINE-ACT trial, a prospective 14-center study that is the first of its kind to evaluate the efficacy of a screening strategy for adrenocortical carcinoma that combines urine steroid profiling with tumor size and imaging characteristics.
The study of 2,017 participants with newly diagnosed adrenal masses, recruited from January 2011 to July 2016 from specialist centers in 11 different countries, assessed the diagnostic accuracy of three components: maximum tumor diameter (≥4 cm vs. <4 cm), imaging characteristics (positive vs. negative), and urine steroid metabolomics (low, medium, or high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma), separately and in combination.
Of the patients, 98 (4.9%) had adrenocortical carcinoma confirmed clinically, histopathologically, or biochemically.
Tumors with diameters of 4 cm or larger were identified in 488 patients (24.2%) and were observed in the vast majority of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma (96 of 98), for a positive predictive value (PPV) of 19.7%.
Likewise, the PPV for imaging characteristics was 19.7%. However, increasing the unenhanced CT tumor attenuation threshold to 20 Hounsfield units (HU) from the recommended 10 HU increased specificity for adrenocortical carcinoma (80.0% vs. 64.0%) while maintaining sensitivity (99.0% vs. 100.0%).
Comparatively, a urine steroid metabolomics result suggesting a high risk of adrenocortical carcinoma had a PPV of 34.6%.
A total of 106 patients (5.3%) met the criteria for all three measures, and the PPV for all three was 76.4%.
Using the criteria, 70 patients (3.5%) were classified as being at moderate risk of adrenocortical carcinoma and 1,841 (91.3%) at low risk, for a negative predictive value (NPV) of 99.7%.
“Use of radiation-free, noninvasive urine steroid metabolomics has a higher PPV than two standard imaging tests, and best performance was seen with the combination of all three tests,” the authors state.
Limit urine test to patients with larger tumors
They note that the use of the combined diagnostic strategy would have led to additional imaging in only 488 (24.2%) of the study’s 2,017 patients, compared with the 2,737 scans that were actually conducted before reaching a diagnostic decision.
“Implementation of urine steroid metabolomics in the routine diagnostic assessment of newly discovered adrenal masses could reduce the number of imaging procedures required to diagnose adrenocortical carcinoma and avoid unnecessary surgery of benign adrenal tumors, potentially yielding beneficial effects with respect to patient burden and health care costs,” they stress.
And regarding imaging parameters, “we also showed that using a cutoff of 20 HU for unenhanced CT tumor attenuation increases the accuracy of imaging characteristic assessment for exclusion of adrenocortical carcinoma, compared with the currently recommended cutoff of 10 HU, which has immediate implications for clinical practice,” they emphasize.
In an accompanying editorial, Adina F. Turcu, MD, of the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Axel K. Walch, MD, of the Helmholtz Zentrum München–German Research Centre for Environmental Health, agree. “The introduction of urine steroid metabolomics into routine clinical practice would provide major advantages,” they state.
However, they point out that, although the overall negative predictive value of the test was excellent, the specificity was weak.
“Thus, urine steroid metabolomics should be limited to patients who have adrenal nodules larger than 4 cm and have qualitative imaging characteristics suggestive of malignancy,” say Dr. Turcu and Dr. Walch.
The EURINE-ACT study results suggest this subgroup would represent roughly only 12% of all patients with adrenal incidentalomas, they add.
Issues that remain to be addressed with regard to the implementation of the screening strategy include how to best respond to patients who are classified as having intermediate or moderate risk of malignancy, and whether the diagnostic value of steroid metabolomics could be refined by adding analytes or parameters, the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the European Commission, U.K. Medical Research Council, Wellcome Trust, U.K. National Institute for Health Research, U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Claire Khan Trust Fund at University Hospitals Birmingham Charities, and the Mayo Clinic Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Positive phase 3 top-line results for migraine prevention drug
AbbVie, the company developing the drug, has announced.
