User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Sticking His Neck Out Leads to Diagnosis
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
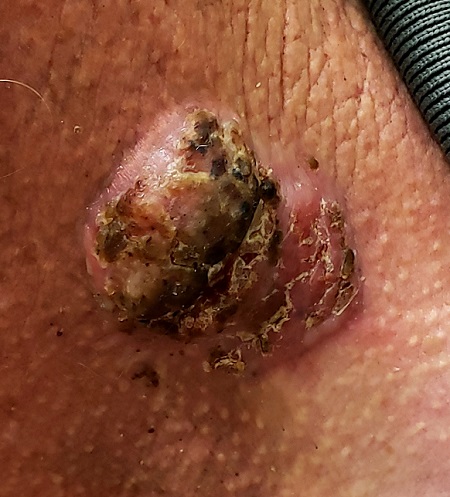
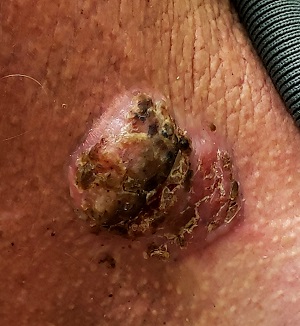
For 5 years, a lesion has been slowly growing on this 50-year-old man’s neck. He has seen several primary care providers who had provided different diagnoses, including wart, seborrheic keratosis, and keratoacanthoma. Throughout these visits, the only treatment he was offered was cryotherapy, but this was not effective at clearing the lesion. One family member convinced him it was time to try a dermatology provider.
In his lifetime, the patient has been exposed to a great deal of UV light. He has had several basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas removed from his face and arms.
He claims to be in otherwise good health, but further questioning reveals a > 40 pack-year history of smoking. He also has a recent diagnosis of early chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Physical examination of the lesion reveals a 4-x-3.5-cm sessile mass located on the left lateral neck. Its surface is rough and irregular, but there is no break in the skin.
On palpation, the lesion is quite firm and only partially mobile. No tenderness is detected. There are no palpable nodes in the region. There is evidence of advanced chronic sun damage on all sun-exposed areas, but especially on the head and neck. The rest of skin has no lesions.
Endocrine Society calls for action to reduce insulin costs
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another lot of extended-release metformin is recalled in the U.S.
Nostrum Laboratories has voluntarily recalled another lot of metformin HCl extended-release tablets 750-mg dosage, expanding their initial announcement in November 2020. According to the new notice, issued by the Food and Drug Administration earlier this week, the recalled tablets are off-white and oblong with a debossed ID “NM7.”
The lot number, NDC, and expiration dates can be found on the FDA website.
Nostrum noted that the tablets were distributed across the United States to wholesalers; these distributors are being notified of the recall and the company is arranging for the drug to be returned.
Metformin is the most prescribed medication worldwide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Nostrum said that anyone in possession of any of the affected lots should consult their physician or pharmacist to obtain a replacement treatment option because it can be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking metformin.
This new announcement expands further the number of metformin HCl extended-release tablets recalled in the United States because they contain potentially high levels of nitrosamines, also known as N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), which are possible carcinogens.
The risks of nitrosamines are not clear. The FDA said they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
As well as the November recall of 2 lots of metformin by Nostrum, 76 more lots of metformin extended-release tablets were flagged in October 2020 from various manufacturers for possible contamination with NDMA, on top of an earlier recall for the same problem in May 2020.
More than 175 different drug combinations, all extended release with either 500 mg or 750 mg of metformin, have now been recalled since late May 2020, and a list of those recalled to November 2020 is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nostrum Laboratories has voluntarily recalled another lot of metformin HCl extended-release tablets 750-mg dosage, expanding their initial announcement in November 2020. According to the new notice, issued by the Food and Drug Administration earlier this week, the recalled tablets are off-white and oblong with a debossed ID “NM7.”
The lot number, NDC, and expiration dates can be found on the FDA website.
Nostrum noted that the tablets were distributed across the United States to wholesalers; these distributors are being notified of the recall and the company is arranging for the drug to be returned.
Metformin is the most prescribed medication worldwide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Nostrum said that anyone in possession of any of the affected lots should consult their physician or pharmacist to obtain a replacement treatment option because it can be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking metformin.
This new announcement expands further the number of metformin HCl extended-release tablets recalled in the United States because they contain potentially high levels of nitrosamines, also known as N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), which are possible carcinogens.
The risks of nitrosamines are not clear. The FDA said they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
As well as the November recall of 2 lots of metformin by Nostrum, 76 more lots of metformin extended-release tablets were flagged in October 2020 from various manufacturers for possible contamination with NDMA, on top of an earlier recall for the same problem in May 2020.
More than 175 different drug combinations, all extended release with either 500 mg or 750 mg of metformin, have now been recalled since late May 2020, and a list of those recalled to November 2020 is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nostrum Laboratories has voluntarily recalled another lot of metformin HCl extended-release tablets 750-mg dosage, expanding their initial announcement in November 2020. According to the new notice, issued by the Food and Drug Administration earlier this week, the recalled tablets are off-white and oblong with a debossed ID “NM7.”
The lot number, NDC, and expiration dates can be found on the FDA website.
Nostrum noted that the tablets were distributed across the United States to wholesalers; these distributors are being notified of the recall and the company is arranging for the drug to be returned.
Metformin is the most prescribed medication worldwide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Nostrum said that anyone in possession of any of the affected lots should consult their physician or pharmacist to obtain a replacement treatment option because it can be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking metformin.
This new announcement expands further the number of metformin HCl extended-release tablets recalled in the United States because they contain potentially high levels of nitrosamines, also known as N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), which are possible carcinogens.
The risks of nitrosamines are not clear. The FDA said they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
As well as the November recall of 2 lots of metformin by Nostrum, 76 more lots of metformin extended-release tablets were flagged in October 2020 from various manufacturers for possible contamination with NDMA, on top of an earlier recall for the same problem in May 2020.
More than 175 different drug combinations, all extended release with either 500 mg or 750 mg of metformin, have now been recalled since late May 2020, and a list of those recalled to November 2020 is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treprostinil offers some benefits for patients with ILD-associated pulmonary hypertension
and was associated with some additional clinical benefits, according to a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To investigate treprostinil therapy for pulmonary hypertension in this subset of patients with lung disease, Aaron Waxman, MD, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and his fellow researchers launched the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled INCREASE trial. They assigned 163 patients to the inhaled treprostinil group – administered via an ultrasonic, pulsed-delivery nebulizer over 16 weeks – and 163 patients to the placebo group. Their average age was 66.5 years, 73% were white, and 47% were female
At baseline, the mean 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) for all patients was 259.6 m. After 16 weeks, the treprostinil group gained a mean of 21.08 m in 6MWD, and the placebo group lost 10.04 m. The least-squares mean difference between the groups from baseline in the 6MWD was 31.12 m (95% confidence interval, 16.85-45.39; P < .001). After sensitivity analysis with multiple imputation, the difference remained significant at 30.97 m (95% CI, 16.53-45.41; P < .001).
In a comparison of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels from baseline to 16 weeks, the treprostinil group saw a decrease of 15% while the placebo group’s levels increased by 46% (treatment ratio 0.58; 95% CI, 0.47-0.72; P < .001). Clinical worsening occurred in 37 patients (23%) in the treprostinil group and 54 patients (33%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.40-0.92; P = .04), while serious adverse events occurred in 23.3% of the patients on treprostinil and 25.8% of the patients on placebo. There was no significant difference between groups in patient-reported quality of life, as assessed via the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire.
“There was no guarantee that this was going to work in this condition,” said Adriano Tonelli, MD, of the department of pulmonary medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, in an interview. “Several small studies have tried different medications, for pulmonary hypertension or otherwise, in patients with interstitial lung disease with minimal effect, if any. Given that all the prior studies were not categorically positive, the expectation, at least on my end, was that we needed to wait and see.” Dr. Tonelli and coauthors published a post hoc analysis of inhaled treprostinil studied in the TRIUMPH and BEAT trials.
Next steps: Assess clinical outcomes after inhaled treprostinil
Although the results of this study by Waxman et al, are encouraging, and the need for a treatment in this type of pulmonary hypertension is very real, more narrowing down will be needed to confirm the benefits of inhaled treprostinil, wrote Darren B. Taichman, MD, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania in an accompanying editorial. He wrote, “After all, patients and physicians may reason, ‘It can’t hurt.’ Unfortunately, however, it could. Therapies approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension have been studied in patients with [ILD]-associated pulmonary hypertension and have shown inconsistent results, with some studies showing no benefit or suggesting harm.”
While the 6MWD has been used as an end point in previous drug trials for pulmonary arterial hypertension, Dr. Taichman wrote that improvements in such a variable were “probably too modest to be unequivocally consequential for many patients.” To confirm the benefits – and detriments – of treatments like inhaled treprostinil, it’s time for studies to focus on clinical end points, he stated, including hospitalizations, disease progression, and death.
He also highlighted the disparity between a treatment that led to increased walk distance and decreased clinical worsening yet did not register an improvement in health-related quality of life. He noted that the oft-cited minimal clinically important difference for 6MWD is approximately 30 m – similar to the difference recorded here. That said, he wrote, “prevention of deterioration is not to be ignored, even if it does not make a patient feel better.”
