User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Tool May Help Prioritize High-Risk Patients for Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.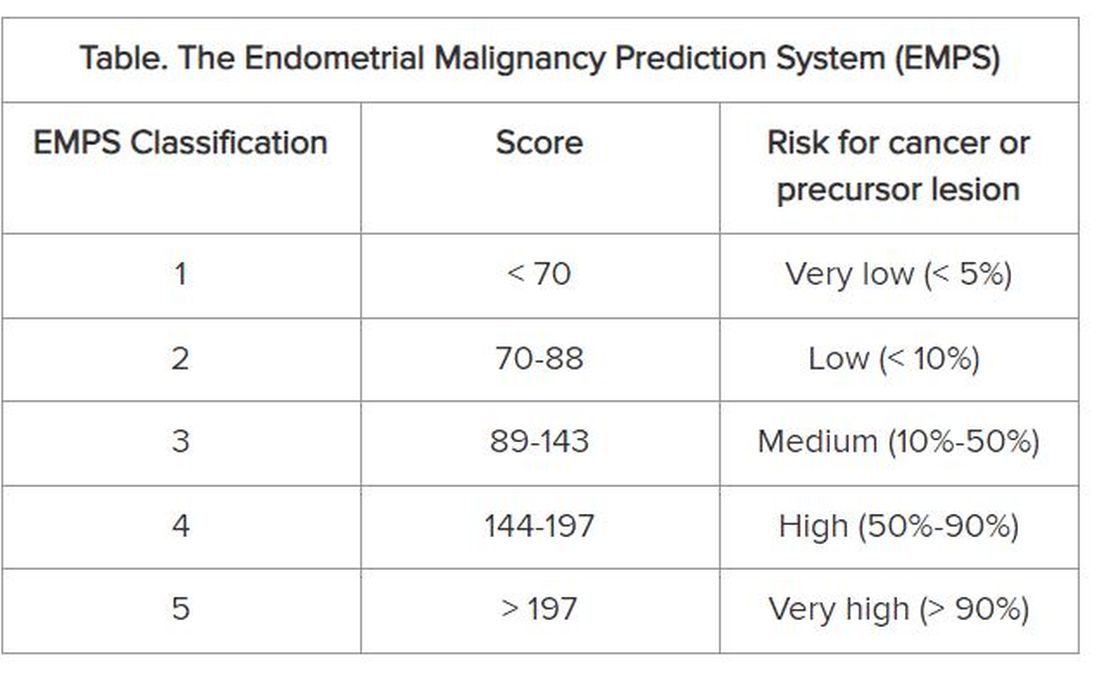
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hysteroscopy is a crucial examination for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. In Brazil, women with postmenopausal bleeding who need to undergo this procedure in the public health system wait in line alongside patients with less severe complaints. Until now, there has been no system to prioritize patients at high risk for cancer. But this situation may change, thanks to a Brazilian study published in February in the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
Researchers from the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina in São Paulo, a public unit managed by Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, have developed the Endometrial Malignancy Prediction System (EMPS), a nomogram to identify patients at high risk for endometrial cancer and prioritize them in the hysteroscopy waiting list.
Bruna Bottura, MD, a gynecologist and obstetrician at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein and the study’s lead author, told this news organization that the idea to create the nomogram arose during the COVID-19 pandemic. “We noticed that ... when outpatient clinics resumed, we were seeing many patients for intrauterine device (IUD) removal. We thought it was unfair for a patient with postmenopausal bleeding, who has a chance of having cancer, to have to wait in the same line as a patient needing IUD removal,” she said. This realization motivated the development of the tool, which was overseen by Renato Moretti-Marques, MD, PhD.
The EMPS Score
The team conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 1945 patients with suspected endometrial cancer who had undergone diagnostic hysteroscopy at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein between March 2019 and March 2022. Among these patients, 107 were diagnosed with precursor lesions or endometrial cancer on the basis of biopsy. The other 1838 participants, who had had cancer ruled out by biopsy, formed the control group.
Through bivariate and multivariate linear regression analysis, the authors determined that the presence or absence of hypertension, diabetes, postmenopausal bleeding, endometrial polyps, uterine volume, number of pregnancies, body mass index, age, and endometrial thickness were the main risk factors for endometrial cancer diagnosis.
On the basis of these data, the group developed the EMPS nomogram. Physicians can use it to classify the patient’s risk according to the sum of the scores assigned to each of these factors.
The Table shows the classification system. The scoring tables available in the supplemental materials of the article can be accessed here.
Focus on Primary Care
The goal is not to remove patients classified as low risk from the hysteroscopy waiting list, but rather to prioritize those classified as high risk to get the examination, according to Dr. Bottura.
At the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina, the average wait time for hysteroscopy was 120 days. But because the unit is focused on oncologic patients and has a high level of organization, this time is much shorter than observed in other parts of Brazil’s National Health Service, said Dr. Bottura. “Many patients are on the hysteroscopy waiting list for 2 years. Considering patients in more advanced stages [of endometrial cancer], it makes a difference,” she said.
Although the nomogram was developed in tertiary care, it is aimed at professionals working in primary care. The reason is that physicians from primary care health units refer women with clinical indications for hysteroscopy to specialized national health services, such as the Municipal Hospital of Vila Santa Catarina. “Our goal is the primary sector, to enable the clinic to refer this high-risk patient sooner. By the time you reach the tertiary sector, where hysteroscopies are performed, all patients will undergo the procedure. Usually, it is not the hospitals that predetermine the line, but rather the health clinics,” she explained.
The researchers hope to continue the research, starting with a prospective study. “We intend to apply and evaluate the tool within our own service to observe whether any patient with a high [EMPS] score patient ended up waiting too long to be referred. In fact, this will be a system validation step,” said Dr. Bottura.
In parallel, the team has a proposal to take the tool to health clinics in the same region as the study hospital. “We know this involves changing the protocol at a national level, so it’s more challenging,” said Dr. Bottura. She added that the final goal is to create a calculator, possibly an app, that allows primary care doctors to calculate the risk score in the office. This calculator could enable risk classification to be linked to patient referrals.
This story was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians Call for Easing FDA Warnings on Low-Dose Estrogen
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Charles Powell, MD, said he sometimes has a hard time persuading patients to start on low-dose vaginal estrogen, which can help prevent urinary tract infections and ease other symptoms of menopause.
Many women fear taking these vaginal products because of what Dr. Powell considers excessively strong warnings about the risk for cancer and cardiovascular disease linked to daily estrogen pills that were issued in the early 2000s.
He is advocating for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to remove the boxed warning on low-dose estrogen. His efforts are separate from his roles as an associate professor of urology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, and as a member of the American Urological Association (AUA), Dr. Powell said.
In his quest to find out how to change labeling, Dr. Powell has gained a quick education about drug regulation. He has enlisted Representative Jim Baird (R-IN) and Senator Mike Braun (R-IN) to contact the FDA on his behalf, while congressional staff guided him through the hurdles of getting the warning label changed. For instance, a manufacturer of low-dose estrogen may need to become involved.
“You don’t learn this in med school,” Dr. Powell said in an interview.
With this work, Dr. Powell is wading into a long-standing argument between the FDA and some clinicians and researchers about the potential harms of low-dose estrogen.
He is doing so at a time of increased interest in understanding genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), a term coined a decade ago by the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society to cover “a constellation of conditions” related to urogenital atrophy.
Symptoms of GSM include vaginal dryness and burning and recurrent urinary tract infections.
The federal government in 2022 began a project budgeted with nearly $1 million to review evidence on treatments, including vaginal and low-dose estrogen. The aim is to eventually help the AUA develop clinical guidelines for addressing GSM.
