User login
Diabetes Drug Improved Symptoms in Small Study of Women With Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case series involving 12 Black women in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, with biopsy-confirmed, treatment-refractory CCCA, a chronic inflammatory hair disorder characterized by permanent hair loss, from the Johns Hopkins University alopecia clinic.
- Participants received CCCA treatment for at least 6 months and had stagnant or worsening symptoms before oral extended-release metformin (500 mg daily) was added to treatment. (Treatments included topical clobetasol, compounded minoxidil, and platelet-rich plasma injections.)
- Scalp biopsies were collected from four patients before and after metformin treatment to evaluate gene expression changes.
- Changes in clinical symptoms were assessed, including pruritus, inflammation, pain, scalp resistance, and hair regrowth, following initiation of metformin treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Metformin led to significant clinical improvement in eight patients, which included reductions in scalp pain, scalp resistance, pruritus, and inflammation. However, two patients experienced worsening symptoms.
- Six patients showed clinical evidence of hair regrowth after at least 6 months of metformin treatment with one experiencing hair loss again 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
- Transcriptomic analysis revealed 34 up-regulated genes, which included up-regulated of 23 hair keratin–associated proteins, and pathways related to keratinization, epidermis development, and the hair cycle. In addition, eight genes were down-regulated, with pathways that included those associated with extracellular matrix organization, collagen fibril organization, and collagen metabolism.
- Gene set variation analysis showed reduced expression of T helper 17 cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways and elevated adenosine monophosphate kinase signaling and keratin-associated proteins after treatment with metformin.
IN PRACTICE:
“Metformin’s ability to concomitantly target fibrosis and inflammation provides a plausible mechanism for its therapeutic effects in CCCA and other fibrosing alopecia disorders,” the authors concluded. But, they added, “larger prospective, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials are needed to rigorously evaluate metformin’s efficacy and optimal dosing for treatment of cicatricial alopecias.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron Bao, Department of Dermatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, and was published online on September 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
A small sample size, retrospective design, lack of a placebo control group, and the single-center setting limited the generalizability of the study findings. Additionally, the absence of a validated activity or severity scale for CCCA and the single posttreatment sampling limit the assessment and comparison of clinical symptoms and transcriptomic changes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the American Academy of Dermatology. One author reported several ties with pharmaceutical companies, a pending patent, and authorship for the UpToDate section on CCCA.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Helps Define Patient-Centered Definition of Atopic Dermatitis Flares
TOPLINE:
, which most agreed would help when communicating with their healthcare providers (HCPs).
METHODOLOGY:
- To develop a patient-centered definition of AD flare, researchers used a modified eDelphi method, which involved a focus group and survey to reach consensus on key aspects of an AD flare.
- The focus group included 26 US adults aged ≥ 18 years with AD who had experienced a flare within the past 12 months. The survey was conducted among 631 adults with AD to validate the identified concepts and assess their agreement with the consensus statements.
- Participants rated 98 statements on a scale from 1 to 9, with consensus defined as at least 70% rating a statement as 7-9 and less than 15% rating it as 1-3.
- In focus groups, participants identified six key concepts for a patient-centered definition of flare, including changes from baseline, mental and emotional consequences, and physical changes in skin.
TAKEAWAY:
- The focus group reached consensus on 15 statements, and survey participants reached consensus on 12 of those statements defining an AD flare, with the highest agreement on symptoms taking more attention than normal, worsening of physical symptoms associated with AD, and worsening of itching associated with AD.
- The statement “acute worsening of symptoms of AD” was ranked as the most important, while “a worsening of physical symptoms” was ranked the least important.
- Most participants (79.7%) reported that prior definitions of AD flare did not resonate with them.
