User login
What's your diagnosis?
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
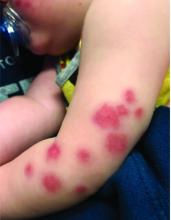
At 3 a.m., you receive a call from the ED for a baby with a new rash on the arms, legs, and face. Some of the lesions appear to be tender. He has a mild fever of 38.4° C (101.1° F) and is not in acute distress. He is drinking, but not eating much.
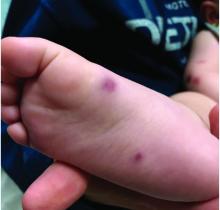
The parents also have noted some swelling on the hands and the feet. He has no upper respiratory or gastrointestinal symptoms. He is not walking yet.
He was admitted to the hospital 3 weeks prior for streptococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. He was treated with ceftriaxone, supportive respiratory care, and an albuterol inhaler. Influenza and respiratory syncytial virus tests were negative.
On physical exam, the child is tired and sleeping in his mom's arms. He has red and some purpuric papules on the face. On the arms and legs, he has purpuric papules and nodules. There is some edema on the face, hands, and feet. His conjunctiva is normal, and he has no oral lesions. He has no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly.
Blood work shows normal complete blood count, coagulation tests, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis, but he has an elevated C-reactive protein of 114 mg/L and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 71 mm/hour.
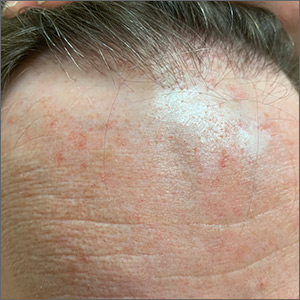
Receding hairline
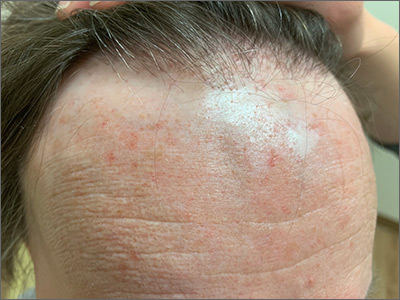
This patient had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), a subtype of lichen planopilaris (LPP), or follicular lichen planus. LPP causes cicatricial (scarring) alopecia where the follicular epithelium is replaced with connective tissue and the hair follicle is permanently lost. LPP is caused by lymphocytic inflammation that initially presents as perifollicular erythema, with scale and keratotic plugs, and later progresses to scarring. If there is uncertainty in the diagnosis, biopsy can be helpful.
The LPP subtype, FFA, usually occurs in postmenopausal women. It follows a distinctive pattern, as in this patient, where the hair is progressively lost along the frontoparietal hair line (and sometimes the eyebrows). A careful physical examination reveals smooth skin where follicles are lost and there is erythema around the base of the hairs due to active inflammation and keratotic plugging. The specific mechanism of FFA is poorly understood, and hormones may play a role, in addition to the inflammatory response.
The goal of treatment is to arrest the progression of additional hair loss (which usually is permanent). Intralesional steroid injections, which also are used for alopecia areata, are the most common therapy. Triamcinolone 2.5 to 5 mg/mL is injected in the affected dermal layer of the scalp. Oral finasteride (a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor to decrease androgens) 1 mg/d can be helpful, as can oral hydroxychloroquine 200 mg bid.
Once the inflammation has subsided, treatment can be discontinued. Hair transplantation has been used, but often fails due to the inflammatory scarring process. Our patient noted that her disease process had been stable and declined treatment.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Text courtesy of Rory Aufderheide, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Drs. Stulberg and Aufderheide are from the Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
To D, Beecker J. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: update and review of challenges and successes. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:182-189.

This patient had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), a subtype of lichen planopilaris (LPP), or follicular lichen planus. LPP causes cicatricial (scarring) alopecia where the follicular epithelium is replaced with connective tissue and the hair follicle is permanently lost. LPP is caused by lymphocytic inflammation that initially presents as perifollicular erythema, with scale and keratotic plugs, and later progresses to scarring. If there is uncertainty in the diagnosis, biopsy can be helpful.
The LPP subtype, FFA, usually occurs in postmenopausal women. It follows a distinctive pattern, as in this patient, where the hair is progressively lost along the frontoparietal hair line (and sometimes the eyebrows). A careful physical examination reveals smooth skin where follicles are lost and there is erythema around the base of the hairs due to active inflammation and keratotic plugging. The specific mechanism of FFA is poorly understood, and hormones may play a role, in addition to the inflammatory response.
The goal of treatment is to arrest the progression of additional hair loss (which usually is permanent). Intralesional steroid injections, which also are used for alopecia areata, are the most common therapy. Triamcinolone 2.5 to 5 mg/mL is injected in the affected dermal layer of the scalp. Oral finasteride (a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor to decrease androgens) 1 mg/d can be helpful, as can oral hydroxychloroquine 200 mg bid.
Once the inflammation has subsided, treatment can be discontinued. Hair transplantation has been used, but often fails due to the inflammatory scarring process. Our patient noted that her disease process had been stable and declined treatment.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Text courtesy of Rory Aufderheide, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Drs. Stulberg and Aufderheide are from the Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

This patient had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), a subtype of lichen planopilaris (LPP), or follicular lichen planus. LPP causes cicatricial (scarring) alopecia where the follicular epithelium is replaced with connective tissue and the hair follicle is permanently lost. LPP is caused by lymphocytic inflammation that initially presents as perifollicular erythema, with scale and keratotic plugs, and later progresses to scarring. If there is uncertainty in the diagnosis, biopsy can be helpful.
The LPP subtype, FFA, usually occurs in postmenopausal women. It follows a distinctive pattern, as in this patient, where the hair is progressively lost along the frontoparietal hair line (and sometimes the eyebrows). A careful physical examination reveals smooth skin where follicles are lost and there is erythema around the base of the hairs due to active inflammation and keratotic plugging. The specific mechanism of FFA is poorly understood, and hormones may play a role, in addition to the inflammatory response.
The goal of treatment is to arrest the progression of additional hair loss (which usually is permanent). Intralesional steroid injections, which also are used for alopecia areata, are the most common therapy. Triamcinolone 2.5 to 5 mg/mL is injected in the affected dermal layer of the scalp. Oral finasteride (a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor to decrease androgens) 1 mg/d can be helpful, as can oral hydroxychloroquine 200 mg bid.
Once the inflammation has subsided, treatment can be discontinued. Hair transplantation has been used, but often fails due to the inflammatory scarring process. Our patient noted that her disease process had been stable and declined treatment.
Photo courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Text courtesy of Rory Aufderheide, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP. Drs. Stulberg and Aufderheide are from the Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
To D, Beecker J. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: update and review of challenges and successes. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:182-189.
To D, Beecker J. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: update and review of challenges and successes. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22:182-189.
Most e-consults not followed by specialist visit
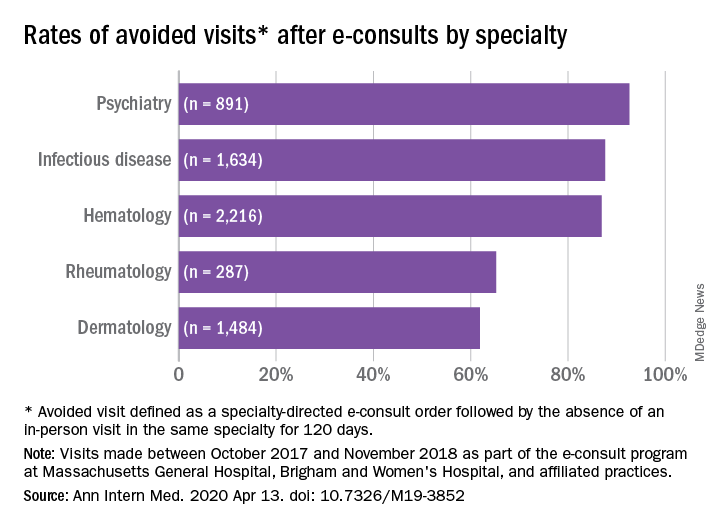
Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.

Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.

Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
A case of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis attributed to HIV treatment
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Expert discusses her approach to using systemic agents in children and adolescents with severe skin disease
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.
When to suspect calciphylaxis and what to do about it
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Dark toenail line
This woman’s linear hyperpigmentation is formally known as longitudinal melanonychia.
After the initial diagnosis, it is important to determine if the melanonychia is due to melanoma or a benign process. Many people with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick skin types V or VI) have several of these lines, so it is reassuring when these lines are present on multiple digits. Additional evaluation is warranted, however, when only 1 longitudinal melanonychia is present.
In this case, it was clear that the pigmentation was homogeneous and in a parallel line format. (Dermoscopy can aid in the evaluation of such lesions.) There was no spreading of the pigmentation onto the skin around the nail (Hutchinson sign), which would be suggestive of melanoma. The patient noted that the lesion had been present (without progression) over a 10-year period, which also was consistent with a benign process. A new lesion, rapid change, a triangular pattern wider at the cuticle vs the distal nail, and nail disruption are worrisome features that would have warranted a biopsy.
If a biopsy is called for, be sure to sample the origin of the pigmentation under the cuticle and the nail at the nail matrix. This requires partial or complete nail removal to reach the matrix, and there is a risk of permanent nail disruption. In light of this, it’s important to discriminate which lesions are at higher risk for melanoma.
In this patient, who had a stable lesion and no concerning history or findings, it was likely that she had a benign nevus or lentigo in the nail matrix. She was instructed to watch for any changes and to notify her physician if any occurred, as such changes might require a biopsy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Singal A, Bisherwal K. Melanonychia: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:1-11.

This woman’s linear hyperpigmentation is formally known as longitudinal melanonychia.
After the initial diagnosis, it is important to determine if the melanonychia is due to melanoma or a benign process. Many people with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick skin types V or VI) have several of these lines, so it is reassuring when these lines are present on multiple digits. Additional evaluation is warranted, however, when only 1 longitudinal melanonychia is present.
In this case, it was clear that the pigmentation was homogeneous and in a parallel line format. (Dermoscopy can aid in the evaluation of such lesions.) There was no spreading of the pigmentation onto the skin around the nail (Hutchinson sign), which would be suggestive of melanoma. The patient noted that the lesion had been present (without progression) over a 10-year period, which also was consistent with a benign process. A new lesion, rapid change, a triangular pattern wider at the cuticle vs the distal nail, and nail disruption are worrisome features that would have warranted a biopsy.
If a biopsy is called for, be sure to sample the origin of the pigmentation under the cuticle and the nail at the nail matrix. This requires partial or complete nail removal to reach the matrix, and there is a risk of permanent nail disruption. In light of this, it’s important to discriminate which lesions are at higher risk for melanoma.
In this patient, who had a stable lesion and no concerning history or findings, it was likely that she had a benign nevus or lentigo in the nail matrix. She was instructed to watch for any changes and to notify her physician if any occurred, as such changes might require a biopsy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

This woman’s linear hyperpigmentation is formally known as longitudinal melanonychia.
After the initial diagnosis, it is important to determine if the melanonychia is due to melanoma or a benign process. Many people with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick skin types V or VI) have several of these lines, so it is reassuring when these lines are present on multiple digits. Additional evaluation is warranted, however, when only 1 longitudinal melanonychia is present.
In this case, it was clear that the pigmentation was homogeneous and in a parallel line format. (Dermoscopy can aid in the evaluation of such lesions.) There was no spreading of the pigmentation onto the skin around the nail (Hutchinson sign), which would be suggestive of melanoma. The patient noted that the lesion had been present (without progression) over a 10-year period, which also was consistent with a benign process. A new lesion, rapid change, a triangular pattern wider at the cuticle vs the distal nail, and nail disruption are worrisome features that would have warranted a biopsy.
If a biopsy is called for, be sure to sample the origin of the pigmentation under the cuticle and the nail at the nail matrix. This requires partial or complete nail removal to reach the matrix, and there is a risk of permanent nail disruption. In light of this, it’s important to discriminate which lesions are at higher risk for melanoma.
In this patient, who had a stable lesion and no concerning history or findings, it was likely that she had a benign nevus or lentigo in the nail matrix. She was instructed to watch for any changes and to notify her physician if any occurred, as such changes might require a biopsy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Singal A, Bisherwal K. Melanonychia: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:1-11.
Singal A, Bisherwal K. Melanonychia: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11:1-11.
Dupilumab hits the mark for severe AD in younger children
The monoclonal antibody , according to new clinical trial results.
In a cohort of children with severe AD, 33% achieved clear or nearly clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment with every 4-week dosing of the injectable medication, while 30% also achieved that mark when receiving a weight-based dose every 2 weeks. Both groups had results that were significantly better than those receiving placebo, with 11% of these children had clear or nearly clear skin by 16 weeks of dupilumab (Dupixent) therapy (P less than .0001 for both therapy arms versus placebo).
“Dupilumab with a topical corticosteroid showed clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in the atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms in children aged 6 to less than 12 years of age with severe atopic dermatitis,” said Amy Paller, MD, the Walter J. Hamlin professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, presenting the results at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. Portions of the conference, which has been rescheduled to December 2020, in Chicago, were presented virtually because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The phase 3 trial of subcutaneously injected dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, dubbed LIBERTY AD PEDS, included children aged 6-11 years with severe AD. The study’s primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) scale by study week 16.
For the purposes of reporting results to the European Medicines Agency, the investigators added a coprimary endpoint of patients reaching 75% clearing on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) by week 16.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial enrolled 367 children with IGA scores of 4, denoting severe AD. The EASI score had to be at least 21 and patients had to endorse peak pruritus of at least 4 on a 0-10 numeric rating scale; body surface involvement had to be at least 15%. Patients went through a washout period of any systemic therapies before beginning the trial, which randomized patients 1:1:1 to receive placebo, dupilumab 300 mg every 4 weeks, or dupilumab every 2 weeks with weight-dependent dosing. All participants were also permitted topical corticosteroids.
Patients were an average of aged 8 years, about half were female, and about two-thirds were white. Most participants had developed AD within their first year of life. Patients were about evenly divided between weighing over and under 30 kg, which was the cutoff for 100 mcg versus 200 mcg dupilumab for the every-2-week dosing group.
Over 90% of patients had other atopic comorbidities, and the mean EASI score was about 38 with average weekly peak pruritus averaging 7.8 on the numeric rating scale.
“When we’re talking about how severe this population is, it’s interesting to note that about 30 to 35% were all that had been previously treated with either systemic steroids or some systemic nonsteroidal immunosuppressants,” Dr. Paller pointed out. “I think that reflects the fact that so many of these very severely affected children are not put on a systemic therapy, but are still staying on topical therapies to try to control their disease.”
Looking at the proportion of patients reaching EASI-75, both dosing strategies for dupilumab out-performed placebo, with 70% of the every 4-week group and 67% of the every 2-week group reaching EASI-75 at 16 weeks, compared with 27% of those on placebo (P less than .0001 for both active arms). “These differences were seen very early on; by 2 weeks already, we can see that we’re starting to see a difference in both of these arms,” noted Dr. Paller, adding that the difference was statistically significant by 4 weeks into the study.
The overall group of dupilumab participants saw their EASI scores drop by about 80%, while those taking placebo saw a 49% drop in EASI scores.
For the group of participants weighing less than 30 kg, the every 4-week strategy resulted in better clearing as measured by both IGA and EASI-75. This effect wasn’t seen for heavier patients. Trough dupilumab concentrations at 16 weeks were higher for lighter patients with every 4-week dosing and for heavier patients with the biweekly strategy, noted Dr. Paller.
In terms of itch, 60% to 68% of participants receiving dupilumab had a drop of at least 3 points in peak pruritus on the numeric rating scale, compared with 21% of those receiving placebo (P less than .001), while about half of the dupilumab groups and 12% of the placebo group saw pruritus improvements of 4 points or more (P less than .001). Pruritus improved early in the active arms of the study, becoming statistically significant at the 2 to 4 week range.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were numerically higher in patients in the placebo group, including infections and adjudicated skin infections. Conjunctivitis occurred more frequently in the dupilumab group, as did injection-site reactions.
“Overall, dupilumab was well tolerated, and data were consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile observed in adults and adolescents,” Dr. Paller said.
Dupilumab has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat moderate to severe AD in those aged 12 years and older whose disease can’t be adequately controlled with topical prescription medications, or when those treatments are not advisable.
The fully human monoclonal antibody blocks a shared receptor component for interleukin-4 and interleukin-13, which contribute to inflammation in AD, as well as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Dr. Paller reported receiving support from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study.
The monoclonal antibody , according to new clinical trial results.
In a cohort of children with severe AD, 33% achieved clear or nearly clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment with every 4-week dosing of the injectable medication, while 30% also achieved that mark when receiving a weight-based dose every 2 weeks. Both groups had results that were significantly better than those receiving placebo, with 11% of these children had clear or nearly clear skin by 16 weeks of dupilumab (Dupixent) therapy (P less than .0001 for both therapy arms versus placebo).
“Dupilumab with a topical corticosteroid showed clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in the atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms in children aged 6 to less than 12 years of age with severe atopic dermatitis,” said Amy Paller, MD, the Walter J. Hamlin professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, presenting the results at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. Portions of the conference, which has been rescheduled to December 2020, in Chicago, were presented virtually because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The phase 3 trial of subcutaneously injected dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, dubbed LIBERTY AD PEDS, included children aged 6-11 years with severe AD. The study’s primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) scale by study week 16.
For the purposes of reporting results to the European Medicines Agency, the investigators added a coprimary endpoint of patients reaching 75% clearing on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) by week 16.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial enrolled 367 children with IGA scores of 4, denoting severe AD. The EASI score had to be at least 21 and patients had to endorse peak pruritus of at least 4 on a 0-10 numeric rating scale; body surface involvement had to be at least 15%. Patients went through a washout period of any systemic therapies before beginning the trial, which randomized patients 1:1:1 to receive placebo, dupilumab 300 mg every 4 weeks, or dupilumab every 2 weeks with weight-dependent dosing. All participants were also permitted topical corticosteroids.
Patients were an average of aged 8 years, about half were female, and about two-thirds were white. Most participants had developed AD within their first year of life. Patients were about evenly divided between weighing over and under 30 kg, which was the cutoff for 100 mcg versus 200 mcg dupilumab for the every-2-week dosing group.
Over 90% of patients had other atopic comorbidities, and the mean EASI score was about 38 with average weekly peak pruritus averaging 7.8 on the numeric rating scale.
“When we’re talking about how severe this population is, it’s interesting to note that about 30 to 35% were all that had been previously treated with either systemic steroids or some systemic nonsteroidal immunosuppressants,” Dr. Paller pointed out. “I think that reflects the fact that so many of these very severely affected children are not put on a systemic therapy, but are still staying on topical therapies to try to control their disease.”
Looking at the proportion of patients reaching EASI-75, both dosing strategies for dupilumab out-performed placebo, with 70% of the every 4-week group and 67% of the every 2-week group reaching EASI-75 at 16 weeks, compared with 27% of those on placebo (P less than .0001 for both active arms). “These differences were seen very early on; by 2 weeks already, we can see that we’re starting to see a difference in both of these arms,” noted Dr. Paller, adding that the difference was statistically significant by 4 weeks into the study.
The overall group of dupilumab participants saw their EASI scores drop by about 80%, while those taking placebo saw a 49% drop in EASI scores.
For the group of participants weighing less than 30 kg, the every 4-week strategy resulted in better clearing as measured by both IGA and EASI-75. This effect wasn’t seen for heavier patients. Trough dupilumab concentrations at 16 weeks were higher for lighter patients with every 4-week dosing and for heavier patients with the biweekly strategy, noted Dr. Paller.
In terms of itch, 60% to 68% of participants receiving dupilumab had a drop of at least 3 points in peak pruritus on the numeric rating scale, compared with 21% of those receiving placebo (P less than .001), while about half of the dupilumab groups and 12% of the placebo group saw pruritus improvements of 4 points or more (P less than .001). Pruritus improved early in the active arms of the study, becoming statistically significant at the 2 to 4 week range.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were numerically higher in patients in the placebo group, including infections and adjudicated skin infections. Conjunctivitis occurred more frequently in the dupilumab group, as did injection-site reactions.
“Overall, dupilumab was well tolerated, and data were consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile observed in adults and adolescents,” Dr. Paller said.
Dupilumab has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat moderate to severe AD in those aged 12 years and older whose disease can’t be adequately controlled with topical prescription medications, or when those treatments are not advisable.
The fully human monoclonal antibody blocks a shared receptor component for interleukin-4 and interleukin-13, which contribute to inflammation in AD, as well as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Dr. Paller reported receiving support from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study.
The monoclonal antibody , according to new clinical trial results.
In a cohort of children with severe AD, 33% achieved clear or nearly clear skin after 16 weeks of treatment with every 4-week dosing of the injectable medication, while 30% also achieved that mark when receiving a weight-based dose every 2 weeks. Both groups had results that were significantly better than those receiving placebo, with 11% of these children had clear or nearly clear skin by 16 weeks of dupilumab (Dupixent) therapy (P less than .0001 for both therapy arms versus placebo).
“Dupilumab with a topical corticosteroid showed clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvement in the atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms in children aged 6 to less than 12 years of age with severe atopic dermatitis,” said Amy Paller, MD, the Walter J. Hamlin professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, presenting the results at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. Portions of the conference, which has been rescheduled to December 2020, in Chicago, were presented virtually because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The phase 3 trial of subcutaneously injected dupilumab for atopic dermatitis, dubbed LIBERTY AD PEDS, included children aged 6-11 years with severe AD. The study’s primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving a score of 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear skin) on the Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) scale by study week 16.
For the purposes of reporting results to the European Medicines Agency, the investigators added a coprimary endpoint of patients reaching 75% clearing on the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75) by week 16.
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial enrolled 367 children with IGA scores of 4, denoting severe AD. The EASI score had to be at least 21 and patients had to endorse peak pruritus of at least 4 on a 0-10 numeric rating scale; body surface involvement had to be at least 15%. Patients went through a washout period of any systemic therapies before beginning the trial, which randomized patients 1:1:1 to receive placebo, dupilumab 300 mg every 4 weeks, or dupilumab every 2 weeks with weight-dependent dosing. All participants were also permitted topical corticosteroids.
Patients were an average of aged 8 years, about half were female, and about two-thirds were white. Most participants had developed AD within their first year of life. Patients were about evenly divided between weighing over and under 30 kg, which was the cutoff for 100 mcg versus 200 mcg dupilumab for the every-2-week dosing group.
Over 90% of patients had other atopic comorbidities, and the mean EASI score was about 38 with average weekly peak pruritus averaging 7.8 on the numeric rating scale.
“When we’re talking about how severe this population is, it’s interesting to note that about 30 to 35% were all that had been previously treated with either systemic steroids or some systemic nonsteroidal immunosuppressants,” Dr. Paller pointed out. “I think that reflects the fact that so many of these very severely affected children are not put on a systemic therapy, but are still staying on topical therapies to try to control their disease.”
Looking at the proportion of patients reaching EASI-75, both dosing strategies for dupilumab out-performed placebo, with 70% of the every 4-week group and 67% of the every 2-week group reaching EASI-75 at 16 weeks, compared with 27% of those on placebo (P less than .0001 for both active arms). “These differences were seen very early on; by 2 weeks already, we can see that we’re starting to see a difference in both of these arms,” noted Dr. Paller, adding that the difference was statistically significant by 4 weeks into the study.
The overall group of dupilumab participants saw their EASI scores drop by about 80%, while those taking placebo saw a 49% drop in EASI scores.
For the group of participants weighing less than 30 kg, the every 4-week strategy resulted in better clearing as measured by both IGA and EASI-75. This effect wasn’t seen for heavier patients. Trough dupilumab concentrations at 16 weeks were higher for lighter patients with every 4-week dosing and for heavier patients with the biweekly strategy, noted Dr. Paller.
In terms of itch, 60% to 68% of participants receiving dupilumab had a drop of at least 3 points in peak pruritus on the numeric rating scale, compared with 21% of those receiving placebo (P less than .001), while about half of the dupilumab groups and 12% of the placebo group saw pruritus improvements of 4 points or more (P less than .001). Pruritus improved early in the active arms of the study, becoming statistically significant at the 2 to 4 week range.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were numerically higher in patients in the placebo group, including infections and adjudicated skin infections. Conjunctivitis occurred more frequently in the dupilumab group, as did injection-site reactions.
“Overall, dupilumab was well tolerated, and data were consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile observed in adults and adolescents,” Dr. Paller said.
Dupilumab has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat moderate to severe AD in those aged 12 years and older whose disease can’t be adequately controlled with topical prescription medications, or when those treatments are not advisable.
The fully human monoclonal antibody blocks a shared receptor component for interleukin-4 and interleukin-13, which contribute to inflammation in AD, as well as asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Dr. Paller reported receiving support from multiple pharmaceutical companies including Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, which sponsored the study.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2020
D.C.-area blacks face increased risk of mortality from SJS/TEN
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
Is There an Association Between Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Fibromyalgia?
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects approximately 1% to 4% of the worldwide population and is 3 times more common in females than in males.1 The condition is characterized by painful inflamed nodules in apocrine gland–bearing regions that can progress to abscesses, sinus tracts, and/or scarring. Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with intense pain, work disability, and poor quality of life.1
Recent evidence has suggested that HS is an autoimmune disease resulting from dysregulation of the γ-secretase/Notch pathway, leading to stimulation of the toll-like receptor–mediated innate immunity that contributes to occlusion and inflammation of the hair follicle. Additionally, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and IL-17 are seen in HS lesions.2 The autoimmune nature of HS may account for its increased association with other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease and potentially with other unexplored conditions such as fibromyalgia.3
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that primarily affects females and is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions.4 The primary objective of this retrospective study was to determine the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients and assess if there is an association between HS disease severity and development of fibromyalgia.
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina) who were 18 years and older and had a diagnosis of both HS and fibromyalgia from January 2008 to November 2018. The primary end point was the prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population. The secondary end point was the association of HS disease severity with the development of fibromyalgia. Hidradenitis disease severity was defined according to the number of body areas affected by HS: mild disease involved 1 body area, moderate disease involved 2 body areas, and severe disease involved 3 or more body areas. Patient age, sex, and race also were recorded.
A total of 1356 patients were seen during this time period for HS. The prevalence of fibromyalgia in the HS population was 3.2% (n=44). Ninety-five percent (42/44) of patients with HS and fibromyalgia were women; 22 (50%) patients had severe disease, 12 (27%) had moderate disease, 7 (16%) had mild disease, and 3 (7%) had an unknown number of affected body areas. Fifty-seven percent (25/44) of patients were diagnosed with HS prior to the diagnosis of fibromyalgia (Table).

In our study, the prevalence of fibromyalgia in HS patients was lower than the overall prevalence estimates of up to 6% in the United States.5 Although fibromyalgia is associated with other autoimmune conditions, it does not appear that fibromyalgia occurs more frequently in the HS population than the general population. A limitation of this study was that we only included academic outpatient clinic visits at one institution, which may not be representative of the entire HS population. Fibromyalgia was one of the many pain disorders in this population of patients. In this population of HS patients, many had pain issues with diagnose
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
- Smith MK, Nichlson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Miller IM, Vinding G, Sorensen HA, et al. Thyroid function in hidradenitis suppurativa: a population-based cross-sectional study from Denmark. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:899-905.
- Giacomelli C, Talarico R, Bombardieri S, et al. The interaction between autoimmune diseases and fibromyalgia: risk, disease course and management. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9:1069-1076.
- Queiroz LP. Worldwide epidemiology of fibromyalgia. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013;17:356.
Practice Point
- Although fibromyalgia does not occur more frequently in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) patients, it is important to recognize that HS patients can have comorbidities that should be addressed when possible to improve overall quality of life.