In addition, a bipartisan Senate bill introduced in May calls for authorizing $125 million over 5 years for the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to fund research on menopause. Senator Patty Murray (D-WA), the lead sponsor of the bill, is a longtime advocate for women’s health and serves as chairwoman for the Senate Appropriations Committee, which largely sets the NIH budget.
“The bottom line is, for too long, menopause has been overlooked, underinvested in and left behind,” Sen. Murray said during a May 2 press conference. “It is well past time to stop treating menopause like some kind of secret and start treating it like the major mainstream public health issue it is.”
Evidence Demands
Increased federal funding for menopause research could help efforts to change the warning label on low-dose estrogen, according to JoAnn Manson, MD, chief of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Dr. Manson was a leader of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a major federally funded research project launched in 1991 to investigate if hormone therapy and diet could protect older women from chronic diseases related to aging.
Before the WHI, clinicians prescribed hormones to prevent cardiovascular disease, based on evidence from earlier research.
But in 2002, a WHI trial that compared estrogen-progestin tablets with placebo was halted early because of disturbing findings, including an association with higher risk for breast cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Compared with placebo, for every 10,000 women taking estrogen plus progestin annually, incidences of cardiovascular disease, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and invasive breast cancer were seven to eight times higher.
In January 2003, the FDA announced it would put a boxed warning about cardiovascular risk and cancer risk on estrogen products, reflecting the WHI finding.
The agency at the time said clinicians should work with patients to assess risks and benefits of these products to manage the effects of menopause.
But more news on the potential harms of estrogen followed in 2004: A WHI study comparing estrogen-only pills with placebo produced signals of a small increased risk for stroke, although it also indicated no excess risk for breast cancer for at least 6.8 years of use.
Dr. Manson and the North American Menopause Society in 2016 filed a petition with the FDA to remove the boxed warning that appears on the front of low-dose estrogen products. The group wanted the information on risks moved to the usual warning section of the label.
Two years later, the FDA rejected the petition, citing the absence of “well-controlled studies,” to prove low-dose topical estrogen poses less risk to women than the high-dose pills studied in the WHI.
The FDA told this news organization that it stands by the decisions in its rejection of the petition.
Persuading the FDA to revise the labels on low-dose estrogen products likely will require evidence from randomized, large-scale studies, Dr. Manson said. The agency has not been satisfied to date with findings from other kinds of studies, including observational research.
“Once that evidence is available that the benefit-risk profile is different for different formulations and the evidence is compelling and definitive, that warning should change,” Dr. Manson told this news organization.
But the warning continues to have a chilling effect on patient willingness to use low-dose vaginal estrogen, even with the FDA’s continued endorsement of estrogen for menopause symptoms, clinicians told this news organization.
Risa Kagan, MD, a gynecologist at Sutter Health in Berkeley, California, said in many cases her patients’ partners also need to be reassured. Dr. Kagan said she still sees women who have had to discontinue sexual intercourse because of pain. In some cases, the patients will bring the medicine home only to find that the warnings frighten their spouses.
“The spouse says, ‘Oh my God, I don’t want you to get dementia, to get breast cancer, it’s not worth it, so let’s keep doing outercourse’,” meaning sexual relations without penetration, Dr. Kagan said.
Difficult Messaging
From the initial unveiling of disappointing WHI results, clinicians and researchers have stressed that women could continue using estrogen products for managing symptoms of menopause, even while advising strongly against their continued use with the intention of preventing heart disease.
Newly published findings from follow-ups of WHI participants may give clinicians and patients even more confidence for the use of estrogen products in early menopause.
According to the study, which Dr. Manson coauthored, younger women have a low risk for cardiovascular disease and other associated conditions when taking hormone therapy. Risks attributed to these drugs were less than one additional adverse event per 1000 women annually. This population may also derive significant quality-of-life benefits for symptom relief.
Dr. Manson told this news organization that estrogen in lower doses and delivered through the skin as a patch or gel may further reduce risks.
“The WHI findings should never be used as a reason to deny hormone therapy to women in early menopause with bothersome menopausal symptoms,” Dr. Manson said. “Many women are good candidates for treatment and, in shared decision-making with their clinicians, should be able to receive appropriate and personalized healthcare for their needs.”
But the current FDA warning label makes it difficult to help women understand the risk and benefits of low-dose estrogen, according to Stephanie Faubion, MD, MBA, medical director at the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health in Jacksonville, Florida.
Clinicians now must set aside time to explain the warnings to women when they prescribe low-dose estrogen, Dr. Faubion said.
“The package insert is going to look scary: I prepare women for that because otherwise they often won’t even fill it or use it.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Molecular Classification of Endometrial Carcinomas
Historically, endometrial cancer has been classified as type I or type II. Type I endometrial cancers are typically estrogen driven, low grade, with endometrioid histology, and have a more favorable prognosis. In contrast, type II endometrial cancers are typically high grade, have more aggressive histologies (eg, serous or clear cell), and have a poorer prognosis.1
While this system provides a helpful schema for understanding endometrial cancers, it fails to represent the immense variation of biologic behavior and outcomes in endometrial cancers and oversimplifies what has come to be understood as a complex and molecularly diverse disease.
In 2013, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) performed genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic characterization of 373 endometrial carcinomas. They identified four categories with distinct genetic profiles corresponding to clinical outcomes: 1) DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE) mutated; 2) mismatch repair deficient; 3) copy number high/p53 abnormal; and 4) copy number low/no specific molecular profile.2 By providing both predictive and prognostic information, these molecular features may be incorporated into treatment planning decisions in the future.
The POLE-mutated subtype are endometrial cancers with recurrent mutations in the POLE gene, which is involved in DNA replication and repair. POLE mutations occur in about 5%-10% of endometrial cancers. Despite some more aggressive histopathologic findings (eg, higher grade, deeper myometrial invasion, positive lymphovascular space invasion), recurrences rarely occur, and patients with POLE mutations have the best prognosis of the four molecular subtypes, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of 92%-100%.3
The mismatch repair–deficient (MMRd) subtype are endometrial cancers with abnormalities in any of the mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6). These alterations may result from hereditary or somatic mutations in any of the MMR genes or epigenetic changes in the MLH1 promoter. Germ-line mutations are associated with Lynch syndrome; thus, patients found to have a germ-line mutation in any of the MMR genes necessitate a genetics referral. The MMRd subtype accounts for about 20%-30% of endometrial cancers, and patients with MMRd tumors have an intermediate prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of about 70%.3. These tumors are more responsive to the use of immunotherapy checkpoint inhibitors. Two recent landmark trials showed improved outcomes in patients with advanced MMRd endometrial cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in addition to standard chemotherapy.4,5
The worst prognosis belongs to the copy number high subgroup, which accounts for approximately 10% of endometrial cancers. Five-year recurrence-free survival is ~50%.3 These tumors often contain TP53 mutations and are composed of aggressive histologies, such as serous, clear cell, high-grade endometrioid, and carcinosarcomas. Recent data suggests that human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) amplification may also be prevalent in this subgroup.6
Endometrial cancers that lack any of the above alterations fall into the no specific molecular profile (NSMP) or copy number low subgroup. Mutations in other genes, such as PTEN, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, KRAS, and ARID1A, are often present in these tumors. As the most common subtype, this heterogeneous group accounts for about 50% of all endometrial cancers. These tumors frequently comprise endometrioid histology with estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity, high rates of response to hormonal therapy, and an overall intermediate to favorable prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of ~75%.3
The use of whole-genome sequencing in TCGA limits the clinical applicability of testing because of the cost and complex methodologies involved. Multiple algorithms have been developed in the interim that approximate TCGA subtypes using relatively less expensive and more widely available testing methods, such as immunohistochemistry and next-generation sequencing. In the ProMisE algorithm, immunohistochemistry for p53 and MMR proteins is used as a surrogate for copy number high and MMRd tumors, respectively, and targeted sequencing is used to identify POLE mutations.7
Full molecular classification of endometrial tumors provides important prognostic information and allows for incorporation into treatment planning. To this end, the new 2023 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) endometrial cancer staging incorporates an option for the addition of molecular subtype, with the stance that it allows for better prognostic prediction.8 While complete molecular classification is not required, it is encouraged. Furthermore, several clinical trials are currently investigating different treatment regimens based on these distinct molecular profiles.
Dr. Haag is a gynecologic oncology fellow in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of North Carolina Hospitals, Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Bokhman JV. Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic Oncology. 1983;15(1):10-17.
2. Kandoth C et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 2013;497(7447):67-73.
3. León-Castillo A et al. Molecular classification of the PORTEC-3 trial for high-risk endometrial cancer: Impact on prognosis and benefit from adjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncology. 2020;38(29):3388-3397.
4. Mirza MR et al. Dostarlimab for primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2145-2158.
5. Eskander RN et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2159-2170.
6. Talia KL et al. The role of HER2 as a therapeutic biomarker in gynaecological malignancy: Potential for use beyond uterine serous carcinoma. Pathology. 2023;55(1):8-18.
7. Kommoss S et al. Final validation of the ProMisE molecular classifier for endometrial carcinoma in a large population-based case series. Annals Oncology. 2018;29(5):1180-1188.
8. Berek JS et al. FIGO staging of endometrial cancer: 2023. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023;162(2):383-394.
Historically, endometrial cancer has been classified as type I or type II. Type I endometrial cancers are typically estrogen driven, low grade, with endometrioid histology, and have a more favorable prognosis. In contrast, type II endometrial cancers are typically high grade, have more aggressive histologies (eg, serous or clear cell), and have a poorer prognosis.1
While this system provides a helpful schema for understanding endometrial cancers, it fails to represent the immense variation of biologic behavior and outcomes in endometrial cancers and oversimplifies what has come to be understood as a complex and molecularly diverse disease.
In 2013, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) performed genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic characterization of 373 endometrial carcinomas. They identified four categories with distinct genetic profiles corresponding to clinical outcomes: 1) DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE) mutated; 2) mismatch repair deficient; 3) copy number high/p53 abnormal; and 4) copy number low/no specific molecular profile.2 By providing both predictive and prognostic information, these molecular features may be incorporated into treatment planning decisions in the future.
The POLE-mutated subtype are endometrial cancers with recurrent mutations in the POLE gene, which is involved in DNA replication and repair. POLE mutations occur in about 5%-10% of endometrial cancers. Despite some more aggressive histopathologic findings (eg, higher grade, deeper myometrial invasion, positive lymphovascular space invasion), recurrences rarely occur, and patients with POLE mutations have the best prognosis of the four molecular subtypes, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of 92%-100%.3
The mismatch repair–deficient (MMRd) subtype are endometrial cancers with abnormalities in any of the mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6). These alterations may result from hereditary or somatic mutations in any of the MMR genes or epigenetic changes in the MLH1 promoter. Germ-line mutations are associated with Lynch syndrome; thus, patients found to have a germ-line mutation in any of the MMR genes necessitate a genetics referral. The MMRd subtype accounts for about 20%-30% of endometrial cancers, and patients with MMRd tumors have an intermediate prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of about 70%.3. These tumors are more responsive to the use of immunotherapy checkpoint inhibitors. Two recent landmark trials showed improved outcomes in patients with advanced MMRd endometrial cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in addition to standard chemotherapy.4,5
The worst prognosis belongs to the copy number high subgroup, which accounts for approximately 10% of endometrial cancers. Five-year recurrence-free survival is ~50%.3 These tumors often contain TP53 mutations and are composed of aggressive histologies, such as serous, clear cell, high-grade endometrioid, and carcinosarcomas. Recent data suggests that human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) amplification may also be prevalent in this subgroup.6
Endometrial cancers that lack any of the above alterations fall into the no specific molecular profile (NSMP) or copy number low subgroup. Mutations in other genes, such as PTEN, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, KRAS, and ARID1A, are often present in these tumors. As the most common subtype, this heterogeneous group accounts for about 50% of all endometrial cancers. These tumors frequently comprise endometrioid histology with estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity, high rates of response to hormonal therapy, and an overall intermediate to favorable prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of ~75%.3
The use of whole-genome sequencing in TCGA limits the clinical applicability of testing because of the cost and complex methodologies involved. Multiple algorithms have been developed in the interim that approximate TCGA subtypes using relatively less expensive and more widely available testing methods, such as immunohistochemistry and next-generation sequencing. In the ProMisE algorithm, immunohistochemistry for p53 and MMR proteins is used as a surrogate for copy number high and MMRd tumors, respectively, and targeted sequencing is used to identify POLE mutations.7
Full molecular classification of endometrial tumors provides important prognostic information and allows for incorporation into treatment planning. To this end, the new 2023 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) endometrial cancer staging incorporates an option for the addition of molecular subtype, with the stance that it allows for better prognostic prediction.8 While complete molecular classification is not required, it is encouraged. Furthermore, several clinical trials are currently investigating different treatment regimens based on these distinct molecular profiles.
Dr. Haag is a gynecologic oncology fellow in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of North Carolina Hospitals, Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Bokhman JV. Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic Oncology. 1983;15(1):10-17.
2. Kandoth C et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 2013;497(7447):67-73.
3. León-Castillo A et al. Molecular classification of the PORTEC-3 trial for high-risk endometrial cancer: Impact on prognosis and benefit from adjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncology. 2020;38(29):3388-3397.
4. Mirza MR et al. Dostarlimab for primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2145-2158.
5. Eskander RN et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2159-2170.
6. Talia KL et al. The role of HER2 as a therapeutic biomarker in gynaecological malignancy: Potential for use beyond uterine serous carcinoma. Pathology. 2023;55(1):8-18.
7. Kommoss S et al. Final validation of the ProMisE molecular classifier for endometrial carcinoma in a large population-based case series. Annals Oncology. 2018;29(5):1180-1188.
8. Berek JS et al. FIGO staging of endometrial cancer: 2023. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023;162(2):383-394.
Historically, endometrial cancer has been classified as type I or type II. Type I endometrial cancers are typically estrogen driven, low grade, with endometrioid histology, and have a more favorable prognosis. In contrast, type II endometrial cancers are typically high grade, have more aggressive histologies (eg, serous or clear cell), and have a poorer prognosis.1
While this system provides a helpful schema for understanding endometrial cancers, it fails to represent the immense variation of biologic behavior and outcomes in endometrial cancers and oversimplifies what has come to be understood as a complex and molecularly diverse disease.
In 2013, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) performed genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic characterization of 373 endometrial carcinomas. They identified four categories with distinct genetic profiles corresponding to clinical outcomes: 1) DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE) mutated; 2) mismatch repair deficient; 3) copy number high/p53 abnormal; and 4) copy number low/no specific molecular profile.2 By providing both predictive and prognostic information, these molecular features may be incorporated into treatment planning decisions in the future.