- More than half (52.9%) agreed with their HCP on what constitutes an AD flare, and the majority (77.6%) indicated that a patient-centered definition would be useful for communication with their HCP and for self-management.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this consensus survey study, we identified statements that are critical to the definition of an AD flare from the patient perspective,” the authors wrote. These findings, they added, “may be useful in clinical practice to improve communication between patients and HCPs who may be using the term flare without a mutual understanding of its meaning” and “may also be applied to the development of outcome measures focused on AD flares, which is an important treatment outcome for people with AD.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron M. Drucker, MD, ScM, of the Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and was published online September 11 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Participants had higher-than-average knowledge about AD, and the study’s findings may not be generalizable to all people with AD. The study included a higher proportion of moderate to severe AD cases than the general population, which may introduce responder bias. The findings may not be applicable to children, caregivers, or individuals in other countries.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by a grant to the National Eczema Association from Pfizer. Dr. Drucker disclosed received compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology, American Academy of Dermatology, and Canadian Dermatology Today, and consultant fees from the National Eczema Association and Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Another author reported receiving personal fees from pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, which most agreed would help when communicating with their healthcare providers (HCPs).
METHODOLOGY:
- To develop a patient-centered definition of AD flare, researchers used a modified eDelphi method, which involved a focus group and survey to reach consensus on key aspects of an AD flare.
- The focus group included 26 US adults aged ≥ 18 years with AD who had experienced a flare within the past 12 months. The survey was conducted among 631 adults with AD to validate the identified concepts and assess their agreement with the consensus statements.
- Participants rated 98 statements on a scale from 1 to 9, with consensus defined as at least 70% rating a statement as 7-9 and less than 15% rating it as 1-3.
- In focus groups, participants identified six key concepts for a patient-centered definition of flare, including changes from baseline, mental and emotional consequences, and physical changes in skin.
TAKEAWAY:
- The focus group reached consensus on 15 statements, and survey participants reached consensus on 12 of those statements defining an AD flare, with the highest agreement on symptoms taking more attention than normal, worsening of physical symptoms associated with AD, and worsening of itching associated with AD.
- The statement “acute worsening of symptoms of AD” was ranked as the most important, while “a worsening of physical symptoms” was ranked the least important.
- Most participants (79.7%) reported that prior definitions of AD flare did not resonate with them.
- More than half (52.9%) agreed with their HCP on what constitutes an AD flare, and the majority (77.6%) indicated that a patient-centered definition would be useful for communication with their HCP and for self-management.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this consensus survey study, we identified statements that are critical to the definition of an AD flare from the patient perspective,” the authors wrote. These findings, they added, “may be useful in clinical practice to improve communication between patients and HCPs who may be using the term flare without a mutual understanding of its meaning” and “may also be applied to the development of outcome measures focused on AD flares, which is an important treatment outcome for people with AD.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron M. Drucker, MD, ScM, of the Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and was published online September 11 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Participants had higher-than-average knowledge about AD, and the study’s findings may not be generalizable to all people with AD. The study included a higher proportion of moderate to severe AD cases than the general population, which may introduce responder bias. The findings may not be applicable to children, caregivers, or individuals in other countries.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by a grant to the National Eczema Association from Pfizer. Dr. Drucker disclosed received compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology, American Academy of Dermatology, and Canadian Dermatology Today, and consultant fees from the National Eczema Association and Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Another author reported receiving personal fees from pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, which most agreed would help when communicating with their healthcare providers (HCPs).
METHODOLOGY:
- To develop a patient-centered definition of AD flare, researchers used a modified eDelphi method, which involved a focus group and survey to reach consensus on key aspects of an AD flare.
- The focus group included 26 US adults aged ≥ 18 years with AD who had experienced a flare within the past 12 months. The survey was conducted among 631 adults with AD to validate the identified concepts and assess their agreement with the consensus statements.
- Participants rated 98 statements on a scale from 1 to 9, with consensus defined as at least 70% rating a statement as 7-9 and less than 15% rating it as 1-3.
- In focus groups, participants identified six key concepts for a patient-centered definition of flare, including changes from baseline, mental and emotional consequences, and physical changes in skin.
TAKEAWAY:
- The focus group reached consensus on 15 statements, and survey participants reached consensus on 12 of those statements defining an AD flare, with the highest agreement on symptoms taking more attention than normal, worsening of physical symptoms associated with AD, and worsening of itching associated with AD.
- The statement “acute worsening of symptoms of AD” was ranked as the most important, while “a worsening of physical symptoms” was ranked the least important.
