User login
77 Million U.S. Residents Have Difficulty Understanding Basic Health Information
The number of U.S. residents who have difficulty understanding basic health information, according to a report developed by the University of California at San Francisco and San Francisco General Hospital and published by the Institute of Medicine.1 The report also suggests ways to bridge the gaps to understanding, such as how to make this a priority at every level of the health organization, avoid stigmatizing patients over literacy issues, and adopt proven educational techniques such as teach-back (see “Teach-Back,” September 2012).
Reference
The number of U.S. residents who have difficulty understanding basic health information, according to a report developed by the University of California at San Francisco and San Francisco General Hospital and published by the Institute of Medicine.1 The report also suggests ways to bridge the gaps to understanding, such as how to make this a priority at every level of the health organization, avoid stigmatizing patients over literacy issues, and adopt proven educational techniques such as teach-back (see “Teach-Back,” September 2012).
Reference
The number of U.S. residents who have difficulty understanding basic health information, according to a report developed by the University of California at San Francisco and San Francisco General Hospital and published by the Institute of Medicine.1 The report also suggests ways to bridge the gaps to understanding, such as how to make this a priority at every level of the health organization, avoid stigmatizing patients over literacy issues, and adopt proven educational techniques such as teach-back (see “Teach-Back,” September 2012).
Reference
Win Whitcomb: Hospital Readmissions Penalties Start Now
The uproar and confusion over readmissions penalties has consumed umpteen hours of senior leaders’ time (especially that of CFOs), not to mention that of front-line nurses, case managers, quality-improvement (QI) coordinators, hospitalists, and others involved in discharge planning and ensuring a safe transition for patients out of the hospital. For many, the math is fuzzy, and for most, the return on investment is even fuzzier. After all, avoided readmissions are lost revenue to those who are running a business known as an acute-care hospital.
Let me start with the conclusion: Eliminating avoidable readmissions is the right thing to do, period. But the financial downside to doing so is probably greater than any upside realized through avoidance of the penalties that began affecting hospital payments on Oct. 1—at least in the fee-for-service world we live in. At some point in the future, when most patients are under a global payment, the math might be clearer, but today, penalties probably won’t offset lost revenue from reduced readmissions added to the cost of paying lots of people to work in meetings (and at the bedside) to devise better care transitions. (Caveat: If your hospital is bursting at the seams with full occupancy, reducing readmissions and replacing them with higher-reimbursing patients, such as those undergoing elective major surgery, likely will be a net financial gain for your hospital.)
Part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) will reduce total Medicare DRG reimbursement for hospitals beginning in fiscal-year 2013 based on actual 30-day readmission rates for myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), and pneumonia that are in excess of risk-adjusted expected rates. The reduction is capped at 1% in 2013, 2% in 2014, and 3% in 2015 and beyond. Hospital readmission rates are based on calculated baseline rates using Medicare data from July 1, 2008, to June 30, 2011.
Cost of a Readmissions-Reduction Program
How much does it cost for a hospital to implement a care-transitions program—such as SHM’s Project BOOST—to reduce readmissions? Last year, I interviewed a dozen hospitals that successfully implemented SHM’s formal mentored implementation program. The result? In the first year of the program, hospitals spent about $170,000 on training and staff time devoted to the project.
Lost Revenue
Let’s look at a sample penalty calculation, then examine a scenario sizing up how revenue is lost when a hospital is successful in reducing readmissions. The ACA defines the payments for excess readmissions as:
The number of patients with the applicable condition (HF, MI, or pneumonia) multiplied by the base DRG payment made for those patients multiplied by the percentage of readmissions beyond the expected.
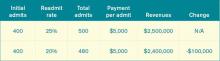
As an example, let’s take a hospital that treats 500 pneumonia patients (# with the applicable condition), has a base DRG payment for pneumonia of $5,000, and a readmission rate that is 4% higher than expected (in this example, the actual rate is 25% and the expected rate is 24%; 1/25=4%). The penalty is 500 X $5,000 X .04, or $100,000. We’ll assume that the readmission rate for myocardial infarction and heart failure are less than expected, so the total penalty is $100,000.
Let’s say the hospital works hard to decrease pneumonia readmissions from 25% to 20% and avoids the penalty. As outlined in Table 1, the hospital will lose $100,000 in revenue (admittedly, reducing readmissions to 20% from 25% represents a big jump, but this is for illustration purposes—we haven’t added in lost revenue from reduced readmissions for other conditions). What’s the final cost of avoiding the $100,000 readmission penalty? Lost revenue of $100,000 plus the cost of implementing the readmission reduction program of $170,000=$270,000.
Why Are We Doing This?
I see the value in care transitions and readmissions-reduction programs, such as Project BOOST, first and foremost as a way to improve patient safety; as such, if implemented effectively, they are likely worth the investment. Second, their value lies in the preparation all hospitals and health systems should be undergoing to remain market-competitive and solvent under global payment systems. Because the penalties in the HRRP might come with lost revenues and the costs of program implementation, be clear about your team’s motivation for reducing readmissions. Your CFO will see to it if I don’t.
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
The uproar and confusion over readmissions penalties has consumed umpteen hours of senior leaders’ time (especially that of CFOs), not to mention that of front-line nurses, case managers, quality-improvement (QI) coordinators, hospitalists, and others involved in discharge planning and ensuring a safe transition for patients out of the hospital. For many, the math is fuzzy, and for most, the return on investment is even fuzzier. After all, avoided readmissions are lost revenue to those who are running a business known as an acute-care hospital.
Let me start with the conclusion: Eliminating avoidable readmissions is the right thing to do, period. But the financial downside to doing so is probably greater than any upside realized through avoidance of the penalties that began affecting hospital payments on Oct. 1—at least in the fee-for-service world we live in. At some point in the future, when most patients are under a global payment, the math might be clearer, but today, penalties probably won’t offset lost revenue from reduced readmissions added to the cost of paying lots of people to work in meetings (and at the bedside) to devise better care transitions. (Caveat: If your hospital is bursting at the seams with full occupancy, reducing readmissions and replacing them with higher-reimbursing patients, such as those undergoing elective major surgery, likely will be a net financial gain for your hospital.)
Part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) will reduce total Medicare DRG reimbursement for hospitals beginning in fiscal-year 2013 based on actual 30-day readmission rates for myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), and pneumonia that are in excess of risk-adjusted expected rates. The reduction is capped at 1% in 2013, 2% in 2014, and 3% in 2015 and beyond. Hospital readmission rates are based on calculated baseline rates using Medicare data from July 1, 2008, to June 30, 2011.
Cost of a Readmissions-Reduction Program
How much does it cost for a hospital to implement a care-transitions program—such as SHM’s Project BOOST—to reduce readmissions? Last year, I interviewed a dozen hospitals that successfully implemented SHM’s formal mentored implementation program. The result? In the first year of the program, hospitals spent about $170,000 on training and staff time devoted to the project.
Lost Revenue
Let’s look at a sample penalty calculation, then examine a scenario sizing up how revenue is lost when a hospital is successful in reducing readmissions. The ACA defines the payments for excess readmissions as:
The number of patients with the applicable condition (HF, MI, or pneumonia) multiplied by the base DRG payment made for those patients multiplied by the percentage of readmissions beyond the expected.
As an example, let’s take a hospital that treats 500 pneumonia patients (# with the applicable condition), has a base DRG payment for pneumonia of $5,000, and a readmission rate that is 4% higher than expected (in this example, the actual rate is 25% and the expected rate is 24%; 1/25=4%). The penalty is 500 X $5,000 X .04, or $100,000. We’ll assume that the readmission rate for myocardial infarction and heart failure are less than expected, so the total penalty is $100,000.
Let’s say the hospital works hard to decrease pneumonia readmissions from 25% to 20% and avoids the penalty. As outlined in Table 1, the hospital will lose $100,000 in revenue (admittedly, reducing readmissions to 20% from 25% represents a big jump, but this is for illustration purposes—we haven’t added in lost revenue from reduced readmissions for other conditions). What’s the final cost of avoiding the $100,000 readmission penalty? Lost revenue of $100,000 plus the cost of implementing the readmission reduction program of $170,000=$270,000.
Why Are We Doing This?
I see the value in care transitions and readmissions-reduction programs, such as Project BOOST, first and foremost as a way to improve patient safety; as such, if implemented effectively, they are likely worth the investment. Second, their value lies in the preparation all hospitals and health systems should be undergoing to remain market-competitive and solvent under global payment systems. Because the penalties in the HRRP might come with lost revenues and the costs of program implementation, be clear about your team’s motivation for reducing readmissions. Your CFO will see to it if I don’t.
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
The uproar and confusion over readmissions penalties has consumed umpteen hours of senior leaders’ time (especially that of CFOs), not to mention that of front-line nurses, case managers, quality-improvement (QI) coordinators, hospitalists, and others involved in discharge planning and ensuring a safe transition for patients out of the hospital. For many, the math is fuzzy, and for most, the return on investment is even fuzzier. After all, avoided readmissions are lost revenue to those who are running a business known as an acute-care hospital.
Let me start with the conclusion: Eliminating avoidable readmissions is the right thing to do, period. But the financial downside to doing so is probably greater than any upside realized through avoidance of the penalties that began affecting hospital payments on Oct. 1—at least in the fee-for-service world we live in. At some point in the future, when most patients are under a global payment, the math might be clearer, but today, penalties probably won’t offset lost revenue from reduced readmissions added to the cost of paying lots of people to work in meetings (and at the bedside) to devise better care transitions. (Caveat: If your hospital is bursting at the seams with full occupancy, reducing readmissions and replacing them with higher-reimbursing patients, such as those undergoing elective major surgery, likely will be a net financial gain for your hospital.)
Part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) will reduce total Medicare DRG reimbursement for hospitals beginning in fiscal-year 2013 based on actual 30-day readmission rates for myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), and pneumonia that are in excess of risk-adjusted expected rates. The reduction is capped at 1% in 2013, 2% in 2014, and 3% in 2015 and beyond. Hospital readmission rates are based on calculated baseline rates using Medicare data from July 1, 2008, to June 30, 2011.
Cost of a Readmissions-Reduction Program
How much does it cost for a hospital to implement a care-transitions program—such as SHM’s Project BOOST—to reduce readmissions? Last year, I interviewed a dozen hospitals that successfully implemented SHM’s formal mentored implementation program. The result? In the first year of the program, hospitals spent about $170,000 on training and staff time devoted to the project.
Lost Revenue
Let’s look at a sample penalty calculation, then examine a scenario sizing up how revenue is lost when a hospital is successful in reducing readmissions. The ACA defines the payments for excess readmissions as:
The number of patients with the applicable condition (HF, MI, or pneumonia) multiplied by the base DRG payment made for those patients multiplied by the percentage of readmissions beyond the expected.
As an example, let’s take a hospital that treats 500 pneumonia patients (# with the applicable condition), has a base DRG payment for pneumonia of $5,000, and a readmission rate that is 4% higher than expected (in this example, the actual rate is 25% and the expected rate is 24%; 1/25=4%). The penalty is 500 X $5,000 X .04, or $100,000. We’ll assume that the readmission rate for myocardial infarction and heart failure are less than expected, so the total penalty is $100,000.
Let’s say the hospital works hard to decrease pneumonia readmissions from 25% to 20% and avoids the penalty. As outlined in Table 1, the hospital will lose $100,000 in revenue (admittedly, reducing readmissions to 20% from 25% represents a big jump, but this is for illustration purposes—we haven’t added in lost revenue from reduced readmissions for other conditions). What’s the final cost of avoiding the $100,000 readmission penalty? Lost revenue of $100,000 plus the cost of implementing the readmission reduction program of $170,000=$270,000.
Why Are We Doing This?
I see the value in care transitions and readmissions-reduction programs, such as Project BOOST, first and foremost as a way to improve patient safety; as such, if implemented effectively, they are likely worth the investment. Second, their value lies in the preparation all hospitals and health systems should be undergoing to remain market-competitive and solvent under global payment systems. Because the penalties in the HRRP might come with lost revenues and the costs of program implementation, be clear about your team’s motivation for reducing readmissions. Your CFO will see to it if I don’t.