The POLE-mutated subtype are endometrial cancers with recurrent mutations in the POLE gene, which is involved in DNA replication and repair. POLE mutations occur in about 5%-10% of endometrial cancers. Despite some more aggressive histopathologic findings (eg, higher grade, deeper myometrial invasion, positive lymphovascular space invasion), recurrences rarely occur, and patients with POLE mutations have the best prognosis of the four molecular subtypes, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of 92%-100%.3
The mismatch repair–deficient (MMRd) subtype are endometrial cancers with abnormalities in any of the mismatch repair proteins (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6). These alterations may result from hereditary or somatic mutations in any of the MMR genes or epigenetic changes in the MLH1 promoter. Germ-line mutations are associated with Lynch syndrome; thus, patients found to have a germ-line mutation in any of the MMR genes necessitate a genetics referral. The MMRd subtype accounts for about 20%-30% of endometrial cancers, and patients with MMRd tumors have an intermediate prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of about 70%.3. These tumors are more responsive to the use of immunotherapy checkpoint inhibitors. Two recent landmark trials showed improved outcomes in patients with advanced MMRd endometrial cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in addition to standard chemotherapy.4,5
The worst prognosis belongs to the copy number high subgroup, which accounts for approximately 10% of endometrial cancers. Five-year recurrence-free survival is ~50%.3 These tumors often contain TP53 mutations and are composed of aggressive histologies, such as serous, clear cell, high-grade endometrioid, and carcinosarcomas. Recent data suggests that human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) amplification may also be prevalent in this subgroup.6
Endometrial cancers that lack any of the above alterations fall into the no specific molecular profile (NSMP) or copy number low subgroup. Mutations in other genes, such as PTEN, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, KRAS, and ARID1A, are often present in these tumors. As the most common subtype, this heterogeneous group accounts for about 50% of all endometrial cancers. These tumors frequently comprise endometrioid histology with estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity, high rates of response to hormonal therapy, and an overall intermediate to favorable prognosis, with a 5-year recurrence-free survival of ~75%.3
The use of whole-genome sequencing in TCGA limits the clinical applicability of testing because of the cost and complex methodologies involved. Multiple algorithms have been developed in the interim that approximate TCGA subtypes using relatively less expensive and more widely available testing methods, such as immunohistochemistry and next-generation sequencing. In the ProMisE algorithm, immunohistochemistry for p53 and MMR proteins is used as a surrogate for copy number high and MMRd tumors, respectively, and targeted sequencing is used to identify POLE mutations.7
Full molecular classification of endometrial tumors provides important prognostic information and allows for incorporation into treatment planning. To this end, the new 2023 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) endometrial cancer staging incorporates an option for the addition of molecular subtype, with the stance that it allows for better prognostic prediction.8 While complete molecular classification is not required, it is encouraged. Furthermore, several clinical trials are currently investigating different treatment regimens based on these distinct molecular profiles.
Dr. Haag is a gynecologic oncology fellow in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of North Carolina Hospitals, Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Bokhman JV. Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic Oncology. 1983;15(1):10-17.
2. Kandoth C et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 2013;497(7447):67-73.
3. León-Castillo A et al. Molecular classification of the PORTEC-3 trial for high-risk endometrial cancer: Impact on prognosis and benefit from adjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncology. 2020;38(29):3388-3397.
4. Mirza MR et al. Dostarlimab for primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2145-2158.
5. Eskander RN et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(23):2159-2170.
6. Talia KL et al. The role of HER2 as a therapeutic biomarker in gynaecological malignancy: Potential for use beyond uterine serous carcinoma. Pathology. 2023;55(1):8-18.
7. Kommoss S et al. Final validation of the ProMisE molecular classifier for endometrial carcinoma in a large population-based case series. Annals Oncology. 2018;29(5):1180-1188.
8. Berek JS et al. FIGO staging of endometrial cancer: 2023. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023;162(2):383-394.
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Limits Toxic Effects in Cervical Cancer
TOPLINE:
results from the phase 2 POHIM-CCRT trial suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no studies have assessed the treatment outcomes and toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT following radical hysterectomy in patients with cervical cancer undergoing curative radiotherapy.
- The team analyzed outcomes from 79 patients undergoing hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection.
- Patients were a median age of 48; 29.5% had stage IB to IIA disease, another 29.5% had stage IIB disease, and 41% had stage III disease. Patients also had at least one of the following criteria following radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: lymph node metastasis (39.7%), parametrial invasion (54.4%), and positive resection margin (5.1%).
- The prescribed dose to the planning target volume was 40 Gy, delivered in 16 fractions to the whole pelvis, with any type of IMRT permitted. Overall, 71 patients also underwent concurrent weekly cisplatin (40 mg/m2 of body surface area for three cycles), and eight received fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2 on days 1-5) with cisplatin (60 mg/m2 for two cycles).
- The primary endpoint was the incidence of acute grade 3 or higher gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary, and hematologic toxic effects during radiotherapy or within 3 months of completing radiotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- After radiotherapy, only two patients (2.5%) experienced acute grade 3 or higher toxic effects. One was hospitalized for enterocolitis on the last day of radiotherapy and developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy; the other experienced hematologic toxic effects and also developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy.
- No patients experienced late grade 3 or higher toxic effects.
- When assessing toxic effects of any grade, acute and late gastrointestinal tract toxicities occurred in 76% and 31.6% of patients, respectively; acute and late genitourinary toxicities, all grade 1, occurred in 19% and 24.1% of patients, respectively; and hematologic toxicities occurred in 29.1% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
- Overall, at 3 years, 79.3% of patients were disease-free and 98% were alive. After a median follow-up of 43 months, 16 patients (20.3%) experienced disease recurrence, four of whom were salvaged and three of whom died.
IN PRACTICE:
“This nonrandomized controlled trial is the first prospective trial, to our knowledge, to show acceptable acute toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer in a postoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy setting,” the authors said, adding that the rate of grade 3 or higher acute toxic effects of 2.5% reported in this study was “substantially lower than our initial hypothesis of less than 15%.”
However , in an accompanying editorial, Mark E. Bernard, MD, of the University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, highlighted caveats to the study design and raised two core questions: “Should acute toxic effects be the primary endpoint of a single-group, phase 2 study using hypofractionation with fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy? Should the primary endpoint rather have been a cancer control endpoint, such as disease-free survival, overall survival, or local control?”
Still, Dr. Bernard wrote, “This trial does help lay the foundation for future pelvic hypofractionated trials with concurrent chemotherapy, especially for gynecological malignant tumors.”
SOURCE:
The research, led by Won Park, MD, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, was published in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The trial is a single-arm study, with a short follow-up time. In the editorial, Bernard listed several limitations, including the fact that patients received fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy than what’s typically given in this population.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results from the phase 2 POHIM-CCRT trial suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no studies have assessed the treatment outcomes and toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT following radical hysterectomy in patients with cervical cancer undergoing curative radiotherapy.
- The team analyzed outcomes from 79 patients undergoing hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection.
- Patients were a median age of 48; 29.5% had stage IB to IIA disease, another 29.5% had stage IIB disease, and 41% had stage III disease. Patients also had at least one of the following criteria following radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: lymph node metastasis (39.7%), parametrial invasion (54.4%), and positive resection margin (5.1%).
- The prescribed dose to the planning target volume was 40 Gy, delivered in 16 fractions to the whole pelvis, with any type of IMRT permitted. Overall, 71 patients also underwent concurrent weekly cisplatin (40 mg/m2 of body surface area for three cycles), and eight received fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2 on days 1-5) with cisplatin (60 mg/m2 for two cycles).
- The primary endpoint was the incidence of acute grade 3 or higher gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary, and hematologic toxic effects during radiotherapy or within 3 months of completing radiotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- After radiotherapy, only two patients (2.5%) experienced acute grade 3 or higher toxic effects. One was hospitalized for enterocolitis on the last day of radiotherapy and developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy; the other experienced hematologic toxic effects and also developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy.
- No patients experienced late grade 3 or higher toxic effects.
- When assessing toxic effects of any grade, acute and late gastrointestinal tract toxicities occurred in 76% and 31.6% of patients, respectively; acute and late genitourinary toxicities, all grade 1, occurred in 19% and 24.1% of patients, respectively; and hematologic toxicities occurred in 29.1% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
- Overall, at 3 years, 79.3% of patients were disease-free and 98% were alive. After a median follow-up of 43 months, 16 patients (20.3%) experienced disease recurrence, four of whom were salvaged and three of whom died.
IN PRACTICE:
“This nonrandomized controlled trial is the first prospective trial, to our knowledge, to show acceptable acute toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer in a postoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy setting,” the authors said, adding that the rate of grade 3 or higher acute toxic effects of 2.5% reported in this study was “substantially lower than our initial hypothesis of less than 15%.”
However , in an accompanying editorial, Mark E. Bernard, MD, of the University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, highlighted caveats to the study design and raised two core questions: “Should acute toxic effects be the primary endpoint of a single-group, phase 2 study using hypofractionation with fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy? Should the primary endpoint rather have been a cancer control endpoint, such as disease-free survival, overall survival, or local control?”
Still, Dr. Bernard wrote, “This trial does help lay the foundation for future pelvic hypofractionated trials with concurrent chemotherapy, especially for gynecological malignant tumors.”
SOURCE:
The research, led by Won Park, MD, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, was published in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The trial is a single-arm study, with a short follow-up time. In the editorial, Bernard listed several limitations, including the fact that patients received fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy than what’s typically given in this population.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results from the phase 2 POHIM-CCRT trial suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- To date, no studies have assessed the treatment outcomes and toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT following radical hysterectomy in patients with cervical cancer undergoing curative radiotherapy.
- The team analyzed outcomes from 79 patients undergoing hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer after radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection.
- Patients were a median age of 48; 29.5% had stage IB to IIA disease, another 29.5% had stage IIB disease, and 41% had stage III disease. Patients also had at least one of the following criteria following radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: lymph node metastasis (39.7%), parametrial invasion (54.4%), and positive resection margin (5.1%).
- The prescribed dose to the planning target volume was 40 Gy, delivered in 16 fractions to the whole pelvis, with any type of IMRT permitted. Overall, 71 patients also underwent concurrent weekly cisplatin (40 mg/m2 of body surface area for three cycles), and eight received fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2 on days 1-5) with cisplatin (60 mg/m2 for two cycles).
- The primary endpoint was the incidence of acute grade 3 or higher gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary, and hematologic toxic effects during radiotherapy or within 3 months of completing radiotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- After radiotherapy, only two patients (2.5%) experienced acute grade 3 or higher toxic effects. One was hospitalized for enterocolitis on the last day of radiotherapy and developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy; the other experienced hematologic toxic effects and also developed grade 3 anemia 3 months after completing radiotherapy.
- No patients experienced late grade 3 or higher toxic effects.
- When assessing toxic effects of any grade, acute and late gastrointestinal tract toxicities occurred in 76% and 31.6% of patients, respectively; acute and late genitourinary toxicities, all grade 1, occurred in 19% and 24.1% of patients, respectively; and hematologic toxicities occurred in 29.1% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
- Overall, at 3 years, 79.3% of patients were disease-free and 98% were alive. After a median follow-up of 43 months, 16 patients (20.3%) experienced disease recurrence, four of whom were salvaged and three of whom died.
IN PRACTICE:
“This nonrandomized controlled trial is the first prospective trial, to our knowledge, to show acceptable acute toxic effects of hypofractionated IMRT for cervical cancer in a postoperative concurrent chemoradiotherapy setting,” the authors said, adding that the rate of grade 3 or higher acute toxic effects of 2.5% reported in this study was “substantially lower than our initial hypothesis of less than 15%.”
However , in an accompanying editorial, Mark E. Bernard, MD, of the University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, highlighted caveats to the study design and raised two core questions: “Should acute toxic effects be the primary endpoint of a single-group, phase 2 study using hypofractionation with fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy? Should the primary endpoint rather have been a cancer control endpoint, such as disease-free survival, overall survival, or local control?”
Still, Dr. Bernard wrote, “This trial does help lay the foundation for future pelvic hypofractionated trials with concurrent chemotherapy, especially for gynecological malignant tumors.”
SOURCE:
The research, led by Won Park, MD, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, was published in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The trial is a single-arm study, with a short follow-up time. In the editorial, Bernard listed several limitations, including the fact that patients received fewer cycles of concurrent chemotherapy than what’s typically given in this population.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey Spotlights Identification of Dermatologic Adverse Events From Cancer Therapies
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“New cancer therapies have brought a diversity of treatment-related dermatologic adverse events (dAEs) beyond those experienced with conventional chemotherapy, which has demanded an evolving assessment of toxicities,” researchers led by Nicole R. LeBoeuf, MD, MPH, of the Department of Dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Boston, wrote in a poster presented at the American Academy of Dermatology annual meeting.
The authors noted that “Version 5.0 of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v5.0)” serves as the current, broadly accepted criteria for classification and grading during routine medical care and clinical trials. But despite extensive utilization of CTCAE, there is little data regarding its application.”
To evaluate how CTCAE is being used in clinical practice, they sent a four-case survey of dAEs to 81 dermatologists and 182 medical oncologists at six US-based academic institutions. For three of the cases, respondents were asked to classify and grade morbilliform, psoriasiform, and papulopustular rashes based on a review of photographs and text descriptions. For the fourth case, respondents were asked to grade a dAE using only a clinic note text description. The researchers used chi-square tests in R software to compare survey responses.
Compared with medical oncologists, dermatologists were significantly more likely to provide correct responses in characterizing morbilliform and psoriasiform eruptions. “As low as 12%” of medical oncologists were correct, and “as low as 87%” of dermatologists were correct (P < .001). Similarly, dermatologists were significantly more likely to grade the psoriasiform, papulopustular, and written cases correctly compared with medical oncologists (P < .001 for all associations).
“These cases demonstrated poor concordance of classification and grading between specialties and across medical oncology,” the authors concluded in their poster, noting that 87% of medical oncologists were interested in additional educational tools on dAEs. “With correct classification as low as 12%, medical oncologists may have more difficulty delivering appropriate, toxicity-specific therapy and may consider banal eruptions dangerous.”
Poor concordance of grading among the two groups of clinicians “raises the question of whether CTCAE v5.0 is an appropriate determinant for patient continuation on therapy or in trials,” they added. “As anticancer therapy becomes more complex — with new toxicities from novel agents and combinations — we must ensure we have a grading system that is valid across investigators and does not harm patients by instituting unnecessary treatment stops.”
Future studies, they said, “can explore what interventions beyond involvement of dermatologists improve classification and grading in practice.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, noted that with the continued expansion and introduction of new targeted and immunotherapies in the oncology space, “you can be sure we will continue to appreciate the importance and value of the field of supportive oncodermatology, as hair, skin, and nails are almost guaranteed collateral damage in this story.
“Ensuring early identification and consistent grading severity is not only important for the plethora of patients who are currently developing the litany of cutaneous adverse events but to evaluate potential mitigation strategies and even push along countermeasures down the FDA approval pathway,” Dr. Friedman said. In this study, the investigators demonstrated that work “is sorely needed, not just in dermatology but even more so for our colleagues across the aisle. A central tenet of supportive oncodermatology must also be education for all stakeholders, and the good news is our oncology partners will welcome it.”
Dr. LeBoeuf disclosed that she is a consultant to and has received honoraria from Bayer, Seattle Genetics, Sanofi, Silverback, Fortress Biotech, and Synox Therapeutics outside the submitted work. No other authors reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman directs the supportive oncodermatology program at GW that received independent funding from La Roche-Posay.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
US Researchers Call for Robust Studies Into Dequalinium, a Bacterial Vaginosis Therapy Common in Europe
Interest is growing in a standard European treatment for bacterial vaginosis (BV).
In a commentary published in JAMA Network Open, researchers and doctors from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the University of Maryland, Baltimore, urged clinical trials in the United States to determine if dequalinium chloride — an antiseptic that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi — is on par with or better than treatments currently available.
