User login
Benefiting from hospitalist-directed transfers
A ‘unique opportunity’ for hospitalists
Emergency department overcrowding is common, and it can result in both increased costs and poor clinical outcomes.
“We sought to evaluate the impact and safety of hospitalist-directed transfers on patients boarding in the ER as a means to alleviate overcrowding,” said Yihan Chen, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles. “High inpatient census has been shown to impair ER throughput by increasing the number of ER ‘boarders,’ which creates a suboptimal care environment for practicing hospitalists. For example, some studies have shown associations with delays in medical decision making when admitted patients remain and receive care in the emergency department.”
Dr. Chen was the lead author of an abstract describing a chart review on 1,016 admissions to the hospitalist service. About half remained at the reference hospital and half were transferred to a nearby affiliate hospital.
In analyzing the data, the researchers’ top takeaway was the many benefits for the transferred patients. “Hospitalist-directed transfer and direct admission of stable ER patients to an affiliate facility with greater bed availability is associated with shorter ER lengths of stay, fewer adverse events, and lower rates of readmission within 30 days of hospitalization,” Dr. Chen said. “Having a system in place to transfer patients to an affiliate hospital with lower census is a way to improve flow.”
Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to take on a triage role in the ED to safely and effectively decrease ED overcrowding and throughput, improve resource utilization at the hospital level, and allow for other hospitalists at their institution to optimize patient care on the inpatient ward rather than in the ED, Dr. Chen said.
“Health systems privileged to have more than one facility should consider an intra–health system transfer process lead by triage hospitalists to identify stable patients who can be directly admitted to the off-site, affiliate hospital,” she said. “By improving patient throughput, hospitalists would play a critical role in relieving institutional stressors, impacting cost and quality of care, and enhancing clinical outcomes.”
Reference
1. Chen Y et al. Hospitalist-Directed Transfers Improve Emergency Room Length of Stay. Hospital Medicine 2018, Abstract 12. Accessed April 3, 2019.
A ‘unique opportunity’ for hospitalists
A ‘unique opportunity’ for hospitalists
Emergency department overcrowding is common, and it can result in both increased costs and poor clinical outcomes.
“We sought to evaluate the impact and safety of hospitalist-directed transfers on patients boarding in the ER as a means to alleviate overcrowding,” said Yihan Chen, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles. “High inpatient census has been shown to impair ER throughput by increasing the number of ER ‘boarders,’ which creates a suboptimal care environment for practicing hospitalists. For example, some studies have shown associations with delays in medical decision making when admitted patients remain and receive care in the emergency department.”
Dr. Chen was the lead author of an abstract describing a chart review on 1,016 admissions to the hospitalist service. About half remained at the reference hospital and half were transferred to a nearby affiliate hospital.
In analyzing the data, the researchers’ top takeaway was the many benefits for the transferred patients. “Hospitalist-directed transfer and direct admission of stable ER patients to an affiliate facility with greater bed availability is associated with shorter ER lengths of stay, fewer adverse events, and lower rates of readmission within 30 days of hospitalization,” Dr. Chen said. “Having a system in place to transfer patients to an affiliate hospital with lower census is a way to improve flow.”
Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to take on a triage role in the ED to safely and effectively decrease ED overcrowding and throughput, improve resource utilization at the hospital level, and allow for other hospitalists at their institution to optimize patient care on the inpatient ward rather than in the ED, Dr. Chen said.
“Health systems privileged to have more than one facility should consider an intra–health system transfer process lead by triage hospitalists to identify stable patients who can be directly admitted to the off-site, affiliate hospital,” she said. “By improving patient throughput, hospitalists would play a critical role in relieving institutional stressors, impacting cost and quality of care, and enhancing clinical outcomes.”
Reference
1. Chen Y et al. Hospitalist-Directed Transfers Improve Emergency Room Length of Stay. Hospital Medicine 2018, Abstract 12. Accessed April 3, 2019.
Emergency department overcrowding is common, and it can result in both increased costs and poor clinical outcomes.
“We sought to evaluate the impact and safety of hospitalist-directed transfers on patients boarding in the ER as a means to alleviate overcrowding,” said Yihan Chen, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles. “High inpatient census has been shown to impair ER throughput by increasing the number of ER ‘boarders,’ which creates a suboptimal care environment for practicing hospitalists. For example, some studies have shown associations with delays in medical decision making when admitted patients remain and receive care in the emergency department.”
Dr. Chen was the lead author of an abstract describing a chart review on 1,016 admissions to the hospitalist service. About half remained at the reference hospital and half were transferred to a nearby affiliate hospital.
In analyzing the data, the researchers’ top takeaway was the many benefits for the transferred patients. “Hospitalist-directed transfer and direct admission of stable ER patients to an affiliate facility with greater bed availability is associated with shorter ER lengths of stay, fewer adverse events, and lower rates of readmission within 30 days of hospitalization,” Dr. Chen said. “Having a system in place to transfer patients to an affiliate hospital with lower census is a way to improve flow.”
Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to take on a triage role in the ED to safely and effectively decrease ED overcrowding and throughput, improve resource utilization at the hospital level, and allow for other hospitalists at their institution to optimize patient care on the inpatient ward rather than in the ED, Dr. Chen said.
“Health systems privileged to have more than one facility should consider an intra–health system transfer process lead by triage hospitalists to identify stable patients who can be directly admitted to the off-site, affiliate hospital,” she said. “By improving patient throughput, hospitalists would play a critical role in relieving institutional stressors, impacting cost and quality of care, and enhancing clinical outcomes.”
Reference
1. Chen Y et al. Hospitalist-Directed Transfers Improve Emergency Room Length of Stay. Hospital Medicine 2018, Abstract 12. Accessed April 3, 2019.
CMS announces application process for Direct Contracting model
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will be accepting letters of intent from physician practices interested in participating in the Direct Contracting model, a new payment model aimed at practices serving at least 5,000 Medicare beneficiaries.
First announced in April 2019, the Direct Contracting program is an advanced alternative payment model designed for organizations that are ready to take on more financial risk and have experience managing large populations through accountable care organizations or working with Medicare Advantage plans.
Interested practices will be able to choose from the Professional population-based payment, which has a lower risk-sharing arrangement (50% savings/losses), and the Global model, which offers a 100% savings/loss risk-sharing arrangement.
“The payment model options available under Direct Contracting aim to reduce expenditures while preserving or enhancing quality of care for beneficiaries,” agency officials said on a web page detailing information for the payment model.
The model offers a prospectively determined and predictable revenue stream for participants and aims to transform risk-sharing arrangements through capitated and partially capitated population-based payments, open up participation in alternative payment models to more physicians, and reduce clinician burden by using smaller sets of quality measures and waivers to help facilitate the delivery of care.
Letters of intent are due to the agency by Dec. 10. CMS noted that submission of a letter of intent will not bind the organization to participating in the program.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will be accepting letters of intent from physician practices interested in participating in the Direct Contracting model, a new payment model aimed at practices serving at least 5,000 Medicare beneficiaries.
First announced in April 2019, the Direct Contracting program is an advanced alternative payment model designed for organizations that are ready to take on more financial risk and have experience managing large populations through accountable care organizations or working with Medicare Advantage plans.
Interested practices will be able to choose from the Professional population-based payment, which has a lower risk-sharing arrangement (50% savings/losses), and the Global model, which offers a 100% savings/loss risk-sharing arrangement.
“The payment model options available under Direct Contracting aim to reduce expenditures while preserving or enhancing quality of care for beneficiaries,” agency officials said on a web page detailing information for the payment model.
The model offers a prospectively determined and predictable revenue stream for participants and aims to transform risk-sharing arrangements through capitated and partially capitated population-based payments, open up participation in alternative payment models to more physicians, and reduce clinician burden by using smaller sets of quality measures and waivers to help facilitate the delivery of care.
Letters of intent are due to the agency by Dec. 10. CMS noted that submission of a letter of intent will not bind the organization to participating in the program.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will be accepting letters of intent from physician practices interested in participating in the Direct Contracting model, a new payment model aimed at practices serving at least 5,000 Medicare beneficiaries.
First announced in April 2019, the Direct Contracting program is an advanced alternative payment model designed for organizations that are ready to take on more financial risk and have experience managing large populations through accountable care organizations or working with Medicare Advantage plans.
Interested practices will be able to choose from the Professional population-based payment, which has a lower risk-sharing arrangement (50% savings/losses), and the Global model, which offers a 100% savings/loss risk-sharing arrangement.
“The payment model options available under Direct Contracting aim to reduce expenditures while preserving or enhancing quality of care for beneficiaries,” agency officials said on a web page detailing information for the payment model.
The model offers a prospectively determined and predictable revenue stream for participants and aims to transform risk-sharing arrangements through capitated and partially capitated population-based payments, open up participation in alternative payment models to more physicians, and reduce clinician burden by using smaller sets of quality measures and waivers to help facilitate the delivery of care.
Letters of intent are due to the agency by Dec. 10. CMS noted that submission of a letter of intent will not bind the organization to participating in the program.
FDA approves Tula system for recurrent pediatric ear infections
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Tubes Under Local Anesthesia (Tula) System for treatment of recurrent ear infections (otitis media) via tympanostomy in young children, according to a release from the agency.
Consisting of Tymbion anesthetic, tympanostomy tubes developed by Tusker Medical, and several devices that deliver them into the ear drum,
“This approval has the potential to expand patient access to a treatment that can be administered in a physician’s office with local anesthesia and minimal discomfort,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health.
The approval was based on data from 222 children treated with the device, with a procedural success rate of 86% in children under 5 years and 89% in children aged 5-12 years. The most common adverse event was insufficient anesthetic.
The system should not be used in children with allergies to some local anesthetics or those younger than 6 months. It also is not intended for patients with preexisting issues with their eardrums, such as perforated ear drums, according to the press release.
The Tula system was granted a Breakthrough Device designation, which means the FDA provided intensive engagement and guidance during its development. The full release can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Tubes Under Local Anesthesia (Tula) System for treatment of recurrent ear infections (otitis media) via tympanostomy in young children, according to a release from the agency.
Consisting of Tymbion anesthetic, tympanostomy tubes developed by Tusker Medical, and several devices that deliver them into the ear drum,
“This approval has the potential to expand patient access to a treatment that can be administered in a physician’s office with local anesthesia and minimal discomfort,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health.
The approval was based on data from 222 children treated with the device, with a procedural success rate of 86% in children under 5 years and 89% in children aged 5-12 years. The most common adverse event was insufficient anesthetic.
The system should not be used in children with allergies to some local anesthetics or those younger than 6 months. It also is not intended for patients with preexisting issues with their eardrums, such as perforated ear drums, according to the press release.
