User login
COVID-19: What now?
“There are decades where nothing happens,” wrote Vladimir Lenin, “and there are weeks where decades happen.” Barely a dozen weeks ago, no one knew that the SARS-CoV-2 virus existed. Now, it has spread to almost every country on Earth, infecting over 1.8 million people whom we know about, and many more whom we do not. In so doing, it has crashed economies and health care systems, filled hospitals, emptied public spaces, and separated people from their workplaces and their friends on a scale that few of us have ever witnessed.
It has also triggered an avalanche of questions as to why our initial response was so thoroughly lethargic, rudderless, and uncoordinated; while there is plenty of blame to go around, that is for another time. The glaring question for many – including physicians trying to keep our private practices viable – is: What now?
The answer depends, of course, on how the pandemic plays out. No one yet knows exactly what will happen, but much depends on two properties of the virus, both of which are currently unknown. First: seasonality. Coronaviruses tend to thrive in winter and wane in the summer. That may also be true for SARS-CoV-2, but seasonal variations might not sufficiently slow the virus when it has so many immunologically naive hosts to infect. As I write this in mid-April, we wait anxiously to see what – if anything – summer temperatures do to its transmission in the Northern Hemisphere.
The second wild card is duration of immunity. Determining that will involve developing accurate serologic tests and administering them widely. Immune citizens, once identified, can return to work, care for the vulnerable, and anchor the economy during future outbreaks.
Even if we do get a summer hiatus, seasonal viruses typically return as winter approaches. We could conceivably still be mopping up from this outbreak when the virus – if it is seasonal – comes roaring back in October or November. Will we be ready? Or will it catch us with our pants amidships yet again?
I can envision two possibilities: Assuming we luck into a seasonal reprieve in the next few weeks, infection rates should drop, which could allow our private practices to return toward some semblance of normal – if health workers and patients alike can be convinced that our offices and clinics are safe. This might be accomplished as part of our overall preparation for a potential winter recurrence, by checking every patient’s temperature at the waiting room door. Similarly, all students should get a daily temperature check at school, as should all commuters, airline passengers, and individuals at any sizable gathering. Every fever should trigger a COVID-19 test, and every positive test should launch aggressive contact tracing and quarantines. Meanwhile, treatments and vaccines should get fast-tracked.
That’s what should happen. If it doesn’t, and COVID-19 recurs next winter, worse than before, it is anybody’s guess whether most private medical practices will be able to weather a second onslaught. Further government funding is not assured. We won’t have a vaccine by November. Chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin might turn out to be helpful, but we can’t count on them.
Even if we do get lucky with seasonality, the question remains of how long it will take to restore public confidence and reboot the economy. Economies generally do not function like light switches that can be turned off for a while then simply turned back on, but act more like campfires. If you pour a bucket of water on one, it takes some time to get it cranked up again. After the “Great Recession” of 2008, it took nearly 10 years.
So now, with great reluctance, I must trot out a hoary old cliché: Hope for the best, but plan for the worst. Everyone’s situation will be different, of course, but I can make a few general suggestions. Perform a difficult mental exercise: What will you do if SARS-CoV-2 outlasts emergency funds from the Paycheck Protection and Economic Injury Disaster programs? Do the math – how long can you keep your practice afloat without floating further loans or dipping into personal savings? If you don’t know how many patients you need to see per day to break even, figure it out – now. On what day will you run out of money? When will you start putting your future at risk?
None of us thought we would ever have to face questions like these, of course – and how ironic is it that a medical emergency has forced them upon us? I sincerely hope that none of us will need to actually confront this Hobson’s choice in the coming months, but far better to address the hypothetical now than the reality later. As always, consult with your own attorney, accountant, and other business advisors before making any life-altering decisions.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected]. He has no disclosures.
“There are decades where nothing happens,” wrote Vladimir Lenin, “and there are weeks where decades happen.” Barely a dozen weeks ago, no one knew that the SARS-CoV-2 virus existed. Now, it has spread to almost every country on Earth, infecting over 1.8 million people whom we know about, and many more whom we do not. In so doing, it has crashed economies and health care systems, filled hospitals, emptied public spaces, and separated people from their workplaces and their friends on a scale that few of us have ever witnessed.
It has also triggered an avalanche of questions as to why our initial response was so thoroughly lethargic, rudderless, and uncoordinated; while there is plenty of blame to go around, that is for another time. The glaring question for many – including physicians trying to keep our private practices viable – is: What now?
The answer depends, of course, on how the pandemic plays out. No one yet knows exactly what will happen, but much depends on two properties of the virus, both of which are currently unknown. First: seasonality. Coronaviruses tend to thrive in winter and wane in the summer. That may also be true for SARS-CoV-2, but seasonal variations might not sufficiently slow the virus when it has so many immunologically naive hosts to infect. As I write this in mid-April, we wait anxiously to see what – if anything – summer temperatures do to its transmission in the Northern Hemisphere.
The second wild card is duration of immunity. Determining that will involve developing accurate serologic tests and administering them widely. Immune citizens, once identified, can return to work, care for the vulnerable, and anchor the economy during future outbreaks.
Even if we do get a summer hiatus, seasonal viruses typically return as winter approaches. We could conceivably still be mopping up from this outbreak when the virus – if it is seasonal – comes roaring back in October or November. Will we be ready? Or will it catch us with our pants amidships yet again?
I can envision two possibilities: Assuming we luck into a seasonal reprieve in the next few weeks, infection rates should drop, which could allow our private practices to return toward some semblance of normal – if health workers and patients alike can be convinced that our offices and clinics are safe. This might be accomplished as part of our overall preparation for a potential winter recurrence, by checking every patient’s temperature at the waiting room door. Similarly, all students should get a daily temperature check at school, as should all commuters, airline passengers, and individuals at any sizable gathering. Every fever should trigger a COVID-19 test, and every positive test should launch aggressive contact tracing and quarantines. Meanwhile, treatments and vaccines should get fast-tracked.
That’s what should happen. If it doesn’t, and COVID-19 recurs next winter, worse than before, it is anybody’s guess whether most private medical practices will be able to weather a second onslaught. Further government funding is not assured. We won’t have a vaccine by November. Chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin might turn out to be helpful, but we can’t count on them.
Even if we do get lucky with seasonality, the question remains of how long it will take to restore public confidence and reboot the economy. Economies generally do not function like light switches that can be turned off for a while then simply turned back on, but act more like campfires. If you pour a bucket of water on one, it takes some time to get it cranked up again. After the “Great Recession” of 2008, it took nearly 10 years.
So now, with great reluctance, I must trot out a hoary old cliché: Hope for the best, but plan for the worst. Everyone’s situation will be different, of course, but I can make a few general suggestions. Perform a difficult mental exercise: What will you do if SARS-CoV-2 outlasts emergency funds from the Paycheck Protection and Economic Injury Disaster programs? Do the math – how long can you keep your practice afloat without floating further loans or dipping into personal savings? If you don’t know how many patients you need to see per day to break even, figure it out – now. On what day will you run out of money? When will you start putting your future at risk?
None of us thought we would ever have to face questions like these, of course – and how ironic is it that a medical emergency has forced them upon us? I sincerely hope that none of us will need to actually confront this Hobson’s choice in the coming months, but far better to address the hypothetical now than the reality later. As always, consult with your own attorney, accountant, and other business advisors before making any life-altering decisions.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected]. He has no disclosures.
“There are decades where nothing happens,” wrote Vladimir Lenin, “and there are weeks where decades happen.” Barely a dozen weeks ago, no one knew that the SARS-CoV-2 virus existed. Now, it has spread to almost every country on Earth, infecting over 1.8 million people whom we know about, and many more whom we do not. In so doing, it has crashed economies and health care systems, filled hospitals, emptied public spaces, and separated people from their workplaces and their friends on a scale that few of us have ever witnessed.
It has also triggered an avalanche of questions as to why our initial response was so thoroughly lethargic, rudderless, and uncoordinated; while there is plenty of blame to go around, that is for another time. The glaring question for many – including physicians trying to keep our private practices viable – is: What now?
The answer depends, of course, on how the pandemic plays out. No one yet knows exactly what will happen, but much depends on two properties of the virus, both of which are currently unknown. First: seasonality. Coronaviruses tend to thrive in winter and wane in the summer. That may also be true for SARS-CoV-2, but seasonal variations might not sufficiently slow the virus when it has so many immunologically naive hosts to infect. As I write this in mid-April, we wait anxiously to see what – if anything – summer temperatures do to its transmission in the Northern Hemisphere.
The second wild card is duration of immunity. Determining that will involve developing accurate serologic tests and administering them widely. Immune citizens, once identified, can return to work, care for the vulnerable, and anchor the economy during future outbreaks.
Even if we do get a summer hiatus, seasonal viruses typically return as winter approaches. We could conceivably still be mopping up from this outbreak when the virus – if it is seasonal – comes roaring back in October or November. Will we be ready? Or will it catch us with our pants amidships yet again?
I can envision two possibilities: Assuming we luck into a seasonal reprieve in the next few weeks, infection rates should drop, which could allow our private practices to return toward some semblance of normal – if health workers and patients alike can be convinced that our offices and clinics are safe. This might be accomplished as part of our overall preparation for a potential winter recurrence, by checking every patient’s temperature at the waiting room door. Similarly, all students should get a daily temperature check at school, as should all commuters, airline passengers, and individuals at any sizable gathering. Every fever should trigger a COVID-19 test, and every positive test should launch aggressive contact tracing and quarantines. Meanwhile, treatments and vaccines should get fast-tracked.
That’s what should happen. If it doesn’t, and COVID-19 recurs next winter, worse than before, it is anybody’s guess whether most private medical practices will be able to weather a second onslaught. Further government funding is not assured. We won’t have a vaccine by November. Chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin might turn out to be helpful, but we can’t count on them.
Even if we do get lucky with seasonality, the question remains of how long it will take to restore public confidence and reboot the economy. Economies generally do not function like light switches that can be turned off for a while then simply turned back on, but act more like campfires. If you pour a bucket of water on one, it takes some time to get it cranked up again. After the “Great Recession” of 2008, it took nearly 10 years.
So now, with great reluctance, I must trot out a hoary old cliché: Hope for the best, but plan for the worst. Everyone’s situation will be different, of course, but I can make a few general suggestions. Perform a difficult mental exercise: What will you do if SARS-CoV-2 outlasts emergency funds from the Paycheck Protection and Economic Injury Disaster programs? Do the math – how long can you keep your practice afloat without floating further loans or dipping into personal savings? If you don’t know how many patients you need to see per day to break even, figure it out – now. On what day will you run out of money? When will you start putting your future at risk?
None of us thought we would ever have to face questions like these, of course – and how ironic is it that a medical emergency has forced them upon us? I sincerely hope that none of us will need to actually confront this Hobson’s choice in the coming months, but far better to address the hypothetical now than the reality later. As always, consult with your own attorney, accountant, and other business advisors before making any life-altering decisions.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected]. He has no disclosures.
Doing things right vs. doing the right things
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
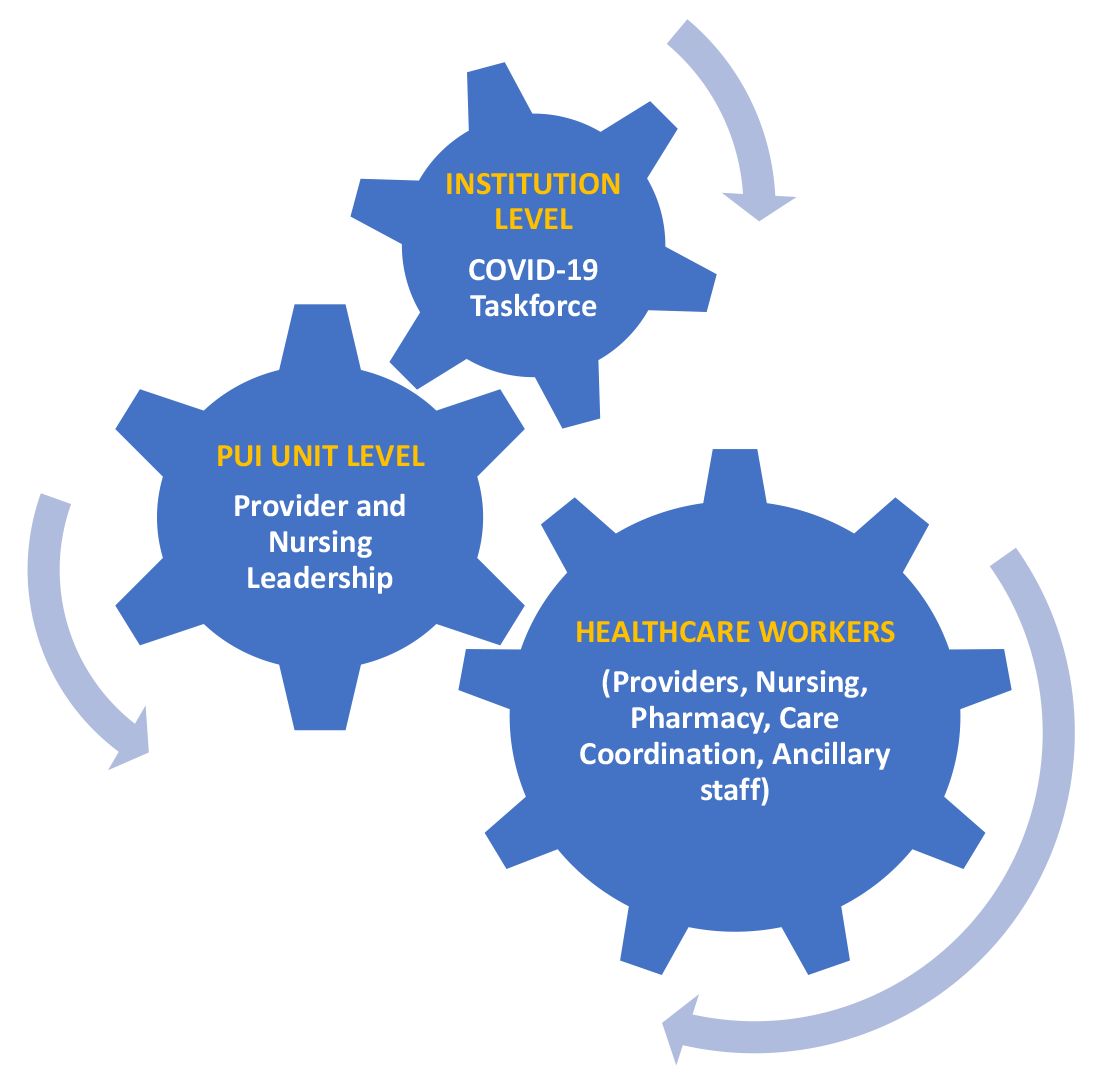
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.)
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.)

Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.)

Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
Can diabetes be cured?
In his Guest Editorial “How to help patients become successful diabetes self-managers” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:8-9), Dr. Unger makes several very good points. I especially liked his recommendation to ask patients why they are concerned about having diabetes; this question alone can kick-start the behavior modification process leading to improved diabetes control.
However, I disagree with Dr. Unger’s assertion that “diabetes cannot be cured.” Based on multiple case studies, clinical trials, results from lifestyle intervention programs, and my own experience as a family physician, it is clear that diabetes can be reversed with lifestyle changes designed to counteract the modifiable factors (eg, diet, lack of exercise) that usually cause this condition.
Rather than merely considering the diabetes measure of success to be blood glucose controlled by prescribed medication, it is important to offer a more collaborative approach to patients willing to make lifestyle changes. We can show many—if not most— that they can achieve the goal of blood glucose control without medication.
Allan Olson MD
Diplomate, American Board of Family Medicine and American Board of Lifestyle Medicine
Kewaunee, WI
In his Guest Editorial “How to help patients become successful diabetes self-managers” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:8-9), Dr. Unger makes several very good points. I especially liked his recommendation to ask patients why they are concerned about having diabetes; this question alone can kick-start the behavior modification process leading to improved diabetes control.
However, I disagree with Dr. Unger’s assertion that “diabetes cannot be cured.” Based on multiple case studies, clinical trials, results from lifestyle intervention programs, and my own experience as a family physician, it is clear that diabetes can be reversed with lifestyle changes designed to counteract the modifiable factors (eg, diet, lack of exercise) that usually cause this condition.
Rather than merely considering the diabetes measure of success to be blood glucose controlled by prescribed medication, it is important to offer a more collaborative approach to patients willing to make lifestyle changes. We can show many—if not most— that they can achieve the goal of blood glucose control without medication.
Allan Olson MD
Diplomate, American Board of Family Medicine and American Board of Lifestyle Medicine
Kewaunee, WI
In his Guest Editorial “How to help patients become successful diabetes self-managers” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:8-9), Dr. Unger makes several very good points. I especially liked his recommendation to ask patients why they are concerned about having diabetes; this question alone can kick-start the behavior modification process leading to improved diabetes control.
However, I disagree with Dr. Unger’s assertion that “diabetes cannot be cured.” Based on multiple case studies, clinical trials, results from lifestyle intervention programs, and my own experience as a family physician, it is clear that diabetes can be reversed with lifestyle changes designed to counteract the modifiable factors (eg, diet, lack of exercise) that usually cause this condition.
Rather than merely considering the diabetes measure of success to be blood glucose controlled by prescribed medication, it is important to offer a more collaborative approach to patients willing to make lifestyle changes. We can show many—if not most— that they can achieve the goal of blood glucose control without medication.
Allan Olson MD
Diplomate, American Board of Family Medicine and American Board of Lifestyle Medicine
Kewaunee, WI
There’s one less weight-loss drug on the market
I would like to provide an update to my article, “10 proven strategies to help patients maintain weight loss” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:20-25), which mentioned lorcaserin as one of several medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for long-term use in weight maintenance. On February 13, 2020, the FDA requested that the manufacturer of Belviq and Belviq XR (lorcaserin), Eisai Inc., voluntarily withdraw the weight-loss drug from the US market because a safety clinical trial demonstrated an increased occurrence of cancer. Eisai Inc. has submitted a request to voluntarily withdraw the drug. The FDA has advised patients to stop taking lorcaserin and talk to their health care provider about alternative weight-loss medicines and weight management programs.
Marijane Hynes, MD
Weight Management Program
The George Washington University
Medical Faculty Associates
Washington, DC
I would like to provide an update to my article, “10 proven strategies to help patients maintain weight loss” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:20-25), which mentioned lorcaserin as one of several medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for long-term use in weight maintenance. On February 13, 2020, the FDA requested that the manufacturer of Belviq and Belviq XR (lorcaserin), Eisai Inc., voluntarily withdraw the weight-loss drug from the US market because a safety clinical trial demonstrated an increased occurrence of cancer. Eisai Inc. has submitted a request to voluntarily withdraw the drug. The FDA has advised patients to stop taking lorcaserin and talk to their health care provider about alternative weight-loss medicines and weight management programs.
Marijane Hynes, MD
Weight Management Program
The George Washington University
Medical Faculty Associates
Washington, DC
I would like to provide an update to my article, “10 proven strategies to help patients maintain weight loss” (J Fam Pract. 2020;69:20-25), which mentioned lorcaserin as one of several medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for long-term use in weight maintenance. On February 13, 2020, the FDA requested that the manufacturer of Belviq and Belviq XR (lorcaserin), Eisai Inc., voluntarily withdraw the weight-loss drug from the US market because a safety clinical trial demonstrated an increased occurrence of cancer. Eisai Inc. has submitted a request to voluntarily withdraw the drug. The FDA has advised patients to stop taking lorcaserin and talk to their health care provider about alternative weight-loss medicines and weight management programs.
Marijane Hynes, MD
Weight Management Program
The George Washington University
Medical Faculty Associates
Washington, DC
The 7 strategies of highly effective people facing the COVID-19 pandemic
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
Learning to live with COVID-19: Postpandemic life will be reflected in how effectively we leverage this crisis
While often compared with the Spanish influenza contagion of 1918, the current COVID-19 pandemic is arguably unprecedented in scale and scope, global reach, and the rate at which it has spread across the world.
Unprecedented times
The United States now has the greatest burden of COVID-19 disease worldwide.1 Although Boston has thus far been spared the full force of the disease’s impact, it is likely only a matter of time before it reaches here. To prepare for the imminent surge, we at Tufts Medical Center defined 4 short-term strategic imperatives to help guide our COVID-19 preparedness. Having a single unified strategy across our organization has helped to maintain focus and consistency in the messaging amidst all of the uncertainty. Our focus areas are outlined below.
1 Flatten the curve
This term refers to the use of “social distancing” and community isolation measures to keep the number of disease cases at a manageable level. COVID-19 is spread almost exclusively through contact with contaminated respiratory droplets. While several categories of risk have been described, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines disease “exposure” as face-to-face contact within 6 feet of an infected individual for more than 15 minutes without wearing a mask.2 Intervening at all 3 of these touchpoints effectively reduces transmission. Interventions include limiting in-person meetings, increasing the space between individuals (both providers and patients), and routinely using personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another effective strategy is to divide frontline providers into smaller units or teams to limit cross-contamination: the inpatient team versus the outpatient team, the day team versus the night team, the “on” team versus the “off” team. If the infection lays one team low, other providers can step in until they recover and return to work.
Visitor policies should be developed and strictly implemented. Many institutions do allow one support person in labor and delivery (L&D) regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status, although that person should not be symptomatic or COVID-19 positive. Whether to test all patients and support persons for COVID-19 on arrival at L&D remains controversial.3 At a minimum, these individuals should be screened for symptoms. Although it was a major focus of initial preventative efforts, taking a travel and exposure history is no longer informative as the virus is now endemic and community spread is common.
Initial preventative efforts focused also on high-risk patients, but routine use of PPE for all encounters clearly is more effective because of the high rate of asymptomatic shedding. The virus can survive suspended in the air for up to 2 hours following an aerosol-generating procedure (AGP) and on surfaces for several hours or even days. Practices such as regular handwashing, cleaning of exposed work surfaces, and avoiding face touching should by now be part of our everyday routine.
Institutions throughout the United States have established inpatient COVID-19 units—so-called “dirty” units—with mixed success. As the pandemic spreads and the number of patients with asymptomatic shedding increases, it is harder to determine who is and who is not infected. Cross-contamination has rendered this approach largely ineffective. Whether this will change with the introduction of rapid point-of-care testing remains to be seen.
Continue to: 2 Preserve PPE...
2 Preserve PPE
PPE use is effective in reducing transmission. This includes tier 1 PPE with or without enhanced droplet precaution (surgical mask, eye protection, gloves, yellow gown) and tier 2 PPE (tier 1 plus N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators [PAPR]). Given the acute PPE shortage in many parts of the country, appropriate use of PPE is critical to maintain an adequate supply. For example, tier 2 PPE is required only in the setting of an AGP. This includes intubation and, in our determination, the second stage of labor for COVID-19–positive patients and patients under investigation (PUIs); we do not employ tier 2 PPE for all patients in the second stage of labor, although some hospitals endorse this practice.
Creative solutions to the impending PPE shortage abound, such as the use of 3D printers to make face shields and novel techniques to sterilize and reuse N95 respirators.
3 Create capacity
In the absence of effective treatment for COVID-19 and with a vaccine still many months away, supportive care is critical. The pulmonary sequelae with cytokine storm and acute hypoxemia can come on quickly, require urgent mechanical ventilatory support, and take several weeks to resolve.
Our ability to create inpatient capacity to accommodate ill patients, monitor them closely, and intubate early will likely be the most critical driver of the case fatality rate. This requires deferring outpatient visits (or doing them via telemedicine), expanding intensive care unit capabilities (especially ventilator beds), and canceling elective surgeries. What constitutes “elective surgery” is not always clear. Our institution, for example, regards abortion services as essential and not elective, but this is not the case throughout the United States.
Creating capacity also refers to staffing. Where necessary, providers should be retrained and redeployed. This may require emergency credentialing of providers in areas outside their usual clinical practice and permission may be needed from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education to engage trainees outside their usual duty hours.
4 Support and protect your workforce
Everyone is anxious, and people convey their anxiety in different ways. I have found it helpful to acknowledge those feelings and provide a forum for staff to express and share their anxieties. That said, hospitals are not a democracy. While staff members should be encouraged to ask questions and voice their opinions, everyone is expected to follow protocol regarding patient care.
Celebrating small successes and finding creative ways to alleviate the stress and inject humor can help. Most institutions are using electronic conferencing platforms (such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams) to stay in touch and to continue education initiatives through interactive didactic sessions, grand rounds, morbidity and mortality conferences, and e-journal clubs. These are also a great platform for social events, such as w(h)ine and book clubs and virtual karaoke.
Since many ObGyn providers are women, the closure of day-care centers and schools is particularly challenging. Share best practices among your staff on how to address this problem, such as alternating on-call shifts or matching providers needing day care with ‘furloughed’ college students who are looking to keep busy and make a little money.
Continue to: Avoid overcommunicating...
Avoid overcommunicating
Clear, concise, and timely communication is key. This can be challenging given the rapidly evolving science of COVID-19 and the daily barrage of information from both reliable and unreliable sources. Setting up regular online meetings with your faculty 2 or 3 times per week can keep people informed, promote engagement, and boost morale.
If an urgent e-mail announcement is needed, keep the message focused. Highlight only updated information and changes to existing policies and guidelines. And consider adding a brief anecdote to illustrate the staff’s creativity and resilience: a “best catch” story, for example, or a staff member who started a “commit to sit” program (spending time in the room with patients who want company but are not able to have their family in attendance).
Look to the future
COVID-19 will pass. Herd immunity will inevitably develop. The question is how quickly and at what cost. Children delivered today are being born into a society already profoundly altered by COVID-19. Some have started to call them Generation C.
Exactly what life will look like at the back end of this pandemic depends on how effectively we leverage this crisis. There are numerous opportunities to change the way we think about health care and educate the next generation of providers. These include increasing the use of telehealth and remote education, redesigning our traditional prenatal care paradigms, and reinforcing the importance of preventive medicine. This is an opportunity to put the “health” back into “health care.”
Look after yourself
Amid all the chaos and uncertainty, do not forget to take care of yourself and your family. Be calm, be kind, and be flexible. Stay safe.
- Kommenda N, Gutierrez P, Adolphe J. Coronavirus world map: which countries have the most cases and deaths? The Guardian. April 1, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/31/coronavirus-mapped-which-countries-have-the-most-cases-and-deaths. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Interim US guidance for risk assessment and public health management of healthcare personnel with potential exposure in a healthcare setting to patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/guidance-risk-assesment-hcp.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Evaluating and testing persons for coronavirus disease 2020 (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/hcp/clinical-criteria.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
While often compared with the Spanish influenza contagion of 1918, the current COVID-19 pandemic is arguably unprecedented in scale and scope, global reach, and the rate at which it has spread across the world.
Unprecedented times
The United States now has the greatest burden of COVID-19 disease worldwide.1 Although Boston has thus far been spared the full force of the disease’s impact, it is likely only a matter of time before it reaches here. To prepare for the imminent surge, we at Tufts Medical Center defined 4 short-term strategic imperatives to help guide our COVID-19 preparedness. Having a single unified strategy across our organization has helped to maintain focus and consistency in the messaging amidst all of the uncertainty. Our focus areas are outlined below.
1 Flatten the curve
This term refers to the use of “social distancing” and community isolation measures to keep the number of disease cases at a manageable level. COVID-19 is spread almost exclusively through contact with contaminated respiratory droplets. While several categories of risk have been described, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines disease “exposure” as face-to-face contact within 6 feet of an infected individual for more than 15 minutes without wearing a mask.2 Intervening at all 3 of these touchpoints effectively reduces transmission. Interventions include limiting in-person meetings, increasing the space between individuals (both providers and patients), and routinely using personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another effective strategy is to divide frontline providers into smaller units or teams to limit cross-contamination: the inpatient team versus the outpatient team, the day team versus the night team, the “on” team versus the “off” team. If the infection lays one team low, other providers can step in until they recover and return to work.
Visitor policies should be developed and strictly implemented. Many institutions do allow one support person in labor and delivery (L&D) regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status, although that person should not be symptomatic or COVID-19 positive. Whether to test all patients and support persons for COVID-19 on arrival at L&D remains controversial.3 At a minimum, these individuals should be screened for symptoms. Although it was a major focus of initial preventative efforts, taking a travel and exposure history is no longer informative as the virus is now endemic and community spread is common.
Initial preventative efforts focused also on high-risk patients, but routine use of PPE for all encounters clearly is more effective because of the high rate of asymptomatic shedding. The virus can survive suspended in the air for up to 2 hours following an aerosol-generating procedure (AGP) and on surfaces for several hours or even days. Practices such as regular handwashing, cleaning of exposed work surfaces, and avoiding face touching should by now be part of our everyday routine.
Institutions throughout the United States have established inpatient COVID-19 units—so-called “dirty” units—with mixed success. As the pandemic spreads and the number of patients with asymptomatic shedding increases, it is harder to determine who is and who is not infected. Cross-contamination has rendered this approach largely ineffective. Whether this will change with the introduction of rapid point-of-care testing remains to be seen.
Continue to: 2 Preserve PPE...
2 Preserve PPE
PPE use is effective in reducing transmission. This includes tier 1 PPE with or without enhanced droplet precaution (surgical mask, eye protection, gloves, yellow gown) and tier 2 PPE (tier 1 plus N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators [PAPR]). Given the acute PPE shortage in many parts of the country, appropriate use of PPE is critical to maintain an adequate supply. For example, tier 2 PPE is required only in the setting of an AGP. This includes intubation and, in our determination, the second stage of labor for COVID-19–positive patients and patients under investigation (PUIs); we do not employ tier 2 PPE for all patients in the second stage of labor, although some hospitals endorse this practice.
Creative solutions to the impending PPE shortage abound, such as the use of 3D printers to make face shields and novel techniques to sterilize and reuse N95 respirators.
3 Create capacity
In the absence of effective treatment for COVID-19 and with a vaccine still many months away, supportive care is critical. The pulmonary sequelae with cytokine storm and acute hypoxemia can come on quickly, require urgent mechanical ventilatory support, and take several weeks to resolve.
Our ability to create inpatient capacity to accommodate ill patients, monitor them closely, and intubate early will likely be the most critical driver of the case fatality rate. This requires deferring outpatient visits (or doing them via telemedicine), expanding intensive care unit capabilities (especially ventilator beds), and canceling elective surgeries. What constitutes “elective surgery” is not always clear. Our institution, for example, regards abortion services as essential and not elective, but this is not the case throughout the United States.
Creating capacity also refers to staffing. Where necessary, providers should be retrained and redeployed. This may require emergency credentialing of providers in areas outside their usual clinical practice and permission may be needed from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education to engage trainees outside their usual duty hours.
4 Support and protect your workforce
Everyone is anxious, and people convey their anxiety in different ways. I have found it helpful to acknowledge those feelings and provide a forum for staff to express and share their anxieties. That said, hospitals are not a democracy. While staff members should be encouraged to ask questions and voice their opinions, everyone is expected to follow protocol regarding patient care.
Celebrating small successes and finding creative ways to alleviate the stress and inject humor can help. Most institutions are using electronic conferencing platforms (such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams) to stay in touch and to continue education initiatives through interactive didactic sessions, grand rounds, morbidity and mortality conferences, and e-journal clubs. These are also a great platform for social events, such as w(h)ine and book clubs and virtual karaoke.
Since many ObGyn providers are women, the closure of day-care centers and schools is particularly challenging. Share best practices among your staff on how to address this problem, such as alternating on-call shifts or matching providers needing day care with ‘furloughed’ college students who are looking to keep busy and make a little money.
Continue to: Avoid overcommunicating...
Avoid overcommunicating
Clear, concise, and timely communication is key. This can be challenging given the rapidly evolving science of COVID-19 and the daily barrage of information from both reliable and unreliable sources. Setting up regular online meetings with your faculty 2 or 3 times per week can keep people informed, promote engagement, and boost morale.
If an urgent e-mail announcement is needed, keep the message focused. Highlight only updated information and changes to existing policies and guidelines. And consider adding a brief anecdote to illustrate the staff’s creativity and resilience: a “best catch” story, for example, or a staff member who started a “commit to sit” program (spending time in the room with patients who want company but are not able to have their family in attendance).
Look to the future
COVID-19 will pass. Herd immunity will inevitably develop. The question is how quickly and at what cost. Children delivered today are being born into a society already profoundly altered by COVID-19. Some have started to call them Generation C.
Exactly what life will look like at the back end of this pandemic depends on how effectively we leverage this crisis. There are numerous opportunities to change the way we think about health care and educate the next generation of providers. These include increasing the use of telehealth and remote education, redesigning our traditional prenatal care paradigms, and reinforcing the importance of preventive medicine. This is an opportunity to put the “health” back into “health care.”
Look after yourself
Amid all the chaos and uncertainty, do not forget to take care of yourself and your family. Be calm, be kind, and be flexible. Stay safe.
While often compared with the Spanish influenza contagion of 1918, the current COVID-19 pandemic is arguably unprecedented in scale and scope, global reach, and the rate at which it has spread across the world.
Unprecedented times
The United States now has the greatest burden of COVID-19 disease worldwide.1 Although Boston has thus far been spared the full force of the disease’s impact, it is likely only a matter of time before it reaches here. To prepare for the imminent surge, we at Tufts Medical Center defined 4 short-term strategic imperatives to help guide our COVID-19 preparedness. Having a single unified strategy across our organization has helped to maintain focus and consistency in the messaging amidst all of the uncertainty. Our focus areas are outlined below.
1 Flatten the curve
This term refers to the use of “social distancing” and community isolation measures to keep the number of disease cases at a manageable level. COVID-19 is spread almost exclusively through contact with contaminated respiratory droplets. While several categories of risk have been described, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines disease “exposure” as face-to-face contact within 6 feet of an infected individual for more than 15 minutes without wearing a mask.2 Intervening at all 3 of these touchpoints effectively reduces transmission. Interventions include limiting in-person meetings, increasing the space between individuals (both providers and patients), and routinely using personal protective equipment (PPE).
Another effective strategy is to divide frontline providers into smaller units or teams to limit cross-contamination: the inpatient team versus the outpatient team, the day team versus the night team, the “on” team versus the “off” team. If the infection lays one team low, other providers can step in until they recover and return to work.
Visitor policies should be developed and strictly implemented. Many institutions do allow one support person in labor and delivery (L&D) regardless of the patient’s COVID-19 status, although that person should not be symptomatic or COVID-19 positive. Whether to test all patients and support persons for COVID-19 on arrival at L&D remains controversial.3 At a minimum, these individuals should be screened for symptoms. Although it was a major focus of initial preventative efforts, taking a travel and exposure history is no longer informative as the virus is now endemic and community spread is common.
Initial preventative efforts focused also on high-risk patients, but routine use of PPE for all encounters clearly is more effective because of the high rate of asymptomatic shedding. The virus can survive suspended in the air for up to 2 hours following an aerosol-generating procedure (AGP) and on surfaces for several hours or even days. Practices such as regular handwashing, cleaning of exposed work surfaces, and avoiding face touching should by now be part of our everyday routine.
Institutions throughout the United States have established inpatient COVID-19 units—so-called “dirty” units—with mixed success. As the pandemic spreads and the number of patients with asymptomatic shedding increases, it is harder to determine who is and who is not infected. Cross-contamination has rendered this approach largely ineffective. Whether this will change with the introduction of rapid point-of-care testing remains to be seen.
Continue to: 2 Preserve PPE...
2 Preserve PPE
PPE use is effective in reducing transmission. This includes tier 1 PPE with or without enhanced droplet precaution (surgical mask, eye protection, gloves, yellow gown) and tier 2 PPE (tier 1 plus N95 respirators or powered air-purifying respirators [PAPR]). Given the acute PPE shortage in many parts of the country, appropriate use of PPE is critical to maintain an adequate supply. For example, tier 2 PPE is required only in the setting of an AGP. This includes intubation and, in our determination, the second stage of labor for COVID-19–positive patients and patients under investigation (PUIs); we do not employ tier 2 PPE for all patients in the second stage of labor, although some hospitals endorse this practice.
Creative solutions to the impending PPE shortage abound, such as the use of 3D printers to make face shields and novel techniques to sterilize and reuse N95 respirators.
3 Create capacity
In the absence of effective treatment for COVID-19 and with a vaccine still many months away, supportive care is critical. The pulmonary sequelae with cytokine storm and acute hypoxemia can come on quickly, require urgent mechanical ventilatory support, and take several weeks to resolve.
Our ability to create inpatient capacity to accommodate ill patients, monitor them closely, and intubate early will likely be the most critical driver of the case fatality rate. This requires deferring outpatient visits (or doing them via telemedicine), expanding intensive care unit capabilities (especially ventilator beds), and canceling elective surgeries. What constitutes “elective surgery” is not always clear. Our institution, for example, regards abortion services as essential and not elective, but this is not the case throughout the United States.
Creating capacity also refers to staffing. Where necessary, providers should be retrained and redeployed. This may require emergency credentialing of providers in areas outside their usual clinical practice and permission may be needed from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education to engage trainees outside their usual duty hours.
4 Support and protect your workforce
Everyone is anxious, and people convey their anxiety in different ways. I have found it helpful to acknowledge those feelings and provide a forum for staff to express and share their anxieties. That said, hospitals are not a democracy. While staff members should be encouraged to ask questions and voice their opinions, everyone is expected to follow protocol regarding patient care.
Celebrating small successes and finding creative ways to alleviate the stress and inject humor can help. Most institutions are using electronic conferencing platforms (such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams) to stay in touch and to continue education initiatives through interactive didactic sessions, grand rounds, morbidity and mortality conferences, and e-journal clubs. These are also a great platform for social events, such as w(h)ine and book clubs and virtual karaoke.
Since many ObGyn providers are women, the closure of day-care centers and schools is particularly challenging. Share best practices among your staff on how to address this problem, such as alternating on-call shifts or matching providers needing day care with ‘furloughed’ college students who are looking to keep busy and make a little money.
Continue to: Avoid overcommunicating...
Avoid overcommunicating
Clear, concise, and timely communication is key. This can be challenging given the rapidly evolving science of COVID-19 and the daily barrage of information from both reliable and unreliable sources. Setting up regular online meetings with your faculty 2 or 3 times per week can keep people informed, promote engagement, and boost morale.
If an urgent e-mail announcement is needed, keep the message focused. Highlight only updated information and changes to existing policies and guidelines. And consider adding a brief anecdote to illustrate the staff’s creativity and resilience: a “best catch” story, for example, or a staff member who started a “commit to sit” program (spending time in the room with patients who want company but are not able to have their family in attendance).
Look to the future
COVID-19 will pass. Herd immunity will inevitably develop. The question is how quickly and at what cost. Children delivered today are being born into a society already profoundly altered by COVID-19. Some have started to call them Generation C.
Exactly what life will look like at the back end of this pandemic depends on how effectively we leverage this crisis. There are numerous opportunities to change the way we think about health care and educate the next generation of providers. These include increasing the use of telehealth and remote education, redesigning our traditional prenatal care paradigms, and reinforcing the importance of preventive medicine. This is an opportunity to put the “health” back into “health care.”
Look after yourself
Amid all the chaos and uncertainty, do not forget to take care of yourself and your family. Be calm, be kind, and be flexible. Stay safe.
- Kommenda N, Gutierrez P, Adolphe J. Coronavirus world map: which countries have the most cases and deaths? The Guardian. April 1, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/31/coronavirus-mapped-which-countries-have-the-most-cases-and-deaths. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Interim US guidance for risk assessment and public health management of healthcare personnel with potential exposure in a healthcare setting to patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/guidance-risk-assesment-hcp.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Evaluating and testing persons for coronavirus disease 2020 (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/hcp/clinical-criteria.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Kommenda N, Gutierrez P, Adolphe J. Coronavirus world map: which countries have the most cases and deaths? The Guardian. April 1, 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/31/coronavirus-mapped-which-countries-have-the-most-cases-and-deaths. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Interim US guidance for risk assessment and public health management of healthcare personnel with potential exposure in a healthcare setting to patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/guidance-risk-assesment-hcp.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Evaluating and testing persons for coronavirus disease 2020 (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/hcp/clinical-criteria.html. Accessed April 1, 2020.
Crisis counseling, not therapy, is what’s needed in the wake of COVID-19
In the wake of the attacks on the World Trade Center, the public mental health system in the New York City area mounted the largest mental health disaster response in history. I was New York City’s mental health commissioner at the time. We called the initiative Project Liberty and over 3 years obtained $137 million in funding from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to support it.
Through Project Liberty, New York established the Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training Program (CCP). And it didn’t take us long to realize that what affected people need following a disaster is not necessarily psychotherapy, as might be expected, but in fact crisis counseling, or helping impacted individuals and their families regain control of their anxieties and effectively respond to an immediate disaster. This proved true not only after 9/11 but also after other recent disasters, including hurricanes Katrina and Sandy. The mental health system must now step up again to assuage fears and anxieties—both individual and collective—around the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic.
So, what is crisis counseling?
A person’s usual adaptive, problem-solving capabilities are often compromised after a disaster, but they are there, and if accessed, they can help those afflicted with mental symptoms following a crisis to mentally endure. thereby making it a different approach from traditional psychotherapy.
The five key concepts in crisis counseling are:
- It is strength-based, which means its foundation is rooted in the assumption that resilience and competence are innate human qualities.
- Crisis counseling also employs anonymity. Impacted individuals should not be diagnosed or labeled. As a result, there are no resulting medical records.
- The approach is outreach-oriented, in which counselors provide services out in the community rather than in traditional mental health settings. This occurs primarily in homes, community centers, and settings, as well as in disaster shelters.
- It is culturally attuned, whereby all staff appreciate and respect a community’s cultural beliefs, values, and primary language.
- It is aimed at supporting, not replacing, existing community support systems (eg, a crisis counselor supports but does not organize, deliver, or manage community recovery activities).
Crisis counselors are required to be licensed psychologists or have obtained a bachelor’s degree or higher in psychology, human services, or another health-related field. In other words, crisis counseling draws on a broad, though related, group of individuals. Before deployment into a disaster area, an applicant must complete the FEMA Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training, which is offered in the disaster area by the FEMA-funded CCP.
Crisis counselors provide trustworthy and actionable information about the disaster at hand and where to turn for resources and assistance. They assist with emotional support. And they aim to educate individuals, families, and communities about how to be resilient.
Crisis counseling, however, may not suffice for everyone impacted. We know that a person’s severity of response to a crisis is highly associated with the intensity and duration of exposure to the disaster (especially when it is life-threatening) and/or the degree of a person’s serious loss (of a loved one, home, job, health). We also know that previous trauma (eg, from childhood, domestic violence, or forced immigration) also predicts the gravity of the response to a current crisis. Which is why crisis counselors also are taught to identify those experiencing significant and persistent mental health and addiction problems because they need to be assisted, literally, in obtaining professional treatment.
Only in recent years has trauma been a recognized driver of stress, distress, and mental and addictive disorders. Until relatively recently, skill with, and access to, crisis counseling—and trauma-informed care—was rare among New York’s large and talented mental health professional community. Few had been trained in it in graduate school or practiced it because New York had been spared a disaster on par with 9/11. Following the attacks, Project Liberty’s programs served nearly 1.5 million affected individuals of very diverse ages, races, cultural backgrounds, and socioeconomic status. Their levels of “psychological distress,” the term we used and measured, ranged from low to very high.
The coronavirus pandemic now presents us with a tragically similar, catastrophic moment. The human consequences we face—psychologically, economically, and socially—are just beginning. But this time, the need is not just in New York but throughout our country.
We humans are resilient. We can bend the arc of crisis toward the light, to recovering our existing but overwhelmed capabilities. We can achieve this in a variety of ways. We can practice self-care. This isn’t an act of selfishness but is rather like putting on your own oxygen mask before trying to help your friend or loved one do the same. We can stay connected to the people we care about. We can eat well, get sufficient sleep, take a walk.
Identifying and pursuing practical goals is also important, like obtaining food, housing that is safe and reliable, transportation to where you need to go, and drawing upon financial and other resources that are issued in a disaster area. We can practice positive thinking and recall how we’ve mastered our troubles in the past; we can remind ourselves that “this too will pass.” Crises create an unusually opportune time for change and self-discovery. As Churchill said to the British people in the darkest moments of the start of World War II, “Never give up.”
Worthy of its own itemization are spiritual beliefs, faith—that however we think about a higher power (religious or secular), that power is on our side. Faith can comfort and sustain hope, particularly at a time when doubt about ourselves and humanity is triggered by disaster.
Maya Angelou’s words remind us at this moment of disaster: “...let us try to help before we have to offer therapy. That is to say, let’s see if we can’t prevent being ill by trying to offer a love of prevention before illness.”
Dr. Sederer is the former chief medical officer for the New York State Office of Mental Health and an adjunct professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the Columbia University School of Public Health. His latest book is The Addiction Solution: Treating Our Dependence on Opioids and Other Drugs.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the attacks on the World Trade Center, the public mental health system in the New York City area mounted the largest mental health disaster response in history. I was New York City’s mental health commissioner at the time. We called the initiative Project Liberty and over 3 years obtained $137 million in funding from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to support it.
Through Project Liberty, New York established the Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training Program (CCP). And it didn’t take us long to realize that what affected people need following a disaster is not necessarily psychotherapy, as might be expected, but in fact crisis counseling, or helping impacted individuals and their families regain control of their anxieties and effectively respond to an immediate disaster. This proved true not only after 9/11 but also after other recent disasters, including hurricanes Katrina and Sandy. The mental health system must now step up again to assuage fears and anxieties—both individual and collective—around the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic.
So, what is crisis counseling?
A person’s usual adaptive, problem-solving capabilities are often compromised after a disaster, but they are there, and if accessed, they can help those afflicted with mental symptoms following a crisis to mentally endure. thereby making it a different approach from traditional psychotherapy.
The five key concepts in crisis counseling are:
- It is strength-based, which means its foundation is rooted in the assumption that resilience and competence are innate human qualities.
- Crisis counseling also employs anonymity. Impacted individuals should not be diagnosed or labeled. As a result, there are no resulting medical records.
- The approach is outreach-oriented, in which counselors provide services out in the community rather than in traditional mental health settings. This occurs primarily in homes, community centers, and settings, as well as in disaster shelters.
- It is culturally attuned, whereby all staff appreciate and respect a community’s cultural beliefs, values, and primary language.
- It is aimed at supporting, not replacing, existing community support systems (eg, a crisis counselor supports but does not organize, deliver, or manage community recovery activities).
Crisis counselors are required to be licensed psychologists or have obtained a bachelor’s degree or higher in psychology, human services, or another health-related field. In other words, crisis counseling draws on a broad, though related, group of individuals. Before deployment into a disaster area, an applicant must complete the FEMA Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training, which is offered in the disaster area by the FEMA-funded CCP.
Crisis counselors provide trustworthy and actionable information about the disaster at hand and where to turn for resources and assistance. They assist with emotional support. And they aim to educate individuals, families, and communities about how to be resilient.
Crisis counseling, however, may not suffice for everyone impacted. We know that a person’s severity of response to a crisis is highly associated with the intensity and duration of exposure to the disaster (especially when it is life-threatening) and/or the degree of a person’s serious loss (of a loved one, home, job, health). We also know that previous trauma (eg, from childhood, domestic violence, or forced immigration) also predicts the gravity of the response to a current crisis. Which is why crisis counselors also are taught to identify those experiencing significant and persistent mental health and addiction problems because they need to be assisted, literally, in obtaining professional treatment.
Only in recent years has trauma been a recognized driver of stress, distress, and mental and addictive disorders. Until relatively recently, skill with, and access to, crisis counseling—and trauma-informed care—was rare among New York’s large and talented mental health professional community. Few had been trained in it in graduate school or practiced it because New York had been spared a disaster on par with 9/11. Following the attacks, Project Liberty’s programs served nearly 1.5 million affected individuals of very diverse ages, races, cultural backgrounds, and socioeconomic status. Their levels of “psychological distress,” the term we used and measured, ranged from low to very high.
The coronavirus pandemic now presents us with a tragically similar, catastrophic moment. The human consequences we face—psychologically, economically, and socially—are just beginning. But this time, the need is not just in New York but throughout our country.
We humans are resilient. We can bend the arc of crisis toward the light, to recovering our existing but overwhelmed capabilities. We can achieve this in a variety of ways. We can practice self-care. This isn’t an act of selfishness but is rather like putting on your own oxygen mask before trying to help your friend or loved one do the same. We can stay connected to the people we care about. We can eat well, get sufficient sleep, take a walk.
Identifying and pursuing practical goals is also important, like obtaining food, housing that is safe and reliable, transportation to where you need to go, and drawing upon financial and other resources that are issued in a disaster area. We can practice positive thinking and recall how we’ve mastered our troubles in the past; we can remind ourselves that “this too will pass.” Crises create an unusually opportune time for change and self-discovery. As Churchill said to the British people in the darkest moments of the start of World War II, “Never give up.”
Worthy of its own itemization are spiritual beliefs, faith—that however we think about a higher power (religious or secular), that power is on our side. Faith can comfort and sustain hope, particularly at a time when doubt about ourselves and humanity is triggered by disaster.
Maya Angelou’s words remind us at this moment of disaster: “...let us try to help before we have to offer therapy. That is to say, let’s see if we can’t prevent being ill by trying to offer a love of prevention before illness.”
Dr. Sederer is the former chief medical officer for the New York State Office of Mental Health and an adjunct professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the Columbia University School of Public Health. His latest book is The Addiction Solution: Treating Our Dependence on Opioids and Other Drugs.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the attacks on the World Trade Center, the public mental health system in the New York City area mounted the largest mental health disaster response in history. I was New York City’s mental health commissioner at the time. We called the initiative Project Liberty and over 3 years obtained $137 million in funding from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to support it.
Through Project Liberty, New York established the Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training Program (CCP). And it didn’t take us long to realize that what affected people need following a disaster is not necessarily psychotherapy, as might be expected, but in fact crisis counseling, or helping impacted individuals and their families regain control of their anxieties and effectively respond to an immediate disaster. This proved true not only after 9/11 but also after other recent disasters, including hurricanes Katrina and Sandy. The mental health system must now step up again to assuage fears and anxieties—both individual and collective—around the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic.
So, what is crisis counseling?
A person’s usual adaptive, problem-solving capabilities are often compromised after a disaster, but they are there, and if accessed, they can help those afflicted with mental symptoms following a crisis to mentally endure. thereby making it a different approach from traditional psychotherapy.
The five key concepts in crisis counseling are:
- It is strength-based, which means its foundation is rooted in the assumption that resilience and competence are innate human qualities.
- Crisis counseling also employs anonymity. Impacted individuals should not be diagnosed or labeled. As a result, there are no resulting medical records.
- The approach is outreach-oriented, in which counselors provide services out in the community rather than in traditional mental health settings. This occurs primarily in homes, community centers, and settings, as well as in disaster shelters.
- It is culturally attuned, whereby all staff appreciate and respect a community’s cultural beliefs, values, and primary language.
- It is aimed at supporting, not replacing, existing community support systems (eg, a crisis counselor supports but does not organize, deliver, or manage community recovery activities).
Crisis counselors are required to be licensed psychologists or have obtained a bachelor’s degree or higher in psychology, human services, or another health-related field. In other words, crisis counseling draws on a broad, though related, group of individuals. Before deployment into a disaster area, an applicant must complete the FEMA Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training, which is offered in the disaster area by the FEMA-funded CCP.
Crisis counselors provide trustworthy and actionable information about the disaster at hand and where to turn for resources and assistance. They assist with emotional support. And they aim to educate individuals, families, and communities about how to be resilient.
Crisis counseling, however, may not suffice for everyone impacted. We know that a person’s severity of response to a crisis is highly associated with the intensity and duration of exposure to the disaster (especially when it is life-threatening) and/or the degree of a person’s serious loss (of a loved one, home, job, health). We also know that previous trauma (eg, from childhood, domestic violence, or forced immigration) also predicts the gravity of the response to a current crisis. Which is why crisis counselors also are taught to identify those experiencing significant and persistent mental health and addiction problems because they need to be assisted, literally, in obtaining professional treatment.
Only in recent years has trauma been a recognized driver of stress, distress, and mental and addictive disorders. Until relatively recently, skill with, and access to, crisis counseling—and trauma-informed care—was rare among New York’s large and talented mental health professional community. Few had been trained in it in graduate school or practiced it because New York had been spared a disaster on par with 9/11. Following the attacks, Project Liberty’s programs served nearly 1.5 million affected individuals of very diverse ages, races, cultural backgrounds, and socioeconomic status. Their levels of “psychological distress,” the term we used and measured, ranged from low to very high.
The coronavirus pandemic now presents us with a tragically similar, catastrophic moment. The human consequences we face—psychologically, economically, and socially—are just beginning. But this time, the need is not just in New York but throughout our country.
We humans are resilient. We can bend the arc of crisis toward the light, to recovering our existing but overwhelmed capabilities. We can achieve this in a variety of ways. We can practice self-care. This isn’t an act of selfishness but is rather like putting on your own oxygen mask before trying to help your friend or loved one do the same. We can stay connected to the people we care about. We can eat well, get sufficient sleep, take a walk.
Identifying and pursuing practical goals is also important, like obtaining food, housing that is safe and reliable, transportation to where you need to go, and drawing upon financial and other resources that are issued in a disaster area. We can practice positive thinking and recall how we’ve mastered our troubles in the past; we can remind ourselves that “this too will pass.” Crises create an unusually opportune time for change and self-discovery. As Churchill said to the British people in the darkest moments of the start of World War II, “Never give up.”
Worthy of its own itemization are spiritual beliefs, faith—that however we think about a higher power (religious or secular), that power is on our side. Faith can comfort and sustain hope, particularly at a time when doubt about ourselves and humanity is triggered by disaster.
Maya Angelou’s words remind us at this moment of disaster: “...let us try to help before we have to offer therapy. That is to say, let’s see if we can’t prevent being ill by trying to offer a love of prevention before illness.”
Dr. Sederer is the former chief medical officer for the New York State Office of Mental Health and an adjunct professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the Columbia University School of Public Health. His latest book is The Addiction Solution: Treating Our Dependence on Opioids and Other Drugs.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Abortion is essential health care
In my New Mexico reproductive health clinic one week in early April, I saw more than twice the number of patients usually scheduled, all seeking abortion care. Two-thirds of those patients were from Texas – some came from towns as close as 6 hours away, and at least two drove for more than 11 hours to receive care at our clinic. In addition to the many reasons women pursue abortion care, all of my patients had an overriding concern about the COVID-19 pandemic. Many worried for the safety of their parents and children; some worried about the safety of continuing a pregnancy during the pandemic; and many were worried for themselves because of the risk involved in their employment or their status as the sole breadwinner for their families. One patient chose an abortion for severe fetal anomalies diagnosed in the early second trimester; she had an appointment with a provider in Texas, which was canceled the day the Texas abortion ban was reinstated. New Mexico, more than 10 hours away, was the closest location to receive the care she needed; she traveled by car with her children.
I am fortunate to live in New Mexico. On March 24, New Mexico Secretary of Health Kathyleen “Kathy” Kunkel affirmed reproductive health care as an essential service. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the U.S. professional organization for reproductive health care, agrees. In a joint statement with seven other professional organizations, they emphasize the importance of abortion access: “Abortion is an essential component of comprehensive health care. It is also a time-sensitive service. The consequences of being unable to obtain an abortion profoundly impact a person’s life, health, and well-being.”
Anti-abortion politicians are using the crisis as an opportunity to restrict health care access as they have done for my patients who have driven hundreds of miles for essential care they should receive in their home communities. My heart goes out to our patients and the burden they have been forced to take on at a time when our politicians should be protecting and ensuring their safety.
Dr. Espey is an obstetrician and gynecologist in New Mexico. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Espey is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News Editorial Advisory Board. Email her at [email protected].
In my New Mexico reproductive health clinic one week in early April, I saw more than twice the number of patients usually scheduled, all seeking abortion care. Two-thirds of those patients were from Texas – some came from towns as close as 6 hours away, and at least two drove for more than 11 hours to receive care at our clinic. In addition to the many reasons women pursue abortion care, all of my patients had an overriding concern about the COVID-19 pandemic. Many worried for the safety of their parents and children; some worried about the safety of continuing a pregnancy during the pandemic; and many were worried for themselves because of the risk involved in their employment or their status as the sole breadwinner for their families. One patient chose an abortion for severe fetal anomalies diagnosed in the early second trimester; she had an appointment with a provider in Texas, which was canceled the day the Texas abortion ban was reinstated. New Mexico, more than 10 hours away, was the closest location to receive the care she needed; she traveled by car with her children.
I am fortunate to live in New Mexico. On March 24, New Mexico Secretary of Health Kathyleen “Kathy” Kunkel affirmed reproductive health care as an essential service. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the U.S. professional organization for reproductive health care, agrees. In a joint statement with seven other professional organizations, they emphasize the importance of abortion access: “Abortion is an essential component of comprehensive health care. It is also a time-sensitive service. The consequences of being unable to obtain an abortion profoundly impact a person’s life, health, and well-being.”
Anti-abortion politicians are using the crisis as an opportunity to restrict health care access as they have done for my patients who have driven hundreds of miles for essential care they should receive in their home communities. My heart goes out to our patients and the burden they have been forced to take on at a time when our politicians should be protecting and ensuring their safety.
Dr. Espey is an obstetrician and gynecologist in New Mexico. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Espey is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News Editorial Advisory Board. Email her at [email protected].
In my New Mexico reproductive health clinic one week in early April, I saw more than twice the number of patients usually scheduled, all seeking abortion care. Two-thirds of those patients were from Texas – some came from towns as close as 6 hours away, and at least two drove for more than 11 hours to receive care at our clinic. In addition to the many reasons women pursue abortion care, all of my patients had an overriding concern about the COVID-19 pandemic. Many worried for the safety of their parents and children; some worried about the safety of continuing a pregnancy during the pandemic; and many were worried for themselves because of the risk involved in their employment or their status as the sole breadwinner for their families. One patient chose an abortion for severe fetal anomalies diagnosed in the early second trimester; she had an appointment with a provider in Texas, which was canceled the day the Texas abortion ban was reinstated. New Mexico, more than 10 hours away, was the closest location to receive the care she needed; she traveled by car with her children.
I am fortunate to live in New Mexico. On March 24, New Mexico Secretary of Health Kathyleen “Kathy” Kunkel affirmed reproductive health care as an essential service. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the U.S. professional organization for reproductive health care, agrees. In a joint statement with seven other professional organizations, they emphasize the importance of abortion access: “Abortion is an essential component of comprehensive health care. It is also a time-sensitive service. The consequences of being unable to obtain an abortion profoundly impact a person’s life, health, and well-being.”
Anti-abortion politicians are using the crisis as an opportunity to restrict health care access as they have done for my patients who have driven hundreds of miles for essential care they should receive in their home communities. My heart goes out to our patients and the burden they have been forced to take on at a time when our politicians should be protecting and ensuring their safety.
Dr. Espey is an obstetrician and gynecologist in New Mexico. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Espey is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News Editorial Advisory Board. Email her at [email protected].
Reproductive health care in the time of COVID-19
It is often said that a crisis brings out the best and worst in people, and I think we are definitely seeing that when it comes to the responses to reproductive health, family planning, and abortion care during this global pandemic.
Many national and international organizations have published strong statements of support for the importance of continuing reproductive health services. These organizations include the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Board of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, the Society of Family Planning, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Society of Family Planning, American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and the Ethiopian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. They state the obvious, which is that
We do not have complete knowledge of what the novel coronavirus 2019 does to a developing pregnancy, especially early in pregnancy. Many people who are struggling with all the uncertainty of this time – job, health, housing, food, school – may decide it is not the best moment to be adding to their family.
These concerns apply as well to the need to maintain and prioritize contraceptive services. Stay-at-home orders have put people in close quarters for long periods of time, and we are already getting reports of increased sexual intercourse, as well as increased sexual violence, both of which could result in a need for abortion if contraception is not accessible. Additionally, many women are expressing a concern for whether they will still have a job or have a job again when this first wave of the crisis passes, so they are wanting to access contraception now when they can afford to do so.
I was personally very proud of and grateful to Barbara A. Goff, MD, the chair of my department at the University of Washington, Seattle, for stating clearly in the first email she sent to faculty about canceling elective procedures and visits that family planning and abortion is not elective. My heart goes out to my colleagues and the patients who are in states that are using this opportunity to act poorly and use COVID-19 as another excuse to legislate against abortion and contraception. It demonstrates horrifying gender discrimination during a time when we should really be focusing on keeping everyone healthy.
I predict there will be an increase in the numbers of abortions after this crisis ebbs, and an increase in the numbers of term deliveries. The time to influence that is now.
Dr. Prager is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, chief of the family planning division, and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of Washington, Seattle. She also is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at St. Paul’s Hospital and Millennium Medical College in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Dr. Prager is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She said she has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Prager at [email protected].
It is often said that a crisis brings out the best and worst in people, and I think we are definitely seeing that when it comes to the responses to reproductive health, family planning, and abortion care during this global pandemic.
Many national and international organizations have published strong statements of support for the importance of continuing reproductive health services. These organizations include the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Board of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, the Society of Family Planning, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Society of Family Planning, American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and the Ethiopian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. They state the obvious, which is that
We do not have complete knowledge of what the novel coronavirus 2019 does to a developing pregnancy, especially early in pregnancy. Many people who are struggling with all the uncertainty of this time – job, health, housing, food, school – may decide it is not the best moment to be adding to their family.
These concerns apply as well to the need to maintain and prioritize contraceptive services. Stay-at-home orders have put people in close quarters for long periods of time, and we are already getting reports of increased sexual intercourse, as well as increased sexual violence, both of which could result in a need for abortion if contraception is not accessible. Additionally, many women are expressing a concern for whether they will still have a job or have a job again when this first wave of the crisis passes, so they are wanting to access contraception now when they can afford to do so.
I was personally very proud of and grateful to Barbara A. Goff, MD, the chair of my department at the University of Washington, Seattle, for stating clearly in the first email she sent to faculty about canceling elective procedures and visits that family planning and abortion is not elective. My heart goes out to my colleagues and the patients who are in states that are using this opportunity to act poorly and use COVID-19 as another excuse to legislate against abortion and contraception. It demonstrates horrifying gender discrimination during a time when we should really be focusing on keeping everyone healthy.
I predict there will be an increase in the numbers of abortions after this crisis ebbs, and an increase in the numbers of term deliveries. The time to influence that is now.
Dr. Prager is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, chief of the family planning division, and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of Washington, Seattle. She also is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at St. Paul’s Hospital and Millennium Medical College in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Dr. Prager is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She said she has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Prager at [email protected].
It is often said that a crisis brings out the best and worst in people, and I think we are definitely seeing that when it comes to the responses to reproductive health, family planning, and abortion care during this global pandemic.
Many national and international organizations have published strong statements of support for the importance of continuing reproductive health services. These organizations include the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Board of Obstetrics & Gynecology, the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, the Society of Family Planning, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Society of Family Planning, American Medical Association, the World Health Organization, and the Ethiopian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. They state the obvious, which is that
We do not have complete knowledge of what the novel coronavirus 2019 does to a developing pregnancy, especially early in pregnancy. Many people who are struggling with all the uncertainty of this time – job, health, housing, food, school – may decide it is not the best moment to be adding to their family.
These concerns apply as well to the need to maintain and prioritize contraceptive services. Stay-at-home orders have put people in close quarters for long periods of time, and we are already getting reports of increased sexual intercourse, as well as increased sexual violence, both of which could result in a need for abortion if contraception is not accessible. Additionally, many women are expressing a concern for whether they will still have a job or have a job again when this first wave of the crisis passes, so they are wanting to access contraception now when they can afford to do so.
I was personally very proud of and grateful to Barbara A. Goff, MD, the chair of my department at the University of Washington, Seattle, for stating clearly in the first email she sent to faculty about canceling elective procedures and visits that family planning and abortion is not elective. My heart goes out to my colleagues and the patients who are in states that are using this opportunity to act poorly and use COVID-19 as another excuse to legislate against abortion and contraception. It demonstrates horrifying gender discrimination during a time when we should really be focusing on keeping everyone healthy.
I predict there will be an increase in the numbers of abortions after this crisis ebbs, and an increase in the numbers of term deliveries. The time to influence that is now.
Dr. Prager is professor of obstetrics and gynecology, chief of the family planning division, and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of Washington, Seattle. She also is professor of obstetrics and gynecology at St. Paul’s Hospital and Millennium Medical College in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Dr. Prager is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She said she has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Prager at [email protected].
Colorectal cancer: Proposed treatment guidelines for the COVID-19 era
In light of the rapid changes affecting cancer clinics due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. David Kerr and Dr. Rachel Kerr, both specialists in gastrointestinal cancers at the University of Oxford in Oxford, United Kingdom, drafted these guidelines for the use of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Dr. Kerr and Dr. Kerr are putting forth this guidance as a topic for discussion and debate.
Our aim in developing these recommendations for the care of colorectal cancer patients in areas affected by the COVID-19 outbreak is to reduce the comorbidity of chemotherapy and decrease the risk of patients dying from COVID-19, weighed against the potential benefits of receiving chemotherapy. These recommendations are also designed to reduce the burden on chemotherapy units during a time of great pressure.
We have modified the guidelines in such a way that, we believe, will decrease the total number of patients receiving chemotherapy – particularly in the adjuvant setting – and reduce the overall immune impact of chemotherapy on these patients. Specifically, we suggest changing doublet chemotherapy to single-agent chemotherapy for some groups; changing to combinations involving capecitabine rather than bolus and infusional 5-FU for other patients; and, finally, making reasonable dose reductions upfront to reduce the risk for cycle 1 complications.
By changing from push-and-pump 5-FU to capecitabine for the vast majority of patients, we will both reduce the rates of neutropenia and decrease throughput in chemotherapy outpatient units, reducing requirements for weekly line flushing, pump disconnections, and other routine maintenance.
We continue to recommend the use of ToxNav germline genetic testing as a genetic screen for DPYD/ENOSF1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify patients at high risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity.
Use of biomarkers to sharpen prognosis should also be considered to refine therapeutic decisions.
Recommendations for stage II-III colorectal cancer

Recommendations for advanced colorectal cancer
Which regimen? Capecitabine/oxaliplatin should be the default backbone chemotherapy (rather than FOLFOX) in order to decrease the stress on infusion units.
Capecitabine plus irinotecan should be considered rather than FOLFIRI. However, in order to increase safety, reduce the dose of the capecitabine and the irinotecan, both to 80%, in all patient groups; and perhaps reduce the capecitabine dose further to 60% in those over the age of 70 or with significant comorbid conditions.
Treatment breaks. Full treatment breaks should be considered after 3 months of treatment in most patients with lower-volume, more indolent disease.
Treatment deintensification to capecitabine alone should be used in those with higher-volume disease (for example, more than 50% of liver replaced by tumor) at the beginning of treatment.
Deferring the start of any chemotherapy. Some older patients, or those with significant other comorbidities (that is, those who will be at increased risk for COVID-19 complications and death); who have low-volume disease, such as a couple of small lung metastases or a single liver metastasis; or who were diagnosed more than 12 months since adjuvant chemotherapy may decide to defer any chemotherapy for a period of time.
In these cases, we suggest rescanning at 3 months and discussing further treatment at that point. Some of these patients will be eligible for other interventions, such as resection, ablation, or stereotactic body radiation therapy. However, it will be important to consider the pressures on these other services during this unprecedented time.
Chemotherapy after resection of metastases. Given the lack of evidence and the present extenuating circumstances, we would not recommend any chemotherapy in this setting.
David J. Kerr, MD, CBE, MD, DSc, is a professor of cancer medicine at the University of Oxford. He is recognized internationally for his work in the research and treatment of colorectal cancer, and has founded three university spin-out companies: COBRA Therapeutics, Celleron Therapeutics, and Oxford Cancer Biomarkers. In 2002, he was appointed Commander of the British Empire by Queen Elizabeth. Rachel S. Kerr, MBChB, is a medical oncologist and associate professor of gastrointestinal oncology at the University of Oxford. She holds a UK Department of Health Fellowship, where she is clinical director of phase 3 trials in the oncology clinical trials office.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In light of the rapid changes affecting cancer clinics due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. David Kerr and Dr. Rachel Kerr, both specialists in gastrointestinal cancers at the University of Oxford in Oxford, United Kingdom, drafted these guidelines for the use of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Dr. Kerr and Dr. Kerr are putting forth this guidance as a topic for discussion and debate.
Our aim in developing these recommendations for the care of colorectal cancer patients in areas affected by the COVID-19 outbreak is to reduce the comorbidity of chemotherapy and decrease the risk of patients dying from COVID-19, weighed against the potential benefits of receiving chemotherapy. These recommendations are also designed to reduce the burden on chemotherapy units during a time of great pressure.
We have modified the guidelines in such a way that, we believe, will decrease the total number of patients receiving chemotherapy – particularly in the adjuvant setting – and reduce the overall immune impact of chemotherapy on these patients. Specifically, we suggest changing doublet chemotherapy to single-agent chemotherapy for some groups; changing to combinations involving capecitabine rather than bolus and infusional 5-FU for other patients; and, finally, making reasonable dose reductions upfront to reduce the risk for cycle 1 complications.
By changing from push-and-pump 5-FU to capecitabine for the vast majority of patients, we will both reduce the rates of neutropenia and decrease throughput in chemotherapy outpatient units, reducing requirements for weekly line flushing, pump disconnections, and other routine maintenance.
We continue to recommend the use of ToxNav germline genetic testing as a genetic screen for DPYD/ENOSF1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify patients at high risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity.
Use of biomarkers to sharpen prognosis should also be considered to refine therapeutic decisions.
Recommendations for stage II-III colorectal cancer

Recommendations for advanced colorectal cancer
Which regimen? Capecitabine/oxaliplatin should be the default backbone chemotherapy (rather than FOLFOX) in order to decrease the stress on infusion units.
Capecitabine plus irinotecan should be considered rather than FOLFIRI. However, in order to increase safety, reduce the dose of the capecitabine and the irinotecan, both to 80%, in all patient groups; and perhaps reduce the capecitabine dose further to 60% in those over the age of 70 or with significant comorbid conditions.
Treatment breaks. Full treatment breaks should be considered after 3 months of treatment in most patients with lower-volume, more indolent disease.
Treatment deintensification to capecitabine alone should be used in those with higher-volume disease (for example, more than 50% of liver replaced by tumor) at the beginning of treatment.
Deferring the start of any chemotherapy. Some older patients, or those with significant other comorbidities (that is, those who will be at increased risk for COVID-19 complications and death); who have low-volume disease, such as a couple of small lung metastases or a single liver metastasis; or who were diagnosed more than 12 months since adjuvant chemotherapy may decide to defer any chemotherapy for a period of time.
In these cases, we suggest rescanning at 3 months and discussing further treatment at that point. Some of these patients will be eligible for other interventions, such as resection, ablation, or stereotactic body radiation therapy. However, it will be important to consider the pressures on these other services during this unprecedented time.
Chemotherapy after resection of metastases. Given the lack of evidence and the present extenuating circumstances, we would not recommend any chemotherapy in this setting.
David J. Kerr, MD, CBE, MD, DSc, is a professor of cancer medicine at the University of Oxford. He is recognized internationally for his work in the research and treatment of colorectal cancer, and has founded three university spin-out companies: COBRA Therapeutics, Celleron Therapeutics, and Oxford Cancer Biomarkers. In 2002, he was appointed Commander of the British Empire by Queen Elizabeth. Rachel S. Kerr, MBChB, is a medical oncologist and associate professor of gastrointestinal oncology at the University of Oxford. She holds a UK Department of Health Fellowship, where she is clinical director of phase 3 trials in the oncology clinical trials office.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In light of the rapid changes affecting cancer clinics due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. David Kerr and Dr. Rachel Kerr, both specialists in gastrointestinal cancers at the University of Oxford in Oxford, United Kingdom, drafted these guidelines for the use of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Dr. Kerr and Dr. Kerr are putting forth this guidance as a topic for discussion and debate.
Our aim in developing these recommendations for the care of colorectal cancer patients in areas affected by the COVID-19 outbreak is to reduce the comorbidity of chemotherapy and decrease the risk of patients dying from COVID-19, weighed against the potential benefits of receiving chemotherapy. These recommendations are also designed to reduce the burden on chemotherapy units during a time of great pressure.
We have modified the guidelines in such a way that, we believe, will decrease the total number of patients receiving chemotherapy – particularly in the adjuvant setting – and reduce the overall immune impact of chemotherapy on these patients. Specifically, we suggest changing doublet chemotherapy to single-agent chemotherapy for some groups; changing to combinations involving capecitabine rather than bolus and infusional 5-FU for other patients; and, finally, making reasonable dose reductions upfront to reduce the risk for cycle 1 complications.
By changing from push-and-pump 5-FU to capecitabine for the vast majority of patients, we will both reduce the rates of neutropenia and decrease throughput in chemotherapy outpatient units, reducing requirements for weekly line flushing, pump disconnections, and other routine maintenance.
We continue to recommend the use of ToxNav germline genetic testing as a genetic screen for DPYD/ENOSF1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify patients at high risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity.
Use of biomarkers to sharpen prognosis should also be considered to refine therapeutic decisions.
Recommendations for stage II-III colorectal cancer

Recommendations for advanced colorectal cancer
Which regimen? Capecitabine/oxaliplatin should be the default backbone chemotherapy (rather than FOLFOX) in order to decrease the stress on infusion units.
Capecitabine plus irinotecan should be considered rather than FOLFIRI. However, in order to increase safety, reduce the dose of the capecitabine and the irinotecan, both to 80%, in all patient groups; and perhaps reduce the capecitabine dose further to 60% in those over the age of 70 or with significant comorbid conditions.
Treatment breaks. Full treatment breaks should be considered after 3 months of treatment in most patients with lower-volume, more indolent disease.
Treatment deintensification to capecitabine alone should be used in those with higher-volume disease (for example, more than 50% of liver replaced by tumor) at the beginning of treatment.
Deferring the start of any chemotherapy. Some older patients, or those with significant other comorbidities (that is, those who will be at increased risk for COVID-19 complications and death); who have low-volume disease, such as a couple of small lung metastases or a single liver metastasis; or who were diagnosed more than 12 months since adjuvant chemotherapy may decide to defer any chemotherapy for a period of time.
In these cases, we suggest rescanning at 3 months and discussing further treatment at that point. Some of these patients will be eligible for other interventions, such as resection, ablation, or stereotactic body radiation therapy. However, it will be important to consider the pressures on these other services during this unprecedented time.
Chemotherapy after resection of metastases. Given the lack of evidence and the present extenuating circumstances, we would not recommend any chemotherapy in this setting.
David J. Kerr, MD, CBE, MD, DSc, is a professor of cancer medicine at the University of Oxford. He is recognized internationally for his work in the research and treatment of colorectal cancer, and has founded three university spin-out companies: COBRA Therapeutics, Celleron Therapeutics, and Oxford Cancer Biomarkers. In 2002, he was appointed Commander of the British Empire by Queen Elizabeth. Rachel S. Kerr, MBChB, is a medical oncologist and associate professor of gastrointestinal oncology at the University of Oxford. She holds a UK Department of Health Fellowship, where she is clinical director of phase 3 trials in the oncology clinical trials office.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.