Dequalinium has been used throughout Europe for decades and is recommended as an alternative or second-line BV treatment by the World Health Organization; the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease; and the Austrian, German, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swiss Societies of Gynecology and Obstetrics. However, the product has not been approved for clinical use in the United States, no trials studying the drug have been registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, and the US Food and Drug Administration has not received an application for approval, according to agency records.
Treatments in the United States for BV include metronidazole and clindamycin that, while effective, have a recurrence rate of up to 60%.
“Current treatments for bacterial vaginosis often fall short, primarily due to frequent recurrences after treatment,” said Rebecca M. Brotman, PhD, MPH, a professor in the Department of Epidemiology and Public Health at the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and the corresponding author of the commentary.
More than 40% of people with recurrent BV do not receive adequate treatment, according to Caroline M. Mitchell, MD, MPH, director of the Vulvovaginal Disorders Program at Massachusetts General Hospital Vincent Center for Reproductive Biology, Boston, Massachusetts.
“BV is very disruptive to people’s daily lives and causes significant distress,” said Dr. Mitchell, who was not a coauthor of the new article. “Additionally, BV is associated with higher risk for HPV [human papillomavirus] infection, progression of HPV to cervical dysplasia, as well as risk for acquisition of other sexually transmitted infections.”
Dr. Mitchell said she hopes a recent trial from Europe comparing dequalinium chloride to metronidazole spurs researchers to study its efficacy and safety among women in the United States.
“Dequalinium has some antifungal activity, so it might offer a lower chance of yeast infection after treatment, which is important because posttreatment vulvovaginal candidiasis is one of the downsides to conventional antibiotic treatments,” Dr. Mitchell said.
The recent clinical trial included 147 premenopausal women with BV who received 10 mg of dequalinium per day for 6 days or oral metronidazole (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
Dr. Brotman said any studies in the United States would need to examine long-term recurrence of vaginosis after treatment with dequalinium chloride and its use during pregnancy.
The study was funded by various grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Gates Foundation. Various authors reported receiving royalties from UpToDate outside the submitted work or receiving a donation of sexually transmitted infection testing kits from Hologic for a study outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Interest is growing in a standard European treatment for bacterial vaginosis (BV).
In a commentary published in JAMA Network Open, researchers and doctors from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the University of Maryland, Baltimore, urged clinical trials in the United States to determine if dequalinium chloride — an antiseptic that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi — is on par with or better than treatments currently available.
Dequalinium has been used throughout Europe for decades and is recommended as an alternative or second-line BV treatment by the World Health Organization; the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease; and the Austrian, German, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swiss Societies of Gynecology and Obstetrics. However, the product has not been approved for clinical use in the United States, no trials studying the drug have been registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, and the US Food and Drug Administration has not received an application for approval, according to agency records.
Treatments in the United States for BV include metronidazole and clindamycin that, while effective, have a recurrence rate of up to 60%.
“Current treatments for bacterial vaginosis often fall short, primarily due to frequent recurrences after treatment,” said Rebecca M. Brotman, PhD, MPH, a professor in the Department of Epidemiology and Public Health at the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and the corresponding author of the commentary.
More than 40% of people with recurrent BV do not receive adequate treatment, according to Caroline M. Mitchell, MD, MPH, director of the Vulvovaginal Disorders Program at Massachusetts General Hospital Vincent Center for Reproductive Biology, Boston, Massachusetts.
“BV is very disruptive to people’s daily lives and causes significant distress,” said Dr. Mitchell, who was not a coauthor of the new article. “Additionally, BV is associated with higher risk for HPV [human papillomavirus] infection, progression of HPV to cervical dysplasia, as well as risk for acquisition of other sexually transmitted infections.”
Dr. Mitchell said she hopes a recent trial from Europe comparing dequalinium chloride to metronidazole spurs researchers to study its efficacy and safety among women in the United States.
“Dequalinium has some antifungal activity, so it might offer a lower chance of yeast infection after treatment, which is important because posttreatment vulvovaginal candidiasis is one of the downsides to conventional antibiotic treatments,” Dr. Mitchell said.
The recent clinical trial included 147 premenopausal women with BV who received 10 mg of dequalinium per day for 6 days or oral metronidazole (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
Dr. Brotman said any studies in the United States would need to examine long-term recurrence of vaginosis after treatment with dequalinium chloride and its use during pregnancy.
The study was funded by various grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Gates Foundation. Various authors reported receiving royalties from UpToDate outside the submitted work or receiving a donation of sexually transmitted infection testing kits from Hologic for a study outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Interest is growing in a standard European treatment for bacterial vaginosis (BV).
In a commentary published in JAMA Network Open, researchers and doctors from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore and the University of Maryland, Baltimore, urged clinical trials in the United States to determine if dequalinium chloride — an antiseptic that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi — is on par with or better than treatments currently available.
Dequalinium has been used throughout Europe for decades and is recommended as an alternative or second-line BV treatment by the World Health Organization; the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease; and the Austrian, German, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swiss Societies of Gynecology and Obstetrics. However, the product has not been approved for clinical use in the United States, no trials studying the drug have been registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, and the US Food and Drug Administration has not received an application for approval, according to agency records.
Treatments in the United States for BV include metronidazole and clindamycin that, while effective, have a recurrence rate of up to 60%.
“Current treatments for bacterial vaginosis often fall short, primarily due to frequent recurrences after treatment,” said Rebecca M. Brotman, PhD, MPH, a professor in the Department of Epidemiology and Public Health at the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and the corresponding author of the commentary.
More than 40% of people with recurrent BV do not receive adequate treatment, according to Caroline M. Mitchell, MD, MPH, director of the Vulvovaginal Disorders Program at Massachusetts General Hospital Vincent Center for Reproductive Biology, Boston, Massachusetts.
“BV is very disruptive to people’s daily lives and causes significant distress,” said Dr. Mitchell, who was not a coauthor of the new article. “Additionally, BV is associated with higher risk for HPV [human papillomavirus] infection, progression of HPV to cervical dysplasia, as well as risk for acquisition of other sexually transmitted infections.”
Dr. Mitchell said she hopes a recent trial from Europe comparing dequalinium chloride to metronidazole spurs researchers to study its efficacy and safety among women in the United States.
“Dequalinium has some antifungal activity, so it might offer a lower chance of yeast infection after treatment, which is important because posttreatment vulvovaginal candidiasis is one of the downsides to conventional antibiotic treatments,” Dr. Mitchell said.
The recent clinical trial included 147 premenopausal women with BV who received 10 mg of dequalinium per day for 6 days or oral metronidazole (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
Dr. Brotman said any studies in the United States would need to examine long-term recurrence of vaginosis after treatment with dequalinium chloride and its use during pregnancy.
The study was funded by various grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Gates Foundation. Various authors reported receiving royalties from UpToDate outside the submitted work or receiving a donation of sexually transmitted infection testing kits from Hologic for a study outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
New mRNA Vaccines in Development for Cancer and Infections
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rural Health System ‘Teetering on Brink’ of Collapse, Says AMA
Physicians are leaving healthcare in droves, “not because they don’t want to practice ... but because the system is making it more and more difficult for them to care for their patients,” Bruce Scott, MD, president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), said at a press conference May 9 at the National Rural Health Association’s Annual Conference in New Orleans.
He said that shrinking reimbursement rates and excessive administrative tasks are pushing doctors out of the workforce, exacerbating physician shortages in rural locations where 46 million Americans live.
A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report found that people living in rural areas are more likely to die early from preventable causes than their urban counterparts, said Dr. Scott.
He said the AMA wants Congress to pass legislation to incentivize more physicians to work in rural areas and expand the number of rural and primary care residency spots. Historically, 80% of residents practice within 80 miles of where they complete residency, he said.
Dr. Scott also hopes Congress will revise the J-1 visa rules to allow qualified international medical graduates to continue to practice in the United States. He’d like to see the pandemic telehealth flexibilities made permanent because these loosened guidelines greatly improved care access for rural areas in recent years.
Lower Pay Affects Care in Rural, Urban Areas
Decreased reimbursements also have hit rural and urban doctors in independent practice particularly hard, Dr. Scott said. When adjusted for inflation, the current Medicare payment rate for physicians has dropped 29% since 2001, he said. Now that commercial payers tie their reimbursement models to the Medicare rate, physicians are experiencing “severe” financial stress amid rising practice costs and student loan debt.
He shared anecdotes about how these issues have affected his private otolaryngology practice in Louisville, Kentucky, a state where more than 2 million people live in federally designated primary care professional shortage areas.
“A major insurance company that controls over 60% of the private payer market in rural Kentucky [recently] offered us ... surgical rates less than they paid us 6 years ago,” he said.
Dr. Scott said physicians must make difficult choices. “Do we not invest in the latest physical equipment? Do we reduce our number of employees? Do we perhaps stop accepting new Medicare patients?”
He noted that physicians now spend twice as much time on prior authorizations and other administrative tasks as they do on direct patient care. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 33% of physicians reported that the cumbersome prior authorization process led to a serious adverse event for a patient. Eighty percent reported it caused their patient to forgo treatment altogether.
Dr. Scott, who will be sworn in as AMA president in June, said he experiences the frustration daily.
“I have to get on the phone and justify to an insurance person who rarely has gone to medical school, has never seen the patient, and heck, in my case, sometimes they can’t even say otolaryngology, much less tell me what the appropriate care is for my patient,” he said.
When asked about the impact of private equity in healthcare, Dr. Scott said there is room for all different modes of practice, but private equity could bring a unique benefit.
“They have deeper pockets to potentially invest in telehealth technology, AI, and better computer systems,” he said.
But, he said, some private equity-owned systems have abandoned rural areas, and in other regions they “push the physicians to move faster, see more patients, and do the things that are profit-driven.
“The key is to continue to provide ... quality medical care that is determined by an individual physician in consultation with the patient.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are leaving healthcare in droves, “not because they don’t want to practice ... but because the system is making it more and more difficult for them to care for their patients,” Bruce Scott, MD, president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), said at a press conference May 9 at the National Rural Health Association’s Annual Conference in New Orleans.
He said that shrinking reimbursement rates and excessive administrative tasks are pushing doctors out of the workforce, exacerbating physician shortages in rural locations where 46 million Americans live.
A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report found that people living in rural areas are more likely to die early from preventable causes than their urban counterparts, said Dr. Scott.
He said the AMA wants Congress to pass legislation to incentivize more physicians to work in rural areas and expand the number of rural and primary care residency spots. Historically, 80% of residents practice within 80 miles of where they complete residency, he said.
Dr. Scott also hopes Congress will revise the J-1 visa rules to allow qualified international medical graduates to continue to practice in the United States. He’d like to see the pandemic telehealth flexibilities made permanent because these loosened guidelines greatly improved care access for rural areas in recent years.
Lower Pay Affects Care in Rural, Urban Areas
Decreased reimbursements also have hit rural and urban doctors in independent practice particularly hard, Dr. Scott said. When adjusted for inflation, the current Medicare payment rate for physicians has dropped 29% since 2001, he said. Now that commercial payers tie their reimbursement models to the Medicare rate, physicians are experiencing “severe” financial stress amid rising practice costs and student loan debt.
He shared anecdotes about how these issues have affected his private otolaryngology practice in Louisville, Kentucky, a state where more than 2 million people live in federally designated primary care professional shortage areas.
“A major insurance company that controls over 60% of the private payer market in rural Kentucky [recently] offered us ... surgical rates less than they paid us 6 years ago,” he said.
Dr. Scott said physicians must make difficult choices. “Do we not invest in the latest physical equipment? Do we reduce our number of employees? Do we perhaps stop accepting new Medicare patients?”
He noted that physicians now spend twice as much time on prior authorizations and other administrative tasks as they do on direct patient care. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 33% of physicians reported that the cumbersome prior authorization process led to a serious adverse event for a patient. Eighty percent reported it caused their patient to forgo treatment altogether.
Dr. Scott, who will be sworn in as AMA president in June, said he experiences the frustration daily.
“I have to get on the phone and justify to an insurance person who rarely has gone to medical school, has never seen the patient, and heck, in my case, sometimes they can’t even say otolaryngology, much less tell me what the appropriate care is for my patient,” he said.
When asked about the impact of private equity in healthcare, Dr. Scott said there is room for all different modes of practice, but private equity could bring a unique benefit.
“They have deeper pockets to potentially invest in telehealth technology, AI, and better computer systems,” he said.
But, he said, some private equity-owned systems have abandoned rural areas, and in other regions they “push the physicians to move faster, see more patients, and do the things that are profit-driven.
“The key is to continue to provide ... quality medical care that is determined by an individual physician in consultation with the patient.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are leaving healthcare in droves, “not because they don’t want to practice ... but because the system is making it more and more difficult for them to care for their patients,” Bruce Scott, MD, president-elect of the American Medical Association (AMA), said at a press conference May 9 at the National Rural Health Association’s Annual Conference in New Orleans.
He said that shrinking reimbursement rates and excessive administrative tasks are pushing doctors out of the workforce, exacerbating physician shortages in rural locations where 46 million Americans live.
A recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report found that people living in rural areas are more likely to die early from preventable causes than their urban counterparts, said Dr. Scott.
He said the AMA wants Congress to pass legislation to incentivize more physicians to work in rural areas and expand the number of rural and primary care residency spots. Historically, 80% of residents practice within 80 miles of where they complete residency, he said.
Dr. Scott also hopes Congress will revise the J-1 visa rules to allow qualified international medical graduates to continue to practice in the United States. He’d like to see the pandemic telehealth flexibilities made permanent because these loosened guidelines greatly improved care access for rural areas in recent years.
Lower Pay Affects Care in Rural, Urban Areas
Decreased reimbursements also have hit rural and urban doctors in independent practice particularly hard, Dr. Scott said. When adjusted for inflation, the current Medicare payment rate for physicians has dropped 29% since 2001, he said. Now that commercial payers tie their reimbursement models to the Medicare rate, physicians are experiencing “severe” financial stress amid rising practice costs and student loan debt.
He shared anecdotes about how these issues have affected his private otolaryngology practice in Louisville, Kentucky, a state where more than 2 million people live in federally designated primary care professional shortage areas.
“A major insurance company that controls over 60% of the private payer market in rural Kentucky [recently] offered us ... surgical rates less than they paid us 6 years ago,” he said.
Dr. Scott said physicians must make difficult choices. “Do we not invest in the latest physical equipment? Do we reduce our number of employees? Do we perhaps stop accepting new Medicare patients?”
He noted that physicians now spend twice as much time on prior authorizations and other administrative tasks as they do on direct patient care. According to a 2022 AMA survey, 33% of physicians reported that the cumbersome prior authorization process led to a serious adverse event for a patient. Eighty percent reported it caused their patient to forgo treatment altogether.
Dr. Scott, who will be sworn in as AMA president in June, said he experiences the frustration daily.
“I have to get on the phone and justify to an insurance person who rarely has gone to medical school, has never seen the patient, and heck, in my case, sometimes they can’t even say otolaryngology, much less tell me what the appropriate care is for my patient,” he said.
When asked about the impact of private equity in healthcare, Dr. Scott said there is room for all different modes of practice, but private equity could bring a unique benefit.
“They have deeper pockets to potentially invest in telehealth technology, AI, and better computer systems,” he said.
But, he said, some private equity-owned systems have abandoned rural areas, and in other regions they “push the physicians to move faster, see more patients, and do the things that are profit-driven.
“The key is to continue to provide ... quality medical care that is determined by an individual physician in consultation with the patient.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can a Risk Score Predict Kidney Injury After Cisplatin?
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cisplatin is a preferred treatment for a wide range of cancers, including breast, head and neck, lung, ovary, and more. However, its side effects — particularly nephrotoxicity — can be severe. Kidney injury on cisplatin is associated with higher mortality and can jeopardize a patient’s eligibility for other therapies.
Now, in a large study using data from six US cancer centers, researchers have developed a risk algorithm to predict acute kidney injury (AKI) after cisplatin administration.
A risk prediction calculator based on the algorithm is available online for patients and providers to determine an individual patient›s risk for kidney injury from cisplatin using readily available clinical data.
Other risk scores and risk prediction models have been developed to help clinicians assess in advance whether a patient might develop AKI after receiving cisplatin, so that more careful monitoring, dose adjustments, or an alternative treatment, if available, might be considered.
However, previous models were limited by factors such as small sample sizes, lack of external validation, older data, and liberal definitions of AKI, said Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, director of onco-nephrology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, director of clinical and translational research in AKI, Division of Renal Medicine, BWH, Boston.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf believe their risk score for predicting severe AKI after intravenous (IV) cisplatin, published online in The BMJ, is “more accurate and generalizable than prior models for several reasons,” they told this news organization in a joint email.
“First, we externally validated our findings across cancer centers other than the one where it was developed,” they said. “Second, we focused on moderate to severe kidney injury, the most clinically relevant form of kidney damage, whereas prior models examined more mild forms of kidney injury. Third, we collected data on nearly 25,000 patients receiving their first dose of IV cisplatin, which is larger than all previous studies combined.”
‘Herculean Effort’
“We conceived of this study back in 2018, contacted collaborators at each participating cancer center, and had numerous meetings to try to gather granular data on patients treated with their first dose of intravenous (IV) cisplatin,” Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf explained. They also incorporated patient feedback from focus groups and surveys.
“This was truly a Herculean effort that involved physicians, programmers, research coordinators, and patients,” they said.
The multicenter study included 24,717 patients — 11,766 in the derivation cohort and 12,951 in the validation cohort. Overall, the median age was about 60 years, about 58% were men, and about 78% were White.
The primary outcome was cisplatin-induced AKI (CP-AKI), defined as a twofold or greater increase in serum creatinine or kidney replacement therapy within 14 days of a first dose of IV cisplatin.
Their simple risk score consisting of nine covariates — age, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin level, white blood cell count, platelet count, serum albumin level, serum magnesium level, and cisplatin dose — predicted a higher risk for CP-AKI in both cohorts.
Notably, adding serum creatinine to the model did not change the area under the curve, and therefore, serum creatinine, though also an independent risk factor for CP-AKI, was not included in the score.
Patients in the highest risk category had 24-fold higher odds of CP-AKI in the derivation cohort and close to 18-fold higher odds in the validation cohort than those in the lowest risk category.
The primary model had a C statistic of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.73-0.76) and showed better discrimination for CP-AKI than previously published models, for which the C statistics ranged from 0.60 to 0.68. The first author of a paper on an earlier model, Shveta Motwani, MD, MMSc, of BWH and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is also a coauthor of the new study.
Greater severity of CP-AKI was associated with shorter 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.63; 95% CI, 3.56-6.02) for stage III CP-AKI vs no CP-AKI.
‘Definitive Work’
Joel M. Topf, MD, a nephrologist with expertise in chronic kidney disease in Detroit, who wasn’t involved in the development of the risk score, called the study “a definitive work on an important concept in oncology and nephrology.”
“While this is not the first attempt to devise a risk score, it is by far the biggest,” he told this news organization. Furthermore, the authors “used a diverse population, recruiting patients with a variety of cancers (previous attempts had often used a homogenous diagnosis, putting into question how generalizable the results were) from six different cancer centers.”
In addition, he said, “The authors did not restrict patients with chronic kidney disease or other significant comorbidities and used the geographic diversity to produce a cohort that has an age, gender, racial, and ethnic distribution, which is more representative of the US than previous, single-center attempts to risk score patients.”
An earlier model used the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus definition of AKI of an increase in serum creatinine of 0.3 mg/dL, he noted. “While a sensitive definition of AKI, it captures mild, hemodynamic increases in creatinine of questionable significance,” he said.
By contrast, the new score uses KDIGO stage II and above to define AKI. “This is a better choice, as we do not want to dissuade patients and doctors from choosing chemotherapy due to a fear of insignificant kidney damage,” he said.
All that said, Dr. Topf noted that neither the current score nor the earlier model included serum creatinine. “This is curious to me and may represent the small number of patients with representative elevated creatinine in the derivation cohort (only 1.3% with an estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 45).”
“Since the cohort is made up of people who received cis-platinum, the low prevalence of eGFRs < 45 may be due to physicians steering away from cis-platinum in this group,” he suggested. “It would be unfortunate if this risk score gave an unintentional ‘green light’ to these patients, exposing them to predictable harm.”
‘Certainly Useful’
Anushree Shirali, MD, an associate professor in the Section of Nephrology and consulting physician, Yale Onco-Nephrology, Yale School of Medicine, in New Haven, Connecticut, said that having a prediction score for which patients are more likely to develop AKI after a single dose of cisplatin would be helpful for oncologists, as well as nephrologists.
As a nephrologist, Dr. Shirali mostly sees patients who already have AKI, she told this news organization. But there are circumstances in which the tool could still be helpful.
“Let’s say someone has abnormal kidney function at baseline — ie, creatinine is higher than the normal range — and they were on dialysis 5 years ago for something else, and now, they have cancer and may be given cisplatin. They worry about their chances of getting AKI and needing dialysis again,” she said. “That’s just one scenario in which I might be asked to answer that question and the tool would certainly be useful.”
Other scenarios could include someone who has just one kidney because they donated a kidney for transplant years ago, and now, they have a malignancy and wonder what their actual risk is of getting kidney issues on cisplatin.
Oncologists could use the tool to determine whether a patient should be treated with cisplatin, or if they’re at high risk, whether an alternative that’s not nephrotoxic might be used. By contrast, “if somebody’s low risk and an oncologist thinks cisplatin is the best agent they have, then they might want to go ahead and use it,” Dr. Shirali said.
Future research could take into consideration that CP-AKI is dose dependent, she suggested, because a prediction score that included the number of cisplatin doses could be even more helpful to determine risk. And, even though the derivation and validation cohorts for the new tool are representative of the US population, additional research should also include more racial/ethnic diversity, she said.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Leaf hope their tool “will be utilized immediately by patients and providers to help predict an individual’s risk of cisplatin-associated kidney damage. It is easy to use, available for free online, and incorporates readily available clinical variables.”
If a patient is at high risk, the clinical team can consider preventive measures such as administering more IV fluids before receiving cisplatin or monitoring kidney function more closely afterward, they suggested.
Dr. Gupta reported research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. She also reported research funding from BTG International, GE HealthCare, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. She is a member of GlaxoSmithKline’s Global Anemia Council, a consultant for Secretome and Proletariat Therapeutics, and founder and president emeritus of the American Society of Onconephrology (unpaid). Dr. Leaf is supported by NIH grants, reported research support from BioPorto, BTG International, and Metro International Biotech, and has served as a consultant. Dr. Topf reported an ownership stake in a few DaVita-run dialysis clinics. He also runs a vascular access center and has participated in advisory boards with Cara Therapeutics, Vifor, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Renibus Therapeutics, Travere Therapeutics, and GlaxoSmithKline. He is president of NephJC, a nonprofit educational organization with no industry support. Dr. Shirali declared no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BMJ
Jumpstart Your AI Learning: The Very Best Resources for Doctors
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.


