User login
Access to care: A nurse practitioner’s plea
Having been a reader of Pediatric News for years, I want to bring to light access-to-care issues involving COVID-19 medical facility restrictions for pediatric patients and their parents.
On March 27, 2020, I received a phone call from the Department of Human Services pleading with me to take a medically fragile child who was entering the foster care system that day. He had very specific needs, and they had no one available who could medically meet those needs. The week prior was my kids’ scheduled spring break; the week I got the call was the week that I was voluntarily furloughed from my job as a pediatric nurse practitioner so that I could stay home with my kids as their school would not be reopening for the year, and someone had to be with them. I was already home with my 3-year-old and 6-year-old, so why not add another?
Leo (name changed for privacy) came to me with a multitude of diagnoses, to say the least. Not only did he require physical, speech, and occupational therapy twice weekly, but he often had appointments with 10 different specialists at the local children’s hospital. The first few weeks he was in my care, we had almost daily visits to either therapists or specialists. Keeping up with these types of appointments in a normal world is difficult ... I was getting the crash course on how to navigate all of it in the COVID-19 world.
So now, I am the primary caregiver during the day for my two children and our medically fragile foster child who has multiple medical appointments a week. Our local children’s hospital allowed only the caregiver to accompany him to his visits. In theory this sounds great, right? Fewer people in a facility equals less exposure, less risk, and fewer COVID-19 infections.
But what about the negative consequences of these hospital policies? I have two other children I was caring for. I couldn’t take them to their grandparents’ house because people over age 65 years are at risk of having COVID-19 complications. I had been furloughed, so our income was half what it typically was. Regardless,
Now imagine if I were a single mom who had three kids and a lesser paying job. Schools are closed and she’s forced to work from home and homeschool her children. Or worse, she’s been laid off and living on unemployment. Do you think she is going to have the time or finances available to hire a babysitter so that she can take her medically fragile child in for his cardiology follow-up? Because not only does she have to pay the copays and whatever insurance doesn’t cover, but now she has to fork over $50 for child care. If you don’t know the answer already, it’s no, she does not have the time or the finances. So her child misses a cardiology appointment, which means that his meds weren’t increased according to his growth, which means his pulmonary hypertension is not controlled, which worsens his heart failure ... you get my drift.
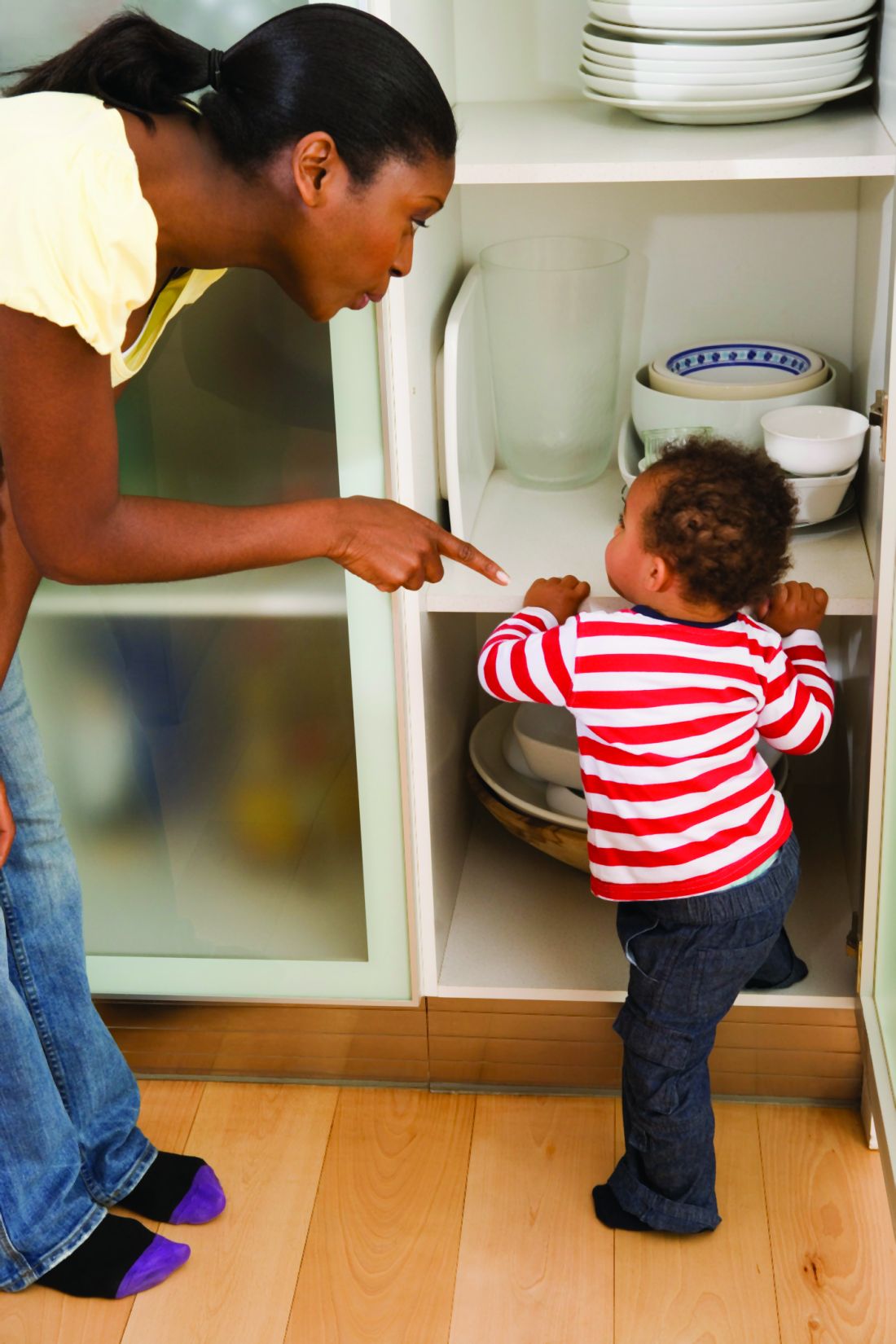
Fast forward to Sept. 22, 2020. I had a cardiology appointment at our local heart hospital for myself. It’s 2020, people, I’ve been having some palpitations that I needed checked out and was going in to have a heart monitor patch placed. I had my 4-year-old son with me because he is on a hybrid schedule where we homeschool 2 days a week. We entered the building wearing masks, and I was immediately stopped by security and informed that, according to the COVID-19 policy for their hospital, children under 16 are not allowed to enter the building. After some discussion, I was ultimately refused care because my son was with me that day. Refused care because I had a masked 4-year-old with a normal temperature at my side.
These policies are not working. We are in health care. It should not matter what pandemic is on the table, we should not be refusing patients access to care based on who is by their side that day. We knew the risks when we entered our profession, and we know the proper measures to protect ourselves. Our patients also know the risks and can protect themselves accordingly.
So this is my plea to all medical facilities out there: Stop. Stop telling people their loved ones can’t accompany them to appointments. Stop telling caregivers to wait in their cars while their elderly, demented mothers have their annual physicals. Stop telling moms they need to leave their other children at home. This is now a huge access-to-care issue nationwide and it needs to stop. Excess deaths in our nation are soaring, and it’s not just because people don’t want to seek medical attention; it’s because medical facilities are making it almost impossible to seek help for many. People are dying, and it’s not only from COVID-19. This is on us as health care providers, and we need to step up to the plate and do what is right.
Ms. Baxendale is a nurse practitioner in Mustang, Okla. Email her at [email protected].
Having been a reader of Pediatric News for years, I want to bring to light access-to-care issues involving COVID-19 medical facility restrictions for pediatric patients and their parents.
On March 27, 2020, I received a phone call from the Department of Human Services pleading with me to take a medically fragile child who was entering the foster care system that day. He had very specific needs, and they had no one available who could medically meet those needs. The week prior was my kids’ scheduled spring break; the week I got the call was the week that I was voluntarily furloughed from my job as a pediatric nurse practitioner so that I could stay home with my kids as their school would not be reopening for the year, and someone had to be with them. I was already home with my 3-year-old and 6-year-old, so why not add another?
Leo (name changed for privacy) came to me with a multitude of diagnoses, to say the least. Not only did he require physical, speech, and occupational therapy twice weekly, but he often had appointments with 10 different specialists at the local children’s hospital. The first few weeks he was in my care, we had almost daily visits to either therapists or specialists. Keeping up with these types of appointments in a normal world is difficult ... I was getting the crash course on how to navigate all of it in the COVID-19 world.
So now, I am the primary caregiver during the day for my two children and our medically fragile foster child who has multiple medical appointments a week. Our local children’s hospital allowed only the caregiver to accompany him to his visits. In theory this sounds great, right? Fewer people in a facility equals less exposure, less risk, and fewer COVID-19 infections.
But what about the negative consequences of these hospital policies? I have two other children I was caring for. I couldn’t take them to their grandparents’ house because people over age 65 years are at risk of having COVID-19 complications. I had been furloughed, so our income was half what it typically was. Regardless,
Now imagine if I were a single mom who had three kids and a lesser paying job. Schools are closed and she’s forced to work from home and homeschool her children. Or worse, she’s been laid off and living on unemployment. Do you think she is going to have the time or finances available to hire a babysitter so that she can take her medically fragile child in for his cardiology follow-up? Because not only does she have to pay the copays and whatever insurance doesn’t cover, but now she has to fork over $50 for child care. If you don’t know the answer already, it’s no, she does not have the time or the finances. So her child misses a cardiology appointment, which means that his meds weren’t increased according to his growth, which means his pulmonary hypertension is not controlled, which worsens his heart failure ... you get my drift.
Fast forward to Sept. 22, 2020. I had a cardiology appointment at our local heart hospital for myself. It’s 2020, people, I’ve been having some palpitations that I needed checked out and was going in to have a heart monitor patch placed. I had my 4-year-old son with me because he is on a hybrid schedule where we homeschool 2 days a week. We entered the building wearing masks, and I was immediately stopped by security and informed that, according to the COVID-19 policy for their hospital, children under 16 are not allowed to enter the building. After some discussion, I was ultimately refused care because my son was with me that day. Refused care because I had a masked 4-year-old with a normal temperature at my side.
These policies are not working. We are in health care. It should not matter what pandemic is on the table, we should not be refusing patients access to care based on who is by their side that day. We knew the risks when we entered our profession, and we know the proper measures to protect ourselves. Our patients also know the risks and can protect themselves accordingly.
So this is my plea to all medical facilities out there: Stop. Stop telling people their loved ones can’t accompany them to appointments. Stop telling caregivers to wait in their cars while their elderly, demented mothers have their annual physicals. Stop telling moms they need to leave their other children at home. This is now a huge access-to-care issue nationwide and it needs to stop. Excess deaths in our nation are soaring, and it’s not just because people don’t want to seek medical attention; it’s because medical facilities are making it almost impossible to seek help for many. People are dying, and it’s not only from COVID-19. This is on us as health care providers, and we need to step up to the plate and do what is right.
Ms. Baxendale is a nurse practitioner in Mustang, Okla. Email her at [email protected].
Having been a reader of Pediatric News for years, I want to bring to light access-to-care issues involving COVID-19 medical facility restrictions for pediatric patients and their parents.
On March 27, 2020, I received a phone call from the Department of Human Services pleading with me to take a medically fragile child who was entering the foster care system that day. He had very specific needs, and they had no one available who could medically meet those needs. The week prior was my kids’ scheduled spring break; the week I got the call was the week that I was voluntarily furloughed from my job as a pediatric nurse practitioner so that I could stay home with my kids as their school would not be reopening for the year, and someone had to be with them. I was already home with my 3-year-old and 6-year-old, so why not add another?
Leo (name changed for privacy) came to me with a multitude of diagnoses, to say the least. Not only did he require physical, speech, and occupational therapy twice weekly, but he often had appointments with 10 different specialists at the local children’s hospital. The first few weeks he was in my care, we had almost daily visits to either therapists or specialists. Keeping up with these types of appointments in a normal world is difficult ... I was getting the crash course on how to navigate all of it in the COVID-19 world.
So now, I am the primary caregiver during the day for my two children and our medically fragile foster child who has multiple medical appointments a week. Our local children’s hospital allowed only the caregiver to accompany him to his visits. In theory this sounds great, right? Fewer people in a facility equals less exposure, less risk, and fewer COVID-19 infections.
But what about the negative consequences of these hospital policies? I have two other children I was caring for. I couldn’t take them to their grandparents’ house because people over age 65 years are at risk of having COVID-19 complications. I had been furloughed, so our income was half what it typically was. Regardless,
Now imagine if I were a single mom who had three kids and a lesser paying job. Schools are closed and she’s forced to work from home and homeschool her children. Or worse, she’s been laid off and living on unemployment. Do you think she is going to have the time or finances available to hire a babysitter so that she can take her medically fragile child in for his cardiology follow-up? Because not only does she have to pay the copays and whatever insurance doesn’t cover, but now she has to fork over $50 for child care. If you don’t know the answer already, it’s no, she does not have the time or the finances. So her child misses a cardiology appointment, which means that his meds weren’t increased according to his growth, which means his pulmonary hypertension is not controlled, which worsens his heart failure ... you get my drift.
Fast forward to Sept. 22, 2020. I had a cardiology appointment at our local heart hospital for myself. It’s 2020, people, I’ve been having some palpitations that I needed checked out and was going in to have a heart monitor patch placed. I had my 4-year-old son with me because he is on a hybrid schedule where we homeschool 2 days a week. We entered the building wearing masks, and I was immediately stopped by security and informed that, according to the COVID-19 policy for their hospital, children under 16 are not allowed to enter the building. After some discussion, I was ultimately refused care because my son was with me that day. Refused care because I had a masked 4-year-old with a normal temperature at my side.
These policies are not working. We are in health care. It should not matter what pandemic is on the table, we should not be refusing patients access to care based on who is by their side that day. We knew the risks when we entered our profession, and we know the proper measures to protect ourselves. Our patients also know the risks and can protect themselves accordingly.
So this is my plea to all medical facilities out there: Stop. Stop telling people their loved ones can’t accompany them to appointments. Stop telling caregivers to wait in their cars while their elderly, demented mothers have their annual physicals. Stop telling moms they need to leave their other children at home. This is now a huge access-to-care issue nationwide and it needs to stop. Excess deaths in our nation are soaring, and it’s not just because people don’t want to seek medical attention; it’s because medical facilities are making it almost impossible to seek help for many. People are dying, and it’s not only from COVID-19. This is on us as health care providers, and we need to step up to the plate and do what is right.
Ms. Baxendale is a nurse practitioner in Mustang, Okla. Email her at [email protected].
Learning about “No”
To say that the pandemic has dropped us into uncharted territory is an understatement of unmeasurable proportions. Every day we learn more about it, and every day that new information brings us new challenges. COVID-19 is playing by its own set of rules. To keep pace with it societies have been forced to adapt to them, and members of those societies have had to realize that these new rules must be obeyed or be prepared to suffer the consequences.
I’m not sure exactly when it happened but gradually over my 7 and a half decades on this planet it appears that following the rules and understanding the value of “No” have become concepts to be ignored and left to gather dust in the attics and basements of our society. The tug of war between well-considered rules and the often misinterpreted concept of freedom has been ebbing and flowing since Eve plucked a forbidden apple off that tree.
In some parts of the world, the twin skills of saying and responding to “No” have become lost arts. I think it is not by chance that, of the four books I have written for parents, the one titled “How to Say No to Your Toddler” has become the most widely distributed, having been translated into Italian, Polish, and Russian. It is only slightly comforting to learn that at least some parents understand that creating rules can be important, but realize they aren’t quite sure how go about it.
As it has become clear that social distancing and mask wearing are associated with curtailing the spread of COVID-19, state and local governments have had to bone up on their long-forgotten No-saying skills. This relearning process has been particularly painful for school administrators who may have been warned that “You’ll never be able to get first and second graders to wear masks” or that “College students just won’t obey the rules.”
Both of these cautions are based on observations by educators with years of experience and certainly have a ring of truth to them. But could it be that these pessimistic predictions reflect a society in which parents and educators have lost the talent for crafting sensible rules and linking them to enforceable and rational consequences?
As colleges throughout the country have reopened using a variety of learning and residential strategies, there have been numerous incidents that validate the gloomy predictions of student misbehavior. Smaller schools seem to be having less difficulty, which is not surprising given their relative ease in fostering a sense of community. Many schools have been forced to rollback their plans for in-person learning because students have failed to follow some very simple but unpopular rules.
In a swift and decisive response to student misbehavior, Northeastern University in Boston dismissed 11 first-year students and will not refund their tuition when officials discovered a prohibited social gathering in one of the resident facilities (“Northeastern Dismisses 11 Students for Gathering in Violation of COVID-19 Policies,” by Ian Thomsen, News at Northwestern). This response seemed to have come as a surprise to many students and parents around the country who have become accustomed a diet of warnings and minor sanctions.
Whether this action by Northeastern will trigger similar responses by other universities remains to be seen. But we can hope that it sets an example of how learning about “No” can be an important part of one’s education.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
To say that the pandemic has dropped us into uncharted territory is an understatement of unmeasurable proportions. Every day we learn more about it, and every day that new information brings us new challenges. COVID-19 is playing by its own set of rules. To keep pace with it societies have been forced to adapt to them, and members of those societies have had to realize that these new rules must be obeyed or be prepared to suffer the consequences.
I’m not sure exactly when it happened but gradually over my 7 and a half decades on this planet it appears that following the rules and understanding the value of “No” have become concepts to be ignored and left to gather dust in the attics and basements of our society. The tug of war between well-considered rules and the often misinterpreted concept of freedom has been ebbing and flowing since Eve plucked a forbidden apple off that tree.
In some parts of the world, the twin skills of saying and responding to “No” have become lost arts. I think it is not by chance that, of the four books I have written for parents, the one titled “How to Say No to Your Toddler” has become the most widely distributed, having been translated into Italian, Polish, and Russian. It is only slightly comforting to learn that at least some parents understand that creating rules can be important, but realize they aren’t quite sure how go about it.
As it has become clear that social distancing and mask wearing are associated with curtailing the spread of COVID-19, state and local governments have had to bone up on their long-forgotten No-saying skills. This relearning process has been particularly painful for school administrators who may have been warned that “You’ll never be able to get first and second graders to wear masks” or that “College students just won’t obey the rules.”
Both of these cautions are based on observations by educators with years of experience and certainly have a ring of truth to them. But could it be that these pessimistic predictions reflect a society in which parents and educators have lost the talent for crafting sensible rules and linking them to enforceable and rational consequences?
As colleges throughout the country have reopened using a variety of learning and residential strategies, there have been numerous incidents that validate the gloomy predictions of student misbehavior. Smaller schools seem to be having less difficulty, which is not surprising given their relative ease in fostering a sense of community. Many schools have been forced to rollback their plans for in-person learning because students have failed to follow some very simple but unpopular rules.
In a swift and decisive response to student misbehavior, Northeastern University in Boston dismissed 11 first-year students and will not refund their tuition when officials discovered a prohibited social gathering in one of the resident facilities (“Northeastern Dismisses 11 Students for Gathering in Violation of COVID-19 Policies,” by Ian Thomsen, News at Northwestern). This response seemed to have come as a surprise to many students and parents around the country who have become accustomed a diet of warnings and minor sanctions.
Whether this action by Northeastern will trigger similar responses by other universities remains to be seen. But we can hope that it sets an example of how learning about “No” can be an important part of one’s education.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
To say that the pandemic has dropped us into uncharted territory is an understatement of unmeasurable proportions. Every day we learn more about it, and every day that new information brings us new challenges. COVID-19 is playing by its own set of rules. To keep pace with it societies have been forced to adapt to them, and members of those societies have had to realize that these new rules must be obeyed or be prepared to suffer the consequences.
I’m not sure exactly when it happened but gradually over my 7 and a half decades on this planet it appears that following the rules and understanding the value of “No” have become concepts to be ignored and left to gather dust in the attics and basements of our society. The tug of war between well-considered rules and the often misinterpreted concept of freedom has been ebbing and flowing since Eve plucked a forbidden apple off that tree.
In some parts of the world, the twin skills of saying and responding to “No” have become lost arts. I think it is not by chance that, of the four books I have written for parents, the one titled “How to Say No to Your Toddler” has become the most widely distributed, having been translated into Italian, Polish, and Russian. It is only slightly comforting to learn that at least some parents understand that creating rules can be important, but realize they aren’t quite sure how go about it.
