User login
Bad Facts Make Bad Policies in Reproductive Health, Says Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Lawyers have the saying, “Bad facts make for bad cases; bad cases make for bad laws.” What we’re seeing, I fear, all too often in discussions about reproductive rights, reproductive behavior, and attempts to regulate and legislate with respect to abortion and contraception are many bad facts.
I do think it’s important that science and medicine speak up in local settings and every opportunity they have, not so much to say what government should do or to say whether they think a particular law is good or bad, but certainly to get the facts straight in their role as doctors, sometimes as scientists, and as caregivers.
Bad facts are making many bad policies in the reproductive behavior space. For example, there are many people, mainly on the conservative side, who are saying things like intrauterine devices, emergency contraception, and even birth control cause abortions. That is simply not true.
There are interventions that prevent fertilization from occurring. There are also interventions that prevent implantation from occurring. Neither of those are abortions. If an embryo has not implanted into a womb, it is not, by any biological definition, a pregnancy.
In situations where a barrier method or something else prevents sperm and egg from meeting or if there is an agent that prevents an egg from implanting, these are facts that legislators, the public, and even your patients need to understand if they’re going to make sound policy about access to methods used to control reproduction.
Similarly, you can see debates about whether embryos are deserving of rights. An Alabama court has ruled that embryos are tiny children. A court can say what it wishes in terms of legal status, but it shouldn’t be deviating from the facts.
The facts are clear. Embryos outside of a uterus implanted are not babies. They are not children. At most, an embryo in a dish might be considered, let’s say, a possible person. Once it implants in a uterus, it may become a potential person because it then still has a failure rate, postimplantation, of not becoming a baby that’s very high. Approximately 40%-50% of such embryos are genetically flawed and aren’t going to be able to turn into a child.
The notion that every embryo, whether it’s stored in a tank or sitting in a dish, is somehow a tiny child, factually is just not true. You can’t make good policy if you ignore the facts. People may wish to protect embryos. They may wish to restrict in vitro fertilization. They may wish to have people implant any embryo that is created and mandate that it has to happen because they don’t want any tiny children not to be brought to term.
Factually, they’re operating outside the realm of what biology and medicine know. There’s no tiny baby, no homunculus, or no preformed baby inside an embryo. An egg that simply fails to implant is not technically even a pregnancy.
I think all of us have an obligation when we’re in disputes, wherever they occur, whether we’re fighting about laws, having an argument with the neighbors, or speaking to younger high school students or even patients, we need to try to make clear the facts about what we know about eggs, how birth control works, and embryos and their failure rate.
We also have to be clear about the significance of saying the facts have to guide public policy. I think the facts should, but unfortunately, I don’t think that’s always been true in recent years. As efforts heat up to intervene more with things like contraception, getting the facts straight becomes even more important and more of a duty for those who know best.
Dr. Caplan is director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York. He served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Lawyers have the saying, “Bad facts make for bad cases; bad cases make for bad laws.” What we’re seeing, I fear, all too often in discussions about reproductive rights, reproductive behavior, and attempts to regulate and legislate with respect to abortion and contraception are many bad facts.
I do think it’s important that science and medicine speak up in local settings and every opportunity they have, not so much to say what government should do or to say whether they think a particular law is good or bad, but certainly to get the facts straight in their role as doctors, sometimes as scientists, and as caregivers.
Bad facts are making many bad policies in the reproductive behavior space. For example, there are many people, mainly on the conservative side, who are saying things like intrauterine devices, emergency contraception, and even birth control cause abortions. That is simply not true.
There are interventions that prevent fertilization from occurring. There are also interventions that prevent implantation from occurring. Neither of those are abortions. If an embryo has not implanted into a womb, it is not, by any biological definition, a pregnancy.
In situations where a barrier method or something else prevents sperm and egg from meeting or if there is an agent that prevents an egg from implanting, these are facts that legislators, the public, and even your patients need to understand if they’re going to make sound policy about access to methods used to control reproduction.
Similarly, you can see debates about whether embryos are deserving of rights. An Alabama court has ruled that embryos are tiny children. A court can say what it wishes in terms of legal status, but it shouldn’t be deviating from the facts.
The facts are clear. Embryos outside of a uterus implanted are not babies. They are not children. At most, an embryo in a dish might be considered, let’s say, a possible person. Once it implants in a uterus, it may become a potential person because it then still has a failure rate, postimplantation, of not becoming a baby that’s very high. Approximately 40%-50% of such embryos are genetically flawed and aren’t going to be able to turn into a child.
The notion that every embryo, whether it’s stored in a tank or sitting in a dish, is somehow a tiny child, factually is just not true. You can’t make good policy if you ignore the facts. People may wish to protect embryos. They may wish to restrict in vitro fertilization. They may wish to have people implant any embryo that is created and mandate that it has to happen because they don’t want any tiny children not to be brought to term.
Factually, they’re operating outside the realm of what biology and medicine know. There’s no tiny baby, no homunculus, or no preformed baby inside an embryo. An egg that simply fails to implant is not technically even a pregnancy.
I think all of us have an obligation when we’re in disputes, wherever they occur, whether we’re fighting about laws, having an argument with the neighbors, or speaking to younger high school students or even patients, we need to try to make clear the facts about what we know about eggs, how birth control works, and embryos and their failure rate.
We also have to be clear about the significance of saying the facts have to guide public policy. I think the facts should, but unfortunately, I don’t think that’s always been true in recent years. As efforts heat up to intervene more with things like contraception, getting the facts straight becomes even more important and more of a duty for those who know best.
Dr. Caplan is director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York. He served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Lawyers have the saying, “Bad facts make for bad cases; bad cases make for bad laws.” What we’re seeing, I fear, all too often in discussions about reproductive rights, reproductive behavior, and attempts to regulate and legislate with respect to abortion and contraception are many bad facts.
I do think it’s important that science and medicine speak up in local settings and every opportunity they have, not so much to say what government should do or to say whether they think a particular law is good or bad, but certainly to get the facts straight in their role as doctors, sometimes as scientists, and as caregivers.
Bad facts are making many bad policies in the reproductive behavior space. For example, there are many people, mainly on the conservative side, who are saying things like intrauterine devices, emergency contraception, and even birth control cause abortions. That is simply not true.
There are interventions that prevent fertilization from occurring. There are also interventions that prevent implantation from occurring. Neither of those are abortions. If an embryo has not implanted into a womb, it is not, by any biological definition, a pregnancy.
In situations where a barrier method or something else prevents sperm and egg from meeting or if there is an agent that prevents an egg from implanting, these are facts that legislators, the public, and even your patients need to understand if they’re going to make sound policy about access to methods used to control reproduction.
Similarly, you can see debates about whether embryos are deserving of rights. An Alabama court has ruled that embryos are tiny children. A court can say what it wishes in terms of legal status, but it shouldn’t be deviating from the facts.
The facts are clear. Embryos outside of a uterus implanted are not babies. They are not children. At most, an embryo in a dish might be considered, let’s say, a possible person. Once it implants in a uterus, it may become a potential person because it then still has a failure rate, postimplantation, of not becoming a baby that’s very high. Approximately 40%-50% of such embryos are genetically flawed and aren’t going to be able to turn into a child.
The notion that every embryo, whether it’s stored in a tank or sitting in a dish, is somehow a tiny child, factually is just not true. You can’t make good policy if you ignore the facts. People may wish to protect embryos. They may wish to restrict in vitro fertilization. They may wish to have people implant any embryo that is created and mandate that it has to happen because they don’t want any tiny children not to be brought to term.
Factually, they’re operating outside the realm of what biology and medicine know. There’s no tiny baby, no homunculus, or no preformed baby inside an embryo. An egg that simply fails to implant is not technically even a pregnancy.
I think all of us have an obligation when we’re in disputes, wherever they occur, whether we’re fighting about laws, having an argument with the neighbors, or speaking to younger high school students or even patients, we need to try to make clear the facts about what we know about eggs, how birth control works, and embryos and their failure rate.
We also have to be clear about the significance of saying the facts have to guide public policy. I think the facts should, but unfortunately, I don’t think that’s always been true in recent years. As efforts heat up to intervene more with things like contraception, getting the facts straight becomes even more important and more of a duty for those who know best.
Dr. Caplan is director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York. He served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). He is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I*DEA in the VA: Optimizing the Physician Workforce to Enhance Quality of Care
Enhancing the quality of care for the evolving American veteran population is critical: many are vulnerable as a result of unique psychological and physical exposures, and many are increasingly coming from populations the federal government considers “potentially vulnerable.”1 To ensure that the needs of veterans enrolled in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) are met, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) workforce must be aware of shifts in the demographics of those who served.
The I*DEA (inclusion, diversity, equity, and access) Council is a new VHA equity team that aims to eliminate gaps in health care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive the treatment they need. The Council is the oversight body for veteran and employee-facing I*DEA programs, policies, and initiatives.2 One strategy to achieve better health outcomes for enrolled veterans is to prioritize the VA health care workforce. In this capacity, the I*DEA Council examines obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees from underserved communities.
This article discusses how diversity encompasses more than gender and ethnicity and proposes applying the following I*DEA strategies to leadership positions within the VA health care workforce: inclusion of diverse perspectives and ideas, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership roles within VHA facilities. Implementing these actions may help attract and retain qualified clinicians as health care leaders and enable the VHA to better serve the diverse veteran population.
Veteran Demographics
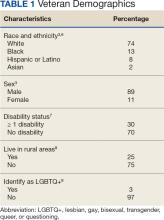
Characteristics of the current population of veterans differ significantly from those of individuals who served in previous eras. Since 2016, Gulf War era veterans have comprised the largest share of the veteran population, even larger than the share of Vietnam War era veterans.3 Among Gulf War veterans, 47% of women and 39% of men are aged < 35 years.4 Another notable change is the increase in the number of female veterans. In 1992, only 4% of veterans were female.5 Now, about 11% of veterans are female, a number projected to grow to 18% by 2046 (Table 1).3
With respect to race and ethnicity, about 74% of the current veteran population identifies as White, 13% as Black, 8% as Hispanic or Latino, and 2% as Asian.3,6 In addition, about 30% of veterans have ≥ 1 disability.7 About 1 million current veterans (3%) identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and/or questioning (LGBTQ+).8 Almost 1 in 4 veterans—about 4.4 million—reside in rural communities, and 55% of these rural veterans are aged > 65 years.9 Of the 4.4 million veterans who live in rural areas, 61% are enrolled in VA health care, and among those individuals 8% are women and 10% are minorities.9
Studies have found that age, sex, race and ethnicity, disability status, and LGBTQ+ identification all significantly affect health care access and outcomes in the general population.10-16 Female patients are more likely to have their symptoms downplayed or dismissed, and are often less likely to receive aggressive treatments when compared with male patients. They are also frequently underrepresented or even excluded from clinical trials.11 Female veterans have unique health care needs and report preferences for being treated by female clinicians.17,18
Higher rates of chronic health conditions and reduced access to mental health services are found among Black Americans compared to White Americans.13 Black veterans are also denied VHA benefits more often than White veterans.19 Patients with disabilities have barriers to accessing care, including difficulty with transportation and a lack of knowledge among clinicians regarding the best course of care.14 Additionally, veterans who identify as LGBTQ+ are less likely than veterans who are cisgender and heterosexual to access Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.20 Veterans in rural communities experience more challenges to accessing health care; up to one-third of veterans in this population are unable to access the internet at home.9
To optimize care for the evolving veteran population, VHA clinicians and leaders need to be aware of the changing demographic characteristics and unique health care needs of the veteran population. Increased inclusion, diversity, and equity within the health care workforce is associated with improved quality of care, improved clinical outcomes, and have had positive financial effects on health care institutions.21-25
VA Workforce Demographics
According to the VA Office of Resolution Management, Diversity, and Inclusion, at the end of fiscal year 2020 57% of VA employees identified as White, 25% as Black, 8% as Asian, 7% as Hispanic or Latino, 2% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 1% belonged to ≥ 2 races.26 Women comprise about 60% of the permanent VA workforce.27 About 12% of VA employees report having a disability, which is similar to the rate of disability among noninstitutionalized civilians in the US (12.7%).28 Five percent of VA employees identified as LGBTQ+.29
Although the general workforce is relatively diverse, there is not as much diversity within VA leadership, and little data exist about the demographic characteristics of VHA physicians. As of September 2020, there were 494 senior executive service and Title 38 (health care workers) senior executive service equivalent leaders in the VHA.26 Almost 78% of these leadership positions belonged to white men and women: about 50% to white men and 28% to white women. In contrast, 8% of these positions were occupied by Black men, 7% by Black women, 3% by Asian men, 2% by Asian women, and 2% by Hispanic or Latino men.26
I*DEA in the VA
The I*DEA Council seeks to eliminate gaps in VHA care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive fair treatment.30 In addition to continued attention to racial disparities, the new initiative will also examine challenges experienced by other groups, including women, individuals who identify as LGBTQ+, tribal communities, and veterans who live in rural areas, aiming to eliminate disparities that exist within the VHA.
Published in 2021, the I*DEA Action Plan discusses recommendations to enhance inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility within the VHA. Its mission statement states that the Council aims to “advance an inclusive environment that values and supports the diverse communities we serve” and “cultivates equitable access to care, benefits and services for all” from 2021 to 2025.31 To achieve better health outcomes for veterans, the I*DEA Council plans to focus on the VHA workforce and examine and address obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees.31
There are several potential benefits of increased I*DEA integration into the health care workforce.21-25 The inclusion of ideas and perspectives from diverse backgrounds, establishing equity of opportunities for all who are appropriately qualified, and accessibility to leadership roles that enable decision making by fostering culture change are direct components of I*DEA that may be beneficial. Diversity encompasses more than race, ethnicity, and gender, and creating a more diverse workforce involves recruiting qualified clinicians with diverse backgrounds and perspectives. Doing so would better reflect the diversity of veteran patients and could enhance the ability of clinicians to learn from each other and be inclusive, while understanding veterans’ unique barriers to accessing health care.
I*DEA integration may reduce the incidence of microaggressions and help transform workplace culture.32 This would be particularly beneficial for patients, as microaggressions can decrease patient satisfaction and may potentially negatively affect health outcomes.33,34 In addition, health care professionals (HCPs) would benefit from fewer microaggressions in the workplace and this would foster a more positive, supportive work environment and improve morale.
Current VHA workforce data reflect changes in the veteran population. The workforce is relatively diverse regarding race and ethnicity, gender, disability, and LGBTQ+ status. However, room for improvement remains with respect to greater inclusion, diversity of perspectives, equity, and accessibility to leadership positions and decision making roles. This would ultimately benefit and improve care for veterans. Prioritizing this within the VHA, as reflected in one of the I*DEA Task Force recommendations, is of great significance.31
It can be difficult to accurately assess the progress made in implementing I*DEA strategies at individual institutions within the VHA. While demographic diversity can be gauged using employee statistics, assessing perceptions of inclusion, incorporation of diverse perspectives, equity, and accessibility is more challenging. We recommend continuing to administer questions focusing specifically on these perceptions to current HCPs via the VHA annual All Employee Survey.35
Implementation
The VA has begun initiating I*DEA concepts in its workforce, starting with the establishment and usage of Special Emphasis Programs.36 The goal of these programs is to increase the employment of historically marginalized groups, including women, people belonging to racial and ethnic minorities, people with disabilities, and individuals identifying as LGBTQ+.28,37-42 For example, each federal agency has a designated Federal Women’s Program whose responsibilities include helping with the recruitment and advancement of female employees.37
The VHA also has an affirmative action plan with goals for recruiting and retaining individuals with disabilities.28 To strengthen equity and inclusion, the VHA offers multiple educational courses (some mandatory), both virtual and in-person, on topics such as understanding microaggressions, managing implicit bias, and understanding the importance of gender and generational diversity.43 Creating awareness and addressing misconceptions about veteran demographics at VA medical centers is important, as is enhancing awareness among the physician workforce about VA strategies and action plans to increase I*DEA. The VHA has hired officers specifically tasked with focusing on these initiatives.
Workforce Strategies
It is important to recognize overlaps between organizational ethics, quality improvement, and I*DEA initiatives. Establishing an I*DEA Council to ensure the delivery of quality care to veterans is commendable. At the facility level, individual I*DEA officers can make observations and recommendations but are not empowered to effect change. Without participation and buy-in from individuals in leadership positions, the efficacy of I*DEA initiatives is limited.
We propose implementing simple strategies to enhance the inclusion of diverse ideas and perspectives, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to clinical leadership roles within the VHA (Table 2). A competitive selection process with specific, objective criteria to enable the selection of qualified clinical leaders is vital. Specific achievements in or contributions to quality improvement, education, research, professional publications, or diversity enhancing efforts should be required qualifications for clinical leadership roles.44
Establishing term limits for clinical leadership positions—something already being implemented at the National Institutes of Health—would be of tremendous value in the VHA.45-47 Term limits would facilitate I*DEA initiatives and accessibility of leadership roles to qualified clinicians fromvarious demographics. Improving diversity of thought among clinical leaders is especially important, given how buy-in from leadership is critical in transforming the culture of an organization. Term limits would enable access to leadership roles for forward thinking, qualified clinical leaders who could institute and support changes that would promote continuous process improvement initiatives. Leaders could have the option to reapply following the completion of a term, with the ability to demonstrate specific achievements.
Another strategy for increasing equity is to ensure transparency of committee structures, with the rotation of committee members and term limits set for committee chairs whenever possible. This provides access to leadership roles, which enables participation in decision making processes. Residents and fellows who work and train at VA hospitals should have awareness of the facility’s organizational structure and the ability to participate in certain committees. The VHA workforce should be regularly informed about educational opportunities, leadership openings, and I*DEA initiatives to increase their access and use.
Exit interviews for clinicians leaving the VA would enable feedback, provide focused reviews of any problematic issues that need to be addressed, and serve as assessments of organizational ethics.48 Transparency and truth telling could be encouraged by having these exit interviews conducted by staff in the human resources department or others outside the home department of the departing clinician.
Mentorship has played a significant role in exposing individuals from historically underrepresented groups to careers in health care, while also advancing and enhancing their careers after they become health care professionals.49-51 Implementing and publicizing VA and veteran health care-focused mentorship and volunteer programs targeted at local communities, rural areas, schools, undergraduate programs, and medical students could increase the likelihood that students and trainees from these groups are exposed to the VHA which may lead them to join the workforce.
Conclusions
Veterans receiving care from the VHA are becoming increasingly diverse. I*DEA strategies could optimize the VHA workforce and enhance the provision of quality care for veterans. The inclusion of diverse perspectives and backgrounds, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership positions is important. Careful selection of qualified clinical leaders within the VHA—with established term limits for leadership positions, rotation of committee chairs and members, and exit interviews to obtain insights from clinicians who leave the VHA—all align with these strategies. This will foster energy and culture change, create an environment conducive to collaboration, learning, and professional growth and will enable continuous process improvement within individual VA medical centers.
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Health equity. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/health_equity.cfm
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Equity action plan. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Department-of-Veterans-Affairs-Equity-Action-Plan.pdf
3. Schaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. March 2021. Updated November 8, 2023. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2021/04/05/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
4. US Department of Labor, Veterans’ Employment and Training Service. 2021 employment situation of women veterans. Accessed May 23, 2024. http://www.dol.gov/agencies/vets/womenveterans/womenveterans-employment
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veteran Analysis and Statistics. National survey of veterans (NSV9503). Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf
6. US Census Bureau. Veterans Day 2022: November 11. News release. October 26, 2022. Updated April 4, 2024. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/facts-for-features/2022/veterans-day.html
7. ADA National Network. Employment data for veterans with disabilities. 2017. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://adata.org/factsheet/employment-data-veterans-disabilities
8. LGBTQ+ Veterans. DAV. Accessed July 26, 2024. https://www.dav.org/get-help-now/veteran-topics-resources/lgbtq-veterans/
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
10. Mikton C, de la Fuente-Núñez V, Officer A, Krug E. Ageism: a social determinant of health that has come of age. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1333-1334.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00524-9
11. Heise L, Greene ME, Opper N, et al. Gender inequality and restrictive gender norms: framing the challenges to health. Lancet. 2019;393(10189):2440-2454.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30652-X
12. Egede LE. Race, ethnicity, culture, and disparities in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(6):667-669. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.0512.x
13. Carratala S, Maxwell C. Health disparities by race and ethnicity. Center for American Progress. Updated May 11, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/health-disparities-race-ethnicity/
14. Clemente KAP, Silva SVD, Vieira GI, et al. Barriers to the access of people with disabilities to health services: a scoping review. Rev Saude Publica. 2022;56:64.
doi:10.11606/s1518-8787.2022056003893
15. Krehely J. How to close the LGBT health disparities gap. Center for American Progress. December 21, 2009. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/how-to-close-the-lgbt-health-disparities-gap/
16. Dawson L, Frederiksen B, Long M, Ranji U, Kates J. LGBT+ people’s health and experiences accessing care. KFF. July 22, 2021. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/report/lgbt-peoples-health-and-experiences-accessing-care
17. Disabled American Veterans. DAV report spotlights issues facing women veterans. September 12, 2018. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.dav.org/learn-more/news/2018/new-report-spotlights-continuing-challenges-facing-women-veterans/
18. Sheahan KL, Goldstein KM, Than CT, et al. Women veterans’ healthcare needs, utilization, and preferences in veterans affairs primary care settings. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl 3):791-798.
doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07585-3
19. Habeshian S. VA denied Black veterans health benefits more often than White vets, data shows. Axios. June 23, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.axios.com/2023/06/23/veterans-benefits-black-white-rate-disproportionate
20. Shipherd JC, Darling JE, Klap RS, Rose D, Yano EM. Experiences in the Veterans Health Administration and impact on healthcare utilization: comparisons between LGBT and non‐LGBT women veterans. LGBT Health. 2018;5(5):303‐311. doi:10.1089/lgbt.2017.0179
21. Gomez LE, Bernet P. Diversity improves performance and outcomes. J Natl Med Assoc. 2019;111(4):383-392. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2019.01.006
22. Gill GK, McNally MJ, Berman V. Effective diversity, equity, and inclusion practices. Healthc Manage Forum. 2018;31(5):196-199. doi:10.1177/0840470418773785
23. Balinda IG, Reza N. Diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging in cardiovascular disease fellowship training. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J. 2022;18(3):67-77. doi:10.14797/mdcvj.1080
24. Parsons SK, Fineberg IC, Lin M, Singer M, Tang M, Erban JK. Promoting high-quality cancer care and equity through disciplinary diversity in team composition. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(11):1141-1147. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.013920
25. Stanford FC. The importance of diversity and inclusion in the healthcare workforce. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112(3):247-249. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2020.03.014
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Diversity and inclusion strategic plan, fiscal years 2021-2022. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/StrategicPlan.pdf
27. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). US EEOC. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.eeoc.gov/federal-sector/department-veterans-affairs-va-0
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Individuals with disabilities employment program. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/IWD.asp
29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). VA workforce diversity: FY 2022. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/Diversity_Inclusion.asp
30. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Same mission, new I-DEA: VA supports inclusion, diversity, equity and access. News release. April 28, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://news.va.gov/118609/same-mission-va-supports-inclusion-diversity/
31. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Inclusion, diversity, equity, & access (I-DEA) action plan. September 2021. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/VA_I-DEA_Action_Plan-SIGNED.pdf
32. Sue DW, Alsaidi S, Awad MN, Glaeser E, Calle CZ. Disarming racial microaggressions: microintervention strategies for targets, White allies, and bystanders. Am Psychol. 2019;74(1):128-142. doi:10.1037/amp0000296
33. Cruz D, Rodriguez Y, Mastropaolo C. Perceived microaggressions in health care: a measurement study. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0211620
 34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
35. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA all employee survey. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.data.va.gov/stories/s/VA-All-Employee-Survey-AES-/r32e-j4vj/
36. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Special emphasis programs (ORMDI). Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Special_Emphasis_Programs.asp
37. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Federal women’s program. Updated August 9, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/FWP.asp
38. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Hispanic Employment program. Updated May 16, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/HEP.asp
39. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). American Indian & Alaska Native Program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AIAN.asp
40. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Asian American, Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AAPI.asp
41. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Black/African American program. Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Black_African_American.asp
42. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). LGBTQ+ program. Updated May 21, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/LGBT.asp
43. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Diversity, equity and inclusion training. Updated March 18, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Diversity_Inclusion_Training.asp
44. Rotenstein LS, Reede JY, Jena AB. Addressing workforce diversity - a quality-improvement framework. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(12):1083-1086. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2032224
45. Beeler WH, Mangurian C, Jagsi R. Unplugging the pipeline - a call for term limits in academic medicine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1508-1511. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1906832
46. Smith DG. Term limits in academic public health administration. Public Health Rep. 2020;135(6):859-863. doi:10.1177/0033354920954495
47. Kaiser J. Shake-up at NIH: Term limits for important positions would open new opportunities for women, minorities. science.org. May 2, 2019. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/shakeup-nih-term-limits-important-positions-would-open-new-opportunities-women
48. Giacalone RA, Jurkiewicz CL, Knouse SB. Exit surveys as assessments of organizational ethicality. Public Pers Manage. 2003;32(3):397-410. doi:10.1177/009102600303200306
49. Bonifacino E, Ufomata EO, Farkas AH, Turner R, Corbelli JA. Mentorship of underrepresented physicians and trainees in academic medicine: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(4):1023-1034. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06478-7
50. Brown IM. Diversity matters: mentorship is the missing ingredient in DEI. Emergency Medicine News. 2021;43(8):28. doi:10.1097/01.EEM.0000771148.76632.35
51. Sinha A, Kuy S. The future of surgery - increasing diversity, equity, and inclusion through early mentorship. Am J Surg. 2023;225(4):800-802. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2022.12.011
Enhancing the quality of care for the evolving American veteran population is critical: many are vulnerable as a result of unique psychological and physical exposures, and many are increasingly coming from populations the federal government considers “potentially vulnerable.”1 To ensure that the needs of veterans enrolled in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) are met, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) workforce must be aware of shifts in the demographics of those who served.
The I*DEA (inclusion, diversity, equity, and access) Council is a new VHA equity team that aims to eliminate gaps in health care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive the treatment they need. The Council is the oversight body for veteran and employee-facing I*DEA programs, policies, and initiatives.2 One strategy to achieve better health outcomes for enrolled veterans is to prioritize the VA health care workforce. In this capacity, the I*DEA Council examines obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees from underserved communities.
This article discusses how diversity encompasses more than gender and ethnicity and proposes applying the following I*DEA strategies to leadership positions within the VA health care workforce: inclusion of diverse perspectives and ideas, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership roles within VHA facilities. Implementing these actions may help attract and retain qualified clinicians as health care leaders and enable the VHA to better serve the diverse veteran population.
Veteran Demographics
Characteristics of the current population of veterans differ significantly from those of individuals who served in previous eras. Since 2016, Gulf War era veterans have comprised the largest share of the veteran population, even larger than the share of Vietnam War era veterans.3 Among Gulf War veterans, 47% of women and 39% of men are aged < 35 years.4 Another notable change is the increase in the number of female veterans. In 1992, only 4% of veterans were female.5 Now, about 11% of veterans are female, a number projected to grow to 18% by 2046 (Table 1).3
With respect to race and ethnicity, about 74% of the current veteran population identifies as White, 13% as Black, 8% as Hispanic or Latino, and 2% as Asian.3,6 In addition, about 30% of veterans have ≥ 1 disability.7 About 1 million current veterans (3%) identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and/or questioning (LGBTQ+).8 Almost 1 in 4 veterans—about 4.4 million—reside in rural communities, and 55% of these rural veterans are aged > 65 years.9 Of the 4.4 million veterans who live in rural areas, 61% are enrolled in VA health care, and among those individuals 8% are women and 10% are minorities.9
Studies have found that age, sex, race and ethnicity, disability status, and LGBTQ+ identification all significantly affect health care access and outcomes in the general population.10-16 Female patients are more likely to have their symptoms downplayed or dismissed, and are often less likely to receive aggressive treatments when compared with male patients. They are also frequently underrepresented or even excluded from clinical trials.11 Female veterans have unique health care needs and report preferences for being treated by female clinicians.17,18
Higher rates of chronic health conditions and reduced access to mental health services are found among Black Americans compared to White Americans.13 Black veterans are also denied VHA benefits more often than White veterans.19 Patients with disabilities have barriers to accessing care, including difficulty with transportation and a lack of knowledge among clinicians regarding the best course of care.14 Additionally, veterans who identify as LGBTQ+ are less likely than veterans who are cisgender and heterosexual to access Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.20 Veterans in rural communities experience more challenges to accessing health care; up to one-third of veterans in this population are unable to access the internet at home.9
To optimize care for the evolving veteran population, VHA clinicians and leaders need to be aware of the changing demographic characteristics and unique health care needs of the veteran population. Increased inclusion, diversity, and equity within the health care workforce is associated with improved quality of care, improved clinical outcomes, and have had positive financial effects on health care institutions.21-25
VA Workforce Demographics
According to the VA Office of Resolution Management, Diversity, and Inclusion, at the end of fiscal year 2020 57% of VA employees identified as White, 25% as Black, 8% as Asian, 7% as Hispanic or Latino, 2% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 1% belonged to ≥ 2 races.26 Women comprise about 60% of the permanent VA workforce.27 About 12% of VA employees report having a disability, which is similar to the rate of disability among noninstitutionalized civilians in the US (12.7%).28 Five percent of VA employees identified as LGBTQ+.29
Although the general workforce is relatively diverse, there is not as much diversity within VA leadership, and little data exist about the demographic characteristics of VHA physicians. As of September 2020, there were 494 senior executive service and Title 38 (health care workers) senior executive service equivalent leaders in the VHA.26 Almost 78% of these leadership positions belonged to white men and women: about 50% to white men and 28% to white women. In contrast, 8% of these positions were occupied by Black men, 7% by Black women, 3% by Asian men, 2% by Asian women, and 2% by Hispanic or Latino men.26
I*DEA in the VA
The I*DEA Council seeks to eliminate gaps in VHA care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive fair treatment.30 In addition to continued attention to racial disparities, the new initiative will also examine challenges experienced by other groups, including women, individuals who identify as LGBTQ+, tribal communities, and veterans who live in rural areas, aiming to eliminate disparities that exist within the VHA.
Published in 2021, the I*DEA Action Plan discusses recommendations to enhance inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility within the VHA. Its mission statement states that the Council aims to “advance an inclusive environment that values and supports the diverse communities we serve” and “cultivates equitable access to care, benefits and services for all” from 2021 to 2025.31 To achieve better health outcomes for veterans, the I*DEA Council plans to focus on the VHA workforce and examine and address obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees.31
There are several potential benefits of increased I*DEA integration into the health care workforce.21-25 The inclusion of ideas and perspectives from diverse backgrounds, establishing equity of opportunities for all who are appropriately qualified, and accessibility to leadership roles that enable decision making by fostering culture change are direct components of I*DEA that may be beneficial. Diversity encompasses more than race, ethnicity, and gender, and creating a more diverse workforce involves recruiting qualified clinicians with diverse backgrounds and perspectives. Doing so would better reflect the diversity of veteran patients and could enhance the ability of clinicians to learn from each other and be inclusive, while understanding veterans’ unique barriers to accessing health care.
I*DEA integration may reduce the incidence of microaggressions and help transform workplace culture.32 This would be particularly beneficial for patients, as microaggressions can decrease patient satisfaction and may potentially negatively affect health outcomes.33,34 In addition, health care professionals (HCPs) would benefit from fewer microaggressions in the workplace and this would foster a more positive, supportive work environment and improve morale.
Current VHA workforce data reflect changes in the veteran population. The workforce is relatively diverse regarding race and ethnicity, gender, disability, and LGBTQ+ status. However, room for improvement remains with respect to greater inclusion, diversity of perspectives, equity, and accessibility to leadership positions and decision making roles. This would ultimately benefit and improve care for veterans. Prioritizing this within the VHA, as reflected in one of the I*DEA Task Force recommendations, is of great significance.31
It can be difficult to accurately assess the progress made in implementing I*DEA strategies at individual institutions within the VHA. While demographic diversity can be gauged using employee statistics, assessing perceptions of inclusion, incorporation of diverse perspectives, equity, and accessibility is more challenging. We recommend continuing to administer questions focusing specifically on these perceptions to current HCPs via the VHA annual All Employee Survey.35
Implementation
The VA has begun initiating I*DEA concepts in its workforce, starting with the establishment and usage of Special Emphasis Programs.36 The goal of these programs is to increase the employment of historically marginalized groups, including women, people belonging to racial and ethnic minorities, people with disabilities, and individuals identifying as LGBTQ+.28,37-42 For example, each federal agency has a designated Federal Women’s Program whose responsibilities include helping with the recruitment and advancement of female employees.37
The VHA also has an affirmative action plan with goals for recruiting and retaining individuals with disabilities.28 To strengthen equity and inclusion, the VHA offers multiple educational courses (some mandatory), both virtual and in-person, on topics such as understanding microaggressions, managing implicit bias, and understanding the importance of gender and generational diversity.43 Creating awareness and addressing misconceptions about veteran demographics at VA medical centers is important, as is enhancing awareness among the physician workforce about VA strategies and action plans to increase I*DEA. The VHA has hired officers specifically tasked with focusing on these initiatives.
Workforce Strategies
It is important to recognize overlaps between organizational ethics, quality improvement, and I*DEA initiatives. Establishing an I*DEA Council to ensure the delivery of quality care to veterans is commendable. At the facility level, individual I*DEA officers can make observations and recommendations but are not empowered to effect change. Without participation and buy-in from individuals in leadership positions, the efficacy of I*DEA initiatives is limited.
We propose implementing simple strategies to enhance the inclusion of diverse ideas and perspectives, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to clinical leadership roles within the VHA (Table 2). A competitive selection process with specific, objective criteria to enable the selection of qualified clinical leaders is vital. Specific achievements in or contributions to quality improvement, education, research, professional publications, or diversity enhancing efforts should be required qualifications for clinical leadership roles.44
Establishing term limits for clinical leadership positions—something already being implemented at the National Institutes of Health—would be of tremendous value in the VHA.45-47 Term limits would facilitate I*DEA initiatives and accessibility of leadership roles to qualified clinicians fromvarious demographics. Improving diversity of thought among clinical leaders is especially important, given how buy-in from leadership is critical in transforming the culture of an organization. Term limits would enable access to leadership roles for forward thinking, qualified clinical leaders who could institute and support changes that would promote continuous process improvement initiatives. Leaders could have the option to reapply following the completion of a term, with the ability to demonstrate specific achievements.
Another strategy for increasing equity is to ensure transparency of committee structures, with the rotation of committee members and term limits set for committee chairs whenever possible. This provides access to leadership roles, which enables participation in decision making processes. Residents and fellows who work and train at VA hospitals should have awareness of the facility’s organizational structure and the ability to participate in certain committees. The VHA workforce should be regularly informed about educational opportunities, leadership openings, and I*DEA initiatives to increase their access and use.
Exit interviews for clinicians leaving the VA would enable feedback, provide focused reviews of any problematic issues that need to be addressed, and serve as assessments of organizational ethics.48 Transparency and truth telling could be encouraged by having these exit interviews conducted by staff in the human resources department or others outside the home department of the departing clinician.
Mentorship has played a significant role in exposing individuals from historically underrepresented groups to careers in health care, while also advancing and enhancing their careers after they become health care professionals.49-51 Implementing and publicizing VA and veteran health care-focused mentorship and volunteer programs targeted at local communities, rural areas, schools, undergraduate programs, and medical students could increase the likelihood that students and trainees from these groups are exposed to the VHA which may lead them to join the workforce.
Conclusions
Veterans receiving care from the VHA are becoming increasingly diverse. I*DEA strategies could optimize the VHA workforce and enhance the provision of quality care for veterans. The inclusion of diverse perspectives and backgrounds, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership positions is important. Careful selection of qualified clinical leaders within the VHA—with established term limits for leadership positions, rotation of committee chairs and members, and exit interviews to obtain insights from clinicians who leave the VHA—all align with these strategies. This will foster energy and culture change, create an environment conducive to collaboration, learning, and professional growth and will enable continuous process improvement within individual VA medical centers.
Enhancing the quality of care for the evolving American veteran population is critical: many are vulnerable as a result of unique psychological and physical exposures, and many are increasingly coming from populations the federal government considers “potentially vulnerable.”1 To ensure that the needs of veterans enrolled in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) are met, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) workforce must be aware of shifts in the demographics of those who served.
The I*DEA (inclusion, diversity, equity, and access) Council is a new VHA equity team that aims to eliminate gaps in health care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive the treatment they need. The Council is the oversight body for veteran and employee-facing I*DEA programs, policies, and initiatives.2 One strategy to achieve better health outcomes for enrolled veterans is to prioritize the VA health care workforce. In this capacity, the I*DEA Council examines obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees from underserved communities.
This article discusses how diversity encompasses more than gender and ethnicity and proposes applying the following I*DEA strategies to leadership positions within the VA health care workforce: inclusion of diverse perspectives and ideas, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership roles within VHA facilities. Implementing these actions may help attract and retain qualified clinicians as health care leaders and enable the VHA to better serve the diverse veteran population.
Veteran Demographics
Characteristics of the current population of veterans differ significantly from those of individuals who served in previous eras. Since 2016, Gulf War era veterans have comprised the largest share of the veteran population, even larger than the share of Vietnam War era veterans.3 Among Gulf War veterans, 47% of women and 39% of men are aged < 35 years.4 Another notable change is the increase in the number of female veterans. In 1992, only 4% of veterans were female.5 Now, about 11% of veterans are female, a number projected to grow to 18% by 2046 (Table 1).3
With respect to race and ethnicity, about 74% of the current veteran population identifies as White, 13% as Black, 8% as Hispanic or Latino, and 2% as Asian.3,6 In addition, about 30% of veterans have ≥ 1 disability.7 About 1 million current veterans (3%) identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and/or questioning (LGBTQ+).8 Almost 1 in 4 veterans—about 4.4 million—reside in rural communities, and 55% of these rural veterans are aged > 65 years.9 Of the 4.4 million veterans who live in rural areas, 61% are enrolled in VA health care, and among those individuals 8% are women and 10% are minorities.9
Studies have found that age, sex, race and ethnicity, disability status, and LGBTQ+ identification all significantly affect health care access and outcomes in the general population.10-16 Female patients are more likely to have their symptoms downplayed or dismissed, and are often less likely to receive aggressive treatments when compared with male patients. They are also frequently underrepresented or even excluded from clinical trials.11 Female veterans have unique health care needs and report preferences for being treated by female clinicians.17,18
Higher rates of chronic health conditions and reduced access to mental health services are found among Black Americans compared to White Americans.13 Black veterans are also denied VHA benefits more often than White veterans.19 Patients with disabilities have barriers to accessing care, including difficulty with transportation and a lack of knowledge among clinicians regarding the best course of care.14 Additionally, veterans who identify as LGBTQ+ are less likely than veterans who are cisgender and heterosexual to access Veterans Health Administration (VHA) care.20 Veterans in rural communities experience more challenges to accessing health care; up to one-third of veterans in this population are unable to access the internet at home.9
To optimize care for the evolving veteran population, VHA clinicians and leaders need to be aware of the changing demographic characteristics and unique health care needs of the veteran population. Increased inclusion, diversity, and equity within the health care workforce is associated with improved quality of care, improved clinical outcomes, and have had positive financial effects on health care institutions.21-25
VA Workforce Demographics
According to the VA Office of Resolution Management, Diversity, and Inclusion, at the end of fiscal year 2020 57% of VA employees identified as White, 25% as Black, 8% as Asian, 7% as Hispanic or Latino, 2% as American Indian or Alaskan Native, and 1% belonged to ≥ 2 races.26 Women comprise about 60% of the permanent VA workforce.27 About 12% of VA employees report having a disability, which is similar to the rate of disability among noninstitutionalized civilians in the US (12.7%).28 Five percent of VA employees identified as LGBTQ+.29
Although the general workforce is relatively diverse, there is not as much diversity within VA leadership, and little data exist about the demographic characteristics of VHA physicians. As of September 2020, there were 494 senior executive service and Title 38 (health care workers) senior executive service equivalent leaders in the VHA.26 Almost 78% of these leadership positions belonged to white men and women: about 50% to white men and 28% to white women. In contrast, 8% of these positions were occupied by Black men, 7% by Black women, 3% by Asian men, 2% by Asian women, and 2% by Hispanic or Latino men.26
I*DEA in the VA
The I*DEA Council seeks to eliminate gaps in VHA care and benefits to ensure that historically underserved veteran communities receive fair treatment.30 In addition to continued attention to racial disparities, the new initiative will also examine challenges experienced by other groups, including women, individuals who identify as LGBTQ+, tribal communities, and veterans who live in rural areas, aiming to eliminate disparities that exist within the VHA.
Published in 2021, the I*DEA Action Plan discusses recommendations to enhance inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility within the VHA. Its mission statement states that the Council aims to “advance an inclusive environment that values and supports the diverse communities we serve” and “cultivates equitable access to care, benefits and services for all” from 2021 to 2025.31 To achieve better health outcomes for veterans, the I*DEA Council plans to focus on the VHA workforce and examine and address obstacles to hiring, promoting, and retaining employees.31
There are several potential benefits of increased I*DEA integration into the health care workforce.21-25 The inclusion of ideas and perspectives from diverse backgrounds, establishing equity of opportunities for all who are appropriately qualified, and accessibility to leadership roles that enable decision making by fostering culture change are direct components of I*DEA that may be beneficial. Diversity encompasses more than race, ethnicity, and gender, and creating a more diverse workforce involves recruiting qualified clinicians with diverse backgrounds and perspectives. Doing so would better reflect the diversity of veteran patients and could enhance the ability of clinicians to learn from each other and be inclusive, while understanding veterans’ unique barriers to accessing health care.
I*DEA integration may reduce the incidence of microaggressions and help transform workplace culture.32 This would be particularly beneficial for patients, as microaggressions can decrease patient satisfaction and may potentially negatively affect health outcomes.33,34 In addition, health care professionals (HCPs) would benefit from fewer microaggressions in the workplace and this would foster a more positive, supportive work environment and improve morale.
Current VHA workforce data reflect changes in the veteran population. The workforce is relatively diverse regarding race and ethnicity, gender, disability, and LGBTQ+ status. However, room for improvement remains with respect to greater inclusion, diversity of perspectives, equity, and accessibility to leadership positions and decision making roles. This would ultimately benefit and improve care for veterans. Prioritizing this within the VHA, as reflected in one of the I*DEA Task Force recommendations, is of great significance.31
It can be difficult to accurately assess the progress made in implementing I*DEA strategies at individual institutions within the VHA. While demographic diversity can be gauged using employee statistics, assessing perceptions of inclusion, incorporation of diverse perspectives, equity, and accessibility is more challenging. We recommend continuing to administer questions focusing specifically on these perceptions to current HCPs via the VHA annual All Employee Survey.35
Implementation
The VA has begun initiating I*DEA concepts in its workforce, starting with the establishment and usage of Special Emphasis Programs.36 The goal of these programs is to increase the employment of historically marginalized groups, including women, people belonging to racial and ethnic minorities, people with disabilities, and individuals identifying as LGBTQ+.28,37-42 For example, each federal agency has a designated Federal Women’s Program whose responsibilities include helping with the recruitment and advancement of female employees.37
The VHA also has an affirmative action plan with goals for recruiting and retaining individuals with disabilities.28 To strengthen equity and inclusion, the VHA offers multiple educational courses (some mandatory), both virtual and in-person, on topics such as understanding microaggressions, managing implicit bias, and understanding the importance of gender and generational diversity.43 Creating awareness and addressing misconceptions about veteran demographics at VA medical centers is important, as is enhancing awareness among the physician workforce about VA strategies and action plans to increase I*DEA. The VHA has hired officers specifically tasked with focusing on these initiatives.
Workforce Strategies
It is important to recognize overlaps between organizational ethics, quality improvement, and I*DEA initiatives. Establishing an I*DEA Council to ensure the delivery of quality care to veterans is commendable. At the facility level, individual I*DEA officers can make observations and recommendations but are not empowered to effect change. Without participation and buy-in from individuals in leadership positions, the efficacy of I*DEA initiatives is limited.
We propose implementing simple strategies to enhance the inclusion of diverse ideas and perspectives, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to clinical leadership roles within the VHA (Table 2). A competitive selection process with specific, objective criteria to enable the selection of qualified clinical leaders is vital. Specific achievements in or contributions to quality improvement, education, research, professional publications, or diversity enhancing efforts should be required qualifications for clinical leadership roles.44
Establishing term limits for clinical leadership positions—something already being implemented at the National Institutes of Health—would be of tremendous value in the VHA.45-47 Term limits would facilitate I*DEA initiatives and accessibility of leadership roles to qualified clinicians fromvarious demographics. Improving diversity of thought among clinical leaders is especially important, given how buy-in from leadership is critical in transforming the culture of an organization. Term limits would enable access to leadership roles for forward thinking, qualified clinical leaders who could institute and support changes that would promote continuous process improvement initiatives. Leaders could have the option to reapply following the completion of a term, with the ability to demonstrate specific achievements.
Another strategy for increasing equity is to ensure transparency of committee structures, with the rotation of committee members and term limits set for committee chairs whenever possible. This provides access to leadership roles, which enables participation in decision making processes. Residents and fellows who work and train at VA hospitals should have awareness of the facility’s organizational structure and the ability to participate in certain committees. The VHA workforce should be regularly informed about educational opportunities, leadership openings, and I*DEA initiatives to increase their access and use.
Exit interviews for clinicians leaving the VA would enable feedback, provide focused reviews of any problematic issues that need to be addressed, and serve as assessments of organizational ethics.48 Transparency and truth telling could be encouraged by having these exit interviews conducted by staff in the human resources department or others outside the home department of the departing clinician.
Mentorship has played a significant role in exposing individuals from historically underrepresented groups to careers in health care, while also advancing and enhancing their careers after they become health care professionals.49-51 Implementing and publicizing VA and veteran health care-focused mentorship and volunteer programs targeted at local communities, rural areas, schools, undergraduate programs, and medical students could increase the likelihood that students and trainees from these groups are exposed to the VHA which may lead them to join the workforce.
Conclusions
Veterans receiving care from the VHA are becoming increasingly diverse. I*DEA strategies could optimize the VHA workforce and enhance the provision of quality care for veterans. The inclusion of diverse perspectives and backgrounds, equity of opportunities, and accessibility to leadership positions is important. Careful selection of qualified clinical leaders within the VHA—with established term limits for leadership positions, rotation of committee chairs and members, and exit interviews to obtain insights from clinicians who leave the VHA—all align with these strategies. This will foster energy and culture change, create an environment conducive to collaboration, learning, and professional growth and will enable continuous process improvement within individual VA medical centers.
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Health equity. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/health_equity.cfm
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Equity action plan. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Department-of-Veterans-Affairs-Equity-Action-Plan.pdf
3. Schaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. March 2021. Updated November 8, 2023. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2021/04/05/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
4. US Department of Labor, Veterans’ Employment and Training Service. 2021 employment situation of women veterans. Accessed May 23, 2024. http://www.dol.gov/agencies/vets/womenveterans/womenveterans-employment
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veteran Analysis and Statistics. National survey of veterans (NSV9503). Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf
6. US Census Bureau. Veterans Day 2022: November 11. News release. October 26, 2022. Updated April 4, 2024. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/facts-for-features/2022/veterans-day.html
7. ADA National Network. Employment data for veterans with disabilities. 2017. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://adata.org/factsheet/employment-data-veterans-disabilities
8. LGBTQ+ Veterans. DAV. Accessed July 26, 2024. https://www.dav.org/get-help-now/veteran-topics-resources/lgbtq-veterans/
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
10. Mikton C, de la Fuente-Núñez V, Officer A, Krug E. Ageism: a social determinant of health that has come of age. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1333-1334.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00524-9
11. Heise L, Greene ME, Opper N, et al. Gender inequality and restrictive gender norms: framing the challenges to health. Lancet. 2019;393(10189):2440-2454.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30652-X
12. Egede LE. Race, ethnicity, culture, and disparities in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(6):667-669. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.0512.x
13. Carratala S, Maxwell C. Health disparities by race and ethnicity. Center for American Progress. Updated May 11, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/health-disparities-race-ethnicity/
14. Clemente KAP, Silva SVD, Vieira GI, et al. Barriers to the access of people with disabilities to health services: a scoping review. Rev Saude Publica. 2022;56:64.
doi:10.11606/s1518-8787.2022056003893
15. Krehely J. How to close the LGBT health disparities gap. Center for American Progress. December 21, 2009. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/how-to-close-the-lgbt-health-disparities-gap/
16. Dawson L, Frederiksen B, Long M, Ranji U, Kates J. LGBT+ people’s health and experiences accessing care. KFF. July 22, 2021. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/report/lgbt-peoples-health-and-experiences-accessing-care
17. Disabled American Veterans. DAV report spotlights issues facing women veterans. September 12, 2018. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.dav.org/learn-more/news/2018/new-report-spotlights-continuing-challenges-facing-women-veterans/
18. Sheahan KL, Goldstein KM, Than CT, et al. Women veterans’ healthcare needs, utilization, and preferences in veterans affairs primary care settings. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl 3):791-798.
doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07585-3
19. Habeshian S. VA denied Black veterans health benefits more often than White vets, data shows. Axios. June 23, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.axios.com/2023/06/23/veterans-benefits-black-white-rate-disproportionate
20. Shipherd JC, Darling JE, Klap RS, Rose D, Yano EM. Experiences in the Veterans Health Administration and impact on healthcare utilization: comparisons between LGBT and non‐LGBT women veterans. LGBT Health. 2018;5(5):303‐311. doi:10.1089/lgbt.2017.0179
21. Gomez LE, Bernet P. Diversity improves performance and outcomes. J Natl Med Assoc. 2019;111(4):383-392. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2019.01.006
22. Gill GK, McNally MJ, Berman V. Effective diversity, equity, and inclusion practices. Healthc Manage Forum. 2018;31(5):196-199. doi:10.1177/0840470418773785
23. Balinda IG, Reza N. Diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging in cardiovascular disease fellowship training. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J. 2022;18(3):67-77. doi:10.14797/mdcvj.1080
24. Parsons SK, Fineberg IC, Lin M, Singer M, Tang M, Erban JK. Promoting high-quality cancer care and equity through disciplinary diversity in team composition. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(11):1141-1147. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.013920
25. Stanford FC. The importance of diversity and inclusion in the healthcare workforce. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112(3):247-249. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2020.03.014
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Diversity and inclusion strategic plan, fiscal years 2021-2022. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/StrategicPlan.pdf
27. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). US EEOC. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.eeoc.gov/federal-sector/department-veterans-affairs-va-0
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Individuals with disabilities employment program. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/IWD.asp
29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). VA workforce diversity: FY 2022. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/Diversity_Inclusion.asp
30. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Same mission, new I-DEA: VA supports inclusion, diversity, equity and access. News release. April 28, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://news.va.gov/118609/same-mission-va-supports-inclusion-diversity/
31. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Inclusion, diversity, equity, & access (I-DEA) action plan. September 2021. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/VA_I-DEA_Action_Plan-SIGNED.pdf
32. Sue DW, Alsaidi S, Awad MN, Glaeser E, Calle CZ. Disarming racial microaggressions: microintervention strategies for targets, White allies, and bystanders. Am Psychol. 2019;74(1):128-142. doi:10.1037/amp0000296
33. Cruz D, Rodriguez Y, Mastropaolo C. Perceived microaggressions in health care: a measurement study. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0211620
 34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
35. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA all employee survey. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.data.va.gov/stories/s/VA-All-Employee-Survey-AES-/r32e-j4vj/
36. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Special emphasis programs (ORMDI). Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Special_Emphasis_Programs.asp
37. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Federal women’s program. Updated August 9, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/FWP.asp
38. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Hispanic Employment program. Updated May 16, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/HEP.asp
39. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). American Indian & Alaska Native Program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AIAN.asp
40. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Asian American, Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AAPI.asp
41. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Black/African American program. Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Black_African_American.asp
42. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). LGBTQ+ program. Updated May 21, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/LGBT.asp
43. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Diversity, equity and inclusion training. Updated March 18, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Diversity_Inclusion_Training.asp
44. Rotenstein LS, Reede JY, Jena AB. Addressing workforce diversity - a quality-improvement framework. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(12):1083-1086. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2032224
45. Beeler WH, Mangurian C, Jagsi R. Unplugging the pipeline - a call for term limits in academic medicine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1508-1511. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1906832
46. Smith DG. Term limits in academic public health administration. Public Health Rep. 2020;135(6):859-863. doi:10.1177/0033354920954495
47. Kaiser J. Shake-up at NIH: Term limits for important positions would open new opportunities for women, minorities. science.org. May 2, 2019. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/shakeup-nih-term-limits-important-positions-would-open-new-opportunities-women
48. Giacalone RA, Jurkiewicz CL, Knouse SB. Exit surveys as assessments of organizational ethicality. Public Pers Manage. 2003;32(3):397-410. doi:10.1177/009102600303200306
49. Bonifacino E, Ufomata EO, Farkas AH, Turner R, Corbelli JA. Mentorship of underrepresented physicians and trainees in academic medicine: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(4):1023-1034. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06478-7
50. Brown IM. Diversity matters: mentorship is the missing ingredient in DEI. Emergency Medicine News. 2021;43(8):28. doi:10.1097/01.EEM.0000771148.76632.35
51. Sinha A, Kuy S. The future of surgery - increasing diversity, equity, and inclusion through early mentorship. Am J Surg. 2023;225(4):800-802. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2022.12.011
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Health equity. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/topics/health_equity.cfm
2. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Equity action plan. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://department.va.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Department-of-Veterans-Affairs-Equity-Action-Plan.pdf
3. Schaeffer K. The changing face of America’s veteran population. Pew Research Center. March 2021. Updated November 8, 2023. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2021/04/05/the-changing-face-of-americas-veteran-population/
4. US Department of Labor, Veterans’ Employment and Training Service. 2021 employment situation of women veterans. Accessed May 23, 2024. http://www.dol.gov/agencies/vets/womenveterans/womenveterans-employment
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veteran Analysis and Statistics. National survey of veterans (NSV9503). Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf
6. US Census Bureau. Veterans Day 2022: November 11. News release. October 26, 2022. Updated April 4, 2024. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/facts-for-features/2022/veterans-day.html
7. ADA National Network. Employment data for veterans with disabilities. 2017. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://adata.org/factsheet/employment-data-veterans-disabilities
8. LGBTQ+ Veterans. DAV. Accessed July 26, 2024. https://www.dav.org/get-help-now/veteran-topics-resources/lgbtq-veterans/
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
10. Mikton C, de la Fuente-Núñez V, Officer A, Krug E. Ageism: a social determinant of health that has come of age. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1333-1334.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00524-9
11. Heise L, Greene ME, Opper N, et al. Gender inequality and restrictive gender norms: framing the challenges to health. Lancet. 2019;393(10189):2440-2454.
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30652-X
12. Egede LE. Race, ethnicity, culture, and disparities in health care. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(6):667-669. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.0512.x
13. Carratala S, Maxwell C. Health disparities by race and ethnicity. Center for American Progress. Updated May 11, 2020. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/health-disparities-race-ethnicity/
14. Clemente KAP, Silva SVD, Vieira GI, et al. Barriers to the access of people with disabilities to health services: a scoping review. Rev Saude Publica. 2022;56:64.
doi:10.11606/s1518-8787.2022056003893
15. Krehely J. How to close the LGBT health disparities gap. Center for American Progress. December 21, 2009. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.americanprogress.org/article/how-to-close-the-lgbt-health-disparities-gap/
16. Dawson L, Frederiksen B, Long M, Ranji U, Kates J. LGBT+ people’s health and experiences accessing care. KFF. July 22, 2021. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.kff.org/womens-health-policy/report/lgbt-peoples-health-and-experiences-accessing-care
17. Disabled American Veterans. DAV report spotlights issues facing women veterans. September 12, 2018. Accessed June 23, 2024. https://www.dav.org/learn-more/news/2018/new-report-spotlights-continuing-challenges-facing-women-veterans/
18. Sheahan KL, Goldstein KM, Than CT, et al. Women veterans’ healthcare needs, utilization, and preferences in veterans affairs primary care settings. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(Suppl 3):791-798.
doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07585-3
19. Habeshian S. VA denied Black veterans health benefits more often than White vets, data shows. Axios. June 23, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.axios.com/2023/06/23/veterans-benefits-black-white-rate-disproportionate
20. Shipherd JC, Darling JE, Klap RS, Rose D, Yano EM. Experiences in the Veterans Health Administration and impact on healthcare utilization: comparisons between LGBT and non‐LGBT women veterans. LGBT Health. 2018;5(5):303‐311. doi:10.1089/lgbt.2017.0179
21. Gomez LE, Bernet P. Diversity improves performance and outcomes. J Natl Med Assoc. 2019;111(4):383-392. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2019.01.006
22. Gill GK, McNally MJ, Berman V. Effective diversity, equity, and inclusion practices. Healthc Manage Forum. 2018;31(5):196-199. doi:10.1177/0840470418773785
23. Balinda IG, Reza N. Diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging in cardiovascular disease fellowship training. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J. 2022;18(3):67-77. doi:10.14797/mdcvj.1080
24. Parsons SK, Fineberg IC, Lin M, Singer M, Tang M, Erban JK. Promoting high-quality cancer care and equity through disciplinary diversity in team composition. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12(11):1141-1147. doi:10.1200/JOP.2016.013920
25. Stanford FC. The importance of diversity and inclusion in the healthcare workforce. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112(3):247-249. doi:10.1016/j.jnma.2020.03.014
26. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Diversity and inclusion strategic plan, fiscal years 2021-2022. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/StrategicPlan.pdf
27. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). US EEOC. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.eeoc.gov/federal-sector/department-veterans-affairs-va-0
28. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Individuals with disabilities employment program. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/IWD.asp
29. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). VA workforce diversity: FY 2022. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/Diversity_Inclusion.asp
30. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Same mission, new I-DEA: VA supports inclusion, diversity, equity and access. News release. April 28, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://news.va.gov/118609/same-mission-va-supports-inclusion-diversity/
31. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Inclusion, diversity, equity, & access (I-DEA) action plan. September 2021. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/docs/VA_I-DEA_Action_Plan-SIGNED.pdf
32. Sue DW, Alsaidi S, Awad MN, Glaeser E, Calle CZ. Disarming racial microaggressions: microintervention strategies for targets, White allies, and bystanders. Am Psychol. 2019;74(1):128-142. doi:10.1037/amp0000296
33. Cruz D, Rodriguez Y, Mastropaolo C. Perceived microaggressions in health care: a measurement study. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0211620
 34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
34. Ehie O, Muse I, Hill L, Bastien A. Professionalism: microaggression in the healthcare setting. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):131-136. doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000966
35. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA all employee survey. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.data.va.gov/stories/s/VA-All-Employee-Survey-AES-/r32e-j4vj/
36. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion. Special emphasis programs (ORMDI). Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Special_Emphasis_Programs.asp
37. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Federal women’s program. Updated August 9, 2022. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/FWP.asp
38. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Hispanic Employment program. Updated May 16, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/HEP.asp
39. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). American Indian & Alaska Native Program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AIAN.asp
40. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Asian American, Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander program. Updated September 27, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/AAPI.asp
41. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Black/African American program. Updated May 3, 2023. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Black_African_American.asp
42. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). LGBTQ+ program. Updated May 21, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/LGBT.asp
43. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Resolution Management, Diversity & Inclusion (ORMDI). Diversity, equity and inclusion training. Updated March 18, 2024. Accessed June 20, 2024. https://www.va.gov/ORMDI/DiversityInclusion/Diversity_Inclusion_Training.asp
44. Rotenstein LS, Reede JY, Jena AB. Addressing workforce diversity - a quality-improvement framework. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(12):1083-1086. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2032224
45. Beeler WH, Mangurian C, Jagsi R. Unplugging the pipeline - a call for term limits in academic medicine. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1508-1511. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1906832
46. Smith DG. Term limits in academic public health administration. Public Health Rep. 2020;135(6):859-863. doi:10.1177/0033354920954495
47. Kaiser J. Shake-up at NIH: Term limits for important positions would open new opportunities for women, minorities. science.org. May 2, 2019. Accessed May 23, 2024. https://www.science.org/content/article/shakeup-nih-term-limits-important-positions-would-open-new-opportunities-women
48. Giacalone RA, Jurkiewicz CL, Knouse SB. Exit surveys as assessments of organizational ethicality. Public Pers Manage. 2003;32(3):397-410. doi:10.1177/009102600303200306
49. Bonifacino E, Ufomata EO, Farkas AH, Turner R, Corbelli JA. Mentorship of underrepresented physicians and trainees in academic medicine: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(4):1023-1034. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06478-7
50. Brown IM. Diversity matters: mentorship is the missing ingredient in DEI. Emergency Medicine News. 2021;43(8):28. doi:10.1097/01.EEM.0000771148.76632.35
51. Sinha A, Kuy S. The future of surgery - increasing diversity, equity, and inclusion through early mentorship. Am J Surg. 2023;225(4):800-802. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2022.12.011
Has the VA Fulfilled its Commitment to Trust and Healing?
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
Trust is built step by step, commitment by commitment, on every level.
Robert C. Solomon1
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was created in response to criticism of its predecessors. Since its establishment in 1930, the VA has never been short of critics who denounced its corruption, called for its dismantling in favor of privatization, and derided its incompetence.2 Despite multiple scandals that have handed more ammunition to those who object to its continued existence, the VA has not only survived, but thrived. This editorial is written in the form of a debate between exemplar opponents and defenders of the VA on whether it is currently fulfilling its commitment to veterans.
In May 2024, the Veterans Signals survey found that 80.4% of respondents reported trust in the VA, the highest level ever recorded.3 At its 2016 launch, the survey found that only 55% of veterans expressed trust in the VA. The survey was conducted 2 years after the scandal over access to care for veterans in Phoenix. Scores would surely have been even lower than 55% during that period when the critique of the VA—even from those who believe in its mission—was most trenchant.4 Administered quarterly, the survey samples > 38,000 of the 9 million enrolled veterans. Veterans surveyed were using services from all 3 branches of the VA: Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Benefits Administration, and National Cemetery Administration. Participants are asked whether they trust the VA to fulfill the country’s commitment to veterans and specifically how they rate the VA in 3 specific criteria: effectiveness, emotional resonance, and overall ease. In the latest survey, 80.5% of veterans rated the VA positively for effectiveness, 78.4% for emotional resonance, and 75.9% for overall ease. Even more impressive is the 91.8% of participants who reported they trust the VA for outpatient health care, capping a 7-year upward trend.3
The paradigmatic VA antagonist will rightly point out the well-known methodological limitations of this type of survey, including self-selection, sampling bias, and especially low response rates. However, VA researchers will counter that the 18% response rate for the latest Veterans Signals survey is higher than the industry average.5
VA critics might say that it would not matter if the response rate were 4 times higher; what matters is not what veterans say on a survey but what decisions they make about their care. The VA defender would be constrained to concede that even the most statistically sophisticated survey remains an indirect measure of veteran trust. They could, though, marshal far stronger evidence. Two direct demonstrations published in the literature suggest that veterans do as they say and are acting on their trust in the agency. First, the VA delivered more services, health care, and benefits to veterans during the 2023 fiscal year than ever before. Importantly for Federal Practitioner readers, the 16 million documented health care visits were 3 million more than previous records.6 Second, and in some ways even more encouraging for the future of the VA as a health care system, is that due in large part to the passage of the PACT Act, there has been a surge in VA enrollment by veterans. The VA recently announced that in the last year, > 400,000 veterans signed up for its health care and services. Enrollments are 30% more than the previous year and represented the highest figure in the past 5 years, a remarkable 50% increase over 2020 pandemic levels.7
VA critics could legitimately rebut this data by asking, “So more veterans are signing up for VA, and you are delivering more care, but what about the quality of that care? Has it improved?” The VA proponent’s rejoinder from multiple converging empirical studies would be a resounding yes. We have space to cite only a few examples of that rigorous recent research. What stands out ethically about these studies is that the VA has a broad program of research into the quality of the care it delivers and then transparently publishes those findings. The VA quality improvement research mission is truly unique and provides a shared open set of data for both critics and defenders to objectively examine VA successes and failures.
Among the most persuasive analysis was a systematic review of 37 studies contrasting VA with non-VA care from 2015 to 2023. The authors examined clinical quality, safety, patient access, experience, cost-efficiency, and equity of outcome. “VA care is consistently as good as or better than non-VA care in terms of clinical quality and safety,” the systematic review authors stated while qualifying that “Access, cost/efficiency, and patient experience between the 2 systems are not well studied.”8
A second systematic review looked specifically at similar key areas of quality, safety, access, patient experience, and comparative cost-efficiency for surgical treatment delivered in the VA and the community from 2015 to 2021. Only 18 studies met the inclusion criteria, but as the authors argued:
Based on limited data, these findings suggest that expanding eligibility for veterans to get care in the community may not provide benefits in terms of increasing access to surgical procedures, will not result in better quality, and may result in worse quality of care, but may reduce inpatient length of stay and perhaps cost less.9
At this juncture, the faultfinder may become frustrated and resort to a new tactic, challenging the very assumption that is the subject of the debate and demanding proof that there is any connection between veterans’ trust in the VA and their health and well-being. “Fair enough,” the VA side would reply, “here is some research that bolsters that connection.” Kopacz and colleagues examined the relationship between trust and healing at 6 sites and included 427 veterans and active-duty service members with combat posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. The researchers found that trust and lack thereof are related to several significant mental, social, and physical health outcomes. The authors indicate the need for more research to better understand the importance and impact of trust and healing, but they show it is significant.10 Finally, veterans recognize the crucial link between trust in the unique expertise of VA practitioners in the treatment of PTSD. In a 2019 study, a majority expressed a preference to receive their PTSD treatment at the VA compared to a smaller group choosing care in the community.11
You be the judge of who won the debate, but knowing the dedication of my fellow federal practitioners, many of you will endorse my sentiment that we all need to stop talking and get back to doing our best to enhance veteran trust and healing; doing our essential part to keep fulfilling our commitment.
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
1. Solomon RC, Fernando F. Building Trust: In Business, Politics, Relationships, and Life. Oxford University Press; 2003:49.
2. Seiken J. 1921: Veterans Bureau is born - precursor to Department of Veterans Affairs. November 12, 2021. Updated September 4, 2023. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/featured-stories/veterans-bureau/
3. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Serving America’s veterans, January 1 - March 31, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://department.va.gov/veterans-experience/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2024/05/veteran-trust-report-fiscal-year-2024-quarter-2.pdf
4. Kizer KW, Jha AK. Restoring trust in VA health care. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):295-297. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1406852
5. Veteran trust in VA has increased 25% since 2016, reached an all-time high. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. May 28, 2024. Accessed July 22, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/veteran-trust-va-increased-25-since-2016-high
6. VA sets all-time records for care and benefits delivered to Veterans in fiscal year 2023. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. November 6, 2023. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-all-time-record-care-benefits-veterans-fy-2023/
7. 400,000+ Veterans enrolled in VA health care over the past 365 days, a 30% increase over last year. News release. US Department of Veterans Affairs. March 29, 2024. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-enrolled-401006-veterans-healthcare-365/
8. Apaydin EA, Paige NM, Begashaw MM, Larkin J, Miake-Lye IM, Shekelle PG. Veterans Health Administration (VA) vs. non-VA healthcare quality: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(9):2179-2188. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08207-2
9. Blegen M, Ko J, Salzman G, et al. Comparing quality of surgical care between the US Department of Veterans Affairs and non-veterans affairs settings: a systematic review. J Am Coll Surg. 2023;237(2):352-361. doi:10.1097/XCS.0000000000000720
10. Kopacz MS, Ames D, Koenig HG. Association between trust and mental, social, and physical health outcomes in veterans and active duty service members with combat-related PTSD symptomatology. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:408. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00408
11. Haro E, Mader M, Noël PH, et al. The impact of trust, satisfaction, and perceived quality on preference for setting of future care among veterans with PTSD. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):e708-e714. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz078
When Is Sexual Behavior Out of Control?
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Insurers’ Rules and AI for Preauthorization: ‘Ethically Nuts,’ Says Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
There are many things screwy with our healthcare system. Many of you [reading] this are dealing with bureaucracy, paperwork, all sorts of constraints, restraints, and requirements that sometimes make the practice of medicine, or even nursing, difficult.
I don’t think I’ve seen anything screwier, from a moral point of view, than the system we have that allows for preauthorization by third-party payers, or insurers, in order to give care to patients. It’s pretty clear that a third-party payer has a conflict of interest. It’s simple: They don’t want to spend money.
Their goal as profit-making companies is to reduce what it is that they’re going to authorize. That clearly is driving how the preauthorization process works. or somebody saying, this is the standard of care and this is what ought to happen.
We’re letting the people who have the pocketbooks and the wallets have prior approval of what the doctor thinks is correct. That is really not the way to practice medicine.
We now have more evidence about what really is going on. A doctor was recently interviewed by ProPublica and said that she had worked for Cigna as a reviewer. Basically, the message she got from that insurer was to speed it up, go fast, and basically “deny, deny, deny” when she got requests. Those are her words, not mine.
We get a peek under the tent of how this works, and Dr. Day is basically saying she had to leave because she just didn’t feel that it was evidence-driven. It was driven by concerns about who’s going to lose money or make money.
If you want to check to see whether something is appropriate, the question becomes, who ought to do prior review?
Who does it now? Sometimes doctors. Sometimes nurses who aren’t in the specialty where the request is coming in for preapproval. I’ve even seen situations where some companies use nurses in other countries, such as the Philippines, to do preapproval. They send them information, like a clip, to use to deny things that basically is boilerplate language, whatever the request is.
Looming up now, some insurers are starting to think, well, maybe artificial intelligence could do it. Just review the written request, trigger certain responses on the part of the artificial intelligence — it can deny the claims just as well as a human — and maybe it’s even cheaper to set up that system for the insurer.
This is ethically nuts. We need to have a system where doctors’ judgments drive what patients get. You listen to doctors, as I do, about preapproval access and they say patients sometimes give up trying to get what they think is needed. Continuity of care is interrupted if they have to keep making requests all the time.
There are adverse events when the thing that the doctor thought was most appropriate isn’t approved and something else is used that is less safe or less efficacious. It isn’t in patient interest to have the person with the wallet saying, this is what we think you need, and then having unqualified people or even automated intelligence with no accountability and no transparency get involved in preauthorization.
This system costs us money because middlemen are doing all this work. It basically becomes one of the huge scandals, in my view, of our health system, that doctors don’t ultimately decide what the patient needs. A preauthorizing third party or robot, without transparency, without accountability, and behind closed doors second-guesses what’s going on.
I’m Art Caplan at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Arthur L. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, New York, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
There are many things screwy with our healthcare system. Many of you [reading] this are dealing with bureaucracy, paperwork, all sorts of constraints, restraints, and requirements that sometimes make the practice of medicine, or even nursing, difficult.
I don’t think I’ve seen anything screwier, from a moral point of view, than the system we have that allows for preauthorization by third-party payers, or insurers, in order to give care to patients. It’s pretty clear that a third-party payer has a conflict of interest. It’s simple: They don’t want to spend money.
Their goal as profit-making companies is to reduce what it is that they’re going to authorize. That clearly is driving how the preauthorization process works. or somebody saying, this is the standard of care and this is what ought to happen.
We’re letting the people who have the pocketbooks and the wallets have prior approval of what the doctor thinks is correct. That is really not the way to practice medicine.
We now have more evidence about what really is going on. A doctor was recently interviewed by ProPublica and said that she had worked for Cigna as a reviewer. Basically, the message she got from that insurer was to speed it up, go fast, and basically “deny, deny, deny” when she got requests. Those are her words, not mine.
We get a peek under the tent of how this works, and Dr. Day is basically saying she had to leave because she just didn’t feel that it was evidence-driven. It was driven by concerns about who’s going to lose money or make money.
If you want to check to see whether something is appropriate, the question becomes, who ought to do prior review?
Who does it now? Sometimes doctors. Sometimes nurses who aren’t in the specialty where the request is coming in for preapproval. I’ve even seen situations where some companies use nurses in other countries, such as the Philippines, to do preapproval. They send them information, like a clip, to use to deny things that basically is boilerplate language, whatever the request is.
Looming up now, some insurers are starting to think, well, maybe artificial intelligence could do it. Just review the written request, trigger certain responses on the part of the artificial intelligence — it can deny the claims just as well as a human — and maybe it’s even cheaper to set up that system for the insurer.
This is ethically nuts. We need to have a system where doctors’ judgments drive what patients get. You listen to doctors, as I do, about preapproval access and they say patients sometimes give up trying to get what they think is needed. Continuity of care is interrupted if they have to keep making requests all the time.
There are adverse events when the thing that the doctor thought was most appropriate isn’t approved and something else is used that is less safe or less efficacious. It isn’t in patient interest to have the person with the wallet saying, this is what we think you need, and then having unqualified people or even automated intelligence with no accountability and no transparency get involved in preauthorization.
This system costs us money because middlemen are doing all this work. It basically becomes one of the huge scandals, in my view, of our health system, that doctors don’t ultimately decide what the patient needs. A preauthorizing third party or robot, without transparency, without accountability, and behind closed doors second-guesses what’s going on.
I’m Art Caplan at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Arthur L. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, New York, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
There are many things screwy with our healthcare system. Many of you [reading] this are dealing with bureaucracy, paperwork, all sorts of constraints, restraints, and requirements that sometimes make the practice of medicine, or even nursing, difficult.
I don’t think I’ve seen anything screwier, from a moral point of view, than the system we have that allows for preauthorization by third-party payers, or insurers, in order to give care to patients. It’s pretty clear that a third-party payer has a conflict of interest. It’s simple: They don’t want to spend money.
Their goal as profit-making companies is to reduce what it is that they’re going to authorize. That clearly is driving how the preauthorization process works. or somebody saying, this is the standard of care and this is what ought to happen.
We’re letting the people who have the pocketbooks and the wallets have prior approval of what the doctor thinks is correct. That is really not the way to practice medicine.
We now have more evidence about what really is going on. A doctor was recently interviewed by ProPublica and said that she had worked for Cigna as a reviewer. Basically, the message she got from that insurer was to speed it up, go fast, and basically “deny, deny, deny” when she got requests. Those are her words, not mine.
We get a peek under the tent of how this works, and Dr. Day is basically saying she had to leave because she just didn’t feel that it was evidence-driven. It was driven by concerns about who’s going to lose money or make money.
If you want to check to see whether something is appropriate, the question becomes, who ought to do prior review?
Who does it now? Sometimes doctors. Sometimes nurses who aren’t in the specialty where the request is coming in for preapproval. I’ve even seen situations where some companies use nurses in other countries, such as the Philippines, to do preapproval. They send them information, like a clip, to use to deny things that basically is boilerplate language, whatever the request is.
Looming up now, some insurers are starting to think, well, maybe artificial intelligence could do it. Just review the written request, trigger certain responses on the part of the artificial intelligence — it can deny the claims just as well as a human — and maybe it’s even cheaper to set up that system for the insurer.
This is ethically nuts. We need to have a system where doctors’ judgments drive what patients get. You listen to doctors, as I do, about preapproval access and they say patients sometimes give up trying to get what they think is needed. Continuity of care is interrupted if they have to keep making requests all the time.
There are adverse events when the thing that the doctor thought was most appropriate isn’t approved and something else is used that is less safe or less efficacious. It isn’t in patient interest to have the person with the wallet saying, this is what we think you need, and then having unqualified people or even automated intelligence with no accountability and no transparency get involved in preauthorization.
This system costs us money because middlemen are doing all this work. It basically becomes one of the huge scandals, in my view, of our health system, that doctors don’t ultimately decide what the patient needs. A preauthorizing third party or robot, without transparency, without accountability, and behind closed doors second-guesses what’s going on.
I’m Art Caplan at the Division of Medical Ethics at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine.
Arthur L. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, New York, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins: So Misunderstood
Recently, a patient of mine was hospitalized with chest pain. She was diagnosed with an acute coronary syndrome and started on a statin in addition to a beta-blocker, aspirin, and clopidogrel. After discharge, she had symptoms of dizziness and recurrent chest pain and her first thought was to stop the statin because she believed that her symptoms were statin-related side effects. I will cover a few areas where I think that there are some misunderstandings about statins.
Statins Are Not Bad For the Liver
When lovastatin first became available for prescription in the 1980s, frequent monitoring of transaminases was recommended. Patients and healthcare professionals became accustomed to frequent liver tests to monitor for statin toxicity, and to this day, some healthcare professionals still obtain liver function tests for this purpose.
But is there a reason to do this? Pfeffer and colleagues reported on the results of over 112,000 people enrolled in the West of Scotland Coronary Protection trial and found that the percentage of patients with any abnormal liver function test was similar (> 3 times the upper limit of normal for ALT) for patients taking pravastatin (1.4%) and for patients taking placebo (1.4%).1 A panel of liver experts concurred that statin-associated transaminase elevations were not indicative of liver damage or dysfunction.2 Furthermore, they noted that chronic liver disease and compensated cirrhosis were not contraindications to statin use.
In a small study, use of low-dose atorvastatin in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis improved transaminase values in 75% of patients and liver steatosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity scores were significantly improved on biopsy in most of the patients.3 The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) removed the recommendation for routine regular monitoring of liver function for patients on statins in 2012.4
Statins Do Not Cause Muscle Pain in Most Patients
Most muscle pain occurring in patients on statins is not due to the statin although patient concerns about muscle pain are common. In a meta-analysis of 19 large statin trials, 27.1% of participants treated with a statin reported at least one episode of muscle pain or weakness during a median of 4.3 years, compared with 26.6% of participants treated with placebo.5 Muscle pain for any reason is common, and patients on statins may stop therapy because of the symptoms.
Cohen and colleagues performed a survey of past and current statin users, asking about muscle symptoms.6 Muscle-related side effects were reported by 60% of former statin users and 25% of current users.
Herrett and colleagues performed an extensive series of n-of-1 trials involving 200 patients who had stopped or were considering stopping statins because of muscle symptoms.7 Participants received either 2-month blocks of atorvastatin 20 mg or 2-month blocks of placebo, six times. They rated their muscle symptoms on a visual analogue scale at the end of each block. There was no difference in muscle symptom scores between the statin and placebo periods.
Wood and colleagues took it a step further when they planned an n-of-1 trial that included statin, placebo, and no treatment.8 Each participant received four bottles of atorvastatin 20 mg, four bottles of placebo, and four empty bottles. Each month they used treatment from the bottles based on a random sequence and reported daily symptom scores. The mean symptom intensity score was 8.0 during no-tablet months, 15.4 during placebo months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months), and 16.3 during statin months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months; P = .39, compared with placebo).
Statins Are Likely Helpful In the Very Elderly
Should we be using statins for primary prevention in our very old patients? For many years the answer was generally “no” on the basis of a lack of evidence. Patients in their 80s often were not included in clinical trials. The much used American Heart Association risk calculator stops at age 79. Given the prevalence of coronary artery disease in patients as they reach their 80s, wouldn’t primary prevention really be secondary prevention? Xu and colleagues in a recent study compared outcomes for patients who were treated with statins for primary prevention with a group who were not. In the patients aged 75-84 there was a risk reduction for major cardiovascular events of 1.2% over 5 years, and for those 85 and older the risk reduction was 4.4%. Importantly, there were no significantly increased risks for myopathies and liver dysfunction in either age group.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pfeffer MA et al. Circulation. 2002;105(20):2341-6.
2. Cohen DE et al. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(8A):77C-81C.
3. Hyogo H et al. Metabolism. 2008;57(12):1711-8.
4. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Important safety label changes to cholesterol-lowering statin drugs. 2012 Feb 28.
5. Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Lancet. 2022;400(10355):832-45.
6. Cohen JD et al. J Clin Lipidol. 2012;6(3):208-15.
7. Herrett E et al. BMJ. 2021 Feb 24;372:n1355.
8. Wood FA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(22):2182-4.
9. Xu W et al. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(6):701-10.
Recently, a patient of mine was hospitalized with chest pain. She was diagnosed with an acute coronary syndrome and started on a statin in addition to a beta-blocker, aspirin, and clopidogrel. After discharge, she had symptoms of dizziness and recurrent chest pain and her first thought was to stop the statin because she believed that her symptoms were statin-related side effects. I will cover a few areas where I think that there are some misunderstandings about statins.
Statins Are Not Bad For the Liver
When lovastatin first became available for prescription in the 1980s, frequent monitoring of transaminases was recommended. Patients and healthcare professionals became accustomed to frequent liver tests to monitor for statin toxicity, and to this day, some healthcare professionals still obtain liver function tests for this purpose.
But is there a reason to do this? Pfeffer and colleagues reported on the results of over 112,000 people enrolled in the West of Scotland Coronary Protection trial and found that the percentage of patients with any abnormal liver function test was similar (> 3 times the upper limit of normal for ALT) for patients taking pravastatin (1.4%) and for patients taking placebo (1.4%).1 A panel of liver experts concurred that statin-associated transaminase elevations were not indicative of liver damage or dysfunction.2 Furthermore, they noted that chronic liver disease and compensated cirrhosis were not contraindications to statin use.
In a small study, use of low-dose atorvastatin in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis improved transaminase values in 75% of patients and liver steatosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity scores were significantly improved on biopsy in most of the patients.3 The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) removed the recommendation for routine regular monitoring of liver function for patients on statins in 2012.4
Statins Do Not Cause Muscle Pain in Most Patients
Most muscle pain occurring in patients on statins is not due to the statin although patient concerns about muscle pain are common. In a meta-analysis of 19 large statin trials, 27.1% of participants treated with a statin reported at least one episode of muscle pain or weakness during a median of 4.3 years, compared with 26.6% of participants treated with placebo.5 Muscle pain for any reason is common, and patients on statins may stop therapy because of the symptoms.
Cohen and colleagues performed a survey of past and current statin users, asking about muscle symptoms.6 Muscle-related side effects were reported by 60% of former statin users and 25% of current users.
Herrett and colleagues performed an extensive series of n-of-1 trials involving 200 patients who had stopped or were considering stopping statins because of muscle symptoms.7 Participants received either 2-month blocks of atorvastatin 20 mg or 2-month blocks of placebo, six times. They rated their muscle symptoms on a visual analogue scale at the end of each block. There was no difference in muscle symptom scores between the statin and placebo periods.
Wood and colleagues took it a step further when they planned an n-of-1 trial that included statin, placebo, and no treatment.8 Each participant received four bottles of atorvastatin 20 mg, four bottles of placebo, and four empty bottles. Each month they used treatment from the bottles based on a random sequence and reported daily symptom scores. The mean symptom intensity score was 8.0 during no-tablet months, 15.4 during placebo months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months), and 16.3 during statin months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months; P = .39, compared with placebo).
Statins Are Likely Helpful In the Very Elderly
Should we be using statins for primary prevention in our very old patients? For many years the answer was generally “no” on the basis of a lack of evidence. Patients in their 80s often were not included in clinical trials. The much used American Heart Association risk calculator stops at age 79. Given the prevalence of coronary artery disease in patients as they reach their 80s, wouldn’t primary prevention really be secondary prevention? Xu and colleagues in a recent study compared outcomes for patients who were treated with statins for primary prevention with a group who were not. In the patients aged 75-84 there was a risk reduction for major cardiovascular events of 1.2% over 5 years, and for those 85 and older the risk reduction was 4.4%. Importantly, there were no significantly increased risks for myopathies and liver dysfunction in either age group.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pfeffer MA et al. Circulation. 2002;105(20):2341-6.
2. Cohen DE et al. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(8A):77C-81C.
3. Hyogo H et al. Metabolism. 2008;57(12):1711-8.
4. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Important safety label changes to cholesterol-lowering statin drugs. 2012 Feb 28.
5. Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Lancet. 2022;400(10355):832-45.
6. Cohen JD et al. J Clin Lipidol. 2012;6(3):208-15.
7. Herrett E et al. BMJ. 2021 Feb 24;372:n1355.
8. Wood FA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(22):2182-4.
9. Xu W et al. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(6):701-10.
Recently, a patient of mine was hospitalized with chest pain. She was diagnosed with an acute coronary syndrome and started on a statin in addition to a beta-blocker, aspirin, and clopidogrel. After discharge, she had symptoms of dizziness and recurrent chest pain and her first thought was to stop the statin because she believed that her symptoms were statin-related side effects. I will cover a few areas where I think that there are some misunderstandings about statins.
Statins Are Not Bad For the Liver
When lovastatin first became available for prescription in the 1980s, frequent monitoring of transaminases was recommended. Patients and healthcare professionals became accustomed to frequent liver tests to monitor for statin toxicity, and to this day, some healthcare professionals still obtain liver function tests for this purpose.
But is there a reason to do this? Pfeffer and colleagues reported on the results of over 112,000 people enrolled in the West of Scotland Coronary Protection trial and found that the percentage of patients with any abnormal liver function test was similar (> 3 times the upper limit of normal for ALT) for patients taking pravastatin (1.4%) and for patients taking placebo (1.4%).1 A panel of liver experts concurred that statin-associated transaminase elevations were not indicative of liver damage or dysfunction.2 Furthermore, they noted that chronic liver disease and compensated cirrhosis were not contraindications to statin use.
In a small study, use of low-dose atorvastatin in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis improved transaminase values in 75% of patients and liver steatosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity scores were significantly improved on biopsy in most of the patients.3 The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) removed the recommendation for routine regular monitoring of liver function for patients on statins in 2012.4
Statins Do Not Cause Muscle Pain in Most Patients
Most muscle pain occurring in patients on statins is not due to the statin although patient concerns about muscle pain are common. In a meta-analysis of 19 large statin trials, 27.1% of participants treated with a statin reported at least one episode of muscle pain or weakness during a median of 4.3 years, compared with 26.6% of participants treated with placebo.5 Muscle pain for any reason is common, and patients on statins may stop therapy because of the symptoms.
Cohen and colleagues performed a survey of past and current statin users, asking about muscle symptoms.6 Muscle-related side effects were reported by 60% of former statin users and 25% of current users.
Herrett and colleagues performed an extensive series of n-of-1 trials involving 200 patients who had stopped or were considering stopping statins because of muscle symptoms.7 Participants received either 2-month blocks of atorvastatin 20 mg or 2-month blocks of placebo, six times. They rated their muscle symptoms on a visual analogue scale at the end of each block. There was no difference in muscle symptom scores between the statin and placebo periods.
Wood and colleagues took it a step further when they planned an n-of-1 trial that included statin, placebo, and no treatment.8 Each participant received four bottles of atorvastatin 20 mg, four bottles of placebo, and four empty bottles. Each month they used treatment from the bottles based on a random sequence and reported daily symptom scores. The mean symptom intensity score was 8.0 during no-tablet months, 15.4 during placebo months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months), and 16.3 during statin months (P < .001, compared with no-tablet months; P = .39, compared with placebo).
Statins Are Likely Helpful In the Very Elderly
Should we be using statins for primary prevention in our very old patients? For many years the answer was generally “no” on the basis of a lack of evidence. Patients in their 80s often were not included in clinical trials. The much used American Heart Association risk calculator stops at age 79. Given the prevalence of coronary artery disease in patients as they reach their 80s, wouldn’t primary prevention really be secondary prevention? Xu and colleagues in a recent study compared outcomes for patients who were treated with statins for primary prevention with a group who were not. In the patients aged 75-84 there was a risk reduction for major cardiovascular events of 1.2% over 5 years, and for those 85 and older the risk reduction was 4.4%. Importantly, there were no significantly increased risks for myopathies and liver dysfunction in either age group.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pfeffer MA et al. Circulation. 2002;105(20):2341-6.
2. Cohen DE et al. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97(8A):77C-81C.
3. Hyogo H et al. Metabolism. 2008;57(12):1711-8.
4. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Important safety label changes to cholesterol-lowering statin drugs. 2012 Feb 28.
5. Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Lancet. 2022;400(10355):832-45.
6. Cohen JD et al. J Clin Lipidol. 2012;6(3):208-15.
7. Herrett E et al. BMJ. 2021 Feb 24;372:n1355.
8. Wood FA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(22):2182-4.
9. Xu W et al. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(6):701-10.
The Shield Sign of Cutaneous Metastases Is Associated With Carcinoma Hemorrhagiectoides
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the Case Letter from Wang et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15) of a 60-year-old man whose metastatic salivary duct adenocarcinoma manifested with the shield sign as well as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. Cutaneous metastases have seldom been described in association with salivary duct carcinoma.2-7 In addition, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign has not been commonly reported.5,8-12
Salivary duct carcinoma—an uncommon head and neck malignancy characterized by androgen receptor expression—rarely is associated with cutaneous metastases. Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms cutaneous, metastatic, salivary duct carcinoma, and/or skin, including the patient described by Wang et al,1 there have been 8 individuals with cutaneous metastases from this cancer. The morphology of the cutaneous metastases has varied from angiomatous to angiokeratomalike (black and keratotic) papules, bullae, macules (red), papules and nodules (erythematous and scaly), plaques (cellulitislike and confluent that were purpuric, hemorrhagic, and violaceous), pseudovesicles, purpuric papules, subcutaneous nodules, and an ulcer (superficial and mimicked a basal cell carcinoma).1-7 Remarkably, 4 of 8 patients (50%) with salivary duct carcinoma cutaneous metastases presented with a shield sign,5,7 including the case reported by Wang et al.1
The shield sign is a distinctive clinical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis.10 It was named to describe the skin metastases located predominantly on the chest area that would be covered by a medieval knight’s shield5,10,12; metastatic lesions also have been noted on the proximal arm and/or the upper back in a similar distribution.8,9 To date, based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms breast cancer, carcinoma, hemorrhagiectoides, metastases, salivary duct carcinoma, shield, and/or sign, the shield sign has been described in 6 patients with cutaneous metastases either from salivary duct carcinoma (4 patients)1,5,7 or breast cancer (2 patients).8,9 The shield sign pathologically corresponds to carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides, an inflammatory pattern of cutaneous metastases.5,11
Inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma has 3 distinctive clinical and pathologic manifestations.11 Carcinoma erysipelatoides and carcinoma telangiectoides were the earlier described variants.11 In 2012, carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides was described as the third pattern of inflammatory cutaneous metastasis.5
Carcinoma erysipelatoides, which clinically mimics cutaneous streptococcal cellulitis, appears as a well-defined erythematous patch or plaque; the tumor cells can be found in the lymphatic vessels and either are absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma telangiectoides, which clinically mimics idiopathic telangiectases, appears as an erythematous patch with prominent telangiectases; the tumor cells can be found in the blood vessels and are either absent or minimally present in the dermis. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides appears as purpuric or violaceous indurated plaques; the tumor cells are not only found in the blood vessels, in the lymphatic vessels, or both, but also can be mildly to extensively present in the dermis.5,10,11
In conclusion, the shield sign is a unique presentation of inflammatory cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, which is associated with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The clinical features of the infiltrated plaques correspond to the presence of tumor cells in the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the dermis; in addition, the purpuric and violaceous appearance correlates with the presence of extravasated erythrocytes or hemorrhage in the dermis. To date, half of the patients with skin metastases from salivary duct carcinoma have presented with carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides–associated shield sign.
Authors’ Response
We appreciate and welcome the comments provided by the authors. Drawing attention to unusual pathologic manifestations of cutaneous metastatic salivary duct carcinoma manifesting with the shield sign, the authors present a comprehensive review of 3 distinctive presentations: carcinoma erysipelatoides, carcinoma telangiectoides, and carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. The inclusion of these variants enriches the discussion and makes this letter a valuable addition to the literature on cutaneous metastatic carcinoma, particularly metastatic salivary duct carcinoma.
Xintong Wang, MD; William H. Westra, MD
From the Department of Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
- Wang X, Vyas NS, Alghamdi AA, et al. Cutaneous presentation of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma. Cutis. 2023;112:E13-E15.
- Pollock JL, Catalano E. Metastatic ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland in a patient with sarcoidosis. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1098-1099.
- Pollock JL. Metastatic carcinoma of the parotid gland resembling carcinoma of the breast. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:1093.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Anderson JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Shin JY, Eun DH, Lee JY, et al. A case of cutaneous metastases of salivary duct carcinoma mimicking radiation recall dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2020;32:436-438.
- Aravena RC, Aravena DC, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hn3z850.
- Smith KA, Basko-Plluska J, Kothari AD, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cutis. 2020;105:E20-E22.
- Cohen PR, Kurzrock R. Cutaneous metastatic cancer: carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides presenting as the shield sign. Cureus. 2021;13:e12627.
- Cohen PR. Pleomorphic appearance of breast cancer cutaneous metastases. Cureus. 2021;13:e20301.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Kurzrock R. Tumor lysis syndrome: introduction of a cutaneous variant and a new classification system. Cureus. 2021;13:e13816.
Undiagnosed, Untreated Tardive Dyskinesia, Hinders Adherence to Antipsychotics
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tardive dyskinesia is a chronic, potentially irreversible, hyperkinetic movement disorder. And the challenge with tardive dyskinesia is that it’s underdiagnosed and undertreated. With the expanded use of dopamine receptor–blocking agents, there are about 7.5 million Americans who are now exposed and at risk for tardive dyskinesia.
It’s thought that about 500,000-750,000 of these patients may in fact have tardive dyskinesia, but only 15% are treated. So why are people not being treated for tardive dyskinesia? Well, there are a number of possible answers.
Until a few years ago, there were no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia, and these antipsychotic medications that the patients were taking, in many cases, were potentially lifesaving drugs, so they couldn’t simply be stopped. As a result of that, I think physicians developed a certain psychic blindness to identifying tardive dyskinesia, because it was their drugs that were causing the disease and yet they couldn’t be stopped. So, there really wasn’t much they could do in terms of making the diagnosis.
In addition, they were trained that tardive dyskinesia doesn’t have much impact on patients. But we now know, through surveys and other studies, that tardive dyskinesia can have a tremendous impact on patients and on your ability to treat the patient’s underlying mental health issues. It’s estimated that 50% of patients with tardive dyskinesia actually reduce the amount of antipsychotic medication they’re taking on their own, and about 40% may in fact stop their antipsychotic medication altogether.
Thirty-five percent of patients stopped seeing their doctor after they developed tardive dyskinesia, and about 20% of patients actually told other patients not to take their antipsychotic medication. So, tardive dyskinesia is impacting your ability to treat patients. In addition, it impacts the patients themselves. Nearly three out of four patients with tardive dyskinesia said, in surveys, that it caused severe impact on their psychosocial functioning.
It also impacted caregivers, with 70% of caregivers saying that the patients with tardive dyskinesia made them more anxious and limited them socially. So, we have this tremendous impact from tardive dyskinesia.
In addition, physicians sometimes don’t identify tardive dyskinesia correctly. They mistake it for another movement disorder: drug-induced parkinsonism. Or it falls under the rubric of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), and they were trained that you treat EPS with benztropine. The challenge with that is that benztropine is only indicated for acute dystonia or for drug-induced parkinsonism. It actually makes tardive dyskinesia worse. And, in the product insert for benztropine, it’s recommended that it should not be used in tardive dyskinesia. So if you have a patient whom you suspect has tardive dyskinesia, you have to discontinue the benztropine. That’s a really important first step.
And then, what else should you do? There are now two FDA-approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia. These are valbenazine and deutetrabenazine. Both of these drugs have been demonstrated in large double-blind, placebo-controlled studies to reduce tardive dyskinesia, as measured by the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale, by about 30%. These drugs have been demonstrated to be safe and well tolerated, with the main side effect being somnolence.
Some people can also develop parkinsonism. Why could there be Parkinsonism? This is because vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors work by reducing the amount of dopamine that can be packaged in the presynaptic neuron. That means that less dopamine is available to the synapse, and this reduces movement. The American Psychiatric Association has issued guidelines for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and has said that moderate to severe tardive dyskinesia should be treated first-line with VMAT2 inhibitors and that mild tardive dyskinesia should also be treated with VMAT2 inhibitors if the tardive dyskinesia is impacting the patient.
Given the impact that tardive dyskinesia has on patients and caregivers, and the physician’s ability to treat these patients’ mental health issues, we need to become aggressive and treat the tardive dyskinesia so that patients can improve and be able to have their movements treated without impacting their underlying mental health issues.
Daniel Kremens, professor, Department of Neurology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, codirector, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Division, Jack and Vickie Farber Center for Neuroscience, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Teva Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Merz, Allergan, Bial, Cerevel, Amneal, Acadia, Supernus, Adamas, Acorda, Kyowa Kirin, and Neurocrine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tardive dyskinesia is a chronic, potentially irreversible, hyperkinetic movement disorder. And the challenge with tardive dyskinesia is that it’s underdiagnosed and undertreated. With the expanded use of dopamine receptor–blocking agents, there are about 7.5 million Americans who are now exposed and at risk for tardive dyskinesia.
It’s thought that about 500,000-750,000 of these patients may in fact have tardive dyskinesia, but only 15% are treated. So why are people not being treated for tardive dyskinesia? Well, there are a number of possible answers.
Until a few years ago, there were no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia, and these antipsychotic medications that the patients were taking, in many cases, were potentially lifesaving drugs, so they couldn’t simply be stopped. As a result of that, I think physicians developed a certain psychic blindness to identifying tardive dyskinesia, because it was their drugs that were causing the disease and yet they couldn’t be stopped. So, there really wasn’t much they could do in terms of making the diagnosis.
In addition, they were trained that tardive dyskinesia doesn’t have much impact on patients. But we now know, through surveys and other studies, that tardive dyskinesia can have a tremendous impact on patients and on your ability to treat the patient’s underlying mental health issues. It’s estimated that 50% of patients with tardive dyskinesia actually reduce the amount of antipsychotic medication they’re taking on their own, and about 40% may in fact stop their antipsychotic medication altogether.
Thirty-five percent of patients stopped seeing their doctor after they developed tardive dyskinesia, and about 20% of patients actually told other patients not to take their antipsychotic medication. So, tardive dyskinesia is impacting your ability to treat patients. In addition, it impacts the patients themselves. Nearly three out of four patients with tardive dyskinesia said, in surveys, that it caused severe impact on their psychosocial functioning.
It also impacted caregivers, with 70% of caregivers saying that the patients with tardive dyskinesia made them more anxious and limited them socially. So, we have this tremendous impact from tardive dyskinesia.
In addition, physicians sometimes don’t identify tardive dyskinesia correctly. They mistake it for another movement disorder: drug-induced parkinsonism. Or it falls under the rubric of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), and they were trained that you treat EPS with benztropine. The challenge with that is that benztropine is only indicated for acute dystonia or for drug-induced parkinsonism. It actually makes tardive dyskinesia worse. And, in the product insert for benztropine, it’s recommended that it should not be used in tardive dyskinesia. So if you have a patient whom you suspect has tardive dyskinesia, you have to discontinue the benztropine. That’s a really important first step.
And then, what else should you do? There are now two FDA-approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia. These are valbenazine and deutetrabenazine. Both of these drugs have been demonstrated in large double-blind, placebo-controlled studies to reduce tardive dyskinesia, as measured by the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale, by about 30%. These drugs have been demonstrated to be safe and well tolerated, with the main side effect being somnolence.
Some people can also develop parkinsonism. Why could there be Parkinsonism? This is because vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors work by reducing the amount of dopamine that can be packaged in the presynaptic neuron. That means that less dopamine is available to the synapse, and this reduces movement. The American Psychiatric Association has issued guidelines for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and has said that moderate to severe tardive dyskinesia should be treated first-line with VMAT2 inhibitors and that mild tardive dyskinesia should also be treated with VMAT2 inhibitors if the tardive dyskinesia is impacting the patient.
Given the impact that tardive dyskinesia has on patients and caregivers, and the physician’s ability to treat these patients’ mental health issues, we need to become aggressive and treat the tardive dyskinesia so that patients can improve and be able to have their movements treated without impacting their underlying mental health issues.
Daniel Kremens, professor, Department of Neurology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, codirector, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Division, Jack and Vickie Farber Center for Neuroscience, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Teva Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Merz, Allergan, Bial, Cerevel, Amneal, Acadia, Supernus, Adamas, Acorda, Kyowa Kirin, and Neurocrine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Tardive dyskinesia is a chronic, potentially irreversible, hyperkinetic movement disorder. And the challenge with tardive dyskinesia is that it’s underdiagnosed and undertreated. With the expanded use of dopamine receptor–blocking agents, there are about 7.5 million Americans who are now exposed and at risk for tardive dyskinesia.
It’s thought that about 500,000-750,000 of these patients may in fact have tardive dyskinesia, but only 15% are treated. So why are people not being treated for tardive dyskinesia? Well, there are a number of possible answers.
Until a few years ago, there were no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia, and these antipsychotic medications that the patients were taking, in many cases, were potentially lifesaving drugs, so they couldn’t simply be stopped. As a result of that, I think physicians developed a certain psychic blindness to identifying tardive dyskinesia, because it was their drugs that were causing the disease and yet they couldn’t be stopped. So, there really wasn’t much they could do in terms of making the diagnosis.
In addition, they were trained that tardive dyskinesia doesn’t have much impact on patients. But we now know, through surveys and other studies, that tardive dyskinesia can have a tremendous impact on patients and on your ability to treat the patient’s underlying mental health issues. It’s estimated that 50% of patients with tardive dyskinesia actually reduce the amount of antipsychotic medication they’re taking on their own, and about 40% may in fact stop their antipsychotic medication altogether.
Thirty-five percent of patients stopped seeing their doctor after they developed tardive dyskinesia, and about 20% of patients actually told other patients not to take their antipsychotic medication. So, tardive dyskinesia is impacting your ability to treat patients. In addition, it impacts the patients themselves. Nearly three out of four patients with tardive dyskinesia said, in surveys, that it caused severe impact on their psychosocial functioning.
It also impacted caregivers, with 70% of caregivers saying that the patients with tardive dyskinesia made them more anxious and limited them socially. So, we have this tremendous impact from tardive dyskinesia.
In addition, physicians sometimes don’t identify tardive dyskinesia correctly. They mistake it for another movement disorder: drug-induced parkinsonism. Or it falls under the rubric of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), and they were trained that you treat EPS with benztropine. The challenge with that is that benztropine is only indicated for acute dystonia or for drug-induced parkinsonism. It actually makes tardive dyskinesia worse. And, in the product insert for benztropine, it’s recommended that it should not be used in tardive dyskinesia. So if you have a patient whom you suspect has tardive dyskinesia, you have to discontinue the benztropine. That’s a really important first step.
And then, what else should you do? There are now two FDA-approved treatments for tardive dyskinesia. These are valbenazine and deutetrabenazine. Both of these drugs have been demonstrated in large double-blind, placebo-controlled studies to reduce tardive dyskinesia, as measured by the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale, by about 30%. These drugs have been demonstrated to be safe and well tolerated, with the main side effect being somnolence.
Some people can also develop parkinsonism. Why could there be Parkinsonism? This is because vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors work by reducing the amount of dopamine that can be packaged in the presynaptic neuron. That means that less dopamine is available to the synapse, and this reduces movement. The American Psychiatric Association has issued guidelines for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and has said that moderate to severe tardive dyskinesia should be treated first-line with VMAT2 inhibitors and that mild tardive dyskinesia should also be treated with VMAT2 inhibitors if the tardive dyskinesia is impacting the patient.
Given the impact that tardive dyskinesia has on patients and caregivers, and the physician’s ability to treat these patients’ mental health issues, we need to become aggressive and treat the tardive dyskinesia so that patients can improve and be able to have their movements treated without impacting their underlying mental health issues.
Daniel Kremens, professor, Department of Neurology, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, codirector, Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Division, Jack and Vickie Farber Center for Neuroscience, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Teva Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Merz, Allergan, Bial, Cerevel, Amneal, Acadia, Supernus, Adamas, Acorda, Kyowa Kirin, and Neurocrine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Retirement Planning for Gastroenterologists
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Fed Worker Health Plans Ban Maximizers and Copay Accumulators: Why Not for the Rest of the US?
The escalating costs of medications and the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country have drawn criticism from governments, regulators, and the media. Federal and state governments are exploring various strategies to mitigate this issue, including the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) for drug price negotiations and the establishment of state Pharmaceutical Drug Affordability Boards (PDABs). However, it’s uncertain whether these measures will effectively reduce patients’ medication expenses, given the tendency of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) to favor more expensive drugs on their formularies and the implementation challenges faced by PDABs.
The question then arises: How can we promptly assist patients, especially those with multiple chronic conditions, in affording their healthcare? Many of these patients are enrolled in high-deductible plans and struggle to cover all their medical and pharmacy costs.
A significant obstacle to healthcare affordability emerged in 2018 with the introduction of Copay Accumulator Programs by PBMs. These programs prevent patients from applying manufacturer copay cards toward their deductible and maximum out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. The impact of these policies has been devastating, leading to decreased adherence to medications and delayed necessary medical procedures, such as colonoscopies. Copay accumulators do nothing to address the high cost of medical care. They merely shift the burden from insurance companies to patients.
There is a direct solution to help patients, particularly those burdened with high pharmacy bills, afford their medical care. It would be that all payments from patients, including manufacturer copay cards, count toward their deductible and maximum OOP costs. This should apply regardless of whether the insurance plan is fully funded or a self-insured employer plan. This would be an immediate step toward making healthcare more affordable for patients.
Copay Accumulator Programs
How did these detrimental policies, which have been proven to harm patients, originate? It’s interesting that health insurance policies for federal employees do not allow these programs and yet the federal government has done little to protect its citizens from these egregious policies. More on that later.
In 2018, insurance companies and PBMs conceived an idea to introduce what they called copay accumulator adjustment programs. These programs would prevent the use of manufacturer copay cards from counting toward patient deductibles or OOP maximums. They justified this by arguing that manufacturer copay cards encouraged patients to opt for higher-priced brand drugs when lower-cost generics were available.
However, data from IQVIA contradicts this claim. An analysis of copay card usage from 2013 to 2017 revealed that a mere 0.4% of these cards were used for brand-name drugs that had already lost their exclusivity. This indicates that the vast majority of copay cards were not being used to purchase more expensive brand-name drugs when cheaper, generic alternatives were available.
Another argument put forth by one of the large PBMs was that patients with high deductibles don’t have enough “skin in the game” due to their low premiums, and therefore don’t deserve to have their deductible covered by a copay card. This raises the question, “Does a patient with hemophilia or systemic lupus who can’t afford a low deductible plan not have ‘skin in the game’? Is that a fair assessment?” It’s disconcerting to see a multibillion-dollar company dictating who deserves to have their deductible covered. These policies clearly disproportionately harm patients with chronic illnesses, especially those with high deductibles. As a result, many organizations have labeled these policies as discriminatory.
Following the implementation of accumulator programs in 2018 and 2019, many patients were unaware that their copay cards weren’t contributing toward their deductibles. They were taken aback when specialty pharmacies informed them of owing substantial amounts because of unmet deductibles. Consequently, patients discontinued their medications, leading to disease progression and increased costs. The only downside for health insurers and PBMs was the negative publicity associated with patients losing medication access.
Maximizer Programs
By the end of 2019, the three major PBMs had devised a strategy to keep patients on their medication throughout the year, without counting copay cards toward the deductible, and found a way to profit more from these cards, sometimes quadrupling their value. This was the birth of the maximizer programs.
Maximizers exploit a “loophole” in the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA defines Essential Healthcare Benefits (EHB); anything not listed as an EHB is deemed “non-essential.” As a result, neither personal payments nor copay cards count toward deductibles or OOP maximums. Patients were informed that neither their own money nor manufacturer copay cards would count toward their deductible/OOP max.
One of my patients was warned that without enrolling in the maximizer program through SaveOnSP (owned by Express Scripts), she would bear the full cost of the drug, and nothing would count toward her OOP max. Frightened, she enrolled and surrendered her manufacturer copay card to SaveOnSP. Maximizers pocket the maximum value of the copay card, even if it exceeds the insurance plan’s yearly cost share by threefold or more. To do this legally, PBMs increase the patient’s original cost share amount during the plan year to match the value of the manufacturer copay card.
Combating These Programs
Nineteen states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico have outlawed copay accumulators in health plans under state jurisdiction. I personally testified in Louisiana, leading to a ban in our state. CSRO’s award-winning map tool can show if your state has passed the ban on copay accumulator programs. However, many states have not passed bans on copay accumulators and self-insured employer groups, which fall under the Department of Labor and not state regulation, are still unaffected. There is also proposed federal legislation, the “Help Ensure Lower Patient Copays Act,” that would prohibit the use of copay accumulators in exchange plans. Despite having bipartisan support, it is having a hard time getting across the finish line in Congress.
In 2020, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued a rule prohibiting accumulator programs in all plans if the product was a brand name without a generic alternative. Unfortunately, this rule was rescinded in 2021, allowing copay accumulators even if a lower-cost generic was available.
In a positive turn of events, the US District Court of the District of Columbia overturned the 2021 rule in late 2023, reinstating the 2020 ban on copay accumulators. However, HHS has yet to enforce this ban.
Double Standard
Why is it that our federal government refrains from enforcing bans on copay accumulators for the American public, yet the US Office of Personnel Management (OPM) in its 2024 health plan for federal employees has explicitly stated that it “will decline any arrangements which may manipulate the prescription drug benefit design or incorporate any programs such as copay maximizers, copay optimizers, or other similar programs as these types of benefit designs are not in the best interest of enrollees or the Government.”
If such practices are deemed unsuitable for federal employees, why are they considered acceptable for the rest of the American population? This discrepancy raises important questions about healthcare equity.
In conclusion, the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. The introduction of copay accumulator programs and maximizers by PBMs has led to decreased adherence to needed medications, as well as delay in important medical procedures, exacerbating this situation. An across-the-board ban on these programs would offer immediate relief to many families that no longer can afford needed care.
It is clear that more needs to be done to ensure that all patients, regardless of their financial situation or the nature of their health insurance plan, can afford the healthcare they need. This includes ensuring that patients are not penalized for using manufacturer copay cards to help cover their costs. As we move forward, it is crucial that we continue to advocate for policies that prioritize the health and well-being of all patients.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
The escalating costs of medications and the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country have drawn criticism from governments, regulators, and the media. Federal and state governments are exploring various strategies to mitigate this issue, including the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) for drug price negotiations and the establishment of state Pharmaceutical Drug Affordability Boards (PDABs). However, it’s uncertain whether these measures will effectively reduce patients’ medication expenses, given the tendency of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) to favor more expensive drugs on their formularies and the implementation challenges faced by PDABs.
The question then arises: How can we promptly assist patients, especially those with multiple chronic conditions, in affording their healthcare? Many of these patients are enrolled in high-deductible plans and struggle to cover all their medical and pharmacy costs.
A significant obstacle to healthcare affordability emerged in 2018 with the introduction of Copay Accumulator Programs by PBMs. These programs prevent patients from applying manufacturer copay cards toward their deductible and maximum out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. The impact of these policies has been devastating, leading to decreased adherence to medications and delayed necessary medical procedures, such as colonoscopies. Copay accumulators do nothing to address the high cost of medical care. They merely shift the burden from insurance companies to patients.
There is a direct solution to help patients, particularly those burdened with high pharmacy bills, afford their medical care. It would be that all payments from patients, including manufacturer copay cards, count toward their deductible and maximum OOP costs. This should apply regardless of whether the insurance plan is fully funded or a self-insured employer plan. This would be an immediate step toward making healthcare more affordable for patients.
Copay Accumulator Programs
How did these detrimental policies, which have been proven to harm patients, originate? It’s interesting that health insurance policies for federal employees do not allow these programs and yet the federal government has done little to protect its citizens from these egregious policies. More on that later.
In 2018, insurance companies and PBMs conceived an idea to introduce what they called copay accumulator adjustment programs. These programs would prevent the use of manufacturer copay cards from counting toward patient deductibles or OOP maximums. They justified this by arguing that manufacturer copay cards encouraged patients to opt for higher-priced brand drugs when lower-cost generics were available.
However, data from IQVIA contradicts this claim. An analysis of copay card usage from 2013 to 2017 revealed that a mere 0.4% of these cards were used for brand-name drugs that had already lost their exclusivity. This indicates that the vast majority of copay cards were not being used to purchase more expensive brand-name drugs when cheaper, generic alternatives were available.
Another argument put forth by one of the large PBMs was that patients with high deductibles don’t have enough “skin in the game” due to their low premiums, and therefore don’t deserve to have their deductible covered by a copay card. This raises the question, “Does a patient with hemophilia or systemic lupus who can’t afford a low deductible plan not have ‘skin in the game’? Is that a fair assessment?” It’s disconcerting to see a multibillion-dollar company dictating who deserves to have their deductible covered. These policies clearly disproportionately harm patients with chronic illnesses, especially those with high deductibles. As a result, many organizations have labeled these policies as discriminatory.
Following the implementation of accumulator programs in 2018 and 2019, many patients were unaware that their copay cards weren’t contributing toward their deductibles. They were taken aback when specialty pharmacies informed them of owing substantial amounts because of unmet deductibles. Consequently, patients discontinued their medications, leading to disease progression and increased costs. The only downside for health insurers and PBMs was the negative publicity associated with patients losing medication access.
Maximizer Programs
By the end of 2019, the three major PBMs had devised a strategy to keep patients on their medication throughout the year, without counting copay cards toward the deductible, and found a way to profit more from these cards, sometimes quadrupling their value. This was the birth of the maximizer programs.
Maximizers exploit a “loophole” in the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA defines Essential Healthcare Benefits (EHB); anything not listed as an EHB is deemed “non-essential.” As a result, neither personal payments nor copay cards count toward deductibles or OOP maximums. Patients were informed that neither their own money nor manufacturer copay cards would count toward their deductible/OOP max.
One of my patients was warned that without enrolling in the maximizer program through SaveOnSP (owned by Express Scripts), she would bear the full cost of the drug, and nothing would count toward her OOP max. Frightened, she enrolled and surrendered her manufacturer copay card to SaveOnSP. Maximizers pocket the maximum value of the copay card, even if it exceeds the insurance plan’s yearly cost share by threefold or more. To do this legally, PBMs increase the patient’s original cost share amount during the plan year to match the value of the manufacturer copay card.
Combating These Programs
Nineteen states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico have outlawed copay accumulators in health plans under state jurisdiction. I personally testified in Louisiana, leading to a ban in our state. CSRO’s award-winning map tool can show if your state has passed the ban on copay accumulator programs. However, many states have not passed bans on copay accumulators and self-insured employer groups, which fall under the Department of Labor and not state regulation, are still unaffected. There is also proposed federal legislation, the “Help Ensure Lower Patient Copays Act,” that would prohibit the use of copay accumulators in exchange plans. Despite having bipartisan support, it is having a hard time getting across the finish line in Congress.
In 2020, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued a rule prohibiting accumulator programs in all plans if the product was a brand name without a generic alternative. Unfortunately, this rule was rescinded in 2021, allowing copay accumulators even if a lower-cost generic was available.
In a positive turn of events, the US District Court of the District of Columbia overturned the 2021 rule in late 2023, reinstating the 2020 ban on copay accumulators. However, HHS has yet to enforce this ban.
Double Standard
Why is it that our federal government refrains from enforcing bans on copay accumulators for the American public, yet the US Office of Personnel Management (OPM) in its 2024 health plan for federal employees has explicitly stated that it “will decline any arrangements which may manipulate the prescription drug benefit design or incorporate any programs such as copay maximizers, copay optimizers, or other similar programs as these types of benefit designs are not in the best interest of enrollees or the Government.”
If such practices are deemed unsuitable for federal employees, why are they considered acceptable for the rest of the American population? This discrepancy raises important questions about healthcare equity.
In conclusion, the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. The introduction of copay accumulator programs and maximizers by PBMs has led to decreased adherence to needed medications, as well as delay in important medical procedures, exacerbating this situation. An across-the-board ban on these programs would offer immediate relief to many families that no longer can afford needed care.
It is clear that more needs to be done to ensure that all patients, regardless of their financial situation or the nature of their health insurance plan, can afford the healthcare they need. This includes ensuring that patients are not penalized for using manufacturer copay cards to help cover their costs. As we move forward, it is crucial that we continue to advocate for policies that prioritize the health and well-being of all patients.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
The escalating costs of medications and the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country have drawn criticism from governments, regulators, and the media. Federal and state governments are exploring various strategies to mitigate this issue, including the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) for drug price negotiations and the establishment of state Pharmaceutical Drug Affordability Boards (PDABs). However, it’s uncertain whether these measures will effectively reduce patients’ medication expenses, given the tendency of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) to favor more expensive drugs on their formularies and the implementation challenges faced by PDABs.
The question then arises: How can we promptly assist patients, especially those with multiple chronic conditions, in affording their healthcare? Many of these patients are enrolled in high-deductible plans and struggle to cover all their medical and pharmacy costs.
A significant obstacle to healthcare affordability emerged in 2018 with the introduction of Copay Accumulator Programs by PBMs. These programs prevent patients from applying manufacturer copay cards toward their deductible and maximum out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. The impact of these policies has been devastating, leading to decreased adherence to medications and delayed necessary medical procedures, such as colonoscopies. Copay accumulators do nothing to address the high cost of medical care. They merely shift the burden from insurance companies to patients.
There is a direct solution to help patients, particularly those burdened with high pharmacy bills, afford their medical care. It would be that all payments from patients, including manufacturer copay cards, count toward their deductible and maximum OOP costs. This should apply regardless of whether the insurance plan is fully funded or a self-insured employer plan. This would be an immediate step toward making healthcare more affordable for patients.
Copay Accumulator Programs
How did these detrimental policies, which have been proven to harm patients, originate? It’s interesting that health insurance policies for federal employees do not allow these programs and yet the federal government has done little to protect its citizens from these egregious policies. More on that later.
In 2018, insurance companies and PBMs conceived an idea to introduce what they called copay accumulator adjustment programs. These programs would prevent the use of manufacturer copay cards from counting toward patient deductibles or OOP maximums. They justified this by arguing that manufacturer copay cards encouraged patients to opt for higher-priced brand drugs when lower-cost generics were available.
However, data from IQVIA contradicts this claim. An analysis of copay card usage from 2013 to 2017 revealed that a mere 0.4% of these cards were used for brand-name drugs that had already lost their exclusivity. This indicates that the vast majority of copay cards were not being used to purchase more expensive brand-name drugs when cheaper, generic alternatives were available.
Another argument put forth by one of the large PBMs was that patients with high deductibles don’t have enough “skin in the game” due to their low premiums, and therefore don’t deserve to have their deductible covered by a copay card. This raises the question, “Does a patient with hemophilia or systemic lupus who can’t afford a low deductible plan not have ‘skin in the game’? Is that a fair assessment?” It’s disconcerting to see a multibillion-dollar company dictating who deserves to have their deductible covered. These policies clearly disproportionately harm patients with chronic illnesses, especially those with high deductibles. As a result, many organizations have labeled these policies as discriminatory.
Following the implementation of accumulator programs in 2018 and 2019, many patients were unaware that their copay cards weren’t contributing toward their deductibles. They were taken aback when specialty pharmacies informed them of owing substantial amounts because of unmet deductibles. Consequently, patients discontinued their medications, leading to disease progression and increased costs. The only downside for health insurers and PBMs was the negative publicity associated with patients losing medication access.
Maximizer Programs
By the end of 2019, the three major PBMs had devised a strategy to keep patients on their medication throughout the year, without counting copay cards toward the deductible, and found a way to profit more from these cards, sometimes quadrupling their value. This was the birth of the maximizer programs.
Maximizers exploit a “loophole” in the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA defines Essential Healthcare Benefits (EHB); anything not listed as an EHB is deemed “non-essential.” As a result, neither personal payments nor copay cards count toward deductibles or OOP maximums. Patients were informed that neither their own money nor manufacturer copay cards would count toward their deductible/OOP max.
One of my patients was warned that without enrolling in the maximizer program through SaveOnSP (owned by Express Scripts), she would bear the full cost of the drug, and nothing would count toward her OOP max. Frightened, she enrolled and surrendered her manufacturer copay card to SaveOnSP. Maximizers pocket the maximum value of the copay card, even if it exceeds the insurance plan’s yearly cost share by threefold or more. To do this legally, PBMs increase the patient’s original cost share amount during the plan year to match the value of the manufacturer copay card.
Combating These Programs
Nineteen states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico have outlawed copay accumulators in health plans under state jurisdiction. I personally testified in Louisiana, leading to a ban in our state. CSRO’s award-winning map tool can show if your state has passed the ban on copay accumulator programs. However, many states have not passed bans on copay accumulators and self-insured employer groups, which fall under the Department of Labor and not state regulation, are still unaffected. There is also proposed federal legislation, the “Help Ensure Lower Patient Copays Act,” that would prohibit the use of copay accumulators in exchange plans. Despite having bipartisan support, it is having a hard time getting across the finish line in Congress.
In 2020, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued a rule prohibiting accumulator programs in all plans if the product was a brand name without a generic alternative. Unfortunately, this rule was rescinded in 2021, allowing copay accumulators even if a lower-cost generic was available.
In a positive turn of events, the US District Court of the District of Columbia overturned the 2021 rule in late 2023, reinstating the 2020 ban on copay accumulators. However, HHS has yet to enforce this ban.
Double Standard
Why is it that our federal government refrains from enforcing bans on copay accumulators for the American public, yet the US Office of Personnel Management (OPM) in its 2024 health plan for federal employees has explicitly stated that it “will decline any arrangements which may manipulate the prescription drug benefit design or incorporate any programs such as copay maximizers, copay optimizers, or other similar programs as these types of benefit designs are not in the best interest of enrollees or the Government.”
If such practices are deemed unsuitable for federal employees, why are they considered acceptable for the rest of the American population? This discrepancy raises important questions about healthcare equity.
In conclusion, the prevalence of medical bankruptcy in our country is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. The introduction of copay accumulator programs and maximizers by PBMs has led to decreased adherence to needed medications, as well as delay in important medical procedures, exacerbating this situation. An across-the-board ban on these programs would offer immediate relief to many families that no longer can afford needed care.
It is clear that more needs to be done to ensure that all patients, regardless of their financial situation or the nature of their health insurance plan, can afford the healthcare they need. This includes ensuring that patients are not penalized for using manufacturer copay cards to help cover their costs. As we move forward, it is crucial that we continue to advocate for policies that prioritize the health and well-being of all patients.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].