Dr. Whitcomb is medical director of healthcare quality at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Mass. He is a co-founder and past president of SHM. Email him at [email protected].
Alternative Healthcare Models Aim to Boost Sagging Critical-Care Workforce
Amid the struggle to boost the country’s sagging critical-care workforce, experts have most commonly proposed creating a tiered or regionalized model of care, investing more in tele-ICU services, and augmenting the role of midlevel providers.
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, with 20 hospitals and roughly 500 ICU beds throughout its network, is adopting a regionalized healthcare delivery system. Some of the center’s most high-risk services, such as its big transplant programs, are centralized within the main university campus hospitals, as are about half of the ICU beds.
“In those hospitals, we’ve decided that we need 24/7 in-house, intensive-care attendings,” says Derek Angus, MD, the center’s chair of critical-care medicine. The doctors work with fellows and a rapidly growing expansion of midlevel providers.
In some of the smaller hospitals, however, some ICU patients are seen and managed by hospitalists. The medical center’s eventual goal is to be more systematic about the kinds of patients managed by intensivists as well as those managed by hospitalists. It’s a task made easier by the specialists’ close working relationship within the same department.
Dr. Angus believes telemedicine could help by providing a sort of mission control that can help track critically ill patients and those at risk of being admitted to ICUs across all 20 hospitals. He concedes, however, that telemedicine for ICU assistance has had mixed results in the medical literature, suggesting that a major key is working out the proper roles and responsibilities of those using the technology.
To improve the consistency of its own frontline providers, the Emory University Center for Critical Care in Atlanta developed a competency-based, critical-care training program for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs).
“It’s very clear that if you have a group of NP and PA providers who can do 90 percent of what the physician does, it really begins to unload the physician to focus on what I call the big-picture pieces of critical care,” says center director Timothy Buchman, PhD, MD.
That attending physician can be trained as a care executive to ensure well-coordinated care and to focus on any process that isn’t working well. “At a big academic health sciences center, that should probably be a critical-care physician,” Dr. Buchman notes. “But for the smaller community and regional hospitals that have a relatively less sick population, the person who will be well-positioned to oversee this nonphysician provider staff could well be a hospitalist who’s received additional guidance and training in critical care.”
For mild or moderate complexity of care, he says, the added training need not necessarily include a traditional two-year fellowship. Under a value-based system, sicker patients could be rapidly transferred to a higher level of care, and telemedicine could provide a “backstop” for providers in smaller hospitals who lack the training and experience of someone with a full critical-care fellowship.
Amid the struggle to boost the country’s sagging critical-care workforce, experts have most commonly proposed creating a tiered or regionalized model of care, investing more in tele-ICU services, and augmenting the role of midlevel providers.
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, with 20 hospitals and roughly 500 ICU beds throughout its network, is adopting a regionalized healthcare delivery system. Some of the center’s most high-risk services, such as its big transplant programs, are centralized within the main university campus hospitals, as are about half of the ICU beds.
“In those hospitals, we’ve decided that we need 24/7 in-house, intensive-care attendings,” says Derek Angus, MD, the center’s chair of critical-care medicine. The doctors work with fellows and a rapidly growing expansion of midlevel providers.
In some of the smaller hospitals, however, some ICU patients are seen and managed by hospitalists. The medical center’s eventual goal is to be more systematic about the kinds of patients managed by intensivists as well as those managed by hospitalists. It’s a task made easier by the specialists’ close working relationship within the same department.
Dr. Angus believes telemedicine could help by providing a sort of mission control that can help track critically ill patients and those at risk of being admitted to ICUs across all 20 hospitals. He concedes, however, that telemedicine for ICU assistance has had mixed results in the medical literature, suggesting that a major key is working out the proper roles and responsibilities of those using the technology.
To improve the consistency of its own frontline providers, the Emory University Center for Critical Care in Atlanta developed a competency-based, critical-care training program for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs).
“It’s very clear that if you have a group of NP and PA providers who can do 90 percent of what the physician does, it really begins to unload the physician to focus on what I call the big-picture pieces of critical care,” says center director Timothy Buchman, PhD, MD.
That attending physician can be trained as a care executive to ensure well-coordinated care and to focus on any process that isn’t working well. “At a big academic health sciences center, that should probably be a critical-care physician,” Dr. Buchman notes. “But for the smaller community and regional hospitals that have a relatively less sick population, the person who will be well-positioned to oversee this nonphysician provider staff could well be a hospitalist who’s received additional guidance and training in critical care.”
For mild or moderate complexity of care, he says, the added training need not necessarily include a traditional two-year fellowship. Under a value-based system, sicker patients could be rapidly transferred to a higher level of care, and telemedicine could provide a “backstop” for providers in smaller hospitals who lack the training and experience of someone with a full critical-care fellowship.
Amid the struggle to boost the country’s sagging critical-care workforce, experts have most commonly proposed creating a tiered or regionalized model of care, investing more in tele-ICU services, and augmenting the role of midlevel providers.
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, with 20 hospitals and roughly 500 ICU beds throughout its network, is adopting a regionalized healthcare delivery system. Some of the center’s most high-risk services, such as its big transplant programs, are centralized within the main university campus hospitals, as are about half of the ICU beds.
“In those hospitals, we’ve decided that we need 24/7 in-house, intensive-care attendings,” says Derek Angus, MD, the center’s chair of critical-care medicine. The doctors work with fellows and a rapidly growing expansion of midlevel providers.
In some of the smaller hospitals, however, some ICU patients are seen and managed by hospitalists. The medical center’s eventual goal is to be more systematic about the kinds of patients managed by intensivists as well as those managed by hospitalists. It’s a task made easier by the specialists’ close working relationship within the same department.
Dr. Angus believes telemedicine could help by providing a sort of mission control that can help track critically ill patients and those at risk of being admitted to ICUs across all 20 hospitals. He concedes, however, that telemedicine for ICU assistance has had mixed results in the medical literature, suggesting that a major key is working out the proper roles and responsibilities of those using the technology.
To improve the consistency of its own frontline providers, the Emory University Center for Critical Care in Atlanta developed a competency-based, critical-care training program for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs).
“It’s very clear that if you have a group of NP and PA providers who can do 90 percent of what the physician does, it really begins to unload the physician to focus on what I call the big-picture pieces of critical care,” says center director Timothy Buchman, PhD, MD.
That attending physician can be trained as a care executive to ensure well-coordinated care and to focus on any process that isn’t working well. “At a big academic health sciences center, that should probably be a critical-care physician,” Dr. Buchman notes. “But for the smaller community and regional hospitals that have a relatively less sick population, the person who will be well-positioned to oversee this nonphysician provider staff could well be a hospitalist who’s received additional guidance and training in critical care.”
For mild or moderate complexity of care, he says, the added training need not necessarily include a traditional two-year fellowship. Under a value-based system, sicker patients could be rapidly transferred to a higher level of care, and telemedicine could provide a “backstop” for providers in smaller hospitals who lack the training and experience of someone with a full critical-care fellowship.
Guidelines Drive Optimal Care for Heart Failure Patients
Cardiologists aren’t shy about repeating it: guidelines, guidelines, guidelines. That is, follow them.
“Evidence-based, guideline-driven optimal care for heart failure truly is beneficial,” Dr. Yancy says. “Every effort should be made to strive to achieve ideal thresholds and meeting best practices.”
There is now compelling evidence that, for patients with heart failure, the higher the degree of adherence to Class I-recommended therapies, the greater the reduction in 24-month mortality risk.5
“It would seem as if practicing best quality is almost a perfunctory statement, but consistently, when we look at surveys of quality improvement and adherence to evidence-based strategies, persistent gaps remain in the broader community,” Dr. Yancy says. “We know what we need to do. We’re still striving to get closer and closer to optimal care.”
Dr. Harold says the guidelines are there to make things simpler. So take advantage of them.
“If anything, hospitalists tend to be ahead of most other groups in terms of knowing evidence-based pathways and really tracking very specific protocols,” he says. “I think one of the advantages of hospitalist care is very often, it is guideline-driven. You have less variation in terms of care and quality outcomes.”
Cardiologists aren’t shy about repeating it: guidelines, guidelines, guidelines. That is, follow them.
“Evidence-based, guideline-driven optimal care for heart failure truly is beneficial,” Dr. Yancy says. “Every effort should be made to strive to achieve ideal thresholds and meeting best practices.”
There is now compelling evidence that, for patients with heart failure, the higher the degree of adherence to Class I-recommended therapies, the greater the reduction in 24-month mortality risk.5
“It would seem as if practicing best quality is almost a perfunctory statement, but consistently, when we look at surveys of quality improvement and adherence to evidence-based strategies, persistent gaps remain in the broader community,” Dr. Yancy says. “We know what we need to do. We’re still striving to get closer and closer to optimal care.”
Dr. Harold says the guidelines are there to make things simpler. So take advantage of them.
“If anything, hospitalists tend to be ahead of most other groups in terms of knowing evidence-based pathways and really tracking very specific protocols,” he says. “I think one of the advantages of hospitalist care is very often, it is guideline-driven. You have less variation in terms of care and quality outcomes.”
Cardiologists aren’t shy about repeating it: guidelines, guidelines, guidelines. That is, follow them.
“Evidence-based, guideline-driven optimal care for heart failure truly is beneficial,” Dr. Yancy says. “Every effort should be made to strive to achieve ideal thresholds and meeting best practices.”
There is now compelling evidence that, for patients with heart failure, the higher the degree of adherence to Class I-recommended therapies, the greater the reduction in 24-month mortality risk.5
“It would seem as if practicing best quality is almost a perfunctory statement, but consistently, when we look at surveys of quality improvement and adherence to evidence-based strategies, persistent gaps remain in the broader community,” Dr. Yancy says. “We know what we need to do. We’re still striving to get closer and closer to optimal care.”
Dr. Harold says the guidelines are there to make things simpler. So take advantage of them.
“If anything, hospitalists tend to be ahead of most other groups in terms of knowing evidence-based pathways and really tracking very specific protocols,” he says. “I think one of the advantages of hospitalist care is very often, it is guideline-driven. You have less variation in terms of care and quality outcomes.”
12 Things Cardiologists Think Hospitalists Need to Know
Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with [aldosterone antagonists], even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines.

—Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief, University of California at Los Angeles division of cardiology, chair, American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program steering committee
You might not have done a fellowship in cardiology, but quite often you probably feel like a cardiologist. Hospitalists frequently attend to patients on observation for heart problems and help manage even the most complex patients.
Often, you are working alongside the cardiologist. But other times, you’re on your own. Hospitalists are expected to carry an increasingly heavy load when it comes to heart-failure patients and many other kinds of patients with specialized disorders. It can be hard to keep up with what you need to know.
Top Twelve
- Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
- It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
- New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
- Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
- Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
- Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
- Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
- Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.
- Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
- Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
- Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
- Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
The Hospitalist spoke to several cardiologists about the latest in treatments, technologies, and HM’s role in the system of care. The following are their suggestions for what you really need to know about treating patients with heart conditions.
1) Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensive receptor blockers have been part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) core measures for heart failure for a long time, but beta-blockers at hospital discharge only recently have been added as American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/American Medical Association–Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement measures for heart failure.1
“For those with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, very old and outdated concepts would have talked about potentially holding the beta-blocker during hospitalization for heart failure—or not initiating until the patient was an outpatient,” says Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief of the University of California at Los Angeles’ division of cardiology and chair of the steering committee for the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program. “[But] the guidelines and evidence, and often performance measures, linked to them are now explicit about initiating or maintaining beta-blockers during the heart-failure hospitalization.”
Beta-blockers should be initiated as patients are stabilized before discharge. Dr. Fonarow suggests hospitalists use only one of the three evidence-based therapies: carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, or bisoprolol.
“Many physicians have been using metoprolol tartrate or atenolol in heart-failure patients,” Dr. Fonarow says. “These are not known to improve clinical outcomes. So here’s an example where the specific medication is absolutely, critically important.”