- Most participants (79.7%) reported that prior definitions of AD flare did not resonate with them.
- More than half (52.9%) agreed with their HCP on what constitutes an AD flare, and the majority (77.6%) indicated that a patient-centered definition would be useful for communication with their HCP and for self-management.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this consensus survey study, we identified statements that are critical to the definition of an AD flare from the patient perspective,” the authors wrote. These findings, they added, “may be useful in clinical practice to improve communication between patients and HCPs who may be using the term flare without a mutual understanding of its meaning” and “may also be applied to the development of outcome measures focused on AD flares, which is an important treatment outcome for people with AD.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron M. Drucker, MD, ScM, of the Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and was published online September 11 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Participants had higher-than-average knowledge about AD, and the study’s findings may not be generalizable to all people with AD. The study included a higher proportion of moderate to severe AD cases than the general population, which may introduce responder bias. The findings may not be applicable to children, caregivers, or individuals in other countries.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by a grant to the National Eczema Association from Pfizer. Dr. Drucker disclosed received compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology, American Academy of Dermatology, and Canadian Dermatology Today, and consultant fees from the National Eczema Association and Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Another author reported receiving personal fees from pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Imaging Tool Helps Identify Features of Nail Disorders
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The single-center, observational cross-sectional pilot study evaluated patients aged ≥ 7 years with newly diagnosed nail disorders between January 2022 and May 2023.
- A total of 128 patients (average age, 46.1 years; range, 8-84 years) with nail psoriasis, onychomycosis, idiopathic/traumatic onycholysis, brittle nail syndrome, nail lichen planus, retronychia, and other nail conditions and those with no nail findings (controls) were enrolled.
- Researchers performed nailfold capillaroscopy imaging and compared capillary features between patients with nail conditions and the controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with nail psoriasis had decreased capillary density and length (P < .001), more crossed and tortuous capillaries (P < .02), and increased abnormal capillary morphology (P = .03) compared with controls. Specific abnormalities, such as branching and meandering capillaries, were more common among those with nail psoriasis (both 26.5%).
- Patients with fingernail and toenail onychomycosis had a higher frequency of abnormal capillary morphology (P < .02), particularly meandering capillaries (75.0% for fingernails and 76.9% for toenails). However, other abnormalities were less frequently observed.
- Patients with nail lichen planus (P < .01), onychopapilloma (P = .01), and retronychia (P = .03) showed significantly shorter capillaries than controls. Retronychia was also associated with increased disorganized polymorphic capillaries (P = .02).
- Patients with brittle nail syndrome and eczema showed no significant differences compared with controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings highlight nailfold capillaroscopy as a potentially quick, cost-effective, and noninvasive imaging modality as an adjunct for diagnosis and treatment initiation for patients with onychodystrophies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan K. Hwang, MD, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, and was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included a small sample size for certain nail conditions and the single-center design, which limited generalizability. Additionally, the uneven surface, scaling, onycholysis, and thickening of toenails made some capillaroscopy images difficult to capture and interpret.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. One author reported serving as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Ortho-Dermatologics, BelleTorus, and Moberg Pharma.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Reports Safety Data in Children on JAK Inhibitors
TOPLINE:
which also found that acne was the most common skin-related AE in children, and serious AEs were less common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 399,649 AEs in 133,216 adult patients and 2883 AEs in 955 pediatric patients (age, < 18 years) from November 2011 to February 2023 using the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System and the Canada Vigilance Adverse Reaction Online Database.
- AEs were categorized on the basis of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities system organ class.
- Five JAK inhibitors approved for use in children were included in the study: Baricitinib, upadacitinib, abrocitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most frequently reported AEs in children were blood and lymphatic system disorders, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia (24%); viral, fungal, and bacterial infections, such as pneumonia and sepsis (17.2%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns, including pyrexia and fatigue (15.7%); gastrointestinal disorders, such as vomiting and abdominal pain (13.6%); and respiratory disorders, such as cough and respiratory distress (5.3%).
- In adults, the most common AEs were viral, fungal, and bacterial infections (16.8%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns (13.5%); musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (7.04%); and gastrointestinal (5.8%) and nervous system (5%) disorders.