The Tula system was granted a Breakthrough Device designation, which means the FDA provided intensive engagement and guidance during its development. The full release can be found on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Tubes Under Local Anesthesia (Tula) System for treatment of recurrent ear infections (otitis media) via tympanostomy in young children, according to a release from the agency.
Consisting of Tymbion anesthetic, tympanostomy tubes developed by Tusker Medical, and several devices that deliver them into the ear drum,
“This approval has the potential to expand patient access to a treatment that can be administered in a physician’s office with local anesthesia and minimal discomfort,” said Jeff Shuren, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health.
The approval was based on data from 222 children treated with the device, with a procedural success rate of 86% in children under 5 years and 89% in children aged 5-12 years. The most common adverse event was insufficient anesthetic.
The system should not be used in children with allergies to some local anesthetics or those younger than 6 months. It also is not intended for patients with preexisting issues with their eardrums, such as perforated ear drums, according to the press release.
The Tula system was granted a Breakthrough Device designation, which means the FDA provided intensive engagement and guidance during its development. The full release can be found on the FDA website.
Question 2
Q2. Correct Answer: D
Rationale
Elbasvir and grazoprevir are hepaticaly metabo¬lized and undergo minimal renal elimination making them safe for use in patients with end stage renal disease. The C-Surfer trial evaluated elbasvir and grazoprevir in genotype 1 patients with advanced renal disease inclusive of patients on hemodialysis. Cure rates in this trial were 94- 99 percent. Sofosbuvir containing regimen are not approved for patient with CKD stage 4-5 or those on hemodialysis, even when given in a dose reduced or post-dialysis fashion.
References
https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-popula¬tions/renal-impairment
Roth D, Nelson DR, Bruchfeld A, et al. Grazoprevir plus elbasvir in treatment-naive and treat¬ment experienced patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (the C-SURFER study): a combination phase 3 study. Lancet. 2015;386(10003):1537-45.
Q2. Correct Answer: D
Rationale
Elbasvir and grazoprevir are hepaticaly metabo¬lized and undergo minimal renal elimination making them safe for use in patients with end stage renal disease. The C-Surfer trial evaluated elbasvir and grazoprevir in genotype 1 patients with advanced renal disease inclusive of patients on hemodialysis. Cure rates in this trial were 94- 99 percent. Sofosbuvir containing regimen are not approved for patient with CKD stage 4-5 or those on hemodialysis, even when given in a dose reduced or post-dialysis fashion.
References
https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-popula¬tions/renal-impairment
Roth D, Nelson DR, Bruchfeld A, et al. Grazoprevir plus elbasvir in treatment-naive and treat¬ment experienced patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (the C-SURFER study): a combination phase 3 study. Lancet. 2015;386(10003):1537-45.
Q2. Correct Answer: D
Rationale
Elbasvir and grazoprevir are hepaticaly metabo¬lized and undergo minimal renal elimination making them safe for use in patients with end stage renal disease. The C-Surfer trial evaluated elbasvir and grazoprevir in genotype 1 patients with advanced renal disease inclusive of patients on hemodialysis. Cure rates in this trial were 94- 99 percent. Sofosbuvir containing regimen are not approved for patient with CKD stage 4-5 or those on hemodialysis, even when given in a dose reduced or post-dialysis fashion.
References
https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-popula¬tions/renal-impairment
Roth D, Nelson DR, Bruchfeld A, et al. Grazoprevir plus elbasvir in treatment-naive and treat¬ment experienced patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (the C-SURFER study): a combination phase 3 study. Lancet. 2015;386(10003):1537-45.
A 47-year-old man with stage 5 chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis is referred to your clinic. He has genotype 1a HCV and F2 fibrosis. He wants to discuss treatment options.
Question 1
Q1. Correct answer: C
Rationale
There are many potential reasons for PPI failure in patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. However, the single most important reason is inappropriate drug administration. Patients should be counseled to take their medication 30-60 minutes prior to meals for optimal physiologic gastric acid inhibition, with the morning meal favored over the evening meal due to relative more gastric acid production at this time.
Reference
Fass R, Shapiro M, Dekel R. Systematic review: proton-pump inhibitor failure in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – where next? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:79-94.
Q1. Correct answer: C
Rationale
There are many potential reasons for PPI failure in patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. However, the single most important reason is inappropriate drug administration. Patients should be counseled to take their medication 30-60 minutes prior to meals for optimal physiologic gastric acid inhibition, with the morning meal favored over the evening meal due to relative more gastric acid production at this time.
Reference
Fass R, Shapiro M, Dekel R. Systematic review: proton-pump inhibitor failure in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – where next? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:79-94.
Q1. Correct answer: C
Rationale
There are many potential reasons for PPI failure in patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. However, the single most important reason is inappropriate drug administration. Patients should be counseled to take their medication 30-60 minutes prior to meals for optimal physiologic gastric acid inhibition, with the morning meal favored over the evening meal due to relative more gastric acid production at this time.
Reference
Fass R, Shapiro M, Dekel R. Systematic review: proton-pump inhibitor failure in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease – where next? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:79-94.
.
What is your diagnosis?
Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver
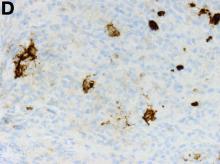
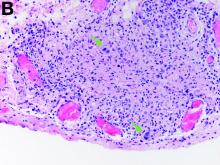
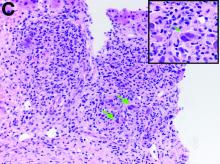
The gallbladder (Figure B) as well as the intraoperative liver biopsy (Figure C; insert showing cells under higher power) showed non-necrotizing granulomas along with scattered infiltration by atypical large cells morphologically consistent with Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells in a lymphoid background (Figures B, C, green arrows). Immunohistochemistry showed these were positive for CD30 (Figure D, liver biopsy), weakly positive for PAX5, and negative for CD15, CD20, CD79a, and ALK-1. Given the pathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with Hodgkins lymphoma.
The patient had a history of mediastinoscopy and lymph node biopsy in the past at an outside hospital with reported noncaseating granulomas and no other abnormalities; those slides could not be obtained for independent review. Primary lymphomas of the liver are exceedingly rare, but advanced lymphoma can have liver involvement.1 Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver is extremely uncommon.2 It can present with fever, hepatomegaly, and jaundice.1 The diagnostic yield of a liver biopsy ranges from 5% to 10% depending on core versus wedge biopsy.1 Pathologically, there is portal inflammation and atypical histiocytic aggregates but Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells are required for diagnosis. These cells stain positive for CD15 and CD30 in around 80% of cases.3 Lymphoma should remain in the differential when granulomas are seen in the liver biopsy. Our patient clinically decompensated by the time the diagnosis was confirmed. The family decided not to pursue aggressive treatment in hospital and the patient was discharged home where she expired.
References
1. in: R.N.M. MacSween (Ed.) Pathology of the liver. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ; 1979
2. Levitan R, Diamond H, Lloyd C. The liver in Hodgkin’s disease. Gut. 1961;2:60.
3. Kanel GC, Korula J. Atlas of liver pathology. Elsevier/Saunders, Philadelphia; 2005.
Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver
The gallbladder (Figure B) as well as the intraoperative liver biopsy (Figure C; insert showing cells under higher power) showed non-necrotizing granulomas along with scattered infiltration by atypical large cells morphologically consistent with Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells in a lymphoid background (Figures B, C, green arrows). Immunohistochemistry showed these were positive for CD30 (Figure D, liver biopsy), weakly positive for PAX5, and negative for CD15, CD20, CD79a, and ALK-1. Given the pathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with Hodgkins lymphoma.
The patient had a history of mediastinoscopy and lymph node biopsy in the past at an outside hospital with reported noncaseating granulomas and no other abnormalities; those slides could not be obtained for independent review. Primary lymphomas of the liver are exceedingly rare, but advanced lymphoma can have liver involvement.1 Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver is extremely uncommon.2 It can present with fever, hepatomegaly, and jaundice.1 The diagnostic yield of a liver biopsy ranges from 5% to 10% depending on core versus wedge biopsy.1 Pathologically, there is portal inflammation and atypical histiocytic aggregates but Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells are required for diagnosis. These cells stain positive for CD15 and CD30 in around 80% of cases.3 Lymphoma should remain in the differential when granulomas are seen in the liver biopsy. Our patient clinically decompensated by the time the diagnosis was confirmed. The family decided not to pursue aggressive treatment in hospital and the patient was discharged home where she expired.
References
1. in: R.N.M. MacSween (Ed.) Pathology of the liver. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ; 1979
2. Levitan R, Diamond H, Lloyd C. The liver in Hodgkin’s disease. Gut. 1961;2:60.
3. Kanel GC, Korula J. Atlas of liver pathology. Elsevier/Saunders, Philadelphia; 2005.
Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver
The gallbladder (Figure B) as well as the intraoperative liver biopsy (Figure C; insert showing cells under higher power) showed non-necrotizing granulomas along with scattered infiltration by atypical large cells morphologically consistent with Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells in a lymphoid background (Figures B, C, green arrows). Immunohistochemistry showed these were positive for CD30 (Figure D, liver biopsy), weakly positive for PAX5, and negative for CD15, CD20, CD79a, and ALK-1. Given the pathologic findings, the patient was diagnosed with Hodgkins lymphoma.
The patient had a history of mediastinoscopy and lymph node biopsy in the past at an outside hospital with reported noncaseating granulomas and no other abnormalities; those slides could not be obtained for independent review. Primary lymphomas of the liver are exceedingly rare, but advanced lymphoma can have liver involvement.1 Hodgkins lymphoma of the liver is extremely uncommon.2 It can present with fever, hepatomegaly, and jaundice.1 The diagnostic yield of a liver biopsy ranges from 5% to 10% depending on core versus wedge biopsy.1 Pathologically, there is portal inflammation and atypical histiocytic aggregates but Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells are required for diagnosis. These cells stain positive for CD15 and CD30 in around 80% of cases.3 Lymphoma should remain in the differential when granulomas are seen in the liver biopsy. Our patient clinically decompensated by the time the diagnosis was confirmed. The family decided not to pursue aggressive treatment in hospital and the patient was discharged home where she expired.
References
1. in: R.N.M. MacSween (Ed.) Pathology of the liver. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ; 1979
2. Levitan R, Diamond H, Lloyd C. The liver in Hodgkin’s disease. Gut. 1961;2:60.
3. Kanel GC, Korula J. Atlas of liver pathology. Elsevier/Saunders, Philadelphia; 2005.
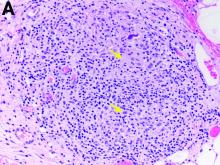
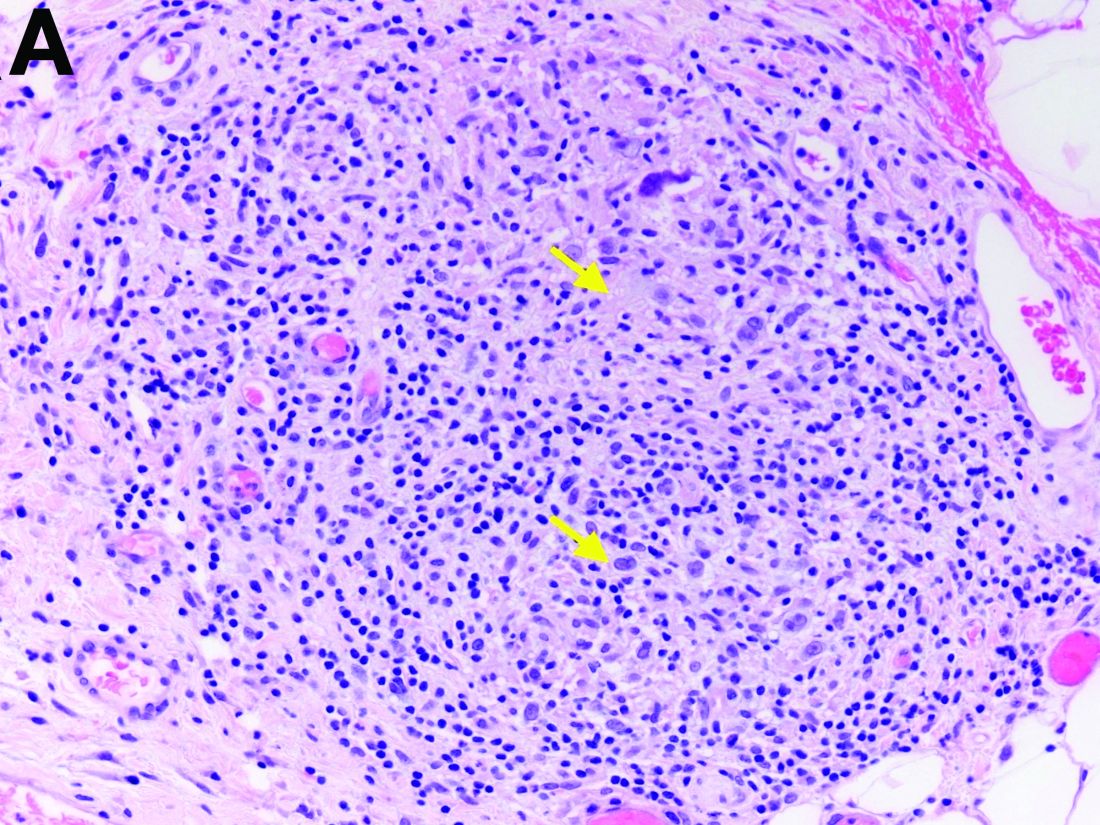
Two months later, repeat laboratory tests showed aspartate aminotransferase of 213 U/L, alanine aminotransferase of 93 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 1,472 U/L, and total bilirubin of 6.0 mg/dL. The initial ultrasound scan was normal. On further assessment, she complained of malaise, weight loss, shortness of breath, dry eyes, dry mouth, and insomnia. She denied any significant alcohol use. No new medications or supplements were started recently. Vital signs were normal. Physical examination was unremarkable. Viral hepatitis serologies were negative. Antinuclear antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibody, and antimitochondrial antibody were negative. She had a magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, which showed splenomegaly but was otherwise unremarkable. She had a liver biopsy (Figure A), which showed non-necrotizing granulomas (yellow arrows) with a chronic inflammatory lymphocytic infiltrate.
Given these findings, prednisone was increased to 20 mg. In the interim, the patient was admitted with acute acalculous cholecystitis. She had a laparoscopic cholecystectomy and an intraoperative liver biopsy. She developed respiratory failure postoperatively and was transferred to intensive care. Stress dose steroids and antibiotics were initiated. Laboratory tests showed a white blood cell count of 13.8 × 109/L, hemoglobin of 9.4 g/dL, platelets at 223 × 109/L, aspartate aminotransferase of 97 U/L, alanine aminotransferase of 63 U/L, alkaline phosphatase of 1,607 U/L, total bilirubin of 5.8 mg/dL (direct 3.3), and albumin of 2.4 g/dL. Pathology from the gallbladder (Figure B) and the intraoperative liver biopsy (Figure C) showed cells pathognomonic for the condition (green arrows).
On the basis of these findings, what is the final diagnosis?
PHM19: MOC Part 4 projects for community pediatric hospitalists
PHM19 session
MOC Part 4 projects for community pediatric hospitalists
Presenters
Jack M. Percelay, MD, MPH, FAAP, MHM
Nancy Chen, MD, FAAP
Elizabeth Dobler, MD, FAAP
Lindsay Fox, MD
Beth C. Natt, MD, MPH, SFHM
Clota Snow, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Jack Percelay, of Sutter Health in San Francisco, started this session at Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2019 by outlining the process of submitting a small group (n = 1-10) project for Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Part 4 credit including the basics of what is needed for the application:
- Aim statement.
- Metrics used.
- Data required (3 data points: pre, post, and sustain).
He also shared the requirement of “meaningful participation” for participants to be eligible for MOC Part 4 credit.
Examples of successful projects were shared by members of the presenting group:
- Dr. Natt: Improving the timing of the birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccination.
- Dr. Dobler: Improving the hepatitis B vaccination rate within 24 hours of birth.
- Dr. Snow: Supplementing vitamin D in the newborn nursery.
- Dr. Fox: Improving newborn discharge efficiency, improving screening for smoking exposure, and offering smoking cessation.
- Dr. Percelay: Improving hospitalist billing and coding using time as a factor.
- Dr. Chen: Improving patient satisfaction through improvement of family-centered rounds.
The workshop audience divided into groups to brainstorm/troubleshoot projects and to elicit general advice regarding the process. Sample submissions were provided.
Key takeaways
- Even small projects (i.e. single metric) can be submitted/accepted with pre- and postintervention data.
- Be creative! Think about changes you are making at your institution and gather the data to support the intervention.
- Always double-dip on QI projects to gain valuable MOC Part 4 credit!
Dr. Fox is site director, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Division at MetroWest Medical Center, Framingham, Mass.
PHM19 session
MOC Part 4 projects for community pediatric hospitalists
Presenters
Jack M. Percelay, MD, MPH, FAAP, MHM
Nancy Chen, MD, FAAP
Elizabeth Dobler, MD, FAAP
Lindsay Fox, MD
Beth C. Natt, MD, MPH, SFHM
Clota Snow, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Jack Percelay, of Sutter Health in San Francisco, started this session at Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2019 by outlining the process of submitting a small group (n = 1-10) project for Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Part 4 credit including the basics of what is needed for the application:
- Aim statement.
- Metrics used.
- Data required (3 data points: pre, post, and sustain).
He also shared the requirement of “meaningful participation” for participants to be eligible for MOC Part 4 credit.
Examples of successful projects were shared by members of the presenting group:
- Dr. Natt: Improving the timing of the birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccination.
- Dr. Dobler: Improving the hepatitis B vaccination rate within 24 hours of birth.
- Dr. Snow: Supplementing vitamin D in the newborn nursery.
- Dr. Fox: Improving newborn discharge efficiency, improving screening for smoking exposure, and offering smoking cessation.
- Dr. Percelay: Improving hospitalist billing and coding using time as a factor.
- Dr. Chen: Improving patient satisfaction through improvement of family-centered rounds.
The workshop audience divided into groups to brainstorm/troubleshoot projects and to elicit general advice regarding the process. Sample submissions were provided.
Key takeaways
- Even small projects (i.e. single metric) can be submitted/accepted with pre- and postintervention data.
- Be creative! Think about changes you are making at your institution and gather the data to support the intervention.
- Always double-dip on QI projects to gain valuable MOC Part 4 credit!
Dr. Fox is site director, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Division at MetroWest Medical Center, Framingham, Mass.
PHM19 session
MOC Part 4 projects for community pediatric hospitalists
Presenters
Jack M. Percelay, MD, MPH, FAAP, MHM
Nancy Chen, MD, FAAP
Elizabeth Dobler, MD, FAAP
Lindsay Fox, MD
Beth C. Natt, MD, MPH, SFHM
Clota Snow, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Jack Percelay, of Sutter Health in San Francisco, started this session at Pediatric Hospital Medicine 2019 by outlining the process of submitting a small group (n = 1-10) project for Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Part 4 credit including the basics of what is needed for the application:
- Aim statement.
- Metrics used.
- Data required (3 data points: pre, post, and sustain).
He also shared the requirement of “meaningful participation” for participants to be eligible for MOC Part 4 credit.
Examples of successful projects were shared by members of the presenting group:
- Dr. Natt: Improving the timing of the birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccination.
- Dr. Dobler: Improving the hepatitis B vaccination rate within 24 hours of birth.
- Dr. Snow: Supplementing vitamin D in the newborn nursery.
- Dr. Fox: Improving newborn discharge efficiency, improving screening for smoking exposure, and offering smoking cessation.
- Dr. Percelay: Improving hospitalist billing and coding using time as a factor.
- Dr. Chen: Improving patient satisfaction through improvement of family-centered rounds.
The workshop audience divided into groups to brainstorm/troubleshoot projects and to elicit general advice regarding the process. Sample submissions were provided.
Key takeaways
- Even small projects (i.e. single metric) can be submitted/accepted with pre- and postintervention data.
- Be creative! Think about changes you are making at your institution and gather the data to support the intervention.
- Always double-dip on QI projects to gain valuable MOC Part 4 credit!
Dr. Fox is site director, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Division at MetroWest Medical Center, Framingham, Mass.
ACGME deepening its commitment to physician well-being, leader says
NEW ORLEANS – When Timothy P. Brigham, MDiv, PhD, thinks about the impact of burnout and stress on the ability of physicians to practice medicine, Lewin’s equation comes to mind.
Developed by psychologist Kurt Lewin in 1936, the equation holds that behavior stems from a person’s personality and the environment that person inhabits.
Dr. Brigham, chief of staff and chief education and organizational development officer at the Chicago-based Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“It’s a toxic mine, in some ways. What we tend to do is when we detect that physicians in general are, or a particular residency program is, too stressed out or burned out, we give them resilience training. Not that that’s unimportant, but it’s like putting a canary in a toxic mine full of poison and saying, ‘We’re going to teach you to hold your breath a little bit longer.’ Our job is to detoxify the mine.”