2) It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
“The modifier is very important,” says Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago. “Heart failure continues to be a problematic disease. Many patients now do really well, but some do not. Those patients are symptomatic and may require frequent hospitalizations for stabilization. We should not disallow or misdirect those patients who need inpatient care from receiving such because of an arbitrary incentive to reduce rehospitalizations out of fear of punitive financial damages. The unforeseen risks here are real.”
Dr. Yancy says studies based on CMS data have found that institutions with higher readmission rates have lower 30-day mortality rates.2 He cautions hospitalists to be “very thoughtful about an overzealous embrace of reducing all readmissions for heart failure.” Instead, the goal should be to limit the “avoidable readmissions.”
“And for the patient that clearly has advanced disease,” he says, “rather than triaging them away from the hospital, we really should be very respectful of their disease. Keep those patients where disease-modifying interventions can be deployed, and we can work to achieve the best possible outcome for those that have the most advanced disease.”
3) New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
Advances in interventional procedures, including transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and endoscopic mitral valve repair, will translate into a new population of highly complex patients. Many of these patients will be in their 80s or 90s.
“It’s a whole new paradigm shift of technology,” says John Harold, MD, president-elect of the American College of Cardiology and past chief of staff and department of medicine clinical chief of staff at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. “Very often, the hospitalist is at the front dealing with all of these issues.”
Many of these patients have other problems, including renal insufficiency, diabetes, and the like.
“They have all sorts of other things going on simultaneously, so very often the hospitalist becomes … the point person in dealing with all of these issues,” Dr. Harold says.
4) Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
Aldosterone antagonists can greatly improve outcomes and reduce hospitalization in heart-failure patients, but they have to be used with very careful dosing and patient selection, Dr. Fonarow says. And they require early follow-up once patients are discharged.
“Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with this agent, even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines,” Dr. Fonarow says. “But this is one where it needs to be started at appropriate low doses, with meticulous monitoring in both the inpatient and the outpatient setting, early follow-up, and early laboratory checks.”
5) Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
Transitioning patients from IV diuretics to oral regimens is an area rife with mistakes, Dr. Fonarow says. It requires a lot of “meticulous attention to proper potassium supplementation and monitoring of renal function and electrolyte levels,” he says.
Medication reconciliation—“med rec”—is especially important during the transition from inpatient to outpatient.
“There are common medication errors that are made during this transition,” Dr. Fonarow says. “Hospitalists, along with other [care team] members, can really play a critically important role in trying to reduce that risk.”
6) Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
“We really can’t exercise a thought economy that just says, ‘Extrapolate the evidence-based therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction’ and expect good outcomes,” Dr. Yancy says. “That’s not the case. We don’t have an evidence base to substantiate that.”
He says one or more common comorbidities (e.g. atrial fibrillation, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, renal insufficiency) are present in 90% of patients with preserved ejection fraction. Treatment of those comorbidities—for example, rate control in afib patients, lowering the blood pressure in hypertension patients—has to be done with care.
“We should recognize that the therapy for this condition, albeit absent any specifically indicated interventions that will change its natural history, can still be skillfully constructed,” Dr. Yancy says. “But that construct needs to reflect the recommended, guideline-driven interventions for the concomitant other comorbidities.”
7) Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
For patients who aren’t in cardiogenic shock, using inotropic agents doesn’t help. In fact, it might actually hurt. Dr. Fonarow says studies have shown these agents can “prolong length of stay, cause complications, and increase mortality risk.”
He notes that the use of inotropes should be avoided, or if it’s being considered, a cardiologist with knowledge and experience in heart failure should be involved in the treatment and care.
Statements about avoiding inotropes in heart failure, except under very specific circumstances, have been “incredibly strengthened” recently in the American College of Cardiology and Heart Failure Society of America guidelines.3
8) Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.

—John Harold, MD, president-elect, American College of Cardiology, former chief of staff, department of medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
Hospitalists caring for acute coronary syndrome patients need to familiarize themselves with updated guidelines and additional therapies that are now available, Dr. Fonarow says. New antiplatelet therapies (e.g. prasugrel and ticagrelor) are available as part of the armamentarium, along with the mainstay clopidogrel.
“These therapies lower the risk of recurrent events, lowered the risk of stent thrombosis,” he says. “In the case of ticagrelor, it actually lowered all-cause mortality. These are important new therapies, with new guideline recommendations, that all hospitalists should be aware of.”
9) Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
“Patients getting such devices as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defribrillators (ICD) installed tend not to need bridging,” says Joaquin Cigarroa, MD, clinical chief of cardiology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
He says it’s actually “safer” to do the procedure when patients “are on oral antithrombotics than switching them from an oral agent, and bridging with low- molecular-weight- or unfractionated heparin.”
“It’s a big deal,” Dr. Cigarroa adds, because it is risky to have elderly and frail patients on multiple antithrombotics. “Hemorrhagic complications in cardiology patients still occurs very frequently, so really be attuned to estimating bleeding risk and making sure that we’re dosing antithrombotics appropriately. Bridging should be the minority of patients, not the majority of patients.”
10) Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
Door-to-balloon time is recognized as critical for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients, but more recent work—such as in the TIMACS trial—finds benefits of early revascularization for some non-STEMI patients as well.2
“This trial showed that among higher-risk patients, using a validated risk score, that those patients did benefit from an early approach, meaning going to the cath lab in the first 12 hours of hospitalization,” Dr. Fonarow says. “We now have more information about the optimal timing of coronary angiography and potential revascularization of higher-risk patients with non-ST-segment elevation MI.”
11) Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
The introduction of dabigatran and rivaroxaban (and, perhaps soon, apixaban) to the array of anticoagulant therapies brings a new slate of considerations for hospitalists, Dr. Harold says.
“For the majority of these, there’s no specific way to reverse the anticoagulant effect in the event of a major bleeding event,” he says. “There’s no simple antidote. And the effect can last up to 12 to 24 hours, depending on the renal function. This is what the hospitalist will be called to deal with: bleeding complications in patients who have these newer anticoagulants on board.”
Dr. Fonarow says that the new CHA2DS2-VASc score has been found to do a better job than the traditional CHADS2 score in assessing afib stroke risk.4
12) Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
Dr. Harold says that most hospitalists probably are up to date on drug-eluting stents and the risk of stopping dual antiplatelet therapy within several months of implant, but that doesn’t mean they won’t treat patients whose primary-care physicians (PCPs) aren’t up to date. He recommends working on these cases with hematologists.
“That knowledge is not widespread in terms of the internal-medicine community,” he says. “I’ve seen situations where patients have had their Plavix stopped for colonoscopies and they’ve had stent thrombosis. It’s this knowledge of cardiac patients who come in with recent deployment of drug-eluting stents who may end up having other issues.”
Tom Collins is a freelance writer in South Florida.
References
- 2009 Focused Update: ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults. Circulation. 2009;119:1977-2016 an HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Cardiac Failure. 2010;16(6):475-539.
- Gorodeski EZ, Starling RC, Blackstone EH. Are all readmissions bad readmissions? N Engl J Med. 2010;363:297-298.
- Mehta SR, Granger CB, Boden WE, et al. Early versus delayed invasive intervention in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(21):2165-2175.
- Olesen JB, Torp-Pedersen C, Hansen ML, Lip GY. The value of the CHA2DS2-VASc score for refining stroke risk stratification in patients with atrial fibrillation with a CHADS2 score 0-1: a nationwide cohort study. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(6):1172-1179.
- Associations between outpatient heart failure process-of-care measures and mortality. Circulation. 2011;123(15):1601-1610.
Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with [aldosterone antagonists], even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines.

—Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief, University of California at Los Angeles division of cardiology, chair, American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program steering committee
You might not have done a fellowship in cardiology, but quite often you probably feel like a cardiologist. Hospitalists frequently attend to patients on observation for heart problems and help manage even the most complex patients.
Often, you are working alongside the cardiologist. But other times, you’re on your own. Hospitalists are expected to carry an increasingly heavy load when it comes to heart-failure patients and many other kinds of patients with specialized disorders. It can be hard to keep up with what you need to know.
Top Twelve
- Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
- It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
- New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
- Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
- Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
- Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
- Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
- Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.
- Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
- Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
- Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
- Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
The Hospitalist spoke to several cardiologists about the latest in treatments, technologies, and HM’s role in the system of care. The following are their suggestions for what you really need to know about treating patients with heart conditions.
1) Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensive receptor blockers have been part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) core measures for heart failure for a long time, but beta-blockers at hospital discharge only recently have been added as American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/American Medical Association–Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement measures for heart failure.1
“For those with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, very old and outdated concepts would have talked about potentially holding the beta-blocker during hospitalization for heart failure—or not initiating until the patient was an outpatient,” says Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief of the University of California at Los Angeles’ division of cardiology and chair of the steering committee for the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program. “[But] the guidelines and evidence, and often performance measures, linked to them are now explicit about initiating or maintaining beta-blockers during the heart-failure hospitalization.”
Beta-blockers should be initiated as patients are stabilized before discharge. Dr. Fonarow suggests hospitalists use only one of the three evidence-based therapies: carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, or bisoprolol.
“Many physicians have been using metoprolol tartrate or atenolol in heart-failure patients,” Dr. Fonarow says. “These are not known to improve clinical outcomes. So here’s an example where the specific medication is absolutely, critically important.”
2) It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
“The modifier is very important,” says Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago. “Heart failure continues to be a problematic disease. Many patients now do really well, but some do not. Those patients are symptomatic and may require frequent hospitalizations for stabilization. We should not disallow or misdirect those patients who need inpatient care from receiving such because of an arbitrary incentive to reduce rehospitalizations out of fear of punitive financial damages. The unforeseen risks here are real.”
Dr. Yancy says studies based on CMS data have found that institutions with higher readmission rates have lower 30-day mortality rates.2 He cautions hospitalists to be “very thoughtful about an overzealous embrace of reducing all readmissions for heart failure.” Instead, the goal should be to limit the “avoidable readmissions.”
“And for the patient that clearly has advanced disease,” he says, “rather than triaging them away from the hospital, we really should be very respectful of their disease. Keep those patients where disease-modifying interventions can be deployed, and we can work to achieve the best possible outcome for those that have the most advanced disease.”
3) New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
Advances in interventional procedures, including transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and endoscopic mitral valve repair, will translate into a new population of highly complex patients. Many of these patients will be in their 80s or 90s.
“It’s a whole new paradigm shift of technology,” says John Harold, MD, president-elect of the American College of Cardiology and past chief of staff and department of medicine clinical chief of staff at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. “Very often, the hospitalist is at the front dealing with all of these issues.”
Many of these patients have other problems, including renal insufficiency, diabetes, and the like.
“They have all sorts of other things going on simultaneously, so very often the hospitalist becomes … the point person in dealing with all of these issues,” Dr. Harold says.
4) Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
Aldosterone antagonists can greatly improve outcomes and reduce hospitalization in heart-failure patients, but they have to be used with very careful dosing and patient selection, Dr. Fonarow says. And they require early follow-up once patients are discharged.
“Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with this agent, even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines,” Dr. Fonarow says. “But this is one where it needs to be started at appropriate low doses, with meticulous monitoring in both the inpatient and the outpatient setting, early follow-up, and early laboratory checks.”
5) Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
Transitioning patients from IV diuretics to oral regimens is an area rife with mistakes, Dr. Fonarow says. It requires a lot of “meticulous attention to proper potassium supplementation and monitoring of renal function and electrolyte levels,” he says.
Medication reconciliation—“med rec”—is especially important during the transition from inpatient to outpatient.
“There are common medication errors that are made during this transition,” Dr. Fonarow says. “Hospitalists, along with other [care team] members, can really play a critically important role in trying to reduce that risk.”
6) Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
“We really can’t exercise a thought economy that just says, ‘Extrapolate the evidence-based therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction’ and expect good outcomes,” Dr. Yancy says. “That’s not the case. We don’t have an evidence base to substantiate that.”
He says one or more common comorbidities (e.g. atrial fibrillation, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, renal insufficiency) are present in 90% of patients with preserved ejection fraction. Treatment of those comorbidities—for example, rate control in afib patients, lowering the blood pressure in hypertension patients—has to be done with care.
“We should recognize that the therapy for this condition, albeit absent any specifically indicated interventions that will change its natural history, can still be skillfully constructed,” Dr. Yancy says. “But that construct needs to reflect the recommended, guideline-driven interventions for the concomitant other comorbidities.”
7) Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
For patients who aren’t in cardiogenic shock, using inotropic agents doesn’t help. In fact, it might actually hurt. Dr. Fonarow says studies have shown these agents can “prolong length of stay, cause complications, and increase mortality risk.”
He notes that the use of inotropes should be avoided, or if it’s being considered, a cardiologist with knowledge and experience in heart failure should be involved in the treatment and care.
Statements about avoiding inotropes in heart failure, except under very specific circumstances, have been “incredibly strengthened” recently in the American College of Cardiology and Heart Failure Society of America guidelines.3
8) Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.

—John Harold, MD, president-elect, American College of Cardiology, former chief of staff, department of medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
Hospitalists caring for acute coronary syndrome patients need to familiarize themselves with updated guidelines and additional therapies that are now available, Dr. Fonarow says. New antiplatelet therapies (e.g. prasugrel and ticagrelor) are available as part of the armamentarium, along with the mainstay clopidogrel.
“These therapies lower the risk of recurrent events, lowered the risk of stent thrombosis,” he says. “In the case of ticagrelor, it actually lowered all-cause mortality. These are important new therapies, with new guideline recommendations, that all hospitalists should be aware of.”
9) Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
“Patients getting such devices as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defribrillators (ICD) installed tend not to need bridging,” says Joaquin Cigarroa, MD, clinical chief of cardiology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
He says it’s actually “safer” to do the procedure when patients “are on oral antithrombotics than switching them from an oral agent, and bridging with low- molecular-weight- or unfractionated heparin.”
“It’s a big deal,” Dr. Cigarroa adds, because it is risky to have elderly and frail patients on multiple antithrombotics. “Hemorrhagic complications in cardiology patients still occurs very frequently, so really be attuned to estimating bleeding risk and making sure that we’re dosing antithrombotics appropriately. Bridging should be the minority of patients, not the majority of patients.”
10) Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
Door-to-balloon time is recognized as critical for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients, but more recent work—such as in the TIMACS trial—finds benefits of early revascularization for some non-STEMI patients as well.2
“This trial showed that among higher-risk patients, using a validated risk score, that those patients did benefit from an early approach, meaning going to the cath lab in the first 12 hours of hospitalization,” Dr. Fonarow says. “We now have more information about the optimal timing of coronary angiography and potential revascularization of higher-risk patients with non-ST-segment elevation MI.”
11) Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
The introduction of dabigatran and rivaroxaban (and, perhaps soon, apixaban) to the array of anticoagulant therapies brings a new slate of considerations for hospitalists, Dr. Harold says.
“For the majority of these, there’s no specific way to reverse the anticoagulant effect in the event of a major bleeding event,” he says. “There’s no simple antidote. And the effect can last up to 12 to 24 hours, depending on the renal function. This is what the hospitalist will be called to deal with: bleeding complications in patients who have these newer anticoagulants on board.”
Dr. Fonarow says that the new CHA2DS2-VASc score has been found to do a better job than the traditional CHADS2 score in assessing afib stroke risk.4
12) Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
Dr. Harold says that most hospitalists probably are up to date on drug-eluting stents and the risk of stopping dual antiplatelet therapy within several months of implant, but that doesn’t mean they won’t treat patients whose primary-care physicians (PCPs) aren’t up to date. He recommends working on these cases with hematologists.
“That knowledge is not widespread in terms of the internal-medicine community,” he says. “I’ve seen situations where patients have had their Plavix stopped for colonoscopies and they’ve had stent thrombosis. It’s this knowledge of cardiac patients who come in with recent deployment of drug-eluting stents who may end up having other issues.”
Tom Collins is a freelance writer in South Florida.
References
- 2009 Focused Update: ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults. Circulation. 2009;119:1977-2016 an HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Cardiac Failure. 2010;16(6):475-539.
- Gorodeski EZ, Starling RC, Blackstone EH. Are all readmissions bad readmissions? N Engl J Med. 2010;363:297-298.
- Mehta SR, Granger CB, Boden WE, et al. Early versus delayed invasive intervention in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(21):2165-2175.
- Olesen JB, Torp-Pedersen C, Hansen ML, Lip GY. The value of the CHA2DS2-VASc score for refining stroke risk stratification in patients with atrial fibrillation with a CHADS2 score 0-1: a nationwide cohort study. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(6):1172-1179.
- Associations between outpatient heart failure process-of-care measures and mortality. Circulation. 2011;123(15):1601-1610.
Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with [aldosterone antagonists], even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines.

—Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief, University of California at Los Angeles division of cardiology, chair, American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program steering committee
You might not have done a fellowship in cardiology, but quite often you probably feel like a cardiologist. Hospitalists frequently attend to patients on observation for heart problems and help manage even the most complex patients.
Often, you are working alongside the cardiologist. But other times, you’re on your own. Hospitalists are expected to carry an increasingly heavy load when it comes to heart-failure patients and many other kinds of patients with specialized disorders. It can be hard to keep up with what you need to know.
Top Twelve
- Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
- It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
- New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
- Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
- Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
- Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
- Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
- Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.
- Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
- Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
- Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
- Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
The Hospitalist spoke to several cardiologists about the latest in treatments, technologies, and HM’s role in the system of care. The following are their suggestions for what you really need to know about treating patients with heart conditions.
1) Recognize the new importance of beta-blockers for heart failure, and go with the best of them.
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensive receptor blockers have been part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) core measures for heart failure for a long time, but beta-blockers at hospital discharge only recently have been added as American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/American Medical Association–Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement measures for heart failure.1
“For those with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, very old and outdated concepts would have talked about potentially holding the beta-blocker during hospitalization for heart failure—or not initiating until the patient was an outpatient,” says Gregg Fonarow, MD, co-chief of the University of California at Los Angeles’ division of cardiology and chair of the steering committee for the American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines program. “[But] the guidelines and evidence, and often performance measures, linked to them are now explicit about initiating or maintaining beta-blockers during the heart-failure hospitalization.”
Beta-blockers should be initiated as patients are stabilized before discharge. Dr. Fonarow suggests hospitalists use only one of the three evidence-based therapies: carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, or bisoprolol.
“Many physicians have been using metoprolol tartrate or atenolol in heart-failure patients,” Dr. Fonarow says. “These are not known to improve clinical outcomes. So here’s an example where the specific medication is absolutely, critically important.”
2) It’s not readmissions that are the problem—it’s avoidable readmissions.
“The modifier is very important,” says Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago. “Heart failure continues to be a problematic disease. Many patients now do really well, but some do not. Those patients are symptomatic and may require frequent hospitalizations for stabilization. We should not disallow or misdirect those patients who need inpatient care from receiving such because of an arbitrary incentive to reduce rehospitalizations out of fear of punitive financial damages. The unforeseen risks here are real.”
Dr. Yancy says studies based on CMS data have found that institutions with higher readmission rates have lower 30-day mortality rates.2 He cautions hospitalists to be “very thoughtful about an overzealous embrace of reducing all readmissions for heart failure.” Instead, the goal should be to limit the “avoidable readmissions.”
“And for the patient that clearly has advanced disease,” he says, “rather than triaging them away from the hospital, we really should be very respectful of their disease. Keep those patients where disease-modifying interventions can be deployed, and we can work to achieve the best possible outcome for those that have the most advanced disease.”
3) New interventional technologies will mean more complex patients, so be ready.
Advances in interventional procedures, including transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and endoscopic mitral valve repair, will translate into a new population of highly complex patients. Many of these patients will be in their 80s or 90s.
“It’s a whole new paradigm shift of technology,” says John Harold, MD, president-elect of the American College of Cardiology and past chief of staff and department of medicine clinical chief of staff at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. “Very often, the hospitalist is at the front dealing with all of these issues.”
Many of these patients have other problems, including renal insufficiency, diabetes, and the like.
“They have all sorts of other things going on simultaneously, so very often the hospitalist becomes … the point person in dealing with all of these issues,” Dr. Harold says.
4) Aldosterone antagonists, though probably underutilized, can be very effective but require caution.
Aldosterone antagonists can greatly improve outcomes and reduce hospitalization in heart-failure patients, but they have to be used with very careful dosing and patient selection, Dr. Fonarow says. And they require early follow-up once patients are discharged.
“Only about a third of ideal candidates with heart failure are currently treated with this agent, even though it markedly improves outcome and is Class I-recommended in the guidelines,” Dr. Fonarow says. “But this is one where it needs to be started at appropriate low doses, with meticulous monitoring in both the inpatient and the outpatient setting, early follow-up, and early laboratory checks.”
5) Switching from IV diuretics to an oral regimen calls for careful monitoring.
Transitioning patients from IV diuretics to oral regimens is an area rife with mistakes, Dr. Fonarow says. It requires a lot of “meticulous attention to proper potassium supplementation and monitoring of renal function and electrolyte levels,” he says.
Medication reconciliation—“med rec”—is especially important during the transition from inpatient to outpatient.
“There are common medication errors that are made during this transition,” Dr. Fonarow says. “Hospitalists, along with other [care team] members, can really play a critically important role in trying to reduce that risk.”
6) Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction have outcomes over the longer haul similar to those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. And in preserved ejection fraction cases, the contributing illnesses must be addressed.
“We really can’t exercise a thought economy that just says, ‘Extrapolate the evidence-based therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction’ and expect good outcomes,” Dr. Yancy says. “That’s not the case. We don’t have an evidence base to substantiate that.”
He says one or more common comorbidities (e.g. atrial fibrillation, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, renal insufficiency) are present in 90% of patients with preserved ejection fraction. Treatment of those comorbidities—for example, rate control in afib patients, lowering the blood pressure in hypertension patients—has to be done with care.
“We should recognize that the therapy for this condition, albeit absent any specifically indicated interventions that will change its natural history, can still be skillfully constructed,” Dr. Yancy says. “But that construct needs to reflect the recommended, guideline-driven interventions for the concomitant other comorbidities.”
7) Inotropic agents can do more harm than good.
For patients who aren’t in cardiogenic shock, using inotropic agents doesn’t help. In fact, it might actually hurt. Dr. Fonarow says studies have shown these agents can “prolong length of stay, cause complications, and increase mortality risk.”
He notes that the use of inotropes should be avoided, or if it’s being considered, a cardiologist with knowledge and experience in heart failure should be involved in the treatment and care.
Statements about avoiding inotropes in heart failure, except under very specific circumstances, have been “incredibly strengthened” recently in the American College of Cardiology and Heart Failure Society of America guidelines.3
8) Pay attention to the ins and outs of new antiplatelet therapies.

—John Harold, MD, president-elect, American College of Cardiology, former chief of staff, department of medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
Hospitalists caring for acute coronary syndrome patients need to familiarize themselves with updated guidelines and additional therapies that are now available, Dr. Fonarow says. New antiplatelet therapies (e.g. prasugrel and ticagrelor) are available as part of the armamentarium, along with the mainstay clopidogrel.
“These therapies lower the risk of recurrent events, lowered the risk of stent thrombosis,” he says. “In the case of ticagrelor, it actually lowered all-cause mortality. These are important new therapies, with new guideline recommendations, that all hospitalists should be aware of.”
9) Bridging anticoagulant therapy in patients going for electrophysiology procedures should be done only some, not most, of the time.
“Patients getting such devices as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defribrillators (ICD) installed tend not to need bridging,” says Joaquin Cigarroa, MD, clinical chief of cardiology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
He says it’s actually “safer” to do the procedure when patients “are on oral antithrombotics than switching them from an oral agent, and bridging with low- molecular-weight- or unfractionated heparin.”
“It’s a big deal,” Dr. Cigarroa adds, because it is risky to have elderly and frail patients on multiple antithrombotics. “Hemorrhagic complications in cardiology patients still occurs very frequently, so really be attuned to estimating bleeding risk and making sure that we’re dosing antithrombotics appropriately. Bridging should be the minority of patients, not the majority of patients.”
10) Some non-STEMI patients might benefit from getting to the catheterization lab quickly.
Door-to-balloon time is recognized as critical for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients, but more recent work—such as in the TIMACS trial—finds benefits of early revascularization for some non-STEMI patients as well.2
“This trial showed that among higher-risk patients, using a validated risk score, that those patients did benefit from an early approach, meaning going to the cath lab in the first 12 hours of hospitalization,” Dr. Fonarow says. “We now have more information about the optimal timing of coronary angiography and potential revascularization of higher-risk patients with non-ST-segment elevation MI.”
11) Beware the idiosyncrasies of new anticoagulants.
The introduction of dabigatran and rivaroxaban (and, perhaps soon, apixaban) to the array of anticoagulant therapies brings a new slate of considerations for hospitalists, Dr. Harold says.
“For the majority of these, there’s no specific way to reverse the anticoagulant effect in the event of a major bleeding event,” he says. “There’s no simple antidote. And the effect can last up to 12 to 24 hours, depending on the renal function. This is what the hospitalist will be called to deal with: bleeding complications in patients who have these newer anticoagulants on board.”
Dr. Fonarow says that the new CHA2DS2-VASc score has been found to do a better job than the traditional CHADS2 score in assessing afib stroke risk.4
12) Be cognizant of stent thrombosis and how to manage it.
Dr. Harold says that most hospitalists probably are up to date on drug-eluting stents and the risk of stopping dual antiplatelet therapy within several months of implant, but that doesn’t mean they won’t treat patients whose primary-care physicians (PCPs) aren’t up to date. He recommends working on these cases with hematologists.
“That knowledge is not widespread in terms of the internal-medicine community,” he says. “I’ve seen situations where patients have had their Plavix stopped for colonoscopies and they’ve had stent thrombosis. It’s this knowledge of cardiac patients who come in with recent deployment of drug-eluting stents who may end up having other issues.”
Tom Collins is a freelance writer in South Florida.
References
- 2009 Focused Update: ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults. Circulation. 2009;119:1977-2016 an HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Cardiac Failure. 2010;16(6):475-539.
- Gorodeski EZ, Starling RC, Blackstone EH. Are all readmissions bad readmissions? N Engl J Med. 2010;363:297-298.
- Mehta SR, Granger CB, Boden WE, et al. Early versus delayed invasive intervention in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(21):2165-2175.
- Olesen JB, Torp-Pedersen C, Hansen ML, Lip GY. The value of the CHA2DS2-VASc score for refining stroke risk stratification in patients with atrial fibrillation with a CHADS2 score 0-1: a nationwide cohort study. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(6):1172-1179.
- Associations between outpatient heart failure process-of-care measures and mortality. Circulation. 2011;123(15):1601-1610.
Follow-Up Appointments Essential for Heart Failure Patients
When heart-failure patients have follow-up appointments with their outpatient doctors, outcomes are good, Dr. Fonarow says. However, they are not done nearly enough.
“Early follow-up is essential,” he says. “Follow-up within seven days—in higher-risk patients, even earlier, within three days—is something that has been associated with a lower risk of rehospitalization.”
Despite the research, only about 30% to 40% of patients hospitalized with heart failure are seen by any outpatient provider in the first week post-discharge.
“We have a real opportunity there,” Dr. Fonarow says. “The inpatient physicians can play a really critical role in ensuring that there’s early and appropriate follow-up, and good communication and handoff to the outpatient physician.”
When heart-failure patients have follow-up appointments with their outpatient doctors, outcomes are good, Dr. Fonarow says. However, they are not done nearly enough.
“Early follow-up is essential,” he says. “Follow-up within seven days—in higher-risk patients, even earlier, within three days—is something that has been associated with a lower risk of rehospitalization.”
Despite the research, only about 30% to 40% of patients hospitalized with heart failure are seen by any outpatient provider in the first week post-discharge.
“We have a real opportunity there,” Dr. Fonarow says. “The inpatient physicians can play a really critical role in ensuring that there’s early and appropriate follow-up, and good communication and handoff to the outpatient physician.”
When heart-failure patients have follow-up appointments with their outpatient doctors, outcomes are good, Dr. Fonarow says. However, they are not done nearly enough.
“Early follow-up is essential,” he says. “Follow-up within seven days—in higher-risk patients, even earlier, within three days—is something that has been associated with a lower risk of rehospitalization.”
Despite the research, only about 30% to 40% of patients hospitalized with heart failure are seen by any outpatient provider in the first week post-discharge.
“We have a real opportunity there,” Dr. Fonarow says. “The inpatient physicians can play a really critical role in ensuring that there’s early and appropriate follow-up, and good communication and handoff to the outpatient physician.”
Managing the Customer Care Experience in Hospital Care
I needed an oil change, so I took my car to Jiffy Lube. I had just pulled into the entrance to one of the service bays when a smiling man whose nametag read “Tony” approached me. “Welcome back, Mr. Wellikson. What can we help you with today?” Well, that was nice and so unexpected, as I had not remembered ever going to that Jiffy Lube. As it turns out, they have a video camera that shows incoming cars in their control room. They can read my license plate and call up my car on their computer system, access my record, and create a personal greeting. They also used my car’s past history as a starting point for this encounter. We were off to a good start.
Once I indicated I just wanted a routine oil change, Tony indicated he would be back in five to 10 minutes. He told me I should wait in the waiting room where they had wireless Internet, TV, magazines, and comfortable chairs.
In less than 10 minutes, Tony was back, clipboard in hand, with an assessment of my car’s status, including previous work and manufacturer’s recommendations, based on my car’s age and mileage. Once we negotiated not replacing all of the fluids and filters, Tony smiled and said the work should be completed in 10 minutes.
Soon, Tony came back to lead me out to my car, which had been wheeled out to the front of the garage bay with an open driver’s door waiting for me. After helping me into my seat, Tony came around and sat in the passenger seat and, once again with his ready clipboard, walked me through the 29 steps of inspections and fluid changes that had been made on my visit, reviewed the frequency of future needs for my vehicle, put a sticker on my inside windshield as a reminder, included $5 off for my next service, then patiently asked me if I had any questions.
Total time at Jiffy Lube: less than 30 minutes. Total cost: $29.99. Total customer experience: exceptional. Considering it was the third Jiffy Lube location I had used in the past three years, I can tell you the experience and system is the same throughout the company, whether the uniform name is Tony or Jose or Gladys.
Can such experiences offer hospitalists lessons about how we manage the customer experience in hospital care?
Scalable Innovation
In August 2012, Atul Gawande, MD, wrote a thought-provoking article in The New Yorker in which he coupled his detailed observation of how the restaurant chain The Cheesecake Factory manages to deliver 8 million meals annually nationwide with high quality at a reasonable cost and strong corporate profits with the emerging trend of healthcare delivery innovations being sought by large hospital chains and such innovations as ICU telemedicine.1
He noted that, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, less than 25% of physicians are currently self-employed, and the growing trend is hospitals being acquired or merged into larger and larger hospital chains. He observed that recent and future financial changes are moving toward payment for results and efficiencies and further away from just rewarding transactions and supplying services, whether of measureable value or with proven results. Cheesecake Factory has built its success on large-scale production-line processes that produce consistent results across hundreds of locations and millions of meals. It may now be time for healthcare, especially hospital care, to come into the 21st century, too.
How did Cheesecake Factory get to where they are? They studied what the best people were doing, figured out a way to standardize it, then looked for ways to bring it to everyone. Although we could look at research as medicine’s way of bringing new concepts forward, where we have fallen down as an industry and culture is our ability to deliver on this at the bedside. Why aren’t most myocardial infarction patients on beta-blockers? Why isn’t DVT prophylaxis universal? Why can’t we all wash our hands on a regular basis?
Medical care, especially the physician portion, has always placed an overwhelming bias on autonomy. We all know that even at the same hospital or within the same physician group of cardiologists or orthopedists (or even hospitalists) that there can be multiple ways to treat chest pain, replace a joint, or manage pneumonia. Dr. Gawande postulates that “customization should be 5%, not 95%, of what we do.” He is not suggesting cookbook medicine—rather, that we bring all of the current proven and consensus medical knowledge together and allow local professionals to agree to narrow their choices down to a consistent and reproducible process for managing care.
Hoag, a health network near my home in Orange County, Calif., has brought this approach to orthopedic care. Hoag purchased a smaller hospital near its main campus and is emphasizing state-of-the-art orthopedic care at the new facility. They aligned the incentives—clinically and financially—with a large but select group of orthopedists, and they have chosen just a few prosthetic choices for hip and knee replacements. They have narrowed their protocols for pre- and post-op care, and now do same-day joint replacements with lower complication rates and better return-to-activity results at lower costs. And trust me, the orthopedists at Hoag were as independent as any physicians you might run into. The demands of the new payor models and competition to provide consumers (i.e. patients) with a 21st-century experience pushed, pulled, and prodded these orthopedists, and an enlightened hospital leadership, to rise to the challenges.
HM Takeaway
So where do hospitalists fit into this emerging world of customer service, standardization, accountability for results, and payment change? As you might imagine, we are right in the middle of all of this. High-functioning HM groups have understood that we must help shape a better system for us to work in. We cannot perpetuate the old paradigm in which the hospital was simply a swap meet where each physician had a booth and performed a procedure with little regard to how efficient or effective the entire enterprise might be.
Hospitalists have always performed in a group setting and worked across the professional disciplines of medicine, surgery, and subspecialties, and with nurses, pharmacists, and therapists. In the best of breed, hospitalists are enculturated to think systemwide yet deliver to an individual patient.
As hospital chains look to standardize and deliver the best results and the most efficient use of resources, hospitalists can be positioned in a variety of ways. You can be an innovative partner, working with other professionals and the administration to seek new ways of doing things. You can be the manager or coordinator of other professionals and the rest of the team. But you also could evolve to be line workers and cogs in a larger machine, replaceable and commoditized. In the end, hospitalists will not only need to create value, but also position themselves to be professionally rewarded and respected for the value they create.
Dr. Gawande considers the perspectives of healthcare providers and patients as he looks to the future. “Patients won’t just look for the best specialist anymore; they’ll look for the best system,” he says. “Nurses and doctors will have to get used to delivering care in which our own convenience counts for less and the patients’ experience counts for more.”
The changes ahead will be rapid and disruptive; some hospitals will be driven out of business, while some will be consolidated. Physicians will aggregate and become employees (although many will still think they are free agents). Standardization will be pushed, and customization and one-offs will be tolerated less and less.
In this new world, hospitalists have the opportunity to be at the leading edge, not just for other physicians but the entire healthcare team. We need to prepare for this challenge, not just with clinical skills, but with a culture and a mindset to adapt and evolve. We need to decide if we will be cogs in a machine or the innovators and managers of change. The time is now; the choice is ours.
Dr. Wellikson is CEO of SHM.
Reference
I needed an oil change, so I took my car to Jiffy Lube. I had just pulled into the entrance to one of the service bays when a smiling man whose nametag read “Tony” approached me. “Welcome back, Mr. Wellikson. What can we help you with today?” Well, that was nice and so unexpected, as I had not remembered ever going to that Jiffy Lube. As it turns out, they have a video camera that shows incoming cars in their control room. They can read my license plate and call up my car on their computer system, access my record, and create a personal greeting. They also used my car’s past history as a starting point for this encounter. We were off to a good start.
Once I indicated I just wanted a routine oil change, Tony indicated he would be back in five to 10 minutes. He told me I should wait in the waiting room where they had wireless Internet, TV, magazines, and comfortable chairs.
In less than 10 minutes, Tony was back, clipboard in hand, with an assessment of my car’s status, including previous work and manufacturer’s recommendations, based on my car’s age and mileage. Once we negotiated not replacing all of the fluids and filters, Tony smiled and said the work should be completed in 10 minutes.
Soon, Tony came back to lead me out to my car, which had been wheeled out to the front of the garage bay with an open driver’s door waiting for me. After helping me into my seat, Tony came around and sat in the passenger seat and, once again with his ready clipboard, walked me through the 29 steps of inspections and fluid changes that had been made on my visit, reviewed the frequency of future needs for my vehicle, put a sticker on my inside windshield as a reminder, included $5 off for my next service, then patiently asked me if I had any questions.
Total time at Jiffy Lube: less than 30 minutes. Total cost: $29.99. Total customer experience: exceptional. Considering it was the third Jiffy Lube location I had used in the past three years, I can tell you the experience and system is the same throughout the company, whether the uniform name is Tony or Jose or Gladys.
Can such experiences offer hospitalists lessons about how we manage the customer experience in hospital care?
Scalable Innovation
In August 2012, Atul Gawande, MD, wrote a thought-provoking article in The New Yorker in which he coupled his detailed observation of how the restaurant chain The Cheesecake Factory manages to deliver 8 million meals annually nationwide with high quality at a reasonable cost and strong corporate profits with the emerging trend of healthcare delivery innovations being sought by large hospital chains and such innovations as ICU telemedicine.1
He noted that, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, less than 25% of physicians are currently self-employed, and the growing trend is hospitals being acquired or merged into larger and larger hospital chains. He observed that recent and future financial changes are moving toward payment for results and efficiencies and further away from just rewarding transactions and supplying services, whether of measureable value or with proven results. Cheesecake Factory has built its success on large-scale production-line processes that produce consistent results across hundreds of locations and millions of meals. It may now be time for healthcare, especially hospital care, to come into the 21st century, too.
How did Cheesecake Factory get to where they are? They studied what the best people were doing, figured out a way to standardize it, then looked for ways to bring it to everyone. Although we could look at research as medicine’s way of bringing new concepts forward, where we have fallen down as an industry and culture is our ability to deliver on this at the bedside. Why aren’t most myocardial infarction patients on beta-blockers? Why isn’t DVT prophylaxis universal? Why can’t we all wash our hands on a regular basis?
Medical care, especially the physician portion, has always placed an overwhelming bias on autonomy. We all know that even at the same hospital or within the same physician group of cardiologists or orthopedists (or even hospitalists) that there can be multiple ways to treat chest pain, replace a joint, or manage pneumonia. Dr. Gawande postulates that “customization should be 5%, not 95%, of what we do.” He is not suggesting cookbook medicine—rather, that we bring all of the current proven and consensus medical knowledge together and allow local professionals to agree to narrow their choices down to a consistent and reproducible process for managing care.
Hoag, a health network near my home in Orange County, Calif., has brought this approach to orthopedic care. Hoag purchased a smaller hospital near its main campus and is emphasizing state-of-the-art orthopedic care at the new facility. They aligned the incentives—clinically and financially—with a large but select group of orthopedists, and they have chosen just a few prosthetic choices for hip and knee replacements. They have narrowed their protocols for pre- and post-op care, and now do same-day joint replacements with lower complication rates and better return-to-activity results at lower costs. And trust me, the orthopedists at Hoag were as independent as any physicians you might run into. The demands of the new payor models and competition to provide consumers (i.e. patients) with a 21st-century experience pushed, pulled, and prodded these orthopedists, and an enlightened hospital leadership, to rise to the challenges.
HM Takeaway
So where do hospitalists fit into this emerging world of customer service, standardization, accountability for results, and payment change? As you might imagine, we are right in the middle of all of this. High-functioning HM groups have understood that we must help shape a better system for us to work in. We cannot perpetuate the old paradigm in which the hospital was simply a swap meet where each physician had a booth and performed a procedure with little regard to how efficient or effective the entire enterprise might be.
Hospitalists have always performed in a group setting and worked across the professional disciplines of medicine, surgery, and subspecialties, and with nurses, pharmacists, and therapists. In the best of breed, hospitalists are enculturated to think systemwide yet deliver to an individual patient.
As hospital chains look to standardize and deliver the best results and the most efficient use of resources, hospitalists can be positioned in a variety of ways. You can be an innovative partner, working with other professionals and the administration to seek new ways of doing things. You can be the manager or coordinator of other professionals and the rest of the team. But you also could evolve to be line workers and cogs in a larger machine, replaceable and commoditized. In the end, hospitalists will not only need to create value, but also position themselves to be professionally rewarded and respected for the value they create.
Dr. Gawande considers the perspectives of healthcare providers and patients as he looks to the future. “Patients won’t just look for the best specialist anymore; they’ll look for the best system,” he says. “Nurses and doctors will have to get used to delivering care in which our own convenience counts for less and the patients’ experience counts for more.”
The changes ahead will be rapid and disruptive; some hospitals will be driven out of business, while some will be consolidated. Physicians will aggregate and become employees (although many will still think they are free agents). Standardization will be pushed, and customization and one-offs will be tolerated less and less.
In this new world, hospitalists have the opportunity to be at the leading edge, not just for other physicians but the entire healthcare team. We need to prepare for this challenge, not just with clinical skills, but with a culture and a mindset to adapt and evolve. We need to decide if we will be cogs in a machine or the innovators and managers of change. The time is now; the choice is ours.
Dr. Wellikson is CEO of SHM.
Reference
I needed an oil change, so I took my car to Jiffy Lube. I had just pulled into the entrance to one of the service bays when a smiling man whose nametag read “Tony” approached me. “Welcome back, Mr. Wellikson. What can we help you with today?” Well, that was nice and so unexpected, as I had not remembered ever going to that Jiffy Lube. As it turns out, they have a video camera that shows incoming cars in their control room. They can read my license plate and call up my car on their computer system, access my record, and create a personal greeting. They also used my car’s past history as a starting point for this encounter. We were off to a good start.
Once I indicated I just wanted a routine oil change, Tony indicated he would be back in five to 10 minutes. He told me I should wait in the waiting room where they had wireless Internet, TV, magazines, and comfortable chairs.
In less than 10 minutes, Tony was back, clipboard in hand, with an assessment of my car’s status, including previous work and manufacturer’s recommendations, based on my car’s age and mileage. Once we negotiated not replacing all of the fluids and filters, Tony smiled and said the work should be completed in 10 minutes.
Soon, Tony came back to lead me out to my car, which had been wheeled out to the front of the garage bay with an open driver’s door waiting for me. After helping me into my seat, Tony came around and sat in the passenger seat and, once again with his ready clipboard, walked me through the 29 steps of inspections and fluid changes that had been made on my visit, reviewed the frequency of future needs for my vehicle, put a sticker on my inside windshield as a reminder, included $5 off for my next service, then patiently asked me if I had any questions.
Total time at Jiffy Lube: less than 30 minutes. Total cost: $29.99. Total customer experience: exceptional. Considering it was the third Jiffy Lube location I had used in the past three years, I can tell you the experience and system is the same throughout the company, whether the uniform name is Tony or Jose or Gladys.
Can such experiences offer hospitalists lessons about how we manage the customer experience in hospital care?
Scalable Innovation
In August 2012, Atul Gawande, MD, wrote a thought-provoking article in The New Yorker in which he coupled his detailed observation of how the restaurant chain The Cheesecake Factory manages to deliver 8 million meals annually nationwide with high quality at a reasonable cost and strong corporate profits with the emerging trend of healthcare delivery innovations being sought by large hospital chains and such innovations as ICU telemedicine.1
He noted that, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, less than 25% of physicians are currently self-employed, and the growing trend is hospitals being acquired or merged into larger and larger hospital chains. He observed that recent and future financial changes are moving toward payment for results and efficiencies and further away from just rewarding transactions and supplying services, whether of measureable value or with proven results. Cheesecake Factory has built its success on large-scale production-line processes that produce consistent results across hundreds of locations and millions of meals. It may now be time for healthcare, especially hospital care, to come into the 21st century, too.
How did Cheesecake Factory get to where they are? They studied what the best people were doing, figured out a way to standardize it, then looked for ways to bring it to everyone. Although we could look at research as medicine’s way of bringing new concepts forward, where we have fallen down as an industry and culture is our ability to deliver on this at the bedside. Why aren’t most myocardial infarction patients on beta-blockers? Why isn’t DVT prophylaxis universal? Why can’t we all wash our hands on a regular basis?
Medical care, especially the physician portion, has always placed an overwhelming bias on autonomy. We all know that even at the same hospital or within the same physician group of cardiologists or orthopedists (or even hospitalists) that there can be multiple ways to treat chest pain, replace a joint, or manage pneumonia. Dr. Gawande postulates that “customization should be 5%, not 95%, of what we do.” He is not suggesting cookbook medicine—rather, that we bring all of the current proven and consensus medical knowledge together and allow local professionals to agree to narrow their choices down to a consistent and reproducible process for managing care.
Hoag, a health network near my home in Orange County, Calif., has brought this approach to orthopedic care. Hoag purchased a smaller hospital near its main campus and is emphasizing state-of-the-art orthopedic care at the new facility. They aligned the incentives—clinically and financially—with a large but select group of orthopedists, and they have chosen just a few prosthetic choices for hip and knee replacements. They have narrowed their protocols for pre- and post-op care, and now do same-day joint replacements with lower complication rates and better return-to-activity results at lower costs. And trust me, the orthopedists at Hoag were as independent as any physicians you might run into. The demands of the new payor models and competition to provide consumers (i.e. patients) with a 21st-century experience pushed, pulled, and prodded these orthopedists, and an enlightened hospital leadership, to rise to the challenges.
HM Takeaway
So where do hospitalists fit into this emerging world of customer service, standardization, accountability for results, and payment change? As you might imagine, we are right in the middle of all of this. High-functioning HM groups have understood that we must help shape a better system for us to work in. We cannot perpetuate the old paradigm in which the hospital was simply a swap meet where each physician had a booth and performed a procedure with little regard to how efficient or effective the entire enterprise might be.
Hospitalists have always performed in a group setting and worked across the professional disciplines of medicine, surgery, and subspecialties, and with nurses, pharmacists, and therapists. In the best of breed, hospitalists are enculturated to think systemwide yet deliver to an individual patient.
As hospital chains look to standardize and deliver the best results and the most efficient use of resources, hospitalists can be positioned in a variety of ways. You can be an innovative partner, working with other professionals and the administration to seek new ways of doing things. You can be the manager or coordinator of other professionals and the rest of the team. But you also could evolve to be line workers and cogs in a larger machine, replaceable and commoditized. In the end, hospitalists will not only need to create value, but also position themselves to be professionally rewarded and respected for the value they create.
Dr. Gawande considers the perspectives of healthcare providers and patients as he looks to the future. “Patients won’t just look for the best specialist anymore; they’ll look for the best system,” he says. “Nurses and doctors will have to get used to delivering care in which our own convenience counts for less and the patients’ experience counts for more.”
The changes ahead will be rapid and disruptive; some hospitals will be driven out of business, while some will be consolidated. Physicians will aggregate and become employees (although many will still think they are free agents). Standardization will be pushed, and customization and one-offs will be tolerated less and less.
In this new world, hospitalists have the opportunity to be at the leading edge, not just for other physicians but the entire healthcare team. We need to prepare for this challenge, not just with clinical skills, but with a culture and a mindset to adapt and evolve. We need to decide if we will be cogs in a machine or the innovators and managers of change. The time is now; the choice is ours.
Dr. Wellikson is CEO of SHM.
Reference
Navigating Rapid Changes in Healthcare Made Easy
This is a tumultuous time in healthcare: regulatory burdens, payment reductions, public scrutiny. And the rapidity of change is mind-boggling. All of this would probably be fine, except that people generally resist change, especially rapid change. Here today, gone tomorrow. That usually does not go over very well.
But given that this is the state of affairs for the foreseeable future, the question is, why is change so hard, and what can we do make it easier?
I thought about this at church the other day. My family and I attend church weekly (except when we don’t) at a small, old, quaint Catholic church built in 1789. My husband and I were raised Catholic, but as you may know, not every Catholic is really a Catholic. Based on my childhood churchgoing routine, my family would best be described as “Creasters,” which are “Catholics” (in quotations on purpose) who dedicate most of their religious energy to showing up only on Christmas and Easter. We are also known as “diet Catholics” or “lite Catholics.” Although I can plow through the “Our Father” with ease and grace, the Lord’s Prayer usually results in some mumbling, hushed tones and ceiling-staring.