Top-line results from the ADVANCE trial, which evaluated atogepant 10, 30, and 60 mg, showed all three doses were associated with a significant reduction from baseline in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
There were also significant improvements in all six secondary endpoints with the two higher doses.
Data from the ADVANCE trial and a previous phase 2/3 trial will be the basis for regulatory submissions in the United States and other countries, AbbVie reported.
Decreased migraine days
The phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of oral atogepant for the prevention of migraine in those who experienced 4-14 migraine days per month.
A total of 910 patients were randomized to one of four treatment groups: 10 mg, 30 mg, or 60 mg of atogepant once daily or placebo. Efficacy analyses were based on the modified intent-to-treat population of 873 patients.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days during the 12-week treatment period. All atogepant dose groups met the primary endpoint and demonstrated significantly greater decreases in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
Mean monthly migraine days were reduced by 3.69 days with the 10-mg dose, 3.86 days with the 30-mg dose, and 4.2 days with the 60-mg dose of atogepant, compared with a reduction of 2.48 migraine days in the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
A key secondary endpoint measured the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% reduction in mean monthly migraine days over 12 weeks. This outcome occurred in 55.6% of the 10-mg atogepant group, 58.7% of the 30-mg group, and 60.8% of the 60-mg group, compared with 29% of the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
Significant improvements
Additional secondary endpoints measured during the 12-week treatment period included change from baseline in mean monthly headache days, mean monthly acute–medication use days, mean monthly performance of daily activities and physical impairment domain scores on the Activity Impairment in Migraine-Diary, and change from baseline in the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire Role Function-Restrictive domain score at week 12. Treatment with the 30-mg and 60-mg doses resulted in significant improvements in all secondary endpoints, and treatment with the 10-mg dose resulted in significant improvements in four of the six secondary endpoints.
No new safety risks were observed when compared with the safety profile of atogepant observed in previous trials, AbbVie said. Serious adverse events occurred in 0.9% of patients in the atogepant 10-mg group versus 0.9% of patients in the placebo group. No patients in the atogepant 30-mg or 60-mg groups experienced a serious adverse event. The most common adverse events (reported in at least 5% of patients and at least one atogepant group and at a rate greater than placebo), across all doses versus placebo, were constipation (6.9%-7.7% vs. 0.5%), nausea (4.4%-6.1% vs. 1.8%), and upper respiratory tract infection (3.9%-5.7% vs. 4.5%).
Most cases of constipation, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to discontinuation. There were no hepatic safety issues identified in the trial.
Full data results will be presented at an upcoming medical congress and/or published in a peer-reviewed journal, the company said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AbbVie, the company developing the drug, has announced.
Top-line results from the ADVANCE trial, which evaluated atogepant 10, 30, and 60 mg, showed all three doses were associated with a significant reduction from baseline in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
There were also significant improvements in all six secondary endpoints with the two higher doses.
Data from the ADVANCE trial and a previous phase 2/3 trial will be the basis for regulatory submissions in the United States and other countries, AbbVie reported.
Decreased migraine days
The phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of oral atogepant for the prevention of migraine in those who experienced 4-14 migraine days per month.
A total of 910 patients were randomized to one of four treatment groups: 10 mg, 30 mg, or 60 mg of atogepant once daily or placebo. Efficacy analyses were based on the modified intent-to-treat population of 873 patients.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days during the 12-week treatment period. All atogepant dose groups met the primary endpoint and demonstrated significantly greater decreases in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
Mean monthly migraine days were reduced by 3.69 days with the 10-mg dose, 3.86 days with the 30-mg dose, and 4.2 days with the 60-mg dose of atogepant, compared with a reduction of 2.48 migraine days in the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
A key secondary endpoint measured the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% reduction in mean monthly migraine days over 12 weeks. This outcome occurred in 55.6% of the 10-mg atogepant group, 58.7% of the 30-mg group, and 60.8% of the 60-mg group, compared with 29% of the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
Significant improvements
Additional secondary endpoints measured during the 12-week treatment period included change from baseline in mean monthly headache days, mean monthly acute–medication use days, mean monthly performance of daily activities and physical impairment domain scores on the Activity Impairment in Migraine-Diary, and change from baseline in the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire Role Function-Restrictive domain score at week 12. Treatment with the 30-mg and 60-mg doses resulted in significant improvements in all secondary endpoints, and treatment with the 10-mg dose resulted in significant improvements in four of the six secondary endpoints.
No new safety risks were observed when compared with the safety profile of atogepant observed in previous trials, AbbVie said. Serious adverse events occurred in 0.9% of patients in the atogepant 10-mg group versus 0.9% of patients in the placebo group. No patients in the atogepant 30-mg or 60-mg groups experienced a serious adverse event. The most common adverse events (reported in at least 5% of patients and at least one atogepant group and at a rate greater than placebo), across all doses versus placebo, were constipation (6.9%-7.7% vs. 0.5%), nausea (4.4%-6.1% vs. 1.8%), and upper respiratory tract infection (3.9%-5.7% vs. 4.5%).
Most cases of constipation, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to discontinuation. There were no hepatic safety issues identified in the trial.
Full data results will be presented at an upcoming medical congress and/or published in a peer-reviewed journal, the company said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AbbVie, the company developing the drug, has announced.
Top-line results from the ADVANCE trial, which evaluated atogepant 10, 30, and 60 mg, showed all three doses were associated with a significant reduction from baseline in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
There were also significant improvements in all six secondary endpoints with the two higher doses.
Data from the ADVANCE trial and a previous phase 2/3 trial will be the basis for regulatory submissions in the United States and other countries, AbbVie reported.
Decreased migraine days
The phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of oral atogepant for the prevention of migraine in those who experienced 4-14 migraine days per month.
A total of 910 patients were randomized to one of four treatment groups: 10 mg, 30 mg, or 60 mg of atogepant once daily or placebo. Efficacy analyses were based on the modified intent-to-treat population of 873 patients.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days during the 12-week treatment period. All atogepant dose groups met the primary endpoint and demonstrated significantly greater decreases in mean monthly migraine days, compared with placebo.
Mean monthly migraine days were reduced by 3.69 days with the 10-mg dose, 3.86 days with the 30-mg dose, and 4.2 days with the 60-mg dose of atogepant, compared with a reduction of 2.48 migraine days in the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
A key secondary endpoint measured the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% reduction in mean monthly migraine days over 12 weeks. This outcome occurred in 55.6% of the 10-mg atogepant group, 58.7% of the 30-mg group, and 60.8% of the 60-mg group, compared with 29% of the placebo group (P < .0001, all dose groups vs. placebo).
Significant improvements
Additional secondary endpoints measured during the 12-week treatment period included change from baseline in mean monthly headache days, mean monthly acute–medication use days, mean monthly performance of daily activities and physical impairment domain scores on the Activity Impairment in Migraine-Diary, and change from baseline in the Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire Role Function-Restrictive domain score at week 12. Treatment with the 30-mg and 60-mg doses resulted in significant improvements in all secondary endpoints, and treatment with the 10-mg dose resulted in significant improvements in four of the six secondary endpoints.
No new safety risks were observed when compared with the safety profile of atogepant observed in previous trials, AbbVie said. Serious adverse events occurred in 0.9% of patients in the atogepant 10-mg group versus 0.9% of patients in the placebo group. No patients in the atogepant 30-mg or 60-mg groups experienced a serious adverse event. The most common adverse events (reported in at least 5% of patients and at least one atogepant group and at a rate greater than placebo), across all doses versus placebo, were constipation (6.9%-7.7% vs. 0.5%), nausea (4.4%-6.1% vs. 1.8%), and upper respiratory tract infection (3.9%-5.7% vs. 4.5%).
Most cases of constipation, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection were mild or moderate in severity and did not lead to discontinuation. There were no hepatic safety issues identified in the trial.
Full data results will be presented at an upcoming medical congress and/or published in a peer-reviewed journal, the company said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.