Regarding quality of life, Dr. Tonelli observed that this questionnaire, standard fare in respiratory research, may not have been perfectly suited for this particular study.
“You have to put it in the context of, ‘How good is the questionnaire to capture a difference in this particular disease over a 16-week period?’ ” he said. “It might not be sensitive enough to capture a significant change. The questionnaire was not developed for pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease, of course. It was developed more generically. It may not capture all that you need to show significance.”
The investigators acknowledged the study’s other potential limitations, including a short duration, a notable percentage of patients who discontinued the trial early, and the fact that clinical worsening and exacerbation of disease were investigator reported and not confirmed by an independent committee.
As for next steps in assessing pulmonary hypertension treatments, Dr. Tonelli pointed to the direction of future research. “The other big study that needs to come out in our field, and I believe it’s being worked on, is inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD],” he said. “That’s a major unmet need; the COPD population is larger than the population for interstitial lung disease, and one would wonder whether inhaled treprostinil would benefit those patients as well. At the moment, we have no treatments for that condition. In the future, a COPD study will be needed.”
The study was supported by United Therapeutics. Author disclosures are listed on the New England Journal of Medicine website.
and was associated with some additional clinical benefits, according to a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To investigate treprostinil therapy for pulmonary hypertension in this subset of patients with lung disease, Aaron Waxman, MD, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and his fellow researchers launched the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled INCREASE trial. They assigned 163 patients to the inhaled treprostinil group – administered via an ultrasonic, pulsed-delivery nebulizer over 16 weeks – and 163 patients to the placebo group. Their average age was 66.5 years, 73% were white, and 47% were female
At baseline, the mean 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) for all patients was 259.6 m. After 16 weeks, the treprostinil group gained a mean of 21.08 m in 6MWD, and the placebo group lost 10.04 m. The least-squares mean difference between the groups from baseline in the 6MWD was 31.12 m (95% confidence interval, 16.85-45.39; P < .001). After sensitivity analysis with multiple imputation, the difference remained significant at 30.97 m (95% CI, 16.53-45.41; P < .001).
In a comparison of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels from baseline to 16 weeks, the treprostinil group saw a decrease of 15% while the placebo group’s levels increased by 46% (treatment ratio 0.58; 95% CI, 0.47-0.72; P < .001). Clinical worsening occurred in 37 patients (23%) in the treprostinil group and 54 patients (33%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.40-0.92; P = .04), while serious adverse events occurred in 23.3% of the patients on treprostinil and 25.8% of the patients on placebo. There was no significant difference between groups in patient-reported quality of life, as assessed via the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire.
“There was no guarantee that this was going to work in this condition,” said Adriano Tonelli, MD, of the department of pulmonary medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, in an interview. “Several small studies have tried different medications, for pulmonary hypertension or otherwise, in patients with interstitial lung disease with minimal effect, if any. Given that all the prior studies were not categorically positive, the expectation, at least on my end, was that we needed to wait and see.” Dr. Tonelli and coauthors published a post hoc analysis of inhaled treprostinil studied in the TRIUMPH and BEAT trials.
Next steps: Assess clinical outcomes after inhaled treprostinil
Although the results of this study by Waxman et al, are encouraging, and the need for a treatment in this type of pulmonary hypertension is very real, more narrowing down will be needed to confirm the benefits of inhaled treprostinil, wrote Darren B. Taichman, MD, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania in an accompanying editorial. He wrote, “After all, patients and physicians may reason, ‘It can’t hurt.’ Unfortunately, however, it could. Therapies approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension have been studied in patients with [ILD]-associated pulmonary hypertension and have shown inconsistent results, with some studies showing no benefit or suggesting harm.”
While the 6MWD has been used as an end point in previous drug trials for pulmonary arterial hypertension, Dr. Taichman wrote that improvements in such a variable were “probably too modest to be unequivocally consequential for many patients.” To confirm the benefits – and detriments – of treatments like inhaled treprostinil, it’s time for studies to focus on clinical end points, he stated, including hospitalizations, disease progression, and death.
He also highlighted the disparity between a treatment that led to increased walk distance and decreased clinical worsening yet did not register an improvement in health-related quality of life. He noted that the oft-cited minimal clinically important difference for 6MWD is approximately 30 m – similar to the difference recorded here. That said, he wrote, “prevention of deterioration is not to be ignored, even if it does not make a patient feel better.”
Regarding quality of life, Dr. Tonelli observed that this questionnaire, standard fare in respiratory research, may not have been perfectly suited for this particular study.
“You have to put it in the context of, ‘How good is the questionnaire to capture a difference in this particular disease over a 16-week period?’ ” he said. “It might not be sensitive enough to capture a significant change. The questionnaire was not developed for pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease, of course. It was developed more generically. It may not capture all that you need to show significance.”
The investigators acknowledged the study’s other potential limitations, including a short duration, a notable percentage of patients who discontinued the trial early, and the fact that clinical worsening and exacerbation of disease were investigator reported and not confirmed by an independent committee.
As for next steps in assessing pulmonary hypertension treatments, Dr. Tonelli pointed to the direction of future research. “The other big study that needs to come out in our field, and I believe it’s being worked on, is inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD],” he said. “That’s a major unmet need; the COPD population is larger than the population for interstitial lung disease, and one would wonder whether inhaled treprostinil would benefit those patients as well. At the moment, we have no treatments for that condition. In the future, a COPD study will be needed.”
The study was supported by United Therapeutics. Author disclosures are listed on the New England Journal of Medicine website.
and was associated with some additional clinical benefits, according to a new study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To investigate treprostinil therapy for pulmonary hypertension in this subset of patients with lung disease, Aaron Waxman, MD, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, and his fellow researchers launched the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled INCREASE trial. They assigned 163 patients to the inhaled treprostinil group – administered via an ultrasonic, pulsed-delivery nebulizer over 16 weeks – and 163 patients to the placebo group. Their average age was 66.5 years, 73% were white, and 47% were female
At baseline, the mean 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) for all patients was 259.6 m. After 16 weeks, the treprostinil group gained a mean of 21.08 m in 6MWD, and the placebo group lost 10.04 m. The least-squares mean difference between the groups from baseline in the 6MWD was 31.12 m (95% confidence interval, 16.85-45.39; P < .001). After sensitivity analysis with multiple imputation, the difference remained significant at 30.97 m (95% CI, 16.53-45.41; P < .001).
In a comparison of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels from baseline to 16 weeks, the treprostinil group saw a decrease of 15% while the placebo group’s levels increased by 46% (treatment ratio 0.58; 95% CI, 0.47-0.72; P < .001). Clinical worsening occurred in 37 patients (23%) in the treprostinil group and 54 patients (33%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.40-0.92; P = .04), while serious adverse events occurred in 23.3% of the patients on treprostinil and 25.8% of the patients on placebo. There was no significant difference between groups in patient-reported quality of life, as assessed via the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire.
“There was no guarantee that this was going to work in this condition,” said Adriano Tonelli, MD, of the department of pulmonary medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, in an interview. “Several small studies have tried different medications, for pulmonary hypertension or otherwise, in patients with interstitial lung disease with minimal effect, if any. Given that all the prior studies were not categorically positive, the expectation, at least on my end, was that we needed to wait and see.” Dr. Tonelli and coauthors published a post hoc analysis of inhaled treprostinil studied in the TRIUMPH and BEAT trials.
Next steps: Assess clinical outcomes after inhaled treprostinil
Although the results of this study by Waxman et al, are encouraging, and the need for a treatment in this type of pulmonary hypertension is very real, more narrowing down will be needed to confirm the benefits of inhaled treprostinil, wrote Darren B. Taichman, MD, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania in an accompanying editorial. He wrote, “After all, patients and physicians may reason, ‘It can’t hurt.’ Unfortunately, however, it could. Therapies approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension have been studied in patients with [ILD]-associated pulmonary hypertension and have shown inconsistent results, with some studies showing no benefit or suggesting harm.”
While the 6MWD has been used as an end point in previous drug trials for pulmonary arterial hypertension, Dr. Taichman wrote that improvements in such a variable were “probably too modest to be unequivocally consequential for many patients.” To confirm the benefits – and detriments – of treatments like inhaled treprostinil, it’s time for studies to focus on clinical end points, he stated, including hospitalizations, disease progression, and death.
He also highlighted the disparity between a treatment that led to increased walk distance and decreased clinical worsening yet did not register an improvement in health-related quality of life. He noted that the oft-cited minimal clinically important difference for 6MWD is approximately 30 m – similar to the difference recorded here. That said, he wrote, “prevention of deterioration is not to be ignored, even if it does not make a patient feel better.”
Regarding quality of life, Dr. Tonelli observed that this questionnaire, standard fare in respiratory research, may not have been perfectly suited for this particular study.
“You have to put it in the context of, ‘How good is the questionnaire to capture a difference in this particular disease over a 16-week period?’ ” he said. “It might not be sensitive enough to capture a significant change. The questionnaire was not developed for pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease, of course. It was developed more generically. It may not capture all that you need to show significance.”
The investigators acknowledged the study’s other potential limitations, including a short duration, a notable percentage of patients who discontinued the trial early, and the fact that clinical worsening and exacerbation of disease were investigator reported and not confirmed by an independent committee.