My husband, on the other hand, was raised a real Catholic. He went to Catholic grade school, received communion six days a week, routinely served as an altar boy, and only missed Sunday Mass for a fever of more than 101 degrees (and even that was a stretch). For years, I have looked to him for cues on when to sit, stand, kneel, talk, sing, and be silent. When Sunday school questions come to the dinner table by way of our 8-year-old, I generally feign a choking episode and defer to my husband.
So this has been our routine for more than a decade: he the leader and I the limper. But then something shocking happened several months ago. In the middle of Mass, I realized my husband had no idea what was going on. He fumbled awkwardly through the service, lowered his speech volume with each passing misstep, and was almost completely silent by the end of the service.
As it ends up, every couple of hundred years, the Catholic Church decides to shake things up and change the Mass around. During key repeatings, the words are now different. What used to be “and also with you” is now “and with your spirit.” These changes were not monumental and went relatively unnoticed by current or former Creasters, but they were mind-boggling for the real Catholics.
The Church must have anticipated that these changes would be difficult to assimilate, as they placed countless numbers of laminated cue cards all over the church, in every pew, the confessional stand, and at all entry and exit points. Undoubtedly, they were hoping (assuming) we would take them home and learn the changes on our own, outside of Mass. So some months passed by, and after a few weeks with a cue card, I was in pretty good shape. My brain rewired the sayings, and I was able to shed my cue-card crutch.
My husband, on the other hand, is still reaching for the cue cards, with a long-standing dependence that now resembles that of an addict. Occasionally feeling confident, he will lay the card down, and will start spewing out the old sayings from a short circuit in the amygdala, programmed in fifth grade and hard-wired for accuracy. Then he will regain consciousness and realize everyone is staring at him.
As hospitalists, we know how hard it is to change, but we also know we have to routinely change to keep pace with the industry. So how do we reconcile the differences?
I recently read the book “Switch,” which describes some techniques on how to change when change is hard.1 The authors write about a rider, an elephant, and a path. If all three are aligned toward a change, it will most likely succeed; without all three, change will be very difficult or unsuccessful altogether.
The rider is the intellectual portion, which will find the rational, statistical, logical solution to get from point A to point B. But the rider is steering an elephant, which is bulky, unruly, and emotional. The rider has to figure out how to motivate and direct the elephant; the two of them then have to get down a common path, which could be winding, confusing, and full of roadblocks. So to overcome all of these, the book gives innumerable, tangible examples of how to maneuver all three of these to facilitate change. In the case of my husband’s Mass issue, a few things could have facilitated the change for many:
Direct the rider:
- Find the bright spots. Find a success story of how others quickly relearned Mass within weeks and see how they accomplished it.
- Script the critical moves. Be very precise about what needs to be done differently; don’t just tell people to “learn the Mass,” but instead tell them to “repeat three new lines every day in the shower” until they have an error-free Mass.
- Point to the destination. Be very specific about the future goal, such as “You will be cue-card-free by October.”
Motivate the elephant:
- Find the feeling. Find a “heavy” emotion that will motivate the change. Shame, embarrassment, or anger from being stared at by a 10-year-old after missing so many lines should be pretty effective.
- Shrink the change. Make it seem like all the lines are easy to learn, if learned only one at a time.
- Grow the person. Motivate the Catholic to learn it as quickly and seamlessly as they did in fifth grade; if you already did it once, you just have do it again!
Shape the path:
- Tweak the environment. Have cue cards all over the place, laminate them, make them easy to fit in a pocket or purse.
- Build habits. Have the Catholic go to church every week until they have an “error-free” Mass.
- Rally the herd. Have them watch others for cues on behavior; this has worked for me for decades!
You can see that many of these techniques should be easier in healthcare than in other industries, especially motivating the elephant and shaping the path. To facilitate change, hospitalists should find ways to direct the rider, motivate the elephant, and shape the path, and we may find that change is not as daunting and overwhelming as it might at first seem.
And when you finally do make a positive change happen, give yourself a high-five—and send a “Hail Mary” to the Creasters.
Dr. Scheurer is physician editor of The Hospitalist.
Reference
This is a tumultuous time in healthcare: regulatory burdens, payment reductions, public scrutiny. And the rapidity of change is mind-boggling. All of this would probably be fine, except that people generally resist change, especially rapid change. Here today, gone tomorrow. That usually does not go over very well.
But given that this is the state of affairs for the foreseeable future, the question is, why is change so hard, and what can we do make it easier?
I thought about this at church the other day. My family and I attend church weekly (except when we don’t) at a small, old, quaint Catholic church built in 1789. My husband and I were raised Catholic, but as you may know, not every Catholic is really a Catholic. Based on my childhood churchgoing routine, my family would best be described as “Creasters,” which are “Catholics” (in quotations on purpose) who dedicate most of their religious energy to showing up only on Christmas and Easter. We are also known as “diet Catholics” or “lite Catholics.” Although I can plow through the “Our Father” with ease and grace, the Lord’s Prayer usually results in some mumbling, hushed tones and ceiling-staring.
My husband, on the other hand, was raised a real Catholic. He went to Catholic grade school, received communion six days a week, routinely served as an altar boy, and only missed Sunday Mass for a fever of more than 101 degrees (and even that was a stretch). For years, I have looked to him for cues on when to sit, stand, kneel, talk, sing, and be silent. When Sunday school questions come to the dinner table by way of our 8-year-old, I generally feign a choking episode and defer to my husband.
So this has been our routine for more than a decade: he the leader and I the limper. But then something shocking happened several months ago. In the middle of Mass, I realized my husband had no idea what was going on. He fumbled awkwardly through the service, lowered his speech volume with each passing misstep, and was almost completely silent by the end of the service.
As it ends up, every couple of hundred years, the Catholic Church decides to shake things up and change the Mass around. During key repeatings, the words are now different. What used to be “and also with you” is now “and with your spirit.” These changes were not monumental and went relatively unnoticed by current or former Creasters, but they were mind-boggling for the real Catholics.
The Church must have anticipated that these changes would be difficult to assimilate, as they placed countless numbers of laminated cue cards all over the church, in every pew, the confessional stand, and at all entry and exit points. Undoubtedly, they were hoping (assuming) we would take them home and learn the changes on our own, outside of Mass. So some months passed by, and after a few weeks with a cue card, I was in pretty good shape. My brain rewired the sayings, and I was able to shed my cue-card crutch.
My husband, on the other hand, is still reaching for the cue cards, with a long-standing dependence that now resembles that of an addict. Occasionally feeling confident, he will lay the card down, and will start spewing out the old sayings from a short circuit in the amygdala, programmed in fifth grade and hard-wired for accuracy. Then he will regain consciousness and realize everyone is staring at him.
As hospitalists, we know how hard it is to change, but we also know we have to routinely change to keep pace with the industry. So how do we reconcile the differences?
I recently read the book “Switch,” which describes some techniques on how to change when change is hard.1 The authors write about a rider, an elephant, and a path. If all three are aligned toward a change, it will most likely succeed; without all three, change will be very difficult or unsuccessful altogether.
The rider is the intellectual portion, which will find the rational, statistical, logical solution to get from point A to point B. But the rider is steering an elephant, which is bulky, unruly, and emotional. The rider has to figure out how to motivate and direct the elephant; the two of them then have to get down a common path, which could be winding, confusing, and full of roadblocks. So to overcome all of these, the book gives innumerable, tangible examples of how to maneuver all three of these to facilitate change. In the case of my husband’s Mass issue, a few things could have facilitated the change for many:
Direct the rider:
- Find the bright spots. Find a success story of how others quickly relearned Mass within weeks and see how they accomplished it.
- Script the critical moves. Be very precise about what needs to be done differently; don’t just tell people to “learn the Mass,” but instead tell them to “repeat three new lines every day in the shower” until they have an error-free Mass.
- Point to the destination. Be very specific about the future goal, such as “You will be cue-card-free by October.”
Motivate the elephant:
- Find the feeling. Find a “heavy” emotion that will motivate the change. Shame, embarrassment, or anger from being stared at by a 10-year-old after missing so many lines should be pretty effective.
- Shrink the change. Make it seem like all the lines are easy to learn, if learned only one at a time.
- Grow the person. Motivate the Catholic to learn it as quickly and seamlessly as they did in fifth grade; if you already did it once, you just have do it again!
Shape the path:
- Tweak the environment. Have cue cards all over the place, laminate them, make them easy to fit in a pocket or purse.
- Build habits. Have the Catholic go to church every week until they have an “error-free” Mass.
- Rally the herd. Have them watch others for cues on behavior; this has worked for me for decades!
You can see that many of these techniques should be easier in healthcare than in other industries, especially motivating the elephant and shaping the path. To facilitate change, hospitalists should find ways to direct the rider, motivate the elephant, and shape the path, and we may find that change is not as daunting and overwhelming as it might at first seem.
And when you finally do make a positive change happen, give yourself a high-five—and send a “Hail Mary” to the Creasters.
Dr. Scheurer is physician editor of The Hospitalist.
Reference
This is a tumultuous time in healthcare: regulatory burdens, payment reductions, public scrutiny. And the rapidity of change is mind-boggling. All of this would probably be fine, except that people generally resist change, especially rapid change. Here today, gone tomorrow. That usually does not go over very well.
But given that this is the state of affairs for the foreseeable future, the question is, why is change so hard, and what can we do make it easier?
I thought about this at church the other day. My family and I attend church weekly (except when we don’t) at a small, old, quaint Catholic church built in 1789. My husband and I were raised Catholic, but as you may know, not every Catholic is really a Catholic. Based on my childhood churchgoing routine, my family would best be described as “Creasters,” which are “Catholics” (in quotations on purpose) who dedicate most of their religious energy to showing up only on Christmas and Easter. We are also known as “diet Catholics” or “lite Catholics.” Although I can plow through the “Our Father” with ease and grace, the Lord’s Prayer usually results in some mumbling, hushed tones and ceiling-staring.
My husband, on the other hand, was raised a real Catholic. He went to Catholic grade school, received communion six days a week, routinely served as an altar boy, and only missed Sunday Mass for a fever of more than 101 degrees (and even that was a stretch). For years, I have looked to him for cues on when to sit, stand, kneel, talk, sing, and be silent. When Sunday school questions come to the dinner table by way of our 8-year-old, I generally feign a choking episode and defer to my husband.
So this has been our routine for more than a decade: he the leader and I the limper. But then something shocking happened several months ago. In the middle of Mass, I realized my husband had no idea what was going on. He fumbled awkwardly through the service, lowered his speech volume with each passing misstep, and was almost completely silent by the end of the service.
As it ends up, every couple of hundred years, the Catholic Church decides to shake things up and change the Mass around. During key repeatings, the words are now different. What used to be “and also with you” is now “and with your spirit.” These changes were not monumental and went relatively unnoticed by current or former Creasters, but they were mind-boggling for the real Catholics.
The Church must have anticipated that these changes would be difficult to assimilate, as they placed countless numbers of laminated cue cards all over the church, in every pew, the confessional stand, and at all entry and exit points. Undoubtedly, they were hoping (assuming) we would take them home and learn the changes on our own, outside of Mass. So some months passed by, and after a few weeks with a cue card, I was in pretty good shape. My brain rewired the sayings, and I was able to shed my cue-card crutch.
My husband, on the other hand, is still reaching for the cue cards, with a long-standing dependence that now resembles that of an addict. Occasionally feeling confident, he will lay the card down, and will start spewing out the old sayings from a short circuit in the amygdala, programmed in fifth grade and hard-wired for accuracy. Then he will regain consciousness and realize everyone is staring at him.
As hospitalists, we know how hard it is to change, but we also know we have to routinely change to keep pace with the industry. So how do we reconcile the differences?
I recently read the book “Switch,” which describes some techniques on how to change when change is hard.1 The authors write about a rider, an elephant, and a path. If all three are aligned toward a change, it will most likely succeed; without all three, change will be very difficult or unsuccessful altogether.
The rider is the intellectual portion, which will find the rational, statistical, logical solution to get from point A to point B. But the rider is steering an elephant, which is bulky, unruly, and emotional. The rider has to figure out how to motivate and direct the elephant; the two of them then have to get down a common path, which could be winding, confusing, and full of roadblocks. So to overcome all of these, the book gives innumerable, tangible examples of how to maneuver all three of these to facilitate change. In the case of my husband’s Mass issue, a few things could have facilitated the change for many:
Direct the rider:
- Find the bright spots. Find a success story of how others quickly relearned Mass within weeks and see how they accomplished it.
- Script the critical moves. Be very precise about what needs to be done differently; don’t just tell people to “learn the Mass,” but instead tell them to “repeat three new lines every day in the shower” until they have an error-free Mass.
- Point to the destination. Be very specific about the future goal, such as “You will be cue-card-free by October.”
Motivate the elephant:
- Find the feeling. Find a “heavy” emotion that will motivate the change. Shame, embarrassment, or anger from being stared at by a 10-year-old after missing so many lines should be pretty effective.
- Shrink the change. Make it seem like all the lines are easy to learn, if learned only one at a time.
- Grow the person. Motivate the Catholic to learn it as quickly and seamlessly as they did in fifth grade; if you already did it once, you just have do it again!
Shape the path:
- Tweak the environment. Have cue cards all over the place, laminate them, make them easy to fit in a pocket or purse.
- Build habits. Have the Catholic go to church every week until they have an “error-free” Mass.
- Rally the herd. Have them watch others for cues on behavior; this has worked for me for decades!
You can see that many of these techniques should be easier in healthcare than in other industries, especially motivating the elephant and shaping the path. To facilitate change, hospitalists should find ways to direct the rider, motivate the elephant, and shape the path, and we may find that change is not as daunting and overwhelming as it might at first seem.
And when you finally do make a positive change happen, give yourself a high-five—and send a “Hail Mary” to the Creasters.
Dr. Scheurer is physician editor of The Hospitalist.
Reference
The New Doctor's Office
The doctor’s office, at least my office, has changed over the last few decades with an increase in personnel added to make my life easier. Much of it has occurred as a response to the increased billing and authentication process that is required for reimbursement.
After all, when doctors were paid in cash or with a dozen eggs, there was little need for all the paperwork. Health insurance, both private and federal, has been the cause of much of this. At the same time, medical assistants, registered nurses, and a variety of ancillary staff have been added to make the patient’s visit smoother and to acquire the requisite information to satiate the vast network of communications that are generated with each office visit. All of these personnel are now an undisputable requirement for the function of today’s medical office.
In the process, the distance between the physician and the patient has increased. In many offices today, the patient may never see the doctor during the visit. To an increasing extent, the office contact with the patient is solely by an RN or physician assistant. In most cases, patients are satisfied with the service and are delighted not to spend a long time waiting to see the "doctor." Many of the visits are check-ups or annual or semiannual visits without any associated symptoms that can often be dealt with by a sympathetic and knowledgeable nurse. The patient is the winner to a great extent in this process by acquiring a sensitive ear and an expeditious visit. What is lost is the continued relationship of the patients and their physician. The biggest loss, I would suggest, is the doctor’s satisfaction of providing medical care that comes with every patient encounter, which keeps many of us energized to keep practicing medicine.
Now we have a new vision of how the primary care office of the future will function as a medical home (N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:891-3). In this vision, the physicians will be energized by a global payment system that will create an environment in which the doctor’s role is to pass real responsibility to their ancillary staff for which they would be held accountable. According to the authors, the physician’s office will be committed to promoting a healthy environment rather than merely treating disease. Why bother with the simple issue of treating sick patients when you can take on the entire environment of your community to prevent disease?
The authors go on to state that the physician would not waste time focusing on the "10% premature mortality that is influenced by medical treatment." In this work environment, the physician would be the team manager of a host of ancillary personnel, including medical assistants, RNs, social workers, nutritionists, and pharmacists, to name but a few. The physician would be energized by his or her role as a team leader. The physician, the authors explain, would see fewer patients and would not be caught running from room to room to see patients. Instead, he or she will become involved with care of the "community and understanding the upstream determinants of downstream sickness" and would spend there time in the community "advocating for the local farmer’s market to accept food stamps, organizing walking clubs for physical exercise, and lobbying ... to reduce emissions to improve air quality."
This, of course, is a far cry from the doctors who negotiated the care for their patient for a dozen eggs. It is clearly a role that is foreign to my generation. To some extent, though, patients may well gain in this futuristic environment. They will acquire an empathetic nurse who will be sensitive to their needs and who may be as good as a crotchety overworked doctor. All of the ancillary medical staff will gain a larger and more responsible role in the medical home. The physicians will morph into a new role that is more characteristic of an administrator and less as a practitioner. The doctors, however, will be the biggest losers as they disengage from the patient contact and care that is so crucial to the satisfaction of being a doctor.
Dr. Goldstein, medical editor of Cardiology News, is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University and division head emeritus of cardiovascular medicine at Henry Ford Hospital, both in Detroit. He is on data safety monitoring committees for the National Institutes of Health and several pharmaceutical companies.
The doctor’s office, at least my office, has changed over the last few decades with an increase in personnel added to make my life easier. Much of it has occurred as a response to the increased billing and authentication process that is required for reimbursement.
After all, when doctors were paid in cash or with a dozen eggs, there was little need for all the paperwork. Health insurance, both private and federal, has been the cause of much of this. At the same time, medical assistants, registered nurses, and a variety of ancillary staff have been added to make the patient’s visit smoother and to acquire the requisite information to satiate the vast network of communications that are generated with each office visit. All of these personnel are now an undisputable requirement for the function of today’s medical office.
In the process, the distance between the physician and the patient has increased. In many offices today, the patient may never see the doctor during the visit. To an increasing extent, the office contact with the patient is solely by an RN or physician assistant. In most cases, patients are satisfied with the service and are delighted not to spend a long time waiting to see the "doctor." Many of the visits are check-ups or annual or semiannual visits without any associated symptoms that can often be dealt with by a sympathetic and knowledgeable nurse. The patient is the winner to a great extent in this process by acquiring a sensitive ear and an expeditious visit. What is lost is the continued relationship of the patients and their physician. The biggest loss, I would suggest, is the doctor’s satisfaction of providing medical care that comes with every patient encounter, which keeps many of us energized to keep practicing medicine.
Now we have a new vision of how the primary care office of the future will function as a medical home (N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:891-3). In this vision, the physicians will be energized by a global payment system that will create an environment in which the doctor’s role is to pass real responsibility to their ancillary staff for which they would be held accountable. According to the authors, the physician’s office will be committed to promoting a healthy environment rather than merely treating disease. Why bother with the simple issue of treating sick patients when you can take on the entire environment of your community to prevent disease?
The authors go on to state that the physician would not waste time focusing on the "10% premature mortality that is influenced by medical treatment." In this work environment, the physician would be the team manager of a host of ancillary personnel, including medical assistants, RNs, social workers, nutritionists, and pharmacists, to name but a few. The physician would be energized by his or her role as a team leader. The physician, the authors explain, would see fewer patients and would not be caught running from room to room to see patients. Instead, he or she will become involved with care of the "community and understanding the upstream determinants of downstream sickness" and would spend there time in the community "advocating for the local farmer’s market to accept food stamps, organizing walking clubs for physical exercise, and lobbying ... to reduce emissions to improve air quality."
This, of course, is a far cry from the doctors who negotiated the care for their patient for a dozen eggs. It is clearly a role that is foreign to my generation. To some extent, though, patients may well gain in this futuristic environment. They will acquire an empathetic nurse who will be sensitive to their needs and who may be as good as a crotchety overworked doctor. All of the ancillary medical staff will gain a larger and more responsible role in the medical home. The physicians will morph into a new role that is more characteristic of an administrator and less as a practitioner. The doctors, however, will be the biggest losers as they disengage from the patient contact and care that is so crucial to the satisfaction of being a doctor.
Dr. Goldstein, medical editor of Cardiology News, is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University and division head emeritus of cardiovascular medicine at Henry Ford Hospital, both in Detroit. He is on data safety monitoring committees for the National Institutes of Health and several pharmaceutical companies.
The doctor’s office, at least my office, has changed over the last few decades with an increase in personnel added to make my life easier. Much of it has occurred as a response to the increased billing and authentication process that is required for reimbursement.
After all, when doctors were paid in cash or with a dozen eggs, there was little need for all the paperwork. Health insurance, both private and federal, has been the cause of much of this. At the same time, medical assistants, registered nurses, and a variety of ancillary staff have been added to make the patient’s visit smoother and to acquire the requisite information to satiate the vast network of communications that are generated with each office visit. All of these personnel are now an undisputable requirement for the function of today’s medical office.
In the process, the distance between the physician and the patient has increased. In many offices today, the patient may never see the doctor during the visit. To an increasing extent, the office contact with the patient is solely by an RN or physician assistant. In most cases, patients are satisfied with the service and are delighted not to spend a long time waiting to see the "doctor." Many of the visits are check-ups or annual or semiannual visits without any associated symptoms that can often be dealt with by a sympathetic and knowledgeable nurse. The patient is the winner to a great extent in this process by acquiring a sensitive ear and an expeditious visit. What is lost is the continued relationship of the patients and their physician. The biggest loss, I would suggest, is the doctor’s satisfaction of providing medical care that comes with every patient encounter, which keeps many of us energized to keep practicing medicine.
Now we have a new vision of how the primary care office of the future will function as a medical home (N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:891-3). In this vision, the physicians will be energized by a global payment system that will create an environment in which the doctor’s role is to pass real responsibility to their ancillary staff for which they would be held accountable. According to the authors, the physician’s office will be committed to promoting a healthy environment rather than merely treating disease. Why bother with the simple issue of treating sick patients when you can take on the entire environment of your community to prevent disease?
The authors go on to state that the physician would not waste time focusing on the "10% premature mortality that is influenced by medical treatment." In this work environment, the physician would be the team manager of a host of ancillary personnel, including medical assistants, RNs, social workers, nutritionists, and pharmacists, to name but a few. The physician would be energized by his or her role as a team leader. The physician, the authors explain, would see fewer patients and would not be caught running from room to room to see patients. Instead, he or she will become involved with care of the "community and understanding the upstream determinants of downstream sickness" and would spend there time in the community "advocating for the local farmer’s market to accept food stamps, organizing walking clubs for physical exercise, and lobbying ... to reduce emissions to improve air quality."
This, of course, is a far cry from the doctors who negotiated the care for their patient for a dozen eggs. It is clearly a role that is foreign to my generation. To some extent, though, patients may well gain in this futuristic environment. They will acquire an empathetic nurse who will be sensitive to their needs and who may be as good as a crotchety overworked doctor. All of the ancillary medical staff will gain a larger and more responsible role in the medical home. The physicians will morph into a new role that is more characteristic of an administrator and less as a practitioner. The doctors, however, will be the biggest losers as they disengage from the patient contact and care that is so crucial to the satisfaction of being a doctor.
Dr. Goldstein, medical editor of Cardiology News, is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University and division head emeritus of cardiovascular medicine at Henry Ford Hospital, both in Detroit. He is on data safety monitoring committees for the National Institutes of Health and several pharmaceutical companies.
Lip Rejuvenation Using Dermal Fillers
Dr. Rossi discusses dermal fillers for a natural approach to lip augmentation. For more information, read Dr. Rossi's article in the June 2012 issue, "Soft Tissue Augmentation With Dermal Fillers, Part 1: Lips and Lower Face."
Dr. Rossi discusses dermal fillers for a natural approach to lip augmentation. For more information, read Dr. Rossi's article in the June 2012 issue, "Soft Tissue Augmentation With Dermal Fillers, Part 1: Lips and Lower Face."
Dr. Rossi discusses dermal fillers for a natural approach to lip augmentation. For more information, read Dr. Rossi's article in the June 2012 issue, "Soft Tissue Augmentation With Dermal Fillers, Part 1: Lips and Lower Face."