User login
Apremilast for Behçet’s oral ulcers: Benefits maintained at 64 weeks
MADRID – of the long-term extension phase of the pivotal RELIEF trial, Alfred Mahr, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We now have strong evidence that apremilast is an effective and safe therapy to treat oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s syndrome. I think this is a major advance in the field,” declared Dr. Mahr, a rheumatologist at St. Gallen (Switzerland) Cantonal Hospital.
Based largely upon the results of the 12-week, double-blind portion of the phase 3 RELIEF trial, the Food and Drug Administration approved apremilast (Otezla) for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease in the summer of 2019.
The safety profile of the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor was as seen in other studies, including in patients with psoriatic arthritis, an FDA-approved indication for the drug since 2014. The main side effects in the long-term extension of RELIEF were diarrhea and nausea, typically mild or moderate in nature and roughly twice as frequent as in placebo-treated controls in the double-blind study phase.
“At the end of the day, at week 64, only 12% of patients treated with apremilast during the entire 64 weeks discontinued the drug due to a treatment-emergent adverse event, which I believe is a good indicator of the safety of this medication,” the rheumatologist said. “The overall feeling is that the benefit-to-risk ratio is very good and it’s a safe drug to prescribe.”
At the close of the initial 12-week, double-blind phase of RELIEF, 178 of the original 207 participants elected to enter the long-term extension, either staying on apremilast at 30 mg twice a day for an additional 52 weeks or switching to that regimen from placebo.
The focus of the long-term extension was on disease activity and quality of life outcomes. The results in patients who had switched from placebo to apremilast after 12 weeks proved to be reassuringly similar to outcomes in patients on the drug for the full duration. For example, the mean improvement on the patient-reported Behçet’s Syndrome Activity Scale was 18.6 points after 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, 16.9 points after 64 weeks of continuous apremilast, and 16.8 points with 12 weeks of placebo followed by 52 weeks of active therapy.
After 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, patients averaged a 3.4-point improvement on the Behçet’s Disease Quality of Life measure. After 64 weeks on the drug, the improvement over baseline was 3.6 points, while in the switch group it was 3.4 points. Similarly, on all three components of the SF-36 quality of life metric, the continuous apremilast group showed maintenance of effect from week 12 to week 64, while the placebo-to-apremilast group caught up. The same was true with regards to the Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Index, which encompasses measures of both the patient’s and clinician’s perception of disease activity.
At the outset of the RELIEF trial, participants averaged four oral ulcers. At week 64, the continuous apremilast group averaged 1.4 and the switch group 0.8, a nonsignificant difference.
Asked if apremilast had a favorable impact upon other manifestations of Behçet’s disease besides the oral ulcers, Dr. Mahr replied, “This is a very good question. People often wonder about it. We do, too. But this trial was not designed to capture less common manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome, such as genital ulcers. There have been some analyses done, but the number of patients who had genital ulcers at 12 weeks were very few. The same was true for eye manifestations. There was sort of a signal that it works, but we can’t prove it in a placebo-controlled trial.”
Dr. Mahr reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to Celgene, the study sponsor.
MADRID – of the long-term extension phase of the pivotal RELIEF trial, Alfred Mahr, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We now have strong evidence that apremilast is an effective and safe therapy to treat oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s syndrome. I think this is a major advance in the field,” declared Dr. Mahr, a rheumatologist at St. Gallen (Switzerland) Cantonal Hospital.
Based largely upon the results of the 12-week, double-blind portion of the phase 3 RELIEF trial, the Food and Drug Administration approved apremilast (Otezla) for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease in the summer of 2019.
The safety profile of the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor was as seen in other studies, including in patients with psoriatic arthritis, an FDA-approved indication for the drug since 2014. The main side effects in the long-term extension of RELIEF were diarrhea and nausea, typically mild or moderate in nature and roughly twice as frequent as in placebo-treated controls in the double-blind study phase.
“At the end of the day, at week 64, only 12% of patients treated with apremilast during the entire 64 weeks discontinued the drug due to a treatment-emergent adverse event, which I believe is a good indicator of the safety of this medication,” the rheumatologist said. “The overall feeling is that the benefit-to-risk ratio is very good and it’s a safe drug to prescribe.”
At the close of the initial 12-week, double-blind phase of RELIEF, 178 of the original 207 participants elected to enter the long-term extension, either staying on apremilast at 30 mg twice a day for an additional 52 weeks or switching to that regimen from placebo.
The focus of the long-term extension was on disease activity and quality of life outcomes. The results in patients who had switched from placebo to apremilast after 12 weeks proved to be reassuringly similar to outcomes in patients on the drug for the full duration. For example, the mean improvement on the patient-reported Behçet’s Syndrome Activity Scale was 18.6 points after 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, 16.9 points after 64 weeks of continuous apremilast, and 16.8 points with 12 weeks of placebo followed by 52 weeks of active therapy.
After 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, patients averaged a 3.4-point improvement on the Behçet’s Disease Quality of Life measure. After 64 weeks on the drug, the improvement over baseline was 3.6 points, while in the switch group it was 3.4 points. Similarly, on all three components of the SF-36 quality of life metric, the continuous apremilast group showed maintenance of effect from week 12 to week 64, while the placebo-to-apremilast group caught up. The same was true with regards to the Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Index, which encompasses measures of both the patient’s and clinician’s perception of disease activity.
At the outset of the RELIEF trial, participants averaged four oral ulcers. At week 64, the continuous apremilast group averaged 1.4 and the switch group 0.8, a nonsignificant difference.
Asked if apremilast had a favorable impact upon other manifestations of Behçet’s disease besides the oral ulcers, Dr. Mahr replied, “This is a very good question. People often wonder about it. We do, too. But this trial was not designed to capture less common manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome, such as genital ulcers. There have been some analyses done, but the number of patients who had genital ulcers at 12 weeks were very few. The same was true for eye manifestations. There was sort of a signal that it works, but we can’t prove it in a placebo-controlled trial.”
Dr. Mahr reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to Celgene, the study sponsor.
MADRID – of the long-term extension phase of the pivotal RELIEF trial, Alfred Mahr, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We now have strong evidence that apremilast is an effective and safe therapy to treat oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s syndrome. I think this is a major advance in the field,” declared Dr. Mahr, a rheumatologist at St. Gallen (Switzerland) Cantonal Hospital.
Based largely upon the results of the 12-week, double-blind portion of the phase 3 RELIEF trial, the Food and Drug Administration approved apremilast (Otezla) for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease in the summer of 2019.
The safety profile of the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor was as seen in other studies, including in patients with psoriatic arthritis, an FDA-approved indication for the drug since 2014. The main side effects in the long-term extension of RELIEF were diarrhea and nausea, typically mild or moderate in nature and roughly twice as frequent as in placebo-treated controls in the double-blind study phase.
“At the end of the day, at week 64, only 12% of patients treated with apremilast during the entire 64 weeks discontinued the drug due to a treatment-emergent adverse event, which I believe is a good indicator of the safety of this medication,” the rheumatologist said. “The overall feeling is that the benefit-to-risk ratio is very good and it’s a safe drug to prescribe.”
At the close of the initial 12-week, double-blind phase of RELIEF, 178 of the original 207 participants elected to enter the long-term extension, either staying on apremilast at 30 mg twice a day for an additional 52 weeks or switching to that regimen from placebo.
The focus of the long-term extension was on disease activity and quality of life outcomes. The results in patients who had switched from placebo to apremilast after 12 weeks proved to be reassuringly similar to outcomes in patients on the drug for the full duration. For example, the mean improvement on the patient-reported Behçet’s Syndrome Activity Scale was 18.6 points after 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, 16.9 points after 64 weeks of continuous apremilast, and 16.8 points with 12 weeks of placebo followed by 52 weeks of active therapy.
After 12 weeks of double-blind apremilast, patients averaged a 3.4-point improvement on the Behçet’s Disease Quality of Life measure. After 64 weeks on the drug, the improvement over baseline was 3.6 points, while in the switch group it was 3.4 points. Similarly, on all three components of the SF-36 quality of life metric, the continuous apremilast group showed maintenance of effect from week 12 to week 64, while the placebo-to-apremilast group caught up. The same was true with regards to the Behçet’s Disease Current Activity Index, which encompasses measures of both the patient’s and clinician’s perception of disease activity.
At the outset of the RELIEF trial, participants averaged four oral ulcers. At week 64, the continuous apremilast group averaged 1.4 and the switch group 0.8, a nonsignificant difference.
Asked if apremilast had a favorable impact upon other manifestations of Behçet’s disease besides the oral ulcers, Dr. Mahr replied, “This is a very good question. People often wonder about it. We do, too. But this trial was not designed to capture less common manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome, such as genital ulcers. There have been some analyses done, but the number of patients who had genital ulcers at 12 weeks were very few. The same was true for eye manifestations. There was sort of a signal that it works, but we can’t prove it in a placebo-controlled trial.”
Dr. Mahr reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to Celgene, the study sponsor.
REPORTING FROM EADV 2019
FDA announces approval of fifth adalimumab biosimilar, Abrilada
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada) as the fifth approved Humira biosimilar and the 25th approved biosimilar drug overall, the agency said in a Nov. 15 announcement.
According to a press release from Pfizer, approval for Abrilada was based on review of a comprehensive data package demonstrating biosimilarity of the drug to the reference product. This included data from a clinical comparative study, which found no clinically meaningful difference between Abrilada and the reference in terms of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In addition to RA, Abrilada is indicated for juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, adult Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis.
Common adverse events in adalimumab clinical trials included infection, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
Pfizer said that it “is working to make Abrilada available to U.S. patients as soon as feasible based on the terms of our agreement with AbbVie [the manufacturer of Humira]. Our current plans are to launch in 2023.”
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada) as the fifth approved Humira biosimilar and the 25th approved biosimilar drug overall, the agency said in a Nov. 15 announcement.
According to a press release from Pfizer, approval for Abrilada was based on review of a comprehensive data package demonstrating biosimilarity of the drug to the reference product. This included data from a clinical comparative study, which found no clinically meaningful difference between Abrilada and the reference in terms of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In addition to RA, Abrilada is indicated for juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, adult Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis.
Common adverse events in adalimumab clinical trials included infection, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
Pfizer said that it “is working to make Abrilada available to U.S. patients as soon as feasible based on the terms of our agreement with AbbVie [the manufacturer of Humira]. Our current plans are to launch in 2023.”
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada) as the fifth approved Humira biosimilar and the 25th approved biosimilar drug overall, the agency said in a Nov. 15 announcement.
According to a press release from Pfizer, approval for Abrilada was based on review of a comprehensive data package demonstrating biosimilarity of the drug to the reference product. This included data from a clinical comparative study, which found no clinically meaningful difference between Abrilada and the reference in terms of efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In addition to RA, Abrilada is indicated for juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, adult Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis.
Common adverse events in adalimumab clinical trials included infection, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
Pfizer said that it “is working to make Abrilada available to U.S. patients as soon as feasible based on the terms of our agreement with AbbVie [the manufacturer of Humira]. Our current plans are to launch in 2023.”
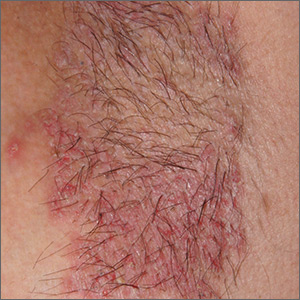
Recurring rash on neck and axilla
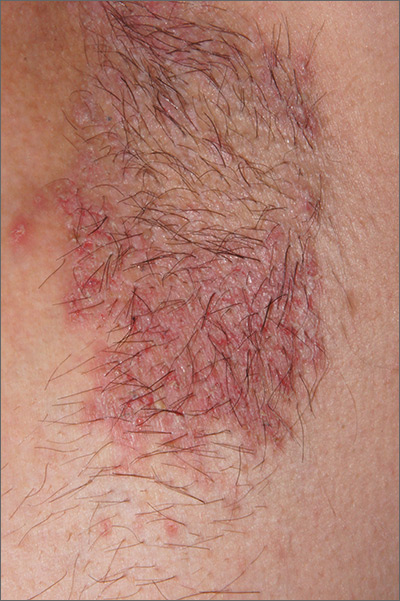
The FP initially treated the area with topical ketoconazole cream, which stung, but partially improved the patient’s symptoms. Because the rash persisted, the FP performed a punch biopsy, which showed widespread epidermal acantholysis or separation of epidermal cells. This is a hallmark of pemphigus vulgaris and benign familial pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease).
