User login
Balancing ethics with empathy
My patients and their families have never been more anxious. In the pediatric ED where I practice, everyone is on edge. The COVID-19 pandemic has amplified the feelings of anxious anticipation and uncertainty that families have when they bring their child to the ED. People are scared that their children have the virus or that they will contract it in this high-risk environment. Both are reasonable fears. As a doctor, it has never been more difficult for me to lessen that anxiety.
Every doctor has a version of an interpersonal toolkit they use to project confidence, maintain calm, and convey empathy. Parts of it are taught in medical school, but most components are learned by trial and error. For me, it starts with speaking clearly and directly. If I can do this successfully, it allows parents to understand my recommendations and feel comfortable with my expertise. But words alone are rarely enough to gain trust. For most people, trusting a doctor requires believing that the physician is empathetic and invested in their care or the care of their loved one.
My experience is that, in the short, high-intensity interactions of the ED, this often has to be achieved with body language and facial expressions. We use so many little movements in interactions with patients: a knowing smile, kind eyes, a timely frown, open arms. These gestures would typically show parents I understand how they feel, and I am invested in the health of their child. Hidden behind my mask, face shield, gown, and gloves, I remain a black box. I dispense advice but struggle to convey that it comes from someone who cares.
At the beginning of the pandemic, I would skirt the rules of personal protective equipment (PPE) usage to try and get a moment of human connection. I might appear in the doorway of a patient’s room, smile, and introduce myself before putting on my mask and goggles. If a parent seemed to expect a firm handshake, I would give one, careful to wash my hands before and after. As the guidelines around PPE usage have become more consistent and the danger of the virus increasingly evident, I have cut out these little indulgences. I wear a mask and eye protection from the moment I enter the ED until I leave. I touch as few patients as possible and generally stand 6 feet or more from everyone I talk to.
I believe most providers would agree; these precautions are the only ethical way to see patients during the pandemic. Patients and families are entitled to health care workers who are doing everything they can to protect themselves and those around them. As long as the pandemic lasts, patients and providers will need to recalibrate their expectations of interpersonal interactions. For the time being, good doctors might be defined as much by their PPE adherence as by their ability to connect with patients.
Dr. Shapiro is a clinical instructor of pediatrics at the George Washington University and a clinical associate in the division of emergency medicine at Children’s National Hospital, both in Washington. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Shapiro at [email protected].
My patients and their families have never been more anxious. In the pediatric ED where I practice, everyone is on edge. The COVID-19 pandemic has amplified the feelings of anxious anticipation and uncertainty that families have when they bring their child to the ED. People are scared that their children have the virus or that they will contract it in this high-risk environment. Both are reasonable fears. As a doctor, it has never been more difficult for me to lessen that anxiety.
Every doctor has a version of an interpersonal toolkit they use to project confidence, maintain calm, and convey empathy. Parts of it are taught in medical school, but most components are learned by trial and error. For me, it starts with speaking clearly and directly. If I can do this successfully, it allows parents to understand my recommendations and feel comfortable with my expertise. But words alone are rarely enough to gain trust. For most people, trusting a doctor requires believing that the physician is empathetic and invested in their care or the care of their loved one.
My experience is that, in the short, high-intensity interactions of the ED, this often has to be achieved with body language and facial expressions. We use so many little movements in interactions with patients: a knowing smile, kind eyes, a timely frown, open arms. These gestures would typically show parents I understand how they feel, and I am invested in the health of their child. Hidden behind my mask, face shield, gown, and gloves, I remain a black box. I dispense advice but struggle to convey that it comes from someone who cares.
At the beginning of the pandemic, I would skirt the rules of personal protective equipment (PPE) usage to try and get a moment of human connection. I might appear in the doorway of a patient’s room, smile, and introduce myself before putting on my mask and goggles. If a parent seemed to expect a firm handshake, I would give one, careful to wash my hands before and after. As the guidelines around PPE usage have become more consistent and the danger of the virus increasingly evident, I have cut out these little indulgences. I wear a mask and eye protection from the moment I enter the ED until I leave. I touch as few patients as possible and generally stand 6 feet or more from everyone I talk to.
I believe most providers would agree; these precautions are the only ethical way to see patients during the pandemic. Patients and families are entitled to health care workers who are doing everything they can to protect themselves and those around them. As long as the pandemic lasts, patients and providers will need to recalibrate their expectations of interpersonal interactions. For the time being, good doctors might be defined as much by their PPE adherence as by their ability to connect with patients.
Dr. Shapiro is a clinical instructor of pediatrics at the George Washington University and a clinical associate in the division of emergency medicine at Children’s National Hospital, both in Washington. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Shapiro at [email protected].
My patients and their families have never been more anxious. In the pediatric ED where I practice, everyone is on edge. The COVID-19 pandemic has amplified the feelings of anxious anticipation and uncertainty that families have when they bring their child to the ED. People are scared that their children have the virus or that they will contract it in this high-risk environment. Both are reasonable fears. As a doctor, it has never been more difficult for me to lessen that anxiety.
Every doctor has a version of an interpersonal toolkit they use to project confidence, maintain calm, and convey empathy. Parts of it are taught in medical school, but most components are learned by trial and error. For me, it starts with speaking clearly and directly. If I can do this successfully, it allows parents to understand my recommendations and feel comfortable with my expertise. But words alone are rarely enough to gain trust. For most people, trusting a doctor requires believing that the physician is empathetic and invested in their care or the care of their loved one.
My experience is that, in the short, high-intensity interactions of the ED, this often has to be achieved with body language and facial expressions. We use so many little movements in interactions with patients: a knowing smile, kind eyes, a timely frown, open arms. These gestures would typically show parents I understand how they feel, and I am invested in the health of their child. Hidden behind my mask, face shield, gown, and gloves, I remain a black box. I dispense advice but struggle to convey that it comes from someone who cares.
At the beginning of the pandemic, I would skirt the rules of personal protective equipment (PPE) usage to try and get a moment of human connection. I might appear in the doorway of a patient’s room, smile, and introduce myself before putting on my mask and goggles. If a parent seemed to expect a firm handshake, I would give one, careful to wash my hands before and after. As the guidelines around PPE usage have become more consistent and the danger of the virus increasingly evident, I have cut out these little indulgences. I wear a mask and eye protection from the moment I enter the ED until I leave. I touch as few patients as possible and generally stand 6 feet or more from everyone I talk to.
I believe most providers would agree; these precautions are the only ethical way to see patients during the pandemic. Patients and families are entitled to health care workers who are doing everything they can to protect themselves and those around them. As long as the pandemic lasts, patients and providers will need to recalibrate their expectations of interpersonal interactions. For the time being, good doctors might be defined as much by their PPE adherence as by their ability to connect with patients.
Dr. Shapiro is a clinical instructor of pediatrics at the George Washington University and a clinical associate in the division of emergency medicine at Children’s National Hospital, both in Washington. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Shapiro at [email protected].
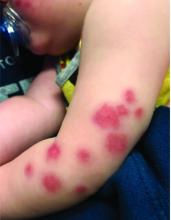
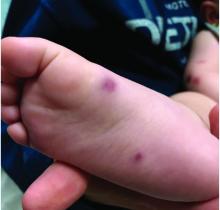
What's your diagnosis?
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
At 3 a.m., you receive a call from the ED for a baby with a new rash on the arms, legs, and face. Some of the lesions appear to be tender. He has a mild fever of 38.4° C (101.1° F) and is not in acute distress. He is drinking, but not eating much.
The parents also have noted some swelling on the hands and the feet. He has no upper respiratory or gastrointestinal symptoms. He is not walking yet.
He was admitted to the hospital 3 weeks prior for streptococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. He was treated with ceftriaxone, supportive respiratory care, and an albuterol inhaler. Influenza and respiratory syncytial virus tests were negative.
On physical exam, the child is tired and sleeping in his mom's arms. He has red and some purpuric papules on the face. On the arms and legs, he has purpuric papules and nodules. There is some edema on the face, hands, and feet. His conjunctiva is normal, and he has no oral lesions. He has no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly.
Blood work shows normal complete blood count, coagulation tests, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis, but he has an elevated C-reactive protein of 114 mg/L and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 71 mm/hour.
“I have to watch my bank accounts closely”: a solo practitioner during COVID-19
Medicine, as often said, is a business.
That’s often forgotten in a crisis, such as COVID-19, and with good reason. Our training in medicine is needed to care for the sick and find ways to prevent disease. Things like money are in the background when it comes to the emergencies of saving lives and helping the sick.
But that doesn’t mean finances don’t matter. They’re always in the background for medical practices of all sizes – just like any business.
Some practices have closed for patient and staff safety. I haven’t gone that far, as some people still need me. I am, after all, a doctor.
So I’m alone in my office, my staff working from home. That helps cut some lines of transmission there.
Like everyone else, I’m also doing telemedicine, and even a few phone appointments. These keep all involved safe, but also have a lot of limitations. They’re fine for checking up on stable, established patients, or following up on test results. But certainly not for new patients or established ones with new problems.
After all, you can’t evaluate a foot drop, extrapyramidal rigidity, or do an EMG/NCV over the video-phone connection.
In-person appointments are spaced out to minimize the number of people in my waiting room. Patients are told not to come in if they’re sick, and I insist we both be wearing masks (of pretty much any kind at this point). Common-use pens, such as those out in the waiting room, are wiped down with alcohol between uses.
With only two staff members, there really isn’t anyone extraneous to cut. I’ve stopped taking a paycheck so I can keep paying them, my rent, and the other miscellaneous costs of running an office.
I’ve always taken a bonus only at the end of the year, after all the other accounts have been paid, and take only a modest regular salary. In this case, that’s worked to my advantage, as I had more cash on hand when the emergency started. While not a huge amount, it’s enough to buy me some time, maybe several weeks, to see how this plays out. After that I’d have to tap into a line of credit, which obviously no one wants to do.
Telemedicine and the few office patients I’m seeing are a trickle of revenue. It’s better than nothing, but certainly isn’t enough to keep the door open and lights on.
That said, I’m not ungrateful. I’m well aware how fortunate my practice and family are compared to many others during this time. I haven’t had to ask for a pass on a mortgage or rent payment – yet. My staff and I have been together since 2004. I’m not going to break up a great team now.
I have no idea when things will turn around and people will start to come in. Your guess is as good as mine. I suspect the trickle will slowly increase at some point, then suddenly there will be a surge of calls for appointments from people who’ve been putting off coming in. Even then, though, I’ll likely space appointments apart and keep using a mask until it appears things are stable. There are going to be further waves of infections, and we don’t know how bad they’ll be.
Like everyone else, I can only hope for the best.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Medicine, as often said, is a business.
That’s often forgotten in a crisis, such as COVID-19, and with good reason. Our training in medicine is needed to care for the sick and find ways to prevent disease. Things like money are in the background when it comes to the emergencies of saving lives and helping the sick.
But that doesn’t mean finances don’t matter. They’re always in the background for medical practices of all sizes – just like any business.
Some practices have closed for patient and staff safety. I haven’t gone that far, as some people still need me. I am, after all, a doctor.
So I’m alone in my office, my staff working from home. That helps cut some lines of transmission there.
Like everyone else, I’m also doing telemedicine, and even a few phone appointments. These keep all involved safe, but also have a lot of limitations. They’re fine for checking up on stable, established patients, or following up on test results. But certainly not for new patients or established ones with new problems.
After all, you can’t evaluate a foot drop, extrapyramidal rigidity, or do an EMG/NCV over the video-phone connection.
In-person appointments are spaced out to minimize the number of people in my waiting room. Patients are told not to come in if they’re sick, and I insist we both be wearing masks (of pretty much any kind at this point). Common-use pens, such as those out in the waiting room, are wiped down with alcohol between uses.
With only two staff members, there really isn’t anyone extraneous to cut. I’ve stopped taking a paycheck so I can keep paying them, my rent, and the other miscellaneous costs of running an office.
I’ve always taken a bonus only at the end of the year, after all the other accounts have been paid, and take only a modest regular salary. In this case, that’s worked to my advantage, as I had more cash on hand when the emergency started. While not a huge amount, it’s enough to buy me some time, maybe several weeks, to see how this plays out. After that I’d have to tap into a line of credit, which obviously no one wants to do.
Telemedicine and the few office patients I’m seeing are a trickle of revenue. It’s better than nothing, but certainly isn’t enough to keep the door open and lights on.
That said, I’m not ungrateful. I’m well aware how fortunate my practice and family are compared to many others during this time. I haven’t had to ask for a pass on a mortgage or rent payment – yet. My staff and I have been together since 2004. I’m not going to break up a great team now.
I have no idea when things will turn around and people will start to come in. Your guess is as good as mine. I suspect the trickle will slowly increase at some point, then suddenly there will be a surge of calls for appointments from people who’ve been putting off coming in. Even then, though, I’ll likely space appointments apart and keep using a mask until it appears things are stable. There are going to be further waves of infections, and we don’t know how bad they’ll be.
Like everyone else, I can only hope for the best.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Medicine, as often said, is a business.
That’s often forgotten in a crisis, such as COVID-19, and with good reason. Our training in medicine is needed to care for the sick and find ways to prevent disease. Things like money are in the background when it comes to the emergencies of saving lives and helping the sick.
But that doesn’t mean finances don’t matter. They’re always in the background for medical practices of all sizes – just like any business.
Some practices have closed for patient and staff safety. I haven’t gone that far, as some people still need me. I am, after all, a doctor.
So I’m alone in my office, my staff working from home. That helps cut some lines of transmission there.
Like everyone else, I’m also doing telemedicine, and even a few phone appointments. These keep all involved safe, but also have a lot of limitations. They’re fine for checking up on stable, established patients, or following up on test results. But certainly not for new patients or established ones with new problems.
After all, you can’t evaluate a foot drop, extrapyramidal rigidity, or do an EMG/NCV over the video-phone connection.
In-person appointments are spaced out to minimize the number of people in my waiting room. Patients are told not to come in if they’re sick, and I insist we both be wearing masks (of pretty much any kind at this point). Common-use pens, such as those out in the waiting room, are wiped down with alcohol between uses.
With only two staff members, there really isn’t anyone extraneous to cut. I’ve stopped taking a paycheck so I can keep paying them, my rent, and the other miscellaneous costs of running an office.
I’ve always taken a bonus only at the end of the year, after all the other accounts have been paid, and take only a modest regular salary. In this case, that’s worked to my advantage, as I had more cash on hand when the emergency started. While not a huge amount, it’s enough to buy me some time, maybe several weeks, to see how this plays out. After that I’d have to tap into a line of credit, which obviously no one wants to do.
Telemedicine and the few office patients I’m seeing are a trickle of revenue. It’s better than nothing, but certainly isn’t enough to keep the door open and lights on.
That said, I’m not ungrateful. I’m well aware how fortunate my practice and family are compared to many others during this time. I haven’t had to ask for a pass on a mortgage or rent payment – yet. My staff and I have been together since 2004. I’m not going to break up a great team now.
I have no idea when things will turn around and people will start to come in. Your guess is as good as mine. I suspect the trickle will slowly increase at some point, then suddenly there will be a surge of calls for appointments from people who’ve been putting off coming in. Even then, though, I’ll likely space appointments apart and keep using a mask until it appears things are stable. There are going to be further waves of infections, and we don’t know how bad they’ll be.
Like everyone else, I can only hope for the best.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Making something ordinary out of the extraordinary
These are tough times for families, children, and practices. In this case, the entire world is going through it at the same time, leaving no escape. There are so many new things each of us needs to do, and for some of the challenges, we are completely thwarted by safety restrictions from doing anything. Adults and children alike are trying to work or learn at home in new ways. This also means that old daily routines have been broken. The sense of disorientation is pervasive. Although it is only one part of what is needed, reestablishing routines can go a long way toward restoring a sense of control and meaning that you can institute for yourself and recommend to your patients.
Examples of such change include natural disasters such as COVID-19, deaths, or separations from loved ones, but also moving, job loss, or new financial instability. Many families and many doctors and staff are experiencing several of these at once these days.
Evidence from studies of times of major disruption such as divorce, a death, war, and natural disasters show that parenting tends to shift to being less organized, with less overall discipline or more arbitrary punishment, and, in some cases, less parent-child connection. Children, on their part, also tend to act differently under these conditions. They are more irritable, upset, anxious, clingy, and aggressive, and also tend to regress in recent developmental achievements such as maintaining toileting and sleep patterns. Parents often do not see the connection to the stress and react to these behaviors in ways that may make things worse by scolding or punishing.
I was really surprised to hear Daniel Kahneman, PhD, Nobel laureate in economics, talk about how even he has trouble judging risk based on mathematical probability. Instead, he recognizes that adults decide about risk based on the behavior of the people around them – when others act worried or agitated, the person does too. Children, even more than adults, must decide if they are safe based on the behavior of the adults around them. When parents maintain routines as closely as possible after a major disruption, children feel reassured that they can expect continuity of their relationship – their most important lifeboat. If their parents keep doing the things they are used to, children basically feel safe.
Simple aspects of sameness important to children are very familiar to pediatricians: always wanting the same spoon, the sandwich cut the same way, only chicken nuggets from a certain store. This tends to be true in typically developing toddlers, preschool, and some school-aged children. The desire to have the same story read to them multiple times – until parents are ready to scream! – is another sign of the importance of predictable routines to children. All of these are best accommodated during times of stress rather than trying to “avoid making a bad habit.” All disruptions of routine are even more disorienting for children with intellectual disabilities or those on the autism spectrum who are generally less able to understand or control their world. Children and adults with preexisting anxiety disorders also are more likely to have more severe reactions to major disruptions and need extra understanding.
Routines for eating at least something at regular times – even if the food is not as interesting as prior fare – provide a sense of security, as well as stabilizing blood sugar and bowel patterns. Keeping patterns of washing hands, sitting together as a family, and interacting in conversation, rather than watching TV news, allow an oasis of respite from ongoing stresses. Family meals are also known to promote learning, vocabulary growth, and better behavior.
Setting a schedule for schooling, play, hygiene, and exercise may seem silly when parents and children are home all day, but it instills a sense of meaning to the day. Making a visual schedule for younger children or a written or online one for older children can be a shared activity in itself. I remember hearing about how important changing clothes and cleaning teeth were to prisoners of war during World War II in maintaining a sense of normalcy in that time of chaos.
Exercise is particularly important to set as a routine as it directly reduces stress – even if it may need to take new forms. While there are lots of online exercise programs for adults, it is better for everyone to go outside if they can manage adequate personal spacing. There they can experience the orderly changing of the seasons and the weather, as well as soak up some sunshine. Interactive parent-child play serves multiple purposes of stress relief, seeing each other more relaxed, interacting, and having fun!
Routines for sleep are especially important. To fall asleep under normal circumstances requires a sense of safety, perhaps for evolutionary reasons because of the vulnerability of the paralysis that is part of REM sleep stages. Fear at bedtime is common in young children, as is disorientation in the elderly. Both respond to reassuring bedtime routines done the same way every night, such as brushing teeth, changing clothes, washing up, reading or being read to, and praying – if these were the previous habit. When there has been a major disruption, these routines take on added importance, even if some modifications need to be made in sleep location, privacy, etc. Keeping schedules for naps, bedtime, and wake time as stable as possible makes sleep onset easier and sleep maintenance more likely. It also increases the chances of adequate sleep duration. Getting enough sleep stabilizes mood, reduces irritability, and improves daytime concentration and problem-solving skills. These all are especially needed by adults as well as children when there are major disruptions.
Maintaining chores at times of disruption can be extra difficult, plus this may seem to parents like an added stress for their already-stressed child. But in fact, children are reassured by adults’ continuing these requirements. Not only is an expectation that chores be done a signal that life can be expected to proceed normally, but having children do things to help – such as cleaning up, restocking soap and towels, or emptying trash – gives them an active role and hence some sense of control.
Discipline is, in essence, also a routine. Maintaining standards for kindness to others and following rules can be especially difficult when life has been disrupted because emotional lability is more likely in both adults and children when severely stressed. It is important for parents to consider the source of the misbehavior as possibly stress related and to interrupt it in a gentle and understanding way. A parent might say: “I know you are upset by all the changes. It is even more important now than ever to be kind to your brother.” Under stressful conditions, it is especially important to ask how the child was feeling when acting up, but also to “speak for them” about possible stress-related reasons for their behavior. While parents may correctly say that their child will “take advantage of this excuse,” it is still a teaching opportunity. Children have little insight into these connections to their feelings and actions, but they can learn.
Times when old patterns are disrupted also are times for making new habits. The main new habit I recommend for stress relief and overall mental health are the practices of mindfulness or meditation. Mindfulness may be easier to teach children as it involves paying close attention to one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations, but doing this without judgment. Children often are naturally better at this than adults, who have layered on more experiences to their thoughts. We pediatricians, as well as the parents we serve, can benefit – especially in stressful times – from sharing in the simple ways children experience the world.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
These are tough times for families, children, and practices. In this case, the entire world is going through it at the same time, leaving no escape. There are so many new things each of us needs to do, and for some of the challenges, we are completely thwarted by safety restrictions from doing anything. Adults and children alike are trying to work or learn at home in new ways. This also means that old daily routines have been broken. The sense of disorientation is pervasive. Although it is only one part of what is needed, reestablishing routines can go a long way toward restoring a sense of control and meaning that you can institute for yourself and recommend to your patients.
Examples of such change include natural disasters such as COVID-19, deaths, or separations from loved ones, but also moving, job loss, or new financial instability. Many families and many doctors and staff are experiencing several of these at once these days.
Evidence from studies of times of major disruption such as divorce, a death, war, and natural disasters show that parenting tends to shift to being less organized, with less overall discipline or more arbitrary punishment, and, in some cases, less parent-child connection. Children, on their part, also tend to act differently under these conditions. They are more irritable, upset, anxious, clingy, and aggressive, and also tend to regress in recent developmental achievements such as maintaining toileting and sleep patterns. Parents often do not see the connection to the stress and react to these behaviors in ways that may make things worse by scolding or punishing.
I was really surprised to hear Daniel Kahneman, PhD, Nobel laureate in economics, talk about how even he has trouble judging risk based on mathematical probability. Instead, he recognizes that adults decide about risk based on the behavior of the people around them – when others act worried or agitated, the person does too. Children, even more than adults, must decide if they are safe based on the behavior of the adults around them. When parents maintain routines as closely as possible after a major disruption, children feel reassured that they can expect continuity of their relationship – their most important lifeboat. If their parents keep doing the things they are used to, children basically feel safe.
Simple aspects of sameness important to children are very familiar to pediatricians: always wanting the same spoon, the sandwich cut the same way, only chicken nuggets from a certain store. This tends to be true in typically developing toddlers, preschool, and some school-aged children. The desire to have the same story read to them multiple times – until parents are ready to scream! – is another sign of the importance of predictable routines to children. All of these are best accommodated during times of stress rather than trying to “avoid making a bad habit.” All disruptions of routine are even more disorienting for children with intellectual disabilities or those on the autism spectrum who are generally less able to understand or control their world. Children and adults with preexisting anxiety disorders also are more likely to have more severe reactions to major disruptions and need extra understanding.
Routines for eating at least something at regular times – even if the food is not as interesting as prior fare – provide a sense of security, as well as stabilizing blood sugar and bowel patterns. Keeping patterns of washing hands, sitting together as a family, and interacting in conversation, rather than watching TV news, allow an oasis of respite from ongoing stresses. Family meals are also known to promote learning, vocabulary growth, and better behavior.
Setting a schedule for schooling, play, hygiene, and exercise may seem silly when parents and children are home all day, but it instills a sense of meaning to the day. Making a visual schedule for younger children or a written or online one for older children can be a shared activity in itself. I remember hearing about how important changing clothes and cleaning teeth were to prisoners of war during World War II in maintaining a sense of normalcy in that time of chaos.
Exercise is particularly important to set as a routine as it directly reduces stress – even if it may need to take new forms. While there are lots of online exercise programs for adults, it is better for everyone to go outside if they can manage adequate personal spacing. There they can experience the orderly changing of the seasons and the weather, as well as soak up some sunshine. Interactive parent-child play serves multiple purposes of stress relief, seeing each other more relaxed, interacting, and having fun!
Routines for sleep are especially important. To fall asleep under normal circumstances requires a sense of safety, perhaps for evolutionary reasons because of the vulnerability of the paralysis that is part of REM sleep stages. Fear at bedtime is common in young children, as is disorientation in the elderly. Both respond to reassuring bedtime routines done the same way every night, such as brushing teeth, changing clothes, washing up, reading or being read to, and praying – if these were the previous habit. When there has been a major disruption, these routines take on added importance, even if some modifications need to be made in sleep location, privacy, etc. Keeping schedules for naps, bedtime, and wake time as stable as possible makes sleep onset easier and sleep maintenance more likely. It also increases the chances of adequate sleep duration. Getting enough sleep stabilizes mood, reduces irritability, and improves daytime concentration and problem-solving skills. These all are especially needed by adults as well as children when there are major disruptions.
Maintaining chores at times of disruption can be extra difficult, plus this may seem to parents like an added stress for their already-stressed child. But in fact, children are reassured by adults’ continuing these requirements. Not only is an expectation that chores be done a signal that life can be expected to proceed normally, but having children do things to help – such as cleaning up, restocking soap and towels, or emptying trash – gives them an active role and hence some sense of control.
Discipline is, in essence, also a routine. Maintaining standards for kindness to others and following rules can be especially difficult when life has been disrupted because emotional lability is more likely in both adults and children when severely stressed. It is important for parents to consider the source of the misbehavior as possibly stress related and to interrupt it in a gentle and understanding way. A parent might say: “I know you are upset by all the changes. It is even more important now than ever to be kind to your brother.” Under stressful conditions, it is especially important to ask how the child was feeling when acting up, but also to “speak for them” about possible stress-related reasons for their behavior. While parents may correctly say that their child will “take advantage of this excuse,” it is still a teaching opportunity. Children have little insight into these connections to their feelings and actions, but they can learn.
Times when old patterns are disrupted also are times for making new habits. The main new habit I recommend for stress relief and overall mental health are the practices of mindfulness or meditation. Mindfulness may be easier to teach children as it involves paying close attention to one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations, but doing this without judgment. Children often are naturally better at this than adults, who have layered on more experiences to their thoughts. We pediatricians, as well as the parents we serve, can benefit – especially in stressful times – from sharing in the simple ways children experience the world.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
These are tough times for families, children, and practices. In this case, the entire world is going through it at the same time, leaving no escape. There are so many new things each of us needs to do, and for some of the challenges, we are completely thwarted by safety restrictions from doing anything. Adults and children alike are trying to work or learn at home in new ways. This also means that old daily routines have been broken. The sense of disorientation is pervasive. Although it is only one part of what is needed, reestablishing routines can go a long way toward restoring a sense of control and meaning that you can institute for yourself and recommend to your patients.
Examples of such change include natural disasters such as COVID-19, deaths, or separations from loved ones, but also moving, job loss, or new financial instability. Many families and many doctors and staff are experiencing several of these at once these days.
Evidence from studies of times of major disruption such as divorce, a death, war, and natural disasters show that parenting tends to shift to being less organized, with less overall discipline or more arbitrary punishment, and, in some cases, less parent-child connection. Children, on their part, also tend to act differently under these conditions. They are more irritable, upset, anxious, clingy, and aggressive, and also tend to regress in recent developmental achievements such as maintaining toileting and sleep patterns. Parents often do not see the connection to the stress and react to these behaviors in ways that may make things worse by scolding or punishing.
I was really surprised to hear Daniel Kahneman, PhD, Nobel laureate in economics, talk about how even he has trouble judging risk based on mathematical probability. Instead, he recognizes that adults decide about risk based on the behavior of the people around them – when others act worried or agitated, the person does too. Children, even more than adults, must decide if they are safe based on the behavior of the adults around them. When parents maintain routines as closely as possible after a major disruption, children feel reassured that they can expect continuity of their relationship – their most important lifeboat. If their parents keep doing the things they are used to, children basically feel safe.
Simple aspects of sameness important to children are very familiar to pediatricians: always wanting the same spoon, the sandwich cut the same way, only chicken nuggets from a certain store. This tends to be true in typically developing toddlers, preschool, and some school-aged children. The desire to have the same story read to them multiple times – until parents are ready to scream! – is another sign of the importance of predictable routines to children. All of these are best accommodated during times of stress rather than trying to “avoid making a bad habit.” All disruptions of routine are even more disorienting for children with intellectual disabilities or those on the autism spectrum who are generally less able to understand or control their world. Children and adults with preexisting anxiety disorders also are more likely to have more severe reactions to major disruptions and need extra understanding.
Routines for eating at least something at regular times – even if the food is not as interesting as prior fare – provide a sense of security, as well as stabilizing blood sugar and bowel patterns. Keeping patterns of washing hands, sitting together as a family, and interacting in conversation, rather than watching TV news, allow an oasis of respite from ongoing stresses. Family meals are also known to promote learning, vocabulary growth, and better behavior.
Setting a schedule for schooling, play, hygiene, and exercise may seem silly when parents and children are home all day, but it instills a sense of meaning to the day. Making a visual schedule for younger children or a written or online one for older children can be a shared activity in itself. I remember hearing about how important changing clothes and cleaning teeth were to prisoners of war during World War II in maintaining a sense of normalcy in that time of chaos.
Exercise is particularly important to set as a routine as it directly reduces stress – even if it may need to take new forms. While there are lots of online exercise programs for adults, it is better for everyone to go outside if they can manage adequate personal spacing. There they can experience the orderly changing of the seasons and the weather, as well as soak up some sunshine. Interactive parent-child play serves multiple purposes of stress relief, seeing each other more relaxed, interacting, and having fun!
Routines for sleep are especially important. To fall asleep under normal circumstances requires a sense of safety, perhaps for evolutionary reasons because of the vulnerability of the paralysis that is part of REM sleep stages. Fear at bedtime is common in young children, as is disorientation in the elderly. Both respond to reassuring bedtime routines done the same way every night, such as brushing teeth, changing clothes, washing up, reading or being read to, and praying – if these were the previous habit. When there has been a major disruption, these routines take on added importance, even if some modifications need to be made in sleep location, privacy, etc. Keeping schedules for naps, bedtime, and wake time as stable as possible makes sleep onset easier and sleep maintenance more likely. It also increases the chances of adequate sleep duration. Getting enough sleep stabilizes mood, reduces irritability, and improves daytime concentration and problem-solving skills. These all are especially needed by adults as well as children when there are major disruptions.
Maintaining chores at times of disruption can be extra difficult, plus this may seem to parents like an added stress for their already-stressed child. But in fact, children are reassured by adults’ continuing these requirements. Not only is an expectation that chores be done a signal that life can be expected to proceed normally, but having children do things to help – such as cleaning up, restocking soap and towels, or emptying trash – gives them an active role and hence some sense of control.
Discipline is, in essence, also a routine. Maintaining standards for kindness to others and following rules can be especially difficult when life has been disrupted because emotional lability is more likely in both adults and children when severely stressed. It is important for parents to consider the source of the misbehavior as possibly stress related and to interrupt it in a gentle and understanding way. A parent might say: “I know you are upset by all the changes. It is even more important now than ever to be kind to your brother.” Under stressful conditions, it is especially important to ask how the child was feeling when acting up, but also to “speak for them” about possible stress-related reasons for their behavior. While parents may correctly say that their child will “take advantage of this excuse,” it is still a teaching opportunity. Children have little insight into these connections to their feelings and actions, but they can learn.
Times when old patterns are disrupted also are times for making new habits. The main new habit I recommend for stress relief and overall mental health are the practices of mindfulness or meditation. Mindfulness may be easier to teach children as it involves paying close attention to one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations, but doing this without judgment. Children often are naturally better at this than adults, who have layered on more experiences to their thoughts. We pediatricians, as well as the parents we serve, can benefit – especially in stressful times – from sharing in the simple ways children experience the world.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. Email her at [email protected].
The role of FOAM and social networks in COVID-19
“Uncertainty creates weakness. Uncertainty makes one tentative, if not fearful, and tentative steps, even when in the right direction, may not overcome significant obstacles.”1
Recently, I spent my vacation time quarantined reading “The Great Influenza,” which recounts the history of the 1918 pandemic. Despite over a century of scientific and medical progress, the parallels to our current situation are indisputable. Just as in 1918, we are limiting social gatherings, quarantining, wearing face masks, and living with the fear and anxiety of keeping ourselves and our families safe. In 1918, use of aspirin, quinine, and digitalis therapies in a desperate search for relief despite limited evidence mirror the current use of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and lopinavir/ritonavir. While there are many similarities between the two situations, in this pandemic our channels for dissemination of scientific literature are better developed, and online networks are enabling physicians across the globe to communicate their experience and findings in near real time.
During this time of uncertainty, our understanding of COVID-19 evolves daily. Without the advantage of robust randomized, controlled trials and large-scale studies to guide us, we are forced to rely on pattern recognition for surveillance and anecdotal or limited case-based accounts to guide clinical care. Fortunately, free open-access medical education (FOAM) and social networks offer a significant advantage in our ability to collect and disseminate information.
Free open access medical education
The concept of FOAM started in 2012 with the intent of creating a collaborative and constantly evolving community to provide open-access medical education. It encompasses multiple platforms – blogs, podcasts, videos, and social media – and features content experts from across the globe. Since its inception, FOAM has grown in popularity and use, especially within emergency medicine and critical care communities, as an adjunct for asynchronous learning.2,3
In a time where knowledge of COVID-19 is dynamically changing, traditional sources like textbooks, journals, and organizational guidelines often lag behind real-time clinical experience and needs. Additionally, many clinicians are now being tasked with taking care of patient populations and a new critical illness profile with which they are not comfortable. It is challenging to find a well-curated and updated repository of information to answer questions surrounding pathophysiology, critical care, ventilator management, caring for adult patients, and personal protective equipment (PPE). During this rapidly evolving reality, FOAM is becoming the ideal modality for timely and efficient sharing of reviews of current literature, expert discussions, and clinical practice guidelines.
A few self-directed hours on EMCrit’s Internet Book of Critical Care’s COVID-19 chapter reveals a bastion of content regarding diagnosis, pathophysiology, transmission, therapies, and ventilator strategies.4 It includes references to major journals and recommendations from international societies. Websites like EMCrit and REBEL EM are updated daily with podcasts, videos, and blog posts surrounding the latest highly debated topics in COVID-19 management.5 Podcasts like EM:RAP and Peds RAP have made COVID segments discussing important topics like pharmacotherapy, telemedicine, and pregnancy available for free.6,7 Many networks, institutions, and individual physicians have created and posted videos online on critical care topics and refreshers.
Social networks
Online social networks composed of international physicians within Facebook and LinkedIn serve as miniature publishing houses. First-hand accounts of patient presentations and patient care act as case reports. As similar accounts accumulate, they become case series. Patterns emerge and new hypotheses are generated, debated, and critiqued through this informal peer review. Personal accounts of frustration with lack of PPE, fear of exposing loved ones, distress at being separated from family, and grief of witnessing multiple patients die alone are opinion and perspective articles.
These networks offer the space for sharing. Those who have had the experience of caring for the surge of COVID-19 patients offer advice and words of caution to those who have yet to experience it. Protocols from a multitude of institutions on triage, surge, disposition, and end-of-life care are disseminated, serving as templates for those that have not yet developed their own. There is an impressive variety of innovative, do-it-yourself projects surrounding PPE, intubation boxes, and three-dimensionally printed ventilator parts.
Finally, these networks provide emotional support. There are offers to ship additional PPE, videos of cities cheering as clinicians go to work, stories of triumph and recovery, pictures depicting ongoing wellness activities, and the occasional much-needed humorous anecdote or illustration. These networks reinforce the message that our lives continue despite this upheaval, and we are not alone in this struggle.
The end of the passage in The Great Influenza concludes with: “Ultimately a scientist has nothing to believe in but the process of inquiry. To move forcefully and aggressively even while uncertain requires a confidence and strength deeper than physical courage.”
They represent a highly adaptable, evolving, and collaborative global community’s determination to persevere through time of uncertainty together.
Dr. Ren is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital, Washington. Dr. Simpson is a pediatric emergency medicine attending and medical director of emergency preparedness at the hospital. They reported that they do not have any disclosures or conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Ren and Dr. Simpson at [email protected].
References
1. “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History.” (New York: Penguin Books, 2005, pp. 261-62).
2. Emerg Med J. 2014 Oct;31(e1):e76-7.
3. Acad Med. 2014 Apr;89(4):598-601.
4. “The Internet Book of Critical Care: COVID-19.” EMCrit Project.
5. “Covid-19.” REBEL EM-Emergency Medicine Blog.
6. “EM:RAP COVID-19 Resources.” EM RAP: Emergency Medicine Reviews and Perspectives.
7. “Episodes.” Peds RAP, Hippo Education.
“Uncertainty creates weakness. Uncertainty makes one tentative, if not fearful, and tentative steps, even when in the right direction, may not overcome significant obstacles.”1
Recently, I spent my vacation time quarantined reading “The Great Influenza,” which recounts the history of the 1918 pandemic. Despite over a century of scientific and medical progress, the parallels to our current situation are indisputable. Just as in 1918, we are limiting social gatherings, quarantining, wearing face masks, and living with the fear and anxiety of keeping ourselves and our families safe. In 1918, use of aspirin, quinine, and digitalis therapies in a desperate search for relief despite limited evidence mirror the current use of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and lopinavir/ritonavir. While there are many similarities between the two situations, in this pandemic our channels for dissemination of scientific literature are better developed, and online networks are enabling physicians across the globe to communicate their experience and findings in near real time.
During this time of uncertainty, our understanding of COVID-19 evolves daily. Without the advantage of robust randomized, controlled trials and large-scale studies to guide us, we are forced to rely on pattern recognition for surveillance and anecdotal or limited case-based accounts to guide clinical care. Fortunately, free open-access medical education (FOAM) and social networks offer a significant advantage in our ability to collect and disseminate information.
Free open access medical education
The concept of FOAM started in 2012 with the intent of creating a collaborative and constantly evolving community to provide open-access medical education. It encompasses multiple platforms – blogs, podcasts, videos, and social media – and features content experts from across the globe. Since its inception, FOAM has grown in popularity and use, especially within emergency medicine and critical care communities, as an adjunct for asynchronous learning.2,3
In a time where knowledge of COVID-19 is dynamically changing, traditional sources like textbooks, journals, and organizational guidelines often lag behind real-time clinical experience and needs. Additionally, many clinicians are now being tasked with taking care of patient populations and a new critical illness profile with which they are not comfortable. It is challenging to find a well-curated and updated repository of information to answer questions surrounding pathophysiology, critical care, ventilator management, caring for adult patients, and personal protective equipment (PPE). During this rapidly evolving reality, FOAM is becoming the ideal modality for timely and efficient sharing of reviews of current literature, expert discussions, and clinical practice guidelines.
A few self-directed hours on EMCrit’s Internet Book of Critical Care’s COVID-19 chapter reveals a bastion of content regarding diagnosis, pathophysiology, transmission, therapies, and ventilator strategies.4 It includes references to major journals and recommendations from international societies. Websites like EMCrit and REBEL EM are updated daily with podcasts, videos, and blog posts surrounding the latest highly debated topics in COVID-19 management.5 Podcasts like EM:RAP and Peds RAP have made COVID segments discussing important topics like pharmacotherapy, telemedicine, and pregnancy available for free.6,7 Many networks, institutions, and individual physicians have created and posted videos online on critical care topics and refreshers.
Social networks
Online social networks composed of international physicians within Facebook and LinkedIn serve as miniature publishing houses. First-hand accounts of patient presentations and patient care act as case reports. As similar accounts accumulate, they become case series. Patterns emerge and new hypotheses are generated, debated, and critiqued through this informal peer review. Personal accounts of frustration with lack of PPE, fear of exposing loved ones, distress at being separated from family, and grief of witnessing multiple patients die alone are opinion and perspective articles.
These networks offer the space for sharing. Those who have had the experience of caring for the surge of COVID-19 patients offer advice and words of caution to those who have yet to experience it. Protocols from a multitude of institutions on triage, surge, disposition, and end-of-life care are disseminated, serving as templates for those that have not yet developed their own. There is an impressive variety of innovative, do-it-yourself projects surrounding PPE, intubation boxes, and three-dimensionally printed ventilator parts.
Finally, these networks provide emotional support. There are offers to ship additional PPE, videos of cities cheering as clinicians go to work, stories of triumph and recovery, pictures depicting ongoing wellness activities, and the occasional much-needed humorous anecdote or illustration. These networks reinforce the message that our lives continue despite this upheaval, and we are not alone in this struggle.
The end of the passage in The Great Influenza concludes with: “Ultimately a scientist has nothing to believe in but the process of inquiry. To move forcefully and aggressively even while uncertain requires a confidence and strength deeper than physical courage.”
They represent a highly adaptable, evolving, and collaborative global community’s determination to persevere through time of uncertainty together.
Dr. Ren is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital, Washington. Dr. Simpson is a pediatric emergency medicine attending and medical director of emergency preparedness at the hospital. They reported that they do not have any disclosures or conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Ren and Dr. Simpson at [email protected].
References
1. “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History.” (New York: Penguin Books, 2005, pp. 261-62).
2. Emerg Med J. 2014 Oct;31(e1):e76-7.
3. Acad Med. 2014 Apr;89(4):598-601.
4. “The Internet Book of Critical Care: COVID-19.” EMCrit Project.
5. “Covid-19.” REBEL EM-Emergency Medicine Blog.
6. “EM:RAP COVID-19 Resources.” EM RAP: Emergency Medicine Reviews and Perspectives.
7. “Episodes.” Peds RAP, Hippo Education.
“Uncertainty creates weakness. Uncertainty makes one tentative, if not fearful, and tentative steps, even when in the right direction, may not overcome significant obstacles.”1
Recently, I spent my vacation time quarantined reading “The Great Influenza,” which recounts the history of the 1918 pandemic. Despite over a century of scientific and medical progress, the parallels to our current situation are indisputable. Just as in 1918, we are limiting social gatherings, quarantining, wearing face masks, and living with the fear and anxiety of keeping ourselves and our families safe. In 1918, use of aspirin, quinine, and digitalis therapies in a desperate search for relief despite limited evidence mirror the current use of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and lopinavir/ritonavir. While there are many similarities between the two situations, in this pandemic our channels for dissemination of scientific literature are better developed, and online networks are enabling physicians across the globe to communicate their experience and findings in near real time.
During this time of uncertainty, our understanding of COVID-19 evolves daily. Without the advantage of robust randomized, controlled trials and large-scale studies to guide us, we are forced to rely on pattern recognition for surveillance and anecdotal or limited case-based accounts to guide clinical care. Fortunately, free open-access medical education (FOAM) and social networks offer a significant advantage in our ability to collect and disseminate information.
Free open access medical education
The concept of FOAM started in 2012 with the intent of creating a collaborative and constantly evolving community to provide open-access medical education. It encompasses multiple platforms – blogs, podcasts, videos, and social media – and features content experts from across the globe. Since its inception, FOAM has grown in popularity and use, especially within emergency medicine and critical care communities, as an adjunct for asynchronous learning.2,3
In a time where knowledge of COVID-19 is dynamically changing, traditional sources like textbooks, journals, and organizational guidelines often lag behind real-time clinical experience and needs. Additionally, many clinicians are now being tasked with taking care of patient populations and a new critical illness profile with which they are not comfortable. It is challenging to find a well-curated and updated repository of information to answer questions surrounding pathophysiology, critical care, ventilator management, caring for adult patients, and personal protective equipment (PPE). During this rapidly evolving reality, FOAM is becoming the ideal modality for timely and efficient sharing of reviews of current literature, expert discussions, and clinical practice guidelines.
A few self-directed hours on EMCrit’s Internet Book of Critical Care’s COVID-19 chapter reveals a bastion of content regarding diagnosis, pathophysiology, transmission, therapies, and ventilator strategies.4 It includes references to major journals and recommendations from international societies. Websites like EMCrit and REBEL EM are updated daily with podcasts, videos, and blog posts surrounding the latest highly debated topics in COVID-19 management.5 Podcasts like EM:RAP and Peds RAP have made COVID segments discussing important topics like pharmacotherapy, telemedicine, and pregnancy available for free.6,7 Many networks, institutions, and individual physicians have created and posted videos online on critical care topics and refreshers.
Social networks
Online social networks composed of international physicians within Facebook and LinkedIn serve as miniature publishing houses. First-hand accounts of patient presentations and patient care act as case reports. As similar accounts accumulate, they become case series. Patterns emerge and new hypotheses are generated, debated, and critiqued through this informal peer review. Personal accounts of frustration with lack of PPE, fear of exposing loved ones, distress at being separated from family, and grief of witnessing multiple patients die alone are opinion and perspective articles.
These networks offer the space for sharing. Those who have had the experience of caring for the surge of COVID-19 patients offer advice and words of caution to those who have yet to experience it. Protocols from a multitude of institutions on triage, surge, disposition, and end-of-life care are disseminated, serving as templates for those that have not yet developed their own. There is an impressive variety of innovative, do-it-yourself projects surrounding PPE, intubation boxes, and three-dimensionally printed ventilator parts.
Finally, these networks provide emotional support. There are offers to ship additional PPE, videos of cities cheering as clinicians go to work, stories of triumph and recovery, pictures depicting ongoing wellness activities, and the occasional much-needed humorous anecdote or illustration. These networks reinforce the message that our lives continue despite this upheaval, and we are not alone in this struggle.
The end of the passage in The Great Influenza concludes with: “Ultimately a scientist has nothing to believe in but the process of inquiry. To move forcefully and aggressively even while uncertain requires a confidence and strength deeper than physical courage.”
They represent a highly adaptable, evolving, and collaborative global community’s determination to persevere through time of uncertainty together.
Dr. Ren is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital, Washington. Dr. Simpson is a pediatric emergency medicine attending and medical director of emergency preparedness at the hospital. They reported that they do not have any disclosures or conflicts of interest. Email Dr. Ren and Dr. Simpson at [email protected].
References
1. “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History.” (New York: Penguin Books, 2005, pp. 261-62).
2. Emerg Med J. 2014 Oct;31(e1):e76-7.
3. Acad Med. 2014 Apr;89(4):598-601.
4. “The Internet Book of Critical Care: COVID-19.” EMCrit Project.
5. “Covid-19.” REBEL EM-Emergency Medicine Blog.
6. “EM:RAP COVID-19 Resources.” EM RAP: Emergency Medicine Reviews and Perspectives.
7. “Episodes.” Peds RAP, Hippo Education.
Learning about the curve
Empty shelves that once cradled toilet paper rolls; lines of shoppers, some with masks; waiting 6 feet or at least a shopping cart length apart to get into grocery stores; hazmat-suited workers loading body bags into makeshift mortuaries ... These are the images we have come to associate with the COVID-19 pandemic. But then there also are the graphs and charts, none of them bearing good news. Some are difficult to interpret because they may be missing a key ingredient, such as a scale. Day to day fluctuations in the timeliness of the data points can make valid comparisons impossible. In most cases, it is too early to look at the graphs and hope for the big picture. Whether you are concerned about the stock market or the number of new cases of the virus in your county, you are hoping to see some graphic depiction of a favorable trend.
We have suddenly learned about the urgency of a process called “flattening the curve.” Are we doing as good a job of flattening as we could be? Are we doing better than France or Spain? Or are we heading toward an Italianesque apocalypse? Who is going to tell us when the flattening is for real and not just a 2- or 3-day statistical aberration?
The curves we are obsessed with today are those showing us new cases and new deaths. But And we won’t be seeing this curve in four-color graphics on the front page of our newspapers. It is the learning curve, and we want it to be as steep as we can make it without any hint of flattening in the foreseeable future.
We need to learn more about corona-like viruses. Why are some of us more vulnerable? We need to learn more about contagion. Does the 6-foot guideline make any sense? How long are viral particles floating in the air capable of initiating disease? What about air flow and dilution? Can we build a cruise ship or airplane that will be less of a health hazard?
More importantly, we need to learn to be better prepared. Even before the pandemic there have been shortages in intravenous solutions and drugs of critical importance to common diseases. Can we learn how to create reliable and affordable supply chains that allow researchers and developers to make a reasonable profit? Can we relearn to value science? Can we learn to invest more heavily in epidemiology and make it a specialty that attracts our best thinkers and communicators? Then can we elect officials who will share our trust in their recommendations?
Can we do a better job of resolving the tension between those who believe in a strong federal government and those who believe in local autonomy because we are seeing every day that this is an issue of survival, not just coexistence? Can we learn that the globalization that has allowed this viral spread can also be leveraged to beat it into submission?
Over the last half century there has been an unfortunate flattening of the learning curve. Ironically we have seen exponential growth among hi-tech industries that have forced us to keep abreast of new developments. But along with this has been a growing skepticism about value of scientific investigation. It is time we climbed back on that steep learning curve. The view gets better the higher we climb.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Empty shelves that once cradled toilet paper rolls; lines of shoppers, some with masks; waiting 6 feet or at least a shopping cart length apart to get into grocery stores; hazmat-suited workers loading body bags into makeshift mortuaries ... These are the images we have come to associate with the COVID-19 pandemic. But then there also are the graphs and charts, none of them bearing good news. Some are difficult to interpret because they may be missing a key ingredient, such as a scale. Day to day fluctuations in the timeliness of the data points can make valid comparisons impossible. In most cases, it is too early to look at the graphs and hope for the big picture. Whether you are concerned about the stock market or the number of new cases of the virus in your county, you are hoping to see some graphic depiction of a favorable trend.
We have suddenly learned about the urgency of a process called “flattening the curve.” Are we doing as good a job of flattening as we could be? Are we doing better than France or Spain? Or are we heading toward an Italianesque apocalypse? Who is going to tell us when the flattening is for real and not just a 2- or 3-day statistical aberration?
The curves we are obsessed with today are those showing us new cases and new deaths. But And we won’t be seeing this curve in four-color graphics on the front page of our newspapers. It is the learning curve, and we want it to be as steep as we can make it without any hint of flattening in the foreseeable future.
We need to learn more about corona-like viruses. Why are some of us more vulnerable? We need to learn more about contagion. Does the 6-foot guideline make any sense? How long are viral particles floating in the air capable of initiating disease? What about air flow and dilution? Can we build a cruise ship or airplane that will be less of a health hazard?
More importantly, we need to learn to be better prepared. Even before the pandemic there have been shortages in intravenous solutions and drugs of critical importance to common diseases. Can we learn how to create reliable and affordable supply chains that allow researchers and developers to make a reasonable profit? Can we relearn to value science? Can we learn to invest more heavily in epidemiology and make it a specialty that attracts our best thinkers and communicators? Then can we elect officials who will share our trust in their recommendations?
Can we do a better job of resolving the tension between those who believe in a strong federal government and those who believe in local autonomy because we are seeing every day that this is an issue of survival, not just coexistence? Can we learn that the globalization that has allowed this viral spread can also be leveraged to beat it into submission?
Over the last half century there has been an unfortunate flattening of the learning curve. Ironically we have seen exponential growth among hi-tech industries that have forced us to keep abreast of new developments. But along with this has been a growing skepticism about value of scientific investigation. It is time we climbed back on that steep learning curve. The view gets better the higher we climb.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Empty shelves that once cradled toilet paper rolls; lines of shoppers, some with masks; waiting 6 feet or at least a shopping cart length apart to get into grocery stores; hazmat-suited workers loading body bags into makeshift mortuaries ... These are the images we have come to associate with the COVID-19 pandemic. But then there also are the graphs and charts, none of them bearing good news. Some are difficult to interpret because they may be missing a key ingredient, such as a scale. Day to day fluctuations in the timeliness of the data points can make valid comparisons impossible. In most cases, it is too early to look at the graphs and hope for the big picture. Whether you are concerned about the stock market or the number of new cases of the virus in your county, you are hoping to see some graphic depiction of a favorable trend.
We have suddenly learned about the urgency of a process called “flattening the curve.” Are we doing as good a job of flattening as we could be? Are we doing better than France or Spain? Or are we heading toward an Italianesque apocalypse? Who is going to tell us when the flattening is for real and not just a 2- or 3-day statistical aberration?
The curves we are obsessed with today are those showing us new cases and new deaths. But And we won’t be seeing this curve in four-color graphics on the front page of our newspapers. It is the learning curve, and we want it to be as steep as we can make it without any hint of flattening in the foreseeable future.
We need to learn more about corona-like viruses. Why are some of us more vulnerable? We need to learn more about contagion. Does the 6-foot guideline make any sense? How long are viral particles floating in the air capable of initiating disease? What about air flow and dilution? Can we build a cruise ship or airplane that will be less of a health hazard?
More importantly, we need to learn to be better prepared. Even before the pandemic there have been shortages in intravenous solutions and drugs of critical importance to common diseases. Can we learn how to create reliable and affordable supply chains that allow researchers and developers to make a reasonable profit? Can we relearn to value science? Can we learn to invest more heavily in epidemiology and make it a specialty that attracts our best thinkers and communicators? Then can we elect officials who will share our trust in their recommendations?
Can we do a better job of resolving the tension between those who believe in a strong federal government and those who believe in local autonomy because we are seeing every day that this is an issue of survival, not just coexistence? Can we learn that the globalization that has allowed this viral spread can also be leveraged to beat it into submission?
Over the last half century there has been an unfortunate flattening of the learning curve. Ironically we have seen exponential growth among hi-tech industries that have forced us to keep abreast of new developments. But along with this has been a growing skepticism about value of scientific investigation. It is time we climbed back on that steep learning curve. The view gets better the higher we climb.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Mother of pearl: The power of pearl powder
Because of its dense protein and mineral composition, it has been used to treat several skin and bone disorders, as well as palpitations, insomnia, and epilepsy.3,4 The pearl-farming industry itself was established in Japan and has existed for more than a century; today, pearls are cultured globally and continue to receive attention for conferring health benefits.5
Calcium carbonate is the primary component of mollusk shells (roughly 95%), with the remainder an organic matrix including proteins, glycoproteins, and polysaccharides.6 Pearl powder is known to have exhibited antiaging, antioxidant, antiradiative, and tonic activities; in recent years, it has been incorporated into health foods for such properties and used in the clinical setting to treat ulcers (aphthous, gastric, and duodenal).4,7 Consisting of multiple active proteins, pearl powder is thought to be conducive to skin cell growth and effective for wound repair.4 This column focuses on recent research into the dermatologic potential of the powder derived from mother of pearl.
Wound healing
A decade ago, Jian-Ping et al. showed in mice that the water-soluble matrix of pearl powder (Hyriopsis cumingii) could significantly induce oral fibroblast proliferation and collagen accumulation, suppress matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity, and significantly foster TIMP-1 synthesis. The investigators concluded that the wound healing facilitated by pearl powder derives, in part, from its capacity to promote fibroblast mitosis, collagen deposition, and production of TIMP-1.8
Two years later, Lee et al. evaluated the effects of water-soluble nacre (mother of pearl) on second-degree burn wound healing in porcine skin as a proxy for human skin. They found that its application quickly led to burn-induced granulation areas filling with collagen, with normal skin appearance restored to wounded dermis and epidermis. Angiogenesis was also promoted by water-soluble nacre as was wound recovery in areas with apoptotic and necrotic cellular damage. Murine fibroblast NIH3T3 cells treated with water-soluble nacre also demonstrated augmented proliferation and collagen production. The researchers cited the restoration of angiogenesis and fibroblast activity as the primary benefits of water-soluble nacre, suggesting its potential as a wound therapy, preferable to powdered nacre due to better biocompatibility with less discomfort.9
The next year, Li et al. found that mother of pearl extract promoted cell migration of fibroblasts in cell culture, demonstrating its potential as a wound healing model.7In 2019, Chen et al. studied the effects of pearl powders of varying particle sizes to treat wounds in vitro and in vivo. They found that micro- and nanosized pearl powders augmented proliferation and migration of skin cells and shortened wound closure time. All powders also improved the biomechanical strength of healed skin, enhanced collagen formation and deposition, and expanded cutaneous angiogenesis, with nanoscale pearl powder displaying greatest efficiency.4
Skin tone and atopic dermatitis
In 2000, Lopez et al. implanted powdered nacre (mother of pearl derived from Pinctada maxima), which can promote and regulate bone-forming cells, into rat dermis to evaluate its effects on skin fibroblasts. They noted that the implant yielded well-vascularized tissue and improved extracellular matrix production, synthesis of substances involved in cellular adhesion and communication, and tissue regeneration (such as collagen types I and III). The investigators concluded that the powdered nacre contributed to the conditions necessary for improved skin tone and proper physiologic functioning of the skin.10
Rousseau et al. extracted lipids from the nacre of the oyster P. margaritifera to test on artificially dehydrated skin explants with the intention of developing new treatments for atopic dermatitis. The researchers determined that the lipids spurred a reconstitution of the intercellular material of the stratum corneum, concluding that new products to treat atopic dermatitis might be based on the signaling activity of nacre lipids.11
Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity
A 2015 study by Yang et al. showed that a room-temperature superextraction system to yield the main active constituents of pearl was successful in enhancing their anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic activity in human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT) exposed to low-dose UVB. The investigators combined pearl extract and poly (gamma-glutamic acid) hydrogels and observed reductions in inflammation and apoptosis of HaCaT cells. They concluded that a marketed pearl extract may be able to suppress radiation dermatitis present in keratinocytes.12
Two years later, Latire et al. used human dermal fibroblasts in primary culture to assess the potential biological activities of the matrix macromolecular components extracted from the shells of two edible mollusks (the blue mussel Mytilus edulis and the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas). The investigators found that both extracts influenced metabolic functions of the cells and reduced type I collagen levels, with an associated rise in matrix metalloproteinase-1 activity. Given their findings implying the effectiveness of the extracts in facilitating the catabolic pathway of human dermal fibroblasts, the authors suggest that these shell matrices present the potential for use in treating fibrosis, especially for scleroderma.6
Antioxidant and antiaging activity
Shao et al. demonstrated 10 years ago that pearl powder provides a moisturizing effect on the skin, with ultramicro pearl powder delivering a more robust moisturizing result than water-soluble pearl powder. These two types of pearl powder, along with another one tested (ultranano pearl powder), also significantly diminished the activation of tyrosinase and free radicals. Water-soluble pearl powder did not perform as well as the other two formulations in free radical scavenging. The investigators suggested that their results support the use of pearl powder to combat aging and enhance beauty, and could be used in the clinical setting.13
In 2017, Yang et al. reported on the in vitro antihemolytic and antioxidant activity of pearl powder in shielding human erythrocytes against 2,2’-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride–induced oxidative damage to membrane proteins/lipids. The researchers contend that the strong antioxidant qualities of pearl powder could be applied to prevent or protect against various diseases resulting from free radical damage.2
Human trials: Antioxidant, antiaging, skin appearance
Chiu et al. studied the antioxidant activity of various pearl powder extracts in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in 2018. They also investigated the life span–prolonging effects of the powders using wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans. Twenty healthy middle-aged subjects were separated into two groups (experimental and placebo), with 3 g of pearl powder administered in capsules to the former and 3 g of placebo to the latter over 8 weeks. Blood samples taken at the beginning and every 2 weeks during the trial and in the 10th week revealed maximum antioxidant activity of the pearl powder and prolongation of C. elegans lifespan by 18.87%. Subjects using pearl powder demonstrated significant increases in total antioxidant capacity, thiols, glutathione, and enzymic antioxidant activity, along with notably inhibited lipid peroxidation products. The investigators concluded that pearl powder extract acted as a potent antioxidant and its use may be warranted to treat degenerative conditions related to aging.3
A recent study of the perception of blue light on Korean women’s faces using blue pearl pigment revealed that the pigment does indeed elicit the perception of the blue-light effect, notably transparency and gloss, which is particularly valued in Korea.14
Conclusion
The use of mother of pearl and pearl powder in traditional Chinese medicine and as a cosmetic and food additive has a rich and lengthy history. Contemporary research clearly suggests interesting avenues for further investigation and some promising results. Much more research is necessary, though, to delineate the potential roles of pearl powder in the skin care arsenal.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Sep Sci. 2015 May;38(9):1552-60.
2. Yang HL et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Oct;25(4):898-907.
3. Chiu HF et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Jan;26(1):309-17.
4. Chen X et al. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Jun;45(6):1009-16.
5. Nagai K. Zoolog Sci. 2013 Oct;30(10):783-93.
6. Latire T et al. Cytotechnology. 2017 Oct;69(5):815-29.
7. Li YC et al. Pharm Biol. 2013 Mar;51(3):289-97.
8. Jian-Ping D et al. Pharm Biol. 2010 Feb;48(2):122-7.
9. Lee K et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Mar;39(3):3211-8.
10. Lopez E et al. Tissue Cell. 2000 Feb;32(1):95-101.
11. Rousseau M et al. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Sep;145(1):1-9.
12. Yang YL et al. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26 Suppl 1:S139-45.
13. Shao DZ et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2010 Mar-Apr;61(2):133-45.
14. Lee M et al. Skin Res Technol. 2020 Jan;26(1):76-80.
Because of its dense protein and mineral composition, it has been used to treat several skin and bone disorders, as well as palpitations, insomnia, and epilepsy.3,4 The pearl-farming industry itself was established in Japan and has existed for more than a century; today, pearls are cultured globally and continue to receive attention for conferring health benefits.5
Calcium carbonate is the primary component of mollusk shells (roughly 95%), with the remainder an organic matrix including proteins, glycoproteins, and polysaccharides.6 Pearl powder is known to have exhibited antiaging, antioxidant, antiradiative, and tonic activities; in recent years, it has been incorporated into health foods for such properties and used in the clinical setting to treat ulcers (aphthous, gastric, and duodenal).4,7 Consisting of multiple active proteins, pearl powder is thought to be conducive to skin cell growth and effective for wound repair.4 This column focuses on recent research into the dermatologic potential of the powder derived from mother of pearl.
Wound healing
A decade ago, Jian-Ping et al. showed in mice that the water-soluble matrix of pearl powder (Hyriopsis cumingii) could significantly induce oral fibroblast proliferation and collagen accumulation, suppress matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity, and significantly foster TIMP-1 synthesis. The investigators concluded that the wound healing facilitated by pearl powder derives, in part, from its capacity to promote fibroblast mitosis, collagen deposition, and production of TIMP-1.8
Two years later, Lee et al. evaluated the effects of water-soluble nacre (mother of pearl) on second-degree burn wound healing in porcine skin as a proxy for human skin. They found that its application quickly led to burn-induced granulation areas filling with collagen, with normal skin appearance restored to wounded dermis and epidermis. Angiogenesis was also promoted by water-soluble nacre as was wound recovery in areas with apoptotic and necrotic cellular damage. Murine fibroblast NIH3T3 cells treated with water-soluble nacre also demonstrated augmented proliferation and collagen production. The researchers cited the restoration of angiogenesis and fibroblast activity as the primary benefits of water-soluble nacre, suggesting its potential as a wound therapy, preferable to powdered nacre due to better biocompatibility with less discomfort.9
The next year, Li et al. found that mother of pearl extract promoted cell migration of fibroblasts in cell culture, demonstrating its potential as a wound healing model.7In 2019, Chen et al. studied the effects of pearl powders of varying particle sizes to treat wounds in vitro and in vivo. They found that micro- and nanosized pearl powders augmented proliferation and migration of skin cells and shortened wound closure time. All powders also improved the biomechanical strength of healed skin, enhanced collagen formation and deposition, and expanded cutaneous angiogenesis, with nanoscale pearl powder displaying greatest efficiency.4
Skin tone and atopic dermatitis
In 2000, Lopez et al. implanted powdered nacre (mother of pearl derived from Pinctada maxima), which can promote and regulate bone-forming cells, into rat dermis to evaluate its effects on skin fibroblasts. They noted that the implant yielded well-vascularized tissue and improved extracellular matrix production, synthesis of substances involved in cellular adhesion and communication, and tissue regeneration (such as collagen types I and III). The investigators concluded that the powdered nacre contributed to the conditions necessary for improved skin tone and proper physiologic functioning of the skin.10
Rousseau et al. extracted lipids from the nacre of the oyster P. margaritifera to test on artificially dehydrated skin explants with the intention of developing new treatments for atopic dermatitis. The researchers determined that the lipids spurred a reconstitution of the intercellular material of the stratum corneum, concluding that new products to treat atopic dermatitis might be based on the signaling activity of nacre lipids.11
Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity
A 2015 study by Yang et al. showed that a room-temperature superextraction system to yield the main active constituents of pearl was successful in enhancing their anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic activity in human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT) exposed to low-dose UVB. The investigators combined pearl extract and poly (gamma-glutamic acid) hydrogels and observed reductions in inflammation and apoptosis of HaCaT cells. They concluded that a marketed pearl extract may be able to suppress radiation dermatitis present in keratinocytes.12
Two years later, Latire et al. used human dermal fibroblasts in primary culture to assess the potential biological activities of the matrix macromolecular components extracted from the shells of two edible mollusks (the blue mussel Mytilus edulis and the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas). The investigators found that both extracts influenced metabolic functions of the cells and reduced type I collagen levels, with an associated rise in matrix metalloproteinase-1 activity. Given their findings implying the effectiveness of the extracts in facilitating the catabolic pathway of human dermal fibroblasts, the authors suggest that these shell matrices present the potential for use in treating fibrosis, especially for scleroderma.6
Antioxidant and antiaging activity
Shao et al. demonstrated 10 years ago that pearl powder provides a moisturizing effect on the skin, with ultramicro pearl powder delivering a more robust moisturizing result than water-soluble pearl powder. These two types of pearl powder, along with another one tested (ultranano pearl powder), also significantly diminished the activation of tyrosinase and free radicals. Water-soluble pearl powder did not perform as well as the other two formulations in free radical scavenging. The investigators suggested that their results support the use of pearl powder to combat aging and enhance beauty, and could be used in the clinical setting.13
In 2017, Yang et al. reported on the in vitro antihemolytic and antioxidant activity of pearl powder in shielding human erythrocytes against 2,2’-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride–induced oxidative damage to membrane proteins/lipids. The researchers contend that the strong antioxidant qualities of pearl powder could be applied to prevent or protect against various diseases resulting from free radical damage.2
Human trials: Antioxidant, antiaging, skin appearance
Chiu et al. studied the antioxidant activity of various pearl powder extracts in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in 2018. They also investigated the life span–prolonging effects of the powders using wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans. Twenty healthy middle-aged subjects were separated into two groups (experimental and placebo), with 3 g of pearl powder administered in capsules to the former and 3 g of placebo to the latter over 8 weeks. Blood samples taken at the beginning and every 2 weeks during the trial and in the 10th week revealed maximum antioxidant activity of the pearl powder and prolongation of C. elegans lifespan by 18.87%. Subjects using pearl powder demonstrated significant increases in total antioxidant capacity, thiols, glutathione, and enzymic antioxidant activity, along with notably inhibited lipid peroxidation products. The investigators concluded that pearl powder extract acted as a potent antioxidant and its use may be warranted to treat degenerative conditions related to aging.3
A recent study of the perception of blue light on Korean women’s faces using blue pearl pigment revealed that the pigment does indeed elicit the perception of the blue-light effect, notably transparency and gloss, which is particularly valued in Korea.14
Conclusion
The use of mother of pearl and pearl powder in traditional Chinese medicine and as a cosmetic and food additive has a rich and lengthy history. Contemporary research clearly suggests interesting avenues for further investigation and some promising results. Much more research is necessary, though, to delineate the potential roles of pearl powder in the skin care arsenal.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Sep Sci. 2015 May;38(9):1552-60.
2. Yang HL et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Oct;25(4):898-907.
3. Chiu HF et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Jan;26(1):309-17.
4. Chen X et al. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Jun;45(6):1009-16.
5. Nagai K. Zoolog Sci. 2013 Oct;30(10):783-93.
6. Latire T et al. Cytotechnology. 2017 Oct;69(5):815-29.
7. Li YC et al. Pharm Biol. 2013 Mar;51(3):289-97.
8. Jian-Ping D et al. Pharm Biol. 2010 Feb;48(2):122-7.
9. Lee K et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Mar;39(3):3211-8.
10. Lopez E et al. Tissue Cell. 2000 Feb;32(1):95-101.
11. Rousseau M et al. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Sep;145(1):1-9.
12. Yang YL et al. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26 Suppl 1:S139-45.
13. Shao DZ et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2010 Mar-Apr;61(2):133-45.
14. Lee M et al. Skin Res Technol. 2020 Jan;26(1):76-80.
Because of its dense protein and mineral composition, it has been used to treat several skin and bone disorders, as well as palpitations, insomnia, and epilepsy.3,4 The pearl-farming industry itself was established in Japan and has existed for more than a century; today, pearls are cultured globally and continue to receive attention for conferring health benefits.5
Calcium carbonate is the primary component of mollusk shells (roughly 95%), with the remainder an organic matrix including proteins, glycoproteins, and polysaccharides.6 Pearl powder is known to have exhibited antiaging, antioxidant, antiradiative, and tonic activities; in recent years, it has been incorporated into health foods for such properties and used in the clinical setting to treat ulcers (aphthous, gastric, and duodenal).4,7 Consisting of multiple active proteins, pearl powder is thought to be conducive to skin cell growth and effective for wound repair.4 This column focuses on recent research into the dermatologic potential of the powder derived from mother of pearl.
Wound healing
A decade ago, Jian-Ping et al. showed in mice that the water-soluble matrix of pearl powder (Hyriopsis cumingii) could significantly induce oral fibroblast proliferation and collagen accumulation, suppress matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity, and significantly foster TIMP-1 synthesis. The investigators concluded that the wound healing facilitated by pearl powder derives, in part, from its capacity to promote fibroblast mitosis, collagen deposition, and production of TIMP-1.8
Two years later, Lee et al. evaluated the effects of water-soluble nacre (mother of pearl) on second-degree burn wound healing in porcine skin as a proxy for human skin. They found that its application quickly led to burn-induced granulation areas filling with collagen, with normal skin appearance restored to wounded dermis and epidermis. Angiogenesis was also promoted by water-soluble nacre as was wound recovery in areas with apoptotic and necrotic cellular damage. Murine fibroblast NIH3T3 cells treated with water-soluble nacre also demonstrated augmented proliferation and collagen production. The researchers cited the restoration of angiogenesis and fibroblast activity as the primary benefits of water-soluble nacre, suggesting its potential as a wound therapy, preferable to powdered nacre due to better biocompatibility with less discomfort.9
The next year, Li et al. found that mother of pearl extract promoted cell migration of fibroblasts in cell culture, demonstrating its potential as a wound healing model.7In 2019, Chen et al. studied the effects of pearl powders of varying particle sizes to treat wounds in vitro and in vivo. They found that micro- and nanosized pearl powders augmented proliferation and migration of skin cells and shortened wound closure time. All powders also improved the biomechanical strength of healed skin, enhanced collagen formation and deposition, and expanded cutaneous angiogenesis, with nanoscale pearl powder displaying greatest efficiency.4
Skin tone and atopic dermatitis
In 2000, Lopez et al. implanted powdered nacre (mother of pearl derived from Pinctada maxima), which can promote and regulate bone-forming cells, into rat dermis to evaluate its effects on skin fibroblasts. They noted that the implant yielded well-vascularized tissue and improved extracellular matrix production, synthesis of substances involved in cellular adhesion and communication, and tissue regeneration (such as collagen types I and III). The investigators concluded that the powdered nacre contributed to the conditions necessary for improved skin tone and proper physiologic functioning of the skin.10
Rousseau et al. extracted lipids from the nacre of the oyster P. margaritifera to test on artificially dehydrated skin explants with the intention of developing new treatments for atopic dermatitis. The researchers determined that the lipids spurred a reconstitution of the intercellular material of the stratum corneum, concluding that new products to treat atopic dermatitis might be based on the signaling activity of nacre lipids.11
Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity
A 2015 study by Yang et al. showed that a room-temperature superextraction system to yield the main active constituents of pearl was successful in enhancing their anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic activity in human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT) exposed to low-dose UVB. The investigators combined pearl extract and poly (gamma-glutamic acid) hydrogels and observed reductions in inflammation and apoptosis of HaCaT cells. They concluded that a marketed pearl extract may be able to suppress radiation dermatitis present in keratinocytes.12
Two years later, Latire et al. used human dermal fibroblasts in primary culture to assess the potential biological activities of the matrix macromolecular components extracted from the shells of two edible mollusks (the blue mussel Mytilus edulis and the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas). The investigators found that both extracts influenced metabolic functions of the cells and reduced type I collagen levels, with an associated rise in matrix metalloproteinase-1 activity. Given their findings implying the effectiveness of the extracts in facilitating the catabolic pathway of human dermal fibroblasts, the authors suggest that these shell matrices present the potential for use in treating fibrosis, especially for scleroderma.6
Antioxidant and antiaging activity
Shao et al. demonstrated 10 years ago that pearl powder provides a moisturizing effect on the skin, with ultramicro pearl powder delivering a more robust moisturizing result than water-soluble pearl powder. These two types of pearl powder, along with another one tested (ultranano pearl powder), also significantly diminished the activation of tyrosinase and free radicals. Water-soluble pearl powder did not perform as well as the other two formulations in free radical scavenging. The investigators suggested that their results support the use of pearl powder to combat aging and enhance beauty, and could be used in the clinical setting.13
In 2017, Yang et al. reported on the in vitro antihemolytic and antioxidant activity of pearl powder in shielding human erythrocytes against 2,2’-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride–induced oxidative damage to membrane proteins/lipids. The researchers contend that the strong antioxidant qualities of pearl powder could be applied to prevent or protect against various diseases resulting from free radical damage.2
Human trials: Antioxidant, antiaging, skin appearance
Chiu et al. studied the antioxidant activity of various pearl powder extracts in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in 2018. They also investigated the life span–prolonging effects of the powders using wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans. Twenty healthy middle-aged subjects were separated into two groups (experimental and placebo), with 3 g of pearl powder administered in capsules to the former and 3 g of placebo to the latter over 8 weeks. Blood samples taken at the beginning and every 2 weeks during the trial and in the 10th week revealed maximum antioxidant activity of the pearl powder and prolongation of C. elegans lifespan by 18.87%. Subjects using pearl powder demonstrated significant increases in total antioxidant capacity, thiols, glutathione, and enzymic antioxidant activity, along with notably inhibited lipid peroxidation products. The investigators concluded that pearl powder extract acted as a potent antioxidant and its use may be warranted to treat degenerative conditions related to aging.3
A recent study of the perception of blue light on Korean women’s faces using blue pearl pigment revealed that the pigment does indeed elicit the perception of the blue-light effect, notably transparency and gloss, which is particularly valued in Korea.14
Conclusion
The use of mother of pearl and pearl powder in traditional Chinese medicine and as a cosmetic and food additive has a rich and lengthy history. Contemporary research clearly suggests interesting avenues for further investigation and some promising results. Much more research is necessary, though, to delineate the potential roles of pearl powder in the skin care arsenal.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Sep Sci. 2015 May;38(9):1552-60.
2. Yang HL et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Oct;25(4):898-907.
3. Chiu HF et al. J Food Drug Anal. 2018 Jan;26(1):309-17.
4. Chen X et al. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Jun;45(6):1009-16.
5. Nagai K. Zoolog Sci. 2013 Oct;30(10):783-93.
6. Latire T et al. Cytotechnology. 2017 Oct;69(5):815-29.
7. Li YC et al. Pharm Biol. 2013 Mar;51(3):289-97.
8. Jian-Ping D et al. Pharm Biol. 2010 Feb;48(2):122-7.
9. Lee K et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Mar;39(3):3211-8.
10. Lopez E et al. Tissue Cell. 2000 Feb;32(1):95-101.
11. Rousseau M et al. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2006 Sep;145(1):1-9.
12. Yang YL et al. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26 Suppl 1:S139-45.
13. Shao DZ et al. J Cosmet Sci. 2010 Mar-Apr;61(2):133-45.
14. Lee M et al. Skin Res Technol. 2020 Jan;26(1):76-80.
Resources for LGBTQ youth during challenging times
If you are anything like me, March 1 came and went as just another first day of the month. Few of us could have imagined that our day-to-day way of life would soon be upended, and our country would be in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. While there is considerable anxiety around protecting our individual health, social distancing and the physical isolation that comes from it have cut off a vital source of support for many of our lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and questioning (or queer) (LGBTQ) youth. Shared experiences with other young people like themselves provide these youth with a sense of community that they may not find in their schools, towns, etc.
LGBTQ youth already face increased rates of anxiety and depression compared with their heterosexual and cisgender peers. According to the 2017 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 63% of LGB youth nationwide reported feeling sad or hopeless compared with 28% of their heterosexual peers. While quarantined at home, many of these youth now are stuck for many more hours per day with families who may not accept them for who they are. Previous research by Ryan et al. shows that LGB adolescents who have higher rates of family rejection are nearly six times more likely to have higher rates of depression and more than eight times more likely to attempt suicide than their peers who come from families with low or no levels of rejection (Pediatrics. 2009 Jan;123[1]:346-52). Going to school for roughly 8 hours a day allows some of these youth an escape from what is otherwise an unpleasant home situation. In addition, educators and other school staff may be among the only allies that a student has in his/her life, and school cancellations remove students from access to these important people.
Due to stay-at-home orders and physical distancing measures, lack of in-person access to medical and psychological care can be distressing for many LGBTQ youth. While many practices have been able to convert to audiovisual telemedicine visits, not all of them have the resources or capability to do so. Consequently, LGBTQ youth may have reduced access to support services that help to bolster their social and emotional health. In addition, many trans youth suffer from physical dysphoria that can make it distressing to see themselves on camera doing teletherapy and so they wish to avoid it for this reason.
This is not to say that everything is bleak. LGBTQ youth can also be resilient in times of stress and worry. “The LGBTQ community has a long history of overcoming adversity and utilizing challenges to build an even stronger sense of community. This pandemic will create yet another opportunity for us to highlight existing health disparities and to support our LGBTQ young people in finding creative responses,” said Heather Newby, LCSW, clinical social worker for the GENECIS (GENder Education and Care Interdisciplinary Support) Program at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. In addition, she reported that many LGBTQ advocacy groups have created excellent online support networks and resources to provide nationwide, regional, and local help.
During these challenging times, there are a number of resources that LGBTQ youth can turn to while trying to maintain their connection to their peers. First, many local LGBTQ service organizations have moved their in-person support groups to a virtual or online platform. Check with your local service organization to see what they are offering during these times. National organizations, such as Gender Spectrum, continue to have online groups as well that youth can participate in. Second, many virtual mental health helplines, such as those through the Trevor Project, remain staffed should LGBTQ youth need to access their services (1-866-488-7386, plus text and chat). They can be reached 24/7 to help those whose mental health has been affected during this pandemic. Third, youth can continue to stay connected to their friends through means such as Zoom, FaceTime, or other virtual audiovisual tools. Lastly, some youth have taken to meeting in school parking lots, mall parking lots, etc., and staying at least 6 feet apart so that they can still see their friends in person.
While the current times may be challenging, they will pass and we will be able to return to those activities that bring us joy. Do not hesitate to reach out if you need help. As Rainer Maria Rilke once said, “In the difficult, we must have our joys, our happiness, our dreams: There against the depth of this background, they stand out, there for the first time we see how beautiful they are.”
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Cooper is on Twitter @teendocmbc. Email him at [email protected].
If you are anything like me, March 1 came and went as just another first day of the month. Few of us could have imagined that our day-to-day way of life would soon be upended, and our country would be in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. While there is considerable anxiety around protecting our individual health, social distancing and the physical isolation that comes from it have cut off a vital source of support for many of our lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and questioning (or queer) (LGBTQ) youth. Shared experiences with other young people like themselves provide these youth with a sense of community that they may not find in their schools, towns, etc.
LGBTQ youth already face increased rates of anxiety and depression compared with their heterosexual and cisgender peers. According to the 2017 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 63% of LGB youth nationwide reported feeling sad or hopeless compared with 28% of their heterosexual peers. While quarantined at home, many of these youth now are stuck for many more hours per day with families who may not accept them for who they are. Previous research by Ryan et al. shows that LGB adolescents who have higher rates of family rejection are nearly six times more likely to have higher rates of depression and more than eight times more likely to attempt suicide than their peers who come from families with low or no levels of rejection (Pediatrics. 2009 Jan;123[1]:346-52). Going to school for roughly 8 hours a day allows some of these youth an escape from what is otherwise an unpleasant home situation. In addition, educators and other school staff may be among the only allies that a student has in his/her life, and school cancellations remove students from access to these important people.
Due to stay-at-home orders and physical distancing measures, lack of in-person access to medical and psychological care can be distressing for many LGBTQ youth. While many practices have been able to convert to audiovisual telemedicine visits, not all of them have the resources or capability to do so. Consequently, LGBTQ youth may have reduced access to support services that help to bolster their social and emotional health. In addition, many trans youth suffer from physical dysphoria that can make it distressing to see themselves on camera doing teletherapy and so they wish to avoid it for this reason.
This is not to say that everything is bleak. LGBTQ youth can also be resilient in times of stress and worry. “The LGBTQ community has a long history of overcoming adversity and utilizing challenges to build an even stronger sense of community. This pandemic will create yet another opportunity for us to highlight existing health disparities and to support our LGBTQ young people in finding creative responses,” said Heather Newby, LCSW, clinical social worker for the GENECIS (GENder Education and Care Interdisciplinary Support) Program at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. In addition, she reported that many LGBTQ advocacy groups have created excellent online support networks and resources to provide nationwide, regional, and local help.
During these challenging times, there are a number of resources that LGBTQ youth can turn to while trying to maintain their connection to their peers. First, many local LGBTQ service organizations have moved their in-person support groups to a virtual or online platform. Check with your local service organization to see what they are offering during these times. National organizations, such as Gender Spectrum, continue to have online groups as well that youth can participate in. Second, many virtual mental health helplines, such as those through the Trevor Project, remain staffed should LGBTQ youth need to access their services (1-866-488-7386, plus text and chat). They can be reached 24/7 to help those whose mental health has been affected during this pandemic. Third, youth can continue to stay connected to their friends through means such as Zoom, FaceTime, or other virtual audiovisual tools. Lastly, some youth have taken to meeting in school parking lots, mall parking lots, etc., and staying at least 6 feet apart so that they can still see their friends in person.
While the current times may be challenging, they will pass and we will be able to return to those activities that bring us joy. Do not hesitate to reach out if you need help. As Rainer Maria Rilke once said, “In the difficult, we must have our joys, our happiness, our dreams: There against the depth of this background, they stand out, there for the first time we see how beautiful they are.”
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Cooper is on Twitter @teendocmbc. Email him at [email protected].
If you are anything like me, March 1 came and went as just another first day of the month. Few of us could have imagined that our day-to-day way of life would soon be upended, and our country would be in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. While there is considerable anxiety around protecting our individual health, social distancing and the physical isolation that comes from it have cut off a vital source of support for many of our lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and questioning (or queer) (LGBTQ) youth. Shared experiences with other young people like themselves provide these youth with a sense of community that they may not find in their schools, towns, etc.
LGBTQ youth already face increased rates of anxiety and depression compared with their heterosexual and cisgender peers. According to the 2017 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 63% of LGB youth nationwide reported feeling sad or hopeless compared with 28% of their heterosexual peers. While quarantined at home, many of these youth now are stuck for many more hours per day with families who may not accept them for who they are. Previous research by Ryan et al. shows that LGB adolescents who have higher rates of family rejection are nearly six times more likely to have higher rates of depression and more than eight times more likely to attempt suicide than their peers who come from families with low or no levels of rejection (Pediatrics. 2009 Jan;123[1]:346-52). Going to school for roughly 8 hours a day allows some of these youth an escape from what is otherwise an unpleasant home situation. In addition, educators and other school staff may be among the only allies that a student has in his/her life, and school cancellations remove students from access to these important people.
Due to stay-at-home orders and physical distancing measures, lack of in-person access to medical and psychological care can be distressing for many LGBTQ youth. While many practices have been able to convert to audiovisual telemedicine visits, not all of them have the resources or capability to do so. Consequently, LGBTQ youth may have reduced access to support services that help to bolster their social and emotional health. In addition, many trans youth suffer from physical dysphoria that can make it distressing to see themselves on camera doing teletherapy and so they wish to avoid it for this reason.
This is not to say that everything is bleak. LGBTQ youth can also be resilient in times of stress and worry. “The LGBTQ community has a long history of overcoming adversity and utilizing challenges to build an even stronger sense of community. This pandemic will create yet another opportunity for us to highlight existing health disparities and to support our LGBTQ young people in finding creative responses,” said Heather Newby, LCSW, clinical social worker for the GENECIS (GENder Education and Care Interdisciplinary Support) Program at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. In addition, she reported that many LGBTQ advocacy groups have created excellent online support networks and resources to provide nationwide, regional, and local help.
During these challenging times, there are a number of resources that LGBTQ youth can turn to while trying to maintain their connection to their peers. First, many local LGBTQ service organizations have moved their in-person support groups to a virtual or online platform. Check with your local service organization to see what they are offering during these times. National organizations, such as Gender Spectrum, continue to have online groups as well that youth can participate in. Second, many virtual mental health helplines, such as those through the Trevor Project, remain staffed should LGBTQ youth need to access their services (1-866-488-7386, plus text and chat). They can be reached 24/7 to help those whose mental health has been affected during this pandemic. Third, youth can continue to stay connected to their friends through means such as Zoom, FaceTime, or other virtual audiovisual tools. Lastly, some youth have taken to meeting in school parking lots, mall parking lots, etc., and staying at least 6 feet apart so that they can still see their friends in person.
While the current times may be challenging, they will pass and we will be able to return to those activities that bring us joy. Do not hesitate to reach out if you need help. As Rainer Maria Rilke once said, “In the difficult, we must have our joys, our happiness, our dreams: There against the depth of this background, they stand out, there for the first time we see how beautiful they are.”
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Cooper is on Twitter @teendocmbc. Email him at [email protected].
COVID-19 pandemic brings unexpected pediatric consequences
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
COVID 19: Confessions of an outpatient psychiatrist during the pandemic
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.