As it has become clear that social distancing and mask wearing are associated with curtailing the spread of COVID-19, state and local governments have had to bone up on their long-forgotten No-saying skills. This relearning process has been particularly painful for school administrators who may have been warned that “You’ll never be able to get first and second graders to wear masks” or that “College students just won’t obey the rules.”
Both of these cautions are based on observations by educators with years of experience and certainly have a ring of truth to them. But could it be that these pessimistic predictions reflect a society in which parents and educators have lost the talent for crafting sensible rules and linking them to enforceable and rational consequences?
As colleges throughout the country have reopened using a variety of learning and residential strategies, there have been numerous incidents that validate the gloomy predictions of student misbehavior. Smaller schools seem to be having less difficulty, which is not surprising given their relative ease in fostering a sense of community. Many schools have been forced to rollback their plans for in-person learning because students have failed to follow some very simple but unpopular rules.
In a swift and decisive response to student misbehavior, Northeastern University in Boston dismissed 11 first-year students and will not refund their tuition when officials discovered a prohibited social gathering in one of the resident facilities (“Northeastern Dismisses 11 Students for Gathering in Violation of COVID-19 Policies,” by Ian Thomsen, News at Northwestern). This response seemed to have come as a surprise to many students and parents around the country who have become accustomed a diet of warnings and minor sanctions.
Whether this action by Northeastern will trigger similar responses by other universities remains to be seen. But we can hope that it sets an example of how learning about “No” can be an important part of one’s education.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Endometriosis, surgical approach impact risk of bowel injury in hysterectomy
Hysterectomies performed using an abdominal surgical approach or in women with endometriosis are more likely to carry an increased risk of bowel injury, according to recent results published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Cici R. Zhu, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Ottawa, and colleagues retrospectively studied the incidence of bowel injury in women participating in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who underwent hysterectomy for a benign surgical indication between 2012 and 2016.
“Although the absolute incidence is low, bowel injuries are among the most devastating complications of hysterectomy, as they can lead to a wide range of complications, including peritonitis, abscess formation, enterocutaneous fistula, sepsis, and even death,” Dr. Zhu and colleagues wrote. “Secondary bowel surgeries are often required, and associated ileostomies and colostomies can be distressing to patients. This not only severely affects quality of life, but the resultant readmissions, reoperations, and prolonged hospitalizations can impose a substantial economic toll on the health care system.”
Overall, 155,557 women were included in the study. The cohort consisted of women who were a mean age of 48 years and had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 31 kg/m2. The researchers evaluated whether baseline characteristics, clinical, and surgical variables impacted the incidence of bowel injury. They analyzed data of participant age, race (White vs. non-White), BMI, comorbid conditions (smoking, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and bleeding disorder), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, surgical approach (abdominal, laparoscopic, or vaginal), hysterectomy type (total or subtotal), lysis of adhesions, operation time, and admission type. Indication for hysterectomy was also evaluated, which included uterine leiomyoma (32.9%), menstrual disorders (22.0%), genital prolapse (13.1%), endometriosis (6.8%) and pelvic pain (3.8%).
Endometriosis, abdominal approach raise risk
There were 610 cases of bowel injury observed in the study, for an overall injury rate of 0.39%. A majority of the repairs were done during surgery (82.3%), with the remainder performed within 30 days of hysterectomy. Women with endometriosis had the most frequent incidence of bowel injury (0.59%), but it also occurred in women with uterine leiomyomas (0.47%), pain (0.24%), menstrual disorders (0.20%), genital prolapse (0.18%) and other indications (0.56%).
Dr. Zhu and colleagues found risk of bowel injury was higher among women 55 years and older, compared with women aged younger than 40 years (odds ratio, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.28-2.15); in non-White women, compared with White women (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.62-2.28); and in women with class 3 obesity, compared with women at a normal BMI (OR, 1.81; 95 CI, 1.40-2.34). Other risk factors for bowel injury included hypertension (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.17-1.64) and ASA III, IV, and V classification, compared with ASA I classification (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.43-2.58).
Researchers noted there was a statistically significant difference in rates of bowel injury between hysterectomy indications (P < .001). When compared with endometriosis, there were lower odds of bowel injury among women with uterine leiomyomas (adjusted odds ratio, 0.44; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.59), genital prolapse (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.67), and menstrual disorder (aOR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.23-0.48).
Surgical factors also impacted the risk for bowel injury. In hysterectomies where the abdominal approach was used, there was an over-tenfold risk of bowel injury, compared with when a vaginal approach was used (OR, 10.80; 95% CI, 7.31-15.95). Lysis of lesions carried an increased risk of bowel injury (OR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.20-4.40), and a subtotal hysterectomy increased the risk of bowel injury, compared with when a total hysterectomy was performed (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.42-2.18).
The researchers acknowledged the lack of detailed clinical information on surgical indications, severity of bowel injury, and training of the surgeons and surgical team, and potential for missing information may limit the application of the study findings.
Findings must be cautiously interpreted
Kate Stampler, DO, assistant program director of minimally invasive gynecologic robotic surgery at Einstein Healthcare Network in Philadelphia, said in an interview that the study by Zhu et al. is a good reminder of the patient and surgical risk factors that can occur that affect outcomes of hysterectomy.
“In my clinical practice, I have not seen a significant difference in route of hysterectomy and bowel injury, however, this must be interpreted carefully in the context of an infrequent complication and as an MIS [minimally invasive surgery]-trained surgeon performing various complex cases,” she said. Other reports in the literature have not identified a difference in the rate of bowel injury based on surgical approach, but the study by Zhu et al. is “unique to the literature in its large sample size,” she explained.
“I would encourage less experienced surgeons to operate with a higher-volume assistant surgeon if the end result means being able to perform an MIS approach, or appropriately offer referral if feasible to another surgeon for best practices. A thorough informed consent of the available route of hysterectomy is integral to good surgical care and allows for shared decision making for the patient,” Dr. Stampler said. “Additionally, participation in a large quality reporting system such as ACS National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database should be considered broadly and we should strive for overall high-value care.”
Regarding endometriosis being a risk factor for bowel injury during hysterectomy, Dr. Stampler noted that severe endometriosis poses a significant challenge for gynecologic surgeons. “Loss of anatomic planes due to dense adhesions and fibrosis, in addition to deep infiltrating lesions, can add significant time, complexity, and risk to the procedure. This can be compounded in a scenario with less experienced surgeons and unplanned disease at the time of surgery.”
Dr. Stampler also applauded the paper for highlighting the differences in White and non-White patient outcomes for hysterectomy, and emphasized that it is not new information. “Their call to continue to address the social determinants of health in an effort to minimize risk and maximize safety for our patients of color is of critical importance now more than ever. While the hypothesis for this study was not meant to address this challenge specifically, the data should serve as a striking reminder that while several factors may be playing a role in surgical complications, ongoing systemic racism is a component that needs dedicated time and attention.”
Dr. Zhu and three coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures. One coauthor received support from the University of Ottawa Clinical Research Chair in Reproductive Population Health and Health Services, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation to conduct this research. Two other coauthors reported financial relationships with various pharmaceutical and medical technology companies. Dr. Stampler reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhu CR et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Oct. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004007.
Hysterectomies performed using an abdominal surgical approach or in women with endometriosis are more likely to carry an increased risk of bowel injury, according to recent results published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Cici R. Zhu, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Ottawa, and colleagues retrospectively studied the incidence of bowel injury in women participating in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who underwent hysterectomy for a benign surgical indication between 2012 and 2016.
“Although the absolute incidence is low, bowel injuries are among the most devastating complications of hysterectomy, as they can lead to a wide range of complications, including peritonitis, abscess formation, enterocutaneous fistula, sepsis, and even death,” Dr. Zhu and colleagues wrote. “Secondary bowel surgeries are often required, and associated ileostomies and colostomies can be distressing to patients. This not only severely affects quality of life, but the resultant readmissions, reoperations, and prolonged hospitalizations can impose a substantial economic toll on the health care system.”
Overall, 155,557 women were included in the study. The cohort consisted of women who were a mean age of 48 years and had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 31 kg/m2. The researchers evaluated whether baseline characteristics, clinical, and surgical variables impacted the incidence of bowel injury. They analyzed data of participant age, race (White vs. non-White), BMI, comorbid conditions (smoking, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and bleeding disorder), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, surgical approach (abdominal, laparoscopic, or vaginal), hysterectomy type (total or subtotal), lysis of adhesions, operation time, and admission type. Indication for hysterectomy was also evaluated, which included uterine leiomyoma (32.9%), menstrual disorders (22.0%), genital prolapse (13.1%), endometriosis (6.8%) and pelvic pain (3.8%).
Endometriosis, abdominal approach raise risk
There were 610 cases of bowel injury observed in the study, for an overall injury rate of 0.39%. A majority of the repairs were done during surgery (82.3%), with the remainder performed within 30 days of hysterectomy. Women with endometriosis had the most frequent incidence of bowel injury (0.59%), but it also occurred in women with uterine leiomyomas (0.47%), pain (0.24%), menstrual disorders (0.20%), genital prolapse (0.18%) and other indications (0.56%).
Dr. Zhu and colleagues found risk of bowel injury was higher among women 55 years and older, compared with women aged younger than 40 years (odds ratio, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.28-2.15); in non-White women, compared with White women (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.62-2.28); and in women with class 3 obesity, compared with women at a normal BMI (OR, 1.81; 95 CI, 1.40-2.34). Other risk factors for bowel injury included hypertension (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.17-1.64) and ASA III, IV, and V classification, compared with ASA I classification (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.43-2.58).
Researchers noted there was a statistically significant difference in rates of bowel injury between hysterectomy indications (P < .001). When compared with endometriosis, there were lower odds of bowel injury among women with uterine leiomyomas (adjusted odds ratio, 0.44; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.59), genital prolapse (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.67), and menstrual disorder (aOR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.23-0.48).
Surgical factors also impacted the risk for bowel injury. In hysterectomies where the abdominal approach was used, there was an over-tenfold risk of bowel injury, compared with when a vaginal approach was used (OR, 10.80; 95% CI, 7.31-15.95). Lysis of lesions carried an increased risk of bowel injury (OR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.20-4.40), and a subtotal hysterectomy increased the risk of bowel injury, compared with when a total hysterectomy was performed (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.42-2.18).
The researchers acknowledged the lack of detailed clinical information on surgical indications, severity of bowel injury, and training of the surgeons and surgical team, and potential for missing information may limit the application of the study findings.
Findings must be cautiously interpreted
Kate Stampler, DO, assistant program director of minimally invasive gynecologic robotic surgery at Einstein Healthcare Network in Philadelphia, said in an interview that the study by Zhu et al. is a good reminder of the patient and surgical risk factors that can occur that affect outcomes of hysterectomy.
“In my clinical practice, I have not seen a significant difference in route of hysterectomy and bowel injury, however, this must be interpreted carefully in the context of an infrequent complication and as an MIS [minimally invasive surgery]-trained surgeon performing various complex cases,” she said. Other reports in the literature have not identified a difference in the rate of bowel injury based on surgical approach, but the study by Zhu et al. is “unique to the literature in its large sample size,” she explained.
“I would encourage less experienced surgeons to operate with a higher-volume assistant surgeon if the end result means being able to perform an MIS approach, or appropriately offer referral if feasible to another surgeon for best practices. A thorough informed consent of the available route of hysterectomy is integral to good surgical care and allows for shared decision making for the patient,” Dr. Stampler said. “Additionally, participation in a large quality reporting system such as ACS National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database should be considered broadly and we should strive for overall high-value care.”
Regarding endometriosis being a risk factor for bowel injury during hysterectomy, Dr. Stampler noted that severe endometriosis poses a significant challenge for gynecologic surgeons. “Loss of anatomic planes due to dense adhesions and fibrosis, in addition to deep infiltrating lesions, can add significant time, complexity, and risk to the procedure. This can be compounded in a scenario with less experienced surgeons and unplanned disease at the time of surgery.”
Dr. Stampler also applauded the paper for highlighting the differences in White and non-White patient outcomes for hysterectomy, and emphasized that it is not new information. “Their call to continue to address the social determinants of health in an effort to minimize risk and maximize safety for our patients of color is of critical importance now more than ever. While the hypothesis for this study was not meant to address this challenge specifically, the data should serve as a striking reminder that while several factors may be playing a role in surgical complications, ongoing systemic racism is a component that needs dedicated time and attention.”
Dr. Zhu and three coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures. One coauthor received support from the University of Ottawa Clinical Research Chair in Reproductive Population Health and Health Services, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation to conduct this research. Two other coauthors reported financial relationships with various pharmaceutical and medical technology companies. Dr. Stampler reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhu CR et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Oct. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004007.
Hysterectomies performed using an abdominal surgical approach or in women with endometriosis are more likely to carry an increased risk of bowel injury, according to recent results published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Cici R. Zhu, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Ottawa, and colleagues retrospectively studied the incidence of bowel injury in women participating in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who underwent hysterectomy for a benign surgical indication between 2012 and 2016.
“Although the absolute incidence is low, bowel injuries are among the most devastating complications of hysterectomy, as they can lead to a wide range of complications, including peritonitis, abscess formation, enterocutaneous fistula, sepsis, and even death,” Dr. Zhu and colleagues wrote. “Secondary bowel surgeries are often required, and associated ileostomies and colostomies can be distressing to patients. This not only severely affects quality of life, but the resultant readmissions, reoperations, and prolonged hospitalizations can impose a substantial economic toll on the health care system.”
Overall, 155,557 women were included in the study. The cohort consisted of women who were a mean age of 48 years and had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 31 kg/m2. The researchers evaluated whether baseline characteristics, clinical, and surgical variables impacted the incidence of bowel injury. They analyzed data of participant age, race (White vs. non-White), BMI, comorbid conditions (smoking, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, and bleeding disorder), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification, surgical approach (abdominal, laparoscopic, or vaginal), hysterectomy type (total or subtotal), lysis of adhesions, operation time, and admission type. Indication for hysterectomy was also evaluated, which included uterine leiomyoma (32.9%), menstrual disorders (22.0%), genital prolapse (13.1%), endometriosis (6.8%) and pelvic pain (3.8%).
Endometriosis, abdominal approach raise risk
There were 610 cases of bowel injury observed in the study, for an overall injury rate of 0.39%. A majority of the repairs were done during surgery (82.3%), with the remainder performed within 30 days of hysterectomy. Women with endometriosis had the most frequent incidence of bowel injury (0.59%), but it also occurred in women with uterine leiomyomas (0.47%), pain (0.24%), menstrual disorders (0.20%), genital prolapse (0.18%) and other indications (0.56%).
Dr. Zhu and colleagues found risk of bowel injury was higher among women 55 years and older, compared with women aged younger than 40 years (odds ratio, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.28-2.15); in non-White women, compared with White women (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.62-2.28); and in women with class 3 obesity, compared with women at a normal BMI (OR, 1.81; 95 CI, 1.40-2.34). Other risk factors for bowel injury included hypertension (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.17-1.64) and ASA III, IV, and V classification, compared with ASA I classification (OR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.43-2.58).
Researchers noted there was a statistically significant difference in rates of bowel injury between hysterectomy indications (P < .001). When compared with endometriosis, there were lower odds of bowel injury among women with uterine leiomyomas (adjusted odds ratio, 0.44; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.59), genital prolapse (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.67), and menstrual disorder (aOR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.23-0.48).
Surgical factors also impacted the risk for bowel injury. In hysterectomies where the abdominal approach was used, there was an over-tenfold risk of bowel injury, compared with when a vaginal approach was used (OR, 10.80; 95% CI, 7.31-15.95). Lysis of lesions carried an increased risk of bowel injury (OR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.20-4.40), and a subtotal hysterectomy increased the risk of bowel injury, compared with when a total hysterectomy was performed (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.42-2.18).
The researchers acknowledged the lack of detailed clinical information on surgical indications, severity of bowel injury, and training of the surgeons and surgical team, and potential for missing information may limit the application of the study findings.
Findings must be cautiously interpreted
Kate Stampler, DO, assistant program director of minimally invasive gynecologic robotic surgery at Einstein Healthcare Network in Philadelphia, said in an interview that the study by Zhu et al. is a good reminder of the patient and surgical risk factors that can occur that affect outcomes of hysterectomy.
“In my clinical practice, I have not seen a significant difference in route of hysterectomy and bowel injury, however, this must be interpreted carefully in the context of an infrequent complication and as an MIS [minimally invasive surgery]-trained surgeon performing various complex cases,” she said. Other reports in the literature have not identified a difference in the rate of bowel injury based on surgical approach, but the study by Zhu et al. is “unique to the literature in its large sample size,” she explained.
“I would encourage less experienced surgeons to operate with a higher-volume assistant surgeon if the end result means being able to perform an MIS approach, or appropriately offer referral if feasible to another surgeon for best practices. A thorough informed consent of the available route of hysterectomy is integral to good surgical care and allows for shared decision making for the patient,” Dr. Stampler said. “Additionally, participation in a large quality reporting system such as ACS National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database should be considered broadly and we should strive for overall high-value care.”
Regarding endometriosis being a risk factor for bowel injury during hysterectomy, Dr. Stampler noted that severe endometriosis poses a significant challenge for gynecologic surgeons. “Loss of anatomic planes due to dense adhesions and fibrosis, in addition to deep infiltrating lesions, can add significant time, complexity, and risk to the procedure. This can be compounded in a scenario with less experienced surgeons and unplanned disease at the time of surgery.”
Dr. Stampler also applauded the paper for highlighting the differences in White and non-White patient outcomes for hysterectomy, and emphasized that it is not new information. “Their call to continue to address the social determinants of health in an effort to minimize risk and maximize safety for our patients of color is of critical importance now more than ever. While the hypothesis for this study was not meant to address this challenge specifically, the data should serve as a striking reminder that while several factors may be playing a role in surgical complications, ongoing systemic racism is a component that needs dedicated time and attention.”
Dr. Zhu and three coauthors reported no relevant financial disclosures. One coauthor received support from the University of Ottawa Clinical Research Chair in Reproductive Population Health and Health Services, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation to conduct this research. Two other coauthors reported financial relationships with various pharmaceutical and medical technology companies. Dr. Stampler reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhu CR et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Oct. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004007.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy ‘somewhat understandable,’ expert says
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 and the superspreaders: Teens
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Pediatric fractures shift during pandemic
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Work-life balance: How 5 surgeons manage life in and out of the operating room
Patrick J. Culligan, MD:
My impression of our younger colleagues, however, is that many of them are not attracted to the traditional ivory tower research model of academic advancement to which many in previous generations aspired. They seem more concerned with work-life balance as their measure of success rather than the classic metrics of money and prestige. Everyone still needs role models and mentors, though, and that’s where all of you come in. I asked each of you to be on this panel because I admire you for your varying approaches to work-life balance while achieving success as gynecologic surgeons. I thought others in the field might be inspired by hearing your stories.
Cultivating your passions
Kristie Greene, MD: What I have come to learn and appreciate is a really simple point: you do not have to do everything. Determining who you want to be both personally and professionally is step 1.
Granted, answering the question, “Who do I want to be?” is not as simple as it sounds. Many factors figure into the decisions we make in our personal and professional lives. Also, it is not a question we often stop and ask ourselves. From early on, we are placed on an escalator moving up through medical school, residency, fellowship, good job, better job, etc. We are so accustomed to being competitive, to winning, and to wanting to be the best that we sometimes forget to ask ourselves, “What is it exactly that I want, and why? What is my endpoint? And does it make me happy?”
Multitasking is regarded as a talent. As much as we would like to believe that we can do everything at the same time and do it all well, we actually can’t. A friend of mine made me read a book a couple of years ago, called Feeling Good, by David Burns. The book encourages you to consider the different tasks you do in a day and rate how good you are at each of them on a scale of 1 to 10. It then asks you to think about how much enjoyment you derive from each of the tasks and about why you are doing the ones that bring you little to no enjoyment.
I ultimately decided that, for me professionally, the most important thing was my interest in global health. So I decided to do whatever it took to make this happen. But you don’t get something for nothing, and everything comes with sacrifices.
Continue to: Charles Rardin, MD...
Charles Rardin, MD: How exactly did you decide that you were going to focus your career toward pursuing international health? How did you know it was more important? And how did you overcome some of those obstacles?
Dr. Greene: You have to ask the hard question again about what brings you the most joy professionally and personally. That was the easy part of it for me because global health has always been that source of happiness and fulfillment for me. The more challenging parts are the sacrifices and hard choices that come with it. With global health, it can be difficult to balance the demands of a clinical practice.
All of our jobs are a business. I am still struggling with the money part of it. For my husband and I, that meant we had to start small—do what we could afford. But then it blossomed into something that was involving residents, fellows, and med students, which requires far more funding than we had. So I reached out to family. Most of our families donate to different organizations or charities every year, so why not donate to a loved one for something they are passionate about?
At the University of South Florida (USF), we set up a fund, a foundation for global health, which helps support our work abroad as well as the costs associated with involvement of our trainees. Right now, what we have is still small potatoes to a country, but we are making it happen by starting at a small level and growing it.
Beyond the money aspect, traveling abroad means less involvement in meetings, missed opportunities to teach courses that might interest me, and time away from my family. I guess my advice on this whole thing is that you can make things happen if they are important enough to you, and if you are willing to make sacrifices in other areas because you can’t have it all.
Making time for you
Dr. Culligan: So you have found what is important to you, and you have found a way to make it happen. But you are faced with more work; you have given yourself additional work on top of your regular work. How do you make time for a personal life?
Catherine Matthews, MD: In preparing for this discussion, I decided to break down my advice into 3 buckets: The first bucket is discovering and knowing your authentic self. The second is building a community, which I’ll elaborate on. And the third, which we have discussed, is to let go of the money.
Dr. Culligan: I love the concept of the authentic self, but how does that jive with a tendency to strive for perfection? We all think we can do it all. How do we narrow down to what really matters?
Dr. Matthews: We often focus on the things that bring us happiness and what we are good at, but it’s the things that make us unhappy that tend to bring us down. It’s the presence of unhappiness, not the absence of happiness, that seems to be the undoing of many, including myself.
None of us are born with dramatic insight. It is experience that leads to insight. People who are actually present are able to gain insight through observation. A person becomes a better surgeon by observing the outcome of doing a stitch this way versus that; you learn how to do it by seeing what it looks like afterward.
Finding our authentic selves happens in much the same way. Having the presence of mind to ask the right questions, such as, “How am I feeling while I’m doing this?” leads to insights into the true self.
Continue to: It takes a village...
It takes a village
Dr. Greene: Catherine mentioned community earlier, and that is extremely important. The people who surround us can have a huge impact on the way we perceive things, including ourselves. Having a mix of people in our lives—some who practice medicine and others who don’t—helps us stay balanced and answer some of the tough questions. Catherine, for example, has helped me in various stages of my career to ask myself meaningful questions and get real answers.
Dr. Rardin: Part of finding balance is luck, and part of it is making a choice between money and everything else. In considering my first job out of training, I knew that money had the potential to distract me from what was important to me. So I chose a position that was almost entirely salaried so that the decisions I made clinically, surgically, and regarding work-life balance would be less likely to directly impact what was important to me.
Sally Huber, MD: I am still in the “getting there” phase of my life, but one thing I have found is that getting my family involved and excited about what I do has made them much more accepting of when I have longer work days or work to do on the weekend. My spouse has become quite involved with what I have been doing with transgender health in Atlanta. It has been a great bonding experience; she shares my passions, and together we are creating something about which we both can be proud.
When work invades home life
Dr. Culligan: That is great. Sally, I think when we talked, you were just learning about the necessity of mental separation and of not taking your work home with you, which is so hard for all of us with all of our devices.
Dr. Huber: Yes, this year has been about seeing what works best as far as being efficient at work and having quality time at home. At the end of every day I ask myself, “What worked well today? What didn’t work well? What else can I do to maximize time with my family?” I am slowly becoming more efficient, but it has been a challenge. During fellowship, your day is pretty set, but once you are practicing on your own, your hours and responsibilities are completely different, and you have to figure out what works best for you, your values, and your expectations of private life. It takes some time, and I am still figuring it out.
Dr. Culligan: How often would you say that you bring work home? I try hard once I am home to quit working, but sometimes on the weekends I break that rule.
Dr. Matthews: I must say that I do feel like there are certain times when I am better at that than others. Work comes in waves with pressing deadlines. If I averaged it out, probably a third of the time I have some email or some conference call or something that I have got to do at home. I do really try to limit the obligations that I have after 5:30 or 6:00 pm. I resent intrusions after that time. As far as weekends, I delegate about one weekend every 2 months to work, instead of doing a little bit every weekend.
Dr. Greene: I agree. I try hard to make 5:30 to 7:30 pm unequivocal time for a family dinner and time for my kids. During that time, I do not have my phone near me so I can’t look at email or texts. I try not to schedule conference calls. I try to be there to read books to my kids at night. Then if I need to do work, I do it later at night, which interferes with time with my spouse, and is not ideal, but that’s what happens.
Dr. Matthews: One of the things that I think is a huge part of work-life balance is work-related travel. When you are present at work on a consistent basis, the work does not pile up to the extent that it does when you are absent on a trip. When you come back, you invariably pay the price by seeing more patients and doing more surgery. Then it becomes a stressful event.
My advice to young people is to be very thoughtful about planning trips, especially distant ones. You do not want to sit on a plane all day when you could be doing something more productive. If I could have done something differently in my mid-career, I would have traveled less.
Continue to: Prioritizing “out of office” time...
Prioritizing “out of office” time
Dr. Greene: How do you all mentally separate yourself from work, so that when you are on vacation with your family you are not thinking about the office, the patients, and all of the things on your to-do list?
Dr. Rardin: I don’t have a great answer for that except that it is about being present. You have to decide that now is the time when I am home, now is the time when I am a parent, now is the time when I am a boy scout leader, etc. I guess maybe it’s a skill, or maybe it’s about making something a priority. Work will always be waiting for you when you turn your attention back to it.
Dr. Matthews: Kristie, the answer to your question goes back to community. Partners in a practice cover for each other. You have to trust them to take care of things so that you can relax during your time away.
Some people recommend not scheduling challenging cases right before going away because invariably something goes wrong, and then you are asking, “Why did I schedule 3 colpopexies before getting on a plane?”
Dr. Rardin: Yes, I completely agree with all of that. Personally, I feel fortunate that I can compartmentalize pretty well. When I am home with my kids, I allow myself to shed some of the doctor/surgeon/leadership persona; I am able to be goofy and completely non–doctor-like. It works to help me leave work behind.
Dr. Matthews: Other things you can do include setting up an out-of-office notice on your email that says when you will be back and what to do in case of urgent matters. This basically says to the world, “Don’t expect to hear from me until X date.” It removes the expectation that you will respond sooner. Otherwise, we would all be on our smartphones all the time and not enjoying our time away.
What I wish I knew then
Dr. Culligan: How would you complete the sentence, “I wish they had told me X when I was embarking on my career?”
Dr. Rardin: I keep coming back to the phrase, “Don’t do anything that you can reasonably pay someone else to do.” By that I mean, if you don’t get energy from housework, consider spending some of your money to get help with the housework. Resolve to make a relatively small expenditure to maximize the quality of the time that you give to yourself and your family. Those are the sorts of things that I think can go a long way.
Dr. Culligan: Charley, your wife is an ObGyn. How do you navigate a dual medical career household? What advice do you have for others?
Dr. Rardin: When I was going into fellowship, we had a conversation about how hard it is for both people in a relationship to have an academic fire in the belly and to be truly engaged in climbing the academic ladder. We made a decision that Jane would go into private practice. There has got to be some give and take in a dual medical relationship; a lot of sacrifices and compromises need to happen. We are fortunate in that there are complementary aspects to our jobs. We both spend about the same number of nights away from the house, but my travel is more in chunks and hers is overnight calls for labor and delivery. We have different ways of (briefly) single-parenting, and you have to come up with ways to handle the domestic chores.
Dr. Matthews: I wish someone had explained to me that the people you work with are much more important than the place. The human connection is what defines your experience, much more than any ego-driven outcome.
Dr. Greene: I wish someone had explained to me the competing aspects of academic medicine. The cards are stacked in a way that make it difficult for you to win. For example, you may love to teach and may be really good at it, but if you let your students handle too many cases, your relative value units plummet and then the hospital is on your back. There are the interests of people, and there are the interests of the business. Everything is a balance, and it’s really tricky.
Dr. Huber: Luckily, Pat counselled me as I was finishing my fellowship about the importance of negotiating a good contract, of being pushy and knowing what you want out of it and knowing what your limitations are. I joined a private practice that had 3 different physical locations. If I had to drive to all of them, as they wanted, it would have meant up to a one-and-a-half-hour commute. But I pushed to stay in one location and to put that extra hour to better use. I am glad I did, but it was terrifying at the time because I didn’t want to lose the offer. I know people that did not do that and took the first thing they got. Now, they are driving all over the place or they have these crazy hours or terrible call responsibilities that if they had just been a little firmer, they probably could have gotten out of. As they start trying to find work-life balance, they are already handicapped.
Continue to: Passions outside the office...
Passions outside the office
Dr. Culligan: One thing I would like to touch on is what is going on in each of your personal lives because all of you have interesting stories to tell outside of what you do professionally. What drives you other than medicine?
Dr. Rardin: I am the father of 3 boys. The oldest one just got his Eagle Scout rank yesterday in Boy Scouts. I would be a woodworker if I wasn’t in medicine. I am a Deacon at church. And I love to spend my downtime reading with my family in front of the fireplace.
Dr. Matthews: For me, it’s music. When my husband and I first met, he asked me if I played a musical instrument. I said I played the cello in primary school. He said, “Great, go rent a cello.” I was never at all interested in playing the cello by myself, but because he plays guitar and piano we became able to play a lot of music together. Our son, Alexander, plays drums. We now have a family band.
In addition, I do yoga. I would never have labeled myself an anxious person, but I learned through this process that I am and need to manage it. It took a lot of years to figure that out. If I don’t leave myself an hour each day to go to a yoga class, I am not a happy person and neither is anyone around me. Also, I get tremendous pleasure from reading books and magazines as opposed to watching a screen.
Dr. Greene: I have found that my passions outside of work often change depending on my stage of life. Right now, I have two young babies and so my life outside of work revolves around them. Before the babies, my dad, who lives in Buffalo, was ill. So for awhile, we were flying to Buffalo almost every weekend that I was not on call. I would say, in general what fuels me is connecting with the people I love as often as I can. A typical night involves me and my husband going for a walk with our kids and dog after dinner and talking to each other. We connect with neighbors and chat on the front porch. It doesn’t really matter what we are doing; it is about being surrounded by people who matter.
Dr. Huber: It’s similar for me. Having a child completely shifts your world view. My goal every day is to give my daughter her first feeding in the morning and to get home as soon as possible at the end of the day to do her last feeding and put her to sleep. She crawled for the first time yesterday, and I was so excited that I could be there for that.
Also, I love being outdoors. I love hiking and camping. Going on a hike and being outside with nature is my way of decompressing.
Continue to: Thinking about upcoming generations...
Thinking about upcoming generations
Dr. Matthews: One other thing I would like to propose is looking at what can we do to make the profession better for the next generation. As a group, our profession is somewhat inflexible. We tend to fall into the trap of, “since this is the way we have always done it this is how we should continue doing it.” The OR still starts at 7:00 or 7:30 am, ignoring the need for school drop-offs, etc. We are not innovative about flexibility in the work week. Honestly, it does not work well for many people, patients and physicians alike. Flexible scheduling should be something that is on the table for both men and women who are trying to balance being full-time parents and full-time surgeons. We need to create an environment in which it is okay for you to spend 10 years instead of 6 as an assistant professor because you are also a young parent, and it will not count against you when you come up for promotion.
Dr. Culligan: I agree with you, Catherine. Full “Professor” is a nice title, but it means time away from family and a lot of other things. Each of us has to decide whether it is worth it, especially since it often does not come with any extra money.
Dr. Huber: A question on a recent survey of residents asked, “Do you see yourself going into private practice or academic medicine when you’ve completed your residency?” When I was a resident, everyone wanted to go into academic medicine, but now it seems like more and more residents have their sights set on private practice because that is where they see the opportunities to create work-life balance.
In the academic world, you have to try to get a promotion in X number of years, and get X number of publications, and be a great teacher, doctor, and administrator all at the same time. I am wondering if we are going to start seeing more and more residents and fellows going into private or hospital-owned practice where there aren’t those added expectations.
Dr. Rardin: I agree, and we are back to what we said in the beginning about doing an honest assessment of what is meaningful and important. We are all trained to try to reach for that shiny brass ring, but do we really want that brass ring? Will it be an asset or a hindrance once we get it? It is okay to be honest and say, “I really don’t want that promotion. I would rather spend more time with my family.” ●
Patrick J. Culligan, MD:
My impression of our younger colleagues, however, is that many of them are not attracted to the traditional ivory tower research model of academic advancement to which many in previous generations aspired. They seem more concerned with work-life balance as their measure of success rather than the classic metrics of money and prestige. Everyone still needs role models and mentors, though, and that’s where all of you come in. I asked each of you to be on this panel because I admire you for your varying approaches to work-life balance while achieving success as gynecologic surgeons. I thought others in the field might be inspired by hearing your stories.
Cultivating your passions
Kristie Greene, MD: What I have come to learn and appreciate is a really simple point: you do not have to do everything. Determining who you want to be both personally and professionally is step 1.
Granted, answering the question, “Who do I want to be?” is not as simple as it sounds. Many factors figure into the decisions we make in our personal and professional lives. Also, it is not a question we often stop and ask ourselves. From early on, we are placed on an escalator moving up through medical school, residency, fellowship, good job, better job, etc. We are so accustomed to being competitive, to winning, and to wanting to be the best that we sometimes forget to ask ourselves, “What is it exactly that I want, and why? What is my endpoint? And does it make me happy?”
Multitasking is regarded as a talent. As much as we would like to believe that we can do everything at the same time and do it all well, we actually can’t. A friend of mine made me read a book a couple of years ago, called Feeling Good, by David Burns. The book encourages you to consider the different tasks you do in a day and rate how good you are at each of them on a scale of 1 to 10. It then asks you to think about how much enjoyment you derive from each of the tasks and about why you are doing the ones that bring you little to no enjoyment.
I ultimately decided that, for me professionally, the most important thing was my interest in global health. So I decided to do whatever it took to make this happen. But you don’t get something for nothing, and everything comes with sacrifices.
Continue to: Charles Rardin, MD...
Charles Rardin, MD: How exactly did you decide that you were going to focus your career toward pursuing international health? How did you know it was more important? And how did you overcome some of those obstacles?
Dr. Greene: You have to ask the hard question again about what brings you the most joy professionally and personally. That was the easy part of it for me because global health has always been that source of happiness and fulfillment for me. The more challenging parts are the sacrifices and hard choices that come with it. With global health, it can be difficult to balance the demands of a clinical practice.
All of our jobs are a business. I am still struggling with the money part of it. For my husband and I, that meant we had to start small—do what we could afford. But then it blossomed into something that was involving residents, fellows, and med students, which requires far more funding than we had. So I reached out to family. Most of our families donate to different organizations or charities every year, so why not donate to a loved one for something they are passionate about?
At the University of South Florida (USF), we set up a fund, a foundation for global health, which helps support our work abroad as well as the costs associated with involvement of our trainees. Right now, what we have is still small potatoes to a country, but we are making it happen by starting at a small level and growing it.
Beyond the money aspect, traveling abroad means less involvement in meetings, missed opportunities to teach courses that might interest me, and time away from my family. I guess my advice on this whole thing is that you can make things happen if they are important enough to you, and if you are willing to make sacrifices in other areas because you can’t have it all.
Making time for you
Dr. Culligan: So you have found what is important to you, and you have found a way to make it happen. But you are faced with more work; you have given yourself additional work on top of your regular work. How do you make time for a personal life?
Catherine Matthews, MD: In preparing for this discussion, I decided to break down my advice into 3 buckets: The first bucket is discovering and knowing your authentic self. The second is building a community, which I’ll elaborate on. And the third, which we have discussed, is to let go of the money.
Dr. Culligan: I love the concept of the authentic self, but how does that jive with a tendency to strive for perfection? We all think we can do it all. How do we narrow down to what really matters?
Dr. Matthews: We often focus on the things that bring us happiness and what we are good at, but it’s the things that make us unhappy that tend to bring us down. It’s the presence of unhappiness, not the absence of happiness, that seems to be the undoing of many, including myself.
None of us are born with dramatic insight. It is experience that leads to insight. People who are actually present are able to gain insight through observation. A person becomes a better surgeon by observing the outcome of doing a stitch this way versus that; you learn how to do it by seeing what it looks like afterward.
Finding our authentic selves happens in much the same way. Having the presence of mind to ask the right questions, such as, “How am I feeling while I’m doing this?” leads to insights into the true self.
Continue to: It takes a village...
It takes a village
Dr. Greene: Catherine mentioned community earlier, and that is extremely important. The people who surround us can have a huge impact on the way we perceive things, including ourselves. Having a mix of people in our lives—some who practice medicine and others who don’t—helps us stay balanced and answer some of the tough questions. Catherine, for example, has helped me in various stages of my career to ask myself meaningful questions and get real answers.
Dr. Rardin: Part of finding balance is luck, and part of it is making a choice between money and everything else. In considering my first job out of training, I knew that money had the potential to distract me from what was important to me. So I chose a position that was almost entirely salaried so that the decisions I made clinically, surgically, and regarding work-life balance would be less likely to directly impact what was important to me.
Sally Huber, MD: I am still in the “getting there” phase of my life, but one thing I have found is that getting my family involved and excited about what I do has made them much more accepting of when I have longer work days or work to do on the weekend. My spouse has become quite involved with what I have been doing with transgender health in Atlanta. It has been a great bonding experience; she shares my passions, and together we are creating something about which we both can be proud.
When work invades home life
Dr. Culligan: That is great. Sally, I think when we talked, you were just learning about the necessity of mental separation and of not taking your work home with you, which is so hard for all of us with all of our devices.
Dr. Huber: Yes, this year has been about seeing what works best as far as being efficient at work and having quality time at home. At the end of every day I ask myself, “What worked well today? What didn’t work well? What else can I do to maximize time with my family?” I am slowly becoming more efficient, but it has been a challenge. During fellowship, your day is pretty set, but once you are practicing on your own, your hours and responsibilities are completely different, and you have to figure out what works best for you, your values, and your expectations of private life. It takes some time, and I am still figuring it out.
Dr. Culligan: How often would you say that you bring work home? I try hard once I am home to quit working, but sometimes on the weekends I break that rule.
Dr. Matthews: I must say that I do feel like there are certain times when I am better at that than others. Work comes in waves with pressing deadlines. If I averaged it out, probably a third of the time I have some email or some conference call or something that I have got to do at home. I do really try to limit the obligations that I have after 5:30 or 6:00 pm. I resent intrusions after that time. As far as weekends, I delegate about one weekend every 2 months to work, instead of doing a little bit every weekend.
Dr. Greene: I agree. I try hard to make 5:30 to 7:30 pm unequivocal time for a family dinner and time for my kids. During that time, I do not have my phone near me so I can’t look at email or texts. I try not to schedule conference calls. I try to be there to read books to my kids at night. Then if I need to do work, I do it later at night, which interferes with time with my spouse, and is not ideal, but that’s what happens.
Dr. Matthews: One of the things that I think is a huge part of work-life balance is work-related travel. When you are present at work on a consistent basis, the work does not pile up to the extent that it does when you are absent on a trip. When you come back, you invariably pay the price by seeing more patients and doing more surgery. Then it becomes a stressful event.
My advice to young people is to be very thoughtful about planning trips, especially distant ones. You do not want to sit on a plane all day when you could be doing something more productive. If I could have done something differently in my mid-career, I would have traveled less.
Continue to: Prioritizing “out of office” time...
Prioritizing “out of office” time
Dr. Greene: How do you all mentally separate yourself from work, so that when you are on vacation with your family you are not thinking about the office, the patients, and all of the things on your to-do list?
Dr. Rardin: I don’t have a great answer for that except that it is about being present. You have to decide that now is the time when I am home, now is the time when I am a parent, now is the time when I am a boy scout leader, etc. I guess maybe it’s a skill, or maybe it’s about making something a priority. Work will always be waiting for you when you turn your attention back to it.
Dr. Matthews: Kristie, the answer to your question goes back to community. Partners in a practice cover for each other. You have to trust them to take care of things so that you can relax during your time away.
Some people recommend not scheduling challenging cases right before going away because invariably something goes wrong, and then you are asking, “Why did I schedule 3 colpopexies before getting on a plane?”
Dr. Rardin: Yes, I completely agree with all of that. Personally, I feel fortunate that I can compartmentalize pretty well. When I am home with my kids, I allow myself to shed some of the doctor/surgeon/leadership persona; I am able to be goofy and completely non–doctor-like. It works to help me leave work behind.
Dr. Matthews: Other things you can do include setting up an out-of-office notice on your email that says when you will be back and what to do in case of urgent matters. This basically says to the world, “Don’t expect to hear from me until X date.” It removes the expectation that you will respond sooner. Otherwise, we would all be on our smartphones all the time and not enjoying our time away.
What I wish I knew then
Dr. Culligan: How would you complete the sentence, “I wish they had told me X when I was embarking on my career?”
Dr. Rardin: I keep coming back to the phrase, “Don’t do anything that you can reasonably pay someone else to do.” By that I mean, if you don’t get energy from housework, consider spending some of your money to get help with the housework. Resolve to make a relatively small expenditure to maximize the quality of the time that you give to yourself and your family. Those are the sorts of things that I think can go a long way.
Dr. Culligan: Charley, your wife is an ObGyn. How do you navigate a dual medical career household? What advice do you have for others?
Dr. Rardin: When I was going into fellowship, we had a conversation about how hard it is for both people in a relationship to have an academic fire in the belly and to be truly engaged in climbing the academic ladder. We made a decision that Jane would go into private practice. There has got to be some give and take in a dual medical relationship; a lot of sacrifices and compromises need to happen. We are fortunate in that there are complementary aspects to our jobs. We both spend about the same number of nights away from the house, but my travel is more in chunks and hers is overnight calls for labor and delivery. We have different ways of (briefly) single-parenting, and you have to come up with ways to handle the domestic chores.
Dr. Matthews: I wish someone had explained to me that the people you work with are much more important than the place. The human connection is what defines your experience, much more than any ego-driven outcome.
Dr. Greene: I wish someone had explained to me the competing aspects of academic medicine. The cards are stacked in a way that make it difficult for you to win. For example, you may love to teach and may be really good at it, but if you let your students handle too many cases, your relative value units plummet and then the hospital is on your back. There are the interests of people, and there are the interests of the business. Everything is a balance, and it’s really tricky.
Dr. Huber: Luckily, Pat counselled me as I was finishing my fellowship about the importance of negotiating a good contract, of being pushy and knowing what you want out of it and knowing what your limitations are. I joined a private practice that had 3 different physical locations. If I had to drive to all of them, as they wanted, it would have meant up to a one-and-a-half-hour commute. But I pushed to stay in one location and to put that extra hour to better use. I am glad I did, but it was terrifying at the time because I didn’t want to lose the offer. I know people that did not do that and took the first thing they got. Now, they are driving all over the place or they have these crazy hours or terrible call responsibilities that if they had just been a little firmer, they probably could have gotten out of. As they start trying to find work-life balance, they are already handicapped.
Continue to: Passions outside the office...
Passions outside the office
Dr. Culligan: One thing I would like to touch on is what is going on in each of your personal lives because all of you have interesting stories to tell outside of what you do professionally. What drives you other than medicine?
Dr. Rardin: I am the father of 3 boys. The oldest one just got his Eagle Scout rank yesterday in Boy Scouts. I would be a woodworker if I wasn’t in medicine. I am a Deacon at church. And I love to spend my downtime reading with my family in front of the fireplace.
Dr. Matthews: For me, it’s music. When my husband and I first met, he asked me if I played a musical instrument. I said I played the cello in primary school. He said, “Great, go rent a cello.” I was never at all interested in playing the cello by myself, but because he plays guitar and piano we became able to play a lot of music together. Our son, Alexander, plays drums. We now have a family band.
In addition, I do yoga. I would never have labeled myself an anxious person, but I learned through this process that I am and need to manage it. It took a lot of years to figure that out. If I don’t leave myself an hour each day to go to a yoga class, I am not a happy person and neither is anyone around me. Also, I get tremendous pleasure from reading books and magazines as opposed to watching a screen.
Dr. Greene: I have found that my passions outside of work often change depending on my stage of life. Right now, I have two young babies and so my life outside of work revolves around them. Before the babies, my dad, who lives in Buffalo, was ill. So for awhile, we were flying to Buffalo almost every weekend that I was not on call. I would say, in general what fuels me is connecting with the people I love as often as I can. A typical night involves me and my husband going for a walk with our kids and dog after dinner and talking to each other. We connect with neighbors and chat on the front porch. It doesn’t really matter what we are doing; it is about being surrounded by people who matter.
Dr. Huber: It’s similar for me. Having a child completely shifts your world view. My goal every day is to give my daughter her first feeding in the morning and to get home as soon as possible at the end of the day to do her last feeding and put her to sleep. She crawled for the first time yesterday, and I was so excited that I could be there for that.
Also, I love being outdoors. I love hiking and camping. Going on a hike and being outside with nature is my way of decompressing.
Continue to: Thinking about upcoming generations...
Thinking about upcoming generations
Dr. Matthews: One other thing I would like to propose is looking at what can we do to make the profession better for the next generation. As a group, our profession is somewhat inflexible. We tend to fall into the trap of, “since this is the way we have always done it this is how we should continue doing it.” The OR still starts at 7:00 or 7:30 am, ignoring the need for school drop-offs, etc. We are not innovative about flexibility in the work week. Honestly, it does not work well for many people, patients and physicians alike. Flexible scheduling should be something that is on the table for both men and women who are trying to balance being full-time parents and full-time surgeons. We need to create an environment in which it is okay for you to spend 10 years instead of 6 as an assistant professor because you are also a young parent, and it will not count against you when you come up for promotion.
Dr. Culligan: I agree with you, Catherine. Full “Professor” is a nice title, but it means time away from family and a lot of other things. Each of us has to decide whether it is worth it, especially since it often does not come with any extra money.
Dr. Huber: A question on a recent survey of residents asked, “Do you see yourself going into private practice or academic medicine when you’ve completed your residency?” When I was a resident, everyone wanted to go into academic medicine, but now it seems like more and more residents have their sights set on private practice because that is where they see the opportunities to create work-life balance.
In the academic world, you have to try to get a promotion in X number of years, and get X number of publications, and be a great teacher, doctor, and administrator all at the same time. I am wondering if we are going to start seeing more and more residents and fellows going into private or hospital-owned practice where there aren’t those added expectations.
Dr. Rardin: I agree, and we are back to what we said in the beginning about doing an honest assessment of what is meaningful and important. We are all trained to try to reach for that shiny brass ring, but do we really want that brass ring? Will it be an asset or a hindrance once we get it? It is okay to be honest and say, “I really don’t want that promotion. I would rather spend more time with my family.” ●
Patrick J. Culligan, MD:
My impression of our younger colleagues, however, is that many of them are not attracted to the traditional ivory tower research model of academic advancement to which many in previous generations aspired. They seem more concerned with work-life balance as their measure of success rather than the classic metrics of money and prestige. Everyone still needs role models and mentors, though, and that’s where all of you come in. I asked each of you to be on this panel because I admire you for your varying approaches to work-life balance while achieving success as gynecologic surgeons. I thought others in the field might be inspired by hearing your stories.
Cultivating your passions
Kristie Greene, MD: What I have come to learn and appreciate is a really simple point: you do not have to do everything. Determining who you want to be both personally and professionally is step 1.
Granted, answering the question, “Who do I want to be?” is not as simple as it sounds. Many factors figure into the decisions we make in our personal and professional lives. Also, it is not a question we often stop and ask ourselves. From early on, we are placed on an escalator moving up through medical school, residency, fellowship, good job, better job, etc. We are so accustomed to being competitive, to winning, and to wanting to be the best that we sometimes forget to ask ourselves, “What is it exactly that I want, and why? What is my endpoint? And does it make me happy?”
Multitasking is regarded as a talent. As much as we would like to believe that we can do everything at the same time and do it all well, we actually can’t. A friend of mine made me read a book a couple of years ago, called Feeling Good, by David Burns. The book encourages you to consider the different tasks you do in a day and rate how good you are at each of them on a scale of 1 to 10. It then asks you to think about how much enjoyment you derive from each of the tasks and about why you are doing the ones that bring you little to no enjoyment.
I ultimately decided that, for me professionally, the most important thing was my interest in global health. So I decided to do whatever it took to make this happen. But you don’t get something for nothing, and everything comes with sacrifices.
Continue to: Charles Rardin, MD...
Charles Rardin, MD: How exactly did you decide that you were going to focus your career toward pursuing international health? How did you know it was more important? And how did you overcome some of those obstacles?
Dr. Greene: You have to ask the hard question again about what brings you the most joy professionally and personally. That was the easy part of it for me because global health has always been that source of happiness and fulfillment for me. The more challenging parts are the sacrifices and hard choices that come with it. With global health, it can be difficult to balance the demands of a clinical practice.
All of our jobs are a business. I am still struggling with the money part of it. For my husband and I, that meant we had to start small—do what we could afford. But then it blossomed into something that was involving residents, fellows, and med students, which requires far more funding than we had. So I reached out to family. Most of our families donate to different organizations or charities every year, so why not donate to a loved one for something they are passionate about?
At the University of South Florida (USF), we set up a fund, a foundation for global health, which helps support our work abroad as well as the costs associated with involvement of our trainees. Right now, what we have is still small potatoes to a country, but we are making it happen by starting at a small level and growing it.
Beyond the money aspect, traveling abroad means less involvement in meetings, missed opportunities to teach courses that might interest me, and time away from my family. I guess my advice on this whole thing is that you can make things happen if they are important enough to you, and if you are willing to make sacrifices in other areas because you can’t have it all.
Making time for you
Dr. Culligan: So you have found what is important to you, and you have found a way to make it happen. But you are faced with more work; you have given yourself additional work on top of your regular work. How do you make time for a personal life?
Catherine Matthews, MD: In preparing for this discussion, I decided to break down my advice into 3 buckets: The first bucket is discovering and knowing your authentic self. The second is building a community, which I’ll elaborate on. And the third, which we have discussed, is to let go of the money.
Dr. Culligan: I love the concept of the authentic self, but how does that jive with a tendency to strive for perfection? We all think we can do it all. How do we narrow down to what really matters?
Dr. Matthews: We often focus on the things that bring us happiness and what we are good at, but it’s the things that make us unhappy that tend to bring us down. It’s the presence of unhappiness, not the absence of happiness, that seems to be the undoing of many, including myself.
None of us are born with dramatic insight. It is experience that leads to insight. People who are actually present are able to gain insight through observation. A person becomes a better surgeon by observing the outcome of doing a stitch this way versus that; you learn how to do it by seeing what it looks like afterward.
Finding our authentic selves happens in much the same way. Having the presence of mind to ask the right questions, such as, “How am I feeling while I’m doing this?” leads to insights into the true self.
Continue to: It takes a village...
It takes a village
Dr. Greene: Catherine mentioned community earlier, and that is extremely important. The people who surround us can have a huge impact on the way we perceive things, including ourselves. Having a mix of people in our lives—some who practice medicine and others who don’t—helps us stay balanced and answer some of the tough questions. Catherine, for example, has helped me in various stages of my career to ask myself meaningful questions and get real answers.
Dr. Rardin: Part of finding balance is luck, and part of it is making a choice between money and everything else. In considering my first job out of training, I knew that money had the potential to distract me from what was important to me. So I chose a position that was almost entirely salaried so that the decisions I made clinically, surgically, and regarding work-life balance would be less likely to directly impact what was important to me.
Sally Huber, MD: I am still in the “getting there” phase of my life, but one thing I have found is that getting my family involved and excited about what I do has made them much more accepting of when I have longer work days or work to do on the weekend. My spouse has become quite involved with what I have been doing with transgender health in Atlanta. It has been a great bonding experience; she shares my passions, and together we are creating something about which we both can be proud.
When work invades home life
Dr. Culligan: That is great. Sally, I think when we talked, you were just learning about the necessity of mental separation and of not taking your work home with you, which is so hard for all of us with all of our devices.
Dr. Huber: Yes, this year has been about seeing what works best as far as being efficient at work and having quality time at home. At the end of every day I ask myself, “What worked well today? What didn’t work well? What else can I do to maximize time with my family?” I am slowly becoming more efficient, but it has been a challenge. During fellowship, your day is pretty set, but once you are practicing on your own, your hours and responsibilities are completely different, and you have to figure out what works best for you, your values, and your expectations of private life. It takes some time, and I am still figuring it out.
Dr. Culligan: How often would you say that you bring work home? I try hard once I am home to quit working, but sometimes on the weekends I break that rule.
Dr. Matthews: I must say that I do feel like there are certain times when I am better at that than others. Work comes in waves with pressing deadlines. If I averaged it out, probably a third of the time I have some email or some conference call or something that I have got to do at home. I do really try to limit the obligations that I have after 5:30 or 6:00 pm. I resent intrusions after that time. As far as weekends, I delegate about one weekend every 2 months to work, instead of doing a little bit every weekend.
Dr. Greene: I agree. I try hard to make 5:30 to 7:30 pm unequivocal time for a family dinner and time for my kids. During that time, I do not have my phone near me so I can’t look at email or texts. I try not to schedule conference calls. I try to be there to read books to my kids at night. Then if I need to do work, I do it later at night, which interferes with time with my spouse, and is not ideal, but that’s what happens.
Dr. Matthews: One of the things that I think is a huge part of work-life balance is work-related travel. When you are present at work on a consistent basis, the work does not pile up to the extent that it does when you are absent on a trip. When you come back, you invariably pay the price by seeing more patients and doing more surgery. Then it becomes a stressful event.
My advice to young people is to be very thoughtful about planning trips, especially distant ones. You do not want to sit on a plane all day when you could be doing something more productive. If I could have done something differently in my mid-career, I would have traveled less.
Continue to: Prioritizing “out of office” time...
Prioritizing “out of office” time
Dr. Greene: How do you all mentally separate yourself from work, so that when you are on vacation with your family you are not thinking about the office, the patients, and all of the things on your to-do list?
Dr. Rardin: I don’t have a great answer for that except that it is about being present. You have to decide that now is the time when I am home, now is the time when I am a parent, now is the time when I am a boy scout leader, etc. I guess maybe it’s a skill, or maybe it’s about making something a priority. Work will always be waiting for you when you turn your attention back to it.
Dr. Matthews: Kristie, the answer to your question goes back to community. Partners in a practice cover for each other. You have to trust them to take care of things so that you can relax during your time away.
Some people recommend not scheduling challenging cases right before going away because invariably something goes wrong, and then you are asking, “Why did I schedule 3 colpopexies before getting on a plane?”
Dr. Rardin: Yes, I completely agree with all of that. Personally, I feel fortunate that I can compartmentalize pretty well. When I am home with my kids, I allow myself to shed some of the doctor/surgeon/leadership persona; I am able to be goofy and completely non–doctor-like. It works to help me leave work behind.
Dr. Matthews: Other things you can do include setting up an out-of-office notice on your email that says when you will be back and what to do in case of urgent matters. This basically says to the world, “Don’t expect to hear from me until X date.” It removes the expectation that you will respond sooner. Otherwise, we would all be on our smartphones all the time and not enjoying our time away.
What I wish I knew then
Dr. Culligan: How would you complete the sentence, “I wish they had told me X when I was embarking on my career?”
Dr. Rardin: I keep coming back to the phrase, “Don’t do anything that you can reasonably pay someone else to do.” By that I mean, if you don’t get energy from housework, consider spending some of your money to get help with the housework. Resolve to make a relatively small expenditure to maximize the quality of the time that you give to yourself and your family. Those are the sorts of things that I think can go a long way.
Dr. Culligan: Charley, your wife is an ObGyn. How do you navigate a dual medical career household? What advice do you have for others?
Dr. Rardin: When I was going into fellowship, we had a conversation about how hard it is for both people in a relationship to have an academic fire in the belly and to be truly engaged in climbing the academic ladder. We made a decision that Jane would go into private practice. There has got to be some give and take in a dual medical relationship; a lot of sacrifices and compromises need to happen. We are fortunate in that there are complementary aspects to our jobs. We both spend about the same number of nights away from the house, but my travel is more in chunks and hers is overnight calls for labor and delivery. We have different ways of (briefly) single-parenting, and you have to come up with ways to handle the domestic chores.
Dr. Matthews: I wish someone had explained to me that the people you work with are much more important than the place. The human connection is what defines your experience, much more than any ego-driven outcome.
Dr. Greene: I wish someone had explained to me the competing aspects of academic medicine. The cards are stacked in a way that make it difficult for you to win. For example, you may love to teach and may be really good at it, but if you let your students handle too many cases, your relative value units plummet and then the hospital is on your back. There are the interests of people, and there are the interests of the business. Everything is a balance, and it’s really tricky.
Dr. Huber: Luckily, Pat counselled me as I was finishing my fellowship about the importance of negotiating a good contract, of being pushy and knowing what you want out of it and knowing what your limitations are. I joined a private practice that had 3 different physical locations. If I had to drive to all of them, as they wanted, it would have meant up to a one-and-a-half-hour commute. But I pushed to stay in one location and to put that extra hour to better use. I am glad I did, but it was terrifying at the time because I didn’t want to lose the offer. I know people that did not do that and took the first thing they got. Now, they are driving all over the place or they have these crazy hours or terrible call responsibilities that if they had just been a little firmer, they probably could have gotten out of. As they start trying to find work-life balance, they are already handicapped.
Continue to: Passions outside the office...
Passions outside the office
Dr. Culligan: One thing I would like to touch on is what is going on in each of your personal lives because all of you have interesting stories to tell outside of what you do professionally. What drives you other than medicine?
Dr. Rardin: I am the father of 3 boys. The oldest one just got his Eagle Scout rank yesterday in Boy Scouts. I would be a woodworker if I wasn’t in medicine. I am a Deacon at church. And I love to spend my downtime reading with my family in front of the fireplace.
Dr. Matthews: For me, it’s music. When my husband and I first met, he asked me if I played a musical instrument. I said I played the cello in primary school. He said, “Great, go rent a cello.” I was never at all interested in playing the cello by myself, but because he plays guitar and piano we became able to play a lot of music together. Our son, Alexander, plays drums. We now have a family band.
In addition, I do yoga. I would never have labeled myself an anxious person, but I learned through this process that I am and need to manage it. It took a lot of years to figure that out. If I don’t leave myself an hour each day to go to a yoga class, I am not a happy person and neither is anyone around me. Also, I get tremendous pleasure from reading books and magazines as opposed to watching a screen.
Dr. Greene: I have found that my passions outside of work often change depending on my stage of life. Right now, I have two young babies and so my life outside of work revolves around them. Before the babies, my dad, who lives in Buffalo, was ill. So for awhile, we were flying to Buffalo almost every weekend that I was not on call. I would say, in general what fuels me is connecting with the people I love as often as I can. A typical night involves me and my husband going for a walk with our kids and dog after dinner and talking to each other. We connect with neighbors and chat on the front porch. It doesn’t really matter what we are doing; it is about being surrounded by people who matter.
Dr. Huber: It’s similar for me. Having a child completely shifts your world view. My goal every day is to give my daughter her first feeding in the morning and to get home as soon as possible at the end of the day to do her last feeding and put her to sleep. She crawled for the first time yesterday, and I was so excited that I could be there for that.
Also, I love being outdoors. I love hiking and camping. Going on a hike and being outside with nature is my way of decompressing.
Continue to: Thinking about upcoming generations...
Thinking about upcoming generations
Dr. Matthews: One other thing I would like to propose is looking at what can we do to make the profession better for the next generation. As a group, our profession is somewhat inflexible. We tend to fall into the trap of, “since this is the way we have always done it this is how we should continue doing it.” The OR still starts at 7:00 or 7:30 am, ignoring the need for school drop-offs, etc. We are not innovative about flexibility in the work week. Honestly, it does not work well for many people, patients and physicians alike. Flexible scheduling should be something that is on the table for both men and women who are trying to balance being full-time parents and full-time surgeons. We need to create an environment in which it is okay for you to spend 10 years instead of 6 as an assistant professor because you are also a young parent, and it will not count against you when you come up for promotion.
Dr. Culligan: I agree with you, Catherine. Full “Professor” is a nice title, but it means time away from family and a lot of other things. Each of us has to decide whether it is worth it, especially since it often does not come with any extra money.
Dr. Huber: A question on a recent survey of residents asked, “Do you see yourself going into private practice or academic medicine when you’ve completed your residency?” When I was a resident, everyone wanted to go into academic medicine, but now it seems like more and more residents have their sights set on private practice because that is where they see the opportunities to create work-life balance.
In the academic world, you have to try to get a promotion in X number of years, and get X number of publications, and be a great teacher, doctor, and administrator all at the same time. I am wondering if we are going to start seeing more and more residents and fellows going into private or hospital-owned practice where there aren’t those added expectations.
Dr. Rardin: I agree, and we are back to what we said in the beginning about doing an honest assessment of what is meaningful and important. We are all trained to try to reach for that shiny brass ring, but do we really want that brass ring? Will it be an asset or a hindrance once we get it? It is okay to be honest and say, “I really don’t want that promotion. I would rather spend more time with my family.” ●
The professional advancement of drug and device innovation

I often say that there are both “guardrail” days and very good days when it comes to the ins and outs of health care builds and product launches. The process is much like starting down the path of a country road in the middle of a blizzard—unless you have dependable wipers and a good defrost system, that path can get murky very quickly. With this article I hope to offer my counsel to inventors, featuring a few of my prior launches as well as case studies of health care launches I was not involved with, and sharing the lessons learned and hurdles that were overcome. I encourage all entrepreneurs to act on their ideas because, in the world of health care startups, the only failure is not acting on an invention.
Case study 1: Cerezyme
Today, Cerezyme is indicated for patients with Gaucher, which is a lysosomal storage disorder. Cerezyme’s first-generation product, called Ceredase, was a human tissue-derived protein that we extracted from human placentas. At the time, the concept of moving this program forward was denied by the Board of Directors because they said that even if you could collect enough placentas to make the enzyme, it would be too expensive to manufacture. In fact, early scale-up modeling for manufacturing the protein demonstrated that Genzyme would need 4 tons of placentas per Gaucher patient per year.
Gaucher is a severe, early-onset disease that has a significant negative outcome for patients. Patients with Gaucher are in dire need of treatment. Genzyme went forward with the Ceredase program by financing it through the families of patients with the disease, by starting an LLC separate from the business and funding the initial clinical trial and the development of the protein through the families of Gaucher patients. That approach was a successful endeavor. A great example of a creative capital structure to advance a program.
This was in the late 1980s/early 1990s, and at the height of the AIDS challenge. Genzyme based the manufacturing in Lille, France, and we cryopreserved placentas in the United States and Europe and shipped them to Lille to be processed into therapy. Genzyme eventually received approval for Ceredase from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency. At the height of the placenta collection, we were gathering about 10% to 15% of the placentas in the United States and 30% to 40% of the placentas in Europe. Resources supply became an issue until we developed a recombinant form of the protein, accomplished by using a manufacturing system called a CHO cell line.
This is a very good success story: If this invention was not pursued, Gaucher patients would not benefit from the treatment today. In addition, there are a plethora of patients with different lysosomal storage disorders treated with additional proteins that have been aided by us going through the entire development, manufacturing, and global commercialization process. We figured out how to manufacture and deliver the treatment, working through multiple countries’ political systems, and today the therapy is paid for by insurance and government systems on a worldwide basis.
Continue to: Case study 2...
Case study 2: ThinPrep
I like to use the approval of ThinPrep as an example of avoiding a false negative—a stoppage in the development of the product or drug for the wrong reasons. False negatives, in my mind, occur when you are developing a technology and you run into issues during the clinical phase and/or with FDA approval, or with a technical failure or you run out of capital prior to knowing whether or not the innovation actually works. In the case of ThinPrep, a poorly run clinical trial almost resulted in a false negative.
The company at the time was Cytyc, and an initial clinical study presented to the FDA yielded a neutral-negative outcome. The FDA said that there were not enough data to show the differentiation from the current Pap smear standard of care.
The founders of the company at that time had inherited the study protocol from a prior leadership team, so they had to finish the trial with the initial protocol. Given the FDA’s advisement, they developed a new trial. It took the persistence of these two founders, who mortgaged their homes and spent their personal dollars to take this through the next wave of clinical development. In the end it was successful. The revised clinical trial yielded an approval for ThinPrep, which is now considered a standard of care.
The use of ThinPrep reduced cervical cancer deaths by 40% from preapproval. The challenging path from clinical development to eventual commercial launch and physician leadership in advancing patient care makes the story of ThinPrep a great example of not allowing an early false negative of a poorly designed and run clinical trial stop important innovation.
Case study 3: Cologuard
The development of Cologuard is a case study demonstrating that, sometimes, when your first attempt does not work, you need to have the persistence to raise additional capital and/or use a slightly different technical approach. The approval story of Cologuard is important to share because it is an important cancer screening diagnostic, using DNA from stool samples to test for colon cancer, giving access to important colon cancer screening to many patients. Currently, caregivers are only scraping the surface with Cologuard’s ability to screen the population. There are many more patients that need access to the test, and I believe they will get it in the years ahead.
Cologuard went through a first- and second-generational technical failure. They could not get the test’s specificity and sensitivity to be at the level of a screening tool; there were too many false-positive results. With the third iteration came the technical breakthrough, and a very large, expensive study was conducted—one the leadership team was criticized for. However, that study yielded the data that achieved a New England Journal of Medicine article, and reimbursement support across the country. The combination of the right technical team and the right leadership team, who planned a proper commercial launch, with a CEO that supported the extensive clinical study, has resulted in the fourth generation of Cologuard—an important breakthrough offering a very useful new standard of care in colon cancer detection and screening.
Continue to: Pearls for moving your innovations forward...
Pearls for moving your innovations forward
Because of my experience in undergoing health care start-ups, and contributing to several of those advancements of innovation, many inventors approach me for advice on their paths from idea to full-concept company. Here are a few of my lessons learned.
Consider purpose, not financial gain, first and foremost. Financial gain is typically the by-product or outcome of a standard-of-care breakthrough for inventors, but it’s a very hard road. Pursue your invention for advancing patient care and moving a new standard of care forward in health care versus financial gain at the end.
Determine whether your invention is a product or a company, or potentially, not capitalizable at all. Figure this out early. Analyze your idea to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and the market dynamics to support a new product. Can the development path be defined very clearly to raise capital? Is your innovation a big enough breakthrough in the market with several current products to actually make a difference in patient outcomes (and eventually achieve product reimbursement)? The creation of a company may be the right strategy if the innovation can support a differentiated enough breakthrough where you can actually support all the infrastructure to build the business. If you find that the market is not there to support and develop your idea to eventual success, backing off early is important to preserve invested capital.
Protect early. Is your invention patentable, or has someone else already thought of the idea? What kind of patent(s) are appropriate? Where, geographically, do you want to protect your invention? Find a good patent attorney in your local area, early in the process, to help you answer all of these critical questions. Patents are expensive to file and maintain, but it is not expensive to do a literature search to find out if your idea is novel. A provisional patent, which would be your first step, is an important cost-effective step.
Capital is out there. If your invention or idea deserves capital, it is available. I will address raising capital in more detail in the next section.
Consider regulatory and manufacturing as achievable hurdles. Inventors often get tripped up here, considering the regulatory hurdles and manufacturing too challenging and abandoning their ideas because the risk is too great. Regulatory and manufacturing are very important aspects of health care standard-of-care builds. Cutting corners is not an option. That said, regulatory and manufacturing should not stop you. Challenges often can be worked through as long as the clinical need is there, and the clinical data support bringing that technology forward.
Consider corporate partnerships. I am a fan of corporate partners. But which ones should you target, and when and why? Corporate partnerships can bring significant capital, which is great, but there is enough investor capital out there that you should not pursue a corporate partner just for capital. The main benefit of a corporate partner is enterprise intellect. They typically know more about the field that you are entering than the investors or a small company leadership team.
Establish and listen to advisors. When thinking about who to trust, research their track record. Advisors who have gone through this process before, and specifically in your product area, are important to have access to.
Persistence is key. I have observed a tremendous “compression of innovation” in the health care areas that I have been involved with—human tissue-derived proteins, robotic surgery, stem cell therapy, and digital health (which is still in its infancy). For each of these breakthrough categories, early on, it appeared that it couldn’t be done. However, after the first 2 or 3 major breakthroughs in each one of these areas, a compression of innovation occurred. For instance, after approximately 15 years of protein development, we came out with the recombinant manufacturing systems for proteins. Very quickly, within 10 years, there were more than 70 proteins on the market. The persistence of the inventors to overcome early obstacles in each of these health care areas was critical to future success in each area.
Continue to: Raising capital...
Raising capital
There are different investors who specialize in different types of investment opportunities. The first phase of raising capital is the seed round—where there is typically early data, or even no data and just a concept. From this seed round forward, there is less risk as you develop your technology; thus, there are different investors that support different stages of development and that specialize in different types of investing. It is important to target the right investors and raise enough capital to be able to go achieve multiple operational milestones. Otherwise, when you go through your first round of capital, or the Series A or B financing rounds, there may not be a set of investors out there to fund the company moving forward. Health care investors will make it known that they invest in certain rounds of capital. You can determine who those investors are by doing a search online.
A mistake health care inventors can make is not taking enough capital from investors, because they are concerned about dilution. I advise investors not to focus on dilution but rather on, how big can you make “the pie” (value of the company) worth? The entire process is about bringing a true product through to a new standard-of-care curve.
Trust is the most important thing to earn with investors, and there is zero tolerance for a lack of trust. Share your vision as the inventor with investors, who want to know where this category could be in the next 5 or 10 years. Clinical data will always win, and health care investors and industry leaders should be focused on executing the most robust clinical data to demonstrate the clearest potential clinical outcome. Investors will follow a good plan that has been developed to achieve FDA approval, successful commercialization or “go to market” launch, and eventual reimbursement to support a true standard-of-care change.
Failure is defined by inaction
The 3 case studies that I have shared were success stories because the ideas and inventions were acted upon. When I was at Genzyme, we built the company up to more than $1 billion in revenue. We commercialized proteins in over 50 countries. Most importantly, many patients benefited from the innovation. If you have an invention and an idea, act on it—and surround yourself with great people in every discipline. Having the right people and team is extremely important. ●

I often say that there are both “guardrail” days and very good days when it comes to the ins and outs of health care builds and product launches. The process is much like starting down the path of a country road in the middle of a blizzard—unless you have dependable wipers and a good defrost system, that path can get murky very quickly. With this article I hope to offer my counsel to inventors, featuring a few of my prior launches as well as case studies of health care launches I was not involved with, and sharing the lessons learned and hurdles that were overcome. I encourage all entrepreneurs to act on their ideas because, in the world of health care startups, the only failure is not acting on an invention.
Case study 1: Cerezyme
Today, Cerezyme is indicated for patients with Gaucher, which is a lysosomal storage disorder. Cerezyme’s first-generation product, called Ceredase, was a human tissue-derived protein that we extracted from human placentas. At the time, the concept of moving this program forward was denied by the Board of Directors because they said that even if you could collect enough placentas to make the enzyme, it would be too expensive to manufacture. In fact, early scale-up modeling for manufacturing the protein demonstrated that Genzyme would need 4 tons of placentas per Gaucher patient per year.
Gaucher is a severe, early-onset disease that has a significant negative outcome for patients. Patients with Gaucher are in dire need of treatment. Genzyme went forward with the Ceredase program by financing it through the families of patients with the disease, by starting an LLC separate from the business and funding the initial clinical trial and the development of the protein through the families of Gaucher patients. That approach was a successful endeavor. A great example of a creative capital structure to advance a program.
This was in the late 1980s/early 1990s, and at the height of the AIDS challenge. Genzyme based the manufacturing in Lille, France, and we cryopreserved placentas in the United States and Europe and shipped them to Lille to be processed into therapy. Genzyme eventually received approval for Ceredase from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency. At the height of the placenta collection, we were gathering about 10% to 15% of the placentas in the United States and 30% to 40% of the placentas in Europe. Resources supply became an issue until we developed a recombinant form of the protein, accomplished by using a manufacturing system called a CHO cell line.
This is a very good success story: If this invention was not pursued, Gaucher patients would not benefit from the treatment today. In addition, there are a plethora of patients with different lysosomal storage disorders treated with additional proteins that have been aided by us going through the entire development, manufacturing, and global commercialization process. We figured out how to manufacture and deliver the treatment, working through multiple countries’ political systems, and today the therapy is paid for by insurance and government systems on a worldwide basis.
Continue to: Case study 2...
Case study 2: ThinPrep
I like to use the approval of ThinPrep as an example of avoiding a false negative—a stoppage in the development of the product or drug for the wrong reasons. False negatives, in my mind, occur when you are developing a technology and you run into issues during the clinical phase and/or with FDA approval, or with a technical failure or you run out of capital prior to knowing whether or not the innovation actually works. In the case of ThinPrep, a poorly run clinical trial almost resulted in a false negative.
The company at the time was Cytyc, and an initial clinical study presented to the FDA yielded a neutral-negative outcome. The FDA said that there were not enough data to show the differentiation from the current Pap smear standard of care.
The founders of the company at that time had inherited the study protocol from a prior leadership team, so they had to finish the trial with the initial protocol. Given the FDA’s advisement, they developed a new trial. It took the persistence of these two founders, who mortgaged their homes and spent their personal dollars to take this through the next wave of clinical development. In the end it was successful. The revised clinical trial yielded an approval for ThinPrep, which is now considered a standard of care.
The use of ThinPrep reduced cervical cancer deaths by 40% from preapproval. The challenging path from clinical development to eventual commercial launch and physician leadership in advancing patient care makes the story of ThinPrep a great example of not allowing an early false negative of a poorly designed and run clinical trial stop important innovation.
Case study 3: Cologuard
The development of Cologuard is a case study demonstrating that, sometimes, when your first attempt does not work, you need to have the persistence to raise additional capital and/or use a slightly different technical approach. The approval story of Cologuard is important to share because it is an important cancer screening diagnostic, using DNA from stool samples to test for colon cancer, giving access to important colon cancer screening to many patients. Currently, caregivers are only scraping the surface with Cologuard’s ability to screen the population. There are many more patients that need access to the test, and I believe they will get it in the years ahead.
Cologuard went through a first- and second-generational technical failure. They could not get the test’s specificity and sensitivity to be at the level of a screening tool; there were too many false-positive results. With the third iteration came the technical breakthrough, and a very large, expensive study was conducted—one the leadership team was criticized for. However, that study yielded the data that achieved a New England Journal of Medicine article, and reimbursement support across the country. The combination of the right technical team and the right leadership team, who planned a proper commercial launch, with a CEO that supported the extensive clinical study, has resulted in the fourth generation of Cologuard—an important breakthrough offering a very useful new standard of care in colon cancer detection and screening.
Continue to: Pearls for moving your innovations forward...
Pearls for moving your innovations forward
Because of my experience in undergoing health care start-ups, and contributing to several of those advancements of innovation, many inventors approach me for advice on their paths from idea to full-concept company. Here are a few of my lessons learned.
Consider purpose, not financial gain, first and foremost. Financial gain is typically the by-product or outcome of a standard-of-care breakthrough for inventors, but it’s a very hard road. Pursue your invention for advancing patient care and moving a new standard of care forward in health care versus financial gain at the end.
Determine whether your invention is a product or a company, or potentially, not capitalizable at all. Figure this out early. Analyze your idea to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and the market dynamics to support a new product. Can the development path be defined very clearly to raise capital? Is your innovation a big enough breakthrough in the market with several current products to actually make a difference in patient outcomes (and eventually achieve product reimbursement)? The creation of a company may be the right strategy if the innovation can support a differentiated enough breakthrough where you can actually support all the infrastructure to build the business. If you find that the market is not there to support and develop your idea to eventual success, backing off early is important to preserve invested capital.
Protect early. Is your invention patentable, or has someone else already thought of the idea? What kind of patent(s) are appropriate? Where, geographically, do you want to protect your invention? Find a good patent attorney in your local area, early in the process, to help you answer all of these critical questions. Patents are expensive to file and maintain, but it is not expensive to do a literature search to find out if your idea is novel. A provisional patent, which would be your first step, is an important cost-effective step.
Capital is out there. If your invention or idea deserves capital, it is available. I will address raising capital in more detail in the next section.
Consider regulatory and manufacturing as achievable hurdles. Inventors often get tripped up here, considering the regulatory hurdles and manufacturing too challenging and abandoning their ideas because the risk is too great. Regulatory and manufacturing are very important aspects of health care standard-of-care builds. Cutting corners is not an option. That said, regulatory and manufacturing should not stop you. Challenges often can be worked through as long as the clinical need is there, and the clinical data support bringing that technology forward.
Consider corporate partnerships. I am a fan of corporate partners. But which ones should you target, and when and why? Corporate partnerships can bring significant capital, which is great, but there is enough investor capital out there that you should not pursue a corporate partner just for capital. The main benefit of a corporate partner is enterprise intellect. They typically know more about the field that you are entering than the investors or a small company leadership team.
Establish and listen to advisors. When thinking about who to trust, research their track record. Advisors who have gone through this process before, and specifically in your product area, are important to have access to.
Persistence is key. I have observed a tremendous “compression of innovation” in the health care areas that I have been involved with—human tissue-derived proteins, robotic surgery, stem cell therapy, and digital health (which is still in its infancy). For each of these breakthrough categories, early on, it appeared that it couldn’t be done. However, after the first 2 or 3 major breakthroughs in each one of these areas, a compression of innovation occurred. For instance, after approximately 15 years of protein development, we came out with the recombinant manufacturing systems for proteins. Very quickly, within 10 years, there were more than 70 proteins on the market. The persistence of the inventors to overcome early obstacles in each of these health care areas was critical to future success in each area.
Continue to: Raising capital...
Raising capital
There are different investors who specialize in different types of investment opportunities. The first phase of raising capital is the seed round—where there is typically early data, or even no data and just a concept. From this seed round forward, there is less risk as you develop your technology; thus, there are different investors that support different stages of development and that specialize in different types of investing. It is important to target the right investors and raise enough capital to be able to go achieve multiple operational milestones. Otherwise, when you go through your first round of capital, or the Series A or B financing rounds, there may not be a set of investors out there to fund the company moving forward. Health care investors will make it known that they invest in certain rounds of capital. You can determine who those investors are by doing a search online.
A mistake health care inventors can make is not taking enough capital from investors, because they are concerned about dilution. I advise investors not to focus on dilution but rather on, how big can you make “the pie” (value of the company) worth? The entire process is about bringing a true product through to a new standard-of-care curve.
Trust is the most important thing to earn with investors, and there is zero tolerance for a lack of trust. Share your vision as the inventor with investors, who want to know where this category could be in the next 5 or 10 years. Clinical data will always win, and health care investors and industry leaders should be focused on executing the most robust clinical data to demonstrate the clearest potential clinical outcome. Investors will follow a good plan that has been developed to achieve FDA approval, successful commercialization or “go to market” launch, and eventual reimbursement to support a true standard-of-care change.
Failure is defined by inaction
The 3 case studies that I have shared were success stories because the ideas and inventions were acted upon. When I was at Genzyme, we built the company up to more than $1 billion in revenue. We commercialized proteins in over 50 countries. Most importantly, many patients benefited from the innovation. If you have an invention and an idea, act on it—and surround yourself with great people in every discipline. Having the right people and team is extremely important. ●

I often say that there are both “guardrail” days and very good days when it comes to the ins and outs of health care builds and product launches. The process is much like starting down the path of a country road in the middle of a blizzard—unless you have dependable wipers and a good defrost system, that path can get murky very quickly. With this article I hope to offer my counsel to inventors, featuring a few of my prior launches as well as case studies of health care launches I was not involved with, and sharing the lessons learned and hurdles that were overcome. I encourage all entrepreneurs to act on their ideas because, in the world of health care startups, the only failure is not acting on an invention.
Case study 1: Cerezyme
Today, Cerezyme is indicated for patients with Gaucher, which is a lysosomal storage disorder. Cerezyme’s first-generation product, called Ceredase, was a human tissue-derived protein that we extracted from human placentas. At the time, the concept of moving this program forward was denied by the Board of Directors because they said that even if you could collect enough placentas to make the enzyme, it would be too expensive to manufacture. In fact, early scale-up modeling for manufacturing the protein demonstrated that Genzyme would need 4 tons of placentas per Gaucher patient per year.
Gaucher is a severe, early-onset disease that has a significant negative outcome for patients. Patients with Gaucher are in dire need of treatment. Genzyme went forward with the Ceredase program by financing it through the families of patients with the disease, by starting an LLC separate from the business and funding the initial clinical trial and the development of the protein through the families of Gaucher patients. That approach was a successful endeavor. A great example of a creative capital structure to advance a program.
This was in the late 1980s/early 1990s, and at the height of the AIDS challenge. Genzyme based the manufacturing in Lille, France, and we cryopreserved placentas in the United States and Europe and shipped them to Lille to be processed into therapy. Genzyme eventually received approval for Ceredase from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency. At the height of the placenta collection, we were gathering about 10% to 15% of the placentas in the United States and 30% to 40% of the placentas in Europe. Resources supply became an issue until we developed a recombinant form of the protein, accomplished by using a manufacturing system called a CHO cell line.
This is a very good success story: If this invention was not pursued, Gaucher patients would not benefit from the treatment today. In addition, there are a plethora of patients with different lysosomal storage disorders treated with additional proteins that have been aided by us going through the entire development, manufacturing, and global commercialization process. We figured out how to manufacture and deliver the treatment, working through multiple countries’ political systems, and today the therapy is paid for by insurance and government systems on a worldwide basis.
Continue to: Case study 2...
Case study 2: ThinPrep
I like to use the approval of ThinPrep as an example of avoiding a false negative—a stoppage in the development of the product or drug for the wrong reasons. False negatives, in my mind, occur when you are developing a technology and you run into issues during the clinical phase and/or with FDA approval, or with a technical failure or you run out of capital prior to knowing whether or not the innovation actually works. In the case of ThinPrep, a poorly run clinical trial almost resulted in a false negative.
The company at the time was Cytyc, and an initial clinical study presented to the FDA yielded a neutral-negative outcome. The FDA said that there were not enough data to show the differentiation from the current Pap smear standard of care.
The founders of the company at that time had inherited the study protocol from a prior leadership team, so they had to finish the trial with the initial protocol. Given the FDA’s advisement, they developed a new trial. It took the persistence of these two founders, who mortgaged their homes and spent their personal dollars to take this through the next wave of clinical development. In the end it was successful. The revised clinical trial yielded an approval for ThinPrep, which is now considered a standard of care.
The use of ThinPrep reduced cervical cancer deaths by 40% from preapproval. The challenging path from clinical development to eventual commercial launch and physician leadership in advancing patient care makes the story of ThinPrep a great example of not allowing an early false negative of a poorly designed and run clinical trial stop important innovation.
Case study 3: Cologuard
The development of Cologuard is a case study demonstrating that, sometimes, when your first attempt does not work, you need to have the persistence to raise additional capital and/or use a slightly different technical approach. The approval story of Cologuard is important to share because it is an important cancer screening diagnostic, using DNA from stool samples to test for colon cancer, giving access to important colon cancer screening to many patients. Currently, caregivers are only scraping the surface with Cologuard’s ability to screen the population. There are many more patients that need access to the test, and I believe they will get it in the years ahead.
Cologuard went through a first- and second-generational technical failure. They could not get the test’s specificity and sensitivity to be at the level of a screening tool; there were too many false-positive results. With the third iteration came the technical breakthrough, and a very large, expensive study was conducted—one the leadership team was criticized for. However, that study yielded the data that achieved a New England Journal of Medicine article, and reimbursement support across the country. The combination of the right technical team and the right leadership team, who planned a proper commercial launch, with a CEO that supported the extensive clinical study, has resulted in the fourth generation of Cologuard—an important breakthrough offering a very useful new standard of care in colon cancer detection and screening.
Continue to: Pearls for moving your innovations forward...
Pearls for moving your innovations forward
Because of my experience in undergoing health care start-ups, and contributing to several of those advancements of innovation, many inventors approach me for advice on their paths from idea to full-concept company. Here are a few of my lessons learned.
Consider purpose, not financial gain, first and foremost. Financial gain is typically the by-product or outcome of a standard-of-care breakthrough for inventors, but it’s a very hard road. Pursue your invention for advancing patient care and moving a new standard of care forward in health care versus financial gain at the end.
Determine whether your invention is a product or a company, or potentially, not capitalizable at all. Figure this out early. Analyze your idea to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and to make sure it is sound and truly novel. Analyze the competition and the market dynamics to support a new product. Can the development path be defined very clearly to raise capital? Is your innovation a big enough breakthrough in the market with several current products to actually make a difference in patient outcomes (and eventually achieve product reimbursement)? The creation of a company may be the right strategy if the innovation can support a differentiated enough breakthrough where you can actually support all the infrastructure to build the business. If you find that the market is not there to support and develop your idea to eventual success, backing off early is important to preserve invested capital.
Protect early. Is your invention patentable, or has someone else already thought of the idea? What kind of patent(s) are appropriate? Where, geographically, do you want to protect your invention? Find a good patent attorney in your local area, early in the process, to help you answer all of these critical questions. Patents are expensive to file and maintain, but it is not expensive to do a literature search to find out if your idea is novel. A provisional patent, which would be your first step, is an important cost-effective step.
Capital is out there. If your invention or idea deserves capital, it is available. I will address raising capital in more detail in the next section.
Consider regulatory and manufacturing as achievable hurdles. Inventors often get tripped up here, considering the regulatory hurdles and manufacturing too challenging and abandoning their ideas because the risk is too great. Regulatory and manufacturing are very important aspects of health care standard-of-care builds. Cutting corners is not an option. That said, regulatory and manufacturing should not stop you. Challenges often can be worked through as long as the clinical need is there, and the clinical data support bringing that technology forward.
Consider corporate partnerships. I am a fan of corporate partners. But which ones should you target, and when and why? Corporate partnerships can bring significant capital, which is great, but there is enough investor capital out there that you should not pursue a corporate partner just for capital. The main benefit of a corporate partner is enterprise intellect. They typically know more about the field that you are entering than the investors or a small company leadership team.
Establish and listen to advisors. When thinking about who to trust, research their track record. Advisors who have gone through this process before, and specifically in your product area, are important to have access to.
Persistence is key. I have observed a tremendous “compression of innovation” in the health care areas that I have been involved with—human tissue-derived proteins, robotic surgery, stem cell therapy, and digital health (which is still in its infancy). For each of these breakthrough categories, early on, it appeared that it couldn’t be done. However, after the first 2 or 3 major breakthroughs in each one of these areas, a compression of innovation occurred. For instance, after approximately 15 years of protein development, we came out with the recombinant manufacturing systems for proteins. Very quickly, within 10 years, there were more than 70 proteins on the market. The persistence of the inventors to overcome early obstacles in each of these health care areas was critical to future success in each area.
Continue to: Raising capital...
Raising capital
There are different investors who specialize in different types of investment opportunities. The first phase of raising capital is the seed round—where there is typically early data, or even no data and just a concept. From this seed round forward, there is less risk as you develop your technology; thus, there are different investors that support different stages of development and that specialize in different types of investing. It is important to target the right investors and raise enough capital to be able to go achieve multiple operational milestones. Otherwise, when you go through your first round of capital, or the Series A or B financing rounds, there may not be a set of investors out there to fund the company moving forward. Health care investors will make it known that they invest in certain rounds of capital. You can determine who those investors are by doing a search online.
A mistake health care inventors can make is not taking enough capital from investors, because they are concerned about dilution. I advise investors not to focus on dilution but rather on, how big can you make “the pie” (value of the company) worth? The entire process is about bringing a true product through to a new standard-of-care curve.
Trust is the most important thing to earn with investors, and there is zero tolerance for a lack of trust. Share your vision as the inventor with investors, who want to know where this category could be in the next 5 or 10 years. Clinical data will always win, and health care investors and industry leaders should be focused on executing the most robust clinical data to demonstrate the clearest potential clinical outcome. Investors will follow a good plan that has been developed to achieve FDA approval, successful commercialization or “go to market” launch, and eventual reimbursement to support a true standard-of-care change.
Failure is defined by inaction
The 3 case studies that I have shared were success stories because the ideas and inventions were acted upon. When I was at Genzyme, we built the company up to more than $1 billion in revenue. We commercialized proteins in over 50 countries. Most importantly, many patients benefited from the innovation. If you have an invention and an idea, act on it—and surround yourself with great people in every discipline. Having the right people and team is extremely important. ●
How ObGyns can best work with radiologists to optimize screening for patients with dense breasts
If your ObGyn practices are anything like ours, every time there is news coverage of a study regarding mammography or about efforts to pass a breast density inform law, your phone rings with patient calls. In fact, every density inform law enacted in the United States, except for in Illinois, directs patients to their referring provider—generally their ObGyn—to discuss the screening and risk implications of dense breast tissue.
The steady increased awareness of breast density means that we, as ObGyns and other primary care providers (PCPs), have additional responsibilities in managing the breast health of our patients. This includes guiding discussions with patients about what breast density means and whether supplemental screening beyond mammography might be beneficial.
As members of the Medical Advisory Board for DenseBreast-info.org (an online educational resource dedicated to providing breast density information to patients and health care professionals), we are aware of the growing body of evidence demonstrating improved detection of early breast cancer using supplemental screening in dense breasts. However, we know that there is confusion among clinicians about how and when to facilitate tailored screening for women with dense breasts or other breast cancer risk factors. Here we answer 6 questions focusing on how to navigate patient discussions around the topic and the best way to collaborate with radiologists to improve breast care for patients.
Play an active role
1. What role should ObGyns and PCPs play in women’s breast health?
Elizabeth Etkin-Kramer, MD: I am a firm believer that ObGyns and all women’s health providers should be able to assess their patients’ risk of breast cancer and explain the process for managing this risk with their patients. This explanation includes the clinical implications of breast density and when supplemental screening should be employed. It is also important for providers to know when to offer genetic testing and when a patient’s personal or family history indicates supplemental screening with breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
DaCarla M. Albright, MD: I absolutely agree that PCPs, ObGyns, and family practitioners should spend the time to be educated about breast density and supplemental screening options. While the exact role providers play in managing patients’ breast health may vary depending on the practice type or location, the need for knowledge and comfort when talking with patients to help them make informed decisions is critical. Breast health and screening, including the importance of breast density, happen to be a particular interest of mine. I have participated in educational webinars, invited lectures, and breast cancer awareness media events on this topic in the past.
Continue to: Join forces with imaging centers...
Join forces with imaging centers
2. How can ObGyns and radiologists collaborate most effectively to use screening results to personalize breast care for patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important to have a close relationship with the radiologists that read our patients’ mammograms. We need to be able to easily contact the radiologist and quickly get clarification on a patient’s report or discuss next steps. Imaging centers should consider running outreach programs to educate their referring providers on how to risk assess, with this assessment inclusive of breast density. Dinner lectures or grand round meetings are effective to facilitate communication between the radiology community and the ObGyn community. Finally, as we all know, supplemental screening is often subject to copays and deductibles per insurance coverage. If advocacy groups, who are working to eliminate these types of costs, cannot get insurers to waive these payments, we need a less expensive self-pay option.
Dr. Albright: I definitely have and encourage an open line of communication between my practice and breast radiology, as well as our breast surgeons and cancer center to set up consultations as needed. We also invite our radiologists as guests to monthly practice meetings or grand rounds within our department to further improve access and open communication, as this environment is one in which greater provider education on density and adjunctive screening can be achieved.
Know when to refer a high-risk patient
3. Most ObGyns routinely collect family history and perform formal risk assessment. What do you need to know about referring patients to a high-risk program?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important as ObGyns to be knowledgeable about breast and ovarian cancer risk assessment and genetic testing for cancer susceptibility genes. Our patients expect that of us. I am comfortable doing risk assessment in my office, but I sometimes refer to other specialists in the community if the patient needs additional counseling. For risk assessment, I look at family and personal history, breast density, and other factors that might lead me to believe the patient might carry a hereditary cancer susceptibility gene, including Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.1 When indicated, I check lifetime as well as short-term (5- to 10-year) risk, usually using Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) or Tyrer-Cuzick/International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) models, as these include breast density.
I discuss risk-reducing medications. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends these agents if my patient’s 5-year risk of breast cancer is 1.67% or greater, and I strongly recommend chemoprevention when the patient’s 5-year BCSC risk exceeds 3%, provided likely benefits exceed risks.2,3 I discuss adding screening breast MRI if lifetime risk by Tyrer-Cuzick exceeds 20%. (Note that Gail and BCSC models are not recommended to be used to determine risk for purposes of supplemental screening with MRI as they do not consider paternal family history nor age of relatives at diagnosis.)
Dr. Albright: ObGyns should be able to ascertain a pertinent history and identify patients at risk for breast cancer based on their personal history, family history, and breast imaging/biopsy history, if relevant. We also need to improve our discussions of supplemental screening for patients who have heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue. I sense that some ObGyns may rely heavily on the radiologist to suggest supplemental screening, but patients actually look to ObGyns as their providers to have this knowledge and give them direction.
Since I practice at a large academic medical center, I have the opportunity to refer patients to our Breast Cancer Genetics Program because I may be limited on time for counseling in the office and do not want to miss salient details. With all of the information I have ascertained about the patient, I am able to determine and encourage appropriate screening and assure insurance coverage for adjunctive breast MRI when appropriate.
Continue to: Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost...
Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost
4. How would you suggest reducing barriers when referring patients for supplemental screening, such as MRI for high-risk women or ultrasound for those with dense breasts? Would you prefer it if such screening could be performed without additional script/referral? How does insurance coverage factor in?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I would love for a screening mammogram with possible ultrasound, on one script, to be the norm. One of the centers that I work with accepts a script written this way. Further, when a patient receives screening at a freestanding facility as opposed to a hospital, the fee for the supplemental screening may be lower because they do not add on a facility fee.
Dr. Albright: We have an order in our electronic health record that allows for screening mammography but adds on diagnostic mammography/bilateral ultrasonography, if indicated by imaging. I am mostly ordering that option now for all of my screening patients; rarely have I had issues with insurance accepting that script. As for when ordering an MRI, I always try to ensure that I have done the patient’s personal risk assessment and included that lifetime breast cancer risk on the order. If the risk is 20% or higher, I typically do not have any insurance coverage issues. If I am ordering MRI as supplemental screening, I typically order the “Fast MRI” protocol that our center offers. This order incurs a $299 out-of-pocket cost for the patient. Any patient with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts on mammography should have this option, but it requires patient education, discussion with the provider, and an additional cost. I definitely think that insurers need to consider covering supplemental screening, since breast density is reportable in a majority of the US states and will soon be the national standard.
Pearls for guiding patients
5. How do you discuss breast density and the need for supplemental screening with your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I strongly feel that my patients need to know when a screening test has limited ability to do its job. This is the case with dense breasts. Visuals help; when discussing breast density, I like the images supplied by DenseBreast-info.org (FIGURE). I explain the two implications of dense tissue:
- First, dense tissue makes it harder to visualize cancers in the breast—the denser the breasts, the less likely the radiologist can pick up a cancer, so mammographic sensitivity for extremely dense breasts can be as low as 25% to 50%.
- Second, high breast density adds to the risk of developing breast cancer. I explain that supplemental screening will pick up additional cancers in women with dense breasts. For example, breast ultrasound will pick up about 2-3/1000 additional breast cancers per year and MRI or molecular breast imaging (MBI) will pick up much more, perhaps 10/1000.
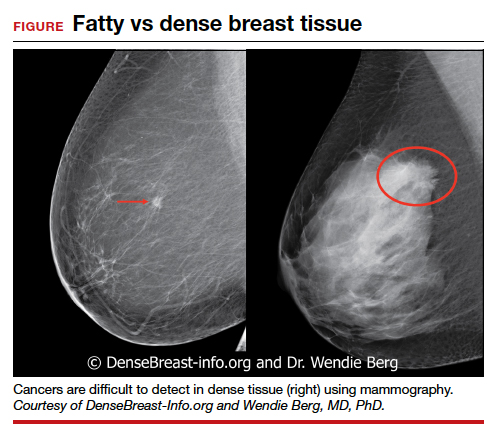
MRI is more invasive than an ultrasound and uses gadolinium, and MBI has more radiation. Supplemental screening is not endorsed by ACOG’s most recent Committee Opinion from 2017; 4 however, patients may choose to have it done. This is where shared-decision making is important.
I strongly recommend that all women’s health care providers complete the CME course on the DenseBreast-info.org website. “ Breast Density: Why It Matters ” is a certified educational program for referring physicians that helps health care professionals learn about breast density, its associated risks, and how best to guide patients regarding breast cancer screening.
Continue to: Dr. Albright...
Dr. Albright: When I discuss breast density, I make sure that patients understand that their mammogram determines the density of their breast tissue. I review that in the higher density categories (heterogeneously dense or extremely dense), there is a higher risk of missing cancer, and that these categories are also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. I also discuss the potential need for supplemental screening, for which my institution primarily offers Fast MRI. However, we can offer breast ultrasonography instead as an option, especially for those concerned about gadolinium exposure. Our center offers either of these supplemental screenings at a cost of $299. I also review the lack of coverage for supplemental screening by some insurance carriers, as both providers and patients may need to advocate for insurer coverage of adjunct studies.
Educational resources
6. What reference materials, illustrations, or other tools do you use to educate your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I frequently use handouts printed from the DenseBreast-info.org website, and there is now a brand new patient fact sheet that I have just started using. I also have an example of breast density categories from fatty replaced to extremely dense on my computer, and I am putting it on a new smart board.
Dr. Albright: The extensive resources available at DenseBreast-info.org can improve both patient and provider knowledge of these important issues, so I suggest patients visit that website, and I use many of the images and visuals to help explain breast density. I even use the materials from the website for educating my resident trainees on breast health and screening. ●
Nearly 16,000 children (up to age 19 years) face cancer-related treatment every year.1 For girls and young women, undergoing chest radiotherapy puts them at higher risk for secondary breast cancer. In fact, they have a 30% chance of developing such cancer by age 50—a risk that is similar to women with a BRCA1 mutation.2 Therefore, current recommendations for breast cancer screening among those who have undergone childhood chest radiation (≥20 Gy) are to begin annual mammography, with adjunct magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), at age 25 years (or 8 years after chest radiotherapy).3
To determine the benefits and risks of these recommendations, as well as of similar strategies, Yeh and colleagues performed simulation modeling using data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and two CISNET (Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network) models.4 For their study they targeted a cohort of female childhood cancer survivors having undergone chest radiotherapy and evaluated breast cancer screening with the following strategies:
- mammography plus MRI, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74
- MRI alone, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74.
They found that both strategies reduced the risk of breast cancer in the targeted cohort but that screening beginning at the earliest ages prevented most deaths. No screening at all was associated with a 10% to 11% lifetime risk of breast cancer, but mammography plus MRI beginning at age 25 reduced that risk by 56% to 71% depending on the model. Screening with MRI alone reduced mortality risk by 56% to 62%. When considering cost per quality adjusted life-year gained, the researchers found that screening beginning at age 30 to be the most cost-effective.4
Yeh and colleagues addressed concerns with mammography and radiation. Although they said the associated amount of radiation exposure is small, the use of mammography in women younger than age 30 is controversial—and not recommended by the American Cancer Society or the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.5,6
Bottom line. Yeh and colleagues conclude that MRI screening, with or without mammography, beginning between the ages of 25 and 30 should be emphasized in screening guidelines. They note the importance of insurance coverage for MRI in those at risk for breast cancer due to childhood radiation exposure.4
References
- National Cancer Institute. How common is cancer in children? https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/child-adolescentcancers-fact-sheet#how-common-is-cancer-in-children. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Moskowitz CS, Chou JF, Wolden SL, et al. Breast cancer after chest radiation therapy for childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2217- 2223.
- Children’s Oncology Group. Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. http:// www.survivorshipguidelines.org/pdf/2018/COG_LTFU_Guidelines_v5.pdf. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Yeh JM, Lowry KP, Schechter CB, et al. Clinical benefits, harms, and cost-effectiveness of breast cancer screening for survivors of childhood cancer treated with chest radiation. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:331-341.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al; American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Advisory Group. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis version 1.2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Bharucha PP, Chiu KE, Francois FM, et al. Genetic testing and screening recommendations for patients with hereditary breast cancer. RadioGraphics. 2020;40:913-936.
- Freedman AN, Yu B, Gail MH, et al. Benefit/risk assessment for breast cancer chemoprevention with raloxifene or tamoxifen for women age 50 years or older. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2327-2333.
- Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3230-3235.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 625: management of women with dense breasts diagnosed by mammography [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:166]. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125(3):750-751.
If your ObGyn practices are anything like ours, every time there is news coverage of a study regarding mammography or about efforts to pass a breast density inform law, your phone rings with patient calls. In fact, every density inform law enacted in the United States, except for in Illinois, directs patients to their referring provider—generally their ObGyn—to discuss the screening and risk implications of dense breast tissue.
The steady increased awareness of breast density means that we, as ObGyns and other primary care providers (PCPs), have additional responsibilities in managing the breast health of our patients. This includes guiding discussions with patients about what breast density means and whether supplemental screening beyond mammography might be beneficial.
As members of the Medical Advisory Board for DenseBreast-info.org (an online educational resource dedicated to providing breast density information to patients and health care professionals), we are aware of the growing body of evidence demonstrating improved detection of early breast cancer using supplemental screening in dense breasts. However, we know that there is confusion among clinicians about how and when to facilitate tailored screening for women with dense breasts or other breast cancer risk factors. Here we answer 6 questions focusing on how to navigate patient discussions around the topic and the best way to collaborate with radiologists to improve breast care for patients.
Play an active role
1. What role should ObGyns and PCPs play in women’s breast health?
Elizabeth Etkin-Kramer, MD: I am a firm believer that ObGyns and all women’s health providers should be able to assess their patients’ risk of breast cancer and explain the process for managing this risk with their patients. This explanation includes the clinical implications of breast density and when supplemental screening should be employed. It is also important for providers to know when to offer genetic testing and when a patient’s personal or family history indicates supplemental screening with breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
DaCarla M. Albright, MD: I absolutely agree that PCPs, ObGyns, and family practitioners should spend the time to be educated about breast density and supplemental screening options. While the exact role providers play in managing patients’ breast health may vary depending on the practice type or location, the need for knowledge and comfort when talking with patients to help them make informed decisions is critical. Breast health and screening, including the importance of breast density, happen to be a particular interest of mine. I have participated in educational webinars, invited lectures, and breast cancer awareness media events on this topic in the past.
Continue to: Join forces with imaging centers...
Join forces with imaging centers
2. How can ObGyns and radiologists collaborate most effectively to use screening results to personalize breast care for patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important to have a close relationship with the radiologists that read our patients’ mammograms. We need to be able to easily contact the radiologist and quickly get clarification on a patient’s report or discuss next steps. Imaging centers should consider running outreach programs to educate their referring providers on how to risk assess, with this assessment inclusive of breast density. Dinner lectures or grand round meetings are effective to facilitate communication between the radiology community and the ObGyn community. Finally, as we all know, supplemental screening is often subject to copays and deductibles per insurance coverage. If advocacy groups, who are working to eliminate these types of costs, cannot get insurers to waive these payments, we need a less expensive self-pay option.
Dr. Albright: I definitely have and encourage an open line of communication between my practice and breast radiology, as well as our breast surgeons and cancer center to set up consultations as needed. We also invite our radiologists as guests to monthly practice meetings or grand rounds within our department to further improve access and open communication, as this environment is one in which greater provider education on density and adjunctive screening can be achieved.
Know when to refer a high-risk patient
3. Most ObGyns routinely collect family history and perform formal risk assessment. What do you need to know about referring patients to a high-risk program?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important as ObGyns to be knowledgeable about breast and ovarian cancer risk assessment and genetic testing for cancer susceptibility genes. Our patients expect that of us. I am comfortable doing risk assessment in my office, but I sometimes refer to other specialists in the community if the patient needs additional counseling. For risk assessment, I look at family and personal history, breast density, and other factors that might lead me to believe the patient might carry a hereditary cancer susceptibility gene, including Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.1 When indicated, I check lifetime as well as short-term (5- to 10-year) risk, usually using Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) or Tyrer-Cuzick/International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) models, as these include breast density.
I discuss risk-reducing medications. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends these agents if my patient’s 5-year risk of breast cancer is 1.67% or greater, and I strongly recommend chemoprevention when the patient’s 5-year BCSC risk exceeds 3%, provided likely benefits exceed risks.2,3 I discuss adding screening breast MRI if lifetime risk by Tyrer-Cuzick exceeds 20%. (Note that Gail and BCSC models are not recommended to be used to determine risk for purposes of supplemental screening with MRI as they do not consider paternal family history nor age of relatives at diagnosis.)
Dr. Albright: ObGyns should be able to ascertain a pertinent history and identify patients at risk for breast cancer based on their personal history, family history, and breast imaging/biopsy history, if relevant. We also need to improve our discussions of supplemental screening for patients who have heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue. I sense that some ObGyns may rely heavily on the radiologist to suggest supplemental screening, but patients actually look to ObGyns as their providers to have this knowledge and give them direction.
Since I practice at a large academic medical center, I have the opportunity to refer patients to our Breast Cancer Genetics Program because I may be limited on time for counseling in the office and do not want to miss salient details. With all of the information I have ascertained about the patient, I am able to determine and encourage appropriate screening and assure insurance coverage for adjunctive breast MRI when appropriate.
Continue to: Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost...
Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost
4. How would you suggest reducing barriers when referring patients for supplemental screening, such as MRI for high-risk women or ultrasound for those with dense breasts? Would you prefer it if such screening could be performed without additional script/referral? How does insurance coverage factor in?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I would love for a screening mammogram with possible ultrasound, on one script, to be the norm. One of the centers that I work with accepts a script written this way. Further, when a patient receives screening at a freestanding facility as opposed to a hospital, the fee for the supplemental screening may be lower because they do not add on a facility fee.
Dr. Albright: We have an order in our electronic health record that allows for screening mammography but adds on diagnostic mammography/bilateral ultrasonography, if indicated by imaging. I am mostly ordering that option now for all of my screening patients; rarely have I had issues with insurance accepting that script. As for when ordering an MRI, I always try to ensure that I have done the patient’s personal risk assessment and included that lifetime breast cancer risk on the order. If the risk is 20% or higher, I typically do not have any insurance coverage issues. If I am ordering MRI as supplemental screening, I typically order the “Fast MRI” protocol that our center offers. This order incurs a $299 out-of-pocket cost for the patient. Any patient with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts on mammography should have this option, but it requires patient education, discussion with the provider, and an additional cost. I definitely think that insurers need to consider covering supplemental screening, since breast density is reportable in a majority of the US states and will soon be the national standard.
Pearls for guiding patients
5. How do you discuss breast density and the need for supplemental screening with your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I strongly feel that my patients need to know when a screening test has limited ability to do its job. This is the case with dense breasts. Visuals help; when discussing breast density, I like the images supplied by DenseBreast-info.org (FIGURE). I explain the two implications of dense tissue:
- First, dense tissue makes it harder to visualize cancers in the breast—the denser the breasts, the less likely the radiologist can pick up a cancer, so mammographic sensitivity for extremely dense breasts can be as low as 25% to 50%.
- Second, high breast density adds to the risk of developing breast cancer. I explain that supplemental screening will pick up additional cancers in women with dense breasts. For example, breast ultrasound will pick up about 2-3/1000 additional breast cancers per year and MRI or molecular breast imaging (MBI) will pick up much more, perhaps 10/1000.

MRI is more invasive than an ultrasound and uses gadolinium, and MBI has more radiation. Supplemental screening is not endorsed by ACOG’s most recent Committee Opinion from 2017; 4 however, patients may choose to have it done. This is where shared-decision making is important.
I strongly recommend that all women’s health care providers complete the CME course on the DenseBreast-info.org website. “ Breast Density: Why It Matters ” is a certified educational program for referring physicians that helps health care professionals learn about breast density, its associated risks, and how best to guide patients regarding breast cancer screening.
Continue to: Dr. Albright...
Dr. Albright: When I discuss breast density, I make sure that patients understand that their mammogram determines the density of their breast tissue. I review that in the higher density categories (heterogeneously dense or extremely dense), there is a higher risk of missing cancer, and that these categories are also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. I also discuss the potential need for supplemental screening, for which my institution primarily offers Fast MRI. However, we can offer breast ultrasonography instead as an option, especially for those concerned about gadolinium exposure. Our center offers either of these supplemental screenings at a cost of $299. I also review the lack of coverage for supplemental screening by some insurance carriers, as both providers and patients may need to advocate for insurer coverage of adjunct studies.
Educational resources
6. What reference materials, illustrations, or other tools do you use to educate your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I frequently use handouts printed from the DenseBreast-info.org website, and there is now a brand new patient fact sheet that I have just started using. I also have an example of breast density categories from fatty replaced to extremely dense on my computer, and I am putting it on a new smart board.
Dr. Albright: The extensive resources available at DenseBreast-info.org can improve both patient and provider knowledge of these important issues, so I suggest patients visit that website, and I use many of the images and visuals to help explain breast density. I even use the materials from the website for educating my resident trainees on breast health and screening. ●
Nearly 16,000 children (up to age 19 years) face cancer-related treatment every year.1 For girls and young women, undergoing chest radiotherapy puts them at higher risk for secondary breast cancer. In fact, they have a 30% chance of developing such cancer by age 50—a risk that is similar to women with a BRCA1 mutation.2 Therefore, current recommendations for breast cancer screening among those who have undergone childhood chest radiation (≥20 Gy) are to begin annual mammography, with adjunct magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), at age 25 years (or 8 years after chest radiotherapy).3
To determine the benefits and risks of these recommendations, as well as of similar strategies, Yeh and colleagues performed simulation modeling using data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and two CISNET (Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network) models.4 For their study they targeted a cohort of female childhood cancer survivors having undergone chest radiotherapy and evaluated breast cancer screening with the following strategies:
- mammography plus MRI, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74
- MRI alone, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74.
They found that both strategies reduced the risk of breast cancer in the targeted cohort but that screening beginning at the earliest ages prevented most deaths. No screening at all was associated with a 10% to 11% lifetime risk of breast cancer, but mammography plus MRI beginning at age 25 reduced that risk by 56% to 71% depending on the model. Screening with MRI alone reduced mortality risk by 56% to 62%. When considering cost per quality adjusted life-year gained, the researchers found that screening beginning at age 30 to be the most cost-effective.4
Yeh and colleagues addressed concerns with mammography and radiation. Although they said the associated amount of radiation exposure is small, the use of mammography in women younger than age 30 is controversial—and not recommended by the American Cancer Society or the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.5,6
Bottom line. Yeh and colleagues conclude that MRI screening, with or without mammography, beginning between the ages of 25 and 30 should be emphasized in screening guidelines. They note the importance of insurance coverage for MRI in those at risk for breast cancer due to childhood radiation exposure.4
References
- National Cancer Institute. How common is cancer in children? https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/child-adolescentcancers-fact-sheet#how-common-is-cancer-in-children. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Moskowitz CS, Chou JF, Wolden SL, et al. Breast cancer after chest radiation therapy for childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2217- 2223.
- Children’s Oncology Group. Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. http:// www.survivorshipguidelines.org/pdf/2018/COG_LTFU_Guidelines_v5.pdf. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Yeh JM, Lowry KP, Schechter CB, et al. Clinical benefits, harms, and cost-effectiveness of breast cancer screening for survivors of childhood cancer treated with chest radiation. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:331-341.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al; American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Advisory Group. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis version 1.2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Accessed September 25, 2020.
If your ObGyn practices are anything like ours, every time there is news coverage of a study regarding mammography or about efforts to pass a breast density inform law, your phone rings with patient calls. In fact, every density inform law enacted in the United States, except for in Illinois, directs patients to their referring provider—generally their ObGyn—to discuss the screening and risk implications of dense breast tissue.
The steady increased awareness of breast density means that we, as ObGyns and other primary care providers (PCPs), have additional responsibilities in managing the breast health of our patients. This includes guiding discussions with patients about what breast density means and whether supplemental screening beyond mammography might be beneficial.
As members of the Medical Advisory Board for DenseBreast-info.org (an online educational resource dedicated to providing breast density information to patients and health care professionals), we are aware of the growing body of evidence demonstrating improved detection of early breast cancer using supplemental screening in dense breasts. However, we know that there is confusion among clinicians about how and when to facilitate tailored screening for women with dense breasts or other breast cancer risk factors. Here we answer 6 questions focusing on how to navigate patient discussions around the topic and the best way to collaborate with radiologists to improve breast care for patients.
Play an active role
1. What role should ObGyns and PCPs play in women’s breast health?
Elizabeth Etkin-Kramer, MD: I am a firm believer that ObGyns and all women’s health providers should be able to assess their patients’ risk of breast cancer and explain the process for managing this risk with their patients. This explanation includes the clinical implications of breast density and when supplemental screening should be employed. It is also important for providers to know when to offer genetic testing and when a patient’s personal or family history indicates supplemental screening with breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
DaCarla M. Albright, MD: I absolutely agree that PCPs, ObGyns, and family practitioners should spend the time to be educated about breast density and supplemental screening options. While the exact role providers play in managing patients’ breast health may vary depending on the practice type or location, the need for knowledge and comfort when talking with patients to help them make informed decisions is critical. Breast health and screening, including the importance of breast density, happen to be a particular interest of mine. I have participated in educational webinars, invited lectures, and breast cancer awareness media events on this topic in the past.
Continue to: Join forces with imaging centers...
Join forces with imaging centers
2. How can ObGyns and radiologists collaborate most effectively to use screening results to personalize breast care for patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important to have a close relationship with the radiologists that read our patients’ mammograms. We need to be able to easily contact the radiologist and quickly get clarification on a patient’s report or discuss next steps. Imaging centers should consider running outreach programs to educate their referring providers on how to risk assess, with this assessment inclusive of breast density. Dinner lectures or grand round meetings are effective to facilitate communication between the radiology community and the ObGyn community. Finally, as we all know, supplemental screening is often subject to copays and deductibles per insurance coverage. If advocacy groups, who are working to eliminate these types of costs, cannot get insurers to waive these payments, we need a less expensive self-pay option.
Dr. Albright: I definitely have and encourage an open line of communication between my practice and breast radiology, as well as our breast surgeons and cancer center to set up consultations as needed. We also invite our radiologists as guests to monthly practice meetings or grand rounds within our department to further improve access and open communication, as this environment is one in which greater provider education on density and adjunctive screening can be achieved.
Know when to refer a high-risk patient
3. Most ObGyns routinely collect family history and perform formal risk assessment. What do you need to know about referring patients to a high-risk program?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: It is important as ObGyns to be knowledgeable about breast and ovarian cancer risk assessment and genetic testing for cancer susceptibility genes. Our patients expect that of us. I am comfortable doing risk assessment in my office, but I sometimes refer to other specialists in the community if the patient needs additional counseling. For risk assessment, I look at family and personal history, breast density, and other factors that might lead me to believe the patient might carry a hereditary cancer susceptibility gene, including Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry.1 When indicated, I check lifetime as well as short-term (5- to 10-year) risk, usually using Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) or Tyrer-Cuzick/International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) models, as these include breast density.
I discuss risk-reducing medications. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends these agents if my patient’s 5-year risk of breast cancer is 1.67% or greater, and I strongly recommend chemoprevention when the patient’s 5-year BCSC risk exceeds 3%, provided likely benefits exceed risks.2,3 I discuss adding screening breast MRI if lifetime risk by Tyrer-Cuzick exceeds 20%. (Note that Gail and BCSC models are not recommended to be used to determine risk for purposes of supplemental screening with MRI as they do not consider paternal family history nor age of relatives at diagnosis.)
Dr. Albright: ObGyns should be able to ascertain a pertinent history and identify patients at risk for breast cancer based on their personal history, family history, and breast imaging/biopsy history, if relevant. We also need to improve our discussions of supplemental screening for patients who have heterogeneously dense or extremely dense breast tissue. I sense that some ObGyns may rely heavily on the radiologist to suggest supplemental screening, but patients actually look to ObGyns as their providers to have this knowledge and give them direction.
Since I practice at a large academic medical center, I have the opportunity to refer patients to our Breast Cancer Genetics Program because I may be limited on time for counseling in the office and do not want to miss salient details. With all of the information I have ascertained about the patient, I am able to determine and encourage appropriate screening and assure insurance coverage for adjunctive breast MRI when appropriate.
Continue to: Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost...
Consider how you order patients’ screening to reduce barriers and cost
4. How would you suggest reducing barriers when referring patients for supplemental screening, such as MRI for high-risk women or ultrasound for those with dense breasts? Would you prefer it if such screening could be performed without additional script/referral? How does insurance coverage factor in?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I would love for a screening mammogram with possible ultrasound, on one script, to be the norm. One of the centers that I work with accepts a script written this way. Further, when a patient receives screening at a freestanding facility as opposed to a hospital, the fee for the supplemental screening may be lower because they do not add on a facility fee.
Dr. Albright: We have an order in our electronic health record that allows for screening mammography but adds on diagnostic mammography/bilateral ultrasonography, if indicated by imaging. I am mostly ordering that option now for all of my screening patients; rarely have I had issues with insurance accepting that script. As for when ordering an MRI, I always try to ensure that I have done the patient’s personal risk assessment and included that lifetime breast cancer risk on the order. If the risk is 20% or higher, I typically do not have any insurance coverage issues. If I am ordering MRI as supplemental screening, I typically order the “Fast MRI” protocol that our center offers. This order incurs a $299 out-of-pocket cost for the patient. Any patient with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts on mammography should have this option, but it requires patient education, discussion with the provider, and an additional cost. I definitely think that insurers need to consider covering supplemental screening, since breast density is reportable in a majority of the US states and will soon be the national standard.
Pearls for guiding patients
5. How do you discuss breast density and the need for supplemental screening with your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I strongly feel that my patients need to know when a screening test has limited ability to do its job. This is the case with dense breasts. Visuals help; when discussing breast density, I like the images supplied by DenseBreast-info.org (FIGURE). I explain the two implications of dense tissue:
- First, dense tissue makes it harder to visualize cancers in the breast—the denser the breasts, the less likely the radiologist can pick up a cancer, so mammographic sensitivity for extremely dense breasts can be as low as 25% to 50%.
- Second, high breast density adds to the risk of developing breast cancer. I explain that supplemental screening will pick up additional cancers in women with dense breasts. For example, breast ultrasound will pick up about 2-3/1000 additional breast cancers per year and MRI or molecular breast imaging (MBI) will pick up much more, perhaps 10/1000.

MRI is more invasive than an ultrasound and uses gadolinium, and MBI has more radiation. Supplemental screening is not endorsed by ACOG’s most recent Committee Opinion from 2017; 4 however, patients may choose to have it done. This is where shared-decision making is important.
I strongly recommend that all women’s health care providers complete the CME course on the DenseBreast-info.org website. “ Breast Density: Why It Matters ” is a certified educational program for referring physicians that helps health care professionals learn about breast density, its associated risks, and how best to guide patients regarding breast cancer screening.
Continue to: Dr. Albright...
Dr. Albright: When I discuss breast density, I make sure that patients understand that their mammogram determines the density of their breast tissue. I review that in the higher density categories (heterogeneously dense or extremely dense), there is a higher risk of missing cancer, and that these categories are also associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. I also discuss the potential need for supplemental screening, for which my institution primarily offers Fast MRI. However, we can offer breast ultrasonography instead as an option, especially for those concerned about gadolinium exposure. Our center offers either of these supplemental screenings at a cost of $299. I also review the lack of coverage for supplemental screening by some insurance carriers, as both providers and patients may need to advocate for insurer coverage of adjunct studies.
Educational resources
6. What reference materials, illustrations, or other tools do you use to educate your patients?
Dr. Etkin-Kramer: I frequently use handouts printed from the DenseBreast-info.org website, and there is now a brand new patient fact sheet that I have just started using. I also have an example of breast density categories from fatty replaced to extremely dense on my computer, and I am putting it on a new smart board.
Dr. Albright: The extensive resources available at DenseBreast-info.org can improve both patient and provider knowledge of these important issues, so I suggest patients visit that website, and I use many of the images and visuals to help explain breast density. I even use the materials from the website for educating my resident trainees on breast health and screening. ●
Nearly 16,000 children (up to age 19 years) face cancer-related treatment every year.1 For girls and young women, undergoing chest radiotherapy puts them at higher risk for secondary breast cancer. In fact, they have a 30% chance of developing such cancer by age 50—a risk that is similar to women with a BRCA1 mutation.2 Therefore, current recommendations for breast cancer screening among those who have undergone childhood chest radiation (≥20 Gy) are to begin annual mammography, with adjunct magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), at age 25 years (or 8 years after chest radiotherapy).3
To determine the benefits and risks of these recommendations, as well as of similar strategies, Yeh and colleagues performed simulation modeling using data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and two CISNET (Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network) models.4 For their study they targeted a cohort of female childhood cancer survivors having undergone chest radiotherapy and evaluated breast cancer screening with the following strategies:
- mammography plus MRI, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74
- MRI alone, starting at ages 25, 30, or 35 years and continuing to age 74.
They found that both strategies reduced the risk of breast cancer in the targeted cohort but that screening beginning at the earliest ages prevented most deaths. No screening at all was associated with a 10% to 11% lifetime risk of breast cancer, but mammography plus MRI beginning at age 25 reduced that risk by 56% to 71% depending on the model. Screening with MRI alone reduced mortality risk by 56% to 62%. When considering cost per quality adjusted life-year gained, the researchers found that screening beginning at age 30 to be the most cost-effective.4
Yeh and colleagues addressed concerns with mammography and radiation. Although they said the associated amount of radiation exposure is small, the use of mammography in women younger than age 30 is controversial—and not recommended by the American Cancer Society or the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.5,6
Bottom line. Yeh and colleagues conclude that MRI screening, with or without mammography, beginning between the ages of 25 and 30 should be emphasized in screening guidelines. They note the importance of insurance coverage for MRI in those at risk for breast cancer due to childhood radiation exposure.4
References
- National Cancer Institute. How common is cancer in children? https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/child-adolescentcancers-fact-sheet#how-common-is-cancer-in-children. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Moskowitz CS, Chou JF, Wolden SL, et al. Breast cancer after chest radiation therapy for childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2217- 2223.
- Children’s Oncology Group. Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers. http:// www.survivorshipguidelines.org/pdf/2018/COG_LTFU_Guidelines_v5.pdf. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Yeh JM, Lowry KP, Schechter CB, et al. Clinical benefits, harms, and cost-effectiveness of breast cancer screening for survivors of childhood cancer treated with chest radiation. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:331-341.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al; American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Advisory Group. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis version 1.2019. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Accessed September 25, 2020.
- Bharucha PP, Chiu KE, Francois FM, et al. Genetic testing and screening recommendations for patients with hereditary breast cancer. RadioGraphics. 2020;40:913-936.
- Freedman AN, Yu B, Gail MH, et al. Benefit/risk assessment for breast cancer chemoprevention with raloxifene or tamoxifen for women age 50 years or older. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2327-2333.
- Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3230-3235.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 625: management of women with dense breasts diagnosed by mammography [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:166]. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125(3):750-751.
- Bharucha PP, Chiu KE, Francois FM, et al. Genetic testing and screening recommendations for patients with hereditary breast cancer. RadioGraphics. 2020;40:913-936.
- Freedman AN, Yu B, Gail MH, et al. Benefit/risk assessment for breast cancer chemoprevention with raloxifene or tamoxifen for women age 50 years or older. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2327-2333.
- Pruthi S, Heisey RE, Bevers TB. Chemoprevention for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3230-3235.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion no. 625: management of women with dense breasts diagnosed by mammography [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:166]. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125(3):750-751.
Please stop using the adjective “elective” to describe the important health services ObGyns provide
During the April 2020 peak of patient admissions to our hospital caused by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we severely limited the number of surgical procedures performed to conserve health system resources. During this stressful time, some administrators and physicians began categorizing operations for cancer as "elective" procedures that could be postponed for months. Personally, I think the use of elective to describe cancer surgery is not optimal, even during a pandemic. In reality, the surgeries for patients with cancer were being postponed to ensure that services were available for patients with severe and critical COVID-19 disease, not because the surgeries were "elective." The health system leaders were making the rational decision to prioritize the needs of patients with COVID-19 infections over the needs of patients with cancer. However, they were using an inappropriate description of the rationale for postponing the surgery for patients with cancer—an intellectual short-cut.
This experience prompted me to explore all the medical interventions commonly described as elective. Surprisingly, among medical specialists, obstetricians excel in using the adjective elective to describe our important work. For example, in the medical record we commonly use terms such as “elective induction of labor,” “elective cesarean delivery” (CD) and “elective termination of pregnancy.” I believe it would advance our field if obstetricians stopped using the term elective to describe the important health services we provide.
Stop using the term “elective induction of labor”
Ghartey and Macones recently advocated for all obstetricians to stop using the term elective when describing induction of labor.1 The ARRIVE trial (A Randomized Trial of Induction vs Expectant Management)2 demonstrated that, among nulliparous women at 39 weeks’ gestation, induction of labor resulted in a lower CD rate than expectant management (18.6% vs 22.2%, respectively; relative risk, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.76-0.93). These findings indicate that induction of labor is not elective because it provides a clear health benefit over the alternative of expectant management. Given current expert guidance, induction of labor prior to 39 weeks’ gestation must be based on an accepted medical indication and provide a health benefit; hence, these inductions are medically indicated. Similarly, since induction of labor at 39 weeks’ gestation also provides a clear health benefit it is also medically indicated and not “elective.” Ghartey and Macones conclude1:
"The words we choose to
describe medical interventions
matter. They send a message
to patients, physicians, nurses,
and hospital administrators.
When the term 'elective' is applied to a medical intervention,
it implies that it is not really
necessary. That is certainly not
the case when it comes to 39-
week nulliparous induction. The
ARRIVE trial provides grade A
(good and consistent) evidence
that labor induction provided
benefit with no harm to women
and their infants. These inductions are not 'elective'."
An alternative descriptor is “medically indicated” induction.
Continue to: Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”...
Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”
I recently searched PubMed for publications using the key words, “elective cesarean delivery,” and more than 7,000 publications were identified by the National Library of Medicine. “Elective cesarean delivery” is clearly an important term used by obstetrical authorities. What do we mean by elective CD?
At 39 weeks’ gestation, a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman has a limited number of options:
- induction of labor
- expectant management awaiting the onset of labor
- scheduled CD before the onset of labor.
For a low-risk pregnant woman at 39 weeks’ gestation, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends vaginal delivery because it best balances the risks and benefits for the woman and newborn.3 When a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman asks a clinician about a scheduled CD, we are trained to thoroughly explore the reasons for the woman’s request, including her intellectual, fact-based, concerns about labor and vaginal birth and her emotional reaction to the thought of a vaginal or cesarean birth. In this situation the clinician will provide information about the risks and benefits of vaginal versus CD. In the vast majority of situations, the pregnant woman will agree to attempting vaginal delivery. In one study of 458,767 births, only 0.2% of women choose a “maternal request cesarean delivery.”4
After thorough counseling, if a woman and her clinician jointly agree to schedule a primary CD it will be the result of hours of intensive discussion, not an imprudent and hasty decision. In this case, the delivery is best characterized as a “maternal request cesarean delivery,” not an “elective” CD.
Stop using the terms “elective termination of pregnancy” and “elective abortion”
Janiak and Goldberg have advocated for the elimination of the phrase elective abortion.5 They write5:
"Support for abortion varies
depending on the reason for
the abortion—whether it is
'elective' or 'indicated.' In the
case of abortion, these terms
generally differentiate between
women seeking abortion for
reasons of maternal or fetal
health (an 'indicated abortion')
defined in contrast to women
seeking abortion for other
reasons (an 'elective abortion').
We argue that such a distinction is impossible to operationalize in a just manner. The use
of the phrase 'elective abortion'
promotes the institutionalization of a false hierarchy of need
among abortion patients."
My experience is that pregnant women never seek an abortion based on whimsy. Most pregnant women who consider an abortion struggle greatly with the choice, using reason and judgment to arrive at their final decision. The choice to seek an abortion is always a difficult one, influenced by a constellation of hard facts that impact the woman’s life. Using the term elective to describe an abortion implies a moral judgment and stigmatizes the choice to have an abortion. Janiak and Goldberg conclude by recommending the elimination of the phrase 'elective abortion' in favor of the phrase “induced abortion.”5
Continue to: Time for change...
Time for change
Shockingly, in searching the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD10), the word elective is most commonly used in the context of health services provided to pregnant women, including: elective induction of labor (Z34.90), elective cesarean delivery (O82), elective termination of pregnancy (Z33.2), and elective fetal reduction (Z031.30X0). In ICD10, other specialties do not describe the scope of their health services with the adjective elective.
There are many definitions and interpretations of elective. The most benign use of the word in the context of surgery is to contrast procedures that can be scheduled in the future with those that need to be performed urgently. In this context elective only refers to the timing, not the medical necessity, of the procedure. By contrast, describing a procedure as elective may signal that it is not medically necessary and is being performed based on the capricious preference of the patient or physician. Given the confusion and misunderstanding that may be caused by describing our important health services as “elective,” I hope that we can permanently sunset use of the term. ●
- Ghartey J, Macones GA. 39-week nulliparous inductions are not elective. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:519-520.
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
- ACOG Committee Opinion No 761: cesarean delivery on maternal request. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133.e73-e77.
- Gossman GL, Joesch JM, Tanfer K. Trends in maternal request cesarean delivery from 1991 to 2004. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1506-1516.
- Janiak E, Goldberg AB. Eliminating the phrase “elective abortion”: why language matters. Contraception. 2016;93:89-92.
During the April 2020 peak of patient admissions to our hospital caused by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we severely limited the number of surgical procedures performed to conserve health system resources. During this stressful time, some administrators and physicians began categorizing operations for cancer as "elective" procedures that could be postponed for months. Personally, I think the use of elective to describe cancer surgery is not optimal, even during a pandemic. In reality, the surgeries for patients with cancer were being postponed to ensure that services were available for patients with severe and critical COVID-19 disease, not because the surgeries were "elective." The health system leaders were making the rational decision to prioritize the needs of patients with COVID-19 infections over the needs of patients with cancer. However, they were using an inappropriate description of the rationale for postponing the surgery for patients with cancer—an intellectual short-cut.
This experience prompted me to explore all the medical interventions commonly described as elective. Surprisingly, among medical specialists, obstetricians excel in using the adjective elective to describe our important work. For example, in the medical record we commonly use terms such as “elective induction of labor,” “elective cesarean delivery” (CD) and “elective termination of pregnancy.” I believe it would advance our field if obstetricians stopped using the term elective to describe the important health services we provide.
Stop using the term “elective induction of labor”
Ghartey and Macones recently advocated for all obstetricians to stop using the term elective when describing induction of labor.1 The ARRIVE trial (A Randomized Trial of Induction vs Expectant Management)2 demonstrated that, among nulliparous women at 39 weeks’ gestation, induction of labor resulted in a lower CD rate than expectant management (18.6% vs 22.2%, respectively; relative risk, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.76-0.93). These findings indicate that induction of labor is not elective because it provides a clear health benefit over the alternative of expectant management. Given current expert guidance, induction of labor prior to 39 weeks’ gestation must be based on an accepted medical indication and provide a health benefit; hence, these inductions are medically indicated. Similarly, since induction of labor at 39 weeks’ gestation also provides a clear health benefit it is also medically indicated and not “elective.” Ghartey and Macones conclude1:
"The words we choose to
describe medical interventions
matter. They send a message
to patients, physicians, nurses,
and hospital administrators.
When the term 'elective' is applied to a medical intervention,
it implies that it is not really
necessary. That is certainly not
the case when it comes to 39-
week nulliparous induction. The
ARRIVE trial provides grade A
(good and consistent) evidence
that labor induction provided
benefit with no harm to women
and their infants. These inductions are not 'elective'."
An alternative descriptor is “medically indicated” induction.
Continue to: Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”...
Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”
I recently searched PubMed for publications using the key words, “elective cesarean delivery,” and more than 7,000 publications were identified by the National Library of Medicine. “Elective cesarean delivery” is clearly an important term used by obstetrical authorities. What do we mean by elective CD?
At 39 weeks’ gestation, a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman has a limited number of options:
- induction of labor
- expectant management awaiting the onset of labor
- scheduled CD before the onset of labor.
For a low-risk pregnant woman at 39 weeks’ gestation, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends vaginal delivery because it best balances the risks and benefits for the woman and newborn.3 When a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman asks a clinician about a scheduled CD, we are trained to thoroughly explore the reasons for the woman’s request, including her intellectual, fact-based, concerns about labor and vaginal birth and her emotional reaction to the thought of a vaginal or cesarean birth. In this situation the clinician will provide information about the risks and benefits of vaginal versus CD. In the vast majority of situations, the pregnant woman will agree to attempting vaginal delivery. In one study of 458,767 births, only 0.2% of women choose a “maternal request cesarean delivery.”4
After thorough counseling, if a woman and her clinician jointly agree to schedule a primary CD it will be the result of hours of intensive discussion, not an imprudent and hasty decision. In this case, the delivery is best characterized as a “maternal request cesarean delivery,” not an “elective” CD.
Stop using the terms “elective termination of pregnancy” and “elective abortion”
Janiak and Goldberg have advocated for the elimination of the phrase elective abortion.5 They write5:
"Support for abortion varies
depending on the reason for
the abortion—whether it is
'elective' or 'indicated.' In the
case of abortion, these terms
generally differentiate between
women seeking abortion for
reasons of maternal or fetal
health (an 'indicated abortion')
defined in contrast to women
seeking abortion for other
reasons (an 'elective abortion').
We argue that such a distinction is impossible to operationalize in a just manner. The use
of the phrase 'elective abortion'
promotes the institutionalization of a false hierarchy of need
among abortion patients."
My experience is that pregnant women never seek an abortion based on whimsy. Most pregnant women who consider an abortion struggle greatly with the choice, using reason and judgment to arrive at their final decision. The choice to seek an abortion is always a difficult one, influenced by a constellation of hard facts that impact the woman’s life. Using the term elective to describe an abortion implies a moral judgment and stigmatizes the choice to have an abortion. Janiak and Goldberg conclude by recommending the elimination of the phrase 'elective abortion' in favor of the phrase “induced abortion.”5
Continue to: Time for change...
Time for change
Shockingly, in searching the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD10), the word elective is most commonly used in the context of health services provided to pregnant women, including: elective induction of labor (Z34.90), elective cesarean delivery (O82), elective termination of pregnancy (Z33.2), and elective fetal reduction (Z031.30X0). In ICD10, other specialties do not describe the scope of their health services with the adjective elective.
There are many definitions and interpretations of elective. The most benign use of the word in the context of surgery is to contrast procedures that can be scheduled in the future with those that need to be performed urgently. In this context elective only refers to the timing, not the medical necessity, of the procedure. By contrast, describing a procedure as elective may signal that it is not medically necessary and is being performed based on the capricious preference of the patient or physician. Given the confusion and misunderstanding that may be caused by describing our important health services as “elective,” I hope that we can permanently sunset use of the term. ●
During the April 2020 peak of patient admissions to our hospital caused by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we severely limited the number of surgical procedures performed to conserve health system resources. During this stressful time, some administrators and physicians began categorizing operations for cancer as "elective" procedures that could be postponed for months. Personally, I think the use of elective to describe cancer surgery is not optimal, even during a pandemic. In reality, the surgeries for patients with cancer were being postponed to ensure that services were available for patients with severe and critical COVID-19 disease, not because the surgeries were "elective." The health system leaders were making the rational decision to prioritize the needs of patients with COVID-19 infections over the needs of patients with cancer. However, they were using an inappropriate description of the rationale for postponing the surgery for patients with cancer—an intellectual short-cut.
This experience prompted me to explore all the medical interventions commonly described as elective. Surprisingly, among medical specialists, obstetricians excel in using the adjective elective to describe our important work. For example, in the medical record we commonly use terms such as “elective induction of labor,” “elective cesarean delivery” (CD) and “elective termination of pregnancy.” I believe it would advance our field if obstetricians stopped using the term elective to describe the important health services we provide.
Stop using the term “elective induction of labor”
Ghartey and Macones recently advocated for all obstetricians to stop using the term elective when describing induction of labor.1 The ARRIVE trial (A Randomized Trial of Induction vs Expectant Management)2 demonstrated that, among nulliparous women at 39 weeks’ gestation, induction of labor resulted in a lower CD rate than expectant management (18.6% vs 22.2%, respectively; relative risk, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.76-0.93). These findings indicate that induction of labor is not elective because it provides a clear health benefit over the alternative of expectant management. Given current expert guidance, induction of labor prior to 39 weeks’ gestation must be based on an accepted medical indication and provide a health benefit; hence, these inductions are medically indicated. Similarly, since induction of labor at 39 weeks’ gestation also provides a clear health benefit it is also medically indicated and not “elective.” Ghartey and Macones conclude1:
"The words we choose to
describe medical interventions
matter. They send a message
to patients, physicians, nurses,
and hospital administrators.
When the term 'elective' is applied to a medical intervention,
it implies that it is not really
necessary. That is certainly not
the case when it comes to 39-
week nulliparous induction. The
ARRIVE trial provides grade A
(good and consistent) evidence
that labor induction provided
benefit with no harm to women
and their infants. These inductions are not 'elective'."
An alternative descriptor is “medically indicated” induction.
Continue to: Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”...
Stop using the term “elective cesarean delivery”
I recently searched PubMed for publications using the key words, “elective cesarean delivery,” and more than 7,000 publications were identified by the National Library of Medicine. “Elective cesarean delivery” is clearly an important term used by obstetrical authorities. What do we mean by elective CD?
At 39 weeks’ gestation, a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman has a limited number of options:
- induction of labor
- expectant management awaiting the onset of labor
- scheduled CD before the onset of labor.
For a low-risk pregnant woman at 39 weeks’ gestation, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends vaginal delivery because it best balances the risks and benefits for the woman and newborn.3 When a low-risk nulliparous pregnant woman asks a clinician about a scheduled CD, we are trained to thoroughly explore the reasons for the woman’s request, including her intellectual, fact-based, concerns about labor and vaginal birth and her emotional reaction to the thought of a vaginal or cesarean birth. In this situation the clinician will provide information about the risks and benefits of vaginal versus CD. In the vast majority of situations, the pregnant woman will agree to attempting vaginal delivery. In one study of 458,767 births, only 0.2% of women choose a “maternal request cesarean delivery.”4
After thorough counseling, if a woman and her clinician jointly agree to schedule a primary CD it will be the result of hours of intensive discussion, not an imprudent and hasty decision. In this case, the delivery is best characterized as a “maternal request cesarean delivery,” not an “elective” CD.
Stop using the terms “elective termination of pregnancy” and “elective abortion”
Janiak and Goldberg have advocated for the elimination of the phrase elective abortion.5 They write5:
"Support for abortion varies
depending on the reason for
the abortion—whether it is
'elective' or 'indicated.' In the
case of abortion, these terms
generally differentiate between
women seeking abortion for
reasons of maternal or fetal
health (an 'indicated abortion')
defined in contrast to women
seeking abortion for other
reasons (an 'elective abortion').
We argue that such a distinction is impossible to operationalize in a just manner. The use
of the phrase 'elective abortion'
promotes the institutionalization of a false hierarchy of need
among abortion patients."
My experience is that pregnant women never seek an abortion based on whimsy. Most pregnant women who consider an abortion struggle greatly with the choice, using reason and judgment to arrive at their final decision. The choice to seek an abortion is always a difficult one, influenced by a constellation of hard facts that impact the woman’s life. Using the term elective to describe an abortion implies a moral judgment and stigmatizes the choice to have an abortion. Janiak and Goldberg conclude by recommending the elimination of the phrase 'elective abortion' in favor of the phrase “induced abortion.”5
Continue to: Time for change...
Time for change
Shockingly, in searching the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision (ICD10), the word elective is most commonly used in the context of health services provided to pregnant women, including: elective induction of labor (Z34.90), elective cesarean delivery (O82), elective termination of pregnancy (Z33.2), and elective fetal reduction (Z031.30X0). In ICD10, other specialties do not describe the scope of their health services with the adjective elective.
There are many definitions and interpretations of elective. The most benign use of the word in the context of surgery is to contrast procedures that can be scheduled in the future with those that need to be performed urgently. In this context elective only refers to the timing, not the medical necessity, of the procedure. By contrast, describing a procedure as elective may signal that it is not medically necessary and is being performed based on the capricious preference of the patient or physician. Given the confusion and misunderstanding that may be caused by describing our important health services as “elective,” I hope that we can permanently sunset use of the term. ●
- Ghartey J, Macones GA. 39-week nulliparous inductions are not elective. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:519-520.
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
- ACOG Committee Opinion No 761: cesarean delivery on maternal request. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133.e73-e77.
- Gossman GL, Joesch JM, Tanfer K. Trends in maternal request cesarean delivery from 1991 to 2004. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1506-1516.
- Janiak E, Goldberg AB. Eliminating the phrase “elective abortion”: why language matters. Contraception. 2016;93:89-92.
- Ghartey J, Macones GA. 39-week nulliparous inductions are not elective. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:519-520.
- Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy UM, et al. Labor induction versus expectant management in low-risk nulliparous women. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:513-523.
- ACOG Committee Opinion No 761: cesarean delivery on maternal request. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133.e73-e77.
- Gossman GL, Joesch JM, Tanfer K. Trends in maternal request cesarean delivery from 1991 to 2004. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1506-1516.
- Janiak E, Goldberg AB. Eliminating the phrase “elective abortion”: why language matters. Contraception. 2016;93:89-92.