User login
With life in the balance, a pediatric palliative care program expands its work to adults
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
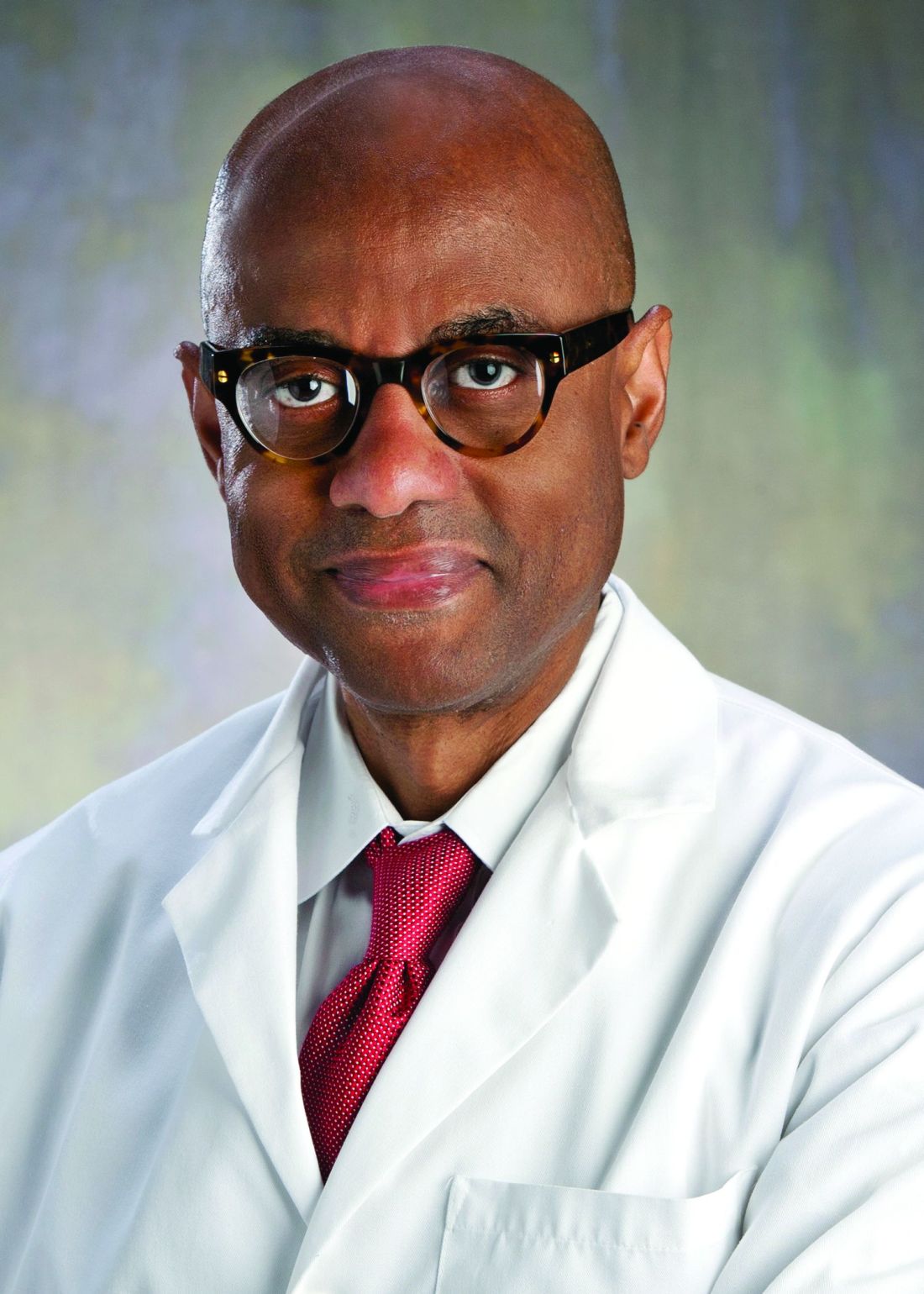
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
Novel inflammatory syndrome in children possibly linked to COVID-19
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
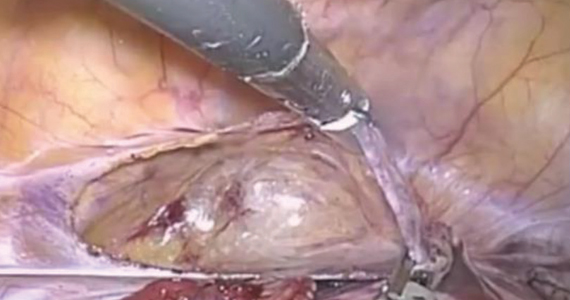
A multicenter RCT makes a case for transabdominal cerclage
Since the 1950s, when Shirodkar (1955) and McDonald (1957) published their seminal works detailing a transvaginal method to suture a “weak” cervix, clinicians and researchers have debated the indications for and utility of cerclage for preventing pregnancy loss and preterm birth.1,2
Originally based on a history of recurrent mid-trimester loss (that is, a clinical diagnosis of cervical insufficiency), cerclage has been expanded to capture both ultrasonography and physical-exam indications. While cerclage has proven useful in select patient populations, an infrequent but vexing problem is what to do when a woman has experienced 1 or more (transvaginal) cerclage “failures.”
With a dearth of well-controlled, randomized data to support the use of cerclage for either history- or physical-exam indications, it is not surprising that we still debate whether the Shirodkar method is superior to the McDonald technique as well as how to best manage a patient when either or both methods previously resulted in an unsatisfactory outcome.
First randomized study to directly compare cerclage techniques
Fortunately, Shennan and colleagues in the United Kingdom have greatly enlarged our knowledge in this area by performing the first well-powered, 3-arm, randomized trial of transabdominal cerclage (TAC) compared with both high and low vaginal cerclage (HVC, LVC).3 They analyzed data for 111 women who were randomly assigned to TAC
(n = 39), HVC (n = 39), or LVC (n = 33).
Interestingly, the investigators chose to not attach conventional eponymous labels to their transvaginal methods, and they do not even provide a reference or detailed description of the surgical methods, telling us instead that, “Techniques used were left to the local clinician’s discretion.” Writing also that HVC cases, like the transabdominal surgeries, were carried out in specialty centers, they implied that additional training was required for the HVC. I inferred that indeed they actually were performing the McDonald and Shirodkar transvaginal methods and with possible by-physician, local modifications.
I am certain that the authors’ results did not surprise proponents of transabdominal cerclage for transvaginal cerclage failures, defined in this trial as prior birth from 14 to 28 weeks’ gestation. Since some clinicians use a more generous definition of cerclage failure (such as birth at less than 34 weeks), this study population was clearly at high risk for poor outcomes; in fact, more than 90% of each group had experienced at least 2 prior mid-trimester losses. As anticipated with randomization, other characteristics were well distributed across the 3 groups.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates...
Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates
Using a primary outcome of preterm birth less than 32 weeks, which concentrates neonatal morbidities, the investigators observed an overall 4.5-fold higher rate of preterm birth in the transvaginal cohorts compared with the transabdominal patients (33% and 38% versus 8%, respectively). Comparing the TAC group individually with both LVC and HVC groups, the relative risk of preterm birth was 0.20 compared with the HVC group and 0.23 compared with the LVC group, reflecting an approximate 80% reduction.
Not surprising to me, the investigators observed nearly identical outcomes between the HVC and LVC cohorts, substantiating my bias that the 2 transvaginal methods are similarly effective. Opponents will quickly remind me that the study was not well-powered to detect a clinically significant difference between these 2 groups; touché!
Risks of TAC. We all know that, despite its now-proven benefits, the transabdominal approach is associated with a risk of special complications, including the surgical risks of placement (and removal) of the cerclage, the management of fetal death beyond approximately 14 weeks, and the absolute requisite for hysterotomy/cesarean birth. While serious complications are rare, in the trial by Shennan and colleagues none were recorded in the 39 TAC cases. Nevertheless, for women with no children or only prior early births, the risks seem to be justified; the number needed to treat was less than 4 to prevent 1 birth at less than 32 weeks and was 5.3 to prevent a fetal loss.
TAC is an option for select patients
Given that TAC now can be successfully placed using minimally invasive surgery, either prior to or following conception, this study provides unique level I evidence that should not be discounted and should further be considered in the context of confirming prior cohort studies that suggested a significant benefit. Although specialized training is required and the procedure may involve travel to a specialty center, the weight of clinical data clearly supports the use of TAC.
In summary, based largely on the trial by Shennan and colleagues, women with prior failed vaginal cerclage can and should be counseled regarding the availability of TAC and given the opportunity to weigh the reported risks and benefits. ●
1. Shirodkar VN. A new method of operative treatment for habitual abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy. Antiseptic. 1955;52:299-303.
2. McDonald IA. Suture of the cervix for inevitable miscarriage. J Obstet Gynecol Br Emp. 1957;64:346-350.
3. Shennan A, Chandiramani M, Bennett P, et al. MAVRIC: a multicenter randomized trial of transabdominal vs transvaginal cervical cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:261.e1-261.e9.
Since the 1950s, when Shirodkar (1955) and McDonald (1957) published their seminal works detailing a transvaginal method to suture a “weak” cervix, clinicians and researchers have debated the indications for and utility of cerclage for preventing pregnancy loss and preterm birth.1,2
Originally based on a history of recurrent mid-trimester loss (that is, a clinical diagnosis of cervical insufficiency), cerclage has been expanded to capture both ultrasonography and physical-exam indications. While cerclage has proven useful in select patient populations, an infrequent but vexing problem is what to do when a woman has experienced 1 or more (transvaginal) cerclage “failures.”
With a dearth of well-controlled, randomized data to support the use of cerclage for either history- or physical-exam indications, it is not surprising that we still debate whether the Shirodkar method is superior to the McDonald technique as well as how to best manage a patient when either or both methods previously resulted in an unsatisfactory outcome.
First randomized study to directly compare cerclage techniques
Fortunately, Shennan and colleagues in the United Kingdom have greatly enlarged our knowledge in this area by performing the first well-powered, 3-arm, randomized trial of transabdominal cerclage (TAC) compared with both high and low vaginal cerclage (HVC, LVC).3 They analyzed data for 111 women who were randomly assigned to TAC
(n = 39), HVC (n = 39), or LVC (n = 33).
Interestingly, the investigators chose to not attach conventional eponymous labels to their transvaginal methods, and they do not even provide a reference or detailed description of the surgical methods, telling us instead that, “Techniques used were left to the local clinician’s discretion.” Writing also that HVC cases, like the transabdominal surgeries, were carried out in specialty centers, they implied that additional training was required for the HVC. I inferred that indeed they actually were performing the McDonald and Shirodkar transvaginal methods and with possible by-physician, local modifications.
I am certain that the authors’ results did not surprise proponents of transabdominal cerclage for transvaginal cerclage failures, defined in this trial as prior birth from 14 to 28 weeks’ gestation. Since some clinicians use a more generous definition of cerclage failure (such as birth at less than 34 weeks), this study population was clearly at high risk for poor outcomes; in fact, more than 90% of each group had experienced at least 2 prior mid-trimester losses. As anticipated with randomization, other characteristics were well distributed across the 3 groups.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates...
Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates
Using a primary outcome of preterm birth less than 32 weeks, which concentrates neonatal morbidities, the investigators observed an overall 4.5-fold higher rate of preterm birth in the transvaginal cohorts compared with the transabdominal patients (33% and 38% versus 8%, respectively). Comparing the TAC group individually with both LVC and HVC groups, the relative risk of preterm birth was 0.20 compared with the HVC group and 0.23 compared with the LVC group, reflecting an approximate 80% reduction.
Not surprising to me, the investigators observed nearly identical outcomes between the HVC and LVC cohorts, substantiating my bias that the 2 transvaginal methods are similarly effective. Opponents will quickly remind me that the study was not well-powered to detect a clinically significant difference between these 2 groups; touché!
Risks of TAC. We all know that, despite its now-proven benefits, the transabdominal approach is associated with a risk of special complications, including the surgical risks of placement (and removal) of the cerclage, the management of fetal death beyond approximately 14 weeks, and the absolute requisite for hysterotomy/cesarean birth. While serious complications are rare, in the trial by Shennan and colleagues none were recorded in the 39 TAC cases. Nevertheless, for women with no children or only prior early births, the risks seem to be justified; the number needed to treat was less than 4 to prevent 1 birth at less than 32 weeks and was 5.3 to prevent a fetal loss.
TAC is an option for select patients
Given that TAC now can be successfully placed using minimally invasive surgery, either prior to or following conception, this study provides unique level I evidence that should not be discounted and should further be considered in the context of confirming prior cohort studies that suggested a significant benefit. Although specialized training is required and the procedure may involve travel to a specialty center, the weight of clinical data clearly supports the use of TAC.
In summary, based largely on the trial by Shennan and colleagues, women with prior failed vaginal cerclage can and should be counseled regarding the availability of TAC and given the opportunity to weigh the reported risks and benefits. ●
Since the 1950s, when Shirodkar (1955) and McDonald (1957) published their seminal works detailing a transvaginal method to suture a “weak” cervix, clinicians and researchers have debated the indications for and utility of cerclage for preventing pregnancy loss and preterm birth.1,2
Originally based on a history of recurrent mid-trimester loss (that is, a clinical diagnosis of cervical insufficiency), cerclage has been expanded to capture both ultrasonography and physical-exam indications. While cerclage has proven useful in select patient populations, an infrequent but vexing problem is what to do when a woman has experienced 1 or more (transvaginal) cerclage “failures.”
With a dearth of well-controlled, randomized data to support the use of cerclage for either history- or physical-exam indications, it is not surprising that we still debate whether the Shirodkar method is superior to the McDonald technique as well as how to best manage a patient when either or both methods previously resulted in an unsatisfactory outcome.
First randomized study to directly compare cerclage techniques
Fortunately, Shennan and colleagues in the United Kingdom have greatly enlarged our knowledge in this area by performing the first well-powered, 3-arm, randomized trial of transabdominal cerclage (TAC) compared with both high and low vaginal cerclage (HVC, LVC).3 They analyzed data for 111 women who were randomly assigned to TAC
(n = 39), HVC (n = 39), or LVC (n = 33).
Interestingly, the investigators chose to not attach conventional eponymous labels to their transvaginal methods, and they do not even provide a reference or detailed description of the surgical methods, telling us instead that, “Techniques used were left to the local clinician’s discretion.” Writing also that HVC cases, like the transabdominal surgeries, were carried out in specialty centers, they implied that additional training was required for the HVC. I inferred that indeed they actually were performing the McDonald and Shirodkar transvaginal methods and with possible by-physician, local modifications.
I am certain that the authors’ results did not surprise proponents of transabdominal cerclage for transvaginal cerclage failures, defined in this trial as prior birth from 14 to 28 weeks’ gestation. Since some clinicians use a more generous definition of cerclage failure (such as birth at less than 34 weeks), this study population was clearly at high risk for poor outcomes; in fact, more than 90% of each group had experienced at least 2 prior mid-trimester losses. As anticipated with randomization, other characteristics were well distributed across the 3 groups.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates...
Transabdominal cerclage significantly reduced preterm birth rates
Using a primary outcome of preterm birth less than 32 weeks, which concentrates neonatal morbidities, the investigators observed an overall 4.5-fold higher rate of preterm birth in the transvaginal cohorts compared with the transabdominal patients (33% and 38% versus 8%, respectively). Comparing the TAC group individually with both LVC and HVC groups, the relative risk of preterm birth was 0.20 compared with the HVC group and 0.23 compared with the LVC group, reflecting an approximate 80% reduction.
Not surprising to me, the investigators observed nearly identical outcomes between the HVC and LVC cohorts, substantiating my bias that the 2 transvaginal methods are similarly effective. Opponents will quickly remind me that the study was not well-powered to detect a clinically significant difference between these 2 groups; touché!
Risks of TAC. We all know that, despite its now-proven benefits, the transabdominal approach is associated with a risk of special complications, including the surgical risks of placement (and removal) of the cerclage, the management of fetal death beyond approximately 14 weeks, and the absolute requisite for hysterotomy/cesarean birth. While serious complications are rare, in the trial by Shennan and colleagues none were recorded in the 39 TAC cases. Nevertheless, for women with no children or only prior early births, the risks seem to be justified; the number needed to treat was less than 4 to prevent 1 birth at less than 32 weeks and was 5.3 to prevent a fetal loss.
TAC is an option for select patients
Given that TAC now can be successfully placed using minimally invasive surgery, either prior to or following conception, this study provides unique level I evidence that should not be discounted and should further be considered in the context of confirming prior cohort studies that suggested a significant benefit. Although specialized training is required and the procedure may involve travel to a specialty center, the weight of clinical data clearly supports the use of TAC.
In summary, based largely on the trial by Shennan and colleagues, women with prior failed vaginal cerclage can and should be counseled regarding the availability of TAC and given the opportunity to weigh the reported risks and benefits. ●
1. Shirodkar VN. A new method of operative treatment for habitual abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy. Antiseptic. 1955;52:299-303.
2. McDonald IA. Suture of the cervix for inevitable miscarriage. J Obstet Gynecol Br Emp. 1957;64:346-350.
3. Shennan A, Chandiramani M, Bennett P, et al. MAVRIC: a multicenter randomized trial of transabdominal vs transvaginal cervical cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:261.e1-261.e9.
1. Shirodkar VN. A new method of operative treatment for habitual abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy. Antiseptic. 1955;52:299-303.
2. McDonald IA. Suture of the cervix for inevitable miscarriage. J Obstet Gynecol Br Emp. 1957;64:346-350.
3. Shennan A, Chandiramani M, Bennett P, et al. MAVRIC: a multicenter randomized trial of transabdominal vs transvaginal cervical cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222:261.e1-261.e9.
Transabdominal cerclage for managing recurrent pregnancy loss
CASE A woman with recurrent pregnancy loss
A 38-year-old woman (G4P0221) presents to your office for preconception counseling. Her history is significant for the following: a spontaneous pregnancy loss at 15 weeks’ gestation; a pregnancy loss at 17 weeks secondary to preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM); a cesarean delivery at 30 weeks and 6 days’ gestation after placement of a transvaginal cerclage at 20 weeks for cervical dilation noted on physical exam (the child now has developmental delays); and most recently a delivery at 24 weeks and 4 days due to preterm labor with subsequent neonatal demise (this followed a transvaginal cerclage placed at 13 weeks and 6 days).
How would you counsel this patient?
Cervical insufficiency describes the inability of the cervix to retain a pregnancy in the absence of the signs and symptoms of clinical contractions, labor, or both in the second trimester.1 This condition affects an estimated 1% of obstetric patients and 8% of women with recurrent losses who have experienced a second-trimester loss.2
Diagnosis of cervical insufficiency is based on a history of painless cervical dilation after the first trimester with expulsion of the pregnancy in the second trimester before 24 weeks of gestation without contractions and in the absence of other pathology, such as bleeding, infection, or ruptured membranes.1 Diagnosis also can be made by noting cervical dilation on physical exam during the second trimester; more recently, short cervical length on transvaginal ultrasonography in the second trimester has been used to try to predict when a cervical cerclage may be indicated, although sonographic cervical length is more a marker for risk of preterm birth than for cervical insufficiency specifically.1,3
Given the considerable emotional and physical distress that patients experience with recurrent second-trimester losses and the significant neonatal morbidity and mortality that can occur with preterm delivery, substantial efforts are made to prevent these outcomes by treating patients with cervical insufficiency and those at risk for preterm delivery.
Transvaginal cerclage: A treatment mainstay
Standard treatment options for cervical insufficiency depend on the patient’s history. One of the treatment mainstays for women with prior second-trimester losses or preterm deliveries is transvaginal cervical cerclage. A transvaginal cerclage can be placed using either a Shirodkar technique, in which the vesicocervical mucosa is dissected and a suture is placed as close to the internal cervical os as possible, or a McDonald technique, in which a purse-string suture is placed around the cervicovaginal junction. No randomized trials have compared the effectiveness of these 2 methods, but most observational studies show no difference, and one suggests that the Shirodkar technique may be more effective in obese women specifically.4-6
Indications for transvaginal cerclage. The indication for transvaginal cerclage is based on history, physical exam, or ultrasonography.
A physical-exam indication is the most straightforward of the 3. Transvaginal cerclage placement is indicated if on physical exam in the second trimester a patient has cervical dilation without contractions or infection.1,7
A history-indicated cerclage (typically placed between 12 and 14 weeks’ gestation) is based on a cerclage having been placed in a prior pregnancy due to painless cervical dilation in the second trimester (either ultrasonography- or physical-exam indicated), and it also can be considered in the case of a history of 1 or more second-trimester pregnancy losses related to painless cervical dilation.1
More recent evidence suggests that in patients with 1 prior second-trimester loss or preterm delivery, serial sonographic cervical length can be measured safely from 16 to 24 weeks, with a cerclage being placed only if cervical length decreases to less than 25 mm. By using the ultrasonography-based indication, unnecessary history-indicated cerclages for 1 prior second-trimester or preterm birth can be avoided in more than one-half of patients (FIGURE 1).1,7
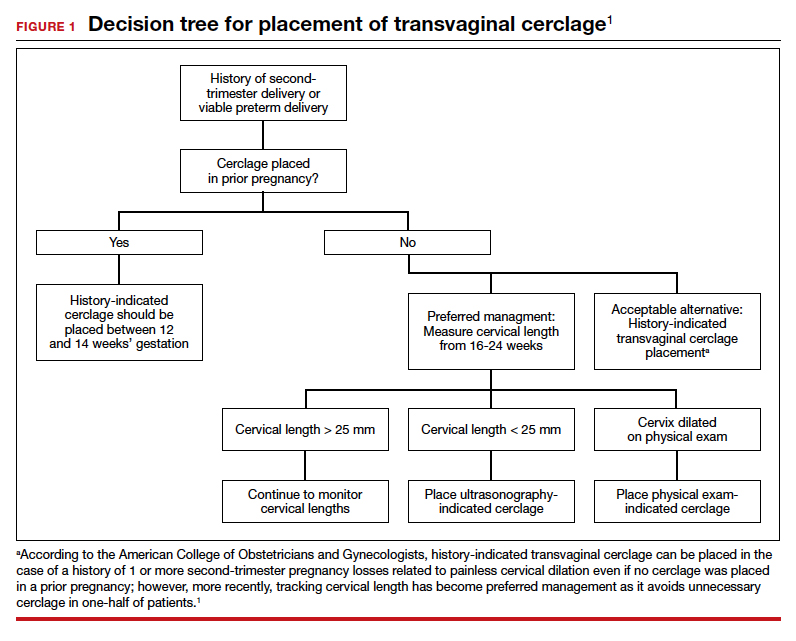
Efficacy. The effectiveness of transvaginal cerclage varies by the indication. Authors of a 2017 Cochrane review found an overall reduced risk of giving birth before 34 weeks’ gestation for any indication, with an average relative risk of 0.77.2 Other recent studies showed the following8-10:
- a 63% delivery rate after 28 weeks’ gestation for physical-exam indicated cerclages in the presence of bulging amniotic membranes
- an 86.2% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for ultrasonography-indicated cerclages
- an 86% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for a history-indicated cerclage in patients with 2 or more prior second-trimester losses.
Success rates, especially for ultrasonography- and history-indicated cerclage, are thus high. For the 14% who still fail these methods, however, a different management strategy is needed, which is where transabdominal cerclage comes into play.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients...
Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients
In transabdominal cerclage, an abdominal approach is used to place a stitch at the cervicouterine junction. With this approach, the cerclage can reach a closer proximity to the internal os compared with the vaginal approach, providing better support of the cervical tissue (FIGURE 2).11 Whether performed via laparotomy or laparoscopy, the transabdominal cerclage procedure likely carries higher morbidity than a transvaginal approach, and cesarean delivery is required after placement.

Since transvaginal cerclage often is successful, in most cases the transabdominal approach should not be viewed as the first-line treatment for cervical insufficiency if a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage has not been attempted. For women who fail a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage, however, a transabdominal cerclage has been proven to decrease the rate of preterm delivery and PPROM compared with attempting another history-indicated transvaginal cerclage.11,12
A recent systematic review of pregnancy outcomes after transabdominal cerclage placement reported neonatal survival of 96.5% and an 83% delivery rate after 34 weeks’ gestation.13 Thus, even among a population that failed transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage has a high success rate in providing a good pregnancy outcome (TABLE). Transabdominal cerclage also can be considered as first-line treatment in patients who had prior cervical surgery or cervical deformities that might preclude the ability to place a cerclage transvaginally.

CASE Continued: A candidate for transabdominal cerclage
Given the patient’s poor obstetric history, which includes a preterm delivery and neonatal loss despite a history-indicated cerclage, you recommend that the patient have a transabdominal cerclage placed as the procedure has been proven to increase the chances of neonatal survival and delivery after 34 weeks in women with a similar obstetric history. The patient is interested in this option and asks about how this cerclage is placed and when it would need to be placed during her next pregnancy.
Surgical technique for transabdominal cerclage placement
A transabdominal cerclage can be placed via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or robot-assisted laparoscopy. No differences in obstetric outcomes have been shown between the laparotomy and laparoscopic approaches.14,15 Given the benefits of minimally invasive surgery, a laparoscopic or robot-assisted approach is preferred when feasible.
Additionally, for ease of placement, transabdominal cerclage can be placed prior to conception—known as interval placement—or during pregnancy between 10 and 14 weeks (preferably closer to 10 weeks). Because of the increased difficulty in placing a cerclage in the gravid uterus, interval transabdominal cerclage placement is recommended when possible.13,16 Authors of one observational study noted that improved obstetric outcomes occurred with interval placement compared with cerclage placement between 9 and 10 weeks’ gestation, with a delivery rate at more than 34 weeks’ gestation in 90% versus 74% of patients, respectively.16
Continue to: Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy...
Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy
Our practice is to place transabdominal cerclage via conventional laparoscopy as an interval procedure when possible. We find no benefit in using robotic assistance.
For an interval procedure, the patient is placed in a dorsal lithotomy position, and we place a 10-mm umbilical port, 2 lateral 5-mm ports, 1 suprapubic 5-mm port, and a uterine manipulator. We use a flexible laparoscope to provide optimal visualization of the pelvis from any angle.
The first step of the surgery involves dissecting the vesicouterine peritoneum in order to move the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 3A). Uterine arteries are then identified lateral to the cervix as part of this dissection, and a window is created in the inferior aspect of the broad ligament just anterior and lateral to the insertion of the uterosacral ligaments onto the uterus, with care taken to avoid the uterine vessels superiorly (FIGURE 3B). Two 5-mm Mersilene tape sutures are then tied together to create 1 suture with a needle at each end. This is then passed into the abdomen, and 1 needle is passed through the parametrial space at the level of the internal os inferior to the uterine vessels on 1 side of the uterus while the other needle is passed through the parametrial space on the opposite side.
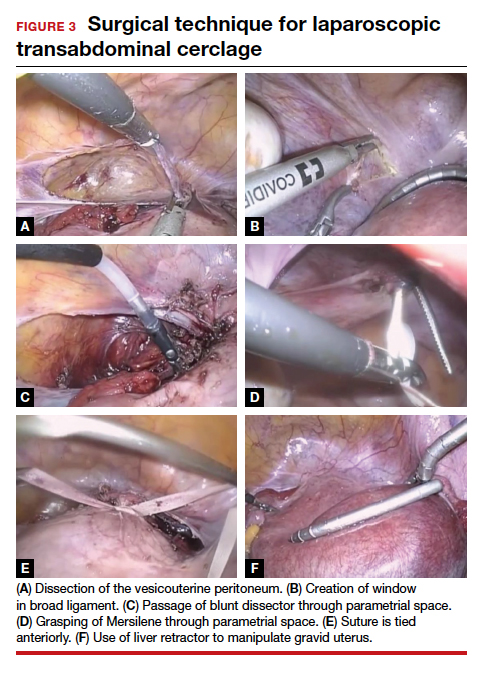
Alternatively, rather than using the suture needles, a blunt dissector can be passed through this same space bilaterally (FIGURE 3C) via the suprapubic port and can pull the Mersilene tape through the parametrial space (FIGURE 3D). The suture is then tied anterior at the level of the internal os intracorporally (FIGURE 3E), and the needles are cut off the suture and removed from the abdomen.
To perform transabdominal cerclage when the patient is pregnant, a few modifications are needed to help with placement. First, the patient may be placed in supine position since a uterine manipulator cannot be used. Second, use of a flexible laparoscope becomes even more imperative in order to properly see around the gravid uterus. Lastly, a 5-mm laparoscopic liver retractor can be used to aid in blunt manipulation of the gravid uterus (FIGURE 3F). (The surgical video below highlights the steps to transabdominal cerclage placement in a pregnant patient.) All other port placements and steps to dissection and suture placement are the same as in interval placement.

CASE Continued: Patient pursues transabdominal cerclage
You explain to your patient that ideally the cerclage should be placed now in a laparoscopic fashion before she becomes pregnant. You then refer her to a local gynecologic surgeon who places many laparoscopic transabdominal cerclages. She undergoes the procedure, becomes pregnant, and after presenting in labor at 35 weeks’ gestation has a cesarean delivery. Her baby is born without any neonatal complications, and the patient is overjoyed with the outcome.
Management during and after pregnancy
Pregnant patients with a transabdominal cerclage are precluded from having a vaginal delivery and must deliver via cesarean. During the antepartum period, patients are managed in the same manner as those who have a transvaginal cerclage. Delivery via cesarean at the onset of regular contractions is recommended to reduce the risk of uterine rupture. In the absence of labor, scheduled cesarean is performed at term.
Our practice is to schedule cesarean delivery at 38 weeks’ gestation, although there are no data or consensus to support a specific gestational age between 37 and 39 weeks. Unlike a transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage can be left in place for use in subsequent pregnancies. Data are limited on whether the transabdominal cerclage should be removed in women who no longer desire childbearing and whether there are long-term sequelae if the suture is left in situ.17
Continue to: Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage...
Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage
As the data suggest and our experience confirms, transabdominal cerclage is highly successful in patients who have failed a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage; however, the transabdominal approach carries a higher surgical risk. Risks include intraoperative hemorrhage, conversion to laparotomy, and a range of rare surgical and obstetric complications, such as bladder injury and PPROM.13,18
If a patient experiences a fetal loss in the first trimester, a dilation and curettage (D&C) can be performed, with good obstetric outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.19 If the patient experiences an early-to-mid second-trimester loss, some studies suggest that a dilation and evacuation (D&E) of the uterus can be done with sufficient dilation of the cervix to accommodate up to a 15-mm cannula and Sopher forceps.19 Laminaria also may be used in this process. However, no data exist regarding success of future pregnancies and transabdominal cerclage integrity after a D&E.20 If the cerclage prevents successful dilation of the cervix, the cerclage must be removed laparoscopically prior to performing the D&E.
In late second-trimester and third-trimester loss, the cerclage must be removed to allow passage of the fetus and placenta prior to a D&E or an induction of labor.20
For patients with PPROM or preterm labor, data are limited regarding management recommendations. However, in these complex cases, we strongly recommend an individualized approach and co-management with maternal-fetal medicine specialists.
CASE Resolved
The cerclage is left in place during the patient’s cesarean delivery, and her postpartum course is uneventful. She continued without complications for the next year, at which time she sees you in the office with plans to have another pregnancy later in the year. You counsel her that her abdominal cerclage will still be effective and that she can get pregnant with expectations of similar outcomes as her previous pregnancy. She thanks you for everything and reports that she hopes to return later in the year for her first prenatal visit. ●
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 142: Cerclage for the management of cervical insufficiency. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 1): 372-379.
- Alfirevic Z, Stampalija T, Medley N. Cervical stitch (cerclage) for preventing preterm birth in singleton pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):CD008991.
- Brown R, Gagnon R, Delisle M-F. No. 373—cervical insufficiency and cervical cerclage. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2019;41:233-247.
- Odibo AO, Berghella V, To MS, et al. Shirodkar versus McDonald cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth in women with short cervical length. Am J Perinatol. 2007;24: 55-60.
- Basbug A, Bayrak M, Dogan O, et al. McDonald versus modified Shirodkar rescue cerclage in women with prolapsed fetal membranes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33: 1075-1097.
- Figueroa R, Crowell R, Martinez A, et al. McDonald versus Shirodkar cervical cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth: impact of body mass index. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:3408-3414.
- Suhag A, Berghella V. Cervical cerclage. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;57:557-567.
- Bayrak M, Gul A, Goynumer G. Rescue cerclage when foetal membranes prolapse into the vagina. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:471-475.
- Drassinower D, Coviello E, Landy HJ, et al. Outcomes after periviable ultrasound-indicated cerclage. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:932-938.
- Lee KN, Whang EJ, Chang KH, et al. History-indicated cerclage: the association between previous preterm history and cerclage outcome. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018;61:23-29. doi:10.5468/ogs.2018.61.1.23.
- Sneider K, Christiansen OB, Sundtoft IB, et al. Recurrence rates after abdominal and vaginal cerclages in women with cervical insufficiency: a validated cohort study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:859-866.
- Davis G, Berghella V, Talucci M, et al. Patients with a prior failed transvaginal cerclage: a comparison of obstetric outcomes with either transabdominal or transvaginal cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:836-839.
- Moawad GN, Tyan P, Bracke T, et al. Systematic review of transabdominal cerclage placed via laparoscopy for the prevention of preterm birth. J Mimim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:277-286.
- Burger NB, Brölmann HAM, Einarsson JI, et al. Effectiveness of abdominal cerclage placed via laparotomy or laparoscopy: systematic review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:696-704.
- Kim S, Hill A, Menderes G, et al. Minimally invasive abdominal cerclage compared to laparotomy: a comparison of surgical and obstetric outcomes. J Robot Surg. 2018;12:295-301.
- Dawood F, Farquharson RG. Transabdominal cerclage: preconceptual versus first trimester insertion. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:27-31.
- Hawkins E, Nimaroff M. Vaginal erosion of an abdominal cerclage 7 years after laparoscopic placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 2 suppl 2):420-423.
- Foster TL, Moore ES, Sumners JE. Operative complications and fetal morbidity encountered in 300 prophylactic transabdominal cervical cerclage procedures by one obstetric surgeon. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:713-717.
- Dethier D, Lassey SC, Pilliod R, et al. Uterine evacuation in the setting of transabdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2020;101:174-177.
- Martin A, Lathrop E. Controversies in family planning: management of second-trimester losses in the setting of an abdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2013;87:728-731.
CASE A woman with recurrent pregnancy loss
A 38-year-old woman (G4P0221) presents to your office for preconception counseling. Her history is significant for the following: a spontaneous pregnancy loss at 15 weeks’ gestation; a pregnancy loss at 17 weeks secondary to preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM); a cesarean delivery at 30 weeks and 6 days’ gestation after placement of a transvaginal cerclage at 20 weeks for cervical dilation noted on physical exam (the child now has developmental delays); and most recently a delivery at 24 weeks and 4 days due to preterm labor with subsequent neonatal demise (this followed a transvaginal cerclage placed at 13 weeks and 6 days).
How would you counsel this patient?
Cervical insufficiency describes the inability of the cervix to retain a pregnancy in the absence of the signs and symptoms of clinical contractions, labor, or both in the second trimester.1 This condition affects an estimated 1% of obstetric patients and 8% of women with recurrent losses who have experienced a second-trimester loss.2
Diagnosis of cervical insufficiency is based on a history of painless cervical dilation after the first trimester with expulsion of the pregnancy in the second trimester before 24 weeks of gestation without contractions and in the absence of other pathology, such as bleeding, infection, or ruptured membranes.1 Diagnosis also can be made by noting cervical dilation on physical exam during the second trimester; more recently, short cervical length on transvaginal ultrasonography in the second trimester has been used to try to predict when a cervical cerclage may be indicated, although sonographic cervical length is more a marker for risk of preterm birth than for cervical insufficiency specifically.1,3
Given the considerable emotional and physical distress that patients experience with recurrent second-trimester losses and the significant neonatal morbidity and mortality that can occur with preterm delivery, substantial efforts are made to prevent these outcomes by treating patients with cervical insufficiency and those at risk for preterm delivery.
Transvaginal cerclage: A treatment mainstay
Standard treatment options for cervical insufficiency depend on the patient’s history. One of the treatment mainstays for women with prior second-trimester losses or preterm deliveries is transvaginal cervical cerclage. A transvaginal cerclage can be placed using either a Shirodkar technique, in which the vesicocervical mucosa is dissected and a suture is placed as close to the internal cervical os as possible, or a McDonald technique, in which a purse-string suture is placed around the cervicovaginal junction. No randomized trials have compared the effectiveness of these 2 methods, but most observational studies show no difference, and one suggests that the Shirodkar technique may be more effective in obese women specifically.4-6
Indications for transvaginal cerclage. The indication for transvaginal cerclage is based on history, physical exam, or ultrasonography.
A physical-exam indication is the most straightforward of the 3. Transvaginal cerclage placement is indicated if on physical exam in the second trimester a patient has cervical dilation without contractions or infection.1,7
A history-indicated cerclage (typically placed between 12 and 14 weeks’ gestation) is based on a cerclage having been placed in a prior pregnancy due to painless cervical dilation in the second trimester (either ultrasonography- or physical-exam indicated), and it also can be considered in the case of a history of 1 or more second-trimester pregnancy losses related to painless cervical dilation.1
More recent evidence suggests that in patients with 1 prior second-trimester loss or preterm delivery, serial sonographic cervical length can be measured safely from 16 to 24 weeks, with a cerclage being placed only if cervical length decreases to less than 25 mm. By using the ultrasonography-based indication, unnecessary history-indicated cerclages for 1 prior second-trimester or preterm birth can be avoided in more than one-half of patients (FIGURE 1).1,7

Efficacy. The effectiveness of transvaginal cerclage varies by the indication. Authors of a 2017 Cochrane review found an overall reduced risk of giving birth before 34 weeks’ gestation for any indication, with an average relative risk of 0.77.2 Other recent studies showed the following8-10:
- a 63% delivery rate after 28 weeks’ gestation for physical-exam indicated cerclages in the presence of bulging amniotic membranes
- an 86.2% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for ultrasonography-indicated cerclages
- an 86% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for a history-indicated cerclage in patients with 2 or more prior second-trimester losses.
Success rates, especially for ultrasonography- and history-indicated cerclage, are thus high. For the 14% who still fail these methods, however, a different management strategy is needed, which is where transabdominal cerclage comes into play.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients...
Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients
In transabdominal cerclage, an abdominal approach is used to place a stitch at the cervicouterine junction. With this approach, the cerclage can reach a closer proximity to the internal os compared with the vaginal approach, providing better support of the cervical tissue (FIGURE 2).11 Whether performed via laparotomy or laparoscopy, the transabdominal cerclage procedure likely carries higher morbidity than a transvaginal approach, and cesarean delivery is required after placement.

Since transvaginal cerclage often is successful, in most cases the transabdominal approach should not be viewed as the first-line treatment for cervical insufficiency if a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage has not been attempted. For women who fail a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage, however, a transabdominal cerclage has been proven to decrease the rate of preterm delivery and PPROM compared with attempting another history-indicated transvaginal cerclage.11,12
A recent systematic review of pregnancy outcomes after transabdominal cerclage placement reported neonatal survival of 96.5% and an 83% delivery rate after 34 weeks’ gestation.13 Thus, even among a population that failed transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage has a high success rate in providing a good pregnancy outcome (TABLE). Transabdominal cerclage also can be considered as first-line treatment in patients who had prior cervical surgery or cervical deformities that might preclude the ability to place a cerclage transvaginally.

CASE Continued: A candidate for transabdominal cerclage
Given the patient’s poor obstetric history, which includes a preterm delivery and neonatal loss despite a history-indicated cerclage, you recommend that the patient have a transabdominal cerclage placed as the procedure has been proven to increase the chances of neonatal survival and delivery after 34 weeks in women with a similar obstetric history. The patient is interested in this option and asks about how this cerclage is placed and when it would need to be placed during her next pregnancy.
Surgical technique for transabdominal cerclage placement
A transabdominal cerclage can be placed via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or robot-assisted laparoscopy. No differences in obstetric outcomes have been shown between the laparotomy and laparoscopic approaches.14,15 Given the benefits of minimally invasive surgery, a laparoscopic or robot-assisted approach is preferred when feasible.
Additionally, for ease of placement, transabdominal cerclage can be placed prior to conception—known as interval placement—or during pregnancy between 10 and 14 weeks (preferably closer to 10 weeks). Because of the increased difficulty in placing a cerclage in the gravid uterus, interval transabdominal cerclage placement is recommended when possible.13,16 Authors of one observational study noted that improved obstetric outcomes occurred with interval placement compared with cerclage placement between 9 and 10 weeks’ gestation, with a delivery rate at more than 34 weeks’ gestation in 90% versus 74% of patients, respectively.16
Continue to: Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy...
Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy
Our practice is to place transabdominal cerclage via conventional laparoscopy as an interval procedure when possible. We find no benefit in using robotic assistance.
For an interval procedure, the patient is placed in a dorsal lithotomy position, and we place a 10-mm umbilical port, 2 lateral 5-mm ports, 1 suprapubic 5-mm port, and a uterine manipulator. We use a flexible laparoscope to provide optimal visualization of the pelvis from any angle.
The first step of the surgery involves dissecting the vesicouterine peritoneum in order to move the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 3A). Uterine arteries are then identified lateral to the cervix as part of this dissection, and a window is created in the inferior aspect of the broad ligament just anterior and lateral to the insertion of the uterosacral ligaments onto the uterus, with care taken to avoid the uterine vessels superiorly (FIGURE 3B). Two 5-mm Mersilene tape sutures are then tied together to create 1 suture with a needle at each end. This is then passed into the abdomen, and 1 needle is passed through the parametrial space at the level of the internal os inferior to the uterine vessels on 1 side of the uterus while the other needle is passed through the parametrial space on the opposite side.

Alternatively, rather than using the suture needles, a blunt dissector can be passed through this same space bilaterally (FIGURE 3C) via the suprapubic port and can pull the Mersilene tape through the parametrial space (FIGURE 3D). The suture is then tied anterior at the level of the internal os intracorporally (FIGURE 3E), and the needles are cut off the suture and removed from the abdomen.
To perform transabdominal cerclage when the patient is pregnant, a few modifications are needed to help with placement. First, the patient may be placed in supine position since a uterine manipulator cannot be used. Second, use of a flexible laparoscope becomes even more imperative in order to properly see around the gravid uterus. Lastly, a 5-mm laparoscopic liver retractor can be used to aid in blunt manipulation of the gravid uterus (FIGURE 3F). (The surgical video below highlights the steps to transabdominal cerclage placement in a pregnant patient.) All other port placements and steps to dissection and suture placement are the same as in interval placement.

CASE Continued: Patient pursues transabdominal cerclage
You explain to your patient that ideally the cerclage should be placed now in a laparoscopic fashion before she becomes pregnant. You then refer her to a local gynecologic surgeon who places many laparoscopic transabdominal cerclages. She undergoes the procedure, becomes pregnant, and after presenting in labor at 35 weeks’ gestation has a cesarean delivery. Her baby is born without any neonatal complications, and the patient is overjoyed with the outcome.
Management during and after pregnancy
Pregnant patients with a transabdominal cerclage are precluded from having a vaginal delivery and must deliver via cesarean. During the antepartum period, patients are managed in the same manner as those who have a transvaginal cerclage. Delivery via cesarean at the onset of regular contractions is recommended to reduce the risk of uterine rupture. In the absence of labor, scheduled cesarean is performed at term.
Our practice is to schedule cesarean delivery at 38 weeks’ gestation, although there are no data or consensus to support a specific gestational age between 37 and 39 weeks. Unlike a transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage can be left in place for use in subsequent pregnancies. Data are limited on whether the transabdominal cerclage should be removed in women who no longer desire childbearing and whether there are long-term sequelae if the suture is left in situ.17
Continue to: Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage...
Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage
As the data suggest and our experience confirms, transabdominal cerclage is highly successful in patients who have failed a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage; however, the transabdominal approach carries a higher surgical risk. Risks include intraoperative hemorrhage, conversion to laparotomy, and a range of rare surgical and obstetric complications, such as bladder injury and PPROM.13,18
If a patient experiences a fetal loss in the first trimester, a dilation and curettage (D&C) can be performed, with good obstetric outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.19 If the patient experiences an early-to-mid second-trimester loss, some studies suggest that a dilation and evacuation (D&E) of the uterus can be done with sufficient dilation of the cervix to accommodate up to a 15-mm cannula and Sopher forceps.19 Laminaria also may be used in this process. However, no data exist regarding success of future pregnancies and transabdominal cerclage integrity after a D&E.20 If the cerclage prevents successful dilation of the cervix, the cerclage must be removed laparoscopically prior to performing the D&E.
In late second-trimester and third-trimester loss, the cerclage must be removed to allow passage of the fetus and placenta prior to a D&E or an induction of labor.20
For patients with PPROM or preterm labor, data are limited regarding management recommendations. However, in these complex cases, we strongly recommend an individualized approach and co-management with maternal-fetal medicine specialists.
CASE Resolved
The cerclage is left in place during the patient’s cesarean delivery, and her postpartum course is uneventful. She continued without complications for the next year, at which time she sees you in the office with plans to have another pregnancy later in the year. You counsel her that her abdominal cerclage will still be effective and that she can get pregnant with expectations of similar outcomes as her previous pregnancy. She thanks you for everything and reports that she hopes to return later in the year for her first prenatal visit. ●
CASE A woman with recurrent pregnancy loss
A 38-year-old woman (G4P0221) presents to your office for preconception counseling. Her history is significant for the following: a spontaneous pregnancy loss at 15 weeks’ gestation; a pregnancy loss at 17 weeks secondary to preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM); a cesarean delivery at 30 weeks and 6 days’ gestation after placement of a transvaginal cerclage at 20 weeks for cervical dilation noted on physical exam (the child now has developmental delays); and most recently a delivery at 24 weeks and 4 days due to preterm labor with subsequent neonatal demise (this followed a transvaginal cerclage placed at 13 weeks and 6 days).
How would you counsel this patient?
Cervical insufficiency describes the inability of the cervix to retain a pregnancy in the absence of the signs and symptoms of clinical contractions, labor, or both in the second trimester.1 This condition affects an estimated 1% of obstetric patients and 8% of women with recurrent losses who have experienced a second-trimester loss.2
Diagnosis of cervical insufficiency is based on a history of painless cervical dilation after the first trimester with expulsion of the pregnancy in the second trimester before 24 weeks of gestation without contractions and in the absence of other pathology, such as bleeding, infection, or ruptured membranes.1 Diagnosis also can be made by noting cervical dilation on physical exam during the second trimester; more recently, short cervical length on transvaginal ultrasonography in the second trimester has been used to try to predict when a cervical cerclage may be indicated, although sonographic cervical length is more a marker for risk of preterm birth than for cervical insufficiency specifically.1,3
Given the considerable emotional and physical distress that patients experience with recurrent second-trimester losses and the significant neonatal morbidity and mortality that can occur with preterm delivery, substantial efforts are made to prevent these outcomes by treating patients with cervical insufficiency and those at risk for preterm delivery.
Transvaginal cerclage: A treatment mainstay
Standard treatment options for cervical insufficiency depend on the patient’s history. One of the treatment mainstays for women with prior second-trimester losses or preterm deliveries is transvaginal cervical cerclage. A transvaginal cerclage can be placed using either a Shirodkar technique, in which the vesicocervical mucosa is dissected and a suture is placed as close to the internal cervical os as possible, or a McDonald technique, in which a purse-string suture is placed around the cervicovaginal junction. No randomized trials have compared the effectiveness of these 2 methods, but most observational studies show no difference, and one suggests that the Shirodkar technique may be more effective in obese women specifically.4-6
Indications for transvaginal cerclage. The indication for transvaginal cerclage is based on history, physical exam, or ultrasonography.
A physical-exam indication is the most straightforward of the 3. Transvaginal cerclage placement is indicated if on physical exam in the second trimester a patient has cervical dilation without contractions or infection.1,7
A history-indicated cerclage (typically placed between 12 and 14 weeks’ gestation) is based on a cerclage having been placed in a prior pregnancy due to painless cervical dilation in the second trimester (either ultrasonography- or physical-exam indicated), and it also can be considered in the case of a history of 1 or more second-trimester pregnancy losses related to painless cervical dilation.1
More recent evidence suggests that in patients with 1 prior second-trimester loss or preterm delivery, serial sonographic cervical length can be measured safely from 16 to 24 weeks, with a cerclage being placed only if cervical length decreases to less than 25 mm. By using the ultrasonography-based indication, unnecessary history-indicated cerclages for 1 prior second-trimester or preterm birth can be avoided in more than one-half of patients (FIGURE 1).1,7

Efficacy. The effectiveness of transvaginal cerclage varies by the indication. Authors of a 2017 Cochrane review found an overall reduced risk of giving birth before 34 weeks’ gestation for any indication, with an average relative risk of 0.77.2 Other recent studies showed the following8-10:
- a 63% delivery rate after 28 weeks’ gestation for physical-exam indicated cerclages in the presence of bulging amniotic membranes
- an 86.2% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for ultrasonography-indicated cerclages
- an 86% delivery rate after 32 weeks’ gestation for a history-indicated cerclage in patients with 2 or more prior second-trimester losses.
Success rates, especially for ultrasonography- and history-indicated cerclage, are thus high. For the 14% who still fail these methods, however, a different management strategy is needed, which is where transabdominal cerclage comes into play.
Continue to: Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients...
Transabdominal cerclage is an option for certain patients
In transabdominal cerclage, an abdominal approach is used to place a stitch at the cervicouterine junction. With this approach, the cerclage can reach a closer proximity to the internal os compared with the vaginal approach, providing better support of the cervical tissue (FIGURE 2).11 Whether performed via laparotomy or laparoscopy, the transabdominal cerclage procedure likely carries higher morbidity than a transvaginal approach, and cesarean delivery is required after placement.

Since transvaginal cerclage often is successful, in most cases the transabdominal approach should not be viewed as the first-line treatment for cervical insufficiency if a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage has not been attempted. For women who fail a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage, however, a transabdominal cerclage has been proven to decrease the rate of preterm delivery and PPROM compared with attempting another history-indicated transvaginal cerclage.11,12
A recent systematic review of pregnancy outcomes after transabdominal cerclage placement reported neonatal survival of 96.5% and an 83% delivery rate after 34 weeks’ gestation.13 Thus, even among a population that failed transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage has a high success rate in providing a good pregnancy outcome (TABLE). Transabdominal cerclage also can be considered as first-line treatment in patients who had prior cervical surgery or cervical deformities that might preclude the ability to place a cerclage transvaginally.

CASE Continued: A candidate for transabdominal cerclage
Given the patient’s poor obstetric history, which includes a preterm delivery and neonatal loss despite a history-indicated cerclage, you recommend that the patient have a transabdominal cerclage placed as the procedure has been proven to increase the chances of neonatal survival and delivery after 34 weeks in women with a similar obstetric history. The patient is interested in this option and asks about how this cerclage is placed and when it would need to be placed during her next pregnancy.
Surgical technique for transabdominal cerclage placement
A transabdominal cerclage can be placed via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or robot-assisted laparoscopy. No differences in obstetric outcomes have been shown between the laparotomy and laparoscopic approaches.14,15 Given the benefits of minimally invasive surgery, a laparoscopic or robot-assisted approach is preferred when feasible.
Additionally, for ease of placement, transabdominal cerclage can be placed prior to conception—known as interval placement—or during pregnancy between 10 and 14 weeks (preferably closer to 10 weeks). Because of the increased difficulty in placing a cerclage in the gravid uterus, interval transabdominal cerclage placement is recommended when possible.13,16 Authors of one observational study noted that improved obstetric outcomes occurred with interval placement compared with cerclage placement between 9 and 10 weeks’ gestation, with a delivery rate at more than 34 weeks’ gestation in 90% versus 74% of patients, respectively.16
Continue to: Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy...
Steps for interval cerclage and during pregnancy
Our practice is to place transabdominal cerclage via conventional laparoscopy as an interval procedure when possible. We find no benefit in using robotic assistance.
For an interval procedure, the patient is placed in a dorsal lithotomy position, and we place a 10-mm umbilical port, 2 lateral 5-mm ports, 1 suprapubic 5-mm port, and a uterine manipulator. We use a flexible laparoscope to provide optimal visualization of the pelvis from any angle.
The first step of the surgery involves dissecting the vesicouterine peritoneum in order to move the bladder inferiorly (FIGURE 3A). Uterine arteries are then identified lateral to the cervix as part of this dissection, and a window is created in the inferior aspect of the broad ligament just anterior and lateral to the insertion of the uterosacral ligaments onto the uterus, with care taken to avoid the uterine vessels superiorly (FIGURE 3B). Two 5-mm Mersilene tape sutures are then tied together to create 1 suture with a needle at each end. This is then passed into the abdomen, and 1 needle is passed through the parametrial space at the level of the internal os inferior to the uterine vessels on 1 side of the uterus while the other needle is passed through the parametrial space on the opposite side.

Alternatively, rather than using the suture needles, a blunt dissector can be passed through this same space bilaterally (FIGURE 3C) via the suprapubic port and can pull the Mersilene tape through the parametrial space (FIGURE 3D). The suture is then tied anterior at the level of the internal os intracorporally (FIGURE 3E), and the needles are cut off the suture and removed from the abdomen.
To perform transabdominal cerclage when the patient is pregnant, a few modifications are needed to help with placement. First, the patient may be placed in supine position since a uterine manipulator cannot be used. Second, use of a flexible laparoscope becomes even more imperative in order to properly see around the gravid uterus. Lastly, a 5-mm laparoscopic liver retractor can be used to aid in blunt manipulation of the gravid uterus (FIGURE 3F). (The surgical video below highlights the steps to transabdominal cerclage placement in a pregnant patient.) All other port placements and steps to dissection and suture placement are the same as in interval placement.

CASE Continued: Patient pursues transabdominal cerclage
You explain to your patient that ideally the cerclage should be placed now in a laparoscopic fashion before she becomes pregnant. You then refer her to a local gynecologic surgeon who places many laparoscopic transabdominal cerclages. She undergoes the procedure, becomes pregnant, and after presenting in labor at 35 weeks’ gestation has a cesarean delivery. Her baby is born without any neonatal complications, and the patient is overjoyed with the outcome.
Management during and after pregnancy
Pregnant patients with a transabdominal cerclage are precluded from having a vaginal delivery and must deliver via cesarean. During the antepartum period, patients are managed in the same manner as those who have a transvaginal cerclage. Delivery via cesarean at the onset of regular contractions is recommended to reduce the risk of uterine rupture. In the absence of labor, scheduled cesarean is performed at term.
Our practice is to schedule cesarean delivery at 38 weeks’ gestation, although there are no data or consensus to support a specific gestational age between 37 and 39 weeks. Unlike a transvaginal cerclage, a transabdominal cerclage can be left in place for use in subsequent pregnancies. Data are limited on whether the transabdominal cerclage should be removed in women who no longer desire childbearing and whether there are long-term sequelae if the suture is left in situ.17
Continue to: Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage...
Complications and risks of abdominal cerclage
As the data suggest and our experience confirms, transabdominal cerclage is highly successful in patients who have failed a history-indicated transvaginal cerclage; however, the transabdominal approach carries a higher surgical risk. Risks include intraoperative hemorrhage, conversion to laparotomy, and a range of rare surgical and obstetric complications, such as bladder injury and PPROM.13,18
If a patient experiences a fetal loss in the first trimester, a dilation and curettage (D&C) can be performed, with good obstetric outcomes in subsequent pregnancies.19 If the patient experiences an early-to-mid second-trimester loss, some studies suggest that a dilation and evacuation (D&E) of the uterus can be done with sufficient dilation of the cervix to accommodate up to a 15-mm cannula and Sopher forceps.19 Laminaria also may be used in this process. However, no data exist regarding success of future pregnancies and transabdominal cerclage integrity after a D&E.20 If the cerclage prevents successful dilation of the cervix, the cerclage must be removed laparoscopically prior to performing the D&E.
In late second-trimester and third-trimester loss, the cerclage must be removed to allow passage of the fetus and placenta prior to a D&E or an induction of labor.20
For patients with PPROM or preterm labor, data are limited regarding management recommendations. However, in these complex cases, we strongly recommend an individualized approach and co-management with maternal-fetal medicine specialists.
CASE Resolved
The cerclage is left in place during the patient’s cesarean delivery, and her postpartum course is uneventful. She continued without complications for the next year, at which time she sees you in the office with plans to have another pregnancy later in the year. You counsel her that her abdominal cerclage will still be effective and that she can get pregnant with expectations of similar outcomes as her previous pregnancy. She thanks you for everything and reports that she hopes to return later in the year for her first prenatal visit. ●
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 142: Cerclage for the management of cervical insufficiency. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 1): 372-379.
- Alfirevic Z, Stampalija T, Medley N. Cervical stitch (cerclage) for preventing preterm birth in singleton pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):CD008991.
- Brown R, Gagnon R, Delisle M-F. No. 373—cervical insufficiency and cervical cerclage. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2019;41:233-247.
- Odibo AO, Berghella V, To MS, et al. Shirodkar versus McDonald cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth in women with short cervical length. Am J Perinatol. 2007;24: 55-60.
- Basbug A, Bayrak M, Dogan O, et al. McDonald versus modified Shirodkar rescue cerclage in women with prolapsed fetal membranes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33: 1075-1097.
- Figueroa R, Crowell R, Martinez A, et al. McDonald versus Shirodkar cervical cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth: impact of body mass index. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:3408-3414.
- Suhag A, Berghella V. Cervical cerclage. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;57:557-567.
- Bayrak M, Gul A, Goynumer G. Rescue cerclage when foetal membranes prolapse into the vagina. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:471-475.
- Drassinower D, Coviello E, Landy HJ, et al. Outcomes after periviable ultrasound-indicated cerclage. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:932-938.
- Lee KN, Whang EJ, Chang KH, et al. History-indicated cerclage: the association between previous preterm history and cerclage outcome. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018;61:23-29. doi:10.5468/ogs.2018.61.1.23.
- Sneider K, Christiansen OB, Sundtoft IB, et al. Recurrence rates after abdominal and vaginal cerclages in women with cervical insufficiency: a validated cohort study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:859-866.
- Davis G, Berghella V, Talucci M, et al. Patients with a prior failed transvaginal cerclage: a comparison of obstetric outcomes with either transabdominal or transvaginal cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:836-839.
- Moawad GN, Tyan P, Bracke T, et al. Systematic review of transabdominal cerclage placed via laparoscopy for the prevention of preterm birth. J Mimim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:277-286.
- Burger NB, Brölmann HAM, Einarsson JI, et al. Effectiveness of abdominal cerclage placed via laparotomy or laparoscopy: systematic review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:696-704.
- Kim S, Hill A, Menderes G, et al. Minimally invasive abdominal cerclage compared to laparotomy: a comparison of surgical and obstetric outcomes. J Robot Surg. 2018;12:295-301.
- Dawood F, Farquharson RG. Transabdominal cerclage: preconceptual versus first trimester insertion. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:27-31.
- Hawkins E, Nimaroff M. Vaginal erosion of an abdominal cerclage 7 years after laparoscopic placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 2 suppl 2):420-423.
- Foster TL, Moore ES, Sumners JE. Operative complications and fetal morbidity encountered in 300 prophylactic transabdominal cervical cerclage procedures by one obstetric surgeon. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:713-717.
- Dethier D, Lassey SC, Pilliod R, et al. Uterine evacuation in the setting of transabdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2020;101:174-177.
- Martin A, Lathrop E. Controversies in family planning: management of second-trimester losses in the setting of an abdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2013;87:728-731.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin no. 142: Cerclage for the management of cervical insufficiency. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 1): 372-379.
- Alfirevic Z, Stampalija T, Medley N. Cervical stitch (cerclage) for preventing preterm birth in singleton pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6(6):CD008991.
- Brown R, Gagnon R, Delisle M-F. No. 373—cervical insufficiency and cervical cerclage. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2019;41:233-247.
- Odibo AO, Berghella V, To MS, et al. Shirodkar versus McDonald cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth in women with short cervical length. Am J Perinatol. 2007;24: 55-60.
- Basbug A, Bayrak M, Dogan O, et al. McDonald versus modified Shirodkar rescue cerclage in women with prolapsed fetal membranes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33: 1075-1097.
- Figueroa R, Crowell R, Martinez A, et al. McDonald versus Shirodkar cervical cerclage for the prevention of preterm birth: impact of body mass index. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:3408-3414.
- Suhag A, Berghella V. Cervical cerclage. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;57:557-567.
- Bayrak M, Gul A, Goynumer G. Rescue cerclage when foetal membranes prolapse into the vagina. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:471-475.
- Drassinower D, Coviello E, Landy HJ, et al. Outcomes after periviable ultrasound-indicated cerclage. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:932-938.
- Lee KN, Whang EJ, Chang KH, et al. History-indicated cerclage: the association between previous preterm history and cerclage outcome. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2018;61:23-29. doi:10.5468/ogs.2018.61.1.23.
- Sneider K, Christiansen OB, Sundtoft IB, et al. Recurrence rates after abdominal and vaginal cerclages in women with cervical insufficiency: a validated cohort study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:859-866.
- Davis G, Berghella V, Talucci M, et al. Patients with a prior failed transvaginal cerclage: a comparison of obstetric outcomes with either transabdominal or transvaginal cerclage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:836-839.
- Moawad GN, Tyan P, Bracke T, et al. Systematic review of transabdominal cerclage placed via laparoscopy for the prevention of preterm birth. J Mimim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:277-286.
- Burger NB, Brölmann HAM, Einarsson JI, et al. Effectiveness of abdominal cerclage placed via laparotomy or laparoscopy: systematic review. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:696-704.
- Kim S, Hill A, Menderes G, et al. Minimally invasive abdominal cerclage compared to laparotomy: a comparison of surgical and obstetric outcomes. J Robot Surg. 2018;12:295-301.
- Dawood F, Farquharson RG. Transabdominal cerclage: preconceptual versus first trimester insertion. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;199:27-31.
- Hawkins E, Nimaroff M. Vaginal erosion of an abdominal cerclage 7 years after laparoscopic placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123(2 pt 2 suppl 2):420-423.
- Foster TL, Moore ES, Sumners JE. Operative complications and fetal morbidity encountered in 300 prophylactic transabdominal cervical cerclage procedures by one obstetric surgeon. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;31:713-717.
- Dethier D, Lassey SC, Pilliod R, et al. Uterine evacuation in the setting of transabdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2020;101:174-177.
- Martin A, Lathrop E. Controversies in family planning: management of second-trimester losses in the setting of an abdominal cerclage. Contraception. 2013;87:728-731.
Triage, L&D, postpartum care during the COVID-19 pandemic
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
Obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
The identification of the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and emergence of the associated infectious respiratory disease, COVID-19, in late 2019 catapulted the citizens of the world, especially those in the health care professions, into an era of considerable uncertainty. At this moment in human history, calm reassurance – founded in fact and evidence – seems its greatest need. Much of the focus within the biomedical community has been on containment, prevention, and treatment of this highly contagious and, for some, extremely virulent disease.
However, for ob.gyns on the front lines of the COVID-19 fight, there is the additional challenge of caring for at least two patients simultaneously: the mother and her unborn baby. Studies in mother-baby dyads, while being published at an incredible pace, are still quite scarce. In addition, published reports are limited by the small sample size of the patient population (many are single-case reports), lack of uniformity in the timing and types of clinical samples collected, testing delays, and varying isolation protocols in cases where the mother has confirmed SARS-CoV-2.
Five months into a pandemic that has swept the world, we still know very little about COVID-19 infection in the general population, let alone the obstetric one. We do not know if having and resolving COVID-19 infection provides any long-term protection against future disease. We do not know if vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs. We do not know if maternal infection confers any immunologic benefit to the neonate. The list goes on.
What we do know is that taking extra precautions works. Use of personal protective equipment saves health care practitioner and patient lives. Prohibiting or restricting visitors to only one person in hospitals reduces risk of transmission to vulnerable patients.
Additionally, we know that leading with compassion is vital to easing patient – and practitioner – anxiety and stress. Most importantly, we know that people are extraordinarily resilient, especially when it comes to safeguarding the health of their families.
To address some of the major concerns that many ob.gyns. have regarding their risk of coronavirus exposure when caring for patients, we have invited Ray Bahado-Singh, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System, who works in a suburb of Detroit, one of our nation’s COVID-19 hot spots.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].
The identification of the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and emergence of the associated infectious respiratory disease, COVID-19, in late 2019 catapulted the citizens of the world, especially those in the health care professions, into an era of considerable uncertainty. At this moment in human history, calm reassurance – founded in fact and evidence – seems its greatest need. Much of the focus within the biomedical community has been on containment, prevention, and treatment of this highly contagious and, for some, extremely virulent disease.
However, for ob.gyns on the front lines of the COVID-19 fight, there is the additional challenge of caring for at least two patients simultaneously: the mother and her unborn baby. Studies in mother-baby dyads, while being published at an incredible pace, are still quite scarce. In addition, published reports are limited by the small sample size of the patient population (many are single-case reports), lack of uniformity in the timing and types of clinical samples collected, testing delays, and varying isolation protocols in cases where the mother has confirmed SARS-CoV-2.
Five months into a pandemic that has swept the world, we still know very little about COVID-19 infection in the general population, let alone the obstetric one. We do not know if having and resolving COVID-19 infection provides any long-term protection against future disease. We do not know if vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs. We do not know if maternal infection confers any immunologic benefit to the neonate. The list goes on.
What we do know is that taking extra precautions works. Use of personal protective equipment saves health care practitioner and patient lives. Prohibiting or restricting visitors to only one person in hospitals reduces risk of transmission to vulnerable patients.
Additionally, we know that leading with compassion is vital to easing patient – and practitioner – anxiety and stress. Most importantly, we know that people are extraordinarily resilient, especially when it comes to safeguarding the health of their families.
To address some of the major concerns that many ob.gyns. have regarding their risk of coronavirus exposure when caring for patients, we have invited Ray Bahado-Singh, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System, who works in a suburb of Detroit, one of our nation’s COVID-19 hot spots.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].
The identification of the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and emergence of the associated infectious respiratory disease, COVID-19, in late 2019 catapulted the citizens of the world, especially those in the health care professions, into an era of considerable uncertainty. At this moment in human history, calm reassurance – founded in fact and evidence – seems its greatest need. Much of the focus within the biomedical community has been on containment, prevention, and treatment of this highly contagious and, for some, extremely virulent disease.
However, for ob.gyns on the front lines of the COVID-19 fight, there is the additional challenge of caring for at least two patients simultaneously: the mother and her unborn baby. Studies in mother-baby dyads, while being published at an incredible pace, are still quite scarce. In addition, published reports are limited by the small sample size of the patient population (many are single-case reports), lack of uniformity in the timing and types of clinical samples collected, testing delays, and varying isolation protocols in cases where the mother has confirmed SARS-CoV-2.
Five months into a pandemic that has swept the world, we still know very little about COVID-19 infection in the general population, let alone the obstetric one. We do not know if having and resolving COVID-19 infection provides any long-term protection against future disease. We do not know if vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs. We do not know if maternal infection confers any immunologic benefit to the neonate. The list goes on.
What we do know is that taking extra precautions works. Use of personal protective equipment saves health care practitioner and patient lives. Prohibiting or restricting visitors to only one person in hospitals reduces risk of transmission to vulnerable patients.
Additionally, we know that leading with compassion is vital to easing patient – and practitioner – anxiety and stress. Most importantly, we know that people are extraordinarily resilient, especially when it comes to safeguarding the health of their families.
To address some of the major concerns that many ob.gyns. have regarding their risk of coronavirus exposure when caring for patients, we have invited Ray Bahado-Singh, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System, who works in a suburb of Detroit, one of our nation’s COVID-19 hot spots.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland School of Medicine as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at [email protected].
COVID-19: Social distancing with young children
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
COVID-19 and pregnancy: Is miscarriage a risk?

- Are you treating pregnant patients with COVID-19? Take this brief survey: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/CDZ7VFK
- Enroll your patients in PRIORITY: Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry
- Second-Trimester Miscarriage in a Pregnant Woman With SARS-CoV-2 Infection JAMA. April 30, 2020

- Are you treating pregnant patients with COVID-19? Take this brief survey: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/CDZ7VFK
- Enroll your patients in PRIORITY: Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry
- Second-Trimester Miscarriage in a Pregnant Woman With SARS-CoV-2 Infection JAMA. April 30, 2020

- Are you treating pregnant patients with COVID-19? Take this brief survey: https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/CDZ7VFK
- Enroll your patients in PRIORITY: Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry
- Second-Trimester Miscarriage in a Pregnant Woman With SARS-CoV-2 Infection JAMA. April 30, 2020
POPCoRN network mobilizes pediatric capacity during pandemic
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
Standing orders for vaccines may improve pediatric vaccination rates
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
FROM PEDIATRICS