User login
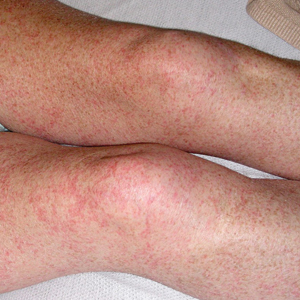
Petechial Rash on the Thighs in an Immunosuppressed Patient
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. In the United States it is most prevalent in the Appalachian region. During the filariform larval stage of the parasite's life cycle, larvae from contaminated soil infect the human skin and spread to the intestinal epithelium,1 then the larvae mature into adult female worms that can produce eggs asexually. Rhabditiform larvae hatch from the eggs and are either excreted in the stool or develop into infectious filariform larvae. The latter can cause autoinfection of the intestinal mucosa or nearby skin; in addition, if the larvae enter the bloodstream, they can spread throughout the body and lead to disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.2 This often fatal progression most commonly occurs in immunosuppressed individuals.3 The mortality rate has been reported to be up to 87%.2,4
Fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea are clinically common in disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.5 Patients also may exhibit dyspnea, cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis.2 Cutaneous manifestations are rare and typically include pruritus and petechiae.6 Eosinophilia may be present but is not a reliable indicator.1
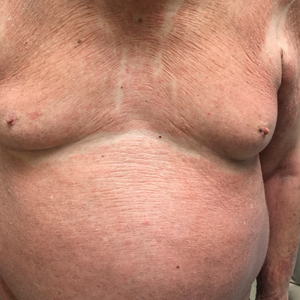
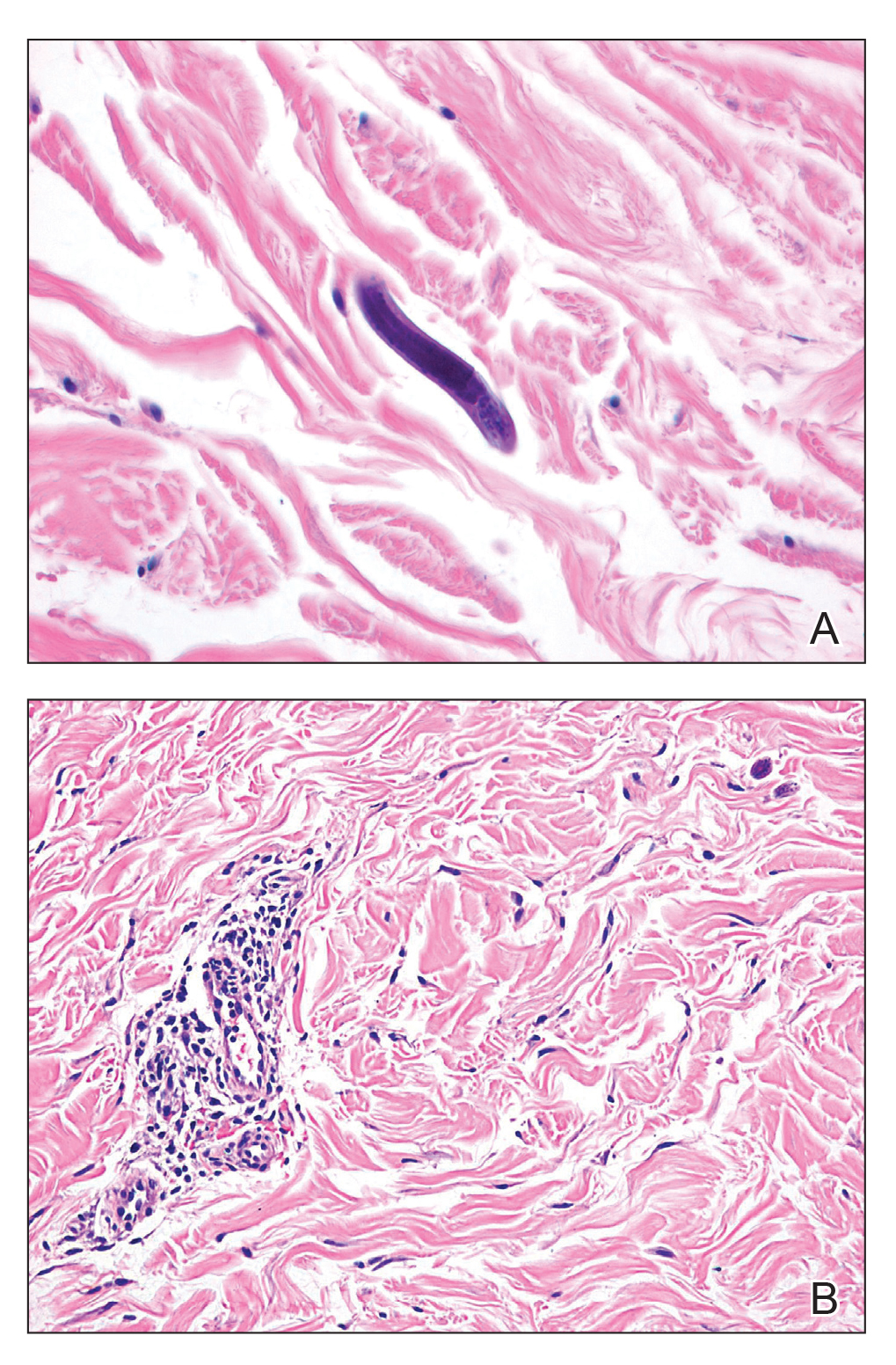
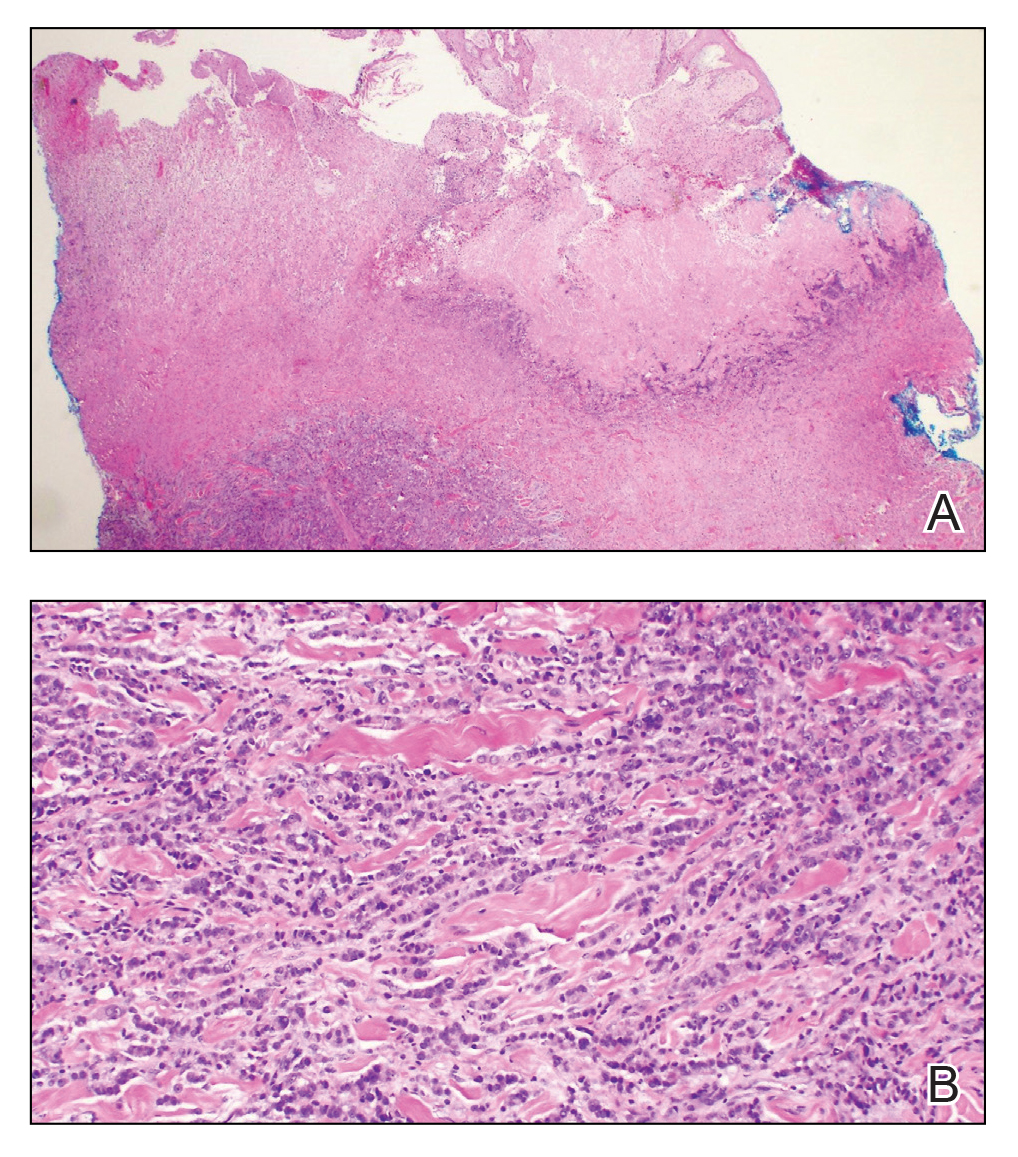
Our patient displayed several risk factors and an early clinical presentation for disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, which evolved over the course of hospitalization. Clues to the diagnosis included an immunosuppressed state; erythematous pruritic macules at presentation that later developed into reticulated petechial patches; and fever, general abdominal symptoms, and dyspnea. However, the patient's overall physical examination findings were subtle and nonspecific. Additionally, the patient did not display the classic larva currens for strongyloidiasis or the pathognomonic periumbilical thumbprint purpura of disseminated infection,6,7 which may indicate that the latter is a later-stage finding. Although graft-vs-host disease initially was suspected, a third skin biopsy revealed basophilic Strongyloides larvae, extravasated erythrocytes, and mild perivascular inflammation (Figure).
Subsequent gastric aspirates and stool cultures revealed S stercoralis. A bronchoalveolar lavage specimen and serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Strongyloides antibody were negative. The patient was treated with an extended 16-day course of ivermectin 12 mg daily until gastric aspirates and stool cultures were negative for the parasite. The rash receded by the end of the patient's 32-day hospital stay.
Because of the high mortality rate of untreated disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, early diagnosis and initiation of anthelmintic treatment is vital in improving patient outcomes. As such, the diagnosis of disseminated strongyloidiasis should be considered in any immunosuppressed patient with multisystemic symptoms and/or petechiae. The differential diagnosis includes graft-vs-host disease, drug-induced urticaria, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and other opportunistic parasites.6,8,9
- Concha R, Harrington W Jr, Rogers AI. Intestinal strongyloidiasis: recognition, management, and determinants of outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:203-211.
- Vadlamudi RS, Chi DS, Krishnaswamy G. Intestinal strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome. Clin Mol Allergy. 2006;4:8.
- Keiser PB, Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004;17:208-217.
- Chan FLY, Kennedy B, Nelson R. Fatal Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome in an immunocompetent adult with review of the literature. Intern Med J. 2018;48:872-875.
- Scowden EB, Schaffner W, Stone WJ. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978;57:527-544.
- von Kuster LC, Genta RM. Cutaneous manifestations of strongyloidiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1826-1830.
- Weiser JA, Scully BE, Bulman WA, et al. Periumbilical parasitic thumbprint purpura: Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome acquired from a cadaveric renal transplant. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13:58-62.
- Berenson CS, Dobuler KJ, Bia FJ. Fever, petechiae, and pulmonary infiltrates in an immunocompromised Peruvian man. Yale J Biol Med. 1987;60:437-445.
- Ly MN, Bethel SL, Usmani AS, et al. Cutaneous Strongyloides stercoralis infection: an unusual presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(2 suppl case reports):S157-S160.
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. In the United States it is most prevalent in the Appalachian region. During the filariform larval stage of the parasite's life cycle, larvae from contaminated soil infect the human skin and spread to the intestinal epithelium,1 then the larvae mature into adult female worms that can produce eggs asexually. Rhabditiform larvae hatch from the eggs and are either excreted in the stool or develop into infectious filariform larvae. The latter can cause autoinfection of the intestinal mucosa or nearby skin; in addition, if the larvae enter the bloodstream, they can spread throughout the body and lead to disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.2 This often fatal progression most commonly occurs in immunosuppressed individuals.3 The mortality rate has been reported to be up to 87%.2,4
Fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea are clinically common in disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.5 Patients also may exhibit dyspnea, cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis.2 Cutaneous manifestations are rare and typically include pruritus and petechiae.6 Eosinophilia may be present but is not a reliable indicator.1
Our patient displayed several risk factors and an early clinical presentation for disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, which evolved over the course of hospitalization. Clues to the diagnosis included an immunosuppressed state; erythematous pruritic macules at presentation that later developed into reticulated petechial patches; and fever, general abdominal symptoms, and dyspnea. However, the patient's overall physical examination findings were subtle and nonspecific. Additionally, the patient did not display the classic larva currens for strongyloidiasis or the pathognomonic periumbilical thumbprint purpura of disseminated infection,6,7 which may indicate that the latter is a later-stage finding. Although graft-vs-host disease initially was suspected, a third skin biopsy revealed basophilic Strongyloides larvae, extravasated erythrocytes, and mild perivascular inflammation (Figure).

Subsequent gastric aspirates and stool cultures revealed S stercoralis. A bronchoalveolar lavage specimen and serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Strongyloides antibody were negative. The patient was treated with an extended 16-day course of ivermectin 12 mg daily until gastric aspirates and stool cultures were negative for the parasite. The rash receded by the end of the patient's 32-day hospital stay.
Because of the high mortality rate of untreated disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, early diagnosis and initiation of anthelmintic treatment is vital in improving patient outcomes. As such, the diagnosis of disseminated strongyloidiasis should be considered in any immunosuppressed patient with multisystemic symptoms and/or petechiae. The differential diagnosis includes graft-vs-host disease, drug-induced urticaria, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and other opportunistic parasites.6,8,9
The Diagnosis: Disseminated Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Strongyloides stercoralis. In the United States it is most prevalent in the Appalachian region. During the filariform larval stage of the parasite's life cycle, larvae from contaminated soil infect the human skin and spread to the intestinal epithelium,1 then the larvae mature into adult female worms that can produce eggs asexually. Rhabditiform larvae hatch from the eggs and are either excreted in the stool or develop into infectious filariform larvae. The latter can cause autoinfection of the intestinal mucosa or nearby skin; in addition, if the larvae enter the bloodstream, they can spread throughout the body and lead to disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.2 This often fatal progression most commonly occurs in immunosuppressed individuals.3 The mortality rate has been reported to be up to 87%.2,4
Fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea are clinically common in disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome.5 Patients also may exhibit dyspnea, cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis.2 Cutaneous manifestations are rare and typically include pruritus and petechiae.6 Eosinophilia may be present but is not a reliable indicator.1
Our patient displayed several risk factors and an early clinical presentation for disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, which evolved over the course of hospitalization. Clues to the diagnosis included an immunosuppressed state; erythematous pruritic macules at presentation that later developed into reticulated petechial patches; and fever, general abdominal symptoms, and dyspnea. However, the patient's overall physical examination findings were subtle and nonspecific. Additionally, the patient did not display the classic larva currens for strongyloidiasis or the pathognomonic periumbilical thumbprint purpura of disseminated infection,6,7 which may indicate that the latter is a later-stage finding. Although graft-vs-host disease initially was suspected, a third skin biopsy revealed basophilic Strongyloides larvae, extravasated erythrocytes, and mild perivascular inflammation (Figure).

Subsequent gastric aspirates and stool cultures revealed S stercoralis. A bronchoalveolar lavage specimen and serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Strongyloides antibody were negative. The patient was treated with an extended 16-day course of ivermectin 12 mg daily until gastric aspirates and stool cultures were negative for the parasite. The rash receded by the end of the patient's 32-day hospital stay.
Because of the high mortality rate of untreated disseminated strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome, early diagnosis and initiation of anthelmintic treatment is vital in improving patient outcomes. As such, the diagnosis of disseminated strongyloidiasis should be considered in any immunosuppressed patient with multisystemic symptoms and/or petechiae. The differential diagnosis includes graft-vs-host disease, drug-induced urticaria, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and other opportunistic parasites.6,8,9
- Concha R, Harrington W Jr, Rogers AI. Intestinal strongyloidiasis: recognition, management, and determinants of outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:203-211.
- Vadlamudi RS, Chi DS, Krishnaswamy G. Intestinal strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome. Clin Mol Allergy. 2006;4:8.
- Keiser PB, Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004;17:208-217.
- Chan FLY, Kennedy B, Nelson R. Fatal Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome in an immunocompetent adult with review of the literature. Intern Med J. 2018;48:872-875.
- Scowden EB, Schaffner W, Stone WJ. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978;57:527-544.
- von Kuster LC, Genta RM. Cutaneous manifestations of strongyloidiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1826-1830.
- Weiser JA, Scully BE, Bulman WA, et al. Periumbilical parasitic thumbprint purpura: Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome acquired from a cadaveric renal transplant. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13:58-62.
- Berenson CS, Dobuler KJ, Bia FJ. Fever, petechiae, and pulmonary infiltrates in an immunocompromised Peruvian man. Yale J Biol Med. 1987;60:437-445.
- Ly MN, Bethel SL, Usmani AS, et al. Cutaneous Strongyloides stercoralis infection: an unusual presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(2 suppl case reports):S157-S160.
- Concha R, Harrington W Jr, Rogers AI. Intestinal strongyloidiasis: recognition, management, and determinants of outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:203-211.
- Vadlamudi RS, Chi DS, Krishnaswamy G. Intestinal strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome. Clin Mol Allergy. 2006;4:8.
- Keiser PB, Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004;17:208-217.
- Chan FLY, Kennedy B, Nelson R. Fatal Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome in an immunocompetent adult with review of the literature. Intern Med J. 2018;48:872-875.
- Scowden EB, Schaffner W, Stone WJ. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978;57:527-544.
- von Kuster LC, Genta RM. Cutaneous manifestations of strongyloidiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:1826-1830.
- Weiser JA, Scully BE, Bulman WA, et al. Periumbilical parasitic thumbprint purpura: Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome acquired from a cadaveric renal transplant. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011;13:58-62.
- Berenson CS, Dobuler KJ, Bia FJ. Fever, petechiae, and pulmonary infiltrates in an immunocompromised Peruvian man. Yale J Biol Med. 1987;60:437-445.
- Ly MN, Bethel SL, Usmani AS, et al. Cutaneous Strongyloides stercoralis infection: an unusual presentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49(2 suppl case reports):S157-S160.
A 48-year-old woman from rural Virginia presented with centrifugally spreading, pruritic, blanchable macules over the lower abdomen and upper thighs noted 4 months after a pancreas transplant. After 3 weeks, the macules coalesced into reticulated nonblanching petechial patches. Fever, dyspnea, increasing xerosis, abdominal pain, and constipation were present. The patient had a medical history of type 1 diabetes mellitus requiring a pancreas transplant. Initial skin biopsy and fluorescence in situ hybridization to test for immune reaction to the XY-donor pancreas were negative. Mild transient eosinophilia was present at admission.
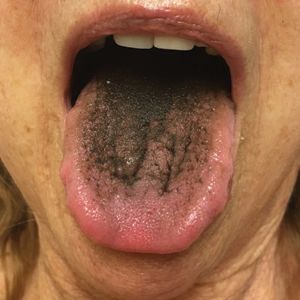
Asymptomatic Transient Lingual Hyperpigmentation
The Diagnosis: Pseudo-Black Hairy Tongue
Pseudo-black hairy tongue is a benign and painless disorder characterized by transient hyperpigmentation of the tongue with a substance that can be easily scraped off. In this case, the patient's lingual discoloration was secondary to the ingestion of bismuth salicylate. The phenomenon is thought to occur due to a reaction between bismuth and sulfur-containing compounds in the saliva, resulting in the characteristic black substance on the surface of the tongue that nestles between the lingual papillae.1 An associated feature may include black stools. Other etiologic factors involved in pseudo-black hairy tongue include food coloring, tobacco, and other drugs such antibiotics and antidepressants.2
The differential diagnosis of lingual hyperpigmentation includes lingua villosa nigra (also known as black hairy tongue), pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue, acanthosis nigricans, and oral hairy leukoplakia. Lingua villosa nigra is a similar condition in which individuals present with a black tongue; however, the tongue also appears hairy. The tongue may appear as other colors such as brown, yellow, or green. Patients additionally may have symptoms of burning, dysgeusia, halitosis, or gagging. Poor oral hygiene, xerostomia, use of tobacco or alcohol, and different medications including antibiotics and antipsychotic medications increase the risk for developing lingua villosa nigra.2,3 This condition is distinguished from pseudo-black hairy tongue by proliferation and elongation of the filiform papillae.3 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a normal variant of tongue morphology, is more common in individuals with darker skin types, and primarily affects the lateral aspect and apex of the tongue.4 Acanthosis nigricans can appear in the oral cavity as multiple pigmented papillary lesions on the dorsal and lateral regions of the tongue and frequently involves the lips; this condition may be associated with metabolic disorders or underlying malignancy.2,3 Oral hairy leukoplakia is caused by Epstein-Barr virus infection and typically presents as white plaques on the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the tongue; this condition largely is found in immunocompromised patients.5
In our patient there was an acute onset of tongue discoloration associated with ingestion of bismuth salicylate, no hypertrophy or lengthening of the lingual papillae, and no involvement of the patient's lips, which was consistent with the diagnosis of pseudo-black hairy tongue. Pseudo-black hairy tongue is transient and treated by discontinuation of offending agents and proper hygiene practices.
- Bradley B, Singleton M, Lin Wan Po A. Bismuth toxicity--a reassessment. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1989;14:423-441.
- Gurvits GE, Tan A. Black hairy tongue syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:10845-10850.
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569.
- Mangold AR, Torgerson RR, Rogers RS. Diseases of the tongue. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:458-469.
- Husak R, Garbe C, Orfanos CE. Oral hairy leukoplakia in 71 HIV-seropositive patients: clinical symptoms, relation to immunologic status, and prognostic significance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:928-934.
The Diagnosis: Pseudo-Black Hairy Tongue
Pseudo-black hairy tongue is a benign and painless disorder characterized by transient hyperpigmentation of the tongue with a substance that can be easily scraped off. In this case, the patient's lingual discoloration was secondary to the ingestion of bismuth salicylate. The phenomenon is thought to occur due to a reaction between bismuth and sulfur-containing compounds in the saliva, resulting in the characteristic black substance on the surface of the tongue that nestles between the lingual papillae.1 An associated feature may include black stools. Other etiologic factors involved in pseudo-black hairy tongue include food coloring, tobacco, and other drugs such antibiotics and antidepressants.2
The differential diagnosis of lingual hyperpigmentation includes lingua villosa nigra (also known as black hairy tongue), pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue, acanthosis nigricans, and oral hairy leukoplakia. Lingua villosa nigra is a similar condition in which individuals present with a black tongue; however, the tongue also appears hairy. The tongue may appear as other colors such as brown, yellow, or green. Patients additionally may have symptoms of burning, dysgeusia, halitosis, or gagging. Poor oral hygiene, xerostomia, use of tobacco or alcohol, and different medications including antibiotics and antipsychotic medications increase the risk for developing lingua villosa nigra.2,3 This condition is distinguished from pseudo-black hairy tongue by proliferation and elongation of the filiform papillae.3 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a normal variant of tongue morphology, is more common in individuals with darker skin types, and primarily affects the lateral aspect and apex of the tongue.4 Acanthosis nigricans can appear in the oral cavity as multiple pigmented papillary lesions on the dorsal and lateral regions of the tongue and frequently involves the lips; this condition may be associated with metabolic disorders or underlying malignancy.2,3 Oral hairy leukoplakia is caused by Epstein-Barr virus infection and typically presents as white plaques on the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the tongue; this condition largely is found in immunocompromised patients.5
In our patient there was an acute onset of tongue discoloration associated with ingestion of bismuth salicylate, no hypertrophy or lengthening of the lingual papillae, and no involvement of the patient's lips, which was consistent with the diagnosis of pseudo-black hairy tongue. Pseudo-black hairy tongue is transient and treated by discontinuation of offending agents and proper hygiene practices.
The Diagnosis: Pseudo-Black Hairy Tongue
Pseudo-black hairy tongue is a benign and painless disorder characterized by transient hyperpigmentation of the tongue with a substance that can be easily scraped off. In this case, the patient's lingual discoloration was secondary to the ingestion of bismuth salicylate. The phenomenon is thought to occur due to a reaction between bismuth and sulfur-containing compounds in the saliva, resulting in the characteristic black substance on the surface of the tongue that nestles between the lingual papillae.1 An associated feature may include black stools. Other etiologic factors involved in pseudo-black hairy tongue include food coloring, tobacco, and other drugs such antibiotics and antidepressants.2
The differential diagnosis of lingual hyperpigmentation includes lingua villosa nigra (also known as black hairy tongue), pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue, acanthosis nigricans, and oral hairy leukoplakia. Lingua villosa nigra is a similar condition in which individuals present with a black tongue; however, the tongue also appears hairy. The tongue may appear as other colors such as brown, yellow, or green. Patients additionally may have symptoms of burning, dysgeusia, halitosis, or gagging. Poor oral hygiene, xerostomia, use of tobacco or alcohol, and different medications including antibiotics and antipsychotic medications increase the risk for developing lingua villosa nigra.2,3 This condition is distinguished from pseudo-black hairy tongue by proliferation and elongation of the filiform papillae.3 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a normal variant of tongue morphology, is more common in individuals with darker skin types, and primarily affects the lateral aspect and apex of the tongue.4 Acanthosis nigricans can appear in the oral cavity as multiple pigmented papillary lesions on the dorsal and lateral regions of the tongue and frequently involves the lips; this condition may be associated with metabolic disorders or underlying malignancy.2,3 Oral hairy leukoplakia is caused by Epstein-Barr virus infection and typically presents as white plaques on the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the tongue; this condition largely is found in immunocompromised patients.5
In our patient there was an acute onset of tongue discoloration associated with ingestion of bismuth salicylate, no hypertrophy or lengthening of the lingual papillae, and no involvement of the patient's lips, which was consistent with the diagnosis of pseudo-black hairy tongue. Pseudo-black hairy tongue is transient and treated by discontinuation of offending agents and proper hygiene practices.
- Bradley B, Singleton M, Lin Wan Po A. Bismuth toxicity--a reassessment. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1989;14:423-441.
- Gurvits GE, Tan A. Black hairy tongue syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:10845-10850.
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569.
- Mangold AR, Torgerson RR, Rogers RS. Diseases of the tongue. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:458-469.
- Husak R, Garbe C, Orfanos CE. Oral hairy leukoplakia in 71 HIV-seropositive patients: clinical symptoms, relation to immunologic status, and prognostic significance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:928-934.
- Bradley B, Singleton M, Lin Wan Po A. Bismuth toxicity--a reassessment. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1989;14:423-441.
- Gurvits GE, Tan A. Black hairy tongue syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:10845-10850.
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569.
- Mangold AR, Torgerson RR, Rogers RS. Diseases of the tongue. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:458-469.
- Husak R, Garbe C, Orfanos CE. Oral hairy leukoplakia in 71 HIV-seropositive patients: clinical symptoms, relation to immunologic status, and prognostic significance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:928-934.
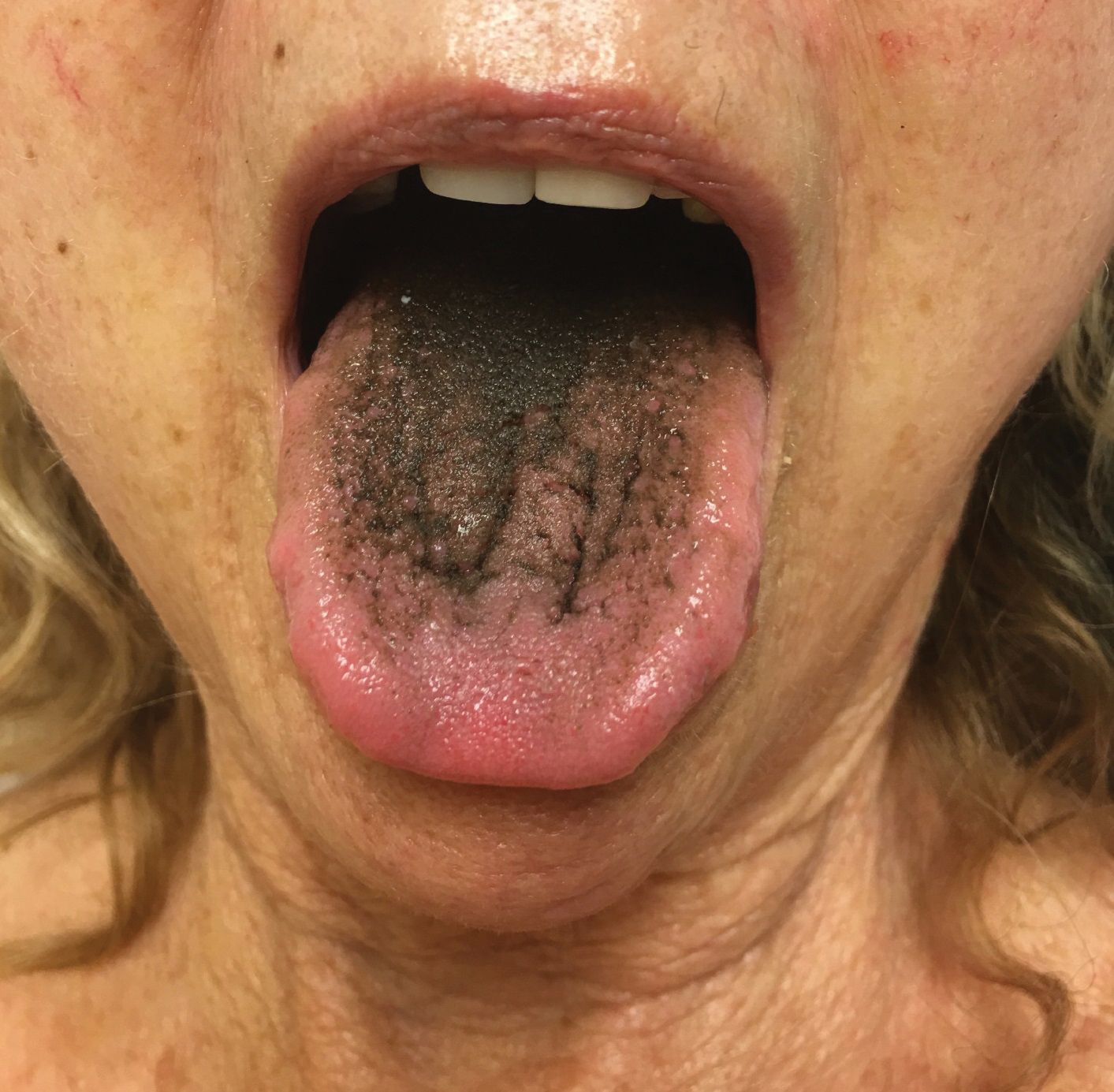
A 77-year-old woman incidentally was noted to have black discoloration of the tongue during a routine dermatologic examination. The patient was unaware of the tongue discoloration and reported that her tongue appeared normal the day prior. The tongue was asymptomatic. Clinical examination revealed black hyperpigmentation on the dorsal aspect of the tongue without appreciable hypertrophy or hyperkeratosis of the filiform papillae. The patient had a half-pack daily smoking habit for many years but had abstained from any smoking or tobacco use for the last 15 years. The patient endorsed good oral hygiene. Upon further questioning, the patient revealed that she had ingested 1 tablet of bismuth salicylate the prior night to relieve postprandial dyspepsia. A cotton-tipped applicator was rubbed gently against the affected area and removed some of the black pigment.
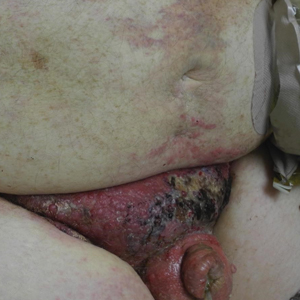
Painful Indurated Plaque on the Groin
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
Histopathology demonstrated ulceration of the epidermis with necrosis of the papillary dermis. There was a diffuse infiltration of pleomorphic and atypical epithelioid cells in the reticular dermis (Figure). Focally there was ductal and glandular differentiation. The stroma was sclerotic. At the deep aspect of the biopsy specimen, tumor cells intercalated between collagen bundles in linear strands. Atypical mitoses were common, and necrosis en masse was seen. An immunohistochemical panel also was performed. Tissue from the biopsy was strongly positive for CDX-2 and cytokeratin 20 and diffusely negative for cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and prostate-specific antigen. The other biopsy was sent for cultures and grew no organisms, which confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from the patient's primary colonic adenocarcinoma. Due to the poor prognosis and his overall poor health, our patient opted for palliative care.
Based on large retrospective studies, the frequency of cutaneous metastasis for patients diagnosed with any malignancy is 0.7% to 9.0%.1-4 The third most common malignancy in both sexes is colorectal cancer, affecting approximately 5% of the US population.3 The frequency of cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancer is 0.81% to 3.9%.1,2,4,5 Generally, cutaneous metastases present within 2 to 3 years from diagnosis of primary malignancy.6,7 The most common sites for cutaneous metastases in a patient with colorectal cancer are the abdomen and pelvic region, often at surgical sites.1-4,6-9
The clinical presentation of cutaneous metastases varies greatly, and as a result, they commonly are misdiagnosed.6,7 Although treatment with many antibiotics and antifungals had failed in our patient, the examination still was concerning for a possible granulomatous infection vs malignancy. With the history of colon cancer, radiation treatment, and chemotherapy, the possible malignancy diagnoses included primary skin cancers, viral tumors, and cutaneous metastasis. The initial evaluations had focused on infectious causes and resulted in 6 weeks of misdiagnosis and inappropriate therapy. Despite cutaneous metastases being uncommon, there should be a high index of suspicion for lesions in patients who have a history of cancer, especially if the lesion does not respond to treatment.2,6,7
Physical examination in our patient showed a high tumor burden as well as evidence of carcinoma erysipeloides on the lower abdomen and thighs, in addition to carcinoma en cuirasse throughout the pubic region. Carcinoma erysipeloides was first described in 1893 in a patient with breast cancer: "The erythematous infiltration of the skin was very superficial, and was attended simply by redness with a slight degree of induration. Until touched by the finger the condition might easily have been taken for a slightly-marked form of erysipelas."10 The clinical findings are a result of lymphatic and vascular obstruction.3,9 The breast is the most common location to find carcinoma erysipeloides.3 It is an unusual occurrence to find it on the abdomen from colonic adenocarcinoma. The term cancer en cuirasse was coined in 1838 to describe the cutaneous manifestation of breast cancer that caused the skin to resemble the metal breastplate of a cuirasser.4 Similar to carcinoma erysipeloides, carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly is found as cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer, not from colonic adenocarcinoma.3
The histologic characteristics of cutaneous metastases in general are similar to the primary malignancy but can be more poorly differentiated.7 Generally, neoplastic cells are seen in the lymphatic and blood vessels, and a large portion of the tumor is confined to the deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat.3,6 Histologic features of colonic adenocarcinoma metastases can demonstrate a well-differentiated, glandular architecture with mucin-secreting cells.3,8,9 There also is a histologic pattern of neoplastic cells arranging themselves between collagen bundles in linear strands; this finding more commonly is seen in adenocarcinoma of the breast but also was seen in our patient.3,9 With immunohistochemical staining, a truncated panel of cytokeratin 7, cytokeratin 20, and S-100 had a diagnostic accuracy of 100% for cutaneous metastases from colonic adenocarcinoma in one study. The pattern of all colonic adenocarcinomas was cytokeratin 20 positive and cytokeratin 7 and S-100 negative.6
Cutaneous metastases typically demonstrate widespread and rapidly progressive disease.3,9 Survival studies of cutaneous metastases showed that 48% to 66% of patients died within the first 6 months.3,6 Specifically, cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancers showed a median survival of 3 to 5 months.6,7 Currently there are no treatment guidelines for cutaneous metastases.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm K. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2 pt 1):228-236.
- Gul U, Kilic A, Gonul M, et al. Spectrum of cutaneous metastases in 1287 cases of internal malignancies: a study from Turkey. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:160-162.
- Hussein MR. Skin metastasis: a pathologist's perspective. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:E1-E20.
- Schwartz RA. Cutaneous metastatic disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):161-182; quiz 183-186.
- Hu S, Chen G, Wu C, et al. Rates of cutaneous metastases from different internal malignancies: experience from a Taiwanese medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:379-387.
- Saeed S, Keehn C, Morgan M. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Sariya D, Ruth K, Adams-McDonnell R. Clinicopathologic correlation of cutaneous metastases: experience of a cancer center. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:613-620.
- Brownstein M, Helwig E. Metastatic tumors of the skin. Cancer. 1972;29:1298-1307.
- McKee PH. Cutaneous metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:239-250.
- Hutchinson J. Notes from congresses and continental hospitals: erythema-scirrhus of the skin in association with cancer of the breast. Arch Surg (London). 1893;4:220-222
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
Histopathology demonstrated ulceration of the epidermis with necrosis of the papillary dermis. There was a diffuse infiltration of pleomorphic and atypical epithelioid cells in the reticular dermis (Figure). Focally there was ductal and glandular differentiation. The stroma was sclerotic. At the deep aspect of the biopsy specimen, tumor cells intercalated between collagen bundles in linear strands. Atypical mitoses were common, and necrosis en masse was seen. An immunohistochemical panel also was performed. Tissue from the biopsy was strongly positive for CDX-2 and cytokeratin 20 and diffusely negative for cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and prostate-specific antigen. The other biopsy was sent for cultures and grew no organisms, which confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from the patient's primary colonic adenocarcinoma. Due to the poor prognosis and his overall poor health, our patient opted for palliative care.

Based on large retrospective studies, the frequency of cutaneous metastasis for patients diagnosed with any malignancy is 0.7% to 9.0%.1-4 The third most common malignancy in both sexes is colorectal cancer, affecting approximately 5% of the US population.3 The frequency of cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancer is 0.81% to 3.9%.1,2,4,5 Generally, cutaneous metastases present within 2 to 3 years from diagnosis of primary malignancy.6,7 The most common sites for cutaneous metastases in a patient with colorectal cancer are the abdomen and pelvic region, often at surgical sites.1-4,6-9
The clinical presentation of cutaneous metastases varies greatly, and as a result, they commonly are misdiagnosed.6,7 Although treatment with many antibiotics and antifungals had failed in our patient, the examination still was concerning for a possible granulomatous infection vs malignancy. With the history of colon cancer, radiation treatment, and chemotherapy, the possible malignancy diagnoses included primary skin cancers, viral tumors, and cutaneous metastasis. The initial evaluations had focused on infectious causes and resulted in 6 weeks of misdiagnosis and inappropriate therapy. Despite cutaneous metastases being uncommon, there should be a high index of suspicion for lesions in patients who have a history of cancer, especially if the lesion does not respond to treatment.2,6,7
Physical examination in our patient showed a high tumor burden as well as evidence of carcinoma erysipeloides on the lower abdomen and thighs, in addition to carcinoma en cuirasse throughout the pubic region. Carcinoma erysipeloides was first described in 1893 in a patient with breast cancer: "The erythematous infiltration of the skin was very superficial, and was attended simply by redness with a slight degree of induration. Until touched by the finger the condition might easily have been taken for a slightly-marked form of erysipelas."10 The clinical findings are a result of lymphatic and vascular obstruction.3,9 The breast is the most common location to find carcinoma erysipeloides.3 It is an unusual occurrence to find it on the abdomen from colonic adenocarcinoma. The term cancer en cuirasse was coined in 1838 to describe the cutaneous manifestation of breast cancer that caused the skin to resemble the metal breastplate of a cuirasser.4 Similar to carcinoma erysipeloides, carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly is found as cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer, not from colonic adenocarcinoma.3
The histologic characteristics of cutaneous metastases in general are similar to the primary malignancy but can be more poorly differentiated.7 Generally, neoplastic cells are seen in the lymphatic and blood vessels, and a large portion of the tumor is confined to the deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat.3,6 Histologic features of colonic adenocarcinoma metastases can demonstrate a well-differentiated, glandular architecture with mucin-secreting cells.3,8,9 There also is a histologic pattern of neoplastic cells arranging themselves between collagen bundles in linear strands; this finding more commonly is seen in adenocarcinoma of the breast but also was seen in our patient.3,9 With immunohistochemical staining, a truncated panel of cytokeratin 7, cytokeratin 20, and S-100 had a diagnostic accuracy of 100% for cutaneous metastases from colonic adenocarcinoma in one study. The pattern of all colonic adenocarcinomas was cytokeratin 20 positive and cytokeratin 7 and S-100 negative.6
Cutaneous metastases typically demonstrate widespread and rapidly progressive disease.3,9 Survival studies of cutaneous metastases showed that 48% to 66% of patients died within the first 6 months.3,6 Specifically, cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancers showed a median survival of 3 to 5 months.6,7 Currently there are no treatment guidelines for cutaneous metastases.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Metastasis
Histopathology demonstrated ulceration of the epidermis with necrosis of the papillary dermis. There was a diffuse infiltration of pleomorphic and atypical epithelioid cells in the reticular dermis (Figure). Focally there was ductal and glandular differentiation. The stroma was sclerotic. At the deep aspect of the biopsy specimen, tumor cells intercalated between collagen bundles in linear strands. Atypical mitoses were common, and necrosis en masse was seen. An immunohistochemical panel also was performed. Tissue from the biopsy was strongly positive for CDX-2 and cytokeratin 20 and diffusely negative for cytokeratin 7, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, and prostate-specific antigen. The other biopsy was sent for cultures and grew no organisms, which confirmed the diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from the patient's primary colonic adenocarcinoma. Due to the poor prognosis and his overall poor health, our patient opted for palliative care.