As for next steps in assessing pulmonary hypertension treatments, Dr. Tonelli pointed to the direction of future research. “The other big study that needs to come out in our field, and I believe it’s being worked on, is inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD],” he said. “That’s a major unmet need; the COPD population is larger than the population for interstitial lung disease, and one would wonder whether inhaled treprostinil would benefit those patients as well. At the moment, we have no treatments for that condition. In the future, a COPD study will be needed.”
The study was supported by United Therapeutics. Author disclosures are listed on the New England Journal of Medicine website.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
COVID-19 in children: Weekly cases trending downward
The United States added over 171,000 new COVID-19 cases in children during the week ending Jan. 7, but that figure is lower than 3 of the previous 4 weeks, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
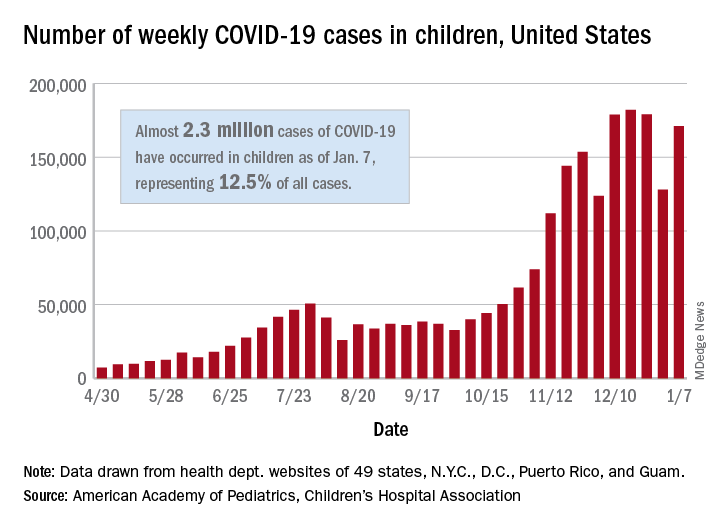
Despite an increase compared with the week ending Dec. 31, the most recent weekly total is down from the high of 182,000 cases reported for the week ending Dec. 17, based on data collected from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Those jurisdictions have recorded a total of almost 2.3 million COVID-19 cases in children since the beginning of the pandemic, which amounts to 12.5% of reported cases among all ages. The 171,000 child cases for the most recent week represented 12.9% of the more than 1.3 million cases nationwide, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly update.
The United States now has a rate of 3,055 COVID-19 cases per 100,000 children in the population, the report shows, with 31 states above that figure and 14 states reporting rates above 4,500 per 100,000 children.
Severe illness, however, continues to be rare among children. So far, children represent 1.8% of all hospitalizations in the jurisdictions reporting such data (24 states and New York City), and just 0.9% of infected children have been hospitalized. There have been 188 deaths among children in 42 states and New York City, which makes up just 0.06% of the total for all ages in those jurisdictions, the AAP and CHA reported.
There are 13 states that have reported no coronavirus-related deaths in children, while Texas (34), New York City (21), Arizona (17), and Illinois (11) are the only jurisdictions with 10 or more. Nevada has the highest proportion of child deaths to all deaths at 0.2%, with Arizona and Nebraska next at 0.18%, according to the AAP/CHA report.
The United States added over 171,000 new COVID-19 cases in children during the week ending Jan. 7, but that figure is lower than 3 of the previous 4 weeks, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Despite an increase compared with the week ending Dec. 31, the most recent weekly total is down from the high of 182,000 cases reported for the week ending Dec. 17, based on data collected from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Those jurisdictions have recorded a total of almost 2.3 million COVID-19 cases in children since the beginning of the pandemic, which amounts to 12.5% of reported cases among all ages. The 171,000 child cases for the most recent week represented 12.9% of the more than 1.3 million cases nationwide, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly update.
The United States now has a rate of 3,055 COVID-19 cases per 100,000 children in the population, the report shows, with 31 states above that figure and 14 states reporting rates above 4,500 per 100,000 children.
Severe illness, however, continues to be rare among children. So far, children represent 1.8% of all hospitalizations in the jurisdictions reporting such data (24 states and New York City), and just 0.9% of infected children have been hospitalized. There have been 188 deaths among children in 42 states and New York City, which makes up just 0.06% of the total for all ages in those jurisdictions, the AAP and CHA reported.
There are 13 states that have reported no coronavirus-related deaths in children, while Texas (34), New York City (21), Arizona (17), and Illinois (11) are the only jurisdictions with 10 or more. Nevada has the highest proportion of child deaths to all deaths at 0.2%, with Arizona and Nebraska next at 0.18%, according to the AAP/CHA report.
The United States added over 171,000 new COVID-19 cases in children during the week ending Jan. 7, but that figure is lower than 3 of the previous 4 weeks, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Despite an increase compared with the week ending Dec. 31, the most recent weekly total is down from the high of 182,000 cases reported for the week ending Dec. 17, based on data collected from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Those jurisdictions have recorded a total of almost 2.3 million COVID-19 cases in children since the beginning of the pandemic, which amounts to 12.5% of reported cases among all ages. The 171,000 child cases for the most recent week represented 12.9% of the more than 1.3 million cases nationwide, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly update.
The United States now has a rate of 3,055 COVID-19 cases per 100,000 children in the population, the report shows, with 31 states above that figure and 14 states reporting rates above 4,500 per 100,000 children.
Severe illness, however, continues to be rare among children. So far, children represent 1.8% of all hospitalizations in the jurisdictions reporting such data (24 states and New York City), and just 0.9% of infected children have been hospitalized. There have been 188 deaths among children in 42 states and New York City, which makes up just 0.06% of the total for all ages in those jurisdictions, the AAP and CHA reported.
There are 13 states that have reported no coronavirus-related deaths in children, while Texas (34), New York City (21), Arizona (17), and Illinois (11) are the only jurisdictions with 10 or more. Nevada has the highest proportion of child deaths to all deaths at 0.2%, with Arizona and Nebraska next at 0.18%, according to the AAP/CHA report.
How to predict successful colonoscopy malpractice lawsuits
Malpractice lawsuits related to colonoscopy continue to pose challenges for practitioners, and a new analysis reveals that errors related to sedation are more likely to be awarded to plaintiffs. Primary care physicians and surgeons are often codefendants, which emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary care in colonoscopy.
Cases involving informed consent were more likely to be ruled for the defendant, while those tied to medication error favored the plaintiff, according to an analysis of cases from the Westlaw legal database. The study, led by Krishan S. Patel and Sushil Ahlawat of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, was published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
According to the authors, 55% of physicians face a malpractice suit at some point in their careers, and gastroenterology ranks as the sixth most common specialty named in malpractice suits. Every year, about 13% of gastroenterologists confront malpractice allegations, and colonoscopy is the most common reason.
The researchers searched the Westlaw legal database for malpractice cases involving colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, identifying 305 cases between 1980 and 2017. The average patient age was 54.9 years, and 52.8% of cases were brought by female patients. The most cases were from New York (21.0%), followed by California (13.4%), Pennsylvania (13.1%), Massachusetts (12.5%), and New Jersey (7.9%). Gastroenterologists were named in 71.1% of cases, internists in 25.6%, and surgeons in 14.8%.
A little more than half (51.8%) of cases were ruled in favor of the defendant, and 25% for the plaintiff; 17% were settled, and 6% had a mixed outcome. Payouts ranged from $30,000 to $500,000,000, with a median of $995,000.
There were multiple causes of litigation listed in 83.6% of cases. The most frequent causes were delayed treatment (65.9%), delayed diagnosis (65.6%), procedural error/negligence (44.3%), and failure to refer/reorder tests (25.6%).
Of 135 cases alleging procedural negligence, 90 (67%) named perforation. Among 79 cases that cited a failure to refer and order appropriate tests, 97% claimed the defendant missed a cancerous lesion. In cases alleging missed cancers, 31% were in the cecum, and 23% in the anus.
A logistic regression analysis of factors associated with a verdict for the defendant found “lack of informed consent” to be an independent predictor of defendant verdict (odds ratio, 4.05; P = .004). “Medication error” was associated with reduced defendant success (OR, 0.17; P=.023). There were nonsignificant trends between reduced odds of a verdict for the defendant and lawsuits that named “delay in diagnosis” (OR, 0.35; P = .060) and “failure to refer” (OR, 0.51; P = .074).
The authors sound a dire note about the number of malpractice suits brought against gastroenterologists, but Lawrence Kosinski, MD, is more sanguine. He notes that gastroenterologists have low insurance premiums, compared with other specialties, but recognizes that colonoscopies are a significant source of risk.
Dr. Kosinski, who is chief medical officer at SonarMD and formerly a managing partner at the Illinois Gastroenterology Group, said in an interview that the study is revealing. “It comes out in the article: Acts of omission are more dangerous to the physician than acts of commission. Not finding that cancer, not acting on that malignant polyp, not pursuing it, is much more likely to get you in trouble than taking it off and perforating a colon,” said Dr. Kosinski, who was not involved in the study.
To gastroenterologists seeking to reduce their risks, he offered advice: You shouldn’t assume that the patient has read the information provided. Risks of anesthesia and the procedure should be directly communicated. It’s also important to document the procedure, including pictures of the cecum and rectal retroflexion. Finally, don’t rush. “This isn’t a race. Clean the colon, make sure you don’t miss something. If that person pops up in 3 years with a cancer, someone may go after you,” said Dr. Kosinski.
