User login
Patients are interrupting DMARD use well into the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in the proportion of patients with rheumatic diseases who stopped taking their disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), but the percentage who interrupted DMARD treatment increased later in the pandemic, according to speakers at the 2022 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
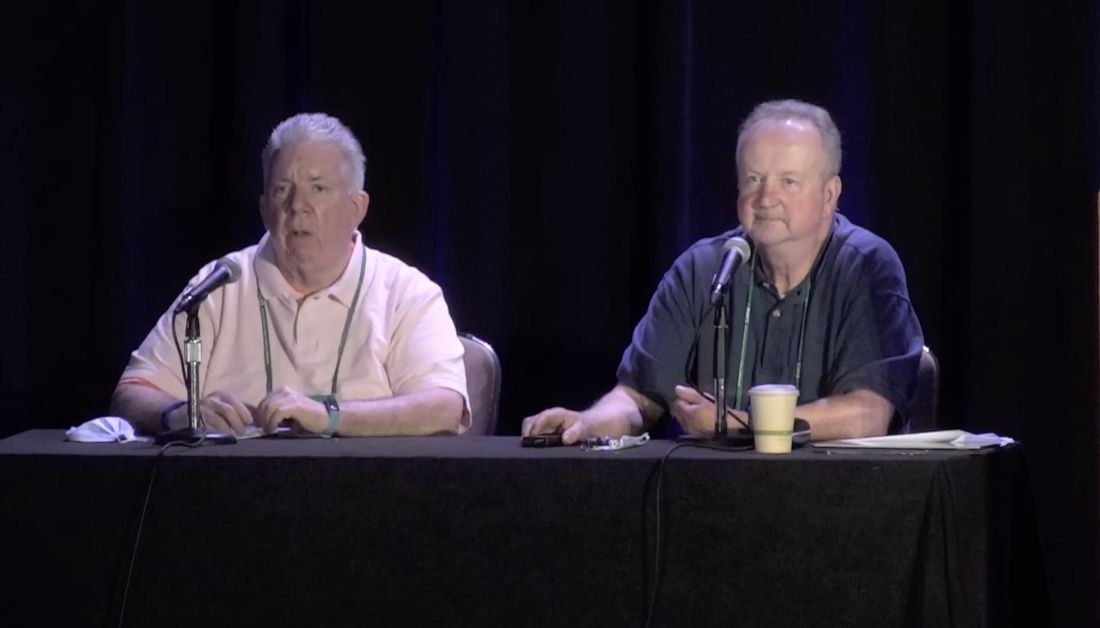
“People seem to be less anxious, but they’re interrupting their DMARD therapy more, more recently than in the pits of COVID, if you will,” said Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and director of RWCS.
Dr. Kavanaugh and his copresenter Jack Cush, MD, were discussing the results of a recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research that evaluated 2,424 patients with rheumatic diseases who completed a baseline and at least one follow-up survey issued by patient organizations between March 2020 and May 2021, with a median of five follow-up surveys completed. The patients included in the study were aged a mean of 57 years, 86.6% were women, 90.5% were White, 41.8% had rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 14.8% had antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, and 12.4% had psoriatic arthritis. Overall, 52.6% were on biologics or a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, 30.0% were receiving methotrexate, 21.4% were taking hydroxychloroquine, and 28.6% were receiving low-dose (24.0%) or high-dose (4.6%) glucocorticoids.
Patients’ T-scores on the anxiety short form Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) survey significantly decreased from a score of 58.7 in April 2020 to a score of 53.7 in May 2021 (P < .001), but there was a significant decrease in the interruption of DMARD treatment between April and December 2020 (11.2% vs. 7.5%; P < .001). This percentage rose significantly to 14.0% by May 2021 (P < .001). Patients who stopped using DMARDs were significantly associated with predicted incidence of severe flare in the next survey in adjusted models (12.9% vs. 8.0%; odds ratio, 1.71; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.36).
The results tell us “that we as a discipline are not doing a good job educating our patients,” said Dr. Cush, a rheumatologist based in Dallas, Tex., and executive editor of RheumNow.com.
“I wish we – and I’m really talking about myself – but myself and my practice were more proactive when COVID happened [in] sending out regular bulletins: ‘Don’t stop your therapy; these are the things you get; get the test that you need to get done,’ ” he said. “We let a lot of things go on autopilot with the patient driving throughout COVID. Even now, it’s happening. And this is a problem, and there are going to be consequences to this.”
Dr. Kavanaugh agreed with Dr. Cush’s assessment, suggesting that the pandemic came up quickly enough that it was difficult to be proactive with the situation.
Patients on JAK inhibitors as new COVID-19 risk group?
Another standout study on COVID-19 from 2021 was an analysis of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registry that examined risk of COVID-19 severity for patients with RA taking biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs), which was presented at the 2021 EULAR congress and later published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The researchers evaluated 2,869 patients March 2020 and April 2021 who were receiving abatacept (237 patients), rituximab (364 patients), interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitors (317 patients), JAK inhibitors (563 patients), or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors such as infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, and golimumab (1,388 patients) before developing COVID-19. Data about biologics or tsDMARDs were collected as a drug class. Patients in the study were mostly White (69.0%) women (80.8%) with a mean age of 56.7 years who lived in Europe (51.8%) or North America (35.0%). The researchers examined the severity of COVID-19 among all patients studied and calculated odds ratios based on drug class, with the TNF inhibitor group serving as a reference.
“[I]n this case, they said that the baseline use of rituximab was associated with more severity, and you see the severity being hospitalization and ICU and deaths. They found a signal for the JAK inhibitors that is not found in the other studies,” Dr. Kavanaugh said.
Overall, they found 21% of patients in the registry were hospitalized and 5.5% died, with rituximab (OR, 4.15; 95% CI, 3.16-5.44) and JAK inhibitors (OR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.60-2.65) associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes. Specifically, rituximab was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 4.53; 95% CI, 3.32-6.18), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.03-4.06), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 4.05; 95% CI, 3.08-5.33), and mortality (OR, 4.57; 95% CI, 3.32-9.01), compared with TNF inhibitors. For JAK inhibitors, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.78-3.24), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.04-2.18), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.56-2.62), and mortality (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.58-2.65), compared with the TNF inhibitors group. Associations between COVID-19 severity and abatacept or IL-6 inhibitors were not identified.
Commenting on the study in a question-and-answer session, Roy Fleischmann, MD, said the part of the study that identified a signal for JAK inhibitors was “very interesting.” He called attention to a rapid response comment to the study, which questioned if it was the drug class itself that caused the risk for severe disease. “This is very important, because actually, the patients who stop the JAK [inhibitor], that’s what drove the illness. The patients [who] continued the JAK [inhibitor], very few of them had illness,” said Dr. Fleischmann, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, Tex.
Confusion among patients during COVID-19
Alvin Wells, MD, PhD, asked the copresenters during the Q&A session whether they had any clinical pearls for the audience on how they manage treatment of patients with rheumatic disease with potential COVID-19 risk. “I think the confusion with our patients and COVID is what the ACR has put out with their guidelines,” said Dr. Wells, director of the department of rheumatology at Advocate Aurora Health in Franklin, Wisc.
Dr. Cush said he has three rules he follows: lower and discontinue steroids, avoid rituximab as a starting treatment and negotiate if patients are already taking it, and don’t stop any therapy.
“I want disease control. I think being under control is what keeps you away from risk of COVID and hospitalization,” Dr. Cush said. “I think being uncontrolled and inflamed, whether it’s our [patients with] inflammatory arthritis or lupus or, worse, vasculitis [or] myositis, those are the ones at high risk of progression from being just infected to being sick and in the hospital.”
Eric Ruderman, MD, professor of rheumatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, posed the question of getting somewhat back to normal during COVID-19 with regard to recently infected patients presenting at infusion centers, whether patients are more likely to continue testing positive, and when patients are cleared to come back. Dr. Ruderman said his center has a 20-day rule for returning after having COVID-19, while Dr. Cush said his center allows patients to come in if they test negative after 7-10 days.
“One of the things we’re struggling with is our infusion center, and one of the questions that keeps coming up is when can people come back after a COVID infection?” he said. “If you’re on a drug at home, that’s up to you and the patient. But in the infusion [center], then you have other people sitting around there.”
Dr. Kavanaugh said there is no current data for how long patients with rheumatic disease shed virus, or how long a positive test can be measured. “You definitely will continue to shed, and you’ll be detectable for a while,” he said.
Dr. Cush and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in the proportion of patients with rheumatic diseases who stopped taking their disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), but the percentage who interrupted DMARD treatment increased later in the pandemic, according to speakers at the 2022 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“People seem to be less anxious, but they’re interrupting their DMARD therapy more, more recently than in the pits of COVID, if you will,” said Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and director of RWCS.
Dr. Kavanaugh and his copresenter Jack Cush, MD, were discussing the results of a recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research that evaluated 2,424 patients with rheumatic diseases who completed a baseline and at least one follow-up survey issued by patient organizations between March 2020 and May 2021, with a median of five follow-up surveys completed. The patients included in the study were aged a mean of 57 years, 86.6% were women, 90.5% were White, 41.8% had rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 14.8% had antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, and 12.4% had psoriatic arthritis. Overall, 52.6% were on biologics or a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, 30.0% were receiving methotrexate, 21.4% were taking hydroxychloroquine, and 28.6% were receiving low-dose (24.0%) or high-dose (4.6%) glucocorticoids.
Patients’ T-scores on the anxiety short form Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) survey significantly decreased from a score of 58.7 in April 2020 to a score of 53.7 in May 2021 (P < .001), but there was a significant decrease in the interruption of DMARD treatment between April and December 2020 (11.2% vs. 7.5%; P < .001). This percentage rose significantly to 14.0% by May 2021 (P < .001). Patients who stopped using DMARDs were significantly associated with predicted incidence of severe flare in the next survey in adjusted models (12.9% vs. 8.0%; odds ratio, 1.71; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.36).
The results tell us “that we as a discipline are not doing a good job educating our patients,” said Dr. Cush, a rheumatologist based in Dallas, Tex., and executive editor of RheumNow.com.
“I wish we – and I’m really talking about myself – but myself and my practice were more proactive when COVID happened [in] sending out regular bulletins: ‘Don’t stop your therapy; these are the things you get; get the test that you need to get done,’ ” he said. “We let a lot of things go on autopilot with the patient driving throughout COVID. Even now, it’s happening. And this is a problem, and there are going to be consequences to this.”
Dr. Kavanaugh agreed with Dr. Cush’s assessment, suggesting that the pandemic came up quickly enough that it was difficult to be proactive with the situation.
Patients on JAK inhibitors as new COVID-19 risk group?
Another standout study on COVID-19 from 2021 was an analysis of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registry that examined risk of COVID-19 severity for patients with RA taking biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs), which was presented at the 2021 EULAR congress and later published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The researchers evaluated 2,869 patients March 2020 and April 2021 who were receiving abatacept (237 patients), rituximab (364 patients), interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitors (317 patients), JAK inhibitors (563 patients), or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors such as infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, and golimumab (1,388 patients) before developing COVID-19. Data about biologics or tsDMARDs were collected as a drug class. Patients in the study were mostly White (69.0%) women (80.8%) with a mean age of 56.7 years who lived in Europe (51.8%) or North America (35.0%). The researchers examined the severity of COVID-19 among all patients studied and calculated odds ratios based on drug class, with the TNF inhibitor group serving as a reference.
“[I]n this case, they said that the baseline use of rituximab was associated with more severity, and you see the severity being hospitalization and ICU and deaths. They found a signal for the JAK inhibitors that is not found in the other studies,” Dr. Kavanaugh said.
Overall, they found 21% of patients in the registry were hospitalized and 5.5% died, with rituximab (OR, 4.15; 95% CI, 3.16-5.44) and JAK inhibitors (OR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.60-2.65) associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes. Specifically, rituximab was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 4.53; 95% CI, 3.32-6.18), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.03-4.06), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 4.05; 95% CI, 3.08-5.33), and mortality (OR, 4.57; 95% CI, 3.32-9.01), compared with TNF inhibitors. For JAK inhibitors, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.78-3.24), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.04-2.18), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.56-2.62), and mortality (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.58-2.65), compared with the TNF inhibitors group. Associations between COVID-19 severity and abatacept or IL-6 inhibitors were not identified.
Commenting on the study in a question-and-answer session, Roy Fleischmann, MD, said the part of the study that identified a signal for JAK inhibitors was “very interesting.” He called attention to a rapid response comment to the study, which questioned if it was the drug class itself that caused the risk for severe disease. “This is very important, because actually, the patients who stop the JAK [inhibitor], that’s what drove the illness. The patients [who] continued the JAK [inhibitor], very few of them had illness,” said Dr. Fleischmann, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, Tex.
Confusion among patients during COVID-19
Alvin Wells, MD, PhD, asked the copresenters during the Q&A session whether they had any clinical pearls for the audience on how they manage treatment of patients with rheumatic disease with potential COVID-19 risk. “I think the confusion with our patients and COVID is what the ACR has put out with their guidelines,” said Dr. Wells, director of the department of rheumatology at Advocate Aurora Health in Franklin, Wisc.
Dr. Cush said he has three rules he follows: lower and discontinue steroids, avoid rituximab as a starting treatment and negotiate if patients are already taking it, and don’t stop any therapy.
“I want disease control. I think being under control is what keeps you away from risk of COVID and hospitalization,” Dr. Cush said. “I think being uncontrolled and inflamed, whether it’s our [patients with] inflammatory arthritis or lupus or, worse, vasculitis [or] myositis, those are the ones at high risk of progression from being just infected to being sick and in the hospital.”
Eric Ruderman, MD, professor of rheumatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, posed the question of getting somewhat back to normal during COVID-19 with regard to recently infected patients presenting at infusion centers, whether patients are more likely to continue testing positive, and when patients are cleared to come back. Dr. Ruderman said his center has a 20-day rule for returning after having COVID-19, while Dr. Cush said his center allows patients to come in if they test negative after 7-10 days.
“One of the things we’re struggling with is our infusion center, and one of the questions that keeps coming up is when can people come back after a COVID infection?” he said. “If you’re on a drug at home, that’s up to you and the patient. But in the infusion [center], then you have other people sitting around there.”
Dr. Kavanaugh said there is no current data for how long patients with rheumatic disease shed virus, or how long a positive test can be measured. “You definitely will continue to shed, and you’ll be detectable for a while,” he said.
Dr. Cush and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in the proportion of patients with rheumatic diseases who stopped taking their disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), but the percentage who interrupted DMARD treatment increased later in the pandemic, according to speakers at the 2022 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“People seem to be less anxious, but they’re interrupting their DMARD therapy more, more recently than in the pits of COVID, if you will,” said Arthur Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and director of RWCS.
Dr. Kavanaugh and his copresenter Jack Cush, MD, were discussing the results of a recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research that evaluated 2,424 patients with rheumatic diseases who completed a baseline and at least one follow-up survey issued by patient organizations between March 2020 and May 2021, with a median of five follow-up surveys completed. The patients included in the study were aged a mean of 57 years, 86.6% were women, 90.5% were White, 41.8% had rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 14.8% had antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, and 12.4% had psoriatic arthritis. Overall, 52.6% were on biologics or a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, 30.0% were receiving methotrexate, 21.4% were taking hydroxychloroquine, and 28.6% were receiving low-dose (24.0%) or high-dose (4.6%) glucocorticoids.
Patients’ T-scores on the anxiety short form Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) survey significantly decreased from a score of 58.7 in April 2020 to a score of 53.7 in May 2021 (P < .001), but there was a significant decrease in the interruption of DMARD treatment between April and December 2020 (11.2% vs. 7.5%; P < .001). This percentage rose significantly to 14.0% by May 2021 (P < .001). Patients who stopped using DMARDs were significantly associated with predicted incidence of severe flare in the next survey in adjusted models (12.9% vs. 8.0%; odds ratio, 1.71; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.36).
The results tell us “that we as a discipline are not doing a good job educating our patients,” said Dr. Cush, a rheumatologist based in Dallas, Tex., and executive editor of RheumNow.com.
“I wish we – and I’m really talking about myself – but myself and my practice were more proactive when COVID happened [in] sending out regular bulletins: ‘Don’t stop your therapy; these are the things you get; get the test that you need to get done,’ ” he said. “We let a lot of things go on autopilot with the patient driving throughout COVID. Even now, it’s happening. And this is a problem, and there are going to be consequences to this.”
Dr. Kavanaugh agreed with Dr. Cush’s assessment, suggesting that the pandemic came up quickly enough that it was difficult to be proactive with the situation.
Patients on JAK inhibitors as new COVID-19 risk group?
Another standout study on COVID-19 from 2021 was an analysis of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registry that examined risk of COVID-19 severity for patients with RA taking biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs), which was presented at the 2021 EULAR congress and later published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The researchers evaluated 2,869 patients March 2020 and April 2021 who were receiving abatacept (237 patients), rituximab (364 patients), interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitors (317 patients), JAK inhibitors (563 patients), or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors such as infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, and golimumab (1,388 patients) before developing COVID-19. Data about biologics or tsDMARDs were collected as a drug class. Patients in the study were mostly White (69.0%) women (80.8%) with a mean age of 56.7 years who lived in Europe (51.8%) or North America (35.0%). The researchers examined the severity of COVID-19 among all patients studied and calculated odds ratios based on drug class, with the TNF inhibitor group serving as a reference.
“[I]n this case, they said that the baseline use of rituximab was associated with more severity, and you see the severity being hospitalization and ICU and deaths. They found a signal for the JAK inhibitors that is not found in the other studies,” Dr. Kavanaugh said.
Overall, they found 21% of patients in the registry were hospitalized and 5.5% died, with rituximab (OR, 4.15; 95% CI, 3.16-5.44) and JAK inhibitors (OR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.60-2.65) associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes. Specifically, rituximab was associated with greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 4.53; 95% CI, 3.32-6.18), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 2.87; 95% CI, 2.03-4.06), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 4.05; 95% CI, 3.08-5.33), and mortality (OR, 4.57; 95% CI, 3.32-9.01), compared with TNF inhibitors. For JAK inhibitors, there was also a greater likelihood of hospitalization (OR, 2.40; 95% CI, 1.78-3.24), hospitalization with oxygen/ventilation (OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.04-2.18), need for mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.56-2.62), and mortality (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.58-2.65), compared with the TNF inhibitors group. Associations between COVID-19 severity and abatacept or IL-6 inhibitors were not identified.
Commenting on the study in a question-and-answer session, Roy Fleischmann, MD, said the part of the study that identified a signal for JAK inhibitors was “very interesting.” He called attention to a rapid response comment to the study, which questioned if it was the drug class itself that caused the risk for severe disease. “This is very important, because actually, the patients who stop the JAK [inhibitor], that’s what drove the illness. The patients [who] continued the JAK [inhibitor], very few of them had illness,” said Dr. Fleischmann, clinical professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and codirector of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center, both in Dallas, Tex.
Confusion among patients during COVID-19
Alvin Wells, MD, PhD, asked the copresenters during the Q&A session whether they had any clinical pearls for the audience on how they manage treatment of patients with rheumatic disease with potential COVID-19 risk. “I think the confusion with our patients and COVID is what the ACR has put out with their guidelines,” said Dr. Wells, director of the department of rheumatology at Advocate Aurora Health in Franklin, Wisc.
Dr. Cush said he has three rules he follows: lower and discontinue steroids, avoid rituximab as a starting treatment and negotiate if patients are already taking it, and don’t stop any therapy.
“I want disease control. I think being under control is what keeps you away from risk of COVID and hospitalization,” Dr. Cush said. “I think being uncontrolled and inflamed, whether it’s our [patients with] inflammatory arthritis or lupus or, worse, vasculitis [or] myositis, those are the ones at high risk of progression from being just infected to being sick and in the hospital.”
Eric Ruderman, MD, professor of rheumatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, posed the question of getting somewhat back to normal during COVID-19 with regard to recently infected patients presenting at infusion centers, whether patients are more likely to continue testing positive, and when patients are cleared to come back. Dr. Ruderman said his center has a 20-day rule for returning after having COVID-19, while Dr. Cush said his center allows patients to come in if they test negative after 7-10 days.
“One of the things we’re struggling with is our infusion center, and one of the questions that keeps coming up is when can people come back after a COVID infection?” he said. “If you’re on a drug at home, that’s up to you and the patient. But in the infusion [center], then you have other people sitting around there.”
Dr. Kavanaugh said there is no current data for how long patients with rheumatic disease shed virus, or how long a positive test can be measured. “You definitely will continue to shed, and you’ll be detectable for a while,” he said.
Dr. Cush and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM RWCS 2022
Eighteen-year study shows inconsistencies in treating, classifying JIA
“Children are not little adults” is a common refrain in pediatric medicine, but when it comes to a condition like juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), rheumatologists might be better off treating pediatric and adult rheumatic disease more similarly.
A recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research followed children diagnosed with JIA for 18 years. Although not the first long-term study to examine children with JIA, it is unique in that it took place “during a time where biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] were emerging as a fundamental therapy in the management of children with JIA,” said Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Additionally, the study highlights the International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) consensus-based classification criteria as an imperfect method to categorize patients with JIA.
Mia Glerup, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues prospectively analyzed 373 patients from Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland with new-onset JIA between 1997 and 2000 and evaluated them at baseline, 8 years, and 18 years. At each visit, the researchers collected data on demographics, disease activity, ILAR category, treatment, and blood samples.
Patients in the cohort were mostly girls (66.7%) with a median age of 5.9 years at onset. Approximately one-third (34.8%) of patients were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive and 21.6% were HLA-B27 positive. The most common JIA categories at baseline were persistent oligoarthritis (53.9%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor (RF) negative (21.1%), and undifferentiated arthritis (10.2%).
Dr. Glerup and colleagues found that the proportion of patients not receiving DMARDs declined from 73.2% at baseline to 59.7% at 8 years, and then rose again to 70% at 18 years (risk ratio, 1.3; P = .003). The group of 103 patients who used conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs) either as monotherapy or in combination with a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) at 8 years dwindled to 44 (42.7%) at 18 years (RR, 0.4; P < .001), whereas 32 of 52 patients (61.5%) using bDMARDs at 8 years were still taking them at 18 years (RR, 0.6; P = .02). Across the whole study, 14.7% of patients never received any JIA treatment, and 33 of 85 patients (38.8%) on continuous DMARDs developed uveitis during the study period.
Overall, 62.7% of patients received DMARDs at least once, including 89.7% with polyarticular RF negative, 77.3% with oligoarticular extended, 76.9% with systemic, 75.7% with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA), 66.7% with polyarticular RF-positive, 65.2% with juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA), 58.9% with undifferentiated JIA, and 27.6% of patients with persistent oligoarticular disease.
The median number of active joints dropped from 3 (range, 1-30) at baseline to 0 at 8 years (range, 0-13), whereas the median cumulative number of affected joints rose from 3 at baseline (range, 1-30) to 6 at 8 years (range, 1-41). At last follow-up, the median number of active joints was 0 (range, 0-5) and median cumulative number of affected joints was 7 (range, 1-47). The percentage of patients in remission barely changed from 52% at 8 years to 51% at 18.
Some patients also changed ILAR categories during the study period, with 7% shifting between baseline and 8 years, and 11% shifting between 8-year and 18-year follow-up. Compared with baseline, by the 18-year follow-up time point there was a significant decrease in the number of patients categorized as oligoarticular (230 vs. 197 patients; P = .02), a significant increase in patients in the psoriatic ILAR category (8 vs. 28 patients; P < .001), and a nonsignificant increase in the number of patients in the undifferentiated category (45 vs. 63 patients; P = .06).
“Almost half of the changes in the distribution between the ILAR categories were caused by updated information on heredity in a first-degree relative obtained at the follow-up visits,” Dr. Glerup and colleagues write.
The results of the long-term study show that patients are “likely to remain in remission – with the converse also evident, as patients still with evidence of disease activity at 8 years after disease onset were more likely to have refractory disease,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, said they are “great news to be able to give parents of young kids with arthritis.” However, she questioned whether the results are generalizable to populations of patients “who are in the worst prognostic group.”
For example, a substantial proportion of patients were classified under the oligoarticular category. “That’s already a group that we know from experience tends to have a better outcome than some of the other groups of JIA,” she said.
“That kind of weaves its way through the whole study, because then they show a lot of patients have come off their medication. Patients who had more severe disease in more joints would be less likely, I think, to just stop their medication and stop going to doctors,” Dr. Imundo explained.
Although the study is valuable for its long-term follow-up, there is also a question of generalizability across a more diverse ethnic and racial group. The authors do not elaborate on the racial breakdown of their patients, Dr. Imundo said, “so we’re going to have to assume that the vast majority are going to [have] Caucasian Nordic ethnic background, and that goes along with them having this high percentage of HLA-B27 positivity, which is a gene that’s more prevalent in northern European populations.”
Jonathan Hausmann, MD, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston,, told this news organization that he believes the overall conclusions from the study – that JIA persists over time and that ILAR classification is a somewhat imprecise measure of assessing JIA types in children – would be generalizable to other groups.
However, long-term registries evaluating JIA in more diverse populations, such as the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) registry, could confirm these results, said Dr. Hausmann, who is a registry informatics associate with CARRA and was not associated with the research.
Long-term management of JIA
In an accompanying editorial, Jaime Guzman, MD, MSc, and Ross E. Petty, MD, PhD, of British Columbia Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said a rheumatologist’s interpretation of the study would be tied to what they learned about children with arthritis in medical school. They would see the glass as “half full” if children who achieved remission stayed in remission if they learned that a child might end up outgrowing JIA but potentially develop lifelong disability, whereas others may focus on the outcome of approximately half of patients not achieving remission.
“When I was going through medical school, I remember learning that JIA is a disease of children, and typically, they outgrow it as they become adults,” Dr. Hausmann said. “I think this study and many other studies have shown that that’s actually not the case – that, in fact, it may be a majority of kids continue having active disease even through adulthood.”
If a rheumatologist knows JIA is likely to continue into adulthood, “that’s huge,” Dr. Hausmann said. “That means when we first diagnose patients with JIA as kids, we need to set expectations with the families that this may not just go away; this may be something that could be more lifelong.”
Education on the part of the patient, their parents, and their clinician on the expected trajectory of the disease is critical so that children can continue their own care as they transition to adulthood, Dr. Hausmann explained. “The earlier the kids develop the skills to discuss their medicines, their side effects, the better they’ll be able to transition to adult medicine,” he said.
For the patients who go into remission and stay in remission, the message is also important. “To have the reassurance that a lot of those kids won’t be having active joint symptoms or need to be on medication, that’s a huge positive message that can get out there, so I think that’s great,” Dr. Imundo said.
Time to move on from ILAR classification?
Another big takeaway from the study was how patients’ ILAR classification changed across the 18-year follow-up. First proposed in 1995, the JIA ILAR classification has been revised several times for clarification purposes. In its current form, the ILAR classification considers a patient’s history when categorizing JIA types but also includes factors such as immediate family history. This system of assessing JIA has been criticized and there are initiatives to create a new JIA classification system to replace it.
“The ILAR criteria were designed to classify patients 6 months after disease onset in an attempt to find some commonality in clinical phenotypes, prognosis, and suggested management,” Dr. Wahezi said. “While there continues to be debate as to whether we can improve our classification of JIA patients, it is not surprising that phenotypes may evolve over time as new clinical features develop. As pediatric rheumatologists, we are well accustomed to having to modify management plans as children manifest with new clinical features over time.”
Although the percentage of patients who switched ILAR classifications over the study period was “much higher” than she would have thought, Dr. Imundo said it was the reasons provided in the study that seemed odd to her. “The classification scheme relies on your family history, like someone else in your family now has psoriasis, so your arthritis classification changes,” she explained.
“We want to head toward a much more unified classification scheme, a simpler one. We now understand that some of the diseases that we see in pediatrics are really the equivalent or same disease in adults,” she said.
“Most of the pediatric categories of JIA have distinct adult correlates,” Dr. Hausmann agreed. RF-positive polyarthritis in children and rheumatoid arthritis in adults are correlated, as are systemic JIA and adult-onset Still’s disease, he explained. “That has been borne out also by genetic susceptibility studies that the genetic predispositions to systemic arthritis in children is the same as the genetic predisposition to adult-onset Still’s disease in adults. By and large, there are a lot of similarities between the two.
“I think we need to incorporate some of that knowledge in better classifying kids with JIA so that we can find the best treatments and the best outcomes, and we can provide information to families about the expected course of the disease over time so that can inform our discussions.”
Some pediatric rheumatologists accept the classification system is flawed, but not all concur with the degree to which these problems impact patient care. “While the ILAR classification criteria may be subject to criticism, it does provide general context and prognostic implications for patients and families,” Dr. Wahezi said.
“The medicines certainly are very similar across the JIA categories, so the implications are not as broad” when classification changes,” Dr. Hausmann said. “But it certainly shows that there are things that we still don’t know. I think classification is actually pretty important because it might give you a sense of how persistent the disease will be.”
Dr. Imundo said the ILAR classification’s “time is limited,” and rheumatologists may soon need to adopt a new way of classifying children with rheumatic disease – “a more data-driven, genetics-driven scheme.”
“These categories are so imperfect, and the patients are changing. I feel like that says to me, let’s find something that’s more predictive that really helps us a little better than what we have now,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors of the study and the editorial have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hausmann reports receiving salary support from CARRA. Dr. Imundo and Dr. Wahezi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Children are not little adults” is a common refrain in pediatric medicine, but when it comes to a condition like juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), rheumatologists might be better off treating pediatric and adult rheumatic disease more similarly.
A recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research followed children diagnosed with JIA for 18 years. Although not the first long-term study to examine children with JIA, it is unique in that it took place “during a time where biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] were emerging as a fundamental therapy in the management of children with JIA,” said Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Additionally, the study highlights the International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) consensus-based classification criteria as an imperfect method to categorize patients with JIA.
Mia Glerup, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues prospectively analyzed 373 patients from Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland with new-onset JIA between 1997 and 2000 and evaluated them at baseline, 8 years, and 18 years. At each visit, the researchers collected data on demographics, disease activity, ILAR category, treatment, and blood samples.
Patients in the cohort were mostly girls (66.7%) with a median age of 5.9 years at onset. Approximately one-third (34.8%) of patients were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive and 21.6% were HLA-B27 positive. The most common JIA categories at baseline were persistent oligoarthritis (53.9%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor (RF) negative (21.1%), and undifferentiated arthritis (10.2%).
Dr. Glerup and colleagues found that the proportion of patients not receiving DMARDs declined from 73.2% at baseline to 59.7% at 8 years, and then rose again to 70% at 18 years (risk ratio, 1.3; P = .003). The group of 103 patients who used conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs) either as monotherapy or in combination with a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) at 8 years dwindled to 44 (42.7%) at 18 years (RR, 0.4; P < .001), whereas 32 of 52 patients (61.5%) using bDMARDs at 8 years were still taking them at 18 years (RR, 0.6; P = .02). Across the whole study, 14.7% of patients never received any JIA treatment, and 33 of 85 patients (38.8%) on continuous DMARDs developed uveitis during the study period.
Overall, 62.7% of patients received DMARDs at least once, including 89.7% with polyarticular RF negative, 77.3% with oligoarticular extended, 76.9% with systemic, 75.7% with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA), 66.7% with polyarticular RF-positive, 65.2% with juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA), 58.9% with undifferentiated JIA, and 27.6% of patients with persistent oligoarticular disease.
The median number of active joints dropped from 3 (range, 1-30) at baseline to 0 at 8 years (range, 0-13), whereas the median cumulative number of affected joints rose from 3 at baseline (range, 1-30) to 6 at 8 years (range, 1-41). At last follow-up, the median number of active joints was 0 (range, 0-5) and median cumulative number of affected joints was 7 (range, 1-47). The percentage of patients in remission barely changed from 52% at 8 years to 51% at 18.
Some patients also changed ILAR categories during the study period, with 7% shifting between baseline and 8 years, and 11% shifting between 8-year and 18-year follow-up. Compared with baseline, by the 18-year follow-up time point there was a significant decrease in the number of patients categorized as oligoarticular (230 vs. 197 patients; P = .02), a significant increase in patients in the psoriatic ILAR category (8 vs. 28 patients; P < .001), and a nonsignificant increase in the number of patients in the undifferentiated category (45 vs. 63 patients; P = .06).
“Almost half of the changes in the distribution between the ILAR categories were caused by updated information on heredity in a first-degree relative obtained at the follow-up visits,” Dr. Glerup and colleagues write.
The results of the long-term study show that patients are “likely to remain in remission – with the converse also evident, as patients still with evidence of disease activity at 8 years after disease onset were more likely to have refractory disease,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, said they are “great news to be able to give parents of young kids with arthritis.” However, she questioned whether the results are generalizable to populations of patients “who are in the worst prognostic group.”
For example, a substantial proportion of patients were classified under the oligoarticular category. “That’s already a group that we know from experience tends to have a better outcome than some of the other groups of JIA,” she said.
“That kind of weaves its way through the whole study, because then they show a lot of patients have come off their medication. Patients who had more severe disease in more joints would be less likely, I think, to just stop their medication and stop going to doctors,” Dr. Imundo explained.
Although the study is valuable for its long-term follow-up, there is also a question of generalizability across a more diverse ethnic and racial group. The authors do not elaborate on the racial breakdown of their patients, Dr. Imundo said, “so we’re going to have to assume that the vast majority are going to [have] Caucasian Nordic ethnic background, and that goes along with them having this high percentage of HLA-B27 positivity, which is a gene that’s more prevalent in northern European populations.”
Jonathan Hausmann, MD, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston,, told this news organization that he believes the overall conclusions from the study – that JIA persists over time and that ILAR classification is a somewhat imprecise measure of assessing JIA types in children – would be generalizable to other groups.
However, long-term registries evaluating JIA in more diverse populations, such as the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) registry, could confirm these results, said Dr. Hausmann, who is a registry informatics associate with CARRA and was not associated with the research.
Long-term management of JIA
In an accompanying editorial, Jaime Guzman, MD, MSc, and Ross E. Petty, MD, PhD, of British Columbia Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said a rheumatologist’s interpretation of the study would be tied to what they learned about children with arthritis in medical school. They would see the glass as “half full” if children who achieved remission stayed in remission if they learned that a child might end up outgrowing JIA but potentially develop lifelong disability, whereas others may focus on the outcome of approximately half of patients not achieving remission.
“When I was going through medical school, I remember learning that JIA is a disease of children, and typically, they outgrow it as they become adults,” Dr. Hausmann said. “I think this study and many other studies have shown that that’s actually not the case – that, in fact, it may be a majority of kids continue having active disease even through adulthood.”
If a rheumatologist knows JIA is likely to continue into adulthood, “that’s huge,” Dr. Hausmann said. “That means when we first diagnose patients with JIA as kids, we need to set expectations with the families that this may not just go away; this may be something that could be more lifelong.”
Education on the part of the patient, their parents, and their clinician on the expected trajectory of the disease is critical so that children can continue their own care as they transition to adulthood, Dr. Hausmann explained. “The earlier the kids develop the skills to discuss their medicines, their side effects, the better they’ll be able to transition to adult medicine,” he said.
For the patients who go into remission and stay in remission, the message is also important. “To have the reassurance that a lot of those kids won’t be having active joint symptoms or need to be on medication, that’s a huge positive message that can get out there, so I think that’s great,” Dr. Imundo said.
Time to move on from ILAR classification?
Another big takeaway from the study was how patients’ ILAR classification changed across the 18-year follow-up. First proposed in 1995, the JIA ILAR classification has been revised several times for clarification purposes. In its current form, the ILAR classification considers a patient’s history when categorizing JIA types but also includes factors such as immediate family history. This system of assessing JIA has been criticized and there are initiatives to create a new JIA classification system to replace it.
“The ILAR criteria were designed to classify patients 6 months after disease onset in an attempt to find some commonality in clinical phenotypes, prognosis, and suggested management,” Dr. Wahezi said. “While there continues to be debate as to whether we can improve our classification of JIA patients, it is not surprising that phenotypes may evolve over time as new clinical features develop. As pediatric rheumatologists, we are well accustomed to having to modify management plans as children manifest with new clinical features over time.”
Although the percentage of patients who switched ILAR classifications over the study period was “much higher” than she would have thought, Dr. Imundo said it was the reasons provided in the study that seemed odd to her. “The classification scheme relies on your family history, like someone else in your family now has psoriasis, so your arthritis classification changes,” she explained.
“We want to head toward a much more unified classification scheme, a simpler one. We now understand that some of the diseases that we see in pediatrics are really the equivalent or same disease in adults,” she said.
“Most of the pediatric categories of JIA have distinct adult correlates,” Dr. Hausmann agreed. RF-positive polyarthritis in children and rheumatoid arthritis in adults are correlated, as are systemic JIA and adult-onset Still’s disease, he explained. “That has been borne out also by genetic susceptibility studies that the genetic predispositions to systemic arthritis in children is the same as the genetic predisposition to adult-onset Still’s disease in adults. By and large, there are a lot of similarities between the two.
“I think we need to incorporate some of that knowledge in better classifying kids with JIA so that we can find the best treatments and the best outcomes, and we can provide information to families about the expected course of the disease over time so that can inform our discussions.”
Some pediatric rheumatologists accept the classification system is flawed, but not all concur with the degree to which these problems impact patient care. “While the ILAR classification criteria may be subject to criticism, it does provide general context and prognostic implications for patients and families,” Dr. Wahezi said.
“The medicines certainly are very similar across the JIA categories, so the implications are not as broad” when classification changes,” Dr. Hausmann said. “But it certainly shows that there are things that we still don’t know. I think classification is actually pretty important because it might give you a sense of how persistent the disease will be.”
Dr. Imundo said the ILAR classification’s “time is limited,” and rheumatologists may soon need to adopt a new way of classifying children with rheumatic disease – “a more data-driven, genetics-driven scheme.”
“These categories are so imperfect, and the patients are changing. I feel like that says to me, let’s find something that’s more predictive that really helps us a little better than what we have now,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors of the study and the editorial have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hausmann reports receiving salary support from CARRA. Dr. Imundo and Dr. Wahezi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Children are not little adults” is a common refrain in pediatric medicine, but when it comes to a condition like juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), rheumatologists might be better off treating pediatric and adult rheumatic disease more similarly.
A recent study published in Arthritis Care & Research followed children diagnosed with JIA for 18 years. Although not the first long-term study to examine children with JIA, it is unique in that it took place “during a time where biologic DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] were emerging as a fundamental therapy in the management of children with JIA,” said Dawn M. Wahezi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Additionally, the study highlights the International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) consensus-based classification criteria as an imperfect method to categorize patients with JIA.
Mia Glerup, MD, PhD, of the department of pediatrics at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital and colleagues prospectively analyzed 373 patients from Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland with new-onset JIA between 1997 and 2000 and evaluated them at baseline, 8 years, and 18 years. At each visit, the researchers collected data on demographics, disease activity, ILAR category, treatment, and blood samples.
Patients in the cohort were mostly girls (66.7%) with a median age of 5.9 years at onset. Approximately one-third (34.8%) of patients were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive and 21.6% were HLA-B27 positive. The most common JIA categories at baseline were persistent oligoarthritis (53.9%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor (RF) negative (21.1%), and undifferentiated arthritis (10.2%).
Dr. Glerup and colleagues found that the proportion of patients not receiving DMARDs declined from 73.2% at baseline to 59.7% at 8 years, and then rose again to 70% at 18 years (risk ratio, 1.3; P = .003). The group of 103 patients who used conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs) either as monotherapy or in combination with a biologic DMARD (bDMARD) at 8 years dwindled to 44 (42.7%) at 18 years (RR, 0.4; P < .001), whereas 32 of 52 patients (61.5%) using bDMARDs at 8 years were still taking them at 18 years (RR, 0.6; P = .02). Across the whole study, 14.7% of patients never received any JIA treatment, and 33 of 85 patients (38.8%) on continuous DMARDs developed uveitis during the study period.
Overall, 62.7% of patients received DMARDs at least once, including 89.7% with polyarticular RF negative, 77.3% with oligoarticular extended, 76.9% with systemic, 75.7% with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA), 66.7% with polyarticular RF-positive, 65.2% with juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA), 58.9% with undifferentiated JIA, and 27.6% of patients with persistent oligoarticular disease.
The median number of active joints dropped from 3 (range, 1-30) at baseline to 0 at 8 years (range, 0-13), whereas the median cumulative number of affected joints rose from 3 at baseline (range, 1-30) to 6 at 8 years (range, 1-41). At last follow-up, the median number of active joints was 0 (range, 0-5) and median cumulative number of affected joints was 7 (range, 1-47). The percentage of patients in remission barely changed from 52% at 8 years to 51% at 18.
Some patients also changed ILAR categories during the study period, with 7% shifting between baseline and 8 years, and 11% shifting between 8-year and 18-year follow-up. Compared with baseline, by the 18-year follow-up time point there was a significant decrease in the number of patients categorized as oligoarticular (230 vs. 197 patients; P = .02), a significant increase in patients in the psoriatic ILAR category (8 vs. 28 patients; P < .001), and a nonsignificant increase in the number of patients in the undifferentiated category (45 vs. 63 patients; P = .06).
“Almost half of the changes in the distribution between the ILAR categories were caused by updated information on heredity in a first-degree relative obtained at the follow-up visits,” Dr. Glerup and colleagues write.
The results of the long-term study show that patients are “likely to remain in remission – with the converse also evident, as patients still with evidence of disease activity at 8 years after disease onset were more likely to have refractory disease,” Dr. Wahezi said.
Commenting on the study’s findings, Lisa F. Imundo, MD, director of adolescent rheumatology at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, said they are “great news to be able to give parents of young kids with arthritis.” However, she questioned whether the results are generalizable to populations of patients “who are in the worst prognostic group.”
For example, a substantial proportion of patients were classified under the oligoarticular category. “That’s already a group that we know from experience tends to have a better outcome than some of the other groups of JIA,” she said.
“That kind of weaves its way through the whole study, because then they show a lot of patients have come off their medication. Patients who had more severe disease in more joints would be less likely, I think, to just stop their medication and stop going to doctors,” Dr. Imundo explained.
Although the study is valuable for its long-term follow-up, there is also a question of generalizability across a more diverse ethnic and racial group. The authors do not elaborate on the racial breakdown of their patients, Dr. Imundo said, “so we’re going to have to assume that the vast majority are going to [have] Caucasian Nordic ethnic background, and that goes along with them having this high percentage of HLA-B27 positivity, which is a gene that’s more prevalent in northern European populations.”
Jonathan Hausmann, MD, a pediatric and adult rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston,, told this news organization that he believes the overall conclusions from the study – that JIA persists over time and that ILAR classification is a somewhat imprecise measure of assessing JIA types in children – would be generalizable to other groups.
However, long-term registries evaluating JIA in more diverse populations, such as the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) registry, could confirm these results, said Dr. Hausmann, who is a registry informatics associate with CARRA and was not associated with the research.
Long-term management of JIA
In an accompanying editorial, Jaime Guzman, MD, MSc, and Ross E. Petty, MD, PhD, of British Columbia Children’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, said a rheumatologist’s interpretation of the study would be tied to what they learned about children with arthritis in medical school. They would see the glass as “half full” if children who achieved remission stayed in remission if they learned that a child might end up outgrowing JIA but potentially develop lifelong disability, whereas others may focus on the outcome of approximately half of patients not achieving remission.
“When I was going through medical school, I remember learning that JIA is a disease of children, and typically, they outgrow it as they become adults,” Dr. Hausmann said. “I think this study and many other studies have shown that that’s actually not the case – that, in fact, it may be a majority of kids continue having active disease even through adulthood.”
If a rheumatologist knows JIA is likely to continue into adulthood, “that’s huge,” Dr. Hausmann said. “That means when we first diagnose patients with JIA as kids, we need to set expectations with the families that this may not just go away; this may be something that could be more lifelong.”
Education on the part of the patient, their parents, and their clinician on the expected trajectory of the disease is critical so that children can continue their own care as they transition to adulthood, Dr. Hausmann explained. “The earlier the kids develop the skills to discuss their medicines, their side effects, the better they’ll be able to transition to adult medicine,” he said.
For the patients who go into remission and stay in remission, the message is also important. “To have the reassurance that a lot of those kids won’t be having active joint symptoms or need to be on medication, that’s a huge positive message that can get out there, so I think that’s great,” Dr. Imundo said.
Time to move on from ILAR classification?
Another big takeaway from the study was how patients’ ILAR classification changed across the 18-year follow-up. First proposed in 1995, the JIA ILAR classification has been revised several times for clarification purposes. In its current form, the ILAR classification considers a patient’s history when categorizing JIA types but also includes factors such as immediate family history. This system of assessing JIA has been criticized and there are initiatives to create a new JIA classification system to replace it.
“The ILAR criteria were designed to classify patients 6 months after disease onset in an attempt to find some commonality in clinical phenotypes, prognosis, and suggested management,” Dr. Wahezi said. “While there continues to be debate as to whether we can improve our classification of JIA patients, it is not surprising that phenotypes may evolve over time as new clinical features develop. As pediatric rheumatologists, we are well accustomed to having to modify management plans as children manifest with new clinical features over time.”
Although the percentage of patients who switched ILAR classifications over the study period was “much higher” than she would have thought, Dr. Imundo said it was the reasons provided in the study that seemed odd to her. “The classification scheme relies on your family history, like someone else in your family now has psoriasis, so your arthritis classification changes,” she explained.
“We want to head toward a much more unified classification scheme, a simpler one. We now understand that some of the diseases that we see in pediatrics are really the equivalent or same disease in adults,” she said.
“Most of the pediatric categories of JIA have distinct adult correlates,” Dr. Hausmann agreed. RF-positive polyarthritis in children and rheumatoid arthritis in adults are correlated, as are systemic JIA and adult-onset Still’s disease, he explained. “That has been borne out also by genetic susceptibility studies that the genetic predispositions to systemic arthritis in children is the same as the genetic predisposition to adult-onset Still’s disease in adults. By and large, there are a lot of similarities between the two.
“I think we need to incorporate some of that knowledge in better classifying kids with JIA so that we can find the best treatments and the best outcomes, and we can provide information to families about the expected course of the disease over time so that can inform our discussions.”
Some pediatric rheumatologists accept the classification system is flawed, but not all concur with the degree to which these problems impact patient care. “While the ILAR classification criteria may be subject to criticism, it does provide general context and prognostic implications for patients and families,” Dr. Wahezi said.
“The medicines certainly are very similar across the JIA categories, so the implications are not as broad” when classification changes,” Dr. Hausmann said. “But it certainly shows that there are things that we still don’t know. I think classification is actually pretty important because it might give you a sense of how persistent the disease will be.”
Dr. Imundo said the ILAR classification’s “time is limited,” and rheumatologists may soon need to adopt a new way of classifying children with rheumatic disease – “a more data-driven, genetics-driven scheme.”
“These categories are so imperfect, and the patients are changing. I feel like that says to me, let’s find something that’s more predictive that really helps us a little better than what we have now,” she said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors of the study and the editorial have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hausmann reports receiving salary support from CARRA. Dr. Imundo and Dr. Wahezi have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Universal hepatitis B screening, vaccination deemed cost effective for pregnant women
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Screening for hepatitis B antibodies and vaccinating pregnant women without immunity appears to be a cost-effective health measure, according to a recent analysis published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Malavika Prabhu, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, said in an interview that the impetus to conduct the study came from the idea that hepatitis B is a concern throughout a woman’s life, but not necessarily during pregnancy. While vaccination is not routine during pregnancy, guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state that at-risk women should be screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B during pregnancy.
“What we thought made more sense just from thinking about other principles of prenatal care was that it would make sense for us to screen, see who’s susceptible, counsel them on the risk of hepatitis B, and then vaccinate them in the course of the pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said.
After writing a commentary arguing in favor of universal screening and vaccination, she and her colleagues noted it was still unclear whether that approach was cost effective, she said. “Health care costs in this country are so expensive at baseline that, as we continue to add more things to health care, we have to make sure that it’s value added.”
Dr. Prabhu and her colleagues evaluated a theoretical cohort of 3.6 million pregnant women in the United States and created a decision-analytic model to determine how universal hepatitis B surface antibody screening and vaccination for hepatitis B affected factors such as cost, cost-effectiveness, and outcomes. They included hepatitis B virus cases as well as long-term problems associated with hepatitis B infection such as hepatocellular carcinoma, decompensated cirrhosis, liver transplant, and death. Assumptions of the model were that 84% of the women would undergo the screening, 61% would receive the vaccine, and 90% would seroconvert after the vaccine series, and were based on probabilities from other studies.
The cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated as the total cost and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) relative to the lifetime of the woman after the index pregnancy, with $50,000 per QALY set as the willingness-to-pay threshold. The researchers also performed an additional analysis and simulations to estimate which variables had the most effect, and an additional model was created to estimate the effect of universal screening and vaccination if at-risk patients were removed.
Dr. Prabhu and colleagues found the universal screening and vaccination program was cost effective, with 1,702 fewer cases of hepatitis B, 11 fewer deaths, 7 fewer decompensated cirrhosis cases, and 4 fewer liver transplants in their model. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was $1,890 per QALY, and the total increased lifetime cohort cost was $13,841,889. The researchers said the model held up in scenarios where there was a high level of hepatitis B immunity, and when at-risk women were removed from the model.
“While it does increase some costs to the health care system to screen everyone and vaccinate those susceptible; overall, it would cost more to not do that because we’re avoiding all of those long-term devastating health outcomes by vaccinating in pregnancy,” Dr. Prabhu said in an interview.
Hepatitis B screening and vaccination for all pregnant women?
Is universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination for pregnant women an upcoming change in prenatal care? In a related editorial, Martina L. Badell, MD, of the division of maternal-fetal medicine and department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, emphasized the hepatitis B vaccine’s safety and effectiveness during pregnancy based on prior studies and compared a universal hepatitis B screening and vaccination program for pregnant women to how clinicians screen universally for rubella as standard of care in this group.
“Owing to the success of rubella vaccination campaigns, today there are fewer than 10 cases of rubella in the United States annually, and, since 2012, all of these cases have been in persons infected when living in or traveling to other countries,” she wrote. “Approximately 850,000 people are living with hepatitis B infection in the United States, and approximately 21,900 acute hepatitis B infections occurred in 2015. Despite the very different prevalence in these infections, we currently screen pregnant and nonpregnant patients for rubella immunity but not hepatitis B.”
If real-world studies bear out that a hepatitis B universal screening and vaccination program is cost effective, guidelines on who should be screened and vaccinated might need to be reconsidered, Dr. Prabhu said. Although following women for decades to see whether hepatitis B screening and vaccination is cost effective is impractical, “a lot of medicine has been predicated on risk-based strategies and risk stratifying, and there is a lot of value to approaching patients like that,” she explained.
How an ob.gyn. determines whether a patient is high risk and qualifies for hepatitis B vaccination under current guidelines is made more complicated by the large amount of information covered in a prenatal visit. There is a “laundry list” of risk factors to consider, and “patients are just meeting you for the first time, and so they may not feel comfortable completely sharing what their risk factors may or may not be,” Dr. Prabhu said. In addition, they may not know the risk factors of their partners.
Under guidelines where all pregnant women are screened and vaccinated for hepatitis B regardless of risk, “it doesn’t harm a woman to check one extra blood test when she’s already having this bevy of blood tests at the first prenatal visit,” she said.
Clinicians may be more aware of the need to add hepatitis B screening to prenatal care given that routine hepatitis C screening for pregnant women was recently released by ACOG as a practice advisory. “I think hepatitis is a little bit more on the forefront of the obstetrician or prenatal care provider’s mind as a result of that recent shift,” she said.
“A lot of women only really access care and access consistent care during their pregnancy, either due to insurance reasons or work reasons. People do things for their developing fetus that they might not do for themselves,” Dr. Prabhu said. “It’s a unique opportunity to have the time to build a relationship, build some trust in the health care system and also educate women about their health and what they can do to keep themselves in good health.
“It’s more than just about the next 9 months and keeping you and your baby safe, so I think there’s a real opportunity for us to think about the public health and the long-term health of a woman.”
One author reported receiving funding from UpToDate; the other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Badell reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Researchers identify growing racial disparity in endometrial cancer mortality
Women in the United States are less likely to die of ovarian cancer, but more likely to die of endometrial cancer than they were 3 decades ago, according to a recent research letter published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“This convergence is because of a steady reduction in the death rate for ovarian cancer, partly because of advances in treatment, alongside a steep increase in the death rate for endometrial cancer,” Rebecca L. Siegel, MPH, corresponding author and senior scientific director of surveillance research at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “Endometrial cancer has not had any major treatment advances in 40 years.”
However, Ms. Siegel and colleagues also found Black women had a twofold higher endometrial cancer–related mortality rate over the same time frame, compared with White women. The disparity in endometrial cancer mortality rates for Black women compared with White women is alarming, the authors said, and might be an underestimate because of a higher rate of hysterectomy among Black women.
The researchers analyzed endometrial and ovarian cancer mortality rates from the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER) with the SEER*Stat software, stratifying the data by whether the person belonged to mutually exclusive racial and ethnic categories of White, Asian or Pacific Islander, Black, or Hispanic. They identified 232,957 women who died from endometrial cancer and 419,085 people who died from ovarian cancer between 1990 and 2019.
Ms. Siegel and colleagues found there was a decrease in ovarian cancer mortality rates between 1990 (9.3 per 100,000 women) and 2019 (6.0 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 22.7%; 95% confidence interval, 23.5%-22.0%). While endometrial cancer mortality decreased between 1990 (4.3 per 100,000 women) and 1997 (4.0 per 100,000 women), it increased between 1997 and 2019 (5.1 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 1.7%; 95% CI, 1.3%-2.1%). When measuring ovarian cancer mortality to endometrial cancer mortality from 1990 (9.3 vs. 4.3 per 100,000), compared with 2019 (6.0 vs. 5.1 per 100,000), there is a significant decline in excess deaths from ovarian cancer.
“Three decades ago, women in the United States were almost twice as likely to die from ovarian cancer as they were to die from endometrial cancer,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. “Today the difference is only 15% higher, or an excess of less than 1 death per of 100,000 women.”
Growing racial disparity in endometrial cancer mortality
While these results persisted for some racial and ethnic subgroups, it did not persist for Black women, who saw an increase in endometrial cancer mortality rate from 7.2 per 100,000 women between 1990 and 1994 to 9.1 per 100,000 women between 2015 and 2019. Compared with White women, there was a significant increase in the mortality rate ratio for uterine cancer for Black women, from 1.83 between 1990 and 1994 (95% CI, 1.77-1.89) to 1.98 between 2015 and 2019 (95% CI, 1.93-2.02) (P < .001).
“Endometrial cancer has one of the largest racial disparities of any cancer. The 5-year relative survival rate for Black women is 63% compared to 84% for White women – a 21% gap in absolute terms. This is largely due to less access to high-quality health care, which is reflected in both later-stage diagnosis and lower survival for every stage of disease,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. Other factors that contribute include lack of guideline-concordant surgical treatment, and increased risk of aggressive tumor subtypes.
Alex A. Francoeur, MD; and Ritu Salani, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who were not involved in the study, said the research by Ms. Siegel and colleagues “highlights growing disparities in uterine cancer between non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White women.”
“Understanding race as a social, not biological construct, and as a proxy for socioeconomic status, is key to understanding this disparity,” said Dr. Francoeur, a third-year ob.gyn. resident at UCLA Health, and Dr. Salani, an Ob.Gyn. News editorial board member. “For example, many studies cite a more advanced stage at diagnosis as an explanation for racial disparities in endometrial cancer; however, this is a substitute for differences in health care access as well as other socioeconomic factors such as income and education.”
Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani also acknowledged other disparities in risk factors may play a role in the differences in endometrial mortality rates such as obesity, which “in non-Hispanic Black women is over 60% greater than non-Hispanic White women.”
In terms of limitations, they noted that SEER’s database is less representative of the population, compared with the United States Cancer Statistics database (36.7% vs. 99%), and that factors such as greater prevalence of hysterectomy may contribute to larger racial disparities.
“Future studies need to examine inequities in treatment by race as well as the importance of health care systems in the stage of diagnosis,” they said.
Ms. Siegel said her team plans to follow the patterns outlined in this analysis and examine factors like cancer subtype, socioeconomic status, and place of residence in the future. “However, health inequalities are rooted in systemic racism, so documentation is necessary but insufficient to effect change, which must occur at the institutional level. A more concerted effort is needed to ensure that every woman receives appropriate treatment, regardless of the color of her skin, and education of providers to reduce racial bias and help increase trust in the health care system should be required.”
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women in the United States are less likely to die of ovarian cancer, but more likely to die of endometrial cancer than they were 3 decades ago, according to a recent research letter published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“This convergence is because of a steady reduction in the death rate for ovarian cancer, partly because of advances in treatment, alongside a steep increase in the death rate for endometrial cancer,” Rebecca L. Siegel, MPH, corresponding author and senior scientific director of surveillance research at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “Endometrial cancer has not had any major treatment advances in 40 years.”
However, Ms. Siegel and colleagues also found Black women had a twofold higher endometrial cancer–related mortality rate over the same time frame, compared with White women. The disparity in endometrial cancer mortality rates for Black women compared with White women is alarming, the authors said, and might be an underestimate because of a higher rate of hysterectomy among Black women.
The researchers analyzed endometrial and ovarian cancer mortality rates from the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER) with the SEER*Stat software, stratifying the data by whether the person belonged to mutually exclusive racial and ethnic categories of White, Asian or Pacific Islander, Black, or Hispanic. They identified 232,957 women who died from endometrial cancer and 419,085 people who died from ovarian cancer between 1990 and 2019.
Ms. Siegel and colleagues found there was a decrease in ovarian cancer mortality rates between 1990 (9.3 per 100,000 women) and 2019 (6.0 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 22.7%; 95% confidence interval, 23.5%-22.0%). While endometrial cancer mortality decreased between 1990 (4.3 per 100,000 women) and 1997 (4.0 per 100,000 women), it increased between 1997 and 2019 (5.1 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 1.7%; 95% CI, 1.3%-2.1%). When measuring ovarian cancer mortality to endometrial cancer mortality from 1990 (9.3 vs. 4.3 per 100,000), compared with 2019 (6.0 vs. 5.1 per 100,000), there is a significant decline in excess deaths from ovarian cancer.
“Three decades ago, women in the United States were almost twice as likely to die from ovarian cancer as they were to die from endometrial cancer,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. “Today the difference is only 15% higher, or an excess of less than 1 death per of 100,000 women.”
Growing racial disparity in endometrial cancer mortality
While these results persisted for some racial and ethnic subgroups, it did not persist for Black women, who saw an increase in endometrial cancer mortality rate from 7.2 per 100,000 women between 1990 and 1994 to 9.1 per 100,000 women between 2015 and 2019. Compared with White women, there was a significant increase in the mortality rate ratio for uterine cancer for Black women, from 1.83 between 1990 and 1994 (95% CI, 1.77-1.89) to 1.98 between 2015 and 2019 (95% CI, 1.93-2.02) (P < .001).
“Endometrial cancer has one of the largest racial disparities of any cancer. The 5-year relative survival rate for Black women is 63% compared to 84% for White women – a 21% gap in absolute terms. This is largely due to less access to high-quality health care, which is reflected in both later-stage diagnosis and lower survival for every stage of disease,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. Other factors that contribute include lack of guideline-concordant surgical treatment, and increased risk of aggressive tumor subtypes.
Alex A. Francoeur, MD; and Ritu Salani, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who were not involved in the study, said the research by Ms. Siegel and colleagues “highlights growing disparities in uterine cancer between non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White women.”
“Understanding race as a social, not biological construct, and as a proxy for socioeconomic status, is key to understanding this disparity,” said Dr. Francoeur, a third-year ob.gyn. resident at UCLA Health, and Dr. Salani, an Ob.Gyn. News editorial board member. “For example, many studies cite a more advanced stage at diagnosis as an explanation for racial disparities in endometrial cancer; however, this is a substitute for differences in health care access as well as other socioeconomic factors such as income and education.”
Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani also acknowledged other disparities in risk factors may play a role in the differences in endometrial mortality rates such as obesity, which “in non-Hispanic Black women is over 60% greater than non-Hispanic White women.”
In terms of limitations, they noted that SEER’s database is less representative of the population, compared with the United States Cancer Statistics database (36.7% vs. 99%), and that factors such as greater prevalence of hysterectomy may contribute to larger racial disparities.
“Future studies need to examine inequities in treatment by race as well as the importance of health care systems in the stage of diagnosis,” they said.
Ms. Siegel said her team plans to follow the patterns outlined in this analysis and examine factors like cancer subtype, socioeconomic status, and place of residence in the future. “However, health inequalities are rooted in systemic racism, so documentation is necessary but insufficient to effect change, which must occur at the institutional level. A more concerted effort is needed to ensure that every woman receives appropriate treatment, regardless of the color of her skin, and education of providers to reduce racial bias and help increase trust in the health care system should be required.”
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Women in the United States are less likely to die of ovarian cancer, but more likely to die of endometrial cancer than they were 3 decades ago, according to a recent research letter published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“This convergence is because of a steady reduction in the death rate for ovarian cancer, partly because of advances in treatment, alongside a steep increase in the death rate for endometrial cancer,” Rebecca L. Siegel, MPH, corresponding author and senior scientific director of surveillance research at the American Cancer Society, said in an interview. “Endometrial cancer has not had any major treatment advances in 40 years.”
However, Ms. Siegel and colleagues also found Black women had a twofold higher endometrial cancer–related mortality rate over the same time frame, compared with White women. The disparity in endometrial cancer mortality rates for Black women compared with White women is alarming, the authors said, and might be an underestimate because of a higher rate of hysterectomy among Black women.
The researchers analyzed endometrial and ovarian cancer mortality rates from the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER) with the SEER*Stat software, stratifying the data by whether the person belonged to mutually exclusive racial and ethnic categories of White, Asian or Pacific Islander, Black, or Hispanic. They identified 232,957 women who died from endometrial cancer and 419,085 people who died from ovarian cancer between 1990 and 2019.
Ms. Siegel and colleagues found there was a decrease in ovarian cancer mortality rates between 1990 (9.3 per 100,000 women) and 2019 (6.0 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 22.7%; 95% confidence interval, 23.5%-22.0%). While endometrial cancer mortality decreased between 1990 (4.3 per 100,000 women) and 1997 (4.0 per 100,000 women), it increased between 1997 and 2019 (5.1 per 100,000 women) (average annual percent change, 1.7%; 95% CI, 1.3%-2.1%). When measuring ovarian cancer mortality to endometrial cancer mortality from 1990 (9.3 vs. 4.3 per 100,000), compared with 2019 (6.0 vs. 5.1 per 100,000), there is a significant decline in excess deaths from ovarian cancer.
“Three decades ago, women in the United States were almost twice as likely to die from ovarian cancer as they were to die from endometrial cancer,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. “Today the difference is only 15% higher, or an excess of less than 1 death per of 100,000 women.”
Growing racial disparity in endometrial cancer mortality
While these results persisted for some racial and ethnic subgroups, it did not persist for Black women, who saw an increase in endometrial cancer mortality rate from 7.2 per 100,000 women between 1990 and 1994 to 9.1 per 100,000 women between 2015 and 2019. Compared with White women, there was a significant increase in the mortality rate ratio for uterine cancer for Black women, from 1.83 between 1990 and 1994 (95% CI, 1.77-1.89) to 1.98 between 2015 and 2019 (95% CI, 1.93-2.02) (P < .001).
“Endometrial cancer has one of the largest racial disparities of any cancer. The 5-year relative survival rate for Black women is 63% compared to 84% for White women – a 21% gap in absolute terms. This is largely due to less access to high-quality health care, which is reflected in both later-stage diagnosis and lower survival for every stage of disease,” Ms. Siegel said in an interview. Other factors that contribute include lack of guideline-concordant surgical treatment, and increased risk of aggressive tumor subtypes.
Alex A. Francoeur, MD; and Ritu Salani, MD, MBA, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who were not involved in the study, said the research by Ms. Siegel and colleagues “highlights growing disparities in uterine cancer between non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White women.”
“Understanding race as a social, not biological construct, and as a proxy for socioeconomic status, is key to understanding this disparity,” said Dr. Francoeur, a third-year ob.gyn. resident at UCLA Health, and Dr. Salani, an Ob.Gyn. News editorial board member. “For example, many studies cite a more advanced stage at diagnosis as an explanation for racial disparities in endometrial cancer; however, this is a substitute for differences in health care access as well as other socioeconomic factors such as income and education.”
Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani also acknowledged other disparities in risk factors may play a role in the differences in endometrial mortality rates such as obesity, which “in non-Hispanic Black women is over 60% greater than non-Hispanic White women.”
In terms of limitations, they noted that SEER’s database is less representative of the population, compared with the United States Cancer Statistics database (36.7% vs. 99%), and that factors such as greater prevalence of hysterectomy may contribute to larger racial disparities.
“Future studies need to examine inequities in treatment by race as well as the importance of health care systems in the stage of diagnosis,” they said.
Ms. Siegel said her team plans to follow the patterns outlined in this analysis and examine factors like cancer subtype, socioeconomic status, and place of residence in the future. “However, health inequalities are rooted in systemic racism, so documentation is necessary but insufficient to effect change, which must occur at the institutional level. A more concerted effort is needed to ensure that every woman receives appropriate treatment, regardless of the color of her skin, and education of providers to reduce racial bias and help increase trust in the health care system should be required.”
The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Francoeur and Dr. Salani reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Rituximab and COVID-19 vaccines: Studies begin to answer key questions
Rituximab has presented something of a conundrum for patients taking the monoclonal antibody during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Used to manage a variety of autoimmune diseases and cancers, rituximab acts against CD20 proteins expressed on the surface of B cells, causing B-cell depletion. However, it is this B-cell depletion that may put these patients at greater risk of COVID-19 development, progression to more severe disease, and in-hospital mortality. Evidence for this appears to be mixed, with studies showing both that patients using rituximab to manage various diseases are and are not at increased risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 progression, and mortality.
As COVID-19 vaccine rollouts take place across the world, more questions have been raised about the relationship between B-cell depletion from anti-CD20 therapies and COVID-19 vaccines. Do rituximab and other anti-CD20 therapies affect a patient’s response to COVID-19 vaccines? If this is the case, does the timing of anti-CD20 treatment matter to maximize B-cell levels and improve the vaccine’s effectiveness? And how do COVID-19 vaccine booster doses factor into the equation?
Humoral and cell-mediated responses following COVID-19 vaccination
First, the bad news: The vaccine is unquestionably safe to administer in patients taking rituximab, but one thing that has been well established is that antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination in these individuals does is reduced. This isn’t entirely unprecedented, as previous studies have shown a weakened immune response to pneumococcal polysaccharide and keyhole limpet hemocyanin vaccines among patients taking rituximab.
“Compromised immunogenicity to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines has been demonstrated in rituximab-treated patients, which is of particular concern given the observation that B-cell–depleting therapies may be associated with worse COVID outcomes,” Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma, Vasculitis, and Myositis Center at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
For example, in a recent study from the Medical University of Vienna, 29 (39%) of 74 patients receiving rituximab (43% as monotherapy, 57% with conventional-synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) who were vaccinated with either the Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) or Spikevax (Moderna) COVID-19 vaccine achieved seroconversion, compared with 100% of patients in a healthy control group, and all but 1 patient without detectable CD19+ peripheral B cells did not develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain antibodies.
“There is an increasing number of studies in this field, and they confirm that patients treated with rituximab and other anti-CD20 agents have severely reduced serological responses to COVID-19 vaccines,” Ingrid Jyssum, MD, of the division of rheumatology and research at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, said in an interview.
One silver lining is that patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies appear to have a cell-mediated response following vaccination even if they don’t develop SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. “Studies that also investigate T-cell responses are starting to emerge, and so far, they show that, even if the patients do not have antibodies, they may have T-cell responses,” Dr. Jyssum said.
One study of 24 patients with autoimmune diseases taking rituximab that evaluated humoral and T-cell responses following vaccination with the Comirnaty vaccine found that none had a humoral response to the vaccine, but the T-cell response from that group did not significantly differ from 35 patients receiving other immunosuppressants and 26 patients in a healthy control group. In another study of rituximab- or ocrelizumab-treated patients who received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, 69.4% developed SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, compared with a control group, but 96.2% of patients taking ocrelizumab and 81.8% of patients taking rituximab mounted a spike-specific CD8+ T-cell response, compared with 66.7% in the control group, and there were comparable rates (85%-90%) of spike-specific CD4+ T cells in all groups. In the study from the Medical University of Vienna, T-cell response was detected in rituximab-treated patients who both did and did not mount an antibody response.
The clinical relevance of how a blunted humoral immune response but a respectable T-cell response to COVID-19 vaccines affects patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said.
While these data are reassuring, they’re also incomplete, Dr. Spiera noted. “The ultimate outcome of relevance to assess vaccine efficacy is protection from COVID and from severe outcomes of COVID infection (i.e., hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, death). That data will require assessment of very large numbers of rituximab-treated vaccinated patients to be compared with rituximab-treated unvaccinated patients, and is unlikely to be forthcoming in the very near future.
“In the meantime, however, achieving serologic positivity, meaning having evidence of serologic as well as cellular immunity following vaccination, is a desired outcome, and likely implies more robust immunity.”
Does treatment timing impact COVID-19 vaccine response?
Given enough time, B-cell reconstitution will occur in patients taking rituximab. With that in mind, is it beneficial to wait a certain amount of time after a patient has stopped rituximab therapy or time since their last dose before giving them a COVID-19 vaccine? In their guidance on COVID-19 vaccines for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, the American College of Rheumatology said there is moderate evidence to consider “optimal timing of dosing and vaccination with the rheumatology provider before proceeding.”
“Guidelines and preliminary studies of serologic response to COVID vaccine in rituximab-treated patients have suggested that longer time from last rituximab exposure is associated with a greater likelihood of a serologic response,” Dr. Spiera said.
In a brief report published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Spiera and colleagues performed a retrospective chart review of 56 patients with varying levels of last exposure to rituximab who received a COVID-19 vaccine. Their results showed that, when patients were vaccinated 6-12 months after the last rituximab dose, 55% were seronegative, and when this was more than 12 months, only 13% were seronegative, compared with seronegativity in 86% who were vaccinated less than 6 months after their last rituximab dose.
The RituxiVac trial, conducted by researchers in Switzerland, also examined vaccine responses of 96 rituximab-treated patients who received Comirnaty or Spikevax; results recently published in The Lancet Rheumatology showed findings similar to other studies, with reduced humoral and cell-mediated responses. In the RituxiVac trial, the median time to last anti-CD20 treatment was 1.07 years.
“The typical interval between rituximab doses [for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis] is typically 6 months, and this has become widely used as the interval from last rituximab to time of COVID vaccination, with a recommendation to wait 4 weeks (if possible) from time of vaccination until the next rituximab administration,” Dr. Spiera explained. However, this window seems to vary depending on the study.
Recent research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates B-cell levels could be a relevant indicator for humoral and cell-mediated response in patients with rheumatic diseases treated with rituximab, with a level of 10 B cells/mcL (0.4% of lymphocytes) identified as one potential marker for likely seroconversion following COVID-19 vaccination.
“In some smaller case series, it has been further recognized that rituximab-treated patients who were beginning to reconstitute peripheral B cells were most likely to respond serologically. Our present study confirmed those findings, demonstrating that the presence of detectable B cells was strongly associated with vaccine responsiveness, and affords complementary information to time from last [rituximab dose] in informing the likelihood of a vaccine response,” Dr. Spiera said.
However, the literature is limited in this area, and an exact cutoff for B-cell counts in these patients isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said. A better metric is time away from anti-CD20 therapies, with CD19 cell count being highly correlated with last infusion.
Dr. Spiera agreed that there is no consistent B-cell percentage that works as a cutoff. “In our study, we looked at it as a binary variable, although we did find that a higher percentage of B cells in the peripheral lymphocyte population was associated with a higher likelihood of seroconversion. We did not, however, identify a ‘threshold’ for vaccine serologic responsiveness.”
Should clinicians measure antibodies?
The Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have recommended that health care providers and the public not use COVID-19 antibody tests as a way to gauge immunity after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and after receiving a COVID-19 vaccination. The ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases strongly recommends against ordering antibody tests for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases as a way to measure immunity.
“Generally, such measurements are not recommended as the clinical correlate of various antibody levels are not known,” Dr. Jyssum said. “With regular infusions of rituximab or other anti-CD20 agents, one cannot expect that these patients will develop significant levels of antibodies.”
However, she said there might be situations where it’s useful to know whether a patient has developed antibodies at all. “Assessing the significance of specific antibody levels is difficult, and the subject of scientific studies. Patients lacking a humoral vaccine response are left to rely on their T-cell responses and on infectious control measures to prevent disease.”
Dr. Spiera said he disagreed with guidelines recommending against checking antibody levels after vaccination, “particularly in patients treated with immunosuppressive medications that might be expected to blunt their serologic response to the vaccines.
“Although we cannot be sure what level of measurable antibodies offer what level of protection, most clinicians would agree that patients who demonstrate no detectable antibodies (which is a common finding in rituximab-treated patients) should be considered at higher risk,” he said. “Indeed, recommendations regarding booster vaccine administration in general was initially based on the observation of declining antibody levels with longer time from vaccination.”
Do COVID-19 vaccine boosters help patients on anti-CD20 therapy?
As of January 2022, the FDA and CDC have recommended a third primary series shot of COVID-19 vaccines for some moderately to severely immunocompromised patients as young as 5 years old (for Comirnaty vaccine) or a booster shot of either Comirnaty or Spikevax for everyone aged 12 years and older, including immunocompromised people, while the ACR goes into more detail and recommends clinicians time a patient’s booster shot with temporary treatment interruption.
In The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Jyssum and colleagues recently published results from the prospective Nor-vaC study examining the humoral and cell-mediated immune responses of 87 patients with RA being treated with rituximab who received the Comirnaty, Spikevax, or Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) COVID-19 vaccines; of these, 49 patients received a booster dose at a median of 70 days after completing their primary series. The results showed 19 patients (28.1%) had a serologic response after their primary series, while 8 of 49 patients (16.3%) who received their booster dose had a serologic response.
All patients who received a third dose in the study had a T-cell response, Dr. Jyssum said. “This is reassuring for patients and clinicians. T cells have been found to be important in countering COVID-19 disease, but whether we can rely on the T-cell response alone in the absence of antibodies to protect patients from infection or from serious COVID disease is still not determined,” she said.
When asked if she would recommend COVID-19 vaccine booster doses for patients on rituximab, Dr. Jyssum replied: “Absolutely.”
Another study, recently published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, examined heterologous and homologous booster doses for 60 patients receiving rituximab without seroconversion after their COVID-19 vaccine primary series. The results showed no significant difference in new seroconversion at 4 weeks based on whether the patient received a vector or mRNA vaccine (22% vs. 32%), but all patients who received a booster dose with a vector vaccine had specific T-cell responses, compared with 81% of patients who received an mRNA vaccine booster. There was a new humoral and/or cellular response in 9 of 11 patients (82%), and most patients with peripheral B cells (12 of 18 patients; 67%) achieved seroconversion.
“Our data show that a cellular and/or humoral immune response can be achieved on a third COVID-19 vaccination in most of the patients who initially developed neither a humoral nor a cellular immune response,” the researchers concluded. “The efficacy data together with the safety data seen in our trial provide a favorable risk/benefit ratio and support the implementation of a third vaccination for nonseroconverted high-risk autoimmune disease patients treated with B-cell–depleting agents.”
Dr. Spiera said booster doses are an important part of the equation, and “it is important to consider factors that would be associated with a greater likelihood of achieving a serologic response, particularly in those patients who did not demonstrate a serologic response to the initial vaccines series.
“Preliminary data shows that the beginnings of B-cell reconstitution is also associated with a positive serologic response following a booster of the COVID-19 vaccine,” he said.
The authors of the cited studies reported numerous relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Spiera and Dr. Jyssum reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Rituximab has presented something of a conundrum for patients taking the monoclonal antibody during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Used to manage a variety of autoimmune diseases and cancers, rituximab acts against CD20 proteins expressed on the surface of B cells, causing B-cell depletion. However, it is this B-cell depletion that may put these patients at greater risk of COVID-19 development, progression to more severe disease, and in-hospital mortality. Evidence for this appears to be mixed, with studies showing both that patients using rituximab to manage various diseases are and are not at increased risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 progression, and mortality.
As COVID-19 vaccine rollouts take place across the world, more questions have been raised about the relationship between B-cell depletion from anti-CD20 therapies and COVID-19 vaccines. Do rituximab and other anti-CD20 therapies affect a patient’s response to COVID-19 vaccines? If this is the case, does the timing of anti-CD20 treatment matter to maximize B-cell levels and improve the vaccine’s effectiveness? And how do COVID-19 vaccine booster doses factor into the equation?
Humoral and cell-mediated responses following COVID-19 vaccination
First, the bad news: The vaccine is unquestionably safe to administer in patients taking rituximab, but one thing that has been well established is that antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination in these individuals does is reduced. This isn’t entirely unprecedented, as previous studies have shown a weakened immune response to pneumococcal polysaccharide and keyhole limpet hemocyanin vaccines among patients taking rituximab.
“Compromised immunogenicity to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines has been demonstrated in rituximab-treated patients, which is of particular concern given the observation that B-cell–depleting therapies may be associated with worse COVID outcomes,” Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma, Vasculitis, and Myositis Center at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
For example, in a recent study from the Medical University of Vienna, 29 (39%) of 74 patients receiving rituximab (43% as monotherapy, 57% with conventional-synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) who were vaccinated with either the Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) or Spikevax (Moderna) COVID-19 vaccine achieved seroconversion, compared with 100% of patients in a healthy control group, and all but 1 patient without detectable CD19+ peripheral B cells did not develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain antibodies.
“There is an increasing number of studies in this field, and they confirm that patients treated with rituximab and other anti-CD20 agents have severely reduced serological responses to COVID-19 vaccines,” Ingrid Jyssum, MD, of the division of rheumatology and research at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, said in an interview.
One silver lining is that patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies appear to have a cell-mediated response following vaccination even if they don’t develop SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. “Studies that also investigate T-cell responses are starting to emerge, and so far, they show that, even if the patients do not have antibodies, they may have T-cell responses,” Dr. Jyssum said.
One study of 24 patients with autoimmune diseases taking rituximab that evaluated humoral and T-cell responses following vaccination with the Comirnaty vaccine found that none had a humoral response to the vaccine, but the T-cell response from that group did not significantly differ from 35 patients receiving other immunosuppressants and 26 patients in a healthy control group. In another study of rituximab- or ocrelizumab-treated patients who received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, 69.4% developed SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, compared with a control group, but 96.2% of patients taking ocrelizumab and 81.8% of patients taking rituximab mounted a spike-specific CD8+ T-cell response, compared with 66.7% in the control group, and there were comparable rates (85%-90%) of spike-specific CD4+ T cells in all groups. In the study from the Medical University of Vienna, T-cell response was detected in rituximab-treated patients who both did and did not mount an antibody response.
The clinical relevance of how a blunted humoral immune response but a respectable T-cell response to COVID-19 vaccines affects patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said.
While these data are reassuring, they’re also incomplete, Dr. Spiera noted. “The ultimate outcome of relevance to assess vaccine efficacy is protection from COVID and from severe outcomes of COVID infection (i.e., hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, death). That data will require assessment of very large numbers of rituximab-treated vaccinated patients to be compared with rituximab-treated unvaccinated patients, and is unlikely to be forthcoming in the very near future.
“In the meantime, however, achieving serologic positivity, meaning having evidence of serologic as well as cellular immunity following vaccination, is a desired outcome, and likely implies more robust immunity.”
Does treatment timing impact COVID-19 vaccine response?
Given enough time, B-cell reconstitution will occur in patients taking rituximab. With that in mind, is it beneficial to wait a certain amount of time after a patient has stopped rituximab therapy or time since their last dose before giving them a COVID-19 vaccine? In their guidance on COVID-19 vaccines for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, the American College of Rheumatology said there is moderate evidence to consider “optimal timing of dosing and vaccination with the rheumatology provider before proceeding.”
“Guidelines and preliminary studies of serologic response to COVID vaccine in rituximab-treated patients have suggested that longer time from last rituximab exposure is associated with a greater likelihood of a serologic response,” Dr. Spiera said.
In a brief report published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Spiera and colleagues performed a retrospective chart review of 56 patients with varying levels of last exposure to rituximab who received a COVID-19 vaccine. Their results showed that, when patients were vaccinated 6-12 months after the last rituximab dose, 55% were seronegative, and when this was more than 12 months, only 13% were seronegative, compared with seronegativity in 86% who were vaccinated less than 6 months after their last rituximab dose.
The RituxiVac trial, conducted by researchers in Switzerland, also examined vaccine responses of 96 rituximab-treated patients who received Comirnaty or Spikevax; results recently published in The Lancet Rheumatology showed findings similar to other studies, with reduced humoral and cell-mediated responses. In the RituxiVac trial, the median time to last anti-CD20 treatment was 1.07 years.
“The typical interval between rituximab doses [for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis] is typically 6 months, and this has become widely used as the interval from last rituximab to time of COVID vaccination, with a recommendation to wait 4 weeks (if possible) from time of vaccination until the next rituximab administration,” Dr. Spiera explained. However, this window seems to vary depending on the study.
Recent research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates B-cell levels could be a relevant indicator for humoral and cell-mediated response in patients with rheumatic diseases treated with rituximab, with a level of 10 B cells/mcL (0.4% of lymphocytes) identified as one potential marker for likely seroconversion following COVID-19 vaccination.
“In some smaller case series, it has been further recognized that rituximab-treated patients who were beginning to reconstitute peripheral B cells were most likely to respond serologically. Our present study confirmed those findings, demonstrating that the presence of detectable B cells was strongly associated with vaccine responsiveness, and affords complementary information to time from last [rituximab dose] in informing the likelihood of a vaccine response,” Dr. Spiera said.
However, the literature is limited in this area, and an exact cutoff for B-cell counts in these patients isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said. A better metric is time away from anti-CD20 therapies, with CD19 cell count being highly correlated with last infusion.
Dr. Spiera agreed that there is no consistent B-cell percentage that works as a cutoff. “In our study, we looked at it as a binary variable, although we did find that a higher percentage of B cells in the peripheral lymphocyte population was associated with a higher likelihood of seroconversion. We did not, however, identify a ‘threshold’ for vaccine serologic responsiveness.”
Should clinicians measure antibodies?
The Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have recommended that health care providers and the public not use COVID-19 antibody tests as a way to gauge immunity after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and after receiving a COVID-19 vaccination. The ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases strongly recommends against ordering antibody tests for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases as a way to measure immunity.
“Generally, such measurements are not recommended as the clinical correlate of various antibody levels are not known,” Dr. Jyssum said. “With regular infusions of rituximab or other anti-CD20 agents, one cannot expect that these patients will develop significant levels of antibodies.”
However, she said there might be situations where it’s useful to know whether a patient has developed antibodies at all. “Assessing the significance of specific antibody levels is difficult, and the subject of scientific studies. Patients lacking a humoral vaccine response are left to rely on their T-cell responses and on infectious control measures to prevent disease.”
Dr. Spiera said he disagreed with guidelines recommending against checking antibody levels after vaccination, “particularly in patients treated with immunosuppressive medications that might be expected to blunt their serologic response to the vaccines.
“Although we cannot be sure what level of measurable antibodies offer what level of protection, most clinicians would agree that patients who demonstrate no detectable antibodies (which is a common finding in rituximab-treated patients) should be considered at higher risk,” he said. “Indeed, recommendations regarding booster vaccine administration in general was initially based on the observation of declining antibody levels with longer time from vaccination.”
Do COVID-19 vaccine boosters help patients on anti-CD20 therapy?
As of January 2022, the FDA and CDC have recommended a third primary series shot of COVID-19 vaccines for some moderately to severely immunocompromised patients as young as 5 years old (for Comirnaty vaccine) or a booster shot of either Comirnaty or Spikevax for everyone aged 12 years and older, including immunocompromised people, while the ACR goes into more detail and recommends clinicians time a patient’s booster shot with temporary treatment interruption.
In The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Jyssum and colleagues recently published results from the prospective Nor-vaC study examining the humoral and cell-mediated immune responses of 87 patients with RA being treated with rituximab who received the Comirnaty, Spikevax, or Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) COVID-19 vaccines; of these, 49 patients received a booster dose at a median of 70 days after completing their primary series. The results showed 19 patients (28.1%) had a serologic response after their primary series, while 8 of 49 patients (16.3%) who received their booster dose had a serologic response.
All patients who received a third dose in the study had a T-cell response, Dr. Jyssum said. “This is reassuring for patients and clinicians. T cells have been found to be important in countering COVID-19 disease, but whether we can rely on the T-cell response alone in the absence of antibodies to protect patients from infection or from serious COVID disease is still not determined,” she said.
When asked if she would recommend COVID-19 vaccine booster doses for patients on rituximab, Dr. Jyssum replied: “Absolutely.”
Another study, recently published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, examined heterologous and homologous booster doses for 60 patients receiving rituximab without seroconversion after their COVID-19 vaccine primary series. The results showed no significant difference in new seroconversion at 4 weeks based on whether the patient received a vector or mRNA vaccine (22% vs. 32%), but all patients who received a booster dose with a vector vaccine had specific T-cell responses, compared with 81% of patients who received an mRNA vaccine booster. There was a new humoral and/or cellular response in 9 of 11 patients (82%), and most patients with peripheral B cells (12 of 18 patients; 67%) achieved seroconversion.
“Our data show that a cellular and/or humoral immune response can be achieved on a third COVID-19 vaccination in most of the patients who initially developed neither a humoral nor a cellular immune response,” the researchers concluded. “The efficacy data together with the safety data seen in our trial provide a favorable risk/benefit ratio and support the implementation of a third vaccination for nonseroconverted high-risk autoimmune disease patients treated with B-cell–depleting agents.”
Dr. Spiera said booster doses are an important part of the equation, and “it is important to consider factors that would be associated with a greater likelihood of achieving a serologic response, particularly in those patients who did not demonstrate a serologic response to the initial vaccines series.
“Preliminary data shows that the beginnings of B-cell reconstitution is also associated with a positive serologic response following a booster of the COVID-19 vaccine,” he said.
The authors of the cited studies reported numerous relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Spiera and Dr. Jyssum reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Rituximab has presented something of a conundrum for patients taking the monoclonal antibody during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Used to manage a variety of autoimmune diseases and cancers, rituximab acts against CD20 proteins expressed on the surface of B cells, causing B-cell depletion. However, it is this B-cell depletion that may put these patients at greater risk of COVID-19 development, progression to more severe disease, and in-hospital mortality. Evidence for this appears to be mixed, with studies showing both that patients using rituximab to manage various diseases are and are not at increased risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 progression, and mortality.
As COVID-19 vaccine rollouts take place across the world, more questions have been raised about the relationship between B-cell depletion from anti-CD20 therapies and COVID-19 vaccines. Do rituximab and other anti-CD20 therapies affect a patient’s response to COVID-19 vaccines? If this is the case, does the timing of anti-CD20 treatment matter to maximize B-cell levels and improve the vaccine’s effectiveness? And how do COVID-19 vaccine booster doses factor into the equation?
Humoral and cell-mediated responses following COVID-19 vaccination
First, the bad news: The vaccine is unquestionably safe to administer in patients taking rituximab, but one thing that has been well established is that antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination in these individuals does is reduced. This isn’t entirely unprecedented, as previous studies have shown a weakened immune response to pneumococcal polysaccharide and keyhole limpet hemocyanin vaccines among patients taking rituximab.
“Compromised immunogenicity to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines has been demonstrated in rituximab-treated patients, which is of particular concern given the observation that B-cell–depleting therapies may be associated with worse COVID outcomes,” Robert F. Spiera, MD, director of the Scleroderma, Vasculitis, and Myositis Center at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview.
For example, in a recent study from the Medical University of Vienna, 29 (39%) of 74 patients receiving rituximab (43% as monotherapy, 57% with conventional-synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) who were vaccinated with either the Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) or Spikevax (Moderna) COVID-19 vaccine achieved seroconversion, compared with 100% of patients in a healthy control group, and all but 1 patient without detectable CD19+ peripheral B cells did not develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain antibodies.
“There is an increasing number of studies in this field, and they confirm that patients treated with rituximab and other anti-CD20 agents have severely reduced serological responses to COVID-19 vaccines,” Ingrid Jyssum, MD, of the division of rheumatology and research at Diakonhjemmet Hospital in Oslo, said in an interview.
One silver lining is that patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies appear to have a cell-mediated response following vaccination even if they don’t develop SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. “Studies that also investigate T-cell responses are starting to emerge, and so far, they show that, even if the patients do not have antibodies, they may have T-cell responses,” Dr. Jyssum said.
One study of 24 patients with autoimmune diseases taking rituximab that evaluated humoral and T-cell responses following vaccination with the Comirnaty vaccine found that none had a humoral response to the vaccine, but the T-cell response from that group did not significantly differ from 35 patients receiving other immunosuppressants and 26 patients in a healthy control group. In another study of rituximab- or ocrelizumab-treated patients who received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, 69.4% developed SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, compared with a control group, but 96.2% of patients taking ocrelizumab and 81.8% of patients taking rituximab mounted a spike-specific CD8+ T-cell response, compared with 66.7% in the control group, and there were comparable rates (85%-90%) of spike-specific CD4+ T cells in all groups. In the study from the Medical University of Vienna, T-cell response was detected in rituximab-treated patients who both did and did not mount an antibody response.
The clinical relevance of how a blunted humoral immune response but a respectable T-cell response to COVID-19 vaccines affects patients treated with anti-CD20 therapies isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said.
While these data are reassuring, they’re also incomplete, Dr. Spiera noted. “The ultimate outcome of relevance to assess vaccine efficacy is protection from COVID and from severe outcomes of COVID infection (i.e., hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, death). That data will require assessment of very large numbers of rituximab-treated vaccinated patients to be compared with rituximab-treated unvaccinated patients, and is unlikely to be forthcoming in the very near future.
“In the meantime, however, achieving serologic positivity, meaning having evidence of serologic as well as cellular immunity following vaccination, is a desired outcome, and likely implies more robust immunity.”
Does treatment timing impact COVID-19 vaccine response?
Given enough time, B-cell reconstitution will occur in patients taking rituximab. With that in mind, is it beneficial to wait a certain amount of time after a patient has stopped rituximab therapy or time since their last dose before giving them a COVID-19 vaccine? In their guidance on COVID-19 vaccines for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, the American College of Rheumatology said there is moderate evidence to consider “optimal timing of dosing and vaccination with the rheumatology provider before proceeding.”
“Guidelines and preliminary studies of serologic response to COVID vaccine in rituximab-treated patients have suggested that longer time from last rituximab exposure is associated with a greater likelihood of a serologic response,” Dr. Spiera said.
In a brief report published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Spiera and colleagues performed a retrospective chart review of 56 patients with varying levels of last exposure to rituximab who received a COVID-19 vaccine. Their results showed that, when patients were vaccinated 6-12 months after the last rituximab dose, 55% were seronegative, and when this was more than 12 months, only 13% were seronegative, compared with seronegativity in 86% who were vaccinated less than 6 months after their last rituximab dose.
The RituxiVac trial, conducted by researchers in Switzerland, also examined vaccine responses of 96 rituximab-treated patients who received Comirnaty or Spikevax; results recently published in The Lancet Rheumatology showed findings similar to other studies, with reduced humoral and cell-mediated responses. In the RituxiVac trial, the median time to last anti-CD20 treatment was 1.07 years.
“The typical interval between rituximab doses [for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for remission maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis] is typically 6 months, and this has become widely used as the interval from last rituximab to time of COVID vaccination, with a recommendation to wait 4 weeks (if possible) from time of vaccination until the next rituximab administration,” Dr. Spiera explained. However, this window seems to vary depending on the study.
Recent research published in Arthritis & Rheumatology indicates B-cell levels could be a relevant indicator for humoral and cell-mediated response in patients with rheumatic diseases treated with rituximab, with a level of 10 B cells/mcL (0.4% of lymphocytes) identified as one potential marker for likely seroconversion following COVID-19 vaccination.
“In some smaller case series, it has been further recognized that rituximab-treated patients who were beginning to reconstitute peripheral B cells were most likely to respond serologically. Our present study confirmed those findings, demonstrating that the presence of detectable B cells was strongly associated with vaccine responsiveness, and affords complementary information to time from last [rituximab dose] in informing the likelihood of a vaccine response,” Dr. Spiera said.
However, the literature is limited in this area, and an exact cutoff for B-cell counts in these patients isn’t currently known, Dr. Jyssum said. A better metric is time away from anti-CD20 therapies, with CD19 cell count being highly correlated with last infusion.
Dr. Spiera agreed that there is no consistent B-cell percentage that works as a cutoff. “In our study, we looked at it as a binary variable, although we did find that a higher percentage of B cells in the peripheral lymphocyte population was associated with a higher likelihood of seroconversion. We did not, however, identify a ‘threshold’ for vaccine serologic responsiveness.”
Should clinicians measure antibodies?
The Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have recommended that health care providers and the public not use COVID-19 antibody tests as a way to gauge immunity after exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and after receiving a COVID-19 vaccination. The ACR’s guidance on COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases strongly recommends against ordering antibody tests for patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases as a way to measure immunity.
“Generally, such measurements are not recommended as the clinical correlate of various antibody levels are not known,” Dr. Jyssum said. “With regular infusions of rituximab or other anti-CD20 agents, one cannot expect that these patients will develop significant levels of antibodies.”
However, she said there might be situations where it’s useful to know whether a patient has developed antibodies at all. “Assessing the significance of specific antibody levels is difficult, and the subject of scientific studies. Patients lacking a humoral vaccine response are left to rely on their T-cell responses and on infectious control measures to prevent disease.”
Dr. Spiera said he disagreed with guidelines recommending against checking antibody levels after vaccination, “particularly in patients treated with immunosuppressive medications that might be expected to blunt their serologic response to the vaccines.
“Although we cannot be sure what level of measurable antibodies offer what level of protection, most clinicians would agree that patients who demonstrate no detectable antibodies (which is a common finding in rituximab-treated patients) should be considered at higher risk,” he said. “Indeed, recommendations regarding booster vaccine administration in general was initially based on the observation of declining antibody levels with longer time from vaccination.”
Do COVID-19 vaccine boosters help patients on anti-CD20 therapy?
As of January 2022, the FDA and CDC have recommended a third primary series shot of COVID-19 vaccines for some moderately to severely immunocompromised patients as young as 5 years old (for Comirnaty vaccine) or a booster shot of either Comirnaty or Spikevax for everyone aged 12 years and older, including immunocompromised people, while the ACR goes into more detail and recommends clinicians time a patient’s booster shot with temporary treatment interruption.
In The Lancet Rheumatology, Dr. Jyssum and colleagues recently published results from the prospective Nor-vaC study examining the humoral and cell-mediated immune responses of 87 patients with RA being treated with rituximab who received the Comirnaty, Spikevax, or Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) COVID-19 vaccines; of these, 49 patients received a booster dose at a median of 70 days after completing their primary series. The results showed 19 patients (28.1%) had a serologic response after their primary series, while 8 of 49 patients (16.3%) who received their booster dose had a serologic response.
All patients who received a third dose in the study had a T-cell response, Dr. Jyssum said. “This is reassuring for patients and clinicians. T cells have been found to be important in countering COVID-19 disease, but whether we can rely on the T-cell response alone in the absence of antibodies to protect patients from infection or from serious COVID disease is still not determined,” she said.
When asked if she would recommend COVID-19 vaccine booster doses for patients on rituximab, Dr. Jyssum replied: “Absolutely.”
Another study, recently published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, examined heterologous and homologous booster doses for 60 patients receiving rituximab without seroconversion after their COVID-19 vaccine primary series. The results showed no significant difference in new seroconversion at 4 weeks based on whether the patient received a vector or mRNA vaccine (22% vs. 32%), but all patients who received a booster dose with a vector vaccine had specific T-cell responses, compared with 81% of patients who received an mRNA vaccine booster. There was a new humoral and/or cellular response in 9 of 11 patients (82%), and most patients with peripheral B cells (12 of 18 patients; 67%) achieved seroconversion.
“Our data show that a cellular and/or humoral immune response can be achieved on a third COVID-19 vaccination in most of the patients who initially developed neither a humoral nor a cellular immune response,” the researchers concluded. “The efficacy data together with the safety data seen in our trial provide a favorable risk/benefit ratio and support the implementation of a third vaccination for nonseroconverted high-risk autoimmune disease patients treated with B-cell–depleting agents.”
Dr. Spiera said booster doses are an important part of the equation, and “it is important to consider factors that would be associated with a greater likelihood of achieving a serologic response, particularly in those patients who did not demonstrate a serologic response to the initial vaccines series.
“Preliminary data shows that the beginnings of B-cell reconstitution is also associated with a positive serologic response following a booster of the COVID-19 vaccine,” he said.
The authors of the cited studies reported numerous relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Spiera and Dr. Jyssum reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Duloxetine added to usual care doesn’t improve hip, knee OA pain
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
A small, open-label, randomized trial of patients with chronic pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis in the Netherlands shows that adding duloxetine to usual care doesn’t significantly improve clinical outcomes.
The results, published on Jan. 6 in Arthritis & Rheumatology, also showed duloxetine did not affect outcomes for a subgroup of patients who had symptoms of centrally sensitized pain, according to Jacoline J. van den Driest, MD, of the department of general practice at Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
The researchers acknowledged their findings contrast with other studies that showed a “small to moderate effect of duloxetine” for patients with chronic pain from hip and knee OA. There was also a higher rate of discontinuation of duloxetine around 3 months in the current trial, compared with previous studies, the authors said, which they attributed to the fact that clinicians were asked to discontinue treatment at 3 months if patients saw no effect or increased side effects.
“This difference in outcome can be due to the fact that we studied the effectiveness of duloxetine in primary care, while the other studies examined the efficacy in placebo-controlled trials in secondary care,” the researchers wrote. Patients in the current trial were also older, had more comorbidities, and had been living with OA symptoms “for a longer time” than patients in other trials, they explained.
“It is known that, in these more ‘real-life’ primary care populations and in effectiveness studies, smaller effects are found than in highly controlled efficacy trials,” they noted.
Dr. van den Driest and colleagues evaluated 132 patients with hip or knee OA between January 2016 and February 2019 who were cluster randomized at 66 general practitioner practice sites to receive duloxetine (30 mg/day in the first week, 60 mg/day in the second week and beyond) in addition to usual care that consisted of analgesics, physiotherapy, patient education, diet, and lifestyle advice. Patients were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old, met the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hip or knee OA, and experienced chronic pain for “most days” over 3 months that was not improved through use of NSAIDs or acetaminophen or were unable to use NSAIDs because of contraindications or adverse effects. They were excluded if taking duloxetine was contraindicated for them, if they were taking an antidepressant or neuropathic pain medication, and if they had rheumatoid arthritis or were scheduled for total hip or total knee replacement.
The researchers assessed patients’ Western Ontario McMaster Universities (WOMAC) Osteoarthritis Index pain scores at 3 months, compared with baseline, as a primary outcome, with secondary outcomes of WOMAC pain and function at 1 year, and cost-effectiveness as measured by the EQ-5D-5L. A modified painDETECT questionnaire was also used at baseline to identify a subset of patients with presence of centralized pain, which was defined as a score >12.
At 12 months, 80.3% of patients in both groups completed follow-up. Patient characteristics differed in duloxetine and usual-care groups, with the duloxetine group being younger (63.2 years vs. 65.4 years) and having fewer women (59.1% vs. 75.8%). The duloxetine group also had a lower percentage of patients with knee OA (77.3% vs. 86.4%) and a lower percentage of patients with two or more comorbidities (15.2% vs. 33.2%).
Duloxetine led to a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months, compared with usual care (adjusted difference, –0.58; 95% confidence interval, –1.80 to 0.63), and at 12 months (adjusted difference, –0.26; 95% CI, –1.86 to 1.34). Among a subgroup of patients with central sensitization symptoms, there was a nonsignificant improvement in WOMAC-measured pain at 3 months (adjusted difference, –0.32; 95% CI, –2.32 to 1.67) and 12 months (adjusted difference, 1.02; 95% CI, –1.22 to 3.27).
Duloxetine also did not significantly improve WOMAC-measured function at 3 months (adjusted difference, –2.10; 95% CI, –6.39 to 2.20) or 12 months (adjusted difference, –1.79; 95% CI, –7.22 to 3.64).
For other secondary outcomes of quality of life, patient satisfaction, and Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT)-Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) responder criteria, Dr. van den Driest and colleagues noted that “none of the differences between the two groups were clinically relevant or statistically significant.”
Some patients may likely still benefit from duloxetine
Commenting on the results, Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania and Philadelphia VA Medical Center, said the study by van den Driest and colleagues is pragmatic and demonstrates the “ ‘real-world’ benefits of trying duloxetine” – one of the study’s strengths.
“As we would probably expect, the benefits are small, and somewhat smaller in this setting than what was observed in more standard clinical trials evaluating this question,” he said, noting that the study is limited by a small sample size and loss to follow-up, as well as its open-label design and the fact that most patients stopped treatment during follow-up.
Dr. Baker also explained that while patients on average did not have a meaningful effect after taking duloxetine, “that doesn’t mean that the therapy didn’t have a meaningful effect for some people.”
“In fact, though most people didn’t receive a meaningful benefit in this study, some did,” he said. “[A]ccording to these data, treating 8 people would be expected to result in 1 person achieving an [OMERACT-OARSI] response. That’s pretty good for a disease with few things that work.”
Future study of duloxetine should focus on who is most likely to benefit from treatment “since while most probably don’t benefit a lot, some probably do,” he said.
Dr. Baker also called attention to the questions surrounding use of antidepressants. “Use of antidepressants has been questioned by some, since the average clinical benefit is low, even for conditions like depression,” he explained. “However, some would argue that even small benefits may be important since there are few things that do work very well, and because a multimodal approach that provides multiple small benefits to patients can add up to a meaningful benefit.”
This study was funded by The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. One author reported receiving grants from The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, the European Union, FOREUM, and the Dutch Arthritis Association, as well as personal fees from OARSI and Pfizer. The other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
* This story was updated 1/6/22.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Case series show no consensus on treatment for palmoplantar pustulosis, generalized pustular psoriasis
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
that evaluated the characteristics and course of the disease in patients diagnosed with PPP or GPP.
“These case series confirm the rarity of both generalized pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis (PPP) and highlight the persistence of symptoms over time and the lack of effective treatment options available to patients,” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, MSCE, first author of both case series and assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview. In both studies, she added, “more than 20 different therapies were utilized, demonstrating a lack of consensus regarding effective treatment.”
The two case series were published in JAMA Dermatology.
Palmoplantar pustulosis
In the case series of 197 patients with PPP , data were obtained from a retrospective review at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. The patients were mostly women (73.6%) who were White (60.9%), with a mean age of 53 years; 38.1% were current smokers, and 27.4% were former smokers, and the mean follow-up time was 22.1 months. About half (48.2%) of patients who presented to their respective centers had skin pain, 19.8% had problems using their hands and feet, 12.7% had arthralgias, and 2% had myalgias. Clinicians who examined these patients found pustules on the palms (80.2%), soles (76.7%), and both palms and soles (59.9%); some nail unit involvement was reported in 10.2%.
Patients were treated with a variety of topical therapies, systemic steroids, systemic anti-infectives, and systemic psoriasis therapies, Dr. Noe and colleagues said. The most common initial treatments included a topical steroid (84.8%), with the vast majority of clinicians using a high-potency topical steroid (153 of 167 patients; 91.6%), or topical therapy only (64.5%).
Other initial treatments used were other types of topical medications in 34 of the patients in the series (17.3%), such as a vitamin D analogue in 27 patients (79.4%); oral systemic treatments such as acitretin in 27 patients (13.7%) or methotrexate in 22 patients (11.2%); narrowband UVB phototherapy in 15 patients (7.7%); systemic steroids in 10 patients (5.1%); or systemic antibiotics in 9 patients (4.6%). Less commonly used were biologic agents like adalimumab, used in 6 patients (3.1%).
The researchers also examined health care utilization in 128 patients and found that 82% had at least one follow-up visit, 31.3% required two to three follow-up visits, and 18.8% had five or more follow-up visits. When adjusted to account for age and sex, there was a decreased risk of requiring five or more healthcare visits per year for women (odds ratio, 0.49; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.95)
Generalized pustular psoriasis
Dr. Noe and colleagues also evaluated 95 patients with GPP in a retrospective longitudinal case series of patients treated at 20 academic dermatology practices in the United States between January 2007 and December 2018. As in the PPP group, most patients in the GPP case series were women (70.5%), and over half were White (53.7%); the mean age was 50.3 years old, and the mean follow-up time was 19.8 months. A majority of patients with GPP were never-smokers (52.6%) or former smokers (20%). When patients with GPP initially presented to the study sites, 36.8% were admitted as inpatients, 9.5% presented in the emergency department, and 53.7% presented in an outpatient or ambulatory dermatology setting.
GPP commonly appeared on the trunk and extremities, but was “also reported on the scalp, face, genitals, nail unit, and mucous membranes in a minority of patients,” the researchers said. Overall, 62.1% of patients had skin pain, 26.2% had joint pain, 16.8% reported tachycardia, and 9.5% reported fever. Hypertension, depression, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and hypothyroidism were common comorbidities of GPP, the researchers noted.
Clinicians reported treating GPP with topical steroids (86.3%) and topical treatments alone (32.3%). Oral systemic treatments such as acitretin (24.2%), cyclosporine (22.1%), and methotrexate (13.7%) were also used, as well as systemic steroids (20%). Other treatments used were narrowband UVB phototherapy (5.3%) and biologic agents like adalimumab (4.2%) and infliximab (4.2%).
For 53 patients with follow-up data of at least 6 months, 19 (35.8%) had been hospitalized because of their symptoms, and 8 patients were hospitalized for further GPP-specific concerns. Patients with GPP had a median 3.2 dermatology visits per year and a maximum of 18 visits. A model that was adjusted for age and sex showed women were at a decreased risk for being admitted to the hospital or emergency department in the follow-up period (odds ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.83).
PPP and GPP in practice
Sylvia Hsu, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at Temple University, Philadelphia, who was not involved with the research, noted that most dermatologists will see few, if any, cases of PPP and GPP in a year. At her center, she estimated that she sees about one PPP case per week, and one or two cases of GPP a year. In general, she said that her clinical experience matched what was found by the authors of both case series.
For patients with PPP, “I would say the average dermatologist would probably start out with a superpotent topical steroid like clobetasol or halobetasol ointment,” Dr. Hsu said.
If they are not of childbearing age, she added, she would also prescribe acitretin, which she avoids giving to patients of childbearing age because of its teratogenicity. “Acitretin has the reputation that it doesn’t work well or fast for psoriasis. It doesn’t work well or fast for plaque-type psoriasis, but it works well and fast for pustular psoriasis,” she said.
In place of acitretin, Dr. Hsu recommended cyclosporine for a patient of childbearing age as a short-term solution to resolve symptoms before transitioning them to another therapy. “A woman of childbearing age, you put on cyclosporine, you’ve got to transition to something else,” she said. “And so many times you wean them off, the pustular psoriasis comes back because the topical steroid doesn’t work that well.”
One possible option is the interluekin-23 inhibitor guselkumab (approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis) but cost and effectiveness can be a factor. Although studies have shown efficacy, biologics as treatments for PPP are “hit or miss,” Dr. Hsu said.
Regarding use of systemic therapies, Dr. Hsu cautioned against using them to treat plaque-type psoriasis. “We always learn, don’t use a systemic steroid like prednisone to treat psoriasis because it helps, but it comes back with a vengeance,” she said. “Sometimes when you treat plaque-type psoriasis with prednisone, it could come back with a vengeance, and it can come back as generalized pustular psoriasis.”
For patients with GPP, “you need a quick fix” because of the painful symptoms associated with the disease, Dr. Hsu said. In this case, she recommended cyclosporine and said she would avoid prescribing topical medications. “You’re going to have to give an oral drug because usually when we’re seeing somebody with GPP, they’re either a hospital consult or they just walked in the door,” she said. After prescribing cyclosporine, you would transition to another treatment like a biologic “as quickly as you can” with the knowledge that the biologic “may or may not work.”
New treatment options needed
Commenting on both case series in a related editorial, Edward W. Cowen, MD, MHSc, senior clinician and head of the dermatology consultation service in the dermatology branch of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, Bethesda, Md., said that “much of the clinical presentation of pustular disease remains a mystery,” including why tobacco use is a risk factor for developing pustular psoriasis, and why tumor necrosis factor inhibitors “induce pustular disease in a small number of patients” with psoriasis vulgaris.
“Most importantly, we still do not know if localized and generalized pustular psoriasis all truly represent different variants of the same disease process, and if not, which biologic treatment represents the best option for a given clinical variant,” he wrote.
Dr. Cowen noted that the multi-institutional approach to collecting the retrospective data in these case series could be used as a “basic framework to build on for future clinical trials for rare skin diseases such as pustular psoriasis.”
In the interview, Dr. Noe said that she hoped that the “Pustular Psoriasis in the US Research Group” she and her coauthors created for the case series could help with the development of prospective clinical trials. “For pustular psoriasis and other rare diseases in dermatology, multi-institutional collaborations are necessary to conduct prospective research,” she said.
“While not directly studied in our research, I think it is important to consider the negative impact on quality of life, experienced by patients with pustular psoriasis. In our study, many patients experienced exacerbations of their disease over time, and it is important to consider the impact this has on patients,” she said in the interview. “Continued research on pustular psoriasis is necessary to decrease the negative impact of these diseases on the lives of our patients.”
The case series were funded in part by an institutional grant from Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors report relationships with various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, technology companies, medical publishing companies, medical journals, and medical societies with connections to the topic area in the form of serving in roles as a chief medical editor, consultant, data safety monitoring board member, deputy editor, principal investigator, research investigator, scientific adviser, or speaker; or having received grants, honoraria, personal fees, or research funding. Dr. Cowen has no disclosures. Dr. Hsu reports serving on a Boehringer Ingelheim advisory board for a product being evaluated as a potential treatment for GPP.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Skin imaging working group releases first guidelines for AI algorithms used in dermatology
The
The guidelines, published in JAMA Dermatology on Dec. 1, 2021, contain a broad range of recommendations stakeholders should consider when developing and assessing image-based AI algorithms in dermatology. The recommendations are divided into categories of data, technique, technical assessment, and application. ISIC is “an academia and industry partnership designed to facilitate the application of digital skin imaging to help reduce melanoma mortality,” and is organized into different working groups, including the AI working group, according to its website.
“Our goal with these guidelines was to create higher-quality reporting of dataset and algorithm characteristics for dermatology AI,” first author Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, clinical scholar in dermatology, in the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview. “We hope these guidelines also aid regulatory bodies around the world when they are assessing algorithms to be used in dermatology.”
Recommendations for data
The authors recommended that datasets used by AI algorithms have image descriptions and details on image artifacts. “For photography, these include the type of camera used; whether images were taken under standardized or varying conditions; whether they were taken by professional photographers, laymen, or health care professionals; and image quality,” they wrote. They also recommended that developers include in an image description the type of lighting used and whether the photo contains pen markings, hair, tattoos, injuries, surgical effects, or other “physical perturbations.”
Exchangeable image file format data obtained from the camera, and preprocessing procedures like color normalization and “postprocessing” of images, such as filtering, should also be disclosed. In addition, developers should disclose and justify inclusion of images that have been created by an algorithm within a dataset. Any public images used in the datasets should have references, and privately used images should be made public where possible, the authors said.
The ISIC working group guidelines also provided recommendations for patient-level metadata. Each image should include a patient’s geographical location and medical center they visited as well as their age, sex and gender, ethnicity and/or race, and skin tone. Dr. Daneshjou said this was one area where she and her colleagues found a lack of transparency in AI datasets in algorithms in a recent review. “We found that many AI papers provided sparse details about the images used to train and test their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou explained. “For example, only 7 out of 70 papers had any information about the skin tones in the images used for developing and/or testing AI algorithms. Understanding the diversity of images used to train and test algorithms is important because algorithms that are developed on images of predominantly white skin likely won’t work as well on Black and brown skin.”
The guideline authors also asked algorithm developers to describe the limitations of not including patient-level metadata information when it is incomplete or unavailable. In addition, “we ask that algorithm developers comment on potential biases of their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm based only on telemedicine images may not capture the full range of diseases seen within an in-person clinic.”
When describing their AI algorithm, developers should detail their reasoning for the dataset size and partitions, inclusion and exclusion criteria for images, and use of any external samples for test sets. “Authors should consider any differences between the image characteristics used for algorithm development and those that might be encountered in the real world,” the guidelines stated.
Recommendations for technique
How the images in a dataset are labeled is a unique challenge in developing AI algorithms for dermatology, the authors noted. Developers should use histopathological diagnosis in their labeling, but this can sometimes result in label noise.
“Many of the AI algorithms in dermatology use supervised learning, which requires labeled examples to help the algorithm ‘learn’ features for discriminating between lesions. We found that some papers use consensus labeling – dermatologists providing a label – to label skin cancers; however, the standard for diagnosing skin cancer is using histopathology from a biopsy,” she said. “Dermatologists can biopsy seven to eight suspected melanomas before discovering a true melanoma, so dermatologist labeling of skin cancers is prone to label noise.”
ISIC’s guidelines stated a gold standard of labeling for dermatologic images is one area that still needs future research, but currently, “diagnoses, labels and diagnostic groups used in data repositories as well as public ontologies” such as ICD-11, AnatomyMapper, and SNOMED-CT should be included in dermatologic image datasets.
AI developers should also provide a detailed description of their algorithm, which includes methods, work flows, mathematical formulas as well as the generalizability of the algorithm across more than one dataset.
Recommendations for technical assessment
“Another important recommendation is that algorithm developers should provide a way for algorithms to be publicly evaluable by researchers,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “Many dermatology AI algorithms do not share either their data or their algorithm. Algorithm sharing is important for assessing reproducibility and robustness.”
Google’s recently announced AI-powered dermatology assistant tool, for example, “has made claims about its accuracy and ability to diagnose skin disease at a dermatologist level, but there is no way for researchers to independently test these claims,” she said. Other options like Model Dermatology, developed by Seung Seog Han, MD, PhD, of the Dermatology Clinic in Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, offer an application programming interface “that allows researchers to test the algorithm,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “This kind of openness is key for assessing algorithm robustness.”
Developers should also note in their algorithm explanations how performance markers and benchmarks would translate to proposed clinical application. “In this context,” the use case – the context in which the AI application is being used – “should be clearly described – who are the intended users and under what clinical scenario are they using the algorithm,” the authors wrote.
Recommendations for application
The guidelines note that use case for the model should also be described by the AI developers. “Our checklist includes delineating use cases for algorithms and describing what use cases may be within the scope of the algorithm versus which use cases are out of scope,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm developed to provide decision support to dermatologists, with a human in the loop, may not be accurate enough to release directly to consumers.”
As the goal of AI algorithms in dermatology is eventual implementation for clinicians and patients, the authors asked developers to consider shortcomings and potential harms of the algorithm during implementation. “Ethical considerations and impact on vulnerable populations should also be considered and discussed,” they wrote. An algorithm “suggesting aesthetic medical treatments may have negative effects given the biased nature of beauty standards,” and “an algorithm that diagnoses basal cell carcinomas but lacks any pigmented basal cell carcinomas, which are more often seen in skin of color, will not perform equitably across populations.”
Prior to implementing an AI algorithm, the ISIC working group recommended developers perform prospective clinical trials for validation. Checklists and guidelines like SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI “provide guidance on how to design clinical trials to test AI algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said.
After implementation, “I believe we need additional research in how we monitor algorithms after they are deployed clinically, Dr. Daneshjou said. “Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved AI algorithms in dermatology; however, there are several applications that have CE mark in Europe, and there are no mechanisms for postmarket surveillance there.
'Timely' recommendations
Commenting on the ISIC working group guidelines, Justin M. Ko, MD, MBA, director and chief of medical dermatology for Stanford Health Care, who was not involved with the work, said that the recommendations are timely and provide “a framework for a ‘common language’ around AI datasets specifically tailored to dermatology.” Dr. Ko, chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on Augmented Intelligence, noted the work by Dr. Daneshjou and colleagues “is consistent with and builds further details” on the position statement released by the AAD AI task force in 2019.
“As machine-learning capabilities and commercial efforts continue to mature, it becomes increasingly important that we are able to ‘look under the hood,’ and evaluate all the critical factors that influence development of these capabilities,” he said in an interview. “A standard set of reporting guidelines not only allows for transparency in evaluating data and performance of models and algorithms, but also forces the consideration of issues of equity, fairness, mitigation of bias, and clinically meaningful outcomes.”
One concern is the impact of AI algorithms on societal or health systems, he noted, which is brought up in the guidelines. “The last thing we would want is the development of robust AI systems that exacerbate access challenges, or generate patient anxiety/worry, or drive low-value utilization, or adds to care team burden, or create a technological barrier to care, or increases inequity in dermatologic care,” he said.
In developing AI algorithms for dermatology, a “major practical issue” is how performance on paper will translate to real-world use, Dr. Ko explained, and the ISIC guidelines “provide a critical step in empowering clinicians, practices, and our field to shape the advent of the AI and augmented intelligence tools and systems to promote and enhance meaningful clinical outcomes, and augment the core patient-clinician relationship and ensure they are grounded in principles of fairness, equity and transparency.”
This research was funded by awards and grants to individual authors from the Charina Fund, a Google Research Award, Melanoma Research Alliance, National Health and Medical Research Council, National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, National Science Foundation, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. The authors disclosed relationships with governmental entities, pharmaceutical companies, technology startups, medical publishers, charitable trusts, consulting firms, dermatology training companies, providers of medical devices, manufacturers of dermatologic products, and other organizations related to the paper in the form of supplied equipment, having founded a company; receiving grants, patents, or personal fees; holding shares; and medical reporting. Dr. Ko reported that he serves as a clinical advisor for Skin Analytics, and has an ongoing research collaboration with Google.
The
The guidelines, published in JAMA Dermatology on Dec. 1, 2021, contain a broad range of recommendations stakeholders should consider when developing and assessing image-based AI algorithms in dermatology. The recommendations are divided into categories of data, technique, technical assessment, and application. ISIC is “an academia and industry partnership designed to facilitate the application of digital skin imaging to help reduce melanoma mortality,” and is organized into different working groups, including the AI working group, according to its website.
“Our goal with these guidelines was to create higher-quality reporting of dataset and algorithm characteristics for dermatology AI,” first author Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, clinical scholar in dermatology, in the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview. “We hope these guidelines also aid regulatory bodies around the world when they are assessing algorithms to be used in dermatology.”
Recommendations for data
The authors recommended that datasets used by AI algorithms have image descriptions and details on image artifacts. “For photography, these include the type of camera used; whether images were taken under standardized or varying conditions; whether they were taken by professional photographers, laymen, or health care professionals; and image quality,” they wrote. They also recommended that developers include in an image description the type of lighting used and whether the photo contains pen markings, hair, tattoos, injuries, surgical effects, or other “physical perturbations.”
Exchangeable image file format data obtained from the camera, and preprocessing procedures like color normalization and “postprocessing” of images, such as filtering, should also be disclosed. In addition, developers should disclose and justify inclusion of images that have been created by an algorithm within a dataset. Any public images used in the datasets should have references, and privately used images should be made public where possible, the authors said.
The ISIC working group guidelines also provided recommendations for patient-level metadata. Each image should include a patient’s geographical location and medical center they visited as well as their age, sex and gender, ethnicity and/or race, and skin tone. Dr. Daneshjou said this was one area where she and her colleagues found a lack of transparency in AI datasets in algorithms in a recent review. “We found that many AI papers provided sparse details about the images used to train and test their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou explained. “For example, only 7 out of 70 papers had any information about the skin tones in the images used for developing and/or testing AI algorithms. Understanding the diversity of images used to train and test algorithms is important because algorithms that are developed on images of predominantly white skin likely won’t work as well on Black and brown skin.”
The guideline authors also asked algorithm developers to describe the limitations of not including patient-level metadata information when it is incomplete or unavailable. In addition, “we ask that algorithm developers comment on potential biases of their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm based only on telemedicine images may not capture the full range of diseases seen within an in-person clinic.”
When describing their AI algorithm, developers should detail their reasoning for the dataset size and partitions, inclusion and exclusion criteria for images, and use of any external samples for test sets. “Authors should consider any differences between the image characteristics used for algorithm development and those that might be encountered in the real world,” the guidelines stated.
Recommendations for technique
How the images in a dataset are labeled is a unique challenge in developing AI algorithms for dermatology, the authors noted. Developers should use histopathological diagnosis in their labeling, but this can sometimes result in label noise.
“Many of the AI algorithms in dermatology use supervised learning, which requires labeled examples to help the algorithm ‘learn’ features for discriminating between lesions. We found that some papers use consensus labeling – dermatologists providing a label – to label skin cancers; however, the standard for diagnosing skin cancer is using histopathology from a biopsy,” she said. “Dermatologists can biopsy seven to eight suspected melanomas before discovering a true melanoma, so dermatologist labeling of skin cancers is prone to label noise.”
ISIC’s guidelines stated a gold standard of labeling for dermatologic images is one area that still needs future research, but currently, “diagnoses, labels and diagnostic groups used in data repositories as well as public ontologies” such as ICD-11, AnatomyMapper, and SNOMED-CT should be included in dermatologic image datasets.
AI developers should also provide a detailed description of their algorithm, which includes methods, work flows, mathematical formulas as well as the generalizability of the algorithm across more than one dataset.
Recommendations for technical assessment
“Another important recommendation is that algorithm developers should provide a way for algorithms to be publicly evaluable by researchers,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “Many dermatology AI algorithms do not share either their data or their algorithm. Algorithm sharing is important for assessing reproducibility and robustness.”
Google’s recently announced AI-powered dermatology assistant tool, for example, “has made claims about its accuracy and ability to diagnose skin disease at a dermatologist level, but there is no way for researchers to independently test these claims,” she said. Other options like Model Dermatology, developed by Seung Seog Han, MD, PhD, of the Dermatology Clinic in Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, offer an application programming interface “that allows researchers to test the algorithm,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “This kind of openness is key for assessing algorithm robustness.”
Developers should also note in their algorithm explanations how performance markers and benchmarks would translate to proposed clinical application. “In this context,” the use case – the context in which the AI application is being used – “should be clearly described – who are the intended users and under what clinical scenario are they using the algorithm,” the authors wrote.
Recommendations for application
The guidelines note that use case for the model should also be described by the AI developers. “Our checklist includes delineating use cases for algorithms and describing what use cases may be within the scope of the algorithm versus which use cases are out of scope,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm developed to provide decision support to dermatologists, with a human in the loop, may not be accurate enough to release directly to consumers.”
As the goal of AI algorithms in dermatology is eventual implementation for clinicians and patients, the authors asked developers to consider shortcomings and potential harms of the algorithm during implementation. “Ethical considerations and impact on vulnerable populations should also be considered and discussed,” they wrote. An algorithm “suggesting aesthetic medical treatments may have negative effects given the biased nature of beauty standards,” and “an algorithm that diagnoses basal cell carcinomas but lacks any pigmented basal cell carcinomas, which are more often seen in skin of color, will not perform equitably across populations.”
Prior to implementing an AI algorithm, the ISIC working group recommended developers perform prospective clinical trials for validation. Checklists and guidelines like SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI “provide guidance on how to design clinical trials to test AI algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said.
After implementation, “I believe we need additional research in how we monitor algorithms after they are deployed clinically, Dr. Daneshjou said. “Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved AI algorithms in dermatology; however, there are several applications that have CE mark in Europe, and there are no mechanisms for postmarket surveillance there.
'Timely' recommendations
Commenting on the ISIC working group guidelines, Justin M. Ko, MD, MBA, director and chief of medical dermatology for Stanford Health Care, who was not involved with the work, said that the recommendations are timely and provide “a framework for a ‘common language’ around AI datasets specifically tailored to dermatology.” Dr. Ko, chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on Augmented Intelligence, noted the work by Dr. Daneshjou and colleagues “is consistent with and builds further details” on the position statement released by the AAD AI task force in 2019.
“As machine-learning capabilities and commercial efforts continue to mature, it becomes increasingly important that we are able to ‘look under the hood,’ and evaluate all the critical factors that influence development of these capabilities,” he said in an interview. “A standard set of reporting guidelines not only allows for transparency in evaluating data and performance of models and algorithms, but also forces the consideration of issues of equity, fairness, mitigation of bias, and clinically meaningful outcomes.”
One concern is the impact of AI algorithms on societal or health systems, he noted, which is brought up in the guidelines. “The last thing we would want is the development of robust AI systems that exacerbate access challenges, or generate patient anxiety/worry, or drive low-value utilization, or adds to care team burden, or create a technological barrier to care, or increases inequity in dermatologic care,” he said.
In developing AI algorithms for dermatology, a “major practical issue” is how performance on paper will translate to real-world use, Dr. Ko explained, and the ISIC guidelines “provide a critical step in empowering clinicians, practices, and our field to shape the advent of the AI and augmented intelligence tools and systems to promote and enhance meaningful clinical outcomes, and augment the core patient-clinician relationship and ensure they are grounded in principles of fairness, equity and transparency.”
This research was funded by awards and grants to individual authors from the Charina Fund, a Google Research Award, Melanoma Research Alliance, National Health and Medical Research Council, National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, National Science Foundation, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. The authors disclosed relationships with governmental entities, pharmaceutical companies, technology startups, medical publishers, charitable trusts, consulting firms, dermatology training companies, providers of medical devices, manufacturers of dermatologic products, and other organizations related to the paper in the form of supplied equipment, having founded a company; receiving grants, patents, or personal fees; holding shares; and medical reporting. Dr. Ko reported that he serves as a clinical advisor for Skin Analytics, and has an ongoing research collaboration with Google.
The
The guidelines, published in JAMA Dermatology on Dec. 1, 2021, contain a broad range of recommendations stakeholders should consider when developing and assessing image-based AI algorithms in dermatology. The recommendations are divided into categories of data, technique, technical assessment, and application. ISIC is “an academia and industry partnership designed to facilitate the application of digital skin imaging to help reduce melanoma mortality,” and is organized into different working groups, including the AI working group, according to its website.
“Our goal with these guidelines was to create higher-quality reporting of dataset and algorithm characteristics for dermatology AI,” first author Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, clinical scholar in dermatology, in the department of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview. “We hope these guidelines also aid regulatory bodies around the world when they are assessing algorithms to be used in dermatology.”
Recommendations for data
The authors recommended that datasets used by AI algorithms have image descriptions and details on image artifacts. “For photography, these include the type of camera used; whether images were taken under standardized or varying conditions; whether they were taken by professional photographers, laymen, or health care professionals; and image quality,” they wrote. They also recommended that developers include in an image description the type of lighting used and whether the photo contains pen markings, hair, tattoos, injuries, surgical effects, or other “physical perturbations.”
Exchangeable image file format data obtained from the camera, and preprocessing procedures like color normalization and “postprocessing” of images, such as filtering, should also be disclosed. In addition, developers should disclose and justify inclusion of images that have been created by an algorithm within a dataset. Any public images used in the datasets should have references, and privately used images should be made public where possible, the authors said.
The ISIC working group guidelines also provided recommendations for patient-level metadata. Each image should include a patient’s geographical location and medical center they visited as well as their age, sex and gender, ethnicity and/or race, and skin tone. Dr. Daneshjou said this was one area where she and her colleagues found a lack of transparency in AI datasets in algorithms in a recent review. “We found that many AI papers provided sparse details about the images used to train and test their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou explained. “For example, only 7 out of 70 papers had any information about the skin tones in the images used for developing and/or testing AI algorithms. Understanding the diversity of images used to train and test algorithms is important because algorithms that are developed on images of predominantly white skin likely won’t work as well on Black and brown skin.”
The guideline authors also asked algorithm developers to describe the limitations of not including patient-level metadata information when it is incomplete or unavailable. In addition, “we ask that algorithm developers comment on potential biases of their algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm based only on telemedicine images may not capture the full range of diseases seen within an in-person clinic.”
When describing their AI algorithm, developers should detail their reasoning for the dataset size and partitions, inclusion and exclusion criteria for images, and use of any external samples for test sets. “Authors should consider any differences between the image characteristics used for algorithm development and those that might be encountered in the real world,” the guidelines stated.
Recommendations for technique
How the images in a dataset are labeled is a unique challenge in developing AI algorithms for dermatology, the authors noted. Developers should use histopathological diagnosis in their labeling, but this can sometimes result in label noise.
“Many of the AI algorithms in dermatology use supervised learning, which requires labeled examples to help the algorithm ‘learn’ features for discriminating between lesions. We found that some papers use consensus labeling – dermatologists providing a label – to label skin cancers; however, the standard for diagnosing skin cancer is using histopathology from a biopsy,” she said. “Dermatologists can biopsy seven to eight suspected melanomas before discovering a true melanoma, so dermatologist labeling of skin cancers is prone to label noise.”
ISIC’s guidelines stated a gold standard of labeling for dermatologic images is one area that still needs future research, but currently, “diagnoses, labels and diagnostic groups used in data repositories as well as public ontologies” such as ICD-11, AnatomyMapper, and SNOMED-CT should be included in dermatologic image datasets.
AI developers should also provide a detailed description of their algorithm, which includes methods, work flows, mathematical formulas as well as the generalizability of the algorithm across more than one dataset.
Recommendations for technical assessment
“Another important recommendation is that algorithm developers should provide a way for algorithms to be publicly evaluable by researchers,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “Many dermatology AI algorithms do not share either their data or their algorithm. Algorithm sharing is important for assessing reproducibility and robustness.”
Google’s recently announced AI-powered dermatology assistant tool, for example, “has made claims about its accuracy and ability to diagnose skin disease at a dermatologist level, but there is no way for researchers to independently test these claims,” she said. Other options like Model Dermatology, developed by Seung Seog Han, MD, PhD, of the Dermatology Clinic in Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, offer an application programming interface “that allows researchers to test the algorithm,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “This kind of openness is key for assessing algorithm robustness.”
Developers should also note in their algorithm explanations how performance markers and benchmarks would translate to proposed clinical application. “In this context,” the use case – the context in which the AI application is being used – “should be clearly described – who are the intended users and under what clinical scenario are they using the algorithm,” the authors wrote.
Recommendations for application
The guidelines note that use case for the model should also be described by the AI developers. “Our checklist includes delineating use cases for algorithms and describing what use cases may be within the scope of the algorithm versus which use cases are out of scope,” Dr. Daneshjou said. “For example, an algorithm developed to provide decision support to dermatologists, with a human in the loop, may not be accurate enough to release directly to consumers.”
As the goal of AI algorithms in dermatology is eventual implementation for clinicians and patients, the authors asked developers to consider shortcomings and potential harms of the algorithm during implementation. “Ethical considerations and impact on vulnerable populations should also be considered and discussed,” they wrote. An algorithm “suggesting aesthetic medical treatments may have negative effects given the biased nature of beauty standards,” and “an algorithm that diagnoses basal cell carcinomas but lacks any pigmented basal cell carcinomas, which are more often seen in skin of color, will not perform equitably across populations.”
Prior to implementing an AI algorithm, the ISIC working group recommended developers perform prospective clinical trials for validation. Checklists and guidelines like SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI “provide guidance on how to design clinical trials to test AI algorithms,” Dr. Daneshjou said.
After implementation, “I believe we need additional research in how we monitor algorithms after they are deployed clinically, Dr. Daneshjou said. “Currently there are no [Food and Drug Administration]–approved AI algorithms in dermatology; however, there are several applications that have CE mark in Europe, and there are no mechanisms for postmarket surveillance there.
'Timely' recommendations
Commenting on the ISIC working group guidelines, Justin M. Ko, MD, MBA, director and chief of medical dermatology for Stanford Health Care, who was not involved with the work, said that the recommendations are timely and provide “a framework for a ‘common language’ around AI datasets specifically tailored to dermatology.” Dr. Ko, chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Ad Hoc Task Force on Augmented Intelligence, noted the work by Dr. Daneshjou and colleagues “is consistent with and builds further details” on the position statement released by the AAD AI task force in 2019.
“As machine-learning capabilities and commercial efforts continue to mature, it becomes increasingly important that we are able to ‘look under the hood,’ and evaluate all the critical factors that influence development of these capabilities,” he said in an interview. “A standard set of reporting guidelines not only allows for transparency in evaluating data and performance of models and algorithms, but also forces the consideration of issues of equity, fairness, mitigation of bias, and clinically meaningful outcomes.”
One concern is the impact of AI algorithms on societal or health systems, he noted, which is brought up in the guidelines. “The last thing we would want is the development of robust AI systems that exacerbate access challenges, or generate patient anxiety/worry, or drive low-value utilization, or adds to care team burden, or create a technological barrier to care, or increases inequity in dermatologic care,” he said.
In developing AI algorithms for dermatology, a “major practical issue” is how performance on paper will translate to real-world use, Dr. Ko explained, and the ISIC guidelines “provide a critical step in empowering clinicians, practices, and our field to shape the advent of the AI and augmented intelligence tools and systems to promote and enhance meaningful clinical outcomes, and augment the core patient-clinician relationship and ensure they are grounded in principles of fairness, equity and transparency.”
This research was funded by awards and grants to individual authors from the Charina Fund, a Google Research Award, Melanoma Research Alliance, National Health and Medical Research Council, National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute, National Science Foundation, and the Department of Veterans Affairs. The authors disclosed relationships with governmental entities, pharmaceutical companies, technology startups, medical publishers, charitable trusts, consulting firms, dermatology training companies, providers of medical devices, manufacturers of dermatologic products, and other organizations related to the paper in the form of supplied equipment, having founded a company; receiving grants, patents, or personal fees; holding shares; and medical reporting. Dr. Ko reported that he serves as a clinical advisor for Skin Analytics, and has an ongoing research collaboration with Google.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
‘Misleading’ results in colchicine COVID-19 trials meta-analysis
A new meta-analysis appears to show that colchicine has no benefit as a treatment for COVID-19, but its inclusion of trials studying differing patient populations and testing different outcomes led to “misleading” results, says a researcher involved in one of the trials.
The meta-analysis, which includes data from the recent Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, was published Nov. 22 in RMD Open.
Kedar Gautambhai Mehta, MBBS, MD, of the GMERS Medical College Gotri in Vadodara, India, and colleagues included outcomes from six studies of 16,148 patients with COVID-19 who received colchicine or supportive care. They evaluated the efficacy outcomes of mortality, need for ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and length of stay in hospital, as well as safety outcomes of adverse events, serious adverse events, and diarrhea.
The studies in the meta-analysis included a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) of 105 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece, the international, open-label RECOVERY RCT of 11,340 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, an RCT of 72 hospitalized patients with moderate or severe COVID-19 in Brazil, an RCT of 100 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Iran, the international COLCORONA trial of 4,488 patients with COVID-19 who were treated with colchicine or placebo on an outpatient basis, and the randomized COLORIT trial of 43 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Russia.
Studies “asked very different questions” about colchicine
Commenting on the meta-analysis, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology with New York University, said the authors combined studies “that are not comparable and that asked very different questions.” Two of the studies in the meta-analysis are very large, and four are very small, which skews the results, he explained.
“The larger studies therefore drive the outcome, and while the small studies are potentially insight providing, the large studies are the only ones worth giving our attention to in the context of the meta-analysis,” he said. The two largest studies – RECOVERY and COLCORONA – taken together show no benefit for colchicine as a treatment, even though the former demonstrated no benefit and the latter did show a benefit, explained Dr. Pillinger, a co–principal investigator for the COLCORONA trial in the United States.
The studies were designed differently and should not have been included in the same analysis, Dr. Pillinger argued. In the case of COLCORONA, early treatment with colchicine was the intervention, whereas RECOVERY focused on hospitalized patients.
“In designing [COLCORONA], the author group (of whom I was a member) expressly rejected the idea that colchicine might be useful for the sicker hospitalized patients, based on the long experience with colchicine of some of us as rheumatologists,” Dr. Pillinger said.
“In short, COLCORONA proved a benefit of colchicine in outpatient COVID-19, and its authors presumed there would be no inpatient benefit; RECOVERY went ahead and proved a lack of inpatient benefit, at least when high-dose steroids were also given,” he said. “While there is no conflict between these results, the combination of the two studies in this meta-analysis suggests there might be no benefit for colchicine overall, which is misleading and can lead physicians to reject the potential of outpatient colchicine, even for future studies.”
Dr. Pillinger said he still believes colchicine has potential value as a COVID-19 treatment option for patients with mild disease, “especially for low–vaccine rate, resource-starved countries.
“It would be unfortunate if meta-analyses such as this one would put a stop to colchicine’s use, or at least its further investigation,” he said.
Study details
The authors of the study assessed heterogeneity of the trials’ data across the outcomes using an I2 test. They evaluated the quality of the evidence for the outcomes using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
The results of their meta-analysis showed that colchicine offered no significant improvement in mortality in six studies (risk difference, –0.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.01 to 0.01; I2 = 15%). It showed no benefit with respect to requiring ventilatory support in five studies of 15,519 patients (risk ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.38-1.21; I2 = 47%); being admitted to the ICU in three studies with 220 patients (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.19-1.25; I2 = 34%); and length of stay while in the hospital in four studies of 11,560 patients (mean difference, –1.17; 95% CI, –3.02 to 0.67; I2 = 77%).
There was no difference in serious adverse events in three studies with 4,665 patients (RD, –0.01; 95% CI, –0.02 to 0.00; I2 = 28%) for patients who received colchicine, compared with supportive care alone. Patients who received colchicine were more likely to have a higher rate of adverse events (RR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.07-2.33; I2 = 81%) and to experience diarrhea (RR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.62-2.29; I2 = 0%) than were patients who received supportive care alone. The researchers note that for most outcomes, the GRADE quality of evidence was moderate.
“Our findings on colchicine should be interpreted cautiously due to the inclusion of open-labeled, randomized clinical trials,” Dr. Mehta and colleagues write. “The analysis of efficacy and safety outcomes are based on a small number of RCTs in control interventions.”
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pillinger is co–principal investigator of the U.S. component of the COLCORONA trial; he reported no other relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new meta-analysis appears to show that colchicine has no benefit as a treatment for COVID-19, but its inclusion of trials studying differing patient populations and testing different outcomes led to “misleading” results, says a researcher involved in one of the trials.
The meta-analysis, which includes data from the recent Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, was published Nov. 22 in RMD Open.
Kedar Gautambhai Mehta, MBBS, MD, of the GMERS Medical College Gotri in Vadodara, India, and colleagues included outcomes from six studies of 16,148 patients with COVID-19 who received colchicine or supportive care. They evaluated the efficacy outcomes of mortality, need for ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and length of stay in hospital, as well as safety outcomes of adverse events, serious adverse events, and diarrhea.
The studies in the meta-analysis included a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) of 105 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece, the international, open-label RECOVERY RCT of 11,340 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, an RCT of 72 hospitalized patients with moderate or severe COVID-19 in Brazil, an RCT of 100 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Iran, the international COLCORONA trial of 4,488 patients with COVID-19 who were treated with colchicine or placebo on an outpatient basis, and the randomized COLORIT trial of 43 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Russia.
Studies “asked very different questions” about colchicine
Commenting on the meta-analysis, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology with New York University, said the authors combined studies “that are not comparable and that asked very different questions.” Two of the studies in the meta-analysis are very large, and four are very small, which skews the results, he explained.
“The larger studies therefore drive the outcome, and while the small studies are potentially insight providing, the large studies are the only ones worth giving our attention to in the context of the meta-analysis,” he said. The two largest studies – RECOVERY and COLCORONA – taken together show no benefit for colchicine as a treatment, even though the former demonstrated no benefit and the latter did show a benefit, explained Dr. Pillinger, a co–principal investigator for the COLCORONA trial in the United States.
The studies were designed differently and should not have been included in the same analysis, Dr. Pillinger argued. In the case of COLCORONA, early treatment with colchicine was the intervention, whereas RECOVERY focused on hospitalized patients.
“In designing [COLCORONA], the author group (of whom I was a member) expressly rejected the idea that colchicine might be useful for the sicker hospitalized patients, based on the long experience with colchicine of some of us as rheumatologists,” Dr. Pillinger said.
“In short, COLCORONA proved a benefit of colchicine in outpatient COVID-19, and its authors presumed there would be no inpatient benefit; RECOVERY went ahead and proved a lack of inpatient benefit, at least when high-dose steroids were also given,” he said. “While there is no conflict between these results, the combination of the two studies in this meta-analysis suggests there might be no benefit for colchicine overall, which is misleading and can lead physicians to reject the potential of outpatient colchicine, even for future studies.”
Dr. Pillinger said he still believes colchicine has potential value as a COVID-19 treatment option for patients with mild disease, “especially for low–vaccine rate, resource-starved countries.
“It would be unfortunate if meta-analyses such as this one would put a stop to colchicine’s use, or at least its further investigation,” he said.
Study details
The authors of the study assessed heterogeneity of the trials’ data across the outcomes using an I2 test. They evaluated the quality of the evidence for the outcomes using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
The results of their meta-analysis showed that colchicine offered no significant improvement in mortality in six studies (risk difference, –0.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.01 to 0.01; I2 = 15%). It showed no benefit with respect to requiring ventilatory support in five studies of 15,519 patients (risk ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.38-1.21; I2 = 47%); being admitted to the ICU in three studies with 220 patients (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.19-1.25; I2 = 34%); and length of stay while in the hospital in four studies of 11,560 patients (mean difference, –1.17; 95% CI, –3.02 to 0.67; I2 = 77%).
There was no difference in serious adverse events in three studies with 4,665 patients (RD, –0.01; 95% CI, –0.02 to 0.00; I2 = 28%) for patients who received colchicine, compared with supportive care alone. Patients who received colchicine were more likely to have a higher rate of adverse events (RR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.07-2.33; I2 = 81%) and to experience diarrhea (RR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.62-2.29; I2 = 0%) than were patients who received supportive care alone. The researchers note that for most outcomes, the GRADE quality of evidence was moderate.
“Our findings on colchicine should be interpreted cautiously due to the inclusion of open-labeled, randomized clinical trials,” Dr. Mehta and colleagues write. “The analysis of efficacy and safety outcomes are based on a small number of RCTs in control interventions.”
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pillinger is co–principal investigator of the U.S. component of the COLCORONA trial; he reported no other relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new meta-analysis appears to show that colchicine has no benefit as a treatment for COVID-19, but its inclusion of trials studying differing patient populations and testing different outcomes led to “misleading” results, says a researcher involved in one of the trials.
The meta-analysis, which includes data from the recent Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy (RECOVERY) trial, was published Nov. 22 in RMD Open.
Kedar Gautambhai Mehta, MBBS, MD, of the GMERS Medical College Gotri in Vadodara, India, and colleagues included outcomes from six studies of 16,148 patients with COVID-19 who received colchicine or supportive care. They evaluated the efficacy outcomes of mortality, need for ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and length of stay in hospital, as well as safety outcomes of adverse events, serious adverse events, and diarrhea.
The studies in the meta-analysis included a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) of 105 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Greece, the international, open-label RECOVERY RCT of 11,340 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, an RCT of 72 hospitalized patients with moderate or severe COVID-19 in Brazil, an RCT of 100 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Iran, the international COLCORONA trial of 4,488 patients with COVID-19 who were treated with colchicine or placebo on an outpatient basis, and the randomized COLORIT trial of 43 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Russia.
Studies “asked very different questions” about colchicine
Commenting on the meta-analysis, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology with New York University, said the authors combined studies “that are not comparable and that asked very different questions.” Two of the studies in the meta-analysis are very large, and four are very small, which skews the results, he explained.
“The larger studies therefore drive the outcome, and while the small studies are potentially insight providing, the large studies are the only ones worth giving our attention to in the context of the meta-analysis,” he said. The two largest studies – RECOVERY and COLCORONA – taken together show no benefit for colchicine as a treatment, even though the former demonstrated no benefit and the latter did show a benefit, explained Dr. Pillinger, a co–principal investigator for the COLCORONA trial in the United States.
The studies were designed differently and should not have been included in the same analysis, Dr. Pillinger argued. In the case of COLCORONA, early treatment with colchicine was the intervention, whereas RECOVERY focused on hospitalized patients.
“In designing [COLCORONA], the author group (of whom I was a member) expressly rejected the idea that colchicine might be useful for the sicker hospitalized patients, based on the long experience with colchicine of some of us as rheumatologists,” Dr. Pillinger said.
“In short, COLCORONA proved a benefit of colchicine in outpatient COVID-19, and its authors presumed there would be no inpatient benefit; RECOVERY went ahead and proved a lack of inpatient benefit, at least when high-dose steroids were also given,” he said. “While there is no conflict between these results, the combination of the two studies in this meta-analysis suggests there might be no benefit for colchicine overall, which is misleading and can lead physicians to reject the potential of outpatient colchicine, even for future studies.”
Dr. Pillinger said he still believes colchicine has potential value as a COVID-19 treatment option for patients with mild disease, “especially for low–vaccine rate, resource-starved countries.
“It would be unfortunate if meta-analyses such as this one would put a stop to colchicine’s use, or at least its further investigation,” he said.
Study details
The authors of the study assessed heterogeneity of the trials’ data across the outcomes using an I2 test. They evaluated the quality of the evidence for the outcomes using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
The results of their meta-analysis showed that colchicine offered no significant improvement in mortality in six studies (risk difference, –0.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.01 to 0.01; I2 = 15%). It showed no benefit with respect to requiring ventilatory support in five studies of 15,519 patients (risk ratio, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.38-1.21; I2 = 47%); being admitted to the ICU in three studies with 220 patients (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.19-1.25; I2 = 34%); and length of stay while in the hospital in four studies of 11,560 patients (mean difference, –1.17; 95% CI, –3.02 to 0.67; I2 = 77%).
There was no difference in serious adverse events in three studies with 4,665 patients (RD, –0.01; 95% CI, –0.02 to 0.00; I2 = 28%) for patients who received colchicine, compared with supportive care alone. Patients who received colchicine were more likely to have a higher rate of adverse events (RR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.07-2.33; I2 = 81%) and to experience diarrhea (RR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.62-2.29; I2 = 0%) than were patients who received supportive care alone. The researchers note that for most outcomes, the GRADE quality of evidence was moderate.
“Our findings on colchicine should be interpreted cautiously due to the inclusion of open-labeled, randomized clinical trials,” Dr. Mehta and colleagues write. “The analysis of efficacy and safety outcomes are based on a small number of RCTs in control interventions.”
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pillinger is co–principal investigator of the U.S. component of the COLCORONA trial; he reported no other relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AI: Skin of color underrepresented in datasets used to identify skin cancer
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.