- Acne (30.6%), atopic dermatitis (22.2%), and psoriasis (16.7%) were the most common skin and subcutaneous tissue AEs reported in children. Skin and subcutaneous AEs were more common with upadacitinib (21.1%), abrocitinib (9.1%), and tofacitinib (6.3%) in children.
- Serious AEs included in the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors — serious infection, mortality, malignancy, cardiovascular events, and thrombosis — were similar for baricitinib in children (4 of 49 patients, 8.2%) and adults (325 of 3707, 8.8%). For other JAK inhibitors, absolute numbers of these AEs in children were small and rates were lower in children than in adults.
IN PRACTICE:
“This information can support customized treatment and minimize the potential for undesired or intolerable AEs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sahithi Talasila, BS, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Pharmacovigilance registries did not fully capture the complete range of AEs because of potential reporting bias or recall bias. Additionally, events lacking sufficient objective evidence were underreported, while common AEs associated with JAK inhibitor therapy were overreported.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding sources for the study were reported. One author reported being a consultant, one reported serving as a principal investigator in clinical trials, and another reported serving on data and safety monitoring boards of various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which also found that acne was the most common skin-related AE in children, and serious AEs were less common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 399,649 AEs in 133,216 adult patients and 2883 AEs in 955 pediatric patients (age, < 18 years) from November 2011 to February 2023 using the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System and the Canada Vigilance Adverse Reaction Online Database.
- AEs were categorized on the basis of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities system organ class.
- Five JAK inhibitors approved for use in children were included in the study: Baricitinib, upadacitinib, abrocitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most frequently reported AEs in children were blood and lymphatic system disorders, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia (24%); viral, fungal, and bacterial infections, such as pneumonia and sepsis (17.2%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns, including pyrexia and fatigue (15.7%); gastrointestinal disorders, such as vomiting and abdominal pain (13.6%); and respiratory disorders, such as cough and respiratory distress (5.3%).
- In adults, the most common AEs were viral, fungal, and bacterial infections (16.8%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns (13.5%); musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (7.04%); and gastrointestinal (5.8%) and nervous system (5%) disorders.
- Acne (30.6%), atopic dermatitis (22.2%), and psoriasis (16.7%) were the most common skin and subcutaneous tissue AEs reported in children. Skin and subcutaneous AEs were more common with upadacitinib (21.1%), abrocitinib (9.1%), and tofacitinib (6.3%) in children.
- Serious AEs included in the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors — serious infection, mortality, malignancy, cardiovascular events, and thrombosis — were similar for baricitinib in children (4 of 49 patients, 8.2%) and adults (325 of 3707, 8.8%). For other JAK inhibitors, absolute numbers of these AEs in children were small and rates were lower in children than in adults.
IN PRACTICE:
“This information can support customized treatment and minimize the potential for undesired or intolerable AEs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sahithi Talasila, BS, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Pharmacovigilance registries did not fully capture the complete range of AEs because of potential reporting bias or recall bias. Additionally, events lacking sufficient objective evidence were underreported, while common AEs associated with JAK inhibitor therapy were overreported.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding sources for the study were reported. One author reported being a consultant, one reported serving as a principal investigator in clinical trials, and another reported serving on data and safety monitoring boards of various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which also found that acne was the most common skin-related AE in children, and serious AEs were less common.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 399,649 AEs in 133,216 adult patients and 2883 AEs in 955 pediatric patients (age, < 18 years) from November 2011 to February 2023 using the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System and the Canada Vigilance Adverse Reaction Online Database.
- AEs were categorized on the basis of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities system organ class.
- Five JAK inhibitors approved for use in children were included in the study: Baricitinib, upadacitinib, abrocitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most frequently reported AEs in children were blood and lymphatic system disorders, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia (24%); viral, fungal, and bacterial infections, such as pneumonia and sepsis (17.2%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns, including pyrexia and fatigue (15.7%); gastrointestinal disorders, such as vomiting and abdominal pain (13.6%); and respiratory disorders, such as cough and respiratory distress (5.3%).
- In adults, the most common AEs were viral, fungal, and bacterial infections (16.8%); constitutional symptoms and administrative concerns (13.5%); musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (7.04%); and gastrointestinal (5.8%) and nervous system (5%) disorders.
- Acne (30.6%), atopic dermatitis (22.2%), and psoriasis (16.7%) were the most common skin and subcutaneous tissue AEs reported in children. Skin and subcutaneous AEs were more common with upadacitinib (21.1%), abrocitinib (9.1%), and tofacitinib (6.3%) in children.
- Serious AEs included in the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors — serious infection, mortality, malignancy, cardiovascular events, and thrombosis — were similar for baricitinib in children (4 of 49 patients, 8.2%) and adults (325 of 3707, 8.8%). For other JAK inhibitors, absolute numbers of these AEs in children were small and rates were lower in children than in adults.
IN PRACTICE:
“This information can support customized treatment and minimize the potential for undesired or intolerable AEs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sahithi Talasila, BS, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Pharmacovigilance registries did not fully capture the complete range of AEs because of potential reporting bias or recall bias. Additionally, events lacking sufficient objective evidence were underreported, while common AEs associated with JAK inhibitor therapy were overreported.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding sources for the study were reported. One author reported being a consultant, one reported serving as a principal investigator in clinical trials, and another reported serving on data and safety monitoring boards of various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs Subcutaneous Atezolizumab Formulation for Multiple Cancer Indications
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
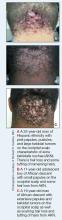
Moving Beyond Traditional Methods for Treatment of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
FDA Approves IL-13 inhibitor for Atopic Dermatitis
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
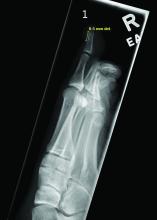
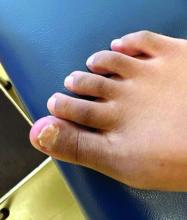
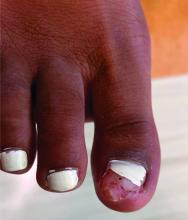
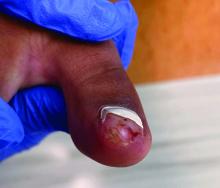
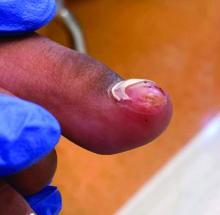
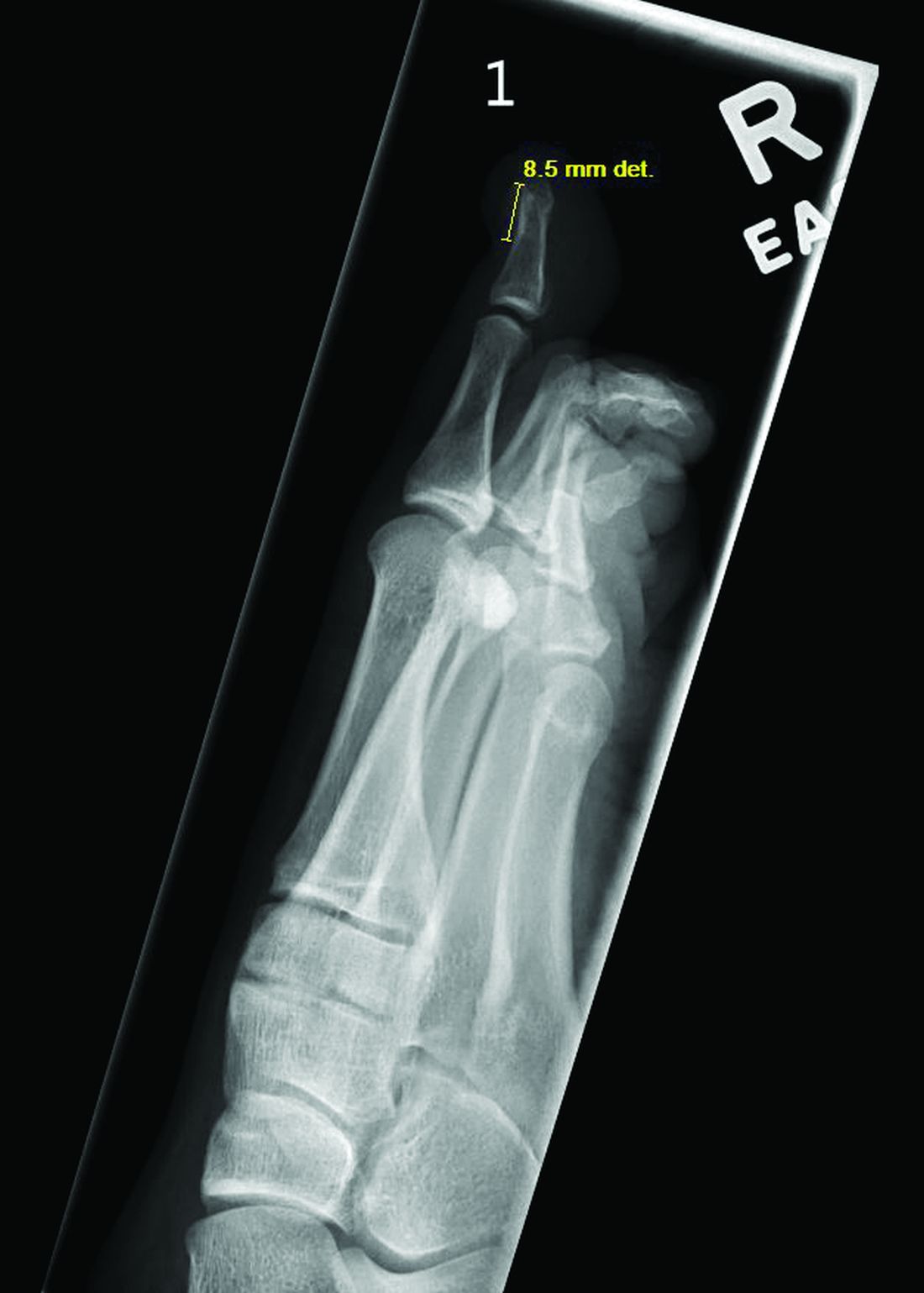
A 14-Year-Old Female Presents With a Growth Under Her Toenail
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
A 14-year-old healthy female presents with a painful nodule under her great toenail. The nodule had been present for 2 months and there was no preceding trauma. Three days prior to presentation, her nail cracked and bled after bumping her toe. The toe is painful to palpation. Given the associated pain, the patient visited urgent care and was prescribed cephalexin and acetaminophen.
Physical examination reveals a skin-colored subungual nodule with hypertrophic tissue originating from the nail bed of the right great toe, but no thickening of the nail plate (Figures 1-3).
Acne: Positive Outcomes Described With Laser Treatment
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical Tapinarof and Roflumilast for Psoriasis: Where Do they Fit In?
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIF. — The Food and Drug Administration and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures were published in 2021, leaving some clinicians to wonder how these two newcomer drugs fit into their clinical practice.
At the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association, Jashin J. Wu, MD, one of the authors of the guidelines and a voluntary associate professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, proposed that tapinarof 1% cream and roflumilast 0.3% cream be considered first-line treatments for mild psoriasis. “The reason is because they’re very fast-acting, effective,” and result in a large improvement over steroids, Dr. Wu said. “You don’t have to worry about steroid atrophy, and it eliminates the need to use many different agents for different parts of the body necessarily, such as a weaker steroid for the face and sensitive areas. It also eliminates the need for patients to switch out steroids, such as 2 weeks on and 2 weeks off.”
Tapinarof 1% cream (Vtama) was approved in May 2022, for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults, and is under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis (AD). “It’s once a day application, which is nice,” Dr. Wu said. “It is a first-in-class topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that can be used for the intertriginous areas. That’s where I find it helpful.”
Roflumilast 0.3% cream (Zoryve), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, was approved in July 2022 for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, in patients aged 12 years and older. It was subsequently approved for treating plaque psoriasis in patients 6 years and older. (Roflumilast 0.15% cream is approved for mild to moderate AD in people aged 6 years or older, and roflumilast 0.3% topical foam is approved for seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children 9 years of age and older.)
The drug is contraindicated for use in patients with certain liver problems. “Patients are not going to be eating tubes of this drug, so I wouldn’t worry about that too much, but be aware if the pharmacist raises a concern about this,” Dr. Wu said.
Dr. Wu disclosed that he is or has been a consultant, investigator, or speaker for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Codex Labs, Dermavant, DermTech, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Zerigo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIF. — The Food and Drug Administration and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures were published in 2021, leaving some clinicians to wonder how these two newcomer drugs fit into their clinical practice.
At the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association, Jashin J. Wu, MD, one of the authors of the guidelines and a voluntary associate professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, proposed that tapinarof 1% cream and roflumilast 0.3% cream be considered first-line treatments for mild psoriasis. “The reason is because they’re very fast-acting, effective,” and result in a large improvement over steroids, Dr. Wu said. “You don’t have to worry about steroid atrophy, and it eliminates the need to use many different agents for different parts of the body necessarily, such as a weaker steroid for the face and sensitive areas. It also eliminates the need for patients to switch out steroids, such as 2 weeks on and 2 weeks off.”
Tapinarof 1% cream (Vtama) was approved in May 2022, for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults, and is under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis (AD). “It’s once a day application, which is nice,” Dr. Wu said. “It is a first-in-class topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that can be used for the intertriginous areas. That’s where I find it helpful.”
Roflumilast 0.3% cream (Zoryve), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, was approved in July 2022 for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, in patients aged 12 years and older. It was subsequently approved for treating plaque psoriasis in patients 6 years and older. (Roflumilast 0.15% cream is approved for mild to moderate AD in people aged 6 years or older, and roflumilast 0.3% topical foam is approved for seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children 9 years of age and older.)
The drug is contraindicated for use in patients with certain liver problems. “Patients are not going to be eating tubes of this drug, so I wouldn’t worry about that too much, but be aware if the pharmacist raises a concern about this,” Dr. Wu said.
Dr. Wu disclosed that he is or has been a consultant, investigator, or speaker for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Codex Labs, Dermavant, DermTech, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Zerigo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIF. — The Food and Drug Administration and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures were published in 2021, leaving some clinicians to wonder how these two newcomer drugs fit into their clinical practice.
At the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association, Jashin J. Wu, MD, one of the authors of the guidelines and a voluntary associate professor of dermatology at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, proposed that tapinarof 1% cream and roflumilast 0.3% cream be considered first-line treatments for mild psoriasis. “The reason is because they’re very fast-acting, effective,” and result in a large improvement over steroids, Dr. Wu said. “You don’t have to worry about steroid atrophy, and it eliminates the need to use many different agents for different parts of the body necessarily, such as a weaker steroid for the face and sensitive areas. It also eliminates the need for patients to switch out steroids, such as 2 weeks on and 2 weeks off.”
Tapinarof 1% cream (Vtama) was approved in May 2022, for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults, and is under FDA review for treating atopic dermatitis (AD). “It’s once a day application, which is nice,” Dr. Wu said. “It is a first-in-class topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that can be used for the intertriginous areas. That’s where I find it helpful.”
Roflumilast 0.3% cream (Zoryve), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, was approved in July 2022 for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, including intertriginous areas, in patients aged 12 years and older. It was subsequently approved for treating plaque psoriasis in patients 6 years and older. (Roflumilast 0.15% cream is approved for mild to moderate AD in people aged 6 years or older, and roflumilast 0.3% topical foam is approved for seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children 9 years of age and older.)
The drug is contraindicated for use in patients with certain liver problems. “Patients are not going to be eating tubes of this drug, so I wouldn’t worry about that too much, but be aware if the pharmacist raises a concern about this,” Dr. Wu said.
Dr. Wu disclosed that he is or has been a consultant, investigator, or speaker for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Aristea Therapeutics, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Codex Labs, Dermavant, DermTech, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly, EPI Health, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Mindera, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi Genzyme, Solius, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Zerigo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PDA 2024