Based on large retrospective studies, the frequency of cutaneous metastasis for patients diagnosed with any malignancy is 0.7% to 9.0%.1-4 The third most common malignancy in both sexes is colorectal cancer, affecting approximately 5% of the US population.3 The frequency of cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancer is 0.81% to 3.9%.1,2,4,5 Generally, cutaneous metastases present within 2 to 3 years from diagnosis of primary malignancy.6,7 The most common sites for cutaneous metastases in a patient with colorectal cancer are the abdomen and pelvic region, often at surgical sites.1-4,6-9
The clinical presentation of cutaneous metastases varies greatly, and as a result, they commonly are misdiagnosed.6,7 Although treatment with many antibiotics and antifungals had failed in our patient, the examination still was concerning for a possible granulomatous infection vs malignancy. With the history of colon cancer, radiation treatment, and chemotherapy, the possible malignancy diagnoses included primary skin cancers, viral tumors, and cutaneous metastasis. The initial evaluations had focused on infectious causes and resulted in 6 weeks of misdiagnosis and inappropriate therapy. Despite cutaneous metastases being uncommon, there should be a high index of suspicion for lesions in patients who have a history of cancer, especially if the lesion does not respond to treatment.2,6,7
Physical examination in our patient showed a high tumor burden as well as evidence of carcinoma erysipeloides on the lower abdomen and thighs, in addition to carcinoma en cuirasse throughout the pubic region. Carcinoma erysipeloides was first described in 1893 in a patient with breast cancer: "The erythematous infiltration of the skin was very superficial, and was attended simply by redness with a slight degree of induration. Until touched by the finger the condition might easily have been taken for a slightly-marked form of erysipelas."10 The clinical findings are a result of lymphatic and vascular obstruction.3,9 The breast is the most common location to find carcinoma erysipeloides.3 It is an unusual occurrence to find it on the abdomen from colonic adenocarcinoma. The term cancer en cuirasse was coined in 1838 to describe the cutaneous manifestation of breast cancer that caused the skin to resemble the metal breastplate of a cuirasser.4 Similar to carcinoma erysipeloides, carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly is found as cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer, not from colonic adenocarcinoma.3
The histologic characteristics of cutaneous metastases in general are similar to the primary malignancy but can be more poorly differentiated.7 Generally, neoplastic cells are seen in the lymphatic and blood vessels, and a large portion of the tumor is confined to the deep dermis and in the subcutaneous fat.3,6 Histologic features of colonic adenocarcinoma metastases can demonstrate a well-differentiated, glandular architecture with mucin-secreting cells.3,8,9 There also is a histologic pattern of neoplastic cells arranging themselves between collagen bundles in linear strands; this finding more commonly is seen in adenocarcinoma of the breast but also was seen in our patient.3,9 With immunohistochemical staining, a truncated panel of cytokeratin 7, cytokeratin 20, and S-100 had a diagnostic accuracy of 100% for cutaneous metastases from colonic adenocarcinoma in one study. The pattern of all colonic adenocarcinomas was cytokeratin 20 positive and cytokeratin 7 and S-100 negative.6
Cutaneous metastases typically demonstrate widespread and rapidly progressive disease.3,9 Survival studies of cutaneous metastases showed that 48% to 66% of patients died within the first 6 months.3,6 Specifically, cutaneous metastases from colorectal cancers showed a median survival of 3 to 5 months.6,7 Currently there are no treatment guidelines for cutaneous metastases.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm K. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2 pt 1):228-236.
- Gul U, Kilic A, Gonul M, et al. Spectrum of cutaneous metastases in 1287 cases of internal malignancies: a study from Turkey. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:160-162.
- Hussein MR. Skin metastasis: a pathologist's perspective. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:E1-E20.
- Schwartz RA. Cutaneous metastatic disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):161-182; quiz 183-186.
- Hu S, Chen G, Wu C, et al. Rates of cutaneous metastases from different internal malignancies: experience from a Taiwanese medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:379-387.
- Saeed S, Keehn C, Morgan M. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Sariya D, Ruth K, Adams-McDonnell R. Clinicopathologic correlation of cutaneous metastases: experience of a cancer center. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:613-620.
- Brownstein M, Helwig E. Metastatic tumors of the skin. Cancer. 1972;29:1298-1307.
- McKee PH. Cutaneous metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:239-250.
- Hutchinson J. Notes from congresses and continental hospitals: erythema-scirrhus of the skin in association with cancer of the breast. Arch Surg (London). 1893;4:220-222
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm K. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(2 pt 1):228-236.
- Gul U, Kilic A, Gonul M, et al. Spectrum of cutaneous metastases in 1287 cases of internal malignancies: a study from Turkey. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:160-162.
- Hussein MR. Skin metastasis: a pathologist's perspective. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:E1-E20.
- Schwartz RA. Cutaneous metastatic disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33(2 pt 1):161-182; quiz 183-186.
- Hu S, Chen G, Wu C, et al. Rates of cutaneous metastases from different internal malignancies: experience from a Taiwanese medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:379-387.
- Saeed S, Keehn C, Morgan M. Cutaneous metastasis: a clinical, pathological, and immunohistochemical appraisal. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:419-430.
- Sariya D, Ruth K, Adams-McDonnell R. Clinicopathologic correlation of cutaneous metastases: experience of a cancer center. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:613-620.
- Brownstein M, Helwig E. Metastatic tumors of the skin. Cancer. 1972;29:1298-1307.
- McKee PH. Cutaneous metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:239-250.
- Hutchinson J. Notes from congresses and continental hospitals: erythema-scirrhus of the skin in association with cancer of the breast. Arch Surg (London). 1893;4:220-222
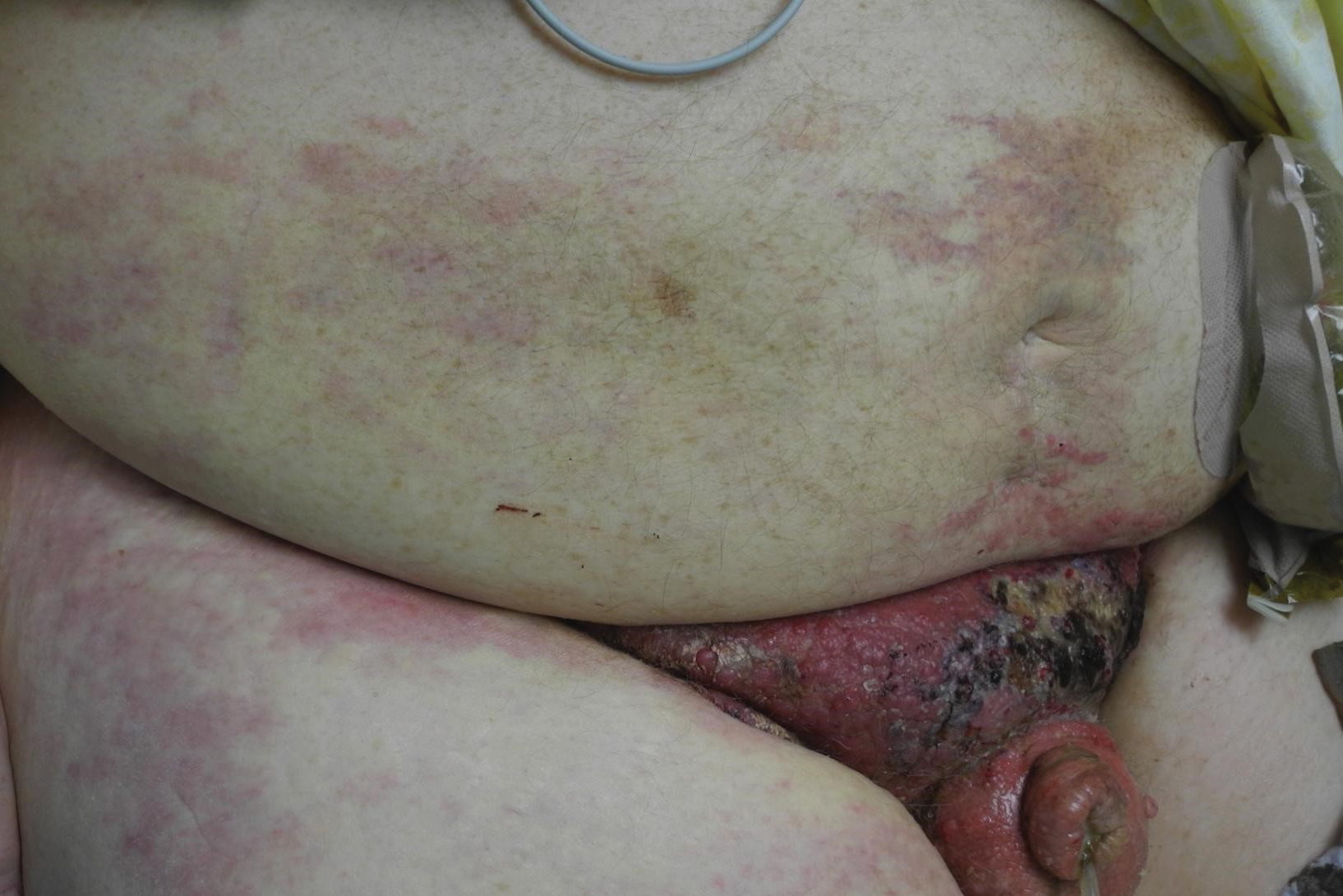
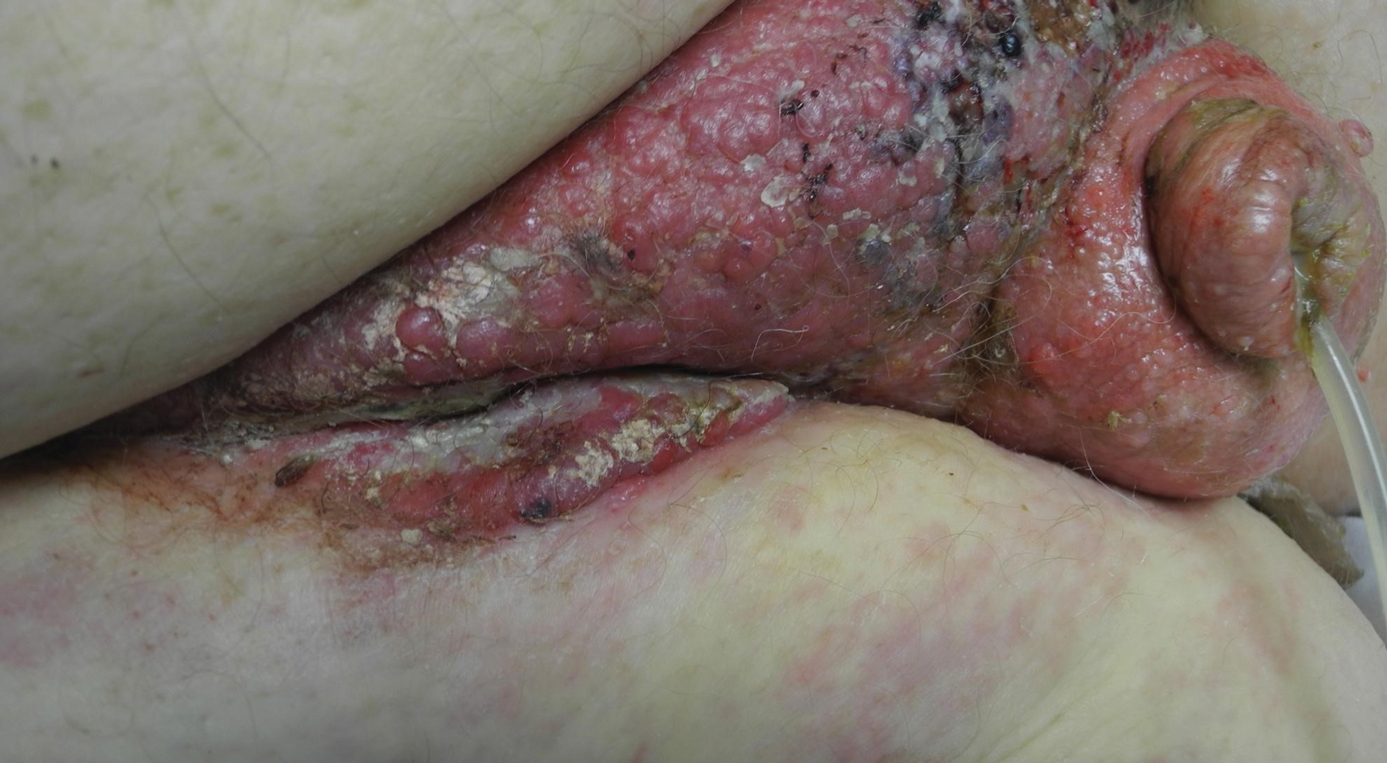
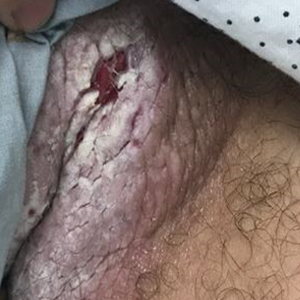
A 67-year-old man presented with a chronic lesion on the groin of 6 weeks' duration. The patient had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and colonic adenocarcinoma diagnosed 4 years prior that was treated with a colectomy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Six weeks prior to the current presentation, the patient first sought treatment of swelling, redness, pain, and a bumpy texture on the groin. He was unsuccessfully managed by several physicians including at a long-term care facility where he was admitted and treated for presumed cellulitis. Attempted treatments included a topical antifungal, fluconazole, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, cefepime, clindamycin, daptomycin, and vancomycin. The affected area continued to worsen along with the patient's overall health. He was transferred to the hospital for more advanced care and was evaluated by inpatient dermatology. Physical examination revealed firm, pink to red-brown, ulcerating papulonodules that coalesced into a large indurated plaque over the pubis, scrotum, penis, and inguinal folds (top). There also were red-violet, indurated plaques on the lower abdomen and bilateral proximal thighs (bottom). Punch biopsies were taken from the indurated area on the left side of the pubis--one for histopathologic evaluation and the other for bacterial, fungal, atypical mycobacterial, and Nocardia tissue cultures.
Solitary Papule on the Shoulder
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma With Sebaceous Induction
The biopsy of the lesion revealed a fibrohistiocytic dermal pattern with overlying benign epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia with a proliferation of fibroblasts in the dermis. Other sections revealed hyperplastic sebaceous glands of the superficial and mid dermis. These findings were suggestive of a dermatofibroma (DF) that had induced epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia.
Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrous soft tissue growths that account for approximately 3% of dermatopathology specimens.1 The etiology of DFs is unknown; however, they are thought to arise from sites of prior trauma or arthropod bites. Multiple or eruptive DFs have been reported in patients with lupus and atopic dermatitis.2 They commonly appear as round firm nodules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter on the extremities of young adults. Eruptive dermatofibromas also have been reported in human immunodeficiency virus-positive and immunosuppressed patients.3,4 On physical examination, gently pinching the lesion causes a downward movement known as the "dimple sign." If left undisturbed, DFs persist but may undergo partial regression, especially in the center; they also may be excised if symptomatic.
The clinical differential for this papule included a scar and sebaceous hyperplasia. The lack of history of skin cancer or prior procedure made a scar less likely. Sebaceous glands are less prominent on the shoulders, making sebaceous hyperplasia less likely, though dermoscopy showed pale yellow lobules. Sebaceous adenomas most commonly are seen on the head or neck and present as a flesh-colored papule. Sebaceous induction by DFs is rare but has been reported in the literature.5,6
The histology of DFs is described as a nodular proliferation of spindle-shaped fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with short intersecting fascicles. A predilection for sebaceous induction from an underlying DF on the shoulder has been reported.5 Sebaceous differentiation has been reported in 16% to 31.6% of DFs.5,6 Seborrheic keratosis-like epidermal hyperplasia frequently has been seen in DFs with sebaceous induction in comparison to DFs without sebaceous induction.5 Immunohistochemical stains are important to help differentiate DF from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, especially when approaching the subcutis. Dermatofibromas stain positive for factor XIIIa and negative for CD34, whereas dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans stain negative for factor XIIIa and positive for CD34.7 Dermatofibromas also demonstrate positive immunostaining for vimentin, stromelysin 3,8 muscle-specific actin, and CD68.
- Rahbari H, Mehregan AH. Adnexal displacement and regression in association with histiocytoma (dermatofibroma). J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:94-102.
- Yazici AC, Baz K, Ikizoglu G, et al. Familial eruptive dermatofibromas in atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:90-92.
- Kanitakis J, Carbonnel E, Delmonte S, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with HIV infection: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:54-56.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Zeidi M, North JP. Sebaceous induction in dermatofibroma: a common feature of dermatofibromas on the shoulder. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:400-405.
- Shuweiter M, Böer A. Spectrum of follicular and sebaceous differentiation induced by dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:778.
- Abenoza P, Lillemoe T. CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Am J Dermatopathol. 1993;15:429-434.
- Kim HJ, Lee JY, Kim SH, et al. Stromelysin-3 expression in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: comparison with factor XIIIa and CD34. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:319-324.
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma With Sebaceous Induction
The biopsy of the lesion revealed a fibrohistiocytic dermal pattern with overlying benign epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia with a proliferation of fibroblasts in the dermis. Other sections revealed hyperplastic sebaceous glands of the superficial and mid dermis. These findings were suggestive of a dermatofibroma (DF) that had induced epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia.
Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrous soft tissue growths that account for approximately 3% of dermatopathology specimens.1 The etiology of DFs is unknown; however, they are thought to arise from sites of prior trauma or arthropod bites. Multiple or eruptive DFs have been reported in patients with lupus and atopic dermatitis.2 They commonly appear as round firm nodules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter on the extremities of young adults. Eruptive dermatofibromas also have been reported in human immunodeficiency virus-positive and immunosuppressed patients.3,4 On physical examination, gently pinching the lesion causes a downward movement known as the "dimple sign." If left undisturbed, DFs persist but may undergo partial regression, especially in the center; they also may be excised if symptomatic.
The clinical differential for this papule included a scar and sebaceous hyperplasia. The lack of history of skin cancer or prior procedure made a scar less likely. Sebaceous glands are less prominent on the shoulders, making sebaceous hyperplasia less likely, though dermoscopy showed pale yellow lobules. Sebaceous adenomas most commonly are seen on the head or neck and present as a flesh-colored papule. Sebaceous induction by DFs is rare but has been reported in the literature.5,6
The histology of DFs is described as a nodular proliferation of spindle-shaped fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with short intersecting fascicles. A predilection for sebaceous induction from an underlying DF on the shoulder has been reported.5 Sebaceous differentiation has been reported in 16% to 31.6% of DFs.5,6 Seborrheic keratosis-like epidermal hyperplasia frequently has been seen in DFs with sebaceous induction in comparison to DFs without sebaceous induction.5 Immunohistochemical stains are important to help differentiate DF from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, especially when approaching the subcutis. Dermatofibromas stain positive for factor XIIIa and negative for CD34, whereas dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans stain negative for factor XIIIa and positive for CD34.7 Dermatofibromas also demonstrate positive immunostaining for vimentin, stromelysin 3,8 muscle-specific actin, and CD68.
The Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma With Sebaceous Induction
The biopsy of the lesion revealed a fibrohistiocytic dermal pattern with overlying benign epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia with a proliferation of fibroblasts in the dermis. Other sections revealed hyperplastic sebaceous glands of the superficial and mid dermis. These findings were suggestive of a dermatofibroma (DF) that had induced epidermal and sebaceous hyperplasia.
Dermatofibromas are common benign fibrous soft tissue growths that account for approximately 3% of dermatopathology specimens.1 The etiology of DFs is unknown; however, they are thought to arise from sites of prior trauma or arthropod bites. Multiple or eruptive DFs have been reported in patients with lupus and atopic dermatitis.2 They commonly appear as round firm nodules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter on the extremities of young adults. Eruptive dermatofibromas also have been reported in human immunodeficiency virus-positive and immunosuppressed patients.3,4 On physical examination, gently pinching the lesion causes a downward movement known as the "dimple sign." If left undisturbed, DFs persist but may undergo partial regression, especially in the center; they also may be excised if symptomatic.
The clinical differential for this papule included a scar and sebaceous hyperplasia. The lack of history of skin cancer or prior procedure made a scar less likely. Sebaceous glands are less prominent on the shoulders, making sebaceous hyperplasia less likely, though dermoscopy showed pale yellow lobules. Sebaceous adenomas most commonly are seen on the head or neck and present as a flesh-colored papule. Sebaceous induction by DFs is rare but has been reported in the literature.5,6
The histology of DFs is described as a nodular proliferation of spindle-shaped fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with short intersecting fascicles. A predilection for sebaceous induction from an underlying DF on the shoulder has been reported.5 Sebaceous differentiation has been reported in 16% to 31.6% of DFs.5,6 Seborrheic keratosis-like epidermal hyperplasia frequently has been seen in DFs with sebaceous induction in comparison to DFs without sebaceous induction.5 Immunohistochemical stains are important to help differentiate DF from dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, especially when approaching the subcutis. Dermatofibromas stain positive for factor XIIIa and negative for CD34, whereas dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans stain negative for factor XIIIa and positive for CD34.7 Dermatofibromas also demonstrate positive immunostaining for vimentin, stromelysin 3,8 muscle-specific actin, and CD68.
- Rahbari H, Mehregan AH. Adnexal displacement and regression in association with histiocytoma (dermatofibroma). J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:94-102.
- Yazici AC, Baz K, Ikizoglu G, et al. Familial eruptive dermatofibromas in atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:90-92.
- Kanitakis J, Carbonnel E, Delmonte S, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with HIV infection: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:54-56.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Zeidi M, North JP. Sebaceous induction in dermatofibroma: a common feature of dermatofibromas on the shoulder. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:400-405.
- Shuweiter M, Böer A. Spectrum of follicular and sebaceous differentiation induced by dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:778.
- Abenoza P, Lillemoe T. CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Am J Dermatopathol. 1993;15:429-434.
- Kim HJ, Lee JY, Kim SH, et al. Stromelysin-3 expression in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: comparison with factor XIIIa and CD34. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:319-324.
- Rahbari H, Mehregan AH. Adnexal displacement and regression in association with histiocytoma (dermatofibroma). J Cutan Pathol. 1985;12:94-102.
- Yazici AC, Baz K, Ikizoglu G, et al. Familial eruptive dermatofibromas in atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:90-92.
- Kanitakis J, Carbonnel E, Delmonte S, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with HIV infection: case report and literature review. J Cutan Pathol. 2000;27:54-56.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Zeidi M, North JP. Sebaceous induction in dermatofibroma: a common feature of dermatofibromas on the shoulder. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:400-405.
- Shuweiter M, Böer A. Spectrum of follicular and sebaceous differentiation induced by dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31:778.
- Abenoza P, Lillemoe T. CD34 and factor XIIIa in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Am J Dermatopathol. 1993;15:429-434.
- Kim HJ, Lee JY, Kim SH, et al. Stromelysin-3 expression in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: comparison with factor XIIIa and CD34. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:319-324.
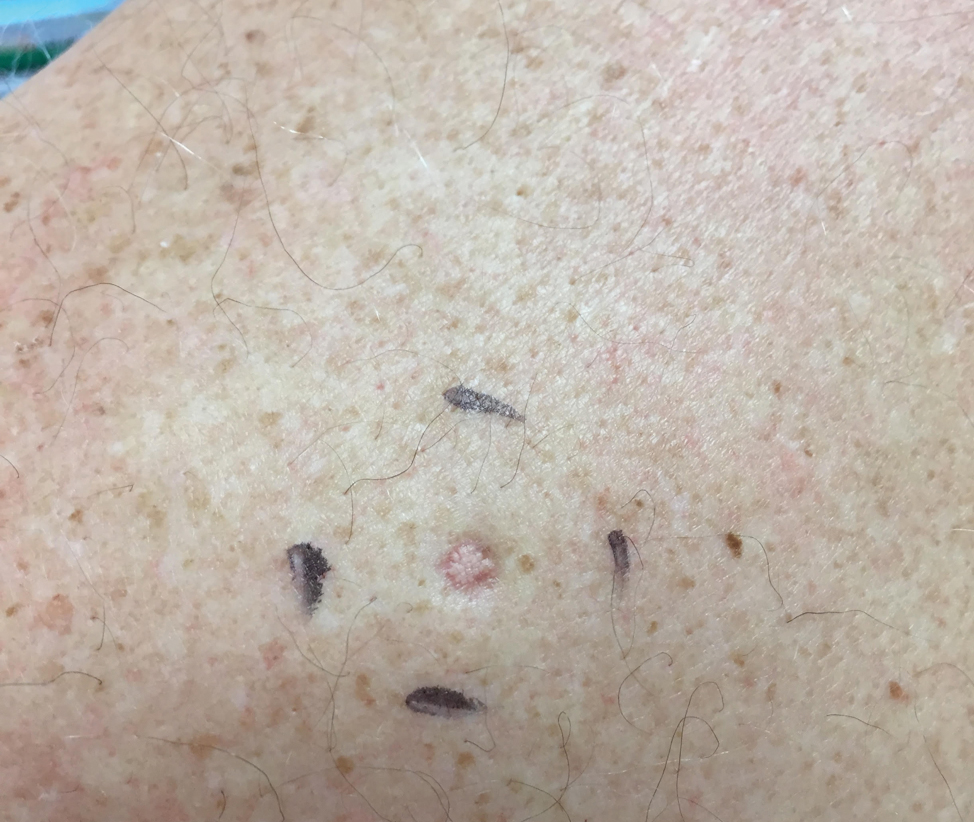

A 64-year-old man presented to dermatology for a full-body skin examination. He had no history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed an asymptomatic, 4-mm, yellowish pink papule on the left posterior shoulder (top). Dermoscopy revealed yellow globules (bottom). The patient was unsure of the duration of the lesion and denied any prior trauma or medical procedure to the area. Subsequently, a shave biopsy was performed.
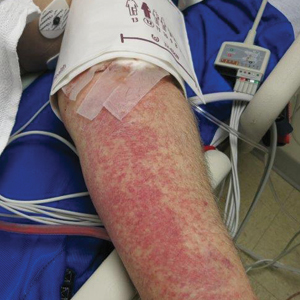
Petechiae and Ecchymoses on the Arm
The Diagnosis: Rumpel-Leede Phenomenon
Rumpel-Leede (R-L) phenomenon describes the rare benign occurrence of dermal capillaries acutely rupturing following the administration of a tourniquetlike force on an extremity,1 which manifests as asymptomatic petechiae and ecchymoses on a distal extremity, usually following noninvasive measurement of blood pressure.2 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon represents an underrecognized entity that either is excluded or minimally referenced in most dermatology textbooks. The R-L sign initially was described in the early 1900s after it was observed that tourniquets applied to the arms of patients with scarlet fever would lead to the development of petechiae in that extremity.3 It later was elucidated that underlying vascular disease predisposes to dermal capillary fragility, a risk factor for R-L phenomenon to occur upon application of a tourniquet. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon has been noted in patients with diabetes mellitus, acute or chronic hypertension, and thrombocytopenia.4 In addition to being hypertensive and diabetic, our patient had been taking amlodipine and diltiazem. Calcium channel blockers have been linked to R-L phenomenon in case reports as well as in a study of calcium channel blockers inducing capillary fragility in vivo.5 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon also has been noted in patients with tightly fitting garments and infants carried in baby carriers.1
The differential diagnosis for R-L phenomenon includes actinic purpura, small vessel vasculitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Actinic purpura, also called solar purpura or senile purpura, represents the petechiae and ecchymoses that are associated with aging skin. It is thought to occur when DNA damage, UV-induced solar elastosis, and decreased lipids in the stratum corneum cause a weakened ability to contain red blood cell extravasation from capillaries.6 Due to the lack of history of trauma and clear association with the blood pressure cuff placement in our patient, a diagnosis of actinic purpura was unlikely. In small vessel vasculitis, patients classically present with nonblanching palpable purpura frequently distributed over the lower extremities. The isolation of the lesions to only the left arm lowered the suspicion for vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestations of DIC and other hypercoagulable states may include purpura, livedo reticularis, atrophie blanche, and in extreme cases purpura fulminans. Routine laboratory examination reveals thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time/partial thromboplastin time, and hemolytic anemia.7 Although our patient had the risk factors of recent infection and surgery, a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0-17.5 g/dL) and platelet count of 279,000/µL (reference range, 150,000-350,000/µL) excluded DIC as the probable diagnosis. Our patient was at an overall increased risk for DVT due to his prolonged hospital stay, increased age, and other factors. Despite these risk factors, the lack of pain or swelling made this diagnosis unlikely. Furthermore, our patient was heparinized throughout his hospital stay, and upper extremity DVT accounts for only 4% to 10% of the total DVT incidence.5
Although R-L phenomenon is a benign, self-limited condition, it may be necessary in some cases to rule out more serious underlying etiologies with investigative workup comprised of a complete blood cell count, coagulation profile, and basic metabolic panel. However, recognition of the R-L phenomenon in the right clinical context of localized petechiae or ecchymoses with a history of a tourniquetlike force may prevent an unnecessary and costly workup. Patients should be encouraged that R-L phenomenon will resolve over time with identification and correction of the tourniquetlike force. In this case, we recommended loosening of the sphygmomanometer cuff and alternating extremities to which the cuff was to be placed, which resulted in complete clearance of the petechiae and ecchymoses within 5 days.
- Nguyen T, Garcia D, Wang A, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon associated with tourniquet-like forces of baby carriers in otherwise healthy infants. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:728-730.
- Chester M, Barwise J, Holzman M, et al. Acute dermal capillary rupture associated with noninvasive blood pressure monitoring. J Clin Anesth. 2007;19:473-475.
- Hartley A, Lim PB, Hayat SA. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon in a hypertensive patient due to mechanical trauma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:150.
- Varela D, Tran D, Ngamdu K, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon presenting as a hypertensive urgency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:200-201.
- Cox NH, Walsh ML, Robson RH. Purpura and bleeding due to calcium-channel blockers: an underestimated problem? case reports and a pilot study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:487-491.
- Ceilley RI. Treatment of actinic purpura. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:44-50.
- Rajagopal R, Thachil J, Monagle P. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in paediatrics. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102:187-193.
- Kraaijpoel N, van Es N, Porreca E, et al. The diagnostic management of upper extremity deep venous thrombosis: a review of the literature. Thromb Res. 2017;156:54-59.
The Diagnosis: Rumpel-Leede Phenomenon
Rumpel-Leede (R-L) phenomenon describes the rare benign occurrence of dermal capillaries acutely rupturing following the administration of a tourniquetlike force on an extremity,1 which manifests as asymptomatic petechiae and ecchymoses on a distal extremity, usually following noninvasive measurement of blood pressure.2 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon represents an underrecognized entity that either is excluded or minimally referenced in most dermatology textbooks. The R-L sign initially was described in the early 1900s after it was observed that tourniquets applied to the arms of patients with scarlet fever would lead to the development of petechiae in that extremity.3 It later was elucidated that underlying vascular disease predisposes to dermal capillary fragility, a risk factor for R-L phenomenon to occur upon application of a tourniquet. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon has been noted in patients with diabetes mellitus, acute or chronic hypertension, and thrombocytopenia.4 In addition to being hypertensive and diabetic, our patient had been taking amlodipine and diltiazem. Calcium channel blockers have been linked to R-L phenomenon in case reports as well as in a study of calcium channel blockers inducing capillary fragility in vivo.5 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon also has been noted in patients with tightly fitting garments and infants carried in baby carriers.1
The differential diagnosis for R-L phenomenon includes actinic purpura, small vessel vasculitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Actinic purpura, also called solar purpura or senile purpura, represents the petechiae and ecchymoses that are associated with aging skin. It is thought to occur when DNA damage, UV-induced solar elastosis, and decreased lipids in the stratum corneum cause a weakened ability to contain red blood cell extravasation from capillaries.6 Due to the lack of history of trauma and clear association with the blood pressure cuff placement in our patient, a diagnosis of actinic purpura was unlikely. In small vessel vasculitis, patients classically present with nonblanching palpable purpura frequently distributed over the lower extremities. The isolation of the lesions to only the left arm lowered the suspicion for vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestations of DIC and other hypercoagulable states may include purpura, livedo reticularis, atrophie blanche, and in extreme cases purpura fulminans. Routine laboratory examination reveals thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time/partial thromboplastin time, and hemolytic anemia.7 Although our patient had the risk factors of recent infection and surgery, a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0-17.5 g/dL) and platelet count of 279,000/µL (reference range, 150,000-350,000/µL) excluded DIC as the probable diagnosis. Our patient was at an overall increased risk for DVT due to his prolonged hospital stay, increased age, and other factors. Despite these risk factors, the lack of pain or swelling made this diagnosis unlikely. Furthermore, our patient was heparinized throughout his hospital stay, and upper extremity DVT accounts for only 4% to 10% of the total DVT incidence.5
Although R-L phenomenon is a benign, self-limited condition, it may be necessary in some cases to rule out more serious underlying etiologies with investigative workup comprised of a complete blood cell count, coagulation profile, and basic metabolic panel. However, recognition of the R-L phenomenon in the right clinical context of localized petechiae or ecchymoses with a history of a tourniquetlike force may prevent an unnecessary and costly workup. Patients should be encouraged that R-L phenomenon will resolve over time with identification and correction of the tourniquetlike force. In this case, we recommended loosening of the sphygmomanometer cuff and alternating extremities to which the cuff was to be placed, which resulted in complete clearance of the petechiae and ecchymoses within 5 days.
The Diagnosis: Rumpel-Leede Phenomenon
Rumpel-Leede (R-L) phenomenon describes the rare benign occurrence of dermal capillaries acutely rupturing following the administration of a tourniquetlike force on an extremity,1 which manifests as asymptomatic petechiae and ecchymoses on a distal extremity, usually following noninvasive measurement of blood pressure.2 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon represents an underrecognized entity that either is excluded or minimally referenced in most dermatology textbooks. The R-L sign initially was described in the early 1900s after it was observed that tourniquets applied to the arms of patients with scarlet fever would lead to the development of petechiae in that extremity.3 It later was elucidated that underlying vascular disease predisposes to dermal capillary fragility, a risk factor for R-L phenomenon to occur upon application of a tourniquet. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon has been noted in patients with diabetes mellitus, acute or chronic hypertension, and thrombocytopenia.4 In addition to being hypertensive and diabetic, our patient had been taking amlodipine and diltiazem. Calcium channel blockers have been linked to R-L phenomenon in case reports as well as in a study of calcium channel blockers inducing capillary fragility in vivo.5 Rumpel-Leede phenomenon also has been noted in patients with tightly fitting garments and infants carried in baby carriers.1
The differential diagnosis for R-L phenomenon includes actinic purpura, small vessel vasculitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Actinic purpura, also called solar purpura or senile purpura, represents the petechiae and ecchymoses that are associated with aging skin. It is thought to occur when DNA damage, UV-induced solar elastosis, and decreased lipids in the stratum corneum cause a weakened ability to contain red blood cell extravasation from capillaries.6 Due to the lack of history of trauma and clear association with the blood pressure cuff placement in our patient, a diagnosis of actinic purpura was unlikely. In small vessel vasculitis, patients classically present with nonblanching palpable purpura frequently distributed over the lower extremities. The isolation of the lesions to only the left arm lowered the suspicion for vasculitis. Cutaneous manifestations of DIC and other hypercoagulable states may include purpura, livedo reticularis, atrophie blanche, and in extreme cases purpura fulminans. Routine laboratory examination reveals thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time/partial thromboplastin time, and hemolytic anemia.7 Although our patient had the risk factors of recent infection and surgery, a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0-17.5 g/dL) and platelet count of 279,000/µL (reference range, 150,000-350,000/µL) excluded DIC as the probable diagnosis. Our patient was at an overall increased risk for DVT due to his prolonged hospital stay, increased age, and other factors. Despite these risk factors, the lack of pain or swelling made this diagnosis unlikely. Furthermore, our patient was heparinized throughout his hospital stay, and upper extremity DVT accounts for only 4% to 10% of the total DVT incidence.5
Although R-L phenomenon is a benign, self-limited condition, it may be necessary in some cases to rule out more serious underlying etiologies with investigative workup comprised of a complete blood cell count, coagulation profile, and basic metabolic panel. However, recognition of the R-L phenomenon in the right clinical context of localized petechiae or ecchymoses with a history of a tourniquetlike force may prevent an unnecessary and costly workup. Patients should be encouraged that R-L phenomenon will resolve over time with identification and correction of the tourniquetlike force. In this case, we recommended loosening of the sphygmomanometer cuff and alternating extremities to which the cuff was to be placed, which resulted in complete clearance of the petechiae and ecchymoses within 5 days.
- Nguyen T, Garcia D, Wang A, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon associated with tourniquet-like forces of baby carriers in otherwise healthy infants. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:728-730.
- Chester M, Barwise J, Holzman M, et al. Acute dermal capillary rupture associated with noninvasive blood pressure monitoring. J Clin Anesth. 2007;19:473-475.
- Hartley A, Lim PB, Hayat SA. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon in a hypertensive patient due to mechanical trauma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:150.
- Varela D, Tran D, Ngamdu K, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon presenting as a hypertensive urgency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:200-201.
- Cox NH, Walsh ML, Robson RH. Purpura and bleeding due to calcium-channel blockers: an underestimated problem? case reports and a pilot study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:487-491.
- Ceilley RI. Treatment of actinic purpura. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:44-50.
- Rajagopal R, Thachil J, Monagle P. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in paediatrics. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102:187-193.
- Kraaijpoel N, van Es N, Porreca E, et al. The diagnostic management of upper extremity deep venous thrombosis: a review of the literature. Thromb Res. 2017;156:54-59.
- Nguyen T, Garcia D, Wang A, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon associated with tourniquet-like forces of baby carriers in otherwise healthy infants. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:728-730.
- Chester M, Barwise J, Holzman M, et al. Acute dermal capillary rupture associated with noninvasive blood pressure monitoring. J Clin Anesth. 2007;19:473-475.
- Hartley A, Lim PB, Hayat SA. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon in a hypertensive patient due to mechanical trauma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:150.
- Varela D, Tran D, Ngamdu K, et al. Rumpel-Leede phenomenon presenting as a hypertensive urgency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2016;29:200-201.
- Cox NH, Walsh ML, Robson RH. Purpura and bleeding due to calcium-channel blockers: an underestimated problem? case reports and a pilot study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:487-491.
- Ceilley RI. Treatment of actinic purpura. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:44-50.
- Rajagopal R, Thachil J, Monagle P. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in paediatrics. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102:187-193.
- Kraaijpoel N, van Es N, Porreca E, et al. The diagnostic management of upper extremity deep venous thrombosis: a review of the literature. Thromb Res. 2017;156:54-59.
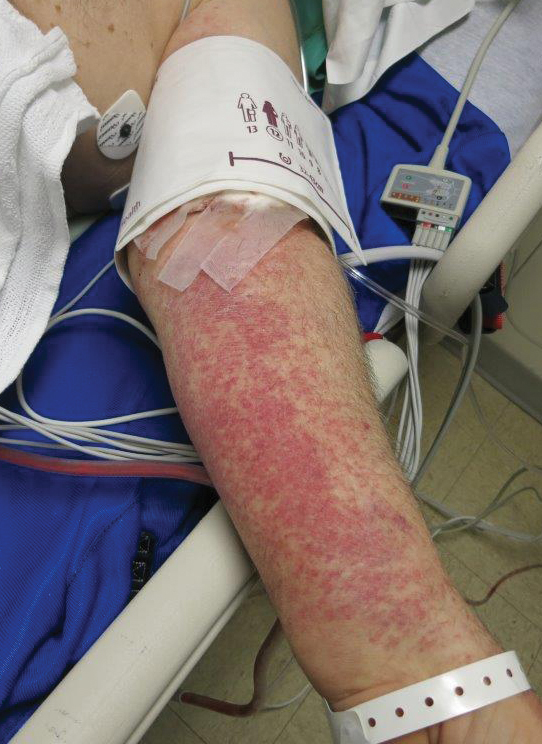
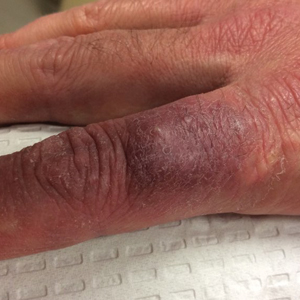
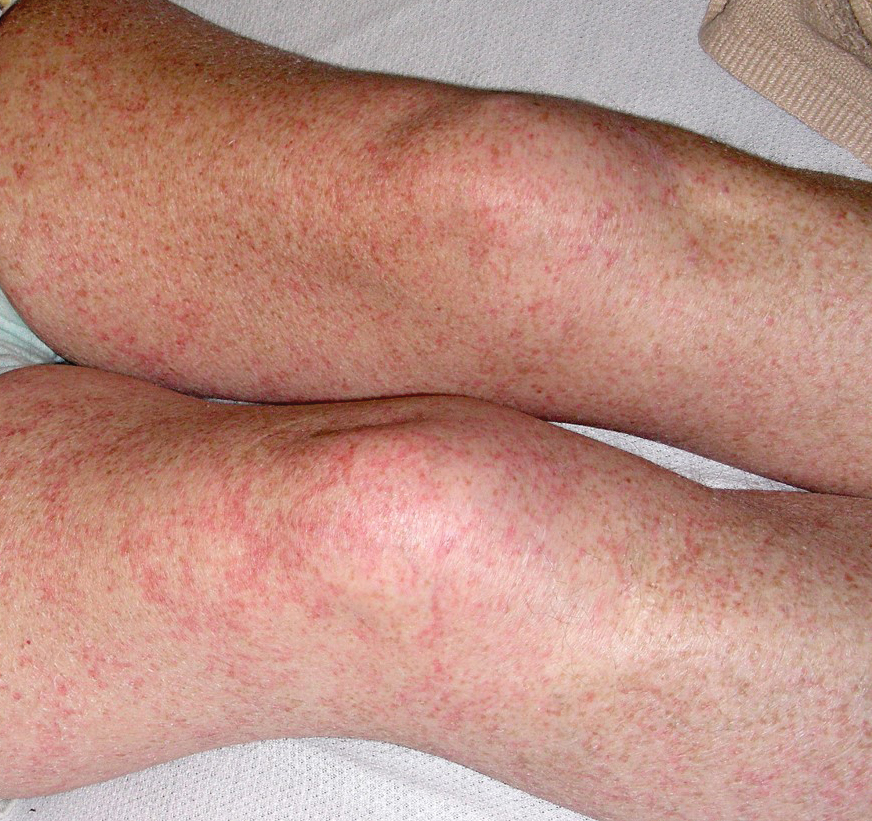
A 70-year-old man who had been admitted to the hospital a week prior for a right groin abscess overlying the site of a femoral graft developed a purpuric rash isolated to the left arm of 1 day's duration. The dermatology service was consulted by vascular surgery. The patient denied prior episodes of a similar rash, and there was no associated pruritus or pain. There was no history of trauma to the area. His medical history was remarkable for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and peripheral vascular disease. His surgical history was notable for bilateral popliteal aneurysm repair and right femoral aneurysm repair. No pertinent family history was elicited. Cefepime, metronidazole, and vancomycin were administered for the groin abscess. Additional medications included amlodipine, atorvastatin, diltiazem, gabapentin, heparin, insulin, oxycodone, and acetaminophen.
Physical examination revealed broad ecchymoses on the left forearm with scattered petechiae as well as linear ecchymoses on the left upper arm distributed in the area where a sphygmomanometer cuff was applied. Full-body skin examination confirmed that the distribution of the petechiae and ecchymoses was limited to the left arm. The patient was normotensive at the time of examination. Laboratory evaluation revealed a hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0-17.5 g/dL), a platelet count of 279,000/µL (reference range, 150,000-350,000/µL), and a glucose level of 121 mg/dL (reference range, 70-110 mg/dL).
Minimally Hyperpigmented Plaque With Skin Thickening on the Neck
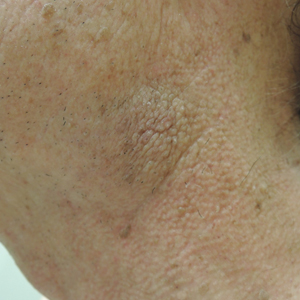
The Diagnosis: Fiddler's Neck
A thorough patient history revealed that the patient was retired and played violin regularly in the local orchestra. Fiddler's neck, or violin hickey, is an uncommon physical examination finding and often is considered a badge of honor by musicians who develop it. Fiddler's neck is a hobby-related callus seen in highly dedicated violin and viola players, and in some circles, it is known as a mark of greatness. In one instance, members of the public were asked to display a violin hickey before they were allowed to play a $3.5 million violin on public display in London, England.1 Fiddler's neck is a benign submandibular lesion caused by pressure and friction on the skin from extensive time spent playing the instrument. The primary cause is thought to be mechanical, but it is not fully understood why the lesion occurs in some musicians and not others, regardless of playing time.1 This submandibular fiddler's neck is distinct from a similarly named supraclavicular lesion, which represents an allergic contact dermatitis to the nickel bracket of the instrument's chin rest and presents with eczematous scale and/or vesicles.2,3 Submandibular fiddler's neck presents with some combination of erythema, edema, lichenification, and scarring just below the angle of the jaw. Occasionally, papules, pustules, and even cyst formation may be noted. Lesions are sometimes mistaken for malignancy or lymphedema. Therefore, a thorough history and clinical expertise are important, as surgical excision should be avoided.2
Depending on presentation, the differential diagnosis also may include malignant melanoma due to irregular pigmentation, branchial cleft cyst or sialolithiasis due to location and texture, or a tumor of the salivary gland.
Management of fiddler's neck may include topical steroids, neck or instrument padding, or decreased playing time. However, the lesion often is worn with pride, seen as a testament to the musician's dedication, and reassurance generally is most appropriate.1
- Roberts C. How to prevent or even cure a violin hickey. Strings. February 1, 2011. https://stringsmagazine.com/how-to-prevent-or-even-cure-a-violin-hickey/. Accessed January 31, 2020.
- Myint CW, Rutt AL, Sataloff RT. Fiddler's neck: a review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017;96:76-79.
- Jue MS, Kim YS, Ro YS. Fiddler's neck accompanied by allergic contact dermatitis to nickel in a viola player. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:88-90.
The Diagnosis: Fiddler's Neck
A thorough patient history revealed that the patient was retired and played violin regularly in the local orchestra. Fiddler's neck, or violin hickey, is an uncommon physical examination finding and often is considered a badge of honor by musicians who develop it. Fiddler's neck is a hobby-related callus seen in highly dedicated violin and viola players, and in some circles, it is known as a mark of greatness. In one instance, members of the public were asked to display a violin hickey before they were allowed to play a $3.5 million violin on public display in London, England.1 Fiddler's neck is a benign submandibular lesion caused by pressure and friction on the skin from extensive time spent playing the instrument. The primary cause is thought to be mechanical, but it is not fully understood why the lesion occurs in some musicians and not others, regardless of playing time.1 This submandibular fiddler's neck is distinct from a similarly named supraclavicular lesion, which represents an allergic contact dermatitis to the nickel bracket of the instrument's chin rest and presents with eczematous scale and/or vesicles.2,3 Submandibular fiddler's neck presents with some combination of erythema, edema, lichenification, and scarring just below the angle of the jaw. Occasionally, papules, pustules, and even cyst formation may be noted. Lesions are sometimes mistaken for malignancy or lymphedema. Therefore, a thorough history and clinical expertise are important, as surgical excision should be avoided.2
Depending on presentation, the differential diagnosis also may include malignant melanoma due to irregular pigmentation, branchial cleft cyst or sialolithiasis due to location and texture, or a tumor of the salivary gland.
Management of fiddler's neck may include topical steroids, neck or instrument padding, or decreased playing time. However, the lesion often is worn with pride, seen as a testament to the musician's dedication, and reassurance generally is most appropriate.1
The Diagnosis: Fiddler's Neck
A thorough patient history revealed that the patient was retired and played violin regularly in the local orchestra. Fiddler's neck, or violin hickey, is an uncommon physical examination finding and often is considered a badge of honor by musicians who develop it. Fiddler's neck is a hobby-related callus seen in highly dedicated violin and viola players, and in some circles, it is known as a mark of greatness. In one instance, members of the public were asked to display a violin hickey before they were allowed to play a $3.5 million violin on public display in London, England.1 Fiddler's neck is a benign submandibular lesion caused by pressure and friction on the skin from extensive time spent playing the instrument. The primary cause is thought to be mechanical, but it is not fully understood why the lesion occurs in some musicians and not others, regardless of playing time.1 This submandibular fiddler's neck is distinct from a similarly named supraclavicular lesion, which represents an allergic contact dermatitis to the nickel bracket of the instrument's chin rest and presents with eczematous scale and/or vesicles.2,3 Submandibular fiddler's neck presents with some combination of erythema, edema, lichenification, and scarring just below the angle of the jaw. Occasionally, papules, pustules, and even cyst formation may be noted. Lesions are sometimes mistaken for malignancy or lymphedema. Therefore, a thorough history and clinical expertise are important, as surgical excision should be avoided.2
Depending on presentation, the differential diagnosis also may include malignant melanoma due to irregular pigmentation, branchial cleft cyst or sialolithiasis due to location and texture, or a tumor of the salivary gland.
Management of fiddler's neck may include topical steroids, neck or instrument padding, or decreased playing time. However, the lesion often is worn with pride, seen as a testament to the musician's dedication, and reassurance generally is most appropriate.1
- Roberts C. How to prevent or even cure a violin hickey. Strings. February 1, 2011. https://stringsmagazine.com/how-to-prevent-or-even-cure-a-violin-hickey/. Accessed January 31, 2020.
- Myint CW, Rutt AL, Sataloff RT. Fiddler's neck: a review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017;96:76-79.
- Jue MS, Kim YS, Ro YS. Fiddler's neck accompanied by allergic contact dermatitis to nickel in a viola player. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:88-90.
- Roberts C. How to prevent or even cure a violin hickey. Strings. February 1, 2011. https://stringsmagazine.com/how-to-prevent-or-even-cure-a-violin-hickey/. Accessed January 31, 2020.
- Myint CW, Rutt AL, Sataloff RT. Fiddler's neck: a review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017;96:76-79.
- Jue MS, Kim YS, Ro YS. Fiddler's neck accompanied by allergic contact dermatitis to nickel in a viola player. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:88-90.
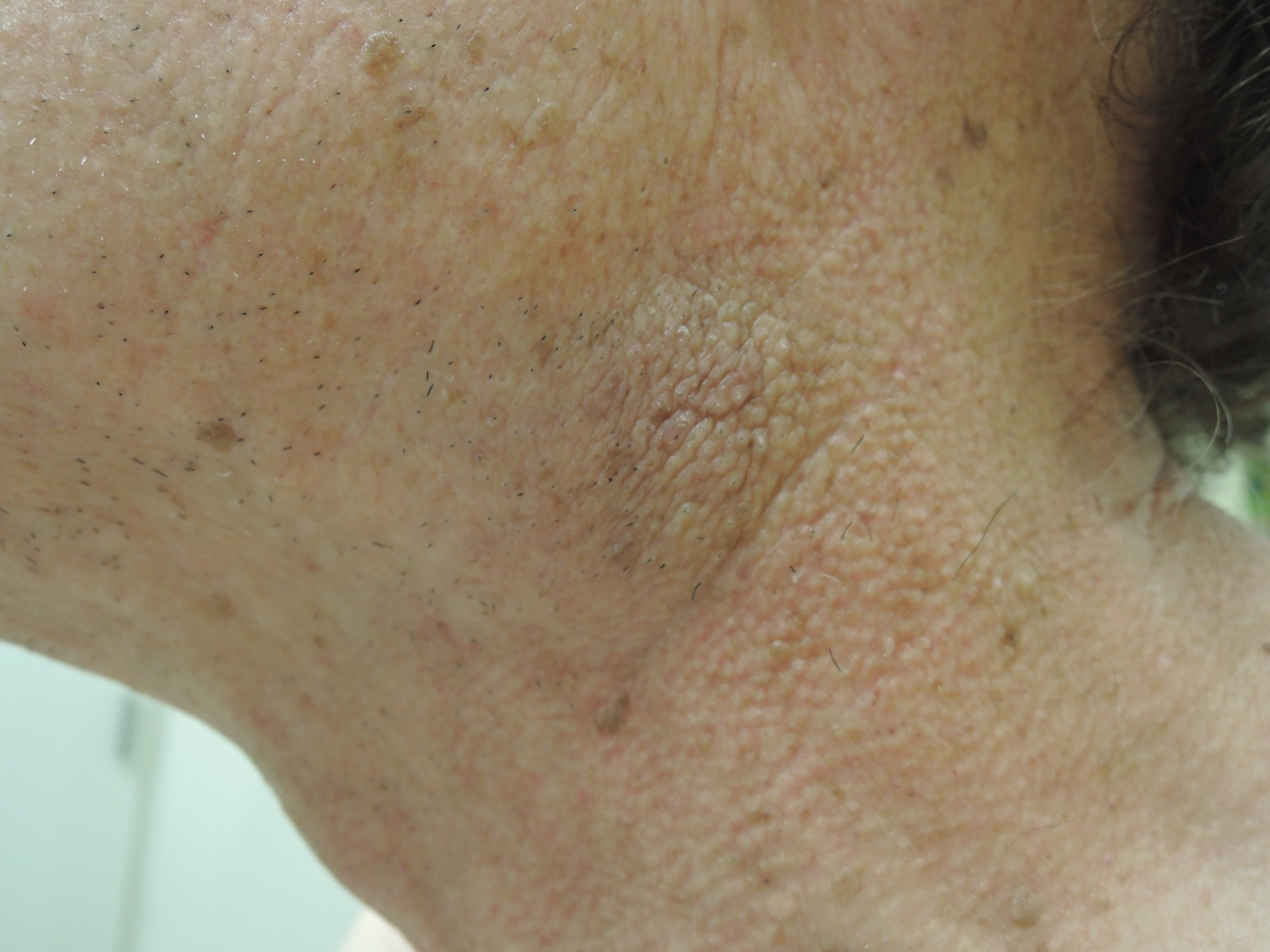
A 74-year-old man with a history of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma presented for an annual skin examination and displayed asymptomatic stable thickening of skin on the left side of the neck below the jawline of several years' duration. Physical examination revealed a 4×2-cm minimally hyperpigmented plaque with skin thickening and a pebbly appearing surface on the left lateral neck just inferior to the angle of the mandible.
Tender White Lesions on the Groin
The Diagnosis: Candidal Intertrigo
The biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of severe hyperkeratotic candidal intertrigo with no evidence of Hailey-Hailey disease. Hematoxylin and eosin- stained sections demonstrated irregular acanthosis and variable spongiosis. The stratum corneum was predominantly orthokeratotic with overlying psuedohyphae and yeast fungal elements (Figure 1).
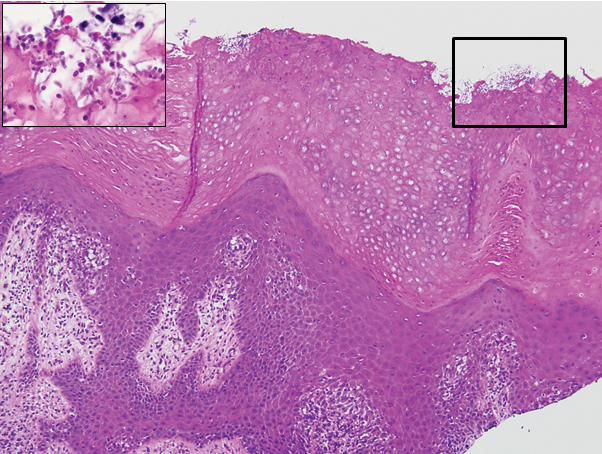
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome (HIES), also known as hyper-IgE syndrome or Job syndrome, is a rare immunodeficiency disorder characterized by an eczematous dermatitis-like rash, recurrent skin and lung abscesses, eosinophilia, and elevated serum IgE. Facial asymmetry, prominent forehead, deep-set eyes, broad nose, and roughened facial skin with large pores are characteristic of the sporadic and autosomal-recessive forms. Other common findings include retained primary teeth, hyperextensible joints, and recurrent mucocutaneous candidiasis.1
Although autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive inheritance patterns exist, sporadic mutations are the most common cause of HIES.2 Several genes have been implicated depending on the inheritance pattern. The majority of autosomal-dominant cases are associated with inactivating STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) mutations, whereas the majority of autosomal-recessive cases are associated with inactivating DOCK8 (dedicator of cytokinesis 8) mutations.1 Ultimately, all of these mutations lead to an impaired helper T cell (TH17) response, which is crucial for clearing fungal and extracellular bacterial infections.3
Skin eruptions typically are the first manifestation of HIES; they appear within the first week to month of life as papulopustular eruptions on the face and scalp and rapidly generalize to the rest of the body, favoring the shoulders, arms, chest, and buttocks. The pustules then coalesce into crusted plaques that resemble atopic dermatitis, frequently with superimposed Staphylococcus aureus infection. On microscopy, the pustules are folliculocentric and often contain eosinophils, whereas the plaques may contain intraepidermal collections of eosinophils.1
Mucocutaneous candidiasis is seen in approximately 60% of HIES cases and is closely linked to STAT3 inactivating mutations.3 Histologically, there is marked acanthosis with neutrophil exocytosis and abundant yeast and pseudohyphal forms within the stratum corneum (Figure 2).4 Cutaneous candidal infections typically require both oral and topical antifungal agents to clear the infection.3 Most cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis are caused by Candida albicans; however, other known culprits include Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei.5,6 Of note, species identification and antifungal susceptibility studies may be useful in refractory cases, especially with C glabrata, which is known to acquire resistance to azoles, such as fluconazole, with emerging resistance to echinocandins.6

The differential diagnosis of this groin eruption included Hailey-Hailey disease; pemphigus vegetans, Hallopeau type; tinea cruris; and inverse psoriasis. Hailey-Hailey disease can be complicated by a superimposed candidal infection with similar clinical features, and biopsy may be required for definitive diagnosis. Hailey-Hailey disease typically presents with macerated fissured plaques that resemble macerated tissue paper with red fissures (Figure 3). Biopsy confirms full-thickness acantholysis resembling a dilapidated brick wall with minimal dyskeratosis.1 Pemphigus vegetans is a localized variant of pemphigus vulgaris with a predilection for flexural surfaces. The lesions progress to vegetating erosive plaques.4 The Hallopeau type often is studded with pustules and typically remains more localized than the Neumann type. Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates intercellular deposition of IgG and C3, and routine sections characteristically show pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses.1,4 Tinea cruris is characterized by erythematous annular lesions with raised scaly borders spreading down the inner thighs.7 The epidermis is variably spongiotic with parakeratosis, and neutrophils often present in a layered stratum corneum with basketweave keratin above a layer of more compact and eosinophilic keratin. Fungal stains, such as periodic acid-Schiff, will highlight the fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum. The inguinal folds are a typical location for inverse psoriasis, which generally appears as thin, sharply demarcated, shiny red plaques with less scale than plaque psoriasis.1 Psoriasiform hyperplasia with a diminished granular layer and tortuous papillary dermal vessels would be expected histologically.1
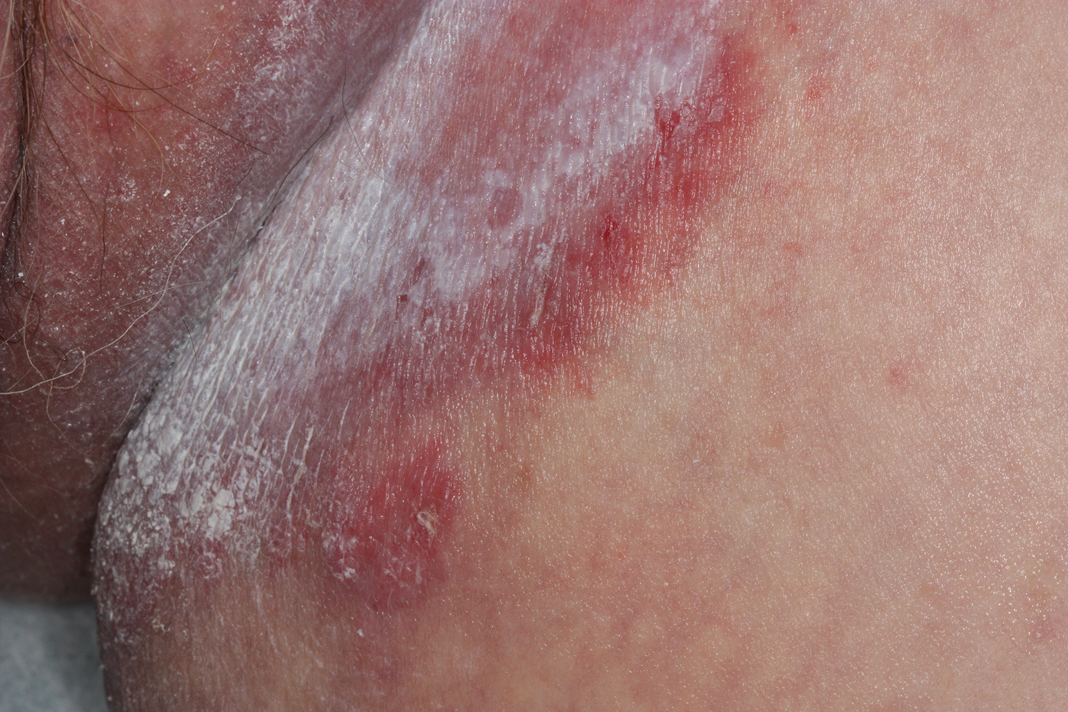
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016.
- Schwartz RA, Tarlow MM. Dermatologic manifestations of Job syndrome. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1050852-overview. Updated April 22, 2019. Accessed March 28, 2020.
- Minegishi Y, Saito M. Cutaneous manifestations of hyper IgE syndrome. Allergol Int. 2012;61:191-196.
- Patterson JW. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2016.
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Executive summary: clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:409-417.
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Antifungal resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/antifungal-resistance.html. Updated March 17, 2020. Accessed April 20, 2020.
- Tinea cruris. DermNet NZ website. https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-cruris/. Published 2003. Accessed March 28, 2020.
The Diagnosis: Candidal Intertrigo
The biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of severe hyperkeratotic candidal intertrigo with no evidence of Hailey-Hailey disease. Hematoxylin and eosin- stained sections demonstrated irregular acanthosis and variable spongiosis. The stratum corneum was predominantly orthokeratotic with overlying psuedohyphae and yeast fungal elements (Figure 1).

Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome (HIES), also known as hyper-IgE syndrome or Job syndrome, is a rare immunodeficiency disorder characterized by an eczematous dermatitis-like rash, recurrent skin and lung abscesses, eosinophilia, and elevated serum IgE. Facial asymmetry, prominent forehead, deep-set eyes, broad nose, and roughened facial skin with large pores are characteristic of the sporadic and autosomal-recessive forms. Other common findings include retained primary teeth, hyperextensible joints, and recurrent mucocutaneous candidiasis.1
Although autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive inheritance patterns exist, sporadic mutations are the most common cause of HIES.2 Several genes have been implicated depending on the inheritance pattern. The majority of autosomal-dominant cases are associated with inactivating STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) mutations, whereas the majority of autosomal-recessive cases are associated with inactivating DOCK8 (dedicator of cytokinesis 8) mutations.1 Ultimately, all of these mutations lead to an impaired helper T cell (TH17) response, which is crucial for clearing fungal and extracellular bacterial infections.3
Skin eruptions typically are the first manifestation of HIES; they appear within the first week to month of life as papulopustular eruptions on the face and scalp and rapidly generalize to the rest of the body, favoring the shoulders, arms, chest, and buttocks. The pustules then coalesce into crusted plaques that resemble atopic dermatitis, frequently with superimposed Staphylococcus aureus infection. On microscopy, the pustules are folliculocentric and often contain eosinophils, whereas the plaques may contain intraepidermal collections of eosinophils.1
Mucocutaneous candidiasis is seen in approximately 60% of HIES cases and is closely linked to STAT3 inactivating mutations.3 Histologically, there is marked acanthosis with neutrophil exocytosis and abundant yeast and pseudohyphal forms within the stratum corneum (Figure 2).4 Cutaneous candidal infections typically require both oral and topical antifungal agents to clear the infection.3 Most cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis are caused by Candida albicans; however, other known culprits include Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei.5,6 Of note, species identification and antifungal susceptibility studies may be useful in refractory cases, especially with C glabrata, which is known to acquire resistance to azoles, such as fluconazole, with emerging resistance to echinocandins.6

The differential diagnosis of this groin eruption included Hailey-Hailey disease; pemphigus vegetans, Hallopeau type; tinea cruris; and inverse psoriasis. Hailey-Hailey disease can be complicated by a superimposed candidal infection with similar clinical features, and biopsy may be required for definitive diagnosis. Hailey-Hailey disease typically presents with macerated fissured plaques that resemble macerated tissue paper with red fissures (Figure 3). Biopsy confirms full-thickness acantholysis resembling a dilapidated brick wall with minimal dyskeratosis.1 Pemphigus vegetans is a localized variant of pemphigus vulgaris with a predilection for flexural surfaces. The lesions progress to vegetating erosive plaques.4 The Hallopeau type often is studded with pustules and typically remains more localized than the Neumann type. Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates intercellular deposition of IgG and C3, and routine sections characteristically show pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses.1,4 Tinea cruris is characterized by erythematous annular lesions with raised scaly borders spreading down the inner thighs.7 The epidermis is variably spongiotic with parakeratosis, and neutrophils often present in a layered stratum corneum with basketweave keratin above a layer of more compact and eosinophilic keratin. Fungal stains, such as periodic acid-Schiff, will highlight the fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum. The inguinal folds are a typical location for inverse psoriasis, which generally appears as thin, sharply demarcated, shiny red plaques with less scale than plaque psoriasis.1 Psoriasiform hyperplasia with a diminished granular layer and tortuous papillary dermal vessels would be expected histologically.1

The Diagnosis: Candidal Intertrigo
The biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of severe hyperkeratotic candidal intertrigo with no evidence of Hailey-Hailey disease. Hematoxylin and eosin- stained sections demonstrated irregular acanthosis and variable spongiosis. The stratum corneum was predominantly orthokeratotic with overlying psuedohyphae and yeast fungal elements (Figure 1).

Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome (HIES), also known as hyper-IgE syndrome or Job syndrome, is a rare immunodeficiency disorder characterized by an eczematous dermatitis-like rash, recurrent skin and lung abscesses, eosinophilia, and elevated serum IgE. Facial asymmetry, prominent forehead, deep-set eyes, broad nose, and roughened facial skin with large pores are characteristic of the sporadic and autosomal-recessive forms. Other common findings include retained primary teeth, hyperextensible joints, and recurrent mucocutaneous candidiasis.1
Although autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive inheritance patterns exist, sporadic mutations are the most common cause of HIES.2 Several genes have been implicated depending on the inheritance pattern. The majority of autosomal-dominant cases are associated with inactivating STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) mutations, whereas the majority of autosomal-recessive cases are associated with inactivating DOCK8 (dedicator of cytokinesis 8) mutations.1 Ultimately, all of these mutations lead to an impaired helper T cell (TH17) response, which is crucial for clearing fungal and extracellular bacterial infections.3
Skin eruptions typically are the first manifestation of HIES; they appear within the first week to month of life as papulopustular eruptions on the face and scalp and rapidly generalize to the rest of the body, favoring the shoulders, arms, chest, and buttocks. The pustules then coalesce into crusted plaques that resemble atopic dermatitis, frequently with superimposed Staphylococcus aureus infection. On microscopy, the pustules are folliculocentric and often contain eosinophils, whereas the plaques may contain intraepidermal collections of eosinophils.1
Mucocutaneous candidiasis is seen in approximately 60% of HIES cases and is closely linked to STAT3 inactivating mutations.3 Histologically, there is marked acanthosis with neutrophil exocytosis and abundant yeast and pseudohyphal forms within the stratum corneum (Figure 2).4 Cutaneous candidal infections typically require both oral and topical antifungal agents to clear the infection.3 Most cases of mucocutaneous candidiasis are caused by Candida albicans; however, other known culprits include Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei.5,6 Of note, species identification and antifungal susceptibility studies may be useful in refractory cases, especially with C glabrata, which is known to acquire resistance to azoles, such as fluconazole, with emerging resistance to echinocandins.6

The differential diagnosis of this groin eruption included Hailey-Hailey disease; pemphigus vegetans, Hallopeau type; tinea cruris; and inverse psoriasis. Hailey-Hailey disease can be complicated by a superimposed candidal infection with similar clinical features, and biopsy may be required for definitive diagnosis. Hailey-Hailey disease typically presents with macerated fissured plaques that resemble macerated tissue paper with red fissures (Figure 3). Biopsy confirms full-thickness acantholysis resembling a dilapidated brick wall with minimal dyskeratosis.1 Pemphigus vegetans is a localized variant of pemphigus vulgaris with a predilection for flexural surfaces. The lesions progress to vegetating erosive plaques.4 The Hallopeau type often is studded with pustules and typically remains more localized than the Neumann type. Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates intercellular deposition of IgG and C3, and routine sections characteristically show pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with intraepidermal eosinophilic microabscesses.1,4 Tinea cruris is characterized by erythematous annular lesions with raised scaly borders spreading down the inner thighs.7 The epidermis is variably spongiotic with parakeratosis, and neutrophils often present in a layered stratum corneum with basketweave keratin above a layer of more compact and eosinophilic keratin. Fungal stains, such as periodic acid-Schiff, will highlight the fungal hyphae within the stratum corneum. The inguinal folds are a typical location for inverse psoriasis, which generally appears as thin, sharply demarcated, shiny red plaques with less scale than plaque psoriasis.1 Psoriasiform hyperplasia with a diminished granular layer and tortuous papillary dermal vessels would be expected histologically.1

- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016.
- Schwartz RA, Tarlow MM. Dermatologic manifestations of Job syndrome. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1050852-overview. Updated April 22, 2019. Accessed March 28, 2020.
- Minegishi Y, Saito M. Cutaneous manifestations of hyper IgE syndrome. Allergol Int. 2012;61:191-196.
- Patterson JW. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2016.
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Executive summary: clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:409-417.
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Antifungal resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/antifungal-resistance.html. Updated March 17, 2020. Accessed April 20, 2020.
- Tinea cruris. DermNet NZ website. https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-cruris/. Published 2003. Accessed March 28, 2020.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016.
- Schwartz RA, Tarlow MM. Dermatologic manifestations of Job syndrome. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1050852-overview. Updated April 22, 2019. Accessed March 28, 2020.
- Minegishi Y, Saito M. Cutaneous manifestations of hyper IgE syndrome. Allergol Int. 2012;61:191-196.
- Patterson JW. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 4th ed. China: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2016.
- Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes DR, et al. Executive summary: clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:409-417.
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Antifungal resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/antifungal-resistance.html. Updated March 17, 2020. Accessed April 20, 2020.
- Tinea cruris. DermNet NZ website. https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-cruris/. Published 2003. Accessed March 28, 2020.
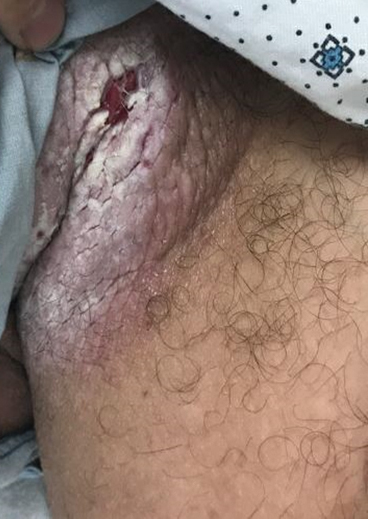
A 28-year-old man with a history of hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome (previously known as Job syndrome), coarse facial features, and multiple skin and soft tissue infections presented to the university dermatology clinic with persistent white, macerated, fissured groin plaques that were present for months. The lesions were tender and pruritic with a burning sensation. Treatment with topical terbinafine and oral fluconazole was attempted without resolution of the eruption. A biopsy of the groin lesion was performed.
Pruritic Papules on the Face and Chest
The Diagnosis: Eosinophilic Folliculitis
A shave biopsy specimen of an intact pustule on the left side of the chest was obtained. Histopathologic examination revealed follicular inflammation with copious eosinophils (Figure, A and B). Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated eosinophilic folliculitis (EF) was made.
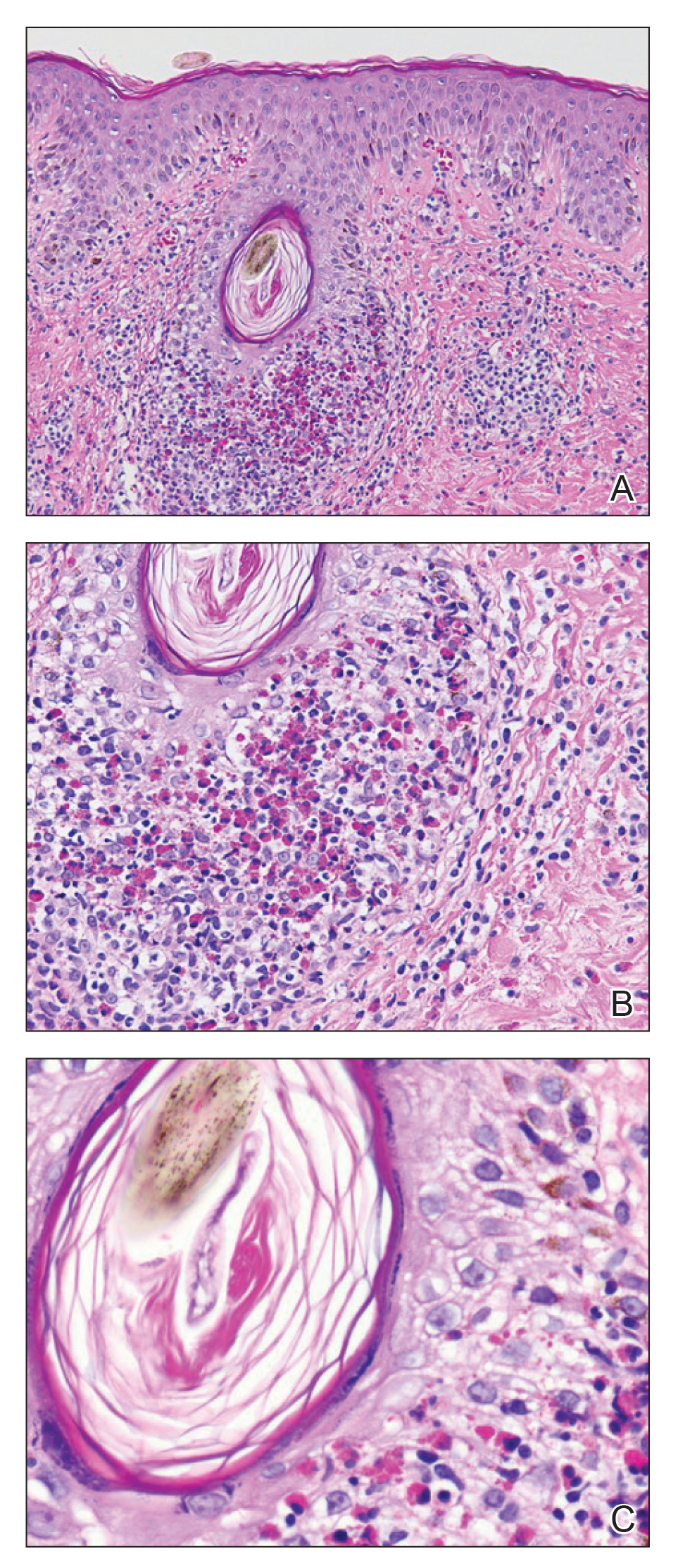
The patient was started on triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily to active lesions, oral cetirizine 10 mg in the morning, and oral hydroxyzine 25 mg at bedtime. Laboratory evaluation at the time of diagnosis showed eosinophilia with a peripheral blood eosinophil count of 0.5 K/μL (reference range, 0.03–0.48 K/μL).
Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF is a pruritic follicular eruption that occurs in HIV-positive individuals with advanced disease. Clinically, it is characterized by intermittent, urticarial, red or flesh-colored, 2- to 5-mm papules with sparse pustules involving the head, neck, arms, and upper trunk.1,2 The cardinal clinical feature of the disorder is intense pruritus, with overlying crusts and excoriations present on physical examination.3
Patients usually have a CD4 count of less than 250 cells/mm3.2,3 Patients with HIV can develop an exacerbation of EF in the first 3 to 6 months after initiating antiretroviral therapy. This clinical pattern is believed to be due to the reconstituted immune system and increased circulation of inflammatory cells.4 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE levels are found in 25% to 50% of patients with HIV-associated EF.2,3
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of intensely pruritic papules with excoriations should include scabies.3 Other diagnoses to consider include opportunistic infections and papular urticaria.5 Acne vulgaris and Demodex folliculitis also may present with lesions similar to HIV-associated EF; however, these lesions tend not to be as intensely pruritic.1,5
The etiology of HIV-associated EF is unknown.3 One proposed mechanism involves a hypersensitivity reaction to Pityrosporum or Demodex mite fragments, as evidenced by studies that found fragments of these microorganisms in biopsied lesions of HIV-associated EF.3,6 In our patient's histopathology, it was noted that the afflicted hair follicle held a single Demodex mite (Figure, C).
The histopathology is characterized by a perifollicular inflammatory infiltrate of eosinophils and CD8+ lymphocytes with areas of sebaceous lysis.3,6 Spongiosis of the follicular epithelium is seen in early lesions of HIV-associated EF.6
The first-line treatment of HIV-associated EF includes antiretroviral therapy with topical steroids and antihistamines. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF improves as CD4 helper T-cell counts rise above 250 cells/mm3 with continued antiretroviral therapy, though it initially can cause a flare of the condition.4 High-potency steroids and antihistamines are added during this period to treat the severe pruritus.1,7 In particular, daily cetirizine has been shown to be effective, which may be due to its ability to block eosinophil migration in addition to H1-receptor antagonist properties.3,7
Various alternative therapies have been described in case reports and case series; however, there have been no controlled studies comparing therapies. Phototherapy with UVB light 3 times weekly for 3 to 6 weeks has been effective and curative in recalcitrant cases.7 Other frequently used treatments include oral metronidazole, oral itraconazole, and permethrin cream 5%. The effectiveness of the latter 2 treatments is believed to be related to the proposed role of Pityrosporum and Demodex in the pathogenesis.3
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his help compiling the histopathological images and their diagnostic descriptions.
- Parker SR, Parker DC, McCall CO. Eosinophilic folliculitis in HIV-infected women: case series and review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:193-200.
- Rosenthal D, LeBoit PE, Klumpp L, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated eosinophilic folliculitis. a unique dermatosis associated with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:206-209.
- Fearfield LA, Rowe A, Francis N, et al. Itchy folliculitis and human immunodeficiency virus infection: clinicopathological and immunological features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:3-11.
- Rajendran PM, Dolev JC, Heaphy MR, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: before and after the introduction of antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:1227-1231.
- Nervi SJ, Schwartz RA, Dmochowski M. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a 40 year retrospect. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:285-289.
- McCalmont TH, Altemus D, Maurer T, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: the histological spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:439-446.
- Ellis E, Scheinfeld N. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a comprehensive review of treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:189-197.
The Diagnosis: Eosinophilic Folliculitis
A shave biopsy specimen of an intact pustule on the left side of the chest was obtained. Histopathologic examination revealed follicular inflammation with copious eosinophils (Figure, A and B). Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated eosinophilic folliculitis (EF) was made.

The patient was started on triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily to active lesions, oral cetirizine 10 mg in the morning, and oral hydroxyzine 25 mg at bedtime. Laboratory evaluation at the time of diagnosis showed eosinophilia with a peripheral blood eosinophil count of 0.5 K/μL (reference range, 0.03–0.48 K/μL).
Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF is a pruritic follicular eruption that occurs in HIV-positive individuals with advanced disease. Clinically, it is characterized by intermittent, urticarial, red or flesh-colored, 2- to 5-mm papules with sparse pustules involving the head, neck, arms, and upper trunk.1,2 The cardinal clinical feature of the disorder is intense pruritus, with overlying crusts and excoriations present on physical examination.3
Patients usually have a CD4 count of less than 250 cells/mm3.2,3 Patients with HIV can develop an exacerbation of EF in the first 3 to 6 months after initiating antiretroviral therapy. This clinical pattern is believed to be due to the reconstituted immune system and increased circulation of inflammatory cells.4 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE levels are found in 25% to 50% of patients with HIV-associated EF.2,3
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of intensely pruritic papules with excoriations should include scabies.3 Other diagnoses to consider include opportunistic infections and papular urticaria.5 Acne vulgaris and Demodex folliculitis also may present with lesions similar to HIV-associated EF; however, these lesions tend not to be as intensely pruritic.1,5
The etiology of HIV-associated EF is unknown.3 One proposed mechanism involves a hypersensitivity reaction to Pityrosporum or Demodex mite fragments, as evidenced by studies that found fragments of these microorganisms in biopsied lesions of HIV-associated EF.3,6 In our patient's histopathology, it was noted that the afflicted hair follicle held a single Demodex mite (Figure, C).
The histopathology is characterized by a perifollicular inflammatory infiltrate of eosinophils and CD8+ lymphocytes with areas of sebaceous lysis.3,6 Spongiosis of the follicular epithelium is seen in early lesions of HIV-associated EF.6
The first-line treatment of HIV-associated EF includes antiretroviral therapy with topical steroids and antihistamines. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF improves as CD4 helper T-cell counts rise above 250 cells/mm3 with continued antiretroviral therapy, though it initially can cause a flare of the condition.4 High-potency steroids and antihistamines are added during this period to treat the severe pruritus.1,7 In particular, daily cetirizine has been shown to be effective, which may be due to its ability to block eosinophil migration in addition to H1-receptor antagonist properties.3,7
Various alternative therapies have been described in case reports and case series; however, there have been no controlled studies comparing therapies. Phototherapy with UVB light 3 times weekly for 3 to 6 weeks has been effective and curative in recalcitrant cases.7 Other frequently used treatments include oral metronidazole, oral itraconazole, and permethrin cream 5%. The effectiveness of the latter 2 treatments is believed to be related to the proposed role of Pityrosporum and Demodex in the pathogenesis.3
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his help compiling the histopathological images and their diagnostic descriptions.
The Diagnosis: Eosinophilic Folliculitis
A shave biopsy specimen of an intact pustule on the left side of the chest was obtained. Histopathologic examination revealed follicular inflammation with copious eosinophils (Figure, A and B). Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated eosinophilic folliculitis (EF) was made.

The patient was started on triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily to active lesions, oral cetirizine 10 mg in the morning, and oral hydroxyzine 25 mg at bedtime. Laboratory evaluation at the time of diagnosis showed eosinophilia with a peripheral blood eosinophil count of 0.5 K/μL (reference range, 0.03–0.48 K/μL).
Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF is a pruritic follicular eruption that occurs in HIV-positive individuals with advanced disease. Clinically, it is characterized by intermittent, urticarial, red or flesh-colored, 2- to 5-mm papules with sparse pustules involving the head, neck, arms, and upper trunk.1,2 The cardinal clinical feature of the disorder is intense pruritus, with overlying crusts and excoriations present on physical examination.3
Patients usually have a CD4 count of less than 250 cells/mm3.2,3 Patients with HIV can develop an exacerbation of EF in the first 3 to 6 months after initiating antiretroviral therapy. This clinical pattern is believed to be due to the reconstituted immune system and increased circulation of inflammatory cells.4 Peripheral eosinophilia and elevated serum IgE levels are found in 25% to 50% of patients with HIV-associated EF.2,3
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of intensely pruritic papules with excoriations should include scabies.3 Other diagnoses to consider include opportunistic infections and papular urticaria.5 Acne vulgaris and Demodex folliculitis also may present with lesions similar to HIV-associated EF; however, these lesions tend not to be as intensely pruritic.1,5
The etiology of HIV-associated EF is unknown.3 One proposed mechanism involves a hypersensitivity reaction to Pityrosporum or Demodex mite fragments, as evidenced by studies that found fragments of these microorganisms in biopsied lesions of HIV-associated EF.3,6 In our patient's histopathology, it was noted that the afflicted hair follicle held a single Demodex mite (Figure, C).
The histopathology is characterized by a perifollicular inflammatory infiltrate of eosinophils and CD8+ lymphocytes with areas of sebaceous lysis.3,6 Spongiosis of the follicular epithelium is seen in early lesions of HIV-associated EF.6
The first-line treatment of HIV-associated EF includes antiretroviral therapy with topical steroids and antihistamines. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated EF improves as CD4 helper T-cell counts rise above 250 cells/mm3 with continued antiretroviral therapy, though it initially can cause a flare of the condition.4 High-potency steroids and antihistamines are added during this period to treat the severe pruritus.1,7 In particular, daily cetirizine has been shown to be effective, which may be due to its ability to block eosinophil migration in addition to H1-receptor antagonist properties.3,7
Various alternative therapies have been described in case reports and case series; however, there have been no controlled studies comparing therapies. Phototherapy with UVB light 3 times weekly for 3 to 6 weeks has been effective and curative in recalcitrant cases.7 Other frequently used treatments include oral metronidazole, oral itraconazole, and permethrin cream 5%. The effectiveness of the latter 2 treatments is believed to be related to the proposed role of Pityrosporum and Demodex in the pathogenesis.3
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Garth Fraga, MD (Kansas City, Kansas), for his help compiling the histopathological images and their diagnostic descriptions.
- Parker SR, Parker DC, McCall CO. Eosinophilic folliculitis in HIV-infected women: case series and review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:193-200.
- Rosenthal D, LeBoit PE, Klumpp L, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated eosinophilic folliculitis. a unique dermatosis associated with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:206-209.
- Fearfield LA, Rowe A, Francis N, et al. Itchy folliculitis and human immunodeficiency virus infection: clinicopathological and immunological features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:3-11.
- Rajendran PM, Dolev JC, Heaphy MR, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: before and after the introduction of antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:1227-1231.
- Nervi SJ, Schwartz RA, Dmochowski M. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a 40 year retrospect. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:285-289.
- McCalmont TH, Altemus D, Maurer T, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: the histological spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:439-446.
- Ellis E, Scheinfeld N. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a comprehensive review of treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:189-197.
- Parker SR, Parker DC, McCall CO. Eosinophilic folliculitis in HIV-infected women: case series and review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:193-200.
- Rosenthal D, LeBoit PE, Klumpp L, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated eosinophilic folliculitis. a unique dermatosis associated with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:206-209.
- Fearfield LA, Rowe A, Francis N, et al. Itchy folliculitis and human immunodeficiency virus infection: clinicopathological and immunological features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:3-11.
- Rajendran PM, Dolev JC, Heaphy MR, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: before and after the introduction of antiretroviral therapy. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:1227-1231.
- Nervi SJ, Schwartz RA, Dmochowski M. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a 40 year retrospect. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:285-289.
- McCalmont TH, Altemus D, Maurer T, et al. Eosinophilic folliculitis: the histological spectrum. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:439-446.
- Ellis E, Scheinfeld N. Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis: a comprehensive review of treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2004;5:189-197.

A 31-year-old man presented with a severely pruritic rash of 2 weeks' duration. Physical examination revealed numerous urticarial papules and rare erythematous pustules over the face (top), upper chest (bottom), and proximal arms; most lesions were excoriated. Additionally, there were numerous hyperpigmented papules with central hypopigmentation on the upper chest and arms. The lower half of the body was spared. His medical history was notable for human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS with a prior episode of Pneumocystis pneumonia. He had been noncompliant with antiretroviral therapy for the last 2 years but restarted therapy 3 weeks prior to presentation. Laboratory test results revealed a CD4 cell count of 13 cells/mm3 (reference range, 500-1500 cells/mm3) with a viral load of 179 copies/mL (reference range, undetectable).
Dusky Pink Nodular Plaque on the Finger
The Diagnosis: Majocchi Granuloma
Majocchi granuloma (MG) is a dermatophytic infection that reveals hyphal elements within the cornified cells of follicles and most commonly is caused by Trichophyton rubrum. However, occasionally other Trichophyton, Trichosporon, and Aspergillus species are involved.1
There typically are 2 forms of MG: (1) the small perifollicular papular form that usually is localized to the dermis and occurs in immunocompetent individuals, and (2) a deep form featuring subcutaneous plaques and nodules that generally occur on the hair-bearing surfaces in immunosuppressed hosts.2 Majocchi granuloma also commonly occurs from the use of potent topical steroids on unsuspected tinea.3
Histopathologically, MG generally presents as granulomatous inflammation with perifollicular neutrophilic infiltration. This polymorphonuclear cell infiltrate was visible clinically as a single pustule overlying the nodular plaque, a clue appreciable only on close inspection. Histopathologic examination revealed segmented branching filaments present within cornified elements of a follicle (Figure). Notably, potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations are unreliable diagnostic aids in MG, as evidenced by the 2 negative KOH preparations in this case. According to Chou and Hsu,4 because KOH preparation can only detect fungi located in the stratum corneum, the result may be negative for MG due to deeper invasion of the fungi into the dermal follicular component. In fact, KOH preparations of MG may reveal no hyphae in 23.3% of cases.2
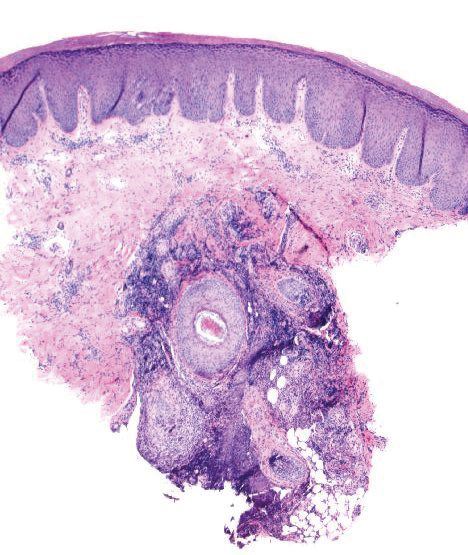
The initiating factor in MG is not entirely known but is thought to be physical trauma that either directly or indirectly leads to follicle disruption and passive introduction of the organism into the dermis (eg, traumatic implantation via gardening or other recreational activities).2 Other proposed mechanisms include the presentation of the membrane-associated ATP-binding cassette transporter on the surface of T rubrum.1 Dermatophytes evade the host immune system through a variety of mechanisms: (1) cell wall glycoproteins, (2) release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and (3) generation of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells.1
Collectively, the clinical and histopathologic findings distinguish MG from other cutaneous conditions. Sporotrichosis, a granulomatous infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii, typically is found in tropical regions of the world and often is associated with floriculture.5 Sporotrichosis initially presents in a subcutaneous papulonodular form, but unlike MG, it later ulcerates and progresses along adjacent lymphatic chains.5 Pathology of sporotrichosis exhibits pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas, possible foci of suppuration, and yeastlike forms called cigar bodies. Chromoblastomycosis clinically is defined by tumorlike lesions on the skin including verrucous, nodular, or scarlike plaques and typically is associated with traumatic injury and implantation of the microorganism. Histologically, chromoblastomycosis demonstrates pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas and characteristic darkly pigmented, thick-walled sclerotic cells called Medlar bodies.6 Mycobacterium marinum is one cause of nontuberculous mycobacterial skin infections in humans. Clinically, M marinum is associated with improper hygiene techniques and contact with fish tanks and other aqueous environments. Mycobacterium marinum can present histopathologically as early neutrophilic infiltration or late dermal granulomatous inflammation.7 Acid-fast bacilli typically are scant, leaving the diagnosis best secured via polymerase chain reaction assay. Nodular Kaposi sarcoma (KS) can present as a dusky nodular plaque on an acral surface but typically is seen in patients with underlying human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS or other immunosuppressive conditions. The pathology for KS shows a proliferation of human herpes virus 8-positive spindle cells with slitlike spaces containing red blood cells instead of granulomatous inflammation.
Treatment regimens with topical corticosteroids can exacerbate the infection due to local suppression of cell-mediated immunity.8 In these scenarios, fungal infection is suspected, and systemic antifungals such as ketoconazole; itraconazole; or terbinafine, which has become the mainstay, are prescribed. Resolution of the infection with these medications usually is seen after 4 weeks.2
A diagnosis of MG can be elusive and often may take multiple visits. Clinicians should note that MG could demonstrate repeated false-negative KOH preparations; therefore, these tests should not be relied on as the sole determination of a diagnosis. Although chromoblastomycosis, sporotrichosis, nodular KS, and infection with M marinum may all present as nodular plaques with granulomatous pathology, a follicular pustule may be a clinical clue to MG, as its mimics typically lack folliculocentric neutrophils.
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Ponce-Olivera RM, Bonifaz A. Majocchi's granuloma (dermatophytic granuloma): updated therapeutic options. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2015;9:204-212.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas¸ M. Majocchi's granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Majocchi granuloma. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1092601-overview. Updated May 14, 2019. Accessed April 13, 2020.
- Chou WY, Hsu CJ. A case report of Majocchi's granuloma associated with combined therapy of topical steroids and adalimumab. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E2245.
- Barros MB, de Almeida Paes R, Schubach AO. Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:633-654.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- Slany M, Jezek P, Bodnarova M. Fish tank granuloma caused by Mycobacterium marinum in two aquarists: two case reports. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:161329.
- Coondoo A, Phiske M, Verma S, et al. Side-effects of topical steroids: a long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:416-425.
The Diagnosis: Majocchi Granuloma
Majocchi granuloma (MG) is a dermatophytic infection that reveals hyphal elements within the cornified cells of follicles and most commonly is caused by Trichophyton rubrum. However, occasionally other Trichophyton, Trichosporon, and Aspergillus species are involved.1
There typically are 2 forms of MG: (1) the small perifollicular papular form that usually is localized to the dermis and occurs in immunocompetent individuals, and (2) a deep form featuring subcutaneous plaques and nodules that generally occur on the hair-bearing surfaces in immunosuppressed hosts.2 Majocchi granuloma also commonly occurs from the use of potent topical steroids on unsuspected tinea.3
Histopathologically, MG generally presents as granulomatous inflammation with perifollicular neutrophilic infiltration. This polymorphonuclear cell infiltrate was visible clinically as a single pustule overlying the nodular plaque, a clue appreciable only on close inspection. Histopathologic examination revealed segmented branching filaments present within cornified elements of a follicle (Figure). Notably, potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations are unreliable diagnostic aids in MG, as evidenced by the 2 negative KOH preparations in this case. According to Chou and Hsu,4 because KOH preparation can only detect fungi located in the stratum corneum, the result may be negative for MG due to deeper invasion of the fungi into the dermal follicular component. In fact, KOH preparations of MG may reveal no hyphae in 23.3% of cases.2

The initiating factor in MG is not entirely known but is thought to be physical trauma that either directly or indirectly leads to follicle disruption and passive introduction of the organism into the dermis (eg, traumatic implantation via gardening or other recreational activities).2 Other proposed mechanisms include the presentation of the membrane-associated ATP-binding cassette transporter on the surface of T rubrum.1 Dermatophytes evade the host immune system through a variety of mechanisms: (1) cell wall glycoproteins, (2) release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and (3) generation of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells.1
Collectively, the clinical and histopathologic findings distinguish MG from other cutaneous conditions. Sporotrichosis, a granulomatous infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii, typically is found in tropical regions of the world and often is associated with floriculture.5 Sporotrichosis initially presents in a subcutaneous papulonodular form, but unlike MG, it later ulcerates and progresses along adjacent lymphatic chains.5 Pathology of sporotrichosis exhibits pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas, possible foci of suppuration, and yeastlike forms called cigar bodies. Chromoblastomycosis clinically is defined by tumorlike lesions on the skin including verrucous, nodular, or scarlike plaques and typically is associated with traumatic injury and implantation of the microorganism. Histologically, chromoblastomycosis demonstrates pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas and characteristic darkly pigmented, thick-walled sclerotic cells called Medlar bodies.6 Mycobacterium marinum is one cause of nontuberculous mycobacterial skin infections in humans. Clinically, M marinum is associated with improper hygiene techniques and contact with fish tanks and other aqueous environments. Mycobacterium marinum can present histopathologically as early neutrophilic infiltration or late dermal granulomatous inflammation.7 Acid-fast bacilli typically are scant, leaving the diagnosis best secured via polymerase chain reaction assay. Nodular Kaposi sarcoma (KS) can present as a dusky nodular plaque on an acral surface but typically is seen in patients with underlying human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS or other immunosuppressive conditions. The pathology for KS shows a proliferation of human herpes virus 8-positive spindle cells with slitlike spaces containing red blood cells instead of granulomatous inflammation.
Treatment regimens with topical corticosteroids can exacerbate the infection due to local suppression of cell-mediated immunity.8 In these scenarios, fungal infection is suspected, and systemic antifungals such as ketoconazole; itraconazole; or terbinafine, which has become the mainstay, are prescribed. Resolution of the infection with these medications usually is seen after 4 weeks.2
A diagnosis of MG can be elusive and often may take multiple visits. Clinicians should note that MG could demonstrate repeated false-negative KOH preparations; therefore, these tests should not be relied on as the sole determination of a diagnosis. Although chromoblastomycosis, sporotrichosis, nodular KS, and infection with M marinum may all present as nodular plaques with granulomatous pathology, a follicular pustule may be a clinical clue to MG, as its mimics typically lack folliculocentric neutrophils.
The Diagnosis: Majocchi Granuloma
Majocchi granuloma (MG) is a dermatophytic infection that reveals hyphal elements within the cornified cells of follicles and most commonly is caused by Trichophyton rubrum. However, occasionally other Trichophyton, Trichosporon, and Aspergillus species are involved.1
There typically are 2 forms of MG: (1) the small perifollicular papular form that usually is localized to the dermis and occurs in immunocompetent individuals, and (2) a deep form featuring subcutaneous plaques and nodules that generally occur on the hair-bearing surfaces in immunosuppressed hosts.2 Majocchi granuloma also commonly occurs from the use of potent topical steroids on unsuspected tinea.3
Histopathologically, MG generally presents as granulomatous inflammation with perifollicular neutrophilic infiltration. This polymorphonuclear cell infiltrate was visible clinically as a single pustule overlying the nodular plaque, a clue appreciable only on close inspection. Histopathologic examination revealed segmented branching filaments present within cornified elements of a follicle (Figure). Notably, potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations are unreliable diagnostic aids in MG, as evidenced by the 2 negative KOH preparations in this case. According to Chou and Hsu,4 because KOH preparation can only detect fungi located in the stratum corneum, the result may be negative for MG due to deeper invasion of the fungi into the dermal follicular component. In fact, KOH preparations of MG may reveal no hyphae in 23.3% of cases.2

The initiating factor in MG is not entirely known but is thought to be physical trauma that either directly or indirectly leads to follicle disruption and passive introduction of the organism into the dermis (eg, traumatic implantation via gardening or other recreational activities).2 Other proposed mechanisms include the presentation of the membrane-associated ATP-binding cassette transporter on the surface of T rubrum.1 Dermatophytes evade the host immune system through a variety of mechanisms: (1) cell wall glycoproteins, (2) release of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and (3) generation of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells.1
Collectively, the clinical and histopathologic findings distinguish MG from other cutaneous conditions. Sporotrichosis, a granulomatous infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii, typically is found in tropical regions of the world and often is associated with floriculture.5 Sporotrichosis initially presents in a subcutaneous papulonodular form, but unlike MG, it later ulcerates and progresses along adjacent lymphatic chains.5 Pathology of sporotrichosis exhibits pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas, possible foci of suppuration, and yeastlike forms called cigar bodies. Chromoblastomycosis clinically is defined by tumorlike lesions on the skin including verrucous, nodular, or scarlike plaques and typically is associated with traumatic injury and implantation of the microorganism. Histologically, chromoblastomycosis demonstrates pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with granulomas and characteristic darkly pigmented, thick-walled sclerotic cells called Medlar bodies.6 Mycobacterium marinum is one cause of nontuberculous mycobacterial skin infections in humans. Clinically, M marinum is associated with improper hygiene techniques and contact with fish tanks and other aqueous environments. Mycobacterium marinum can present histopathologically as early neutrophilic infiltration or late dermal granulomatous inflammation.7 Acid-fast bacilli typically are scant, leaving the diagnosis best secured via polymerase chain reaction assay. Nodular Kaposi sarcoma (KS) can present as a dusky nodular plaque on an acral surface but typically is seen in patients with underlying human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS or other immunosuppressive conditions. The pathology for KS shows a proliferation of human herpes virus 8-positive spindle cells with slitlike spaces containing red blood cells instead of granulomatous inflammation.
Treatment regimens with topical corticosteroids can exacerbate the infection due to local suppression of cell-mediated immunity.8 In these scenarios, fungal infection is suspected, and systemic antifungals such as ketoconazole; itraconazole; or terbinafine, which has become the mainstay, are prescribed. Resolution of the infection with these medications usually is seen after 4 weeks.2
A diagnosis of MG can be elusive and often may take multiple visits. Clinicians should note that MG could demonstrate repeated false-negative KOH preparations; therefore, these tests should not be relied on as the sole determination of a diagnosis. Although chromoblastomycosis, sporotrichosis, nodular KS, and infection with M marinum may all present as nodular plaques with granulomatous pathology, a follicular pustule may be a clinical clue to MG, as its mimics typically lack folliculocentric neutrophils.
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Ponce-Olivera RM, Bonifaz A. Majocchi's granuloma (dermatophytic granuloma): updated therapeutic options. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2015;9:204-212.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas¸ M. Majocchi's granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Majocchi granuloma. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1092601-overview. Updated May 14, 2019. Accessed April 13, 2020.
- Chou WY, Hsu CJ. A case report of Majocchi's granuloma associated with combined therapy of topical steroids and adalimumab. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E2245.
- Barros MB, de Almeida Paes R, Schubach AO. Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:633-654.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- Slany M, Jezek P, Bodnarova M. Fish tank granuloma caused by Mycobacterium marinum in two aquarists: two case reports. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:161329.
- Coondoo A, Phiske M, Verma S, et al. Side-effects of topical steroids: a long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:416-425.
- Tirado-Sánchez A, Ponce-Olivera RM, Bonifaz A. Majocchi's granuloma (dermatophytic granuloma): updated therapeutic options. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2015;9:204-212.
- Ilkit M, Durdu M, Karakas¸ M. Majocchi's granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457.
- Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Majocchi granuloma. Medscape website. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1092601-overview. Updated May 14, 2019. Accessed April 13, 2020.
- Chou WY, Hsu CJ. A case report of Majocchi's granuloma associated with combined therapy of topical steroids and adalimumab. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E2245.
- Barros MB, de Almeida Paes R, Schubach AO. Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:633-654.
- Guarner J, Brandt ME. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011;24:247-280.
- Slany M, Jezek P, Bodnarova M. Fish tank granuloma caused by Mycobacterium marinum in two aquarists: two case reports. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:161329.
- Coondoo A, Phiske M, Verma S, et al. Side-effects of topical steroids: a long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:416-425.
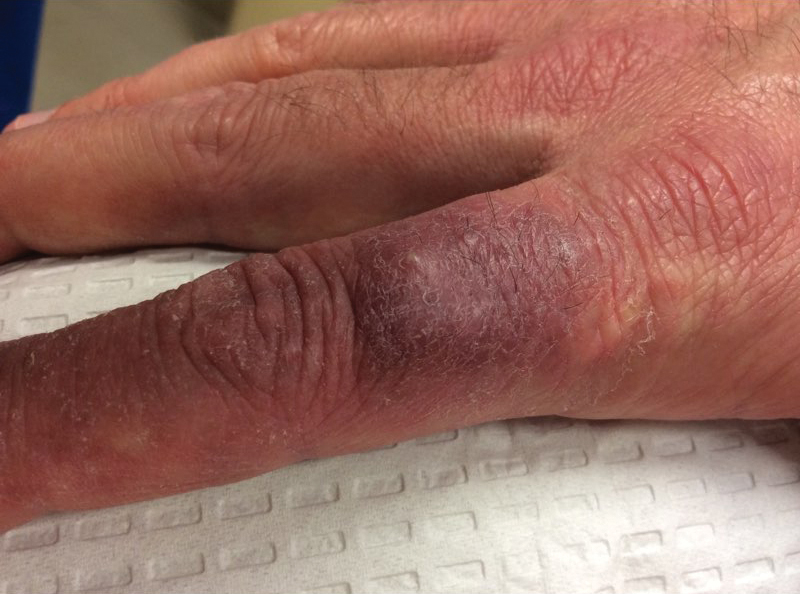
A 38-year-old man presented with a persistent pruritic nodular plaque on the proximal right index finger of 4 months' duration. He reported pruning roses in the garden but denied any trauma. The patient previously had been treated by another clinician with fluocinonide cream 0.05%, clobetasol cream 0.05%, intramuscular methylprednisolone 40 mg, and oral doxycycline hyclate 100 mg with no improvement. Two potassium hydroxide preparations were performed as well as a bacterial culture and sensitivity, with all results returning as negative. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink to purple, scaly, nodular plaque on the right index finger. A punch biopsy was obtained for histopathology with hematoxylin and eosin stain.
Pruritic Eruption With Skinfold Sparing
The Diagnosis: Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji
The patient presented with a characteristic finding of skinfold sparing, known as the "deck-chair sign" (Figure 1).1 A repeat biopsy at our institution revealed a dermal perivascular and bandlike infiltrate with lymphocytes and occasional eosinophils (Figure 2). The epidermis showed mild spongiosis, lymphocytic exocytosis, and rare necrotic keratinocytes. A T-cell gene rearrangement assay was negative for a monoclonal population of T lymphocytes. Based on the clinical and histologic features, the diagnosis was most consistent with papuloerythroderma of Ofuji (PEO); however, a lymphoproliferative disorder needed to be excluded. Further workup included a peripheral smear, complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, IgE level, and hepatitis panel; all were normal, except for an elevated serum IgE level. Human immunodeficiency virus and age-appropriate malignancy screening were negative. The patient was prescribed betamethasone dipropionate cream 0.05% twice daily, which resulted in near-complete resolution of the rash and marked improvement in pruritus.
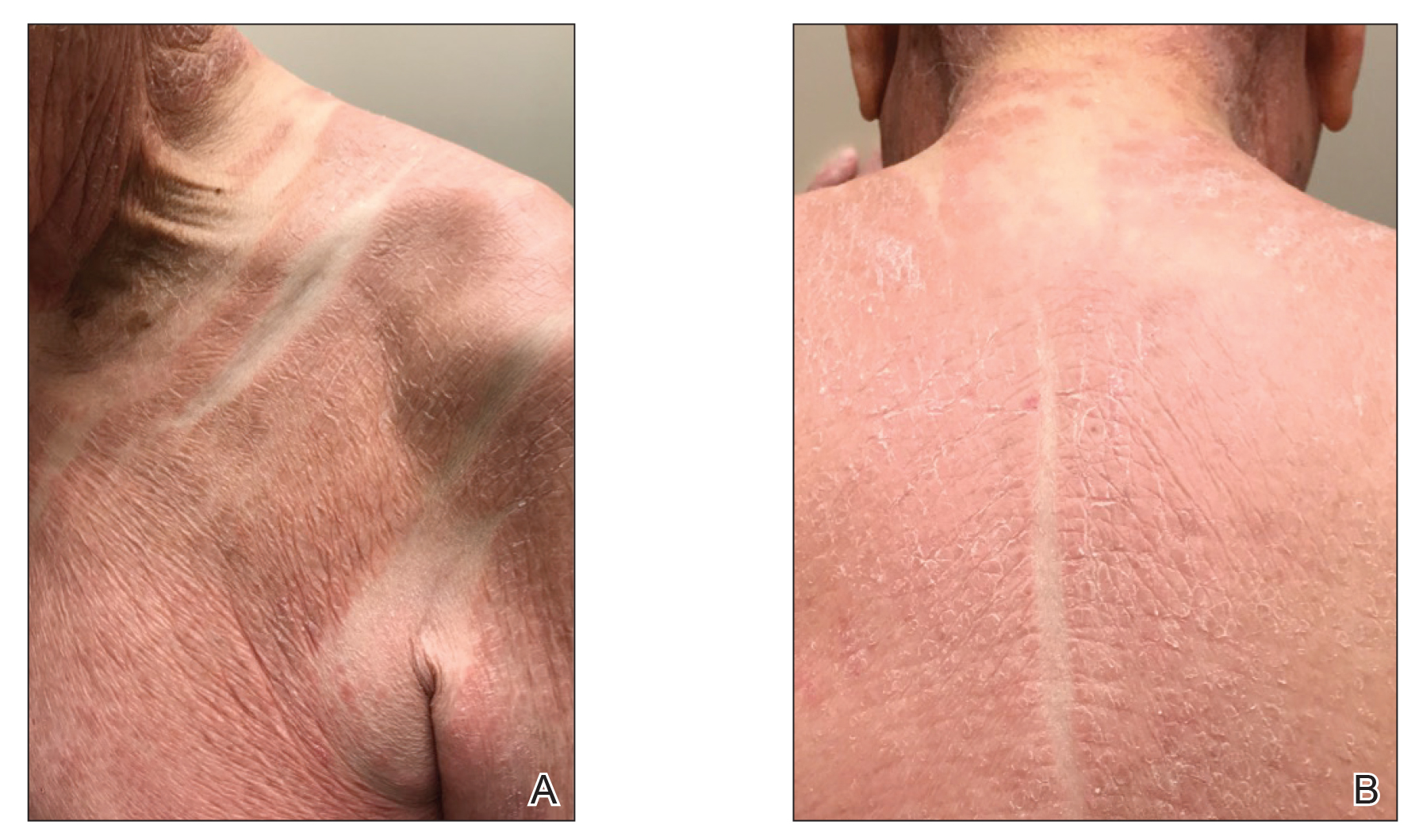
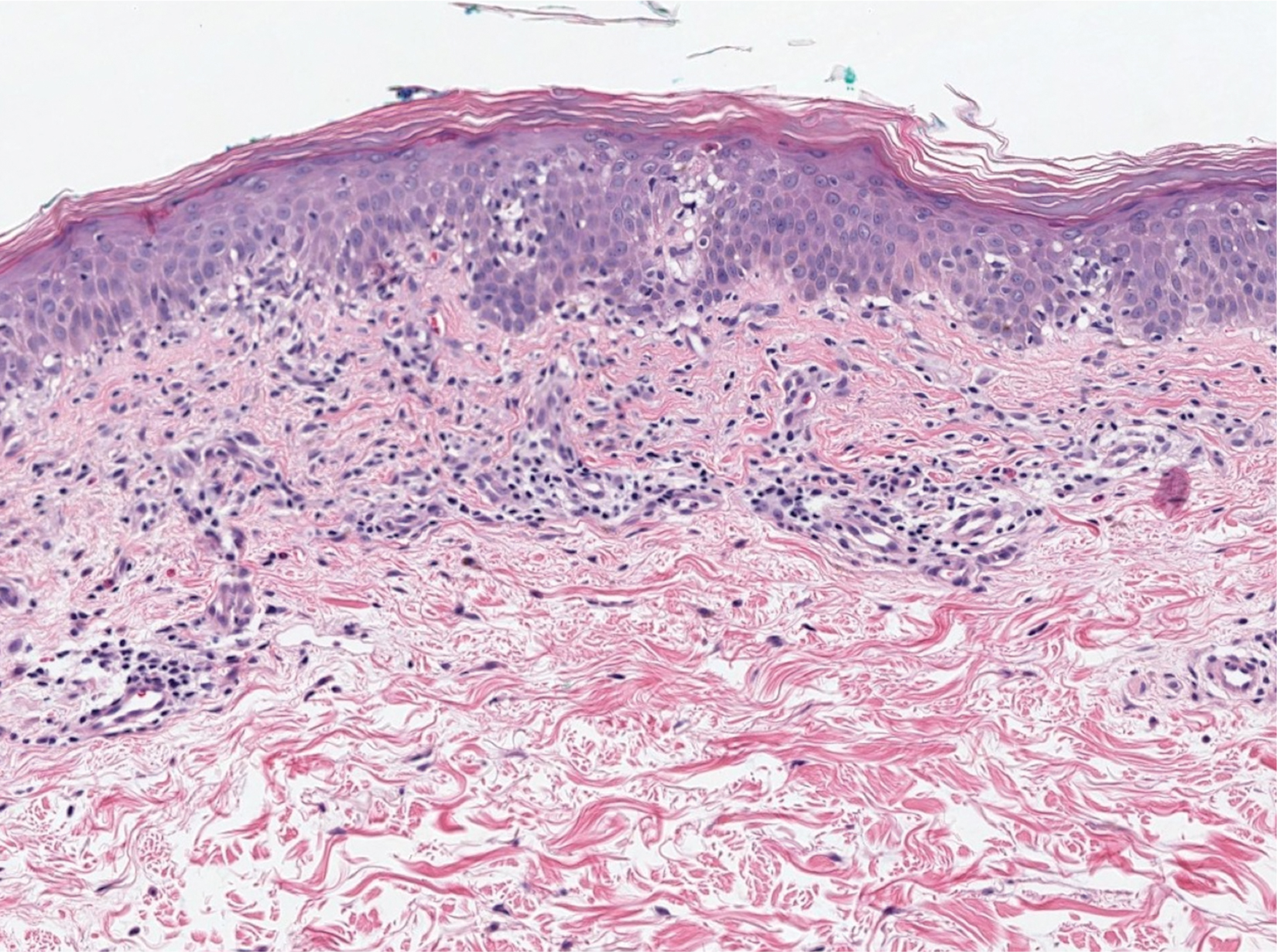
In 1984, PEO was described as an entity of generalized pruritic erythroderma characterized by flat-topped, red to brown, coalescing papules with sparing of the skinfolds, later coined the deck-chair sign.1,2 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji commonly presents in elderly Asian males with a male to female ratio of 4:1.3 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji is a T cell-mediated skin disease; however, the etiology of the signature rash remains unclear. One explanation includes circulating factors in the skin that elicit an inflammatory response, which does not occur in areas of external pressure.3 The deck-chair sign may occur more frequently in elderly individuals due to increased skin laxity, which creates crease lines that are spared from rubbing and excoriations.4
Although Ofuji et al2 initially reported 4 idiopathic cases, subsequent authors described PEO in association with other conditions, including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and atopic diathesis, and infections, as well as secondary to medications. Some authors have suggested that PEO may be an early variant of mycosis fungoides; therefore, physicians should monitor patients closely.5-7 Maher et al6 commented that multiple causative factors including CTCL underlie the development of papuloerythroderma.
In a review of PEO, Torchia et al3 proposed diagnostic criteria and an etiologic classification to address whether PEO represents an independent entity or an unusual manifestation of other dermatoses. They established 4 categories of papuloerythroderma--primary, secondary, papuloerythrodermalike CTCL, and pseudopapuloerythroderma--and proposed that primary PEO is a diagnosis of exclusion. If no secondary association is found, they proposed 10 criteria for primary PEO: 5 major criteria include coalescing flat-topped papules, the deck-chair sign, pruritus, histopathologic exclusion of diseases such as CTCL, and a negative workup to exclude other causes.3 In 2018, Maher et al6 recommended workup to rule out cutaneous malignancy, including skin biopsy, flow cytometry, Sézary cell count, T-cell rearrangement, lactate dehydrogenase, and human T-cell lymphotropic virus 1. The 5 minor criteria proposed by Torchia et al3 include age older than 55 years, male sex, eosinophilia, elevated IgE level, and lymphopenia. Our patient fulfilled all 5 major criteria and 3 minor criteria; eosinophilia and lymphopenia were absent.
Clinically, PEO has been associated with the deck-chair sign, a pattern of selective sparing of skinfolds, including axillary, inguinal, submammary, and other flexural areas. Although the deck-chair sign was originally considered pathognomonic for PEO, this clinical pattern also has been observed in other entities, such as angioimmunoblastic lymphoma, cutaneous Waldenström macroglobulinemia, and acanthosis nigricans.5,8,9
Specific characteristics of the rash and certain clinical symptoms may help to distinguish the deck-chair sign of PEO from its other causes. Although malignant acanthosis nigricans may spare the skinfolds, lesions have a classic velvety thickening and brownish hyperpigmentation, which is not characteristic of the reddish brown, flat-topped papules of PEO.9 Pai et al5 described a patient with parthenium dermatitis presenting with the deck-chair sign that developed years after repeated exposure to the allergen. Our patient did not have a history of repeated episodes of allergic contact dermatitis. In addition, areas of sparing may mimic the appearance of pityriasis rubra pilaris. As in our patient, those with PEO generally lack the follicular hyperkeratotic papules, palmoplantar keratoderma, widespread orange-red erythema, and characteristic histopathologic finding of hyperkeratosis with alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis, allowing these entities to be easily distinguished in most instances.10
Histopathologically, primary PEO shows a nonspecific spongiotic dermatitis-like pattern characterized by slight epidermal hyperplasia with spongiosis and a predominantly perivascular dermal infiltrate with lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils.3 These histologic findings may at times show some overlap with CTCL, and therefore T-cell gene rearrangement and flow cytometry may be performed in those instances.6
Treatment includes the management of any underlying condition causing the papuloerythroderma.3,6 There are no large clinical trials of treatment options for primary PEO due to its rarity. Topical or systemic corticosteroids remain the mainstay of treatment.3 Alternative treatments used with variable success include phototherapy, interferon, etretinate, cyclosporine, and azathioprine.11 Allegue et al11 successfully used methotrexate to treat a patient with primary PEO and postulated that methotrexate may act through an immunosuppressive mechanism on activated T cells due to the involvement of helper T cells TH2 and TH22 in its pathogenesis.
Although the cutaneous manifestations of PEO may respond well to topical steroids, it is important to consider the possible presence of an underlying malignancy and other associated systemic conditions.
- Farthing CF, Staughton RC, Harper JI, et al. Papuloerythroderma--a further case with the 'deck chair sign.' Dermatologica. 1986;172:65-66.
- Ofuji S, Furukawa F, Miyachi Y, et al. Papuloerythroderma. Dermatologica. 1984;169:125-130.
- Torchia D, Miteva M, Hu S, et al. Papuloerythroderma 2009: two new cases and systematic review of the worldwide literature 25 years after its identification by Ofuji et al. Dermatology. 2010;220:311-320.
- Ochi H, Ang CC. Novel association of a papuloerythroderma of Ofuji phenotype with dermatitis herpetiformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:856-857.
- Pai S, Shetty S, Rao R. Parthenium dermatitis with deck-chair sign. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:906-907.
- Maher AM, Ward CE, Glassman S, et al. The importance of excluding cutaneous T-cell lymphomas in patients with a working diagnosis of papuloerythroderma of Ofuji: a case series. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:46-54.
- Grob JJ, Collet-Villette AM, Horchowski N, et al. Ofuji papuloerythroderma. report of a case with T cell skin lymphoma and discussion of the nature of this disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(5 pt 2):927-931.
- Ferran M, Gallardo F, Baena V, et al. The 'deck chair sign' in specific cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Dermatology. 2006;213:50-52.
- Murao K, Sadamoto Y, Kubo Y, et al. Generalized malignant acanthosis nigricans with "deck-chair sign." Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:377-378.
- Regina G, Paramita L, Radiono S, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji in Indonesia: the first case report. JDVI. 2016;1:93-98.
- Allegue F, Fachal C, Gonzalez-Vilas D, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji successfully treated with methotrexate. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12638.
The Diagnosis: Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji
The patient presented with a characteristic finding of skinfold sparing, known as the "deck-chair sign" (Figure 1).1 A repeat biopsy at our institution revealed a dermal perivascular and bandlike infiltrate with lymphocytes and occasional eosinophils (Figure 2). The epidermis showed mild spongiosis, lymphocytic exocytosis, and rare necrotic keratinocytes. A T-cell gene rearrangement assay was negative for a monoclonal population of T lymphocytes. Based on the clinical and histologic features, the diagnosis was most consistent with papuloerythroderma of Ofuji (PEO); however, a lymphoproliferative disorder needed to be excluded. Further workup included a peripheral smear, complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, IgE level, and hepatitis panel; all were normal, except for an elevated serum IgE level. Human immunodeficiency virus and age-appropriate malignancy screening were negative. The patient was prescribed betamethasone dipropionate cream 0.05% twice daily, which resulted in near-complete resolution of the rash and marked improvement in pruritus.


In 1984, PEO was described as an entity of generalized pruritic erythroderma characterized by flat-topped, red to brown, coalescing papules with sparing of the skinfolds, later coined the deck-chair sign.1,2 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji commonly presents in elderly Asian males with a male to female ratio of 4:1.3 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji is a T cell-mediated skin disease; however, the etiology of the signature rash remains unclear. One explanation includes circulating factors in the skin that elicit an inflammatory response, which does not occur in areas of external pressure.3 The deck-chair sign may occur more frequently in elderly individuals due to increased skin laxity, which creates crease lines that are spared from rubbing and excoriations.4
Although Ofuji et al2 initially reported 4 idiopathic cases, subsequent authors described PEO in association with other conditions, including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and atopic diathesis, and infections, as well as secondary to medications. Some authors have suggested that PEO may be an early variant of mycosis fungoides; therefore, physicians should monitor patients closely.5-7 Maher et al6 commented that multiple causative factors including CTCL underlie the development of papuloerythroderma.
In a review of PEO, Torchia et al3 proposed diagnostic criteria and an etiologic classification to address whether PEO represents an independent entity or an unusual manifestation of other dermatoses. They established 4 categories of papuloerythroderma--primary, secondary, papuloerythrodermalike CTCL, and pseudopapuloerythroderma--and proposed that primary PEO is a diagnosis of exclusion. If no secondary association is found, they proposed 10 criteria for primary PEO: 5 major criteria include coalescing flat-topped papules, the deck-chair sign, pruritus, histopathologic exclusion of diseases such as CTCL, and a negative workup to exclude other causes.3 In 2018, Maher et al6 recommended workup to rule out cutaneous malignancy, including skin biopsy, flow cytometry, Sézary cell count, T-cell rearrangement, lactate dehydrogenase, and human T-cell lymphotropic virus 1. The 5 minor criteria proposed by Torchia et al3 include age older than 55 years, male sex, eosinophilia, elevated IgE level, and lymphopenia. Our patient fulfilled all 5 major criteria and 3 minor criteria; eosinophilia and lymphopenia were absent.
Clinically, PEO has been associated with the deck-chair sign, a pattern of selective sparing of skinfolds, including axillary, inguinal, submammary, and other flexural areas. Although the deck-chair sign was originally considered pathognomonic for PEO, this clinical pattern also has been observed in other entities, such as angioimmunoblastic lymphoma, cutaneous Waldenström macroglobulinemia, and acanthosis nigricans.5,8,9
Specific characteristics of the rash and certain clinical symptoms may help to distinguish the deck-chair sign of PEO from its other causes. Although malignant acanthosis nigricans may spare the skinfolds, lesions have a classic velvety thickening and brownish hyperpigmentation, which is not characteristic of the reddish brown, flat-topped papules of PEO.9 Pai et al5 described a patient with parthenium dermatitis presenting with the deck-chair sign that developed years after repeated exposure to the allergen. Our patient did not have a history of repeated episodes of allergic contact dermatitis. In addition, areas of sparing may mimic the appearance of pityriasis rubra pilaris. As in our patient, those with PEO generally lack the follicular hyperkeratotic papules, palmoplantar keratoderma, widespread orange-red erythema, and characteristic histopathologic finding of hyperkeratosis with alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis, allowing these entities to be easily distinguished in most instances.10
Histopathologically, primary PEO shows a nonspecific spongiotic dermatitis-like pattern characterized by slight epidermal hyperplasia with spongiosis and a predominantly perivascular dermal infiltrate with lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils.3 These histologic findings may at times show some overlap with CTCL, and therefore T-cell gene rearrangement and flow cytometry may be performed in those instances.6
Treatment includes the management of any underlying condition causing the papuloerythroderma.3,6 There are no large clinical trials of treatment options for primary PEO due to its rarity. Topical or systemic corticosteroids remain the mainstay of treatment.3 Alternative treatments used with variable success include phototherapy, interferon, etretinate, cyclosporine, and azathioprine.11 Allegue et al11 successfully used methotrexate to treat a patient with primary PEO and postulated that methotrexate may act through an immunosuppressive mechanism on activated T cells due to the involvement of helper T cells TH2 and TH22 in its pathogenesis.
Although the cutaneous manifestations of PEO may respond well to topical steroids, it is important to consider the possible presence of an underlying malignancy and other associated systemic conditions.
The Diagnosis: Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji
The patient presented with a characteristic finding of skinfold sparing, known as the "deck-chair sign" (Figure 1).1 A repeat biopsy at our institution revealed a dermal perivascular and bandlike infiltrate with lymphocytes and occasional eosinophils (Figure 2). The epidermis showed mild spongiosis, lymphocytic exocytosis, and rare necrotic keratinocytes. A T-cell gene rearrangement assay was negative for a monoclonal population of T lymphocytes. Based on the clinical and histologic features, the diagnosis was most consistent with papuloerythroderma of Ofuji (PEO); however, a lymphoproliferative disorder needed to be excluded. Further workup included a peripheral smear, complete blood cell count with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, IgE level, and hepatitis panel; all were normal, except for an elevated serum IgE level. Human immunodeficiency virus and age-appropriate malignancy screening were negative. The patient was prescribed betamethasone dipropionate cream 0.05% twice daily, which resulted in near-complete resolution of the rash and marked improvement in pruritus.


In 1984, PEO was described as an entity of generalized pruritic erythroderma characterized by flat-topped, red to brown, coalescing papules with sparing of the skinfolds, later coined the deck-chair sign.1,2 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji commonly presents in elderly Asian males with a male to female ratio of 4:1.3 Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji is a T cell-mediated skin disease; however, the etiology of the signature rash remains unclear. One explanation includes circulating factors in the skin that elicit an inflammatory response, which does not occur in areas of external pressure.3 The deck-chair sign may occur more frequently in elderly individuals due to increased skin laxity, which creates crease lines that are spared from rubbing and excoriations.4
Although Ofuji et al2 initially reported 4 idiopathic cases, subsequent authors described PEO in association with other conditions, including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and atopic diathesis, and infections, as well as secondary to medications. Some authors have suggested that PEO may be an early variant of mycosis fungoides; therefore, physicians should monitor patients closely.5-7 Maher et al6 commented that multiple causative factors including CTCL underlie the development of papuloerythroderma.
In a review of PEO, Torchia et al3 proposed diagnostic criteria and an etiologic classification to address whether PEO represents an independent entity or an unusual manifestation of other dermatoses. They established 4 categories of papuloerythroderma--primary, secondary, papuloerythrodermalike CTCL, and pseudopapuloerythroderma--and proposed that primary PEO is a diagnosis of exclusion. If no secondary association is found, they proposed 10 criteria for primary PEO: 5 major criteria include coalescing flat-topped papules, the deck-chair sign, pruritus, histopathologic exclusion of diseases such as CTCL, and a negative workup to exclude other causes.3 In 2018, Maher et al6 recommended workup to rule out cutaneous malignancy, including skin biopsy, flow cytometry, Sézary cell count, T-cell rearrangement, lactate dehydrogenase, and human T-cell lymphotropic virus 1. The 5 minor criteria proposed by Torchia et al3 include age older than 55 years, male sex, eosinophilia, elevated IgE level, and lymphopenia. Our patient fulfilled all 5 major criteria and 3 minor criteria; eosinophilia and lymphopenia were absent.
Clinically, PEO has been associated with the deck-chair sign, a pattern of selective sparing of skinfolds, including axillary, inguinal, submammary, and other flexural areas. Although the deck-chair sign was originally considered pathognomonic for PEO, this clinical pattern also has been observed in other entities, such as angioimmunoblastic lymphoma, cutaneous Waldenström macroglobulinemia, and acanthosis nigricans.5,8,9
Specific characteristics of the rash and certain clinical symptoms may help to distinguish the deck-chair sign of PEO from its other causes. Although malignant acanthosis nigricans may spare the skinfolds, lesions have a classic velvety thickening and brownish hyperpigmentation, which is not characteristic of the reddish brown, flat-topped papules of PEO.9 Pai et al5 described a patient with parthenium dermatitis presenting with the deck-chair sign that developed years after repeated exposure to the allergen. Our patient did not have a history of repeated episodes of allergic contact dermatitis. In addition, areas of sparing may mimic the appearance of pityriasis rubra pilaris. As in our patient, those with PEO generally lack the follicular hyperkeratotic papules, palmoplantar keratoderma, widespread orange-red erythema, and characteristic histopathologic finding of hyperkeratosis with alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis, allowing these entities to be easily distinguished in most instances.10
Histopathologically, primary PEO shows a nonspecific spongiotic dermatitis-like pattern characterized by slight epidermal hyperplasia with spongiosis and a predominantly perivascular dermal infiltrate with lymphocytes, histiocytes, and eosinophils.3 These histologic findings may at times show some overlap with CTCL, and therefore T-cell gene rearrangement and flow cytometry may be performed in those instances.6
Treatment includes the management of any underlying condition causing the papuloerythroderma.3,6 There are no large clinical trials of treatment options for primary PEO due to its rarity. Topical or systemic corticosteroids remain the mainstay of treatment.3 Alternative treatments used with variable success include phototherapy, interferon, etretinate, cyclosporine, and azathioprine.11 Allegue et al11 successfully used methotrexate to treat a patient with primary PEO and postulated that methotrexate may act through an immunosuppressive mechanism on activated T cells due to the involvement of helper T cells TH2 and TH22 in its pathogenesis.
Although the cutaneous manifestations of PEO may respond well to topical steroids, it is important to consider the possible presence of an underlying malignancy and other associated systemic conditions.
- Farthing CF, Staughton RC, Harper JI, et al. Papuloerythroderma--a further case with the 'deck chair sign.' Dermatologica. 1986;172:65-66.
- Ofuji S, Furukawa F, Miyachi Y, et al. Papuloerythroderma. Dermatologica. 1984;169:125-130.
- Torchia D, Miteva M, Hu S, et al. Papuloerythroderma 2009: two new cases and systematic review of the worldwide literature 25 years after its identification by Ofuji et al. Dermatology. 2010;220:311-320.
- Ochi H, Ang CC. Novel association of a papuloerythroderma of Ofuji phenotype with dermatitis herpetiformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:856-857.
- Pai S, Shetty S, Rao R. Parthenium dermatitis with deck-chair sign. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:906-907.
- Maher AM, Ward CE, Glassman S, et al. The importance of excluding cutaneous T-cell lymphomas in patients with a working diagnosis of papuloerythroderma of Ofuji: a case series. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:46-54.
- Grob JJ, Collet-Villette AM, Horchowski N, et al. Ofuji papuloerythroderma. report of a case with T cell skin lymphoma and discussion of the nature of this disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(5 pt 2):927-931.
- Ferran M, Gallardo F, Baena V, et al. The 'deck chair sign' in specific cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Dermatology. 2006;213:50-52.
- Murao K, Sadamoto Y, Kubo Y, et al. Generalized malignant acanthosis nigricans with "deck-chair sign." Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:377-378.
- Regina G, Paramita L, Radiono S, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji in Indonesia: the first case report. JDVI. 2016;1:93-98.
- Allegue F, Fachal C, Gonzalez-Vilas D, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji successfully treated with methotrexate. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12638.
- Farthing CF, Staughton RC, Harper JI, et al. Papuloerythroderma--a further case with the 'deck chair sign.' Dermatologica. 1986;172:65-66.
- Ofuji S, Furukawa F, Miyachi Y, et al. Papuloerythroderma. Dermatologica. 1984;169:125-130.
- Torchia D, Miteva M, Hu S, et al. Papuloerythroderma 2009: two new cases and systematic review of the worldwide literature 25 years after its identification by Ofuji et al. Dermatology. 2010;220:311-320.
- Ochi H, Ang CC. Novel association of a papuloerythroderma of Ofuji phenotype with dermatitis herpetiformis. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:856-857.
- Pai S, Shetty S, Rao R. Parthenium dermatitis with deck-chair sign. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:906-907.
- Maher AM, Ward CE, Glassman S, et al. The importance of excluding cutaneous T-cell lymphomas in patients with a working diagnosis of papuloerythroderma of Ofuji: a case series. Case Rep Dermatol. 2018;10:46-54.
- Grob JJ, Collet-Villette AM, Horchowski N, et al. Ofuji papuloerythroderma. report of a case with T cell skin lymphoma and discussion of the nature of this disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(5 pt 2):927-931.
- Ferran M, Gallardo F, Baena V, et al. The 'deck chair sign' in specific cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. Dermatology. 2006;213:50-52.
- Murao K, Sadamoto Y, Kubo Y, et al. Generalized malignant acanthosis nigricans with "deck-chair sign." Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:377-378.
- Regina G, Paramita L, Radiono S, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji in Indonesia: the first case report. JDVI. 2016;1:93-98.
- Allegue F, Fachal C, Gonzalez-Vilas D, et al. Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji successfully treated with methotrexate. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31:E12638.
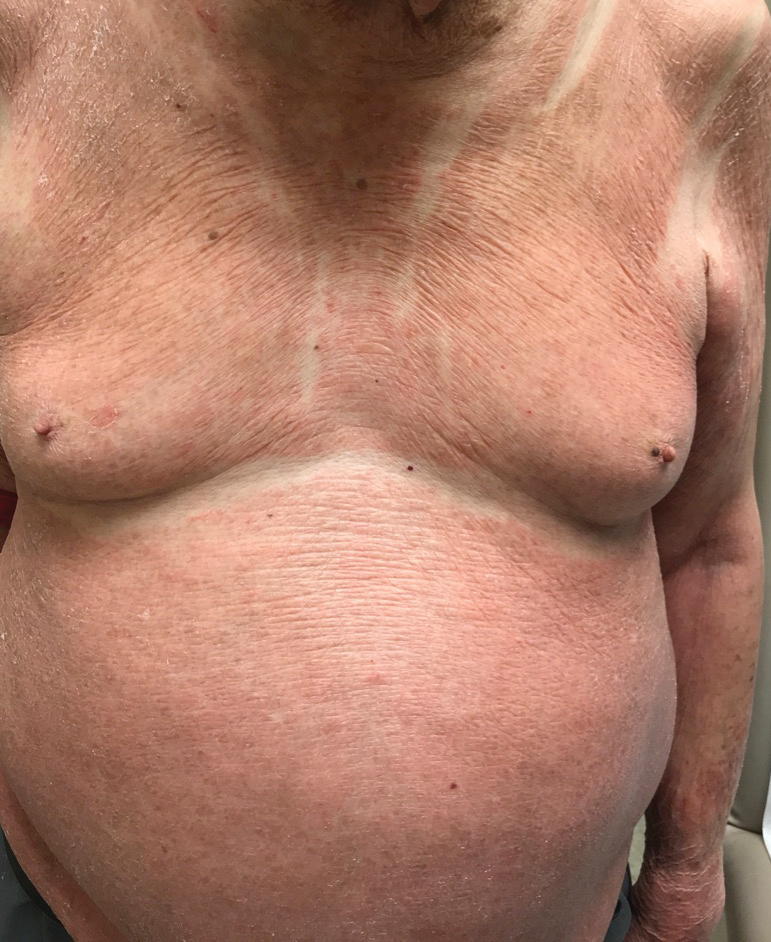
An 89-year-old Asian man presented with a generalized pruritic eruption of 2 months' duration. The rash started on the flanks and later spread to the arms and legs, abdomen, and back; the face and palms were spared. Physical examination revealed numerous erythematous papules coalescing into large scaly plaques on the trunk, arms, and legs. There were noticeable areas of sparing of the skinfolds, especially the axillary, inframammary, and inguinal folds, as well as the midline of the back. A biopsy performed by an outside physician showed findings consistent with a possible pityriasiform drug eruption; however, there were no recent changes in medication history.