Hailey-Hailey disease is an uncommon autosomal dominant inherited blistering disorder that affects connecting proteins in the epidermis, which is why histology overlaps with pemphigus. Symptoms may not present until the second or third decade of life and often occur in flexural or high friction areas, including the axilla and inguinal folds. Any skin injury may trigger a flare, including sunburn, infections, heavy sweating, or friction from clothes. Bacterial overgrowth or colonization can cause a bad odor and social isolation in severe cases.
The differential diagnosis of axillary skin disorders is broad and includes irritant contact dermatitis, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, candida intertrigo, and psoriasis. Clinical clues that favor Hailey-Hailey disease include fragile vesicles or pustules at the periphery and small focal erosions. The family history is helpful but not always known.
Some patients require topical therapy sequentially, in combination, or personalized through trial and error that addresses the inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and fungal disease. Patients also may require long-term doxycycline therapy to suppress flares. Most patients will benefit from at least prn use of topical steroids for inflammation. Addressing sweating with topical aluminum chloride or botulinum injections can be beneficial. Low dose naltrexone, as well as afamelanotide, has shown promise in a few small case series.
The patient in this case improved with topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid and systemic doxycycline 100 mg bid for 2 weeks. However, he continued to require occasional rounds of oral doxycycline with flares.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

The FP initially treated the area with topical ketoconazole cream, which stung, but partially improved the patient’s symptoms. Because the rash persisted, the FP performed a punch biopsy, which showed widespread epidermal acantholysis or separation of epidermal cells. This is a hallmark of pemphigus vulgaris and benign familial pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease).
Hailey-Hailey disease is an uncommon autosomal dominant inherited blistering disorder that affects connecting proteins in the epidermis, which is why histology overlaps with pemphigus. Symptoms may not present until the second or third decade of life and often occur in flexural or high friction areas, including the axilla and inguinal folds. Any skin injury may trigger a flare, including sunburn, infections, heavy sweating, or friction from clothes. Bacterial overgrowth or colonization can cause a bad odor and social isolation in severe cases.
The differential diagnosis of axillary skin disorders is broad and includes irritant contact dermatitis, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, candida intertrigo, and psoriasis. Clinical clues that favor Hailey-Hailey disease include fragile vesicles or pustules at the periphery and small focal erosions. The family history is helpful but not always known.
Some patients require topical therapy sequentially, in combination, or personalized through trial and error that addresses the inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and fungal disease. Patients also may require long-term doxycycline therapy to suppress flares. Most patients will benefit from at least prn use of topical steroids for inflammation. Addressing sweating with topical aluminum chloride or botulinum injections can be beneficial. Low dose naltrexone, as well as afamelanotide, has shown promise in a few small case series.
The patient in this case improved with topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid and systemic doxycycline 100 mg bid for 2 weeks. However, he continued to require occasional rounds of oral doxycycline with flares.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

The FP initially treated the area with topical ketoconazole cream, which stung, but partially improved the patient’s symptoms. Because the rash persisted, the FP performed a punch biopsy, which showed widespread epidermal acantholysis or separation of epidermal cells. This is a hallmark of pemphigus vulgaris and benign familial pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease).
Hailey-Hailey disease is an uncommon autosomal dominant inherited blistering disorder that affects connecting proteins in the epidermis, which is why histology overlaps with pemphigus. Symptoms may not present until the second or third decade of life and often occur in flexural or high friction areas, including the axilla and inguinal folds. Any skin injury may trigger a flare, including sunburn, infections, heavy sweating, or friction from clothes. Bacterial overgrowth or colonization can cause a bad odor and social isolation in severe cases.
The differential diagnosis of axillary skin disorders is broad and includes irritant contact dermatitis, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, candida intertrigo, and psoriasis. Clinical clues that favor Hailey-Hailey disease include fragile vesicles or pustules at the periphery and small focal erosions. The family history is helpful but not always known.
Some patients require topical therapy sequentially, in combination, or personalized through trial and error that addresses the inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and fungal disease. Patients also may require long-term doxycycline therapy to suppress flares. Most patients will benefit from at least prn use of topical steroids for inflammation. Addressing sweating with topical aluminum chloride or botulinum injections can be beneficial. Low dose naltrexone, as well as afamelanotide, has shown promise in a few small case series.
The patient in this case improved with topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment bid and systemic doxycycline 100 mg bid for 2 weeks. However, he continued to require occasional rounds of oral doxycycline with flares.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
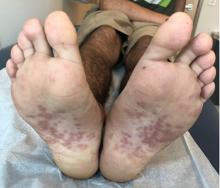
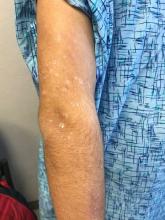
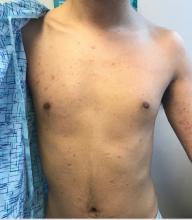
Pink scaly rash on torso and extremities
Tumor necrosis factor–alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors are therapeutic agents used to treat a variety of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as psoriasis of the skin (PSO) and psoriatic arthritis. In a 2017 systematic review, there were 216 reported cases of new-onset TNF-alpha inhibitor–induced psoriasis, with an estimated rate of 1 per 1,000. The cases thus far have had a wide range of presentations, the most common being plaque psoriasis, scalp psoriasis, as well as palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.1
A retrospective chart review study at Mayo clinic published in 2017 evaluated children younger than 19 years seen in 2003-2015 who developed new-onset or recurrent PSO with a history of inflammatory bowel disease being treated with anti-TNF-alpha therapy. The review showed variable latency in the development of PSO in these patients, although it typically occurred during inflammatory bowel disease remission.2 It is unclear whether there is an association between a personal or family history of psoriasis and development of these lesions.
TNF-alpha, interleukin (IL)–17) and interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) are main cytokines that contribute to the development of psoriasis. The mechanism of action for paradoxical PSO/psoriasis in patients treated with anti-TNF is not clearly understood; however, many hypotheses are based on an imbalance between TNF-alpha and interferon-alpha – more specifically, an increased production of interferon-alpha. TNF-alpha inhibits the activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells which are key producers of IFN-alpha. Because of this blockade, there is unopposed IFN-alpha production. Interferon-alpha allows for the expression of chemokines such as CXCR3, which favor T cells homing to the skin. IFN-alpha also stimulates and activates T cells to produce TNF-alpha and IL-17, which in turn sustains inflammatory mechanisms and allows for the development of psoriatic lesions.3
There are no universal management guidelines. Most of these patients’ treatment plans mirror standard psoriasis therapies while the main question remains the decision to continue the same anti-TNF therapy, change anti-TNF agents, or entirely switch classes of biologic or other systemic therapy. This decision in management requires several considerations: treatability of TNF-alpha inhibitor-induced psoriasis, the severity of background disease (i.e., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, other systemic condition), and whether the underlying disease is well controlled on current therapy, as well as the consideration of possible loss in efficacy if a drug is discontinued and then restarted at a later date.4
A reasonable initial approach in patients with well-controlled underlying disease and mild skin eruption is to continue anti-TNF therapy and manage skin topically with topical corticosteroids and/or phototherapy. In patients that either do not have well-controlled underlying disease or moderate skin involvement, changing to an alternative anti-TNF or other agent may be reasonable, and requires coordinated care with involved specialists. In the 2017 pediatric review mentioned previously, nearly half of the patients required a change in their initial anti-TNF-alpha agent despite conventional skin-directed therapies, and one-third of patients discontinued all anti-TNF-alpha therapy because of PSO.2
The psoriasiform papulosquamous features of this case along with the history suggests the diagnosis. Pityriasis rosea would be highly atypical on the feet and with the duration of findings. Lichen planus and atopic dermatitis morphology are inconsistent with this eruption, and coxsackie viral infection would have a shorter course.
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Feb;76(2):334-41.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 May;34(3):253-60.
3. RMD Open. 2016 Jul 15;2(2):e000239.
4. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80.
Tumor necrosis factor–alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors are therapeutic agents used to treat a variety of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as psoriasis of the skin (PSO) and psoriatic arthritis. In a 2017 systematic review, there were 216 reported cases of new-onset TNF-alpha inhibitor–induced psoriasis, with an estimated rate of 1 per 1,000. The cases thus far have had a wide range of presentations, the most common being plaque psoriasis, scalp psoriasis, as well as palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.1
A retrospective chart review study at Mayo clinic published in 2017 evaluated children younger than 19 years seen in 2003-2015 who developed new-onset or recurrent PSO with a history of inflammatory bowel disease being treated with anti-TNF-alpha therapy. The review showed variable latency in the development of PSO in these patients, although it typically occurred during inflammatory bowel disease remission.2 It is unclear whether there is an association between a personal or family history of psoriasis and development of these lesions.
TNF-alpha, interleukin (IL)–17) and interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) are main cytokines that contribute to the development of psoriasis. The mechanism of action for paradoxical PSO/psoriasis in patients treated with anti-TNF is not clearly understood; however, many hypotheses are based on an imbalance between TNF-alpha and interferon-alpha – more specifically, an increased production of interferon-alpha. TNF-alpha inhibits the activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells which are key producers of IFN-alpha. Because of this blockade, there is unopposed IFN-alpha production. Interferon-alpha allows for the expression of chemokines such as CXCR3, which favor T cells homing to the skin. IFN-alpha also stimulates and activates T cells to produce TNF-alpha and IL-17, which in turn sustains inflammatory mechanisms and allows for the development of psoriatic lesions.3
There are no universal management guidelines. Most of these patients’ treatment plans mirror standard psoriasis therapies while the main question remains the decision to continue the same anti-TNF therapy, change anti-TNF agents, or entirely switch classes of biologic or other systemic therapy. This decision in management requires several considerations: treatability of TNF-alpha inhibitor-induced psoriasis, the severity of background disease (i.e., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, other systemic condition), and whether the underlying disease is well controlled on current therapy, as well as the consideration of possible loss in efficacy if a drug is discontinued and then restarted at a later date.4
A reasonable initial approach in patients with well-controlled underlying disease and mild skin eruption is to continue anti-TNF therapy and manage skin topically with topical corticosteroids and/or phototherapy. In patients that either do not have well-controlled underlying disease or moderate skin involvement, changing to an alternative anti-TNF or other agent may be reasonable, and requires coordinated care with involved specialists. In the 2017 pediatric review mentioned previously, nearly half of the patients required a change in their initial anti-TNF-alpha agent despite conventional skin-directed therapies, and one-third of patients discontinued all anti-TNF-alpha therapy because of PSO.2
The psoriasiform papulosquamous features of this case along with the history suggests the diagnosis. Pityriasis rosea would be highly atypical on the feet and with the duration of findings. Lichen planus and atopic dermatitis morphology are inconsistent with this eruption, and coxsackie viral infection would have a shorter course.
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Feb;76(2):334-41.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 May;34(3):253-60.
3. RMD Open. 2016 Jul 15;2(2):e000239.
4. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80.
Tumor necrosis factor–alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors are therapeutic agents used to treat a variety of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as psoriasis of the skin (PSO) and psoriatic arthritis. In a 2017 systematic review, there were 216 reported cases of new-onset TNF-alpha inhibitor–induced psoriasis, with an estimated rate of 1 per 1,000. The cases thus far have had a wide range of presentations, the most common being plaque psoriasis, scalp psoriasis, as well as palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.1
A retrospective chart review study at Mayo clinic published in 2017 evaluated children younger than 19 years seen in 2003-2015 who developed new-onset or recurrent PSO with a history of inflammatory bowel disease being treated with anti-TNF-alpha therapy. The review showed variable latency in the development of PSO in these patients, although it typically occurred during inflammatory bowel disease remission.2 It is unclear whether there is an association between a personal or family history of psoriasis and development of these lesions.
TNF-alpha, interleukin (IL)–17) and interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) are main cytokines that contribute to the development of psoriasis. The mechanism of action for paradoxical PSO/psoriasis in patients treated with anti-TNF is not clearly understood; however, many hypotheses are based on an imbalance between TNF-alpha and interferon-alpha – more specifically, an increased production of interferon-alpha. TNF-alpha inhibits the activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells which are key producers of IFN-alpha. Because of this blockade, there is unopposed IFN-alpha production. Interferon-alpha allows for the expression of chemokines such as CXCR3, which favor T cells homing to the skin. IFN-alpha also stimulates and activates T cells to produce TNF-alpha and IL-17, which in turn sustains inflammatory mechanisms and allows for the development of psoriatic lesions.3
There are no universal management guidelines. Most of these patients’ treatment plans mirror standard psoriasis therapies while the main question remains the decision to continue the same anti-TNF therapy, change anti-TNF agents, or entirely switch classes of biologic or other systemic therapy. This decision in management requires several considerations: treatability of TNF-alpha inhibitor-induced psoriasis, the severity of background disease (i.e., rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, other systemic condition), and whether the underlying disease is well controlled on current therapy, as well as the consideration of possible loss in efficacy if a drug is discontinued and then restarted at a later date.4
A reasonable initial approach in patients with well-controlled underlying disease and mild skin eruption is to continue anti-TNF therapy and manage skin topically with topical corticosteroids and/or phototherapy. In patients that either do not have well-controlled underlying disease or moderate skin involvement, changing to an alternative anti-TNF or other agent may be reasonable, and requires coordinated care with involved specialists. In the 2017 pediatric review mentioned previously, nearly half of the patients required a change in their initial anti-TNF-alpha agent despite conventional skin-directed therapies, and one-third of patients discontinued all anti-TNF-alpha therapy because of PSO.2
The psoriasiform papulosquamous features of this case along with the history suggests the diagnosis. Pityriasis rosea would be highly atypical on the feet and with the duration of findings. Lichen planus and atopic dermatitis morphology are inconsistent with this eruption, and coxsackie viral infection would have a shorter course.
Dr. Tracy is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Feb;76(2):334-41.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 May;34(3):253-60.
3. RMD Open. 2016 Jul 15;2(2):e000239.
4. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019 Apr;4(2):70-80.
A 17-year-old male with a history of Crohn's disease, well controlled on infliximab, is seen for evaluation of a pink scaly rash on the torso, upper extremities, and lower extremities. The rash began 5 months previously and has been mostly asymptomatic. The patient denies pruritus or pain at the affected areas. There is no fever or drainage from any of the sites. The patient has not undergone any treatments. He does not have a personal or family history of chronic skin conditions.
On physical exam, he is noted to have numerous pink papules and plaques with overlying scale on his trunk, as well as the dorsal aspects of bilateral hands and the plantar surfaces of bilateral feet. His skin is otherwise unremarkable.
Expert shares tips for TNF-alpha inhibitor use in special populations
LAS VEGAS – Francisco A. Kerdel, BSc, MBBS, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Kerdel, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Florida International University, Miami, noted that, while tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors are category B drugs, inadequate data exist regarding lactation and exposure throughout pregnancy. “Rates of malformations and spontaneous abortions with therapy are similar to those in the general population, higher concentrations of infliximab and adalimumab have been found in infant and cord blood, compared with certolizumab pegol,” an anti-TNF biologic, he said.
In a prospective, postmarketing, multicenter pharmacokinetic study, researchers found a lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-33). Specifically, certolizumab levels were below the lower limit of quantification (less than 0.032 mcg/mL) in 13 of 14 infant samples at birth and in all infant samples at weeks 4 and 8. Only one infant had a minimal certolizumab level at birth (infant/mother ratio of 0.0009). No antibodies were detected at any time point during the study. Safety data in mothers were in line with the known safety profile of certolizumab and pregnancy profile of these underlying diseases. Adverse events experienced by the infants did not show any patterns or clusters of events suggesting a specific safety signal in children.
In a separate postmarketing pharmacokinetic study, investigators evaluated the transfer of certolizumab into breast milk (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1890-6). They found that the average daily infant dose of certolizumab was minimal. Specifically, the highest concentration of certolizumab in breast milk (0.0758 mcg/mL) was less than 1% of the expected mean plasma trough concentration of a therapeutic dose.
How do TNF-alpha inhibitors fare in the pediatric population? In a retrospective study of 390 children with psoriasis treated at 20 centers in the United States, Canada, and Europe, researchers evaluated the safety of systemic agents (JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153[11]:1147-57). Most (69%) were prescribed methotrexate, followed by biologics, acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid. Drug discontinuation (because of adverse events), which is sometimes used as an efficacy parameter, occurred in 12% of those who were on methotrexate, compared with 3% of those on biologics, 67% of those on acitretin, and 68% of those on fumaric acid.
At the other end of the age spectrum, biologic therapy is generally effective and well tolerated in elderly patients. “Sometimes, they may be more effective than other traditional drugs,” Dr. Kerdel said. “We’re a little bit concerned about immunosenescence, which can increase the risk for severe infections and malignancies. And, 90% of elderly patients with psoriasis may have comorbidities that need to be taken into account when treating psoriasis.”
Other factors come into play when choosing the right anti-TNF agent, including weight. While clinical trials show efficacy across weight groups, infliximab has weight-based dosing, “which may make it a better choice,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Patients taking etanercept may need a biweekly dose.”
Treatment flexibility also comes into play. For example, stopping therapy because of an infection or surgery may be problematic in drugs with a long half-life. Then there’s the issue of patient preference. “Some people don’t want to be injected frequently,” he said. “Some people don’t want to be injected at all and may require a simpler dosing regimen.”
Optimizing anti-TNF-alpha treatment starts with recognizing that there is a loss of response over time, Dr. Kerdel said, “or there may not be a response at all.” Contributing factors may include immunogenicity, suboptimal dosing, and poor patient adherence. In order to optimize treatment, clinicians can try switching agents or combination therapy, and explore continuous versus intermittent dosing.
“We really don’t have good data on the best protocol for switching treatment after failure of an anti-TNF-alpha agent,” he added. In cases of primary and secondary treatment failure, there is no consensus or guidelines on which second-line agent to use, nor good data on which measures to use.
No evidence-based guidelines are available for screening and monitoring patients receiving biologic therapy for psoriasis, either. “Evidence is strongest [grade B] for tuberculosis screening in patients treated with biologic agents,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Among known hepatitis B virus carriers, consider monitoring liver function tests and viral load [grade C]. High-grade evidence is lacking to support other routine testing. Physicians should use clinical judgment when screening and monitoring patients.”
He concluded his presentation by noting that there are a number of biosimilar agents available or in the pipeline for infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept. This raises a number of questions for current and future consideration. For one, “will biosimilars show the same long-term efficacy and safety as the innovator products?” he asked. “Real-world, postmarketing, and registry data are needed. Will biosimilar agents offer significant cost benefits? Will biosimilar labeling be adequately transparent? Will we find biomarkers to help us target biologic agents to specific patients and subtypes of psoriasis?”
Dr. Kerdel reported that he is a member of the speaker’s bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Leo, Ortho, and Novartis. He has also received grant/research support from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, and XBiotech.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Francisco A. Kerdel, BSc, MBBS, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Kerdel, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Florida International University, Miami, noted that, while tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors are category B drugs, inadequate data exist regarding lactation and exposure throughout pregnancy. “Rates of malformations and spontaneous abortions with therapy are similar to those in the general population, higher concentrations of infliximab and adalimumab have been found in infant and cord blood, compared with certolizumab pegol,” an anti-TNF biologic, he said.
In a prospective, postmarketing, multicenter pharmacokinetic study, researchers found a lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-33). Specifically, certolizumab levels were below the lower limit of quantification (less than 0.032 mcg/mL) in 13 of 14 infant samples at birth and in all infant samples at weeks 4 and 8. Only one infant had a minimal certolizumab level at birth (infant/mother ratio of 0.0009). No antibodies were detected at any time point during the study. Safety data in mothers were in line with the known safety profile of certolizumab and pregnancy profile of these underlying diseases. Adverse events experienced by the infants did not show any patterns or clusters of events suggesting a specific safety signal in children.
In a separate postmarketing pharmacokinetic study, investigators evaluated the transfer of certolizumab into breast milk (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1890-6). They found that the average daily infant dose of certolizumab was minimal. Specifically, the highest concentration of certolizumab in breast milk (0.0758 mcg/mL) was less than 1% of the expected mean plasma trough concentration of a therapeutic dose.
How do TNF-alpha inhibitors fare in the pediatric population? In a retrospective study of 390 children with psoriasis treated at 20 centers in the United States, Canada, and Europe, researchers evaluated the safety of systemic agents (JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153[11]:1147-57). Most (69%) were prescribed methotrexate, followed by biologics, acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid. Drug discontinuation (because of adverse events), which is sometimes used as an efficacy parameter, occurred in 12% of those who were on methotrexate, compared with 3% of those on biologics, 67% of those on acitretin, and 68% of those on fumaric acid.
At the other end of the age spectrum, biologic therapy is generally effective and well tolerated in elderly patients. “Sometimes, they may be more effective than other traditional drugs,” Dr. Kerdel said. “We’re a little bit concerned about immunosenescence, which can increase the risk for severe infections and malignancies. And, 90% of elderly patients with psoriasis may have comorbidities that need to be taken into account when treating psoriasis.”
Other factors come into play when choosing the right anti-TNF agent, including weight. While clinical trials show efficacy across weight groups, infliximab has weight-based dosing, “which may make it a better choice,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Patients taking etanercept may need a biweekly dose.”
Treatment flexibility also comes into play. For example, stopping therapy because of an infection or surgery may be problematic in drugs with a long half-life. Then there’s the issue of patient preference. “Some people don’t want to be injected frequently,” he said. “Some people don’t want to be injected at all and may require a simpler dosing regimen.”
Optimizing anti-TNF-alpha treatment starts with recognizing that there is a loss of response over time, Dr. Kerdel said, “or there may not be a response at all.” Contributing factors may include immunogenicity, suboptimal dosing, and poor patient adherence. In order to optimize treatment, clinicians can try switching agents or combination therapy, and explore continuous versus intermittent dosing.
“We really don’t have good data on the best protocol for switching treatment after failure of an anti-TNF-alpha agent,” he added. In cases of primary and secondary treatment failure, there is no consensus or guidelines on which second-line agent to use, nor good data on which measures to use.
No evidence-based guidelines are available for screening and monitoring patients receiving biologic therapy for psoriasis, either. “Evidence is strongest [grade B] for tuberculosis screening in patients treated with biologic agents,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Among known hepatitis B virus carriers, consider monitoring liver function tests and viral load [grade C]. High-grade evidence is lacking to support other routine testing. Physicians should use clinical judgment when screening and monitoring patients.”
He concluded his presentation by noting that there are a number of biosimilar agents available or in the pipeline for infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept. This raises a number of questions for current and future consideration. For one, “will biosimilars show the same long-term efficacy and safety as the innovator products?” he asked. “Real-world, postmarketing, and registry data are needed. Will biosimilar agents offer significant cost benefits? Will biosimilar labeling be adequately transparent? Will we find biomarkers to help us target biologic agents to specific patients and subtypes of psoriasis?”
Dr. Kerdel reported that he is a member of the speaker’s bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Leo, Ortho, and Novartis. He has also received grant/research support from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, and XBiotech.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Francisco A. Kerdel, BSc, MBBS, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Kerdel, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Florida International University, Miami, noted that, while tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors are category B drugs, inadequate data exist regarding lactation and exposure throughout pregnancy. “Rates of malformations and spontaneous abortions with therapy are similar to those in the general population, higher concentrations of infliximab and adalimumab have been found in infant and cord blood, compared with certolizumab pegol,” an anti-TNF biologic, he said.
In a prospective, postmarketing, multicenter pharmacokinetic study, researchers found a lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-33). Specifically, certolizumab levels were below the lower limit of quantification (less than 0.032 mcg/mL) in 13 of 14 infant samples at birth and in all infant samples at weeks 4 and 8. Only one infant had a minimal certolizumab level at birth (infant/mother ratio of 0.0009). No antibodies were detected at any time point during the study. Safety data in mothers were in line with the known safety profile of certolizumab and pregnancy profile of these underlying diseases. Adverse events experienced by the infants did not show any patterns or clusters of events suggesting a specific safety signal in children.
In a separate postmarketing pharmacokinetic study, investigators evaluated the transfer of certolizumab into breast milk (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1890-6). They found that the average daily infant dose of certolizumab was minimal. Specifically, the highest concentration of certolizumab in breast milk (0.0758 mcg/mL) was less than 1% of the expected mean plasma trough concentration of a therapeutic dose.
How do TNF-alpha inhibitors fare in the pediatric population? In a retrospective study of 390 children with psoriasis treated at 20 centers in the United States, Canada, and Europe, researchers evaluated the safety of systemic agents (JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153[11]:1147-57). Most (69%) were prescribed methotrexate, followed by biologics, acitretin, cyclosporine, and fumaric acid. Drug discontinuation (because of adverse events), which is sometimes used as an efficacy parameter, occurred in 12% of those who were on methotrexate, compared with 3% of those on biologics, 67% of those on acitretin, and 68% of those on fumaric acid.
At the other end of the age spectrum, biologic therapy is generally effective and well tolerated in elderly patients. “Sometimes, they may be more effective than other traditional drugs,” Dr. Kerdel said. “We’re a little bit concerned about immunosenescence, which can increase the risk for severe infections and malignancies. And, 90% of elderly patients with psoriasis may have comorbidities that need to be taken into account when treating psoriasis.”
Other factors come into play when choosing the right anti-TNF agent, including weight. While clinical trials show efficacy across weight groups, infliximab has weight-based dosing, “which may make it a better choice,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Patients taking etanercept may need a biweekly dose.”
Treatment flexibility also comes into play. For example, stopping therapy because of an infection or surgery may be problematic in drugs with a long half-life. Then there’s the issue of patient preference. “Some people don’t want to be injected frequently,” he said. “Some people don’t want to be injected at all and may require a simpler dosing regimen.”
Optimizing anti-TNF-alpha treatment starts with recognizing that there is a loss of response over time, Dr. Kerdel said, “or there may not be a response at all.” Contributing factors may include immunogenicity, suboptimal dosing, and poor patient adherence. In order to optimize treatment, clinicians can try switching agents or combination therapy, and explore continuous versus intermittent dosing.
“We really don’t have good data on the best protocol for switching treatment after failure of an anti-TNF-alpha agent,” he added. In cases of primary and secondary treatment failure, there is no consensus or guidelines on which second-line agent to use, nor good data on which measures to use.
No evidence-based guidelines are available for screening and monitoring patients receiving biologic therapy for psoriasis, either. “Evidence is strongest [grade B] for tuberculosis screening in patients treated with biologic agents,” Dr. Kerdel said. “Among known hepatitis B virus carriers, consider monitoring liver function tests and viral load [grade C]. High-grade evidence is lacking to support other routine testing. Physicians should use clinical judgment when screening and monitoring patients.”
He concluded his presentation by noting that there are a number of biosimilar agents available or in the pipeline for infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept. This raises a number of questions for current and future consideration. For one, “will biosimilars show the same long-term efficacy and safety as the innovator products?” he asked. “Real-world, postmarketing, and registry data are needed. Will biosimilar agents offer significant cost benefits? Will biosimilar labeling be adequately transparent? Will we find biomarkers to help us target biologic agents to specific patients and subtypes of psoriasis?”
Dr. Kerdel reported that he is a member of the speaker’s bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Lilly, Leo, Ortho, and Novartis. He has also received grant/research support from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, and XBiotech.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Guselkumab improves psoriatic arthritis regardless of prior TNFi use
ATLANTA – Guselkumab improved outcomes in psoriatic arthritis patients regardless of past treatment with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in the phase 3 DISCOVER-1 trial.
The anti-interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody is approved in the United States for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO).
Benefits in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) were seen in both biologic-naive and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)–treated patients and occurred with both 4- and 8-week dosing regimens, Atul Deodhar, MD, reported during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
For example, the primary endpoint of ACR 20 response at 24 weeks was achieved in 58.6% and 52.8% of patients randomized to receive 100 mg of guselkumab delivered subcutaneously either at baseline and every 4 weeks or at baseline, week 4, and then every 8 weeks, respectively, compared with 22.2% of those randomized to receive placebo, said Dr. Deodhar, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Greater proportions of patients in the guselkumab groups achieved ACR 20 response at week 16; ACR 50 response at weeks 16 and 24; ACR 70 response at week 24; Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 24; and minimal disease activity response at week 24, he said, adding that improvements were also seen with guselkumab versus placebo for the controlled major secondary endpoints of change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index score, Short Form 36 Health Survey score, and investigator global assessment (IGA) of PsO response.
The response rates with guselkumab versus placebo were seen regardless of prior TNFi use, he said.
The study included 381 patients with active PsA, defined as three or more swollen joints, three or more tender joints, and C-reactive protein of 0.3 mg/dL or greater despite standard therapies. About 30% were exposed to up to two TNFi therapies and 10% were nonresponders or inadequate responders to those therapies.
Concomitant use of select nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, and NSAIDs was allowed, and patients with less than 5% improvement in tender plus swollen joints at week 16 could initiate or increase the dose of the permitted medications while continuing study treatment, Dr. Deodhar said.
The mean body surface area with PsO involvement was 13.4%; 42.5% of patients had an IGA of 3-4 for skin involvement. Mean swollen and tender joint counts were 9.8 and 19.3, respectively, indicating a population with moderate to severe disease, he added.
Serious adverse events, serious infections, and death occurred in 2.4%, 0.5%, and 0.3% of patients, respectively.
“Both guselkumab regimens were safe and well tolerated through week 24,” Dr. Deodhar said, noting that the safety profile was consistent with that established in the treatment of PsO and described in the label.
DISCOVER-1 was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Deodhar reported relationships (advisory board activity, consulting, and/or research grant funding) with several pharmaceutical companies including Janssen. Several coauthors are employees of Janssen.
SOURCE: Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 807.
ATLANTA – Guselkumab improved outcomes in psoriatic arthritis patients regardless of past treatment with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in the phase 3 DISCOVER-1 trial.
The anti-interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody is approved in the United States for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO).
Benefits in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) were seen in both biologic-naive and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)–treated patients and occurred with both 4- and 8-week dosing regimens, Atul Deodhar, MD, reported during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
For example, the primary endpoint of ACR 20 response at 24 weeks was achieved in 58.6% and 52.8% of patients randomized to receive 100 mg of guselkumab delivered subcutaneously either at baseline and every 4 weeks or at baseline, week 4, and then every 8 weeks, respectively, compared with 22.2% of those randomized to receive placebo, said Dr. Deodhar, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Greater proportions of patients in the guselkumab groups achieved ACR 20 response at week 16; ACR 50 response at weeks 16 and 24; ACR 70 response at week 24; Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 24; and minimal disease activity response at week 24, he said, adding that improvements were also seen with guselkumab versus placebo for the controlled major secondary endpoints of change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index score, Short Form 36 Health Survey score, and investigator global assessment (IGA) of PsO response.
The response rates with guselkumab versus placebo were seen regardless of prior TNFi use, he said.
The study included 381 patients with active PsA, defined as three or more swollen joints, three or more tender joints, and C-reactive protein of 0.3 mg/dL or greater despite standard therapies. About 30% were exposed to up to two TNFi therapies and 10% were nonresponders or inadequate responders to those therapies.
Concomitant use of select nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, and NSAIDs was allowed, and patients with less than 5% improvement in tender plus swollen joints at week 16 could initiate or increase the dose of the permitted medications while continuing study treatment, Dr. Deodhar said.
The mean body surface area with PsO involvement was 13.4%; 42.5% of patients had an IGA of 3-4 for skin involvement. Mean swollen and tender joint counts were 9.8 and 19.3, respectively, indicating a population with moderate to severe disease, he added.
Serious adverse events, serious infections, and death occurred in 2.4%, 0.5%, and 0.3% of patients, respectively.
“Both guselkumab regimens were safe and well tolerated through week 24,” Dr. Deodhar said, noting that the safety profile was consistent with that established in the treatment of PsO and described in the label.
DISCOVER-1 was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Deodhar reported relationships (advisory board activity, consulting, and/or research grant funding) with several pharmaceutical companies including Janssen. Several coauthors are employees of Janssen.
SOURCE: Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 807.
ATLANTA – Guselkumab improved outcomes in psoriatic arthritis patients regardless of past treatment with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in the phase 3 DISCOVER-1 trial.
The anti-interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody is approved in the United States for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO).
Benefits in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) were seen in both biologic-naive and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)–treated patients and occurred with both 4- and 8-week dosing regimens, Atul Deodhar, MD, reported during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
For example, the primary endpoint of ACR 20 response at 24 weeks was achieved in 58.6% and 52.8% of patients randomized to receive 100 mg of guselkumab delivered subcutaneously either at baseline and every 4 weeks or at baseline, week 4, and then every 8 weeks, respectively, compared with 22.2% of those randomized to receive placebo, said Dr. Deodhar, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Greater proportions of patients in the guselkumab groups achieved ACR 20 response at week 16; ACR 50 response at weeks 16 and 24; ACR 70 response at week 24; Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 24; and minimal disease activity response at week 24, he said, adding that improvements were also seen with guselkumab versus placebo for the controlled major secondary endpoints of change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index score, Short Form 36 Health Survey score, and investigator global assessment (IGA) of PsO response.
The response rates with guselkumab versus placebo were seen regardless of prior TNFi use, he said.
The study included 381 patients with active PsA, defined as three or more swollen joints, three or more tender joints, and C-reactive protein of 0.3 mg/dL or greater despite standard therapies. About 30% were exposed to up to two TNFi therapies and 10% were nonresponders or inadequate responders to those therapies.
Concomitant use of select nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, and NSAIDs was allowed, and patients with less than 5% improvement in tender plus swollen joints at week 16 could initiate or increase the dose of the permitted medications while continuing study treatment, Dr. Deodhar said.
The mean body surface area with PsO involvement was 13.4%; 42.5% of patients had an IGA of 3-4 for skin involvement. Mean swollen and tender joint counts were 9.8 and 19.3, respectively, indicating a population with moderate to severe disease, he added.
Serious adverse events, serious infections, and death occurred in 2.4%, 0.5%, and 0.3% of patients, respectively.
“Both guselkumab regimens were safe and well tolerated through week 24,” Dr. Deodhar said, noting that the safety profile was consistent with that established in the treatment of PsO and described in the label.
DISCOVER-1 was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Deodhar reported relationships (advisory board activity, consulting, and/or research grant funding) with several pharmaceutical companies including Janssen. Several coauthors are employees of Janssen.
SOURCE: Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 807.
AAD-NPF Pediatric psoriasis guideline advises on physical and mental care
Psoriasis management in children involves attention not only to treatment of the physical condition but also psychosocial wellness and quality of life, according to
Psoriasis affects approximately 1% of children, either alone or associated with comorbid conditions such as psoriatic arthritis (PsA), wrote Alan Menter, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and coauthors of the guideline.
In the guideline, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, the multidisciplinary work group identified screening tools to measure disease severity, strategies for management of comorbidities, and the safety and effectiveness of topical, systemic, and phototherapy treatments.
To assess disease severity, the work group recommended not only the use of body surface area (BSA), similar to measurement of severity in adults, but also the use of the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index, a 10-question quality of life survey, as BSA alone does not account for the potential negative impact of the disease on quality of life in terms of physical, emotional, social, and psychological function.
“For example, a child with psoriasis limited to the face or the entire scalp does not have severe disease based on BSA definitions, but if this involvement causes shame, social withdrawal, or bullying, it satisfies criteria for severe disease based on impact beyond the skin,” they said.
The work group stated that a variety of conditions may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis in children, including infections, cutaneous trauma, or physiological, emotional, and environmental stressors.
The majority of children with PsA develop joint inflammation before skin disease, the work group wrote. In addition, children with psoriasis are at increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis, so clinicians may need to distinguish between a combination of psoriasis and musculoskeletal issues and cases of either psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis in young patients.
The cardiovascular risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome are greater in children with psoriasis, compared with children without psoriasis, the work group noted. In addition, pediatric psoriasis patients have a higher prevalence of obesity than children without psoriasis, and they recommended that children with psoriasis be monitored for the development of obesity, and that obese children with psoriasis should be referred for weight management.
The work group noted that data are insufficient in children to support the link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease that has been documented in adults with psoriasis. However, “patients with pediatric psoriasis should have American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)–recommended age-related cardiovascular screening regardless of the presence of signs or symptoms,” they said.
The guideline also recommends screening for dyslipidemia and hypertension according to AAP guidelines and educating pediatric psoriasis patients about the risk of diabetes and regularly screening for diabetes and insulin resistance in those who are obese. Overweight children with psoriasis may be screened at the provider’s discretion, they wrote. Patients with signs of inflammatory bowel disease, which also is associated with psoriasis in adults, should be considered for referral to a gastroenterologist, they noted.
Children with psoriasis should be screened regularly for mental health conditions regardless of age, and they should be asked about substance abuse, according to the guideline, and those with concerns should be referred for additional assessment and management.
The guideline divides treatment of psoriasis in children into three categories: topical, phototherapy and photochemotherapy, and systemic treatments (nonbiologic or biologic).
For topicals, the guideline recommendations include corticosteroids as an off-label therapy, as well as ultra-high-potency topical corticosteroids as monotherapy. Overall, “selection of a therapeutic routine (potency, delivery vehicle, frequency of application) should take into account sites of involvement, type and thickness of psoriasis, age of the patient, total BSA of application, anticipated occlusion, and disease acuity, among other patient-, disease-, and drug-related factors,” the authors wrote. Other topical options included in the recommendations: calcineurin inhibitors, topical vitamin D analogues, tazarotene (off label), anthralin, and coal tar.
Phototherapy has a history of use in psoriasis treatment and remains part of the current recommendations, although data in children are limited, and data on the use of phototherapy for pustular psoriasis in children are insufficient to make specific treatment and dosing recommendations, the work group noted. The researchers also noted that in-office phototherapy may not be feasible for many patients, but that in-home ultraviolet light equipment or natural sunlight in moderation could be recommended as an alternative.
The use of systemic, nonbiologic treatments for pediatric psoriasis should be “based on baseline severity of disease, subtype of psoriasis, speed of disease progression, lack of response to more conservative therapies such as topical agents and phototherapy (when appropriate), impaired physical or psychological functioning or [quality of life] due to disease extent, and the presence of comorbidities such as PsA,” the workgroup said.
Options for systemic treatment include methotrexate, cyclosporine (notably for pustular as well as plaque and erythrodermic psoriasis), and systemic retinoids. In addition, fumaric acid esters may be an option for children with moderate to severe psoriasis, with recommended clinical and laboratory monitoring.
The increasing safety and efficacy data on biologics in pediatric psoriasis patients support their consideration among first-line systemic treatments, the work group suggested. “Etanercept and ustekinumab are now [Food and Drug Administration] approved for patients with psoriasis 4 years and older and 12 years and older, respectively,” they said, and infliximab and adalimumab have been used off label in children.
The work group concluded that research and knowledge gaps about pediatric psoriasis persist and include mechanism of disease onset, development of comorbidities, and identification of ideal dosing for various treatments.
Finally, the work group emphasized the importance of collaboration between dermatologists and primary care providers for managing psoriasis in children, as well as the importance of patient education.
“Dermatologists should be mindful of the unique aspects of the emotional development of children and the social dynamics of having a visible difference,” they wrote. “Shared decision making with the patient (if age appropriate) and the caregivers is a useful approach, particularly as related to the use of off-label medications to treat severe disease,” they said.
“This is the first time that pediatric psoriasis has been discussed as an independent topic within the guideline,” said one of the guideline authors, Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in an interview. “Children have unique physiology and psychosocial aspects to their care relative to adults. In addition, psoriasis has some clinical manifestations that are oftentimes distinctly seen in children,” she commented. “Creation of a guideline specific to children allows us to summarize the similarities and differences of disease presentation and management. It also allows an opportunity to clarify what research data (especially therapeutics) have been studied in children and their uses, safety profiles, and dosing,” she noted.
Psoriasis can be a psychosocially debilitating disease, she emphasized. “In children, for example, isolated or prominent facial involvement is common, which can be embarrassing and impact relationships.”
The take-home message for clinicians, Dr. Davis said, is to keep in mind the multisystemic nature of psoriasis. “It is not limited to the skin,” she said. “Treating a patient with psoriasis necessitates practicing whole-person care” and considering the multiple comorbidities that impact quality of life and overall health in children, as well as adults with psoriasis, she commented. “Dermatologists can empower patients and their caregivers by educating them on the multifocal, complex nature of the disease.” She added, “We have much to learn regarding psoriasis in the pediatric population. More research into therapeutics, topical and systemic, is necessary to optimize patient care.”
The guideline was based on studies published in the PubMed and MEDLINE databases from January 2011 through December 31, 2017.
Dr. Menter and Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology, at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, were cochairs of the work group. The pediatric guideline is the latest in a multipart series of AAD-NPF guidelines on psoriasis being published this year in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Many of the guideline authors, including lead author Dr. Menter, disclosed relationships with multiple companies; however, a minimum 51% of workgroup members had no relevant conflicts of interest in accordance with AAD policy. There was no funding source. Dr. Davis disclosed serving as an investigator for Regeneron, with no compensation.
SOURCE: Menter et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.049.
Psoriasis management in children involves attention not only to treatment of the physical condition but also psychosocial wellness and quality of life, according to
Psoriasis affects approximately 1% of children, either alone or associated with comorbid conditions such as psoriatic arthritis (PsA), wrote Alan Menter, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and coauthors of the guideline.
In the guideline, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, the multidisciplinary work group identified screening tools to measure disease severity, strategies for management of comorbidities, and the safety and effectiveness of topical, systemic, and phototherapy treatments.
To assess disease severity, the work group recommended not only the use of body surface area (BSA), similar to measurement of severity in adults, but also the use of the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index, a 10-question quality of life survey, as BSA alone does not account for the potential negative impact of the disease on quality of life in terms of physical, emotional, social, and psychological function.
“For example, a child with psoriasis limited to the face or the entire scalp does not have severe disease based on BSA definitions, but if this involvement causes shame, social withdrawal, or bullying, it satisfies criteria for severe disease based on impact beyond the skin,” they said.
The work group stated that a variety of conditions may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis in children, including infections, cutaneous trauma, or physiological, emotional, and environmental stressors.
The majority of children with PsA develop joint inflammation before skin disease, the work group wrote. In addition, children with psoriasis are at increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis, so clinicians may need to distinguish between a combination of psoriasis and musculoskeletal issues and cases of either psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis in young patients.
The cardiovascular risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome are greater in children with psoriasis, compared with children without psoriasis, the work group noted. In addition, pediatric psoriasis patients have a higher prevalence of obesity than children without psoriasis, and they recommended that children with psoriasis be monitored for the development of obesity, and that obese children with psoriasis should be referred for weight management.
The work group noted that data are insufficient in children to support the link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease that has been documented in adults with psoriasis. However, “patients with pediatric psoriasis should have American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)–recommended age-related cardiovascular screening regardless of the presence of signs or symptoms,” they said.
The guideline also recommends screening for dyslipidemia and hypertension according to AAP guidelines and educating pediatric psoriasis patients about the risk of diabetes and regularly screening for diabetes and insulin resistance in those who are obese. Overweight children with psoriasis may be screened at the provider’s discretion, they wrote. Patients with signs of inflammatory bowel disease, which also is associated with psoriasis in adults, should be considered for referral to a gastroenterologist, they noted.
Children with psoriasis should be screened regularly for mental health conditions regardless of age, and they should be asked about substance abuse, according to the guideline, and those with concerns should be referred for additional assessment and management.
The guideline divides treatment of psoriasis in children into three categories: topical, phototherapy and photochemotherapy, and systemic treatments (nonbiologic or biologic).
For topicals, the guideline recommendations include corticosteroids as an off-label therapy, as well as ultra-high-potency topical corticosteroids as monotherapy. Overall, “selection of a therapeutic routine (potency, delivery vehicle, frequency of application) should take into account sites of involvement, type and thickness of psoriasis, age of the patient, total BSA of application, anticipated occlusion, and disease acuity, among other patient-, disease-, and drug-related factors,” the authors wrote. Other topical options included in the recommendations: calcineurin inhibitors, topical vitamin D analogues, tazarotene (off label), anthralin, and coal tar.
Phototherapy has a history of use in psoriasis treatment and remains part of the current recommendations, although data in children are limited, and data on the use of phototherapy for pustular psoriasis in children are insufficient to make specific treatment and dosing recommendations, the work group noted. The researchers also noted that in-office phototherapy may not be feasible for many patients, but that in-home ultraviolet light equipment or natural sunlight in moderation could be recommended as an alternative.
The use of systemic, nonbiologic treatments for pediatric psoriasis should be “based on baseline severity of disease, subtype of psoriasis, speed of disease progression, lack of response to more conservative therapies such as topical agents and phototherapy (when appropriate), impaired physical or psychological functioning or [quality of life] due to disease extent, and the presence of comorbidities such as PsA,” the workgroup said.
Options for systemic treatment include methotrexate, cyclosporine (notably for pustular as well as plaque and erythrodermic psoriasis), and systemic retinoids. In addition, fumaric acid esters may be an option for children with moderate to severe psoriasis, with recommended clinical and laboratory monitoring.
The increasing safety and efficacy data on biologics in pediatric psoriasis patients support their consideration among first-line systemic treatments, the work group suggested. “Etanercept and ustekinumab are now [Food and Drug Administration] approved for patients with psoriasis 4 years and older and 12 years and older, respectively,” they said, and infliximab and adalimumab have been used off label in children.
The work group concluded that research and knowledge gaps about pediatric psoriasis persist and include mechanism of disease onset, development of comorbidities, and identification of ideal dosing for various treatments.
Finally, the work group emphasized the importance of collaboration between dermatologists and primary care providers for managing psoriasis in children, as well as the importance of patient education.
“Dermatologists should be mindful of the unique aspects of the emotional development of children and the social dynamics of having a visible difference,” they wrote. “Shared decision making with the patient (if age appropriate) and the caregivers is a useful approach, particularly as related to the use of off-label medications to treat severe disease,” they said.
“This is the first time that pediatric psoriasis has been discussed as an independent topic within the guideline,” said one of the guideline authors, Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in an interview. “Children have unique physiology and psychosocial aspects to their care relative to adults. In addition, psoriasis has some clinical manifestations that are oftentimes distinctly seen in children,” she commented. “Creation of a guideline specific to children allows us to summarize the similarities and differences of disease presentation and management. It also allows an opportunity to clarify what research data (especially therapeutics) have been studied in children and their uses, safety profiles, and dosing,” she noted.
Psoriasis can be a psychosocially debilitating disease, she emphasized. “In children, for example, isolated or prominent facial involvement is common, which can be embarrassing and impact relationships.”
The take-home message for clinicians, Dr. Davis said, is to keep in mind the multisystemic nature of psoriasis. “It is not limited to the skin,” she said. “Treating a patient with psoriasis necessitates practicing whole-person care” and considering the multiple comorbidities that impact quality of life and overall health in children, as well as adults with psoriasis, she commented. “Dermatologists can empower patients and their caregivers by educating them on the multifocal, complex nature of the disease.” She added, “We have much to learn regarding psoriasis in the pediatric population. More research into therapeutics, topical and systemic, is necessary to optimize patient care.”
The guideline was based on studies published in the PubMed and MEDLINE databases from January 2011 through December 31, 2017.
Dr. Menter and Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology, at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, were cochairs of the work group. The pediatric guideline is the latest in a multipart series of AAD-NPF guidelines on psoriasis being published this year in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Many of the guideline authors, including lead author Dr. Menter, disclosed relationships with multiple companies; however, a minimum 51% of workgroup members had no relevant conflicts of interest in accordance with AAD policy. There was no funding source. Dr. Davis disclosed serving as an investigator for Regeneron, with no compensation.
SOURCE: Menter et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.049.
Psoriasis management in children involves attention not only to treatment of the physical condition but also psychosocial wellness and quality of life, according to
Psoriasis affects approximately 1% of children, either alone or associated with comorbid conditions such as psoriatic arthritis (PsA), wrote Alan Menter, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, and coauthors of the guideline.
In the guideline, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, the multidisciplinary work group identified screening tools to measure disease severity, strategies for management of comorbidities, and the safety and effectiveness of topical, systemic, and phototherapy treatments.
To assess disease severity, the work group recommended not only the use of body surface area (BSA), similar to measurement of severity in adults, but also the use of the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index, a 10-question quality of life survey, as BSA alone does not account for the potential negative impact of the disease on quality of life in terms of physical, emotional, social, and psychological function.
“For example, a child with psoriasis limited to the face or the entire scalp does not have severe disease based on BSA definitions, but if this involvement causes shame, social withdrawal, or bullying, it satisfies criteria for severe disease based on impact beyond the skin,” they said.
The work group stated that a variety of conditions may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis in children, including infections, cutaneous trauma, or physiological, emotional, and environmental stressors.
The majority of children with PsA develop joint inflammation before skin disease, the work group wrote. In addition, children with psoriasis are at increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis, so clinicians may need to distinguish between a combination of psoriasis and musculoskeletal issues and cases of either psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis in young patients.
The cardiovascular risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome are greater in children with psoriasis, compared with children without psoriasis, the work group noted. In addition, pediatric psoriasis patients have a higher prevalence of obesity than children without psoriasis, and they recommended that children with psoriasis be monitored for the development of obesity, and that obese children with psoriasis should be referred for weight management.
The work group noted that data are insufficient in children to support the link between psoriasis and cardiovascular disease that has been documented in adults with psoriasis. However, “patients with pediatric psoriasis should have American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)–recommended age-related cardiovascular screening regardless of the presence of signs or symptoms,” they said.
The guideline also recommends screening for dyslipidemia and hypertension according to AAP guidelines and educating pediatric psoriasis patients about the risk of diabetes and regularly screening for diabetes and insulin resistance in those who are obese. Overweight children with psoriasis may be screened at the provider’s discretion, they wrote. Patients with signs of inflammatory bowel disease, which also is associated with psoriasis in adults, should be considered for referral to a gastroenterologist, they noted.
Children with psoriasis should be screened regularly for mental health conditions regardless of age, and they should be asked about substance abuse, according to the guideline, and those with concerns should be referred for additional assessment and management.
The guideline divides treatment of psoriasis in children into three categories: topical, phototherapy and photochemotherapy, and systemic treatments (nonbiologic or biologic).
For topicals, the guideline recommendations include corticosteroids as an off-label therapy, as well as ultra-high-potency topical corticosteroids as monotherapy. Overall, “selection of a therapeutic routine (potency, delivery vehicle, frequency of application) should take into account sites of involvement, type and thickness of psoriasis, age of the patient, total BSA of application, anticipated occlusion, and disease acuity, among other patient-, disease-, and drug-related factors,” the authors wrote. Other topical options included in the recommendations: calcineurin inhibitors, topical vitamin D analogues, tazarotene (off label), anthralin, and coal tar.
Phototherapy has a history of use in psoriasis treatment and remains part of the current recommendations, although data in children are limited, and data on the use of phototherapy for pustular psoriasis in children are insufficient to make specific treatment and dosing recommendations, the work group noted. The researchers also noted that in-office phototherapy may not be feasible for many patients, but that in-home ultraviolet light equipment or natural sunlight in moderation could be recommended as an alternative.
The use of systemic, nonbiologic treatments for pediatric psoriasis should be “based on baseline severity of disease, subtype of psoriasis, speed of disease progression, lack of response to more conservative therapies such as topical agents and phototherapy (when appropriate), impaired physical or psychological functioning or [quality of life] due to disease extent, and the presence of comorbidities such as PsA,” the workgroup said.
Options for systemic treatment include methotrexate, cyclosporine (notably for pustular as well as plaque and erythrodermic psoriasis), and systemic retinoids. In addition, fumaric acid esters may be an option for children with moderate to severe psoriasis, with recommended clinical and laboratory monitoring.
The increasing safety and efficacy data on biologics in pediatric psoriasis patients support their consideration among first-line systemic treatments, the work group suggested. “Etanercept and ustekinumab are now [Food and Drug Administration] approved for patients with psoriasis 4 years and older and 12 years and older, respectively,” they said, and infliximab and adalimumab have been used off label in children.
The work group concluded that research and knowledge gaps about pediatric psoriasis persist and include mechanism of disease onset, development of comorbidities, and identification of ideal dosing for various treatments.
Finally, the work group emphasized the importance of collaboration between dermatologists and primary care providers for managing psoriasis in children, as well as the importance of patient education.
“Dermatologists should be mindful of the unique aspects of the emotional development of children and the social dynamics of having a visible difference,” they wrote. “Shared decision making with the patient (if age appropriate) and the caregivers is a useful approach, particularly as related to the use of off-label medications to treat severe disease,” they said.
“This is the first time that pediatric psoriasis has been discussed as an independent topic within the guideline,” said one of the guideline authors, Dawn M.R. Davis, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., in an interview. “Children have unique physiology and psychosocial aspects to their care relative to adults. In addition, psoriasis has some clinical manifestations that are oftentimes distinctly seen in children,” she commented. “Creation of a guideline specific to children allows us to summarize the similarities and differences of disease presentation and management. It also allows an opportunity to clarify what research data (especially therapeutics) have been studied in children and their uses, safety profiles, and dosing,” she noted.
Psoriasis can be a psychosocially debilitating disease, she emphasized. “In children, for example, isolated or prominent facial involvement is common, which can be embarrassing and impact relationships.”
The take-home message for clinicians, Dr. Davis said, is to keep in mind the multisystemic nature of psoriasis. “It is not limited to the skin,” she said. “Treating a patient with psoriasis necessitates practicing whole-person care” and considering the multiple comorbidities that impact quality of life and overall health in children, as well as adults with psoriasis, she commented. “Dermatologists can empower patients and their caregivers by educating them on the multifocal, complex nature of the disease.” She added, “We have much to learn regarding psoriasis in the pediatric population. More research into therapeutics, topical and systemic, is necessary to optimize patient care.”
The guideline was based on studies published in the PubMed and MEDLINE databases from January 2011 through December 31, 2017.
Dr. Menter and Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology, at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, were cochairs of the work group. The pediatric guideline is the latest in a multipart series of AAD-NPF guidelines on psoriasis being published this year in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Many of the guideline authors, including lead author Dr. Menter, disclosed relationships with multiple companies; however, a minimum 51% of workgroup members had no relevant conflicts of interest in accordance with AAD policy. There was no funding source. Dr. Davis disclosed serving as an investigator for Regeneron, with no compensation.
SOURCE: Menter et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.08.049.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Options for acne treatment continue to advance
LAS VEGAS – according to Linda Stein Gold, MD, who reviewed the data on these two therapies, as well as cannabidiol (CBD) and an androgen receptor antagonist, which are currently in clinical trials, at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
When considering antibiotic therapy for patients with moderate to severe acne, sarecycline, approved for that indication in October 2018, has improved anti-inflammatory properties and a narrower spectrum of activity, compared with other tetracycline-class antibiotics used for the condition, according to Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology research at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit. In two identically designed, 12-week randomized trials, SC 1401 and SC1402, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of an approximate 1.5–mg/kg per day dose of sarecycline in comparison with placebo in patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-45 years (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Sept 1;17[9]:987-96). “We started to see separation in the inflammatory lesions as early as week 3, and a nice separation versus placebo over the course of 12 weeks,” said Dr. Stein Gold, one of the study investigators. “In all, 22% of patients got clear or almost clear with monotherapy. That’s fairly good.”
She noted that there was consistency in the reductions of lesion count achieved in both studies. Improvements were seen through to 12 weeks, with statistically significant reduction seen as early as 3 weeks in both studies. Sarecycline was also statistically superior to placebo at every time point studied in both trials.
In order to be judged a successful outcome, the subject had to have a 12-week Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score with a 2-point or greater decrease (improvement) from baseline score on the IGA in each location, for patients who have a baseline IGA of 2 or greater, and to be clear (0) or almost clear (1). The same IGA scale was used for the chest and back assessments as was used for facial acne; the researchers observed statistically significant improvements in IGA score for both chest and back acne across both studies at week 12.
Sarecycline also had a favorable safety profile, with no treatment-emergent vertigo or tinnitus adverse events, she noted. Treatment-emergent vestibular and phototoxic adverse events both occurred in fewer than 1% of sarecycline patients. Among females, rates of yeast infections were low. When she recommends a course of this drug for her patients, “I never overpromise,” she said. “I tell my acne patients, ‘We measure your success in weeks and months, not days.’ I always tell them, ‘Take a selfie today and take a selfie every few weeks. When you come back in, we’ll review your progress and see how things went.’ ”
Researchers have also been studying topical minocycline as a treatment option. Minocycline is a large molecule that Dr. Stein Gold characterized as being “very challenging” to deliver topically. “It’s also challenging to keep it stable in a topical formulation.” However, results from two identical phase 3 trials found 4% topical minocycline foam significantly reduced both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions and improved IGA scores in patients with moderate to severe acne when treated daily for 12 weeks (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan;80[1]:168-77).
“This drug has an interesting vehicle,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was one of the study investigators. “If you take the vehicle itself and you put it next to sebum, it causes sebum to melt at lower temperatures. Why does this matter? If you’re dissolving sebum, maybe you’re creating an easier pathway for the drug to get delivered into the skin and into the hair follicles. We don’t know all the details.” In the two trials, 15%-31% of patients achieved clearance or near clearance of all lesions. “How did it do in terms of decreasing papules and pustules? It did pretty well,” she said. “We want drugs to meet their match in everything that we do.” In terms of tolerability, skin-related adverse events were reported in fewer than 1% of subjects treated with 4% topical minocycline foam. She noted that by delivering minocycline topically, “we get huge concentrations in the skin, but almost negligible amounts in the systemic circulation, which is important. We want to keep [the drug] in the skin; we don’t want it in our system.”
(The Food and Drug Administration approved minocycline foam 4% in October 2019 for treating inflammatory lesions associated with non-nodular moderate to severe acne).
Another potential treatment on the horizon is cortexolone 17a-propionate, a novel androgen receptor antagonist that inhibits production of lipids and inflammatory cytokines from sebocytes in vitro. “When used around the sebaceous gland, we find that the amount of sebum produced goes down,” she said, noting that phase 3 trials of the agent have been completed.
“We also find that abnormal keratinization subsequently goes down. Just putting this on the skin significantly reduced acne as monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe acne. We were able to get them to clear or almost clear. It worked on comedones, papules, and pustules. Hopefully, it will get FDA approval. This fills the one unmet need we haven’t had topically in terms of decreasing sebum production.”
Clinical trials of CBD are also under way for acne and atopic dermatitis. “It could work for acne because there are some studies showing that might work on sebaceous glands to decrease sebum production,” she said. “CBD has been shown to have positive effects on abnormal keratinization, and it has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Maybe we’ll have another mechanism of action for acne.”
Dr. Gold disclosed that she is on the speakers bureau for Almirall, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron. She is a consultant for Dermavant, Foamix, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and holds stock/stock options in AbbVie, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Foamix, Galderma, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sol-Gel.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – according to Linda Stein Gold, MD, who reviewed the data on these two therapies, as well as cannabidiol (CBD) and an androgen receptor antagonist, which are currently in clinical trials, at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
When considering antibiotic therapy for patients with moderate to severe acne, sarecycline, approved for that indication in October 2018, has improved anti-inflammatory properties and a narrower spectrum of activity, compared with other tetracycline-class antibiotics used for the condition, according to Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology research at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit. In two identically designed, 12-week randomized trials, SC 1401 and SC1402, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of an approximate 1.5–mg/kg per day dose of sarecycline in comparison with placebo in patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-45 years (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Sept 1;17[9]:987-96). “We started to see separation in the inflammatory lesions as early as week 3, and a nice separation versus placebo over the course of 12 weeks,” said Dr. Stein Gold, one of the study investigators. “In all, 22% of patients got clear or almost clear with monotherapy. That’s fairly good.”
She noted that there was consistency in the reductions of lesion count achieved in both studies. Improvements were seen through to 12 weeks, with statistically significant reduction seen as early as 3 weeks in both studies. Sarecycline was also statistically superior to placebo at every time point studied in both trials.
In order to be judged a successful outcome, the subject had to have a 12-week Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score with a 2-point or greater decrease (improvement) from baseline score on the IGA in each location, for patients who have a baseline IGA of 2 or greater, and to be clear (0) or almost clear (1). The same IGA scale was used for the chest and back assessments as was used for facial acne; the researchers observed statistically significant improvements in IGA score for both chest and back acne across both studies at week 12.
Sarecycline also had a favorable safety profile, with no treatment-emergent vertigo or tinnitus adverse events, she noted. Treatment-emergent vestibular and phototoxic adverse events both occurred in fewer than 1% of sarecycline patients. Among females, rates of yeast infections were low. When she recommends a course of this drug for her patients, “I never overpromise,” she said. “I tell my acne patients, ‘We measure your success in weeks and months, not days.’ I always tell them, ‘Take a selfie today and take a selfie every few weeks. When you come back in, we’ll review your progress and see how things went.’ ”
Researchers have also been studying topical minocycline as a treatment option. Minocycline is a large molecule that Dr. Stein Gold characterized as being “very challenging” to deliver topically. “It’s also challenging to keep it stable in a topical formulation.” However, results from two identical phase 3 trials found 4% topical minocycline foam significantly reduced both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions and improved IGA scores in patients with moderate to severe acne when treated daily for 12 weeks (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan;80[1]:168-77).