No source of funding was disclosed. Dr. Kosinski has no relevant financial disclosures.
Malpractice lawsuits related to colonoscopy continue to pose challenges for practitioners, and a new analysis reveals that errors related to sedation are more likely to be awarded to plaintiffs. Primary care physicians and surgeons are often codefendants, which emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary care in colonoscopy.
Cases involving informed consent were more likely to be ruled for the defendant, while those tied to medication error favored the plaintiff, according to an analysis of cases from the Westlaw legal database. The study, led by Krishan S. Patel and Sushil Ahlawat of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, was published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
According to the authors, 55% of physicians face a malpractice suit at some point in their careers, and gastroenterology ranks as the sixth most common specialty named in malpractice suits. Every year, about 13% of gastroenterologists confront malpractice allegations, and colonoscopy is the most common reason.
The researchers searched the Westlaw legal database for malpractice cases involving colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, identifying 305 cases between 1980 and 2017. The average patient age was 54.9 years, and 52.8% of cases were brought by female patients. The most cases were from New York (21.0%), followed by California (13.4%), Pennsylvania (13.1%), Massachusetts (12.5%), and New Jersey (7.9%). Gastroenterologists were named in 71.1% of cases, internists in 25.6%, and surgeons in 14.8%.
A little more than half (51.8%) of cases were ruled in favor of the defendant, and 25% for the plaintiff; 17% were settled, and 6% had a mixed outcome. Payouts ranged from $30,000 to $500,000,000, with a median of $995,000.
There were multiple causes of litigation listed in 83.6% of cases. The most frequent causes were delayed treatment (65.9%), delayed diagnosis (65.6%), procedural error/negligence (44.3%), and failure to refer/reorder tests (25.6%).
Of 135 cases alleging procedural negligence, 90 (67%) named perforation. Among 79 cases that cited a failure to refer and order appropriate tests, 97% claimed the defendant missed a cancerous lesion. In cases alleging missed cancers, 31% were in the cecum, and 23% in the anus.
A logistic regression analysis of factors associated with a verdict for the defendant found “lack of informed consent” to be an independent predictor of defendant verdict (odds ratio, 4.05; P = .004). “Medication error” was associated with reduced defendant success (OR, 0.17; P=.023). There were nonsignificant trends between reduced odds of a verdict for the defendant and lawsuits that named “delay in diagnosis” (OR, 0.35; P = .060) and “failure to refer” (OR, 0.51; P = .074).
The authors sound a dire note about the number of malpractice suits brought against gastroenterologists, but Lawrence Kosinski, MD, is more sanguine. He notes that gastroenterologists have low insurance premiums, compared with other specialties, but recognizes that colonoscopies are a significant source of risk.
Dr. Kosinski, who is chief medical officer at SonarMD and formerly a managing partner at the Illinois Gastroenterology Group, said in an interview that the study is revealing. “It comes out in the article: Acts of omission are more dangerous to the physician than acts of commission. Not finding that cancer, not acting on that malignant polyp, not pursuing it, is much more likely to get you in trouble than taking it off and perforating a colon,” said Dr. Kosinski, who was not involved in the study.
To gastroenterologists seeking to reduce their risks, he offered advice: You shouldn’t assume that the patient has read the information provided. Risks of anesthesia and the procedure should be directly communicated. It’s also important to document the procedure, including pictures of the cecum and rectal retroflexion. Finally, don’t rush. “This isn’t a race. Clean the colon, make sure you don’t miss something. If that person pops up in 3 years with a cancer, someone may go after you,” said Dr. Kosinski.
No source of funding was disclosed. Dr. Kosinski has no relevant financial disclosures.
Malpractice lawsuits related to colonoscopy continue to pose challenges for practitioners, and a new analysis reveals that errors related to sedation are more likely to be awarded to plaintiffs. Primary care physicians and surgeons are often codefendants, which emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary care in colonoscopy.
Cases involving informed consent were more likely to be ruled for the defendant, while those tied to medication error favored the plaintiff, according to an analysis of cases from the Westlaw legal database. The study, led by Krishan S. Patel and Sushil Ahlawat of Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, was published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.
According to the authors, 55% of physicians face a malpractice suit at some point in their careers, and gastroenterology ranks as the sixth most common specialty named in malpractice suits. Every year, about 13% of gastroenterologists confront malpractice allegations, and colonoscopy is the most common reason.
The researchers searched the Westlaw legal database for malpractice cases involving colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, identifying 305 cases between 1980 and 2017. The average patient age was 54.9 years, and 52.8% of cases were brought by female patients. The most cases were from New York (21.0%), followed by California (13.4%), Pennsylvania (13.1%), Massachusetts (12.5%), and New Jersey (7.9%). Gastroenterologists were named in 71.1% of cases, internists in 25.6%, and surgeons in 14.8%.
A little more than half (51.8%) of cases were ruled in favor of the defendant, and 25% for the plaintiff; 17% were settled, and 6% had a mixed outcome. Payouts ranged from $30,000 to $500,000,000, with a median of $995,000.
There were multiple causes of litigation listed in 83.6% of cases. The most frequent causes were delayed treatment (65.9%), delayed diagnosis (65.6%), procedural error/negligence (44.3%), and failure to refer/reorder tests (25.6%).
Of 135 cases alleging procedural negligence, 90 (67%) named perforation. Among 79 cases that cited a failure to refer and order appropriate tests, 97% claimed the defendant missed a cancerous lesion. In cases alleging missed cancers, 31% were in the cecum, and 23% in the anus.
A logistic regression analysis of factors associated with a verdict for the defendant found “lack of informed consent” to be an independent predictor of defendant verdict (odds ratio, 4.05; P = .004). “Medication error” was associated with reduced defendant success (OR, 0.17; P=.023). There were nonsignificant trends between reduced odds of a verdict for the defendant and lawsuits that named “delay in diagnosis” (OR, 0.35; P = .060) and “failure to refer” (OR, 0.51; P = .074).
The authors sound a dire note about the number of malpractice suits brought against gastroenterologists, but Lawrence Kosinski, MD, is more sanguine. He notes that gastroenterologists have low insurance premiums, compared with other specialties, but recognizes that colonoscopies are a significant source of risk.
Dr. Kosinski, who is chief medical officer at SonarMD and formerly a managing partner at the Illinois Gastroenterology Group, said in an interview that the study is revealing. “It comes out in the article: Acts of omission are more dangerous to the physician than acts of commission. Not finding that cancer, not acting on that malignant polyp, not pursuing it, is much more likely to get you in trouble than taking it off and perforating a colon,” said Dr. Kosinski, who was not involved in the study.
To gastroenterologists seeking to reduce their risks, he offered advice: You shouldn’t assume that the patient has read the information provided. Risks of anesthesia and the procedure should be directly communicated. It’s also important to document the procedure, including pictures of the cecum and rectal retroflexion. Finally, don’t rush. “This isn’t a race. Clean the colon, make sure you don’t miss something. If that person pops up in 3 years with a cancer, someone may go after you,” said Dr. Kosinski.
No source of funding was disclosed. Dr. Kosinski has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
Updated USPSTF HBV screening recommendation may be a ‘lost opportunity’
An update of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation for hepatitis B screening shows little change from the 2014 version, but some wonder if it should have gone farther than a risk-based approach.
The recommendation, which was published in JAMA, reinforces that screening should be conducted among adolescents and adults who are at increased risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The USPSTF named six categories of individuals at increased risk of infection: Persons born in countries with a 2% or higher prevalence of hepatitis B, such as Asia, Africa, the Pacific Islands, and some areas of South America; unvaccinated individuals born in the United States to parents from regions with a very high prevalence of HBV (≥8%); HIV-positive individuals; those who use injected drugs; men who have sex with men; and people who live with people who have HBV or who have HBV-infected sexual partners. It also recommended that pregnant women be screened for HBV infection during their first prenatal visit.
“I view the updated recommendations as an important document because it validates the importance of HBV screening, and the Grade B recommendation supports mandated insurance coverage for the screening test,” said Joseph Lim, MD, who is a professor of medicine at Yale University and director of the Yale Viral Hepatitis Program, both in New Haven, Conn.
Still, the recommendation could have gone further. Notably absent from the USPSTF document, yet featured in recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, are patients who have diabetes, are on immunosuppressive therapy, or have elevated liver enzymes or liver disease. Furthermore, a single-center study found that, among physicians administering immunosuppressive therapy, a setting in which HBV reactivation is a concern, there were low rates of screening for HBV infection, and the physicians did not reliably identify high-risk patients.
“This may also be viewed as a lost opportunity. Evidence suggests that risk factor–based screening is ineffective for the identification of chronic conditions such as hepatitis B. Risk factor–based screening is difficult to implement across health systems and exacerbates the burden on community-based organizations that are motivated to address viral hepatitis. It may further exacerbate labeling, stigma, and discrimination within already marginalized communities that are deemed to be at high risk,” said Dr. Lim.
A similar view was expressed by Avegail Flores, MD, medical director of liver transplantation at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, both in Houston. “This is a good launching point, and with further evidence provided, hopefully it will also bring in a broader conversation about other persons who are at risk but not included in these criteria.” Neither Dr. Lim nor Dr. Flores were involved in the study.
She noted that resistance to universal screening may be caused by the relatively low prevalence of hepatitis B infection in the United States. However, the CDC estimates that only about 61% of people infected with HBV are aware of it. “I don’t think we have done a good job screening those who are at risk,” said Dr. Flores.
Universal screening could help, but would have a low yield. Dr. Flores suggested expansion into other at-risk groups, such as Baby Boomers. With respect to other risk groups that could be stigmatized or discriminated against, Dr. Flores recalled her medical school days when some students went directly into underserved communities to provide information and screening services. “We have to think of creative ways of how to reach out to people, not just relying on the usual physician-patient relationship.”
The issue is especially timely because the World Health Organization has declared a target to reduce new hepatitis B infections by 90% by 2030, and that will require addressing gaps in diagnosis. “That’s why these recommendations are so consequential. We are at a critical juncture in terms of global hepatitis elimination efforts. There is a time sensitive need to have multistakeholder engagement in ensuring that all aspects of the care cascade are addressed. Because of the central role of screening and diagnosis, it’s of critical importance that organizations such as USPSTF are in alignment with other organizations that have already issued clear guidance on who should be screened. It is (my) hope that further examination of the evidence-base will further support broadening USPSTF guidance to include a larger group of at-risk individuals, or ideally a universal screening strategy,” said Dr. Lim.
The recommendation’s authors received travel reimbursement for their involvement, and one author reported receiving grants and personal fees from Healthwise. Dr. Flores has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lim is a member of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Viral Hepatitis Elimination Task Force.
SOURCE: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2020 Dec 15. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22980.
Updated Jan. 20, 2021
An update of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation for hepatitis B screening shows little change from the 2014 version, but some wonder if it should have gone farther than a risk-based approach.
The recommendation, which was published in JAMA, reinforces that screening should be conducted among adolescents and adults who are at increased risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The USPSTF named six categories of individuals at increased risk of infection: Persons born in countries with a 2% or higher prevalence of hepatitis B, such as Asia, Africa, the Pacific Islands, and some areas of South America; unvaccinated individuals born in the United States to parents from regions with a very high prevalence of HBV (≥8%); HIV-positive individuals; those who use injected drugs; men who have sex with men; and people who live with people who have HBV or who have HBV-infected sexual partners. It also recommended that pregnant women be screened for HBV infection during their first prenatal visit.
“I view the updated recommendations as an important document because it validates the importance of HBV screening, and the Grade B recommendation supports mandated insurance coverage for the screening test,” said Joseph Lim, MD, who is a professor of medicine at Yale University and director of the Yale Viral Hepatitis Program, both in New Haven, Conn.
Still, the recommendation could have gone further. Notably absent from the USPSTF document, yet featured in recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, are patients who have diabetes, are on immunosuppressive therapy, or have elevated liver enzymes or liver disease. Furthermore, a single-center study found that, among physicians administering immunosuppressive therapy, a setting in which HBV reactivation is a concern, there were low rates of screening for HBV infection, and the physicians did not reliably identify high-risk patients.
“This may also be viewed as a lost opportunity. Evidence suggests that risk factor–based screening is ineffective for the identification of chronic conditions such as hepatitis B. Risk factor–based screening is difficult to implement across health systems and exacerbates the burden on community-based organizations that are motivated to address viral hepatitis. It may further exacerbate labeling, stigma, and discrimination within already marginalized communities that are deemed to be at high risk,” said Dr. Lim.
A similar view was expressed by Avegail Flores, MD, medical director of liver transplantation at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, both in Houston. “This is a good launching point, and with further evidence provided, hopefully it will also bring in a broader conversation about other persons who are at risk but not included in these criteria.” Neither Dr. Lim nor Dr. Flores were involved in the study.
She noted that resistance to universal screening may be caused by the relatively low prevalence of hepatitis B infection in the United States. However, the CDC estimates that only about 61% of people infected with HBV are aware of it. “I don’t think we have done a good job screening those who are at risk,” said Dr. Flores.
Universal screening could help, but would have a low yield. Dr. Flores suggested expansion into other at-risk groups, such as Baby Boomers. With respect to other risk groups that could be stigmatized or discriminated against, Dr. Flores recalled her medical school days when some students went directly into underserved communities to provide information and screening services. “We have to think of creative ways of how to reach out to people, not just relying on the usual physician-patient relationship.”
The issue is especially timely because the World Health Organization has declared a target to reduce new hepatitis B infections by 90% by 2030, and that will require addressing gaps in diagnosis. “That’s why these recommendations are so consequential. We are at a critical juncture in terms of global hepatitis elimination efforts. There is a time sensitive need to have multistakeholder engagement in ensuring that all aspects of the care cascade are addressed. Because of the central role of screening and diagnosis, it’s of critical importance that organizations such as USPSTF are in alignment with other organizations that have already issued clear guidance on who should be screened. It is (my) hope that further examination of the evidence-base will further support broadening USPSTF guidance to include a larger group of at-risk individuals, or ideally a universal screening strategy,” said Dr. Lim.
The recommendation’s authors received travel reimbursement for their involvement, and one author reported receiving grants and personal fees from Healthwise. Dr. Flores has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lim is a member of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Viral Hepatitis Elimination Task Force.
SOURCE: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2020 Dec 15. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22980.
Updated Jan. 20, 2021
An update of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation for hepatitis B screening shows little change from the 2014 version, but some wonder if it should have gone farther than a risk-based approach.
The recommendation, which was published in JAMA, reinforces that screening should be conducted among adolescents and adults who are at increased risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The USPSTF named six categories of individuals at increased risk of infection: Persons born in countries with a 2% or higher prevalence of hepatitis B, such as Asia, Africa, the Pacific Islands, and some areas of South America; unvaccinated individuals born in the United States to parents from regions with a very high prevalence of HBV (≥8%); HIV-positive individuals; those who use injected drugs; men who have sex with men; and people who live with people who have HBV or who have HBV-infected sexual partners. It also recommended that pregnant women be screened for HBV infection during their first prenatal visit.
“I view the updated recommendations as an important document because it validates the importance of HBV screening, and the Grade B recommendation supports mandated insurance coverage for the screening test,” said Joseph Lim, MD, who is a professor of medicine at Yale University and director of the Yale Viral Hepatitis Program, both in New Haven, Conn.
Still, the recommendation could have gone further. Notably absent from the USPSTF document, yet featured in recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, are patients who have diabetes, are on immunosuppressive therapy, or have elevated liver enzymes or liver disease. Furthermore, a single-center study found that, among physicians administering immunosuppressive therapy, a setting in which HBV reactivation is a concern, there were low rates of screening for HBV infection, and the physicians did not reliably identify high-risk patients.
“This may also be viewed as a lost opportunity. Evidence suggests that risk factor–based screening is ineffective for the identification of chronic conditions such as hepatitis B. Risk factor–based screening is difficult to implement across health systems and exacerbates the burden on community-based organizations that are motivated to address viral hepatitis. It may further exacerbate labeling, stigma, and discrimination within already marginalized communities that are deemed to be at high risk,” said Dr. Lim.
A similar view was expressed by Avegail Flores, MD, medical director of liver transplantation at the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, both in Houston. “This is a good launching point, and with further evidence provided, hopefully it will also bring in a broader conversation about other persons who are at risk but not included in these criteria.” Neither Dr. Lim nor Dr. Flores were involved in the study.
She noted that resistance to universal screening may be caused by the relatively low prevalence of hepatitis B infection in the United States. However, the CDC estimates that only about 61% of people infected with HBV are aware of it. “I don’t think we have done a good job screening those who are at risk,” said Dr. Flores.
Universal screening could help, but would have a low yield. Dr. Flores suggested expansion into other at-risk groups, such as Baby Boomers. With respect to other risk groups that could be stigmatized or discriminated against, Dr. Flores recalled her medical school days when some students went directly into underserved communities to provide information and screening services. “We have to think of creative ways of how to reach out to people, not just relying on the usual physician-patient relationship.”
The issue is especially timely because the World Health Organization has declared a target to reduce new hepatitis B infections by 90% by 2030, and that will require addressing gaps in diagnosis. “That’s why these recommendations are so consequential. We are at a critical juncture in terms of global hepatitis elimination efforts. There is a time sensitive need to have multistakeholder engagement in ensuring that all aspects of the care cascade are addressed. Because of the central role of screening and diagnosis, it’s of critical importance that organizations such as USPSTF are in alignment with other organizations that have already issued clear guidance on who should be screened. It is (my) hope that further examination of the evidence-base will further support broadening USPSTF guidance to include a larger group of at-risk individuals, or ideally a universal screening strategy,” said Dr. Lim.
The recommendation’s authors received travel reimbursement for their involvement, and one author reported receiving grants and personal fees from Healthwise. Dr. Flores has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Lim is a member of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Viral Hepatitis Elimination Task Force.
SOURCE: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2020 Dec 15. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.22980.
Updated Jan. 20, 2021
FROM JAMA
In COVID-19 patients, risk of bleeding rivals risk of thromboembolism
There is no question that COVID-19 infection increases the risks of serious thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), but it also increases the risk of bleeding, complicating the benefit-to-risk calculations for anticoagulation, according to a review of data at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“Bleeding is a significant cause of morbidity in patients with COVID-19, and this is an important concept to appreciate,” reported Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, director of thrombosis research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
At least five guidelines, including those issued by the American College of Cardiology, International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH), and the American College of Chest Physicians, have recently addressed anticoagulation in patients infected with COVID-19, but there are “substantive differences” between them, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason is that they are essentially no high quality trials to guide practice. Rather, the recommendations are based primarily on retrospective studies and expert opinion.
The single most common theme from the guidelines is that anticoagulation must be individualized to balance patient-specific risks of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding, said Dr. Rosovsky, whose group published a recent comparison of these guidelines (Flaczyk A et al. Crit Care 2020;24:559).
Although there is general consensus that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive anticoagulation unless there are contraindications, there are differences in the recommended intensity of the anticoagulation for different risk groups and there is even less is less consensus on the need to anticoagulate outpatients or patients after discharge, according to Dr. Rosovsky
In her own center, the standard is a prophylactic dose of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in an algorithm that calls for dose adjustments for some groups such as those with renal impairment or obesity. Alternative forms of anticoagulation are recommended for patients with a history of thrombocytopenia or are at high risk for hemorrhage. Full dose LMWH is recommended in patients already on an oral anticoagulant at time of hospitalization.
“The biggest question right now is when to consider increasing from a prophylactic dose to intermediate or full dose anticoagulation in high risk patients, especially those in the ICU patients,” Dr. Rosovsky said.
Current practices are diverse, according to a recently published survey led by Dr. Rosovsky (Rosovsky RP et al. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2020;4:969-83). According to the survey, which had responses from more than 500 physicians in 41 countries, 30% of centers escalate from a prophylactic dose of anticoagulation to an intermediate dose when patients move to the ICU. Although not all answered this question, 25% reported that they do not escalate at ICU transfer. For 15% of respondents, dose escalation is being offered to patients with a D-dimer exceeding six-times the upper limit of normal.
These practices have developed in the absence of prospective clinical trials, which are urgently needed, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason that trials specific to COVID-19 are particularly important is that this infection also engenders a high risk of major bleeding.
For example, in a multicenter retrospective study of 400 hospital-admitted COVID-19 patients the rates of major bleeding was 4.8% or exactly the same as the rate of radiographically confirmed VTE. At 7.6%, the rates of VTE and major bleeding were also exactly the same for ICU patients (Al-Samkari H et al. Blood 2020;136:489-500).
“An elevated D-dimer was a marker for both VTE and major bleeding,” reported Dr. Rosovsky, who was the senior author of this study. On the basis of odds ratio (OR), the risk of VTE was increased more than six-fold (OR, 6.79) and the risk of major bleeding by more than three-fold (OR, 3.56) when the D-dimer exceeded 2,500 ng/mL.
The risk of VTE from COVID-19 infection is well documented. For example, autopsy studies have shown widespread thrombosis, including PE, in patients who have died from COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Rosovsky.
There is also evidence of benefit from anticoagulation. In an retrospective study from China undertaken early in the pandemic, there was no overall mortality benefit at 28 days among those who did receive LMWH when compared to those who did not, but there was a 20% absolute mortality benefit (52.4% vs. 32.8%; P = .017) in those with a D-dimer six-fold ULN (Tang N et al. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1094-9).
These types of data support the use of anticoagulation to manage VTE risk in at least some patients, but the reported rates of VTE across institutions and across inpatient and outpatient settings have varied “dramatically,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. The balance of VTE and major bleeding is delicate. In one retrospective study, the mortality advantage for therapeutic versus prophylactic dose of LMWH did not reach statistical significance, but the rate of major bleeding was nearly doubled (3.0% vs. 1.7%) (Nadkarni GN et al J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:1815-26).
Because of the many variables that might affect risk of VTE and risk of major bleeding in any individual patient, the benefit-to-risk calculation of anticoagulation is “complex,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. It is for this reason she urged clinicians to consider entering patients into clinical trials designed to generate evidence-based answers.
There is large and growing body of retrospective data that have helped characterize the risk of VTE and bleeding in patients with COVID-19, but “there is no substitute for a well-controlled clinical trial,” agreed Robert A. Harrington, MD, chairman of the department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
He and the comoderator of the session in which these data were presented agreed that anticoagulation must be administered within a narrow therapeutic window that will be best defined through controlled trial designs.
“There is a significant risk of doing harm,” said Fatima Rodriguez, MD, assistant professor of cardiology at Stanford University. She seconded the critical role of trial participation when possible and the need for clinical trials to better guide treatment decisions.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There is no question that COVID-19 infection increases the risks of serious thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), but it also increases the risk of bleeding, complicating the benefit-to-risk calculations for anticoagulation, according to a review of data at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“Bleeding is a significant cause of morbidity in patients with COVID-19, and this is an important concept to appreciate,” reported Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, director of thrombosis research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
At least five guidelines, including those issued by the American College of Cardiology, International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH), and the American College of Chest Physicians, have recently addressed anticoagulation in patients infected with COVID-19, but there are “substantive differences” between them, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason is that they are essentially no high quality trials to guide practice. Rather, the recommendations are based primarily on retrospective studies and expert opinion.
The single most common theme from the guidelines is that anticoagulation must be individualized to balance patient-specific risks of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding, said Dr. Rosovsky, whose group published a recent comparison of these guidelines (Flaczyk A et al. Crit Care 2020;24:559).
Although there is general consensus that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive anticoagulation unless there are contraindications, there are differences in the recommended intensity of the anticoagulation for different risk groups and there is even less is less consensus on the need to anticoagulate outpatients or patients after discharge, according to Dr. Rosovsky
In her own center, the standard is a prophylactic dose of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in an algorithm that calls for dose adjustments for some groups such as those with renal impairment or obesity. Alternative forms of anticoagulation are recommended for patients with a history of thrombocytopenia or are at high risk for hemorrhage. Full dose LMWH is recommended in patients already on an oral anticoagulant at time of hospitalization.
“The biggest question right now is when to consider increasing from a prophylactic dose to intermediate or full dose anticoagulation in high risk patients, especially those in the ICU patients,” Dr. Rosovsky said.
Current practices are diverse, according to a recently published survey led by Dr. Rosovsky (Rosovsky RP et al. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2020;4:969-83). According to the survey, which had responses from more than 500 physicians in 41 countries, 30% of centers escalate from a prophylactic dose of anticoagulation to an intermediate dose when patients move to the ICU. Although not all answered this question, 25% reported that they do not escalate at ICU transfer. For 15% of respondents, dose escalation is being offered to patients with a D-dimer exceeding six-times the upper limit of normal.
These practices have developed in the absence of prospective clinical trials, which are urgently needed, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason that trials specific to COVID-19 are particularly important is that this infection also engenders a high risk of major bleeding.
For example, in a multicenter retrospective study of 400 hospital-admitted COVID-19 patients the rates of major bleeding was 4.8% or exactly the same as the rate of radiographically confirmed VTE. At 7.6%, the rates of VTE and major bleeding were also exactly the same for ICU patients (Al-Samkari H et al. Blood 2020;136:489-500).
“An elevated D-dimer was a marker for both VTE and major bleeding,” reported Dr. Rosovsky, who was the senior author of this study. On the basis of odds ratio (OR), the risk of VTE was increased more than six-fold (OR, 6.79) and the risk of major bleeding by more than three-fold (OR, 3.56) when the D-dimer exceeded 2,500 ng/mL.
The risk of VTE from COVID-19 infection is well documented. For example, autopsy studies have shown widespread thrombosis, including PE, in patients who have died from COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Rosovsky.
There is also evidence of benefit from anticoagulation. In an retrospective study from China undertaken early in the pandemic, there was no overall mortality benefit at 28 days among those who did receive LMWH when compared to those who did not, but there was a 20% absolute mortality benefit (52.4% vs. 32.8%; P = .017) in those with a D-dimer six-fold ULN (Tang N et al. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1094-9).
These types of data support the use of anticoagulation to manage VTE risk in at least some patients, but the reported rates of VTE across institutions and across inpatient and outpatient settings have varied “dramatically,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. The balance of VTE and major bleeding is delicate. In one retrospective study, the mortality advantage for therapeutic versus prophylactic dose of LMWH did not reach statistical significance, but the rate of major bleeding was nearly doubled (3.0% vs. 1.7%) (Nadkarni GN et al J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:1815-26).
Because of the many variables that might affect risk of VTE and risk of major bleeding in any individual patient, the benefit-to-risk calculation of anticoagulation is “complex,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. It is for this reason she urged clinicians to consider entering patients into clinical trials designed to generate evidence-based answers.
There is large and growing body of retrospective data that have helped characterize the risk of VTE and bleeding in patients with COVID-19, but “there is no substitute for a well-controlled clinical trial,” agreed Robert A. Harrington, MD, chairman of the department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
He and the comoderator of the session in which these data were presented agreed that anticoagulation must be administered within a narrow therapeutic window that will be best defined through controlled trial designs.
“There is a significant risk of doing harm,” said Fatima Rodriguez, MD, assistant professor of cardiology at Stanford University. She seconded the critical role of trial participation when possible and the need for clinical trials to better guide treatment decisions.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There is no question that COVID-19 infection increases the risks of serious thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), but it also increases the risk of bleeding, complicating the benefit-to-risk calculations for anticoagulation, according to a review of data at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“Bleeding is a significant cause of morbidity in patients with COVID-19, and this is an important concept to appreciate,” reported Rachel P. Rosovsky, MD, director of thrombosis research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
At least five guidelines, including those issued by the American College of Cardiology, International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH), and the American College of Chest Physicians, have recently addressed anticoagulation in patients infected with COVID-19, but there are “substantive differences” between them, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason is that they are essentially no high quality trials to guide practice. Rather, the recommendations are based primarily on retrospective studies and expert opinion.
The single most common theme from the guidelines is that anticoagulation must be individualized to balance patient-specific risks of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding, said Dr. Rosovsky, whose group published a recent comparison of these guidelines (Flaczyk A et al. Crit Care 2020;24:559).
Although there is general consensus that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive anticoagulation unless there are contraindications, there are differences in the recommended intensity of the anticoagulation for different risk groups and there is even less is less consensus on the need to anticoagulate outpatients or patients after discharge, according to Dr. Rosovsky
In her own center, the standard is a prophylactic dose of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in an algorithm that calls for dose adjustments for some groups such as those with renal impairment or obesity. Alternative forms of anticoagulation are recommended for patients with a history of thrombocytopenia or are at high risk for hemorrhage. Full dose LMWH is recommended in patients already on an oral anticoagulant at time of hospitalization.
“The biggest question right now is when to consider increasing from a prophylactic dose to intermediate or full dose anticoagulation in high risk patients, especially those in the ICU patients,” Dr. Rosovsky said.
Current practices are diverse, according to a recently published survey led by Dr. Rosovsky (Rosovsky RP et al. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2020;4:969-83). According to the survey, which had responses from more than 500 physicians in 41 countries, 30% of centers escalate from a prophylactic dose of anticoagulation to an intermediate dose when patients move to the ICU. Although not all answered this question, 25% reported that they do not escalate at ICU transfer. For 15% of respondents, dose escalation is being offered to patients with a D-dimer exceeding six-times the upper limit of normal.
These practices have developed in the absence of prospective clinical trials, which are urgently needed, according to Dr. Rosovsky. The reason that trials specific to COVID-19 are particularly important is that this infection also engenders a high risk of major bleeding.
For example, in a multicenter retrospective study of 400 hospital-admitted COVID-19 patients the rates of major bleeding was 4.8% or exactly the same as the rate of radiographically confirmed VTE. At 7.6%, the rates of VTE and major bleeding were also exactly the same for ICU patients (Al-Samkari H et al. Blood 2020;136:489-500).
“An elevated D-dimer was a marker for both VTE and major bleeding,” reported Dr. Rosovsky, who was the senior author of this study. On the basis of odds ratio (OR), the risk of VTE was increased more than six-fold (OR, 6.79) and the risk of major bleeding by more than three-fold (OR, 3.56) when the D-dimer exceeded 2,500 ng/mL.
The risk of VTE from COVID-19 infection is well documented. For example, autopsy studies have shown widespread thrombosis, including PE, in patients who have died from COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Rosovsky.
There is also evidence of benefit from anticoagulation. In an retrospective study from China undertaken early in the pandemic, there was no overall mortality benefit at 28 days among those who did receive LMWH when compared to those who did not, but there was a 20% absolute mortality benefit (52.4% vs. 32.8%; P = .017) in those with a D-dimer six-fold ULN (Tang N et al. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1094-9).
These types of data support the use of anticoagulation to manage VTE risk in at least some patients, but the reported rates of VTE across institutions and across inpatient and outpatient settings have varied “dramatically,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. The balance of VTE and major bleeding is delicate. In one retrospective study, the mortality advantage for therapeutic versus prophylactic dose of LMWH did not reach statistical significance, but the rate of major bleeding was nearly doubled (3.0% vs. 1.7%) (Nadkarni GN et al J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:1815-26).
Because of the many variables that might affect risk of VTE and risk of major bleeding in any individual patient, the benefit-to-risk calculation of anticoagulation is “complex,” according to Dr. Rosovsky. It is for this reason she urged clinicians to consider entering patients into clinical trials designed to generate evidence-based answers.
There is large and growing body of retrospective data that have helped characterize the risk of VTE and bleeding in patients with COVID-19, but “there is no substitute for a well-controlled clinical trial,” agreed Robert A. Harrington, MD, chairman of the department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
He and the comoderator of the session in which these data were presented agreed that anticoagulation must be administered within a narrow therapeutic window that will be best defined through controlled trial designs.
“There is a significant risk of doing harm,” said Fatima Rodriguez, MD, assistant professor of cardiology at Stanford University. She seconded the critical role of trial participation when possible and the need for clinical trials to better guide treatment decisions.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE GOING BACK TO THE HEART OF CARDIOLOGY MEETING
Risk of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer linked to number of oral sex partners
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Large study links brown fat with lower rates of cardiometabolic disease
People who have brown fat detected on imaging seem to be at reduced risk of cardiac and metabolic conditions, ranging from type 2 diabetes to hypertension and coronary artery disease, with a notably strong effect in people with obesity, according to a new study of more than 52,000 individuals who had PET/CT scans as part of cancer evaluation.
Although this has been studied for decades in newborns and animals, only in the past decade have scientists appreciated that some adults have brown fat, typically around the neck and shoulders.
The new study, by far the largest of its kind in humans, appears to confirm the health benefits of brown fat suggested by previous studies, Tobias Becher, MD, and colleagues from The Rockefeller University, New York, wrote in their article published online Jan. 4 in Nature Medicine.
“Our study indicates an important contribution of brown adipose tissue to cardiometabolic health and suggests ... [it] has therapeutic potential in humans,” they stated.
But Caroline M. Apovian, MD, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, is more cautious in her interpretation of the findings.
“It’s nice to see that what we believe about this is correct, and it’s great to see that with obesity and more brown fat there is reduced diabetes and hypertension, but it’s only an association,” she said in an interview.
“This is a good study, but I don’t think we have an understanding of exactly why some people have more brown fat than others, how white fat becomes brown fat, the role of therapeutics, or if it’s important to try to create more brown fat.
“We don’t know if it’s a matter of exercise or something like living in a colder environment, so we need to find out whether or not brown fat is, for instance, a genetic issue, and if it is, if there is a way to increase it in humans,” she added.
And the fact that the study included patients with or being screened for cancer is one of the most important limitations of the study, Dr. Apovian noted.
Brown fat detected in 10% of participants
Contrary to white fat, which stores energy, brown fat is thermogenic, activated by cold conditions, and instead burns energy. And although animal studies have shown a link between brown fat and improvements in glucose and lipid homeostasis, the effects of brown fat in humans are not well understood.
Dr. Becher and colleagues explained that large-scale studies of brown fat have been practically impossible because the tissue only shows up on medical imaging and it would be unethical to expose people to radiation just to study brown fat.
But they realized that, across the street from their lab, many thousands of people visit Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center each year to undergo PET/CT scans for cancer evaluation.
Because radiologists routinely take note when brown adipose tissue is detected to prevent its misinterpretation as a tumor, the information was readily available with the scan data.
“We realized this could be a valuable resource to get us started with looking at brown fat at a population scale,” Dr. Becher said in a press statement from The Rockefeller University.
So they reviewed 134,529 PET/CT scans from 52,487 individuals attending Memorial Sloan Kettering between June 2009 and March 2018 for indications ranging from cancer diagnosis to treatment or surveillance.
Participants were classified by the presence or absence of brown adipose tissue and researchers were able to use electronic health records to comprehensively examine associations between brown fat and rates of disease.
Overall, brown adipose tissue was identified in 5,070 (9.7%) of patients, with higher rates of brown fat among women than men (13.8% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and reduced rates with advancing age (P < .0001), as has been observed in previous studies.
The researchers noted, however, that this rate of around 10% of people having brown fat is likely an underestimate because the patients had been instructed to avoid cold exposure, exercise, and caffeine – all of which are thought to increase brown adipose tissue – prior to having their scans.
Does brown fat mitigate some harms of obesity?
Among those with brown fat, the rate of type 2 diabetes was 4.6% compared with 9.5% in those with no detected brown fat (P < .0001), and in a multivariate analysis, the odds ratio (OR) for type 2 diabetes in the presence of brown fat was 0.44.
The occurrence of coronary artery disease was significantly lower in those with brown fat (OR, 0.68; P = .0002), as was cerebrovascular disease (OR, 0.77; P = .0317), heart failure (OR, 0.62; P = .0043), and hypertension (OR, 0.85; P = .0014).
Brown fat also was associated with notable improvements in glucose, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels (all P < .0001), while no differences were seen in measures of LDL-Cs or total cholesterol.
Leukocyte and platelet counts were significantly decreased in individuals with brown fat (both P < .0001).
The findings “suggest potential roles for brown adipose beyond regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism,” the authors wrote.
Most notably, the effects were more pronounced in people with obesity. For example, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in those with obesity and brown fat was less than half the rate in those with obesity without brown fat (7.5% vs. 20.3%; P < .0001).
This could indicate that brown adipose tissue “might play a role in mitigating the deleterious effects of obesity,” the researchers stated.
“Future research should aim to improve our understanding of brown adipose tissue regulation in humans and to develop mechanisms to safely modulate [its activity],” they concluded.
The study received funding from the American Diabetes Association, the Sinsheimer Foundation, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The authors and Dr. Apovian have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who have brown fat detected on imaging seem to be at reduced risk of cardiac and metabolic conditions, ranging from type 2 diabetes to hypertension and coronary artery disease, with a notably strong effect in people with obesity, according to a new study of more than 52,000 individuals who had PET/CT scans as part of cancer evaluation.
Although this has been studied for decades in newborns and animals, only in the past decade have scientists appreciated that some adults have brown fat, typically around the neck and shoulders.
The new study, by far the largest of its kind in humans, appears to confirm the health benefits of brown fat suggested by previous studies, Tobias Becher, MD, and colleagues from The Rockefeller University, New York, wrote in their article published online Jan. 4 in Nature Medicine.
“Our study indicates an important contribution of brown adipose tissue to cardiometabolic health and suggests ... [it] has therapeutic potential in humans,” they stated.
But Caroline M. Apovian, MD, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, is more cautious in her interpretation of the findings.
“It’s nice to see that what we believe about this is correct, and it’s great to see that with obesity and more brown fat there is reduced diabetes and hypertension, but it’s only an association,” she said in an interview.
“This is a good study, but I don’t think we have an understanding of exactly why some people have more brown fat than others, how white fat becomes brown fat, the role of therapeutics, or if it’s important to try to create more brown fat.
“We don’t know if it’s a matter of exercise or something like living in a colder environment, so we need to find out whether or not brown fat is, for instance, a genetic issue, and if it is, if there is a way to increase it in humans,” she added.
And the fact that the study included patients with or being screened for cancer is one of the most important limitations of the study, Dr. Apovian noted.
Brown fat detected in 10% of participants
Contrary to white fat, which stores energy, brown fat is thermogenic, activated by cold conditions, and instead burns energy. And although animal studies have shown a link between brown fat and improvements in glucose and lipid homeostasis, the effects of brown fat in humans are not well understood.
Dr. Becher and colleagues explained that large-scale studies of brown fat have been practically impossible because the tissue only shows up on medical imaging and it would be unethical to expose people to radiation just to study brown fat.
But they realized that, across the street from their lab, many thousands of people visit Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center each year to undergo PET/CT scans for cancer evaluation.
Because radiologists routinely take note when brown adipose tissue is detected to prevent its misinterpretation as a tumor, the information was readily available with the scan data.
“We realized this could be a valuable resource to get us started with looking at brown fat at a population scale,” Dr. Becher said in a press statement from The Rockefeller University.
So they reviewed 134,529 PET/CT scans from 52,487 individuals attending Memorial Sloan Kettering between June 2009 and March 2018 for indications ranging from cancer diagnosis to treatment or surveillance.
Participants were classified by the presence or absence of brown adipose tissue and researchers were able to use electronic health records to comprehensively examine associations between brown fat and rates of disease.
Overall, brown adipose tissue was identified in 5,070 (9.7%) of patients, with higher rates of brown fat among women than men (13.8% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and reduced rates with advancing age (P < .0001), as has been observed in previous studies.
The researchers noted, however, that this rate of around 10% of people having brown fat is likely an underestimate because the patients had been instructed to avoid cold exposure, exercise, and caffeine – all of which are thought to increase brown adipose tissue – prior to having their scans.
Does brown fat mitigate some harms of obesity?
Among those with brown fat, the rate of type 2 diabetes was 4.6% compared with 9.5% in those with no detected brown fat (P < .0001), and in a multivariate analysis, the odds ratio (OR) for type 2 diabetes in the presence of brown fat was 0.44.
The occurrence of coronary artery disease was significantly lower in those with brown fat (OR, 0.68; P = .0002), as was cerebrovascular disease (OR, 0.77; P = .0317), heart failure (OR, 0.62; P = .0043), and hypertension (OR, 0.85; P = .0014).
Brown fat also was associated with notable improvements in glucose, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels (all P < .0001), while no differences were seen in measures of LDL-Cs or total cholesterol.
Leukocyte and platelet counts were significantly decreased in individuals with brown fat (both P < .0001).
The findings “suggest potential roles for brown adipose beyond regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism,” the authors wrote.
Most notably, the effects were more pronounced in people with obesity. For example, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in those with obesity and brown fat was less than half the rate in those with obesity without brown fat (7.5% vs. 20.3%; P < .0001).
This could indicate that brown adipose tissue “might play a role in mitigating the deleterious effects of obesity,” the researchers stated.
“Future research should aim to improve our understanding of brown adipose tissue regulation in humans and to develop mechanisms to safely modulate [its activity],” they concluded.
The study received funding from the American Diabetes Association, the Sinsheimer Foundation, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The authors and Dr. Apovian have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who have brown fat detected on imaging seem to be at reduced risk of cardiac and metabolic conditions, ranging from type 2 diabetes to hypertension and coronary artery disease, with a notably strong effect in people with obesity, according to a new study of more than 52,000 individuals who had PET/CT scans as part of cancer evaluation.
Although this has been studied for decades in newborns and animals, only in the past decade have scientists appreciated that some adults have brown fat, typically around the neck and shoulders.
The new study, by far the largest of its kind in humans, appears to confirm the health benefits of brown fat suggested by previous studies, Tobias Becher, MD, and colleagues from The Rockefeller University, New York, wrote in their article published online Jan. 4 in Nature Medicine.
“Our study indicates an important contribution of brown adipose tissue to cardiometabolic health and suggests ... [it] has therapeutic potential in humans,” they stated.
But Caroline M. Apovian, MD, Center for Weight Management and Wellness, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, is more cautious in her interpretation of the findings.
“It’s nice to see that what we believe about this is correct, and it’s great to see that with obesity and more brown fat there is reduced diabetes and hypertension, but it’s only an association,” she said in an interview.
“This is a good study, but I don’t think we have an understanding of exactly why some people have more brown fat than others, how white fat becomes brown fat, the role of therapeutics, or if it’s important to try to create more brown fat.
“We don’t know if it’s a matter of exercise or something like living in a colder environment, so we need to find out whether or not brown fat is, for instance, a genetic issue, and if it is, if there is a way to increase it in humans,” she added.
And the fact that the study included patients with or being screened for cancer is one of the most important limitations of the study, Dr. Apovian noted.
Brown fat detected in 10% of participants
Contrary to white fat, which stores energy, brown fat is thermogenic, activated by cold conditions, and instead burns energy. And although animal studies have shown a link between brown fat and improvements in glucose and lipid homeostasis, the effects of brown fat in humans are not well understood.
Dr. Becher and colleagues explained that large-scale studies of brown fat have been practically impossible because the tissue only shows up on medical imaging and it would be unethical to expose people to radiation just to study brown fat.
But they realized that, across the street from their lab, many thousands of people visit Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center each year to undergo PET/CT scans for cancer evaluation.
Because radiologists routinely take note when brown adipose tissue is detected to prevent its misinterpretation as a tumor, the information was readily available with the scan data.
“We realized this could be a valuable resource to get us started with looking at brown fat at a population scale,” Dr. Becher said in a press statement from The Rockefeller University.
So they reviewed 134,529 PET/CT scans from 52,487 individuals attending Memorial Sloan Kettering between June 2009 and March 2018 for indications ranging from cancer diagnosis to treatment or surveillance.
Participants were classified by the presence or absence of brown adipose tissue and researchers were able to use electronic health records to comprehensively examine associations between brown fat and rates of disease.
Overall, brown adipose tissue was identified in 5,070 (9.7%) of patients, with higher rates of brown fat among women than men (13.8% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and reduced rates with advancing age (P < .0001), as has been observed in previous studies.
The researchers noted, however, that this rate of around 10% of people having brown fat is likely an underestimate because the patients had been instructed to avoid cold exposure, exercise, and caffeine – all of which are thought to increase brown adipose tissue – prior to having their scans.
Does brown fat mitigate some harms of obesity?
Among those with brown fat, the rate of type 2 diabetes was 4.6% compared with 9.5% in those with no detected brown fat (P < .0001), and in a multivariate analysis, the odds ratio (OR) for type 2 diabetes in the presence of brown fat was 0.44.
The occurrence of coronary artery disease was significantly lower in those with brown fat (OR, 0.68; P = .0002), as was cerebrovascular disease (OR, 0.77; P = .0317), heart failure (OR, 0.62; P = .0043), and hypertension (OR, 0.85; P = .0014).
Brown fat also was associated with notable improvements in glucose, triglycerides, and HDL-C levels (all P < .0001), while no differences were seen in measures of LDL-Cs or total cholesterol.
Leukocyte and platelet counts were significantly decreased in individuals with brown fat (both P < .0001).
The findings “suggest potential roles for brown adipose beyond regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism,” the authors wrote.
Most notably, the effects were more pronounced in people with obesity. For example, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in those with obesity and brown fat was less than half the rate in those with obesity without brown fat (7.5% vs. 20.3%; P < .0001).
This could indicate that brown adipose tissue “might play a role in mitigating the deleterious effects of obesity,” the researchers stated.
“Future research should aim to improve our understanding of brown adipose tissue regulation in humans and to develop mechanisms to safely modulate [its activity],” they concluded.
The study received funding from the American Diabetes Association, the Sinsheimer Foundation, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The authors and Dr. Apovian have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.