Troubled by the rise of suicides among physicians in recent years as well as mounting evidence about the adverse impact of burnout and stress on the practice of medicine, Dr. Brigham said that the ACGME is deepening its commitment to the well-being of faculty, residents, patients, and all members of the health care team. Since launching a “call to arms” on the topic at its annual educational conference in 2015, the ACGME has added courses on well-being to its annual meeting and remolded its Clinical Learning Environmental Review program to include all clinicians, “because everybody is affected by this: nurses, coordinators, et cetera,” he said. The ACGME also has revised Common Program Requirements, disseminated tools and resources to promote well-being and new knowledge on the topic, and partnered with the National Academy of Medicine Action Collaborative on Clinician Well-Being and Resilience – all in an effort to bring about culture change.
“But we’re well aware that the ACGME can’t do this alone,” Dr. Brigham said. “We can’t ‘requirement’ our way out of this problem. It’s going to take a culture shift. Only you physicians, in collaboration with everyone in your community of learning, can create the systemic change required to improve our culture. We have a good handle on the problem at this point, but the solutions are a little bit more difficult to get a hold of. As Martin Luther King Jr. once said, ‘You don’t have to see the whole staircase, just take the first step.’ ”
The ACGME wants to work with physicians “to collect data and do joint research, to share insights, and to share tools and resources to create a better world for practicing physicians, for other members of the health care team, and for patients. After all, clinicians who care for themselves provide better care for others. They’re less likely to make errors or leave the profession,” Dr. Brigham told attendees.
He added that clinicians can gauge their risk for burnout by asking themselves three simple questions about their work environment: Does it support self-care? Does it increase and support connection with colleagues? Does it connect people to purpose and meaningful work?
“One of the problems with our resident clinical work hours is not terrible program directors saying, ‘work longer.’ It’s residents who want to take care of families for 1 more hour,” Dr. Brigham continued. “It’s residents who want to take care of patients who are going through a difficult time. You represent the top 2% in the world in terms of your intelligence and achievement, yet that’s not what makes you special. What makes you special is that the level of self-doubt in this room exceeds that of the general population by about 10 times. You also tend to run toward what everyone else runs away from: disease, despair, people who are injured and suffering. That takes a toll.”
He emphasized that positive social relationships with others are crucial to joy and well-being in the practice of medicine. “Burnout isn’t just about exhaustion; it’s about loneliness,” Dr. Brigham said. “There’s a surprising power in just asking people how they’re doing, and really wanting to know the answer.”
Negative social connections are highly correlated with burnout and depression, such as harassment, bullying, mistreatment, discrimination, “and using the power gradient to squash somebody who’s trying their best to be a physician,” he said.
Dr. Brigham acknowledged the tall task of bringing a spotlight to well-being as physicians continue to engage in tasks such as the burden and lack of standardization of prior authorization requirements, the burden of clinical documentation requirements, electronic health records and related work flow, and quality payment programs. “This is what we need to shift; this is what we need to take away so you can get back in touch with why you became a physician in the first place.”
Dr. Brigham reported having no financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – When Timothy P. Brigham, MDiv, PhD, thinks about the impact of burnout and stress on the ability of physicians to practice medicine, Lewin’s equation comes to mind.
Developed by psychologist Kurt Lewin in 1936, the equation holds that behavior stems from a person’s personality and the environment that person inhabits.
Dr. Brigham, chief of staff and chief education and organizational development officer at the Chicago-based Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“It’s a toxic mine, in some ways. What we tend to do is when we detect that physicians in general are, or a particular residency program is, too stressed out or burned out, we give them resilience training. Not that that’s unimportant, but it’s like putting a canary in a toxic mine full of poison and saying, ‘We’re going to teach you to hold your breath a little bit longer.’ Our job is to detoxify the mine.”
Troubled by the rise of suicides among physicians in recent years as well as mounting evidence about the adverse impact of burnout and stress on the practice of medicine, Dr. Brigham said that the ACGME is deepening its commitment to the well-being of faculty, residents, patients, and all members of the health care team. Since launching a “call to arms” on the topic at its annual educational conference in 2015, the ACGME has added courses on well-being to its annual meeting and remolded its Clinical Learning Environmental Review program to include all clinicians, “because everybody is affected by this: nurses, coordinators, et cetera,” he said. The ACGME also has revised Common Program Requirements, disseminated tools and resources to promote well-being and new knowledge on the topic, and partnered with the National Academy of Medicine Action Collaborative on Clinician Well-Being and Resilience – all in an effort to bring about culture change.
“But we’re well aware that the ACGME can’t do this alone,” Dr. Brigham said. “We can’t ‘requirement’ our way out of this problem. It’s going to take a culture shift. Only you physicians, in collaboration with everyone in your community of learning, can create the systemic change required to improve our culture. We have a good handle on the problem at this point, but the solutions are a little bit more difficult to get a hold of. As Martin Luther King Jr. once said, ‘You don’t have to see the whole staircase, just take the first step.’ ”
The ACGME wants to work with physicians “to collect data and do joint research, to share insights, and to share tools and resources to create a better world for practicing physicians, for other members of the health care team, and for patients. After all, clinicians who care for themselves provide better care for others. They’re less likely to make errors or leave the profession,” Dr. Brigham told attendees.
He added that clinicians can gauge their risk for burnout by asking themselves three simple questions about their work environment: Does it support self-care? Does it increase and support connection with colleagues? Does it connect people to purpose and meaningful work?
“One of the problems with our resident clinical work hours is not terrible program directors saying, ‘work longer.’ It’s residents who want to take care of families for 1 more hour,” Dr. Brigham continued. “It’s residents who want to take care of patients who are going through a difficult time. You represent the top 2% in the world in terms of your intelligence and achievement, yet that’s not what makes you special. What makes you special is that the level of self-doubt in this room exceeds that of the general population by about 10 times. You also tend to run toward what everyone else runs away from: disease, despair, people who are injured and suffering. That takes a toll.”
He emphasized that positive social relationships with others are crucial to joy and well-being in the practice of medicine. “Burnout isn’t just about exhaustion; it’s about loneliness,” Dr. Brigham said. “There’s a surprising power in just asking people how they’re doing, and really wanting to know the answer.”
Negative social connections are highly correlated with burnout and depression, such as harassment, bullying, mistreatment, discrimination, “and using the power gradient to squash somebody who’s trying their best to be a physician,” he said.
Dr. Brigham acknowledged the tall task of bringing a spotlight to well-being as physicians continue to engage in tasks such as the burden and lack of standardization of prior authorization requirements, the burden of clinical documentation requirements, electronic health records and related work flow, and quality payment programs. “This is what we need to shift; this is what we need to take away so you can get back in touch with why you became a physician in the first place.”
Dr. Brigham reported having no financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – When Timothy P. Brigham, MDiv, PhD, thinks about the impact of burnout and stress on the ability of physicians to practice medicine, Lewin’s equation comes to mind.
Developed by psychologist Kurt Lewin in 1936, the equation holds that behavior stems from a person’s personality and the environment that person inhabits.
Dr. Brigham, chief of staff and chief education and organizational development officer at the Chicago-based Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“It’s a toxic mine, in some ways. What we tend to do is when we detect that physicians in general are, or a particular residency program is, too stressed out or burned out, we give them resilience training. Not that that’s unimportant, but it’s like putting a canary in a toxic mine full of poison and saying, ‘We’re going to teach you to hold your breath a little bit longer.’ Our job is to detoxify the mine.”
Troubled by the rise of suicides among physicians in recent years as well as mounting evidence about the adverse impact of burnout and stress on the practice of medicine, Dr. Brigham said that the ACGME is deepening its commitment to the well-being of faculty, residents, patients, and all members of the health care team. Since launching a “call to arms” on the topic at its annual educational conference in 2015, the ACGME has added courses on well-being to its annual meeting and remolded its Clinical Learning Environmental Review program to include all clinicians, “because everybody is affected by this: nurses, coordinators, et cetera,” he said. The ACGME also has revised Common Program Requirements, disseminated tools and resources to promote well-being and new knowledge on the topic, and partnered with the National Academy of Medicine Action Collaborative on Clinician Well-Being and Resilience – all in an effort to bring about culture change.
“But we’re well aware that the ACGME can’t do this alone,” Dr. Brigham said. “We can’t ‘requirement’ our way out of this problem. It’s going to take a culture shift. Only you physicians, in collaboration with everyone in your community of learning, can create the systemic change required to improve our culture. We have a good handle on the problem at this point, but the solutions are a little bit more difficult to get a hold of. As Martin Luther King Jr. once said, ‘You don’t have to see the whole staircase, just take the first step.’ ”
The ACGME wants to work with physicians “to collect data and do joint research, to share insights, and to share tools and resources to create a better world for practicing physicians, for other members of the health care team, and for patients. After all, clinicians who care for themselves provide better care for others. They’re less likely to make errors or leave the profession,” Dr. Brigham told attendees.
He added that clinicians can gauge their risk for burnout by asking themselves three simple questions about their work environment: Does it support self-care? Does it increase and support connection with colleagues? Does it connect people to purpose and meaningful work?
“One of the problems with our resident clinical work hours is not terrible program directors saying, ‘work longer.’ It’s residents who want to take care of families for 1 more hour,” Dr. Brigham continued. “It’s residents who want to take care of patients who are going through a difficult time. You represent the top 2% in the world in terms of your intelligence and achievement, yet that’s not what makes you special. What makes you special is that the level of self-doubt in this room exceeds that of the general population by about 10 times. You also tend to run toward what everyone else runs away from: disease, despair, people who are injured and suffering. That takes a toll.”
He emphasized that positive social relationships with others are crucial to joy and well-being in the practice of medicine. “Burnout isn’t just about exhaustion; it’s about loneliness,” Dr. Brigham said. “There’s a surprising power in just asking people how they’re doing, and really wanting to know the answer.”
Negative social connections are highly correlated with burnout and depression, such as harassment, bullying, mistreatment, discrimination, “and using the power gradient to squash somebody who’s trying their best to be a physician,” he said.
Dr. Brigham acknowledged the tall task of bringing a spotlight to well-being as physicians continue to engage in tasks such as the burden and lack of standardization of prior authorization requirements, the burden of clinical documentation requirements, electronic health records and related work flow, and quality payment programs. “This is what we need to shift; this is what we need to take away so you can get back in touch with why you became a physician in the first place.”
Dr. Brigham reported having no financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS AT AAP 2019
Application of Hand Therapy Extensor Tendon Protocol to Toe Extensor Tendon Rehabilitation
Plastic and orthopedic surgeons worked closely with therapists in military hospitals to rehabilitate soldiers afflicted with upper extremity trauma during World War II. Together, they developed treatment protocols. In 1975, the American Society for Hand Therapists (ASHT) was created during the American Society for Surgery of the Hand meeting. The ASHT application process required case studies, patient logs, and clinical hours, so membership was equivalent to competency. In May 1991, the first hand certification examination took place and designated the first group of certified hand therapists (CHT).1
In the US Department of Veterans Affairs collaboration takes place between different services and communication is facilitated using the electronic heath record. The case presented here is an example of several services (emergency medicine, plastic/hand surgery, and occupational therapy) working together to develop a treatment plan for a condition that often goes undiagnosed or untreated. This article describes an innovative application of hand extensor tendon therapy clinical decision making to rehabilitate foot extensor tendons when the plastic surgery service was called on to work outside its usual comfort zone of the hand and upper extremity. The hand therapist applied hand extensor tendon rehabilitation principles to recover toe extensor lacerations.
Certified hand therapists (CHTs) are key to a successful hand surgery practice. The Plastic Surgery Service at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida, relies heavily on the CHTs to optimize patient outcomes. The hand surgery clinic and hand therapy clinics are in the same hospital building, allowing for easy face-to-face communication. Hand therapy students are able to observe cases in the operating room. Immediately after surgery, follow-up consults are scheduled to coordinate postoperative care between the services.
Case Presentation
The next day, the patient was examined in the plastic surgery clinic and found to have a completely lacerated extensor digitorum brevis to the second toe and a completely lacerated extensor digitorum longus to the third toe. These were located proximal to the metatarsal phalangeal joints. Surgery was scheduled for the following week.
In surgery, the tendons were sharply debrided and repaired using a 3.0 Ethibond suture placed in a modified Kessler technique followed by a horizontal mattress for a total of a 4-core repair. This was reinforced with a No. 6 Prolene to the paratendon. The surgery was performed under IV sedation and an ankle block, using 17 minutes of tourniquet time.
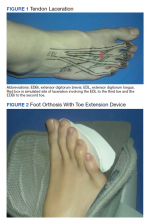
On postoperative day 1, the patient was seen in plastic surgery and occupational therapy clinic. The hand therapist modified the hand extensor tendon repair protocol since there was no known protocol for repairs of the foot and toe extensor tendon. The patient was placed in an ankle foot orthosis with a toe extension device created by heating and molding a low-temperature thermoplastic sheet (Figure 2). The toes were boosted into slight hyper extension. This was done to reduce tension across the extensor tendon repair site. All of the toes were held in about 20°of extension, as the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) has a common origin, to aide in adherence of wearing and for comfort. No standing or weight bearing was permitted for 3 weeks.
A wheelchair was issued in lieu of crutches to inhibit the work of toe extension with gait swing-through. Otherwise, the patient would generate tension on the extensor tendon in order for the toes to clear the ground. It was postulated that it would be difficult to turn off the toe extensors while using crutches. Maximal laxity was desired because edema and early scar formation could increase tension on the repair, resulting in rupture if the patient tried to fire the muscle belly even while in passive extension.
The patient kept his appointments and progressed steadily. He started passive toe extension and relaxation once per day for 30 repetitions at 1 week to aide in tendon glide. He started place and hold techniques in toe extension at 3 weeks. This progressed to active extension 50% effort plus active flexion at 4 weeks after surgery, then 75% extension effort plus toe towel crunches at 5 weeks. Toe crunches are toe flexion exercises with a washcloth on the floor with active bending of the toes with light resistance similar to picking up a marble with the toes. He was found to have a third toe extensor lag at that time that was correctible. The patient was actively able to flex and extend the toe independently. The early extension lag was felt to be secondary to edema and scar formation, which, over time are anticipated to resolve and contract and effectively shorten the tendon. Tendon gliding, and scar massage were reviewed. The patient’s last therapy session occurred 7 weeks after surgery, and he was cleared for full activity at 12 weeks. There was no further follow-up as he was planning on back surgery 2 weeks later.
Discussion
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System is fortunate to have 4 CHTs on staff. CHTs take a 200 question 4 hour certifying exam after being licensed for a minimum of 3 years as a physical or occupational therapist and completing 4,000 hours of direct upper extremity patient experience. Pass rates from 2008 to 2018 ranged from 52% to 68%.3 These clinicians are key to the success of our hand surgery service, utilizing their education and skills on our elective and trauma cases. The hand therapy service applied their knowledge of hand extensor rehabilitation protocols to rehabilitate the patient’s toe extensor in the absence of clear guidelines.
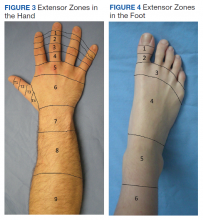
Hand extensor tendon rehabilitation protocols are based on the location of the repair on the hand or forearm. Nine extensor zones are named, distal to proximal, from the distal interphalangeal joints to the proximal forearm (Figure 3). In his review of extensor hallucis longus (EHL) repairs, Al-Qattan described 6 foot-extensor tendon zones, distal to proximal, from the first toe at the insertion of the big toe extensor to the distal leg proximal to the extensor retinaculum (Figure 4).4 Zone 3 is over the metatarsophalangeal joint; zone 5 is under the extensor retinaculum. The extensor tendon repairs described in this report were in dorsal foot zone 4 (proximal to the metatarsophalangeal joint and over the metatarsals), which would be most comparable to hand extensor zone 6 (proximal to the metacarpal phalangeal joint and over the metacarpals).
The EDL originates on the lateral condyle of the tibia and anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane, passes under the extensor retinaculum, and divides into 4 separate tendons. The 4 tendons split into 3 slips; the central one inserts on the middle phalanx, and the lateral ones insert onto the distal phalanx of the 4 lateral toes, which allows for toe extension.5 The EDL common origin for the muscle belly that serves 4 tendon slips has clinical significance because rehabilitation for one digit will affect the others. Knowledge of the anatomical structures guides the clinical decision making whether it is in the hand or foot. The EDL works synergistically with the extensor digitorum brevis (EDBr) to dorsiflex (extend) the toe phalanges. The EDB originates at the supralateral surface of the calcaneus, lateral talocalcaneal ligament and cruciate crural ligament and inserts at the lateral side of the EDL of second, third, and fourth toes at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint.6
Repair of lacerated extensor tendons in the foot is the recommended treatment. Chronic extensor lag of the phalanges can result in a claw toe deformity, difficulty controlling the toes when putting on shoes or socks, and catching of the toe on fabric or insoles.7 The extensor tendons are close to the deep and superficial peroneal nerves and to the dorsalis pedis artery, none of which were involved in this case report.
There are case reports and series of EHL repairs that all involves at least 3 weeks of immobilization.4,8,9 The EHL dorsiflexes the big toe. Al-Qattan’s series involved placing K wires across the interphalangeal joint of the big toe and across the metatarsophalangeal joint, which were removed at 6 weeks, in addition to 3.0 polypropylene tendon mattress sutures. All patients in this series healed without tendon rupture or infection. Our PubMed search did not reveal any specific protocol for the EDL or EDB tendons, which are anatomically most comparable to the extensor digitorum communis (EDC) tendons in the hand. The EDC originates at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, also divides into 4 separate tendons and is responsible for extending the 4 ulnar sided fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joint.10
Tendon repair protocols are a balance between preventing tendon rupture by too aggressive therapy and with preventing tendon adhesions from prolonged immobilization. Orthotic fabrication plays a key early role with blocking possible forces creating unacceptable strain or tension across the surgical repair site. Traditionally, extensor tendon repairs in the hand were immobilized for at least 3 weeks to prevent rupture. This is still the preferred protocol for the patient unwilling or unable to follow instructions. The downside to this method is extension lags, extrinsic tightness, and adhesions that prevent flexion, which can require prolonged therapy or tenolysis surgery to correct.11-13
Early passive motion (EPM) was promoted in the 1980s when studies found better functional outcomes and fewer adhesions. This involved either a dynamic extension splint that relied on elastic bands (Louisville protocol) to keep tension off the repair or the Duran protocol that relied on a static splint and the patient doing the passive exercises with his other uninjured hand. Critics of the EPM protocol point to the costs of the splints and demands of postoperative hand therapy.11
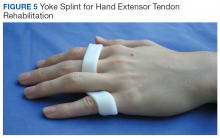
Early active motion (EAM) is the most recent development in hand tendon rehabilitation and starts within days of surgery. Studies have found an earlier regain of total active motion in patients who are mobilized earlier.12 EAM protocols can be divided into controlled active motion (CAM) and relative motion extension splinting (RMES). CAM splints are forearm based and cross more joints. Relative motion splinting is the least restrictive, which makes it less likely that the patient will remove it. Patient friendly splints are ideal because tendon ruptures are often secondary to nonadherence.13 The yoke splint is an example of a RMES, which places the repaired digit in slightly greater extension at the metacarpal phalangeal joint than the other digits (Figure 5), allowing use of the uninjured digits.
The toe extensors do not have the juncturae tendinum connecting the individual EDL tendons to each other, as found between the EDC tendons in the hand. These connective bands can mask a single extensor tendon laceration in the hand when the patient is still able to extend the digit to neutral in the event of a more proximal dorsal hand laceration. A case can be made for closing the skin only in lesser toe extensor injuries in poor surgical candidates because the extensor lag would not be appreciated functionally when wearing shoes. There would be less functional impact when letting a toe extensor go untreated compared with that of a hand extensor. Routine activities such as typing or getting the fingers into a tight pocket could be challenging if hand extensors were untreated. The rehabilitation for toe extensors is more inconvenient when a patient is nonweight bearing, compared with wearing a hand yoke splint.
Conclusion
The case described used an early passive motion protocol without the dynamic splint to rehabilitate the third toe EDL and second toe EDB. This was felt to be the most patient and therapist friendly option, given the previously unchartered territory. The foot orthosis was in stock at the adjacent physical therapy clinic, and the toe booster was created in the hand therapy clinic with readily available supplies. Ideally, one would like to return structures to their anatomic site and control the healing process in the event of a traumatic injury to prevent nonanatomic healing between structures and painful scar adhesions in an area with little subcutaneous tissue. This patient’s tendon repair was still intact at 7 weeks and on his way to recovery, demonstrating good scar management techniques. The risks and benefits to lesser toe tendon repair and recovery would have to be weighed on an individual basis.
Acknowledgments
This project is the result of work supported with resources and use of facilities at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
1. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. History of HTCC. https://www.htcc.org/consumer-information/about-htcc/history-of-htcc. Accessed November 8, 2019.
2. Coady-Fariborzian L, McGreane A. Comparison of hand emergency triage before and after specialty templates (2007 vs 2012). Hand (N Y). 2015;10(2):215-220.
3. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. Passing rates for the CHT exam. https://www.htcc.org/certify/exam-results/passing-rates. Accessed November 8, 2019.
4. Al-Qattan MM. Surgical treatment and results in 17 cases of open lacerations of the extensor hallucis longus tendon. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60(4):360-367.
5. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum longus. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_longus. Updated December 8, 2011. Accessed November 8, 2019.
6. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum brevis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_brevis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
7. Coughlin M, Schon L. Disorders of tendons. https://musculoskeletalkey.com/disorders-of-tendons-2/#s0035. Published August 27, 2016. Accessed November 8, 2019.
8. Bronner S, Ojofeitimi S, Rose D. Repair and rehabilitation of extensor hallucis longus and brevis tendon lacerations in a professional dancer. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(6):362-370.
9. Wong JC, Daniel JN, Raikin SM. Repair of acute extensor hallucis longus tendon injuries: a retrospective review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014;7(1):45-51.
10. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum communis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_communis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
11. Hall B, Lee H, Page R, Rosenwax L, Lee AH. Comparing three postoperative treatment protocols for extensor tendon repair in zones V and VI of the hand. Am J Occup Ther. 2010;64(5):682-688.
12. Wong AL, Wilson M, Girnary S, Nojoomi M, Acharya S, Paul SM. The optimal orthosis and motion protocol for extensor tendon injury in zones IV-VIII: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017;30(4):447-456.
13. Collocott SJ, Kelly E, Ellis RF. Optimal early active mobilisation protocol after extensor tendon repairs in zones V and VI: a systematic review of literature. Hand Ther. 2018;23(1):3-18.
Plastic and orthopedic surgeons worked closely with therapists in military hospitals to rehabilitate soldiers afflicted with upper extremity trauma during World War II. Together, they developed treatment protocols. In 1975, the American Society for Hand Therapists (ASHT) was created during the American Society for Surgery of the Hand meeting. The ASHT application process required case studies, patient logs, and clinical hours, so membership was equivalent to competency. In May 1991, the first hand certification examination took place and designated the first group of certified hand therapists (CHT).1
In the US Department of Veterans Affairs collaboration takes place between different services and communication is facilitated using the electronic heath record. The case presented here is an example of several services (emergency medicine, plastic/hand surgery, and occupational therapy) working together to develop a treatment plan for a condition that often goes undiagnosed or untreated. This article describes an innovative application of hand extensor tendon therapy clinical decision making to rehabilitate foot extensor tendons when the plastic surgery service was called on to work outside its usual comfort zone of the hand and upper extremity. The hand therapist applied hand extensor tendon rehabilitation principles to recover toe extensor lacerations.
Certified hand therapists (CHTs) are key to a successful hand surgery practice. The Plastic Surgery Service at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida, relies heavily on the CHTs to optimize patient outcomes. The hand surgery clinic and hand therapy clinics are in the same hospital building, allowing for easy face-to-face communication. Hand therapy students are able to observe cases in the operating room. Immediately after surgery, follow-up consults are scheduled to coordinate postoperative care between the services.
Case Presentation
The next day, the patient was examined in the plastic surgery clinic and found to have a completely lacerated extensor digitorum brevis to the second toe and a completely lacerated extensor digitorum longus to the third toe. These were located proximal to the metatarsal phalangeal joints. Surgery was scheduled for the following week.
In surgery, the tendons were sharply debrided and repaired using a 3.0 Ethibond suture placed in a modified Kessler technique followed by a horizontal mattress for a total of a 4-core repair. This was reinforced with a No. 6 Prolene to the paratendon. The surgery was performed under IV sedation and an ankle block, using 17 minutes of tourniquet time.
On postoperative day 1, the patient was seen in plastic surgery and occupational therapy clinic. The hand therapist modified the hand extensor tendon repair protocol since there was no known protocol for repairs of the foot and toe extensor tendon. The patient was placed in an ankle foot orthosis with a toe extension device created by heating and molding a low-temperature thermoplastic sheet (Figure 2). The toes were boosted into slight hyper extension. This was done to reduce tension across the extensor tendon repair site. All of the toes were held in about 20°of extension, as the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) has a common origin, to aide in adherence of wearing and for comfort. No standing or weight bearing was permitted for 3 weeks.
A wheelchair was issued in lieu of crutches to inhibit the work of toe extension with gait swing-through. Otherwise, the patient would generate tension on the extensor tendon in order for the toes to clear the ground. It was postulated that it would be difficult to turn off the toe extensors while using crutches. Maximal laxity was desired because edema and early scar formation could increase tension on the repair, resulting in rupture if the patient tried to fire the muscle belly even while in passive extension.
The patient kept his appointments and progressed steadily. He started passive toe extension and relaxation once per day for 30 repetitions at 1 week to aide in tendon glide. He started place and hold techniques in toe extension at 3 weeks. This progressed to active extension 50% effort plus active flexion at 4 weeks after surgery, then 75% extension effort plus toe towel crunches at 5 weeks. Toe crunches are toe flexion exercises with a washcloth on the floor with active bending of the toes with light resistance similar to picking up a marble with the toes. He was found to have a third toe extensor lag at that time that was correctible. The patient was actively able to flex and extend the toe independently. The early extension lag was felt to be secondary to edema and scar formation, which, over time are anticipated to resolve and contract and effectively shorten the tendon. Tendon gliding, and scar massage were reviewed. The patient’s last therapy session occurred 7 weeks after surgery, and he was cleared for full activity at 12 weeks. There was no further follow-up as he was planning on back surgery 2 weeks later.
Discussion
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System is fortunate to have 4 CHTs on staff. CHTs take a 200 question 4 hour certifying exam after being licensed for a minimum of 3 years as a physical or occupational therapist and completing 4,000 hours of direct upper extremity patient experience. Pass rates from 2008 to 2018 ranged from 52% to 68%.3 These clinicians are key to the success of our hand surgery service, utilizing their education and skills on our elective and trauma cases. The hand therapy service applied their knowledge of hand extensor rehabilitation protocols to rehabilitate the patient’s toe extensor in the absence of clear guidelines.
Hand extensor tendon rehabilitation protocols are based on the location of the repair on the hand or forearm. Nine extensor zones are named, distal to proximal, from the distal interphalangeal joints to the proximal forearm (Figure 3). In his review of extensor hallucis longus (EHL) repairs, Al-Qattan described 6 foot-extensor tendon zones, distal to proximal, from the first toe at the insertion of the big toe extensor to the distal leg proximal to the extensor retinaculum (Figure 4).4 Zone 3 is over the metatarsophalangeal joint; zone 5 is under the extensor retinaculum. The extensor tendon repairs described in this report were in dorsal foot zone 4 (proximal to the metatarsophalangeal joint and over the metatarsals), which would be most comparable to hand extensor zone 6 (proximal to the metacarpal phalangeal joint and over the metacarpals).
The EDL originates on the lateral condyle of the tibia and anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane, passes under the extensor retinaculum, and divides into 4 separate tendons. The 4 tendons split into 3 slips; the central one inserts on the middle phalanx, and the lateral ones insert onto the distal phalanx of the 4 lateral toes, which allows for toe extension.5 The EDL common origin for the muscle belly that serves 4 tendon slips has clinical significance because rehabilitation for one digit will affect the others. Knowledge of the anatomical structures guides the clinical decision making whether it is in the hand or foot. The EDL works synergistically with the extensor digitorum brevis (EDBr) to dorsiflex (extend) the toe phalanges. The EDB originates at the supralateral surface of the calcaneus, lateral talocalcaneal ligament and cruciate crural ligament and inserts at the lateral side of the EDL of second, third, and fourth toes at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint.6
Repair of lacerated extensor tendons in the foot is the recommended treatment. Chronic extensor lag of the phalanges can result in a claw toe deformity, difficulty controlling the toes when putting on shoes or socks, and catching of the toe on fabric or insoles.7 The extensor tendons are close to the deep and superficial peroneal nerves and to the dorsalis pedis artery, none of which were involved in this case report.
There are case reports and series of EHL repairs that all involves at least 3 weeks of immobilization.4,8,9 The EHL dorsiflexes the big toe. Al-Qattan’s series involved placing K wires across the interphalangeal joint of the big toe and across the metatarsophalangeal joint, which were removed at 6 weeks, in addition to 3.0 polypropylene tendon mattress sutures. All patients in this series healed without tendon rupture or infection. Our PubMed search did not reveal any specific protocol for the EDL or EDB tendons, which are anatomically most comparable to the extensor digitorum communis (EDC) tendons in the hand. The EDC originates at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, also divides into 4 separate tendons and is responsible for extending the 4 ulnar sided fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joint.10
Tendon repair protocols are a balance between preventing tendon rupture by too aggressive therapy and with preventing tendon adhesions from prolonged immobilization. Orthotic fabrication plays a key early role with blocking possible forces creating unacceptable strain or tension across the surgical repair site. Traditionally, extensor tendon repairs in the hand were immobilized for at least 3 weeks to prevent rupture. This is still the preferred protocol for the patient unwilling or unable to follow instructions. The downside to this method is extension lags, extrinsic tightness, and adhesions that prevent flexion, which can require prolonged therapy or tenolysis surgery to correct.11-13
Early passive motion (EPM) was promoted in the 1980s when studies found better functional outcomes and fewer adhesions. This involved either a dynamic extension splint that relied on elastic bands (Louisville protocol) to keep tension off the repair or the Duran protocol that relied on a static splint and the patient doing the passive exercises with his other uninjured hand. Critics of the EPM protocol point to the costs of the splints and demands of postoperative hand therapy.11
Early active motion (EAM) is the most recent development in hand tendon rehabilitation and starts within days of surgery. Studies have found an earlier regain of total active motion in patients who are mobilized earlier.12 EAM protocols can be divided into controlled active motion (CAM) and relative motion extension splinting (RMES). CAM splints are forearm based and cross more joints. Relative motion splinting is the least restrictive, which makes it less likely that the patient will remove it. Patient friendly splints are ideal because tendon ruptures are often secondary to nonadherence.13 The yoke splint is an example of a RMES, which places the repaired digit in slightly greater extension at the metacarpal phalangeal joint than the other digits (Figure 5), allowing use of the uninjured digits.
The toe extensors do not have the juncturae tendinum connecting the individual EDL tendons to each other, as found between the EDC tendons in the hand. These connective bands can mask a single extensor tendon laceration in the hand when the patient is still able to extend the digit to neutral in the event of a more proximal dorsal hand laceration. A case can be made for closing the skin only in lesser toe extensor injuries in poor surgical candidates because the extensor lag would not be appreciated functionally when wearing shoes. There would be less functional impact when letting a toe extensor go untreated compared with that of a hand extensor. Routine activities such as typing or getting the fingers into a tight pocket could be challenging if hand extensors were untreated. The rehabilitation for toe extensors is more inconvenient when a patient is nonweight bearing, compared with wearing a hand yoke splint.