“This drug has an interesting vehicle,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was one of the study investigators. “If you take the vehicle itself and you put it next to sebum, it causes sebum to melt at lower temperatures. Why does this matter? If you’re dissolving sebum, maybe you’re creating an easier pathway for the drug to get delivered into the skin and into the hair follicles. We don’t know all the details.” In the two trials, 15%-31% of patients achieved clearance or near clearance of all lesions. “How did it do in terms of decreasing papules and pustules? It did pretty well,” she said. “We want drugs to meet their match in everything that we do.” In terms of tolerability, skin-related adverse events were reported in fewer than 1% of subjects treated with 4% topical minocycline foam. She noted that by delivering minocycline topically, “we get huge concentrations in the skin, but almost negligible amounts in the systemic circulation, which is important. We want to keep [the drug] in the skin; we don’t want it in our system.”
(The Food and Drug Administration approved minocycline foam 4% in October 2019 for treating inflammatory lesions associated with non-nodular moderate to severe acne).
Another potential treatment on the horizon is cortexolone 17a-propionate, a novel androgen receptor antagonist that inhibits production of lipids and inflammatory cytokines from sebocytes in vitro. “When used around the sebaceous gland, we find that the amount of sebum produced goes down,” she said, noting that phase 3 trials of the agent have been completed.
“We also find that abnormal keratinization subsequently goes down. Just putting this on the skin significantly reduced acne as monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe acne. We were able to get them to clear or almost clear. It worked on comedones, papules, and pustules. Hopefully, it will get FDA approval. This fills the one unmet need we haven’t had topically in terms of decreasing sebum production.”
Clinical trials of CBD are also under way for acne and atopic dermatitis. “It could work for acne because there are some studies showing that might work on sebaceous glands to decrease sebum production,” she said. “CBD has been shown to have positive effects on abnormal keratinization, and it has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Maybe we’ll have another mechanism of action for acne.”
Dr. Gold disclosed that she is on the speakers bureau for Almirall, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron. She is a consultant for Dermavant, Foamix, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and holds stock/stock options in AbbVie, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Foamix, Galderma, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sol-Gel.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – according to Linda Stein Gold, MD, who reviewed the data on these two therapies, as well as cannabidiol (CBD) and an androgen receptor antagonist, which are currently in clinical trials, at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
When considering antibiotic therapy for patients with moderate to severe acne, sarecycline, approved for that indication in October 2018, has improved anti-inflammatory properties and a narrower spectrum of activity, compared with other tetracycline-class antibiotics used for the condition, according to Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology research at Henry Ford Health System in Detroit. In two identically designed, 12-week randomized trials, SC 1401 and SC1402, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of an approximate 1.5–mg/kg per day dose of sarecycline in comparison with placebo in patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-45 years (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Sept 1;17[9]:987-96). “We started to see separation in the inflammatory lesions as early as week 3, and a nice separation versus placebo over the course of 12 weeks,” said Dr. Stein Gold, one of the study investigators. “In all, 22% of patients got clear or almost clear with monotherapy. That’s fairly good.”
She noted that there was consistency in the reductions of lesion count achieved in both studies. Improvements were seen through to 12 weeks, with statistically significant reduction seen as early as 3 weeks in both studies. Sarecycline was also statistically superior to placebo at every time point studied in both trials.
In order to be judged a successful outcome, the subject had to have a 12-week Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score with a 2-point or greater decrease (improvement) from baseline score on the IGA in each location, for patients who have a baseline IGA of 2 or greater, and to be clear (0) or almost clear (1). The same IGA scale was used for the chest and back assessments as was used for facial acne; the researchers observed statistically significant improvements in IGA score for both chest and back acne across both studies at week 12.
Sarecycline also had a favorable safety profile, with no treatment-emergent vertigo or tinnitus adverse events, she noted. Treatment-emergent vestibular and phototoxic adverse events both occurred in fewer than 1% of sarecycline patients. Among females, rates of yeast infections were low. When she recommends a course of this drug for her patients, “I never overpromise,” she said. “I tell my acne patients, ‘We measure your success in weeks and months, not days.’ I always tell them, ‘Take a selfie today and take a selfie every few weeks. When you come back in, we’ll review your progress and see how things went.’ ”
Researchers have also been studying topical minocycline as a treatment option. Minocycline is a large molecule that Dr. Stein Gold characterized as being “very challenging” to deliver topically. “It’s also challenging to keep it stable in a topical formulation.” However, results from two identical phase 3 trials found 4% topical minocycline foam significantly reduced both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions and improved IGA scores in patients with moderate to severe acne when treated daily for 12 weeks (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan;80[1]:168-77).
“This drug has an interesting vehicle,” said Dr. Stein Gold, who was one of the study investigators. “If you take the vehicle itself and you put it next to sebum, it causes sebum to melt at lower temperatures. Why does this matter? If you’re dissolving sebum, maybe you’re creating an easier pathway for the drug to get delivered into the skin and into the hair follicles. We don’t know all the details.” In the two trials, 15%-31% of patients achieved clearance or near clearance of all lesions. “How did it do in terms of decreasing papules and pustules? It did pretty well,” she said. “We want drugs to meet their match in everything that we do.” In terms of tolerability, skin-related adverse events were reported in fewer than 1% of subjects treated with 4% topical minocycline foam. She noted that by delivering minocycline topically, “we get huge concentrations in the skin, but almost negligible amounts in the systemic circulation, which is important. We want to keep [the drug] in the skin; we don’t want it in our system.”
(The Food and Drug Administration approved minocycline foam 4% in October 2019 for treating inflammatory lesions associated with non-nodular moderate to severe acne).
Another potential treatment on the horizon is cortexolone 17a-propionate, a novel androgen receptor antagonist that inhibits production of lipids and inflammatory cytokines from sebocytes in vitro. “When used around the sebaceous gland, we find that the amount of sebum produced goes down,” she said, noting that phase 3 trials of the agent have been completed.
“We also find that abnormal keratinization subsequently goes down. Just putting this on the skin significantly reduced acne as monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe acne. We were able to get them to clear or almost clear. It worked on comedones, papules, and pustules. Hopefully, it will get FDA approval. This fills the one unmet need we haven’t had topically in terms of decreasing sebum production.”
Clinical trials of CBD are also under way for acne and atopic dermatitis. “It could work for acne because there are some studies showing that might work on sebaceous glands to decrease sebum production,” she said. “CBD has been shown to have positive effects on abnormal keratinization, and it has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Maybe we’ll have another mechanism of action for acne.”
Dr. Gold disclosed that she is on the speakers bureau for Almirall, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sanofi/Regeneron. She is a consultant for Dermavant, Foamix, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, and holds stock/stock options in AbbVie, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Foamix, Galderma, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sol-Gel.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Expert reviews strategies for diagnosing, treating onychomycosis
LAS VEGAS – The way Neal Bhatia, MD, sees it, there is no such thing as a classical presentation of onychomycosis.
“This is where proving your diagnosis is half the battle, even though we are sometimes using empiric therapy in suspected cases,” he said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “Prove the diagnosis and get the extra tests necessary.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, director of clinical dermatology research at San Diego-based Therapeutics Clinical Research, . With onychomycosis, the ultimate treatment goal from the standpoint of clinicians is no more fungus, he noted, while the desired endpoint from the standpoint of some patients is normal-looking nails.
“Endpoint failures in a research trial are not the same as what we tell patients in the clinic,” Dr. Bhatia said. “If you have a patient using something topical for 52 weeks and they see two-thirds of their nail improve, you’re not going to say, ‘Stop; you’re a failure now.’ You tell them, ‘Keep going and we’ll keep watching.’ But in the research world, it’s very different when you look at all of the different endpoints that have to be met at the finish line. It’s very important to measure success based on what that patient’s experiencing.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, diagnosing onychomycosis by visual assessment has a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 47%, while KOH has a sensitivity between 67% and 93% and specificity between 38% and 78%. PCR, meanwhile, “is quick, but it’s expensive and it has a high false-positive rate. So, in those difficult patients who aren’t responding [to treatment], maybe we can’t just trust our eyes alone [to make a diagnosis].”
Tests such as a KOH stain have low sensitivity, with high costs of more sensitive tests such as the periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain. In a recent study, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of 600 patients with toenail clippings sent for PAS stain during January 2000–December 2013 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May; 72(5):AB116). They reviewed records to determine which PAS stains were performed to confirm probable clinical diagnosis of onychomycosis.
The researchers found that 30% of toenail clippings were sent for confirmatory PAS staining by dermatologists, compared with 37% by podiatrists and 34% by other clinicians. Of these tests, 75% ordered by dermatologists were positive for fungus, compared with 81% ordered by podiatrists, and 66% ordered by other physicians. “The positive predictive value of clinical suspicion for true onychomycosis was high, and the findings question whether or not a confirmatory test is really necessary,” Dr. Bhatia said.
Preventative strategies to control recurrence of onychomycosis include using maintenance regimens of the recommended antifungal agent, discarding old shoes, alternating wearing different pairs of shoes, periodically disinfecting shoes, washing feet regularly, and alerting the physician to the first sign of infection.
In an effort to investigate strategies to minimize recurrence of onychomycosis, Dr. Bhatia and colleagues evaluated 73 patients over the course of 7 years who were taking either terbinafine or itraconazole (J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15[3]:279-82). Thirty-six months later, the overall mean recurrence rate among patients was 14%. Prognostic factors influencing recurrence included patient’s family history; lifestyle; underlying physiology (presence of a very thick nail, extensive involvement of the entire nail unit, lateral nail disease and yellow spikes); physical trauma, especially in the elderly; concomitant disease, such as peripheral artery disease and/or diabetes; immunocompromised or immunosuppressed patients, and the presence of tinea pedis.
Based on their analysis, they recommended the following strategies to prevent or limit recurrence: prophylactic use of a topical antifungal twice-weekly for 2-3 years; periodic application of a topical antifungal to plantar surface and/or interdigital spaces; treatment of any coexisting tinea pedis; treating immediate family members; footwear and sock decontamination with antifungal powder; ultraviolet light or ozone; avoidance of activities known to risk spread of disease, such as communal swimming pools.
Dr. Bhatia concluded his presentation by noting that the ideal treatment for onychomycosis would not pose a systemic risk to the liver, heart, or other organs; would not require monitoring of labs; would not require debridement; and would not interact with other drugs. It would also penetrate the nail plate – especially the diseased nail – and would be quick drying.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed having affiliations with Actavis, Allergan, Anacor, Aqua, Bayer, Biofrontera, BiopharmX, Cipher, Dermira, Dusa, Exeltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novan, Novartis, PharmaDerm, Promius, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Valeant.
LAS VEGAS – The way Neal Bhatia, MD, sees it, there is no such thing as a classical presentation of onychomycosis.
“This is where proving your diagnosis is half the battle, even though we are sometimes using empiric therapy in suspected cases,” he said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “Prove the diagnosis and get the extra tests necessary.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, director of clinical dermatology research at San Diego-based Therapeutics Clinical Research, . With onychomycosis, the ultimate treatment goal from the standpoint of clinicians is no more fungus, he noted, while the desired endpoint from the standpoint of some patients is normal-looking nails.
“Endpoint failures in a research trial are not the same as what we tell patients in the clinic,” Dr. Bhatia said. “If you have a patient using something topical for 52 weeks and they see two-thirds of their nail improve, you’re not going to say, ‘Stop; you’re a failure now.’ You tell them, ‘Keep going and we’ll keep watching.’ But in the research world, it’s very different when you look at all of the different endpoints that have to be met at the finish line. It’s very important to measure success based on what that patient’s experiencing.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, diagnosing onychomycosis by visual assessment has a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 47%, while KOH has a sensitivity between 67% and 93% and specificity between 38% and 78%. PCR, meanwhile, “is quick, but it’s expensive and it has a high false-positive rate. So, in those difficult patients who aren’t responding [to treatment], maybe we can’t just trust our eyes alone [to make a diagnosis].”
Tests such as a KOH stain have low sensitivity, with high costs of more sensitive tests such as the periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain. In a recent study, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of 600 patients with toenail clippings sent for PAS stain during January 2000–December 2013 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May; 72(5):AB116). They reviewed records to determine which PAS stains were performed to confirm probable clinical diagnosis of onychomycosis.
The researchers found that 30% of toenail clippings were sent for confirmatory PAS staining by dermatologists, compared with 37% by podiatrists and 34% by other clinicians. Of these tests, 75% ordered by dermatologists were positive for fungus, compared with 81% ordered by podiatrists, and 66% ordered by other physicians. “The positive predictive value of clinical suspicion for true onychomycosis was high, and the findings question whether or not a confirmatory test is really necessary,” Dr. Bhatia said.
Preventative strategies to control recurrence of onychomycosis include using maintenance regimens of the recommended antifungal agent, discarding old shoes, alternating wearing different pairs of shoes, periodically disinfecting shoes, washing feet regularly, and alerting the physician to the first sign of infection.
In an effort to investigate strategies to minimize recurrence of onychomycosis, Dr. Bhatia and colleagues evaluated 73 patients over the course of 7 years who were taking either terbinafine or itraconazole (J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15[3]:279-82). Thirty-six months later, the overall mean recurrence rate among patients was 14%. Prognostic factors influencing recurrence included patient’s family history; lifestyle; underlying physiology (presence of a very thick nail, extensive involvement of the entire nail unit, lateral nail disease and yellow spikes); physical trauma, especially in the elderly; concomitant disease, such as peripheral artery disease and/or diabetes; immunocompromised or immunosuppressed patients, and the presence of tinea pedis.
Based on their analysis, they recommended the following strategies to prevent or limit recurrence: prophylactic use of a topical antifungal twice-weekly for 2-3 years; periodic application of a topical antifungal to plantar surface and/or interdigital spaces; treatment of any coexisting tinea pedis; treating immediate family members; footwear and sock decontamination with antifungal powder; ultraviolet light or ozone; avoidance of activities known to risk spread of disease, such as communal swimming pools.
Dr. Bhatia concluded his presentation by noting that the ideal treatment for onychomycosis would not pose a systemic risk to the liver, heart, or other organs; would not require monitoring of labs; would not require debridement; and would not interact with other drugs. It would also penetrate the nail plate – especially the diseased nail – and would be quick drying.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed having affiliations with Actavis, Allergan, Anacor, Aqua, Bayer, Biofrontera, BiopharmX, Cipher, Dermira, Dusa, Exeltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novan, Novartis, PharmaDerm, Promius, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Valeant.
LAS VEGAS – The way Neal Bhatia, MD, sees it, there is no such thing as a classical presentation of onychomycosis.
“This is where proving your diagnosis is half the battle, even though we are sometimes using empiric therapy in suspected cases,” he said at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “Prove the diagnosis and get the extra tests necessary.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, director of clinical dermatology research at San Diego-based Therapeutics Clinical Research, . With onychomycosis, the ultimate treatment goal from the standpoint of clinicians is no more fungus, he noted, while the desired endpoint from the standpoint of some patients is normal-looking nails.
“Endpoint failures in a research trial are not the same as what we tell patients in the clinic,” Dr. Bhatia said. “If you have a patient using something topical for 52 weeks and they see two-thirds of their nail improve, you’re not going to say, ‘Stop; you’re a failure now.’ You tell them, ‘Keep going and we’ll keep watching.’ But in the research world, it’s very different when you look at all of the different endpoints that have to be met at the finish line. It’s very important to measure success based on what that patient’s experiencing.”
According to Dr. Bhatia, diagnosing onychomycosis by visual assessment has a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 47%, while KOH has a sensitivity between 67% and 93% and specificity between 38% and 78%. PCR, meanwhile, “is quick, but it’s expensive and it has a high false-positive rate. So, in those difficult patients who aren’t responding [to treatment], maybe we can’t just trust our eyes alone [to make a diagnosis].”
Tests such as a KOH stain have low sensitivity, with high costs of more sensitive tests such as the periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain. In a recent study, researchers conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of 600 patients with toenail clippings sent for PAS stain during January 2000–December 2013 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May; 72(5):AB116). They reviewed records to determine which PAS stains were performed to confirm probable clinical diagnosis of onychomycosis.
The researchers found that 30% of toenail clippings were sent for confirmatory PAS staining by dermatologists, compared with 37% by podiatrists and 34% by other clinicians. Of these tests, 75% ordered by dermatologists were positive for fungus, compared with 81% ordered by podiatrists, and 66% ordered by other physicians. “The positive predictive value of clinical suspicion for true onychomycosis was high, and the findings question whether or not a confirmatory test is really necessary,” Dr. Bhatia said.
Preventative strategies to control recurrence of onychomycosis include using maintenance regimens of the recommended antifungal agent, discarding old shoes, alternating wearing different pairs of shoes, periodically disinfecting shoes, washing feet regularly, and alerting the physician to the first sign of infection.
In an effort to investigate strategies to minimize recurrence of onychomycosis, Dr. Bhatia and colleagues evaluated 73 patients over the course of 7 years who were taking either terbinafine or itraconazole (J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15[3]:279-82). Thirty-six months later, the overall mean recurrence rate among patients was 14%. Prognostic factors influencing recurrence included patient’s family history; lifestyle; underlying physiology (presence of a very thick nail, extensive involvement of the entire nail unit, lateral nail disease and yellow spikes); physical trauma, especially in the elderly; concomitant disease, such as peripheral artery disease and/or diabetes; immunocompromised or immunosuppressed patients, and the presence of tinea pedis.
Based on their analysis, they recommended the following strategies to prevent or limit recurrence: prophylactic use of a topical antifungal twice-weekly for 2-3 years; periodic application of a topical antifungal to plantar surface and/or interdigital spaces; treatment of any coexisting tinea pedis; treating immediate family members; footwear and sock decontamination with antifungal powder; ultraviolet light or ozone; avoidance of activities known to risk spread of disease, such as communal swimming pools.
Dr. Bhatia concluded his presentation by noting that the ideal treatment for onychomycosis would not pose a systemic risk to the liver, heart, or other organs; would not require monitoring of labs; would not require debridement; and would not interact with other drugs. It would also penetrate the nail plate – especially the diseased nail – and would be quick drying.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed having affiliations with Actavis, Allergan, Anacor, Aqua, Bayer, Biofrontera, BiopharmX, Cipher, Dermira, Dusa, Exeltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novan, Novartis, PharmaDerm, Promius, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and Valeant.
AT THE SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
In Oregon, ‘war on melanoma’ takes flight
LAS VEGAS – with the goal of dramatically reducing melanoma deaths in the state of 4.2 million people.
Research shows that “early detection works in melanoma. And awareness seems to be important for the public in detecting melanoma early,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Leachman, who is also the John D. Gray chair in melanoma research at OHSU, directs the “War on Melanoma” project, which was inspired by a project in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein that aimed to screen all residents aged over 21 years for melanoma. The project featured an education campaign and population-wide skin cancer screening, and mandated that certain patients – those at high risk and those who needed biopsies – would be referred to dermatologists (Br J Cancer. 2012 Feb 28;106[5]:970-4).
According to Dr. Leachman, the German project was initially a success, and was linked to a 50% decrease in melanoma mortality.
“In Oregon, we thought ‘that sounds very good, so we’re going to try that.’ ” But when it went national, the German project failed, she said, providing lessons for dermatologists in Oregon. “We’re going to try to improve upon the first [German] experiment by making ours controlled with a defined baseline. If it works, the plan is to extend it to select states nationwide.”
The War on Melanoma project was launched earlier this year. According to the university, the program is featuring or will feature the following elements:
- A media campaign called “Start Seeing Melanoma” that’s devoted to educating the public about the early detection of melanoma.
- The release of an iPhone app called MoleMapper that allows users to monitor moles over time.
- Education of medical professionals and partnerships with state-licensed skin care professionals such as massage therapists, cosmetologists, and tattoo artists.
In an interview at the meeting, Dr. Leachman said the project is expected to cost $1 million to $1.5 million over the first 18 months. At that time, she said, researchers will survey residents of Oregon and two control states – Washington and Utah– to see if their knowledge of melanoma has improved, compared with baseline survey results.
In 5 years, researchers plan to begin analyzing melanoma mortality in Oregon and the other states. “We hope to see a decline,” and to link it to increased awareness of melanoma, she said.
Dr. Leachman reported no relevant disclosures. She spoke during a forum on cutaneous malignancies at the meeting.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – with the goal of dramatically reducing melanoma deaths in the state of 4.2 million people.
Research shows that “early detection works in melanoma. And awareness seems to be important for the public in detecting melanoma early,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Leachman, who is also the John D. Gray chair in melanoma research at OHSU, directs the “War on Melanoma” project, which was inspired by a project in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein that aimed to screen all residents aged over 21 years for melanoma. The project featured an education campaign and population-wide skin cancer screening, and mandated that certain patients – those at high risk and those who needed biopsies – would be referred to dermatologists (Br J Cancer. 2012 Feb 28;106[5]:970-4).
According to Dr. Leachman, the German project was initially a success, and was linked to a 50% decrease in melanoma mortality.
“In Oregon, we thought ‘that sounds very good, so we’re going to try that.’ ” But when it went national, the German project failed, she said, providing lessons for dermatologists in Oregon. “We’re going to try to improve upon the first [German] experiment by making ours controlled with a defined baseline. If it works, the plan is to extend it to select states nationwide.”
The War on Melanoma project was launched earlier this year. According to the university, the program is featuring or will feature the following elements:
- A media campaign called “Start Seeing Melanoma” that’s devoted to educating the public about the early detection of melanoma.
- The release of an iPhone app called MoleMapper that allows users to monitor moles over time.
- Education of medical professionals and partnerships with state-licensed skin care professionals such as massage therapists, cosmetologists, and tattoo artists.
In an interview at the meeting, Dr. Leachman said the project is expected to cost $1 million to $1.5 million over the first 18 months. At that time, she said, researchers will survey residents of Oregon and two control states – Washington and Utah– to see if their knowledge of melanoma has improved, compared with baseline survey results.
In 5 years, researchers plan to begin analyzing melanoma mortality in Oregon and the other states. “We hope to see a decline,” and to link it to increased awareness of melanoma, she said.
Dr. Leachman reported no relevant disclosures. She spoke during a forum on cutaneous malignancies at the meeting.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – with the goal of dramatically reducing melanoma deaths in the state of 4.2 million people.
Research shows that “early detection works in melanoma. And awareness seems to be important for the public in detecting melanoma early,” said Sancy Leachman, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Dr. Leachman, who is also the John D. Gray chair in melanoma research at OHSU, directs the “War on Melanoma” project, which was inspired by a project in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein that aimed to screen all residents aged over 21 years for melanoma. The project featured an education campaign and population-wide skin cancer screening, and mandated that certain patients – those at high risk and those who needed biopsies – would be referred to dermatologists (Br J Cancer. 2012 Feb 28;106[5]:970-4).
According to Dr. Leachman, the German project was initially a success, and was linked to a 50% decrease in melanoma mortality.
“In Oregon, we thought ‘that sounds very good, so we’re going to try that.’ ” But when it went national, the German project failed, she said, providing lessons for dermatologists in Oregon. “We’re going to try to improve upon the first [German] experiment by making ours controlled with a defined baseline. If it works, the plan is to extend it to select states nationwide.”
The War on Melanoma project was launched earlier this year. According to the university, the program is featuring or will feature the following elements:
- A media campaign called “Start Seeing Melanoma” that’s devoted to educating the public about the early detection of melanoma.
- The release of an iPhone app called MoleMapper that allows users to monitor moles over time.
- Education of medical professionals and partnerships with state-licensed skin care professionals such as massage therapists, cosmetologists, and tattoo artists.
In an interview at the meeting, Dr. Leachman said the project is expected to cost $1 million to $1.5 million over the first 18 months. At that time, she said, researchers will survey residents of Oregon and two control states – Washington and Utah– to see if their knowledge of melanoma has improved, compared with baseline survey results.
In 5 years, researchers plan to begin analyzing melanoma mortality in Oregon and the other states. “We hope to see a decline,” and to link it to increased awareness of melanoma, she said.
Dr. Leachman reported no relevant disclosures. She spoke during a forum on cutaneous malignancies at the meeting.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR