User login
Thyroid hormone analogues can reverse NASH
Background: Fat toxicity results in inflammation of the liver and eventual hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Thyroid hormones can greatly reduce this hepatic steatosis by restoring metabolic pathways in damaged liver, prevent fibrosis progression, and have broad atherogenic lipid-lowering actions by activating hepatic thyroid beta-receptors.
However, hyperthyroidism also leads to osteoporosis, tachyarrhythmias, muscle wasting, and psychiatric side effects, mediated by the alpha-thyroid receptor. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) is a novel, highly selective thyroid beta-agonist, with a minimal side-effect profile, which avoids the alpha–side effects.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Setting: 25 centers in the United States.
Synopsis: Of 125 adults with NASH fibrosis 1-3 and greater than 10% hepatic fat, 84 received resmetirom and 41 received placebo. Resmetirom resulted in a nearly 30% decrease over placebo in hepatic fat, compared with baseline, significant improvement in lipid profile, improvement in liver enzymes, fibrosis markers, and histologic resolution of NASH in some patients.
While the study showed resolution of inflammation, the 36-week study was likely not long enough to show improvement of fibrosis. The relatively small sample size also limited results. Placebo patients who lost significant weight also showed improvement and were discarded from analysis, suggesting that weight loss itself is also an excellent alternative to reverse NASH. Resmetirom use in NASH is now moving into a large phase 3 trial.
Bottom line: Resmetirom results in major liver and cardiovascular benefits in patients with NASH.
Citation: Harrison SA et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2019 Nov 11;394(10213):2012-24.
Dr. Raghavan is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Fat toxicity results in inflammation of the liver and eventual hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Thyroid hormones can greatly reduce this hepatic steatosis by restoring metabolic pathways in damaged liver, prevent fibrosis progression, and have broad atherogenic lipid-lowering actions by activating hepatic thyroid beta-receptors.
However, hyperthyroidism also leads to osteoporosis, tachyarrhythmias, muscle wasting, and psychiatric side effects, mediated by the alpha-thyroid receptor. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) is a novel, highly selective thyroid beta-agonist, with a minimal side-effect profile, which avoids the alpha–side effects.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Setting: 25 centers in the United States.
Synopsis: Of 125 adults with NASH fibrosis 1-3 and greater than 10% hepatic fat, 84 received resmetirom and 41 received placebo. Resmetirom resulted in a nearly 30% decrease over placebo in hepatic fat, compared with baseline, significant improvement in lipid profile, improvement in liver enzymes, fibrosis markers, and histologic resolution of NASH in some patients.
While the study showed resolution of inflammation, the 36-week study was likely not long enough to show improvement of fibrosis. The relatively small sample size also limited results. Placebo patients who lost significant weight also showed improvement and were discarded from analysis, suggesting that weight loss itself is also an excellent alternative to reverse NASH. Resmetirom use in NASH is now moving into a large phase 3 trial.
Bottom line: Resmetirom results in major liver and cardiovascular benefits in patients with NASH.
Citation: Harrison SA et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2019 Nov 11;394(10213):2012-24.
Dr. Raghavan is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Fat toxicity results in inflammation of the liver and eventual hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Thyroid hormones can greatly reduce this hepatic steatosis by restoring metabolic pathways in damaged liver, prevent fibrosis progression, and have broad atherogenic lipid-lowering actions by activating hepatic thyroid beta-receptors.
However, hyperthyroidism also leads to osteoporosis, tachyarrhythmias, muscle wasting, and psychiatric side effects, mediated by the alpha-thyroid receptor. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) is a novel, highly selective thyroid beta-agonist, with a minimal side-effect profile, which avoids the alpha–side effects.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Setting: 25 centers in the United States.
Synopsis: Of 125 adults with NASH fibrosis 1-3 and greater than 10% hepatic fat, 84 received resmetirom and 41 received placebo. Resmetirom resulted in a nearly 30% decrease over placebo in hepatic fat, compared with baseline, significant improvement in lipid profile, improvement in liver enzymes, fibrosis markers, and histologic resolution of NASH in some patients.
While the study showed resolution of inflammation, the 36-week study was likely not long enough to show improvement of fibrosis. The relatively small sample size also limited results. Placebo patients who lost significant weight also showed improvement and were discarded from analysis, suggesting that weight loss itself is also an excellent alternative to reverse NASH. Resmetirom use in NASH is now moving into a large phase 3 trial.
Bottom line: Resmetirom results in major liver and cardiovascular benefits in patients with NASH.
Citation: Harrison SA et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2019 Nov 11;394(10213):2012-24.
Dr. Raghavan is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Assessing the efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with HFrEF
Background: Guideline-directed medical therapy (use of beta-blockers, ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid antagonists) provides clear benefits on mortality and morbidity in patients with HFrEF. Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) belongs to a class of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors that inhibits reabsorption of sodium and glucose in the kidney and treats type 2 diabetes. This new class of drugs is emerging as an effective tool in the management of HFrEF based on the recent publication of the primary results of the DAPA-HF trial (Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Worsening Heart Failure or Cardiovascular Death in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure). It demonstrated substantial benefits in terms of heart failure symptoms, hospitalizations, and mortality when added to triple therapy for patients with chronic HFrEF regardless of the presence of diabetes.
Study design: Randomized, controlled double-blind trials.
Setting: 410 participating institutions in 20 countries.
Synopsis: Men and women aged 18 years and older with HFrEF who had New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II or higher, and optimally treated with pharmacologic and device therapy for HF were randomized to receive dapagliflozin or placebo. A total of 4,744 patients, aged 22-94 years were enrolled in the study.
- Dapagliflozin showed a clinically significant benefit on health status (symptoms, physical function, and quality of life). Improved health-related quality of life (as measured by the well-validated Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score) with dapagliflozin in comparison with placebo was sustained for more than 8 months.
- Dapagliflozin reduced the risk of death and worsening heart failure and improved symptoms across the broad spectrum of ages studied in DAPA-HF. There was no significant imbalance in tolerability or safety events between dapagliflozin and placebo, even in elderly individuals.
Bottom line: Follow-up DAPA-HF studies further support the role of SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in improving mortality, reducing hospitalization, and improving the quality of life in patients with HFrEF and is considered a safe option across all age groups.
Citations: Kosiborod MN et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on symptoms, function, and quality of life in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: Results from the DAPA-HF trial. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141(2):90-9. Martinez FA et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction according to age. Insights from DAPA-HF. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141:100-11.
Dr. Garg is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Guideline-directed medical therapy (use of beta-blockers, ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid antagonists) provides clear benefits on mortality and morbidity in patients with HFrEF. Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) belongs to a class of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors that inhibits reabsorption of sodium and glucose in the kidney and treats type 2 diabetes. This new class of drugs is emerging as an effective tool in the management of HFrEF based on the recent publication of the primary results of the DAPA-HF trial (Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Worsening Heart Failure or Cardiovascular Death in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure). It demonstrated substantial benefits in terms of heart failure symptoms, hospitalizations, and mortality when added to triple therapy for patients with chronic HFrEF regardless of the presence of diabetes.
Study design: Randomized, controlled double-blind trials.
Setting: 410 participating institutions in 20 countries.
Synopsis: Men and women aged 18 years and older with HFrEF who had New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II or higher, and optimally treated with pharmacologic and device therapy for HF were randomized to receive dapagliflozin or placebo. A total of 4,744 patients, aged 22-94 years were enrolled in the study.
- Dapagliflozin showed a clinically significant benefit on health status (symptoms, physical function, and quality of life). Improved health-related quality of life (as measured by the well-validated Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score) with dapagliflozin in comparison with placebo was sustained for more than 8 months.
- Dapagliflozin reduced the risk of death and worsening heart failure and improved symptoms across the broad spectrum of ages studied in DAPA-HF. There was no significant imbalance in tolerability or safety events between dapagliflozin and placebo, even in elderly individuals.
Bottom line: Follow-up DAPA-HF studies further support the role of SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in improving mortality, reducing hospitalization, and improving the quality of life in patients with HFrEF and is considered a safe option across all age groups.
Citations: Kosiborod MN et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on symptoms, function, and quality of life in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: Results from the DAPA-HF trial. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141(2):90-9. Martinez FA et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction according to age. Insights from DAPA-HF. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141:100-11.
Dr. Garg is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Guideline-directed medical therapy (use of beta-blockers, ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid antagonists) provides clear benefits on mortality and morbidity in patients with HFrEF. Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) belongs to a class of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors that inhibits reabsorption of sodium and glucose in the kidney and treats type 2 diabetes. This new class of drugs is emerging as an effective tool in the management of HFrEF based on the recent publication of the primary results of the DAPA-HF trial (Study to Evaluate the Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Incidence of Worsening Heart Failure or Cardiovascular Death in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure). It demonstrated substantial benefits in terms of heart failure symptoms, hospitalizations, and mortality when added to triple therapy for patients with chronic HFrEF regardless of the presence of diabetes.
Study design: Randomized, controlled double-blind trials.
Setting: 410 participating institutions in 20 countries.
Synopsis: Men and women aged 18 years and older with HFrEF who had New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II or higher, and optimally treated with pharmacologic and device therapy for HF were randomized to receive dapagliflozin or placebo. A total of 4,744 patients, aged 22-94 years were enrolled in the study.
- Dapagliflozin showed a clinically significant benefit on health status (symptoms, physical function, and quality of life). Improved health-related quality of life (as measured by the well-validated Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire score) with dapagliflozin in comparison with placebo was sustained for more than 8 months.
- Dapagliflozin reduced the risk of death and worsening heart failure and improved symptoms across the broad spectrum of ages studied in DAPA-HF. There was no significant imbalance in tolerability or safety events between dapagliflozin and placebo, even in elderly individuals.
Bottom line: Follow-up DAPA-HF studies further support the role of SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in improving mortality, reducing hospitalization, and improving the quality of life in patients with HFrEF and is considered a safe option across all age groups.
Citations: Kosiborod MN et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on symptoms, function, and quality of life in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: Results from the DAPA-HF trial. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141(2):90-9. Martinez FA et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction according to age. Insights from DAPA-HF. Circulation. 2020 Jan 14;141:100-11.
Dr. Garg is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Cushing’s death rate ‘unacceptable,’ triple that of general population
Excess mortality among people with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome (CS) has declined in the past 20 years yet remains three times higher than in the general population, new research finds.
Among more than 90,000 individuals with endogenous CS, the overall proportion of mortality – defined as the ratio of the number of deaths from CS divided by the total number of CS patients – was 0.05, and the standardized mortality rate was an “unacceptable” three times that of the general population, Padiporn Limumpornpetch, MD, reported on March 20 at ENDO 2021: The Endocrine Society Annual Meeting.
Excess deaths were higher among those with adrenal CS, compared with those with Cushing’s disease. The most common causes of death among those with CS were cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular accident, infection, and malignancy, noted Dr. Limumpornpetch, of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand, who is also a PhD student at the University of Leeds, United Kingdom.
“While mortality has improved since 2000, it is still significantly compromised compared to the background population ... The causes of death highlight the need for aggressive management of cardiovascular risk, prevention of thromboembolism, infection control, and a normalized cortisol level,” she said.
Asked to comment, Maria Fleseriu, MD, told this news organization that the new data show “we are making improvements in the care of patients with CS and thus outcomes, but we are not there yet ... This meta-analysis highlights the whole spectrum of acute and life-threatening complications in CS and their high prevalence, even before disease diagnosis and after successful surgery.”
She noted that although she wasn’t surprised by the overall results, “the improvement over time was indeed lower than I expected. However, interestingly here, the risk of mortality in adrenal Cushing’s was unexpectedly high despite patients with adrenal cancer being excluded.”
Dr. Fleseriu, who is director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, advised, “Management of hyperglycemia and diabetes, hypertension, hypokalemia, hyperlipidemia, and other cardiovascular risk factors is generally undertaken in accordance with standard of clinical care.”
“But we should focus more on optimizing more aggressively this care in addition to the specific Cushing’s treatment,” she stressed.
In addition, she noted, “Medical therapy for CS may be needed even prior to surgery in severe and/or prolonged hypercortisolism to decrease complications ... We definitely need a multidisciplinary approach to address complications and etiologic treatment as well as the reduced long-term quality of life in patients with CS.”
Largest study in scale and scope of Cushing’s syndrome mortality
Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome occurs when the body overproduces cortisol. The most common cause of the latter is a tumor of the pituitary gland (Cushing’s disease), but another cause is a usually benign tumor of the adrenal glands (adrenal Cushing’s syndrome). Surgery is the mainstay of initial treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. If an operation to remove the tumor fails to cause remission, medications are available.
Prior to this new meta-analysis, there had been limited data on mortality among patients with endogenous CS. Research has mostly been limited to single-cohort studies. A previous systematic review/meta-analysis comprised only seven articles with 780 patients. All the studies were conducted prior to 2012, and most were limited to Cushing’s disease.
“In 2021, we lacked a detailed understanding of patient outcomes and mortality because of the rarity of Cushing’s syndrome,” Dr. Limumpornpetch noted.
The current meta-analysis included 91 articles that reported mortality among patients with endogenous CS. There was a total of 19,181 patients from 92 study cohorts, including 49 studies on CD (n = 14,971), 24 studies on adrenal CS (n = 2304), and 19 studies that included both (n = 1906).
Among 21 studies that reported standardized mortality rate (SMR) data, including 13 CD studies (n = 2160) and seven on adrenal CS (n = 1531), the overall increase in mortality compared to the background population was a significant 3.00 (range, 1.15-7.84).
This SMR was higher among patients with adrenal Cushing’s syndrome (3.3) versus Cushing’s disease (2.8) (P = .003) and among patients who had active disease (5.7) versus those whose disease was in remission (2.3) (P < .001).
The SMR was also worse among patients with Cushing’s disease with larger tumors (macroadenomas), at 7.4, than among patients with very small tumors (microadenomas), at 1.9 (P = .004).
The proportion of death was 0.05 for CS overall, with 0.04 for CD and 0.02 for adrenal adenomas.
Compared to studies published prior to the year 2000, more recent studies seem to reflect advances in treatment and care. The overall proportion of death for all CS cohorts dropped from 0.10 to 0.03 (P < .001); for all CD cohorts, it dropped from 0.14 to 0.03; and for adrenal CS cohorts, it dropped from 0.09 to 0.03 (P = .04).
Causes of death were cardiovascular diseases (29.5% of cases), cerebrovascular accident (11.5%), infection (10.5%), and malignancy (10.1%). Less common causes of death were gastrointestinal bleeding and acute pancreatitis (3.7%), active CS (3.5%), adrenal insufficiency (2.5%), suicide (2.5%), and surgery (1.6%).
Overall, in the CS groups, the proportion of deaths within 30 days of surgery dropped from 0.04 prior to 2000 to 0.01 since (P = .07). For CD, the proportion dropped from 0.02 to 0.01 (P = .25).
Preventing perioperative mortality: Consider thromboprophylaxis
Dr. Fleseriu told this news organization that she believes hypercoagulability is “the least recognized complication with a big role in mortality.” Because most of the perioperative mortality is due to venous thromboembolism and infections, “thromboprophylaxis should be considered for CS patients with severe hypercortisolism and/or postoperatively, based on individual risk factors of thromboembolism and bleeding.”
Recently, Dr. Fleseriu’s group showed in a single retrospective study that the risk for arterial and venous thromboembolic events among patients with CS was approximately 20%. Many patients experienced more than one event. Risk was higher 30 to 60 days postoperatively.
The odds ratio of venous thromoboembolism among patients with CS was 18 times higher than in the normal population.
“Due to the additional thrombotic risk of surgery or any invasive procedure, anticoagulation prophylaxis should be at least considered in all patients with Cushing’s syndrome and balanced with individual bleeding risk,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A recent Pituitary Society workshop discussed the management of complications of CS at length; proceedings will be published soon, she noted.
Dr. Limumpornpetch commented, “We look forward to the day when our interdisciplinary approach to managing these challenging patients can deliver outcomes similar to the background population.”
Dr. Limumpornpetch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fleseriu has been a scientific consultant to Recordati, Sparrow, and Strongbridge and has received grants (inst) from Novartis and Strongbridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Excess mortality among people with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome (CS) has declined in the past 20 years yet remains three times higher than in the general population, new research finds.
Among more than 90,000 individuals with endogenous CS, the overall proportion of mortality – defined as the ratio of the number of deaths from CS divided by the total number of CS patients – was 0.05, and the standardized mortality rate was an “unacceptable” three times that of the general population, Padiporn Limumpornpetch, MD, reported on March 20 at ENDO 2021: The Endocrine Society Annual Meeting.
Excess deaths were higher among those with adrenal CS, compared with those with Cushing’s disease. The most common causes of death among those with CS were cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular accident, infection, and malignancy, noted Dr. Limumpornpetch, of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand, who is also a PhD student at the University of Leeds, United Kingdom.
“While mortality has improved since 2000, it is still significantly compromised compared to the background population ... The causes of death highlight the need for aggressive management of cardiovascular risk, prevention of thromboembolism, infection control, and a normalized cortisol level,” she said.
Asked to comment, Maria Fleseriu, MD, told this news organization that the new data show “we are making improvements in the care of patients with CS and thus outcomes, but we are not there yet ... This meta-analysis highlights the whole spectrum of acute and life-threatening complications in CS and their high prevalence, even before disease diagnosis and after successful surgery.”
She noted that although she wasn’t surprised by the overall results, “the improvement over time was indeed lower than I expected. However, interestingly here, the risk of mortality in adrenal Cushing’s was unexpectedly high despite patients with adrenal cancer being excluded.”
Dr. Fleseriu, who is director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, advised, “Management of hyperglycemia and diabetes, hypertension, hypokalemia, hyperlipidemia, and other cardiovascular risk factors is generally undertaken in accordance with standard of clinical care.”
“But we should focus more on optimizing more aggressively this care in addition to the specific Cushing’s treatment,” she stressed.
In addition, she noted, “Medical therapy for CS may be needed even prior to surgery in severe and/or prolonged hypercortisolism to decrease complications ... We definitely need a multidisciplinary approach to address complications and etiologic treatment as well as the reduced long-term quality of life in patients with CS.”
Largest study in scale and scope of Cushing’s syndrome mortality
Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome occurs when the body overproduces cortisol. The most common cause of the latter is a tumor of the pituitary gland (Cushing’s disease), but another cause is a usually benign tumor of the adrenal glands (adrenal Cushing’s syndrome). Surgery is the mainstay of initial treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. If an operation to remove the tumor fails to cause remission, medications are available.
Prior to this new meta-analysis, there had been limited data on mortality among patients with endogenous CS. Research has mostly been limited to single-cohort studies. A previous systematic review/meta-analysis comprised only seven articles with 780 patients. All the studies were conducted prior to 2012, and most were limited to Cushing’s disease.
“In 2021, we lacked a detailed understanding of patient outcomes and mortality because of the rarity of Cushing’s syndrome,” Dr. Limumpornpetch noted.
The current meta-analysis included 91 articles that reported mortality among patients with endogenous CS. There was a total of 19,181 patients from 92 study cohorts, including 49 studies on CD (n = 14,971), 24 studies on adrenal CS (n = 2304), and 19 studies that included both (n = 1906).
Among 21 studies that reported standardized mortality rate (SMR) data, including 13 CD studies (n = 2160) and seven on adrenal CS (n = 1531), the overall increase in mortality compared to the background population was a significant 3.00 (range, 1.15-7.84).
This SMR was higher among patients with adrenal Cushing’s syndrome (3.3) versus Cushing’s disease (2.8) (P = .003) and among patients who had active disease (5.7) versus those whose disease was in remission (2.3) (P < .001).
The SMR was also worse among patients with Cushing’s disease with larger tumors (macroadenomas), at 7.4, than among patients with very small tumors (microadenomas), at 1.9 (P = .004).
The proportion of death was 0.05 for CS overall, with 0.04 for CD and 0.02 for adrenal adenomas.
Compared to studies published prior to the year 2000, more recent studies seem to reflect advances in treatment and care. The overall proportion of death for all CS cohorts dropped from 0.10 to 0.03 (P < .001); for all CD cohorts, it dropped from 0.14 to 0.03; and for adrenal CS cohorts, it dropped from 0.09 to 0.03 (P = .04).
Causes of death were cardiovascular diseases (29.5% of cases), cerebrovascular accident (11.5%), infection (10.5%), and malignancy (10.1%). Less common causes of death were gastrointestinal bleeding and acute pancreatitis (3.7%), active CS (3.5%), adrenal insufficiency (2.5%), suicide (2.5%), and surgery (1.6%).
Overall, in the CS groups, the proportion of deaths within 30 days of surgery dropped from 0.04 prior to 2000 to 0.01 since (P = .07). For CD, the proportion dropped from 0.02 to 0.01 (P = .25).
Preventing perioperative mortality: Consider thromboprophylaxis
Dr. Fleseriu told this news organization that she believes hypercoagulability is “the least recognized complication with a big role in mortality.” Because most of the perioperative mortality is due to venous thromboembolism and infections, “thromboprophylaxis should be considered for CS patients with severe hypercortisolism and/or postoperatively, based on individual risk factors of thromboembolism and bleeding.”
Recently, Dr. Fleseriu’s group showed in a single retrospective study that the risk for arterial and venous thromboembolic events among patients with CS was approximately 20%. Many patients experienced more than one event. Risk was higher 30 to 60 days postoperatively.
The odds ratio of venous thromoboembolism among patients with CS was 18 times higher than in the normal population.
“Due to the additional thrombotic risk of surgery or any invasive procedure, anticoagulation prophylaxis should be at least considered in all patients with Cushing’s syndrome and balanced with individual bleeding risk,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A recent Pituitary Society workshop discussed the management of complications of CS at length; proceedings will be published soon, she noted.
Dr. Limumpornpetch commented, “We look forward to the day when our interdisciplinary approach to managing these challenging patients can deliver outcomes similar to the background population.”
Dr. Limumpornpetch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fleseriu has been a scientific consultant to Recordati, Sparrow, and Strongbridge and has received grants (inst) from Novartis and Strongbridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Excess mortality among people with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome (CS) has declined in the past 20 years yet remains three times higher than in the general population, new research finds.
Among more than 90,000 individuals with endogenous CS, the overall proportion of mortality – defined as the ratio of the number of deaths from CS divided by the total number of CS patients – was 0.05, and the standardized mortality rate was an “unacceptable” three times that of the general population, Padiporn Limumpornpetch, MD, reported on March 20 at ENDO 2021: The Endocrine Society Annual Meeting.
Excess deaths were higher among those with adrenal CS, compared with those with Cushing’s disease. The most common causes of death among those with CS were cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular accident, infection, and malignancy, noted Dr. Limumpornpetch, of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand, who is also a PhD student at the University of Leeds, United Kingdom.
“While mortality has improved since 2000, it is still significantly compromised compared to the background population ... The causes of death highlight the need for aggressive management of cardiovascular risk, prevention of thromboembolism, infection control, and a normalized cortisol level,” she said.
Asked to comment, Maria Fleseriu, MD, told this news organization that the new data show “we are making improvements in the care of patients with CS and thus outcomes, but we are not there yet ... This meta-analysis highlights the whole spectrum of acute and life-threatening complications in CS and their high prevalence, even before disease diagnosis and after successful surgery.”
She noted that although she wasn’t surprised by the overall results, “the improvement over time was indeed lower than I expected. However, interestingly here, the risk of mortality in adrenal Cushing’s was unexpectedly high despite patients with adrenal cancer being excluded.”
Dr. Fleseriu, who is director of the Pituitary Center at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, advised, “Management of hyperglycemia and diabetes, hypertension, hypokalemia, hyperlipidemia, and other cardiovascular risk factors is generally undertaken in accordance with standard of clinical care.”
“But we should focus more on optimizing more aggressively this care in addition to the specific Cushing’s treatment,” she stressed.
In addition, she noted, “Medical therapy for CS may be needed even prior to surgery in severe and/or prolonged hypercortisolism to decrease complications ... We definitely need a multidisciplinary approach to address complications and etiologic treatment as well as the reduced long-term quality of life in patients with CS.”
Largest study in scale and scope of Cushing’s syndrome mortality
Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome occurs when the body overproduces cortisol. The most common cause of the latter is a tumor of the pituitary gland (Cushing’s disease), but another cause is a usually benign tumor of the adrenal glands (adrenal Cushing’s syndrome). Surgery is the mainstay of initial treatment of Cushing’s syndrome. If an operation to remove the tumor fails to cause remission, medications are available.
Prior to this new meta-analysis, there had been limited data on mortality among patients with endogenous CS. Research has mostly been limited to single-cohort studies. A previous systematic review/meta-analysis comprised only seven articles with 780 patients. All the studies were conducted prior to 2012, and most were limited to Cushing’s disease.
“In 2021, we lacked a detailed understanding of patient outcomes and mortality because of the rarity of Cushing’s syndrome,” Dr. Limumpornpetch noted.
The current meta-analysis included 91 articles that reported mortality among patients with endogenous CS. There was a total of 19,181 patients from 92 study cohorts, including 49 studies on CD (n = 14,971), 24 studies on adrenal CS (n = 2304), and 19 studies that included both (n = 1906).
Among 21 studies that reported standardized mortality rate (SMR) data, including 13 CD studies (n = 2160) and seven on adrenal CS (n = 1531), the overall increase in mortality compared to the background population was a significant 3.00 (range, 1.15-7.84).
This SMR was higher among patients with adrenal Cushing’s syndrome (3.3) versus Cushing’s disease (2.8) (P = .003) and among patients who had active disease (5.7) versus those whose disease was in remission (2.3) (P < .001).
The SMR was also worse among patients with Cushing’s disease with larger tumors (macroadenomas), at 7.4, than among patients with very small tumors (microadenomas), at 1.9 (P = .004).
The proportion of death was 0.05 for CS overall, with 0.04 for CD and 0.02 for adrenal adenomas.
Compared to studies published prior to the year 2000, more recent studies seem to reflect advances in treatment and care. The overall proportion of death for all CS cohorts dropped from 0.10 to 0.03 (P < .001); for all CD cohorts, it dropped from 0.14 to 0.03; and for adrenal CS cohorts, it dropped from 0.09 to 0.03 (P = .04).
Causes of death were cardiovascular diseases (29.5% of cases), cerebrovascular accident (11.5%), infection (10.5%), and malignancy (10.1%). Less common causes of death were gastrointestinal bleeding and acute pancreatitis (3.7%), active CS (3.5%), adrenal insufficiency (2.5%), suicide (2.5%), and surgery (1.6%).
Overall, in the CS groups, the proportion of deaths within 30 days of surgery dropped from 0.04 prior to 2000 to 0.01 since (P = .07). For CD, the proportion dropped from 0.02 to 0.01 (P = .25).
Preventing perioperative mortality: Consider thromboprophylaxis
Dr. Fleseriu told this news organization that she believes hypercoagulability is “the least recognized complication with a big role in mortality.” Because most of the perioperative mortality is due to venous thromboembolism and infections, “thromboprophylaxis should be considered for CS patients with severe hypercortisolism and/or postoperatively, based on individual risk factors of thromboembolism and bleeding.”
Recently, Dr. Fleseriu’s group showed in a single retrospective study that the risk for arterial and venous thromboembolic events among patients with CS was approximately 20%. Many patients experienced more than one event. Risk was higher 30 to 60 days postoperatively.
The odds ratio of venous thromoboembolism among patients with CS was 18 times higher than in the normal population.
“Due to the additional thrombotic risk of surgery or any invasive procedure, anticoagulation prophylaxis should be at least considered in all patients with Cushing’s syndrome and balanced with individual bleeding risk,” Dr. Fleseriu advised.
A recent Pituitary Society workshop discussed the management of complications of CS at length; proceedings will be published soon, she noted.
Dr. Limumpornpetch commented, “We look forward to the day when our interdisciplinary approach to managing these challenging patients can deliver outcomes similar to the background population.”
Dr. Limumpornpetch has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fleseriu has been a scientific consultant to Recordati, Sparrow, and Strongbridge and has received grants (inst) from Novartis and Strongbridge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Don’t screen for vitamin D in general population, says USPSTF
Seven years after concluding that evidence was insufficient to recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in the general population, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has revisited the issue – and come up with the same conclusion.
Overall, “the current evidence is inadequate to determine whether screening for and treatment of asymptomatic low 25(OH)D levels improve clinical outcomes in community dwelling adults,” the task force concluded in its statement, recommending an “I” for insufficient.
The statement was published online April 13 in JAMA.
In the absence of screening recommendations, clinicians may be best advised to instead focus on diet and supplementation for those considered at risk, said Anne R. Cappola, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Rather than posing the question of screening the general population for vitamin D deficiency, let’s focus on ensuring that everyone consumes the age-based recommended daily allowance of vitamin D instead,” Dr. Cappola, a coauthor of the accompanying editorial, said in an interview.
No studies have directly evaluated benefits of screening
The latest USPSTF recommendation is based on a systematic review of the benefits and harms of screening and early treatment for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic, community-dwelling nonpregnant adults aged 18 or older in the primary care setting with no signs or symptoms of deficiency.
The review found no studies that directly evaluated the benefits of screening for vitamin D deficiency.
However, 26 randomized clinical trials and one nested case-control study evaluated the effectiveness of treatment of vitamin D deficiency with supplementation.
And while observational studies have linked lower vitamin D levels with a multitude of conditions and risks, evidence of any benefit was inconsistent, with none identified for most major outcomes in asymptomatic adults – the focus of the Task Force recommendation.
“Among asymptomatic, community-dwelling populations with low vitamin D levels, the evidence suggests that treatment with vitamin D has no effect on mortality or the incidence of fractures, falls, depression, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, or adverse events,” the review authors stress.
“The evidence is inconclusive about the effect of treatment on physical functioning and infection.”
One in four are vitamin D deficient
In terms of the further question of the potential harms of vitamin D screening of asymptomatic individuals, a key concern is the potential for misclassification and over- or underdiagnosis due to inconsistent cutoffs and variability of different screening assays, the review concluded.
However, with the rare exception of vitamin D toxicity from supplementation well above sufficient levels, treatment with vitamin D supplementation appears relatively safe.
With a lack of consensus even over the basic cutoff for vitamin D deficiency, the National Academy of Medicine determined in 2011 that hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels below 20 ng/mL are deficient for bone health, with no evidence of different thresholds for any other health condition.
Based on that cutoff, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), reported in 2014 that 25% of the U.S. population over the age of 1 was vitamin D deficient, with 18% of the population having 25(OH)D levels of 12-19 ng/mL and 5% having very low levels (< 12 ng/mL).
More work needed to determine groups at risk
While the task force report did not delve into testing or treatment recommendations for symptomatic adults, key established risk factors that may help clinicians identify those who are vitamin D deficient include obesity, receiving little or no UVB light exposure, and older age.
In general, obesity is associated with a 1.3- to 2-fold risk of being vitamin D deficient based on the criteria used, while non-Hispanic Blacks are 2-10 times more likely to be deficient compared with non-Hispanic White patients, the task force noted.
However, the implications of vitamin D deficiency in certain populations can vary. For instance, non-Hispanic Black people, despite having a higher prevalence of lower vitamin D levels compared with White people, in fact, have lower reported rates of fractures.
To address the various issues and gain a better understanding of the complexities of vitamin D deficiency, the task force calls for further research in key areas.
“More research is needed to determine whether total serum 25(OH)D levels are the best measure of vitamin D deficiency and whether the best measure of vitamin D deficiency varies by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex,” the authors indicated.
Furthermore, “more research is needed to determine the cutoff that defines vitamin D deficiency and whether that cutoff varies by specific clinical outcome or by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex.”
No support for population-based screening in guidelines
With the lack of conclusive evidence, no organizations currently recommend population-based screening for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic patients, and the American Society for Clinical Pathology endorses this stance.
The Endocrine Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists meanwhile do recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in patients considered at risk.
Data show there was as much as an 80-fold increase in Medicare reimbursement volumes for vitamin D testing among clinicians from 2000 to 2010; however, that rate may have leveled off after the National Academy of Medicine reported on set deficiency levels, said Sherri-Ann M. Burnett-Bowie, MD, MPH, Dr. Cappola’s editorial coauthor.
Dr. Burnett-Bowie noted that she regularly tests her patients’ vitamin D levels, however most of her patients have osteoporosis or fractures.
“I do screen them for vitamin D deficiency since optimizing their vitamin D will improve calcium absorption, which is important for treating their osteoporosis,” Dr. Burnett-Bowie, of the endocrine division, department of medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In terms of broader testing of asymptomatic patients in the general population, however, any changes in screening will likely be contingent on developments in the effects of treatment, she said.
“Given the challenge in finding benefits of vitamin D supplementation in those who are deficient, it will likely be more challenging to find benefits from wider screening,” she concluded.
The USPSTF and editorialists reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven years after concluding that evidence was insufficient to recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in the general population, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has revisited the issue – and come up with the same conclusion.
Overall, “the current evidence is inadequate to determine whether screening for and treatment of asymptomatic low 25(OH)D levels improve clinical outcomes in community dwelling adults,” the task force concluded in its statement, recommending an “I” for insufficient.
The statement was published online April 13 in JAMA.
In the absence of screening recommendations, clinicians may be best advised to instead focus on diet and supplementation for those considered at risk, said Anne R. Cappola, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Rather than posing the question of screening the general population for vitamin D deficiency, let’s focus on ensuring that everyone consumes the age-based recommended daily allowance of vitamin D instead,” Dr. Cappola, a coauthor of the accompanying editorial, said in an interview.
No studies have directly evaluated benefits of screening
The latest USPSTF recommendation is based on a systematic review of the benefits and harms of screening and early treatment for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic, community-dwelling nonpregnant adults aged 18 or older in the primary care setting with no signs or symptoms of deficiency.
The review found no studies that directly evaluated the benefits of screening for vitamin D deficiency.
However, 26 randomized clinical trials and one nested case-control study evaluated the effectiveness of treatment of vitamin D deficiency with supplementation.
And while observational studies have linked lower vitamin D levels with a multitude of conditions and risks, evidence of any benefit was inconsistent, with none identified for most major outcomes in asymptomatic adults – the focus of the Task Force recommendation.
“Among asymptomatic, community-dwelling populations with low vitamin D levels, the evidence suggests that treatment with vitamin D has no effect on mortality or the incidence of fractures, falls, depression, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, or adverse events,” the review authors stress.
“The evidence is inconclusive about the effect of treatment on physical functioning and infection.”
One in four are vitamin D deficient
In terms of the further question of the potential harms of vitamin D screening of asymptomatic individuals, a key concern is the potential for misclassification and over- or underdiagnosis due to inconsistent cutoffs and variability of different screening assays, the review concluded.
However, with the rare exception of vitamin D toxicity from supplementation well above sufficient levels, treatment with vitamin D supplementation appears relatively safe.
With a lack of consensus even over the basic cutoff for vitamin D deficiency, the National Academy of Medicine determined in 2011 that hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels below 20 ng/mL are deficient for bone health, with no evidence of different thresholds for any other health condition.
Based on that cutoff, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), reported in 2014 that 25% of the U.S. population over the age of 1 was vitamin D deficient, with 18% of the population having 25(OH)D levels of 12-19 ng/mL and 5% having very low levels (< 12 ng/mL).
More work needed to determine groups at risk
While the task force report did not delve into testing or treatment recommendations for symptomatic adults, key established risk factors that may help clinicians identify those who are vitamin D deficient include obesity, receiving little or no UVB light exposure, and older age.
In general, obesity is associated with a 1.3- to 2-fold risk of being vitamin D deficient based on the criteria used, while non-Hispanic Blacks are 2-10 times more likely to be deficient compared with non-Hispanic White patients, the task force noted.
However, the implications of vitamin D deficiency in certain populations can vary. For instance, non-Hispanic Black people, despite having a higher prevalence of lower vitamin D levels compared with White people, in fact, have lower reported rates of fractures.
To address the various issues and gain a better understanding of the complexities of vitamin D deficiency, the task force calls for further research in key areas.
“More research is needed to determine whether total serum 25(OH)D levels are the best measure of vitamin D deficiency and whether the best measure of vitamin D deficiency varies by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex,” the authors indicated.
Furthermore, “more research is needed to determine the cutoff that defines vitamin D deficiency and whether that cutoff varies by specific clinical outcome or by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex.”
No support for population-based screening in guidelines
With the lack of conclusive evidence, no organizations currently recommend population-based screening for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic patients, and the American Society for Clinical Pathology endorses this stance.
The Endocrine Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists meanwhile do recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in patients considered at risk.
Data show there was as much as an 80-fold increase in Medicare reimbursement volumes for vitamin D testing among clinicians from 2000 to 2010; however, that rate may have leveled off after the National Academy of Medicine reported on set deficiency levels, said Sherri-Ann M. Burnett-Bowie, MD, MPH, Dr. Cappola’s editorial coauthor.
Dr. Burnett-Bowie noted that she regularly tests her patients’ vitamin D levels, however most of her patients have osteoporosis or fractures.
“I do screen them for vitamin D deficiency since optimizing their vitamin D will improve calcium absorption, which is important for treating their osteoporosis,” Dr. Burnett-Bowie, of the endocrine division, department of medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In terms of broader testing of asymptomatic patients in the general population, however, any changes in screening will likely be contingent on developments in the effects of treatment, she said.
“Given the challenge in finding benefits of vitamin D supplementation in those who are deficient, it will likely be more challenging to find benefits from wider screening,” she concluded.
The USPSTF and editorialists reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven years after concluding that evidence was insufficient to recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in the general population, the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has revisited the issue – and come up with the same conclusion.
Overall, “the current evidence is inadequate to determine whether screening for and treatment of asymptomatic low 25(OH)D levels improve clinical outcomes in community dwelling adults,” the task force concluded in its statement, recommending an “I” for insufficient.
The statement was published online April 13 in JAMA.
In the absence of screening recommendations, clinicians may be best advised to instead focus on diet and supplementation for those considered at risk, said Anne R. Cappola, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Rather than posing the question of screening the general population for vitamin D deficiency, let’s focus on ensuring that everyone consumes the age-based recommended daily allowance of vitamin D instead,” Dr. Cappola, a coauthor of the accompanying editorial, said in an interview.
No studies have directly evaluated benefits of screening
The latest USPSTF recommendation is based on a systematic review of the benefits and harms of screening and early treatment for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic, community-dwelling nonpregnant adults aged 18 or older in the primary care setting with no signs or symptoms of deficiency.
The review found no studies that directly evaluated the benefits of screening for vitamin D deficiency.
However, 26 randomized clinical trials and one nested case-control study evaluated the effectiveness of treatment of vitamin D deficiency with supplementation.
And while observational studies have linked lower vitamin D levels with a multitude of conditions and risks, evidence of any benefit was inconsistent, with none identified for most major outcomes in asymptomatic adults – the focus of the Task Force recommendation.
“Among asymptomatic, community-dwelling populations with low vitamin D levels, the evidence suggests that treatment with vitamin D has no effect on mortality or the incidence of fractures, falls, depression, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, or adverse events,” the review authors stress.
“The evidence is inconclusive about the effect of treatment on physical functioning and infection.”
One in four are vitamin D deficient
In terms of the further question of the potential harms of vitamin D screening of asymptomatic individuals, a key concern is the potential for misclassification and over- or underdiagnosis due to inconsistent cutoffs and variability of different screening assays, the review concluded.
However, with the rare exception of vitamin D toxicity from supplementation well above sufficient levels, treatment with vitamin D supplementation appears relatively safe.
With a lack of consensus even over the basic cutoff for vitamin D deficiency, the National Academy of Medicine determined in 2011 that hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels below 20 ng/mL are deficient for bone health, with no evidence of different thresholds for any other health condition.
Based on that cutoff, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), reported in 2014 that 25% of the U.S. population over the age of 1 was vitamin D deficient, with 18% of the population having 25(OH)D levels of 12-19 ng/mL and 5% having very low levels (< 12 ng/mL).
More work needed to determine groups at risk
While the task force report did not delve into testing or treatment recommendations for symptomatic adults, key established risk factors that may help clinicians identify those who are vitamin D deficient include obesity, receiving little or no UVB light exposure, and older age.
In general, obesity is associated with a 1.3- to 2-fold risk of being vitamin D deficient based on the criteria used, while non-Hispanic Blacks are 2-10 times more likely to be deficient compared with non-Hispanic White patients, the task force noted.
However, the implications of vitamin D deficiency in certain populations can vary. For instance, non-Hispanic Black people, despite having a higher prevalence of lower vitamin D levels compared with White people, in fact, have lower reported rates of fractures.
To address the various issues and gain a better understanding of the complexities of vitamin D deficiency, the task force calls for further research in key areas.
“More research is needed to determine whether total serum 25(OH)D levels are the best measure of vitamin D deficiency and whether the best measure of vitamin D deficiency varies by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex,” the authors indicated.
Furthermore, “more research is needed to determine the cutoff that defines vitamin D deficiency and whether that cutoff varies by specific clinical outcome or by subgroups defined by race, ethnicity, or sex.”
No support for population-based screening in guidelines
With the lack of conclusive evidence, no organizations currently recommend population-based screening for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic patients, and the American Society for Clinical Pathology endorses this stance.
The Endocrine Society and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists meanwhile do recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency in patients considered at risk.
Data show there was as much as an 80-fold increase in Medicare reimbursement volumes for vitamin D testing among clinicians from 2000 to 2010; however, that rate may have leveled off after the National Academy of Medicine reported on set deficiency levels, said Sherri-Ann M. Burnett-Bowie, MD, MPH, Dr. Cappola’s editorial coauthor.
Dr. Burnett-Bowie noted that she regularly tests her patients’ vitamin D levels, however most of her patients have osteoporosis or fractures.
“I do screen them for vitamin D deficiency since optimizing their vitamin D will improve calcium absorption, which is important for treating their osteoporosis,” Dr. Burnett-Bowie, of the endocrine division, department of medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In terms of broader testing of asymptomatic patients in the general population, however, any changes in screening will likely be contingent on developments in the effects of treatment, she said.
“Given the challenge in finding benefits of vitamin D supplementation in those who are deficient, it will likely be more challenging to find benefits from wider screening,” she concluded.
The USPSTF and editorialists reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How physicians can provide better care to transgender patients
People who identify as transgender experience many health disparities, in addition to lack of access to quality care. The most commonly cited barrier is the lack of providers who are knowledgeable about transgender health care, according to past surveys.
Even those who do seek care often have unpleasant experiences. A 2015 survey conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality found that 33% of those who saw a health care provider reported at least one unfavorable experience related to being transgender, such as being verbally harassed or refused treatment because of their gender identity. In fact, 23% of those surveyed say they did not seek health care they needed in the past year because of fear of being mistreated as a transgender person.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Question: Surveys have shown that many people who identify as transgender will seek only transition care, not primary or preventive care. Why is that?
Dr. Brandt: My answer is multifactorial. Transgender patients do seek primary care – just not as readily. There’s a lot of misconceptions about health care needs for the LGBT community in general. For example, lesbian or bisexual women may be not as well informed about the need for Pap smears compared with their heterosexual counterparts. These misconceptions are further exacerbated in the transgender community.
The fact that a lot of patients seek only transition-related care, but not preventive services, such as primary care and gynecologic care, is also related to fears of discrimination and lack of education of providers. These patients are afraid when they walk into an office that they will be misgendered or their physician won’t be familiar with their health care needs.
What can clinics and clinicians do to create a safe and welcoming environment?
Dr. Brandt: It starts with educating office staff about terminology and gender identities.
A key feature of our EHR is the sexual orientation and gender identity platform, which asks questions about a patient’s gender identity, sexual orientation, sex assigned at birth, and organ inventory. These data are then found in the patient information tab and are just as relevant as their insurance status, age, and date of birth.
There are many ways a doctor’s office can signal to patients that they are inclusive. They can hang LGBTQ-friendly flags or symbols or a sign saying, “We have an anti-discrimination policy” in the waiting room. A welcoming environment can also be achieved by revising patient questionnaires or forms so that they aren’t gender-specific or binary.
Given that the patient may have limited contact with a primary care clinician, how do you prioritize what you address during the visit?
Dr. Brandt: Similar to cisgender patients, it depends initially on the age of the patient and the reason for the visit. The priorities of an otherwise healthy transgender patient in their 20s are going to be largely the same as for a cisgender patient of the same age. As patients age in the primary care world, you’re addressing more issues, such as colorectal screening, lipid disorders, and mammograms, and that doesn’t change. For the most part, the problems that you address should be specific for that age group.
It becomes more complicated when you add in factors such as hormone therapy and whether patients have had any type of gender-affirming surgery. Those things can change the usual recommendations for screening or risk assessment. We try to figure out what routine health maintenance and cancer screening a patient needs based on age and risk factors, in addition to hormone status and surgical state.
Do you think that many physicians are educated about the care of underserved populations such as transgender patients?
Dr. Brandt: Yes and no. We are definitely getting better at it. For example, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published a committee opinion highlighting transgender care. So organizations are starting to prioritize these populations and recognize that they are, in fact, underserved and they have special health care needs.
However, the knowledge gaps are still pretty big. I get calls daily from providers asking questions about how to manage patients on hormones, or how to examine a patient who has undergone a vaginoplasty. I hear a lot of horror stories from transgender patients who had their hormones stopped for absurd and medically misinformed reasons.
But I definitely think it’s getting better and it’s being addressed at all levels – the medical school level, the residency level, and the attending level. It just takes time to inform people and for people to get used to the health care needs of these patients.
What should physicians keep in mind when treating patients who identify as transgender?
Dr. Brandt: First and foremost, understanding the terminology and the difference between gender identity, sex, and sexual orientation. Being familiar with that language and being able to speak that language very comfortably and not being awkward about it is a really important thing for primary care physicians and indeed any physician who treats transgender patients.
Physicians should also be aware that any underserved population has higher rates of mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. Obviously, that goes along with being underserved and the stigma and the disparities that exist for these patients. Having providers educate themselves about what those disparities are and how they impact a patient’s daily life and health is paramount to knowing how to treat patients.
What are your top health concerns for these patients and how do you address them?
Dr. Brandt: I think mental health and safety is probably the number one for me. About 41% of transgender adults have attempted suicide. That number is roughly 51% in transgender youth. That is an astonishing number. These patients have much higher rates of domestic violence, intimate partner violence, and sexual assault, especially trans women and trans women of color. So understanding those statistics is huge.
Obesity, smoking, and substance abuse are my next three. Again, those are things that should be addressed at any visit, regardless of the gender identity or sexual orientation of the patient, but those rates are particularly high in this population.
Fertility and long-term care for patients should be addressed. Many patients who identify as transgender are told they can’t have a family. As a primary care physician, you may see a patient before they are seen by an ob.gyn. or surgeon. Talking about what a patient’s long-term life goals are with fertility and family planning, and what that looks like for them, is a big thing for me. Other providers may not feel that’s a concern, but I believe it should be discussed before initiation of hormone therapy, which can significantly impact fertility in some patients.
Are there nuances to the physical examination that primary care physicians should be aware of when dealing with transmasculine patients vs. transfeminine patients?
Dr. Brandt: Absolutely. And this interview can’t cover the scope of those nuances. An example that comes to mind is the genital exam. For transgender women who have undergone a vaginoplasty, the pelvic exam can be very affirming. Whereas for transgender men, a gynecologic exam can significantly exacerbate dysphoria and there are ways to conduct the exam to limit this discomfort and avoid creating a traumatic experience for the patient. It’s important to be aware that the genital exam, or any type of genitourinary exam, can be either affirming or not affirming.
Sexually transmitted infections are up in the general population, and the trans population is at even higher risk. What should physicians think about when they assess this risk?
Dr. Brandt: It’s really important for primary care clinicians and for gynecologists to learn to be comfortable talking about sexual practices, because what people do behind closed doors is really a key to how to counsel patients about safe sex.
People are well aware of the need to have safe sex. However, depending on the type of sex that you’re having, what body parts go where, what is truly safe can vary and people may not know, for example, to wear a condom when sex toys are involved or that a transgender male on testosterone can become pregnant during penile-vaginal intercourse. Providers really should be very educated on the array of sexual practices that people have and how to counsel them about those. They should know how to ask patients the gender identity of their sexual partners, the sexual orientation of their partners, and what parts go where during sex.
Providers should also talk to patients about PrEP [pre-exposure prophylaxis], whether they identify as cisgender or transgender. My trans patients tend to be a lot more educated about PrEP than other patients. It’s something that many of the residents, even in a standard gynecologic clinic, for example, don’t talk to cisgender patients about because of the stigma surrounding HIV. Many providers still think that the only people who are at risk for HIV are men who have sex with men. And while those rates are higher in some populations, depending on sexual practices, those aren’t the only patients who qualify for PrEP.
Overall, in order to counsel patients about STIs and safe sexual practices, providers should learn to be comfortable talking about sex.
Do you have any strategies on how to make the appointment more successful in addressing those issues?
Dr. Brandt: Bedside manner is a hard thing to teach, and comfort in talking about sex, gender identity, and sexual orientation can vary – but there are a lot of continuing medical education courses that physicians can utilize through the World Professional Association for Transgender Health.
If providers start to notice an influx of patients who identify as transgender or if they want to start seeing transgender patients, it’s really important for them to have that training before they start interacting with patients. In all of medicine, we sort of learn as we go, but this patient population has been subjected to discrimination, violence, error, and misgendering. They have dealt with providers who didn’t understand their health care needs. While this field is evolving, knowing how to appropriately address a patient (using their correct name, pronouns, etc.) is an absolute must.
That needs to be part of a provider’s routine vernacular and not something that they sort of stumble through. You can scare a patient away as soon as they walk into the office with an uneducated front desk staff and things that are seen in the office. Seeking out those educational tools, being aware of your own deficits as a provider and the educational needs of your office, and addressing those needs is really key.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who identify as transgender experience many health disparities, in addition to lack of access to quality care. The most commonly cited barrier is the lack of providers who are knowledgeable about transgender health care, according to past surveys.
Even those who do seek care often have unpleasant experiences. A 2015 survey conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality found that 33% of those who saw a health care provider reported at least one unfavorable experience related to being transgender, such as being verbally harassed or refused treatment because of their gender identity. In fact, 23% of those surveyed say they did not seek health care they needed in the past year because of fear of being mistreated as a transgender person.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Question: Surveys have shown that many people who identify as transgender will seek only transition care, not primary or preventive care. Why is that?
Dr. Brandt: My answer is multifactorial. Transgender patients do seek primary care – just not as readily. There’s a lot of misconceptions about health care needs for the LGBT community in general. For example, lesbian or bisexual women may be not as well informed about the need for Pap smears compared with their heterosexual counterparts. These misconceptions are further exacerbated in the transgender community.
The fact that a lot of patients seek only transition-related care, but not preventive services, such as primary care and gynecologic care, is also related to fears of discrimination and lack of education of providers. These patients are afraid when they walk into an office that they will be misgendered or their physician won’t be familiar with their health care needs.
What can clinics and clinicians do to create a safe and welcoming environment?
Dr. Brandt: It starts with educating office staff about terminology and gender identities.
A key feature of our EHR is the sexual orientation and gender identity platform, which asks questions about a patient’s gender identity, sexual orientation, sex assigned at birth, and organ inventory. These data are then found in the patient information tab and are just as relevant as their insurance status, age, and date of birth.
There are many ways a doctor’s office can signal to patients that they are inclusive. They can hang LGBTQ-friendly flags or symbols or a sign saying, “We have an anti-discrimination policy” in the waiting room. A welcoming environment can also be achieved by revising patient questionnaires or forms so that they aren’t gender-specific or binary.
Given that the patient may have limited contact with a primary care clinician, how do you prioritize what you address during the visit?
Dr. Brandt: Similar to cisgender patients, it depends initially on the age of the patient and the reason for the visit. The priorities of an otherwise healthy transgender patient in their 20s are going to be largely the same as for a cisgender patient of the same age. As patients age in the primary care world, you’re addressing more issues, such as colorectal screening, lipid disorders, and mammograms, and that doesn’t change. For the most part, the problems that you address should be specific for that age group.
It becomes more complicated when you add in factors such as hormone therapy and whether patients have had any type of gender-affirming surgery. Those things can change the usual recommendations for screening or risk assessment. We try to figure out what routine health maintenance and cancer screening a patient needs based on age and risk factors, in addition to hormone status and surgical state.
Do you think that many physicians are educated about the care of underserved populations such as transgender patients?
Dr. Brandt: Yes and no. We are definitely getting better at it. For example, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published a committee opinion highlighting transgender care. So organizations are starting to prioritize these populations and recognize that they are, in fact, underserved and they have special health care needs.
However, the knowledge gaps are still pretty big. I get calls daily from providers asking questions about how to manage patients on hormones, or how to examine a patient who has undergone a vaginoplasty. I hear a lot of horror stories from transgender patients who had their hormones stopped for absurd and medically misinformed reasons.
But I definitely think it’s getting better and it’s being addressed at all levels – the medical school level, the residency level, and the attending level. It just takes time to inform people and for people to get used to the health care needs of these patients.
What should physicians keep in mind when treating patients who identify as transgender?
Dr. Brandt: First and foremost, understanding the terminology and the difference between gender identity, sex, and sexual orientation. Being familiar with that language and being able to speak that language very comfortably and not being awkward about it is a really important thing for primary care physicians and indeed any physician who treats transgender patients.
Physicians should also be aware that any underserved population has higher rates of mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. Obviously, that goes along with being underserved and the stigma and the disparities that exist for these patients. Having providers educate themselves about what those disparities are and how they impact a patient’s daily life and health is paramount to knowing how to treat patients.
What are your top health concerns for these patients and how do you address them?
Dr. Brandt: I think mental health and safety is probably the number one for me. About 41% of transgender adults have attempted suicide. That number is roughly 51% in transgender youth. That is an astonishing number. These patients have much higher rates of domestic violence, intimate partner violence, and sexual assault, especially trans women and trans women of color. So understanding those statistics is huge.
Obesity, smoking, and substance abuse are my next three. Again, those are things that should be addressed at any visit, regardless of the gender identity or sexual orientation of the patient, but those rates are particularly high in this population.
Fertility and long-term care for patients should be addressed. Many patients who identify as transgender are told they can’t have a family. As a primary care physician, you may see a patient before they are seen by an ob.gyn. or surgeon. Talking about what a patient’s long-term life goals are with fertility and family planning, and what that looks like for them, is a big thing for me. Other providers may not feel that’s a concern, but I believe it should be discussed before initiation of hormone therapy, which can significantly impact fertility in some patients.
Are there nuances to the physical examination that primary care physicians should be aware of when dealing with transmasculine patients vs. transfeminine patients?
Dr. Brandt: Absolutely. And this interview can’t cover the scope of those nuances. An example that comes to mind is the genital exam. For transgender women who have undergone a vaginoplasty, the pelvic exam can be very affirming. Whereas for transgender men, a gynecologic exam can significantly exacerbate dysphoria and there are ways to conduct the exam to limit this discomfort and avoid creating a traumatic experience for the patient. It’s important to be aware that the genital exam, or any type of genitourinary exam, can be either affirming or not affirming.
Sexually transmitted infections are up in the general population, and the trans population is at even higher risk. What should physicians think about when they assess this risk?
Dr. Brandt: It’s really important for primary care clinicians and for gynecologists to learn to be comfortable talking about sexual practices, because what people do behind closed doors is really a key to how to counsel patients about safe sex.
People are well aware of the need to have safe sex. However, depending on the type of sex that you’re having, what body parts go where, what is truly safe can vary and people may not know, for example, to wear a condom when sex toys are involved or that a transgender male on testosterone can become pregnant during penile-vaginal intercourse. Providers really should be very educated on the array of sexual practices that people have and how to counsel them about those. They should know how to ask patients the gender identity of their sexual partners, the sexual orientation of their partners, and what parts go where during sex.
Providers should also talk to patients about PrEP [pre-exposure prophylaxis], whether they identify as cisgender or transgender. My trans patients tend to be a lot more educated about PrEP than other patients. It’s something that many of the residents, even in a standard gynecologic clinic, for example, don’t talk to cisgender patients about because of the stigma surrounding HIV. Many providers still think that the only people who are at risk for HIV are men who have sex with men. And while those rates are higher in some populations, depending on sexual practices, those aren’t the only patients who qualify for PrEP.
Overall, in order to counsel patients about STIs and safe sexual practices, providers should learn to be comfortable talking about sex.
Do you have any strategies on how to make the appointment more successful in addressing those issues?
Dr. Brandt: Bedside manner is a hard thing to teach, and comfort in talking about sex, gender identity, and sexual orientation can vary – but there are a lot of continuing medical education courses that physicians can utilize through the World Professional Association for Transgender Health.
If providers start to notice an influx of patients who identify as transgender or if they want to start seeing transgender patients, it’s really important for them to have that training before they start interacting with patients. In all of medicine, we sort of learn as we go, but this patient population has been subjected to discrimination, violence, error, and misgendering. They have dealt with providers who didn’t understand their health care needs. While this field is evolving, knowing how to appropriately address a patient (using their correct name, pronouns, etc.) is an absolute must.
That needs to be part of a provider’s routine vernacular and not something that they sort of stumble through. You can scare a patient away as soon as they walk into the office with an uneducated front desk staff and things that are seen in the office. Seeking out those educational tools, being aware of your own deficits as a provider and the educational needs of your office, and addressing those needs is really key.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who identify as transgender experience many health disparities, in addition to lack of access to quality care. The most commonly cited barrier is the lack of providers who are knowledgeable about transgender health care, according to past surveys.
Even those who do seek care often have unpleasant experiences. A 2015 survey conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality found that 33% of those who saw a health care provider reported at least one unfavorable experience related to being transgender, such as being verbally harassed or refused treatment because of their gender identity. In fact, 23% of those surveyed say they did not seek health care they needed in the past year because of fear of being mistreated as a transgender person.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
Question: Surveys have shown that many people who identify as transgender will seek only transition care, not primary or preventive care. Why is that?
Dr. Brandt: My answer is multifactorial. Transgender patients do seek primary care – just not as readily. There’s a lot of misconceptions about health care needs for the LGBT community in general. For example, lesbian or bisexual women may be not as well informed about the need for Pap smears compared with their heterosexual counterparts. These misconceptions are further exacerbated in the transgender community.
The fact that a lot of patients seek only transition-related care, but not preventive services, such as primary care and gynecologic care, is also related to fears of discrimination and lack of education of providers. These patients are afraid when they walk into an office that they will be misgendered or their physician won’t be familiar with their health care needs.
What can clinics and clinicians do to create a safe and welcoming environment?
Dr. Brandt: It starts with educating office staff about terminology and gender identities.
A key feature of our EHR is the sexual orientation and gender identity platform, which asks questions about a patient’s gender identity, sexual orientation, sex assigned at birth, and organ inventory. These data are then found in the patient information tab and are just as relevant as their insurance status, age, and date of birth.
There are many ways a doctor’s office can signal to patients that they are inclusive. They can hang LGBTQ-friendly flags or symbols or a sign saying, “We have an anti-discrimination policy” in the waiting room. A welcoming environment can also be achieved by revising patient questionnaires or forms so that they aren’t gender-specific or binary.
Given that the patient may have limited contact with a primary care clinician, how do you prioritize what you address during the visit?
Dr. Brandt: Similar to cisgender patients, it depends initially on the age of the patient and the reason for the visit. The priorities of an otherwise healthy transgender patient in their 20s are going to be largely the same as for a cisgender patient of the same age. As patients age in the primary care world, you’re addressing more issues, such as colorectal screening, lipid disorders, and mammograms, and that doesn’t change. For the most part, the problems that you address should be specific for that age group.
It becomes more complicated when you add in factors such as hormone therapy and whether patients have had any type of gender-affirming surgery. Those things can change the usual recommendations for screening or risk assessment. We try to figure out what routine health maintenance and cancer screening a patient needs based on age and risk factors, in addition to hormone status and surgical state.
Do you think that many physicians are educated about the care of underserved populations such as transgender patients?
Dr. Brandt: Yes and no. We are definitely getting better at it. For example, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published a committee opinion highlighting transgender care. So organizations are starting to prioritize these populations and recognize that they are, in fact, underserved and they have special health care needs.
However, the knowledge gaps are still pretty big. I get calls daily from providers asking questions about how to manage patients on hormones, or how to examine a patient who has undergone a vaginoplasty. I hear a lot of horror stories from transgender patients who had their hormones stopped for absurd and medically misinformed reasons.
But I definitely think it’s getting better and it’s being addressed at all levels – the medical school level, the residency level, and the attending level. It just takes time to inform people and for people to get used to the health care needs of these patients.
What should physicians keep in mind when treating patients who identify as transgender?
Dr. Brandt: First and foremost, understanding the terminology and the difference between gender identity, sex, and sexual orientation. Being familiar with that language and being able to speak that language very comfortably and not being awkward about it is a really important thing for primary care physicians and indeed any physician who treats transgender patients.
Physicians should also be aware that any underserved population has higher rates of mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. Obviously, that goes along with being underserved and the stigma and the disparities that exist for these patients. Having providers educate themselves about what those disparities are and how they impact a patient’s daily life and health is paramount to knowing how to treat patients.
What are your top health concerns for these patients and how do you address them?
Dr. Brandt: I think mental health and safety is probably the number one for me. About 41% of transgender adults have attempted suicide. That number is roughly 51% in transgender youth. That is an astonishing number. These patients have much higher rates of domestic violence, intimate partner violence, and sexual assault, especially trans women and trans women of color. So understanding those statistics is huge.
Obesity, smoking, and substance abuse are my next three. Again, those are things that should be addressed at any visit, regardless of the gender identity or sexual orientation of the patient, but those rates are particularly high in this population.
Fertility and long-term care for patients should be addressed. Many patients who identify as transgender are told they can’t have a family. As a primary care physician, you may see a patient before they are seen by an ob.gyn. or surgeon. Talking about what a patient’s long-term life goals are with fertility and family planning, and what that looks like for them, is a big thing for me. Other providers may not feel that’s a concern, but I believe it should be discussed before initiation of hormone therapy, which can significantly impact fertility in some patients.
Are there nuances to the physical examination that primary care physicians should be aware of when dealing with transmasculine patients vs. transfeminine patients?
Dr. Brandt: Absolutely. And this interview can’t cover the scope of those nuances. An example that comes to mind is the genital exam. For transgender women who have undergone a vaginoplasty, the pelvic exam can be very affirming. Whereas for transgender men, a gynecologic exam can significantly exacerbate dysphoria and there are ways to conduct the exam to limit this discomfort and avoid creating a traumatic experience for the patient. It’s important to be aware that the genital exam, or any type of genitourinary exam, can be either affirming or not affirming.
Sexually transmitted infections are up in the general population, and the trans population is at even higher risk. What should physicians think about when they assess this risk?
Dr. Brandt: It’s really important for primary care clinicians and for gynecologists to learn to be comfortable talking about sexual practices, because what people do behind closed doors is really a key to how to counsel patients about safe sex.
People are well aware of the need to have safe sex. However, depending on the type of sex that you’re having, what body parts go where, what is truly safe can vary and people may not know, for example, to wear a condom when sex toys are involved or that a transgender male on testosterone can become pregnant during penile-vaginal intercourse. Providers really should be very educated on the array of sexual practices that people have and how to counsel them about those. They should know how to ask patients the gender identity of their sexual partners, the sexual orientation of their partners, and what parts go where during sex.
Providers should also talk to patients about PrEP [pre-exposure prophylaxis], whether they identify as cisgender or transgender. My trans patients tend to be a lot more educated about PrEP than other patients. It’s something that many of the residents, even in a standard gynecologic clinic, for example, don’t talk to cisgender patients about because of the stigma surrounding HIV. Many providers still think that the only people who are at risk for HIV are men who have sex with men. And while those rates are higher in some populations, depending on sexual practices, those aren’t the only patients who qualify for PrEP.
Overall, in order to counsel patients about STIs and safe sexual practices, providers should learn to be comfortable talking about sex.
Do you have any strategies on how to make the appointment more successful in addressing those issues?
Dr. Brandt: Bedside manner is a hard thing to teach, and comfort in talking about sex, gender identity, and sexual orientation can vary – but there are a lot of continuing medical education courses that physicians can utilize through the World Professional Association for Transgender Health.
If providers start to notice an influx of patients who identify as transgender or if they want to start seeing transgender patients, it’s really important for them to have that training before they start interacting with patients. In all of medicine, we sort of learn as we go, but this patient population has been subjected to discrimination, violence, error, and misgendering. They have dealt with providers who didn’t understand their health care needs. While this field is evolving, knowing how to appropriately address a patient (using their correct name, pronouns, etc.) is an absolute must.
That needs to be part of a provider’s routine vernacular and not something that they sort of stumble through. You can scare a patient away as soon as they walk into the office with an uneducated front desk staff and things that are seen in the office. Seeking out those educational tools, being aware of your own deficits as a provider and the educational needs of your office, and addressing those needs is really key.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Everyday chemicals are linked to declines in human fertility
Chemicals that pervade our modern world – plastics, pesticides, stain repellents, components of personal hygiene products – are contributing to a decades-long decline in fertility and could pose health risks even into future generations, according to an explosive new book by Shanna Swan, PhD, an environmental and reproductive epidemiologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Dr. Swan laid out the case that endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) threaten human existence, a conclusion that stems in part from her 2017 meta-analysis that showed a 52% drop in sperm counts from 1973 to 2011 in men in North America, Europe, and Australia.
“This alarming rate of decline could mean the human race will be unable to reproduce itself if the trend continues,” Dr. Swan said in her book, “Count Down: How Our Modern World Is Threatening Sperm Counts, Altering Male and Female Reproductive Development, and Imperiling the Future of the Human Race,” (New York: Scribner, 2021) coauthored with health journalist Stacey Colino.
Her premise that EDCs pose a risk to both male and female fertility is underscored by new research. A March 2021 article in Human Reproduction links prenatal chemical exposures to lowered fertility in a study of 1,045 Swiss military conscripts.
The Swiss men, aged 18-22 years, were significantly more likely to have low semen volume and low total sperm count if their mothers reported that they had occupational exposures to four or more endocrine-disrupting chemicals while they were pregnant. These EDCs, which mimic natural hormones, included pesticides, heavy metals, phthalates, alkylphenolic compounds, and solvents that can be found in agricultural work or hair and beauty salons.
These chemicals are not so-called “forever chemicals” that persist in the human body. But the Swiss study still showed an association between exposure during pregnancy and the future fertility of the male children. “Those apparently small exposures that pass quickly can affect development,” said Dr. Swan, who was not affiliated with the research. “It takes very little in terms of time and amount of chemicals to alter fetal development.”
Health risks beyond reproduction
While Count Down is placing a new spotlight on chemical hazards, some major medical organizations have already taken positions on the risks. “Reducing exposure to toxic environmental agents is a critical area of intervention for ob.gyns.,” the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said in an environmental policy priority. “The Endocrine Society is concerned that human health is at risk because the current extensive scientific knowledge on EDCs and their health effects is not effectively translated to regulatory policies that fully protect populations from EDC exposures.”
But for the medical community, addressing the impact of EDCs goes beyond advocacy for regulatory and legislative changes, Dr. Swan said in an interview. Physicians should talk to patients about the importance of reducing their chemical exposure to safeguard their overall health.
“Reproductive health and particularly sperm count, subfertility, and infertility are predictors of lifelong health,” she said. That includes associations between reproductive disorders and “the risk of heart disease, obesity, reproductive cancers and, perhaps most dramatically, with a shortened lifespan.”
Some medical schools are including information on environmental health and exposure risks in the curriculum, said Tracey Woodruff, PhD, MPH, director of the program on reproductive health and the environment at the University of California, San Francisco. She urged physicians to ask patients about potential occupational exposures to hazardous chemicals and provide information about ways to reduce everyday exposures.
For example, safer options include buying organic produce, microwaving food in glass rather than plastic containers and avoiding products that contain phthalate or BPA. “If you’re going to talk to people about what they eat, that’s a perfect venue for talking about the environment,” said Dr. Woodruff, who coedited the textbook, Environmental Impacts on Reproductive Health and Fertility (Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England, 2010).
The UCSF program provides patient guides in English and Spanish with suggestions of ways to reduce chemical exposures at work and at home.
Limits in the data
Michael Eisenberg, MD, a urologist and director of male reproductive medicine and surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, often gets questions from patients about how lifestyle and environmental exposures affect male fertility. (In her book, Dr. Swan also discusses how factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and stress can affect male and female fertility.)
He found the evidence convincing that certain chemicals impact fertility – although, of course, it isn’t ethically possible to do randomized, controlled trials in which some people are intentionally exposed to chemicals to measure the effects. Along with adopting other healthy habits, he advised patients to avoid chemical exposures.
“It’s reasonable to try to eat organic and be mindful of where some of these exposures come from and try to minimize them to the extent possible,” he said.
Rebecca Sokol, MD, MPH, an endocrinologist and expert in male reproductive health, demonstrated the toxic effects of lead on sperm production in studies conducted on rats. But she views low-dose chemical exposure from everyday products as just one aspect of modern reproductive risks, some of which have stronger associations. For example, testosterone therapy impairs sperm production, and finasteride (a medication for male pattern baldness) has been linked to a reversible decline in sperm count.
“When it comes to these ubiquitous chemicals like phthalate and BPA, we explain to the patient that maybe they’re harmful, but we can’t say for sure,” because of the lack of causal data, said Dr. Sokol, professor emerita at the University of Southern California, who was on the panel that drafted the American Urological Association and American Society of Reproductive Medicine guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility.
Nonetheless, she advised patients to try to reduce exposures. “I don’t see us eradicating all the chemicals that might be bad for us unless we go back to another era. But we can do the best we can to avoid what we can.”
A call to action
Dr. Swan likened awareness of the health threat of chemical exposures to the gradual recognition of the climate crisis as a global imperative. Yet in some ways, the scientific work on chemical effects is even more daunting. The Environmental Protection Agency lists more than 86,000 chemicals on its inventory of chemical substances manufactured or imported into the United States.
Little is known about the potential effects of many chemicals that we inhale, ingest or absorb through our skin, Dr. Swan said. In her book, she noted the impact on wildlife – for example, reproductive abnormalities in frogs, alligators, and birds that were exposed to EDCs.
Yet Dr. Swan also takes solace in the lessons from the animal kingdom. Decades after the pesticide DDT, a neurotoxin and endocrine-disruptor, was banned in the United States in 1972, the bald eagle has made a comeback from near-extinction. She also pointed to a 2018 study which found that, while mice exposed to bisphenols passed on reproductive effects to offspring, when the exposures stopped, the effects disappeared after several generations.
“If we stop poisoning ourselves, we can turn this around,” said Dr. Swan. “That’s what I want people to know.”
Count Down frames the issues in language that is much starker than typically found in academic publications. But that is what’s necessary to draw attention to the effects of chemical exposures on human health and reproduction, Dr. Swan said. “I’m saying this in fairly extreme terms to alarm people, to make them realize it is a crisis and they have to act.”
No disclosures were reported.
Chemicals that pervade our modern world – plastics, pesticides, stain repellents, components of personal hygiene products – are contributing to a decades-long decline in fertility and could pose health risks even into future generations, according to an explosive new book by Shanna Swan, PhD, an environmental and reproductive epidemiologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Dr. Swan laid out the case that endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) threaten human existence, a conclusion that stems in part from her 2017 meta-analysis that showed a 52% drop in sperm counts from 1973 to 2011 in men in North America, Europe, and Australia.
“This alarming rate of decline could mean the human race will be unable to reproduce itself if the trend continues,” Dr. Swan said in her book, “Count Down: How Our Modern World Is Threatening Sperm Counts, Altering Male and Female Reproductive Development, and Imperiling the Future of the Human Race,” (New York: Scribner, 2021) coauthored with health journalist Stacey Colino.
Her premise that EDCs pose a risk to both male and female fertility is underscored by new research. A March 2021 article in Human Reproduction links prenatal chemical exposures to lowered fertility in a study of 1,045 Swiss military conscripts.
The Swiss men, aged 18-22 years, were significantly more likely to have low semen volume and low total sperm count if their mothers reported that they had occupational exposures to four or more endocrine-disrupting chemicals while they were pregnant. These EDCs, which mimic natural hormones, included pesticides, heavy metals, phthalates, alkylphenolic compounds, and solvents that can be found in agricultural work or hair and beauty salons.
These chemicals are not so-called “forever chemicals” that persist in the human body. But the Swiss study still showed an association between exposure during pregnancy and the future fertility of the male children. “Those apparently small exposures that pass quickly can affect development,” said Dr. Swan, who was not affiliated with the research. “It takes very little in terms of time and amount of chemicals to alter fetal development.”
Health risks beyond reproduction
While Count Down is placing a new spotlight on chemical hazards, some major medical organizations have already taken positions on the risks. “Reducing exposure to toxic environmental agents is a critical area of intervention for ob.gyns.,” the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said in an environmental policy priority. “The Endocrine Society is concerned that human health is at risk because the current extensive scientific knowledge on EDCs and their health effects is not effectively translated to regulatory policies that fully protect populations from EDC exposures.”
But for the medical community, addressing the impact of EDCs goes beyond advocacy for regulatory and legislative changes, Dr. Swan said in an interview. Physicians should talk to patients about the importance of reducing their chemical exposure to safeguard their overall health.
“Reproductive health and particularly sperm count, subfertility, and infertility are predictors of lifelong health,” she said. That includes associations between reproductive disorders and “the risk of heart disease, obesity, reproductive cancers and, perhaps most dramatically, with a shortened lifespan.”
Some medical schools are including information on environmental health and exposure risks in the curriculum, said Tracey Woodruff, PhD, MPH, director of the program on reproductive health and the environment at the University of California, San Francisco. She urged physicians to ask patients about potential occupational exposures to hazardous chemicals and provide information about ways to reduce everyday exposures.
For example, safer options include buying organic produce, microwaving food in glass rather than plastic containers and avoiding products that contain phthalate or BPA. “If you’re going to talk to people about what they eat, that’s a perfect venue for talking about the environment,” said Dr. Woodruff, who coedited the textbook, Environmental Impacts on Reproductive Health and Fertility (Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England, 2010).
The UCSF program provides patient guides in English and Spanish with suggestions of ways to reduce chemical exposures at work and at home.
Limits in the data
Michael Eisenberg, MD, a urologist and director of male reproductive medicine and surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, often gets questions from patients about how lifestyle and environmental exposures affect male fertility. (In her book, Dr. Swan also discusses how factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and stress can affect male and female fertility.)
He found the evidence convincing that certain chemicals impact fertility – although, of course, it isn’t ethically possible to do randomized, controlled trials in which some people are intentionally exposed to chemicals to measure the effects. Along with adopting other healthy habits, he advised patients to avoid chemical exposures.
“It’s reasonable to try to eat organic and be mindful of where some of these exposures come from and try to minimize them to the extent possible,” he said.
Rebecca Sokol, MD, MPH, an endocrinologist and expert in male reproductive health, demonstrated the toxic effects of lead on sperm production in studies conducted on rats. But she views low-dose chemical exposure from everyday products as just one aspect of modern reproductive risks, some of which have stronger associations. For example, testosterone therapy impairs sperm production, and finasteride (a medication for male pattern baldness) has been linked to a reversible decline in sperm count.
“When it comes to these ubiquitous chemicals like phthalate and BPA, we explain to the patient that maybe they’re harmful, but we can’t say for sure,” because of the lack of causal data, said Dr. Sokol, professor emerita at the University of Southern California, who was on the panel that drafted the American Urological Association and American Society of Reproductive Medicine guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility.
Nonetheless, she advised patients to try to reduce exposures. “I don’t see us eradicating all the chemicals that might be bad for us unless we go back to another era. But we can do the best we can to avoid what we can.”
A call to action
Dr. Swan likened awareness of the health threat of chemical exposures to the gradual recognition of the climate crisis as a global imperative. Yet in some ways, the scientific work on chemical effects is even more daunting. The Environmental Protection Agency lists more than 86,000 chemicals on its inventory of chemical substances manufactured or imported into the United States.
Little is known about the potential effects of many chemicals that we inhale, ingest or absorb through our skin, Dr. Swan said. In her book, she noted the impact on wildlife – for example, reproductive abnormalities in frogs, alligators, and birds that were exposed to EDCs.
Yet Dr. Swan also takes solace in the lessons from the animal kingdom. Decades after the pesticide DDT, a neurotoxin and endocrine-disruptor, was banned in the United States in 1972, the bald eagle has made a comeback from near-extinction. She also pointed to a 2018 study which found that, while mice exposed to bisphenols passed on reproductive effects to offspring, when the exposures stopped, the effects disappeared after several generations.
“If we stop poisoning ourselves, we can turn this around,” said Dr. Swan. “That’s what I want people to know.”
Count Down frames the issues in language that is much starker than typically found in academic publications. But that is what’s necessary to draw attention to the effects of chemical exposures on human health and reproduction, Dr. Swan said. “I’m saying this in fairly extreme terms to alarm people, to make them realize it is a crisis and they have to act.”
No disclosures were reported.
Chemicals that pervade our modern world – plastics, pesticides, stain repellents, components of personal hygiene products – are contributing to a decades-long decline in fertility and could pose health risks even into future generations, according to an explosive new book by Shanna Swan, PhD, an environmental and reproductive epidemiologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Dr. Swan laid out the case that endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) such as phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) threaten human existence, a conclusion that stems in part from her 2017 meta-analysis that showed a 52% drop in sperm counts from 1973 to 2011 in men in North America, Europe, and Australia.
“This alarming rate of decline could mean the human race will be unable to reproduce itself if the trend continues,” Dr. Swan said in her book, “Count Down: How Our Modern World Is Threatening Sperm Counts, Altering Male and Female Reproductive Development, and Imperiling the Future of the Human Race,” (New York: Scribner, 2021) coauthored with health journalist Stacey Colino.
Her premise that EDCs pose a risk to both male and female fertility is underscored by new research. A March 2021 article in Human Reproduction links prenatal chemical exposures to lowered fertility in a study of 1,045 Swiss military conscripts.
The Swiss men, aged 18-22 years, were significantly more likely to have low semen volume and low total sperm count if their mothers reported that they had occupational exposures to four or more endocrine-disrupting chemicals while they were pregnant. These EDCs, which mimic natural hormones, included pesticides, heavy metals, phthalates, alkylphenolic compounds, and solvents that can be found in agricultural work or hair and beauty salons.
These chemicals are not so-called “forever chemicals” that persist in the human body. But the Swiss study still showed an association between exposure during pregnancy and the future fertility of the male children. “Those apparently small exposures that pass quickly can affect development,” said Dr. Swan, who was not affiliated with the research. “It takes very little in terms of time and amount of chemicals to alter fetal development.”
Health risks beyond reproduction
While Count Down is placing a new spotlight on chemical hazards, some major medical organizations have already taken positions on the risks. “Reducing exposure to toxic environmental agents is a critical area of intervention for ob.gyns.,” the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists said in an environmental policy priority. “The Endocrine Society is concerned that human health is at risk because the current extensive scientific knowledge on EDCs and their health effects is not effectively translated to regulatory policies that fully protect populations from EDC exposures.”
But for the medical community, addressing the impact of EDCs goes beyond advocacy for regulatory and legislative changes, Dr. Swan said in an interview. Physicians should talk to patients about the importance of reducing their chemical exposure to safeguard their overall health.
“Reproductive health and particularly sperm count, subfertility, and infertility are predictors of lifelong health,” she said. That includes associations between reproductive disorders and “the risk of heart disease, obesity, reproductive cancers and, perhaps most dramatically, with a shortened lifespan.”
Some medical schools are including information on environmental health and exposure risks in the curriculum, said Tracey Woodruff, PhD, MPH, director of the program on reproductive health and the environment at the University of California, San Francisco. She urged physicians to ask patients about potential occupational exposures to hazardous chemicals and provide information about ways to reduce everyday exposures.
For example, safer options include buying organic produce, microwaving food in glass rather than plastic containers and avoiding products that contain phthalate or BPA. “If you’re going to talk to people about what they eat, that’s a perfect venue for talking about the environment,” said Dr. Woodruff, who coedited the textbook, Environmental Impacts on Reproductive Health and Fertility (Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England, 2010).
The UCSF program provides patient guides in English and Spanish with suggestions of ways to reduce chemical exposures at work and at home.
Limits in the data
Michael Eisenberg, MD, a urologist and director of male reproductive medicine and surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center, often gets questions from patients about how lifestyle and environmental exposures affect male fertility. (In her book, Dr. Swan also discusses how factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and stress can affect male and female fertility.)
He found the evidence convincing that certain chemicals impact fertility – although, of course, it isn’t ethically possible to do randomized, controlled trials in which some people are intentionally exposed to chemicals to measure the effects. Along with adopting other healthy habits, he advised patients to avoid chemical exposures.
“It’s reasonable to try to eat organic and be mindful of where some of these exposures come from and try to minimize them to the extent possible,” he said.
Rebecca Sokol, MD, MPH, an endocrinologist and expert in male reproductive health, demonstrated the toxic effects of lead on sperm production in studies conducted on rats. But she views low-dose chemical exposure from everyday products as just one aspect of modern reproductive risks, some of which have stronger associations. For example, testosterone therapy impairs sperm production, and finasteride (a medication for male pattern baldness) has been linked to a reversible decline in sperm count.
“When it comes to these ubiquitous chemicals like phthalate and BPA, we explain to the patient that maybe they’re harmful, but we can’t say for sure,” because of the lack of causal data, said Dr. Sokol, professor emerita at the University of Southern California, who was on the panel that drafted the American Urological Association and American Society of Reproductive Medicine guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility.
Nonetheless, she advised patients to try to reduce exposures. “I don’t see us eradicating all the chemicals that might be bad for us unless we go back to another era. But we can do the best we can to avoid what we can.”
A call to action
Dr. Swan likened awareness of the health threat of chemical exposures to the gradual recognition of the climate crisis as a global imperative. Yet in some ways, the scientific work on chemical effects is even more daunting. The Environmental Protection Agency lists more than 86,000 chemicals on its inventory of chemical substances manufactured or imported into the United States.
Little is known about the potential effects of many chemicals that we inhale, ingest or absorb through our skin, Dr. Swan said. In her book, she noted the impact on wildlife – for example, reproductive abnormalities in frogs, alligators, and birds that were exposed to EDCs.
Yet Dr. Swan also takes solace in the lessons from the animal kingdom. Decades after the pesticide DDT, a neurotoxin and endocrine-disruptor, was banned in the United States in 1972, the bald eagle has made a comeback from near-extinction. She also pointed to a 2018 study which found that, while mice exposed to bisphenols passed on reproductive effects to offspring, when the exposures stopped, the effects disappeared after several generations.
“If we stop poisoning ourselves, we can turn this around,” said Dr. Swan. “That’s what I want people to know.”
Count Down frames the issues in language that is much starker than typically found in academic publications. But that is what’s necessary to draw attention to the effects of chemical exposures on human health and reproduction, Dr. Swan said. “I’m saying this in fairly extreme terms to alarm people, to make them realize it is a crisis and they have to act.”
No disclosures were reported.
Helping your obese patient achieve a healthier weight
In 2015-2016, almost 40% of adults and 18.5% of children ages 2 to 19 years in the United States met the definition for obesity—a chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that results in adverse metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial health consequences.1,2
Tremendous resources have been invested in research, policy development, and public education to try to prevent obesity and its related complications. Despite this, the obesity epidemic has worsened. Here, we explore how to evaluate and treat obese patients in a primary care setting based on the evidence and our experience seeing patients specifically for weight management in a family medicine residency teaching clinic. Pharmacotherapy and surgery, while often helpful, are outside the scope of this article.
It begins withan obesity-friendly office
Patients may have reservations about health care interactions specific to obesity, so it is important to invite them into a setting that facilitates trust and encourages collaboration. Actively engage patients with unhealthy weight by creating an environment where they feel comfortable. Offer wide chairs without armrests, which will easily accommodate patients of all sizes, and ensure that scales have a weight capacity > 400 lb. Communicate a message to patients, via waiting room materials and videos, that focuses on health rather than on weight or body mass index (BMI).
Understand the patient’s goals and challenges
Most (although not all) family physicians will see obese patients in the context of a visit for diabetes, hypertension, or another condition. However, we feel that having visits specifically to address weight in the initial stages of weight management is helpful. The focus of an initial visit should be getting to know how obesity has affected the patient and what his or her motive is in attempting to lose weight. Explore previous attempts at weight loss and establish what the patient’s highest weight has been, as this will impact weight-loss goals. For example, if a patient has weighed > 300 lb all her adult life, it will be extremely difficult to maintain a weight loss of 150 lb.
What else to ask about. Discuss stressors that may be causing increased food intake or poor food choices, including hunger, anger, loneliness, and sleep difficulties. Multidisciplinary care including a psychologist can aid in addressing these issues. Ask patients if they keep a food diary (and if not, recommend that they start), as food diaries are often helpful in elucidating eating and drinking patterns. Determine a patient’s current and past levels of physical activity, as this will guide the fitness goals you develop for him or her.
Screen for psychosocial disorders
As noted earlier, the physical component of obesity is commonly associated with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.2 This requires a multidisciplinary team effort to facilitate healing in the patient struggling with obesity.
Screening for depression and anxiety using standardized tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 is encouraged in patients who are overweight or obese. Positive screens should be addressed as part of the patient’s treatment plan, as untreated depression and anxiety can inhibit success with weight loss. Be mindful that many medications commonly used to treat these conditions can impair weight loss and even promote weight gain.
Continue to: Don't overlook binge-eating disorders
Don’t overlook binge-eating disorders. Screening specifically for binge-eating disorders is important, given the implications on treatment. The US Department of Veterans Affairs developed a single-item tool for this purpose, the VA Binge Eating Screener. The validated questionnaire asks, “On average, how often have you eaten extremely large amounts of food at one time and felt that your eating was out of control at that time?” Response options are: “Never,” “< 1 time/week,” “1 time/week,” “2-4 times/week,” and “5+ times/week.” A response of ≥ 2 times/week had a sensitivity of 88.9% and specificity of 83.2% for binge-eating disorder.3
Patients with positive screens should undergo psychotherapy and consider pharmacotherapy with lisdexamfetamine as part of their treatment plan. Caution should be used if recommending intermittent fasting for someone with binge-eating disorder.
Evaluate for underlying causes and assess for comorbidities
Review the patient’s current medication list and history. Many medications can cause weight gain, and weight loss can often be achieved by deprescribing such medications. When feasible, prescribe an alternative medication with a more favorable weight profile. A previous article in The Journal of Family Practice addresses this in more depth.4
Laboratory and other testing
Laboratory analysis should primarily be focused on determining treatment alterations specific to underlying pathophysiology. Tests to consider ordering are outlined in the Table
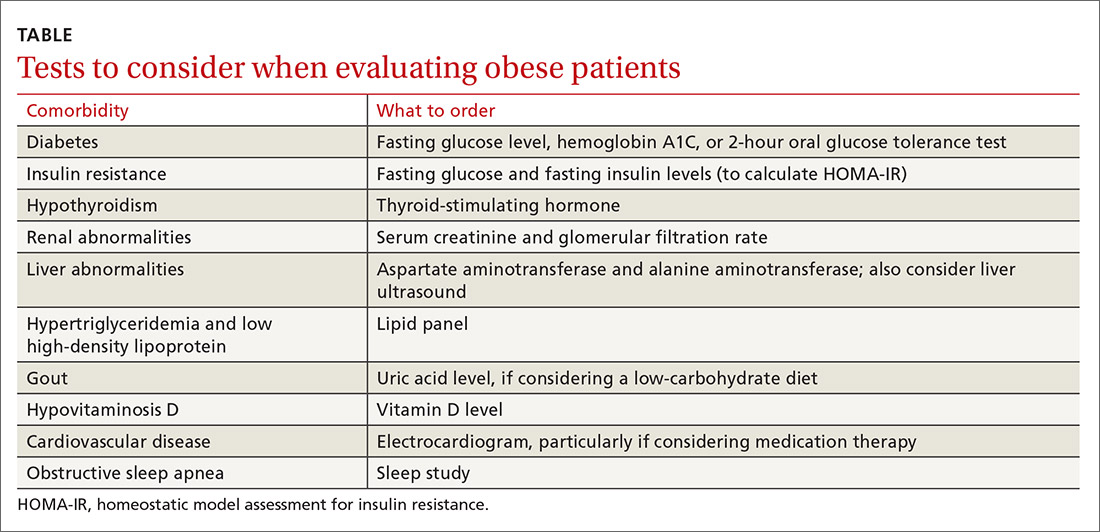
Diabetes and insulin resistance. The American Diabetes Association recommends screening patients who are overweight or obese and have an additional risk factor for diabetes.5 This can be done by obtaining a fasting glucose level, hemoglobin A1C, or a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test.
Continue to: Since it is known that...
Since it is known that insulin resistance increases the risk for coronary heart disease6 and can be treated effectively,7 we recommend testing for insulin resistance in patients who do not already have impaired fasting glucose, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance. The homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)8 is a measure of insulin resistance and can be calculated from the fasting insulin and fasting glucose levels. This measure should not be done in isolation, but it can be a useful adjunct in identifying patients with insulin resistance and directing treatment.
If there is evidence of diabetes or insulin resistance, consider treatment with metformin ± initiation of a low-carbohydrate diet.
Hypothyroidism. Consider screening for thyroid dysfunction with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level, if it has not been checked previously.
Renal abnormalities. When serum creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate indicate chronic kidney disease, consider recommending a protein-restricted diet and adjust medications according to renal dosing protocols, as indicated.
Liver abnormalities, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Monitor aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase for resolution of elevations as weight loss is achieved. If abnormalities persist, consider ordering a liver ultrasound. Traditionally, low-calorie diets have been prescribed to treat NAFLD, but evidence shows that low-carbohydrate diets can also be effective.9
Continue to: Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Obtain a lipid panel if one has not been completed within the past several years, as hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL can improve dramatically with specific dietary changes.7 Observe trends to assess for resolution of lipid abnormalities as weight loss is achieved.
Gout. Consider checking a uric acid level if you are thinking about recommending a low-carbohydrate diet, particularly in patients with a history of gout, as this may temporarily increase the risk of gout flare.
Hypovitaminosis D. If the patient’s vitamin D level is low, consider appropriate supplementation to support the patient’s overall health. While vitamin D deficiency is common in obesity, the role of supplementation in this population is unclear.
Cardiovascular disease. Consider ordering an electrocardiogram, particularly if you are thinking of prescribing medication therapy. Use caution with initiation of certain medications, such as phentermine or diethylproprion, in the presence of arrhythmias or active cardiovascular disease.
Obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep health is important to address, since obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea.10 If your patient is given a diagnosis of OSA following a sleep study, consider treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), although there are conflicting studies regarding the effects of CPAP therapy in OSA on weight.11,12
Continue to: Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Addressing obesity with patients can be challenging in a busy primary care clinic, but it is imperative to helping patients achieve overall health. Counseling on nutrition and physical activity is an important part of this process.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition counseling. Focus on creating individualized plans through which patients can achieve success. Some guidance follows, but also beware of common pitfalls that we have observed in clinical practice which, when addressed, can enable significant weight loss (see “Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss”).
SIDEBAR
Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss
On the part of the patient:
- Continuing to consume substantial amounts of high-calorie drinks.
- Taking in excessive amounts of sugar-rich foods, including cough drops.
- Using non-nutritive sweeteners (eg, aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and erythritol). Although the mechanism is not certain, some people are able to lose weight while consuming these substances, while others are not.
On the part of the provider:
- Prescribing a diet that the patient cannot sustain long term.
- Overlooking the issue of food availability for the patient.
Choose an approach that works for the patient. Commonly prescribed diets to address obesity include, but are not limited to, Atkins, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Glycemic Index, Mediterranean, Ornish, Paleolithic, Zone, whole food plant-based, and ketogenic. We attempt to engage patients in making the decision on what food choices are appropriate for them considering their food availability, culture, and belief systems. For patients who prefer a vegan or vegetarian whole food diet, it is important to note that these diets are generally deficient in vitamin B12 and omega 3 fatty acids, so supplementing these should be considered.
Rather than focus on a specific diet, which may not be sustainable long term, encourage healthy eating habits. Low-carbohydrate diets have been shown to promote greater weight loss compared to low-fat diets.13,14 Low-calorie diets can also be quite effective in promoting short-term weight loss. In our clinic, when weight loss is the primary goal, patients are typically encouraged to focus on either calorie or carbohydrate restriction in the initial stages of weight loss.
Eliminate sugar and refined carbohydrates. While rigorous mortality data are not available, more recent trials have demonstrated significant improvements in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk markers, including weight reduction and diabetes reversal, when following a diet that markedly decreases carbohydrate intake, especially sugar and refined carbohydrates.7,14-17
Continue to: We recommend that patients focus...
We recommend that patients focus on eliminating sweetened beverages, such as soft drinks, sports drinks, energy drinks, vitamin water, sweet tea, chocolate milk, and Frappuccinos. We also recommend substantially limiting or eliminating fruit juices and fruit smoothies due to their high sugar content. For example, 8 oz of orange juice contains 26 g of carbohydrates, which is almost as much as 8 oz of soda.
Compared with eating whole fruit, consuming fruit juice has demonstrated a small amount of weight gain in young children and adults.18,19 It also has shown a higher insulin response compared with eating the same amount of carbohydrates in whole fruit.20 Better options to drink include water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee. Also, avoid ultra-processed carbohydrates from foods such as breads, cereals, and pastries, as they have similar effects on blood glucose when compared to sugar.21
Greatly restrict highly processed foods. The evidence suggests that the availability of processed food is associated with increasing obesity.22 Simple advice to offer your patients is to encourage them to shop the perimeter of the grocery store, where fresh produce, meat, and dairy products are primarily located, and avoid the inner aisles, which contain primarily processed foods. Choosing food items with 5 or fewer ingredients is a starting point when teaching patients to read labels.
Consider limiting saturated fats. In 1977, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommended that Americans eat no more than 30% of total energy intake from fat and less than 10% of total energy intake from saturated fat; however, no randomized controlled trials had been done that supported this recommendation and epidemiologic data supporting it were weak.23
The 2015 Dietary Guidelines continue to recommend limiting total energy intake from saturated fats.24 While there may be a small decrease in cardiovascular risk with a reduction of saturated fat intake and replacement with unsaturated fats, no overall mortality benefit has been demonstrated.24,25 More research is needed in this area to guide patients in decisions regarding consumption of saturated fats and what types of unsaturated fats are best for their health.
Continue to: Eat only 3 meals per day
Eat only 3 meals per day, but aim for fewer than that. The prescription of fasting is a modality that can be used for weight loss and improved health. Fasting has been a prescribed healing practice for thousands of years.26 It is a practice that virtually every major religion in the world embraces. Studies have demonstrated fasting to be safe and effective in the setting of obesity without significant comorbidities, and it may promote weight loss and metabolic health.26-29
There are multiple types of intermittent fasting. A practical way for patients to start is by restricting the number of hours in which they eat or drink calorie-containing beverages to 8 hours per day. In our experience, this regimen is easier for most patients to follow than alternate-day or other longer fasts. While there has been caution in the prescription of intermittent fasting due to concerns about causing eating disorders, a recent small study did not demonstrate increased risk of eating disorders with daily intermittent fasting.30
Participate in healthy exercise. Nonpharmacologic office-based strategies for treating obesity have generally focused on increasing exercise and decreasing caloric intake.31 While exercise has significant health benefits, including preventing weight regain, evidence does not support monotherapy with exercise as an effective long-term weight-loss strategy.32 There are no studies available that adequately support prescribing an exact dose of exercise.33 Generally, less than 150 minutes of exercise per week is not effective and more than that does have a dose-related response.33
Follow up to help patients stay on target
There is no ideal interval for follow-up visits. However, frequent visits—anywhere from weekly to monthly—in the initial stages of weight loss increase the patient’s sense of accountability and, in our experience, seem to be helpful.
Patients may also choose to track their progress by weighing themselves regularly. A small study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that patients who weighed themselves daily had greater and more sustained weight loss than those who didn’t.34 But the decision of whether to weigh one’s self at home should be individualized for each patient.
CORRESPONDENCE
Wesley Eichorn, DO, 1000 Oakland Drive, Kalamazoo, MI 49008; [email protected]
1. Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015-2016 key findings data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NCHS Data Brief. 2017;(288):1-8.
2. Seger JC, Horn DB, Westman EC, et al. Obesity Algorithm, presented by the Obesity Medicine Association. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.obesityalgorithm.org. 2016-2017
3. Dorflinger LM, Ruser CB, Masheb RM. A brief screening measure for binge eating in primary care. Eat Behav. 2017;26:163-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.03.009
4. Saunders KH, Igel LI, Shukla AP, et al. Drug-induced weight gain: rethinking our choices. J Fam Pract. 2016;65:780-788.
5. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(suppl 1):S13-S28. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S002
6. Reaven G. Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease in nondiabetic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:1754-1759. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241885/-/DC1
7. Hallberg S, McKenzie A, Williams P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of a novel care model for the management of type 2 diabetes at 1 year: an open-label, non-randomized, controlled study. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9:583-612. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare
8. Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1487-1495.
9. Vilar-Gomez E, Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, et al. Post hoc analyses of surrogate markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes in a digitally supported continuous care intervention: an open-label, non-randomised controlled study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e023597. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023597
10. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217-1239. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2109080
11. Drager LF, Brunoni AR, Jenner R, et al. Effects of CPAP on body weight in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Thorax. 2015;70:258-264. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205361
12. Bosworth T. CPAP use associated with greater weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea. CHEST Physician. Published March 29, 2019. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.mdedge.com/chestphysician/article/197827/sleep-medicine/cpap-use-associated-greater-weight-loss-obese-patients
13. Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JAE, et al. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:968-979. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00367-8
14. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
15. Bezerra Bueno N, Vieira De Melo IS, Lima De Oliveira S, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513000548
16. Santos FL, Esteves SS, da Costa Pereira A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of the effects of low carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors. Obes Rev. 2012;13:1048-1066. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01021.x
17. Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, Hallberg SJ, et al. Long-term effects of a novel continuous remote care intervention including nutritional ketosis for the management of type 2 diabetes: a 2-year non-randomized clinical trial. bioRxiv. 2018;10:348. https://doi.org/10.1101/476275
18. Auerbach BJ, Dibey S, Vallila-Buchman P, et al. Review of 100% fruit juice and chronic health conditions: implications for sugar-sweetened beverage policy. Adv Nutr. 2018;9:78-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmx006
19. Faith MS, Dennison BA, Edmunds LS, et al. Fruit juice intake predicts increased adiposity gain in children from low-income families: weight status-by-environment interaction. Pediatrics. 2006;118:2066-2075. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-1117
20. Bolton RP, Burroughs LF, Heaton KW. The role of dietary fiber in satiety, insulin: studies with fruit and fruit. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;84:211-217. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/34.2.211
21. Unwin D, Haslam D, Livesey G. It is the glycaemic response to, not the carbohydrate content of food that matters in diabetes and obesity: the glycaemic index revisited. J Insul Resist. 2016;1(1):a8. https://doi.org/10.4102/jir.v1i1.8
22. Monteiro CA, Moubarac JC, Levy RB, et al. Household availability of ultra-processed foods and obesity in nineteen European countries. Public Health Nutr. 2018;21:18-26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980017001379
23. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, Cooper SM, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials did not support the introduction of dietary fat guidelines in 1977 and 1983: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2015;2:e000196. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2014
24. US Department of Health and Human Services and US Department of Agriculture. 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th edition. Published December 2015. Accessed March 5, 2021. http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/
25. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, DiNicolantonio JJ, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials does not support current dietary fat guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2016;3:e000409. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2016-000409
26. Fung J. The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight Loss. Greystone Books; 2016.
27. Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;39:46-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.005
28. Patterson RE, Sears DD. Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting. Annu Rev Nutr. 2017; 37:371-393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
29. Duncan GG. Intermittent fasts in the correction and control of intractable obesity. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1962;74:121-129.
30. Gabel K, Hoddy KK, Varady KA. Safety of 8-h time restricted feeding in adults with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44:107-109. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2018-0389
31. Erlandson M, Ivey LC, Seikel K. Update on office-based strategies for the management of obesity. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:361-368.
32. Malhotra A, Noakes T, Phinney S. It is time to bust the myth of physical inactivity and obesity: you cannot outrun a bad diet. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49:967-968. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-094911
33. Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, et al. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:459-471. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181949333
34. Zheng Y, Burke LE, Danford CA, et al. Patterns of self-weighing behavior and weight change in a weight loss trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40:1392-1396. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.68
In 2015-2016, almost 40% of adults and 18.5% of children ages 2 to 19 years in the United States met the definition for obesity—a chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that results in adverse metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial health consequences.1,2
Tremendous resources have been invested in research, policy development, and public education to try to prevent obesity and its related complications. Despite this, the obesity epidemic has worsened. Here, we explore how to evaluate and treat obese patients in a primary care setting based on the evidence and our experience seeing patients specifically for weight management in a family medicine residency teaching clinic. Pharmacotherapy and surgery, while often helpful, are outside the scope of this article.
It begins withan obesity-friendly office
Patients may have reservations about health care interactions specific to obesity, so it is important to invite them into a setting that facilitates trust and encourages collaboration. Actively engage patients with unhealthy weight by creating an environment where they feel comfortable. Offer wide chairs without armrests, which will easily accommodate patients of all sizes, and ensure that scales have a weight capacity > 400 lb. Communicate a message to patients, via waiting room materials and videos, that focuses on health rather than on weight or body mass index (BMI).
Understand the patient’s goals and challenges
Most (although not all) family physicians will see obese patients in the context of a visit for diabetes, hypertension, or another condition. However, we feel that having visits specifically to address weight in the initial stages of weight management is helpful. The focus of an initial visit should be getting to know how obesity has affected the patient and what his or her motive is in attempting to lose weight. Explore previous attempts at weight loss and establish what the patient’s highest weight has been, as this will impact weight-loss goals. For example, if a patient has weighed > 300 lb all her adult life, it will be extremely difficult to maintain a weight loss of 150 lb.
What else to ask about. Discuss stressors that may be causing increased food intake or poor food choices, including hunger, anger, loneliness, and sleep difficulties. Multidisciplinary care including a psychologist can aid in addressing these issues. Ask patients if they keep a food diary (and if not, recommend that they start), as food diaries are often helpful in elucidating eating and drinking patterns. Determine a patient’s current and past levels of physical activity, as this will guide the fitness goals you develop for him or her.
Screen for psychosocial disorders
As noted earlier, the physical component of obesity is commonly associated with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.2 This requires a multidisciplinary team effort to facilitate healing in the patient struggling with obesity.
Screening for depression and anxiety using standardized tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 is encouraged in patients who are overweight or obese. Positive screens should be addressed as part of the patient’s treatment plan, as untreated depression and anxiety can inhibit success with weight loss. Be mindful that many medications commonly used to treat these conditions can impair weight loss and even promote weight gain.
Continue to: Don't overlook binge-eating disorders
Don’t overlook binge-eating disorders. Screening specifically for binge-eating disorders is important, given the implications on treatment. The US Department of Veterans Affairs developed a single-item tool for this purpose, the VA Binge Eating Screener. The validated questionnaire asks, “On average, how often have you eaten extremely large amounts of food at one time and felt that your eating was out of control at that time?” Response options are: “Never,” “< 1 time/week,” “1 time/week,” “2-4 times/week,” and “5+ times/week.” A response of ≥ 2 times/week had a sensitivity of 88.9% and specificity of 83.2% for binge-eating disorder.3
Patients with positive screens should undergo psychotherapy and consider pharmacotherapy with lisdexamfetamine as part of their treatment plan. Caution should be used if recommending intermittent fasting for someone with binge-eating disorder.
Evaluate for underlying causes and assess for comorbidities
Review the patient’s current medication list and history. Many medications can cause weight gain, and weight loss can often be achieved by deprescribing such medications. When feasible, prescribe an alternative medication with a more favorable weight profile. A previous article in The Journal of Family Practice addresses this in more depth.4
Laboratory and other testing
Laboratory analysis should primarily be focused on determining treatment alterations specific to underlying pathophysiology. Tests to consider ordering are outlined in the Table

Diabetes and insulin resistance. The American Diabetes Association recommends screening patients who are overweight or obese and have an additional risk factor for diabetes.5 This can be done by obtaining a fasting glucose level, hemoglobin A1C, or a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test.
Continue to: Since it is known that...
Since it is known that insulin resistance increases the risk for coronary heart disease6 and can be treated effectively,7 we recommend testing for insulin resistance in patients who do not already have impaired fasting glucose, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance. The homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)8 is a measure of insulin resistance and can be calculated from the fasting insulin and fasting glucose levels. This measure should not be done in isolation, but it can be a useful adjunct in identifying patients with insulin resistance and directing treatment.
If there is evidence of diabetes or insulin resistance, consider treatment with metformin ± initiation of a low-carbohydrate diet.
Hypothyroidism. Consider screening for thyroid dysfunction with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level, if it has not been checked previously.
Renal abnormalities. When serum creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate indicate chronic kidney disease, consider recommending a protein-restricted diet and adjust medications according to renal dosing protocols, as indicated.
Liver abnormalities, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Monitor aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase for resolution of elevations as weight loss is achieved. If abnormalities persist, consider ordering a liver ultrasound. Traditionally, low-calorie diets have been prescribed to treat NAFLD, but evidence shows that low-carbohydrate diets can also be effective.9
Continue to: Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Obtain a lipid panel if one has not been completed within the past several years, as hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL can improve dramatically with specific dietary changes.7 Observe trends to assess for resolution of lipid abnormalities as weight loss is achieved.
Gout. Consider checking a uric acid level if you are thinking about recommending a low-carbohydrate diet, particularly in patients with a history of gout, as this may temporarily increase the risk of gout flare.
Hypovitaminosis D. If the patient’s vitamin D level is low, consider appropriate supplementation to support the patient’s overall health. While vitamin D deficiency is common in obesity, the role of supplementation in this population is unclear.
Cardiovascular disease. Consider ordering an electrocardiogram, particularly if you are thinking of prescribing medication therapy. Use caution with initiation of certain medications, such as phentermine or diethylproprion, in the presence of arrhythmias or active cardiovascular disease.
Obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep health is important to address, since obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea.10 If your patient is given a diagnosis of OSA following a sleep study, consider treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), although there are conflicting studies regarding the effects of CPAP therapy in OSA on weight.11,12
Continue to: Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Addressing obesity with patients can be challenging in a busy primary care clinic, but it is imperative to helping patients achieve overall health. Counseling on nutrition and physical activity is an important part of this process.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition counseling. Focus on creating individualized plans through which patients can achieve success. Some guidance follows, but also beware of common pitfalls that we have observed in clinical practice which, when addressed, can enable significant weight loss (see “Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss”).
SIDEBAR
Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss
On the part of the patient:
- Continuing to consume substantial amounts of high-calorie drinks.
- Taking in excessive amounts of sugar-rich foods, including cough drops.
- Using non-nutritive sweeteners (eg, aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and erythritol). Although the mechanism is not certain, some people are able to lose weight while consuming these substances, while others are not.
On the part of the provider:
- Prescribing a diet that the patient cannot sustain long term.
- Overlooking the issue of food availability for the patient.
Choose an approach that works for the patient. Commonly prescribed diets to address obesity include, but are not limited to, Atkins, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Glycemic Index, Mediterranean, Ornish, Paleolithic, Zone, whole food plant-based, and ketogenic. We attempt to engage patients in making the decision on what food choices are appropriate for them considering their food availability, culture, and belief systems. For patients who prefer a vegan or vegetarian whole food diet, it is important to note that these diets are generally deficient in vitamin B12 and omega 3 fatty acids, so supplementing these should be considered.
Rather than focus on a specific diet, which may not be sustainable long term, encourage healthy eating habits. Low-carbohydrate diets have been shown to promote greater weight loss compared to low-fat diets.13,14 Low-calorie diets can also be quite effective in promoting short-term weight loss. In our clinic, when weight loss is the primary goal, patients are typically encouraged to focus on either calorie or carbohydrate restriction in the initial stages of weight loss.
Eliminate sugar and refined carbohydrates. While rigorous mortality data are not available, more recent trials have demonstrated significant improvements in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk markers, including weight reduction and diabetes reversal, when following a diet that markedly decreases carbohydrate intake, especially sugar and refined carbohydrates.7,14-17
Continue to: We recommend that patients focus...
We recommend that patients focus on eliminating sweetened beverages, such as soft drinks, sports drinks, energy drinks, vitamin water, sweet tea, chocolate milk, and Frappuccinos. We also recommend substantially limiting or eliminating fruit juices and fruit smoothies due to their high sugar content. For example, 8 oz of orange juice contains 26 g of carbohydrates, which is almost as much as 8 oz of soda.
Compared with eating whole fruit, consuming fruit juice has demonstrated a small amount of weight gain in young children and adults.18,19 It also has shown a higher insulin response compared with eating the same amount of carbohydrates in whole fruit.20 Better options to drink include water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee. Also, avoid ultra-processed carbohydrates from foods such as breads, cereals, and pastries, as they have similar effects on blood glucose when compared to sugar.21
Greatly restrict highly processed foods. The evidence suggests that the availability of processed food is associated with increasing obesity.22 Simple advice to offer your patients is to encourage them to shop the perimeter of the grocery store, where fresh produce, meat, and dairy products are primarily located, and avoid the inner aisles, which contain primarily processed foods. Choosing food items with 5 or fewer ingredients is a starting point when teaching patients to read labels.
Consider limiting saturated fats. In 1977, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommended that Americans eat no more than 30% of total energy intake from fat and less than 10% of total energy intake from saturated fat; however, no randomized controlled trials had been done that supported this recommendation and epidemiologic data supporting it were weak.23
The 2015 Dietary Guidelines continue to recommend limiting total energy intake from saturated fats.24 While there may be a small decrease in cardiovascular risk with a reduction of saturated fat intake and replacement with unsaturated fats, no overall mortality benefit has been demonstrated.24,25 More research is needed in this area to guide patients in decisions regarding consumption of saturated fats and what types of unsaturated fats are best for their health.
Continue to: Eat only 3 meals per day
Eat only 3 meals per day, but aim for fewer than that. The prescription of fasting is a modality that can be used for weight loss and improved health. Fasting has been a prescribed healing practice for thousands of years.26 It is a practice that virtually every major religion in the world embraces. Studies have demonstrated fasting to be safe and effective in the setting of obesity without significant comorbidities, and it may promote weight loss and metabolic health.26-29
There are multiple types of intermittent fasting. A practical way for patients to start is by restricting the number of hours in which they eat or drink calorie-containing beverages to 8 hours per day. In our experience, this regimen is easier for most patients to follow than alternate-day or other longer fasts. While there has been caution in the prescription of intermittent fasting due to concerns about causing eating disorders, a recent small study did not demonstrate increased risk of eating disorders with daily intermittent fasting.30
Participate in healthy exercise. Nonpharmacologic office-based strategies for treating obesity have generally focused on increasing exercise and decreasing caloric intake.31 While exercise has significant health benefits, including preventing weight regain, evidence does not support monotherapy with exercise as an effective long-term weight-loss strategy.32 There are no studies available that adequately support prescribing an exact dose of exercise.33 Generally, less than 150 minutes of exercise per week is not effective and more than that does have a dose-related response.33
Follow up to help patients stay on target
There is no ideal interval for follow-up visits. However, frequent visits—anywhere from weekly to monthly—in the initial stages of weight loss increase the patient’s sense of accountability and, in our experience, seem to be helpful.
Patients may also choose to track their progress by weighing themselves regularly. A small study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that patients who weighed themselves daily had greater and more sustained weight loss than those who didn’t.34 But the decision of whether to weigh one’s self at home should be individualized for each patient.
CORRESPONDENCE
Wesley Eichorn, DO, 1000 Oakland Drive, Kalamazoo, MI 49008; [email protected]
In 2015-2016, almost 40% of adults and 18.5% of children ages 2 to 19 years in the United States met the definition for obesity—a chronic, relapsing, multifactorial, neurobehavioral disease that results in adverse metabolic, biomechanical, and psychosocial health consequences.1,2
Tremendous resources have been invested in research, policy development, and public education to try to prevent obesity and its related complications. Despite this, the obesity epidemic has worsened. Here, we explore how to evaluate and treat obese patients in a primary care setting based on the evidence and our experience seeing patients specifically for weight management in a family medicine residency teaching clinic. Pharmacotherapy and surgery, while often helpful, are outside the scope of this article.
It begins withan obesity-friendly office
Patients may have reservations about health care interactions specific to obesity, so it is important to invite them into a setting that facilitates trust and encourages collaboration. Actively engage patients with unhealthy weight by creating an environment where they feel comfortable. Offer wide chairs without armrests, which will easily accommodate patients of all sizes, and ensure that scales have a weight capacity > 400 lb. Communicate a message to patients, via waiting room materials and videos, that focuses on health rather than on weight or body mass index (BMI).
Understand the patient’s goals and challenges
Most (although not all) family physicians will see obese patients in the context of a visit for diabetes, hypertension, or another condition. However, we feel that having visits specifically to address weight in the initial stages of weight management is helpful. The focus of an initial visit should be getting to know how obesity has affected the patient and what his or her motive is in attempting to lose weight. Explore previous attempts at weight loss and establish what the patient’s highest weight has been, as this will impact weight-loss goals. For example, if a patient has weighed > 300 lb all her adult life, it will be extremely difficult to maintain a weight loss of 150 lb.
What else to ask about. Discuss stressors that may be causing increased food intake or poor food choices, including hunger, anger, loneliness, and sleep difficulties. Multidisciplinary care including a psychologist can aid in addressing these issues. Ask patients if they keep a food diary (and if not, recommend that they start), as food diaries are often helpful in elucidating eating and drinking patterns. Determine a patient’s current and past levels of physical activity, as this will guide the fitness goals you develop for him or her.
Screen for psychosocial disorders
As noted earlier, the physical component of obesity is commonly associated with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.2 This requires a multidisciplinary team effort to facilitate healing in the patient struggling with obesity.
Screening for depression and anxiety using standardized tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 is encouraged in patients who are overweight or obese. Positive screens should be addressed as part of the patient’s treatment plan, as untreated depression and anxiety can inhibit success with weight loss. Be mindful that many medications commonly used to treat these conditions can impair weight loss and even promote weight gain.
Continue to: Don't overlook binge-eating disorders
Don’t overlook binge-eating disorders. Screening specifically for binge-eating disorders is important, given the implications on treatment. The US Department of Veterans Affairs developed a single-item tool for this purpose, the VA Binge Eating Screener. The validated questionnaire asks, “On average, how often have you eaten extremely large amounts of food at one time and felt that your eating was out of control at that time?” Response options are: “Never,” “< 1 time/week,” “1 time/week,” “2-4 times/week,” and “5+ times/week.” A response of ≥ 2 times/week had a sensitivity of 88.9% and specificity of 83.2% for binge-eating disorder.3
Patients with positive screens should undergo psychotherapy and consider pharmacotherapy with lisdexamfetamine as part of their treatment plan. Caution should be used if recommending intermittent fasting for someone with binge-eating disorder.
Evaluate for underlying causes and assess for comorbidities
Review the patient’s current medication list and history. Many medications can cause weight gain, and weight loss can often be achieved by deprescribing such medications. When feasible, prescribe an alternative medication with a more favorable weight profile. A previous article in The Journal of Family Practice addresses this in more depth.4
Laboratory and other testing
Laboratory analysis should primarily be focused on determining treatment alterations specific to underlying pathophysiology. Tests to consider ordering are outlined in the Table

Diabetes and insulin resistance. The American Diabetes Association recommends screening patients who are overweight or obese and have an additional risk factor for diabetes.5 This can be done by obtaining a fasting glucose level, hemoglobin A1C, or a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test.
Continue to: Since it is known that...
Since it is known that insulin resistance increases the risk for coronary heart disease6 and can be treated effectively,7 we recommend testing for insulin resistance in patients who do not already have impaired fasting glucose, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance. The homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)8 is a measure of insulin resistance and can be calculated from the fasting insulin and fasting glucose levels. This measure should not be done in isolation, but it can be a useful adjunct in identifying patients with insulin resistance and directing treatment.
If there is evidence of diabetes or insulin resistance, consider treatment with metformin ± initiation of a low-carbohydrate diet.
Hypothyroidism. Consider screening for thyroid dysfunction with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level, if it has not been checked previously.
Renal abnormalities. When serum creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate indicate chronic kidney disease, consider recommending a protein-restricted diet and adjust medications according to renal dosing protocols, as indicated.
Liver abnormalities, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Monitor aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase for resolution of elevations as weight loss is achieved. If abnormalities persist, consider ordering a liver ultrasound. Traditionally, low-calorie diets have been prescribed to treat NAFLD, but evidence shows that low-carbohydrate diets can also be effective.9
Continue to: Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
Hypertriglyceridemia and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Obtain a lipid panel if one has not been completed within the past several years, as hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL can improve dramatically with specific dietary changes.7 Observe trends to assess for resolution of lipid abnormalities as weight loss is achieved.
Gout. Consider checking a uric acid level if you are thinking about recommending a low-carbohydrate diet, particularly in patients with a history of gout, as this may temporarily increase the risk of gout flare.
Hypovitaminosis D. If the patient’s vitamin D level is low, consider appropriate supplementation to support the patient’s overall health. While vitamin D deficiency is common in obesity, the role of supplementation in this population is unclear.
Cardiovascular disease. Consider ordering an electrocardiogram, particularly if you are thinking of prescribing medication therapy. Use caution with initiation of certain medications, such as phentermine or diethylproprion, in the presence of arrhythmias or active cardiovascular disease.
Obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep health is important to address, since obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea.10 If your patient is given a diagnosis of OSA following a sleep study, consider treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), although there are conflicting studies regarding the effects of CPAP therapy in OSA on weight.11,12
Continue to: Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Provide guidance on lifestyle changes
Addressing obesity with patients can be challenging in a busy primary care clinic, but it is imperative to helping patients achieve overall health. Counseling on nutrition and physical activity is an important part of this process.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition counseling. Focus on creating individualized plans through which patients can achieve success. Some guidance follows, but also beware of common pitfalls that we have observed in clinical practice which, when addressed, can enable significant weight loss (see “Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss”).
SIDEBAR
Common pitfalls inhibiting weight loss
On the part of the patient:
- Continuing to consume substantial amounts of high-calorie drinks.
- Taking in excessive amounts of sugar-rich foods, including cough drops.
- Using non-nutritive sweeteners (eg, aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and erythritol). Although the mechanism is not certain, some people are able to lose weight while consuming these substances, while others are not.
On the part of the provider:
- Prescribing a diet that the patient cannot sustain long term.
- Overlooking the issue of food availability for the patient.
Choose an approach that works for the patient. Commonly prescribed diets to address obesity include, but are not limited to, Atkins, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), Glycemic Index, Mediterranean, Ornish, Paleolithic, Zone, whole food plant-based, and ketogenic. We attempt to engage patients in making the decision on what food choices are appropriate for them considering their food availability, culture, and belief systems. For patients who prefer a vegan or vegetarian whole food diet, it is important to note that these diets are generally deficient in vitamin B12 and omega 3 fatty acids, so supplementing these should be considered.
Rather than focus on a specific diet, which may not be sustainable long term, encourage healthy eating habits. Low-carbohydrate diets have been shown to promote greater weight loss compared to low-fat diets.13,14 Low-calorie diets can also be quite effective in promoting short-term weight loss. In our clinic, when weight loss is the primary goal, patients are typically encouraged to focus on either calorie or carbohydrate restriction in the initial stages of weight loss.
Eliminate sugar and refined carbohydrates. While rigorous mortality data are not available, more recent trials have demonstrated significant improvements in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk markers, including weight reduction and diabetes reversal, when following a diet that markedly decreases carbohydrate intake, especially sugar and refined carbohydrates.7,14-17
Continue to: We recommend that patients focus...
We recommend that patients focus on eliminating sweetened beverages, such as soft drinks, sports drinks, energy drinks, vitamin water, sweet tea, chocolate milk, and Frappuccinos. We also recommend substantially limiting or eliminating fruit juices and fruit smoothies due to their high sugar content. For example, 8 oz of orange juice contains 26 g of carbohydrates, which is almost as much as 8 oz of soda.
Compared with eating whole fruit, consuming fruit juice has demonstrated a small amount of weight gain in young children and adults.18,19 It also has shown a higher insulin response compared with eating the same amount of carbohydrates in whole fruit.20 Better options to drink include water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee. Also, avoid ultra-processed carbohydrates from foods such as breads, cereals, and pastries, as they have similar effects on blood glucose when compared to sugar.21
Greatly restrict highly processed foods. The evidence suggests that the availability of processed food is associated with increasing obesity.22 Simple advice to offer your patients is to encourage them to shop the perimeter of the grocery store, where fresh produce, meat, and dairy products are primarily located, and avoid the inner aisles, which contain primarily processed foods. Choosing food items with 5 or fewer ingredients is a starting point when teaching patients to read labels.
Consider limiting saturated fats. In 1977, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommended that Americans eat no more than 30% of total energy intake from fat and less than 10% of total energy intake from saturated fat; however, no randomized controlled trials had been done that supported this recommendation and epidemiologic data supporting it were weak.23
The 2015 Dietary Guidelines continue to recommend limiting total energy intake from saturated fats.24 While there may be a small decrease in cardiovascular risk with a reduction of saturated fat intake and replacement with unsaturated fats, no overall mortality benefit has been demonstrated.24,25 More research is needed in this area to guide patients in decisions regarding consumption of saturated fats and what types of unsaturated fats are best for their health.
Continue to: Eat only 3 meals per day
Eat only 3 meals per day, but aim for fewer than that. The prescription of fasting is a modality that can be used for weight loss and improved health. Fasting has been a prescribed healing practice for thousands of years.26 It is a practice that virtually every major religion in the world embraces. Studies have demonstrated fasting to be safe and effective in the setting of obesity without significant comorbidities, and it may promote weight loss and metabolic health.26-29
There are multiple types of intermittent fasting. A practical way for patients to start is by restricting the number of hours in which they eat or drink calorie-containing beverages to 8 hours per day. In our experience, this regimen is easier for most patients to follow than alternate-day or other longer fasts. While there has been caution in the prescription of intermittent fasting due to concerns about causing eating disorders, a recent small study did not demonstrate increased risk of eating disorders with daily intermittent fasting.30
Participate in healthy exercise. Nonpharmacologic office-based strategies for treating obesity have generally focused on increasing exercise and decreasing caloric intake.31 While exercise has significant health benefits, including preventing weight regain, evidence does not support monotherapy with exercise as an effective long-term weight-loss strategy.32 There are no studies available that adequately support prescribing an exact dose of exercise.33 Generally, less than 150 minutes of exercise per week is not effective and more than that does have a dose-related response.33
Follow up to help patients stay on target
There is no ideal interval for follow-up visits. However, frequent visits—anywhere from weekly to monthly—in the initial stages of weight loss increase the patient’s sense of accountability and, in our experience, seem to be helpful.
Patients may also choose to track their progress by weighing themselves regularly. A small study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that patients who weighed themselves daily had greater and more sustained weight loss than those who didn’t.34 But the decision of whether to weigh one’s self at home should be individualized for each patient.
CORRESPONDENCE
Wesley Eichorn, DO, 1000 Oakland Drive, Kalamazoo, MI 49008; [email protected]
1. Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015-2016 key findings data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NCHS Data Brief. 2017;(288):1-8.
2. Seger JC, Horn DB, Westman EC, et al. Obesity Algorithm, presented by the Obesity Medicine Association. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.obesityalgorithm.org. 2016-2017
3. Dorflinger LM, Ruser CB, Masheb RM. A brief screening measure for binge eating in primary care. Eat Behav. 2017;26:163-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.03.009
4. Saunders KH, Igel LI, Shukla AP, et al. Drug-induced weight gain: rethinking our choices. J Fam Pract. 2016;65:780-788.
5. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(suppl 1):S13-S28. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S002
6. Reaven G. Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease in nondiabetic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:1754-1759. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241885/-/DC1
7. Hallberg S, McKenzie A, Williams P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of a novel care model for the management of type 2 diabetes at 1 year: an open-label, non-randomized, controlled study. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9:583-612. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare
8. Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1487-1495.
9. Vilar-Gomez E, Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, et al. Post hoc analyses of surrogate markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes in a digitally supported continuous care intervention: an open-label, non-randomised controlled study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e023597. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023597
10. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217-1239. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2109080
11. Drager LF, Brunoni AR, Jenner R, et al. Effects of CPAP on body weight in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Thorax. 2015;70:258-264. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205361
12. Bosworth T. CPAP use associated with greater weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea. CHEST Physician. Published March 29, 2019. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.mdedge.com/chestphysician/article/197827/sleep-medicine/cpap-use-associated-greater-weight-loss-obese-patients
13. Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JAE, et al. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:968-979. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00367-8
14. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
15. Bezerra Bueno N, Vieira De Melo IS, Lima De Oliveira S, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513000548
16. Santos FL, Esteves SS, da Costa Pereira A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of the effects of low carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors. Obes Rev. 2012;13:1048-1066. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01021.x
17. Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, Hallberg SJ, et al. Long-term effects of a novel continuous remote care intervention including nutritional ketosis for the management of type 2 diabetes: a 2-year non-randomized clinical trial. bioRxiv. 2018;10:348. https://doi.org/10.1101/476275
18. Auerbach BJ, Dibey S, Vallila-Buchman P, et al. Review of 100% fruit juice and chronic health conditions: implications for sugar-sweetened beverage policy. Adv Nutr. 2018;9:78-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmx006
19. Faith MS, Dennison BA, Edmunds LS, et al. Fruit juice intake predicts increased adiposity gain in children from low-income families: weight status-by-environment interaction. Pediatrics. 2006;118:2066-2075. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-1117
20. Bolton RP, Burroughs LF, Heaton KW. The role of dietary fiber in satiety, insulin: studies with fruit and fruit. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;84:211-217. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/34.2.211
21. Unwin D, Haslam D, Livesey G. It is the glycaemic response to, not the carbohydrate content of food that matters in diabetes and obesity: the glycaemic index revisited. J Insul Resist. 2016;1(1):a8. https://doi.org/10.4102/jir.v1i1.8
22. Monteiro CA, Moubarac JC, Levy RB, et al. Household availability of ultra-processed foods and obesity in nineteen European countries. Public Health Nutr. 2018;21:18-26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980017001379
23. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, Cooper SM, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials did not support the introduction of dietary fat guidelines in 1977 and 1983: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2015;2:e000196. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2014
24. US Department of Health and Human Services and US Department of Agriculture. 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th edition. Published December 2015. Accessed March 5, 2021. http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/
25. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, DiNicolantonio JJ, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials does not support current dietary fat guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2016;3:e000409. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2016-000409
26. Fung J. The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight Loss. Greystone Books; 2016.
27. Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;39:46-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.005
28. Patterson RE, Sears DD. Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting. Annu Rev Nutr. 2017; 37:371-393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
29. Duncan GG. Intermittent fasts in the correction and control of intractable obesity. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1962;74:121-129.
30. Gabel K, Hoddy KK, Varady KA. Safety of 8-h time restricted feeding in adults with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44:107-109. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2018-0389
31. Erlandson M, Ivey LC, Seikel K. Update on office-based strategies for the management of obesity. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:361-368.
32. Malhotra A, Noakes T, Phinney S. It is time to bust the myth of physical inactivity and obesity: you cannot outrun a bad diet. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49:967-968. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-094911
33. Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, et al. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:459-471. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181949333
34. Zheng Y, Burke LE, Danford CA, et al. Patterns of self-weighing behavior and weight change in a weight loss trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40:1392-1396. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.68
1. Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015-2016 key findings data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. NCHS Data Brief. 2017;(288):1-8.
2. Seger JC, Horn DB, Westman EC, et al. Obesity Algorithm, presented by the Obesity Medicine Association. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.obesityalgorithm.org. 2016-2017
3. Dorflinger LM, Ruser CB, Masheb RM. A brief screening measure for binge eating in primary care. Eat Behav. 2017;26:163-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2017.03.009
4. Saunders KH, Igel LI, Shukla AP, et al. Drug-induced weight gain: rethinking our choices. J Fam Pract. 2016;65:780-788.
5. American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(suppl 1):S13-S28. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S002
6. Reaven G. Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease in nondiabetic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:1754-1759. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241885/-/DC1
7. Hallberg S, McKenzie A, Williams P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of a novel care model for the management of type 2 diabetes at 1 year: an open-label, non-randomized, controlled study. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9:583-612. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare
8. Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1487-1495.
9. Vilar-Gomez E, Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, et al. Post hoc analyses of surrogate markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes in a digitally supported continuous care intervention: an open-label, non-randomised controlled study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e023597. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023597
10. Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217-1239. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2109080
11. Drager LF, Brunoni AR, Jenner R, et al. Effects of CPAP on body weight in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Thorax. 2015;70:258-264. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205361
12. Bosworth T. CPAP use associated with greater weight loss in obese patients with sleep apnea. CHEST Physician. Published March 29, 2019. Accessed March 5, 2021. www.mdedge.com/chestphysician/article/197827/sleep-medicine/cpap-use-associated-greater-weight-loss-obese-patients
13. Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JAE, et al. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:968-979. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00367-8
14. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
15. Bezerra Bueno N, Vieira De Melo IS, Lima De Oliveira S, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513000548
16. Santos FL, Esteves SS, da Costa Pereira A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of the effects of low carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors. Obes Rev. 2012;13:1048-1066. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01021.x
17. Athinarayanan SJ, Adams RN, Hallberg SJ, et al. Long-term effects of a novel continuous remote care intervention including nutritional ketosis for the management of type 2 diabetes: a 2-year non-randomized clinical trial. bioRxiv. 2018;10:348. https://doi.org/10.1101/476275
18. Auerbach BJ, Dibey S, Vallila-Buchman P, et al. Review of 100% fruit juice and chronic health conditions: implications for sugar-sweetened beverage policy. Adv Nutr. 2018;9:78-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmx006
19. Faith MS, Dennison BA, Edmunds LS, et al. Fruit juice intake predicts increased adiposity gain in children from low-income families: weight status-by-environment interaction. Pediatrics. 2006;118:2066-2075. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-1117
20. Bolton RP, Burroughs LF, Heaton KW. The role of dietary fiber in satiety, insulin: studies with fruit and fruit. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;84:211-217. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/34.2.211
21. Unwin D, Haslam D, Livesey G. It is the glycaemic response to, not the carbohydrate content of food that matters in diabetes and obesity: the glycaemic index revisited. J Insul Resist. 2016;1(1):a8. https://doi.org/10.4102/jir.v1i1.8
22. Monteiro CA, Moubarac JC, Levy RB, et al. Household availability of ultra-processed foods and obesity in nineteen European countries. Public Health Nutr. 2018;21:18-26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980017001379
23. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, Cooper SM, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials did not support the introduction of dietary fat guidelines in 1977 and 1983: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2015;2:e000196. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2014
24. US Department of Health and Human Services and US Department of Agriculture. 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th edition. Published December 2015. Accessed March 5, 2021. http://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/
25. Harcombe Z, Baker JS, DiNicolantonio JJ, et al. Evidence from randomised controlled trials does not support current dietary fat guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Hear. 2016;3:e000409. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2016-000409
26. Fung J. The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight Loss. Greystone Books; 2016.
27. Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;39:46-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.10.005
28. Patterson RE, Sears DD. Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting. Annu Rev Nutr. 2017; 37:371-393. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064634
29. Duncan GG. Intermittent fasts in the correction and control of intractable obesity. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1962;74:121-129.
30. Gabel K, Hoddy KK, Varady KA. Safety of 8-h time restricted feeding in adults with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44:107-109. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2018-0389
31. Erlandson M, Ivey LC, Seikel K. Update on office-based strategies for the management of obesity. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:361-368.
32. Malhotra A, Noakes T, Phinney S. It is time to bust the myth of physical inactivity and obesity: you cannot outrun a bad diet. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49:967-968. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2015-094911
33. Donnelly JE, Blair SN, Jakicic JM, et al. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41:459-471. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181949333
34. Zheng Y, Burke LE, Danford CA, et al. Patterns of self-weighing behavior and weight change in a weight loss trial. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40:1392-1396. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.68
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Create an office environment where patients feel comfortable discussing their weight. C
› Screen overweight and obese patients for comorbidities. B
› Focus on nutritional changes more than exercise when working with patients who want to lose weight. C
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Risk for erectile dysfunction sixfold higher in men with COVID-19
COVID-19 increases the risk of developing erectile dysfunction (ED) by nearly sixfold, according to data from the first study to investigate the association between ED and COVID-19 in young men in a real-life setting.
Men with ED are more than five times more likely to have COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.27).
For men with a history of COVID-19, the odds ratio of developing ED was 5.66. The strength of the association remained after adjusting for factors considered to affect ED.
The study, which was led by Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD, professor of endocrinology and medical sexology, University of Rome Tor Vergata, was published on March 20 in Andrology.
‘Mask up to keep it up’
ED can be both a short-term and a long-term complication of COVID-19, Dr. Jannini suggests.
“When offered, men should have the COVID vaccination. It also gives a whole new meaning to wearing the mask – mask up to keep it up,” he said. “It could possibly have the added benefit of preventing sexual dysfunction.”
He points out that older age, diabetes, high body mass index, and smoking increase the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“These are the same as risk factors for ED. Results of our study agree with the pathophysiological mechanisms linking ED, endothelial dysfunction, and COVID-19. Basically, endothelial dysfunction is common in both conditions [COVID-10 and ED].
“We would like to find some sort of biomarker of endothelial dysfunction post COVID, because it seems that there are many sequelae that coexist for a long time after infection,” added Dr. Jannini. “Asking a patient if they have ED after COVID might provide a measure of systemic wellness.”
Allan Pacey, MD, professor of andrology at the University of Sheffield (England), welcomed the research, noting, “This seems to be a well-conducted study. However, at the moment, the relationship is just a correlation, and it might be that some of the comorbidities that increased the men’s chances of getting a significant COVID-19 infection may have also independently increased their chances of erectile dysfunction.
“But the authors offer a plausible mechanism by which COVID-19 may impact directly on erectile function,” agrees Dr. Pacey. However, “There’s more work to be done,” he said. “I’d also argue it’s a good reason for men to wear a mask, practice social distancing, and take the vaccine when it’s offered to them.”
Urologist John Mulhall, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, remarked, “It was a highly preliminary study, but the data are suggestive of a potential link between COVID-19 infection and ED.
“However, it raises enough questions such that further large, more long-term analyses are required to define causation. Future studies assessing testosterone levels and erectile hemodynamics will be needed to provide definite evidence of a causative link,» he stressed.
Erectile problems a ‘hallmark’ of systemic endothelial dysfunction
Prior research has suggested that asymptomatic COVID-19 could be associated with subclinical microvascular involvement with long-term cardiovascular effects.
“Indeed, COVID-19 is by all means an endothelial disease, in which systemic manifestations ... can potentially be due to alterations in the endothelial thrombotic/fibrinolytic balance,” emphasized Dr. Jannini. “In addition, endothelial cells express many of the cofactors used by SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells.
“Erectile dysfunction has often been considered a hallmark of endothelial dysfunction, and as such, a potential association between ED and COVID-19 has also been postulated and underpinned the investigation in this study,” he explained.
The study was predicated on the fact that ED is often considered a clinical marker of impaired overall health status, which often features cardiovascular events at an early age. It aimed to investigate the bidirectional relationship between COVID-19 and ED. It asked whether ED could be a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 and whether having COVID-19 predisposes to developing ED.
“This would possibly suggest that men with ED, due to the underlying conditions which impair erectile response, could also be more susceptible to contracting COVID-19,” said Dr. Jannini.
Data were drawn from the Sex@COVID online survey, which was conducted from April 7 to May 4, 2020, in Italy. The survey included 6,821 participants aged 18 years or older (4,177 women; 2,644 men; mean age, 32.83 ± 11.24 years). Participants were stratified on the basis of marital status and sexual activity during lockdown. From these participants, 985 sexually active men were identified, among whom 25 (2.54%) reported having tested positive for COVID-19. These persons were matched with 75 COVID-19–negative men using propensity score matching in a 1:3 ratio.
The researchers used standardized psychometric tools to measure the effects of lockdown and social distancing on the intrapsychic, relational, and sexual health of the participants.
Erectile function was measured with the International Index of Erectile Function or the Sexual Health Inventory for Men, which are often used in clinical settings. In light of the two-way interaction between sexual activity and psychological well-being, results were adjusted for any influence of anxiety and depression, which were measured with recognized scales for use in patients with a history of COVID-19.
Results showed that the prevalence of ED was significantly higher among men who self-reported a history of COVID-19, compared with a matching COVID-negative population (28% vs. 9.33%; P = .027).
After adjusting for variables that are considered to have a bearing on the development of ED, such as psychological status, age, and BMI, the odds ratio for developing ED after having had COVID-19 was 5.66 (95% confidence interval, 1.50-24.01).
Similarly, after adjusting for age and BMI, men with ED were more likely to have COVID‐19 (OR, 5.27; 95% CI, 1.49-20.09).
The authors note that persons who experience “a sudden onset or worsening of ED might also consider precautionary quarantine or nasopharyngeal swab, as COVID‐19 might act as a potential initiating trigger for the onset of erectile impairment, or an aggravating factor for its progression to more severe forms.”
Similarly, patients who have ED “should consider their erectile impairment as a sign of possible underlying conditions that could increase the likelihood of suffering from COVID‐19,” they write.
Dr. Mulhall highlighted several limitations of the study, including its retrospective nature, recall bias associated with the use of online questionnaires, and the inclusion of COVID‐19 diagnoses that were based on the response to the survey rather than on testing with nasopharyngeal swabs. In addition, comorbidity data were incomplete, and there was no indication of duration after COVID-19 infection, the severity of COVID-19, or the severity of ED.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pacey is chairman of the advisory committee of the U.K. National External Quality Assurance Schemes in Andrology, editor-in-chief of Human Fertility, trustee of the Progress Educational Trust, and trustee of the British Fertility Society (all unpaid). Dr. Mulhall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 increases the risk of developing erectile dysfunction (ED) by nearly sixfold, according to data from the first study to investigate the association between ED and COVID-19 in young men in a real-life setting.
Men with ED are more than five times more likely to have COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.27).
For men with a history of COVID-19, the odds ratio of developing ED was 5.66. The strength of the association remained after adjusting for factors considered to affect ED.
The study, which was led by Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD, professor of endocrinology and medical sexology, University of Rome Tor Vergata, was published on March 20 in Andrology.
‘Mask up to keep it up’
ED can be both a short-term and a long-term complication of COVID-19, Dr. Jannini suggests.
“When offered, men should have the COVID vaccination. It also gives a whole new meaning to wearing the mask – mask up to keep it up,” he said. “It could possibly have the added benefit of preventing sexual dysfunction.”
He points out that older age, diabetes, high body mass index, and smoking increase the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“These are the same as risk factors for ED. Results of our study agree with the pathophysiological mechanisms linking ED, endothelial dysfunction, and COVID-19. Basically, endothelial dysfunction is common in both conditions [COVID-10 and ED].
“We would like to find some sort of biomarker of endothelial dysfunction post COVID, because it seems that there are many sequelae that coexist for a long time after infection,” added Dr. Jannini. “Asking a patient if they have ED after COVID might provide a measure of systemic wellness.”
Allan Pacey, MD, professor of andrology at the University of Sheffield (England), welcomed the research, noting, “This seems to be a well-conducted study. However, at the moment, the relationship is just a correlation, and it might be that some of the comorbidities that increased the men’s chances of getting a significant COVID-19 infection may have also independently increased their chances of erectile dysfunction.
“But the authors offer a plausible mechanism by which COVID-19 may impact directly on erectile function,” agrees Dr. Pacey. However, “There’s more work to be done,” he said. “I’d also argue it’s a good reason for men to wear a mask, practice social distancing, and take the vaccine when it’s offered to them.”
Urologist John Mulhall, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, remarked, “It was a highly preliminary study, but the data are suggestive of a potential link between COVID-19 infection and ED.
“However, it raises enough questions such that further large, more long-term analyses are required to define causation. Future studies assessing testosterone levels and erectile hemodynamics will be needed to provide definite evidence of a causative link,» he stressed.
Erectile problems a ‘hallmark’ of systemic endothelial dysfunction
Prior research has suggested that asymptomatic COVID-19 could be associated with subclinical microvascular involvement with long-term cardiovascular effects.
“Indeed, COVID-19 is by all means an endothelial disease, in which systemic manifestations ... can potentially be due to alterations in the endothelial thrombotic/fibrinolytic balance,” emphasized Dr. Jannini. “In addition, endothelial cells express many of the cofactors used by SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells.
“Erectile dysfunction has often been considered a hallmark of endothelial dysfunction, and as such, a potential association between ED and COVID-19 has also been postulated and underpinned the investigation in this study,” he explained.
The study was predicated on the fact that ED is often considered a clinical marker of impaired overall health status, which often features cardiovascular events at an early age. It aimed to investigate the bidirectional relationship between COVID-19 and ED. It asked whether ED could be a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 and whether having COVID-19 predisposes to developing ED.
“This would possibly suggest that men with ED, due to the underlying conditions which impair erectile response, could also be more susceptible to contracting COVID-19,” said Dr. Jannini.
Data were drawn from the Sex@COVID online survey, which was conducted from April 7 to May 4, 2020, in Italy. The survey included 6,821 participants aged 18 years or older (4,177 women; 2,644 men; mean age, 32.83 ± 11.24 years). Participants were stratified on the basis of marital status and sexual activity during lockdown. From these participants, 985 sexually active men were identified, among whom 25 (2.54%) reported having tested positive for COVID-19. These persons were matched with 75 COVID-19–negative men using propensity score matching in a 1:3 ratio.
The researchers used standardized psychometric tools to measure the effects of lockdown and social distancing on the intrapsychic, relational, and sexual health of the participants.
Erectile function was measured with the International Index of Erectile Function or the Sexual Health Inventory for Men, which are often used in clinical settings. In light of the two-way interaction between sexual activity and psychological well-being, results were adjusted for any influence of anxiety and depression, which were measured with recognized scales for use in patients with a history of COVID-19.
Results showed that the prevalence of ED was significantly higher among men who self-reported a history of COVID-19, compared with a matching COVID-negative population (28% vs. 9.33%; P = .027).
After adjusting for variables that are considered to have a bearing on the development of ED, such as psychological status, age, and BMI, the odds ratio for developing ED after having had COVID-19 was 5.66 (95% confidence interval, 1.50-24.01).
Similarly, after adjusting for age and BMI, men with ED were more likely to have COVID‐19 (OR, 5.27; 95% CI, 1.49-20.09).
The authors note that persons who experience “a sudden onset or worsening of ED might also consider precautionary quarantine or nasopharyngeal swab, as COVID‐19 might act as a potential initiating trigger for the onset of erectile impairment, or an aggravating factor for its progression to more severe forms.”
Similarly, patients who have ED “should consider their erectile impairment as a sign of possible underlying conditions that could increase the likelihood of suffering from COVID‐19,” they write.
Dr. Mulhall highlighted several limitations of the study, including its retrospective nature, recall bias associated with the use of online questionnaires, and the inclusion of COVID‐19 diagnoses that were based on the response to the survey rather than on testing with nasopharyngeal swabs. In addition, comorbidity data were incomplete, and there was no indication of duration after COVID-19 infection, the severity of COVID-19, or the severity of ED.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pacey is chairman of the advisory committee of the U.K. National External Quality Assurance Schemes in Andrology, editor-in-chief of Human Fertility, trustee of the Progress Educational Trust, and trustee of the British Fertility Society (all unpaid). Dr. Mulhall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 increases the risk of developing erectile dysfunction (ED) by nearly sixfold, according to data from the first study to investigate the association between ED and COVID-19 in young men in a real-life setting.
Men with ED are more than five times more likely to have COVID-19 (odds ratio, 5.27).
For men with a history of COVID-19, the odds ratio of developing ED was 5.66. The strength of the association remained after adjusting for factors considered to affect ED.
The study, which was led by Emmanuele A. Jannini, MD, professor of endocrinology and medical sexology, University of Rome Tor Vergata, was published on March 20 in Andrology.
‘Mask up to keep it up’
ED can be both a short-term and a long-term complication of COVID-19, Dr. Jannini suggests.
“When offered, men should have the COVID vaccination. It also gives a whole new meaning to wearing the mask – mask up to keep it up,” he said. “It could possibly have the added benefit of preventing sexual dysfunction.”
He points out that older age, diabetes, high body mass index, and smoking increase the risk of contracting COVID-19.
“These are the same as risk factors for ED. Results of our study agree with the pathophysiological mechanisms linking ED, endothelial dysfunction, and COVID-19. Basically, endothelial dysfunction is common in both conditions [COVID-10 and ED].
“We would like to find some sort of biomarker of endothelial dysfunction post COVID, because it seems that there are many sequelae that coexist for a long time after infection,” added Dr. Jannini. “Asking a patient if they have ED after COVID might provide a measure of systemic wellness.”
Allan Pacey, MD, professor of andrology at the University of Sheffield (England), welcomed the research, noting, “This seems to be a well-conducted study. However, at the moment, the relationship is just a correlation, and it might be that some of the comorbidities that increased the men’s chances of getting a significant COVID-19 infection may have also independently increased their chances of erectile dysfunction.
“But the authors offer a plausible mechanism by which COVID-19 may impact directly on erectile function,” agrees Dr. Pacey. However, “There’s more work to be done,” he said. “I’d also argue it’s a good reason for men to wear a mask, practice social distancing, and take the vaccine when it’s offered to them.”
Urologist John Mulhall, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, remarked, “It was a highly preliminary study, but the data are suggestive of a potential link between COVID-19 infection and ED.
“However, it raises enough questions such that further large, more long-term analyses are required to define causation. Future studies assessing testosterone levels and erectile hemodynamics will be needed to provide definite evidence of a causative link,» he stressed.
Erectile problems a ‘hallmark’ of systemic endothelial dysfunction
Prior research has suggested that asymptomatic COVID-19 could be associated with subclinical microvascular involvement with long-term cardiovascular effects.
“Indeed, COVID-19 is by all means an endothelial disease, in which systemic manifestations ... can potentially be due to alterations in the endothelial thrombotic/fibrinolytic balance,” emphasized Dr. Jannini. “In addition, endothelial cells express many of the cofactors used by SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells.
“Erectile dysfunction has often been considered a hallmark of endothelial dysfunction, and as such, a potential association between ED and COVID-19 has also been postulated and underpinned the investigation in this study,” he explained.
The study was predicated on the fact that ED is often considered a clinical marker of impaired overall health status, which often features cardiovascular events at an early age. It aimed to investigate the bidirectional relationship between COVID-19 and ED. It asked whether ED could be a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 and whether having COVID-19 predisposes to developing ED.
“This would possibly suggest that men with ED, due to the underlying conditions which impair erectile response, could also be more susceptible to contracting COVID-19,” said Dr. Jannini.
Data were drawn from the Sex@COVID online survey, which was conducted from April 7 to May 4, 2020, in Italy. The survey included 6,821 participants aged 18 years or older (4,177 women; 2,644 men; mean age, 32.83 ± 11.24 years). Participants were stratified on the basis of marital status and sexual activity during lockdown. From these participants, 985 sexually active men were identified, among whom 25 (2.54%) reported having tested positive for COVID-19. These persons were matched with 75 COVID-19–negative men using propensity score matching in a 1:3 ratio.
The researchers used standardized psychometric tools to measure the effects of lockdown and social distancing on the intrapsychic, relational, and sexual health of the participants.
Erectile function was measured with the International Index of Erectile Function or the Sexual Health Inventory for Men, which are often used in clinical settings. In light of the two-way interaction between sexual activity and psychological well-being, results were adjusted for any influence of anxiety and depression, which were measured with recognized scales for use in patients with a history of COVID-19.
Results showed that the prevalence of ED was significantly higher among men who self-reported a history of COVID-19, compared with a matching COVID-negative population (28% vs. 9.33%; P = .027).
After adjusting for variables that are considered to have a bearing on the development of ED, such as psychological status, age, and BMI, the odds ratio for developing ED after having had COVID-19 was 5.66 (95% confidence interval, 1.50-24.01).
Similarly, after adjusting for age and BMI, men with ED were more likely to have COVID‐19 (OR, 5.27; 95% CI, 1.49-20.09).
The authors note that persons who experience “a sudden onset or worsening of ED might also consider precautionary quarantine or nasopharyngeal swab, as COVID‐19 might act as a potential initiating trigger for the onset of erectile impairment, or an aggravating factor for its progression to more severe forms.”
Similarly, patients who have ED “should consider their erectile impairment as a sign of possible underlying conditions that could increase the likelihood of suffering from COVID‐19,” they write.
Dr. Mulhall highlighted several limitations of the study, including its retrospective nature, recall bias associated with the use of online questionnaires, and the inclusion of COVID‐19 diagnoses that were based on the response to the survey rather than on testing with nasopharyngeal swabs. In addition, comorbidity data were incomplete, and there was no indication of duration after COVID-19 infection, the severity of COVID-19, or the severity of ED.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pacey is chairman of the advisory committee of the U.K. National External Quality Assurance Schemes in Andrology, editor-in-chief of Human Fertility, trustee of the Progress Educational Trust, and trustee of the British Fertility Society (all unpaid). Dr. Mulhall has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular risks elevated in transgender youth
Cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors are increased among transgender youths, compared with youths who are not transgender. Elevations in lipid levels and body mass index (BMI) also occur in adult transgender patients, new research shows.
“This is the first study of its size in the United States of which we are aware that looks at the odds of youth with a diagnosis of gender dysphoria having medical diagnoses that relate to overall metabolic and cardiovascular health,” first author Anna Valentine, MD, of Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, said in a press statement.
Although previous studies have shown that among transgender adults, BMI is higher and there is an increased risk for cardiovascular events, such as stroke or heart attack, compared with nontransgender people, research on adolescent transgender patients has been lacking.
With a recent survey showing that nearly 2% of adolescents identify as transgender, interest in health outcomes among younger patients is high.
To investigate, Dr. Valentine, and colleagues evaluated data from the PEDSnet pediatric database on 4,177 youths who had received a diagnosis of gender dysphoria. The participants had been enrolled at six sites from 2009 to 2019. The researchers compared these patients in a ratio of 1:4 with 16,664 control persons who had not been diagnosed with gender dysphoria. They reported their findings as a poster at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
For the propensity-score analysis, participants were matched according to year of birth, age at last visit, site, race, ethnicity, insurance status, and duration in the database.
In both the transgender and control groups, about 66% were female at birth, 73% were White, and 9% Hispanic. For both groups, the average age was 16.2 years at the last visit. The average duration in the database was 7 years.
Study didn’t distinguish between those receiving and those not receiving gender-affirming hormones
In the retrospective study, among those who identified as transgender, the rates of diagnoses of dyslipidemia (odds ratio, 1.6; P < .0001) and metabolic syndrome (OR, 1.9; P = .0086) were significantly higher, compared with those without gender dysphoria.
Among the transgender male patients (born female) but not transgender female patients (born male), rates of diagnoses of overweight/obesity (OR, 1.7; P < .0001) and polycystic ovary syndrome were higher (OR, 1.9, P = .0006), compared with controls.
Gender-affirming hormone therapy, such as with testosterone or estradiol, is among the suspected culprits for the cardiovascular effects. However, importantly, this study did not differentiate between patients who had received estradiol or testosterone for gender affirmation and those who had not, Dr. Valentine said.
“We don’t know [whether gender-affirming hormone therapy is a cause], as we have not looked at this yet,” she said in an interview. “We are looking at that in our next analyses and will be including that in our future publication.
“We’ll also be looking at the relationship between having overweight/obesity and the other diagnoses that influence cardiovascular health (high blood pressure, liver dysfunction, and abnormal cholesterol), as that could certainly be playing a role as well,” she said.
For many transgender patients, gender-affirming hormone therapy is lifelong. One question that needs to be evaluated concerns whether the dose of such therapy has a role on cardiovascular effects and if so, whether adjustments could be made without compromising the therapeutic effect, Dr. Valentine noted.
“This is an important question, and future research is needed to evaluate whether doses [of gender-affirming hormones] are related to cardiometabolic outcomes,” she said.
Potential confounders in the study include the fact that rates of overweight and obesity are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. This can in itself can increase the risk for other disorders, Dr. Valentine noted.
Furthermore, rates of mental health comorbidities are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. One consequence of this may be that they engage in less physical activity, she said.
Hormone therapy, health care disparities, or both could explain risk
In commenting on the study, Joshua D. Safer, MD, executive director of the Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, the Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said that although similar cardiovascular effects are known to occur in transgender adults as well, they may or may not be hormone related. Other factors can increase the risk.
“With transgender adults, any differences in lipids or cardiac risk factors relative to cisgender people might be attributable either to hormone therapy or to health care disparities,” he said in an interview.
“The data are mixed. It may be that most differences relate to lack of access to care and to mistreatment by society,” he said. “Even studies that focus on hormones see a worsened situation for trans women versus trans men.”
Other recent research that shows potential cardiovascular effects among adult transgender men includes a study of more than 1,000 transgender men (born female) who received testosterone. That study, which was also presented at the ENDO meeting and was reported by this news organization, found an increased risk for high hematocrit levels, which could lead to a thrombotic event.
However, a study published in Pediatrics, which was also reported by this news organization, that included 611 transgender youths who had taken gender-affirming hormone therapy for more than a year found no increased risk for thrombosis, even in the presence of thrombosis risk factors, including obesity, tobacco use, and family history of thrombosis. However, the senior author of that study pointed out that the duration of follow-up in that study was relatively short, which may have been why they did not find an increased risk for thrombosis.
Dr. Safer noted that transgender youths and adults alike face a host of cultural factors that could play a role in increased cardiovascular risks.
“For adults, the major candidate explanations for worse BMI and cardiac risk factors are societal mistreatment, and for trans women specifically, progestins. For youth, the major candidate explanations are societal mistreatment and lack of access to athletics,” he said.
The authors and Dr. Safer disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors are increased among transgender youths, compared with youths who are not transgender. Elevations in lipid levels and body mass index (BMI) also occur in adult transgender patients, new research shows.
“This is the first study of its size in the United States of which we are aware that looks at the odds of youth with a diagnosis of gender dysphoria having medical diagnoses that relate to overall metabolic and cardiovascular health,” first author Anna Valentine, MD, of Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, said in a press statement.
Although previous studies have shown that among transgender adults, BMI is higher and there is an increased risk for cardiovascular events, such as stroke or heart attack, compared with nontransgender people, research on adolescent transgender patients has been lacking.
With a recent survey showing that nearly 2% of adolescents identify as transgender, interest in health outcomes among younger patients is high.
To investigate, Dr. Valentine, and colleagues evaluated data from the PEDSnet pediatric database on 4,177 youths who had received a diagnosis of gender dysphoria. The participants had been enrolled at six sites from 2009 to 2019. The researchers compared these patients in a ratio of 1:4 with 16,664 control persons who had not been diagnosed with gender dysphoria. They reported their findings as a poster at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
For the propensity-score analysis, participants were matched according to year of birth, age at last visit, site, race, ethnicity, insurance status, and duration in the database.
In both the transgender and control groups, about 66% were female at birth, 73% were White, and 9% Hispanic. For both groups, the average age was 16.2 years at the last visit. The average duration in the database was 7 years.
Study didn’t distinguish between those receiving and those not receiving gender-affirming hormones
In the retrospective study, among those who identified as transgender, the rates of diagnoses of dyslipidemia (odds ratio, 1.6; P < .0001) and metabolic syndrome (OR, 1.9; P = .0086) were significantly higher, compared with those without gender dysphoria.
Among the transgender male patients (born female) but not transgender female patients (born male), rates of diagnoses of overweight/obesity (OR, 1.7; P < .0001) and polycystic ovary syndrome were higher (OR, 1.9, P = .0006), compared with controls.
Gender-affirming hormone therapy, such as with testosterone or estradiol, is among the suspected culprits for the cardiovascular effects. However, importantly, this study did not differentiate between patients who had received estradiol or testosterone for gender affirmation and those who had not, Dr. Valentine said.
“We don’t know [whether gender-affirming hormone therapy is a cause], as we have not looked at this yet,” she said in an interview. “We are looking at that in our next analyses and will be including that in our future publication.
“We’ll also be looking at the relationship between having overweight/obesity and the other diagnoses that influence cardiovascular health (high blood pressure, liver dysfunction, and abnormal cholesterol), as that could certainly be playing a role as well,” she said.
For many transgender patients, gender-affirming hormone therapy is lifelong. One question that needs to be evaluated concerns whether the dose of such therapy has a role on cardiovascular effects and if so, whether adjustments could be made without compromising the therapeutic effect, Dr. Valentine noted.
“This is an important question, and future research is needed to evaluate whether doses [of gender-affirming hormones] are related to cardiometabolic outcomes,” she said.
Potential confounders in the study include the fact that rates of overweight and obesity are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. This can in itself can increase the risk for other disorders, Dr. Valentine noted.
Furthermore, rates of mental health comorbidities are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. One consequence of this may be that they engage in less physical activity, she said.
Hormone therapy, health care disparities, or both could explain risk
In commenting on the study, Joshua D. Safer, MD, executive director of the Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, the Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said that although similar cardiovascular effects are known to occur in transgender adults as well, they may or may not be hormone related. Other factors can increase the risk.
“With transgender adults, any differences in lipids or cardiac risk factors relative to cisgender people might be attributable either to hormone therapy or to health care disparities,” he said in an interview.
“The data are mixed. It may be that most differences relate to lack of access to care and to mistreatment by society,” he said. “Even studies that focus on hormones see a worsened situation for trans women versus trans men.”
Other recent research that shows potential cardiovascular effects among adult transgender men includes a study of more than 1,000 transgender men (born female) who received testosterone. That study, which was also presented at the ENDO meeting and was reported by this news organization, found an increased risk for high hematocrit levels, which could lead to a thrombotic event.
However, a study published in Pediatrics, which was also reported by this news organization, that included 611 transgender youths who had taken gender-affirming hormone therapy for more than a year found no increased risk for thrombosis, even in the presence of thrombosis risk factors, including obesity, tobacco use, and family history of thrombosis. However, the senior author of that study pointed out that the duration of follow-up in that study was relatively short, which may have been why they did not find an increased risk for thrombosis.
Dr. Safer noted that transgender youths and adults alike face a host of cultural factors that could play a role in increased cardiovascular risks.
“For adults, the major candidate explanations for worse BMI and cardiac risk factors are societal mistreatment, and for trans women specifically, progestins. For youth, the major candidate explanations are societal mistreatment and lack of access to athletics,” he said.
The authors and Dr. Safer disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors are increased among transgender youths, compared with youths who are not transgender. Elevations in lipid levels and body mass index (BMI) also occur in adult transgender patients, new research shows.
“This is the first study of its size in the United States of which we are aware that looks at the odds of youth with a diagnosis of gender dysphoria having medical diagnoses that relate to overall metabolic and cardiovascular health,” first author Anna Valentine, MD, of Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, said in a press statement.
Although previous studies have shown that among transgender adults, BMI is higher and there is an increased risk for cardiovascular events, such as stroke or heart attack, compared with nontransgender people, research on adolescent transgender patients has been lacking.
With a recent survey showing that nearly 2% of adolescents identify as transgender, interest in health outcomes among younger patients is high.
To investigate, Dr. Valentine, and colleagues evaluated data from the PEDSnet pediatric database on 4,177 youths who had received a diagnosis of gender dysphoria. The participants had been enrolled at six sites from 2009 to 2019. The researchers compared these patients in a ratio of 1:4 with 16,664 control persons who had not been diagnosed with gender dysphoria. They reported their findings as a poster at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
For the propensity-score analysis, participants were matched according to year of birth, age at last visit, site, race, ethnicity, insurance status, and duration in the database.
In both the transgender and control groups, about 66% were female at birth, 73% were White, and 9% Hispanic. For both groups, the average age was 16.2 years at the last visit. The average duration in the database was 7 years.
Study didn’t distinguish between those receiving and those not receiving gender-affirming hormones
In the retrospective study, among those who identified as transgender, the rates of diagnoses of dyslipidemia (odds ratio, 1.6; P < .0001) and metabolic syndrome (OR, 1.9; P = .0086) were significantly higher, compared with those without gender dysphoria.
Among the transgender male patients (born female) but not transgender female patients (born male), rates of diagnoses of overweight/obesity (OR, 1.7; P < .0001) and polycystic ovary syndrome were higher (OR, 1.9, P = .0006), compared with controls.
Gender-affirming hormone therapy, such as with testosterone or estradiol, is among the suspected culprits for the cardiovascular effects. However, importantly, this study did not differentiate between patients who had received estradiol or testosterone for gender affirmation and those who had not, Dr. Valentine said.
“We don’t know [whether gender-affirming hormone therapy is a cause], as we have not looked at this yet,” she said in an interview. “We are looking at that in our next analyses and will be including that in our future publication.
“We’ll also be looking at the relationship between having overweight/obesity and the other diagnoses that influence cardiovascular health (high blood pressure, liver dysfunction, and abnormal cholesterol), as that could certainly be playing a role as well,” she said.
For many transgender patients, gender-affirming hormone therapy is lifelong. One question that needs to be evaluated concerns whether the dose of such therapy has a role on cardiovascular effects and if so, whether adjustments could be made without compromising the therapeutic effect, Dr. Valentine noted.
“This is an important question, and future research is needed to evaluate whether doses [of gender-affirming hormones] are related to cardiometabolic outcomes,” she said.
Potential confounders in the study include the fact that rates of overweight and obesity are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. This can in itself can increase the risk for other disorders, Dr. Valentine noted.
Furthermore, rates of mental health comorbidities are higher among youths with gender dysphoria. One consequence of this may be that they engage in less physical activity, she said.
Hormone therapy, health care disparities, or both could explain risk
In commenting on the study, Joshua D. Safer, MD, executive director of the Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, the Mount Sinai Health System, New York, said that although similar cardiovascular effects are known to occur in transgender adults as well, they may or may not be hormone related. Other factors can increase the risk.
“With transgender adults, any differences in lipids or cardiac risk factors relative to cisgender people might be attributable either to hormone therapy or to health care disparities,” he said in an interview.
“The data are mixed. It may be that most differences relate to lack of access to care and to mistreatment by society,” he said. “Even studies that focus on hormones see a worsened situation for trans women versus trans men.”
Other recent research that shows potential cardiovascular effects among adult transgender men includes a study of more than 1,000 transgender men (born female) who received testosterone. That study, which was also presented at the ENDO meeting and was reported by this news organization, found an increased risk for high hematocrit levels, which could lead to a thrombotic event.
However, a study published in Pediatrics, which was also reported by this news organization, that included 611 transgender youths who had taken gender-affirming hormone therapy for more than a year found no increased risk for thrombosis, even in the presence of thrombosis risk factors, including obesity, tobacco use, and family history of thrombosis. However, the senior author of that study pointed out that the duration of follow-up in that study was relatively short, which may have been why they did not find an increased risk for thrombosis.
Dr. Safer noted that transgender youths and adults alike face a host of cultural factors that could play a role in increased cardiovascular risks.
“For adults, the major candidate explanations for worse BMI and cardiac risk factors are societal mistreatment, and for trans women specifically, progestins. For youth, the major candidate explanations are societal mistreatment and lack of access to athletics,” he said.
The authors and Dr. Safer disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hyperphagia, anxiety eased with carbetocin in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome
Children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) who received three daily, intranasal doses of carbetocin, an investigational, long-acting oxytocin analogue, had significant improvement in hyperphagia and anxiety during 8 weeks on treatment, compared with placebo in a multicenter, phase 3 trial with 119 patients.
The treatment also appeared safe during up to 56 additional weeks on active treatment, with no serious adverse effects nor “unexpected” events, and once completing the study about 95% of enrolled patients opted to remain on active treatment, Cheri L. Deal, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on “the significant results for the placebo-controlled period, as well as for those finishing the 56-week extension, we may well have a new armament for helping these kids and their families deal with the unrelenting hunger of patients with PWS as well as some of the behavioral symptoms,” Dr. Deal, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at the Sainte-Justine Mother-Child University of Montreal Hospital, said in an interview. No treatment currently has labeling for addressing the hyperphagia or anxiety that is characteristic and often problematic for children and adolescents with PWS, an autosomal dominant genetic disease with an incidence of about 1 in 15,000 births and an estimated U.S. prevalence of about 9,000 cases, or about 1 case for every 37,000 people.
‘Gorgeous’ safety
“The results looked pretty positive, and we’re encouraged by what appears to be a good safety profile, so overall I think the PWS community is very excited by the results and is very interested in getting access to this drug,” commented Theresa V. Strong, PhD, director of research programs for the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research in Walnut, Calif., a group not involved with the study. Currently, “we have no effective treatments for these difficult behaviors” of hyperphagia and anxiety. Surveys and studies run by the foundation have documented that hyperphagia and anxiety “were the two most important symptoms that families would like to see treated,” Dr. Strong added in an interview.
PWS “is complex and affects almost every aspect of the lives of affected people and their families. Any treatment that can chip away at some of the problems these patients have can be a huge benefit to the patients and their families,” said Jennifer L. Miller, MD, a professor of pediatric endocrinology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and a coinvestigator on the study.
But the finding that carbetocin appeared to address, at least in part, this unmet need while compiling a safety record that Dr. Miller called “gorgeous” and “remarkable,” also came with a few limitations.
Fewer patients than planned, and muddled outcomes
The CARE-PWS trial aimed to enroll 175 patients, but fell short once the COVID-19 pandemic hit. Plus the trial had two prespecified primary endpoints – improvements in a measure of hyperphagia, and in a measure of obsessive and compulsive behaviors – specifically in the 40 patients who received the higher of the two dosages studied, 9.6 mg t.i.d. intranasally. Neither endpoint showed significant improvement among the patients on this dosage, compared with the 40 patients who received placebo, although both outcomes trended in the right direction in the actively treated patients.
The study’s positive results came in a secondary treatment group, 39 patients who received 3.2 mg t.i.d., also intranasally. This subgroup had significant benefit, compared with placebo, for reducing hyperphagia symptoms as measured on the Hyperphagia Questionnaire for Clinical Trials (HQ-CT) Total Score. After the first 8 weeks on treatment, patients on the lower carbetocin dosage had an average reduction in their HQ-CT score of greater than 5 points, more than double the reduction seen among control patients who received placebo.
Those on the 3.2-mg t.i.d. dosage also showed significant improvements, compared with placebo, for anxiety, measured by the PWS Anxiety and Distress Questionnaire Total Score, as well as on measures of clinical global impression of severity, and of clinical global impression of change. Like the higher-dosage patients the lower-dosage subgroup did not show a significant difference compared with placebo for the other primary endpoint, change in obsessive and compulsive behaviors as measured by the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale Total Score, although also like the higher dosage the effect from the lower dosage trended toward benefit.
A further limitation was that, at the time of her report, presented in abstract OR16-3 at the meeting, Dr. Deal could only present complete 64-week follow-up for 72 patients, although this reassuringly showed that, as time on the 9.6-mg t.i.d. dosage continued beyond 8 weeks, patients gradually improved their HQ-CT response so that by 64 weeks on treatment their hyperphagia score had improved as much as in the patients who received the lower dosage.
In short, documented benefits occurred on the lower dosage, especially for clinically meaningful symptoms like hyperphagia and anxiety, but the study’s overall results were not fully consistent by statistical criteria.
Benefiting an unmet need?
“While it is regrettable that we did not get to 175 patients because of COVID-19, the dataset is significant enough for me to feel that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] needs to take a very serious look and consider approval,” Dr. Deal said in an interview. “Once safety is assured, which I think it is, I can only hope that regulatory officials understand their unmet needs of this rare disease community and will allow the drug to move to the next stage.”
“This is a very rare disease, and having families participate in trials is really challenging,” especially while the COVID-19 pandemic continues, Dr. Strong said. For the pediatric and adolescent patients targeted in this study “it will take a while for COVID to go away and for families to feel safe again being in a trial, so a real concern is that a need for more clinical trials is not terribly feasible now. Given that the safety profile looked good and one dose seemed to have good efficacy, as long as the long-term data continue to look good we’d love for the FDA to look at the existing data and see whether there is a path forward.”
Dr. Miller highlighted the limitations of what the CARE-PWS findings show.
“Given that it was only an 8-week trial of drug against placebo, and the fact that the primary outcomes weren’t met for the higher dose, my thought is that potentially we need to study more patients for a longer period at the 3.2-mg dose,” she said. She acknowledged that the metric used in the study to assess obsessive and compulsive behaviors is “very difficult” to apply to patients with PWS because of uncertainties in scoring obsessions in patients “who are not very good at telling you what they’re thinking.” Plus, “it’s absolutely not a problem that we did not see an effect on obsession and compulsions if the treatment potentially improves anxiety and hyperphagia, which are very common.” A treatment that reliably reduces these symptoms “would be amazing,” Dr. Miller added.
“PWS is very rare, so it’s very hard to do trials. Maybe the FDA will approve carbetocin because it was safe and gave a signal of efficacy at the lower dose. But my thought is that additional treatment trials are needed with only the lower dose and with longer duration,” she said.
CARE-PWS enrolled patients with nutritional phase 3 PWS who were aged 7-18 years at any of 24 sites in the United States, Canada, or Australia during 2018-2020. They averaged about 12 years of age, and 56% were girls.
The most common adverse effect from carbetocin was flushing, occurring in 14% of those on the lower dose and 21% on the higher dose, but not in any placebo patient. Other adverse effects more common on the lower dose than in the placebo group included headache in 16%, and diarrhea in 9%.
Carbetocin is not only long-lasting in circulation, it also has better affinity for oxytocin receptors than for vasopressin receptors, reducing the potential for causing hyponatremia. The idea to use it in patients with PWS followed prior studies with oxytocin, which had shown dopamine interactions that reduced anxiety and influenced food ingestion behavior. Brain autopsy studies had shown that patients with Prader-Willi syndrome have substantially fewer neurons than usual producing oxytocin. Treatment with intranasal carbetocin had shown efficacy for improving hyperphagia and behavior in a controlled phase 2 study with 37 patients.
Carbetocin is approved for use in reducing excessive bleeding after childbirth, particularly cesarean, in more than 20 countries outside the United States.
CARE-PWS was sponsored by Levo Therapeutics, the company developing carbetocin. Dr. Deal has been an adviser to Levo Therapeutics. Dr. Strong is an employee of the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research, which has received support from Levo Therapeutics as well as from other drug companies, but which receives most of its funding from individuals. Dr. Miller has received research funding from Levo Therapeutics and also from Harmony Biosciences, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and Soleno Therapeutics.
Children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) who received three daily, intranasal doses of carbetocin, an investigational, long-acting oxytocin analogue, had significant improvement in hyperphagia and anxiety during 8 weeks on treatment, compared with placebo in a multicenter, phase 3 trial with 119 patients.
The treatment also appeared safe during up to 56 additional weeks on active treatment, with no serious adverse effects nor “unexpected” events, and once completing the study about 95% of enrolled patients opted to remain on active treatment, Cheri L. Deal, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on “the significant results for the placebo-controlled period, as well as for those finishing the 56-week extension, we may well have a new armament for helping these kids and their families deal with the unrelenting hunger of patients with PWS as well as some of the behavioral symptoms,” Dr. Deal, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at the Sainte-Justine Mother-Child University of Montreal Hospital, said in an interview. No treatment currently has labeling for addressing the hyperphagia or anxiety that is characteristic and often problematic for children and adolescents with PWS, an autosomal dominant genetic disease with an incidence of about 1 in 15,000 births and an estimated U.S. prevalence of about 9,000 cases, or about 1 case for every 37,000 people.
‘Gorgeous’ safety
“The results looked pretty positive, and we’re encouraged by what appears to be a good safety profile, so overall I think the PWS community is very excited by the results and is very interested in getting access to this drug,” commented Theresa V. Strong, PhD, director of research programs for the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research in Walnut, Calif., a group not involved with the study. Currently, “we have no effective treatments for these difficult behaviors” of hyperphagia and anxiety. Surveys and studies run by the foundation have documented that hyperphagia and anxiety “were the two most important symptoms that families would like to see treated,” Dr. Strong added in an interview.
PWS “is complex and affects almost every aspect of the lives of affected people and their families. Any treatment that can chip away at some of the problems these patients have can be a huge benefit to the patients and their families,” said Jennifer L. Miller, MD, a professor of pediatric endocrinology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and a coinvestigator on the study.
But the finding that carbetocin appeared to address, at least in part, this unmet need while compiling a safety record that Dr. Miller called “gorgeous” and “remarkable,” also came with a few limitations.
Fewer patients than planned, and muddled outcomes
The CARE-PWS trial aimed to enroll 175 patients, but fell short once the COVID-19 pandemic hit. Plus the trial had two prespecified primary endpoints – improvements in a measure of hyperphagia, and in a measure of obsessive and compulsive behaviors – specifically in the 40 patients who received the higher of the two dosages studied, 9.6 mg t.i.d. intranasally. Neither endpoint showed significant improvement among the patients on this dosage, compared with the 40 patients who received placebo, although both outcomes trended in the right direction in the actively treated patients.
The study’s positive results came in a secondary treatment group, 39 patients who received 3.2 mg t.i.d., also intranasally. This subgroup had significant benefit, compared with placebo, for reducing hyperphagia symptoms as measured on the Hyperphagia Questionnaire for Clinical Trials (HQ-CT) Total Score. After the first 8 weeks on treatment, patients on the lower carbetocin dosage had an average reduction in their HQ-CT score of greater than 5 points, more than double the reduction seen among control patients who received placebo.
Those on the 3.2-mg t.i.d. dosage also showed significant improvements, compared with placebo, for anxiety, measured by the PWS Anxiety and Distress Questionnaire Total Score, as well as on measures of clinical global impression of severity, and of clinical global impression of change. Like the higher-dosage patients the lower-dosage subgroup did not show a significant difference compared with placebo for the other primary endpoint, change in obsessive and compulsive behaviors as measured by the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale Total Score, although also like the higher dosage the effect from the lower dosage trended toward benefit.
A further limitation was that, at the time of her report, presented in abstract OR16-3 at the meeting, Dr. Deal could only present complete 64-week follow-up for 72 patients, although this reassuringly showed that, as time on the 9.6-mg t.i.d. dosage continued beyond 8 weeks, patients gradually improved their HQ-CT response so that by 64 weeks on treatment their hyperphagia score had improved as much as in the patients who received the lower dosage.
In short, documented benefits occurred on the lower dosage, especially for clinically meaningful symptoms like hyperphagia and anxiety, but the study’s overall results were not fully consistent by statistical criteria.
Benefiting an unmet need?
“While it is regrettable that we did not get to 175 patients because of COVID-19, the dataset is significant enough for me to feel that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] needs to take a very serious look and consider approval,” Dr. Deal said in an interview. “Once safety is assured, which I think it is, I can only hope that regulatory officials understand their unmet needs of this rare disease community and will allow the drug to move to the next stage.”
“This is a very rare disease, and having families participate in trials is really challenging,” especially while the COVID-19 pandemic continues, Dr. Strong said. For the pediatric and adolescent patients targeted in this study “it will take a while for COVID to go away and for families to feel safe again being in a trial, so a real concern is that a need for more clinical trials is not terribly feasible now. Given that the safety profile looked good and one dose seemed to have good efficacy, as long as the long-term data continue to look good we’d love for the FDA to look at the existing data and see whether there is a path forward.”
Dr. Miller highlighted the limitations of what the CARE-PWS findings show.
“Given that it was only an 8-week trial of drug against placebo, and the fact that the primary outcomes weren’t met for the higher dose, my thought is that potentially we need to study more patients for a longer period at the 3.2-mg dose,” she said. She acknowledged that the metric used in the study to assess obsessive and compulsive behaviors is “very difficult” to apply to patients with PWS because of uncertainties in scoring obsessions in patients “who are not very good at telling you what they’re thinking.” Plus, “it’s absolutely not a problem that we did not see an effect on obsession and compulsions if the treatment potentially improves anxiety and hyperphagia, which are very common.” A treatment that reliably reduces these symptoms “would be amazing,” Dr. Miller added.
“PWS is very rare, so it’s very hard to do trials. Maybe the FDA will approve carbetocin because it was safe and gave a signal of efficacy at the lower dose. But my thought is that additional treatment trials are needed with only the lower dose and with longer duration,” she said.
CARE-PWS enrolled patients with nutritional phase 3 PWS who were aged 7-18 years at any of 24 sites in the United States, Canada, or Australia during 2018-2020. They averaged about 12 years of age, and 56% were girls.
The most common adverse effect from carbetocin was flushing, occurring in 14% of those on the lower dose and 21% on the higher dose, but not in any placebo patient. Other adverse effects more common on the lower dose than in the placebo group included headache in 16%, and diarrhea in 9%.
Carbetocin is not only long-lasting in circulation, it also has better affinity for oxytocin receptors than for vasopressin receptors, reducing the potential for causing hyponatremia. The idea to use it in patients with PWS followed prior studies with oxytocin, which had shown dopamine interactions that reduced anxiety and influenced food ingestion behavior. Brain autopsy studies had shown that patients with Prader-Willi syndrome have substantially fewer neurons than usual producing oxytocin. Treatment with intranasal carbetocin had shown efficacy for improving hyperphagia and behavior in a controlled phase 2 study with 37 patients.
Carbetocin is approved for use in reducing excessive bleeding after childbirth, particularly cesarean, in more than 20 countries outside the United States.
CARE-PWS was sponsored by Levo Therapeutics, the company developing carbetocin. Dr. Deal has been an adviser to Levo Therapeutics. Dr. Strong is an employee of the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research, which has received support from Levo Therapeutics as well as from other drug companies, but which receives most of its funding from individuals. Dr. Miller has received research funding from Levo Therapeutics and also from Harmony Biosciences, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and Soleno Therapeutics.
Children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) who received three daily, intranasal doses of carbetocin, an investigational, long-acting oxytocin analogue, had significant improvement in hyperphagia and anxiety during 8 weeks on treatment, compared with placebo in a multicenter, phase 3 trial with 119 patients.
The treatment also appeared safe during up to 56 additional weeks on active treatment, with no serious adverse effects nor “unexpected” events, and once completing the study about 95% of enrolled patients opted to remain on active treatment, Cheri L. Deal, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on “the significant results for the placebo-controlled period, as well as for those finishing the 56-week extension, we may well have a new armament for helping these kids and their families deal with the unrelenting hunger of patients with PWS as well as some of the behavioral symptoms,” Dr. Deal, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at the Sainte-Justine Mother-Child University of Montreal Hospital, said in an interview. No treatment currently has labeling for addressing the hyperphagia or anxiety that is characteristic and often problematic for children and adolescents with PWS, an autosomal dominant genetic disease with an incidence of about 1 in 15,000 births and an estimated U.S. prevalence of about 9,000 cases, or about 1 case for every 37,000 people.
‘Gorgeous’ safety
“The results looked pretty positive, and we’re encouraged by what appears to be a good safety profile, so overall I think the PWS community is very excited by the results and is very interested in getting access to this drug,” commented Theresa V. Strong, PhD, director of research programs for the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research in Walnut, Calif., a group not involved with the study. Currently, “we have no effective treatments for these difficult behaviors” of hyperphagia and anxiety. Surveys and studies run by the foundation have documented that hyperphagia and anxiety “were the two most important symptoms that families would like to see treated,” Dr. Strong added in an interview.
PWS “is complex and affects almost every aspect of the lives of affected people and their families. Any treatment that can chip away at some of the problems these patients have can be a huge benefit to the patients and their families,” said Jennifer L. Miller, MD, a professor of pediatric endocrinology at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and a coinvestigator on the study.
But the finding that carbetocin appeared to address, at least in part, this unmet need while compiling a safety record that Dr. Miller called “gorgeous” and “remarkable,” also came with a few limitations.
Fewer patients than planned, and muddled outcomes
The CARE-PWS trial aimed to enroll 175 patients, but fell short once the COVID-19 pandemic hit. Plus the trial had two prespecified primary endpoints – improvements in a measure of hyperphagia, and in a measure of obsessive and compulsive behaviors – specifically in the 40 patients who received the higher of the two dosages studied, 9.6 mg t.i.d. intranasally. Neither endpoint showed significant improvement among the patients on this dosage, compared with the 40 patients who received placebo, although both outcomes trended in the right direction in the actively treated patients.
The study’s positive results came in a secondary treatment group, 39 patients who received 3.2 mg t.i.d., also intranasally. This subgroup had significant benefit, compared with placebo, for reducing hyperphagia symptoms as measured on the Hyperphagia Questionnaire for Clinical Trials (HQ-CT) Total Score. After the first 8 weeks on treatment, patients on the lower carbetocin dosage had an average reduction in their HQ-CT score of greater than 5 points, more than double the reduction seen among control patients who received placebo.
Those on the 3.2-mg t.i.d. dosage also showed significant improvements, compared with placebo, for anxiety, measured by the PWS Anxiety and Distress Questionnaire Total Score, as well as on measures of clinical global impression of severity, and of clinical global impression of change. Like the higher-dosage patients the lower-dosage subgroup did not show a significant difference compared with placebo for the other primary endpoint, change in obsessive and compulsive behaviors as measured by the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale Total Score, although also like the higher dosage the effect from the lower dosage trended toward benefit.
A further limitation was that, at the time of her report, presented in abstract OR16-3 at the meeting, Dr. Deal could only present complete 64-week follow-up for 72 patients, although this reassuringly showed that, as time on the 9.6-mg t.i.d. dosage continued beyond 8 weeks, patients gradually improved their HQ-CT response so that by 64 weeks on treatment their hyperphagia score had improved as much as in the patients who received the lower dosage.
In short, documented benefits occurred on the lower dosage, especially for clinically meaningful symptoms like hyperphagia and anxiety, but the study’s overall results were not fully consistent by statistical criteria.
Benefiting an unmet need?
“While it is regrettable that we did not get to 175 patients because of COVID-19, the dataset is significant enough for me to feel that the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] needs to take a very serious look and consider approval,” Dr. Deal said in an interview. “Once safety is assured, which I think it is, I can only hope that regulatory officials understand their unmet needs of this rare disease community and will allow the drug to move to the next stage.”
“This is a very rare disease, and having families participate in trials is really challenging,” especially while the COVID-19 pandemic continues, Dr. Strong said. For the pediatric and adolescent patients targeted in this study “it will take a while for COVID to go away and for families to feel safe again being in a trial, so a real concern is that a need for more clinical trials is not terribly feasible now. Given that the safety profile looked good and one dose seemed to have good efficacy, as long as the long-term data continue to look good we’d love for the FDA to look at the existing data and see whether there is a path forward.”
Dr. Miller highlighted the limitations of what the CARE-PWS findings show.
“Given that it was only an 8-week trial of drug against placebo, and the fact that the primary outcomes weren’t met for the higher dose, my thought is that potentially we need to study more patients for a longer period at the 3.2-mg dose,” she said. She acknowledged that the metric used in the study to assess obsessive and compulsive behaviors is “very difficult” to apply to patients with PWS because of uncertainties in scoring obsessions in patients “who are not very good at telling you what they’re thinking.” Plus, “it’s absolutely not a problem that we did not see an effect on obsession and compulsions if the treatment potentially improves anxiety and hyperphagia, which are very common.” A treatment that reliably reduces these symptoms “would be amazing,” Dr. Miller added.
“PWS is very rare, so it’s very hard to do trials. Maybe the FDA will approve carbetocin because it was safe and gave a signal of efficacy at the lower dose. But my thought is that additional treatment trials are needed with only the lower dose and with longer duration,” she said.
CARE-PWS enrolled patients with nutritional phase 3 PWS who were aged 7-18 years at any of 24 sites in the United States, Canada, or Australia during 2018-2020. They averaged about 12 years of age, and 56% were girls.
The most common adverse effect from carbetocin was flushing, occurring in 14% of those on the lower dose and 21% on the higher dose, but not in any placebo patient. Other adverse effects more common on the lower dose than in the placebo group included headache in 16%, and diarrhea in 9%.
Carbetocin is not only long-lasting in circulation, it also has better affinity for oxytocin receptors than for vasopressin receptors, reducing the potential for causing hyponatremia. The idea to use it in patients with PWS followed prior studies with oxytocin, which had shown dopamine interactions that reduced anxiety and influenced food ingestion behavior. Brain autopsy studies had shown that patients with Prader-Willi syndrome have substantially fewer neurons than usual producing oxytocin. Treatment with intranasal carbetocin had shown efficacy for improving hyperphagia and behavior in a controlled phase 2 study with 37 patients.
Carbetocin is approved for use in reducing excessive bleeding after childbirth, particularly cesarean, in more than 20 countries outside the United States.
CARE-PWS was sponsored by Levo Therapeutics, the company developing carbetocin. Dr. Deal has been an adviser to Levo Therapeutics. Dr. Strong is an employee of the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research, which has received support from Levo Therapeutics as well as from other drug companies, but which receives most of its funding from individuals. Dr. Miller has received research funding from Levo Therapeutics and also from Harmony Biosciences, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and Soleno Therapeutics.
FROM ENDO 2021










