User login
Spinosad: New kid on the block for treating scabies
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
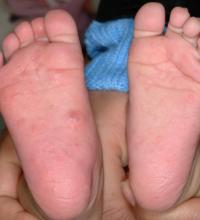
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – , Anthony J. Mancini, MD, said during a presentation at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE!
In April 2021, spinosad topical suspension 0.9%, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating scabies infestations in adult and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older – a first-in-class drug and the first new scabicide approved in 31 years. It was also approved for treating head lice in adults and children aged 6 months of age and older.
“Scabies has been described as the worst itch one can experience,” said Dr. Mancini, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago. “It’s a hallmark of the disease, it can persist for weeks, it’s most intense at night, and patients report various sensations. It’s believed to be a both type I and type IV hypersensitivity reaction.”
The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Besides intense itching, the classic presentation consists of a skin rash composed of inflammatory papules, linear burrows and crusted papules (especially on the hands, feet, and groin), and at times, larger red nodules. “Scabies nodules can persist for many months,” he said.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 cited scabies as having the greatest burden of disease in tropical regions, especially among children, adolescents, and the elderly. The greatest burden of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) occurred in East and Southeast Asia, Oceana, and tropical South America, but in North America, there was a 24% increase in the DALY rate between 1990 and 2015.
In addition, the World Health Organization designated scabies as a neglected tropical disease in 2017 and included it in its 10-year road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021-2030 with goals of promoting disease awareness and encouraging research and achieving global control.
“In our country, we typically see scabies treated successfully without complications, but there can be complications, especially in underdeveloped areas, like Staph aureus and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections,” which can be fatal, said Dr. Mancini, who is also head of pediatric dermatology at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
Permethrin 5% cream is typically offered as first-line topical therapy in the United States for the treatment of scabies. However, in vitro studies and small investigator-initiated in vivo studies have reported that efficacy appears to be decreasing. In one of the trials, Italian researchers enrolled 155 patients who were treated with permethrin 5% for 8 hours for 2 consecutive days and repeated the treatment 5 days later . Following the course of permethrin, only 34 responded, 96 failed treatment, and 25 were lost to follow-up.
“The study authors concluded that mite resistance to permethrin 5% seems to be increasing, following a path like other ectoparasite resistance,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved with the study. “We may even be seeing more ivermectin resistance in some geographic locations, as well.”
According to new scabicide efficacy criteria established by the FDA in 2016, complete cure is now defined as meeting both clinical and confirmatory criteria. A clinical cure means that all signs and symptoms of scabies have completely resolved, including burrows, inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions, and pruritus. A confirmatory cure means there is an absence of mites, eggs, scybala (feces), and burrows via microscopy or dermoscopy.
Enter spinosad, which is derived from a naturally occurring soil microorganism known as Saccharopolyspora spinosa and is composed of two active molecules: spinosyn A and spinosyn D. According to Dr. Mancini, spinosad’s mechanism of action is unique from other medications used to treat ectoparasites. It activates nicotinic and GABA-gated sodium channels, leads to sodium influx in the insect nerves, hyperexcitation, then paralysis and death. Cross-resistance to other insecticides has not been reported, he added, and there is no known evidence of resistance to its active compound.
Approval of the drug was based on data from two phase 3 randomized clinical trials involving 551 index cases and household contacts. In the intent-to-treat population, with the two trials combined, complete cure was achieved in 78.1% of the spinosad-treated group, compared with 39.6% in the vehicle group (P < .0001), clinical cure was achieved in 79.6% of the spinosad group, compared with 41.2% in the vehicle group (P < .001), and microscopic cure occurred in 85.9% of the spinosad group, compared with 52.6% in the vehicle group (P < .001).
Of the 306 participants in the study, the only adverse events reported by more than one patient each included abdominal pain, back pain, cough, headache, neck pain, and decreased weight in two patients each (0.8%), which investigators believed were not attributable to the study drug. Adverse events that investigators considered to be potentially related to the study drug included burning sensation in two participants (0.7%) and dry skin in another (0.3%). In clinical trials reported in the prescribing information, adverse events occurring in greater than 1% of subjects included application-site irritation (3% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle) and dry skin (2% spinosad vs. 0% vehicle).
“Spinosad met the FDA’s new stringent criteria, with all signs and symptoms of scabies completely resolved and confirmed via microscopy or dermoscopy,” said Dr. Mancini, who was not involved in the trials. “The patented formulation drives the active compound to the stratum corneum, where mites live and breed. It’s a single full-body application, without any resistance observed to date. This is an exciting newer option for treating our scabies patients.”
In an interview at the meeting, John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said that, while he has no clinical experience with spinosad for scabies, he welcomes a new option for the condition. “The fact that it has a different mechanism of action than permethrin is a good thing,” he said.
Dr. Mancini disclosed that he is a consultant or an adviser for ParaPRO, the manufacturer of spinosad, and Cassiopea, Castle Creek, Novan, Novartis, and Verrica. He was not involved in clinical trials of spinosad. Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
FDA OKs first drug for Rett syndrome
Rett syndrome is a rare, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder that affects about 6,000-9,000 people in the United States, mostly females.
Symptoms typically present between 6 and 18 months of age, with patients experiencing a rapid decline with loss of fine motor and communication skills.
Trofinetide is a synthetic analogue of the amino-terminal tripeptide of insulinlike growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which occurs naturally in the brain. The drug is designed to treat the core symptoms of Rett syndrome by potentially reducing neuroinflammation and supporting synaptic function.
The approval of trofinetide was supported by results from the pivotal phase 3 LAVENDER study that tested the efficacy and safety of trofinetide vs. placebo in 187 female patients with Rett syndrome, aged 5-20 years.
A total of 93 participants were randomly assigned to twice-daily oral trofinetide, and 94 received placebo for 12 weeks.
After 12 weeks, trofinetide showed a statistically significant improvement from baseline, compared with placebo, on both the caregiver-assessed Rett Syndrome Behavior Questionnaire (RSBQ) and 7-point Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) scale.
The drug also outperformed placebo at 12 weeks in a key secondary endpoint: the composite score on the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant-Toddler Checklist-Social (CSBS-DP-IT Social), a scale on which caregivers assess nonverbal communication.
The most common adverse events with trofinetide treatment were diarrhea and vomiting. Almost all these events were considered mild or moderate.
‘Historic day’
“This is a historic day for the Rett syndrome community and a meaningful moment for the patients and caregivers who have eagerly awaited the arrival of an approved treatment for this condition,” Melissa Kennedy, MHA, chief executive officer of the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, said in a news release issued by Acadia.
“Rett syndrome is a complicated, devastating disease that affects not only the individual patient, but whole families. With today’s FDA decision, those impacted by Rett have a promising new treatment option that has demonstrated benefit across a variety of Rett symptoms, including those that impact the daily lives of those living with Rett and their loved ones,” Ms. Kennedy said.
Trofinetide is expected to be available in the United States by the end of April.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rett syndrome is a rare, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder that affects about 6,000-9,000 people in the United States, mostly females.
Symptoms typically present between 6 and 18 months of age, with patients experiencing a rapid decline with loss of fine motor and communication skills.
Trofinetide is a synthetic analogue of the amino-terminal tripeptide of insulinlike growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which occurs naturally in the brain. The drug is designed to treat the core symptoms of Rett syndrome by potentially reducing neuroinflammation and supporting synaptic function.
The approval of trofinetide was supported by results from the pivotal phase 3 LAVENDER study that tested the efficacy and safety of trofinetide vs. placebo in 187 female patients with Rett syndrome, aged 5-20 years.
A total of 93 participants were randomly assigned to twice-daily oral trofinetide, and 94 received placebo for 12 weeks.
After 12 weeks, trofinetide showed a statistically significant improvement from baseline, compared with placebo, on both the caregiver-assessed Rett Syndrome Behavior Questionnaire (RSBQ) and 7-point Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) scale.
The drug also outperformed placebo at 12 weeks in a key secondary endpoint: the composite score on the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant-Toddler Checklist-Social (CSBS-DP-IT Social), a scale on which caregivers assess nonverbal communication.
The most common adverse events with trofinetide treatment were diarrhea and vomiting. Almost all these events were considered mild or moderate.
‘Historic day’
“This is a historic day for the Rett syndrome community and a meaningful moment for the patients and caregivers who have eagerly awaited the arrival of an approved treatment for this condition,” Melissa Kennedy, MHA, chief executive officer of the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, said in a news release issued by Acadia.
“Rett syndrome is a complicated, devastating disease that affects not only the individual patient, but whole families. With today’s FDA decision, those impacted by Rett have a promising new treatment option that has demonstrated benefit across a variety of Rett symptoms, including those that impact the daily lives of those living with Rett and their loved ones,” Ms. Kennedy said.
Trofinetide is expected to be available in the United States by the end of April.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rett syndrome is a rare, genetic neurodevelopmental disorder that affects about 6,000-9,000 people in the United States, mostly females.
Symptoms typically present between 6 and 18 months of age, with patients experiencing a rapid decline with loss of fine motor and communication skills.
Trofinetide is a synthetic analogue of the amino-terminal tripeptide of insulinlike growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which occurs naturally in the brain. The drug is designed to treat the core symptoms of Rett syndrome by potentially reducing neuroinflammation and supporting synaptic function.
The approval of trofinetide was supported by results from the pivotal phase 3 LAVENDER study that tested the efficacy and safety of trofinetide vs. placebo in 187 female patients with Rett syndrome, aged 5-20 years.
A total of 93 participants were randomly assigned to twice-daily oral trofinetide, and 94 received placebo for 12 weeks.
After 12 weeks, trofinetide showed a statistically significant improvement from baseline, compared with placebo, on both the caregiver-assessed Rett Syndrome Behavior Questionnaire (RSBQ) and 7-point Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) scale.
The drug also outperformed placebo at 12 weeks in a key secondary endpoint: the composite score on the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant-Toddler Checklist-Social (CSBS-DP-IT Social), a scale on which caregivers assess nonverbal communication.
The most common adverse events with trofinetide treatment were diarrhea and vomiting. Almost all these events were considered mild or moderate.
‘Historic day’
“This is a historic day for the Rett syndrome community and a meaningful moment for the patients and caregivers who have eagerly awaited the arrival of an approved treatment for this condition,” Melissa Kennedy, MHA, chief executive officer of the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, said in a news release issued by Acadia.
“Rett syndrome is a complicated, devastating disease that affects not only the individual patient, but whole families. With today’s FDA decision, those impacted by Rett have a promising new treatment option that has demonstrated benefit across a variety of Rett symptoms, including those that impact the daily lives of those living with Rett and their loved ones,” Ms. Kennedy said.
Trofinetide is expected to be available in the United States by the end of April.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Add-on antipsychotic beats switching meds in older adults with resistant depression
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAGP 2023
‘Unheard of’ PAH improvement with novel drug: STELLAR
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – An investigational, first-in class agent that delivers a completely new type of intervention to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) scored a clear win in the STELLAR trial, the first to complete among three phase 3 trials that are testing this agent.
Sotatercept, administered subcutaneously every 3 weeks for 24 weeks, improved from baseline average 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) by a significant and clinically meaningful 40.8 meters, compared with placebo, for the trial’s primary efficacy endpoint (P < .001). The treatment also “delivered broad clinical benefit across multiple domains including hemodynamics, World Health Organization functional class, disease biomarkers, risk scores and patient-reported outcomes,” Marius M. Hoeper, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“These results establish the clinical utility of sotatercept, administered in combination with approved PAH therapies, as a new treatment for PAH,” added Dr. Hoeper, professor and deputy director of the department of respiratory medicine at Hannover (Germany) Medical School,
“The most important aspect was the hemodynamic improvement,” with sotatercept treatment, which led to an average 235 dyn/sec per cm−5 reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance from baseline and an average cut in pulmonary artery pressure of 13.9 mm Hg from baseline, compared with placebo, a result that’s “unheard of,” Dr. Hoeper said in a press conference during the meeting.
“With other tested agents we usually see very little improvement in pulmonary artery pressure. This is a signal that we achieved some reversing of the pathological changes in the pulmonary vessels that lead to” PAH, he added.
Simultaneously with his report the findings also appeared online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
‘A new hope’ for patients with PAH
Based on the reported findings, sotatercept is a “very exciting boutique molecule” that will “offer patients with PAH a very exciting new treatment,” commented Rhonda Cooper-DeHoff, PharmD, a designated discussant and a researcher at the University of Florida, Gainesville.
“This study is a new hope for patients with PAH. Until now, they’ve had really bad outcomes, but [in this study] we see significant differences in 6MWD, hemodynamics, and risk factors. Overall, I think the benefit is greater than the risk” it may pose to patients through potential adverse effects, commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, and another discussant at the meeting.
“The results are impressive” and “encouraging,” and “suggest that sotatercept may represent a new and clinically consequential addition to current medications for PAH,” wrote three clinicians from Canyons Region Intermountain Medical Center in Murray, Utah, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
But the authors of the editorial also raised several cautions and concerns. They questioned the generalizability of the findings, noting that the patients with PAH enrolled in the study were all adults who were clinically stable and an average of more than 8 years out from their initial PAH diagnosis, and more than 90% were on stable treatment for PAH with two or three agents specific for treating the disorder. The study cohort also had a disproportionately high enrollment of patients with idiopathic (59%) or heritable (18%) forms of PAH, and the 15% of patients in the trial with connective tissue disease represented a disproportionately low prevalence of this PAH subtype.
The editorialists also called for “ongoing vigilance” for adverse effects from sotatercept treatment, although they acknowledged that the adverse effects reported to date from sotatercept are “largely reassuring.”
Death or clinical worsening cut by 84%
STELLAR randomized 323 patients at 91 sites in 21 countries with WHO Group 1 PAH and with WHO functional class II or III disease to receive either sotatercept or placebo for 24 weeks, with an option for treatment to continue beyond that until the last patient in the study reached 24 weeks on treatment, resulting in an overall median treatment duration of nearly 33 weeks.
In addition to the significant result for the primary endpoint, the 163 patients who received sotatercept had significant improvements, compared with 160 placebo-treated patients, for eight of nine secondary endpoints. The only secondary endpoint with a neutral result was for a measure of cognitive and emotional wellbeing, a parameter that was already at a normal level at baseline in most enrolled patients, Dr. Hoeper explained.
The incidence of either death or an event indicative of clinical worsening during the overall median follow-up of almost 33 weeks was 26.3% among the control patients and 5.5% among those who received sotatercept. This translated into a significant reduction for this endpoint of 84% with sotatercept treatment, compared with placebo.
The rates of treatment-emergent adverse events leading to discontinuation were roughly the same in the control and sotatercept arms, and the incidence of severe or serious treatment-emergent adverse events was higher among the control patients.
The most common adverse event on sotatercept was bleeding events, which occurred in 32% of those on sotatercept and in 16% of the control patients, but the events in the sotatercept arm were “mostly mild,” said Dr. Hoeper. The next most frequent adverse event during sotatercept treatment was appearance of telangiectasias, which occurred in 14% of those on sotatercept and in 4% of control patients.
“It’s an uncommon adverse event profile, but not unexpected for a drug with its mechanism of action,” he said.
Drug binds activin, a pathologic driver of PAH
Sotatercept is an engineered molecule that combines a section of a human immunoglobulin G molecule with a portion of the receptor for activin. This structure allows sotatercept to bind free activin molecules in a patient’s blood, thereby removing a key driver of the pulmonary vascular wall remodeling that is at the pathologic root of PAH.
“Hyperproliferation of blood vessel–wall cells” caused by activin signaling “is perhaps the most important driver of PAH,” Dr. Hoeper said. “Sotatercept allows us for the first time to target the underlying mechanism behind PAH.”
Still ongoing are the HYPERION and ZENITH phase 3 trials of sotatercept. HYPERION is enrolling patients with newly diagnosed or high-risk PAH and is expected to complete in 2028. ZENITH is enrolling patients with more advanced PAH and a higher mortality risk, with results expected in 2026.
Sotatercept has received “Breakthrough Therapy” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and “Priority Medicines” designation and “Orphan Drug” designation by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of PAH. One recent review estimated a worldwide PAH prevalence of about 3-4 cases/100,000, which for the United States translates into a total prevalence of perhaps 10,000-15,000 affected people.
STELLAR was funded by Acceleron Pharma, a subsidiary of Merck. Dr. Hoeper is a consultant to Acceleron. Dr. Cooper-DeHoff, Dr. Grapsa, and the authors of the editorial on STELLAR have no relevant disclosures.
At ACC 2023
Once-daily stimulant for ADHD safe, effective at 1 year
A once-daily oral stimulant medication for treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in individuals aged 6 years or older is safe and effective after 1 year of treatment, new research shows.
Results from a phase 3, multicenter dose optimization, open-label safety study of Azstarys (KemPharm) found that most treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were mild to moderate.
“This data show that Azstarys remains safe and effective for the treatment of ADHD when given for up to a year,” lead investigator Ann Childress, MD, president of the Center for Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology.
Safety at 1 year
The drug is a combination of extended-release serdexmethylphenidate (SDX), KemPharm’s prodrug of dexmethylphenidate (d-MPH), co-formulated with immediate-release d-MPH.
SDX is converted to d-MPH after it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The d-MPH is released gradually throughout the day, providing quick symptom control with the d-MPH and extended control with SDX.
As reported by this news organization, Azstarys was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021 on the basis of results from a laboratory classroom phase 3 trial, which showed significant improvement in ADHD symptoms, compared with placebo.
For this study, the second phase 3 trial of Azstarys, investigators analyzed data from 282 children aged 6-12 years in the United States, including 70 who participated in an earlier 1-month efficacy trial as well.
After screening and a 3-week dose-optimization phase for new participants, patients received once-daily treatment with doses of 26.1 mg/5.2 mg, 39.2 mg/7.8 mg, or 52.3 mg/10.4 mg of SDX/d-MPH.
After 1 year of treatment, 60.1% of participants reported at least one TEAE, the majority of which were moderate. Twelve patients reported severe TEAEs. Six children (2.5%) discontinued the study due to a TEAE during the treatment phase.
Investigators also measured growth and changes in sleep with the Children’s Sleep Habits Questionnaire during the 12-month study. Sleep improved on most measures and the impact on growth was mild.
There were no life-threatening TEAEs and no deaths reported during the study.
The most common TEAEs during the treatment phase were decreased appetite, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, decreased weight, irritability, and increased weight.
Efficacy at 1 year
ADHD symptoms improved considerably after 1 month of treatment, with responses continuing at 1 year.
At baseline, participants’ mean ADHD Rating Scale-5 (ADHD-RS-5) score was 41.5. After 1 month of treatment, scores averaged 16.1, a decline of –25.3 (P < .001).
The mean score stabilized in the 12-15 range for the remainder of the study. After 1 year of treatment, ADHD symptoms had decreased approximately 70% from baseline.
Investigators found similar results in clinical severity. After 1 month of treatment, the average Clinical Global Impressions–Severity (CGI-S) scale score was 2.5, a decline of –2.2 (P < .0001).
CGI-S scale scores remained in the 2.2-2.4 range for the remainder of the study.
These results, combined with the results of the original classroom trial, suggest Azstarys may offer advantages over other ADHD drugs, Dr. Childress said.
“In the laboratory classroom trial, subjects taking Azstarys completed significantly more math problems than subjects taking placebo beginning at 30 minutes and up to 13 hours after dosing,” Dr. Childress said. “No other methylphenidate extended-release product currently marketed in the United States has a 13-hour duration of effect.”
‘Reassuring data’
Aditya Pawar, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with the Kennedy Krieger Institute and an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, said that the study suggests the drug may be a valuable addition to ADHD treatment options for pediatric patients.
“The study provides reassuring data on the safety of stimulants in patients without significant history of cardiac events or blood pressure changes, which are usual concerns among patients and clinicians despite the evidence supporting safety, said Dr. Pawar, who was not part of the study.
“Additionally, the 1-year data on efficacy and safety of a new stimulant medication is valuable for clinicians looking for sustained relief for their patients, despite the limitations of an open-label trial,” she added.
Overall, the safety data reported here are fairly consistent with the safety profile of other methylphenidates used for treating ADHD, Dr. Pawar said.
However, she noted, the study does have some limitations, including its open-label design and lack of blinding. The research also excluded children with autism, disruptive mood dysregulation disorders, and other common comorbidities of ADHD, which may limit the generalizability of the results.
“These comorbidities often require stimulants as a part of treatment and yet have a higher risk of side effects,” Dr. Pawar said. “Future studies with a broader population may be needed to better understand treatment effectiveness and potential risks.”
The study was funded by KemPharm. Dr. Childress serves as consultant for Aardvark, Arbor, Attentive, Cingulate, Ironshore, Neos Therapeutics, Neurocentria, Otsuka, Purdue, Rhodes, Sunovion, Tris Pharma, KemPharm, Supernus, Jazz, Corium, Tulex, and Lumos. Full disclosures are reported in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A once-daily oral stimulant medication for treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in individuals aged 6 years or older is safe and effective after 1 year of treatment, new research shows.
Results from a phase 3, multicenter dose optimization, open-label safety study of Azstarys (KemPharm) found that most treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were mild to moderate.
“This data show that Azstarys remains safe and effective for the treatment of ADHD when given for up to a year,” lead investigator Ann Childress, MD, president of the Center for Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology.
Safety at 1 year
The drug is a combination of extended-release serdexmethylphenidate (SDX), KemPharm’s prodrug of dexmethylphenidate (d-MPH), co-formulated with immediate-release d-MPH.
SDX is converted to d-MPH after it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The d-MPH is released gradually throughout the day, providing quick symptom control with the d-MPH and extended control with SDX.
As reported by this news organization, Azstarys was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021 on the basis of results from a laboratory classroom phase 3 trial, which showed significant improvement in ADHD symptoms, compared with placebo.
For this study, the second phase 3 trial of Azstarys, investigators analyzed data from 282 children aged 6-12 years in the United States, including 70 who participated in an earlier 1-month efficacy trial as well.
After screening and a 3-week dose-optimization phase for new participants, patients received once-daily treatment with doses of 26.1 mg/5.2 mg, 39.2 mg/7.8 mg, or 52.3 mg/10.4 mg of SDX/d-MPH.
After 1 year of treatment, 60.1% of participants reported at least one TEAE, the majority of which were moderate. Twelve patients reported severe TEAEs. Six children (2.5%) discontinued the study due to a TEAE during the treatment phase.
Investigators also measured growth and changes in sleep with the Children’s Sleep Habits Questionnaire during the 12-month study. Sleep improved on most measures and the impact on growth was mild.
There were no life-threatening TEAEs and no deaths reported during the study.
The most common TEAEs during the treatment phase were decreased appetite, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, decreased weight, irritability, and increased weight.
Efficacy at 1 year
ADHD symptoms improved considerably after 1 month of treatment, with responses continuing at 1 year.
At baseline, participants’ mean ADHD Rating Scale-5 (ADHD-RS-5) score was 41.5. After 1 month of treatment, scores averaged 16.1, a decline of –25.3 (P < .001).
The mean score stabilized in the 12-15 range for the remainder of the study. After 1 year of treatment, ADHD symptoms had decreased approximately 70% from baseline.
Investigators found similar results in clinical severity. After 1 month of treatment, the average Clinical Global Impressions–Severity (CGI-S) scale score was 2.5, a decline of –2.2 (P < .0001).
CGI-S scale scores remained in the 2.2-2.4 range for the remainder of the study.
These results, combined with the results of the original classroom trial, suggest Azstarys may offer advantages over other ADHD drugs, Dr. Childress said.
“In the laboratory classroom trial, subjects taking Azstarys completed significantly more math problems than subjects taking placebo beginning at 30 minutes and up to 13 hours after dosing,” Dr. Childress said. “No other methylphenidate extended-release product currently marketed in the United States has a 13-hour duration of effect.”
‘Reassuring data’
Aditya Pawar, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with the Kennedy Krieger Institute and an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, said that the study suggests the drug may be a valuable addition to ADHD treatment options for pediatric patients.
“The study provides reassuring data on the safety of stimulants in patients without significant history of cardiac events or blood pressure changes, which are usual concerns among patients and clinicians despite the evidence supporting safety, said Dr. Pawar, who was not part of the study.
“Additionally, the 1-year data on efficacy and safety of a new stimulant medication is valuable for clinicians looking for sustained relief for their patients, despite the limitations of an open-label trial,” she added.
Overall, the safety data reported here are fairly consistent with the safety profile of other methylphenidates used for treating ADHD, Dr. Pawar said.
However, she noted, the study does have some limitations, including its open-label design and lack of blinding. The research also excluded children with autism, disruptive mood dysregulation disorders, and other common comorbidities of ADHD, which may limit the generalizability of the results.
“These comorbidities often require stimulants as a part of treatment and yet have a higher risk of side effects,” Dr. Pawar said. “Future studies with a broader population may be needed to better understand treatment effectiveness and potential risks.”
The study was funded by KemPharm. Dr. Childress serves as consultant for Aardvark, Arbor, Attentive, Cingulate, Ironshore, Neos Therapeutics, Neurocentria, Otsuka, Purdue, Rhodes, Sunovion, Tris Pharma, KemPharm, Supernus, Jazz, Corium, Tulex, and Lumos. Full disclosures are reported in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A once-daily oral stimulant medication for treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in individuals aged 6 years or older is safe and effective after 1 year of treatment, new research shows.
Results from a phase 3, multicenter dose optimization, open-label safety study of Azstarys (KemPharm) found that most treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were mild to moderate.
“This data show that Azstarys remains safe and effective for the treatment of ADHD when given for up to a year,” lead investigator Ann Childress, MD, president of the Center for Psychiatry and Behavioral Medicine, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology.
Safety at 1 year
The drug is a combination of extended-release serdexmethylphenidate (SDX), KemPharm’s prodrug of dexmethylphenidate (d-MPH), co-formulated with immediate-release d-MPH.
SDX is converted to d-MPH after it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The d-MPH is released gradually throughout the day, providing quick symptom control with the d-MPH and extended control with SDX.
As reported by this news organization, Azstarys was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021 on the basis of results from a laboratory classroom phase 3 trial, which showed significant improvement in ADHD symptoms, compared with placebo.
For this study, the second phase 3 trial of Azstarys, investigators analyzed data from 282 children aged 6-12 years in the United States, including 70 who participated in an earlier 1-month efficacy trial as well.
After screening and a 3-week dose-optimization phase for new participants, patients received once-daily treatment with doses of 26.1 mg/5.2 mg, 39.2 mg/7.8 mg, or 52.3 mg/10.4 mg of SDX/d-MPH.
After 1 year of treatment, 60.1% of participants reported at least one TEAE, the majority of which were moderate. Twelve patients reported severe TEAEs. Six children (2.5%) discontinued the study due to a TEAE during the treatment phase.
Investigators also measured growth and changes in sleep with the Children’s Sleep Habits Questionnaire during the 12-month study. Sleep improved on most measures and the impact on growth was mild.
There were no life-threatening TEAEs and no deaths reported during the study.
The most common TEAEs during the treatment phase were decreased appetite, upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, decreased weight, irritability, and increased weight.
Efficacy at 1 year
ADHD symptoms improved considerably after 1 month of treatment, with responses continuing at 1 year.
At baseline, participants’ mean ADHD Rating Scale-5 (ADHD-RS-5) score was 41.5. After 1 month of treatment, scores averaged 16.1, a decline of –25.3 (P < .001).
The mean score stabilized in the 12-15 range for the remainder of the study. After 1 year of treatment, ADHD symptoms had decreased approximately 70% from baseline.
Investigators found similar results in clinical severity. After 1 month of treatment, the average Clinical Global Impressions–Severity (CGI-S) scale score was 2.5, a decline of –2.2 (P < .0001).
CGI-S scale scores remained in the 2.2-2.4 range for the remainder of the study.
These results, combined with the results of the original classroom trial, suggest Azstarys may offer advantages over other ADHD drugs, Dr. Childress said.
“In the laboratory classroom trial, subjects taking Azstarys completed significantly more math problems than subjects taking placebo beginning at 30 minutes and up to 13 hours after dosing,” Dr. Childress said. “No other methylphenidate extended-release product currently marketed in the United States has a 13-hour duration of effect.”
‘Reassuring data’
Aditya Pawar, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist with the Kennedy Krieger Institute and an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, said that the study suggests the drug may be a valuable addition to ADHD treatment options for pediatric patients.
“The study provides reassuring data on the safety of stimulants in patients without significant history of cardiac events or blood pressure changes, which are usual concerns among patients and clinicians despite the evidence supporting safety, said Dr. Pawar, who was not part of the study.
“Additionally, the 1-year data on efficacy and safety of a new stimulant medication is valuable for clinicians looking for sustained relief for their patients, despite the limitations of an open-label trial,” she added.
Overall, the safety data reported here are fairly consistent with the safety profile of other methylphenidates used for treating ADHD, Dr. Pawar said.
However, she noted, the study does have some limitations, including its open-label design and lack of blinding. The research also excluded children with autism, disruptive mood dysregulation disorders, and other common comorbidities of ADHD, which may limit the generalizability of the results.
“These comorbidities often require stimulants as a part of treatment and yet have a higher risk of side effects,” Dr. Pawar said. “Future studies with a broader population may be needed to better understand treatment effectiveness and potential risks.”
The study was funded by KemPharm. Dr. Childress serves as consultant for Aardvark, Arbor, Attentive, Cingulate, Ironshore, Neos Therapeutics, Neurocentria, Otsuka, Purdue, Rhodes, Sunovion, Tris Pharma, KemPharm, Supernus, Jazz, Corium, Tulex, and Lumos. Full disclosures are reported in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antipsychotic cuts Alzheimer’s-related agitation
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
AT AAGP 2023
Venetoclax shows promise for r/r hairy cell leukemia
Venetoclax is already approved for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic leukemia, and as part of a treatment combination in certain patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
The new findings suggest that the drug could also be a chemotherapy-free treatment option for HCL patients after the failure of multiple prior lines of therapy, including vemurafenib plus rituximab, the investigators wrote in a letter to the editor published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Treatment options for such patients are limited, they noted.
Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University of Perugia (Italy), and colleagues decided to explore the use of venetoclax in this patient population after reports of in vitro findings showing a possible benefit.
The investigators administered the drug off-label to six patients who had received vemurafenib plus rituximab as their most recent prior therapy; one was resistant and five relapsed after that therapy, they reported. Venetoclax was delivered in 29-day cycles.
After 6 or 12 cycles, two patients experienced complete remission with minimal residual disease (MRD), and one had partial remission, although each had incomplete platelet recovery.
Adding rituximab at a dose of 375 mg per square meter of body-surface area for three to eight cycles improved the depth of response in a patient who had a previous minor response, further reduced MRD in one who had a complete remission to venetoclax, and led to hematologic remission in one who had no response to venetoclax, they noted.
Progression-free survival ranged from 23 to 53-plus months in all five patients who did not have early progression and was similar or better than PFS seen after vemurafenib plus rituximab.
The main toxic effect of venetoclax was worsening of baseline neutropenia, which was sometimes complicated by infections or febrile neutropenia and was managed by dose reductions and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
“Thus, venetoclax with or without rituximab may serve as a safe and effective salvage option after failure of vemurafenib plus rituximab treatment, especially in patients who do not require a rapid recovery of blood count,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from Fondazione Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Venetoclax is already approved for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic leukemia, and as part of a treatment combination in certain patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
The new findings suggest that the drug could also be a chemotherapy-free treatment option for HCL patients after the failure of multiple prior lines of therapy, including vemurafenib plus rituximab, the investigators wrote in a letter to the editor published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Treatment options for such patients are limited, they noted.
Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University of Perugia (Italy), and colleagues decided to explore the use of venetoclax in this patient population after reports of in vitro findings showing a possible benefit.
The investigators administered the drug off-label to six patients who had received vemurafenib plus rituximab as their most recent prior therapy; one was resistant and five relapsed after that therapy, they reported. Venetoclax was delivered in 29-day cycles.
After 6 or 12 cycles, two patients experienced complete remission with minimal residual disease (MRD), and one had partial remission, although each had incomplete platelet recovery.
Adding rituximab at a dose of 375 mg per square meter of body-surface area for three to eight cycles improved the depth of response in a patient who had a previous minor response, further reduced MRD in one who had a complete remission to venetoclax, and led to hematologic remission in one who had no response to venetoclax, they noted.
Progression-free survival ranged from 23 to 53-plus months in all five patients who did not have early progression and was similar or better than PFS seen after vemurafenib plus rituximab.
The main toxic effect of venetoclax was worsening of baseline neutropenia, which was sometimes complicated by infections or febrile neutropenia and was managed by dose reductions and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
“Thus, venetoclax with or without rituximab may serve as a safe and effective salvage option after failure of vemurafenib plus rituximab treatment, especially in patients who do not require a rapid recovery of blood count,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from Fondazione Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Venetoclax is already approved for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic leukemia, and as part of a treatment combination in certain patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
The new findings suggest that the drug could also be a chemotherapy-free treatment option for HCL patients after the failure of multiple prior lines of therapy, including vemurafenib plus rituximab, the investigators wrote in a letter to the editor published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Treatment options for such patients are limited, they noted.
Enrico Tiacci, MD, of the University of Perugia (Italy), and colleagues decided to explore the use of venetoclax in this patient population after reports of in vitro findings showing a possible benefit.
The investigators administered the drug off-label to six patients who had received vemurafenib plus rituximab as their most recent prior therapy; one was resistant and five relapsed after that therapy, they reported. Venetoclax was delivered in 29-day cycles.
After 6 or 12 cycles, two patients experienced complete remission with minimal residual disease (MRD), and one had partial remission, although each had incomplete platelet recovery.
Adding rituximab at a dose of 375 mg per square meter of body-surface area for three to eight cycles improved the depth of response in a patient who had a previous minor response, further reduced MRD in one who had a complete remission to venetoclax, and led to hematologic remission in one who had no response to venetoclax, they noted.
Progression-free survival ranged from 23 to 53-plus months in all five patients who did not have early progression and was similar or better than PFS seen after vemurafenib plus rituximab.
The main toxic effect of venetoclax was worsening of baseline neutropenia, which was sometimes complicated by infections or febrile neutropenia and was managed by dose reductions and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
“Thus, venetoclax with or without rituximab may serve as a safe and effective salvage option after failure of vemurafenib plus rituximab treatment, especially in patients who do not require a rapid recovery of blood count,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from Fondazione Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro and the Italian Ministry of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Phase 3 results: Ponatinib bests imatinib for Ph+ALL
The agents were evaluated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PhALLCON study, the first head-to-head comparison of ponatinib and imatinib in combination with reduced-intensity chemotherapy in the Ph+ALL population.
Overall, patients in the ponatinib arm experienced a significantly higher minimal residual disease (MRD)–negative complete response rate as well as deeper and more durable responses compared with those in the imatinib arm, the investigators reported.
The findings were presented during an American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual plenary session.
In adults with ALL, Ph+ disease is the most frequent genetic subtype, accounting for about one third of cases. The current standard of care for newly diagnosed Ph+ALL, also known as BCR-ABL-1–positive ALL, is BCR-ABL1 TKIs in combination with chemotherapy or steroids. However, when treated with first- or second-generation TKIs, patients eventually progress due to the emergence of treatment resistance.
Before the advent of TKI therapies, Ph+ALL had a very poor prognosis, but the development of imatinib in 2001 was transformative, said Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, in the ASCO plenary session, exploring the state of the science.
Added to “backbone” chemotherapy regimens, imatinib improved complete response rates, increased eligibility for stem cell transplantation, and improved overall survival. Second-generation TKIs, including dasatinib and nilotinib further improved outcomes, said Dr. Luskin, also assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
More recently, ponatinib has emerged as a promising treatment given its unique action against the ABLA1 T315I KD mutation present in about 75% of cases that relapse as well as the findings of improved MRD-negative complete response rates and event-free survival in retrospective studies, Dr. Luskin said.
The PhALLCON study was designed to further investigate promising results seen in retrospective studies of ponatinib.
To assess ponatinib versus imatinib, patients were enrolled and randomized two to one to receive either a 30-mg once-daily starting dose of ponatinib or a once-daily 600 mg dose of imatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy. After cycle 20, patients received single agent ponatinib or imatinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 245 enrolled, 78 remained on treatment at the August 2022 data cutoff, including 42% of those in the ponatinib arm and 12% in the imatinib arm. The most common reasons for discontinuation included hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (31% for ponatinib and 37% for imatinib), adverse events (12% in both arms), and lack of efficacy (7% and 26%, respectively).
At median follow-up of 20 months among 164 patients in the ponatinib arm and 18 months among 81 patients in the imatinib arm, the MRD-negative complete response rates were 34.4% and 16.7%, respectively, said first author Elias J. Jabbour, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
A trend toward improved event-free survival was also observed in the ponatinib arm, but the data were not mature at the time of the analysis, Dr. Jabbour noted.
The two treatments showed comparable safety. Treatment-emergent adverse event rates of any grade and of grade 3 or higher were similar in the two study arms. Arterial occlusive events were infrequent and were also similar between the arms.
“Taken together, for this patient population, the efficacy and safety results demonstrate a favorable risk-benefit assessment for ponatinib, which should be considered a standard of care for frontline therapy in patents with newly diagnosed Ph+ALL,” Dr. Jabbour said.
Although the PhALLCON findings are encouraging, invited discussant Anjali S. Advani, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, noted some study “pitfalls and caveats,” including the generally younger age and low incidence of cardiovascular risk factors in the study population, which raises questions about the ability to extrapolate the findings to “the larger population, which may be older and have more comorbidities.”
Dr. Advani also said that the ponatinib versus imatinib comparison is a reasonable one, but that most clinicians are now using dasatinib, so “it would have been nice to have this comparison.”
Additionally, “the landscape is now changing with the use of blinatumomab plus TKIs – either dasatinib or ponatinib – in the up-front setting.”
“There is data now from various groups ... showing excellent results, although longer follow-up is needed on all of these,” she said.
One such study is the GIMEMA ALL2820 trial looking at ponatinib plus blinatumomab versus imatinib plus chemotherapy, said Nicolas Boissel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, an invited discussant who addressed the European perspective on the PhALLCON results.
“It is expected that access to ponatinib will be delayed in Europe, compared with the U.S., so meanwhile, clinical trials remain a good option to give access to ponatinib frontline,” he said.
Going forward, Dr. Boissel said it will be important to determine the role of second-generation TKIs in patients who are ineligible to receive ponatinib, the treatment duration needed to reduce long-term risk of relapse, and the potential for eliminating the need for postremission chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation in certain patients.
Dr. Advani added that when evaluating and comparing treatments, it will be important to look at genomic alterations and BCR-ABL mutation status, age and comorbidities, and patterns of disease relapse, including relapse sites and genomics. Longer follow-up results for event-free survival and overall survival are also needed.
“I think, particularly in younger patients with relatively few or no cardiovascular comorbidities, [ponatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy] represents a really exciting option,” Dr. Advani said. “What’s difficult is that the landscape is changing quickly in this field, and so is the standard of care. I think what we struggle with is whether we should be using antibody-based therapies plus TKIs or look at an approach such as this, and further studies are going to be needed to answer that question.”
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with Pfizer, Takeda, Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Astellas Pharma, Genentech, and Ascentage Pharma. Dr. Luskin reported relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, and Abbvie. Dr. Advani disclosed ties with Novartis, Glycomimetics, Kite Pharma, Seattle Genetics, Amgen, Beam Therapeutics, Mkarta, Taiho Oncology, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Kura Oncology. Dr. Boissel reported relationships with Amgen, ARIAD/Incyte, Novartis, SERVIER, and Astellas Pharma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The agents were evaluated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PhALLCON study, the first head-to-head comparison of ponatinib and imatinib in combination with reduced-intensity chemotherapy in the Ph+ALL population.
Overall, patients in the ponatinib arm experienced a significantly higher minimal residual disease (MRD)–negative complete response rate as well as deeper and more durable responses compared with those in the imatinib arm, the investigators reported.
The findings were presented during an American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual plenary session.
In adults with ALL, Ph+ disease is the most frequent genetic subtype, accounting for about one third of cases. The current standard of care for newly diagnosed Ph+ALL, also known as BCR-ABL-1–positive ALL, is BCR-ABL1 TKIs in combination with chemotherapy or steroids. However, when treated with first- or second-generation TKIs, patients eventually progress due to the emergence of treatment resistance.
Before the advent of TKI therapies, Ph+ALL had a very poor prognosis, but the development of imatinib in 2001 was transformative, said Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, in the ASCO plenary session, exploring the state of the science.
Added to “backbone” chemotherapy regimens, imatinib improved complete response rates, increased eligibility for stem cell transplantation, and improved overall survival. Second-generation TKIs, including dasatinib and nilotinib further improved outcomes, said Dr. Luskin, also assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
More recently, ponatinib has emerged as a promising treatment given its unique action against the ABLA1 T315I KD mutation present in about 75% of cases that relapse as well as the findings of improved MRD-negative complete response rates and event-free survival in retrospective studies, Dr. Luskin said.
The PhALLCON study was designed to further investigate promising results seen in retrospective studies of ponatinib.
To assess ponatinib versus imatinib, patients were enrolled and randomized two to one to receive either a 30-mg once-daily starting dose of ponatinib or a once-daily 600 mg dose of imatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy. After cycle 20, patients received single agent ponatinib or imatinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 245 enrolled, 78 remained on treatment at the August 2022 data cutoff, including 42% of those in the ponatinib arm and 12% in the imatinib arm. The most common reasons for discontinuation included hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (31% for ponatinib and 37% for imatinib), adverse events (12% in both arms), and lack of efficacy (7% and 26%, respectively).
At median follow-up of 20 months among 164 patients in the ponatinib arm and 18 months among 81 patients in the imatinib arm, the MRD-negative complete response rates were 34.4% and 16.7%, respectively, said first author Elias J. Jabbour, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
A trend toward improved event-free survival was also observed in the ponatinib arm, but the data were not mature at the time of the analysis, Dr. Jabbour noted.
The two treatments showed comparable safety. Treatment-emergent adverse event rates of any grade and of grade 3 or higher were similar in the two study arms. Arterial occlusive events were infrequent and were also similar between the arms.
“Taken together, for this patient population, the efficacy and safety results demonstrate a favorable risk-benefit assessment for ponatinib, which should be considered a standard of care for frontline therapy in patents with newly diagnosed Ph+ALL,” Dr. Jabbour said.
Although the PhALLCON findings are encouraging, invited discussant Anjali S. Advani, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, noted some study “pitfalls and caveats,” including the generally younger age and low incidence of cardiovascular risk factors in the study population, which raises questions about the ability to extrapolate the findings to “the larger population, which may be older and have more comorbidities.”
Dr. Advani also said that the ponatinib versus imatinib comparison is a reasonable one, but that most clinicians are now using dasatinib, so “it would have been nice to have this comparison.”
Additionally, “the landscape is now changing with the use of blinatumomab plus TKIs – either dasatinib or ponatinib – in the up-front setting.”
“There is data now from various groups ... showing excellent results, although longer follow-up is needed on all of these,” she said.
One such study is the GIMEMA ALL2820 trial looking at ponatinib plus blinatumomab versus imatinib plus chemotherapy, said Nicolas Boissel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, an invited discussant who addressed the European perspective on the PhALLCON results.
“It is expected that access to ponatinib will be delayed in Europe, compared with the U.S., so meanwhile, clinical trials remain a good option to give access to ponatinib frontline,” he said.
Going forward, Dr. Boissel said it will be important to determine the role of second-generation TKIs in patients who are ineligible to receive ponatinib, the treatment duration needed to reduce long-term risk of relapse, and the potential for eliminating the need for postremission chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation in certain patients.
Dr. Advani added that when evaluating and comparing treatments, it will be important to look at genomic alterations and BCR-ABL mutation status, age and comorbidities, and patterns of disease relapse, including relapse sites and genomics. Longer follow-up results for event-free survival and overall survival are also needed.
“I think, particularly in younger patients with relatively few or no cardiovascular comorbidities, [ponatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy] represents a really exciting option,” Dr. Advani said. “What’s difficult is that the landscape is changing quickly in this field, and so is the standard of care. I think what we struggle with is whether we should be using antibody-based therapies plus TKIs or look at an approach such as this, and further studies are going to be needed to answer that question.”
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with Pfizer, Takeda, Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Astellas Pharma, Genentech, and Ascentage Pharma. Dr. Luskin reported relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, and Abbvie. Dr. Advani disclosed ties with Novartis, Glycomimetics, Kite Pharma, Seattle Genetics, Amgen, Beam Therapeutics, Mkarta, Taiho Oncology, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Kura Oncology. Dr. Boissel reported relationships with Amgen, ARIAD/Incyte, Novartis, SERVIER, and Astellas Pharma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The agents were evaluated in the randomized, open-label, phase 3 PhALLCON study, the first head-to-head comparison of ponatinib and imatinib in combination with reduced-intensity chemotherapy in the Ph+ALL population.
Overall, patients in the ponatinib arm experienced a significantly higher minimal residual disease (MRD)–negative complete response rate as well as deeper and more durable responses compared with those in the imatinib arm, the investigators reported.
The findings were presented during an American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual plenary session.
In adults with ALL, Ph+ disease is the most frequent genetic subtype, accounting for about one third of cases. The current standard of care for newly diagnosed Ph+ALL, also known as BCR-ABL-1–positive ALL, is BCR-ABL1 TKIs in combination with chemotherapy or steroids. However, when treated with first- or second-generation TKIs, patients eventually progress due to the emergence of treatment resistance.
Before the advent of TKI therapies, Ph+ALL had a very poor prognosis, but the development of imatinib in 2001 was transformative, said Marlise R. Luskin, MD, a senior physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, in the ASCO plenary session, exploring the state of the science.
Added to “backbone” chemotherapy regimens, imatinib improved complete response rates, increased eligibility for stem cell transplantation, and improved overall survival. Second-generation TKIs, including dasatinib and nilotinib further improved outcomes, said Dr. Luskin, also assistant professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
More recently, ponatinib has emerged as a promising treatment given its unique action against the ABLA1 T315I KD mutation present in about 75% of cases that relapse as well as the findings of improved MRD-negative complete response rates and event-free survival in retrospective studies, Dr. Luskin said.
The PhALLCON study was designed to further investigate promising results seen in retrospective studies of ponatinib.
To assess ponatinib versus imatinib, patients were enrolled and randomized two to one to receive either a 30-mg once-daily starting dose of ponatinib or a once-daily 600 mg dose of imatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy. After cycle 20, patients received single agent ponatinib or imatinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 245 enrolled, 78 remained on treatment at the August 2022 data cutoff, including 42% of those in the ponatinib arm and 12% in the imatinib arm. The most common reasons for discontinuation included hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (31% for ponatinib and 37% for imatinib), adverse events (12% in both arms), and lack of efficacy (7% and 26%, respectively).
At median follow-up of 20 months among 164 patients in the ponatinib arm and 18 months among 81 patients in the imatinib arm, the MRD-negative complete response rates were 34.4% and 16.7%, respectively, said first author Elias J. Jabbour, MD, a professor of medicine at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
A trend toward improved event-free survival was also observed in the ponatinib arm, but the data were not mature at the time of the analysis, Dr. Jabbour noted.
The two treatments showed comparable safety. Treatment-emergent adverse event rates of any grade and of grade 3 or higher were similar in the two study arms. Arterial occlusive events were infrequent and were also similar between the arms.
“Taken together, for this patient population, the efficacy and safety results demonstrate a favorable risk-benefit assessment for ponatinib, which should be considered a standard of care for frontline therapy in patents with newly diagnosed Ph+ALL,” Dr. Jabbour said.
Although the PhALLCON findings are encouraging, invited discussant Anjali S. Advani, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, noted some study “pitfalls and caveats,” including the generally younger age and low incidence of cardiovascular risk factors in the study population, which raises questions about the ability to extrapolate the findings to “the larger population, which may be older and have more comorbidities.”
Dr. Advani also said that the ponatinib versus imatinib comparison is a reasonable one, but that most clinicians are now using dasatinib, so “it would have been nice to have this comparison.”
Additionally, “the landscape is now changing with the use of blinatumomab plus TKIs – either dasatinib or ponatinib – in the up-front setting.”
“There is data now from various groups ... showing excellent results, although longer follow-up is needed on all of these,” she said.
One such study is the GIMEMA ALL2820 trial looking at ponatinib plus blinatumomab versus imatinib plus chemotherapy, said Nicolas Boissel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, an invited discussant who addressed the European perspective on the PhALLCON results.
“It is expected that access to ponatinib will be delayed in Europe, compared with the U.S., so meanwhile, clinical trials remain a good option to give access to ponatinib frontline,” he said.
Going forward, Dr. Boissel said it will be important to determine the role of second-generation TKIs in patients who are ineligible to receive ponatinib, the treatment duration needed to reduce long-term risk of relapse, and the potential for eliminating the need for postremission chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation in certain patients.
Dr. Advani added that when evaluating and comparing treatments, it will be important to look at genomic alterations and BCR-ABL mutation status, age and comorbidities, and patterns of disease relapse, including relapse sites and genomics. Longer follow-up results for event-free survival and overall survival are also needed.
“I think, particularly in younger patients with relatively few or no cardiovascular comorbidities, [ponatinib plus reduced-intensity chemotherapy] represents a really exciting option,” Dr. Advani said. “What’s difficult is that the landscape is changing quickly in this field, and so is the standard of care. I think what we struggle with is whether we should be using antibody-based therapies plus TKIs or look at an approach such as this, and further studies are going to be needed to answer that question.”
Dr. Jabbour disclosed ties with Pfizer, Takeda, Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Astellas Pharma, Genentech, and Ascentage Pharma. Dr. Luskin reported relationships with Pfizer, Novartis, and Abbvie. Dr. Advani disclosed ties with Novartis, Glycomimetics, Kite Pharma, Seattle Genetics, Amgen, Beam Therapeutics, Mkarta, Taiho Oncology, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Kura Oncology. Dr. Boissel reported relationships with Amgen, ARIAD/Incyte, Novartis, SERVIER, and Astellas Pharma.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Two FDA clearances add diabetes technology options
Two diabetes management devices that aid in the precision of insulin delivery have been recently cleared by the Food and Drug Administration.
On March 2, the FDA cleared the Android version of Bigfoot Biomedical’s Unity Mobile App for use with its system of smart pen caps that are compatible with different disposable insulin pens for administering both long-acting and rapid-acting insulin.
The system, which has been compatible with iOS devices since May 2021, is “the first and only FDA-cleared smart injection system that turns CGM [continuous glucose monitoring] data into dosing recommendations displayed right on the pen cap for people using multiple daily [insulin] injection therapy,” according to a company statement.
The Bigfoot app allows users to input and review provider treatment recommendations, displays current glucose ranges, and delivers real-time alerts.
Once it is commercially launched, the Android phone application will be available via the Google Play Store. “Given that 41% of U.S. smartphone users choose Android devices, this clearance enables expanded access to a large group of people with diabetes,” the company said.
On March 6, the FDA cleared the Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 devices as “integrated” CGM sensors. This means that they can now be used as components in automated insulin delivery systems, along with insulin pumps and connectivity software.
Abbott is working with insulin pump manufacturers Insulet and Tandem in the United States for integration with the FreeStyle Libre versions 2 and 3. Outside the United States, the Libre 3 is already authorized to work with mylife Loop from Ypsomed and CamDiab in Germany. Further launches are expected in the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and the Netherlands later this year.
The modified FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 sensors have been cleared for use by patients as young as age 2 years and for up to 15 days, in contrast to the previous versions, which were available for patients as young as 4 years for use up to 14 days. The FDA has cleared all Libre sensors – 2 and 3, current and future versions – for use by pregnant women with any type of diabetes.
The modified sensors will be available in the United States later this year and will eventually replace the Libre sensors in current use, the company said in a statement.
“The FreeStyle Libre portfolio is still the most affordable CGM on the market,” an Abbott representative said in an interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two diabetes management devices that aid in the precision of insulin delivery have been recently cleared by the Food and Drug Administration.
On March 2, the FDA cleared the Android version of Bigfoot Biomedical’s Unity Mobile App for use with its system of smart pen caps that are compatible with different disposable insulin pens for administering both long-acting and rapid-acting insulin.
The system, which has been compatible with iOS devices since May 2021, is “the first and only FDA-cleared smart injection system that turns CGM [continuous glucose monitoring] data into dosing recommendations displayed right on the pen cap for people using multiple daily [insulin] injection therapy,” according to a company statement.
The Bigfoot app allows users to input and review provider treatment recommendations, displays current glucose ranges, and delivers real-time alerts.
Once it is commercially launched, the Android phone application will be available via the Google Play Store. “Given that 41% of U.S. smartphone users choose Android devices, this clearance enables expanded access to a large group of people with diabetes,” the company said.
On March 6, the FDA cleared the Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 devices as “integrated” CGM sensors. This means that they can now be used as components in automated insulin delivery systems, along with insulin pumps and connectivity software.
Abbott is working with insulin pump manufacturers Insulet and Tandem in the United States for integration with the FreeStyle Libre versions 2 and 3. Outside the United States, the Libre 3 is already authorized to work with mylife Loop from Ypsomed and CamDiab in Germany. Further launches are expected in the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and the Netherlands later this year.
The modified FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 sensors have been cleared for use by patients as young as age 2 years and for up to 15 days, in contrast to the previous versions, which were available for patients as young as 4 years for use up to 14 days. The FDA has cleared all Libre sensors – 2 and 3, current and future versions – for use by pregnant women with any type of diabetes.
The modified sensors will be available in the United States later this year and will eventually replace the Libre sensors in current use, the company said in a statement.
“The FreeStyle Libre portfolio is still the most affordable CGM on the market,” an Abbott representative said in an interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two diabetes management devices that aid in the precision of insulin delivery have been recently cleared by the Food and Drug Administration.
On March 2, the FDA cleared the Android version of Bigfoot Biomedical’s Unity Mobile App for use with its system of smart pen caps that are compatible with different disposable insulin pens for administering both long-acting and rapid-acting insulin.
The system, which has been compatible with iOS devices since May 2021, is “the first and only FDA-cleared smart injection system that turns CGM [continuous glucose monitoring] data into dosing recommendations displayed right on the pen cap for people using multiple daily [insulin] injection therapy,” according to a company statement.
The Bigfoot app allows users to input and review provider treatment recommendations, displays current glucose ranges, and delivers real-time alerts.
Once it is commercially launched, the Android phone application will be available via the Google Play Store. “Given that 41% of U.S. smartphone users choose Android devices, this clearance enables expanded access to a large group of people with diabetes,” the company said.
On March 6, the FDA cleared the Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 devices as “integrated” CGM sensors. This means that they can now be used as components in automated insulin delivery systems, along with insulin pumps and connectivity software.
Abbott is working with insulin pump manufacturers Insulet and Tandem in the United States for integration with the FreeStyle Libre versions 2 and 3. Outside the United States, the Libre 3 is already authorized to work with mylife Loop from Ypsomed and CamDiab in Germany. Further launches are expected in the United Kingdom, Switzerland, and the Netherlands later this year.
The modified FreeStyle Libre 2 and FreeStyle Libre 3 sensors have been cleared for use by patients as young as age 2 years and for up to 15 days, in contrast to the previous versions, which were available for patients as young as 4 years for use up to 14 days. The FDA has cleared all Libre sensors – 2 and 3, current and future versions – for use by pregnant women with any type of diabetes.
The modified sensors will be available in the United States later this year and will eventually replace the Libre sensors in current use, the company said in a statement.
“The FreeStyle Libre portfolio is still the most affordable CGM on the market,” an Abbott representative said in an interview.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taking a break from TKIs unlikely to shorten survival
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That might soon change with the publication of a unique study. Lasting 10 years, the phase 3 STAR trial involved 920 patients across 60 cancer centers. These patients had advanced kidney cancer and were taking either sunitinib (Sutent) or pazopanib (Votrient).
The results showed that taking an occasional respite from TKI therapy had little impact on the patient’s survival.
The study was published online in The Lancet Oncology.
The study was funded by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Research because drug companies never run studies on how to reduce the use of their drug, commented lead author Janet Brown, MD, of the University of Sheffield (England).
“We rely on the NIHR to do these important trials that … companies wouldn’t do,” she commented to this news organization.
Commenting on the rationale for STAR, coauthor Jenny Hewison, PhD, of Leeds (England) University School of Medicine, explained that patients often find it difficult to tolerate TKIs. “Although these patients are getting the best treatment that we can offer them, it’s very demanding. … It could make them feel tired, quite unwell. And there can be a range of other effects including sickness and diarrhea.”
As an example, 77% of patients in the pivotal trial of sunitinib in kidney cancer experienced grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as hypertension (13%), fatigue (15%), diarrhea (10%) and hand-foot syndrome (8%).
Both sunitinib and pazopanib carry label warnings of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity.
Also, in contrast to conventional chemotherapy, which is usually given in a finite number of courses, treatment with TKIs carries on indefinitely.
“It feels like you’re taking [TKIs] for the whole of the rest of your life,” said Dr. Brown.
Study details
The STAR trial, an open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled study, is the first phase 3 study of treatment breaks in renal cell carcinoma. The participants had inoperable locoregional or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and had received no systemic therapy for advanced disease.
They were randomly assigned before TKI treatment to a conventional continuation strategy or a drug-free interval approach. The treating physician decided whether a patient would take sunitinib or pazopanib.
All participants took their drugs for four cycles (6 weeks each cycle). At the 24-week point, those with a complete response, partial response, or stable disease began their randomized assignment.
Individuals who took a break continued until their disease progressed, at which point therapy was resumed. They could take further treatment breaks once their disease was back under control. The group on continuous treatment kept going until disease progression or intolerable toxicities. Median follow up was 58 months.
In both the per-protocol and intent-to-treat (ITT) populations, overall survival was 28 months for the people who received continuous treatment vs. 27 months for those who took a break. Statistical noninferiority was established in the ITT population but not in the per-protocol population.
The median length of all treatment breaks was 87 days. Many people took two or more breaks; one patient took nine breaks overall. The breaks were popular: only 3% of participants who were meant to stop therapy withdrew from the study in order to continue their treatment.
Said Dr. Hewison: “In the very early days of planning the study there were some doubts as to whether it would succeed because of potential unwillingness of people to stop treatment for a while.”
Dr. Brown agreed: “People did worry about that initially, but it actually seemed to be more the other way around. By that time – 6 months – people were relieved to be there. …We actually had some people from the other arm asking, could they also have a break?”
To understand better the benefits of treatment breaks to patients, Janine Bestall, PhD, a senior research fellow in applied health research at the University of Leeds, conducted a qualitative study in parallel with the main trial.
Summing up the patients’ experiences, Dr. Bestall said the drug-free periods “gave them more time.”
Dr. Bestall quoted one patient who said: “I know that things can happen and it grows back, but you’ve always got the buffer there knowing that you can go back and get help. But you actually lead a normal life and the advantage is, yeah, you can go on holiday, you can actually do more things in the garden, cleaning up, painting, whatever needs doing, you do it.”
Dr. Brown said, “I had a lady who, when she was on the trial, had four breaks in total, one when her daughter got married, and [she said] that was really nice for her to do all the shopping and all the normal things that you do, and not be on something that was making her tired and causing sore hands and diarrhea.”
The drug-free interval strategy provided annual cost savings of 3,235 pounds sterling ($3,850) and a noninferior quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) benefit in both the ITT and per-protocol populations.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients in the treatment-break group versus 12% of the continuous-treatment group.
The authors of the study concluded, “Treatment breaks might be a feasible and cost-effective option with lifestyle benefits for patients during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with renal cell carcinoma.”
Changes in treatment strategies
The STAR trial started recruiting in January 2012.
Since that time, immunotherapy has taken over as first-line treatment for many patients with advanced ccRCC in both the United Kingdom and the United States.
However, TKIs still have a place. The NCCN Kidney Cancer 2022 Guidelines recommend both sunitinib and pazopanib as options for first-line therapy in advanced disease. The 2022 ASCO Metastatic ccRCC guidelines recommend either drug as first-line treatment in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or in monotherapy if there are “coexisting medical problems.”
In the United States, intermittent sunitinib in metastatic RCC was tested in a small study in 2017 with little activity in the literature since then. The authors, led by Moshe Ornstein, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic, concluded at the time that sunitinib treatment breaks were feasible and “clinical efficacy does not seem to be compromised.” Dr. Ornstein was approached for comment on this latest U.K. study but declined.
Back in the United Kingdom, the results of STAR arrived just in time.
Said Dr. Brown: “This has … been really helpful in the U.K. in the pandemic when people said, can these patients have extra breaks? At the worst of the pandemic we were able to say, sure, if it’s stable, we can keep them off for 3-6 months. …And so that’s already had a powerful impact.”
Dr. Brown concluded, “I think what the trial does allow us to do, as individual oncologists, is to look at the patients that this might be suitable for – it won’t be everybody – and to say yes, it’s okay to personalize things.”
The study was funded by the U.K.’s National Institute for Health and Care Research. Dr. Bestall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hewison reported funding to her institution from the NIHR Health Technology Assessment. Dr. Brown reports having served as a consultant or adviser for Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen, Amgen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer; research funding paid to their institution from the National Institute for Health and Care Research; and travel expenses from Ipsen. Other coauthors reported numerous relationships with industry.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY