User login
Free Clinic Diagnosis Data Improvement Project Using International Classification of Diseases and Electronic Health Record
From Pacific Lutheran School of Nursing, Tacoma, WA.
Objective: This quality improvement project aimed to enhance The Olympia Free Clinic’s (TOFC) data availability using
Methods: A new system was implemented for inputting ICD codes into Practice Fusion, the clinic’s EHR. During the initial phase, TOFC’s 21 volunteer providers entered the codes associated with the appropriate diagnosis for each of 157 encounters using a simplified map of options, including a map of the 20 most common diagnoses and a more comprehensive 60-code map.
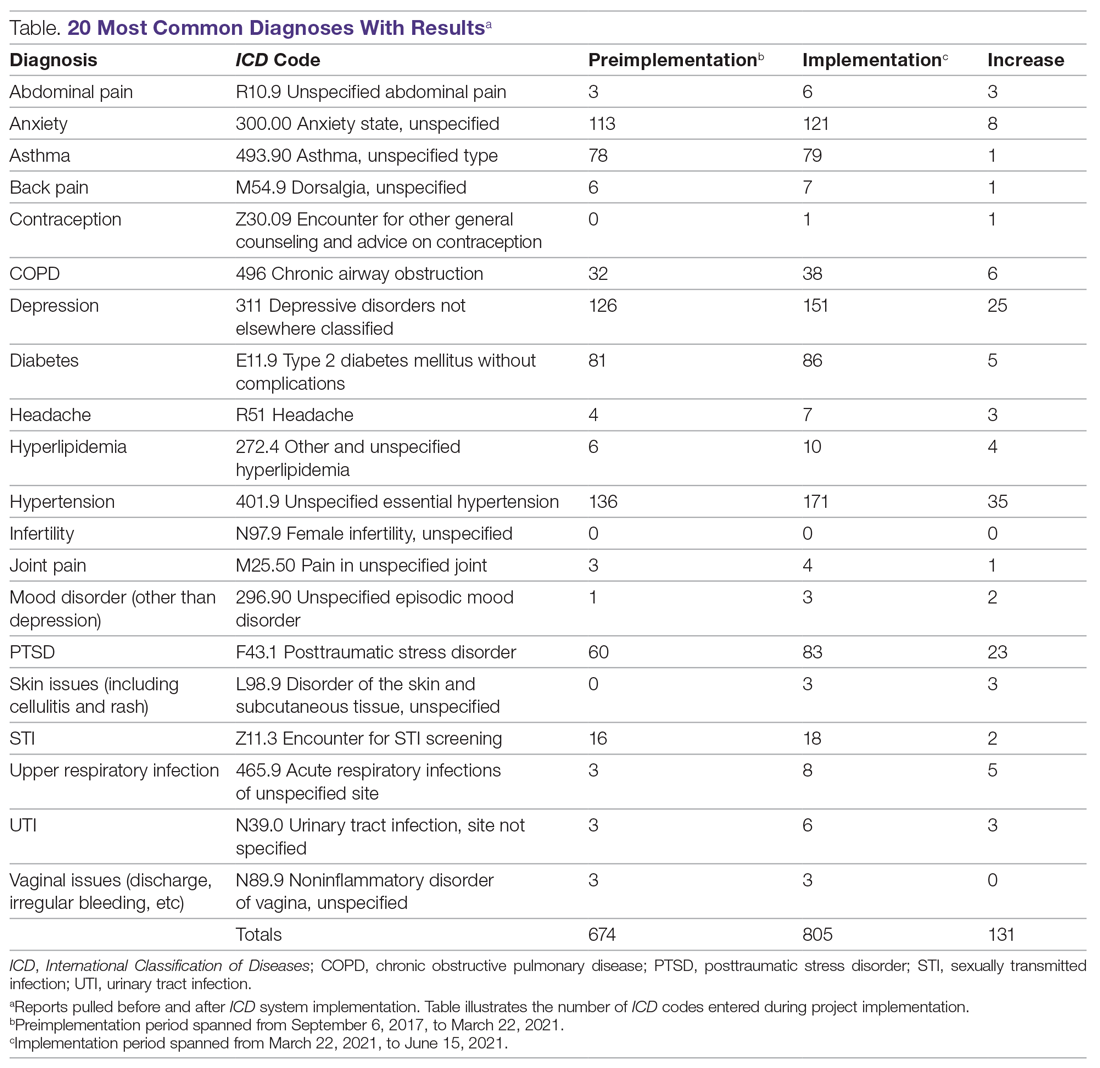
Results: An EHR report found that 128 new diagnoses were entered during project implementation, hypertension being the most common diagnosis, followed by depression, then posttraumatic stress disorder.
Conclusion: The knowledge of patient diagnoses enabled the clinic to make more-informed decisions.
Keywords: free clinic, data, quality improvement, electronic health record, International Classification of Diseases
Data creates a starting point, a goal, background, understanding of needs and context, and allows for tracking and improvement over time. This quality improvement (QI) project for The Olympia Free Clinic (TOFC) implemented a new system for tracking patient diagnoses. The 21 primary TOFC providers were encouraged to input mapped International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) codes into the electronic health record (EHR). The clinic’s providers consisted of mostly retired, but some actively practicing, medical doctors, doctors of osteopathy, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and psychiatrists.
Previous to this project, the clinic lacked any concrete data on patient demographics or diagnoses. For example, the clinic was unable to accurately answer the National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics’ questions about how many patients TOFC providers saw with diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and hyperlipidemia.1 Additionally, the needs of the clinic and its population were based on educated guesses.
As a free clinic staffed by volunteers and open 2 days a week, TOFC focused solely on giving care to those who needed it, operating pragmatically and addressing any issues as they arose. However, this strategy left the clinic unable to answer questions like “How many TOFC patients have diabetes?” By answering these questions, the clinic can better assess their resource and staffing needs.
Purpose
The project enlisted 21 volunteer providers to record diagnoses through ICD codes on the approximately 2000 active patients between March 22, 2021, and June 15, 2021. Tracking patient diagnoses improves clinic data, outcomes, and decision-making. By working on data improvement, the clinic can better understand its patient population and their needs, enhance clinical care, create better outcomes, make informed decisions, and raise eligibility for grants. The clinic was at a turning point as they reevaluated their mission statement and decided whether they would continue to focus on acute ailments or expand to formally manage chronic diseases as well. This decision needed to be made with knowledge, understanding, and context, which diagnosis data can provide. For example, the knowledge that the clinic’s 3 most common diagnoses are chronic conditions demonstrated that an official shift in their mission may have been warranted.
Literature Review
QI projects are effective and common in the free clinic setting.2-4 To the author’s knowledge, no literature to date shows the implementation of a system to better track diagnoses using a free clinic’s EHR with ICD codes.
Data bring value to clinics in many ways. It can also lead to more informed and better distribution of resources, such as preventative health and social services, patient education, and medical inventory.4
The focus of the US health care system is shifting to a value-based system under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.5 Outcome measurements and improvement play a key role in this.6 Without knowing diagnoses, we cannot effectively track outcomes and have no data on which to base improvements. Insurance and reimbursement requirements typically hold health care facilities accountable for making these outcomes and improvements a reality.5,6 Free clinics, however, lack these motivations, which explains why a free clinic may be deficient in data and tracking methods. Tracking diagnosis codes will, going forward, allow TOFC to see outcomes and trends over time, track the effectiveness of the treatments, and change course if need be.6
TOFC fully implemented the EHR in 2018, giving the clinic better capabilities for pulling reports and tracking data. Although there were growing pains, many TOFC providers were already familiar with ICD codes, which, along with an EHR, provide a system to easily retrieve, store, and analyze diagnoses for evidence-based and informed decision-making.7 This made using ICD codes and the EHR an obvious choice to track patient diagnoses. However, most of the providers were not putting them in ICD codes before this project was implemented. Instead, diagnoses were typed in the notes and, therefore, not easy to generate in a report without having to open each chart for each individual encounter and combing through the notes. To make matters worse, providers were never trained on how to enter the codes in the EHR, and most providers saw no reason to, because the clinic does not bill for services.
Methods
A needs assessment determined that TOFC lacked data. This QI project used a combination of primary and secondary continuous quality improvement data.8 The primary data came from pulling the reports on Practice Fusion to see how many times each diagnosis code was put in during the implementation phase of this project. Secondary data came from interviewing the providers and asking whether they put in the diagnosis codes.
ICD diagnosis entry
Practice Fusion is the EHR TOFC uses and was therefore the platform for this QI project. Two ICD maps were created, which incorporated both International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes. There are tens of thousands of ICD codes in existence, but because TOFC is a free clinic that does not bill or receive reimbursement, the codes did not need to be as specific as they do in a paid clinic. Therefore, the maps put all the variations of each disease into a single category. For example, every patient with diabetes would receive the same ICD code regardless of whether their diabetes was controlled, uncontrolled, or any other variation. The goal of simplifying the codes was to improve compliance with ICD code entry and make reports easier to generate. The maps allowed the options to be simplified and, therefore, more user friendly for both the providers and the data collectors pulling reports. As some ICD-9 codes were already being used, these codes were incorporated so providers could keep using what they were already familiar with. To create the map, generic ICD codes were selected to represent each disease.
An initial survey was conducted prior to implementation with 10 providers, 2 nurses, and 2 staff members, asking which diagnoses they thought were seen most often in the clinic. Based off those answers, a map was created with the 20 most commonly used ICD codes, which can be seen in the Table. A more comprehensive map was also created, with 61 encompassing diagnoses.
To start the implementation process, providers were emailed an explanation of the project, the ICD code maps, and step-by-step instructions on how to enter a diagnosis into the EHR. Additionally, the 20 most common diagnoses forms were posted on the walls at the provider stations along with pictures illustrating how to input the codes in the EHR. The more comprehensive map was attached to the nurse clipboards that accompanied each encounter. The first night the providers volunteered after receiving the email, the researcher would review with them how to input the diagnosis code and have them test the method on a practice patient, either in person or over the phone.
A starting report was pulled March 22, 2021, covering encounters between September 6, 2017, and March 22, 2021, for the 20 most common diagnoses. Another report was pulled at the completion of the implementation phase, on June 15, 2021, covering March 22, 2021, to June 15, 2021. Willing providers and staff members were surveyed after implementation completion. The providers were asked whether they use the ICD codes, whether they would do so in the future, and whether they found it helpful when other providers had entered diagnoses. If they answered no to any of the questions, there were asked why, and whether they had any suggestions for improvements. The 4 staff members were asked whether they thought the data were helpful for their role and, if so, how they would use it.
Surveys
Surveys were conducted after the project was completed with willing and available providers and staff members in order to assess the utility of the project as well as to ensure future improvements and sustainability of the system.
Provider surveys
Do you currently input mapped ICD-10 codes when you chart for each encounter?
Yes No
If yes, do you intend to continue inputting the ICD codes in your encounters in the future?
Yes No
If no to either question above, please explain:
Do you have any recommendations for making it easier to input ICD codes or another way to track patients’ diagnoses?
Staff surveys
Is this data helpful for your role?
Yes No
If yes, how will you use this data?
Results
During the implementation phase, hypertension was the most common diagnosis seen at TOFC, accounting for 35 of 131 (27%) top 20 diagnoses entered. Depression was second, accounting for about 20% of diagnoses. Posttraumatic stress disorder was the third most common, making up 18% of diagnoses. There were 157 encounters during the implementation phase and 128 ICD diagnoses entered into the chart during this time period, suggesting that most encounters had a corresponding diagnosis code entered. See the Table for more details.
Survey results
Provider surveys
Six providers answered the survey questions. Four answered “yes” to both questions and 2 answered “no” to both questions. Reasons cited for why they did not input the ICD codes included not remembering to enter the codes or not remembering how to enter the codes. Recommendations for making it easier included incorporating the diagnosis in the assessment section of the EHR instead of standing alone as its own section, replacing ICD-9 codes with ICD-10 codes on the maps, making more specific codes for options, like typing more mental health diagnoses, and implementing more training on how to enter the codes.
Staff surveys
Three of 4 staff members responded to the survey. All 3 indicated that the data collected from this project assisted in their role. Stated uses for this data included grant applications and funding; community education, such as presentations and outreach; program development and monitoring; quality improvement; supply purchasing (eg, medications in stock to treat most commonly seen conditions), scheduling clinics and providers; allocating resources and supplies; and accepting or rejecting medical supply donations.
Discussion
Before this project, 668 of the top 20 most common diagnosis codes were entered from when TOFC introduced use of the EHR in the clinic in 2017, until the beginning of the implementation phase of this project in March 2021. During the 3 months of the implementation phase, 131 diagnoses were entered, representing almost 20% of the amount that were entered in 3 and a half years. Pulling the reports for these 20 diagnoses took less than 1 hour. During the needs assessment phase of this project, diagnoses for 3 months were extracted from the EHR by combing through provider notes and extracting the data from the notes—a process that took 11 hours.
Knowledge of diagnoses and the reasons for clinic attendance help the clinic make decisions about staffing, resources, and services. The TOFC board of directors used this data to assist with the decision of whether or not to change the clinic’s mission to include primary care as an official clinic function. The original purpose of the clinic was to address acute issues for people who lacked the resources for medical care. For example, a homeless person with an abscess could come to the clinic and have the abscess drained and treated. The results of this project illustrate that, in reality, most of the diagnoses actually seen in the clinic are more chronic in nature and require consistent, ongoing care. For instance, the project identified 52 clinic patients receiving consistent diabetic care. This type of data can help the clinic determine whether it should accept diabetes-associated donations and whether it needs to recruit a volunteer diabetes educator. Generally, this data can help guide other decisions as well, like what medications should be kept in the pharmacy, whether there are certain specialists the clinic should seek to partner with, and whether the clinic should embark on any particular education campaigns. By inputting ICD codes, diagnosis data are easily obtained to assist with future decisions.
A limitation of this project was that the reports could only be pulled within a certain time frame if the start date of the diagnosis was specified. As most providers did not indicate a start date with their entered diagnosis code, the only way to compare the before and after was to count the total before and the total after the implementation time frame. In other words, comparison reports could not be pulled retroactively, so some data on the less common diagnosis codes are missing from this paper, as reports for the comprehensive map were not pulled ahead of time. Providers may have omitted the start date when entering the diagnosis codes because many of these patients had their diagnoses for years—seeing different providers each time—so starting the diagnosis at that particular encounter did not make sense. Additionally, during training, although how to enter the start date was demonstrated, the emphasis and priority was placed on actually entering the ICD code, in an effort to keep the process simple and increase participation.
Conclusion
Evidence-based care and informed decision-making require data. In a free clinic, this can be difficult to obtain due to limited staffing and the absence of billing and insurance requirements. ICD codes and EHRs are powerful tools to collect data and information about clinic needs. This project improved TOFC’s knowledge about what kind of patients and diagnoses they see.
Corresponding author: Sarah M. Shanahan, MSN, RN, Pacific Lutheran University School of Nursing, Ramstad, Room 214, Tacoma, WA 98447; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics. 2021 NAFC Member Data & Standards Report. https://www.nafcclinics.org/sites/default/files/NAFC%202021%20Data%20Report%20Final.pdf
2. Lee JS, Combs K, Pasarica M; KNIGHTS Research Group. Improving efficiency while improving patient care in a student-run free clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2017;30(4):513-519. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2017.04.170044
3. Lu KB, Thiel B, Atkins CA, et al. Satisfaction with healthcare received at an interprofessional student-run free clinic: invested in training the next generation of healthcare professionals. Cureus. 2018;10(3):e2282. doi:10.7759/cureus.2282
4. Tran T, Briones C, Gillet AS, et al. “Knowing” your population: who are we caring for at Tulane University School of Medicine’s student-run free clinics? J Public Health (Oxf). 2020:1-7. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01389-7
5. Sennett C. Healthcare reform: quality outcomes measurement and reporting. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2010;3(5):350-352.
6. Mazzali C, Duca P. Use of administrative data in healthcare research. Intern Emerg Med. 2015;10(4):517-524. doi:10.1007/s11739-015-1213-9
7. Moons E, Khanna A, Akkasi A, Moens MF. A comparison of deep learning methods for ICD coding of clinical records. Appl Sci. 2020;10(15):5262. doi:10.3390/app10155262
8. Finkelman A. Quality Improvement: A Guide for Integration in Nursing. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2018.
From Pacific Lutheran School of Nursing, Tacoma, WA.
Objective: This quality improvement project aimed to enhance The Olympia Free Clinic’s (TOFC) data availability using
Methods: A new system was implemented for inputting ICD codes into Practice Fusion, the clinic’s EHR. During the initial phase, TOFC’s 21 volunteer providers entered the codes associated with the appropriate diagnosis for each of 157 encounters using a simplified map of options, including a map of the 20 most common diagnoses and a more comprehensive 60-code map.
Results: An EHR report found that 128 new diagnoses were entered during project implementation, hypertension being the most common diagnosis, followed by depression, then posttraumatic stress disorder.
Conclusion: The knowledge of patient diagnoses enabled the clinic to make more-informed decisions.
Keywords: free clinic, data, quality improvement, electronic health record, International Classification of Diseases
Data creates a starting point, a goal, background, understanding of needs and context, and allows for tracking and improvement over time. This quality improvement (QI) project for The Olympia Free Clinic (TOFC) implemented a new system for tracking patient diagnoses. The 21 primary TOFC providers were encouraged to input mapped International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) codes into the electronic health record (EHR). The clinic’s providers consisted of mostly retired, but some actively practicing, medical doctors, doctors of osteopathy, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and psychiatrists.
Previous to this project, the clinic lacked any concrete data on patient demographics or diagnoses. For example, the clinic was unable to accurately answer the National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics’ questions about how many patients TOFC providers saw with diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and hyperlipidemia.1 Additionally, the needs of the clinic and its population were based on educated guesses.
As a free clinic staffed by volunteers and open 2 days a week, TOFC focused solely on giving care to those who needed it, operating pragmatically and addressing any issues as they arose. However, this strategy left the clinic unable to answer questions like “How many TOFC patients have diabetes?” By answering these questions, the clinic can better assess their resource and staffing needs.
Purpose
The project enlisted 21 volunteer providers to record diagnoses through ICD codes on the approximately 2000 active patients between March 22, 2021, and June 15, 2021. Tracking patient diagnoses improves clinic data, outcomes, and decision-making. By working on data improvement, the clinic can better understand its patient population and their needs, enhance clinical care, create better outcomes, make informed decisions, and raise eligibility for grants. The clinic was at a turning point as they reevaluated their mission statement and decided whether they would continue to focus on acute ailments or expand to formally manage chronic diseases as well. This decision needed to be made with knowledge, understanding, and context, which diagnosis data can provide. For example, the knowledge that the clinic’s 3 most common diagnoses are chronic conditions demonstrated that an official shift in their mission may have been warranted.
Literature Review
QI projects are effective and common in the free clinic setting.2-4 To the author’s knowledge, no literature to date shows the implementation of a system to better track diagnoses using a free clinic’s EHR with ICD codes.
Data bring value to clinics in many ways. It can also lead to more informed and better distribution of resources, such as preventative health and social services, patient education, and medical inventory.4
The focus of the US health care system is shifting to a value-based system under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.5 Outcome measurements and improvement play a key role in this.6 Without knowing diagnoses, we cannot effectively track outcomes and have no data on which to base improvements. Insurance and reimbursement requirements typically hold health care facilities accountable for making these outcomes and improvements a reality.5,6 Free clinics, however, lack these motivations, which explains why a free clinic may be deficient in data and tracking methods. Tracking diagnosis codes will, going forward, allow TOFC to see outcomes and trends over time, track the effectiveness of the treatments, and change course if need be.6
TOFC fully implemented the EHR in 2018, giving the clinic better capabilities for pulling reports and tracking data. Although there were growing pains, many TOFC providers were already familiar with ICD codes, which, along with an EHR, provide a system to easily retrieve, store, and analyze diagnoses for evidence-based and informed decision-making.7 This made using ICD codes and the EHR an obvious choice to track patient diagnoses. However, most of the providers were not putting them in ICD codes before this project was implemented. Instead, diagnoses were typed in the notes and, therefore, not easy to generate in a report without having to open each chart for each individual encounter and combing through the notes. To make matters worse, providers were never trained on how to enter the codes in the EHR, and most providers saw no reason to, because the clinic does not bill for services.
Methods
A needs assessment determined that TOFC lacked data. This QI project used a combination of primary and secondary continuous quality improvement data.8 The primary data came from pulling the reports on Practice Fusion to see how many times each diagnosis code was put in during the implementation phase of this project. Secondary data came from interviewing the providers and asking whether they put in the diagnosis codes.
ICD diagnosis entry
Practice Fusion is the EHR TOFC uses and was therefore the platform for this QI project. Two ICD maps were created, which incorporated both International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes. There are tens of thousands of ICD codes in existence, but because TOFC is a free clinic that does not bill or receive reimbursement, the codes did not need to be as specific as they do in a paid clinic. Therefore, the maps put all the variations of each disease into a single category. For example, every patient with diabetes would receive the same ICD code regardless of whether their diabetes was controlled, uncontrolled, or any other variation. The goal of simplifying the codes was to improve compliance with ICD code entry and make reports easier to generate. The maps allowed the options to be simplified and, therefore, more user friendly for both the providers and the data collectors pulling reports. As some ICD-9 codes were already being used, these codes were incorporated so providers could keep using what they were already familiar with. To create the map, generic ICD codes were selected to represent each disease.
An initial survey was conducted prior to implementation with 10 providers, 2 nurses, and 2 staff members, asking which diagnoses they thought were seen most often in the clinic. Based off those answers, a map was created with the 20 most commonly used ICD codes, which can be seen in the Table. A more comprehensive map was also created, with 61 encompassing diagnoses.

To start the implementation process, providers were emailed an explanation of the project, the ICD code maps, and step-by-step instructions on how to enter a diagnosis into the EHR. Additionally, the 20 most common diagnoses forms were posted on the walls at the provider stations along with pictures illustrating how to input the codes in the EHR. The more comprehensive map was attached to the nurse clipboards that accompanied each encounter. The first night the providers volunteered after receiving the email, the researcher would review with them how to input the diagnosis code and have them test the method on a practice patient, either in person or over the phone.
A starting report was pulled March 22, 2021, covering encounters between September 6, 2017, and March 22, 2021, for the 20 most common diagnoses. Another report was pulled at the completion of the implementation phase, on June 15, 2021, covering March 22, 2021, to June 15, 2021. Willing providers and staff members were surveyed after implementation completion. The providers were asked whether they use the ICD codes, whether they would do so in the future, and whether they found it helpful when other providers had entered diagnoses. If they answered no to any of the questions, there were asked why, and whether they had any suggestions for improvements. The 4 staff members were asked whether they thought the data were helpful for their role and, if so, how they would use it.
Surveys
Surveys were conducted after the project was completed with willing and available providers and staff members in order to assess the utility of the project as well as to ensure future improvements and sustainability of the system.
Provider surveys
Do you currently input mapped ICD-10 codes when you chart for each encounter?
Yes No
If yes, do you intend to continue inputting the ICD codes in your encounters in the future?
Yes No
If no to either question above, please explain:
Do you have any recommendations for making it easier to input ICD codes or another way to track patients’ diagnoses?
Staff surveys
Is this data helpful for your role?
Yes No
If yes, how will you use this data?
Results
During the implementation phase, hypertension was the most common diagnosis seen at TOFC, accounting for 35 of 131 (27%) top 20 diagnoses entered. Depression was second, accounting for about 20% of diagnoses. Posttraumatic stress disorder was the third most common, making up 18% of diagnoses. There were 157 encounters during the implementation phase and 128 ICD diagnoses entered into the chart during this time period, suggesting that most encounters had a corresponding diagnosis code entered. See the Table for more details.
Survey results
Provider surveys
Six providers answered the survey questions. Four answered “yes” to both questions and 2 answered “no” to both questions. Reasons cited for why they did not input the ICD codes included not remembering to enter the codes or not remembering how to enter the codes. Recommendations for making it easier included incorporating the diagnosis in the assessment section of the EHR instead of standing alone as its own section, replacing ICD-9 codes with ICD-10 codes on the maps, making more specific codes for options, like typing more mental health diagnoses, and implementing more training on how to enter the codes.
Staff surveys
Three of 4 staff members responded to the survey. All 3 indicated that the data collected from this project assisted in their role. Stated uses for this data included grant applications and funding; community education, such as presentations and outreach; program development and monitoring; quality improvement; supply purchasing (eg, medications in stock to treat most commonly seen conditions), scheduling clinics and providers; allocating resources and supplies; and accepting or rejecting medical supply donations.
Discussion
Before this project, 668 of the top 20 most common diagnosis codes were entered from when TOFC introduced use of the EHR in the clinic in 2017, until the beginning of the implementation phase of this project in March 2021. During the 3 months of the implementation phase, 131 diagnoses were entered, representing almost 20% of the amount that were entered in 3 and a half years. Pulling the reports for these 20 diagnoses took less than 1 hour. During the needs assessment phase of this project, diagnoses for 3 months were extracted from the EHR by combing through provider notes and extracting the data from the notes—a process that took 11 hours.
Knowledge of diagnoses and the reasons for clinic attendance help the clinic make decisions about staffing, resources, and services. The TOFC board of directors used this data to assist with the decision of whether or not to change the clinic’s mission to include primary care as an official clinic function. The original purpose of the clinic was to address acute issues for people who lacked the resources for medical care. For example, a homeless person with an abscess could come to the clinic and have the abscess drained and treated. The results of this project illustrate that, in reality, most of the diagnoses actually seen in the clinic are more chronic in nature and require consistent, ongoing care. For instance, the project identified 52 clinic patients receiving consistent diabetic care. This type of data can help the clinic determine whether it should accept diabetes-associated donations and whether it needs to recruit a volunteer diabetes educator. Generally, this data can help guide other decisions as well, like what medications should be kept in the pharmacy, whether there are certain specialists the clinic should seek to partner with, and whether the clinic should embark on any particular education campaigns. By inputting ICD codes, diagnosis data are easily obtained to assist with future decisions.
A limitation of this project was that the reports could only be pulled within a certain time frame if the start date of the diagnosis was specified. As most providers did not indicate a start date with their entered diagnosis code, the only way to compare the before and after was to count the total before and the total after the implementation time frame. In other words, comparison reports could not be pulled retroactively, so some data on the less common diagnosis codes are missing from this paper, as reports for the comprehensive map were not pulled ahead of time. Providers may have omitted the start date when entering the diagnosis codes because many of these patients had their diagnoses for years—seeing different providers each time—so starting the diagnosis at that particular encounter did not make sense. Additionally, during training, although how to enter the start date was demonstrated, the emphasis and priority was placed on actually entering the ICD code, in an effort to keep the process simple and increase participation.
Conclusion
Evidence-based care and informed decision-making require data. In a free clinic, this can be difficult to obtain due to limited staffing and the absence of billing and insurance requirements. ICD codes and EHRs are powerful tools to collect data and information about clinic needs. This project improved TOFC’s knowledge about what kind of patients and diagnoses they see.
Corresponding author: Sarah M. Shanahan, MSN, RN, Pacific Lutheran University School of Nursing, Ramstad, Room 214, Tacoma, WA 98447; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
From Pacific Lutheran School of Nursing, Tacoma, WA.
Objective: This quality improvement project aimed to enhance The Olympia Free Clinic’s (TOFC) data availability using
Methods: A new system was implemented for inputting ICD codes into Practice Fusion, the clinic’s EHR. During the initial phase, TOFC’s 21 volunteer providers entered the codes associated with the appropriate diagnosis for each of 157 encounters using a simplified map of options, including a map of the 20 most common diagnoses and a more comprehensive 60-code map.
Results: An EHR report found that 128 new diagnoses were entered during project implementation, hypertension being the most common diagnosis, followed by depression, then posttraumatic stress disorder.
Conclusion: The knowledge of patient diagnoses enabled the clinic to make more-informed decisions.
Keywords: free clinic, data, quality improvement, electronic health record, International Classification of Diseases
Data creates a starting point, a goal, background, understanding of needs and context, and allows for tracking and improvement over time. This quality improvement (QI) project for The Olympia Free Clinic (TOFC) implemented a new system for tracking patient diagnoses. The 21 primary TOFC providers were encouraged to input mapped International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) codes into the electronic health record (EHR). The clinic’s providers consisted of mostly retired, but some actively practicing, medical doctors, doctors of osteopathy, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and psychiatrists.
Previous to this project, the clinic lacked any concrete data on patient demographics or diagnoses. For example, the clinic was unable to accurately answer the National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics’ questions about how many patients TOFC providers saw with diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and hyperlipidemia.1 Additionally, the needs of the clinic and its population were based on educated guesses.
As a free clinic staffed by volunteers and open 2 days a week, TOFC focused solely on giving care to those who needed it, operating pragmatically and addressing any issues as they arose. However, this strategy left the clinic unable to answer questions like “How many TOFC patients have diabetes?” By answering these questions, the clinic can better assess their resource and staffing needs.
Purpose
The project enlisted 21 volunteer providers to record diagnoses through ICD codes on the approximately 2000 active patients between March 22, 2021, and June 15, 2021. Tracking patient diagnoses improves clinic data, outcomes, and decision-making. By working on data improvement, the clinic can better understand its patient population and their needs, enhance clinical care, create better outcomes, make informed decisions, and raise eligibility for grants. The clinic was at a turning point as they reevaluated their mission statement and decided whether they would continue to focus on acute ailments or expand to formally manage chronic diseases as well. This decision needed to be made with knowledge, understanding, and context, which diagnosis data can provide. For example, the knowledge that the clinic’s 3 most common diagnoses are chronic conditions demonstrated that an official shift in their mission may have been warranted.
Literature Review
QI projects are effective and common in the free clinic setting.2-4 To the author’s knowledge, no literature to date shows the implementation of a system to better track diagnoses using a free clinic’s EHR with ICD codes.
Data bring value to clinics in many ways. It can also lead to more informed and better distribution of resources, such as preventative health and social services, patient education, and medical inventory.4
The focus of the US health care system is shifting to a value-based system under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.5 Outcome measurements and improvement play a key role in this.6 Without knowing diagnoses, we cannot effectively track outcomes and have no data on which to base improvements. Insurance and reimbursement requirements typically hold health care facilities accountable for making these outcomes and improvements a reality.5,6 Free clinics, however, lack these motivations, which explains why a free clinic may be deficient in data and tracking methods. Tracking diagnosis codes will, going forward, allow TOFC to see outcomes and trends over time, track the effectiveness of the treatments, and change course if need be.6
TOFC fully implemented the EHR in 2018, giving the clinic better capabilities for pulling reports and tracking data. Although there were growing pains, many TOFC providers were already familiar with ICD codes, which, along with an EHR, provide a system to easily retrieve, store, and analyze diagnoses for evidence-based and informed decision-making.7 This made using ICD codes and the EHR an obvious choice to track patient diagnoses. However, most of the providers were not putting them in ICD codes before this project was implemented. Instead, diagnoses were typed in the notes and, therefore, not easy to generate in a report without having to open each chart for each individual encounter and combing through the notes. To make matters worse, providers were never trained on how to enter the codes in the EHR, and most providers saw no reason to, because the clinic does not bill for services.
Methods
A needs assessment determined that TOFC lacked data. This QI project used a combination of primary and secondary continuous quality improvement data.8 The primary data came from pulling the reports on Practice Fusion to see how many times each diagnosis code was put in during the implementation phase of this project. Secondary data came from interviewing the providers and asking whether they put in the diagnosis codes.
ICD diagnosis entry
Practice Fusion is the EHR TOFC uses and was therefore the platform for this QI project. Two ICD maps were created, which incorporated both International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes. There are tens of thousands of ICD codes in existence, but because TOFC is a free clinic that does not bill or receive reimbursement, the codes did not need to be as specific as they do in a paid clinic. Therefore, the maps put all the variations of each disease into a single category. For example, every patient with diabetes would receive the same ICD code regardless of whether their diabetes was controlled, uncontrolled, or any other variation. The goal of simplifying the codes was to improve compliance with ICD code entry and make reports easier to generate. The maps allowed the options to be simplified and, therefore, more user friendly for both the providers and the data collectors pulling reports. As some ICD-9 codes were already being used, these codes were incorporated so providers could keep using what they were already familiar with. To create the map, generic ICD codes were selected to represent each disease.
An initial survey was conducted prior to implementation with 10 providers, 2 nurses, and 2 staff members, asking which diagnoses they thought were seen most often in the clinic. Based off those answers, a map was created with the 20 most commonly used ICD codes, which can be seen in the Table. A more comprehensive map was also created, with 61 encompassing diagnoses.

To start the implementation process, providers were emailed an explanation of the project, the ICD code maps, and step-by-step instructions on how to enter a diagnosis into the EHR. Additionally, the 20 most common diagnoses forms were posted on the walls at the provider stations along with pictures illustrating how to input the codes in the EHR. The more comprehensive map was attached to the nurse clipboards that accompanied each encounter. The first night the providers volunteered after receiving the email, the researcher would review with them how to input the diagnosis code and have them test the method on a practice patient, either in person or over the phone.
A starting report was pulled March 22, 2021, covering encounters between September 6, 2017, and March 22, 2021, for the 20 most common diagnoses. Another report was pulled at the completion of the implementation phase, on June 15, 2021, covering March 22, 2021, to June 15, 2021. Willing providers and staff members were surveyed after implementation completion. The providers were asked whether they use the ICD codes, whether they would do so in the future, and whether they found it helpful when other providers had entered diagnoses. If they answered no to any of the questions, there were asked why, and whether they had any suggestions for improvements. The 4 staff members were asked whether they thought the data were helpful for their role and, if so, how they would use it.
Surveys
Surveys were conducted after the project was completed with willing and available providers and staff members in order to assess the utility of the project as well as to ensure future improvements and sustainability of the system.
Provider surveys
Do you currently input mapped ICD-10 codes when you chart for each encounter?
Yes No
If yes, do you intend to continue inputting the ICD codes in your encounters in the future?
Yes No
If no to either question above, please explain:
Do you have any recommendations for making it easier to input ICD codes or another way to track patients’ diagnoses?
Staff surveys
Is this data helpful for your role?
Yes No
If yes, how will you use this data?
Results
During the implementation phase, hypertension was the most common diagnosis seen at TOFC, accounting for 35 of 131 (27%) top 20 diagnoses entered. Depression was second, accounting for about 20% of diagnoses. Posttraumatic stress disorder was the third most common, making up 18% of diagnoses. There were 157 encounters during the implementation phase and 128 ICD diagnoses entered into the chart during this time period, suggesting that most encounters had a corresponding diagnosis code entered. See the Table for more details.
Survey results
Provider surveys
Six providers answered the survey questions. Four answered “yes” to both questions and 2 answered “no” to both questions. Reasons cited for why they did not input the ICD codes included not remembering to enter the codes or not remembering how to enter the codes. Recommendations for making it easier included incorporating the diagnosis in the assessment section of the EHR instead of standing alone as its own section, replacing ICD-9 codes with ICD-10 codes on the maps, making more specific codes for options, like typing more mental health diagnoses, and implementing more training on how to enter the codes.
Staff surveys
Three of 4 staff members responded to the survey. All 3 indicated that the data collected from this project assisted in their role. Stated uses for this data included grant applications and funding; community education, such as presentations and outreach; program development and monitoring; quality improvement; supply purchasing (eg, medications in stock to treat most commonly seen conditions), scheduling clinics and providers; allocating resources and supplies; and accepting or rejecting medical supply donations.
Discussion
Before this project, 668 of the top 20 most common diagnosis codes were entered from when TOFC introduced use of the EHR in the clinic in 2017, until the beginning of the implementation phase of this project in March 2021. During the 3 months of the implementation phase, 131 diagnoses were entered, representing almost 20% of the amount that were entered in 3 and a half years. Pulling the reports for these 20 diagnoses took less than 1 hour. During the needs assessment phase of this project, diagnoses for 3 months were extracted from the EHR by combing through provider notes and extracting the data from the notes—a process that took 11 hours.
Knowledge of diagnoses and the reasons for clinic attendance help the clinic make decisions about staffing, resources, and services. The TOFC board of directors used this data to assist with the decision of whether or not to change the clinic’s mission to include primary care as an official clinic function. The original purpose of the clinic was to address acute issues for people who lacked the resources for medical care. For example, a homeless person with an abscess could come to the clinic and have the abscess drained and treated. The results of this project illustrate that, in reality, most of the diagnoses actually seen in the clinic are more chronic in nature and require consistent, ongoing care. For instance, the project identified 52 clinic patients receiving consistent diabetic care. This type of data can help the clinic determine whether it should accept diabetes-associated donations and whether it needs to recruit a volunteer diabetes educator. Generally, this data can help guide other decisions as well, like what medications should be kept in the pharmacy, whether there are certain specialists the clinic should seek to partner with, and whether the clinic should embark on any particular education campaigns. By inputting ICD codes, diagnosis data are easily obtained to assist with future decisions.
A limitation of this project was that the reports could only be pulled within a certain time frame if the start date of the diagnosis was specified. As most providers did not indicate a start date with their entered diagnosis code, the only way to compare the before and after was to count the total before and the total after the implementation time frame. In other words, comparison reports could not be pulled retroactively, so some data on the less common diagnosis codes are missing from this paper, as reports for the comprehensive map were not pulled ahead of time. Providers may have omitted the start date when entering the diagnosis codes because many of these patients had their diagnoses for years—seeing different providers each time—so starting the diagnosis at that particular encounter did not make sense. Additionally, during training, although how to enter the start date was demonstrated, the emphasis and priority was placed on actually entering the ICD code, in an effort to keep the process simple and increase participation.
Conclusion
Evidence-based care and informed decision-making require data. In a free clinic, this can be difficult to obtain due to limited staffing and the absence of billing and insurance requirements. ICD codes and EHRs are powerful tools to collect data and information about clinic needs. This project improved TOFC’s knowledge about what kind of patients and diagnoses they see.
Corresponding author: Sarah M. Shanahan, MSN, RN, Pacific Lutheran University School of Nursing, Ramstad, Room 214, Tacoma, WA 98447; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics. 2021 NAFC Member Data & Standards Report. https://www.nafcclinics.org/sites/default/files/NAFC%202021%20Data%20Report%20Final.pdf
2. Lee JS, Combs K, Pasarica M; KNIGHTS Research Group. Improving efficiency while improving patient care in a student-run free clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2017;30(4):513-519. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2017.04.170044
3. Lu KB, Thiel B, Atkins CA, et al. Satisfaction with healthcare received at an interprofessional student-run free clinic: invested in training the next generation of healthcare professionals. Cureus. 2018;10(3):e2282. doi:10.7759/cureus.2282
4. Tran T, Briones C, Gillet AS, et al. “Knowing” your population: who are we caring for at Tulane University School of Medicine’s student-run free clinics? J Public Health (Oxf). 2020:1-7. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01389-7
5. Sennett C. Healthcare reform: quality outcomes measurement and reporting. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2010;3(5):350-352.
6. Mazzali C, Duca P. Use of administrative data in healthcare research. Intern Emerg Med. 2015;10(4):517-524. doi:10.1007/s11739-015-1213-9
7. Moons E, Khanna A, Akkasi A, Moens MF. A comparison of deep learning methods for ICD coding of clinical records. Appl Sci. 2020;10(15):5262. doi:10.3390/app10155262
8. Finkelman A. Quality Improvement: A Guide for Integration in Nursing. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2018.
1. National Association of Free and Charitable Clinics. 2021 NAFC Member Data & Standards Report. https://www.nafcclinics.org/sites/default/files/NAFC%202021%20Data%20Report%20Final.pdf
2. Lee JS, Combs K, Pasarica M; KNIGHTS Research Group. Improving efficiency while improving patient care in a student-run free clinic. J Am Board Fam Med. 2017;30(4):513-519. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2017.04.170044
3. Lu KB, Thiel B, Atkins CA, et al. Satisfaction with healthcare received at an interprofessional student-run free clinic: invested in training the next generation of healthcare professionals. Cureus. 2018;10(3):e2282. doi:10.7759/cureus.2282
4. Tran T, Briones C, Gillet AS, et al. “Knowing” your population: who are we caring for at Tulane University School of Medicine’s student-run free clinics? J Public Health (Oxf). 2020:1-7. doi:10.1007/s10389-020-01389-7
5. Sennett C. Healthcare reform: quality outcomes measurement and reporting. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2010;3(5):350-352.
6. Mazzali C, Duca P. Use of administrative data in healthcare research. Intern Emerg Med. 2015;10(4):517-524. doi:10.1007/s11739-015-1213-9
7. Moons E, Khanna A, Akkasi A, Moens MF. A comparison of deep learning methods for ICD coding of clinical records. Appl Sci. 2020;10(15):5262. doi:10.3390/app10155262
8. Finkelman A. Quality Improvement: A Guide for Integration in Nursing. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2018.
Gratitude, reflection, and catnaps with the dog
Now we’re in the final sprint.
Thanksgiving week is the first pause. I’m lucky. I have more things to be grateful for than I can count. I try to keep that in mind and instill it in my kids.
The second pause comes in December. I always close my office for the last 2 weeks of the year, since most patients are too busy during that time to see me. That means, in a little less than a month from now, my 2021 will be (from a practice point of view) pretty much over.
Of course, it’s really not. Just because the office is closed doesn’t mean there isn’t stuff to do. Patients will call in with pressing issues; refills have to be sent; test results come in and need to be handled correctly.
And that’s just the clinical part. The business part is there, too. It’s time to start wrapping up the corporate year, doing quarterly 941 forms, and preparing stuff for my accountant to file my taxes in the new year. Sifting through receipts, bills, and Quickbooks to get things ready.
But it’s still a relaxing time. My kids will all be home. We’ll have family dinners again for a few weeks. My hot tub will (hopefully) be up and running. I’ll have more time for walks, or talks, or naps (the last one usually with a dog sprawled out on the bed). For 2 weeks I can sleep in.
It also brings reflection. The same applies to personal thoughts: What can I do in the coming year to be a better person and a better doctor?
Two weeks off never seems like long enough, but it’s a good time to pause and think about my little world, and what I can change to make it better for all involved.
That kind of perspective should always be kept in mind, but in the day-to-day hectic world, often it isn’t. It’s important to put it back in place when I can.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Now we’re in the final sprint.
Thanksgiving week is the first pause. I’m lucky. I have more things to be grateful for than I can count. I try to keep that in mind and instill it in my kids.
The second pause comes in December. I always close my office for the last 2 weeks of the year, since most patients are too busy during that time to see me. That means, in a little less than a month from now, my 2021 will be (from a practice point of view) pretty much over.
Of course, it’s really not. Just because the office is closed doesn’t mean there isn’t stuff to do. Patients will call in with pressing issues; refills have to be sent; test results come in and need to be handled correctly.
And that’s just the clinical part. The business part is there, too. It’s time to start wrapping up the corporate year, doing quarterly 941 forms, and preparing stuff for my accountant to file my taxes in the new year. Sifting through receipts, bills, and Quickbooks to get things ready.
But it’s still a relaxing time. My kids will all be home. We’ll have family dinners again for a few weeks. My hot tub will (hopefully) be up and running. I’ll have more time for walks, or talks, or naps (the last one usually with a dog sprawled out on the bed). For 2 weeks I can sleep in.
It also brings reflection. The same applies to personal thoughts: What can I do in the coming year to be a better person and a better doctor?
Two weeks off never seems like long enough, but it’s a good time to pause and think about my little world, and what I can change to make it better for all involved.
That kind of perspective should always be kept in mind, but in the day-to-day hectic world, often it isn’t. It’s important to put it back in place when I can.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Now we’re in the final sprint.
Thanksgiving week is the first pause. I’m lucky. I have more things to be grateful for than I can count. I try to keep that in mind and instill it in my kids.
The second pause comes in December. I always close my office for the last 2 weeks of the year, since most patients are too busy during that time to see me. That means, in a little less than a month from now, my 2021 will be (from a practice point of view) pretty much over.
Of course, it’s really not. Just because the office is closed doesn’t mean there isn’t stuff to do. Patients will call in with pressing issues; refills have to be sent; test results come in and need to be handled correctly.
And that’s just the clinical part. The business part is there, too. It’s time to start wrapping up the corporate year, doing quarterly 941 forms, and preparing stuff for my accountant to file my taxes in the new year. Sifting through receipts, bills, and Quickbooks to get things ready.
But it’s still a relaxing time. My kids will all be home. We’ll have family dinners again for a few weeks. My hot tub will (hopefully) be up and running. I’ll have more time for walks, or talks, or naps (the last one usually with a dog sprawled out on the bed). For 2 weeks I can sleep in.
It also brings reflection. The same applies to personal thoughts: What can I do in the coming year to be a better person and a better doctor?
Two weeks off never seems like long enough, but it’s a good time to pause and think about my little world, and what I can change to make it better for all involved.
That kind of perspective should always be kept in mind, but in the day-to-day hectic world, often it isn’t. It’s important to put it back in place when I can.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Neurologist guilty of overprescribing thousands of doses of painkillers
Ohio doctor convicted of prescribing unnecessary controlled substances, fraud
A federal jury found William R. Bauer, 84, of Port Clinton, Ohio, guilty of prescribing powerful controlled substances, including opioids, to patients without medical necessity and outside the usual course of medical practice.
Dr. Bauer, a neurologist with over 50 years of experience, was convicted of 76 counts of distribution of controlled substances and 25 counts of healthcare fraud. According to television station WTOL, a federal indictment from 2019 listed 270 charges against the physician.
Federal officials claim that through his practice in Bellevue, Ohio, Dr. Bauer repeatedly prescribed controlled substances, including oxycodone, fentanyl, morphine, and tramadol, outside the usual course of professional practice and without legitimate medical purpose. The charges focused on 14 of his patients, to whom he prescribed high doses of opioids and other controlled substances without medical necessity. He also prescribed dangerous drug combinations. He ignored patients’ signs of addiction and abuse, such as early requests for refills, claims that medications had been lost, and claims that family members were stealing pills.
Dr. Bauer was also convicted of healthcare fraud for regularly administering epidural injections and trigger-point injections without medical necessity. Because these injections failed to meet the procedural requirements, they were rendered ineffective and were fraudulently billed to insurers. Dr. Bauer’s illegal prescriptions resulted in insurers paying for these medically unnecessary controlled substances.
Evidence at trial indicated that between January 2007 and August 16, 2019, Dr. Bauer prescribed controlled substances outside the usual course of medical practice and for illegitimate medical purposes. Insurers paid for these medically unnecessary controlled substances as well.
He will be sentenced at a later date.
Lab pays $1.2 million to resolve allegations of false claims for drug testing
Bluewater Toxicology, LLC, a clinical laboratory in Mount Washington, Ky., has agreed to pay $1.2 million to resolve civil allegations that it violated the False Claims Act.
The U.S. Department of Justice alleged three issues relating to claims for urine drug testing services that Bluewater submitted to Medicare, Kentucky Medicaid, Indiana Medicaid, TRICARE, and CHAMPVA. First, Bluewater submitted claims in which it misrepresented the number of drug classes it tested. Bluewater claimed it conducted definitive urine drug tests of 22 or more drug classes. In truth, Bluewater tested for fewer than 22 drug classes and secured reimbursement for drug tests that it did not conduct.
Second, Bluewater submitted certain claims without sufficient documentation to support the physician’s intent to order the test that was billed. In this way Bluewater obtained further unwarranted reimbursements.
Finally, Bluewater billed Medicare for specimen validity testing, a quality control process used to analyze a urine specimen to ensure that it has not been diluted or adulterated. Since January 2014, Medicare’s guidance has stated that specimen validity testing should not be separately billed to Medicare, but Bluewater did so anyway.
Home care company owner pays $1 million in Medicare fraud restitution
Richard Wennerberg, 72, of Grantham, N.H., pleaded guilty and was sentenced to two counts of class B felony Medicaid fraud, according to the New Hampshire Department of Justice.
Mr. Wennerberg is the owner of Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, a company licensed to provide in-home personal care services to Medicaid beneficiaries. He also pleaded guilty to a third charge of Medicaid fraud, through which Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, will be excluded from future participation in federal healthcare programs.
According to New Hampshire officials, Mr. Wennerberg submitted claims for reimbursement for in-home, personal care services that were never provided. Wennerberg billed Medicaid up to the maximum hours allowed under certain clients’ service authorizations, knowing that his employees did not provide care for all of those hours. He would use the difference to reimburse some caregivers for mileage.
Mr. Wennerberg will serve 1 year in state prison and will pay $1 million in restitution.
North Carolina wins two “Operation Root Canal” settlements
North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein announced two separate civil settlements with ProHealth Dental Inc and Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS, as part of Operation Root Canal, an ongoing effort to find and stop healthcare fraud among dental practitioners. The settlements, totaling $75,000, resolve allegations of the submission of false claims to the North Carolina Medicaid program.
In Operation Root Canal, the state Medicaid investigations department reviews billing practices for a wide variety of dental services, including dental cleanings, use of nitrous oxide, repetitive restorations on the same tooth, palliative care, and upcoding of patient examinations. In total, the operation has netted more than $7 million for the state.
The recent settlement relates to a prior criminal plea the attorney general’s Medicaid Investigations Division obtained involving Mr. Christian Ekberg, of Maryland, who was sentenced to 18 months in prison for healthcare fraud and was ordered to pay $173,870.12 to the North Carolina Medicaid Fund in restitution. Ekberg was an officer and minority shareholder of ProHealth Dental, a company that entered into a practice management agreement with Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS., a North Carolina dentist and Medicaid practitioner who provided dental services to patients living in skilled nursing facilities throughout North Carolina. ProHealth Dental would provide professional management services to Dr. Davis, including submitting Medicaid claims. The company submitted claims for dental services that Dr. Davis did not perform on Medicaid recipients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ohio doctor convicted of prescribing unnecessary controlled substances, fraud
Ohio doctor convicted of prescribing unnecessary controlled substances, fraud
A federal jury found William R. Bauer, 84, of Port Clinton, Ohio, guilty of prescribing powerful controlled substances, including opioids, to patients without medical necessity and outside the usual course of medical practice.
Dr. Bauer, a neurologist with over 50 years of experience, was convicted of 76 counts of distribution of controlled substances and 25 counts of healthcare fraud. According to television station WTOL, a federal indictment from 2019 listed 270 charges against the physician.
Federal officials claim that through his practice in Bellevue, Ohio, Dr. Bauer repeatedly prescribed controlled substances, including oxycodone, fentanyl, morphine, and tramadol, outside the usual course of professional practice and without legitimate medical purpose. The charges focused on 14 of his patients, to whom he prescribed high doses of opioids and other controlled substances without medical necessity. He also prescribed dangerous drug combinations. He ignored patients’ signs of addiction and abuse, such as early requests for refills, claims that medications had been lost, and claims that family members were stealing pills.
Dr. Bauer was also convicted of healthcare fraud for regularly administering epidural injections and trigger-point injections without medical necessity. Because these injections failed to meet the procedural requirements, they were rendered ineffective and were fraudulently billed to insurers. Dr. Bauer’s illegal prescriptions resulted in insurers paying for these medically unnecessary controlled substances.
Evidence at trial indicated that between January 2007 and August 16, 2019, Dr. Bauer prescribed controlled substances outside the usual course of medical practice and for illegitimate medical purposes. Insurers paid for these medically unnecessary controlled substances as well.
He will be sentenced at a later date.
Lab pays $1.2 million to resolve allegations of false claims for drug testing
Bluewater Toxicology, LLC, a clinical laboratory in Mount Washington, Ky., has agreed to pay $1.2 million to resolve civil allegations that it violated the False Claims Act.
The U.S. Department of Justice alleged three issues relating to claims for urine drug testing services that Bluewater submitted to Medicare, Kentucky Medicaid, Indiana Medicaid, TRICARE, and CHAMPVA. First, Bluewater submitted claims in which it misrepresented the number of drug classes it tested. Bluewater claimed it conducted definitive urine drug tests of 22 or more drug classes. In truth, Bluewater tested for fewer than 22 drug classes and secured reimbursement for drug tests that it did not conduct.
Second, Bluewater submitted certain claims without sufficient documentation to support the physician’s intent to order the test that was billed. In this way Bluewater obtained further unwarranted reimbursements.
Finally, Bluewater billed Medicare for specimen validity testing, a quality control process used to analyze a urine specimen to ensure that it has not been diluted or adulterated. Since January 2014, Medicare’s guidance has stated that specimen validity testing should not be separately billed to Medicare, but Bluewater did so anyway.
Home care company owner pays $1 million in Medicare fraud restitution
Richard Wennerberg, 72, of Grantham, N.H., pleaded guilty and was sentenced to two counts of class B felony Medicaid fraud, according to the New Hampshire Department of Justice.
Mr. Wennerberg is the owner of Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, a company licensed to provide in-home personal care services to Medicaid beneficiaries. He also pleaded guilty to a third charge of Medicaid fraud, through which Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, will be excluded from future participation in federal healthcare programs.
According to New Hampshire officials, Mr. Wennerberg submitted claims for reimbursement for in-home, personal care services that were never provided. Wennerberg billed Medicaid up to the maximum hours allowed under certain clients’ service authorizations, knowing that his employees did not provide care for all of those hours. He would use the difference to reimburse some caregivers for mileage.
Mr. Wennerberg will serve 1 year in state prison and will pay $1 million in restitution.
North Carolina wins two “Operation Root Canal” settlements
North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein announced two separate civil settlements with ProHealth Dental Inc and Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS, as part of Operation Root Canal, an ongoing effort to find and stop healthcare fraud among dental practitioners. The settlements, totaling $75,000, resolve allegations of the submission of false claims to the North Carolina Medicaid program.
In Operation Root Canal, the state Medicaid investigations department reviews billing practices for a wide variety of dental services, including dental cleanings, use of nitrous oxide, repetitive restorations on the same tooth, palliative care, and upcoding of patient examinations. In total, the operation has netted more than $7 million for the state.
The recent settlement relates to a prior criminal plea the attorney general’s Medicaid Investigations Division obtained involving Mr. Christian Ekberg, of Maryland, who was sentenced to 18 months in prison for healthcare fraud and was ordered to pay $173,870.12 to the North Carolina Medicaid Fund in restitution. Ekberg was an officer and minority shareholder of ProHealth Dental, a company that entered into a practice management agreement with Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS., a North Carolina dentist and Medicaid practitioner who provided dental services to patients living in skilled nursing facilities throughout North Carolina. ProHealth Dental would provide professional management services to Dr. Davis, including submitting Medicaid claims. The company submitted claims for dental services that Dr. Davis did not perform on Medicaid recipients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A federal jury found William R. Bauer, 84, of Port Clinton, Ohio, guilty of prescribing powerful controlled substances, including opioids, to patients without medical necessity and outside the usual course of medical practice.
Dr. Bauer, a neurologist with over 50 years of experience, was convicted of 76 counts of distribution of controlled substances and 25 counts of healthcare fraud. According to television station WTOL, a federal indictment from 2019 listed 270 charges against the physician.
Federal officials claim that through his practice in Bellevue, Ohio, Dr. Bauer repeatedly prescribed controlled substances, including oxycodone, fentanyl, morphine, and tramadol, outside the usual course of professional practice and without legitimate medical purpose. The charges focused on 14 of his patients, to whom he prescribed high doses of opioids and other controlled substances without medical necessity. He also prescribed dangerous drug combinations. He ignored patients’ signs of addiction and abuse, such as early requests for refills, claims that medications had been lost, and claims that family members were stealing pills.
Dr. Bauer was also convicted of healthcare fraud for regularly administering epidural injections and trigger-point injections without medical necessity. Because these injections failed to meet the procedural requirements, they were rendered ineffective and were fraudulently billed to insurers. Dr. Bauer’s illegal prescriptions resulted in insurers paying for these medically unnecessary controlled substances.
Evidence at trial indicated that between January 2007 and August 16, 2019, Dr. Bauer prescribed controlled substances outside the usual course of medical practice and for illegitimate medical purposes. Insurers paid for these medically unnecessary controlled substances as well.
He will be sentenced at a later date.
Lab pays $1.2 million to resolve allegations of false claims for drug testing
Bluewater Toxicology, LLC, a clinical laboratory in Mount Washington, Ky., has agreed to pay $1.2 million to resolve civil allegations that it violated the False Claims Act.
The U.S. Department of Justice alleged three issues relating to claims for urine drug testing services that Bluewater submitted to Medicare, Kentucky Medicaid, Indiana Medicaid, TRICARE, and CHAMPVA. First, Bluewater submitted claims in which it misrepresented the number of drug classes it tested. Bluewater claimed it conducted definitive urine drug tests of 22 or more drug classes. In truth, Bluewater tested for fewer than 22 drug classes and secured reimbursement for drug tests that it did not conduct.
Second, Bluewater submitted certain claims without sufficient documentation to support the physician’s intent to order the test that was billed. In this way Bluewater obtained further unwarranted reimbursements.
Finally, Bluewater billed Medicare for specimen validity testing, a quality control process used to analyze a urine specimen to ensure that it has not been diluted or adulterated. Since January 2014, Medicare’s guidance has stated that specimen validity testing should not be separately billed to Medicare, but Bluewater did so anyway.
Home care company owner pays $1 million in Medicare fraud restitution
Richard Wennerberg, 72, of Grantham, N.H., pleaded guilty and was sentenced to two counts of class B felony Medicaid fraud, according to the New Hampshire Department of Justice.
Mr. Wennerberg is the owner of Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, a company licensed to provide in-home personal care services to Medicaid beneficiaries. He also pleaded guilty to a third charge of Medicaid fraud, through which Alternative Care @ Home, LLC, will be excluded from future participation in federal healthcare programs.
According to New Hampshire officials, Mr. Wennerberg submitted claims for reimbursement for in-home, personal care services that were never provided. Wennerberg billed Medicaid up to the maximum hours allowed under certain clients’ service authorizations, knowing that his employees did not provide care for all of those hours. He would use the difference to reimburse some caregivers for mileage.
Mr. Wennerberg will serve 1 year in state prison and will pay $1 million in restitution.
North Carolina wins two “Operation Root Canal” settlements
North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein announced two separate civil settlements with ProHealth Dental Inc and Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS, as part of Operation Root Canal, an ongoing effort to find and stop healthcare fraud among dental practitioners. The settlements, totaling $75,000, resolve allegations of the submission of false claims to the North Carolina Medicaid program.
In Operation Root Canal, the state Medicaid investigations department reviews billing practices for a wide variety of dental services, including dental cleanings, use of nitrous oxide, repetitive restorations on the same tooth, palliative care, and upcoding of patient examinations. In total, the operation has netted more than $7 million for the state.
The recent settlement relates to a prior criminal plea the attorney general’s Medicaid Investigations Division obtained involving Mr. Christian Ekberg, of Maryland, who was sentenced to 18 months in prison for healthcare fraud and was ordered to pay $173,870.12 to the North Carolina Medicaid Fund in restitution. Ekberg was an officer and minority shareholder of ProHealth Dental, a company that entered into a practice management agreement with Henry W. Davis, Jr, DDS., a North Carolina dentist and Medicaid practitioner who provided dental services to patients living in skilled nursing facilities throughout North Carolina. ProHealth Dental would provide professional management services to Dr. Davis, including submitting Medicaid claims. The company submitted claims for dental services that Dr. Davis did not perform on Medicaid recipients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patient whips out smartphone and starts recording: Trouble ahead?
Joe Lindsey, a 48-year old Colorado-based journalist, has dealt with complex hearing loss for about 15 years. which has led to countless doctor’s visits, treatments, and even surgery in hopes of finding improvement. As time went on and Mr. Lindsey’s hearing deteriorated, he began recording his appointments in order to retain important information.
Mr. Lindsey had positive intentions, but not every patient does.
With smartphones everywhere, recording medical appointments can be fraught with downsides too. While there are clear-cut reasons for recording doctor visits, patients’ goals and how they carry out the taping are key. Audio only? Or also video? With the physician’s knowledge and permission, or without?
These are the legal and ethical weeds doctors find themselves in today, so it’s important to understand all sides of the issue.
The medical world is divided on its sentiments about patients recording their visits. The American Medical Association, in fact, failed to make progress on a recent policy (resolution 007) proposal to encourage that any “audio or video recording made during a medical encounter should require both physician and patient notification and consent.” Rather than voting on the resolution, the AMA house of delegates tabled it and chose to gather more information on the issue.
In most cases, patients are recording their visits in good faith, says Jeffrey Segal, MD, JD, the CEO and founder of Medical Justice, a risk mitigation and reputation management firm for healthcare clinicians. “When it comes to ‘Team, let’s record this,’ I’m a fan,” he says. “The most common reason patients record visits is that there’s a lot of information transferred from the doctor to the patient, and there’s just not enough time to absorb it all.”
While the option is there for patients to take notes, in the give-and-take nature of conversation, this can get difficult. “If they record the visit, they can then digest it all down the road,” says Dr. Segal. “A compliant patient is one who understands what’s expected. That’s the charitable explanation for recording, and I support it.”
It’s that question of good intent, however, that concerns some physicians in today’s highly litigious society. “The worry is that there’s a small subset of patients with an ulterior motive,” says Dr. Segal.
“Some patients do record in case of an event down the road,” he adds. “They want the recording to potentially talk to a lawyer, or to file a board complaint.”
Laws in the United States surrounding recordings are confusing, with variations from state to state. Currently, 39 U.S. states allow for one-party consent — meaning a patient can record a visit without consenting with the physician.
Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at University of Texas Health, San Antonio, resides in Texas, which is one of the 39 one-consent states. “Physicians must be aware of this fact and consider how it might be used against them,” she says. “A good practice is to set expectations with the patient from the start. Also, know your hospital’s policy — some may have boundaries surrounding recordings.”
The first step is to know what type of state you practice in. Regardless of whether you are in a one- or two-party consent state — but especially a one-party state — it’s a smart move to add a sign at your office saying that you support the recording of visits, provided the patient is open and transparent about it. “Let the patient know that if they plan to record, they should ask your permission,” says Dr. Segal. “Let them know it’s not appropriate if they haven’t received your permission.”
There are, of course, the occasional horror stories involving surreptitious recordings. “I remember a case where a patient left a phone actively recording in his bag of clothing, which went into the OR with him,” he says. “The background conversation was not flattering to the patient, who happened to be an employee of the hospital. When he came to and listened to the recording, he sued, winning his case.”
The age of video and telehealth
What about the rare situation when a patient pulls out a phone and begins to videotape a conversation? It can be a big slippery slope. “Patients can abuse a video recording with editing, and the recording becomes one-dimensional, which is unfair to the physician,” adds Dr. Segal.
Patients sometimes have other motives as well. “I’m aware of occasions where a doctor/patient visit got heated and the patient took out the phone to video record, sharing it to social media,” says Dr. Segal. “Once someone uses a phone to take video, just stop the conversation. Tell the patient, ‘We’re having a disagreement,’ and that it’s time to put an end to it.”
He adds that from the physician side, a video can be a protagonist in a conversation. “Frankly, a camera on your face changes the nature of things,” Dr. Segal says. “It’s much easier to have the phone sitting in a corner, quietly recording.”
Other scenarios might involve a patient’s family member accompanying the patient and bringing out their phone to record. “Doctors should consider how this might be used against them — it can blow up,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Draw boundaries on this behavior, using your hospital’s policy if it has one.”
In today’s pandemic landscape, this is particularly important, she adds. “There’s generally more mistrust in the medical system right now,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “People are getting misinformation from sources that aren’t credible, and then want to record their visits because they aren’t receiving the treatment they want, for instance.”
COVID has also added the tricky element of telehealth, which has exploded since 2020. “You don’t know what a patient is doing on the other side of the screen,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez explains. “Face-to-face, you might see them with their phones out, but anything goes with telehealth. You have to be open and communicative with your patients about your policies from the start to avoid any negative connotations.”
How taping can help patients
Mr. Lindsey, the Colorado journalist, is far from alone in his desire to use visit recordings in order to retain valuable information — and with good reason. According to the Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice’s Open Recordings Project, at least 1 in 10 patients records their doctor’s visits.
“I realized I was missing things and in a medical setting, that matters,” Mr. Lindsey says. “Last year, once COVID hit and we all began wearing masks, I lost my ability to read lips, one of my coping mechanisms. It became even more important that I had a backup recording to ensure I understood everything.”
Even if a patient doesn’t have hearing loss like Mr. Lindsey, having an audio record of a visit can be useful. According to a 2018 study on patient recall of key information 1 week out from their visits, 49% of decisions and recommendations were recalled accurately without prompting; 36% recalled with a prompt; and 15% recalled erroneously or not at all.
This squares with the personal experiences of Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “I even see this with my mom, who doesn’t remember many details of her doctor’s visits when I ask her,” she says. “This can definitely impact treatment.”
For better or worse
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez says that often it comes down to how a patient learns best. “I teach my residents to keep this in mind and to ask the patient in advance what works best for them,” she says. “If a patient is a visual learner, they might want to take notes or have access to the appointment notes after the visit. If they will learn and retain the information best with an audio recording, then offer that option.”
Mr. Lindsey makes it a habit to inform his physicians that he will be making an audio recording of his visits. “I always let them know that I’m recording for accuracy and not to catch them in some sort of falsehood,” he says. “I can get the doctor’s notes, but those are often short and to the point; I can get more information by going back over the recording.”
To date, Mr. Lindsey hasn’t experienced any pushback from his physicians. “No one has balked at the idea or acted surprised that I want to do it,” he explains. “I think most doctors appreciate that we have a tool we can make use of for better care.”
In past coverage of the topic, some healthcare providers weighed in with support for recordings, usually citing personal reasons. “I am so very grateful for the physicians that allowed me to record the medical appointments that I attended with my parents,” said one. “As their adult daughter, I was painfully aware that my parents struggled to process and understand all of the new information coming their way.”
Another expressed support as well, stating that as a patient, he prefers recordings to notes, because the latter “bears little resemblance to the content of the meeting and discussion with the physician. If the patient straightforwardly asks for permission to record, then why not honor the good intent expressed thereby?”
More often than not, patients have good intentions when they decide to hit the record button in a medical visit. A little preparation goes a long way, however, says Dr. Segal: “Assume you’re being recorded, and act accordingly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Joe Lindsey, a 48-year old Colorado-based journalist, has dealt with complex hearing loss for about 15 years. which has led to countless doctor’s visits, treatments, and even surgery in hopes of finding improvement. As time went on and Mr. Lindsey’s hearing deteriorated, he began recording his appointments in order to retain important information.
Mr. Lindsey had positive intentions, but not every patient does.
With smartphones everywhere, recording medical appointments can be fraught with downsides too. While there are clear-cut reasons for recording doctor visits, patients’ goals and how they carry out the taping are key. Audio only? Or also video? With the physician’s knowledge and permission, or without?
These are the legal and ethical weeds doctors find themselves in today, so it’s important to understand all sides of the issue.
The medical world is divided on its sentiments about patients recording their visits. The American Medical Association, in fact, failed to make progress on a recent policy (resolution 007) proposal to encourage that any “audio or video recording made during a medical encounter should require both physician and patient notification and consent.” Rather than voting on the resolution, the AMA house of delegates tabled it and chose to gather more information on the issue.
In most cases, patients are recording their visits in good faith, says Jeffrey Segal, MD, JD, the CEO and founder of Medical Justice, a risk mitigation and reputation management firm for healthcare clinicians. “When it comes to ‘Team, let’s record this,’ I’m a fan,” he says. “The most common reason patients record visits is that there’s a lot of information transferred from the doctor to the patient, and there’s just not enough time to absorb it all.”
While the option is there for patients to take notes, in the give-and-take nature of conversation, this can get difficult. “If they record the visit, they can then digest it all down the road,” says Dr. Segal. “A compliant patient is one who understands what’s expected. That’s the charitable explanation for recording, and I support it.”
It’s that question of good intent, however, that concerns some physicians in today’s highly litigious society. “The worry is that there’s a small subset of patients with an ulterior motive,” says Dr. Segal.
“Some patients do record in case of an event down the road,” he adds. “They want the recording to potentially talk to a lawyer, or to file a board complaint.”
Laws in the United States surrounding recordings are confusing, with variations from state to state. Currently, 39 U.S. states allow for one-party consent — meaning a patient can record a visit without consenting with the physician.
Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at University of Texas Health, San Antonio, resides in Texas, which is one of the 39 one-consent states. “Physicians must be aware of this fact and consider how it might be used against them,” she says. “A good practice is to set expectations with the patient from the start. Also, know your hospital’s policy — some may have boundaries surrounding recordings.”
The first step is to know what type of state you practice in. Regardless of whether you are in a one- or two-party consent state — but especially a one-party state — it’s a smart move to add a sign at your office saying that you support the recording of visits, provided the patient is open and transparent about it. “Let the patient know that if they plan to record, they should ask your permission,” says Dr. Segal. “Let them know it’s not appropriate if they haven’t received your permission.”
There are, of course, the occasional horror stories involving surreptitious recordings. “I remember a case where a patient left a phone actively recording in his bag of clothing, which went into the OR with him,” he says. “The background conversation was not flattering to the patient, who happened to be an employee of the hospital. When he came to and listened to the recording, he sued, winning his case.”
The age of video and telehealth
What about the rare situation when a patient pulls out a phone and begins to videotape a conversation? It can be a big slippery slope. “Patients can abuse a video recording with editing, and the recording becomes one-dimensional, which is unfair to the physician,” adds Dr. Segal.
Patients sometimes have other motives as well. “I’m aware of occasions where a doctor/patient visit got heated and the patient took out the phone to video record, sharing it to social media,” says Dr. Segal. “Once someone uses a phone to take video, just stop the conversation. Tell the patient, ‘We’re having a disagreement,’ and that it’s time to put an end to it.”
He adds that from the physician side, a video can be a protagonist in a conversation. “Frankly, a camera on your face changes the nature of things,” Dr. Segal says. “It’s much easier to have the phone sitting in a corner, quietly recording.”
Other scenarios might involve a patient’s family member accompanying the patient and bringing out their phone to record. “Doctors should consider how this might be used against them — it can blow up,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Draw boundaries on this behavior, using your hospital’s policy if it has one.”
In today’s pandemic landscape, this is particularly important, she adds. “There’s generally more mistrust in the medical system right now,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “People are getting misinformation from sources that aren’t credible, and then want to record their visits because they aren’t receiving the treatment they want, for instance.”
COVID has also added the tricky element of telehealth, which has exploded since 2020. “You don’t know what a patient is doing on the other side of the screen,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez explains. “Face-to-face, you might see them with their phones out, but anything goes with telehealth. You have to be open and communicative with your patients about your policies from the start to avoid any negative connotations.”
How taping can help patients
Mr. Lindsey, the Colorado journalist, is far from alone in his desire to use visit recordings in order to retain valuable information — and with good reason. According to the Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice’s Open Recordings Project, at least 1 in 10 patients records their doctor’s visits.
“I realized I was missing things and in a medical setting, that matters,” Mr. Lindsey says. “Last year, once COVID hit and we all began wearing masks, I lost my ability to read lips, one of my coping mechanisms. It became even more important that I had a backup recording to ensure I understood everything.”
Even if a patient doesn’t have hearing loss like Mr. Lindsey, having an audio record of a visit can be useful. According to a 2018 study on patient recall of key information 1 week out from their visits, 49% of decisions and recommendations were recalled accurately without prompting; 36% recalled with a prompt; and 15% recalled erroneously or not at all.
This squares with the personal experiences of Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “I even see this with my mom, who doesn’t remember many details of her doctor’s visits when I ask her,” she says. “This can definitely impact treatment.”
For better or worse
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez says that often it comes down to how a patient learns best. “I teach my residents to keep this in mind and to ask the patient in advance what works best for them,” she says. “If a patient is a visual learner, they might want to take notes or have access to the appointment notes after the visit. If they will learn and retain the information best with an audio recording, then offer that option.”
Mr. Lindsey makes it a habit to inform his physicians that he will be making an audio recording of his visits. “I always let them know that I’m recording for accuracy and not to catch them in some sort of falsehood,” he says. “I can get the doctor’s notes, but those are often short and to the point; I can get more information by going back over the recording.”
To date, Mr. Lindsey hasn’t experienced any pushback from his physicians. “No one has balked at the idea or acted surprised that I want to do it,” he explains. “I think most doctors appreciate that we have a tool we can make use of for better care.”
In past coverage of the topic, some healthcare providers weighed in with support for recordings, usually citing personal reasons. “I am so very grateful for the physicians that allowed me to record the medical appointments that I attended with my parents,” said one. “As their adult daughter, I was painfully aware that my parents struggled to process and understand all of the new information coming their way.”
Another expressed support as well, stating that as a patient, he prefers recordings to notes, because the latter “bears little resemblance to the content of the meeting and discussion with the physician. If the patient straightforwardly asks for permission to record, then why not honor the good intent expressed thereby?”
More often than not, patients have good intentions when they decide to hit the record button in a medical visit. A little preparation goes a long way, however, says Dr. Segal: “Assume you’re being recorded, and act accordingly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Joe Lindsey, a 48-year old Colorado-based journalist, has dealt with complex hearing loss for about 15 years. which has led to countless doctor’s visits, treatments, and even surgery in hopes of finding improvement. As time went on and Mr. Lindsey’s hearing deteriorated, he began recording his appointments in order to retain important information.
Mr. Lindsey had positive intentions, but not every patient does.
With smartphones everywhere, recording medical appointments can be fraught with downsides too. While there are clear-cut reasons for recording doctor visits, patients’ goals and how they carry out the taping are key. Audio only? Or also video? With the physician’s knowledge and permission, or without?
These are the legal and ethical weeds doctors find themselves in today, so it’s important to understand all sides of the issue.
The medical world is divided on its sentiments about patients recording their visits. The American Medical Association, in fact, failed to make progress on a recent policy (resolution 007) proposal to encourage that any “audio or video recording made during a medical encounter should require both physician and patient notification and consent.” Rather than voting on the resolution, the AMA house of delegates tabled it and chose to gather more information on the issue.
In most cases, patients are recording their visits in good faith, says Jeffrey Segal, MD, JD, the CEO and founder of Medical Justice, a risk mitigation and reputation management firm for healthcare clinicians. “When it comes to ‘Team, let’s record this,’ I’m a fan,” he says. “The most common reason patients record visits is that there’s a lot of information transferred from the doctor to the patient, and there’s just not enough time to absorb it all.”
While the option is there for patients to take notes, in the give-and-take nature of conversation, this can get difficult. “If they record the visit, they can then digest it all down the road,” says Dr. Segal. “A compliant patient is one who understands what’s expected. That’s the charitable explanation for recording, and I support it.”
It’s that question of good intent, however, that concerns some physicians in today’s highly litigious society. “The worry is that there’s a small subset of patients with an ulterior motive,” says Dr. Segal.
“Some patients do record in case of an event down the road,” he adds. “They want the recording to potentially talk to a lawyer, or to file a board complaint.”
Laws in the United States surrounding recordings are confusing, with variations from state to state. Currently, 39 U.S. states allow for one-party consent — meaning a patient can record a visit without consenting with the physician.
Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at University of Texas Health, San Antonio, resides in Texas, which is one of the 39 one-consent states. “Physicians must be aware of this fact and consider how it might be used against them,” she says. “A good practice is to set expectations with the patient from the start. Also, know your hospital’s policy — some may have boundaries surrounding recordings.”
The first step is to know what type of state you practice in. Regardless of whether you are in a one- or two-party consent state — but especially a one-party state — it’s a smart move to add a sign at your office saying that you support the recording of visits, provided the patient is open and transparent about it. “Let the patient know that if they plan to record, they should ask your permission,” says Dr. Segal. “Let them know it’s not appropriate if they haven’t received your permission.”
There are, of course, the occasional horror stories involving surreptitious recordings. “I remember a case where a patient left a phone actively recording in his bag of clothing, which went into the OR with him,” he says. “The background conversation was not flattering to the patient, who happened to be an employee of the hospital. When he came to and listened to the recording, he sued, winning his case.”
The age of video and telehealth
What about the rare situation when a patient pulls out a phone and begins to videotape a conversation? It can be a big slippery slope. “Patients can abuse a video recording with editing, and the recording becomes one-dimensional, which is unfair to the physician,” adds Dr. Segal.
Patients sometimes have other motives as well. “I’m aware of occasions where a doctor/patient visit got heated and the patient took out the phone to video record, sharing it to social media,” says Dr. Segal. “Once someone uses a phone to take video, just stop the conversation. Tell the patient, ‘We’re having a disagreement,’ and that it’s time to put an end to it.”
He adds that from the physician side, a video can be a protagonist in a conversation. “Frankly, a camera on your face changes the nature of things,” Dr. Segal says. “It’s much easier to have the phone sitting in a corner, quietly recording.”
Other scenarios might involve a patient’s family member accompanying the patient and bringing out their phone to record. “Doctors should consider how this might be used against them — it can blow up,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Draw boundaries on this behavior, using your hospital’s policy if it has one.”
In today’s pandemic landscape, this is particularly important, she adds. “There’s generally more mistrust in the medical system right now,” says Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “People are getting misinformation from sources that aren’t credible, and then want to record their visits because they aren’t receiving the treatment they want, for instance.”
COVID has also added the tricky element of telehealth, which has exploded since 2020. “You don’t know what a patient is doing on the other side of the screen,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez explains. “Face-to-face, you might see them with their phones out, but anything goes with telehealth. You have to be open and communicative with your patients about your policies from the start to avoid any negative connotations.”
How taping can help patients
Mr. Lindsey, the Colorado journalist, is far from alone in his desire to use visit recordings in order to retain valuable information — and with good reason. According to the Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice’s Open Recordings Project, at least 1 in 10 patients records their doctor’s visits.
“I realized I was missing things and in a medical setting, that matters,” Mr. Lindsey says. “Last year, once COVID hit and we all began wearing masks, I lost my ability to read lips, one of my coping mechanisms. It became even more important that I had a backup recording to ensure I understood everything.”
Even if a patient doesn’t have hearing loss like Mr. Lindsey, having an audio record of a visit can be useful. According to a 2018 study on patient recall of key information 1 week out from their visits, 49% of decisions and recommendations were recalled accurately without prompting; 36% recalled with a prompt; and 15% recalled erroneously or not at all.
This squares with the personal experiences of Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “I even see this with my mom, who doesn’t remember many details of her doctor’s visits when I ask her,” she says. “This can definitely impact treatment.”
For better or worse
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez says that often it comes down to how a patient learns best. “I teach my residents to keep this in mind and to ask the patient in advance what works best for them,” she says. “If a patient is a visual learner, they might want to take notes or have access to the appointment notes after the visit. If they will learn and retain the information best with an audio recording, then offer that option.”
Mr. Lindsey makes it a habit to inform his physicians that he will be making an audio recording of his visits. “I always let them know that I’m recording for accuracy and not to catch them in some sort of falsehood,” he says. “I can get the doctor’s notes, but those are often short and to the point; I can get more information by going back over the recording.”
To date, Mr. Lindsey hasn’t experienced any pushback from his physicians. “No one has balked at the idea or acted surprised that I want to do it,” he explains. “I think most doctors appreciate that we have a tool we can make use of for better care.”
In past coverage of the topic, some healthcare providers weighed in with support for recordings, usually citing personal reasons. “I am so very grateful for the physicians that allowed me to record the medical appointments that I attended with my parents,” said one. “As their adult daughter, I was painfully aware that my parents struggled to process and understand all of the new information coming their way.”
Another expressed support as well, stating that as a patient, he prefers recordings to notes, because the latter “bears little resemblance to the content of the meeting and discussion with the physician. If the patient straightforwardly asks for permission to record, then why not honor the good intent expressed thereby?”
More often than not, patients have good intentions when they decide to hit the record button in a medical visit. A little preparation goes a long way, however, says Dr. Segal: “Assume you’re being recorded, and act accordingly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC unveils mental health protection plan for health care workers
Federal health officials have outlined a five-part plan to improve and protect the mental health and well-being of America’s health care workers (HCWs) and create sustainable change for the next generation of HCWs.
“It’s long past time for us to care for the people who care for all of us and address burnout in our health care workers,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, said during a webinar hosted by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, part of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“My hope is that, going forward, we will be able to embark on this journey together to create a health care system, a health care environment, a country where we can not only provide extraordinary care to all those who need it, but where we can take good care of those who have sacrificed so much and make sure that they are well,” Dr. Murthy said.
Burnout is not selective
There are 20 million HCWs in the United States, and no one is immune from burnout, said NIOSH Director John Howard, MD.
He noted that from June through Sept. of 2020 – the height of the COVID-19 pandemic – 93% of HCWs experienced some degree of stress, with 22% reporting moderate depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Looking at subsets of HCWs, a recent survey showed that one in five nurses contemplated leaving the profession because of insufficient staffing, intensity of workload, emotional and physical toll of the job, and lack of support, Dr. Howard noted.
Physician burnout was a significant issue even before the pandemic, with about 79% of physicians reporting burnout. , Dr. Howard said.
Women in health care jobs are especially vulnerable to burnout; 76% of health care jobs are held by women and 64% of physicians that feel burned-out are women, according to federal data.
“We have significant work to do in shoring up the safety and health of women in health care,” Dr. Howard said.
Mental health is also suffering among local and state public health workers. In a recent CDC survey of 26,000 of these workers, 53% reported symptoms of at least one mental health condition in the past 2 weeks.
“That is really an alarming proportion of public health workers who are as vital and essential as nurses and doctors are in our health care system,” Dr. Howard said.
Primary prevention approach
To tackle the burnout crisis, NIOSH plans to:
- Take a deep dive into understanding the personal, social, and economic burdens HCWs face on a daily basis.
- Assimilate the evidence and create a repository of best practices, resources, and interventions.
- Partner with key stakeholders, including the American Hospital Association, the American Nurses Association, National Nurses United, the Joint Commission.
- Identify and adapt tools for the health care workplace that emphasize stress reduction.
NIOSH also plans to “generate awareness through a national, multidimensional social marketing campaign to get the word out about stress so health care workers don’t feel so alone,” Dr. Howard said.
This five-part plan takes a primary prevention approach to identifying and eliminating risk factors for burnout and stress, he added.
Secondary prevention, “when damage has already been done and you’re trying to save a health care worker who is suffering from a mental health issue, that’s a lot harder than taking a good look at what you can do to organizational practices that lead to health care workers’ stress and burnout,” Dr. Howard said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal health officials have outlined a five-part plan to improve and protect the mental health and well-being of America’s health care workers (HCWs) and create sustainable change for the next generation of HCWs.
“It’s long past time for us to care for the people who care for all of us and address burnout in our health care workers,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, said during a webinar hosted by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, part of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“My hope is that, going forward, we will be able to embark on this journey together to create a health care system, a health care environment, a country where we can not only provide extraordinary care to all those who need it, but where we can take good care of those who have sacrificed so much and make sure that they are well,” Dr. Murthy said.
Burnout is not selective
There are 20 million HCWs in the United States, and no one is immune from burnout, said NIOSH Director John Howard, MD.
He noted that from June through Sept. of 2020 – the height of the COVID-19 pandemic – 93% of HCWs experienced some degree of stress, with 22% reporting moderate depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Looking at subsets of HCWs, a recent survey showed that one in five nurses contemplated leaving the profession because of insufficient staffing, intensity of workload, emotional and physical toll of the job, and lack of support, Dr. Howard noted.
Physician burnout was a significant issue even before the pandemic, with about 79% of physicians reporting burnout. , Dr. Howard said.
Women in health care jobs are especially vulnerable to burnout; 76% of health care jobs are held by women and 64% of physicians that feel burned-out are women, according to federal data.
“We have significant work to do in shoring up the safety and health of women in health care,” Dr. Howard said.
Mental health is also suffering among local and state public health workers. In a recent CDC survey of 26,000 of these workers, 53% reported symptoms of at least one mental health condition in the past 2 weeks.
“That is really an alarming proportion of public health workers who are as vital and essential as nurses and doctors are in our health care system,” Dr. Howard said.
Primary prevention approach
To tackle the burnout crisis, NIOSH plans to:
- Take a deep dive into understanding the personal, social, and economic burdens HCWs face on a daily basis.
- Assimilate the evidence and create a repository of best practices, resources, and interventions.
- Partner with key stakeholders, including the American Hospital Association, the American Nurses Association, National Nurses United, the Joint Commission.
- Identify and adapt tools for the health care workplace that emphasize stress reduction.
NIOSH also plans to “generate awareness through a national, multidimensional social marketing campaign to get the word out about stress so health care workers don’t feel so alone,” Dr. Howard said.
This five-part plan takes a primary prevention approach to identifying and eliminating risk factors for burnout and stress, he added.
Secondary prevention, “when damage has already been done and you’re trying to save a health care worker who is suffering from a mental health issue, that’s a lot harder than taking a good look at what you can do to organizational practices that lead to health care workers’ stress and burnout,” Dr. Howard said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal health officials have outlined a five-part plan to improve and protect the mental health and well-being of America’s health care workers (HCWs) and create sustainable change for the next generation of HCWs.
“It’s long past time for us to care for the people who care for all of us and address burnout in our health care workers,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, said during a webinar hosted by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, part of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“My hope is that, going forward, we will be able to embark on this journey together to create a health care system, a health care environment, a country where we can not only provide extraordinary care to all those who need it, but where we can take good care of those who have sacrificed so much and make sure that they are well,” Dr. Murthy said.
Burnout is not selective
There are 20 million HCWs in the United States, and no one is immune from burnout, said NIOSH Director John Howard, MD.
He noted that from June through Sept. of 2020 – the height of the COVID-19 pandemic – 93% of HCWs experienced some degree of stress, with 22% reporting moderate depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Looking at subsets of HCWs, a recent survey showed that one in five nurses contemplated leaving the profession because of insufficient staffing, intensity of workload, emotional and physical toll of the job, and lack of support, Dr. Howard noted.
Physician burnout was a significant issue even before the pandemic, with about 79% of physicians reporting burnout. , Dr. Howard said.
Women in health care jobs are especially vulnerable to burnout; 76% of health care jobs are held by women and 64% of physicians that feel burned-out are women, according to federal data.
“We have significant work to do in shoring up the safety and health of women in health care,” Dr. Howard said.
Mental health is also suffering among local and state public health workers. In a recent CDC survey of 26,000 of these workers, 53% reported symptoms of at least one mental health condition in the past 2 weeks.
“That is really an alarming proportion of public health workers who are as vital and essential as nurses and doctors are in our health care system,” Dr. Howard said.
Primary prevention approach
To tackle the burnout crisis, NIOSH plans to:
- Take a deep dive into understanding the personal, social, and economic burdens HCWs face on a daily basis.
- Assimilate the evidence and create a repository of best practices, resources, and interventions.
- Partner with key stakeholders, including the American Hospital Association, the American Nurses Association, National Nurses United, the Joint Commission.
- Identify and adapt tools for the health care workplace that emphasize stress reduction.
NIOSH also plans to “generate awareness through a national, multidimensional social marketing campaign to get the word out about stress so health care workers don’t feel so alone,” Dr. Howard said.
This five-part plan takes a primary prevention approach to identifying and eliminating risk factors for burnout and stress, he added.
Secondary prevention, “when damage has already been done and you’re trying to save a health care worker who is suffering from a mental health issue, that’s a lot harder than taking a good look at what you can do to organizational practices that lead to health care workers’ stress and burnout,” Dr. Howard said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Beware of private equity–owned nursing homes: study
When you have to help a parent choose a nursing home or you need nursing home care yourself, you can consult a health care professional, talk to friends, or look at the Nursing Home Compare website of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The CMS website includes star ratings for each nursing home, both overall and on health inspections, staffing and certain quality measures.
But what you might not know is what financial incentives a particular nursing home might have to provide high-quality care, depending on what kind of entity owns the facility.
According to the study, you can expect a somewhat lower level of quality in a PE-owned nursing home than in other for-profit facilities.
The researchers compared CMS data on 302 nursing homes owned by 79 PE firms to data on 9,562 for-profit facilities not owned by such companies from 2013 to 2017. Among fee-for-service Medicare patients in long-term care, private equity acquisitions of nursing homes were associated with an 11.1% increase in ambulatory-care-sensitive (ACS) visits to the emergency department (ED) and an 8.7% increase in ACS hospitalizations per quarter, compared to the changes that occurred in the non-PE-owned facilities, they found.
What’s more, Medicare costs per beneficiary increased 3.9% more – or about $1,000 a year – in the PE-owned nursing homes than they did in the other cohort during the study period.
And when the acquired nursing homes were compared to the nursing homes prior to their acquisition by PE firms, there were no statistically significant differences in unadjusted outcomes, the researchers found. That means the two cohorts were broadly comparable.
The researchers adjusted the numbers in their study for various characteristics of the facilities and their residents. For example, the PE-acquired nursing homes were likely to have a higher percentage of patients covered by Medicare and a lower percentage covered by Medicaid than their non-PE counterparts.
The mean percentages of Black residents, female residents, and residents aged 85 or older were 12.4%, 65.4%, and 36.2%, respectively, for the PE-owned nursing homes and 15.7%, 67.8%, and 39%, respectively, for the non–PE-owned facilities.
Less than optimal outcomes
On average, the residents of non–PE-owned nursing homes had better outcomes than did the patients in the PE-owned facilities. But that doesn’t mean that the average for-profit nursing home had terrific outcomes.
For all the nursing homes in the study, the mean quarterly rate of ACS emergency department visits was 14.1%, and the mean quarterly rate of ACS hospitalizations was 17.3%.
“These events should be largely, although not completely, preventable with appropriate care,” the researchers pointed out.
To date, PE firms have invested about $750 billion in U.S. health care, with nursing homes being a major target of these companies, which currently own 5% of skilled nursing facilities, per the study. PE companies seek annual returns of 20% or more, the paper says, and thus feel pressure to generate high short-term profits. That could lead to reduced staffing, services, supplies, or equipment in their facilities.
Some nursing homes purchased by PE firms may be responsible for the debt incurred in their own leveraged buyouts, the researchers noted. There is also concern that PE firms may focus their properties disproportionately on short-term post-acute care, which is reimbursed at a higher rate than long-term care, the study says.
For all these reasons, some health policy makers are concerned about the long-term impact of private-equity nursing home acquisitions, according to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When you have to help a parent choose a nursing home or you need nursing home care yourself, you can consult a health care professional, talk to friends, or look at the Nursing Home Compare website of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The CMS website includes star ratings for each nursing home, both overall and on health inspections, staffing and certain quality measures.
But what you might not know is what financial incentives a particular nursing home might have to provide high-quality care, depending on what kind of entity owns the facility.
According to the study, you can expect a somewhat lower level of quality in a PE-owned nursing home than in other for-profit facilities.
The researchers compared CMS data on 302 nursing homes owned by 79 PE firms to data on 9,562 for-profit facilities not owned by such companies from 2013 to 2017. Among fee-for-service Medicare patients in long-term care, private equity acquisitions of nursing homes were associated with an 11.1% increase in ambulatory-care-sensitive (ACS) visits to the emergency department (ED) and an 8.7% increase in ACS hospitalizations per quarter, compared to the changes that occurred in the non-PE-owned facilities, they found.
What’s more, Medicare costs per beneficiary increased 3.9% more – or about $1,000 a year – in the PE-owned nursing homes than they did in the other cohort during the study period.
And when the acquired nursing homes were compared to the nursing homes prior to their acquisition by PE firms, there were no statistically significant differences in unadjusted outcomes, the researchers found. That means the two cohorts were broadly comparable.
The researchers adjusted the numbers in their study for various characteristics of the facilities and their residents. For example, the PE-acquired nursing homes were likely to have a higher percentage of patients covered by Medicare and a lower percentage covered by Medicaid than their non-PE counterparts.
The mean percentages of Black residents, female residents, and residents aged 85 or older were 12.4%, 65.4%, and 36.2%, respectively, for the PE-owned nursing homes and 15.7%, 67.8%, and 39%, respectively, for the non–PE-owned facilities.
Less than optimal outcomes
On average, the residents of non–PE-owned nursing homes had better outcomes than did the patients in the PE-owned facilities. But that doesn’t mean that the average for-profit nursing home had terrific outcomes.
For all the nursing homes in the study, the mean quarterly rate of ACS emergency department visits was 14.1%, and the mean quarterly rate of ACS hospitalizations was 17.3%.
“These events should be largely, although not completely, preventable with appropriate care,” the researchers pointed out.
To date, PE firms have invested about $750 billion in U.S. health care, with nursing homes being a major target of these companies, which currently own 5% of skilled nursing facilities, per the study. PE companies seek annual returns of 20% or more, the paper says, and thus feel pressure to generate high short-term profits. That could lead to reduced staffing, services, supplies, or equipment in their facilities.
Some nursing homes purchased by PE firms may be responsible for the debt incurred in their own leveraged buyouts, the researchers noted. There is also concern that PE firms may focus their properties disproportionately on short-term post-acute care, which is reimbursed at a higher rate than long-term care, the study says.
For all these reasons, some health policy makers are concerned about the long-term impact of private-equity nursing home acquisitions, according to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When you have to help a parent choose a nursing home or you need nursing home care yourself, you can consult a health care professional, talk to friends, or look at the Nursing Home Compare website of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). The CMS website includes star ratings for each nursing home, both overall and on health inspections, staffing and certain quality measures.
But what you might not know is what financial incentives a particular nursing home might have to provide high-quality care, depending on what kind of entity owns the facility.
According to the study, you can expect a somewhat lower level of quality in a PE-owned nursing home than in other for-profit facilities.
The researchers compared CMS data on 302 nursing homes owned by 79 PE firms to data on 9,562 for-profit facilities not owned by such companies from 2013 to 2017. Among fee-for-service Medicare patients in long-term care, private equity acquisitions of nursing homes were associated with an 11.1% increase in ambulatory-care-sensitive (ACS) visits to the emergency department (ED) and an 8.7% increase in ACS hospitalizations per quarter, compared to the changes that occurred in the non-PE-owned facilities, they found.
What’s more, Medicare costs per beneficiary increased 3.9% more – or about $1,000 a year – in the PE-owned nursing homes than they did in the other cohort during the study period.
And when the acquired nursing homes were compared to the nursing homes prior to their acquisition by PE firms, there were no statistically significant differences in unadjusted outcomes, the researchers found. That means the two cohorts were broadly comparable.
The researchers adjusted the numbers in their study for various characteristics of the facilities and their residents. For example, the PE-acquired nursing homes were likely to have a higher percentage of patients covered by Medicare and a lower percentage covered by Medicaid than their non-PE counterparts.
The mean percentages of Black residents, female residents, and residents aged 85 or older were 12.4%, 65.4%, and 36.2%, respectively, for the PE-owned nursing homes and 15.7%, 67.8%, and 39%, respectively, for the non–PE-owned facilities.
Less than optimal outcomes
On average, the residents of non–PE-owned nursing homes had better outcomes than did the patients in the PE-owned facilities. But that doesn’t mean that the average for-profit nursing home had terrific outcomes.
For all the nursing homes in the study, the mean quarterly rate of ACS emergency department visits was 14.1%, and the mean quarterly rate of ACS hospitalizations was 17.3%.
“These events should be largely, although not completely, preventable with appropriate care,” the researchers pointed out.
To date, PE firms have invested about $750 billion in U.S. health care, with nursing homes being a major target of these companies, which currently own 5% of skilled nursing facilities, per the study. PE companies seek annual returns of 20% or more, the paper says, and thus feel pressure to generate high short-term profits. That could lead to reduced staffing, services, supplies, or equipment in their facilities.
Some nursing homes purchased by PE firms may be responsible for the debt incurred in their own leveraged buyouts, the researchers noted. There is also concern that PE firms may focus their properties disproportionately on short-term post-acute care, which is reimbursed at a higher rate than long-term care, the study says.
For all these reasons, some health policy makers are concerned about the long-term impact of private-equity nursing home acquisitions, according to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When should psychiatrists retire?
I remember a conversation I had at the end of my training with an older psychiatrist who was closing his practice. I was very excited to finally be a psychiatrist, and therefore a bit shocked that someone would voluntarily end a career I was just beginning. After all, psychiatry is a field where people can practice with flexibility, and a private practice is not an all-or-none endeavor.
“Dinah,” this gentleman said to me, sensing my dismay, “I’m 74. I’m allowed to retire.”
Like many retired psychiatrists, this one continued to come to grand rounds every Monday, dressed in a suit, which was followed by lunch with friends in the dining room. He continued to be involved in professional activities and lived to be 96.
Another dear friend practiced psychiatry until she entered hospice after a 2-year battle with cancer. Others have whittled down their practices, hanging on to a few hours of patient care along with supervision, teaching, and involvement with professional organizations.
In discussing retirement with some of my peers, it’s become immediately clear that each psychiatrist approaches this decision – and how they choose to live after it’s made – with a unique set of concerns and goals.
Fatigued by bureaucracy
Robin Weiss, MD, is in the process of “shrinking” her private practice. She is quick to say she is not retiring, but planning to scale back to 1 day a week starting next summer.
“I want to work less so I have more time for my grandchildren, friends, and travel, and to finally write more.” She also hopes to improve her ping-pong game and exercise habits.
“I’m so tired of prior authorizations, and the one day a week of patients I’ve been committed to feels just about right.”
During the pandemic, Dr. Weiss relinquished her office and she plans to continue with a virtual practice, which allows her more flexibility in terms of where she is physically located.
“The pandemic didn’t influence my decision to scale back, but it did play a role in deciding to give up my office,” she said.
A decision precipitated by medical reasons
Stephen Warres, MD, is a child and adolescent psychiatrist in Maryland who fully retired from practice in June 2021. He started scaling back a few years ago, when he had to give up his office because the building was undergoing renovations.
“I was seeing some patients from my home, but for 2 years I had been working 1 or 2 weekends a month at the Baltimore city jail, and I thought of that as my final act. It was a setting I had never worked in, and I left there 4 months before the pandemic started.”
Dr. Warres noted that his decision to retire was propelled by his diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease at the end of 2019.
“So far I only have a resting tremor, but this is an illness in which cognitive decline is a possibility.”
The emotional roller-coaster that can await
“Why am I leaving when others practice longer? I read about a psychiatrist in California who was still practicing when he died at 102. And the last patient whom I saw when I left practice was a man I started treating just 2 days after I started residency in 1976! When I told him I would be retiring, he found a new psychiatrist who is 82 years old.”
This was followed, he said, by a sense of shame.
“My father was a radiologist and he retired at 76, the same age that I am now, but he volunteered 2 days a week for the state attorney’s office until he was 92, and I’m not doing that.”
What Dr. Warres is choosing to do instead is indulge his many interests, including reading; writing; and practicing on the instrument he’s recently taken up, the harmonium.
This cascade of emotions led to one that was arguably more pleasurable: a sense of immense relief.
“When I got my first request after retirement for a prior authorization, I felt jubilant, like I wanted to throw a party! I felt like I had been walking with a backpack full of weights, and only after the weights were removed did I realize how much lighter it was.
“I loved doing psychotherapy, but more and more psychiatry was not what I had signed up for. I’m relieved that I no longer have to keep up with psychopharmacology. In a way, the Parkinson’s diagnosis sealed the deal. I felt that it gave me license, like a get out of jail card, to retire.”
But even this sense of palpable relief hasn’t closed the cycle of emotions Dr. Warres is experiencing over his retirement.
“You know, the more relieved I am, the more guilt I feel.”
As intellectually adventurous as ever
Marshal Folstein, MD, of Miami retired over a decade ago after a long academic career at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and as chairman of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. His Facebook profile states: “Leading the quiet life of a retired professor.”
He said retirement was an easy decision for he and his wife Susan, herself a former academic psychiatrist, which allowed them to immediately change gears.
“At the beginning, we traveled a bit. I wanted to continue with music, so I took flute lessons, and then I played flute in my synagogue, so now I have recently retired from that. I spend my time reading Talmud and the Bible and I keep asking questions. I found a new group of people, some are physicians, and we study and argue. I just turned 80 and I’m intellectually busy and happy.”
The retirement coach
Barbara Fowler, PhD, is a lifespan services consultant at Johns Hopkins who works with faculty and staff getting ready to retire. She said that the university has methods in place to make this decision less jarring.
“The school of medicine has a faculty transition plan that lets people cut back over a set period of time while still keeping benefits. It gives doctors a way to wind up their research and clinical responsibilities, and this is negotiated on an individual level.”
When she’s discussing with someone the possibility of retirement, Dr. Fowler likes to begin by asking them to define what exactly they mean by that word.
“The stereotyped concept is that someone stops what they are doing completely and spends their time playing golf or canasta,” she said. “But the baby boomers are redefining that. Physicians often continue to see some patients or participate in professional organizations. Some people are happy to stop doing the work they have done for years and go do something different, whereas others are interested in scaling back on work activities while adding new ones.”
Timing it right
So, when should psychiatrists retire? The most obvious time to reconsider is when the doctor is no longer able to perform work-related obligations owing to physical or cognitive limitations.
Financial constraints are another factor that comes into play. How necessary is it to work to pay the bills?
“When the kids are out of college and the mortgage is paid off, then there may be the financial means to reconceptualize work life and how you want to rebuild it,” Dr. Fowler said. “Because whether or not people are getting paid, they want to be productive.”
For some, this may come in the form of working in a reduced capacity. Certain practices are more amenable to part-time work or a gradual decrease in hours. A private practice may allow for more control than a position with an institution where an employee may have to continue working full time or not at all.
For others, that productivity might be measured in pursuing their own interests or assisting with family members who need their help. Grandchildren can be an important factor, especially if they live at a distance or childcare is needed. These issues became all the more salient when the pandemic shuttered day care centers and schools, and people limited contact with those outside their households.
Retirement for all physicians is wrapped in issues of identity; for those who have not cultivated other interests, retirement can be a huge loss with no clear path forward. And in an environment where there is a psychiatrist shortage, health care workers are deemed heroes, and human distress is mounting, retirement may come with mixed feelings of guilt, even when the psychiatrist wants a change and is ready for the next chapter. Finally, for those who have launched programs or research projects, there may be the fear that there is no one else who can or will carry on, and that all will be lost.
Yet these considerations focus on the negative, whereas Dr. Fowler said she likes to frame retirement in a positive light. “The key is having more choices; looking for activities that inspire passion; and asking, how can you live your best life?”
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I remember a conversation I had at the end of my training with an older psychiatrist who was closing his practice. I was very excited to finally be a psychiatrist, and therefore a bit shocked that someone would voluntarily end a career I was just beginning. After all, psychiatry is a field where people can practice with flexibility, and a private practice is not an all-or-none endeavor.
“Dinah,” this gentleman said to me, sensing my dismay, “I’m 74. I’m allowed to retire.”
Like many retired psychiatrists, this one continued to come to grand rounds every Monday, dressed in a suit, which was followed by lunch with friends in the dining room. He continued to be involved in professional activities and lived to be 96.
Another dear friend practiced psychiatry until she entered hospice after a 2-year battle with cancer. Others have whittled down their practices, hanging on to a few hours of patient care along with supervision, teaching, and involvement with professional organizations.
In discussing retirement with some of my peers, it’s become immediately clear that each psychiatrist approaches this decision – and how they choose to live after it’s made – with a unique set of concerns and goals.
Fatigued by bureaucracy
Robin Weiss, MD, is in the process of “shrinking” her private practice. She is quick to say she is not retiring, but planning to scale back to 1 day a week starting next summer.
“I want to work less so I have more time for my grandchildren, friends, and travel, and to finally write more.” She also hopes to improve her ping-pong game and exercise habits.
“I’m so tired of prior authorizations, and the one day a week of patients I’ve been committed to feels just about right.”
During the pandemic, Dr. Weiss relinquished her office and she plans to continue with a virtual practice, which allows her more flexibility in terms of where she is physically located.
“The pandemic didn’t influence my decision to scale back, but it did play a role in deciding to give up my office,” she said.
A decision precipitated by medical reasons
Stephen Warres, MD, is a child and adolescent psychiatrist in Maryland who fully retired from practice in June 2021. He started scaling back a few years ago, when he had to give up his office because the building was undergoing renovations.
“I was seeing some patients from my home, but for 2 years I had been working 1 or 2 weekends a month at the Baltimore city jail, and I thought of that as my final act. It was a setting I had never worked in, and I left there 4 months before the pandemic started.”
Dr. Warres noted that his decision to retire was propelled by his diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease at the end of 2019.
“So far I only have a resting tremor, but this is an illness in which cognitive decline is a possibility.”
The emotional roller-coaster that can await
“Why am I leaving when others practice longer? I read about a psychiatrist in California who was still practicing when he died at 102. And the last patient whom I saw when I left practice was a man I started treating just 2 days after I started residency in 1976! When I told him I would be retiring, he found a new psychiatrist who is 82 years old.”
This was followed, he said, by a sense of shame.
“My father was a radiologist and he retired at 76, the same age that I am now, but he volunteered 2 days a week for the state attorney’s office until he was 92, and I’m not doing that.”
What Dr. Warres is choosing to do instead is indulge his many interests, including reading; writing; and practicing on the instrument he’s recently taken up, the harmonium.
This cascade of emotions led to one that was arguably more pleasurable: a sense of immense relief.
“When I got my first request after retirement for a prior authorization, I felt jubilant, like I wanted to throw a party! I felt like I had been walking with a backpack full of weights, and only after the weights were removed did I realize how much lighter it was.
“I loved doing psychotherapy, but more and more psychiatry was not what I had signed up for. I’m relieved that I no longer have to keep up with psychopharmacology. In a way, the Parkinson’s diagnosis sealed the deal. I felt that it gave me license, like a get out of jail card, to retire.”
But even this sense of palpable relief hasn’t closed the cycle of emotions Dr. Warres is experiencing over his retirement.
“You know, the more relieved I am, the more guilt I feel.”
As intellectually adventurous as ever
Marshal Folstein, MD, of Miami retired over a decade ago after a long academic career at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and as chairman of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. His Facebook profile states: “Leading the quiet life of a retired professor.”
He said retirement was an easy decision for he and his wife Susan, herself a former academic psychiatrist, which allowed them to immediately change gears.
“At the beginning, we traveled a bit. I wanted to continue with music, so I took flute lessons, and then I played flute in my synagogue, so now I have recently retired from that. I spend my time reading Talmud and the Bible and I keep asking questions. I found a new group of people, some are physicians, and we study and argue. I just turned 80 and I’m intellectually busy and happy.”
The retirement coach
Barbara Fowler, PhD, is a lifespan services consultant at Johns Hopkins who works with faculty and staff getting ready to retire. She said that the university has methods in place to make this decision less jarring.
“The school of medicine has a faculty transition plan that lets people cut back over a set period of time while still keeping benefits. It gives doctors a way to wind up their research and clinical responsibilities, and this is negotiated on an individual level.”
When she’s discussing with someone the possibility of retirement, Dr. Fowler likes to begin by asking them to define what exactly they mean by that word.
“The stereotyped concept is that someone stops what they are doing completely and spends their time playing golf or canasta,” she said. “But the baby boomers are redefining that. Physicians often continue to see some patients or participate in professional organizations. Some people are happy to stop doing the work they have done for years and go do something different, whereas others are interested in scaling back on work activities while adding new ones.”
Timing it right
So, when should psychiatrists retire? The most obvious time to reconsider is when the doctor is no longer able to perform work-related obligations owing to physical or cognitive limitations.
Financial constraints are another factor that comes into play. How necessary is it to work to pay the bills?
“When the kids are out of college and the mortgage is paid off, then there may be the financial means to reconceptualize work life and how you want to rebuild it,” Dr. Fowler said. “Because whether or not people are getting paid, they want to be productive.”
For some, this may come in the form of working in a reduced capacity. Certain practices are more amenable to part-time work or a gradual decrease in hours. A private practice may allow for more control than a position with an institution where an employee may have to continue working full time or not at all.
For others, that productivity might be measured in pursuing their own interests or assisting with family members who need their help. Grandchildren can be an important factor, especially if they live at a distance or childcare is needed. These issues became all the more salient when the pandemic shuttered day care centers and schools, and people limited contact with those outside their households.
Retirement for all physicians is wrapped in issues of identity; for those who have not cultivated other interests, retirement can be a huge loss with no clear path forward. And in an environment where there is a psychiatrist shortage, health care workers are deemed heroes, and human distress is mounting, retirement may come with mixed feelings of guilt, even when the psychiatrist wants a change and is ready for the next chapter. Finally, for those who have launched programs or research projects, there may be the fear that there is no one else who can or will carry on, and that all will be lost.
Yet these considerations focus on the negative, whereas Dr. Fowler said she likes to frame retirement in a positive light. “The key is having more choices; looking for activities that inspire passion; and asking, how can you live your best life?”
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I remember a conversation I had at the end of my training with an older psychiatrist who was closing his practice. I was very excited to finally be a psychiatrist, and therefore a bit shocked that someone would voluntarily end a career I was just beginning. After all, psychiatry is a field where people can practice with flexibility, and a private practice is not an all-or-none endeavor.
“Dinah,” this gentleman said to me, sensing my dismay, “I’m 74. I’m allowed to retire.”
Like many retired psychiatrists, this one continued to come to grand rounds every Monday, dressed in a suit, which was followed by lunch with friends in the dining room. He continued to be involved in professional activities and lived to be 96.
Another dear friend practiced psychiatry until she entered hospice after a 2-year battle with cancer. Others have whittled down their practices, hanging on to a few hours of patient care along with supervision, teaching, and involvement with professional organizations.
In discussing retirement with some of my peers, it’s become immediately clear that each psychiatrist approaches this decision – and how they choose to live after it’s made – with a unique set of concerns and goals.
Fatigued by bureaucracy
Robin Weiss, MD, is in the process of “shrinking” her private practice. She is quick to say she is not retiring, but planning to scale back to 1 day a week starting next summer.
“I want to work less so I have more time for my grandchildren, friends, and travel, and to finally write more.” She also hopes to improve her ping-pong game and exercise habits.
“I’m so tired of prior authorizations, and the one day a week of patients I’ve been committed to feels just about right.”
During the pandemic, Dr. Weiss relinquished her office and she plans to continue with a virtual practice, which allows her more flexibility in terms of where she is physically located.
“The pandemic didn’t influence my decision to scale back, but it did play a role in deciding to give up my office,” she said.
A decision precipitated by medical reasons
Stephen Warres, MD, is a child and adolescent psychiatrist in Maryland who fully retired from practice in June 2021. He started scaling back a few years ago, when he had to give up his office because the building was undergoing renovations.
“I was seeing some patients from my home, but for 2 years I had been working 1 or 2 weekends a month at the Baltimore city jail, and I thought of that as my final act. It was a setting I had never worked in, and I left there 4 months before the pandemic started.”
Dr. Warres noted that his decision to retire was propelled by his diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease at the end of 2019.
“So far I only have a resting tremor, but this is an illness in which cognitive decline is a possibility.”
The emotional roller-coaster that can await
“Why am I leaving when others practice longer? I read about a psychiatrist in California who was still practicing when he died at 102. And the last patient whom I saw when I left practice was a man I started treating just 2 days after I started residency in 1976! When I told him I would be retiring, he found a new psychiatrist who is 82 years old.”
This was followed, he said, by a sense of shame.
“My father was a radiologist and he retired at 76, the same age that I am now, but he volunteered 2 days a week for the state attorney’s office until he was 92, and I’m not doing that.”
What Dr. Warres is choosing to do instead is indulge his many interests, including reading; writing; and practicing on the instrument he’s recently taken up, the harmonium.
This cascade of emotions led to one that was arguably more pleasurable: a sense of immense relief.
“When I got my first request after retirement for a prior authorization, I felt jubilant, like I wanted to throw a party! I felt like I had been walking with a backpack full of weights, and only after the weights were removed did I realize how much lighter it was.
“I loved doing psychotherapy, but more and more psychiatry was not what I had signed up for. I’m relieved that I no longer have to keep up with psychopharmacology. In a way, the Parkinson’s diagnosis sealed the deal. I felt that it gave me license, like a get out of jail card, to retire.”
But even this sense of palpable relief hasn’t closed the cycle of emotions Dr. Warres is experiencing over his retirement.
“You know, the more relieved I am, the more guilt I feel.”
As intellectually adventurous as ever
Marshal Folstein, MD, of Miami retired over a decade ago after a long academic career at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and as chairman of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. His Facebook profile states: “Leading the quiet life of a retired professor.”
He said retirement was an easy decision for he and his wife Susan, herself a former academic psychiatrist, which allowed them to immediately change gears.
“At the beginning, we traveled a bit. I wanted to continue with music, so I took flute lessons, and then I played flute in my synagogue, so now I have recently retired from that. I spend my time reading Talmud and the Bible and I keep asking questions. I found a new group of people, some are physicians, and we study and argue. I just turned 80 and I’m intellectually busy and happy.”
The retirement coach
Barbara Fowler, PhD, is a lifespan services consultant at Johns Hopkins who works with faculty and staff getting ready to retire. She said that the university has methods in place to make this decision less jarring.
“The school of medicine has a faculty transition plan that lets people cut back over a set period of time while still keeping benefits. It gives doctors a way to wind up their research and clinical responsibilities, and this is negotiated on an individual level.”
When she’s discussing with someone the possibility of retirement, Dr. Fowler likes to begin by asking them to define what exactly they mean by that word.
“The stereotyped concept is that someone stops what they are doing completely and spends their time playing golf or canasta,” she said. “But the baby boomers are redefining that. Physicians often continue to see some patients or participate in professional organizations. Some people are happy to stop doing the work they have done for years and go do something different, whereas others are interested in scaling back on work activities while adding new ones.”
Timing it right
So, when should psychiatrists retire? The most obvious time to reconsider is when the doctor is no longer able to perform work-related obligations owing to physical or cognitive limitations.
Financial constraints are another factor that comes into play. How necessary is it to work to pay the bills?
“When the kids are out of college and the mortgage is paid off, then there may be the financial means to reconceptualize work life and how you want to rebuild it,” Dr. Fowler said. “Because whether or not people are getting paid, they want to be productive.”
For some, this may come in the form of working in a reduced capacity. Certain practices are more amenable to part-time work or a gradual decrease in hours. A private practice may allow for more control than a position with an institution where an employee may have to continue working full time or not at all.
For others, that productivity might be measured in pursuing their own interests or assisting with family members who need their help. Grandchildren can be an important factor, especially if they live at a distance or childcare is needed. These issues became all the more salient when the pandemic shuttered day care centers and schools, and people limited contact with those outside their households.
Retirement for all physicians is wrapped in issues of identity; for those who have not cultivated other interests, retirement can be a huge loss with no clear path forward. And in an environment where there is a psychiatrist shortage, health care workers are deemed heroes, and human distress is mounting, retirement may come with mixed feelings of guilt, even when the psychiatrist wants a change and is ready for the next chapter. Finally, for those who have launched programs or research projects, there may be the fear that there is no one else who can or will carry on, and that all will be lost.
Yet these considerations focus on the negative, whereas Dr. Fowler said she likes to frame retirement in a positive light. “The key is having more choices; looking for activities that inspire passion; and asking, how can you live your best life?”
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to deal with offensive or impaired doctors
Knowing what to say and do can lead to a positive outcome for the physician involved and the organization.
Misbehaving and impaired physicians put their organizations at risk, which can lead to malpractice/patient injury lawsuits, labor law and harassment claims, and a damaged reputation through negative social media reviews, said Debra Phairas, MBA, president of Practice and Liability Consultants LLC, at the annual meeting of the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) .
“Verbal harassment or bullying claims can result in large dollar awards against the organizations that knew about the behavior and did nothing to stop it. Organizations can be sued for that,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls a doctor who called a female doctor “an entitled bitch” and the administrator “incompetent” in front of other staff. “He would pick on one department manager at every meeting and humiliate them in front of the others,” says Ms. Phairas.
After working with a human resources (HR) attorney and conducting independent reviews, they used a strategy Ms. Phairas calls her “3 C’s” for dealing with disruptive doctors.
Confront, correct, and/or counsel
The three C’s can work individually or together, depending on the doctor’s situation. Confronting a physician can start with an informal discussion; correcting can involve seeking a written apology that directly addresses the problem or sending a letter of admonition; and coaching or counseling can be offered. If the doctor resists those efforts, practice administrators can issue a final letter of warning and then suspend or terminate the physician, says Ms. Phairas.
Sometimes having a conversation with a disruptive doctor about the risks and consequences is enough to change the offending behavior, says Ms. Phairas.
She recalled being asked by a medical group to meet with a physician who she says was “snapping the bra straps of medical assistants in the hall — everyone there was horrified. I told him that’s not appropriate, that he was placing everyone at risk and they will terminate him if he didn’t stop. I asked for his commitment to stop, and he agreed,” says Ms. Phairas.
She also recommends implementing these strategies to prevent and deal with disruptive physicians:
- Implement a code of conduct and share it during interviews;
- Have zero tolerance policies and procedures for documenting behavior;
- Get advice from a good employment attorney;
- Implement written performance improvement plans;
- Provide resources to change the behavior;
- Follow through with suspension and termination; and
- Add to shareholder agreements a clause stating that partners/shareholders can gently ask or insist that the physician obtain counseling or help.
Getting impaired doctors help
Doctors can be impaired through substance abuse, a serious medical illness, mental illness, or age-related deterioration.
Life events such as divorce or the death of a spouse, child, or a physician partner can affect a doctor’s mental health. “In those cases, you need to have the courage to say you’re really depressed and we all agree you need to get help,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls one occasion in which a practice administration staff member could not locate a doctor whose patients were waiting to be seen. “He was so devastated from his divorce that he had crawled into a ball beneath his desk. She had to coax him out and tell him that they were worried about him and he needed to get help.”
Another reason doctors may not be performing well may be because of an undiagnosed medical illness. Doctors in an orthopedic group were mad at another partner who had slowed down and couldn’t help pay the expenses. “They were ready to terminate him when he went to the doctor and learned he had colon cancer,” says Ms. Phairas.
Ms. Phairas recommends that practices update their partner shareholder agreements regularly with the following:
- Include “fit for duty” examinations, especially after age 65.
- Insist that a physician be evaluated by a doctor outside the practice. The doctor may be one that they agree upon or one chosen by the local medical society president.
- Include in the agreement the clause, “Partners and employees will be subject to review for impairment due to matters including but not limited to age-related, physical, or mental conditions.”
- Establish a voting mechanism for terminating a physician.
Aging doctors who won’t retire
Some doctors have retired early because of COVID, whereas others are staying on because they are feeling financial pressures — they lost a lot of money last year and need to make up for it, says Ms. Phairas.
She warned that administrators have to be careful in dealing with older doctors because of age discrimination laws.
Doctors may not notice they are declining mentally until it becomes a problem. Ms. Phairas recalls an internist senior partner who started behaving erratically when he was 78 years old. “He wrote himself a $25,000 check from the organization’s funds without telling his partners, left a patient he should have been watching and she fell over and sued the practice, and the staff started noticing that he was forgetting or not doing things,” says Ms. Phairas.
She sought guidance from a good HR attorney and involved a malpractice attorney. She then met with the senior partner. “I reminded him of his Hippocratic Oath that he took when he became a doctor and told him that his actions were harming patients. I pleaded with him that it was time to retire. He didn’t.”
Because this physician wouldn’t retire, the practice referred to their updated shareholder agreement, which stated that they could insist that the physician undergo a neuropsychiatric assessment from a certified specialist. He didn’t pass the evaluation, which then provided evidence of his declining cognitive skills.
“All the doctors, myself, and the HR attorney talked to him about this and laid out all the facts. It was hard to say these things, but he listened and left. We went through the termination process to protect the practice and avoid litigation. The malpractice insurer also refused to renew his policy,” says Ms. Phairas.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Knowing what to say and do can lead to a positive outcome for the physician involved and the organization.
Misbehaving and impaired physicians put their organizations at risk, which can lead to malpractice/patient injury lawsuits, labor law and harassment claims, and a damaged reputation through negative social media reviews, said Debra Phairas, MBA, president of Practice and Liability Consultants LLC, at the annual meeting of the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) .
“Verbal harassment or bullying claims can result in large dollar awards against the organizations that knew about the behavior and did nothing to stop it. Organizations can be sued for that,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls a doctor who called a female doctor “an entitled bitch” and the administrator “incompetent” in front of other staff. “He would pick on one department manager at every meeting and humiliate them in front of the others,” says Ms. Phairas.
After working with a human resources (HR) attorney and conducting independent reviews, they used a strategy Ms. Phairas calls her “3 C’s” for dealing with disruptive doctors.
Confront, correct, and/or counsel
The three C’s can work individually or together, depending on the doctor’s situation. Confronting a physician can start with an informal discussion; correcting can involve seeking a written apology that directly addresses the problem or sending a letter of admonition; and coaching or counseling can be offered. If the doctor resists those efforts, practice administrators can issue a final letter of warning and then suspend or terminate the physician, says Ms. Phairas.
Sometimes having a conversation with a disruptive doctor about the risks and consequences is enough to change the offending behavior, says Ms. Phairas.
She recalled being asked by a medical group to meet with a physician who she says was “snapping the bra straps of medical assistants in the hall — everyone there was horrified. I told him that’s not appropriate, that he was placing everyone at risk and they will terminate him if he didn’t stop. I asked for his commitment to stop, and he agreed,” says Ms. Phairas.
She also recommends implementing these strategies to prevent and deal with disruptive physicians:
- Implement a code of conduct and share it during interviews;
- Have zero tolerance policies and procedures for documenting behavior;
- Get advice from a good employment attorney;
- Implement written performance improvement plans;
- Provide resources to change the behavior;
- Follow through with suspension and termination; and
- Add to shareholder agreements a clause stating that partners/shareholders can gently ask or insist that the physician obtain counseling or help.
Getting impaired doctors help
Doctors can be impaired through substance abuse, a serious medical illness, mental illness, or age-related deterioration.
Life events such as divorce or the death of a spouse, child, or a physician partner can affect a doctor’s mental health. “In those cases, you need to have the courage to say you’re really depressed and we all agree you need to get help,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls one occasion in which a practice administration staff member could not locate a doctor whose patients were waiting to be seen. “He was so devastated from his divorce that he had crawled into a ball beneath his desk. She had to coax him out and tell him that they were worried about him and he needed to get help.”
Another reason doctors may not be performing well may be because of an undiagnosed medical illness. Doctors in an orthopedic group were mad at another partner who had slowed down and couldn’t help pay the expenses. “They were ready to terminate him when he went to the doctor and learned he had colon cancer,” says Ms. Phairas.
Ms. Phairas recommends that practices update their partner shareholder agreements regularly with the following:
- Include “fit for duty” examinations, especially after age 65.
- Insist that a physician be evaluated by a doctor outside the practice. The doctor may be one that they agree upon or one chosen by the local medical society president.
- Include in the agreement the clause, “Partners and employees will be subject to review for impairment due to matters including but not limited to age-related, physical, or mental conditions.”
- Establish a voting mechanism for terminating a physician.
Aging doctors who won’t retire
Some doctors have retired early because of COVID, whereas others are staying on because they are feeling financial pressures — they lost a lot of money last year and need to make up for it, says Ms. Phairas.
She warned that administrators have to be careful in dealing with older doctors because of age discrimination laws.
Doctors may not notice they are declining mentally until it becomes a problem. Ms. Phairas recalls an internist senior partner who started behaving erratically when he was 78 years old. “He wrote himself a $25,000 check from the organization’s funds without telling his partners, left a patient he should have been watching and she fell over and sued the practice, and the staff started noticing that he was forgetting or not doing things,” says Ms. Phairas.
She sought guidance from a good HR attorney and involved a malpractice attorney. She then met with the senior partner. “I reminded him of his Hippocratic Oath that he took when he became a doctor and told him that his actions were harming patients. I pleaded with him that it was time to retire. He didn’t.”
Because this physician wouldn’t retire, the practice referred to their updated shareholder agreement, which stated that they could insist that the physician undergo a neuropsychiatric assessment from a certified specialist. He didn’t pass the evaluation, which then provided evidence of his declining cognitive skills.
“All the doctors, myself, and the HR attorney talked to him about this and laid out all the facts. It was hard to say these things, but he listened and left. We went through the termination process to protect the practice and avoid litigation. The malpractice insurer also refused to renew his policy,” says Ms. Phairas.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Knowing what to say and do can lead to a positive outcome for the physician involved and the organization.
Misbehaving and impaired physicians put their organizations at risk, which can lead to malpractice/patient injury lawsuits, labor law and harassment claims, and a damaged reputation through negative social media reviews, said Debra Phairas, MBA, president of Practice and Liability Consultants LLC, at the annual meeting of the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) .
“Verbal harassment or bullying claims can result in large dollar awards against the organizations that knew about the behavior and did nothing to stop it. Organizations can be sued for that,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls a doctor who called a female doctor “an entitled bitch” and the administrator “incompetent” in front of other staff. “He would pick on one department manager at every meeting and humiliate them in front of the others,” says Ms. Phairas.
After working with a human resources (HR) attorney and conducting independent reviews, they used a strategy Ms. Phairas calls her “3 C’s” for dealing with disruptive doctors.
Confront, correct, and/or counsel
The three C’s can work individually or together, depending on the doctor’s situation. Confronting a physician can start with an informal discussion; correcting can involve seeking a written apology that directly addresses the problem or sending a letter of admonition; and coaching or counseling can be offered. If the doctor resists those efforts, practice administrators can issue a final letter of warning and then suspend or terminate the physician, says Ms. Phairas.
Sometimes having a conversation with a disruptive doctor about the risks and consequences is enough to change the offending behavior, says Ms. Phairas.
She recalled being asked by a medical group to meet with a physician who she says was “snapping the bra straps of medical assistants in the hall — everyone there was horrified. I told him that’s not appropriate, that he was placing everyone at risk and they will terminate him if he didn’t stop. I asked for his commitment to stop, and he agreed,” says Ms. Phairas.
She also recommends implementing these strategies to prevent and deal with disruptive physicians:
- Implement a code of conduct and share it during interviews;
- Have zero tolerance policies and procedures for documenting behavior;
- Get advice from a good employment attorney;
- Implement written performance improvement plans;
- Provide resources to change the behavior;
- Follow through with suspension and termination; and
- Add to shareholder agreements a clause stating that partners/shareholders can gently ask or insist that the physician obtain counseling or help.
Getting impaired doctors help
Doctors can be impaired through substance abuse, a serious medical illness, mental illness, or age-related deterioration.
Life events such as divorce or the death of a spouse, child, or a physician partner can affect a doctor’s mental health. “In those cases, you need to have the courage to say you’re really depressed and we all agree you need to get help,” says Ms. Phairas.
She recalls one occasion in which a practice administration staff member could not locate a doctor whose patients were waiting to be seen. “He was so devastated from his divorce that he had crawled into a ball beneath his desk. She had to coax him out and tell him that they were worried about him and he needed to get help.”
Another reason doctors may not be performing well may be because of an undiagnosed medical illness. Doctors in an orthopedic group were mad at another partner who had slowed down and couldn’t help pay the expenses. “They were ready to terminate him when he went to the doctor and learned he had colon cancer,” says Ms. Phairas.
Ms. Phairas recommends that practices update their partner shareholder agreements regularly with the following:
- Include “fit for duty” examinations, especially after age 65.
- Insist that a physician be evaluated by a doctor outside the practice. The doctor may be one that they agree upon or one chosen by the local medical society president.
- Include in the agreement the clause, “Partners and employees will be subject to review for impairment due to matters including but not limited to age-related, physical, or mental conditions.”
- Establish a voting mechanism for terminating a physician.
Aging doctors who won’t retire
Some doctors have retired early because of COVID, whereas others are staying on because they are feeling financial pressures — they lost a lot of money last year and need to make up for it, says Ms. Phairas.
She warned that administrators have to be careful in dealing with older doctors because of age discrimination laws.
Doctors may not notice they are declining mentally until it becomes a problem. Ms. Phairas recalls an internist senior partner who started behaving erratically when he was 78 years old. “He wrote himself a $25,000 check from the organization’s funds without telling his partners, left a patient he should have been watching and she fell over and sued the practice, and the staff started noticing that he was forgetting or not doing things,” says Ms. Phairas.
She sought guidance from a good HR attorney and involved a malpractice attorney. She then met with the senior partner. “I reminded him of his Hippocratic Oath that he took when he became a doctor and told him that his actions were harming patients. I pleaded with him that it was time to retire. He didn’t.”
Because this physician wouldn’t retire, the practice referred to their updated shareholder agreement, which stated that they could insist that the physician undergo a neuropsychiatric assessment from a certified specialist. He didn’t pass the evaluation, which then provided evidence of his declining cognitive skills.
“All the doctors, myself, and the HR attorney talked to him about this and laid out all the facts. It was hard to say these things, but he listened and left. We went through the termination process to protect the practice and avoid litigation. The malpractice insurer also refused to renew his policy,” says Ms. Phairas.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
California plans for a post-Roe world as abortion access shrinks elsewhere
SACRAMENTO – With access to abortion at stake across America, California is preparing to become the nation’s abortion provider.
Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom and legislative leaders have asked a group of reproductive health experts to propose policies to bolster the state’s abortion infrastructure and ready it for more patients. Lawmakers plan to begin debating the ideas when they reconvene in January.
Abortion clinics are already girding themselves for a surge in demand.
Janet Jacobson, MD, medical director of Planned Parenthood of Orange and San Bernardino Counties, said three or four out-of-state patients visit her clinics each day – about double the number that sought treatment before a near-total ban on abortion took effect in Texas in September.
While the nine clinics can absorb that slow trickle, they expect up to 50 out-of-state patients a week if the U.S. Supreme Court’s conservative majority guts abortion rights nationally, Dr. Jacobson said. She bases her estimate on new data from the Guttmacher Institute, a research organization that supports abortion and reproductive health rights.
She is adding staff members and appointment capacity, hoping to accommodate everyone.
“We have to make sure we can still continue to care for all of our California patients,” Dr. Jacobson said. “We don’t want them getting squeezed out” of appointments.
The Texas law banned nearly all abortions after about 6 weeks of pregnancy and empowered private citizens to sue anyone who performs or “aids and abets” an abortion after that time. The Supreme Court heard arguments in that case on Nov. 1 and is expected to announce a ruling on its constitutionality in June. Nonetheless, Florida and Ohio have announced plans for copycat laws.
Next month the high court will hear another abortion case with even broader implications, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, a lawsuit challenging the constitutionality of a 2018 Mississippi law that prohibited abortion after 15 weeks. If the court sides with Mississippi, its decision could overturn existing abortion rights set by the landmark Roe v. Wade case.
Should that happen, reproductive rights experts predict, 26 states will ban the procedure altogether, and states with stronger protections for abortion, like California, will draw even more patients. There could be up to a 3,000% increase in people who “may drive to California for abortion care” each year, according to the Guttmacher data.
In 2017, the most recent year for which data are available from Guttmacher, California – by far the nation’s most populous state – had more abortion providers than any other state, with 419 hospitals, clinics, or doctors’ offices performing the procedure. The next highest were New York, with 252, and Florida, with 85. Neighboring Arizona and Nevada each had 11. Of the 862,320 abortions performed in the United States that year, 132.680, about 15% were in California.
Planned Parenthood clinics in California say they already serve about 7,000 out-of-state patients a year and are expecting a surge of new ones, especially in travel hubs like the Los Angeles area.
In September, Planned Parenthood and groups such as Black Women for Wellness convened the California Future of Abortion Council with backing from influential Democratic leaders including Gov. Newsom, state Senate leader Toni Atkins, and Assembly Speaker Anthony Rendon.
Ms. Atkins, who was the director of a San Diego women’s health clinic in the 1980s, said she spent time with women from states where it was hard to get an abortion. She said California is committed to ensuring abortion access in the state and beyond.
The council is focused on increasing funding for abortion services, providing logistical and financial help for women who need to travel, increasing the number of health care providers who perform abortions, and strengthening legal protections for them.
Increasing capacity could mean licensing more practitioners to provide abortions or pumping more resources into telehealth so people can see a doctor online to prescribe pills for a medical abortion – a service California doctors currently can provide to patients only in California.
The most important thing the state should do is fix its shortage of providers, especially those who perform second-trimester abortions, which are more expensive and complicated than first-trimester abortions, said council member Daniel Grossman, MD, director of the Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health program at the University of California, San Francisco.
It’s not feasible to place an abortion provider in every corner of the state, Dr. Grossman said. Instead, the council should focus on creating “hubs that can provide abortion care for large numbers of people” in easy-to-get-to locations.
California already struggles to provide abortions to all who seek them, especially low-income women covered by Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program. For example, 28 counties – home to 10% of Medi-Cal recipients of childbearing age – don’t have facilities that provide abortions to Medi-Cal patients.
A medical abortion, in which pills are used to terminate a pregnancy, costs California patients an average of $306 out-of-pocket, according to an analysis by the California Health Benefits Review Program, but isn’t available after 10 weeks. After that, the only option is a surgical abortion, which costs an average of $887 out-of-pocket in California.
One of the council’s recommendations will likely be to increase the rate Medi-Cal payments for abortions so more providers will perform them, said council member Fabiola Carrión, interim director for reproductive and sexual health at the National Health Law Program.
Medi-Cal pays $354.43 for a second-trimester abortion. A 2020 study in the journal Contraception found that states paid between $79 and $626 for a second-trimester abortion in 2017.
Increasing Medi-Cal rates won’t help patients traveling from outside California. Generally, private insurance doesn’t cover out-of-state abortions, so most women will be on the hook for the full cost, and those enrolled in other states’ Medicaid programs must pay out-of-pocket, too.
The council hopes to reduce costs for state residents and visitors, said Brandon Richards, director of communications for Planned Parenthood Affiliates of California. “It’s about making it easy for people to access abortion in California, whether they reside here or are coming in from out of state,” he said.
One way to target costs is by funding the practical support, like helping to pay for transportation, child care, hotels, or time off work, said council member Jessica Pinckney, executive director of Access Reproductive Justice, a fund that helps people pay for abortions.
Ms. Pinckney said she’s working with Los Angeles County to set up a public abortion fund to cover some of those costs for anyone seeking an abortion in the county. It would be modeled after similar pots maintained by the cities of New York; Austin, Tex.; and Portland, Ore., and could eventually be a template for the first statewide fund, Ms. Pinckney said.
Most Texans seeking abortions since that state’s law took effect are going to nearby states like Colorado, New Mexico, and Oklahoma, said Sierra Harris, deputy director of network strategies for the National Network of Abortion Funds. Women in those states, in turn, are having trouble getting care and are looking to California for appointments.
Practical support is important for out-of-state patients, said Alissa Perrucci, PhD, MPH, operations manager at the Women’s Options Center at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, one of five abortion clinics inside California hospitals.
Dr. Perrucci’s clinic is focusing on telemedicine, phone counseling, and other ways to save time so it can add appointments for out-of-state patients if necessary.
But more slots are useless if women can’t make it to California. The clinic has booked about 10 appointments for Texans since the state’s ban went into effect, but only half have shown up, mostly women with family connections in California.
“Most people just don’t have the money to get here,” she said. “If the burden of abortion was borne predominantly by the wealthy, yeah, they’d just fly here.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
SACRAMENTO – With access to abortion at stake across America, California is preparing to become the nation’s abortion provider.
Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom and legislative leaders have asked a group of reproductive health experts to propose policies to bolster the state’s abortion infrastructure and ready it for more patients. Lawmakers plan to begin debating the ideas when they reconvene in January.
Abortion clinics are already girding themselves for a surge in demand.
Janet Jacobson, MD, medical director of Planned Parenthood of Orange and San Bernardino Counties, said three or four out-of-state patients visit her clinics each day – about double the number that sought treatment before a near-total ban on abortion took effect in Texas in September.
While the nine clinics can absorb that slow trickle, they expect up to 50 out-of-state patients a week if the U.S. Supreme Court’s conservative majority guts abortion rights nationally, Dr. Jacobson said. She bases her estimate on new data from the Guttmacher Institute, a research organization that supports abortion and reproductive health rights.
She is adding staff members and appointment capacity, hoping to accommodate everyone.
“We have to make sure we can still continue to care for all of our California patients,” Dr. Jacobson said. “We don’t want them getting squeezed out” of appointments.
The Texas law banned nearly all abortions after about 6 weeks of pregnancy and empowered private citizens to sue anyone who performs or “aids and abets” an abortion after that time. The Supreme Court heard arguments in that case on Nov. 1 and is expected to announce a ruling on its constitutionality in June. Nonetheless, Florida and Ohio have announced plans for copycat laws.
Next month the high court will hear another abortion case with even broader implications, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, a lawsuit challenging the constitutionality of a 2018 Mississippi law that prohibited abortion after 15 weeks. If the court sides with Mississippi, its decision could overturn existing abortion rights set by the landmark Roe v. Wade case.
Should that happen, reproductive rights experts predict, 26 states will ban the procedure altogether, and states with stronger protections for abortion, like California, will draw even more patients. There could be up to a 3,000% increase in people who “may drive to California for abortion care” each year, according to the Guttmacher data.
In 2017, the most recent year for which data are available from Guttmacher, California – by far the nation’s most populous state – had more abortion providers than any other state, with 419 hospitals, clinics, or doctors’ offices performing the procedure. The next highest were New York, with 252, and Florida, with 85. Neighboring Arizona and Nevada each had 11. Of the 862,320 abortions performed in the United States that year, 132.680, about 15% were in California.
Planned Parenthood clinics in California say they already serve about 7,000 out-of-state patients a year and are expecting a surge of new ones, especially in travel hubs like the Los Angeles area.
In September, Planned Parenthood and groups such as Black Women for Wellness convened the California Future of Abortion Council with backing from influential Democratic leaders including Gov. Newsom, state Senate leader Toni Atkins, and Assembly Speaker Anthony Rendon.
Ms. Atkins, who was the director of a San Diego women’s health clinic in the 1980s, said she spent time with women from states where it was hard to get an abortion. She said California is committed to ensuring abortion access in the state and beyond.
The council is focused on increasing funding for abortion services, providing logistical and financial help for women who need to travel, increasing the number of health care providers who perform abortions, and strengthening legal protections for them.
Increasing capacity could mean licensing more practitioners to provide abortions or pumping more resources into telehealth so people can see a doctor online to prescribe pills for a medical abortion – a service California doctors currently can provide to patients only in California.
The most important thing the state should do is fix its shortage of providers, especially those who perform second-trimester abortions, which are more expensive and complicated than first-trimester abortions, said council member Daniel Grossman, MD, director of the Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health program at the University of California, San Francisco.
It’s not feasible to place an abortion provider in every corner of the state, Dr. Grossman said. Instead, the council should focus on creating “hubs that can provide abortion care for large numbers of people” in easy-to-get-to locations.
California already struggles to provide abortions to all who seek them, especially low-income women covered by Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program. For example, 28 counties – home to 10% of Medi-Cal recipients of childbearing age – don’t have facilities that provide abortions to Medi-Cal patients.
A medical abortion, in which pills are used to terminate a pregnancy, costs California patients an average of $306 out-of-pocket, according to an analysis by the California Health Benefits Review Program, but isn’t available after 10 weeks. After that, the only option is a surgical abortion, which costs an average of $887 out-of-pocket in California.
One of the council’s recommendations will likely be to increase the rate Medi-Cal payments for abortions so more providers will perform them, said council member Fabiola Carrión, interim director for reproductive and sexual health at the National Health Law Program.
Medi-Cal pays $354.43 for a second-trimester abortion. A 2020 study in the journal Contraception found that states paid between $79 and $626 for a second-trimester abortion in 2017.
Increasing Medi-Cal rates won’t help patients traveling from outside California. Generally, private insurance doesn’t cover out-of-state abortions, so most women will be on the hook for the full cost, and those enrolled in other states’ Medicaid programs must pay out-of-pocket, too.
The council hopes to reduce costs for state residents and visitors, said Brandon Richards, director of communications for Planned Parenthood Affiliates of California. “It’s about making it easy for people to access abortion in California, whether they reside here or are coming in from out of state,” he said.
One way to target costs is by funding the practical support, like helping to pay for transportation, child care, hotels, or time off work, said council member Jessica Pinckney, executive director of Access Reproductive Justice, a fund that helps people pay for abortions.
Ms. Pinckney said she’s working with Los Angeles County to set up a public abortion fund to cover some of those costs for anyone seeking an abortion in the county. It would be modeled after similar pots maintained by the cities of New York; Austin, Tex.; and Portland, Ore., and could eventually be a template for the first statewide fund, Ms. Pinckney said.
Most Texans seeking abortions since that state’s law took effect are going to nearby states like Colorado, New Mexico, and Oklahoma, said Sierra Harris, deputy director of network strategies for the National Network of Abortion Funds. Women in those states, in turn, are having trouble getting care and are looking to California for appointments.
Practical support is important for out-of-state patients, said Alissa Perrucci, PhD, MPH, operations manager at the Women’s Options Center at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, one of five abortion clinics inside California hospitals.
Dr. Perrucci’s clinic is focusing on telemedicine, phone counseling, and other ways to save time so it can add appointments for out-of-state patients if necessary.
But more slots are useless if women can’t make it to California. The clinic has booked about 10 appointments for Texans since the state’s ban went into effect, but only half have shown up, mostly women with family connections in California.
“Most people just don’t have the money to get here,” she said. “If the burden of abortion was borne predominantly by the wealthy, yeah, they’d just fly here.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
SACRAMENTO – With access to abortion at stake across America, California is preparing to become the nation’s abortion provider.
Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom and legislative leaders have asked a group of reproductive health experts to propose policies to bolster the state’s abortion infrastructure and ready it for more patients. Lawmakers plan to begin debating the ideas when they reconvene in January.
Abortion clinics are already girding themselves for a surge in demand.
Janet Jacobson, MD, medical director of Planned Parenthood of Orange and San Bernardino Counties, said three or four out-of-state patients visit her clinics each day – about double the number that sought treatment before a near-total ban on abortion took effect in Texas in September.
While the nine clinics can absorb that slow trickle, they expect up to 50 out-of-state patients a week if the U.S. Supreme Court’s conservative majority guts abortion rights nationally, Dr. Jacobson said. She bases her estimate on new data from the Guttmacher Institute, a research organization that supports abortion and reproductive health rights.
She is adding staff members and appointment capacity, hoping to accommodate everyone.
“We have to make sure we can still continue to care for all of our California patients,” Dr. Jacobson said. “We don’t want them getting squeezed out” of appointments.
The Texas law banned nearly all abortions after about 6 weeks of pregnancy and empowered private citizens to sue anyone who performs or “aids and abets” an abortion after that time. The Supreme Court heard arguments in that case on Nov. 1 and is expected to announce a ruling on its constitutionality in June. Nonetheless, Florida and Ohio have announced plans for copycat laws.
Next month the high court will hear another abortion case with even broader implications, Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, a lawsuit challenging the constitutionality of a 2018 Mississippi law that prohibited abortion after 15 weeks. If the court sides with Mississippi, its decision could overturn existing abortion rights set by the landmark Roe v. Wade case.
Should that happen, reproductive rights experts predict, 26 states will ban the procedure altogether, and states with stronger protections for abortion, like California, will draw even more patients. There could be up to a 3,000% increase in people who “may drive to California for abortion care” each year, according to the Guttmacher data.
In 2017, the most recent year for which data are available from Guttmacher, California – by far the nation’s most populous state – had more abortion providers than any other state, with 419 hospitals, clinics, or doctors’ offices performing the procedure. The next highest were New York, with 252, and Florida, with 85. Neighboring Arizona and Nevada each had 11. Of the 862,320 abortions performed in the United States that year, 132.680, about 15% were in California.
Planned Parenthood clinics in California say they already serve about 7,000 out-of-state patients a year and are expecting a surge of new ones, especially in travel hubs like the Los Angeles area.
In September, Planned Parenthood and groups such as Black Women for Wellness convened the California Future of Abortion Council with backing from influential Democratic leaders including Gov. Newsom, state Senate leader Toni Atkins, and Assembly Speaker Anthony Rendon.
Ms. Atkins, who was the director of a San Diego women’s health clinic in the 1980s, said she spent time with women from states where it was hard to get an abortion. She said California is committed to ensuring abortion access in the state and beyond.
The council is focused on increasing funding for abortion services, providing logistical and financial help for women who need to travel, increasing the number of health care providers who perform abortions, and strengthening legal protections for them.
Increasing capacity could mean licensing more practitioners to provide abortions or pumping more resources into telehealth so people can see a doctor online to prescribe pills for a medical abortion – a service California doctors currently can provide to patients only in California.
The most important thing the state should do is fix its shortage of providers, especially those who perform second-trimester abortions, which are more expensive and complicated than first-trimester abortions, said council member Daniel Grossman, MD, director of the Advancing New Standards in Reproductive Health program at the University of California, San Francisco.
It’s not feasible to place an abortion provider in every corner of the state, Dr. Grossman said. Instead, the council should focus on creating “hubs that can provide abortion care for large numbers of people” in easy-to-get-to locations.
California already struggles to provide abortions to all who seek them, especially low-income women covered by Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program. For example, 28 counties – home to 10% of Medi-Cal recipients of childbearing age – don’t have facilities that provide abortions to Medi-Cal patients.
A medical abortion, in which pills are used to terminate a pregnancy, costs California patients an average of $306 out-of-pocket, according to an analysis by the California Health Benefits Review Program, but isn’t available after 10 weeks. After that, the only option is a surgical abortion, which costs an average of $887 out-of-pocket in California.
One of the council’s recommendations will likely be to increase the rate Medi-Cal payments for abortions so more providers will perform them, said council member Fabiola Carrión, interim director for reproductive and sexual health at the National Health Law Program.
Medi-Cal pays $354.43 for a second-trimester abortion. A 2020 study in the journal Contraception found that states paid between $79 and $626 for a second-trimester abortion in 2017.
Increasing Medi-Cal rates won’t help patients traveling from outside California. Generally, private insurance doesn’t cover out-of-state abortions, so most women will be on the hook for the full cost, and those enrolled in other states’ Medicaid programs must pay out-of-pocket, too.
The council hopes to reduce costs for state residents and visitors, said Brandon Richards, director of communications for Planned Parenthood Affiliates of California. “It’s about making it easy for people to access abortion in California, whether they reside here or are coming in from out of state,” he said.
One way to target costs is by funding the practical support, like helping to pay for transportation, child care, hotels, or time off work, said council member Jessica Pinckney, executive director of Access Reproductive Justice, a fund that helps people pay for abortions.
Ms. Pinckney said she’s working with Los Angeles County to set up a public abortion fund to cover some of those costs for anyone seeking an abortion in the county. It would be modeled after similar pots maintained by the cities of New York; Austin, Tex.; and Portland, Ore., and could eventually be a template for the first statewide fund, Ms. Pinckney said.
Most Texans seeking abortions since that state’s law took effect are going to nearby states like Colorado, New Mexico, and Oklahoma, said Sierra Harris, deputy director of network strategies for the National Network of Abortion Funds. Women in those states, in turn, are having trouble getting care and are looking to California for appointments.
Practical support is important for out-of-state patients, said Alissa Perrucci, PhD, MPH, operations manager at the Women’s Options Center at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, one of five abortion clinics inside California hospitals.
Dr. Perrucci’s clinic is focusing on telemedicine, phone counseling, and other ways to save time so it can add appointments for out-of-state patients if necessary.
But more slots are useless if women can’t make it to California. The clinic has booked about 10 appointments for Texans since the state’s ban went into effect, but only half have shown up, mostly women with family connections in California.
“Most people just don’t have the money to get here,” she said. “If the burden of abortion was borne predominantly by the wealthy, yeah, they’d just fly here.”
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Medical technology should keep patient in mind
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.
Indeed, science and technology provide opportunities to improve outcomes in ways not even imagined 100 years ago, yet we must acknowledge that technology also threatens to erect barriers between us and our patients. We can be easily tempted to confuse new care delivery tools with the actual care itself.
Threats to the physician-patient relationship
Medical history provides many examples of how our zeal to innovate can have untoward consequences to the physician-patient relationship.
In the late 1800s, for example, to convey a sense of science, purity of intent, and trust, the medical community began wearing white coats. Those white coats have been discussed as creating emotional distance between physicians and their patients.1
Even when we in the medical community are slow and reluctant to change, the external forces propelling us forward often seem unstoppable; kinetic aspirations to innovate electronic information systems and new applications seem suddenly to revolutionize care delivery when we least expect it. The rapidity of change in technology can sometimes be dizzying but can at the same time can occur so swiftly we don’t even notice it.
After René Laennec invented the stethoscope in the early 1800s, clinicians no longer needed to physically lean in and place an ear directly onto patients to hear their hearts beating. This created a distance from patients that was still lamented 50 years later, when a professor of medicine is reported to have said, “he that hath ears to hear, let him use his ears and not a stethoscope.” Still, while the stethoscope has literally distanced us from patients, it is such an important tool that we no longer think about this distancing. We have adapted over time to remain close to our patients, to sincerely listen to their thoughts and reassure them that we hear them without the need to feel our ears on their chests.
Francis Peabody, the eminent Harvard physician, wrote an essay in 1927 titled, “The Care of the Patient.” At the end of the first paragraph, he states: “The most common criticism made at present by older practitioners is that young graduates ... are too “scientific” and do not know how to take care of patients.” He goes on to say that “one of the essential qualities of the clinician is interest in humanity, for the secret of the care of the patient is in caring for the patient.”2
We agree with Dr. Peabody. As we embrace science and technology that can change health outcomes, our patients’ needs to feel understood and cared for will not diminish. Instead, that need will continue to be an important aspect of our struggle and joy in providing holistic, humane, competent care into the future.
Twenty-first century physicians have access to an ever-growing trove of data, yet our ability to truly know our patients seems somehow less accessible. Home health devices have begun to provide a flow of information about parameters, ranging from continuous glucose readings to home blood pressures, weights, and inspiratory flow readings. These data can provide much more accurate insight into patients than what we can glean from one point in time during an office visit. Yet we need to remember that behind the data are people with dreams and desires, not just table entries in an electronic health record.
In 1923, the German philosopher Martin Buber published the book for which he is best known, “I and Thou.” In that book, Mr. Buber says that there are two ways we can approach relationships: “I-Thou” or “I-It.” In I-It relationships, we view the other person as an “it” to be used to accomplish a purpose, or to be experienced without his or her full involvement. In an I-Thou relationship, we appreciate the other people for all their complexity, in their full humanness. We must consciously remind ourselves amid the rush of technology that there are real people behind those data. We must acknowledge and approach each person as a unique individual who has dreams, goals, fears, and wishes that may be different from ours but to which we can still relate.
‘From the Beating End of the Stethoscope’
John Ciardi, an American poet, said the following in a poem titled, “Lines From the Beating End of the Stethoscope”:
I speak, as I say, the patient’s point of view.
But, given time, doctors are patients, too.
And there’s our bond: beyond anatomy,
Or in it, through it, to the mystery
Medicine takes the pulse of and lets go
Forever unexplained. It’s art, we know,
Not science at the heart. Doctor be whole,
I won’t insist the patient is a soul,
But he’s a something, possibly laughable,
Or possibly sublime, but not quite graphable.
Not quite containable on a bed chart.
Where science touches man it turns to art.3
This poem is a reminder of the subtle needs of patients during their encounters with doctors, especially around many of the most important decisions and events in their lives. Patients’ needs are varied, complex, difficult to discern, and not able to be fully explained or understood through math and science.
Einstein warned us that the modern age would be characterized by a perfection of means and a confusion of goals.4 As clinicians, we should strive to clarify and align our goals with those of our patients, providing care that is real, compassionate, and personal, not just an optimized means to achieve standardized metrics. While technology can assist us in this pursuit, we’ll need be careful that our enchantment with innovation does not cloud our actual goal: truly caring for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Jones VA. The white coat: Why not follow suit? JAMA. 1999;281(5):478. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.5.478-JMS0203-5-1
2. Peabody, Francis (1927). “The care of the patient.” JAMA. 88(12):877-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.1927.02680380001001.
3. Ciardi, John. Lines from the Beating End of the Stethoscope. Saturday Review, Nov. 18, 1968.
4. Albert Einstein, Out of My Later Years, 1950.