Conclusion
The case described used an early passive motion protocol without the dynamic splint to rehabilitate the third toe EDL and second toe EDB. This was felt to be the most patient and therapist friendly option, given the previously unchartered territory. The foot orthosis was in stock at the adjacent physical therapy clinic, and the toe booster was created in the hand therapy clinic with readily available supplies. Ideally, one would like to return structures to their anatomic site and control the healing process in the event of a traumatic injury to prevent nonanatomic healing between structures and painful scar adhesions in an area with little subcutaneous tissue. This patient’s tendon repair was still intact at 7 weeks and on his way to recovery, demonstrating good scar management techniques. The risks and benefits to lesser toe tendon repair and recovery would have to be weighed on an individual basis.
Acknowledgments
This project is the result of work supported with resources and use of facilities at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
Plastic and orthopedic surgeons worked closely with therapists in military hospitals to rehabilitate soldiers afflicted with upper extremity trauma during World War II. Together, they developed treatment protocols. In 1975, the American Society for Hand Therapists (ASHT) was created during the American Society for Surgery of the Hand meeting. The ASHT application process required case studies, patient logs, and clinical hours, so membership was equivalent to competency. In May 1991, the first hand certification examination took place and designated the first group of certified hand therapists (CHT).1
In the US Department of Veterans Affairs collaboration takes place between different services and communication is facilitated using the electronic heath record. The case presented here is an example of several services (emergency medicine, plastic/hand surgery, and occupational therapy) working together to develop a treatment plan for a condition that often goes undiagnosed or untreated. This article describes an innovative application of hand extensor tendon therapy clinical decision making to rehabilitate foot extensor tendons when the plastic surgery service was called on to work outside its usual comfort zone of the hand and upper extremity. The hand therapist applied hand extensor tendon rehabilitation principles to recover toe extensor lacerations.
Certified hand therapists (CHTs) are key to a successful hand surgery practice. The Plastic Surgery Service at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida, relies heavily on the CHTs to optimize patient outcomes. The hand surgery clinic and hand therapy clinics are in the same hospital building, allowing for easy face-to-face communication. Hand therapy students are able to observe cases in the operating room. Immediately after surgery, follow-up consults are scheduled to coordinate postoperative care between the services.
Case Presentation
The next day, the patient was examined in the plastic surgery clinic and found to have a completely lacerated extensor digitorum brevis to the second toe and a completely lacerated extensor digitorum longus to the third toe. These were located proximal to the metatarsal phalangeal joints. Surgery was scheduled for the following week.
In surgery, the tendons were sharply debrided and repaired using a 3.0 Ethibond suture placed in a modified Kessler technique followed by a horizontal mattress for a total of a 4-core repair. This was reinforced with a No. 6 Prolene to the paratendon. The surgery was performed under IV sedation and an ankle block, using 17 minutes of tourniquet time.
On postoperative day 1, the patient was seen in plastic surgery and occupational therapy clinic. The hand therapist modified the hand extensor tendon repair protocol since there was no known protocol for repairs of the foot and toe extensor tendon. The patient was placed in an ankle foot orthosis with a toe extension device created by heating and molding a low-temperature thermoplastic sheet (Figure 2). The toes were boosted into slight hyper extension. This was done to reduce tension across the extensor tendon repair site. All of the toes were held in about 20°of extension, as the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) has a common origin, to aide in adherence of wearing and for comfort. No standing or weight bearing was permitted for 3 weeks.
A wheelchair was issued in lieu of crutches to inhibit the work of toe extension with gait swing-through. Otherwise, the patient would generate tension on the extensor tendon in order for the toes to clear the ground. It was postulated that it would be difficult to turn off the toe extensors while using crutches. Maximal laxity was desired because edema and early scar formation could increase tension on the repair, resulting in rupture if the patient tried to fire the muscle belly even while in passive extension.
The patient kept his appointments and progressed steadily. He started passive toe extension and relaxation once per day for 30 repetitions at 1 week to aide in tendon glide. He started place and hold techniques in toe extension at 3 weeks. This progressed to active extension 50% effort plus active flexion at 4 weeks after surgery, then 75% extension effort plus toe towel crunches at 5 weeks. Toe crunches are toe flexion exercises with a washcloth on the floor with active bending of the toes with light resistance similar to picking up a marble with the toes. He was found to have a third toe extensor lag at that time that was correctible. The patient was actively able to flex and extend the toe independently. The early extension lag was felt to be secondary to edema and scar formation, which, over time are anticipated to resolve and contract and effectively shorten the tendon. Tendon gliding, and scar massage were reviewed. The patient’s last therapy session occurred 7 weeks after surgery, and he was cleared for full activity at 12 weeks. There was no further follow-up as he was planning on back surgery 2 weeks later.
Discussion
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System is fortunate to have 4 CHTs on staff. CHTs take a 200 question 4 hour certifying exam after being licensed for a minimum of 3 years as a physical or occupational therapist and completing 4,000 hours of direct upper extremity patient experience. Pass rates from 2008 to 2018 ranged from 52% to 68%.3 These clinicians are key to the success of our hand surgery service, utilizing their education and skills on our elective and trauma cases. The hand therapy service applied their knowledge of hand extensor rehabilitation protocols to rehabilitate the patient’s toe extensor in the absence of clear guidelines.
Hand extensor tendon rehabilitation protocols are based on the location of the repair on the hand or forearm. Nine extensor zones are named, distal to proximal, from the distal interphalangeal joints to the proximal forearm (Figure 3). In his review of extensor hallucis longus (EHL) repairs, Al-Qattan described 6 foot-extensor tendon zones, distal to proximal, from the first toe at the insertion of the big toe extensor to the distal leg proximal to the extensor retinaculum (Figure 4).4 Zone 3 is over the metatarsophalangeal joint; zone 5 is under the extensor retinaculum. The extensor tendon repairs described in this report were in dorsal foot zone 4 (proximal to the metatarsophalangeal joint and over the metatarsals), which would be most comparable to hand extensor zone 6 (proximal to the metacarpal phalangeal joint and over the metacarpals).
The EDL originates on the lateral condyle of the tibia and anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane, passes under the extensor retinaculum, and divides into 4 separate tendons. The 4 tendons split into 3 slips; the central one inserts on the middle phalanx, and the lateral ones insert onto the distal phalanx of the 4 lateral toes, which allows for toe extension.5 The EDL common origin for the muscle belly that serves 4 tendon slips has clinical significance because rehabilitation for one digit will affect the others. Knowledge of the anatomical structures guides the clinical decision making whether it is in the hand or foot. The EDL works synergistically with the extensor digitorum brevis (EDBr) to dorsiflex (extend) the toe phalanges. The EDB originates at the supralateral surface of the calcaneus, lateral talocalcaneal ligament and cruciate crural ligament and inserts at the lateral side of the EDL of second, third, and fourth toes at the level of the metatarsophalangeal joint.6
Repair of lacerated extensor tendons in the foot is the recommended treatment. Chronic extensor lag of the phalanges can result in a claw toe deformity, difficulty controlling the toes when putting on shoes or socks, and catching of the toe on fabric or insoles.7 The extensor tendons are close to the deep and superficial peroneal nerves and to the dorsalis pedis artery, none of which were involved in this case report.
There are case reports and series of EHL repairs that all involves at least 3 weeks of immobilization.4,8,9 The EHL dorsiflexes the big toe. Al-Qattan’s series involved placing K wires across the interphalangeal joint of the big toe and across the metatarsophalangeal joint, which were removed at 6 weeks, in addition to 3.0 polypropylene tendon mattress sutures. All patients in this series healed without tendon rupture or infection. Our PubMed search did not reveal any specific protocol for the EDL or EDB tendons, which are anatomically most comparable to the extensor digitorum communis (EDC) tendons in the hand. The EDC originates at the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, also divides into 4 separate tendons and is responsible for extending the 4 ulnar sided fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joint.10
Tendon repair protocols are a balance between preventing tendon rupture by too aggressive therapy and with preventing tendon adhesions from prolonged immobilization. Orthotic fabrication plays a key early role with blocking possible forces creating unacceptable strain or tension across the surgical repair site. Traditionally, extensor tendon repairs in the hand were immobilized for at least 3 weeks to prevent rupture. This is still the preferred protocol for the patient unwilling or unable to follow instructions. The downside to this method is extension lags, extrinsic tightness, and adhesions that prevent flexion, which can require prolonged therapy or tenolysis surgery to correct.11-13
Early passive motion (EPM) was promoted in the 1980s when studies found better functional outcomes and fewer adhesions. This involved either a dynamic extension splint that relied on elastic bands (Louisville protocol) to keep tension off the repair or the Duran protocol that relied on a static splint and the patient doing the passive exercises with his other uninjured hand. Critics of the EPM protocol point to the costs of the splints and demands of postoperative hand therapy.11
Early active motion (EAM) is the most recent development in hand tendon rehabilitation and starts within days of surgery. Studies have found an earlier regain of total active motion in patients who are mobilized earlier.12 EAM protocols can be divided into controlled active motion (CAM) and relative motion extension splinting (RMES). CAM splints are forearm based and cross more joints. Relative motion splinting is the least restrictive, which makes it less likely that the patient will remove it. Patient friendly splints are ideal because tendon ruptures are often secondary to nonadherence.13 The yoke splint is an example of a RMES, which places the repaired digit in slightly greater extension at the metacarpal phalangeal joint than the other digits (Figure 5), allowing use of the uninjured digits.
The toe extensors do not have the juncturae tendinum connecting the individual EDL tendons to each other, as found between the EDC tendons in the hand. These connective bands can mask a single extensor tendon laceration in the hand when the patient is still able to extend the digit to neutral in the event of a more proximal dorsal hand laceration. A case can be made for closing the skin only in lesser toe extensor injuries in poor surgical candidates because the extensor lag would not be appreciated functionally when wearing shoes. There would be less functional impact when letting a toe extensor go untreated compared with that of a hand extensor. Routine activities such as typing or getting the fingers into a tight pocket could be challenging if hand extensors were untreated. The rehabilitation for toe extensors is more inconvenient when a patient is nonweight bearing, compared with wearing a hand yoke splint.
Conclusion
The case described used an early passive motion protocol without the dynamic splint to rehabilitate the third toe EDL and second toe EDB. This was felt to be the most patient and therapist friendly option, given the previously unchartered territory. The foot orthosis was in stock at the adjacent physical therapy clinic, and the toe booster was created in the hand therapy clinic with readily available supplies. Ideally, one would like to return structures to their anatomic site and control the healing process in the event of a traumatic injury to prevent nonanatomic healing between structures and painful scar adhesions in an area with little subcutaneous tissue. This patient’s tendon repair was still intact at 7 weeks and on his way to recovery, demonstrating good scar management techniques. The risks and benefits to lesser toe tendon repair and recovery would have to be weighed on an individual basis.
Acknowledgments
This project is the result of work supported with resources and use of facilities at the Malcom Randall VA Medical Center in Gainesville, Florida.
1. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. History of HTCC. https://www.htcc.org/consumer-information/about-htcc/history-of-htcc. Accessed November 8, 2019.
2. Coady-Fariborzian L, McGreane A. Comparison of hand emergency triage before and after specialty templates (2007 vs 2012). Hand (N Y). 2015;10(2):215-220.
3. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. Passing rates for the CHT exam. https://www.htcc.org/certify/exam-results/passing-rates. Accessed November 8, 2019.
4. Al-Qattan MM. Surgical treatment and results in 17 cases of open lacerations of the extensor hallucis longus tendon. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60(4):360-367.
5. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum longus. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_longus. Updated December 8, 2011. Accessed November 8, 2019.
6. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum brevis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_brevis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
7. Coughlin M, Schon L. Disorders of tendons. https://musculoskeletalkey.com/disorders-of-tendons-2/#s0035. Published August 27, 2016. Accessed November 8, 2019.
8. Bronner S, Ojofeitimi S, Rose D. Repair and rehabilitation of extensor hallucis longus and brevis tendon lacerations in a professional dancer. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(6):362-370.
9. Wong JC, Daniel JN, Raikin SM. Repair of acute extensor hallucis longus tendon injuries: a retrospective review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014;7(1):45-51.
10. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum communis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_communis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
11. Hall B, Lee H, Page R, Rosenwax L, Lee AH. Comparing three postoperative treatment protocols for extensor tendon repair in zones V and VI of the hand. Am J Occup Ther. 2010;64(5):682-688.
12. Wong AL, Wilson M, Girnary S, Nojoomi M, Acharya S, Paul SM. The optimal orthosis and motion protocol for extensor tendon injury in zones IV-VIII: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017;30(4):447-456.
13. Collocott SJ, Kelly E, Ellis RF. Optimal early active mobilisation protocol after extensor tendon repairs in zones V and VI: a systematic review of literature. Hand Ther. 2018;23(1):3-18.
1. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. History of HTCC. https://www.htcc.org/consumer-information/about-htcc/history-of-htcc. Accessed November 8, 2019.
2. Coady-Fariborzian L, McGreane A. Comparison of hand emergency triage before and after specialty templates (2007 vs 2012). Hand (N Y). 2015;10(2):215-220.
3. Hand Therapy Certification Commission. Passing rates for the CHT exam. https://www.htcc.org/certify/exam-results/passing-rates. Accessed November 8, 2019.
4. Al-Qattan MM. Surgical treatment and results in 17 cases of open lacerations of the extensor hallucis longus tendon. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60(4):360-367.
5. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum longus. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_longus. Updated December 8, 2011. Accessed November 8, 2019.
6. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum brevis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_brevis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
7. Coughlin M, Schon L. Disorders of tendons. https://musculoskeletalkey.com/disorders-of-tendons-2/#s0035. Published August 27, 2016. Accessed November 8, 2019.
8. Bronner S, Ojofeitimi S, Rose D. Repair and rehabilitation of extensor hallucis longus and brevis tendon lacerations in a professional dancer. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(6):362-370.
9. Wong JC, Daniel JN, Raikin SM. Repair of acute extensor hallucis longus tendon injuries: a retrospective review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014;7(1):45-51.
10. Wheeless CR. Wheeless’ textbook of orthopaedics: extensor digitorum communis. http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/extensor_digitorum_communis. Updated March 4, 2018. Accessed November 8, 2019.
11. Hall B, Lee H, Page R, Rosenwax L, Lee AH. Comparing three postoperative treatment protocols for extensor tendon repair in zones V and VI of the hand. Am J Occup Ther. 2010;64(5):682-688.
12. Wong AL, Wilson M, Girnary S, Nojoomi M, Acharya S, Paul SM. The optimal orthosis and motion protocol for extensor tendon injury in zones IV-VIII: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2017;30(4):447-456.
13. Collocott SJ, Kelly E, Ellis RF. Optimal early active mobilisation protocol after extensor tendon repairs in zones V and VI: a systematic review of literature. Hand Ther. 2018;23(1):3-18.
‘Remarkable’ seizure-free rates seen with adjunctive cenobamate
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
In addition, “high rates of seizure freedom were observed with doses of 200 mg and 400 mg,” investigators reported in the Lancet Neurology.
During a 12-week maintenance phase, 21% of patients who received cenobamate 400 mg/day and 11% who received cenobamate 200 mg/day were seizure free, compared with 1% who received placebo. “These data suggest that cenobamate might be a safe and effective treatment option in patients with uncontrolled focal (partial)-onset seizures,” the authors wrote.
On Nov. 21, 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved cenobamate tablets, marketed as Xcopri, to treat focal-onset seizures in adults. The agency noted that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with cenobamate in two randomized, controlled studies and that one patient died when the drug was titrated rapidly during one of the studies that has not been published yet.
Researchers think that cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative, reduces neuronal excitability “by enhancing the fast and slow inactivation of sodium channels and by inhibiting the persistent component of the sodium channel current,” wrote Gregory L. Krauss, MD, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
The rates of seizure freedom with adjunctive cenobamate in the published trial are “a remarkable finding,” wrote Stephan Arnold, MD, an epilepsy specialist at Neurozentrum Nymphenburg in Munich, in an accompanying commentary. Twenty of 95 patients in the 400-mg/day group and 11 of 98 patients in the 200-mg/day group “had no seizures during the 12-week maintenance phase, whereas only 1 patient (1%) of the placebo group remained free of seizures during this period,” Dr. Arnold wrote. “To my knowledge, a seizure freedom rate of 20% or higher has not yet been reported in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of anticonvulsive drugs.”
Still, clinical trials in general are limited by their inclusion and exclusion criteria, relatively short maintenance phases, and the need to keep the dosage of concomitant drugs unchanged during the study, Dr. Arnold noted. “Thus, future findings under real-life conditions will reveal the clinical relevance of cenobamate.”
Hypersensitivity reactions led to protocol adjustments
During the trial, the investigators amended the protocol to lower the starting dose of cenobamate and slow the rate of up-titration to address a risk of allergic drug reactions. “Three hypersensitivity reactions, characterized as rash with involvement of at least one other body system, were reported in three patients” who were assigned to receive cenobamate 200 mg/day, the authors wrote. One case of pruritic rash accompanied by pyrexia occurred on day 10 during the initial faster titration protocol. In another case, “a rash and facial swelling occurred on day 57 in a patient who underwent the amended titration protocol.” These two patients discontinued treatment, and the rashes resolved.
“The third hypersensitivity reaction was a serious case of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms that occurred starting on day 24 of treatment in a patient randomly assigned to receive 200 mg/day of cenobamate during the faster initial titration protocol,” the authors wrote. “Treatment was discontinued and the patient was treated with corticosteroids and recovered within 2 months.”
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue. Most events were mild or moderate. The rate of titration and an inability to adjust the dose of concomitant medications may have contributed to the rate of adverse events, the researchers noted. Treatment-emergent adverse events were most frequent in the 400-mg/day group and led to treatment discontinuation in 20% of patients in this group. An ongoing phase 3 study is assessing a lower starting dose and slower titration rate.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
The 18-week, double-blind, randomized trial published in Lancet Neurology is one of two phase 2 clinical trials of cenobamate. The other phase 2 study, which lasted 12 weeks, is pending publication. For the 18-week study, researchers at 107 centers in 16 countries enrolled more than 430 adults aged 18-70 years with uncontrolled focal epilepsy. Patients were taking one to three concomitant antiepileptic drugs at stable doses for at least 4 weeks before screening. Patients completed an 8-week baseline assessment, followed by a 6-week titration phase and a 12-week maintenance phase.
“During the 8-week baseline assessment, patients had to have eight or more focal aware (simple partial) seizures with a motor component, focal impaired awareness (complex partial) seizures, or focal to bilateral tonic-clonic (secondarily generalized) seizures, with a seizure-free interval of less than 25 days,” Dr. Krauss and colleagues wrote. In addition, participants had to have at least three of these seizures during the first 4 weeks of the baseline assessment and at least three during the last 4 weeks.
The investigators excluded patients who were taking diazepam, phenytoin, or phenobarbital within 1 month of screening because of a potential drug-drug interaction with cenobamate. Other exclusion criteria included clinically significant psychiatric illness and status epilepticus within 3 months of screening.
The researchers assigned patients 1:1:1:1 to receive cenobamate 100 mg/day, cenobamate 200 mg/day, cenobamate 400 mg/day, or placebo. Percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency averaged over 28 days during the 18-week treatment period was the primary efficacy outcome for the FDA. The responder rate (the percentage of patients with at least a 50% reduction from baseline in focal seizure frequency) during the 12-week maintenance phase was the primary efficacy outcome for the European Medicines Agency.
The investigators screened 533 patients and assigned 437 to treatment groups. The modified intention-to-treat population included 434 patients, the modified intention-to-treat maintenance-phase population included 397 patients, and the safety population included 437 patients. The most frequently used concomitant medications were levetiracetam (43%), lamotrigine (32%), and carbamazepine (28%).
The median percentage change from baseline in focal seizure frequency per 28 days during treatment was –24% for the placebo group and –35.5% for the cenobamate 100-mg group. The cenobamate 200 mg group and the cenobamate 400-mg/day group each had a change of –55%.
Responder rates during the maintenance phase were 25% for the placebo group, 40% for the 100-mg group, 56% for the 200-mg group, and 64% for the 400-mg group.
The implications of seizure freedom
The authors acknowledged that it is “difficult to interpret seizure freedom in clinical trials given the constraints of the study designs ... which do not reflect real-life practice. Nonetheless, seizure freedom is of great clinical significance to patient quality of life and the rates reported in this study are notable relative to all other pivotal studies of antiepileptic drug treatment in uncontrolled focal seizures over the past 25 years.”
Rates of seizure freedom represent a crucial outcome measure, Dr. Arnold wrote in his commentary.
“For individual patients, it is not a seizure reduction of 50% or even higher that counts, since this effect will not allow them to drive a car or to work under circumstances bearing increased health risks,” he wrote. “Even when seizure are infrequent, patients nevertheless face the risks of falls, fractures, drowning, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. It is complete seizure control that gives rise for hope of an independent lifestyle.”
The study was funded by SK Life Science, the developer of cenobamate. One of the study authors is an employee of SK Life Science. Dr. Krauss is a consultant or advisor for Eisai, Otsuka, and Shire and has received research support from Biogen, SK Life Science, and UCB. Dr. Arnold had no competing interests.
SOURCE: Krauss GL et al. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Nov 13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30399-0.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY