User login
Asboe-Hansen Sign in Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
To the Editor:
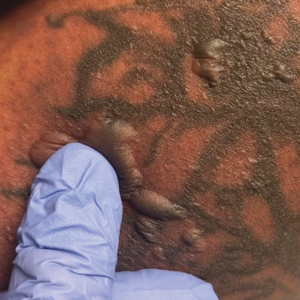
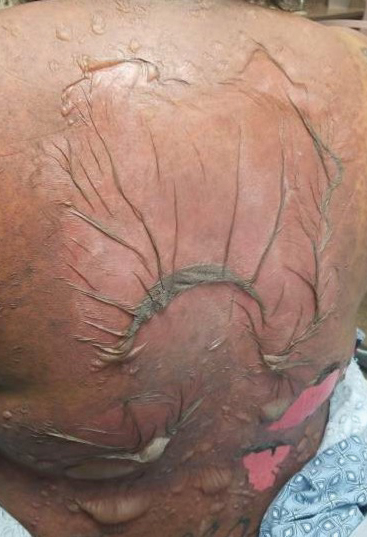
A 25-year-old woman with no notable medical history was admitted to the hospital for suspected Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS). The patient was started on amoxicillin 7 days prior to the skin eruption for prophylaxis before removal of an intrauterine device. On the day of admission, she reported ocular discomfort, dysphagia, and dysuria. She developed erythema of the conjunctivae, face, chest, and proximal upper extremities, as well as erosions of the vermilion lips. She presented to the local emergency department and was transferred to our institution for urgent dermatologic consultation. On physical examination by the dermatology service, the patient had erythematous macules coalescing into patches with overlying flaccid bullae, some denuded, involving the face, chest, abdomen, back (Figure 1), bilateral upper extremities, bilateral thighs, and labia majora and minora. Additionally, she had conjunctivitis, superficial erosions of the vermilion lips, and tense bullae of the palms and soles. On palpation of the flaccid bullae, the Asboe-Hansen sign was elicited (Figure 2 and video). A shave biopsy of the newly elicited bullae was performed. Pathology showed a subepidermal bulla with confluent necrosis of the epidermis and minimal inflammatory infiltrate. An additional shave biopsy of perilesional skin was obtained for direct immunofluorescence, which was negative for IgG, C3, IgM, and IgA. Based on the clinical presentation involving more than 30% of the patient’s body surface area (BSA) and the pathology findings, a diagnosis of toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) was made. The patient remained in the intensive care unit with a multidisciplinary team consisting of dermatology, ophthalmology, gynecology, gastroenterology, and the general surgery burn group. Following treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, systemic corticosteroids, and aggressive wound care, the patient made a full recovery.
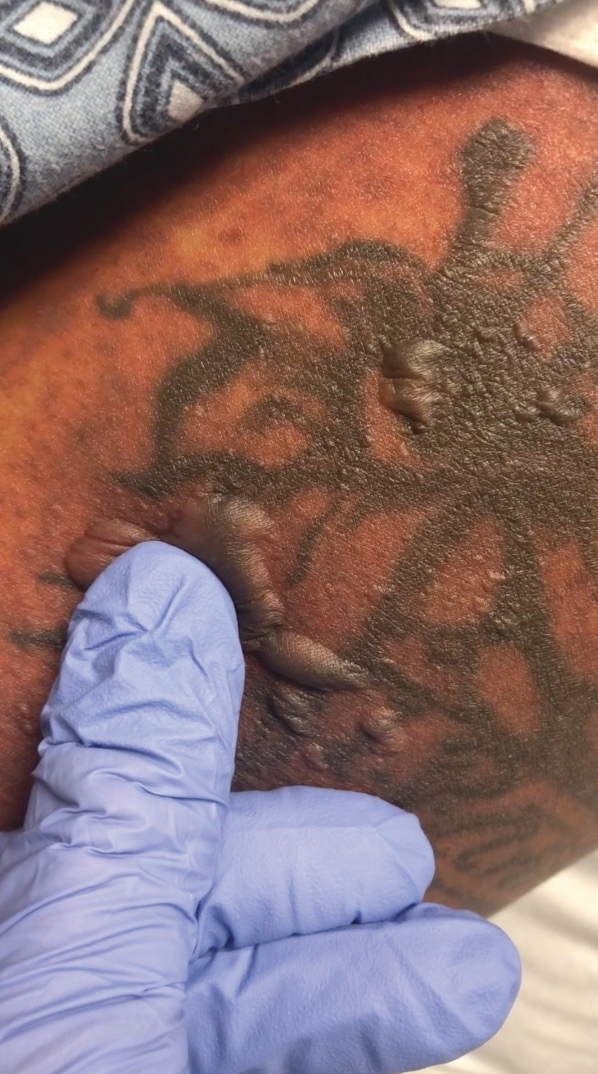
applied to an intact bulla.

Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare, acute, life-threatening mucocutaneous disease within a spectrum of adverse cutaneous drug reactions. The estimated worldwide incidence of TEN is 0.4 to 1.9 per million individuals annually.1 Toxic epidermal necrolysis is clinically characterized by diffuse exfoliation of the skin and mucosae with flaccid bullae. These clinical features are a consequence of extensive keratinocyte death, leading to dermoepidermal junction dissociation. Commonly, there is a prodrome of fever, pharyngitis, and painful skin preceding the diffuse erythema and sloughing of skin and mucous membranes. Lesions typically first appear on the trunk and then follow a centrifugal spread, often sparing the distal aspects of the arms and legs.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis is part of a continuous spectrum with SJS. Less than 10% BSA involvement is considered SJS, 10% to 30% BSA involvement is SJS/TEN overlap, and more than 30% BSA detachment is TEN. Stevens-Johnson syndrome can progress to TEN. In TEN, the distribution of cutaneous lesions is more confluent, and mucosal involvement is more severe.2 The differential diagnosis may include staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis, severe acute graft-vs-host disease, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and invasive fungal dermatitis. An accurate diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as the management and morbidity of these diseases are vastly different. Toxic epidermal necrolysis has an estimated mortality rate of 25% to 30%, with sepsis leading to multiorgan failure being the most common cause of death.3
Although the pathophysiology of TEN has yet to be fully elucidated, it is thought to be a T cell–mediated process with CD8+ cells acting as the primary means of keratinocyte death. An estimated 80% to 95% of cases are due to drug reactions.3 The medications that are most commonly associated with TEN include allopurinol, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticonvulsants. Symptoms typically begin 7 to 21 days after starting the drug. Less commonly, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, dengue virus, cytomegalovirus, and contrast medium have been reported as inciting factors for TEN.2
The diagnosis of TEN is established by correlating clinical features with a histopathologic examination obtained from a lesional skin biopsy. The classic cutaneous features of TEN begin as erythematous, flesh-colored, dusky to violaceous macules and/or morbilliform or targetoid lesions. These early lesions have the tendency to coalesce. The cutaneous findings will eventually progress into flaccid bullae, diffuse epidermal sloughing, and full-thickness skin necrosis.2,3 The evolution of skin lesions may be rapid or may take several days to develop. On palpation, the Nikolsky (lateral shearing of epidermis with minimal pressure) and Asboe-Hansen sign will be positive in patients with SJS/TEN, demonstrating that the associated blisters are flaccid and may be displaced peripherally.4 For an accurate diagnosis, the biopsy must contain full-thickness epidermis. It is imperative to choose a biopsy site from an acute blister, as old lesions of other diseases, such as erythema multiforme, will eventually become necrotic and mimic the histopathologic appearance of SJS/TEN, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.4 Full-thickness epidermal necrosis has a high sensitivity but low specificity for TEN.3 The histologic features of TEN vary depending on the stage of the disease. Classic histologic findings include satellite necrosis of keratinocytes followed by full-thickness necrosis of keratinocytes and perivascular lymphoid infiltrates. The stratum corneum retains its original structure.4
The Asboe-Hansen sign, also known as the bulla spread sign, was originally described in 1960 as a diagnostic sign for pemphigus vulgaris.5 A positive Asboe-Hansen sign demonstrates the ability to enlarge a bulla in the lateral direction by applying perpendicular mechanical pressure to the roof of an intact bulla. The bulla is extended to adjacent nonblistered skin.6 A positive sign demonstrates decreased adhesion between keratinocytes or between the basal epidermal cells and the dermal connective tissue.5 In addition to pemphigus vulgaris, the Asboe-Hansen sign may be positive in TEN and SJS, as well as other diseases affecting the dermoepidermal junction including pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus vegetans, and bullous pemphigoid. Asboe-Hansen5 made the argument that a fresh bulla should be biopsied if histopathologic diagnosis is necessary, as older bullae may exhibit epithelial cell regeneration and disturb an accurate diagnosis.
Accurate and early diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as prognosis is strongly correlated with the speed at which the offending drug is discontinued and appropriate medical treatment is initiated. Prompt withdrawal of the offending drug has been reported to reduce the risk for morbidity by 30% per day.7 Although classically associated with the pemphigus group of diseases, the Asboe-Hansen sign is of diagnostic value to the pathologist in diagnosing TEN by reproducing the same microscopic appearance of a fresh spontaneous blister. Due to the notable morbidity and mortality in SJS and TEN, the Asboe-Hansen sign should be attempted for the site of a lesional biopsy, as an accurate diagnosis relies on clinicopathologic correlation.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part I. introduction, history, classification, clinical features, systemic manifestations, etiology, and immunopathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:173.e1-173.e13.
- Frech LE, Prins C. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Schaffer J, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2012:332-347.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part II. prognosis, sequelae, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:187.e1–187.e16.
- Elston D, Stratman E, Miller S. Skin biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1-16.
- Asboe-Hansen G. Blister-spread induced by finger-pressure, a diagnostic sign in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1960;34:5-9.
- Ganapati S. Eponymous dermatological signs in bullous dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:21-23.
- Garcia-Doval I, Lecleach L, Bocquet H, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:323-327.
To the Editor:
A 25-year-old woman with no notable medical history was admitted to the hospital for suspected Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS). The patient was started on amoxicillin 7 days prior to the skin eruption for prophylaxis before removal of an intrauterine device. On the day of admission, she reported ocular discomfort, dysphagia, and dysuria. She developed erythema of the conjunctivae, face, chest, and proximal upper extremities, as well as erosions of the vermilion lips. She presented to the local emergency department and was transferred to our institution for urgent dermatologic consultation. On physical examination by the dermatology service, the patient had erythematous macules coalescing into patches with overlying flaccid bullae, some denuded, involving the face, chest, abdomen, back (Figure 1), bilateral upper extremities, bilateral thighs, and labia majora and minora. Additionally, she had conjunctivitis, superficial erosions of the vermilion lips, and tense bullae of the palms and soles. On palpation of the flaccid bullae, the Asboe-Hansen sign was elicited (Figure 2 and video). A shave biopsy of the newly elicited bullae was performed. Pathology showed a subepidermal bulla with confluent necrosis of the epidermis and minimal inflammatory infiltrate. An additional shave biopsy of perilesional skin was obtained for direct immunofluorescence, which was negative for IgG, C3, IgM, and IgA. Based on the clinical presentation involving more than 30% of the patient’s body surface area (BSA) and the pathology findings, a diagnosis of toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) was made. The patient remained in the intensive care unit with a multidisciplinary team consisting of dermatology, ophthalmology, gynecology, gastroenterology, and the general surgery burn group. Following treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, systemic corticosteroids, and aggressive wound care, the patient made a full recovery.


applied to an intact bulla.

Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare, acute, life-threatening mucocutaneous disease within a spectrum of adverse cutaneous drug reactions. The estimated worldwide incidence of TEN is 0.4 to 1.9 per million individuals annually.1 Toxic epidermal necrolysis is clinically characterized by diffuse exfoliation of the skin and mucosae with flaccid bullae. These clinical features are a consequence of extensive keratinocyte death, leading to dermoepidermal junction dissociation. Commonly, there is a prodrome of fever, pharyngitis, and painful skin preceding the diffuse erythema and sloughing of skin and mucous membranes. Lesions typically first appear on the trunk and then follow a centrifugal spread, often sparing the distal aspects of the arms and legs.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis is part of a continuous spectrum with SJS. Less than 10% BSA involvement is considered SJS, 10% to 30% BSA involvement is SJS/TEN overlap, and more than 30% BSA detachment is TEN. Stevens-Johnson syndrome can progress to TEN. In TEN, the distribution of cutaneous lesions is more confluent, and mucosal involvement is more severe.2 The differential diagnosis may include staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis, severe acute graft-vs-host disease, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and invasive fungal dermatitis. An accurate diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as the management and morbidity of these diseases are vastly different. Toxic epidermal necrolysis has an estimated mortality rate of 25% to 30%, with sepsis leading to multiorgan failure being the most common cause of death.3
Although the pathophysiology of TEN has yet to be fully elucidated, it is thought to be a T cell–mediated process with CD8+ cells acting as the primary means of keratinocyte death. An estimated 80% to 95% of cases are due to drug reactions.3 The medications that are most commonly associated with TEN include allopurinol, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticonvulsants. Symptoms typically begin 7 to 21 days after starting the drug. Less commonly, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, dengue virus, cytomegalovirus, and contrast medium have been reported as inciting factors for TEN.2
The diagnosis of TEN is established by correlating clinical features with a histopathologic examination obtained from a lesional skin biopsy. The classic cutaneous features of TEN begin as erythematous, flesh-colored, dusky to violaceous macules and/or morbilliform or targetoid lesions. These early lesions have the tendency to coalesce. The cutaneous findings will eventually progress into flaccid bullae, diffuse epidermal sloughing, and full-thickness skin necrosis.2,3 The evolution of skin lesions may be rapid or may take several days to develop. On palpation, the Nikolsky (lateral shearing of epidermis with minimal pressure) and Asboe-Hansen sign will be positive in patients with SJS/TEN, demonstrating that the associated blisters are flaccid and may be displaced peripherally.4 For an accurate diagnosis, the biopsy must contain full-thickness epidermis. It is imperative to choose a biopsy site from an acute blister, as old lesions of other diseases, such as erythema multiforme, will eventually become necrotic and mimic the histopathologic appearance of SJS/TEN, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.4 Full-thickness epidermal necrosis has a high sensitivity but low specificity for TEN.3 The histologic features of TEN vary depending on the stage of the disease. Classic histologic findings include satellite necrosis of keratinocytes followed by full-thickness necrosis of keratinocytes and perivascular lymphoid infiltrates. The stratum corneum retains its original structure.4
The Asboe-Hansen sign, also known as the bulla spread sign, was originally described in 1960 as a diagnostic sign for pemphigus vulgaris.5 A positive Asboe-Hansen sign demonstrates the ability to enlarge a bulla in the lateral direction by applying perpendicular mechanical pressure to the roof of an intact bulla. The bulla is extended to adjacent nonblistered skin.6 A positive sign demonstrates decreased adhesion between keratinocytes or between the basal epidermal cells and the dermal connective tissue.5 In addition to pemphigus vulgaris, the Asboe-Hansen sign may be positive in TEN and SJS, as well as other diseases affecting the dermoepidermal junction including pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus vegetans, and bullous pemphigoid. Asboe-Hansen5 made the argument that a fresh bulla should be biopsied if histopathologic diagnosis is necessary, as older bullae may exhibit epithelial cell regeneration and disturb an accurate diagnosis.
Accurate and early diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as prognosis is strongly correlated with the speed at which the offending drug is discontinued and appropriate medical treatment is initiated. Prompt withdrawal of the offending drug has been reported to reduce the risk for morbidity by 30% per day.7 Although classically associated with the pemphigus group of diseases, the Asboe-Hansen sign is of diagnostic value to the pathologist in diagnosing TEN by reproducing the same microscopic appearance of a fresh spontaneous blister. Due to the notable morbidity and mortality in SJS and TEN, the Asboe-Hansen sign should be attempted for the site of a lesional biopsy, as an accurate diagnosis relies on clinicopathologic correlation.
To the Editor:
A 25-year-old woman with no notable medical history was admitted to the hospital for suspected Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS). The patient was started on amoxicillin 7 days prior to the skin eruption for prophylaxis before removal of an intrauterine device. On the day of admission, she reported ocular discomfort, dysphagia, and dysuria. She developed erythema of the conjunctivae, face, chest, and proximal upper extremities, as well as erosions of the vermilion lips. She presented to the local emergency department and was transferred to our institution for urgent dermatologic consultation. On physical examination by the dermatology service, the patient had erythematous macules coalescing into patches with overlying flaccid bullae, some denuded, involving the face, chest, abdomen, back (Figure 1), bilateral upper extremities, bilateral thighs, and labia majora and minora. Additionally, she had conjunctivitis, superficial erosions of the vermilion lips, and tense bullae of the palms and soles. On palpation of the flaccid bullae, the Asboe-Hansen sign was elicited (Figure 2 and video). A shave biopsy of the newly elicited bullae was performed. Pathology showed a subepidermal bulla with confluent necrosis of the epidermis and minimal inflammatory infiltrate. An additional shave biopsy of perilesional skin was obtained for direct immunofluorescence, which was negative for IgG, C3, IgM, and IgA. Based on the clinical presentation involving more than 30% of the patient’s body surface area (BSA) and the pathology findings, a diagnosis of toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) was made. The patient remained in the intensive care unit with a multidisciplinary team consisting of dermatology, ophthalmology, gynecology, gastroenterology, and the general surgery burn group. Following treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin, systemic corticosteroids, and aggressive wound care, the patient made a full recovery.


applied to an intact bulla.

Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a rare, acute, life-threatening mucocutaneous disease within a spectrum of adverse cutaneous drug reactions. The estimated worldwide incidence of TEN is 0.4 to 1.9 per million individuals annually.1 Toxic epidermal necrolysis is clinically characterized by diffuse exfoliation of the skin and mucosae with flaccid bullae. These clinical features are a consequence of extensive keratinocyte death, leading to dermoepidermal junction dissociation. Commonly, there is a prodrome of fever, pharyngitis, and painful skin preceding the diffuse erythema and sloughing of skin and mucous membranes. Lesions typically first appear on the trunk and then follow a centrifugal spread, often sparing the distal aspects of the arms and legs.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis is part of a continuous spectrum with SJS. Less than 10% BSA involvement is considered SJS, 10% to 30% BSA involvement is SJS/TEN overlap, and more than 30% BSA detachment is TEN. Stevens-Johnson syndrome can progress to TEN. In TEN, the distribution of cutaneous lesions is more confluent, and mucosal involvement is more severe.2 The differential diagnosis may include staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis, severe acute graft-vs-host disease, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and invasive fungal dermatitis. An accurate diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as the management and morbidity of these diseases are vastly different. Toxic epidermal necrolysis has an estimated mortality rate of 25% to 30%, with sepsis leading to multiorgan failure being the most common cause of death.3
Although the pathophysiology of TEN has yet to be fully elucidated, it is thought to be a T cell–mediated process with CD8+ cells acting as the primary means of keratinocyte death. An estimated 80% to 95% of cases are due to drug reactions.3 The medications that are most commonly associated with TEN include allopurinol, antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticonvulsants. Symptoms typically begin 7 to 21 days after starting the drug. Less commonly, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, dengue virus, cytomegalovirus, and contrast medium have been reported as inciting factors for TEN.2
The diagnosis of TEN is established by correlating clinical features with a histopathologic examination obtained from a lesional skin biopsy. The classic cutaneous features of TEN begin as erythematous, flesh-colored, dusky to violaceous macules and/or morbilliform or targetoid lesions. These early lesions have the tendency to coalesce. The cutaneous findings will eventually progress into flaccid bullae, diffuse epidermal sloughing, and full-thickness skin necrosis.2,3 The evolution of skin lesions may be rapid or may take several days to develop. On palpation, the Nikolsky (lateral shearing of epidermis with minimal pressure) and Asboe-Hansen sign will be positive in patients with SJS/TEN, demonstrating that the associated blisters are flaccid and may be displaced peripherally.4 For an accurate diagnosis, the biopsy must contain full-thickness epidermis. It is imperative to choose a biopsy site from an acute blister, as old lesions of other diseases, such as erythema multiforme, will eventually become necrotic and mimic the histopathologic appearance of SJS/TEN, potentially leading to an incorrect diagnosis.4 Full-thickness epidermal necrosis has a high sensitivity but low specificity for TEN.3 The histologic features of TEN vary depending on the stage of the disease. Classic histologic findings include satellite necrosis of keratinocytes followed by full-thickness necrosis of keratinocytes and perivascular lymphoid infiltrates. The stratum corneum retains its original structure.4
The Asboe-Hansen sign, also known as the bulla spread sign, was originally described in 1960 as a diagnostic sign for pemphigus vulgaris.5 A positive Asboe-Hansen sign demonstrates the ability to enlarge a bulla in the lateral direction by applying perpendicular mechanical pressure to the roof of an intact bulla. The bulla is extended to adjacent nonblistered skin.6 A positive sign demonstrates decreased adhesion between keratinocytes or between the basal epidermal cells and the dermal connective tissue.5 In addition to pemphigus vulgaris, the Asboe-Hansen sign may be positive in TEN and SJS, as well as other diseases affecting the dermoepidermal junction including pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus vegetans, and bullous pemphigoid. Asboe-Hansen5 made the argument that a fresh bulla should be biopsied if histopathologic diagnosis is necessary, as older bullae may exhibit epithelial cell regeneration and disturb an accurate diagnosis.
Accurate and early diagnosis of TEN is imperative, as prognosis is strongly correlated with the speed at which the offending drug is discontinued and appropriate medical treatment is initiated. Prompt withdrawal of the offending drug has been reported to reduce the risk for morbidity by 30% per day.7 Although classically associated with the pemphigus group of diseases, the Asboe-Hansen sign is of diagnostic value to the pathologist in diagnosing TEN by reproducing the same microscopic appearance of a fresh spontaneous blister. Due to the notable morbidity and mortality in SJS and TEN, the Asboe-Hansen sign should be attempted for the site of a lesional biopsy, as an accurate diagnosis relies on clinicopathologic correlation.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part I. introduction, history, classification, clinical features, systemic manifestations, etiology, and immunopathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:173.e1-173.e13.
- Frech LE, Prins C. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Schaffer J, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2012:332-347.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part II. prognosis, sequelae, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:187.e1–187.e16.
- Elston D, Stratman E, Miller S. Skin biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1-16.
- Asboe-Hansen G. Blister-spread induced by finger-pressure, a diagnostic sign in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1960;34:5-9.
- Ganapati S. Eponymous dermatological signs in bullous dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:21-23.
- Garcia-Doval I, Lecleach L, Bocquet H, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:323-327.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part I. introduction, history, classification, clinical features, systemic manifestations, etiology, and immunopathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:173.e1-173.e13.
- Frech LE, Prins C. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo J, Schaffer J, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Elsevier; 2012:332-347.
- Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part II. prognosis, sequelae, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:187.e1–187.e16.
- Elston D, Stratman E, Miller S. Skin biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1-16.
- Asboe-Hansen G. Blister-spread induced by finger-pressure, a diagnostic sign in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1960;34:5-9.
- Ganapati S. Eponymous dermatological signs in bullous dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:21-23.
- Garcia-Doval I, Lecleach L, Bocquet H, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:323-327.
Practice Points
- Asboe-Hansen sign is a useful clinical tool for diagnosing toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
- Asboe-Hansen sign can be employed to generate a fresh bulla for lesional skin biopsy in the evaluation of TEN.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in gastroenterology
SAN FRANCISCO – Artificial intelligence (AI) is using computer technology to solve particular kinds of medical problems, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD, AGAF, chair, division of gastroenterology, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.

Computers are good at doing many processes in a short period of time and executing repetitive tasks with no errors, whereas humans tend to introduce errors after many repetitions. Using algorithms by which physicians assess and diagnose colonic lesions, computer software can learn the criteria that diagnose adenomas and assist in the process of diagnosis, Dr. Guha said.
Computers are also ideal for managing and analyzing large amounts of data – this ability has so far been used to personalize cancer treatment – and is now being used to suggest the best treatment and predict remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. AI can use anatomical data combined with endoscopy to predict GI bleeding so that physicians can target therapy. Dr. Guha predicts that there will be an “explosion” of applications of AI in gastroenterology in the next 5-10 years.
SAN FRANCISCO – Artificial intelligence (AI) is using computer technology to solve particular kinds of medical problems, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD, AGAF, chair, division of gastroenterology, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.

Computers are good at doing many processes in a short period of time and executing repetitive tasks with no errors, whereas humans tend to introduce errors after many repetitions. Using algorithms by which physicians assess and diagnose colonic lesions, computer software can learn the criteria that diagnose adenomas and assist in the process of diagnosis, Dr. Guha said.
Computers are also ideal for managing and analyzing large amounts of data – this ability has so far been used to personalize cancer treatment – and is now being used to suggest the best treatment and predict remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. AI can use anatomical data combined with endoscopy to predict GI bleeding so that physicians can target therapy. Dr. Guha predicts that there will be an “explosion” of applications of AI in gastroenterology in the next 5-10 years.
SAN FRANCISCO – Artificial intelligence (AI) is using computer technology to solve particular kinds of medical problems, Sushovan Guha, MD, PhD, AGAF, chair, division of gastroenterology, University of Arizona, Phoenix, said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.

Computers are good at doing many processes in a short period of time and executing repetitive tasks with no errors, whereas humans tend to introduce errors after many repetitions. Using algorithms by which physicians assess and diagnose colonic lesions, computer software can learn the criteria that diagnose adenomas and assist in the process of diagnosis, Dr. Guha said.
Computers are also ideal for managing and analyzing large amounts of data – this ability has so far been used to personalize cancer treatment – and is now being used to suggest the best treatment and predict remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. AI can use anatomical data combined with endoscopy to predict GI bleeding so that physicians can target therapy. Dr. Guha predicts that there will be an “explosion” of applications of AI in gastroenterology in the next 5-10 years.
REPORTING FROM 2019 AGA TECH SUMMIT
Symmetric Lichen Amyloidosis: An Atypical Location on the Bilateral Extensor Surfaces of the Arms
To the Editor:
Lichen amyloidosis (LA) classically presents as a pruritic, hyperkeratotic, papular eruption localized to the pretibial surface of the legs.1 Nonpruritic and generalized variants have been reported but are rare.2 Although it is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, LA is a benign condition but is difficult to eradicate.1 The precise pathophysiology is poorly understood, but chronic frictional irritation is closely associated with the eruption. We present a nongeneralized case of LA in an atypical location.
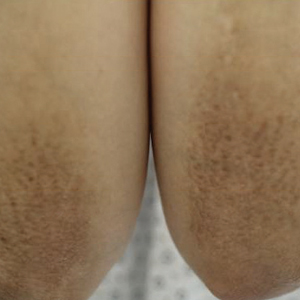
A healthy 30-year-old woman presented with an intermittent itchy rash on the elbows and knees of 2 years’ duration. The patient was first diagnosed with lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) and initially responded well to treatment with fluocinonide ointment 0.05%. Nearly 2 years after the initial presentation, she developed recurrent symptoms and sought further treatment. She reported frequent scratching in association with episodes of anxiety. Examination revealed numerous 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored to light brown, monomorphic, dome-shaped papules over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms and left pretibial surface (Figure 1).
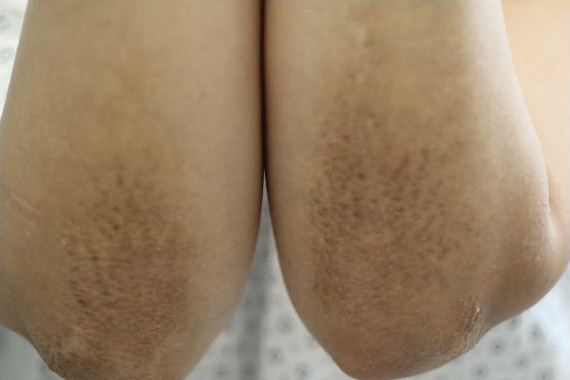
papules (1–3 mm) over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms.
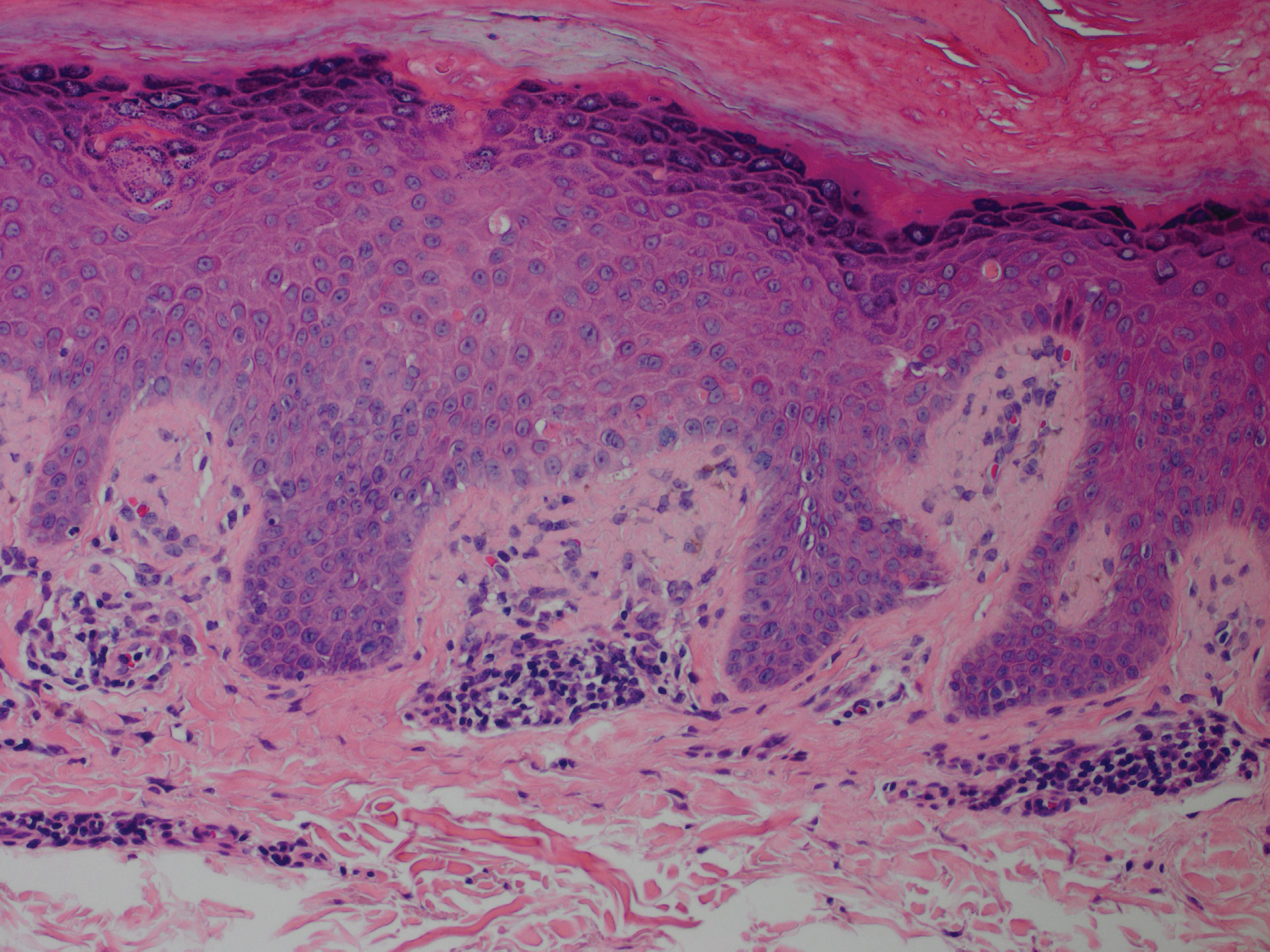
Although in an atypical location, LA was clinically suspected due to the morphology, and a biopsy was performed given the evolving nature of the lesions. The differential diagnosis included LSC, hypertrophic lichen planus, papular mucinosis, prurigo nodularis, and pretibial myxedema. Pathology revealed small eosinophilic globules in the papillary dermis (Figure 2), and cytokeratin 5/6 immunostaining showed amorphous papillary dermal deposits consistent with keratin-derived amyloid deposition (Figure 3). The deposits stained positive for Congo red and displayed apple green birefringence under polarized light. Thus, the diagnosis of LA was confirmed. After limited success with triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, the patient was transitioned to clobetasol cream 0.05% with notable physical and symptomatic improvement.
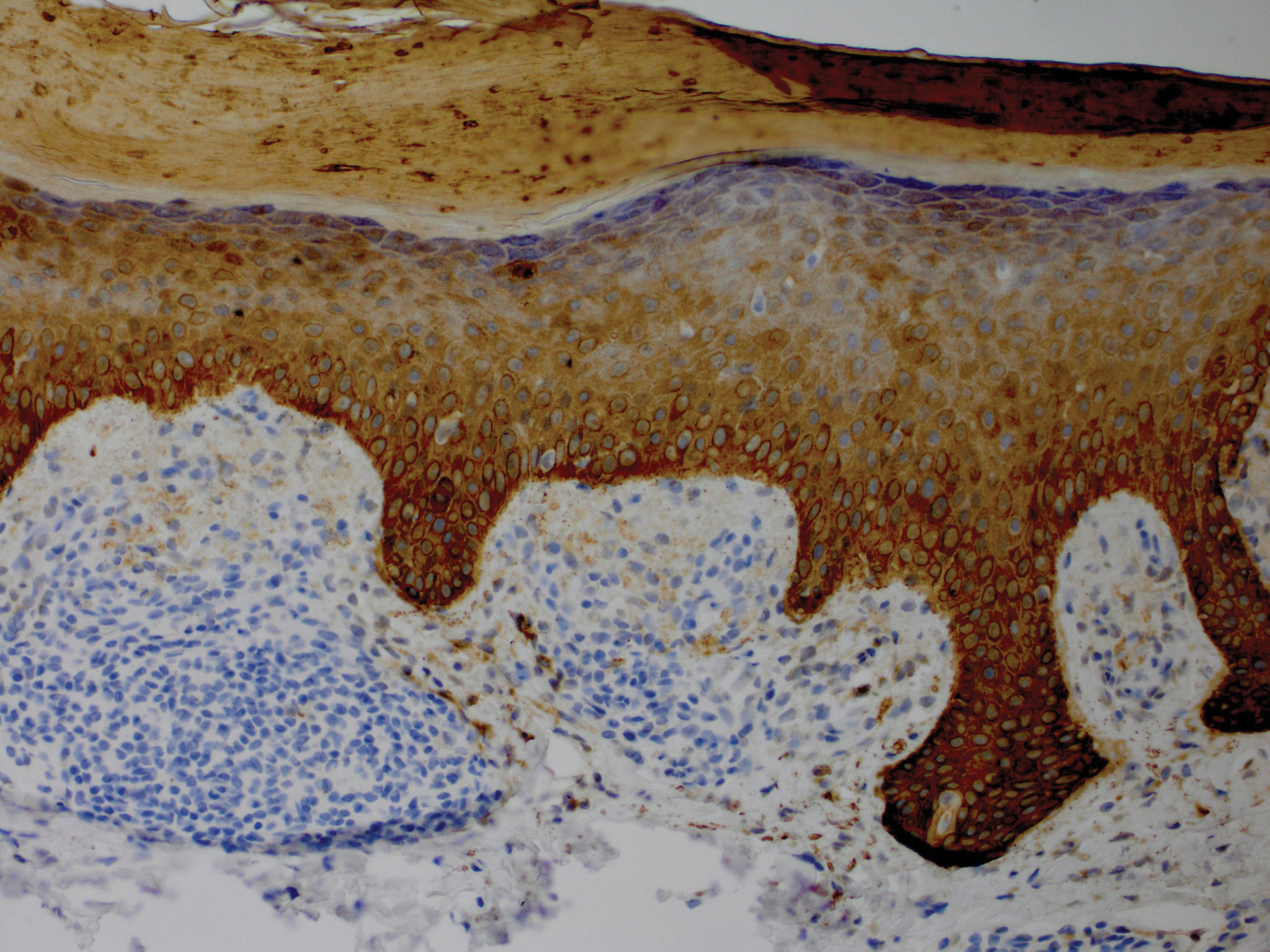
Amyloidosis is histopathologically characterized by extracellular deposits of amyloid, a polypeptide that polymerizes to form cross-β sheets.3 It is believed that the deposits seen in localized amyloidosis result from local production of amyloid, as opposed to the deposition of circulating light chains that is characteristic of systemic amyloidosis.3 Lichen amyloidosis is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis.1 The amyloid in this condition has been found to react immunohistochemically with antikeratin antibody, leading to the conclusion that the amyloid is formed by degeneration of keratinocytes locally due to chronic rubbing and scratching.
4-6
The possibility remains that this patient first presented with LSC 2 years prior and secondarily developed LA due to chronic trauma. Indeed, LA has been proposed as a variant of LSC. In both conditions, scratching seems to be the most important factor in the development of lesions. It has been proposed that treatment should primarily focus on the amelioration of pruritus.5
Five percent to 10% of cases of LA have been found to have some form of upper extremity involvement.7 However, these cases typically are associated with a generalized presentation involving the trunk and arms.2,7 Our patient had no evidence of disease elsewhere. When evaluating a localized, pruritic, monomorphic, papular eruption on the extensor surfaces of the arms, LA may be an important consideration.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis. clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Kandhari R, Ramesh V, Singh A. A generalized, non-pruritic variant of lichen amyloidosis: a case report and a brief review. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:328.
- Biewend ML, Menke DM, Calamia KT. The spectrum of localized amyloidosis: a case series of 20 patients and review of the literature. Amyloid. 2006;13:135-142.
- Jambrosic J, From L, Hanna W. Lichen amyloidosus. ultrastructure and pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:151-158.
- Weyers W, Weyers I, Bonczkowitz M, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a consequence of scratching. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:923-928.
- Kumakiri M, Hashimoto K. Histogenesis of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: sequential change of epidermal keratinocytes to amyloid via filamentous degeneration. J Invest Dermatol. 1979;73:150-162.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosus: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
To the Editor:
Lichen amyloidosis (LA) classically presents as a pruritic, hyperkeratotic, papular eruption localized to the pretibial surface of the legs.1 Nonpruritic and generalized variants have been reported but are rare.2 Although it is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, LA is a benign condition but is difficult to eradicate.1 The precise pathophysiology is poorly understood, but chronic frictional irritation is closely associated with the eruption. We present a nongeneralized case of LA in an atypical location.
A healthy 30-year-old woman presented with an intermittent itchy rash on the elbows and knees of 2 years’ duration. The patient was first diagnosed with lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) and initially responded well to treatment with fluocinonide ointment 0.05%. Nearly 2 years after the initial presentation, she developed recurrent symptoms and sought further treatment. She reported frequent scratching in association with episodes of anxiety. Examination revealed numerous 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored to light brown, monomorphic, dome-shaped papules over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms and left pretibial surface (Figure 1).

papules (1–3 mm) over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms.
Although in an atypical location, LA was clinically suspected due to the morphology, and a biopsy was performed given the evolving nature of the lesions. The differential diagnosis included LSC, hypertrophic lichen planus, papular mucinosis, prurigo nodularis, and pretibial myxedema. Pathology revealed small eosinophilic globules in the papillary dermis (Figure 2), and cytokeratin 5/6 immunostaining showed amorphous papillary dermal deposits consistent with keratin-derived amyloid deposition (Figure 3). The deposits stained positive for Congo red and displayed apple green birefringence under polarized light. Thus, the diagnosis of LA was confirmed. After limited success with triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, the patient was transitioned to clobetasol cream 0.05% with notable physical and symptomatic improvement.


Amyloidosis is histopathologically characterized by extracellular deposits of amyloid, a polypeptide that polymerizes to form cross-β sheets.3 It is believed that the deposits seen in localized amyloidosis result from local production of amyloid, as opposed to the deposition of circulating light chains that is characteristic of systemic amyloidosis.3 Lichen amyloidosis is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis.1 The amyloid in this condition has been found to react immunohistochemically with antikeratin antibody, leading to the conclusion that the amyloid is formed by degeneration of keratinocytes locally due to chronic rubbing and scratching.
4-6
The possibility remains that this patient first presented with LSC 2 years prior and secondarily developed LA due to chronic trauma. Indeed, LA has been proposed as a variant of LSC. In both conditions, scratching seems to be the most important factor in the development of lesions. It has been proposed that treatment should primarily focus on the amelioration of pruritus.5
Five percent to 10% of cases of LA have been found to have some form of upper extremity involvement.7 However, these cases typically are associated with a generalized presentation involving the trunk and arms.2,7 Our patient had no evidence of disease elsewhere. When evaluating a localized, pruritic, monomorphic, papular eruption on the extensor surfaces of the arms, LA may be an important consideration.
To the Editor:
Lichen amyloidosis (LA) classically presents as a pruritic, hyperkeratotic, papular eruption localized to the pretibial surface of the legs.1 Nonpruritic and generalized variants have been reported but are rare.2 Although it is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, LA is a benign condition but is difficult to eradicate.1 The precise pathophysiology is poorly understood, but chronic frictional irritation is closely associated with the eruption. We present a nongeneralized case of LA in an atypical location.
A healthy 30-year-old woman presented with an intermittent itchy rash on the elbows and knees of 2 years’ duration. The patient was first diagnosed with lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) and initially responded well to treatment with fluocinonide ointment 0.05%. Nearly 2 years after the initial presentation, she developed recurrent symptoms and sought further treatment. She reported frequent scratching in association with episodes of anxiety. Examination revealed numerous 1- to 3-mm, flesh-colored to light brown, monomorphic, dome-shaped papules over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms and left pretibial surface (Figure 1).

papules (1–3 mm) over the extensor surfaces of the bilateral arms.
Although in an atypical location, LA was clinically suspected due to the morphology, and a biopsy was performed given the evolving nature of the lesions. The differential diagnosis included LSC, hypertrophic lichen planus, papular mucinosis, prurigo nodularis, and pretibial myxedema. Pathology revealed small eosinophilic globules in the papillary dermis (Figure 2), and cytokeratin 5/6 immunostaining showed amorphous papillary dermal deposits consistent with keratin-derived amyloid deposition (Figure 3). The deposits stained positive for Congo red and displayed apple green birefringence under polarized light. Thus, the diagnosis of LA was confirmed. After limited success with triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, the patient was transitioned to clobetasol cream 0.05% with notable physical and symptomatic improvement.


Amyloidosis is histopathologically characterized by extracellular deposits of amyloid, a polypeptide that polymerizes to form cross-β sheets.3 It is believed that the deposits seen in localized amyloidosis result from local production of amyloid, as opposed to the deposition of circulating light chains that is characteristic of systemic amyloidosis.3 Lichen amyloidosis is the most common subtype of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis.1 The amyloid in this condition has been found to react immunohistochemically with antikeratin antibody, leading to the conclusion that the amyloid is formed by degeneration of keratinocytes locally due to chronic rubbing and scratching.
4-6
The possibility remains that this patient first presented with LSC 2 years prior and secondarily developed LA due to chronic trauma. Indeed, LA has been proposed as a variant of LSC. In both conditions, scratching seems to be the most important factor in the development of lesions. It has been proposed that treatment should primarily focus on the amelioration of pruritus.5
Five percent to 10% of cases of LA have been found to have some form of upper extremity involvement.7 However, these cases typically are associated with a generalized presentation involving the trunk and arms.2,7 Our patient had no evidence of disease elsewhere. When evaluating a localized, pruritic, monomorphic, papular eruption on the extensor surfaces of the arms, LA may be an important consideration.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis. clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Kandhari R, Ramesh V, Singh A. A generalized, non-pruritic variant of lichen amyloidosis: a case report and a brief review. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:328.
- Biewend ML, Menke DM, Calamia KT. The spectrum of localized amyloidosis: a case series of 20 patients and review of the literature. Amyloid. 2006;13:135-142.
- Jambrosic J, From L, Hanna W. Lichen amyloidosus. ultrastructure and pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:151-158.
- Weyers W, Weyers I, Bonczkowitz M, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a consequence of scratching. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:923-928.
- Kumakiri M, Hashimoto K. Histogenesis of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: sequential change of epidermal keratinocytes to amyloid via filamentous degeneration. J Invest Dermatol. 1979;73:150-162.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosus: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
- Tay CH, Dacosta JL. Lichen amyloidosis. clinical study of 40 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1970;82:129-136.
- Kandhari R, Ramesh V, Singh A. A generalized, non-pruritic variant of lichen amyloidosis: a case report and a brief review. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:328.
- Biewend ML, Menke DM, Calamia KT. The spectrum of localized amyloidosis: a case series of 20 patients and review of the literature. Amyloid. 2006;13:135-142.
- Jambrosic J, From L, Hanna W. Lichen amyloidosus. ultrastructure and pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1984;6:151-158.
- Weyers W, Weyers I, Bonczkowitz M, et al. Lichen amyloidosis: a consequence of scratching. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:923-928.
- Kumakiri M, Hashimoto K. Histogenesis of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis: sequential change of epidermal keratinocytes to amyloid via filamentous degeneration. J Invest Dermatol. 1979;73:150-162.
- Salim T, Shenoi SD, Balachandran C, et al. Lichen amyloidosus: a study of clinical, histopathologic and immunofluorescence findings in 30 cases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2005;71:166-169.
Practice Points
- Lichen amyloidosis (LA) classically presents as a pruritic and papular eruption localized to the pretibial surface of the legs.
- Nonpruritic and generalized variants are rare.
- This case represents a pruritic and nongeneralized
case located on the arms; LA should be considered
for any localized and pruritic eruption on the arms.
Bipartisanship breaks out at House hearing on insulin prices
Who’s responsible for the rising cost of insulin? Manufacturers and pharmacy benefit managers pointed their fingers at each other on April 10 at a congressional hearing.
In response, Democrats and Republicans on the House Energy & Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations said they might just take matters into their own hands.
Rebates and discounts are the drivers, according to leaders from three insulin manufacturers.
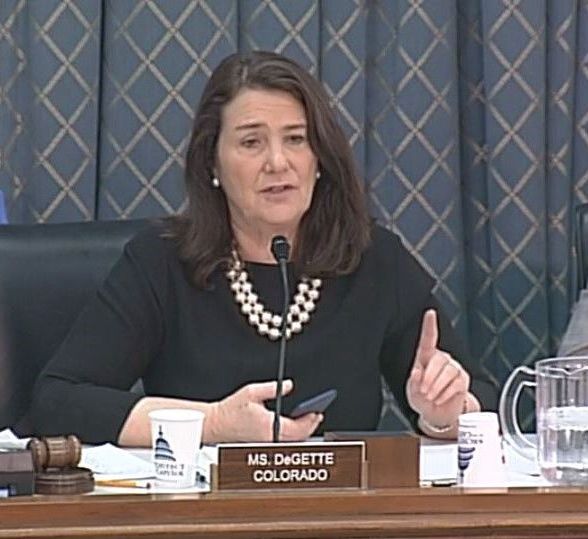
Mike Mason, a senior vice president of Eli Lilly & Co., was put on the defensive immediately by Subcommittee Chairman Diana DeGette (D-Colo.), who asked him to justify the increases in list prices during the last 10 years.
“Seventy-five percent of our list price is paid for rebates and discounts to secure access so people have affordable access,” Mr. Mason said.
He was cut off in his response as Rep. DeGette pressed further: “So that’s what’s making the price go up and up.”
To which Mr. Mason responded, “$210 of a vial of Humalog is paid for discounts and rebates.” It was noted during the hearing that a vial has a list price of $275.
Doug Langa, an executive vice president at Novo Nordisk, agreed. “There is significant demand for rebates.”
Kathleen Tregoning, an executive vice president at Sanofi, added that, as part of setting the list price, “we have to look at the dynamics of the supply chain, including the rebates.”
Leaders of several pharmacy benefit managers disagreed.
Rep. DeGette asked Thomas M. Moriarty, an executive vice president and general counsel at CVS Health whether he thought rebates were forcing manufacturers to raise list prices. His response? “I do not, no.”
Amy Bricker, a senior vice president at Express Scripts concurred. “I have no idea why list prices are high, and it’s not a result of rebates.”
Sumit Dutta, MD, a senior vice president and chief medical officer at OptumRx, added that there have been list prices rising double digits in nonrebated drugs, in generics where a manufacturer buys out the market to create a monopoly.
“We can’t see a correlation just when rebates raise list prices,” Dr. Dutta said.
While the PBMs denied the rebate system played any role in the setting of list prices, they were firm in maintaining secrecy in rebating process.
When asked by Rep. John Sarbanes (D-Md.) whether the public should be able to track the list price and see the rebates, the net prices, and the savings that are passed along to the consumer, Ms. Bricker said “we don’t believe so.”
She continued: “The reason I’m able to get the discounts that I can from the manufacturer is because it is confidential.”
And while Ms. Tregoning offered support for full transparency in every facet of the supply chain, Ms. Bricker did not. “It will hurt the consumer, Congressman, because prices will be held high.”
“I’m not buying it,” Rep. Sarbanes replied. “I think a system has been built that allows for gaming to go on and you’ve all got your talking points.”
Rep. Buddy Carter (R-Ga.), Congress’ only pharmacist, does not on the committee but was allowed to participate in the hearing. He shared with his colleagues stories of customers leaving prescriptions behind because of cost.
He asked Mr. Langa whether he thought PBM consolidation played a role in driving up rebates and list prices, to which Mr. Langa said, “I think it was a factor.”
Rep. Carter offering a sarcastic congratulations to the panel.
“You’ve done something here today that we’ve been trying to do in Congress for the 4 years and 3 months I’ve been here, and that is to create bipartisanship.”
He then cautioned PBM leaders on the panel that the status quo “is going to end. ... I have seen what you have done with the PBMs” and all the various fees that have been created over time and said that Congress will make sure rebate reform will happen, specifically for Medicare and Medicaid. But he added, “we are not going to stop there.”
During the hearing, the manufacturers, while being not completely committal, suggested that list prices could in fact come down if rebates and discounts were done away with, while the PBMs would not commit to flat administrative fees as opposed to current fees that are based on list prices.
Rep. DeGette said that work will continue until all parties come up with a viable solution. Action “is not optional and it is going to happen.”
Who’s responsible for the rising cost of insulin? Manufacturers and pharmacy benefit managers pointed their fingers at each other on April 10 at a congressional hearing.
In response, Democrats and Republicans on the House Energy & Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations said they might just take matters into their own hands.
Rebates and discounts are the drivers, according to leaders from three insulin manufacturers.
Mike Mason, a senior vice president of Eli Lilly & Co., was put on the defensive immediately by Subcommittee Chairman Diana DeGette (D-Colo.), who asked him to justify the increases in list prices during the last 10 years.
“Seventy-five percent of our list price is paid for rebates and discounts to secure access so people have affordable access,” Mr. Mason said.
He was cut off in his response as Rep. DeGette pressed further: “So that’s what’s making the price go up and up.”
To which Mr. Mason responded, “$210 of a vial of Humalog is paid for discounts and rebates.” It was noted during the hearing that a vial has a list price of $275.
Doug Langa, an executive vice president at Novo Nordisk, agreed. “There is significant demand for rebates.”
Kathleen Tregoning, an executive vice president at Sanofi, added that, as part of setting the list price, “we have to look at the dynamics of the supply chain, including the rebates.”
Leaders of several pharmacy benefit managers disagreed.
Rep. DeGette asked Thomas M. Moriarty, an executive vice president and general counsel at CVS Health whether he thought rebates were forcing manufacturers to raise list prices. His response? “I do not, no.”
Amy Bricker, a senior vice president at Express Scripts concurred. “I have no idea why list prices are high, and it’s not a result of rebates.”
Sumit Dutta, MD, a senior vice president and chief medical officer at OptumRx, added that there have been list prices rising double digits in nonrebated drugs, in generics where a manufacturer buys out the market to create a monopoly.
“We can’t see a correlation just when rebates raise list prices,” Dr. Dutta said.
While the PBMs denied the rebate system played any role in the setting of list prices, they were firm in maintaining secrecy in rebating process.
When asked by Rep. John Sarbanes (D-Md.) whether the public should be able to track the list price and see the rebates, the net prices, and the savings that are passed along to the consumer, Ms. Bricker said “we don’t believe so.”
She continued: “The reason I’m able to get the discounts that I can from the manufacturer is because it is confidential.”
And while Ms. Tregoning offered support for full transparency in every facet of the supply chain, Ms. Bricker did not. “It will hurt the consumer, Congressman, because prices will be held high.”
“I’m not buying it,” Rep. Sarbanes replied. “I think a system has been built that allows for gaming to go on and you’ve all got your talking points.”
Rep. Buddy Carter (R-Ga.), Congress’ only pharmacist, does not on the committee but was allowed to participate in the hearing. He shared with his colleagues stories of customers leaving prescriptions behind because of cost.
He asked Mr. Langa whether he thought PBM consolidation played a role in driving up rebates and list prices, to which Mr. Langa said, “I think it was a factor.”
Rep. Carter offering a sarcastic congratulations to the panel.
“You’ve done something here today that we’ve been trying to do in Congress for the 4 years and 3 months I’ve been here, and that is to create bipartisanship.”
He then cautioned PBM leaders on the panel that the status quo “is going to end. ... I have seen what you have done with the PBMs” and all the various fees that have been created over time and said that Congress will make sure rebate reform will happen, specifically for Medicare and Medicaid. But he added, “we are not going to stop there.”
During the hearing, the manufacturers, while being not completely committal, suggested that list prices could in fact come down if rebates and discounts were done away with, while the PBMs would not commit to flat administrative fees as opposed to current fees that are based on list prices.
Rep. DeGette said that work will continue until all parties come up with a viable solution. Action “is not optional and it is going to happen.”
Who’s responsible for the rising cost of insulin? Manufacturers and pharmacy benefit managers pointed their fingers at each other on April 10 at a congressional hearing.
In response, Democrats and Republicans on the House Energy & Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations said they might just take matters into their own hands.
Rebates and discounts are the drivers, according to leaders from three insulin manufacturers.
Mike Mason, a senior vice president of Eli Lilly & Co., was put on the defensive immediately by Subcommittee Chairman Diana DeGette (D-Colo.), who asked him to justify the increases in list prices during the last 10 years.
“Seventy-five percent of our list price is paid for rebates and discounts to secure access so people have affordable access,” Mr. Mason said.
He was cut off in his response as Rep. DeGette pressed further: “So that’s what’s making the price go up and up.”
To which Mr. Mason responded, “$210 of a vial of Humalog is paid for discounts and rebates.” It was noted during the hearing that a vial has a list price of $275.
Doug Langa, an executive vice president at Novo Nordisk, agreed. “There is significant demand for rebates.”
Kathleen Tregoning, an executive vice president at Sanofi, added that, as part of setting the list price, “we have to look at the dynamics of the supply chain, including the rebates.”
Leaders of several pharmacy benefit managers disagreed.
Rep. DeGette asked Thomas M. Moriarty, an executive vice president and general counsel at CVS Health whether he thought rebates were forcing manufacturers to raise list prices. His response? “I do not, no.”
Amy Bricker, a senior vice president at Express Scripts concurred. “I have no idea why list prices are high, and it’s not a result of rebates.”
Sumit Dutta, MD, a senior vice president and chief medical officer at OptumRx, added that there have been list prices rising double digits in nonrebated drugs, in generics where a manufacturer buys out the market to create a monopoly.
“We can’t see a correlation just when rebates raise list prices,” Dr. Dutta said.
While the PBMs denied the rebate system played any role in the setting of list prices, they were firm in maintaining secrecy in rebating process.
When asked by Rep. John Sarbanes (D-Md.) whether the public should be able to track the list price and see the rebates, the net prices, and the savings that are passed along to the consumer, Ms. Bricker said “we don’t believe so.”
She continued: “The reason I’m able to get the discounts that I can from the manufacturer is because it is confidential.”
And while Ms. Tregoning offered support for full transparency in every facet of the supply chain, Ms. Bricker did not. “It will hurt the consumer, Congressman, because prices will be held high.”
“I’m not buying it,” Rep. Sarbanes replied. “I think a system has been built that allows for gaming to go on and you’ve all got your talking points.”
Rep. Buddy Carter (R-Ga.), Congress’ only pharmacist, does not on the committee but was allowed to participate in the hearing. He shared with his colleagues stories of customers leaving prescriptions behind because of cost.
He asked Mr. Langa whether he thought PBM consolidation played a role in driving up rebates and list prices, to which Mr. Langa said, “I think it was a factor.”
Rep. Carter offering a sarcastic congratulations to the panel.
“You’ve done something here today that we’ve been trying to do in Congress for the 4 years and 3 months I’ve been here, and that is to create bipartisanship.”
He then cautioned PBM leaders on the panel that the status quo “is going to end. ... I have seen what you have done with the PBMs” and all the various fees that have been created over time and said that Congress will make sure rebate reform will happen, specifically for Medicare and Medicaid. But he added, “we are not going to stop there.”
During the hearing, the manufacturers, while being not completely committal, suggested that list prices could in fact come down if rebates and discounts were done away with, while the PBMs would not commit to flat administrative fees as opposed to current fees that are based on list prices.
Rep. DeGette said that work will continue until all parties come up with a viable solution. Action “is not optional and it is going to happen.”
REPORTING FROM A HOUSE ENERGY AND COMMERCE SUBCOMMITTEE HEARING
MRI predicts ALK status of NSCLC via brain lesions
GENEVA – Radiogenomic MRI signatures may be able to identify anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)–positive brain metastases in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), offering a minimally invasive option that could allow for initiation of treatment while waiting for molecular results, according to investigators.
In the future, artificial intelligence may be able to detect these imaging patterns, allowing for rapid and accurate mutation subtyping, reported lead author Shweta Wadhwa, MD, of Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai, India, who presented the findings at the European Lung Cancer Conference.
“Radiogenomics is a concept used to associate genetic information with medical images,” Dr. Wadhwa explained at the meeting presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology. “It creates imaging biomarkers noninvasively without using biopsy. … The aim of my study was to analyze certain MRI data genomic parameters and correlate with the ALK mutation status.”
Dr. Wadhwa and her colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 75 patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who underwent multiparametric MRI at the time of diagnosis. Univariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to look for associations between ALK mutation status and various clinical factors, including sex, age, smoking, histology, TNM stage, and imaging characteristics.
Out of 75 patients, 46 were ALK positive and 29 were ALK negative. Analysis showed that ALK positivity was associated with a variety of lesion morphology characteristics. ALK-positive lesions more often exhibited a fuzzy and infiltrative T2w border with hypointense peripheral solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which frequently had a well-defined T2w border with no solid rim (P less than .001). On T1w, most ALK-positive lesions were heterogeneous, whereas ALK-negative lesions were predominantly hypointense (P less than .001). Diffusion-weighted images showed that ALK-positive lesions often had peripheral restriction of the solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which were associated with central restriction (P = .001). MRI also revealed that about half of ALK-positive patients (54.3%) had meningeal involvement, compared with just 17.2% of ALK-negative patients (P = .02). ALK positivity was also associated with younger age and lack of smoking history. Considering these findings, Dr. Wadhwa concluded that “radiogenomics has a potential role in personalized management of ALK-positive NSCLC brain metastases.”
In an interview, Dr. Wadhwa provided more insight regarding the clinical need for this technology. “We have to wait for 10 days [for molecular diagnostic results], and ALK is usually aggressive disease, so if we wait for 10 days, patients can undergo rapid progression.”
Dr. Wadhwa noted that these results are similar to that of her colleague, Abhishek Mahajan, MD, who recently published results showing potential for radiogenomic detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status. According to Dr. Wadhwa, the two investigators plan to build on their collective findings in an effort to automate radiogenomic detection of NSCLC mutation subtypes.
“My upcoming project with my coinvestigator is to take a bigger sample,” Dr. Wadhwa said. “We will be further generalizing [this process] to all patients in a prospective study. We will also be sending this to the University of Pennsylvania for automatic brain segmentation.” Dr. Wadhwa estimated that adding automation will provide an accuracy rate of around 90%.
“We will train the computer accordingly,” Dr. Wadhwa said, “and then the computer will tell us, yes, this is ALK positive, this is EGFR positive.”
The investigators reported no external study funding and reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wadhwa S et al. ELCC 2019, Abstract 55O.
GENEVA – Radiogenomic MRI signatures may be able to identify anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)–positive brain metastases in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), offering a minimally invasive option that could allow for initiation of treatment while waiting for molecular results, according to investigators.
In the future, artificial intelligence may be able to detect these imaging patterns, allowing for rapid and accurate mutation subtyping, reported lead author Shweta Wadhwa, MD, of Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai, India, who presented the findings at the European Lung Cancer Conference.
“Radiogenomics is a concept used to associate genetic information with medical images,” Dr. Wadhwa explained at the meeting presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology. “It creates imaging biomarkers noninvasively without using biopsy. … The aim of my study was to analyze certain MRI data genomic parameters and correlate with the ALK mutation status.”
Dr. Wadhwa and her colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 75 patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who underwent multiparametric MRI at the time of diagnosis. Univariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to look for associations between ALK mutation status and various clinical factors, including sex, age, smoking, histology, TNM stage, and imaging characteristics.
Out of 75 patients, 46 were ALK positive and 29 were ALK negative. Analysis showed that ALK positivity was associated with a variety of lesion morphology characteristics. ALK-positive lesions more often exhibited a fuzzy and infiltrative T2w border with hypointense peripheral solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which frequently had a well-defined T2w border with no solid rim (P less than .001). On T1w, most ALK-positive lesions were heterogeneous, whereas ALK-negative lesions were predominantly hypointense (P less than .001). Diffusion-weighted images showed that ALK-positive lesions often had peripheral restriction of the solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which were associated with central restriction (P = .001). MRI also revealed that about half of ALK-positive patients (54.3%) had meningeal involvement, compared with just 17.2% of ALK-negative patients (P = .02). ALK positivity was also associated with younger age and lack of smoking history. Considering these findings, Dr. Wadhwa concluded that “radiogenomics has a potential role in personalized management of ALK-positive NSCLC brain metastases.”
In an interview, Dr. Wadhwa provided more insight regarding the clinical need for this technology. “We have to wait for 10 days [for molecular diagnostic results], and ALK is usually aggressive disease, so if we wait for 10 days, patients can undergo rapid progression.”
Dr. Wadhwa noted that these results are similar to that of her colleague, Abhishek Mahajan, MD, who recently published results showing potential for radiogenomic detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status. According to Dr. Wadhwa, the two investigators plan to build on their collective findings in an effort to automate radiogenomic detection of NSCLC mutation subtypes.
“My upcoming project with my coinvestigator is to take a bigger sample,” Dr. Wadhwa said. “We will be further generalizing [this process] to all patients in a prospective study. We will also be sending this to the University of Pennsylvania for automatic brain segmentation.” Dr. Wadhwa estimated that adding automation will provide an accuracy rate of around 90%.
“We will train the computer accordingly,” Dr. Wadhwa said, “and then the computer will tell us, yes, this is ALK positive, this is EGFR positive.”
The investigators reported no external study funding and reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wadhwa S et al. ELCC 2019, Abstract 55O.
GENEVA – Radiogenomic MRI signatures may be able to identify anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)–positive brain metastases in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), offering a minimally invasive option that could allow for initiation of treatment while waiting for molecular results, according to investigators.
In the future, artificial intelligence may be able to detect these imaging patterns, allowing for rapid and accurate mutation subtyping, reported lead author Shweta Wadhwa, MD, of Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai, India, who presented the findings at the European Lung Cancer Conference.
“Radiogenomics is a concept used to associate genetic information with medical images,” Dr. Wadhwa explained at the meeting presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology. “It creates imaging biomarkers noninvasively without using biopsy. … The aim of my study was to analyze certain MRI data genomic parameters and correlate with the ALK mutation status.”
Dr. Wadhwa and her colleagues retrospectively analyzed data from 75 patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who underwent multiparametric MRI at the time of diagnosis. Univariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to look for associations between ALK mutation status and various clinical factors, including sex, age, smoking, histology, TNM stage, and imaging characteristics.
Out of 75 patients, 46 were ALK positive and 29 were ALK negative. Analysis showed that ALK positivity was associated with a variety of lesion morphology characteristics. ALK-positive lesions more often exhibited a fuzzy and infiltrative T2w border with hypointense peripheral solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which frequently had a well-defined T2w border with no solid rim (P less than .001). On T1w, most ALK-positive lesions were heterogeneous, whereas ALK-negative lesions were predominantly hypointense (P less than .001). Diffusion-weighted images showed that ALK-positive lesions often had peripheral restriction of the solid rim, compared with ALK-negative lesions, which were associated with central restriction (P = .001). MRI also revealed that about half of ALK-positive patients (54.3%) had meningeal involvement, compared with just 17.2% of ALK-negative patients (P = .02). ALK positivity was also associated with younger age and lack of smoking history. Considering these findings, Dr. Wadhwa concluded that “radiogenomics has a potential role in personalized management of ALK-positive NSCLC brain metastases.”
In an interview, Dr. Wadhwa provided more insight regarding the clinical need for this technology. “We have to wait for 10 days [for molecular diagnostic results], and ALK is usually aggressive disease, so if we wait for 10 days, patients can undergo rapid progression.”
Dr. Wadhwa noted that these results are similar to that of her colleague, Abhishek Mahajan, MD, who recently published results showing potential for radiogenomic detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status. According to Dr. Wadhwa, the two investigators plan to build on their collective findings in an effort to automate radiogenomic detection of NSCLC mutation subtypes.
“My upcoming project with my coinvestigator is to take a bigger sample,” Dr. Wadhwa said. “We will be further generalizing [this process] to all patients in a prospective study. We will also be sending this to the University of Pennsylvania for automatic brain segmentation.” Dr. Wadhwa estimated that adding automation will provide an accuracy rate of around 90%.
“We will train the computer accordingly,” Dr. Wadhwa said, “and then the computer will tell us, yes, this is ALK positive, this is EGFR positive.”
The investigators reported no external study funding and reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Wadhwa S et al. ELCC 2019, Abstract 55O.
REPORTING FROM ELCC 2019
European NAVIGATE data support safety of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy
GENEVA – For lung lesion biopsy, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) offers high navigational success with a relatively low rate of pneumothorax, according to European data from the international NAVIGATE study.
In addition to lung lesion biopsy, ENB can facilitate concurrent lymph node sampling and fiducial placement during a single anesthetic event, reported lead author Kelvin Lau, MD, chief of thoracic surgery at Barts Thorax Centre in London, and his colleagues. According to Dr. Lau, who presented at the European Lung Cancer Conference, the findings from this European cohort add weight to previously published data from the NAVIGATE trial, which aims to demonstrate real-world use of ENB.
“The outcomes show that [ENB] is very safe in terms of pneumothorax rate, despite the fact that many of these patients were challenging and actually were turned down by the percutaneous radiologist before they came to us,” Dr. Lau said at the meeting, presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Out of 1,200 patients enrolled in the NAVIGATE trial in the United States and Europe, the present 1-month interim analysis showed experiences with 175 patients treated at eight European centers. Anyone undergoing navigational bronchoscopy was eligible. The primary outcome was pneumothorax rate and the secondary outcome was diagnostic yield.
Data analysis showed that lesions were most frequently in the upper lobe (62.6%) and in the peripheral third of the lung (72.7%), the latter of which is beyond the reach of a conventional bronchoscope. In two out of three patients (66.8%), a bronchus sign was present, which “means that the bronchoscope runs straight into the lesion, and theoretically means it’s easier to access,” Dr. Lau said. Almost all patients had ENB for lung biopsy (99.4%), while in a small minority (8.0%), ENB was used for fiducial marking. The median total procedure time was 43.5 minutes, of which 32.9 minutes were spent navigating and sampling with ENB.
The ENB-related pneumothorax rate was 7.4%, although a slightly lower percentage, 5.1%, required intervention or hospitalization. According to the ENB-related Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, 2.3% of patients had grade 2 or higher bronchopulmonary hemorrhage and 0.6% of patients had grade 4 or higher respiratory failure. Although the secondary endpoint, diagnostic yield, was not met because of inadequate follow-up time, the navigational success rate, defined as access to the intended lung lesion, was 96.6%, which offers some sense of efficacy.
“The purpose of this study is to show that [ENB] is very safe,” Dr. Lau said in an interview. “And the numbers are significantly better than historic CT-guided biopsy data.”
Considering the choice between ENB and CT-guided biopsy, invited discussant Anne-Marie Dingemans, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, offered a different viewpoint.
“CT-guided biopsies are low cost ... and the sensitivity is very, very high,” Dr. Dingemans said. “In good hands, with a good radiologist, you have a high chance that you will have a good diagnosis of the nodules.” She also noted that a bronchus sign does not impact efficacy.
“I’m very into CT-guided biopsies,” Dr. Dingemans continued, noting that the radiologist at her treatment center takes biopsies with a 10-gauge large-core needle. With this technique, Dr. Dingemans reported a 5.7% pneumothorax rate, which is comparable with the present NAVIGATE data.
However, Dr. Lau contested this figure.
“The pneumothorax rates [for CT-guided biopsy] in larger studies have always been about 20% to 40%,” Dr. Lau said. “You can’t compare large overall practice in a pragmatic study capturing everyone versus one single center. The truth is, most centers will have a 20% pneumothorax rate.”
Dr. Lau added that patient experiences are likely to be better with ENB than with CT-guided percutaneous biopsy.
“To me, patient comfort for biopsy is essential,” Dr. Lau said. “Having a needle stuck into your chest – it’s very uncomfortable. I’ve had patients who’ve come to me after they had a percutaneous biopsy and who for some reason needed a re-biopsy ... those patients almost always wish they had navigational bronchoscopy the first time because there would be no pain for them.”
When asked about capital cost concerns surrounding ENB, Dr. Lau suggested that the benefits outweigh the costs.
“The most expensive procedure is the one you have to do again,” Dr. Lau said. “So what we do is put a brush in, and a needle, and a biopsy, and hopefully, one of those three, if not all three, gets tissue, and we can do that with navigational bronchoscopy because there is one channel down. You can’t repeatedly stick needles into patients. By definition, you can’t throw three needle jabs, because you will get a 90% pneumothorax rate. And that’s the beauty of navigational bronchoscopy as well, because in the NAVIGATE series, a number of patients, about 10%, had multiple lesions biopsied.” Furthermore, Dr. Lau noted, percutaneous biopsy is “almost never” performed bilaterally, for fear of collapsing both lungs, but this is not the case with ENB. “We’ve done it on patients who have one lung,” he said.
Dr. Lau predicted that costs of ENB will come down with time. “Because of the number of products increasing, the price will drop,” he said.
Concluding the interview, Dr. Lau offered a summarizing message: “If you want to give the patient the safe option, you should do [ENB], and when it becomes more popular, the price will fall,” he said.
Medtronic funded the study. The investigators reported financial relationships with Olympus, Ambu, PulmonX, Boston Scientific, and others.
SOURCE: Lau et al. ELCC 2019. Abstract 68O.
GENEVA – For lung lesion biopsy, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) offers high navigational success with a relatively low rate of pneumothorax, according to European data from the international NAVIGATE study.
In addition to lung lesion biopsy, ENB can facilitate concurrent lymph node sampling and fiducial placement during a single anesthetic event, reported lead author Kelvin Lau, MD, chief of thoracic surgery at Barts Thorax Centre in London, and his colleagues. According to Dr. Lau, who presented at the European Lung Cancer Conference, the findings from this European cohort add weight to previously published data from the NAVIGATE trial, which aims to demonstrate real-world use of ENB.
“The outcomes show that [ENB] is very safe in terms of pneumothorax rate, despite the fact that many of these patients were challenging and actually were turned down by the percutaneous radiologist before they came to us,” Dr. Lau said at the meeting, presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Out of 1,200 patients enrolled in the NAVIGATE trial in the United States and Europe, the present 1-month interim analysis showed experiences with 175 patients treated at eight European centers. Anyone undergoing navigational bronchoscopy was eligible. The primary outcome was pneumothorax rate and the secondary outcome was diagnostic yield.
Data analysis showed that lesions were most frequently in the upper lobe (62.6%) and in the peripheral third of the lung (72.7%), the latter of which is beyond the reach of a conventional bronchoscope. In two out of three patients (66.8%), a bronchus sign was present, which “means that the bronchoscope runs straight into the lesion, and theoretically means it’s easier to access,” Dr. Lau said. Almost all patients had ENB for lung biopsy (99.4%), while in a small minority (8.0%), ENB was used for fiducial marking. The median total procedure time was 43.5 minutes, of which 32.9 minutes were spent navigating and sampling with ENB.
The ENB-related pneumothorax rate was 7.4%, although a slightly lower percentage, 5.1%, required intervention or hospitalization. According to the ENB-related Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, 2.3% of patients had grade 2 or higher bronchopulmonary hemorrhage and 0.6% of patients had grade 4 or higher respiratory failure. Although the secondary endpoint, diagnostic yield, was not met because of inadequate follow-up time, the navigational success rate, defined as access to the intended lung lesion, was 96.6%, which offers some sense of efficacy.
“The purpose of this study is to show that [ENB] is very safe,” Dr. Lau said in an interview. “And the numbers are significantly better than historic CT-guided biopsy data.”
Considering the choice between ENB and CT-guided biopsy, invited discussant Anne-Marie Dingemans, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, offered a different viewpoint.
“CT-guided biopsies are low cost ... and the sensitivity is very, very high,” Dr. Dingemans said. “In good hands, with a good radiologist, you have a high chance that you will have a good diagnosis of the nodules.” She also noted that a bronchus sign does not impact efficacy.
“I’m very into CT-guided biopsies,” Dr. Dingemans continued, noting that the radiologist at her treatment center takes biopsies with a 10-gauge large-core needle. With this technique, Dr. Dingemans reported a 5.7% pneumothorax rate, which is comparable with the present NAVIGATE data.
However, Dr. Lau contested this figure.
“The pneumothorax rates [for CT-guided biopsy] in larger studies have always been about 20% to 40%,” Dr. Lau said. “You can’t compare large overall practice in a pragmatic study capturing everyone versus one single center. The truth is, most centers will have a 20% pneumothorax rate.”
Dr. Lau added that patient experiences are likely to be better with ENB than with CT-guided percutaneous biopsy.
“To me, patient comfort for biopsy is essential,” Dr. Lau said. “Having a needle stuck into your chest – it’s very uncomfortable. I’ve had patients who’ve come to me after they had a percutaneous biopsy and who for some reason needed a re-biopsy ... those patients almost always wish they had navigational bronchoscopy the first time because there would be no pain for them.”
When asked about capital cost concerns surrounding ENB, Dr. Lau suggested that the benefits outweigh the costs.
“The most expensive procedure is the one you have to do again,” Dr. Lau said. “So what we do is put a brush in, and a needle, and a biopsy, and hopefully, one of those three, if not all three, gets tissue, and we can do that with navigational bronchoscopy because there is one channel down. You can’t repeatedly stick needles into patients. By definition, you can’t throw three needle jabs, because you will get a 90% pneumothorax rate. And that’s the beauty of navigational bronchoscopy as well, because in the NAVIGATE series, a number of patients, about 10%, had multiple lesions biopsied.” Furthermore, Dr. Lau noted, percutaneous biopsy is “almost never” performed bilaterally, for fear of collapsing both lungs, but this is not the case with ENB. “We’ve done it on patients who have one lung,” he said.
Dr. Lau predicted that costs of ENB will come down with time. “Because of the number of products increasing, the price will drop,” he said.
Concluding the interview, Dr. Lau offered a summarizing message: “If you want to give the patient the safe option, you should do [ENB], and when it becomes more popular, the price will fall,” he said.
Medtronic funded the study. The investigators reported financial relationships with Olympus, Ambu, PulmonX, Boston Scientific, and others.
SOURCE: Lau et al. ELCC 2019. Abstract 68O.
GENEVA – For lung lesion biopsy, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) offers high navigational success with a relatively low rate of pneumothorax, according to European data from the international NAVIGATE study.
In addition to lung lesion biopsy, ENB can facilitate concurrent lymph node sampling and fiducial placement during a single anesthetic event, reported lead author Kelvin Lau, MD, chief of thoracic surgery at Barts Thorax Centre in London, and his colleagues. According to Dr. Lau, who presented at the European Lung Cancer Conference, the findings from this European cohort add weight to previously published data from the NAVIGATE trial, which aims to demonstrate real-world use of ENB.
“The outcomes show that [ENB] is very safe in terms of pneumothorax rate, despite the fact that many of these patients were challenging and actually were turned down by the percutaneous radiologist before they came to us,” Dr. Lau said at the meeting, presented by the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Out of 1,200 patients enrolled in the NAVIGATE trial in the United States and Europe, the present 1-month interim analysis showed experiences with 175 patients treated at eight European centers. Anyone undergoing navigational bronchoscopy was eligible. The primary outcome was pneumothorax rate and the secondary outcome was diagnostic yield.
Data analysis showed that lesions were most frequently in the upper lobe (62.6%) and in the peripheral third of the lung (72.7%), the latter of which is beyond the reach of a conventional bronchoscope. In two out of three patients (66.8%), a bronchus sign was present, which “means that the bronchoscope runs straight into the lesion, and theoretically means it’s easier to access,” Dr. Lau said. Almost all patients had ENB for lung biopsy (99.4%), while in a small minority (8.0%), ENB was used for fiducial marking. The median total procedure time was 43.5 minutes, of which 32.9 minutes were spent navigating and sampling with ENB.
The ENB-related pneumothorax rate was 7.4%, although a slightly lower percentage, 5.1%, required intervention or hospitalization. According to the ENB-related Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, 2.3% of patients had grade 2 or higher bronchopulmonary hemorrhage and 0.6% of patients had grade 4 or higher respiratory failure. Although the secondary endpoint, diagnostic yield, was not met because of inadequate follow-up time, the navigational success rate, defined as access to the intended lung lesion, was 96.6%, which offers some sense of efficacy.
“The purpose of this study is to show that [ENB] is very safe,” Dr. Lau said in an interview. “And the numbers are significantly better than historic CT-guided biopsy data.”
Considering the choice between ENB and CT-guided biopsy, invited discussant Anne-Marie Dingemans, MD, of Maastricht University, the Netherlands, offered a different viewpoint.
“CT-guided biopsies are low cost ... and the sensitivity is very, very high,” Dr. Dingemans said. “In good hands, with a good radiologist, you have a high chance that you will have a good diagnosis of the nodules.” She also noted that a bronchus sign does not impact efficacy.
“I’m very into CT-guided biopsies,” Dr. Dingemans continued, noting that the radiologist at her treatment center takes biopsies with a 10-gauge large-core needle. With this technique, Dr. Dingemans reported a 5.7% pneumothorax rate, which is comparable with the present NAVIGATE data.
However, Dr. Lau contested this figure.
“The pneumothorax rates [for CT-guided biopsy] in larger studies have always been about 20% to 40%,” Dr. Lau said. “You can’t compare large overall practice in a pragmatic study capturing everyone versus one single center. The truth is, most centers will have a 20% pneumothorax rate.”
Dr. Lau added that patient experiences are likely to be better with ENB than with CT-guided percutaneous biopsy.
“To me, patient comfort for biopsy is essential,” Dr. Lau said. “Having a needle stuck into your chest – it’s very uncomfortable. I’ve had patients who’ve come to me after they had a percutaneous biopsy and who for some reason needed a re-biopsy ... those patients almost always wish they had navigational bronchoscopy the first time because there would be no pain for them.”
When asked about capital cost concerns surrounding ENB, Dr. Lau suggested that the benefits outweigh the costs.
“The most expensive procedure is the one you have to do again,” Dr. Lau said. “So what we do is put a brush in, and a needle, and a biopsy, and hopefully, one of those three, if not all three, gets tissue, and we can do that with navigational bronchoscopy because there is one channel down. You can’t repeatedly stick needles into patients. By definition, you can’t throw three needle jabs, because you will get a 90% pneumothorax rate. And that’s the beauty of navigational bronchoscopy as well, because in the NAVIGATE series, a number of patients, about 10%, had multiple lesions biopsied.” Furthermore, Dr. Lau noted, percutaneous biopsy is “almost never” performed bilaterally, for fear of collapsing both lungs, but this is not the case with ENB. “We’ve done it on patients who have one lung,” he said.
Dr. Lau predicted that costs of ENB will come down with time. “Because of the number of products increasing, the price will drop,” he said.
Concluding the interview, Dr. Lau offered a summarizing message: “If you want to give the patient the safe option, you should do [ENB], and when it becomes more popular, the price will fall,” he said.
Medtronic funded the study. The investigators reported financial relationships with Olympus, Ambu, PulmonX, Boston Scientific, and others.
SOURCE: Lau et al. ELCC 2019. Abstract 68O.
REPORTING FROM ELCC 2019
No clear benefit seen for postdischarge oxygen in preemies with BPD
Preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) discharged with supplemental oxygen showed slightly better weight and significantly improved weight-for-length scores, but were more likely to use medical resources and had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants not discharged with oxygen, according to research published in Pediatrics.
“With this study, we provide important and novel information that may aid the decision of whether to discharge an infant with supplemental oxygen, particularly for those infants who might be weaned off by some clinicians and not by others,” wrote Sara B. DeMauro, MD, MSCE, of University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and her colleagues. “This study helps to clarify, both for clinicians and parents, the potential benefits and harms that might be expected from home oxygen therapy among the subset of infants for whom the best course of action is unclear.”
Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues examined 1,039 preterm infants with BPD given supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula between January 2006 and December 2014, who were propensity matched to infants in a control group with a similar severity of BPD who were not discharged with oxygen. The infants were born at less than 27 weeks’ gestation and began receiving oxygen therapy or respiratory support at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. These infants were then measured for growth, neurodevelopment, and resource use from discharge to follow-up at 22-26 months corrected age.
At follow-up, infants discharged with oxygen showed marginal weight improvement scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.11) and significantly improved weight-for-length scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.13), but they had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants with BPD discharged without supplemental oxygen. In addition, infants discharged with oxygen had a greater likelihood of rehospitalization due to respiratory illness (adjusted relative risk, 1.33), use of asthma or BPD medication (adjusted RR, 1.30), and use of medical equipment such as a pulse oximeter (adjusted RR, 2.94).
The researchers noted that their study’s design prevented them from examining all infants with BPD discharged with supplemental oxygen and what factors influenced discharge of infants with supplemental oxygen, as well as the effects of various durations of supplemental oxygen exposure.
“Definitive evaluation of the risk/benefit ratio of this therapy will require prospective controlled trials,” Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues wrote. “Such research will facilitate a more evidence-based approach to clinical decisions about postdischarge care of infants with BPD.”
This study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: DeMauro SB et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2956.
While oxygen use recommendations for preterm infants in the delivery room and neonatal ICU have changed, postdischarge oxygen instructions have largely not, with variations among practices and evidence for its use not well established.
The results from DeMauro et al., while not establishing causality, can instead be used to design a prospective trial to identify which preterm infants with BPD require oxygen post discharge, Reese H. Clark, MD, and Veeral N. Tolia, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
Supplemental oxygen also was associated with greater resource use among infants in the study, and they were more likely to require medications for asthma and BPD, procedures such as tracheotomy, and rehospitalization, which is in line with previous clinical studies analyzing oxygen use in the NICU, they noted.
The findings by DeMauro et al. could be used to improve the design and safety of a prospective study. For example, “it may not be feasible or ethical to include some infants with more severe BPD in future trials,” they noted. “Once again, we are challenged to reevaluate our clinical beliefs and biases about the use of oxygen,” said Dr. Clark and Dr. Tolia. “Now we must collaborate to design and implement a trial to help us determine which infants should receive oxygen after discharge. We look forward to seeing those results.”
Dr. Clark is from the Center for Research and Education at MEDNAX in Sunrise, Fla., and Dr. Tolia is at Baylor University Medical Center and Pediatrix Medical Group in Dallas. This is a summary of the editorial accompanying the report by DeMauro et al. (Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0372). They reported no relevant financial disclosures or external funding.
While oxygen use recommendations for preterm infants in the delivery room and neonatal ICU have changed, postdischarge oxygen instructions have largely not, with variations among practices and evidence for its use not well established.
The results from DeMauro et al., while not establishing causality, can instead be used to design a prospective trial to identify which preterm infants with BPD require oxygen post discharge, Reese H. Clark, MD, and Veeral N. Tolia, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
Supplemental oxygen also was associated with greater resource use among infants in the study, and they were more likely to require medications for asthma and BPD, procedures such as tracheotomy, and rehospitalization, which is in line with previous clinical studies analyzing oxygen use in the NICU, they noted.
The findings by DeMauro et al. could be used to improve the design and safety of a prospective study. For example, “it may not be feasible or ethical to include some infants with more severe BPD in future trials,” they noted. “Once again, we are challenged to reevaluate our clinical beliefs and biases about the use of oxygen,” said Dr. Clark and Dr. Tolia. “Now we must collaborate to design and implement a trial to help us determine which infants should receive oxygen after discharge. We look forward to seeing those results.”
Dr. Clark is from the Center for Research and Education at MEDNAX in Sunrise, Fla., and Dr. Tolia is at Baylor University Medical Center and Pediatrix Medical Group in Dallas. This is a summary of the editorial accompanying the report by DeMauro et al. (Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0372). They reported no relevant financial disclosures or external funding.
While oxygen use recommendations for preterm infants in the delivery room and neonatal ICU have changed, postdischarge oxygen instructions have largely not, with variations among practices and evidence for its use not well established.
The results from DeMauro et al., while not establishing causality, can instead be used to design a prospective trial to identify which preterm infants with BPD require oxygen post discharge, Reese H. Clark, MD, and Veeral N. Tolia, MD, wrote in a related editorial.
Supplemental oxygen also was associated with greater resource use among infants in the study, and they were more likely to require medications for asthma and BPD, procedures such as tracheotomy, and rehospitalization, which is in line with previous clinical studies analyzing oxygen use in the NICU, they noted.
The findings by DeMauro et al. could be used to improve the design and safety of a prospective study. For example, “it may not be feasible or ethical to include some infants with more severe BPD in future trials,” they noted. “Once again, we are challenged to reevaluate our clinical beliefs and biases about the use of oxygen,” said Dr. Clark and Dr. Tolia. “Now we must collaborate to design and implement a trial to help us determine which infants should receive oxygen after discharge. We look forward to seeing those results.”
Dr. Clark is from the Center for Research and Education at MEDNAX in Sunrise, Fla., and Dr. Tolia is at Baylor University Medical Center and Pediatrix Medical Group in Dallas. This is a summary of the editorial accompanying the report by DeMauro et al. (Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0372). They reported no relevant financial disclosures or external funding.
Preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) discharged with supplemental oxygen showed slightly better weight and significantly improved weight-for-length scores, but were more likely to use medical resources and had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants not discharged with oxygen, according to research published in Pediatrics.
“With this study, we provide important and novel information that may aid the decision of whether to discharge an infant with supplemental oxygen, particularly for those infants who might be weaned off by some clinicians and not by others,” wrote Sara B. DeMauro, MD, MSCE, of University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and her colleagues. “This study helps to clarify, both for clinicians and parents, the potential benefits and harms that might be expected from home oxygen therapy among the subset of infants for whom the best course of action is unclear.”
Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues examined 1,039 preterm infants with BPD given supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula between January 2006 and December 2014, who were propensity matched to infants in a control group with a similar severity of BPD who were not discharged with oxygen. The infants were born at less than 27 weeks’ gestation and began receiving oxygen therapy or respiratory support at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. These infants were then measured for growth, neurodevelopment, and resource use from discharge to follow-up at 22-26 months corrected age.
At follow-up, infants discharged with oxygen showed marginal weight improvement scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.11) and significantly improved weight-for-length scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.13), but they had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants with BPD discharged without supplemental oxygen. In addition, infants discharged with oxygen had a greater likelihood of rehospitalization due to respiratory illness (adjusted relative risk, 1.33), use of asthma or BPD medication (adjusted RR, 1.30), and use of medical equipment such as a pulse oximeter (adjusted RR, 2.94).
The researchers noted that their study’s design prevented them from examining all infants with BPD discharged with supplemental oxygen and what factors influenced discharge of infants with supplemental oxygen, as well as the effects of various durations of supplemental oxygen exposure.
“Definitive evaluation of the risk/benefit ratio of this therapy will require prospective controlled trials,” Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues wrote. “Such research will facilitate a more evidence-based approach to clinical decisions about postdischarge care of infants with BPD.”
This study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: DeMauro SB et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2956.
Preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) discharged with supplemental oxygen showed slightly better weight and significantly improved weight-for-length scores, but were more likely to use medical resources and had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants not discharged with oxygen, according to research published in Pediatrics.
“With this study, we provide important and novel information that may aid the decision of whether to discharge an infant with supplemental oxygen, particularly for those infants who might be weaned off by some clinicians and not by others,” wrote Sara B. DeMauro, MD, MSCE, of University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and her colleagues. “This study helps to clarify, both for clinicians and parents, the potential benefits and harms that might be expected from home oxygen therapy among the subset of infants for whom the best course of action is unclear.”
Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues examined 1,039 preterm infants with BPD given supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula between January 2006 and December 2014, who were propensity matched to infants in a control group with a similar severity of BPD who were not discharged with oxygen. The infants were born at less than 27 weeks’ gestation and began receiving oxygen therapy or respiratory support at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. These infants were then measured for growth, neurodevelopment, and resource use from discharge to follow-up at 22-26 months corrected age.
At follow-up, infants discharged with oxygen showed marginal weight improvement scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.11) and significantly improved weight-for-length scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.13), but they had rates of neurodevelopmental impairment similar to those of infants with BPD discharged without supplemental oxygen. In addition, infants discharged with oxygen had a greater likelihood of rehospitalization due to respiratory illness (adjusted relative risk, 1.33), use of asthma or BPD medication (adjusted RR, 1.30), and use of medical equipment such as a pulse oximeter (adjusted RR, 2.94).
The researchers noted that their study’s design prevented them from examining all infants with BPD discharged with supplemental oxygen and what factors influenced discharge of infants with supplemental oxygen, as well as the effects of various durations of supplemental oxygen exposure.
“Definitive evaluation of the risk/benefit ratio of this therapy will require prospective controlled trials,” Dr. DeMauro and her colleagues wrote. “Such research will facilitate a more evidence-based approach to clinical decisions about postdischarge care of infants with BPD.”
This study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: DeMauro SB et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2956.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: compared with controls.
Major finding: At 22-26 months of age, infants discharged with oxygen showed marginal improvement in weight z scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.11) and significantly improved weight-for-length z scores (adjusted mean difference, 0.13), but similar rates of neurodevelopmental impairment.
Study details: A retrospective propensity-matched cohort study of 1,039 preterm infants given supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula between January 2006 and December 2014 and analyzed over 2 years of life.
Disclosures: This study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: DeMauro SB et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2956.
Research coalition issues plan for curing hepatitis B virus
VIENNA – They hope either to have a cure or to have made substantial progress toward this goal over the next 10 years.
Treatments already are on the market that effectively inhibit hepatitis B replication in infected patients (and an effective preventive vaccine also exists). Still, these treatments are not curative, and for the vast majority of patients treatment must continue indefinitely, while their risk for liver cancer and their virally induced immune system abnormalities remain, Peter A. Revill, PhD, said during a press briefing that introduced a strategy for hepatitis B virus (HBV) cure development from the International Coalition to Eliminate HBV. Concurrently with the briefing session, the strategy appeared in an article published online (Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30119-0).
The way forward will likely be a “two-pronged approach or restoring immune responses and targeting the virus,” Dr. Revill, head of molecular virology at the Doherty Institute in Melbourne, said in a video interview.
The new strategy recognizes the huge challenge of devising a treatment that produces a total cure that includes elimination of all traces of viral DNA from patients and for the immediate future focuses on the goal of functional cure. The term functional cure means a sustained period without detectable HBV surface antigen or HBV DNA in a patient’s serum, as well as suppressed virus release. Another feature of a functional cure would be a halt to progression of liver disease, replaced by liver regeneration, said Anna S. Lok, MD, professor of medicine and director of clinical hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a member of the strategy-writing group. She and her colleagues who wrote the strategy foresee the need for drug combinations with agents that can hit multiple viral targets as well as agents that restore normal immune function.
Several novel drug classes aimed at new viral targets, such as capsid inhibitors, are in various stages of clinical development, said Fabien Zoulim, MD, head of the gastroenterology and hepatology service at the Red Cross Hospital in Lyon, France, and another member of the writing panel. “We have many drug candidates” that use novel approaches to further restrict viral growth, roughly 50 agents in phase 1 and 2 studies, he said during the press briefing, held during the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The other, immunologic aspect of the two-part cure strategy – restoring the “exhausted” HBV-specific T-cell population and stimulating production of neutralizing antibody to HBV – remains hypothetical right now, however. “It’s a concept that needs development,” Dr. Zoulim said.
A reason members of the coalition are optimistic about eventual prospects for a cure is that currently about 1% of patients on HBV antiviral treatments have a functional cure after relatively brief treatment, and the percentage of cured patients plateaus at about 10% among those who remain on current HBV antiviral drugs for several years. In addition, a substantial fraction of patients spontaneously resolve their HBV infection without any treatment. Experts estimate that more than 1 billion people worldwide have been infected by HBV and then later had their infection clear “naturally,” said Dr. Revill. But the mechanism by which this happens is currently a mystery. “We don’t know how or why” so many infected people are “cured” naturally, Dr. Revill admitted, but it gives him and his colleagues hope that the numbers can expand once more and better treatments for HBV infection are available.
VIENNA – They hope either to have a cure or to have made substantial progress toward this goal over the next 10 years.
Treatments already are on the market that effectively inhibit hepatitis B replication in infected patients (and an effective preventive vaccine also exists). Still, these treatments are not curative, and for the vast majority of patients treatment must continue indefinitely, while their risk for liver cancer and their virally induced immune system abnormalities remain, Peter A. Revill, PhD, said during a press briefing that introduced a strategy for hepatitis B virus (HBV) cure development from the International Coalition to Eliminate HBV. Concurrently with the briefing session, the strategy appeared in an article published online (Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30119-0).
The way forward will likely be a “two-pronged approach or restoring immune responses and targeting the virus,” Dr. Revill, head of molecular virology at the Doherty Institute in Melbourne, said in a video interview.
The new strategy recognizes the huge challenge of devising a treatment that produces a total cure that includes elimination of all traces of viral DNA from patients and for the immediate future focuses on the goal of functional cure. The term functional cure means a sustained period without detectable HBV surface antigen or HBV DNA in a patient’s serum, as well as suppressed virus release. Another feature of a functional cure would be a halt to progression of liver disease, replaced by liver regeneration, said Anna S. Lok, MD, professor of medicine and director of clinical hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a member of the strategy-writing group. She and her colleagues who wrote the strategy foresee the need for drug combinations with agents that can hit multiple viral targets as well as agents that restore normal immune function.
Several novel drug classes aimed at new viral targets, such as capsid inhibitors, are in various stages of clinical development, said Fabien Zoulim, MD, head of the gastroenterology and hepatology service at the Red Cross Hospital in Lyon, France, and another member of the writing panel. “We have many drug candidates” that use novel approaches to further restrict viral growth, roughly 50 agents in phase 1 and 2 studies, he said during the press briefing, held during the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The other, immunologic aspect of the two-part cure strategy – restoring the “exhausted” HBV-specific T-cell population and stimulating production of neutralizing antibody to HBV – remains hypothetical right now, however. “It’s a concept that needs development,” Dr. Zoulim said.
A reason members of the coalition are optimistic about eventual prospects for a cure is that currently about 1% of patients on HBV antiviral treatments have a functional cure after relatively brief treatment, and the percentage of cured patients plateaus at about 10% among those who remain on current HBV antiviral drugs for several years. In addition, a substantial fraction of patients spontaneously resolve their HBV infection without any treatment. Experts estimate that more than 1 billion people worldwide have been infected by HBV and then later had their infection clear “naturally,” said Dr. Revill. But the mechanism by which this happens is currently a mystery. “We don’t know how or why” so many infected people are “cured” naturally, Dr. Revill admitted, but it gives him and his colleagues hope that the numbers can expand once more and better treatments for HBV infection are available.
VIENNA – They hope either to have a cure or to have made substantial progress toward this goal over the next 10 years.
Treatments already are on the market that effectively inhibit hepatitis B replication in infected patients (and an effective preventive vaccine also exists). Still, these treatments are not curative, and for the vast majority of patients treatment must continue indefinitely, while their risk for liver cancer and their virally induced immune system abnormalities remain, Peter A. Revill, PhD, said during a press briefing that introduced a strategy for hepatitis B virus (HBV) cure development from the International Coalition to Eliminate HBV. Concurrently with the briefing session, the strategy appeared in an article published online (Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30119-0).
The way forward will likely be a “two-pronged approach or restoring immune responses and targeting the virus,” Dr. Revill, head of molecular virology at the Doherty Institute in Melbourne, said in a video interview.
The new strategy recognizes the huge challenge of devising a treatment that produces a total cure that includes elimination of all traces of viral DNA from patients and for the immediate future focuses on the goal of functional cure. The term functional cure means a sustained period without detectable HBV surface antigen or HBV DNA in a patient’s serum, as well as suppressed virus release. Another feature of a functional cure would be a halt to progression of liver disease, replaced by liver regeneration, said Anna S. Lok, MD, professor of medicine and director of clinical hepatology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a member of the strategy-writing group. She and her colleagues who wrote the strategy foresee the need for drug combinations with agents that can hit multiple viral targets as well as agents that restore normal immune function.
Several novel drug classes aimed at new viral targets, such as capsid inhibitors, are in various stages of clinical development, said Fabien Zoulim, MD, head of the gastroenterology and hepatology service at the Red Cross Hospital in Lyon, France, and another member of the writing panel. “We have many drug candidates” that use novel approaches to further restrict viral growth, roughly 50 agents in phase 1 and 2 studies, he said during the press briefing, held during the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. The other, immunologic aspect of the two-part cure strategy – restoring the “exhausted” HBV-specific T-cell population and stimulating production of neutralizing antibody to HBV – remains hypothetical right now, however. “It’s a concept that needs development,” Dr. Zoulim said.
A reason members of the coalition are optimistic about eventual prospects for a cure is that currently about 1% of patients on HBV antiviral treatments have a functional cure after relatively brief treatment, and the percentage of cured patients plateaus at about 10% among those who remain on current HBV antiviral drugs for several years. In addition, a substantial fraction of patients spontaneously resolve their HBV infection without any treatment. Experts estimate that more than 1 billion people worldwide have been infected by HBV and then later had their infection clear “naturally,” said Dr. Revill. But the mechanism by which this happens is currently a mystery. “We don’t know how or why” so many infected people are “cured” naturally, Dr. Revill admitted, but it gives him and his colleagues hope that the numbers can expand once more and better treatments for HBV infection are available.
REPORTING FROM ILC 2019
Furosemide speeds ureteral patency confirmation, but is time savings worth the risk?
TUCSON, ARIZ. – according to results from a new randomized, controlled trial.
“It does make a difference, but is that really a [meaningful] difference? Every medication has adverse effects, so is it worth that extra time [savings] to take on that potential for side effects? It highlights the importance of statistical significance versus clinical significance, and I think [the clinical significance] can just be answered by each individual physician,” Simon Patton, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Patton is a urogynecologist at Ascension Via Christi Medical Group in Wichita, Kan. He presented the study, which was conducted during his time as a fellow at the University of South Florida, Tampa, at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. Dr. Patton isn’t sure just how often physicians use furosemide during routine cystoscopy. “It would be great to do a survey to find out how many people use it in their practice,” he said.
Cystoscopy is used to during a surgery to ensure that no injury has been done to the bladder or the urethra, and the American Urogynecological Society recommends that it be performed during any pelvic reconstructive surgery. A key element of the test is confirming that the ureters are open. By increasing urine flow, furosemide can reduce the time to confirmation. But after conferring with a colleague who used the procedure, Dr. Patton looked for some data to support the practice and couldn’t find any.
Although the cystoscopy itself generally is safe, furosemide can cause hypotension, change in renal function, and even dehydration at higher doses. During the question-and-answer period, one attendee noted these issues and pointed out that furosemide can potentiate renal failure, especially among patients taking cephalosporins. “If you’re going to do this sort of trial, you have to consider potential adverse events. A single dose is probably not going to [cause an issue], but in the context of a study you want to monitor the adverse events that have been reported,” this attendee said.
The researchers did not observe any of these adverse events during the study, but Dr. Patton noted that the study was not powered to detect them. “We felt that with the low-dose, single-time [exposure], it was appropriate to not worry too much about those side effects,” he replied.
Another potential concern is that the increased urine flow could mask a kink in the ureter by forcing it open.
In the study, his team randomized 145 patients with a planned cystoscopy as part of a procedure to receive 10-mg furosemide (1 cc) or saline (1 cc) during a cystoscopy performed by an attending or a fellow. The median time to confirmation of ureteral patency was 86.5 seconds in the furosemide group, compared with 165.0 seconds in the saline group (difference, 78.5 seconds; P less than .001). The time to the first ureteral jet was 59 seconds versus 74 seconds, respectively (P less than .006). A Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis also showed a significant improvement in time to ureteral patency confirmation (log-rank P less than .001).
The study was not funded. Dr. Patton has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patton S et al. SGS 2019, Abstract 10.
TUCSON, ARIZ. – according to results from a new randomized, controlled trial.
“It does make a difference, but is that really a [meaningful] difference? Every medication has adverse effects, so is it worth that extra time [savings] to take on that potential for side effects? It highlights the importance of statistical significance versus clinical significance, and I think [the clinical significance] can just be answered by each individual physician,” Simon Patton, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Patton is a urogynecologist at Ascension Via Christi Medical Group in Wichita, Kan. He presented the study, which was conducted during his time as a fellow at the University of South Florida, Tampa, at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. Dr. Patton isn’t sure just how often physicians use furosemide during routine cystoscopy. “It would be great to do a survey to find out how many people use it in their practice,” he said.
Cystoscopy is used to during a surgery to ensure that no injury has been done to the bladder or the urethra, and the American Urogynecological Society recommends that it be performed during any pelvic reconstructive surgery. A key element of the test is confirming that the ureters are open. By increasing urine flow, furosemide can reduce the time to confirmation. But after conferring with a colleague who used the procedure, Dr. Patton looked for some data to support the practice and couldn’t find any.
Although the cystoscopy itself generally is safe, furosemide can cause hypotension, change in renal function, and even dehydration at higher doses. During the question-and-answer period, one attendee noted these issues and pointed out that furosemide can potentiate renal failure, especially among patients taking cephalosporins. “If you’re going to do this sort of trial, you have to consider potential adverse events. A single dose is probably not going to [cause an issue], but in the context of a study you want to monitor the adverse events that have been reported,” this attendee said.
The researchers did not observe any of these adverse events during the study, but Dr. Patton noted that the study was not powered to detect them. “We felt that with the low-dose, single-time [exposure], it was appropriate to not worry too much about those side effects,” he replied.
Another potential concern is that the increased urine flow could mask a kink in the ureter by forcing it open.
In the study, his team randomized 145 patients with a planned cystoscopy as part of a procedure to receive 10-mg furosemide (1 cc) or saline (1 cc) during a cystoscopy performed by an attending or a fellow. The median time to confirmation of ureteral patency was 86.5 seconds in the furosemide group, compared with 165.0 seconds in the saline group (difference, 78.5 seconds; P less than .001). The time to the first ureteral jet was 59 seconds versus 74 seconds, respectively (P less than .006). A Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis also showed a significant improvement in time to ureteral patency confirmation (log-rank P less than .001).
The study was not funded. Dr. Patton has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patton S et al. SGS 2019, Abstract 10.
TUCSON, ARIZ. – according to results from a new randomized, controlled trial.
“It does make a difference, but is that really a [meaningful] difference? Every medication has adverse effects, so is it worth that extra time [savings] to take on that potential for side effects? It highlights the importance of statistical significance versus clinical significance, and I think [the clinical significance] can just be answered by each individual physician,” Simon Patton, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Patton is a urogynecologist at Ascension Via Christi Medical Group in Wichita, Kan. He presented the study, which was conducted during his time as a fellow at the University of South Florida, Tampa, at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons. Dr. Patton isn’t sure just how often physicians use furosemide during routine cystoscopy. “It would be great to do a survey to find out how many people use it in their practice,” he said.
Cystoscopy is used to during a surgery to ensure that no injury has been done to the bladder or the urethra, and the American Urogynecological Society recommends that it be performed during any pelvic reconstructive surgery. A key element of the test is confirming that the ureters are open. By increasing urine flow, furosemide can reduce the time to confirmation. But after conferring with a colleague who used the procedure, Dr. Patton looked for some data to support the practice and couldn’t find any.
Although the cystoscopy itself generally is safe, furosemide can cause hypotension, change in renal function, and even dehydration at higher doses. During the question-and-answer period, one attendee noted these issues and pointed out that furosemide can potentiate renal failure, especially among patients taking cephalosporins. “If you’re going to do this sort of trial, you have to consider potential adverse events. A single dose is probably not going to [cause an issue], but in the context of a study you want to monitor the adverse events that have been reported,” this attendee said.
The researchers did not observe any of these adverse events during the study, but Dr. Patton noted that the study was not powered to detect them. “We felt that with the low-dose, single-time [exposure], it was appropriate to not worry too much about those side effects,” he replied.
Another potential concern is that the increased urine flow could mask a kink in the ureter by forcing it open.
In the study, his team randomized 145 patients with a planned cystoscopy as part of a procedure to receive 10-mg furosemide (1 cc) or saline (1 cc) during a cystoscopy performed by an attending or a fellow. The median time to confirmation of ureteral patency was 86.5 seconds in the furosemide group, compared with 165.0 seconds in the saline group (difference, 78.5 seconds; P less than .001). The time to the first ureteral jet was 59 seconds versus 74 seconds, respectively (P less than .006). A Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis also showed a significant improvement in time to ureteral patency confirmation (log-rank P less than .001).
The study was not funded. Dr. Patton has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Patton S et al. SGS 2019, Abstract 10.
REPORTING FROM SGS 2019
SUI cure definition may need updating
TUCSON, ARIZ. – The definition of a surgical cure for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) varies significantly from one clinical trial to another, but the best choice might be an International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ) score of 5 or less, according to a study that correlated a patient’s definition of success with various measures of success or failure.
Adoption of a standard definition could make clinical trial results easier to interpret, as well as improve consistency in clinical practice.
The study was a planned secondary analysis of a randomized, controlled trial that compared midurethral sling to Burch colpopexy in women undergoing abdominal sacrocolpopexy. The original study found no difference in outcomes between the two approaches with respect to stress-specific incontinence rates at 6 months, although the midurethral sling was associated with better secondary, patient-reported outcomes.
That incongruity between objective and subjective outcomes raised questions. “I would frequently have the nurse tell me that a patient didn’t do well [on the stress incontinence test], but you would talk to the patient, and she was happy as could be. She wasn’t using pads, she was perfectly dry. So I thought there was a little bit of a disconnect between the definitions we were using, and what the patients wanted from the procedure,” Emanuel Trabuco, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Trabuco is a consultant and the chair of the division of urogynecology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. He presented the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons.
because as things currently stand, different clinical trials use a range of different outcomes, and as the nurse’s experience shows, an objective outcome might not match patient perception. In fact, objective urinary incontinence tests may not be so objective at all.
“Urodynamics is inherently [challenging]. You can have women that come in with stress incontinence symptoms asking for treatment, and we do urodynamics and they don’t leak. It’s a false negative. Conversely, other women presenting with other issues like overactive bladder – you do urodynamics, and they leak. So that’s a false positive. We have this desire for objectivity, but the tests we have are neither sensitive nor specific,” said Dr. Trabuco.
The researchers examined 13 different methods of determining SUI cure, and then linked them to answers to two questions from 104 trial participants. The first question: “In your opinion, how successful has treatment for your urinary leakage been?” Responses ranged from 0 (not at all) to 10 (very successful). The second question: “Compared to how you were before your recent surgery, how are your urinary leakage symptoms now?” Responses ranged from 0 (much worse) to 10 (much better).
At 6 months, the largest Cohen’s d value for patient perception of symptom improvement was associated with ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (–13.5, mean ratings of 9.7 versus 4.6), which was better than definitions based on a negative cough stress test (–6.5) and the strict composite definition, which included a negative cough stress test, ICIQ = 0, and no retreatment (–6.4).
The researchers examined the correlation between each definition of SUI cure and the answers to the above questions, and found that the highest Cohen’s d values for agreement with patient’s perception of symptom improvement were: ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (Cohen’s d at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months; –13.5; –13.0; –12.6, respectively); ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no (“not-at-all” or “somewhat”) SUI symptoms on Urinary Distress Inventory, Short Form (UDI-6) (–7.2; –7.2; and –8.1); and ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no SUI symptoms (never or rarely) on Medical, Epidemiologic, and Social aspects of Aging (MESA) urinary incontinence questionnaire (–7.0, –7.0, –6.4).
The results argue against the use of cough stress test, said Dr. Trabuco. “If you think about the time commitment that our patients give us to participate in a trial, we should make that participation as least onerous as we can. If the cough stress test doesn’t really add anything to patient perception of surgical success and improvement, why put the poor patient through a catheterization and a cough test and a prolonged visit? For all of those reasons, I hope this is something that others will look at and try to standardize,” said Dr. Trabuco.
Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., funded the study. Dr. Trabuco has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Trabuco E et al. SGS 2019, oral poster 14.
TUCSON, ARIZ. – The definition of a surgical cure for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) varies significantly from one clinical trial to another, but the best choice might be an International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ) score of 5 or less, according to a study that correlated a patient’s definition of success with various measures of success or failure.
Adoption of a standard definition could make clinical trial results easier to interpret, as well as improve consistency in clinical practice.
The study was a planned secondary analysis of a randomized, controlled trial that compared midurethral sling to Burch colpopexy in women undergoing abdominal sacrocolpopexy. The original study found no difference in outcomes between the two approaches with respect to stress-specific incontinence rates at 6 months, although the midurethral sling was associated with better secondary, patient-reported outcomes.
That incongruity between objective and subjective outcomes raised questions. “I would frequently have the nurse tell me that a patient didn’t do well [on the stress incontinence test], but you would talk to the patient, and she was happy as could be. She wasn’t using pads, she was perfectly dry. So I thought there was a little bit of a disconnect between the definitions we were using, and what the patients wanted from the procedure,” Emanuel Trabuco, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Trabuco is a consultant and the chair of the division of urogynecology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. He presented the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons.
because as things currently stand, different clinical trials use a range of different outcomes, and as the nurse’s experience shows, an objective outcome might not match patient perception. In fact, objective urinary incontinence tests may not be so objective at all.
“Urodynamics is inherently [challenging]. You can have women that come in with stress incontinence symptoms asking for treatment, and we do urodynamics and they don’t leak. It’s a false negative. Conversely, other women presenting with other issues like overactive bladder – you do urodynamics, and they leak. So that’s a false positive. We have this desire for objectivity, but the tests we have are neither sensitive nor specific,” said Dr. Trabuco.
The researchers examined 13 different methods of determining SUI cure, and then linked them to answers to two questions from 104 trial participants. The first question: “In your opinion, how successful has treatment for your urinary leakage been?” Responses ranged from 0 (not at all) to 10 (very successful). The second question: “Compared to how you were before your recent surgery, how are your urinary leakage symptoms now?” Responses ranged from 0 (much worse) to 10 (much better).
At 6 months, the largest Cohen’s d value for patient perception of symptom improvement was associated with ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (–13.5, mean ratings of 9.7 versus 4.6), which was better than definitions based on a negative cough stress test (–6.5) and the strict composite definition, which included a negative cough stress test, ICIQ = 0, and no retreatment (–6.4).
The researchers examined the correlation between each definition of SUI cure and the answers to the above questions, and found that the highest Cohen’s d values for agreement with patient’s perception of symptom improvement were: ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (Cohen’s d at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months; –13.5; –13.0; –12.6, respectively); ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no (“not-at-all” or “somewhat”) SUI symptoms on Urinary Distress Inventory, Short Form (UDI-6) (–7.2; –7.2; and –8.1); and ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no SUI symptoms (never or rarely) on Medical, Epidemiologic, and Social aspects of Aging (MESA) urinary incontinence questionnaire (–7.0, –7.0, –6.4).
The results argue against the use of cough stress test, said Dr. Trabuco. “If you think about the time commitment that our patients give us to participate in a trial, we should make that participation as least onerous as we can. If the cough stress test doesn’t really add anything to patient perception of surgical success and improvement, why put the poor patient through a catheterization and a cough test and a prolonged visit? For all of those reasons, I hope this is something that others will look at and try to standardize,” said Dr. Trabuco.
Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., funded the study. Dr. Trabuco has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Trabuco E et al. SGS 2019, oral poster 14.
TUCSON, ARIZ. – The definition of a surgical cure for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) varies significantly from one clinical trial to another, but the best choice might be an International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ) score of 5 or less, according to a study that correlated a patient’s definition of success with various measures of success or failure.
Adoption of a standard definition could make clinical trial results easier to interpret, as well as improve consistency in clinical practice.
The study was a planned secondary analysis of a randomized, controlled trial that compared midurethral sling to Burch colpopexy in women undergoing abdominal sacrocolpopexy. The original study found no difference in outcomes between the two approaches with respect to stress-specific incontinence rates at 6 months, although the midurethral sling was associated with better secondary, patient-reported outcomes.
That incongruity between objective and subjective outcomes raised questions. “I would frequently have the nurse tell me that a patient didn’t do well [on the stress incontinence test], but you would talk to the patient, and she was happy as could be. She wasn’t using pads, she was perfectly dry. So I thought there was a little bit of a disconnect between the definitions we were using, and what the patients wanted from the procedure,” Emanuel Trabuco, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Trabuco is a consultant and the chair of the division of urogynecology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. He presented the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons.
because as things currently stand, different clinical trials use a range of different outcomes, and as the nurse’s experience shows, an objective outcome might not match patient perception. In fact, objective urinary incontinence tests may not be so objective at all.
“Urodynamics is inherently [challenging]. You can have women that come in with stress incontinence symptoms asking for treatment, and we do urodynamics and they don’t leak. It’s a false negative. Conversely, other women presenting with other issues like overactive bladder – you do urodynamics, and they leak. So that’s a false positive. We have this desire for objectivity, but the tests we have are neither sensitive nor specific,” said Dr. Trabuco.
The researchers examined 13 different methods of determining SUI cure, and then linked them to answers to two questions from 104 trial participants. The first question: “In your opinion, how successful has treatment for your urinary leakage been?” Responses ranged from 0 (not at all) to 10 (very successful). The second question: “Compared to how you were before your recent surgery, how are your urinary leakage symptoms now?” Responses ranged from 0 (much worse) to 10 (much better).
At 6 months, the largest Cohen’s d value for patient perception of symptom improvement was associated with ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (–13.5, mean ratings of 9.7 versus 4.6), which was better than definitions based on a negative cough stress test (–6.5) and the strict composite definition, which included a negative cough stress test, ICIQ = 0, and no retreatment (–6.4).
The researchers examined the correlation between each definition of SUI cure and the answers to the above questions, and found that the highest Cohen’s d values for agreement with patient’s perception of symptom improvement were: ICIQ score greater than or equal to 5 (Cohen’s d at 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months; –13.5; –13.0; –12.6, respectively); ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no (“not-at-all” or “somewhat”) SUI symptoms on Urinary Distress Inventory, Short Form (UDI-6) (–7.2; –7.2; and –8.1); and ICIQ score less than or equal to 5 with no SUI symptoms (never or rarely) on Medical, Epidemiologic, and Social aspects of Aging (MESA) urinary incontinence questionnaire (–7.0, –7.0, –6.4).
The results argue against the use of cough stress test, said Dr. Trabuco. “If you think about the time commitment that our patients give us to participate in a trial, we should make that participation as least onerous as we can. If the cough stress test doesn’t really add anything to patient perception of surgical success and improvement, why put the poor patient through a catheterization and a cough test and a prolonged visit? For all of those reasons, I hope this is something that others will look at and try to standardize,” said Dr. Trabuco.
Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., funded the study. Dr. Trabuco has no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Trabuco E et al. SGS 2019, oral poster 14.
REPORTING FROM SGS 2019